Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Efficient productivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
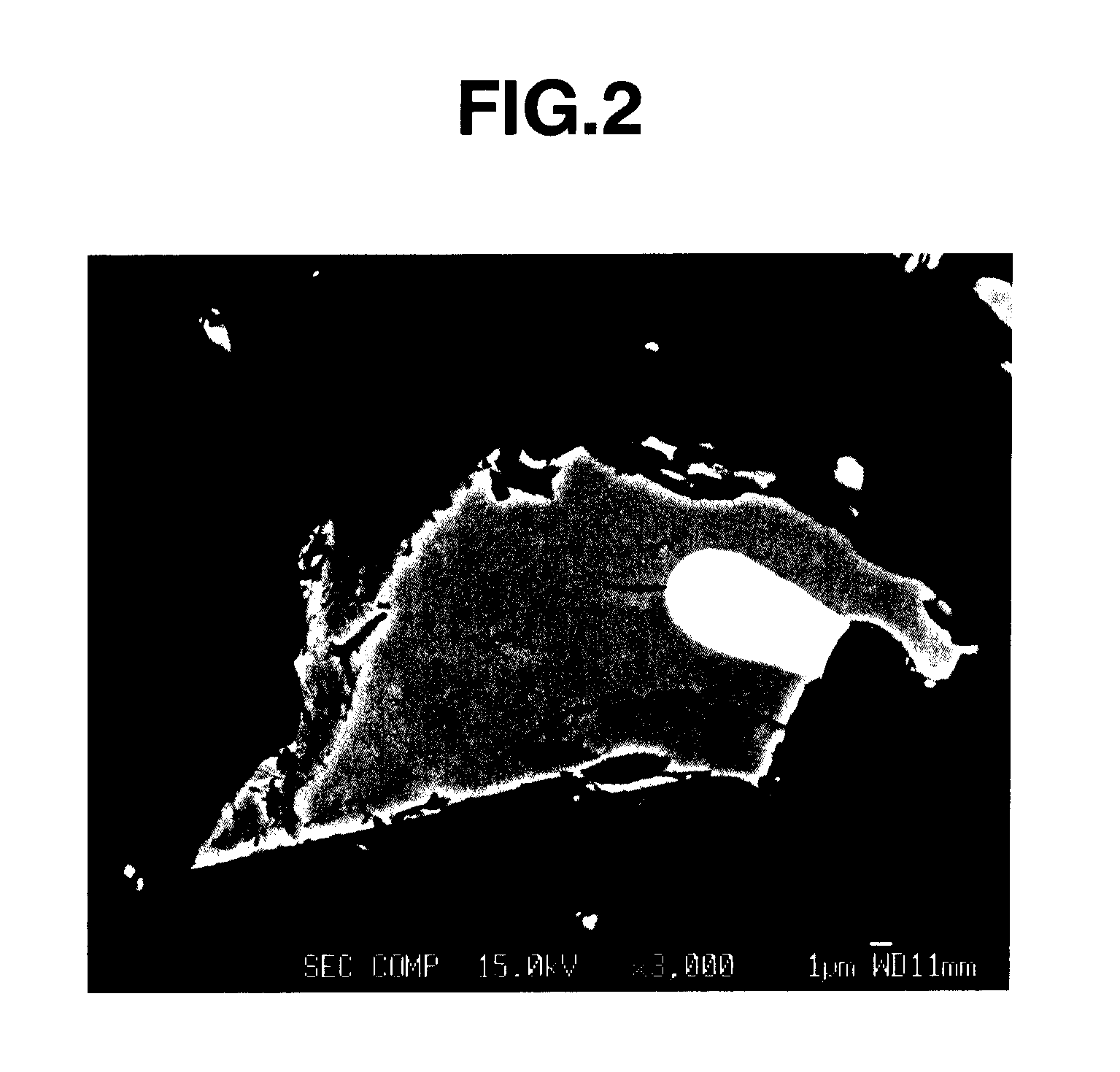
