Fluorescence probe for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological system and application of fluorescence probe
A technology of fluorescent probe and hypochlorous acid, which is applied in the field of fluorescence analysis, can solve the problems of incomparable fluorescence imaging technology, etc., and achieve the effects of good fluorescence emission spectrum characteristics, low preparation cost, and cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Preparation of fluorescent probe 1a for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological systems according to the present invention
[0030] 3-acetyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (204mg, 10mmol), 4-(diethylamino) salicylaldehyde (193mg, 10mmol) and methanesulfonic acid (5mL) were added to a 50mL single-necked flask, refluxed for 6 hours, cooled, poured into 10g of ice, filtered, and dried.
[0031] The resulting solid was purified by column chromatography (dichloromethane:methanol=10:1) to obtain 371 mg of a dark blue product, which is the fluorescent probe 1a for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological systems according to the present invention, with a yield of 67%.
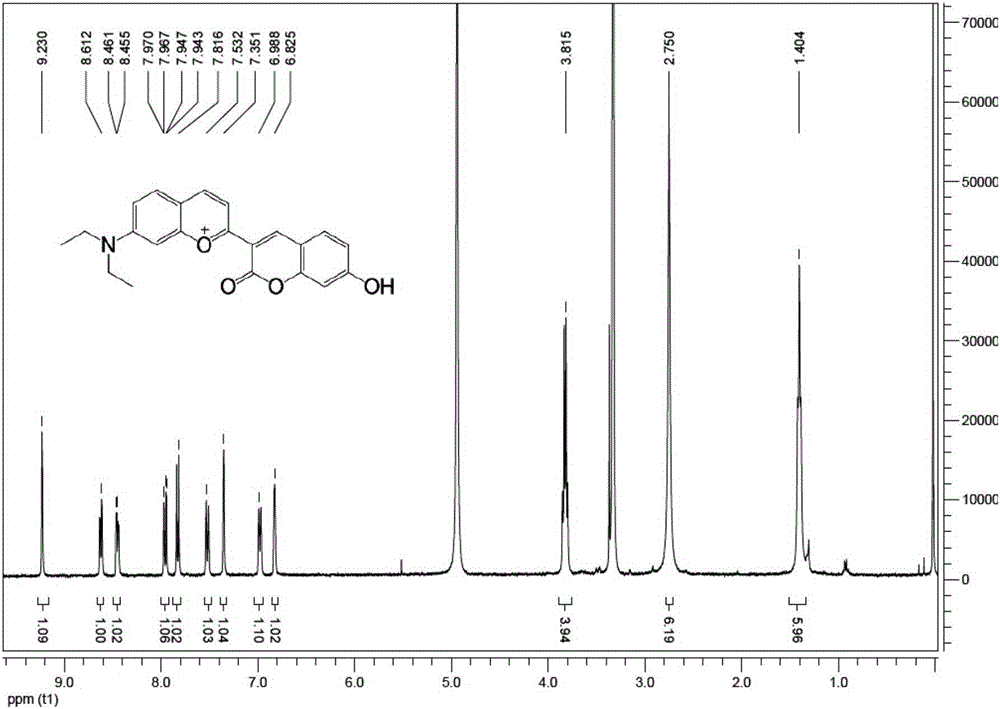
[0032] The above-mentioned fluorescent probe 1a for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological systems 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: The selectivity of fluorescent probe 1a for detecting hypochlorous acid in biological systems according to the present invention to different substances
