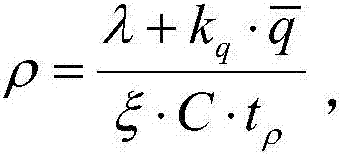Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51results about How to "Eliminate latency effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
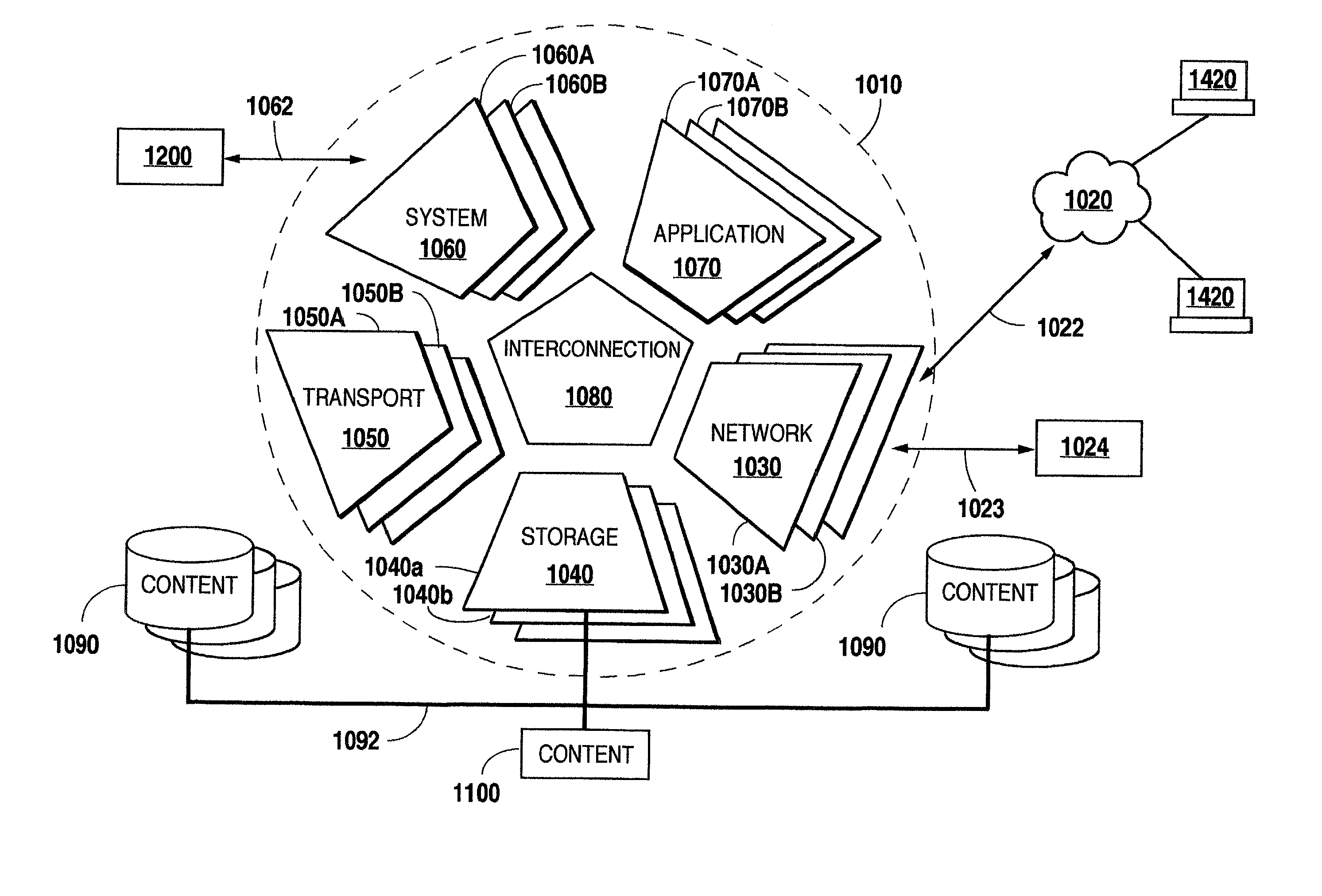
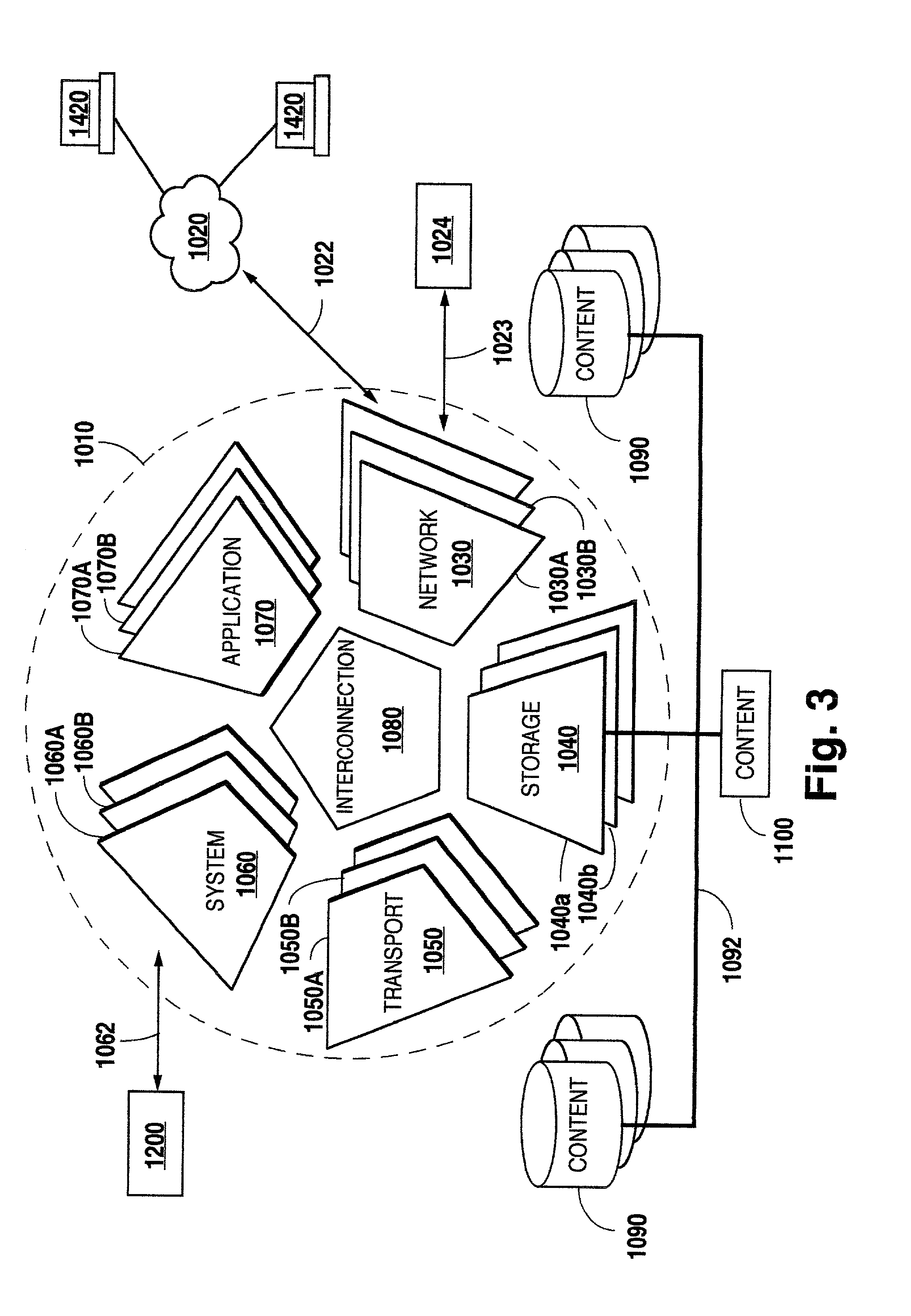
Systems and methods for intelligent information retrieval and delivery in an information management environment
InactiveUS20020129123A1Eliminate effectEnhance efficient useMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation retrievalInformation delivery
Methods and systems for intelligent information retrieval and delivery in information delivery environments that may be employed in a variety of information management system environments, including those employing high-end streaming servers. The disclosed methods and systems may be implemented to achieve a variety of information delivery goals, including delivery of continuous content in a manner that is free or substantially free of interruptions and hiccups, to enhance the efficient use of information retrieval resources such as buffer / cache memory, and / or to allocate information retrieval resources among simultaneous users, such as during periods of system congestion or overuse.
Owner:SURGIENT NETWORKS
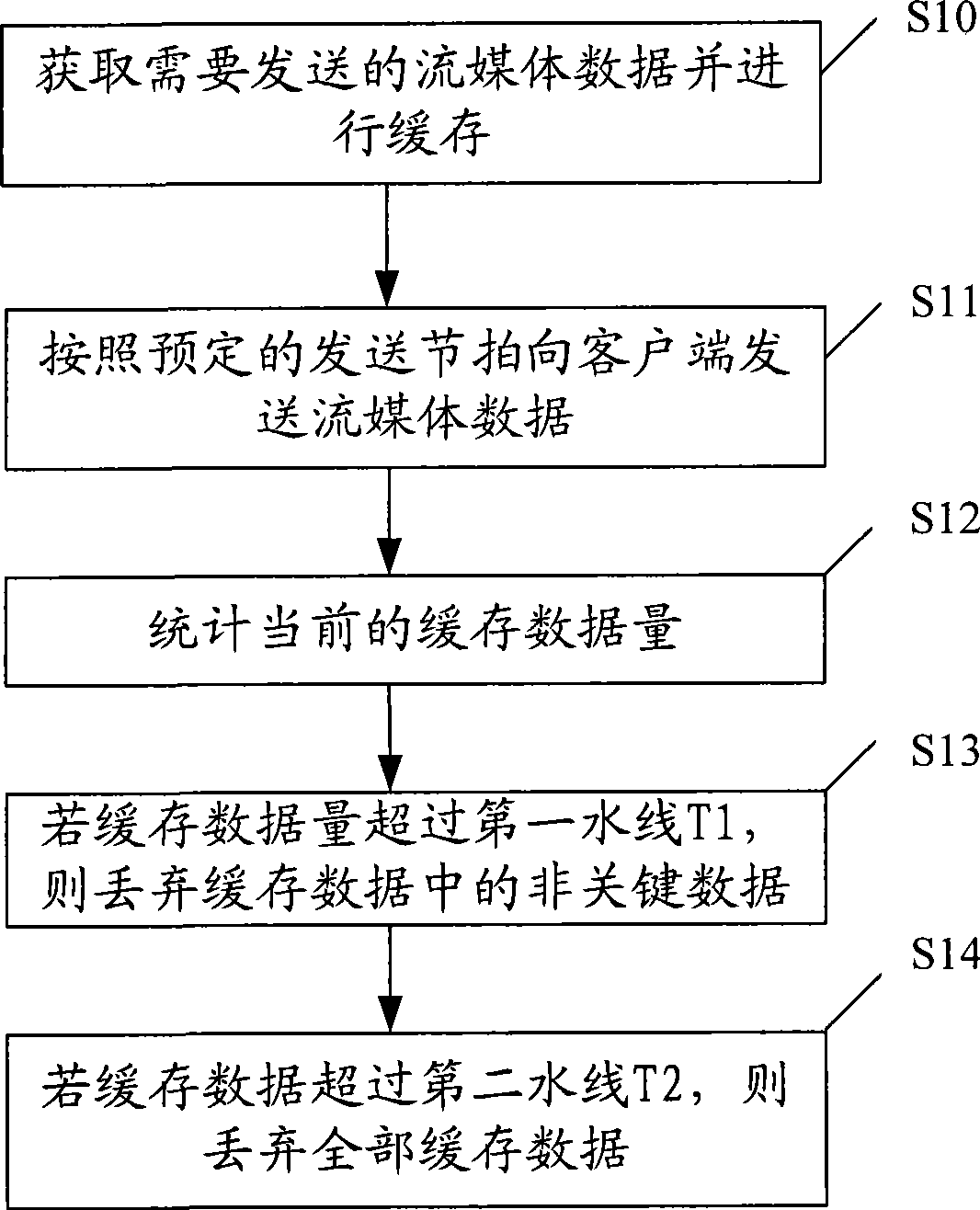
Method and device for sending and playing stream medium data and stream medium program request system
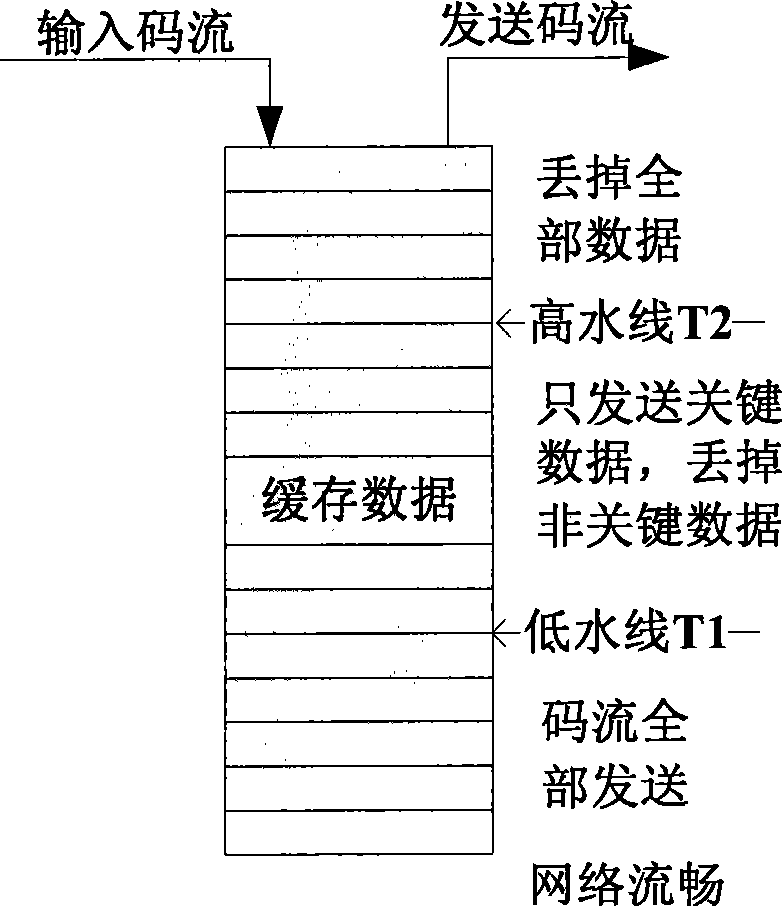
InactiveCN101466034AEliminate latency effectsLower latencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionSelective content distributionTime lagMedia on demand
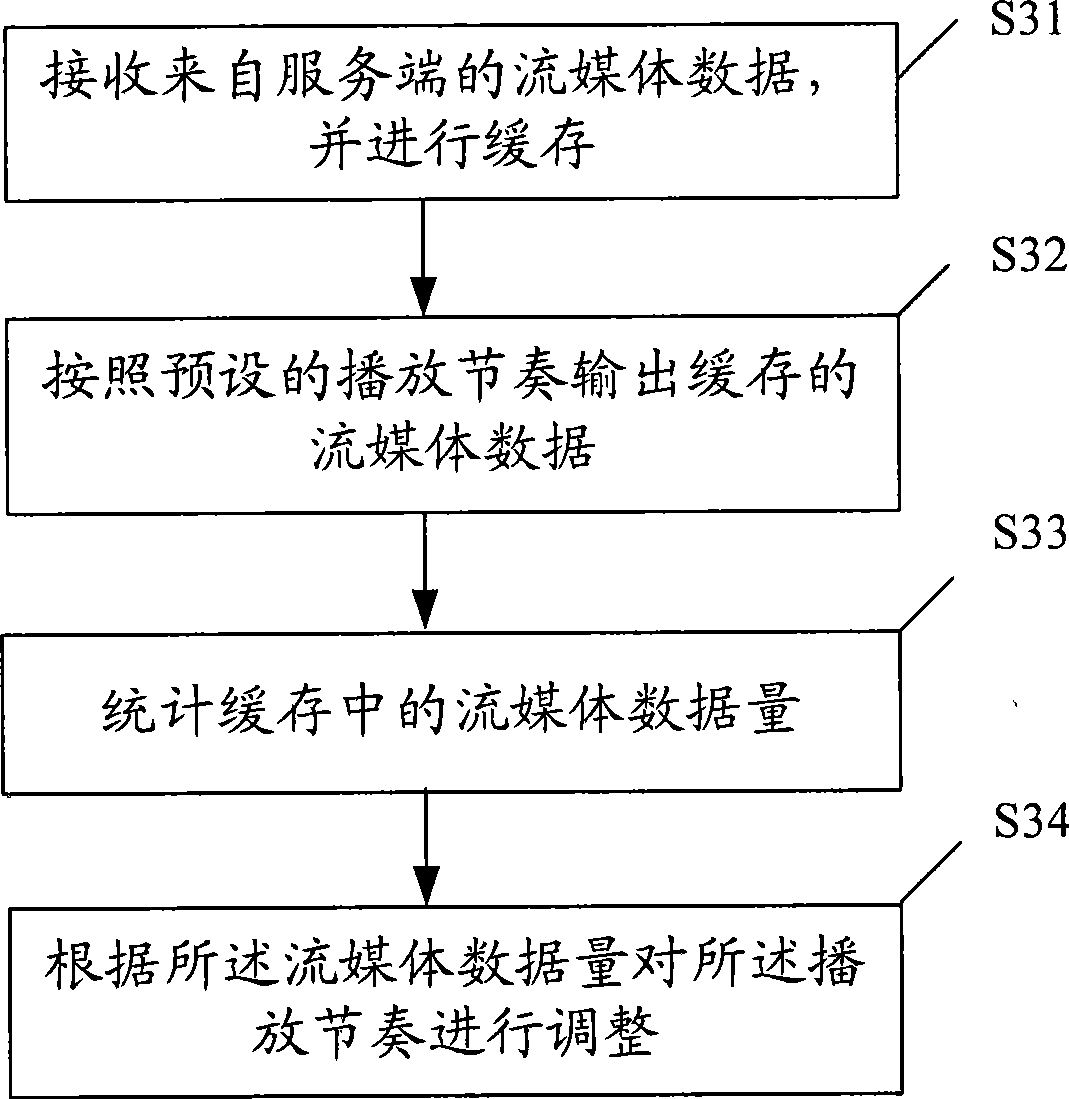
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method of sending and playing streaming media data and a device thereof, and a streaming media playing on demand system. The method of playing the streaming media data comprises: the streaming media data coming from a service terminal is received and cached; the cached streaming media data is output according to the preset playing rhythm. The volume of the streaming media data in caching is calculated; the playing rhythm is adjusted according to the volume of the streaming media data. A sending terminal can send the streaming media data to a client as soon as possible and only caches less data; the controlling of the playing rhythm is carried out at the client, thus lessening the impact on time lag played by the network jittering and reducing the time lag of the playing of the streaming media.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
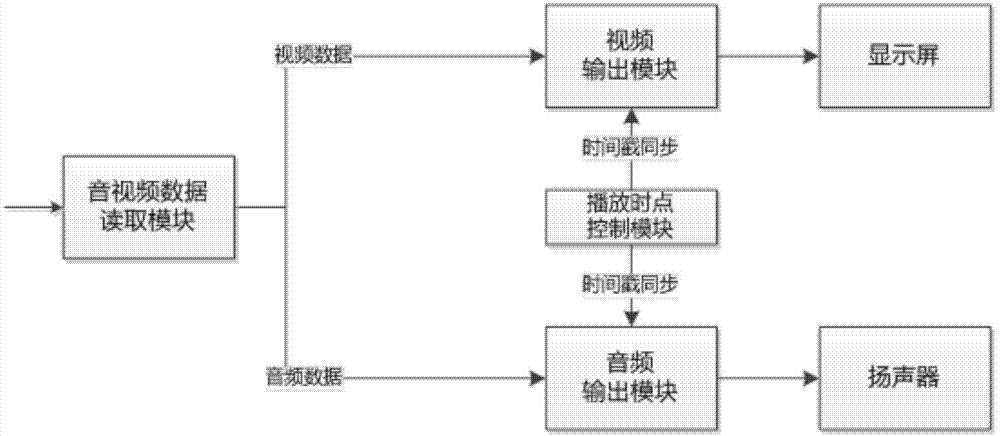
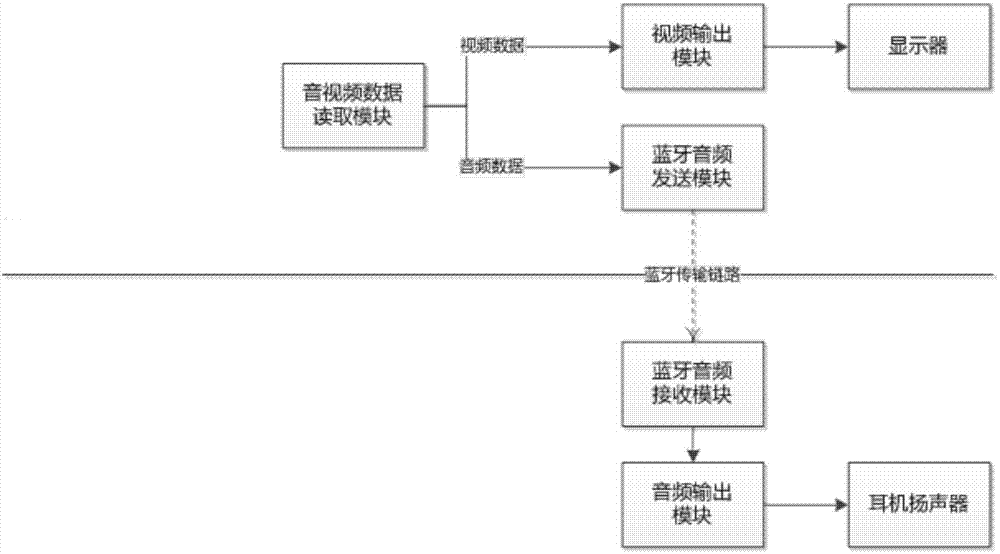
Video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment
InactiveCN103905876AEasy to operateAvoid buyingSelective content distributionComputer hardwareWireless transmission
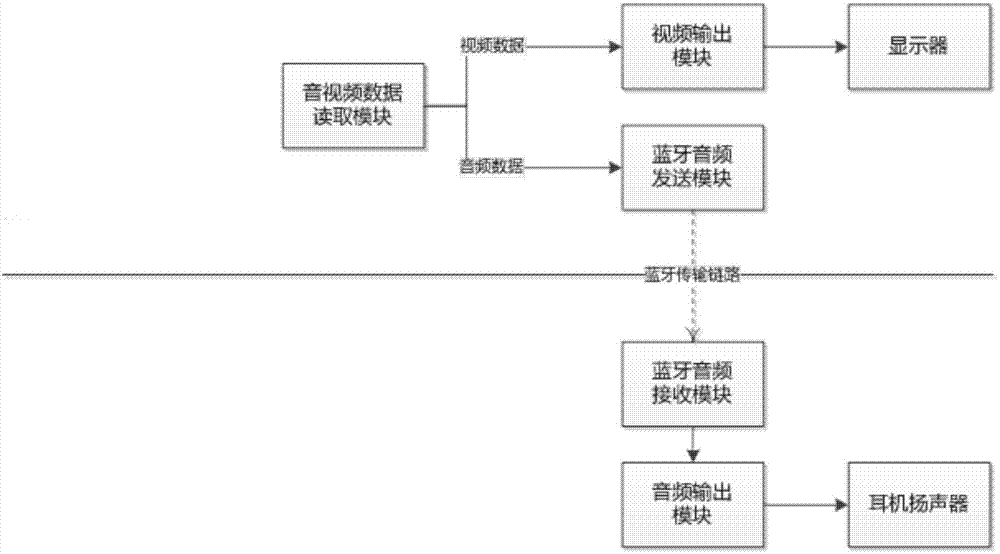
The embodiment of the invention provides a video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment. The method includes the steps that multimedia data are received on a display terminal side; the multimedia data comprise video data and audio data; the video data carry one or more video timestamps; the audio data are sent to a mobile device side; the display terminal side is connected with the mobile device side in a wireless transmission mode; playing object timestamps returned by the mobile device side are received; the playing object timestamps are timestamps generated according to currently-played audio timestamps when the audio data are played by the mobile device side; the video data corresponding to the playing object timestamps are played on the display terminal side. With the video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and the equipment, the constraint caused when wired earphones are directly connected with a display terminal can be gotten rid of by a user, operation of the user is facilitated, and synchronized playing of the audio data and the video data is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
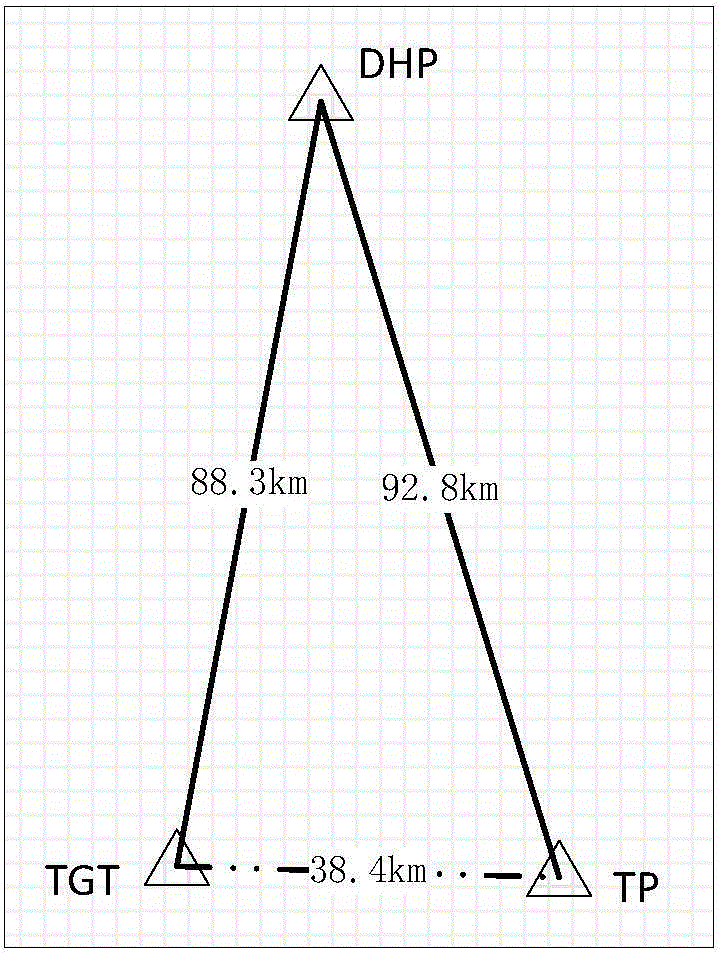
Quick resolving method for multi-constellation long-base-line network RTK partial ambiguity
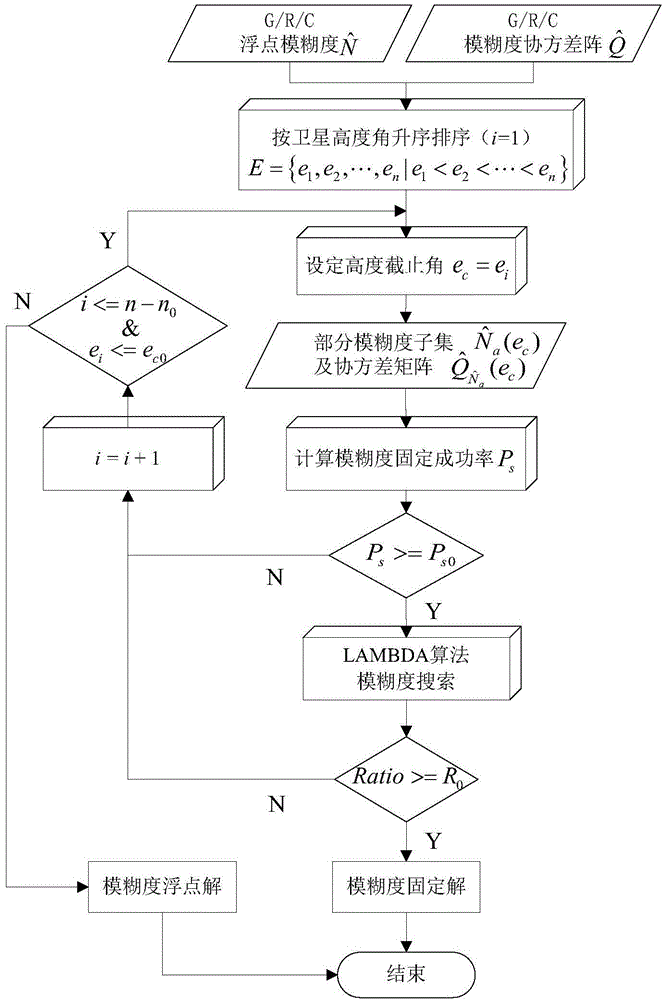
ActiveCN104459745AShorten the timeEliminate latency effectsSatellite radio beaconingSystem combinationComputer science
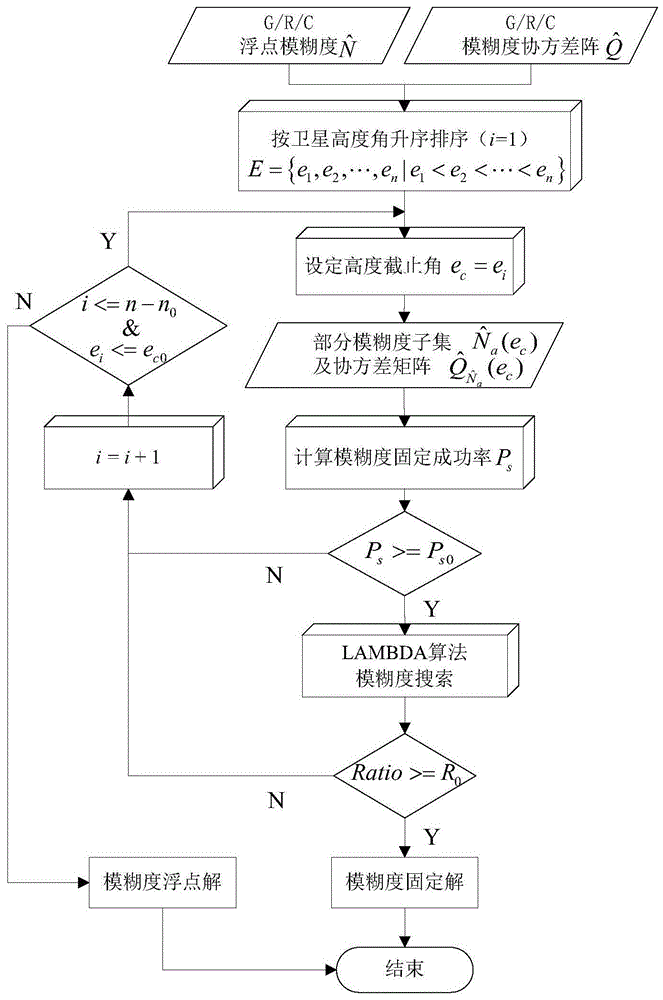
The invention discloses a quick resolving method for multi-constellation long-base-line network RTK partial ambiguity. After combination of multiple systems, it is hard to obtain accurate integer values of all ambiguities at the same time through resolving due to the influence of observation noise, atmosphere residual errors and other factors; especially for a long base line, the problem is intensified by complexity of atmosphere errors. According to the method, the three-step resolving strategy of wide-lane ambiguity solution, ionized-layer-free ambiguity solution and basic ambiguity fixing is adopted, in the basic ambiguity fixing process, a partial ambiguity fixing method with cut-off satellite elevation, the ambiguity searching prior success rate and Ratio values as main parameters is provided, and quick and accurate fixing of network RTK long-base-line ambiguity is achieved through an optimized partial ambiguity fixing subset. By means of the quick resolving method, the prior success rate and Ratio values can be obviously improved in the ambiguity fixing process, and therefore time needed by ambiguity fixing between network RTK base stations is shortened.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
