Application of near infrared-emission fluorescent probe in quick pesticide residue detection
A technology for fluorescent probes and pesticide residues, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, measurement devices, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of being easily affected by biomass fluorescence, short fluorescence wavelength, etc., and achieve a simple and easy synthesis process and fast metabolism. , responsive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The chemical synthesis of embodiment 1 compound 2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoic acid DHBA
[0026] (1) Dissolve 22mmol 3-hydroxy-N,N-diethylaniline (DAHO) and 20mmol phthalic anhydride in 100mL toluene solution, N 2 Protection, heated to reflux for 15h.
[0027] (2) The solvent of the reaction solution was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the solid mixture was separated by column chromatography (developing solvent: dichloromethane:methanol=20:1, v:v).
[0028] (3) Add 10% NaOH solution to the separated solution for washing, and ultrasonically so that the product is fully dissolved in the water phase. Let the mixture stand and take the aqueous phase. 20% HCl was added to the water phase to adjust the pH of the system to 4-5, a large amount of white solids were precipitated, and finally about 2.8 g of the white solid compound DNBA was obtained. 1 H NMR (500MHz, DMSO) δ13.06(s,1H),12.57(s,1H),8.00–7.93(m,1H),7.69(td,J=7.5,1.1Hz,1H),7.61(td, J=7.7...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Chemical synthesis of 10-(diethylamino)-3-hydroxyl-3'H-spiro[benzo[c]xanthene-7,1'-isobenzofuran]-3'-one NDRO
[0030] (1) Dissolve 8 mmol of DHBA and 8.5 mmol of 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene in 30 mL of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). Stir and reflux, and control the reaction temperature to 90°C.
[0031] (2) Stir the reaction for 12h, stop the reaction, and the solution returns to room temperature;
[0032] (3) The solvent trifluoroacetic acid was rotary evaporated to dryness. The reaction mixture was separated by column chromatography (developing solvent: dichloromethane:methanol=15:1, v:v) to finally obtain 1.4 g of red solid compound NDRO. 1 H NMR (500MHz,DMSO)δ10.50(s,1H),8.60(s,1H),8.13(s,1H),7.92–7.71(m,2H),7.50(s,1H),7.35(dd, J = 18.2, 7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.23 (s, 1H), 6.76 (s, 4H), 3.54 (s, 4H), 1.19 (s, 6H).
Embodiment 3
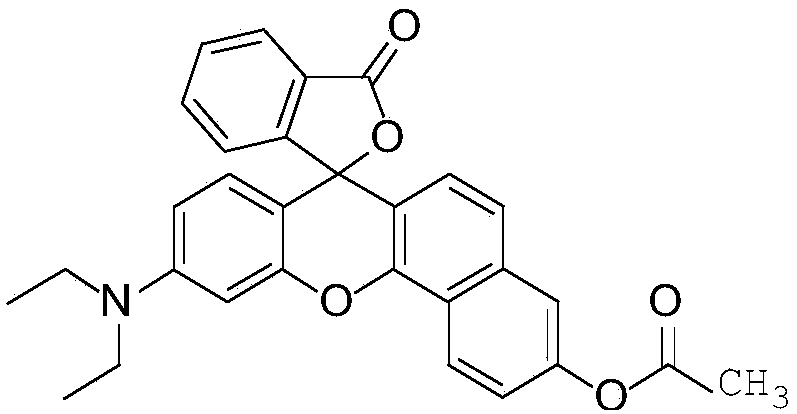
[0033] Example 3 10-(Diethylamino)-3'-oxo-3'H-spiro[benzo[c]xanthene-7,1'-isobenzofuran]-3-yl acetate Chemical Synthesis of NDRO-1
[0034] (1) Dissolve 120mg of the intermediate product NDRO in 26mL of dichloromethane, add about 70mg of acetyl chloride, then dropwise add 4-5 drops of triethylamine, and stir at room temperature for 25min;
[0035] (2) Add 35 mg of acetyl chloride, continue stirring for 40 min, and add water to quench the reaction.
[0036] (3) The organic layer was washed with water for 3 times, and then the dichloromethane was rotary evaporated to dryness. The reaction mixture was separated by column chromatography (developing solvent: dichloromethane:methanol=80:1, v:v) to obtain NDRO-153 mg as a red solid compound. 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl3) δ8.63 (d, J = 8.9Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 7.3Hz, 1H), 7.62 (dd, J = 16.5, 7.7Hz, 2H), 7.53 (s ,1H),7.38(d,J=8.6Hz,2H),7.15(d,J=7.2Hz,1H),6.78(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),6.66(s,2H),6.45(s , 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 6.4Hz, 4H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com