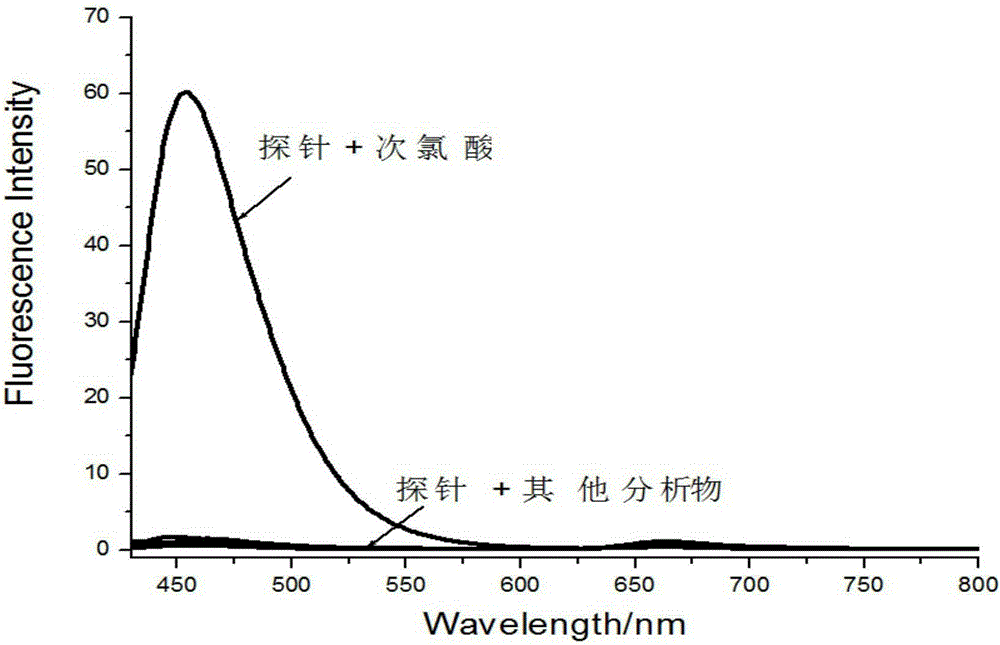
[0034] Prepare 8 parts of 5 mL of 5 μM probe PBS solution (containing 5% methanol, pH=7.4), and then add 50 μL of 10 mM NaClO, Na 2 S, Na 2 SO 3 , NO, H 2 o 2 、CH 3 COOOH, HClO 4 , cys, GSH, NaNO 2 , VC, etc. in PBS solution. Fluorescence detection was then performed (λ Ex =410nm,λ Em =452nm); Calculate the fluorescence intensity in each system; Evaluate the selectivity of the probe to hypochlorous acid (see image 3 ).
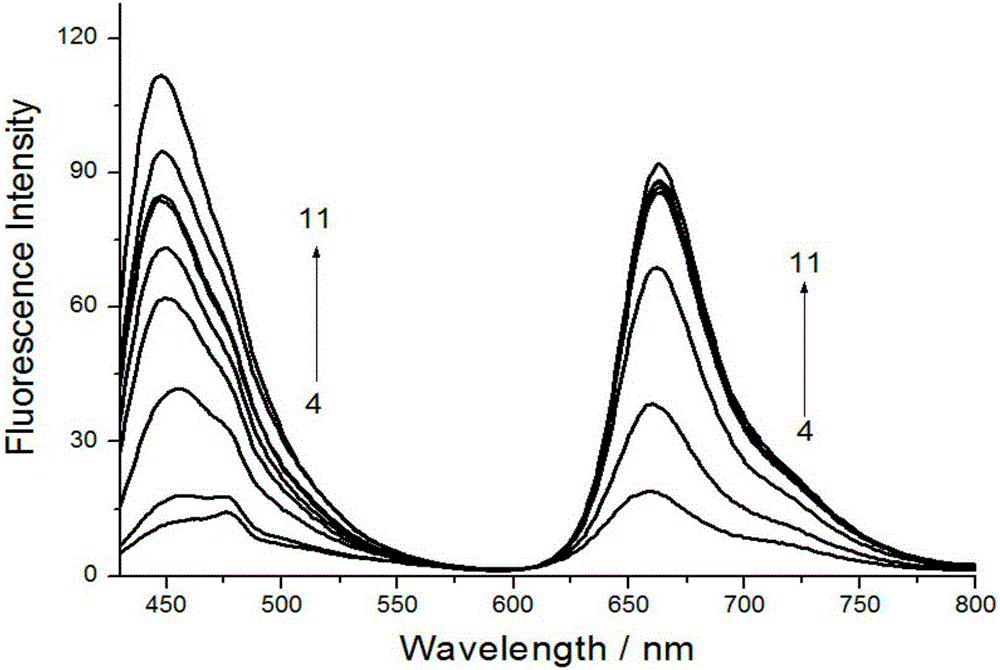
[0035] Similar method analyzes the fluorescent spectrum of the fluorescent probe 1a of detecting hypochlorous acid in the biological system of the present invention under different pH conditions, the results are shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: Absorption and fluorescence change analysis of fluorescent probe 1a for detecting hypochlorous acid in a biological system reacted with different concentrations of hypochlorous acid according to the present invention
[0037] Prepare 1 mL of acetonitrile solution with a concentration of 0-1 mM hypochlorous acid, and then add 9 mL of a probe PBS solution (containing 5% methanol, pH=7.4) with a concentration of 5 μM. After reacting 10min, carry out absorption spectrum test (see Figure 4 ); for fluorescence detection (λ Ex =410nm,λ Em =452nm), calculate the fluorescence intensity in each system, establish the standard curve of fluorescence intensity and hypochlorous acid concentration (see Figure 5 ) to determine the lower limit of the probe for hypochlorous acid detection.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com