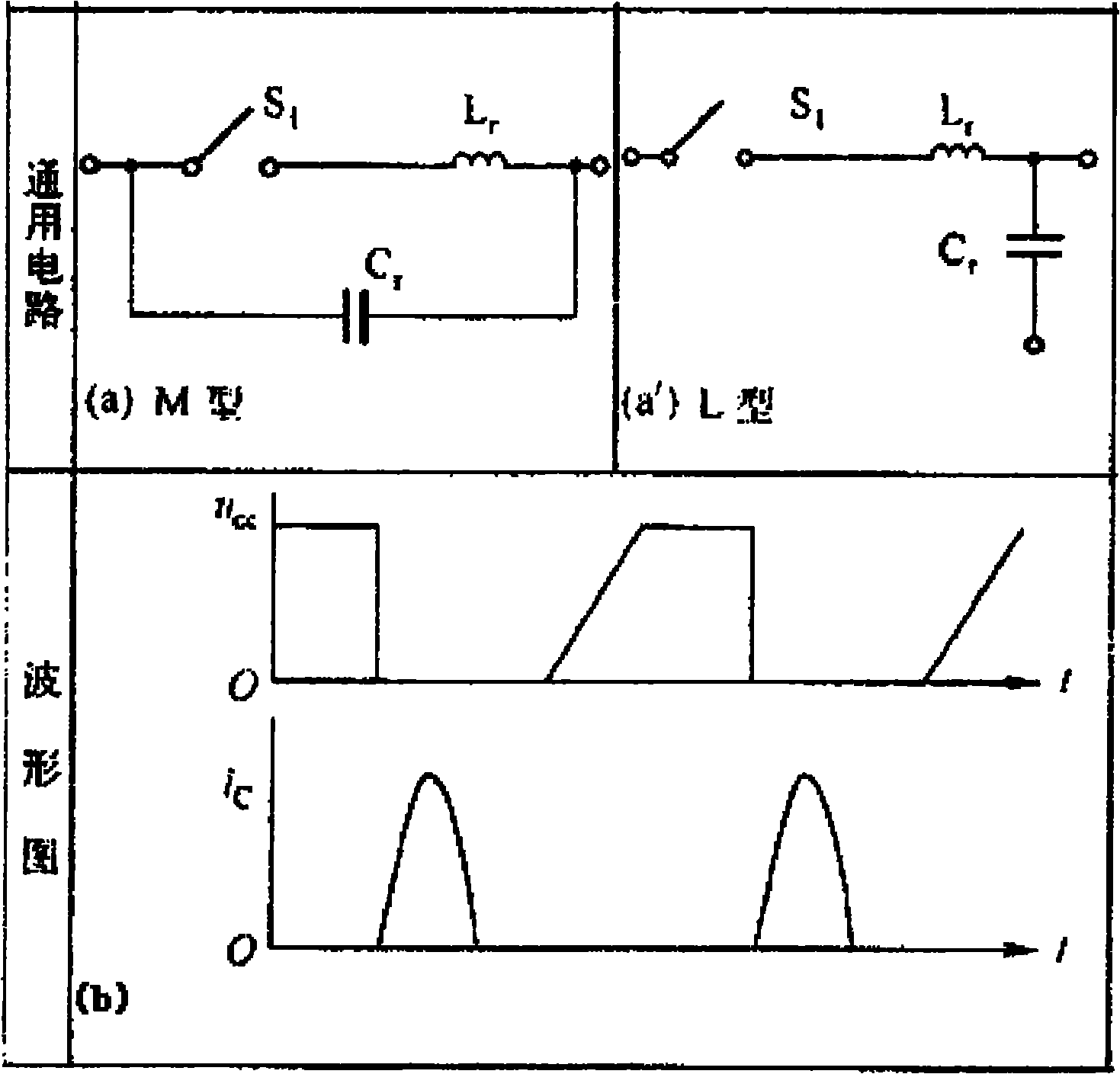
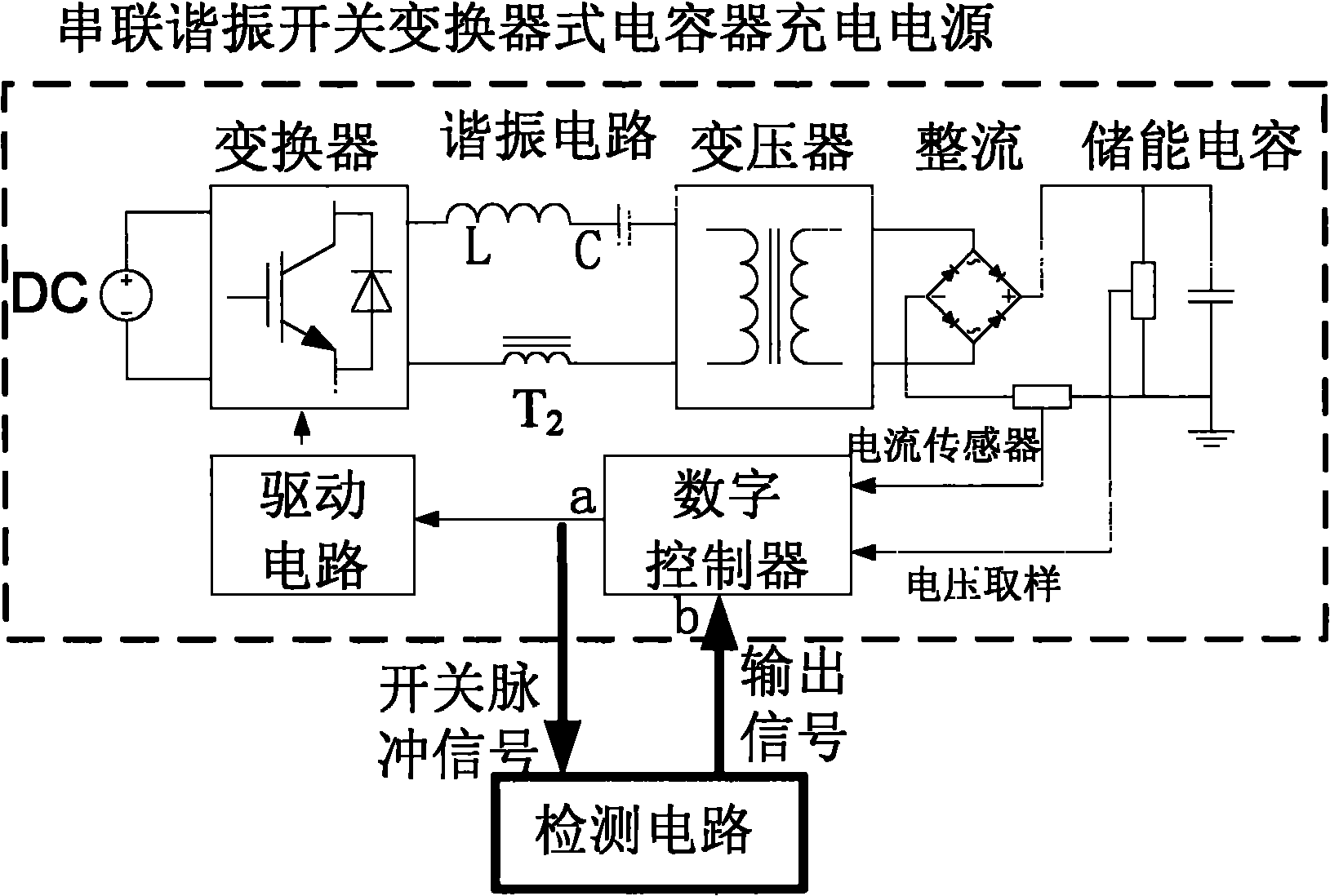
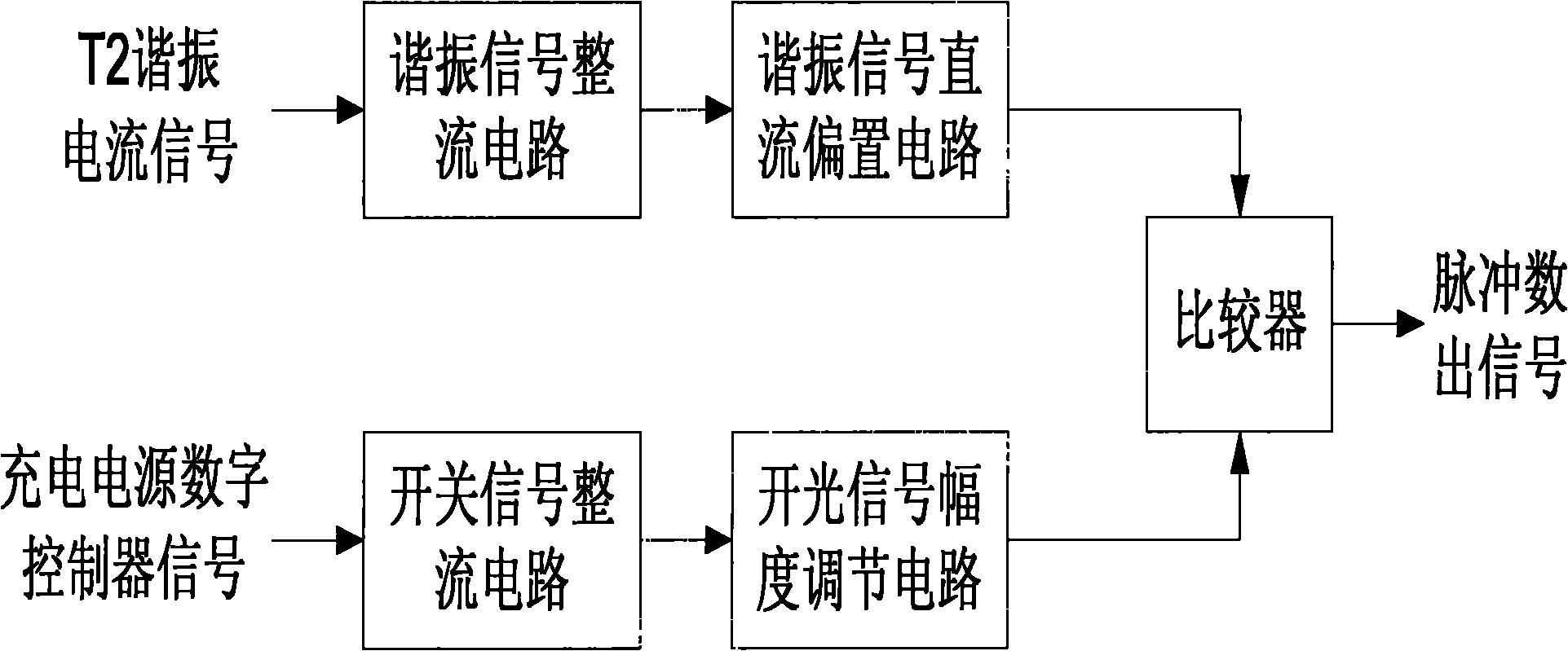
Zero current detection circuit for series resonance charging source and design method thereof
InactiveCN102023286AImprove efficiencyEliminate latency effectsCurrent/voltage measurementPower supply testingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to a detection circuit for charging source working state and a design method thereof, particularly to a zero current detection circuit for a series resonance charging source and the design method thereof. The invention solves the problem of the prior art that the converter switch nonzero turn-off is caused by the capacitor charging source resonant frequency drift designed based on series resonance switch convertor technique. The invention provides a detection circuit guiding a series resonance convertor type capacitor charging source convertor switch to keep working under the condition of zero current. The technical scheme is that a resonance voltage signal is generated by rectifying a resonance current signal and bias adjusting direct current, an amplitude-adjustable threshold voltage is generated by rectifying a convertor switch signal of the charging source, and the resonance voltage signal and a switch voltage signal are sent to a comparator so as to treat correspondingly according to a comparison result. The invention is mainly applied to the situation at zero current switch state in the design process of a series resonance convertor type capacitor charging source.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
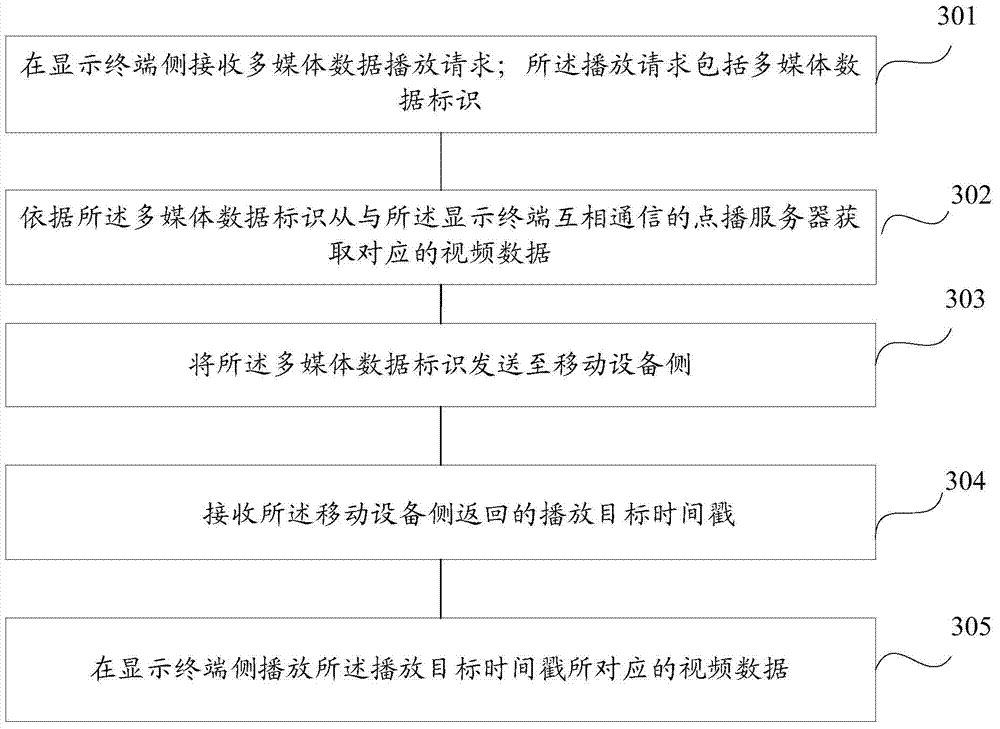
Video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment
ActiveCN103905881AEasy to operateRealize synchronous playbackSelective content distributionWireless transmissionTimestamp
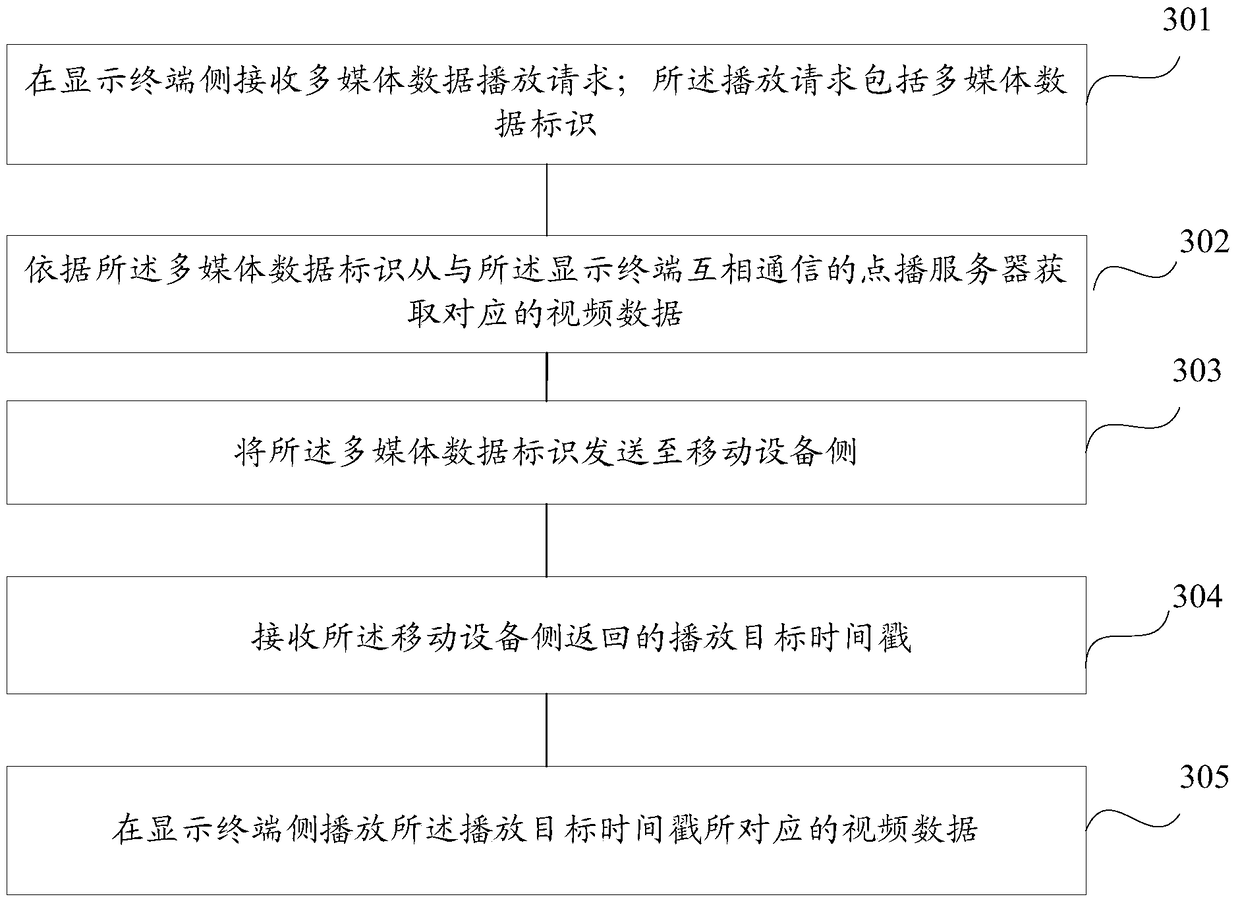
The embodiment of the invention provides a video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment. The method includes the steps that a multimedia data playing request is received on a display terminal side; the playing request comprises multimedia data identification; by depending on the multimedia data identification, corresponding video data are acquired from a request-playing server in communication with the display terminal side; the multimedia data identification is transmitted to a mobile device side; the display terminal side is connected with the mobile device side in a wireless transmission mode; playing object timestamps returned by the mobile device side are received; the playing object timestamps are timestamps generated according to currently-played audio timestamps when the audio data are played by the mobile device side; the video data corresponding to the playing object timestamps are played on the display terminal side. With the video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and the equipment, synchronized playing of the audio data and the video data is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
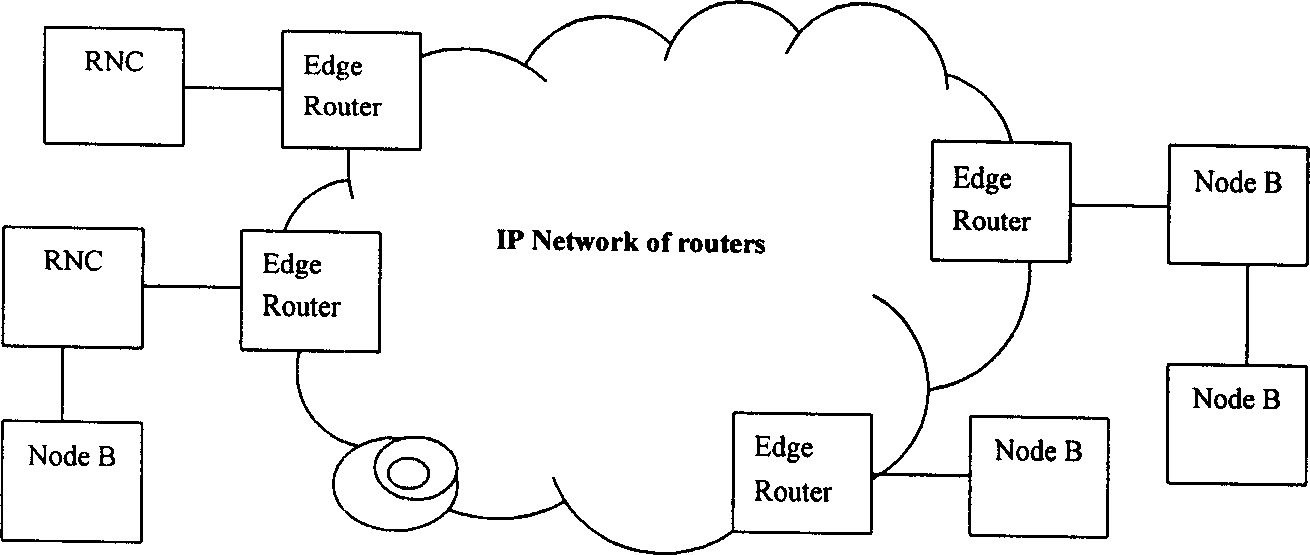
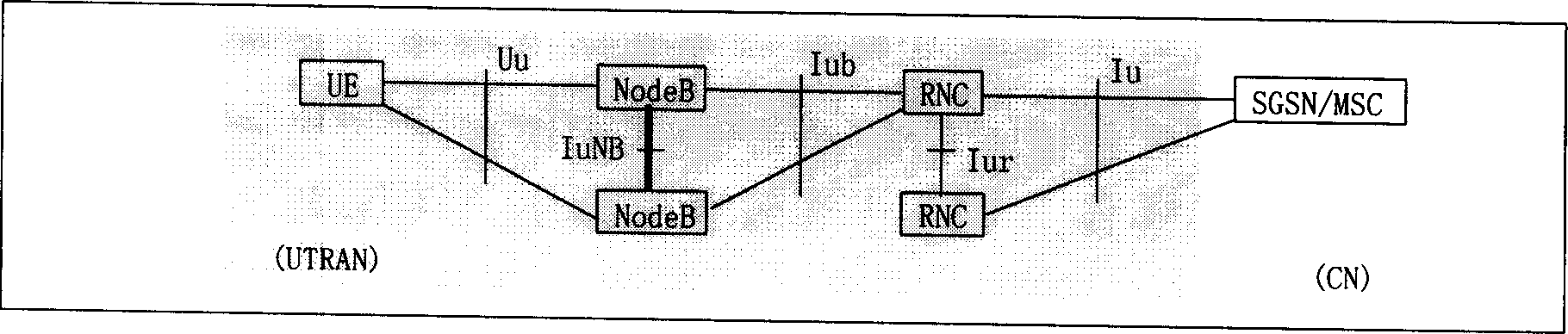
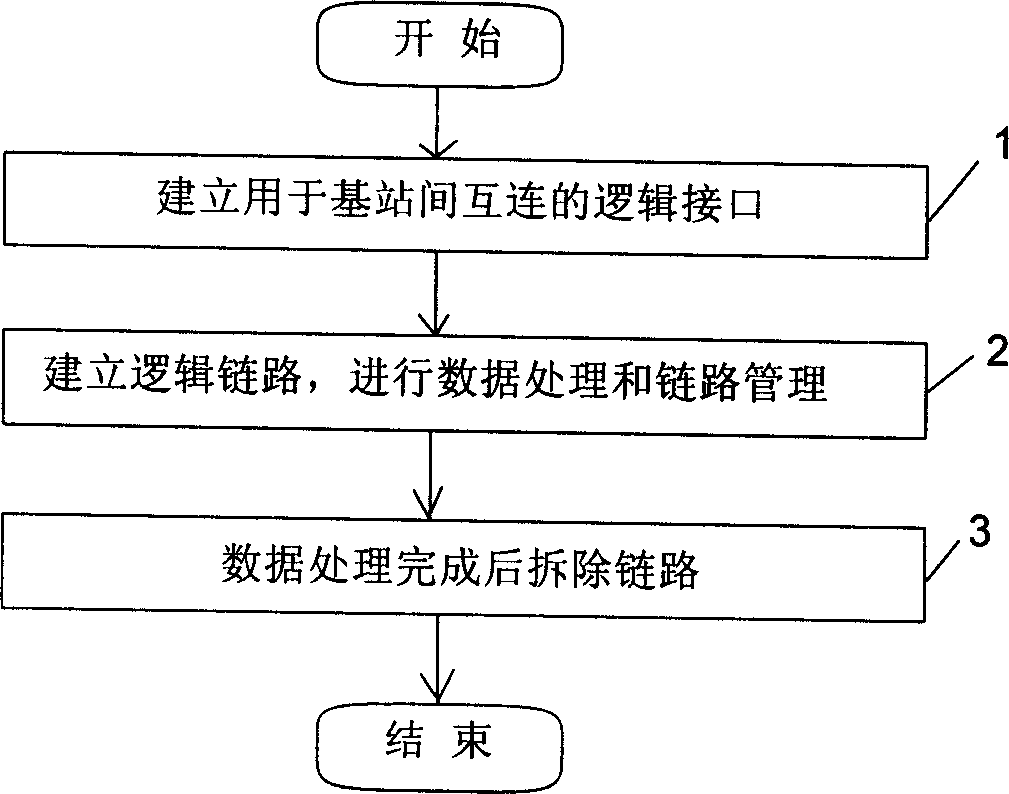
Method of implementing direct communication between base stations
InactiveCN1414804AReduce data processing burdenEliminate latency effectsWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBusiness managementStructure of Management Information
A method to realize the direct communication on data and signalling between the base stations includes the logic interface IuNB used for interconnections between the base stations and its supporting on the transmission of data and signalling between two base stations as well as fulfilling the management and maintenance of transmission network, business management of transmission channel and interface resources between the base stations, setting up the logic link between two base stations through above-mentioned interface and using it for finishing the transmission and management function of data and signalling, releasing the logic link between the base stations at last, and the said method also establishing the protocol stack between the control face of abovesaid IuNB interface and user face.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
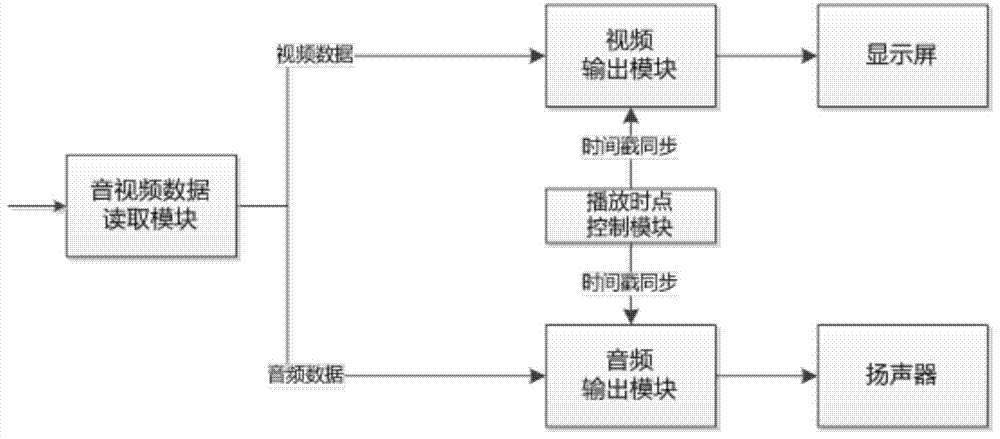
Video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment
InactiveCN103905878AEasy to operateAvoid buyingSelective content distributionComputer hardwareWireless transmission
The embodiment of the invention provides a video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment. The method includes the steps that multimedia data are received on a display terminal side; the multimedia data comprise video data and audio data; the video data carry one or more video timestamps; the audio data are sent to a mobile device side; the display terminal side is connected with the mobile device side in a wireless transmission mode; when the video data are played, playing object timestamps are generated according to currently-played video timestamps; the playing object timestamps are sent to the mobile device side; the mobile device side is used for playing the audio data corresponding to the playing object timestamps. With the video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and the equipment, the constraint caused when wired earphones are directly connected with a display terminal can be gotten rid of by a user, operation of the user is facilitated, and synchronized playing of the audio data and the video data is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
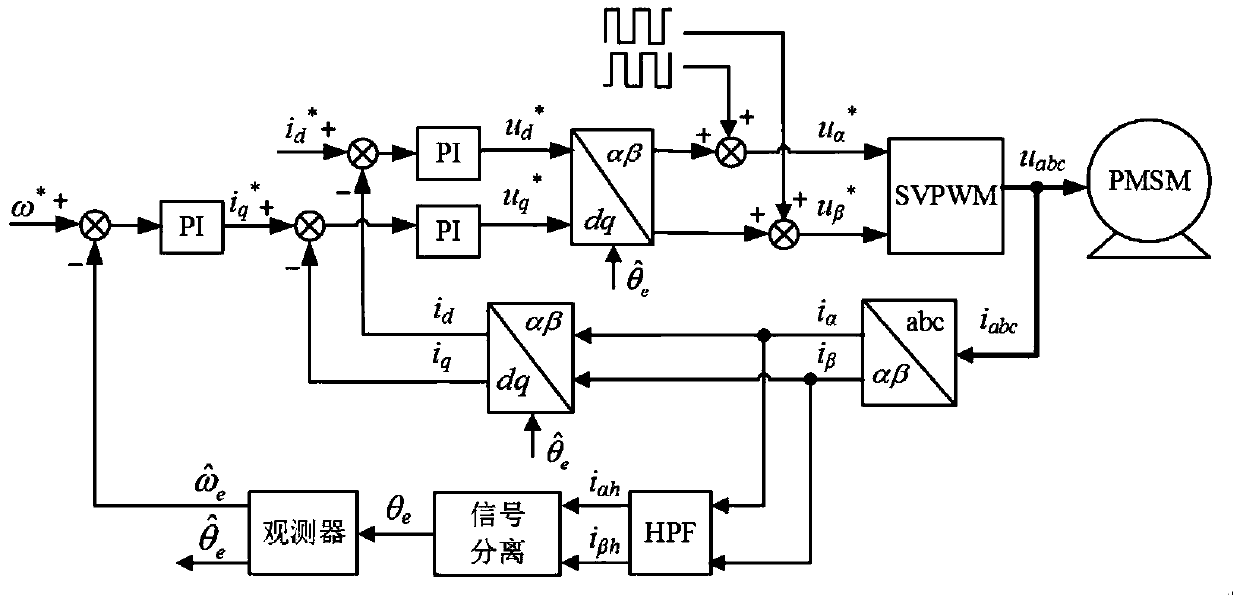
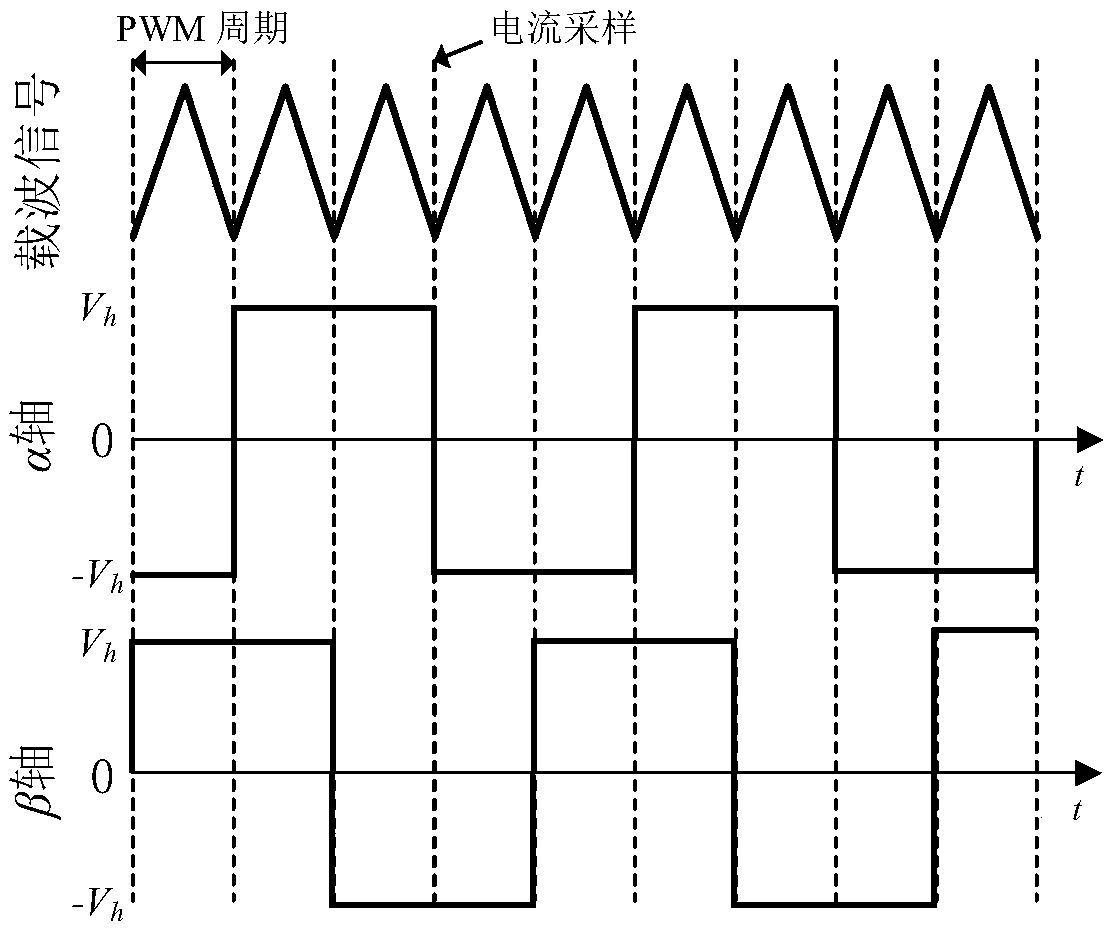
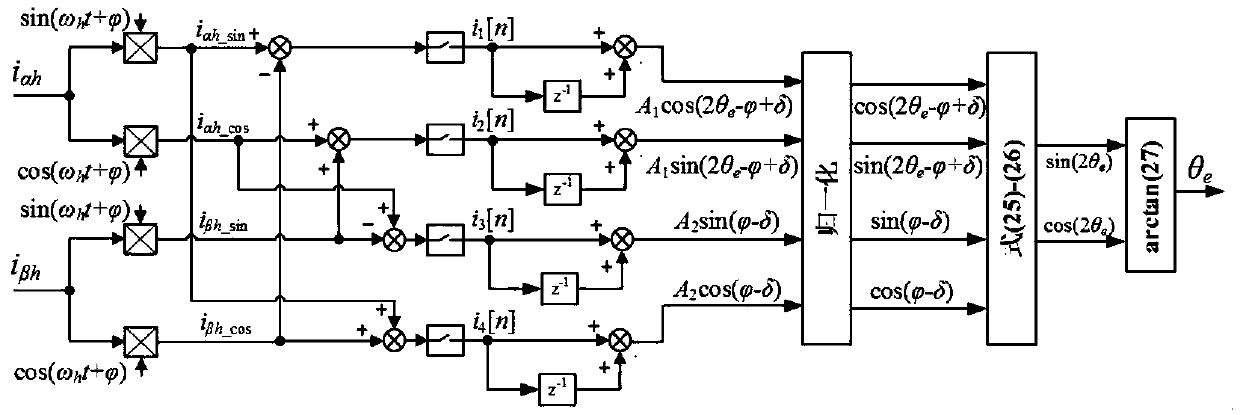
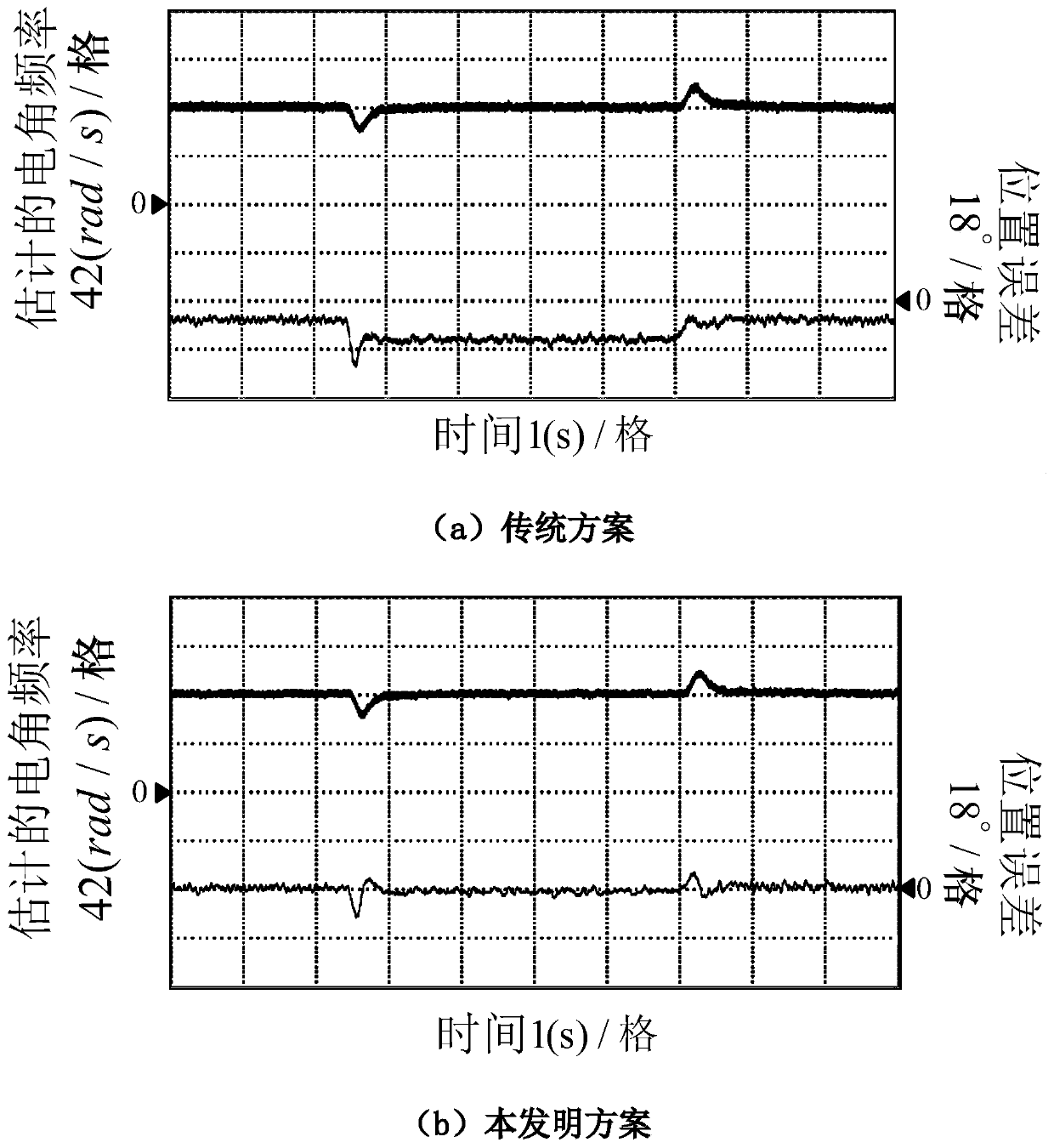
Sensorless control method of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN108847795AHigh precisionImprove controllabilityElectric motor controlVector control systemsLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a sensorless control method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and aims to solve the problems of instability and negative influences caused by a digital filter and systemdelay in a voltage injection method used in the traditional zero-low-speed process in the sensorless control of a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor. The sensorless control method comprises the steps that 1, the operating process of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is controlled by a microprocessor, and a high-frequency orthogonal square-wave voltage is injected into a static shaftsystem of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; 2, according to the high-frequency current information extracted in the static shaft system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a signal processing link of a discrete sequence is designed, and the negative effects of the digital filter and a digital control system are considered and eliminated; and 3, a position observer is designed, so thatthe position and the rotating speed of a rotor are obtained for performing motor rotating speed and current closed loop control, so that sensorless control is realized. The invention is used for thetechnical field of motor control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
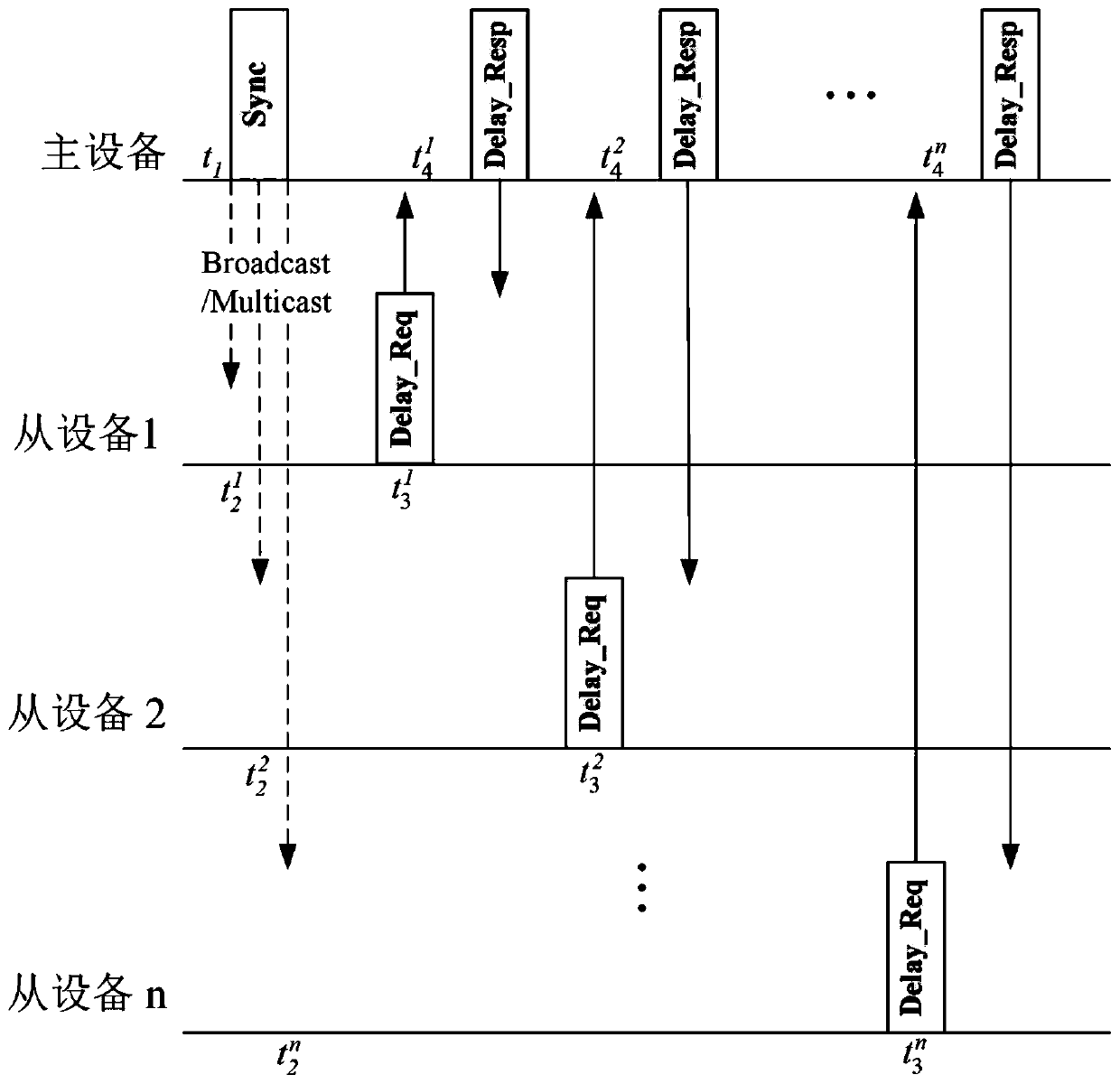
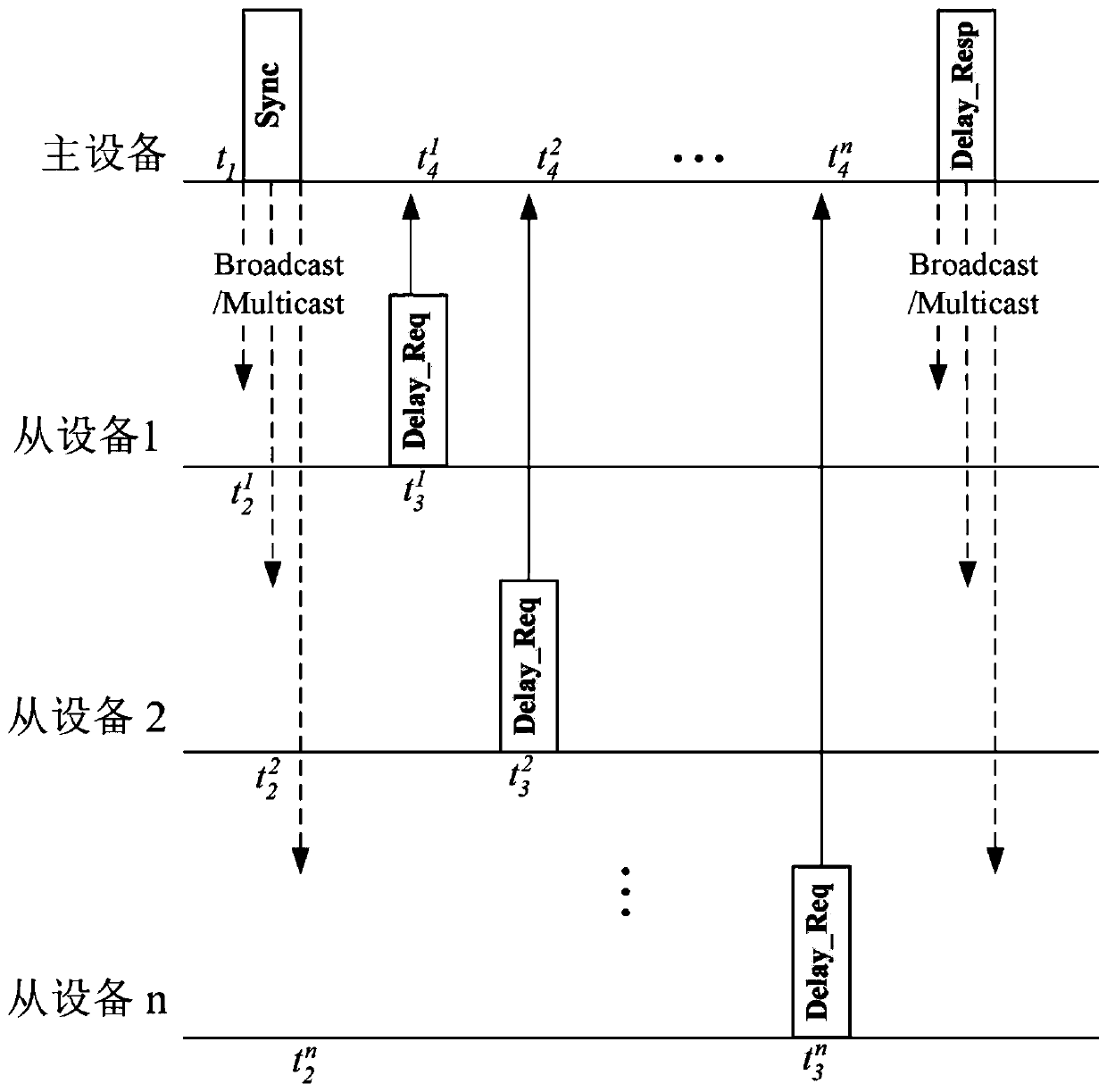
Wireless network accurate time synchronization method
InactiveCN110401505AHigh synchronization accuracyReduce Uncertain JitterSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime informationData synchronization
The invention discloses a wireless network accurate time synchronization method. The method comprises the following steps: taking a clock of main equipment as a reference clock; the master device sending a message to each slave device in a broadcast or multicast form or by using an MU-MIMO technology; exchanging messages carrying time information between a master device and slave devices twice ormore, each slave device determining time offset between the slave device and the master device according to the time information carried by the messages, and adjusting local clocks according to the time offset, so that the respective clocks are in time synchronization with the master device. According to the invention, each slave device can calibrate its own clock according to the calculated clockand respectively complete time synchronization with the master device, so that time synchronization among all devices in the whole local area network is realized, and a traditional point-to-point communication mode is replaced by a broadcast or multicast mode, so that the time synchronization efficiency is improved. The timestamp is completed in the wireless device driving layer, the influence ofuncertain jitter and delay is reduced to the maximum extent without additional hardware support, and the synchronization precision is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
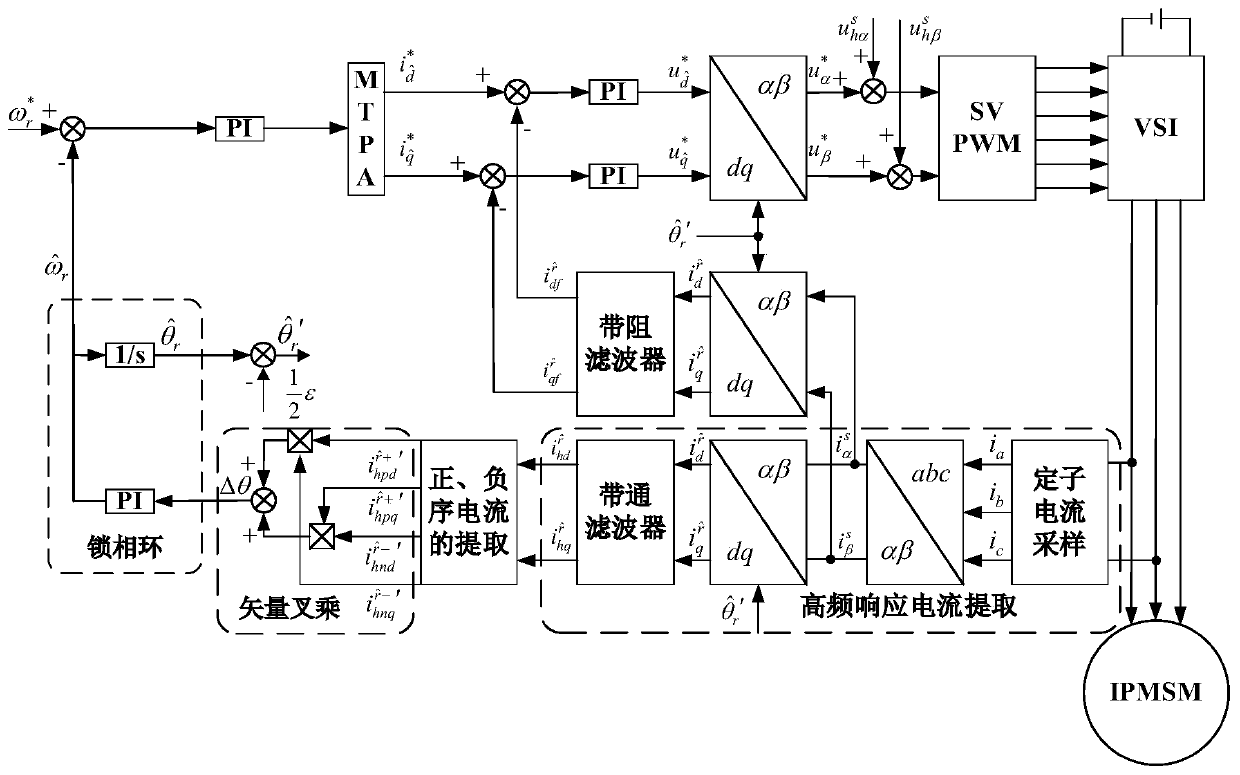
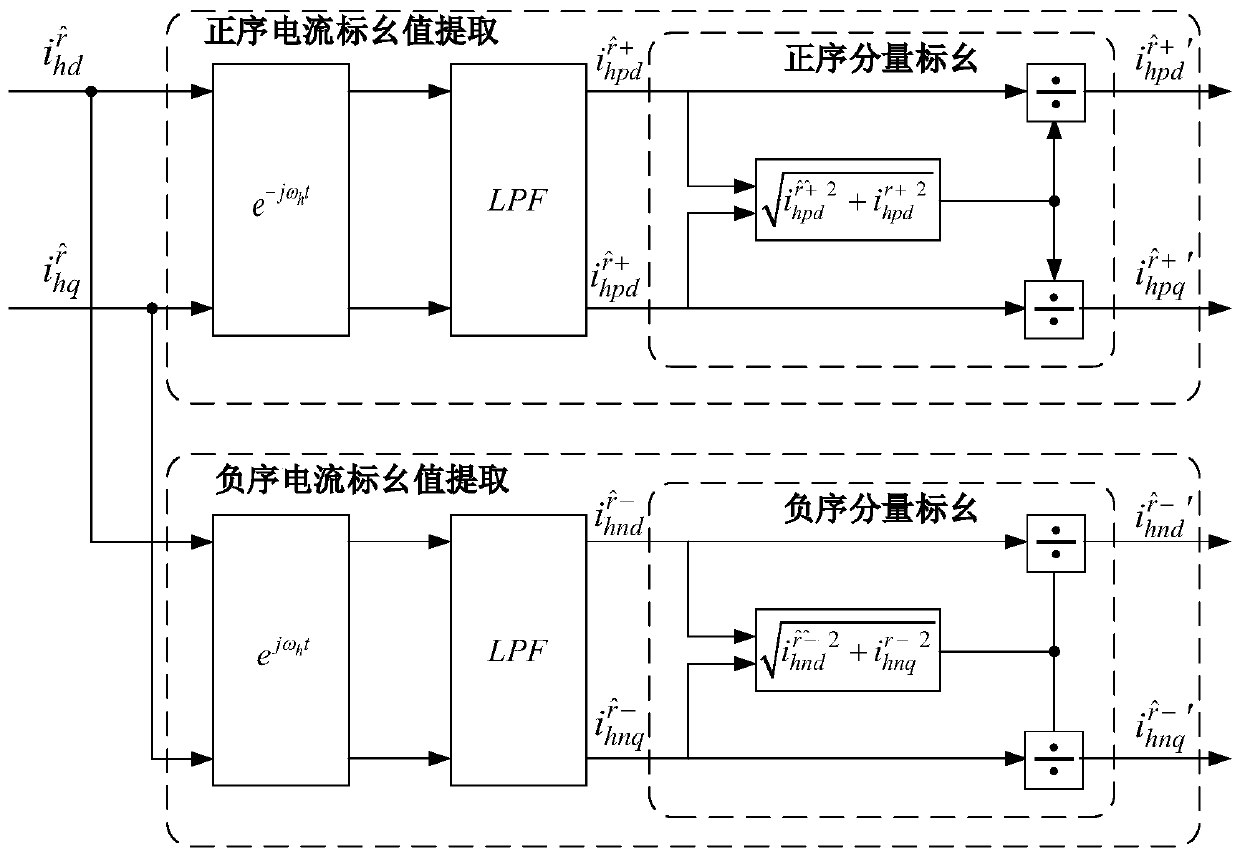
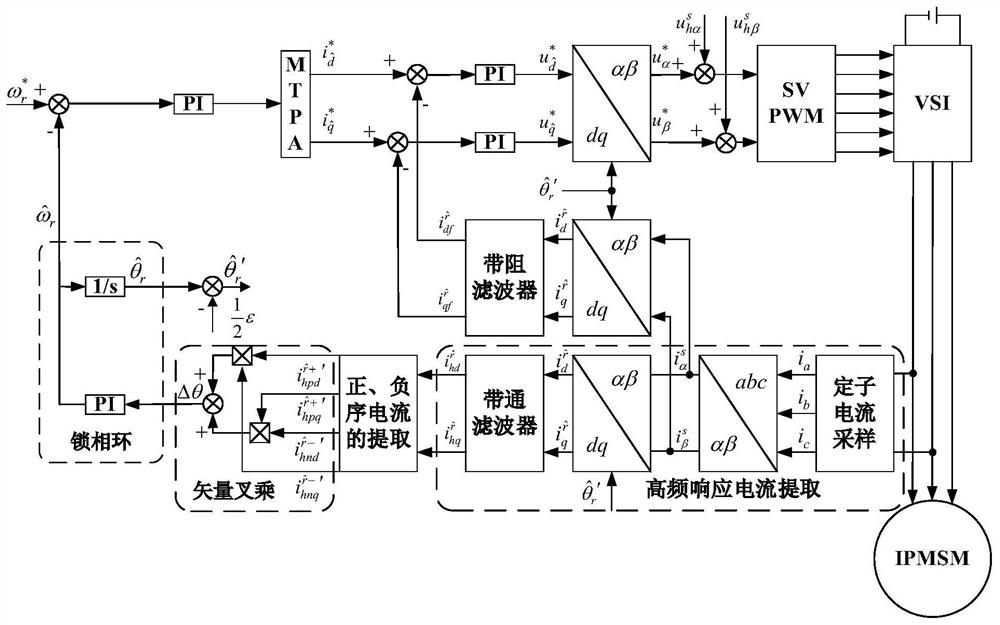
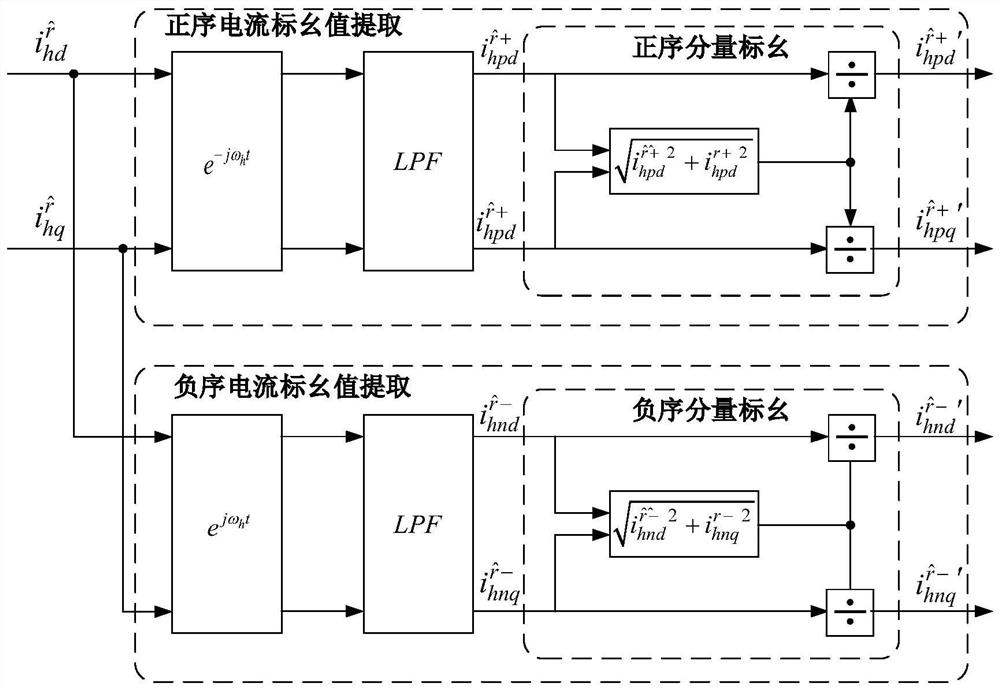
IPMSM position observation method and system based on rotary high-frequency injection method, and driving system
ActiveCN109889117AHigh Position Observation AccuracyReduce design requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLow speedLow-pass filter
The invention discloses an IPMSM position observation method based on a rotary high-frequency injection method. The method comprises the following steps that a high-frequency voltage signal is injected into a motor static alpha beta coordinate system after the motor finishes initial position detection; a stator current sampling module is used for performing sampling to obtain three-phase currentsof the motor, and conversion is carried out to obtain an estimated d-q coordinate axis; namely, target currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in a shafting which is a formula as shown in the specification; the target currents which are formulas as shown in the specification are subjected to band-pass filter extraction to obtain high-frequency response currents which are formulasas shown in the specification in a coordinate system which is a formula as shown in the specification; the positive sequence components of the high-frequency response currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in the axis of a formula which is as shown in the specification are extracted through transformation of coordinates and a low-pass filter, and the positive sequence current component per-unit unit processing is carried out; the negative sequence components of the high-frequency response currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in the axis of a formula which is as shown in the specification are extracted through transformation of coordinates and a low-pass filter, and the negative sequence current component per-unit value processing is carried out; andthe obtained high-frequency positive sequence current per-unit value and the high-frequency negative sequence current per-unit value are subjected to vector fork multiplication, and the estimated motor rotating speed and position are obtained. The invention further provides an observation system and an IPMSM driving system. The method has the advantages that no matter whether the IPMSM driving system runs at zero speed or a low speed, relatively high position observation precision is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
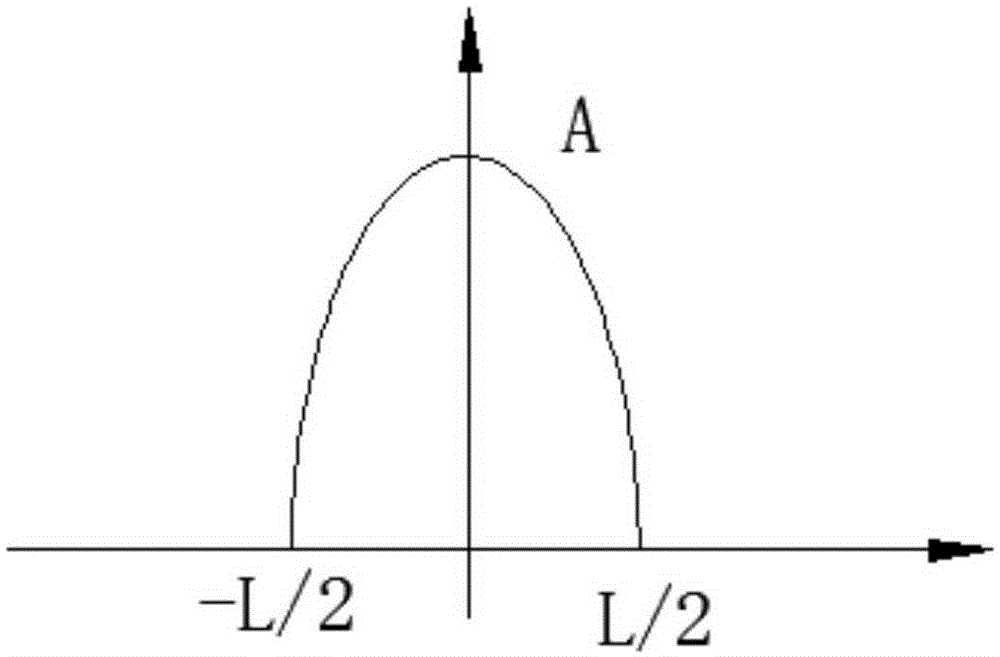
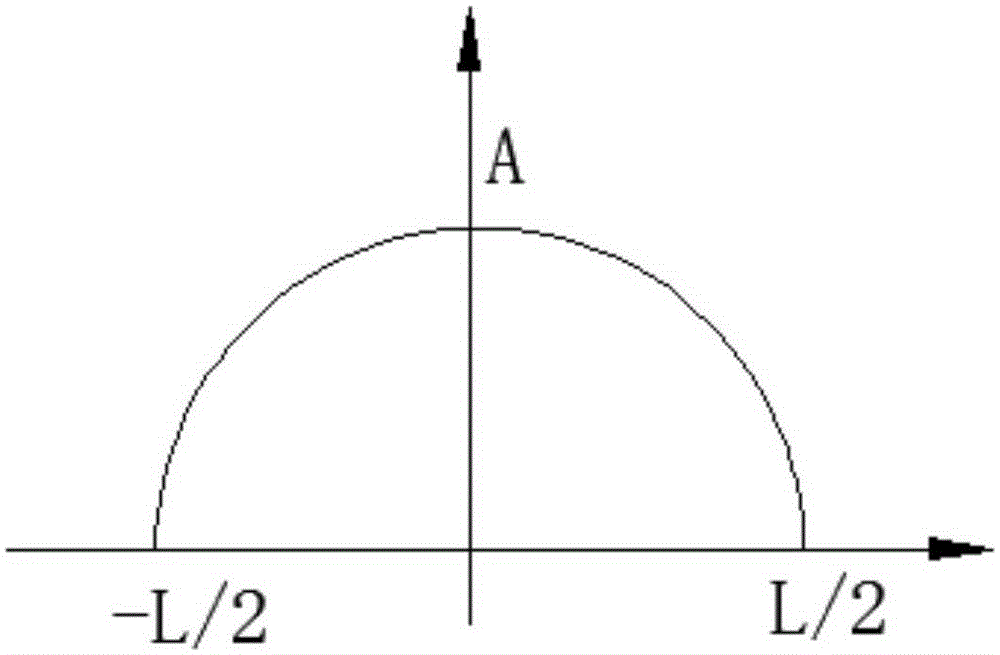
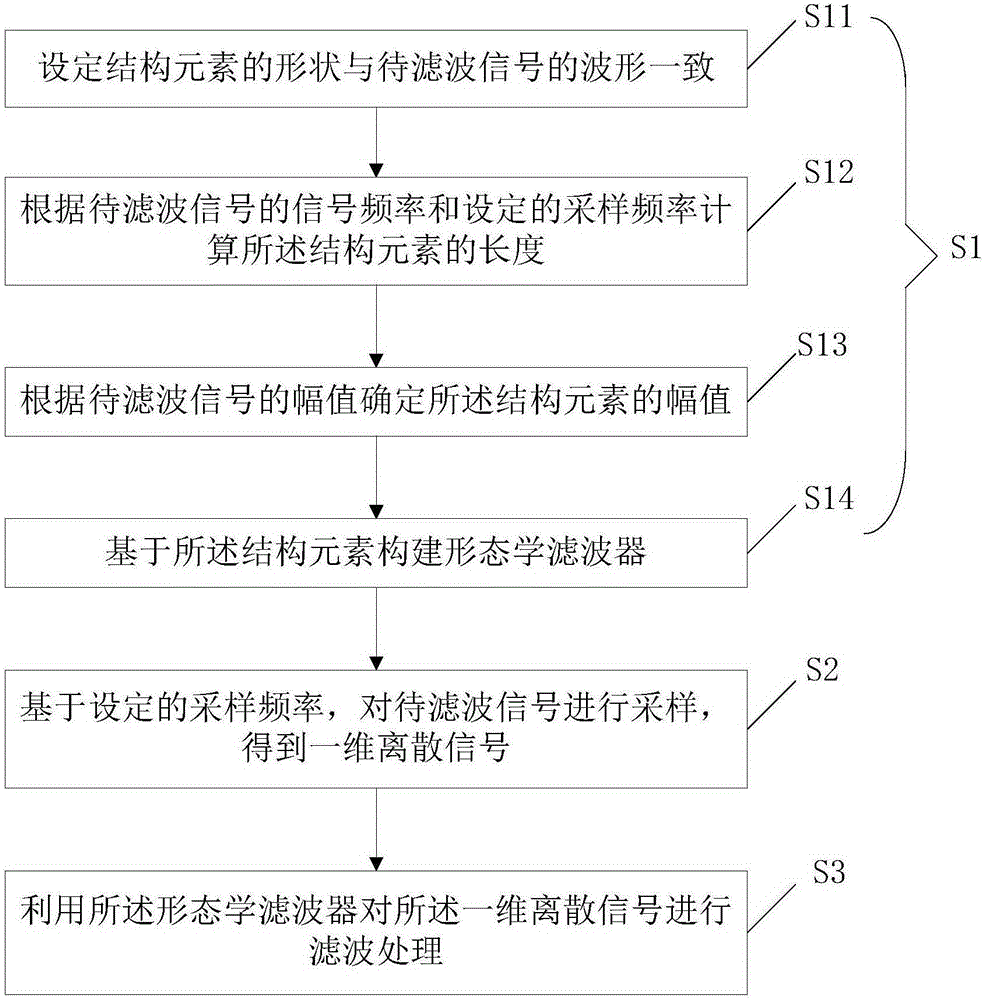
Filtering method based on mathematical morphology and filtering system thereof
ActiveCN105207645AAdaptableSuitable for engineering applicationsDigital technique networkFilter systemFilter algorithm
The invention provides a filtering method based on mathematical morphology and a filtering system thereof. The filtering method comprises the steps that S1, a morphological filter is constructed based on the selected structural elements; and the shape of the structural elements is consistent with the waveform of signals to be processed, length of the structural elements is obtained according to signal frequency of the signals to be processed and the set sampling frequency through calculation, and the amplitude of the structural elements is determined based on the amplitude of the signals to be processed; S2, sampling is performed on the signals to be processed according to the set sampling frequency so that one-dimensional discrete signals are obtained; and S3, filtering processing is performed on the one-dimensional discrete signals by utilizing the morphological filter. The structural elements are not fixed and are obtained according to signal frequency of the signals to be processed and the set sampling frequency through calculation so that the structural elements are high in adaptability and suitable for engineering application. Furthermore, erosion operation involved in filtering processing is improved through combination of length of the selected structural elements and concretely improved into (fthetag)(n)=min[f(n+m-L-g(m)] so that intrinsic delay in a filtering algorithm can be eliminated and the filtering effect can be enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU INOVANCE TECH CO LTD
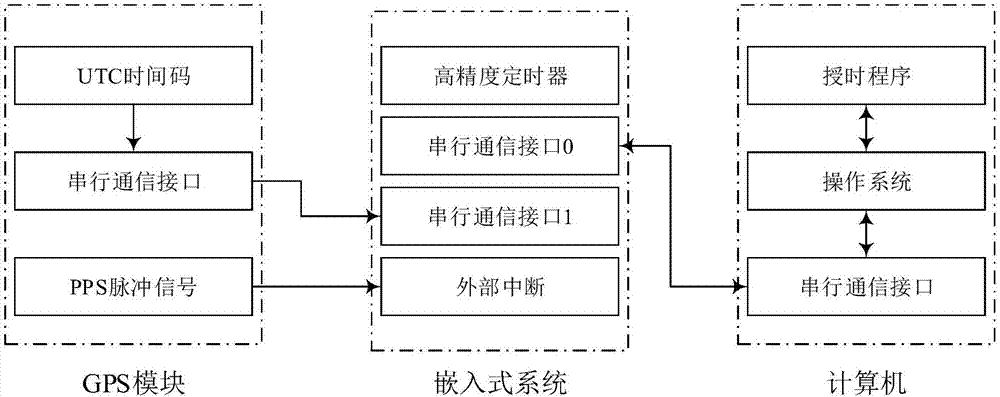
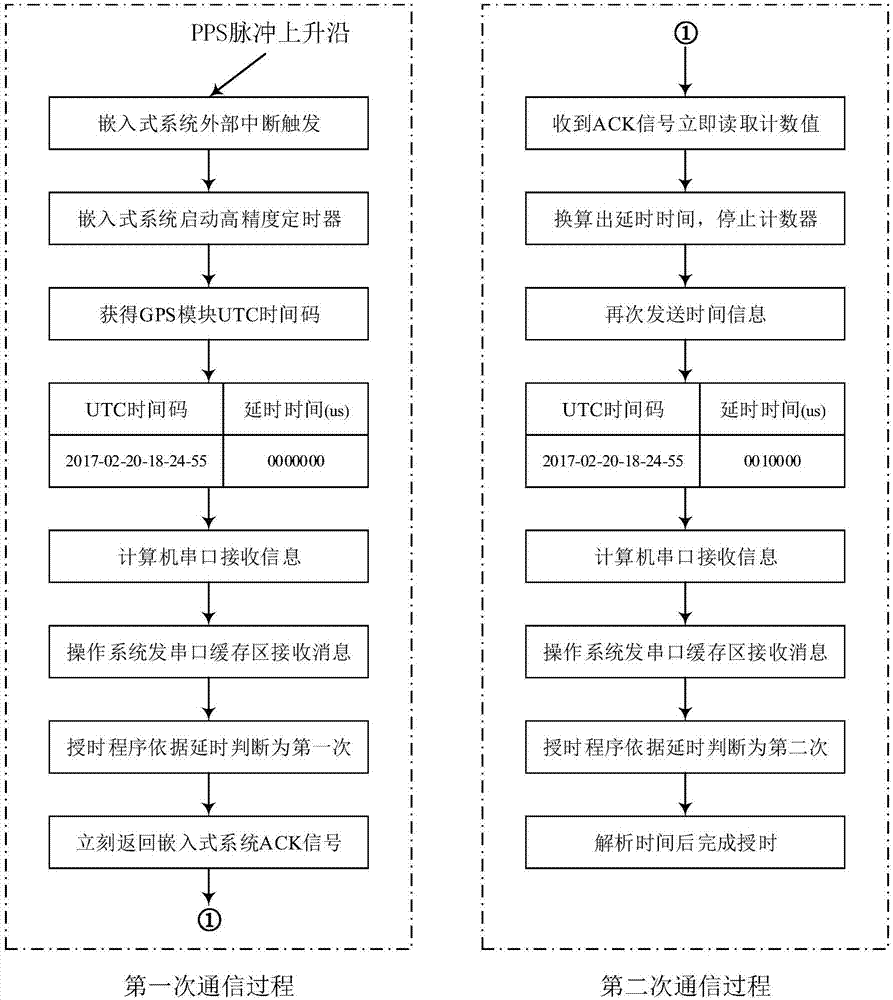
Computer accurate timing method based on GPS module and embedded system and realization system of computer accurate timing method
InactiveCN107229219ARealize time serviceAccurate timingRadio-controlled time-piecesNon real timeOperational system
The invention relates to a computer accurate timing method based on a GPS module and an embedded system and a realization system of the computer accurate timing method. According to the method, the GPS module generates UTC time codes and PPS signals in real time; the external interrupt of the embedded system obtains the PPS signals emitted by the GPS module; the embedded system communicates with a computer; and the embedded system is utilized to calculate communication process time delay and computer system time delay, the communication process time delay and the computer system time delay are added, so that accurate time can be obtained. According to the method and the system of the invention, the embedded system is used because the embedded system has the advantages of high real-time performance, portability and low cost. Since the real-time performance of the embedded system is high, the embedded system can be utilized to accurately record time delay caused by the non-real-time performance of a computer operating system; and since the embedded system is low in cost and is convenient to carry, the method can be conveniently applied to special work environments such as field work environments.
Owner:SHANDONG CHAOYUE DATA CONTROL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
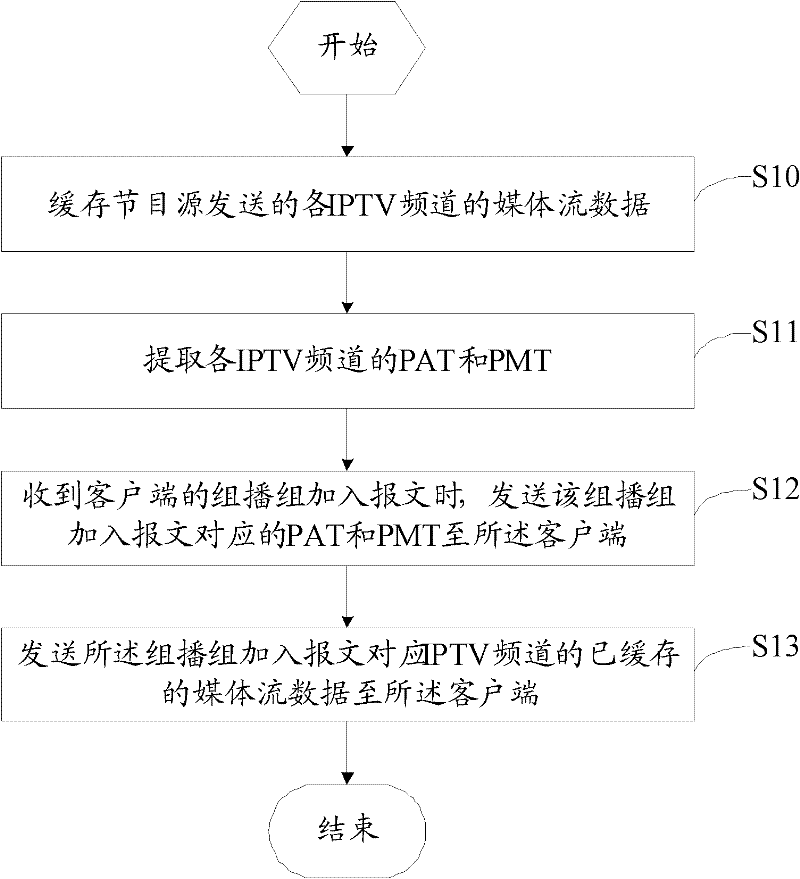
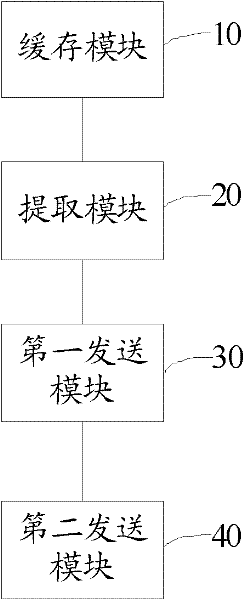
IPTV channel switching method and apparatus thereof
The invention reveals an IPTV channel switching method. The method comprises the following steps: buffering media stream data of all IPTV channels, wherein the data are sent by a program source; extracting program associate tables (PATs) and program mapping tables (PMTs) of the all IPTV channels; sending a PAT and a PMT to a client after reception of an added message of a multicast group of the client, wherein the PAT and the PMT correspond to the added message of the multicast group; and sending the buffered media stream data of the IPTV channel to the client, wherein the IPTV channel corresponds to the added message of the multicast group. Besides, the invention also provides a corresponding apparatus. According to the IPTV channel switching method and the apparatus thereof provided in the invention, a switching speed of the IPTV channel is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Concurrent transmission method and system of uniform interface test of power consumption information collection system
ActiveCN107276850AImprove throughputEliminate latency effectsData switching networksCollection systemDynamic programming
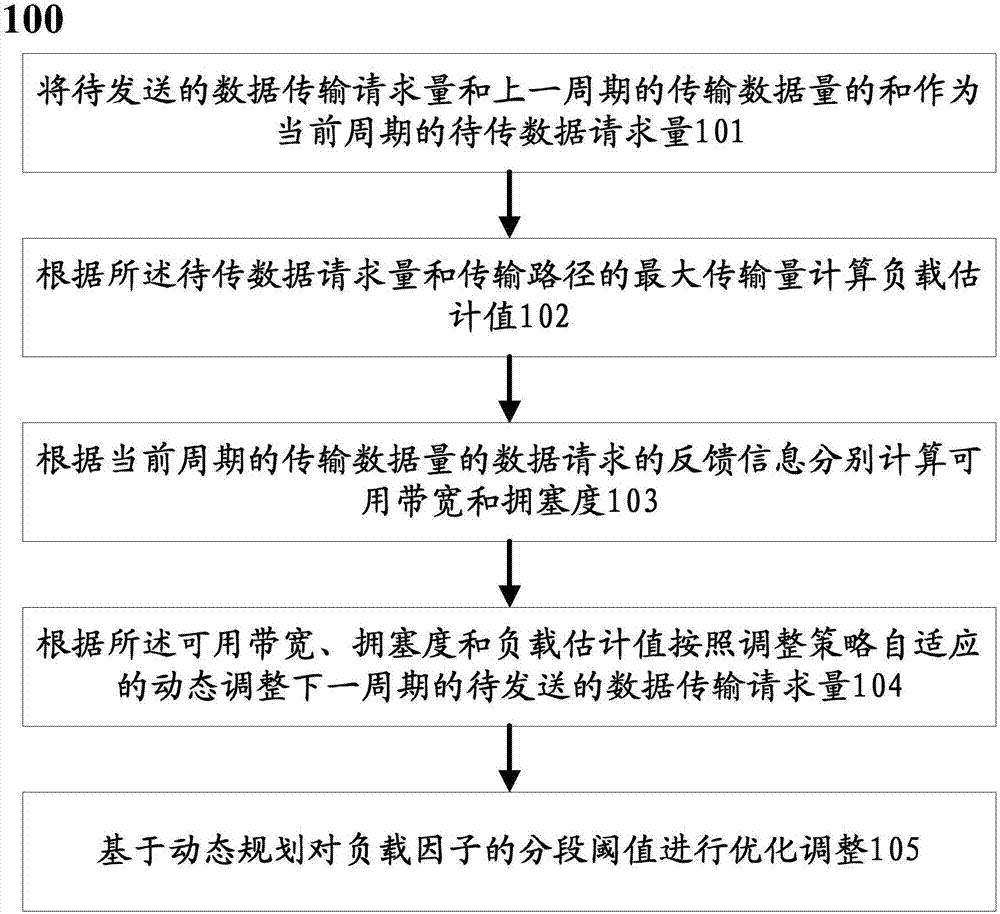
The invention discloses a concurrent transmission method of a uniform interface test of a power consumption information collection system. The method comprises the following steps: using a sum of a to-be-sent data transmission request amount and a transmission data size in a last period as a to-be-transmitted data request amount in the current period; calculating a load estimation value according to the to-be-transmitted data request amount and the maximum transmission amount of a transmission path; separately calculating an available bandwidth and a congestion degree according to the feedback information of the data request of the transmission data size in the current period; adjusting the to-be-sent data transmission request amount in the next period adaptively and dynamically according to the available bandwidth, the congestion degree and the load estimation value depending on an adjustment strategy; and performing optimization and adjustment on the segmentation threshold of a load factor based on a dynamic plan. The concurrent transmission method has the beneficial effects that the dynamic adjustment of key segmentation threshold of the data transmission request amount based on the optimum control algorithm, and the high efficiency of concurrent processing of test data is ensured.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +7
Liquid damping time delayer
ActiveCN102102725AReduce volumeEliminate latency effectsSpringsLiquid based dampersFire protectionTime delays
The invention provides a liquid damping time delayer for a fire protection safety control system. The liquid damping time delayer comprises a gas exchange device and a damping device which are connected mutually, wherein the gas exchange device comprises a gas inlet interface, a gas outlet interface, a small piston and a piston reduction end, wherein the gas inlet interface and the gas outlet interface are arranged at two ends of the gas exchange device and are communicated with the cavity of the gas exchange device; the small piston and the piston reduction end are arranged in the cavity of the gas exchange device and are connected mutually; the damping device comprises liquid, a liquid adding port, a large damping piston, a guide column, a display rod and a return spring, wherein the liquid fills in the cavity of the damping device; the liquid adding port is communicated with the cavity of the damping device; the large damping piston, the guide column and the display rod are positioned in the cavity of the damping device and are connected mutually; and the return spring is positioned at the circumference of a guiding column. By utilizing the liquid damping time delayer disclosed by the invention, the influence on time delay by the temperature can be reduced, the volume of a container can be reduced, and more reliability and safety can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINDUN FIRE FIGHTING SECURITY TECHCO
Method for reducing display unevenness of liquid crystal display panel
InactiveCN106297708ALower latencyReduce display unevennessStatic indicating devicesResistance capacitanceLiquid-crystal display
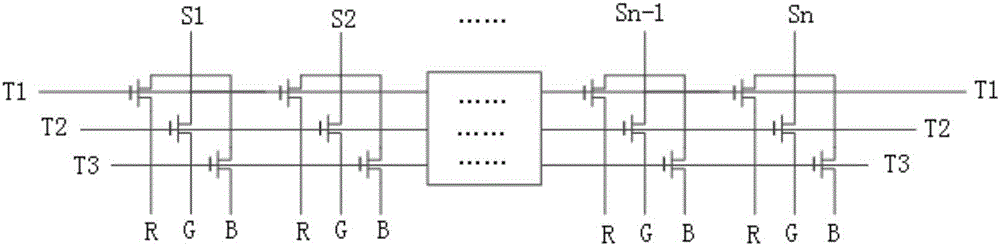
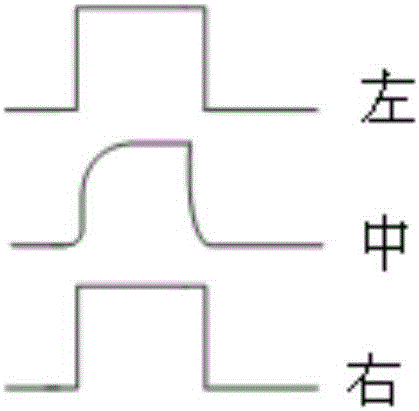
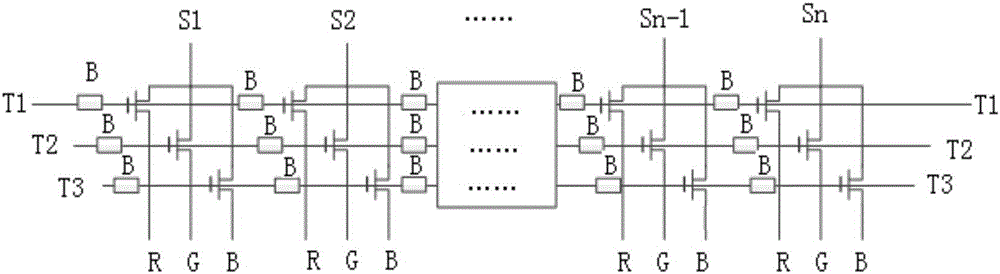
The invention provides a method for reducing display unevenness of a liquid crystal display panel. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a multipath demultiplexing circuit into multiple levels of circuits according to the demultiplexing signal transmission direction, and using a signal compensation circuit to implement signal compensation on a circuit on the post level of the demultiplexing signal transmission direction. According to the method, the signal compensation circuit is added in the multipath demultiplexing circuit to reduce delay of a drive signal after the demultiplexing signal of the multipath demultiplexing circuit passes an RC circuit (Resistance-Capacitance network), so that the phenomenon of display unevenness of the liquid crystal display panel, caused by the signal delay difference of the RC circuit, is reduced, and the display effect of the liquid crystal display panel is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
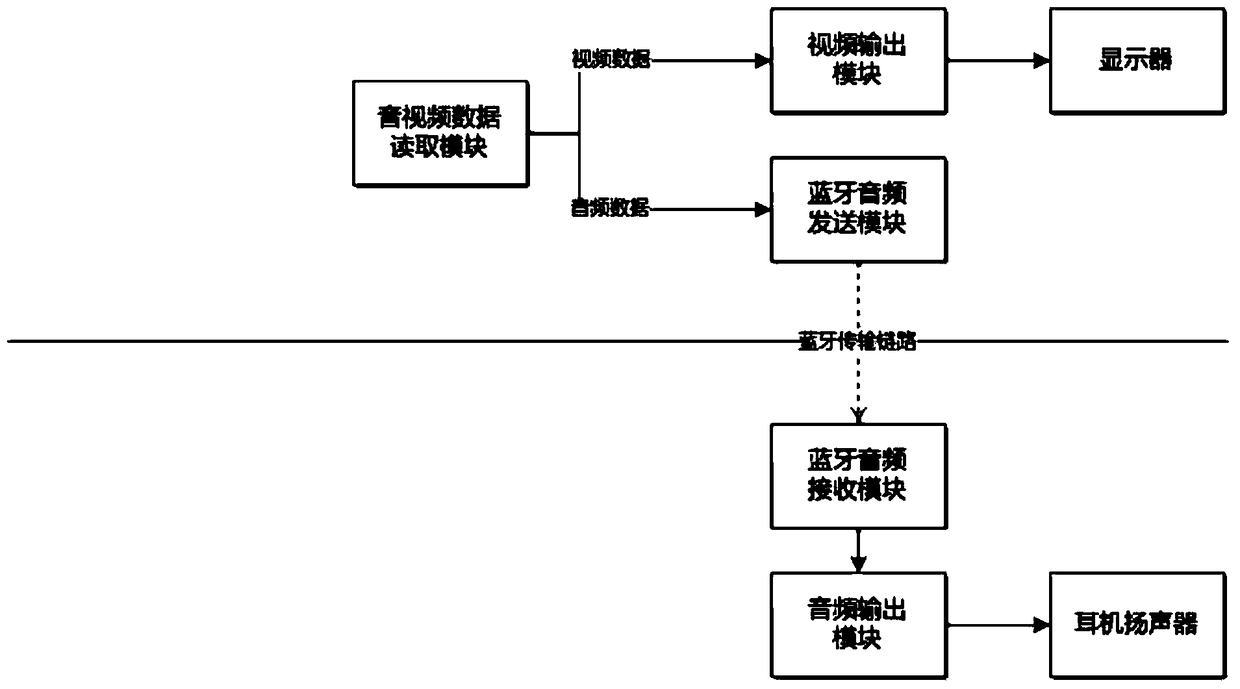
Accurate and synchronous video playing method, apparatus and device among multiple devices, and storage medium
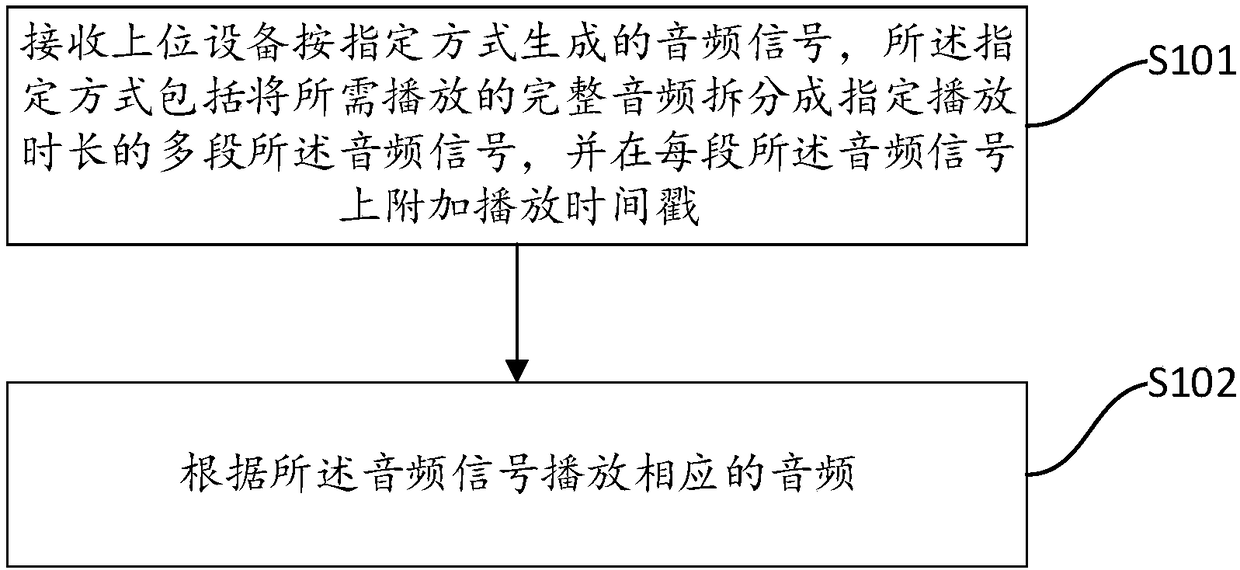
ActiveCN108495239AEliminate latency effectsReduce dependencyStereophonic circuit arrangementsLoudspeaker signals distributionTimestampMultiple device
The invention discloses an accurate and synchronous video playing method, apparatus and device among multiple devices, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: receiving an audio signal generated by an upper device in a specified manner, wherein the specified manner comprises splitting complete audio needing to be played into multiple segments of the audio signal with specified playing time lengths, and adding a playing timestamp to each segment of the audio signal; and playing corresponding audio according to the audio signal. The accurate and synchronous video playingmethod, apparatus and device among multiple devices, and the storage medium disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that synchronous playing errors among the multiple devices are reduced, the synchronization precision is improved, an error jitter range after synchronization is small, the influence of the network delay in the synchronization process is low, the dependence on the hardware during the synchronous playing of the multiple devices is also reduced, the synchronous playing can be completed as long as the multiple devices can access each other through the network, and theversatility is high.
Owner:深圳聚点互动科技有限公司
Novel driving topology and driving method and crosstalk suppression method thereof
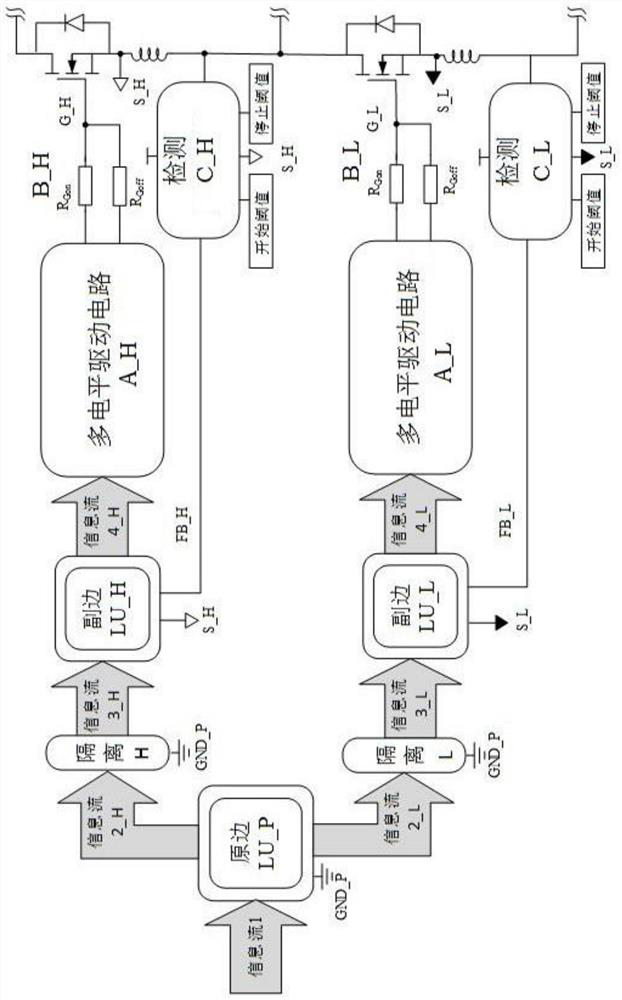
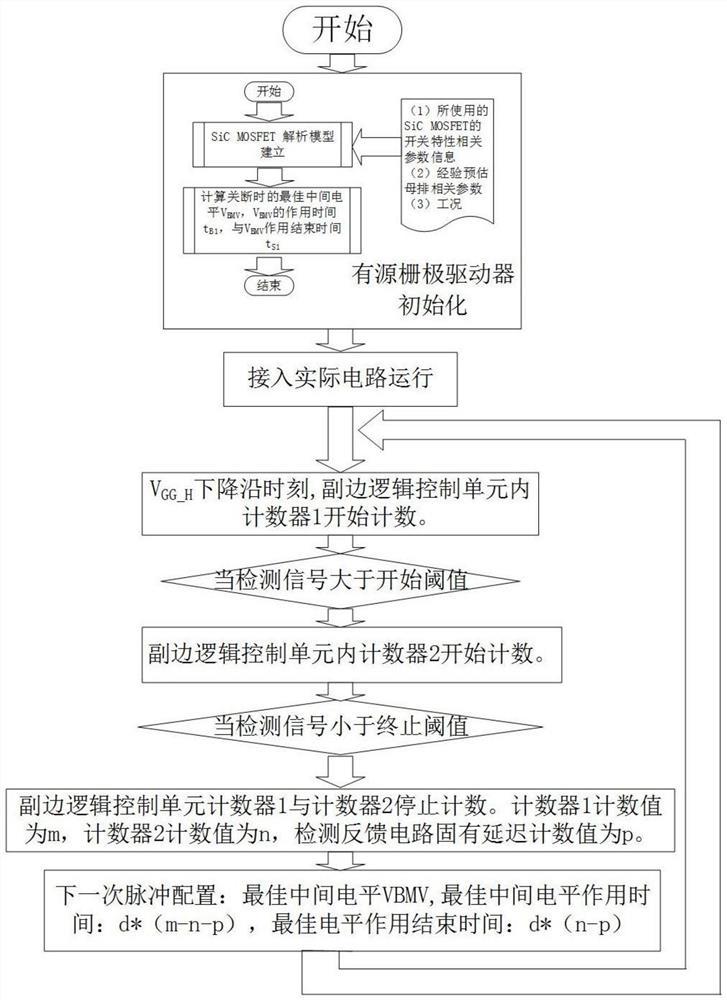
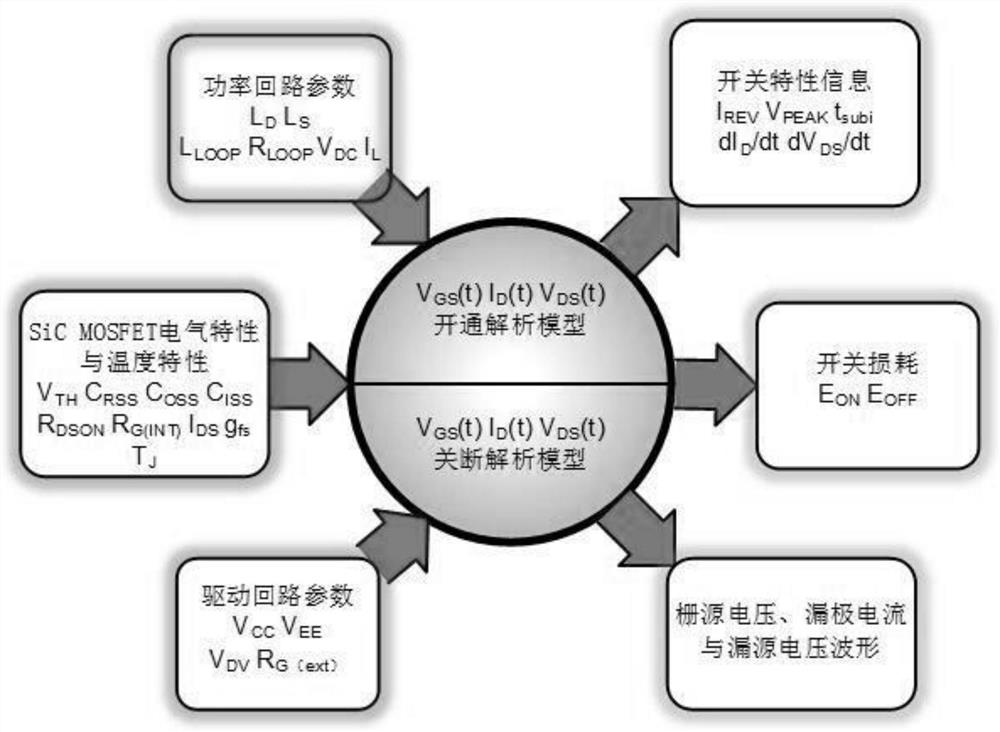
PendingCN112821730AEliminate latency effectsSuppress voltage overshootEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsOxide semiconductorDrain current
The invention discloses a novel driving topology and a driving method and a crosstalk suppression method thereof, which are suitable for a silicon carbide metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor of a half-bridge circuit. The novel driving topology comprises a primary side logic processing unit, two isolation units, two secondary side logic processing units, two multi-level driving circuits, two driving resistance networks and two turn-off drain current detection feedback circuits. According to the present invention, the next multi-level pulse signal is determined according to the feedback information of a detection circuit, the feedback self-adaption can be detected to optimize the turn-off characteristic, and the influence of inherent detection circuit hardware delay of the detection circuit is effectively eliminated through the subtraction of the secondary side logic control units. Therefore, the turn-off transient oscillation and voltage overshoot of a half-bridge circuit switching tube are suppressed. When an active tube acts, the influence of crosstalk is suppressed by adjusting the grid-source electrode level of a passive tube, so that parasitic opening and grid-source electrode negative voltage overshoot are prevented, the use reliability of the device is improved, and the service life of the device is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Time synchronization method and system
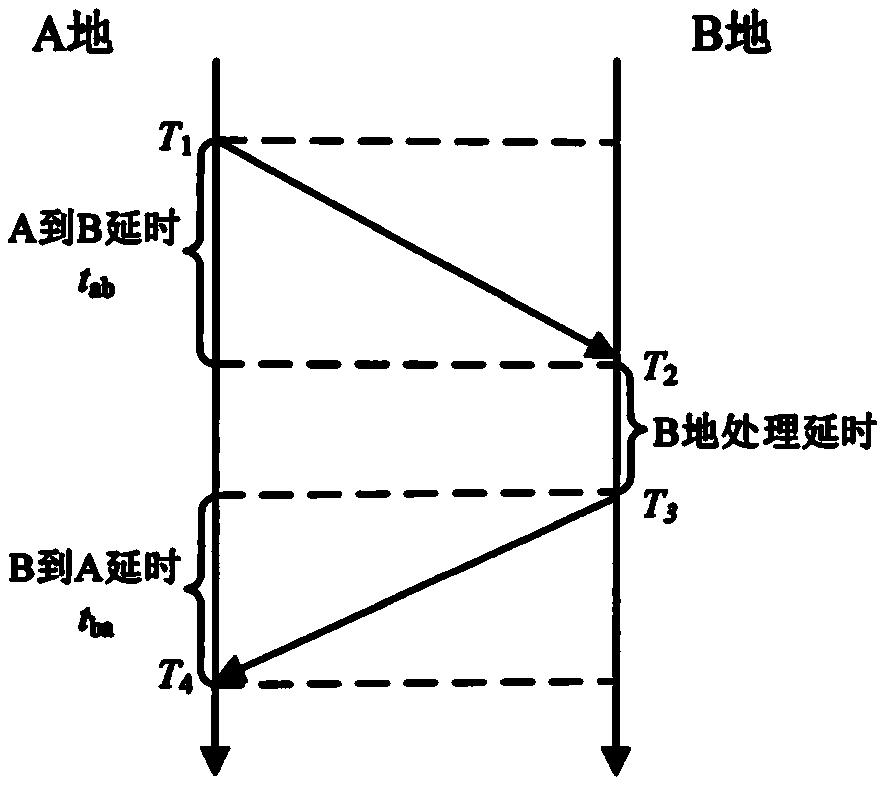
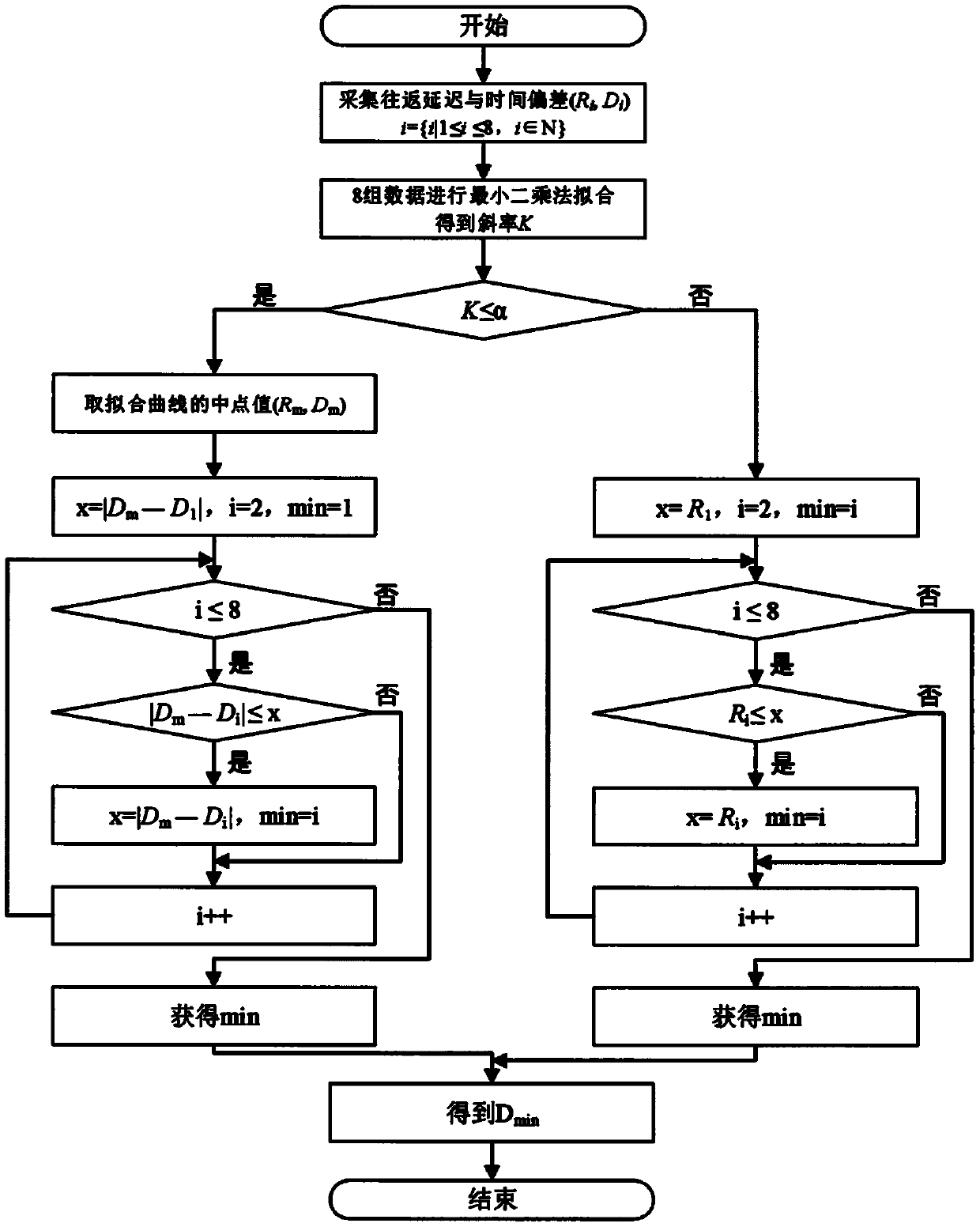
ActiveCN110278049AHigh time accuracyImprove time synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexTime deviationDelayed time
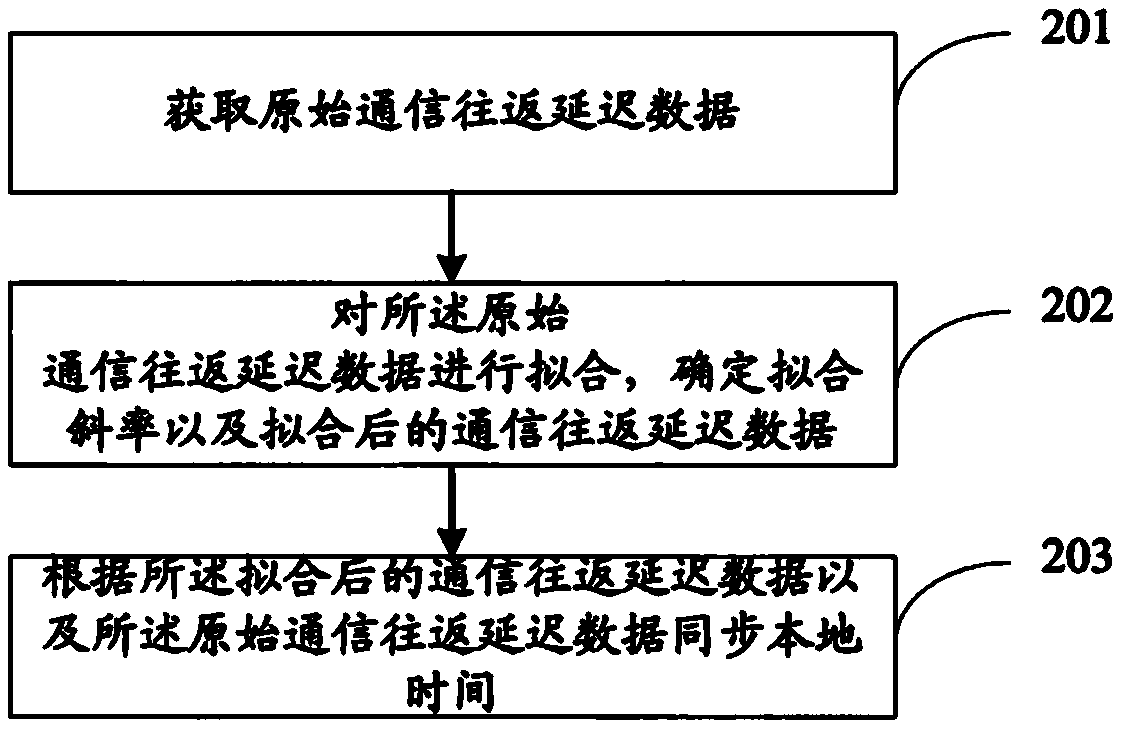
The invention discloses a time synchronization method and system. The time synchronization method comprises the following steps of acquiring the original communication round-trip delay data, wherein the original communication round-trip delay data comprises the original round-trip delay time and the original time deviation, and the original round-trip delay time and the original time deviation are in one-to-one correspondence; fitting the original communication round-trip delay data, and determining a fitting slope and the fitted communication round-trip delay data, wherein the fitted communication round-trip delay data comprises fitted round-trip delay time and fitted time deviation; and synchronizing the local time according to the fitted communication round-trip delay data and the original communication round-trip delay data. By adopting the time synchronization method and system provided by the invention, the network time service precision and the time synchronization precision can be improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU METROLOGY & TESTING INST
Optical fiber one-way time-frequency synchronization signal transmission method and device, medium and equipment
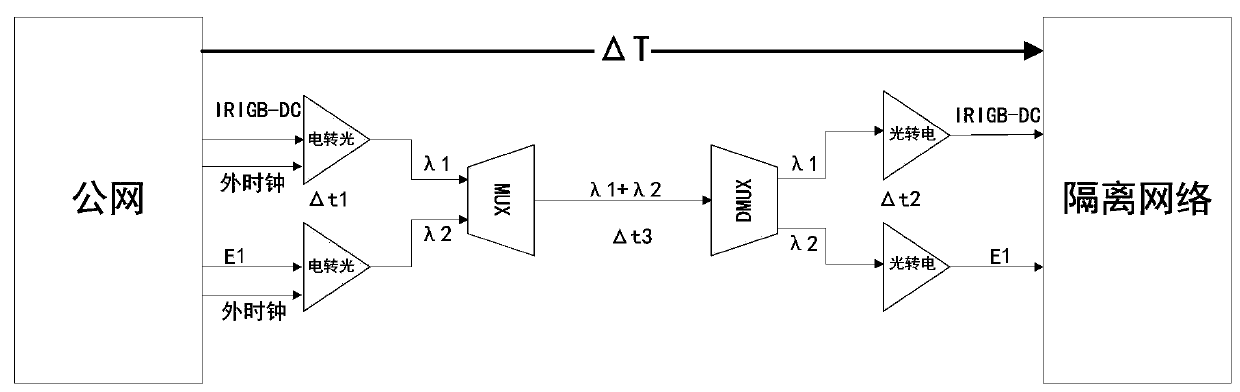
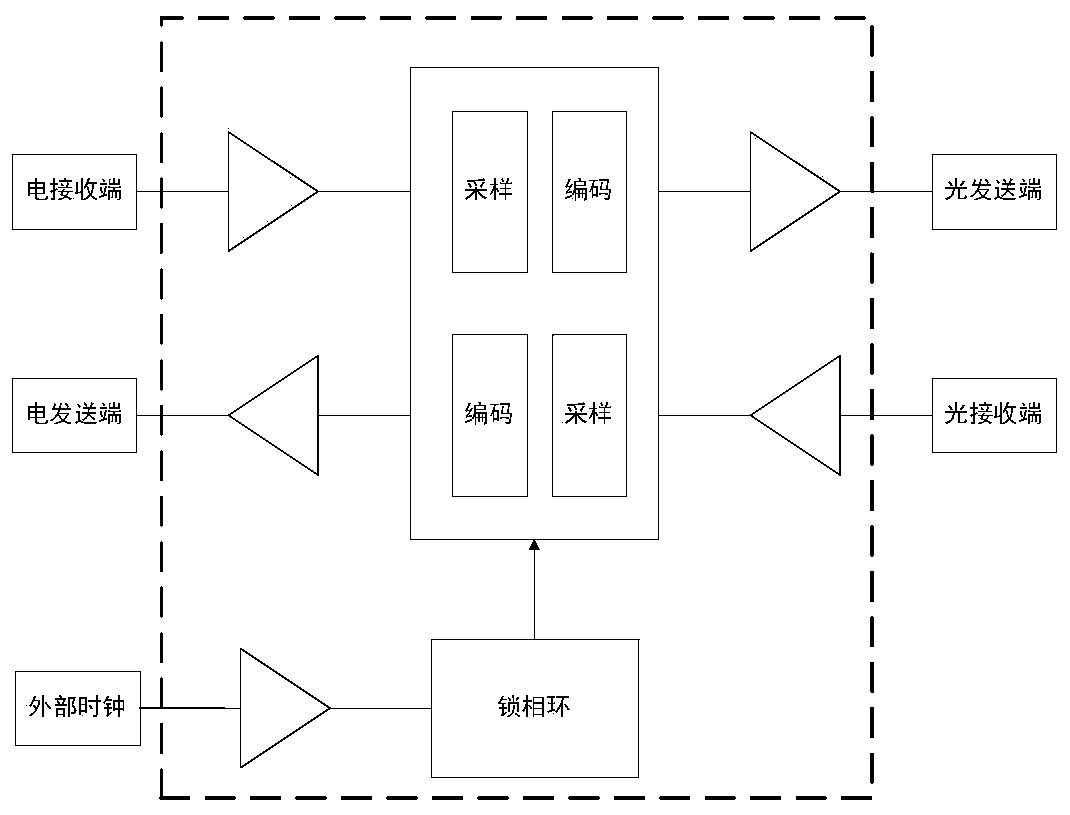
ActiveCN110995389AEliminates Inherent Latency EffectsLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexEngineeringReal-time computing
The invention discloses an optical fiber one-way time-frequency synchronization signal transmission method and device, a medium and equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: correspondingly converting a high-precision time electric signal and a high-precision frequency electric signal of a public network into a time optical signal and a frequency optical signal through a photoelectric converter, multiplexing the time optical signal and the frequency optical signal into the same single optical fiber link through an optical multiplexer, recovering a high-precision time optical signal and a high-precision frequency optical signal from the single optical fiber link through a demultiplexer, and correspondingly converting the high-precision time optical signal and the high-precision frequency optical signal into a high-precision time electric signal and a high-precision frequency electric signal through a photoelectric converter. According to the method, under the condition that a time-frequency taming device does not need to be added to an isolation network side, a public network with a close physical distance is selected as the isolation network to import single-fiber same-fiber one-way low-loss high-precision time-frequency signals, and isolation network time and frequency equipment directly uses imported time-frequency electric signals to perform time-frequency synchronization with the public network.
Owner:电信科学技术第五研究所有限公司
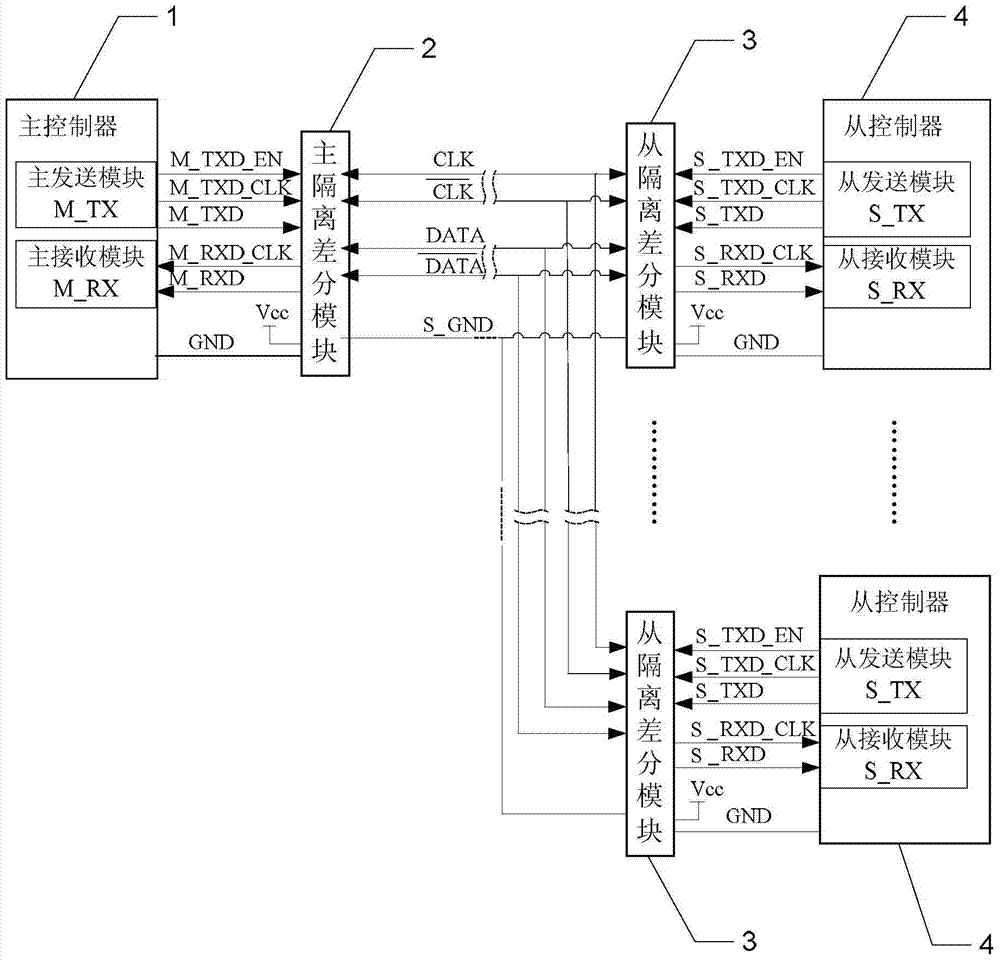
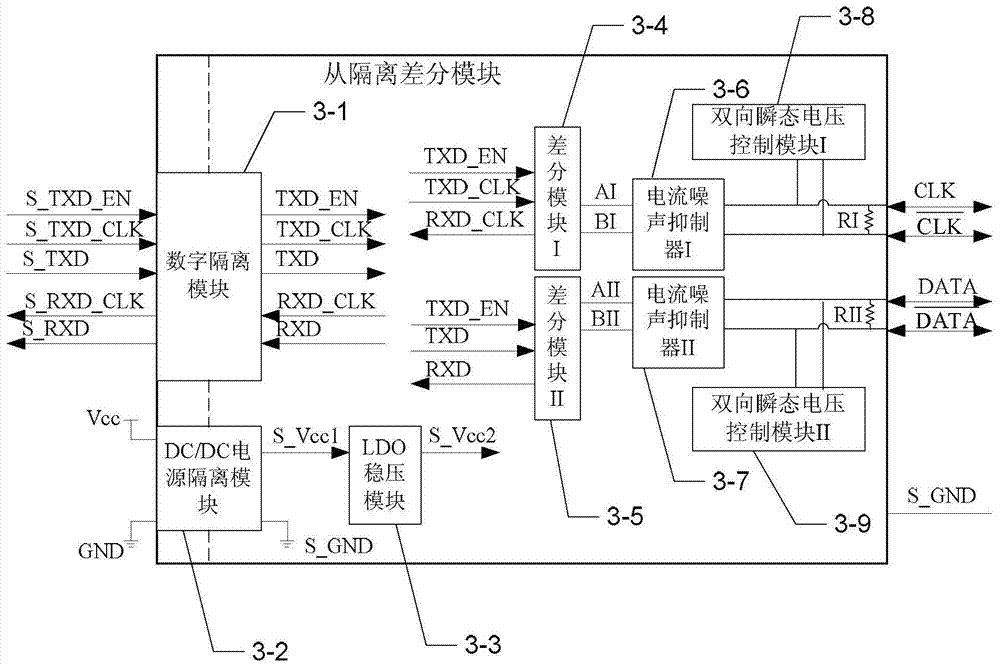
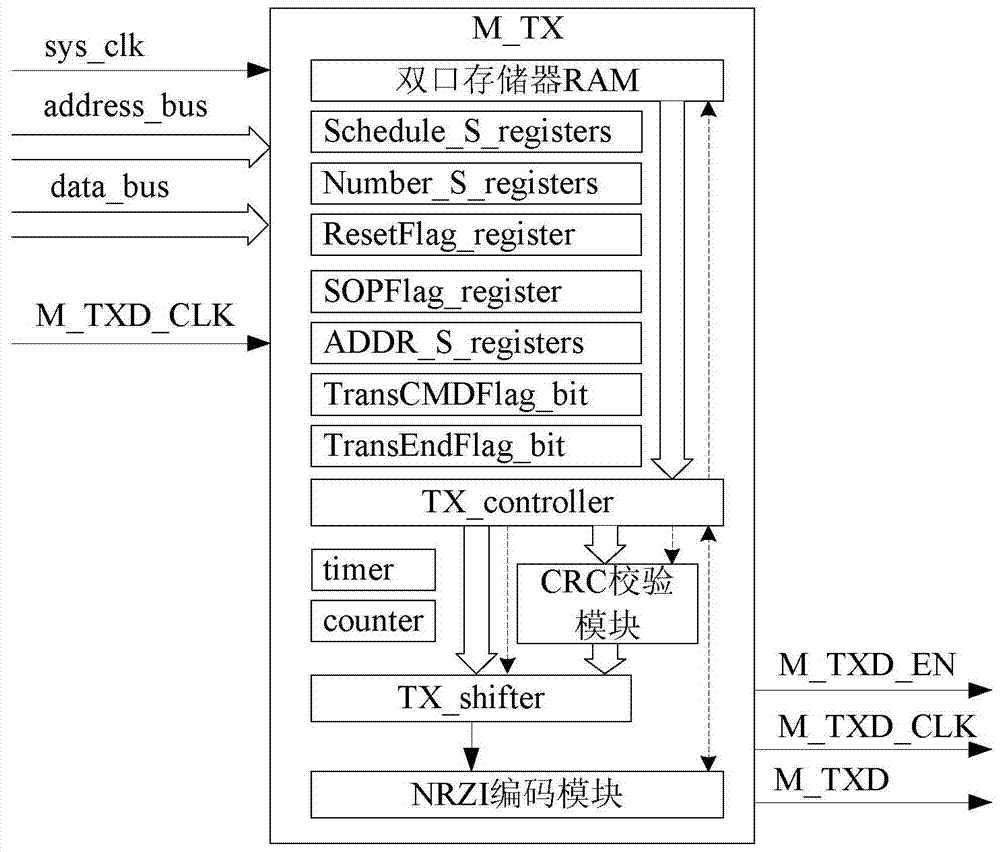
Master-slave synchronous serial communication bus based on differential signal and its realization method
ActiveCN104484306BEliminate latency effectsGuaranteed timing relationshipElectric digital data processingVoltage regulator moduleDifferential signaling
The invention provides a master-slave synchronous serial communication bus based on a differential signal and a realization method of the master-slave synchronous serial communication bus, relates to a master-slave synchronous serial communication bus, and aims at solving the problems that the existing master-slave synchronous serial communication is low in transmission speed, the real-time transmission of massive data cannot be guaranteed, and only the single byte check can be realized through code error detection. A master-slave synchronous serial communication bus based on the differential signal comprises a master controller, a master isolation difference module, n slave isolation difference modules and n slave controllers; the master controller comprises a master transmitting module and a master receiving module; each of the slave controllers comprises a slave transmitting module and a slave receiving module; the slave isolation difference modules are same in structure; each of the slave isolation difference modules comprises a digital isolation module, a DC / DC (Direct Current / Direct Current) power isolation module, an LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) voltage regulator module, two difference modules, two current noise suppressors, two two-way transient voltage control modules and two impedance matching resistors. The master-slave synchronous serial communication bus and the realization method of the master-slave synchronous serial communication bus are mainly used for master-slave synchronous serial communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
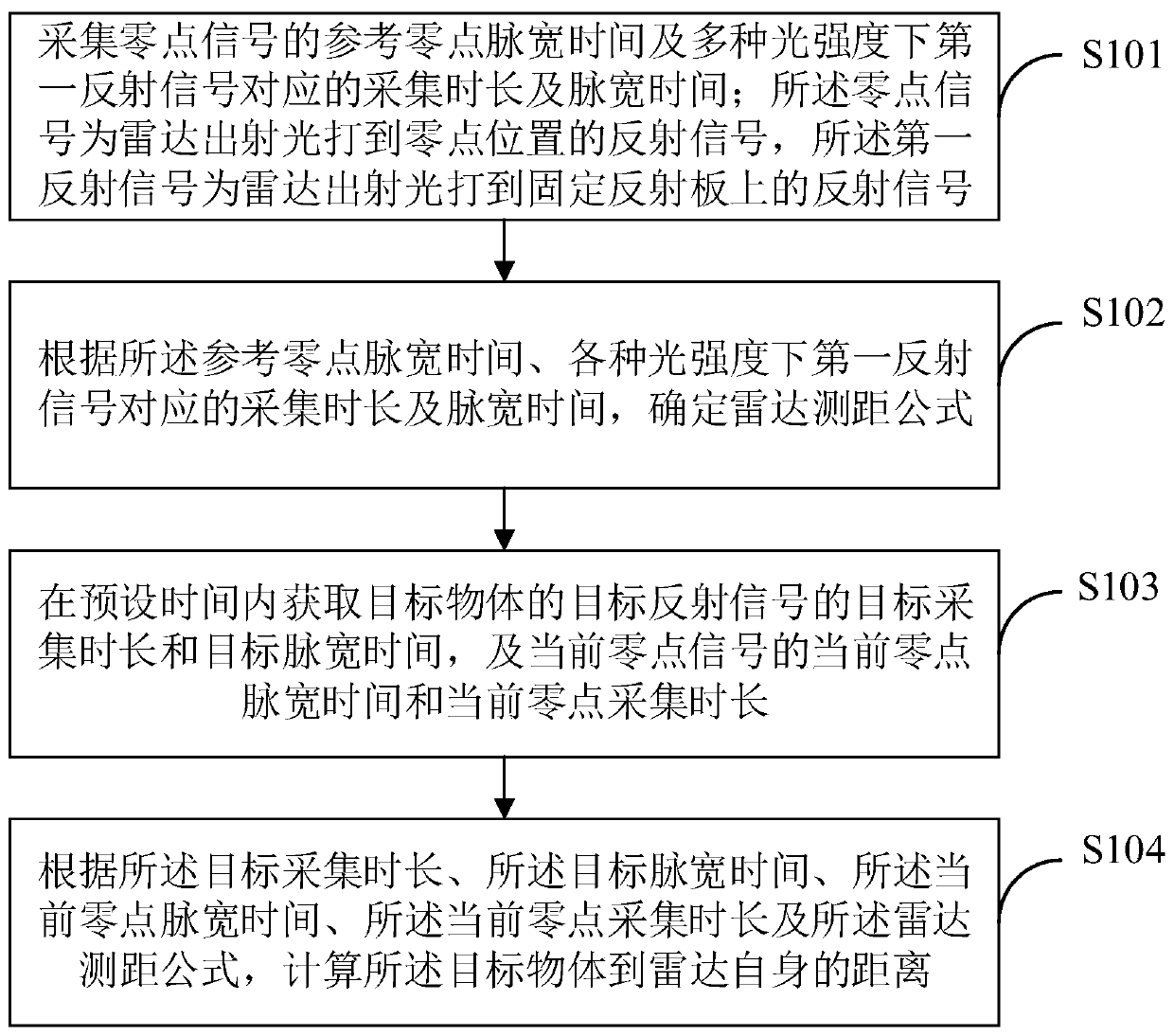
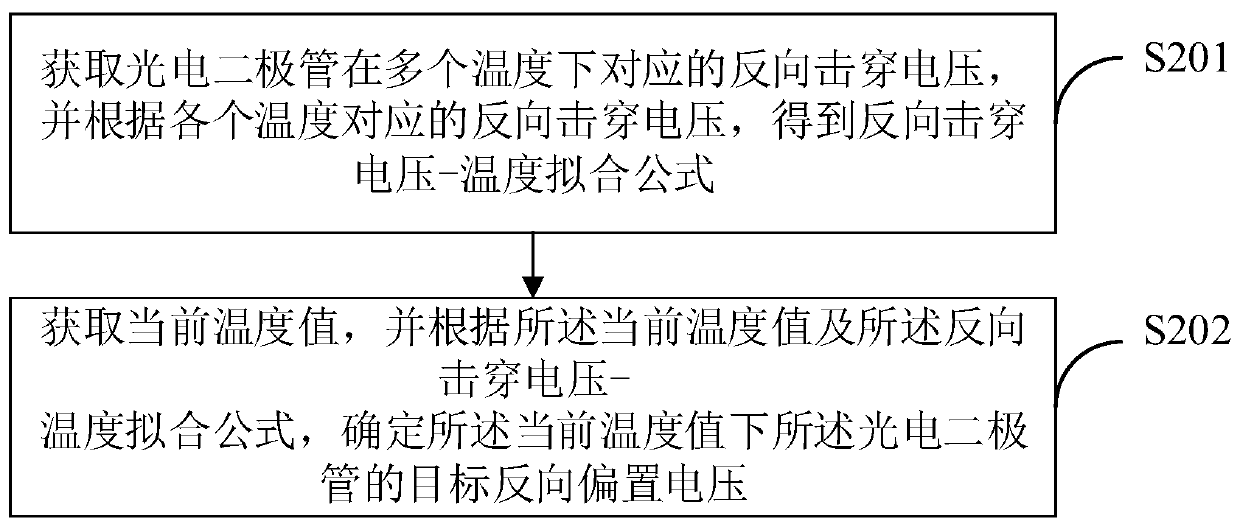
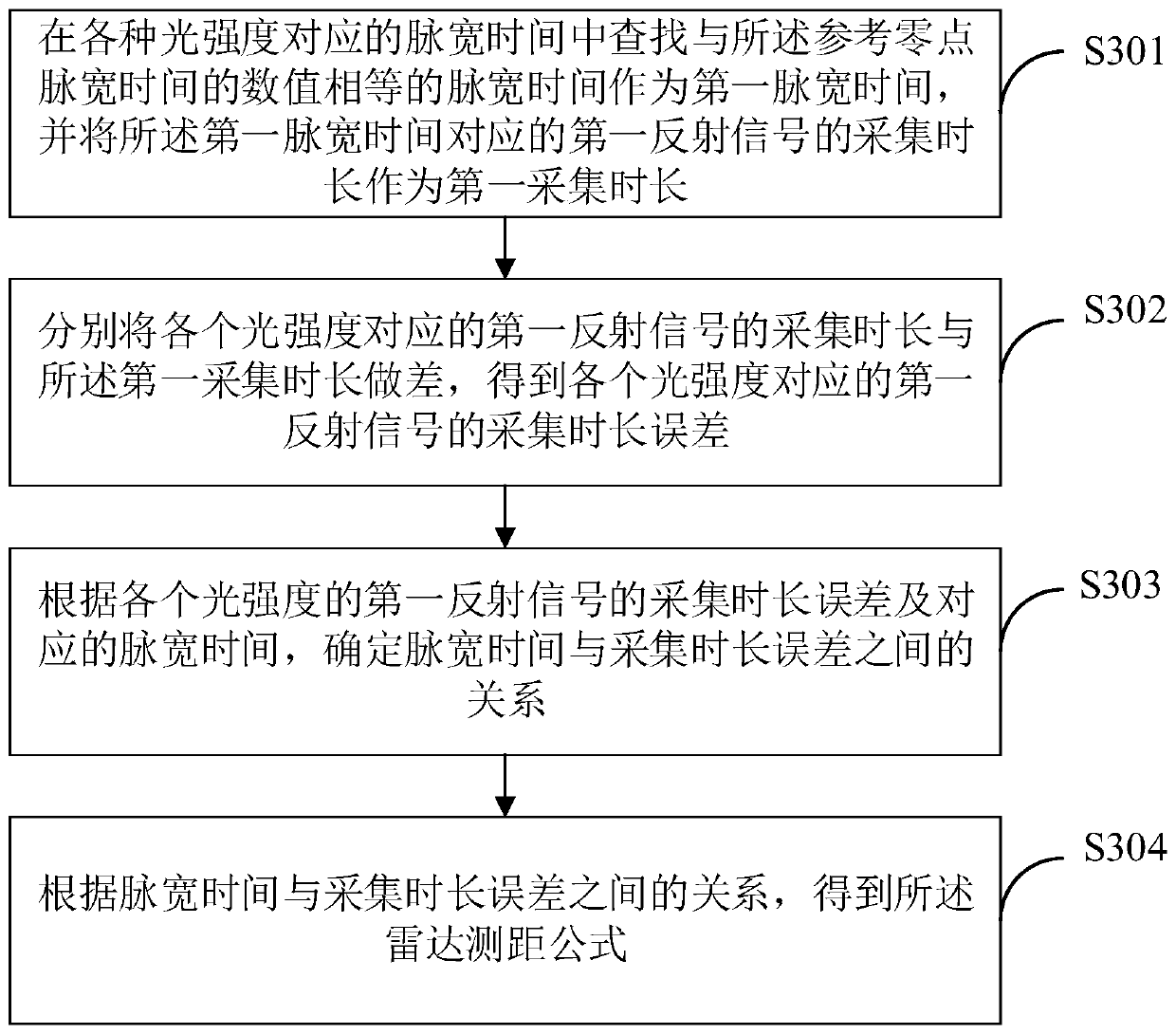
Radar ranging method, device and terminal device
ActiveCN110471075AEliminate latency effectsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhysicsTarget acquisition
The invention belongs to the technical field of radars and provides a radar ranging method, a radar ranging device and a terminal device. The method comprises the following steps that: the reference zero point pulse width time of zero point signals, and acquisition durations and pulse width time corresponding to first reflection signals under a plurality of optical intensities are acquired; a radar ranging formula is determined according to the reference zero point pulse width time, and the acquisition durations and pulse width time corresponding to the various light intensities; the target acquisition duration and target pulse width time of a target object as well as the current zero point pulse width time and current zero point acquisition duration of current zero point signals are acquired within preset time; and a distance from the target object to a radar is calculated according to the radar ranging formula. According to the radar ranging method, a zero point position is set; thereflection signals of the zero point position and the reflection signals of the target object can be acquired within the preset time; the delay influence of temperature on a circuit within the presettime is nearly the same; and therefore, distance calculation can be performed according to target zero point signals and target reflection signals, and the influence of the temperature on the delay ofthe circuit is eliminated.
Owner:WHST CO LTD
IPMSM position observation method, system and drive system based on rotating high-frequency injection method
ActiveCN109889117BHigh Position Observation AccuracyReduce design requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMotor speedPhase currents
The invention discloses an IPMSM position observation method based on a rotary high-frequency injection method. The method comprises the following steps that a high-frequency voltage signal is injected into a motor static alpha beta coordinate system after the motor finishes initial position detection; a stator current sampling module is used for performing sampling to obtain three-phase currentsof the motor, and conversion is carried out to obtain an estimated d-q coordinate axis; namely, target currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in a shafting which is a formula as shown in the specification; the target currents which are formulas as shown in the specification are subjected to band-pass filter extraction to obtain high-frequency response currents which are formulasas shown in the specification in a coordinate system which is a formula as shown in the specification; the positive sequence components of the high-frequency response currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in the axis of a formula which is as shown in the specification are extracted through transformation of coordinates and a low-pass filter, and the positive sequence current component per-unit unit processing is carried out; the negative sequence components of the high-frequency response currents which are formulas as shown in the specification in the axis of a formula which is as shown in the specification are extracted through transformation of coordinates and a low-pass filter, and the negative sequence current component per-unit value processing is carried out; andthe obtained high-frequency positive sequence current per-unit value and the high-frequency negative sequence current per-unit value are subjected to vector fork multiplication, and the estimated motor rotating speed and position are obtained. The invention further provides an observation system and an IPMSM driving system. The method has the advantages that no matter whether the IPMSM driving system runs at zero speed or a low speed, relatively high position observation precision is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Desulfurization system multi-working-condition prediction method based on extreme learning machine
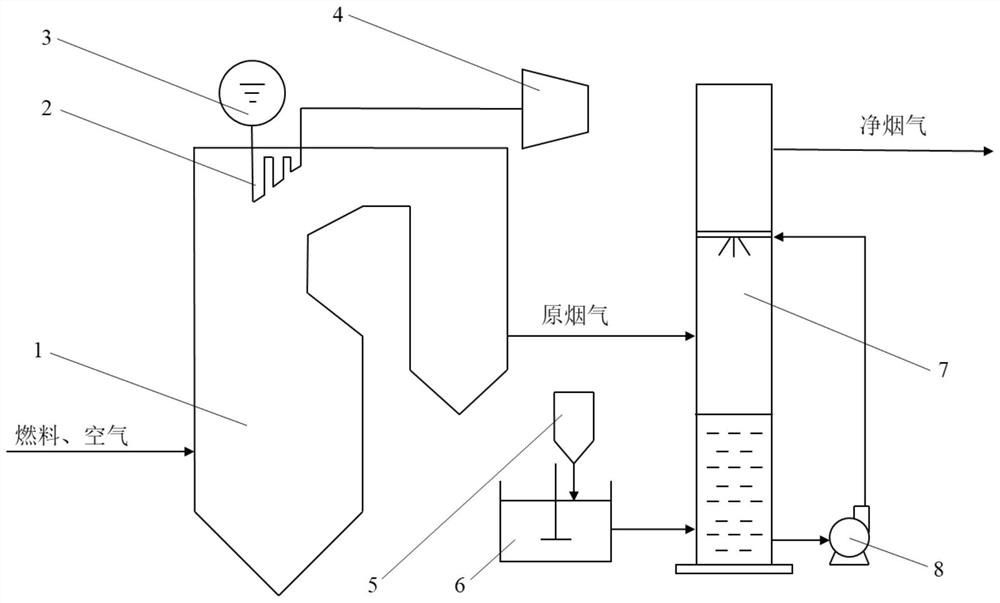
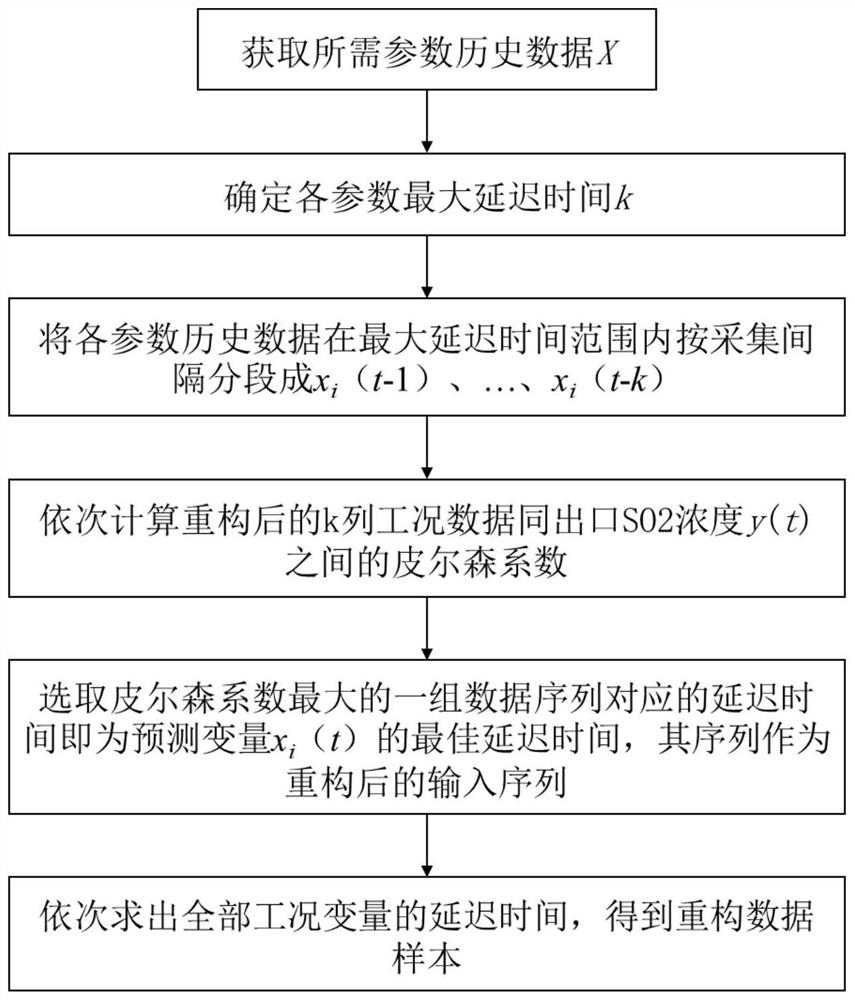
PendingCN114881355AImprove forecasting efficiencyImprove forecast accuracyForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning machineData set
The invention provides a desulfurization system multi-working-condition prediction method based on an extreme learning machine, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the historical data of the operation parameters of a thermal power plant boiler and a desulfurization system, carrying out the working condition classification according to the feature parameters of six flag bits, and determining a corresponding working condition training data set; for the training data set, based on a Bayesian algorithm, establishing classification models of different working conditions, and selecting a proper modeling sample set; estimating the delay time of a variable by using a Pearson coefficient, and recombining modeling data through the delay time; establishing SO2 prediction models under different marking conditions based on an extreme learning machine algorithm by using the recombined data set; and inputting the real-time data of the system into the classification model, judging the real-time working condition category of the system, and predicting the SO2 emission concentration by adopting a corresponding prediction model. According to the method, on the premise that the delay time influence is reduced, the current working condition of the system is judged based on the boiler operation data, different working condition prediction models are switched, and the prediction efficiency and precision of outlet SO2 are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable gear hobbing device for gear machining
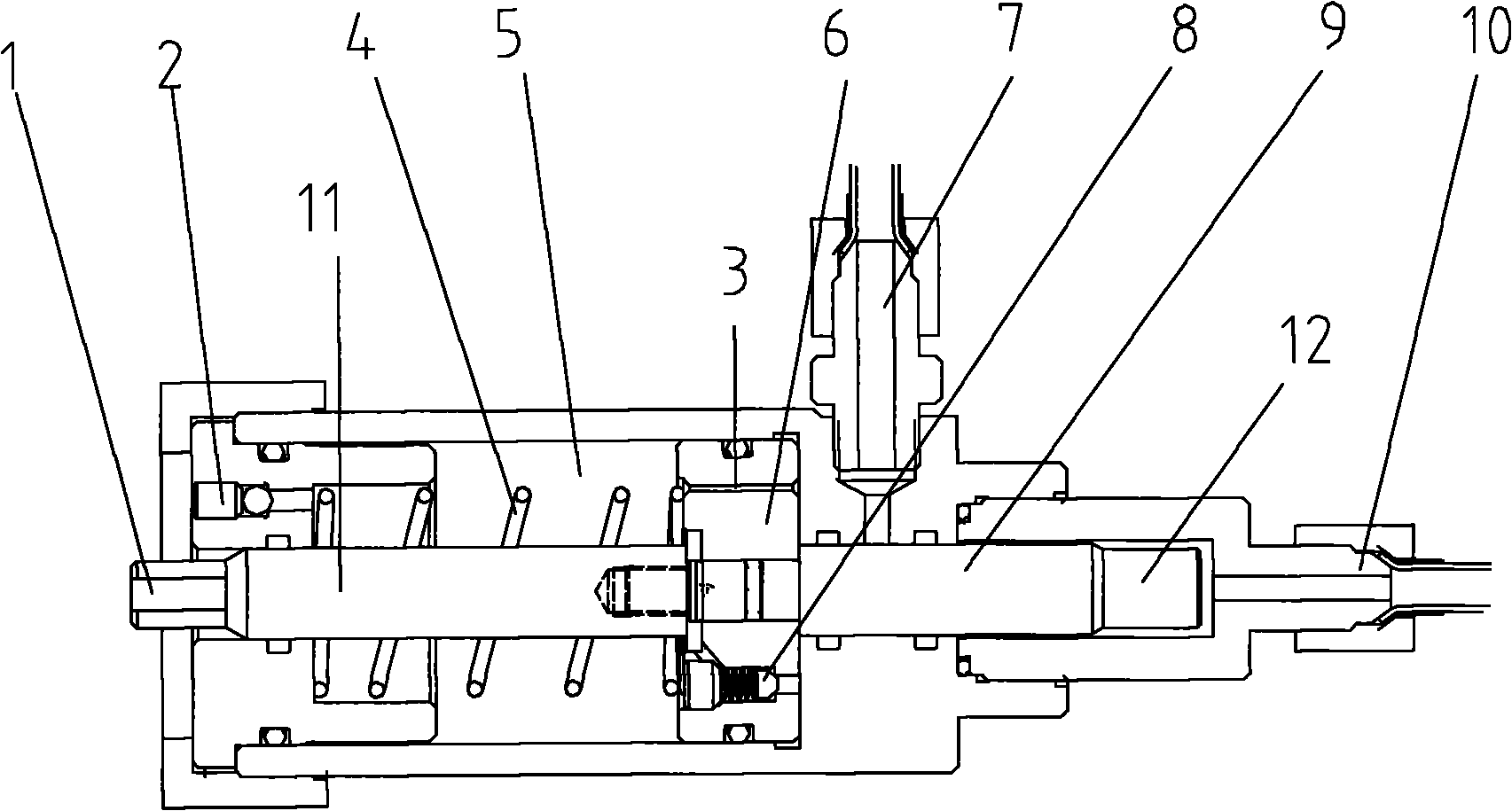
ActiveCN114192895AGuaranteed cleanlinessReduce detection errorMeasurement/indication equipmentsDriving apparatusHobbingBrake
The invention relates to the field of gear hobbing machines, and discloses an adjustable gear hobbing device for gear machining, which comprises a mounting table and a to-be-machined gear, and the mounting table is provided with a bearing mechanism capable of driving the to-be-machined gear to rotate and lift and a forming hobbing used for hobbing the to-be-machined gear. The detection assembly can perform flaw detection on the outer wall of the gear to be machined by adopting an ultrasonic flaw detection technology, and can also obtain the gear forming condition in a backlight projection mode to detect the gear hobbing shape of the gear; an arc-shaped sealing gasket attached to the upper side and the lower side of the gear to be machined is arranged on one side of the detection assembly, and a braking assembly and a speed reduction assembly are further arranged on the mounting table. Compared with the prior art, the gear hobbing device has the advantages that gear detection errors during gear hobbing are reduced, industrial hazards caused by the fact that defective gears after gear hobbing are put into use are avoided, the time delay influence caused when defective gears appear can be reduced, abrasion of the brake assembly and the main shaft is relieved, the overall practicability of the device is improved, and the service life of the device is prolonged.
Owner:TAIZHOU LIHUA GEAR MFG
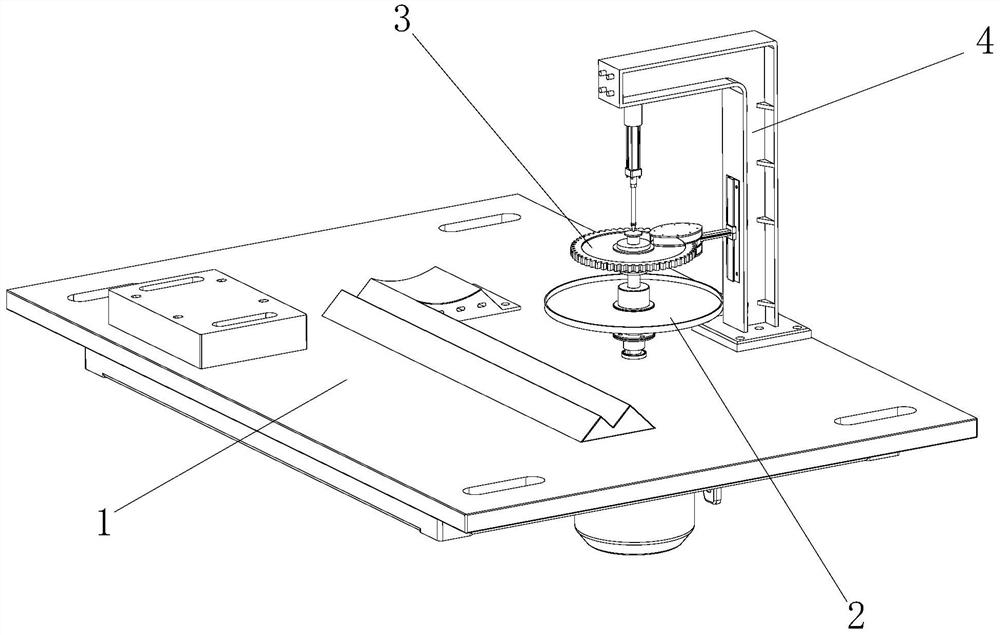
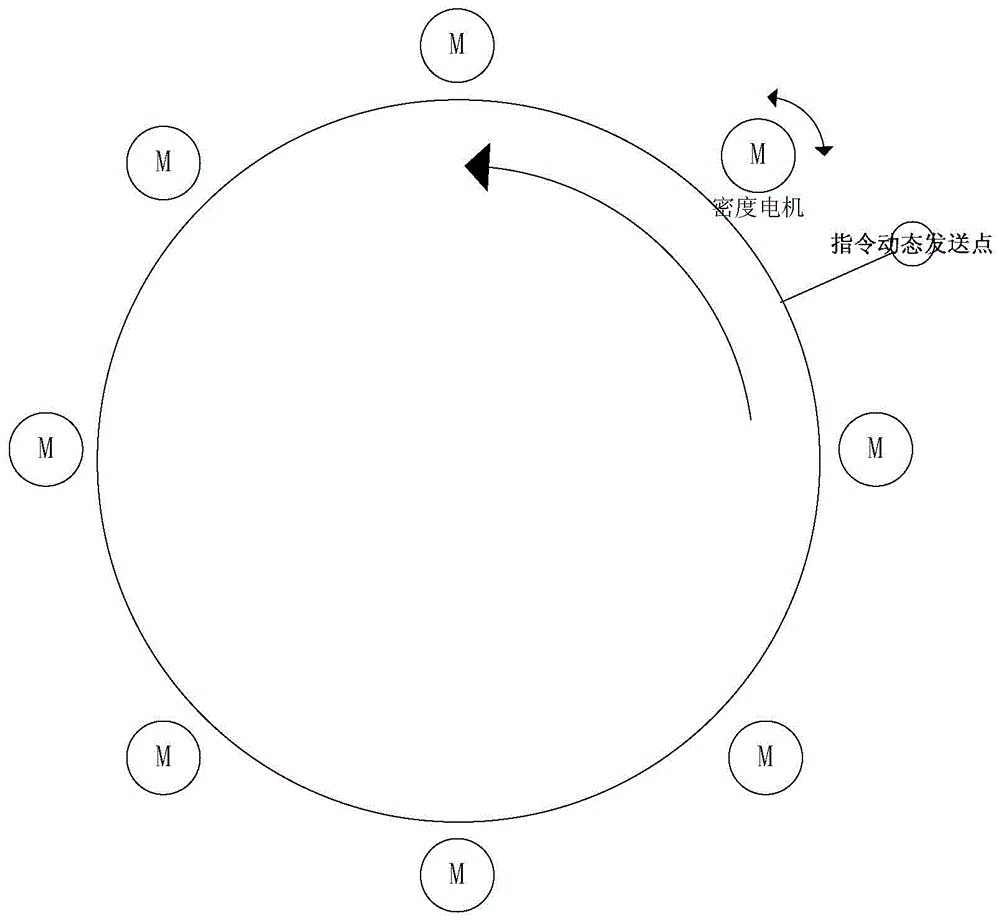
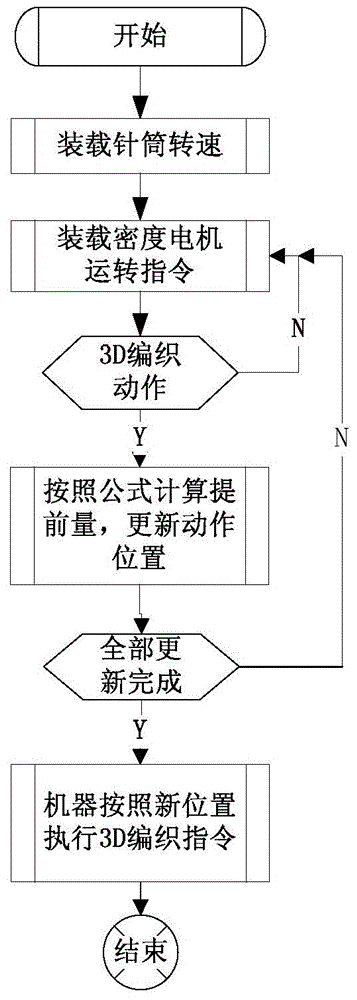
High-speed 3D weaving method for seamless underwear machine
ActiveCN104099717BEliminate latency effectsIncrease productivityWeft knittingControl systemElectric machinery
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGQIANG TECH CO LTD
A method, device and equipment for synchronously playing video data and audio data
ActiveCN103905881BEasy to operateRealize synchronous playbackSelective content distributionComputer hardwareWireless transmission
The embodiment of the invention provides a video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and equipment. The method includes the steps that a multimedia data playing request is received on a display terminal side; the playing request comprises multimedia data identification; by depending on the multimedia data identification, corresponding video data are acquired from a request-playing server in communication with the display terminal side; the multimedia data identification is transmitted to a mobile device side; the display terminal side is connected with the mobile device side in a wireless transmission mode; playing object timestamps returned by the mobile device side are received; the playing object timestamps are timestamps generated according to currently-played audio timestamps when the audio data are played by the mobile device side; the video data corresponding to the playing object timestamps are played on the display terminal side. With the video data and audio data synchronized playing method and device and the equipment, synchronized playing of the audio data and the video data is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
Low motion to photon latency rapid target acquisition
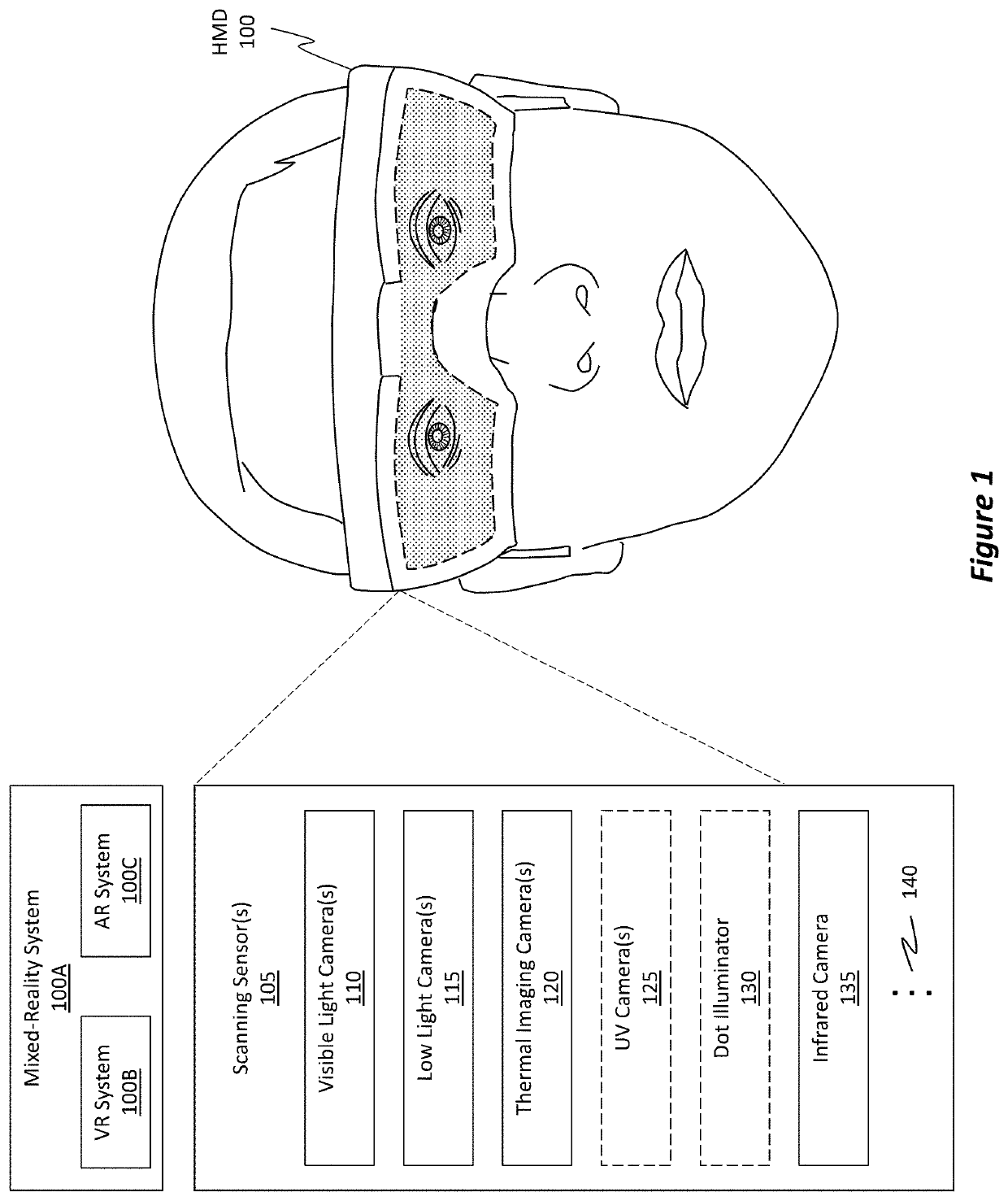
ActiveUS20220171187A1Minimize latency effectMinimize, orInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
Techniques for updating a position of overlaid image content using IMU data to reflect subsequent changes in camera positions to minimize latency effects are disclosed. A “system camera” refers to an integrated camera that is a part of an HMD. An “external camera” is a camera that is separated from the HMD. The system camera and the external camera generate images. These images are overlaid on one another and aligned to form an overlaid image. Content from the external camera image is surrounded by a bounding element in the overlaid image. IMU data associated with both the system camera and the external camera is obtained. Based on that IMU data, an amount of movement that the system camera and / or the external camera have moved since the images were originally generated is determined. Based on that movement, the bounding element is shifted to a new position in the overlaid image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
A fast solution method for rtk partial ambiguity in multi-constellation long-baseline network
ActiveCN104459745BShorten the timeEliminate latency effectsSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteComputer science
The invention discloses a quick resolving method for multi-constellation long-base-line network RTK partial ambiguity. After combination of multiple systems, it is hard to obtain accurate integer values of all ambiguities at the same time through resolving due to the influence of observation noise, atmosphere residual errors and other factors; especially for a long base line, the problem is intensified by complexity of atmosphere errors. According to the method, the three-step resolving strategy of wide-lane ambiguity solution, ionized-layer-free ambiguity solution and basic ambiguity fixing is adopted, in the basic ambiguity fixing process, a partial ambiguity fixing method with cut-off satellite elevation, the ambiguity searching prior success rate and Ratio values as main parameters is provided, and quick and accurate fixing of network RTK long-base-line ambiguity is achieved through an optimized partial ambiguity fixing subset. By means of the quick resolving method, the prior success rate and Ratio values can be obviously improved in the ambiguity fixing process, and therefore time needed by ambiguity fixing between network RTK base stations is shortened.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com