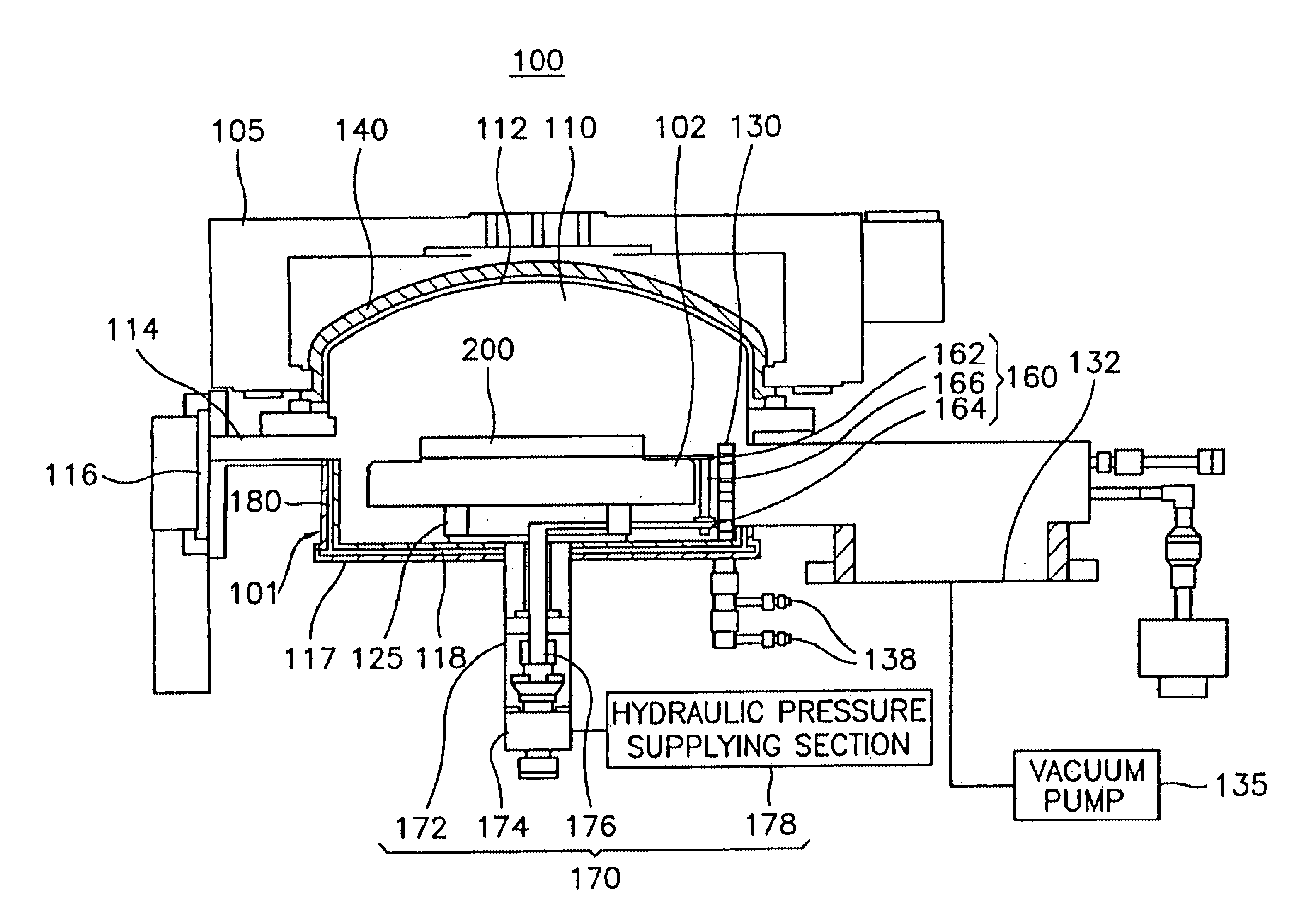
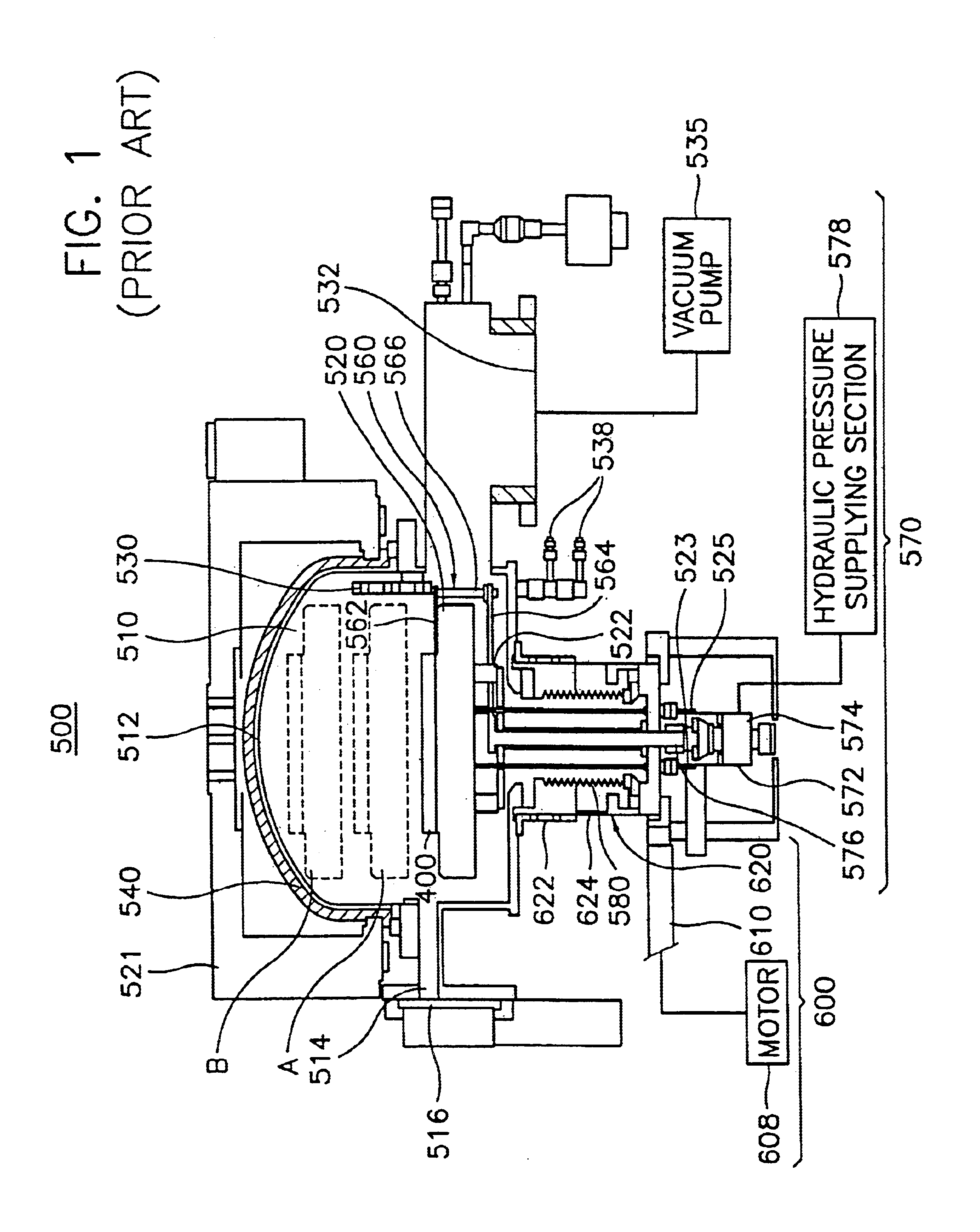
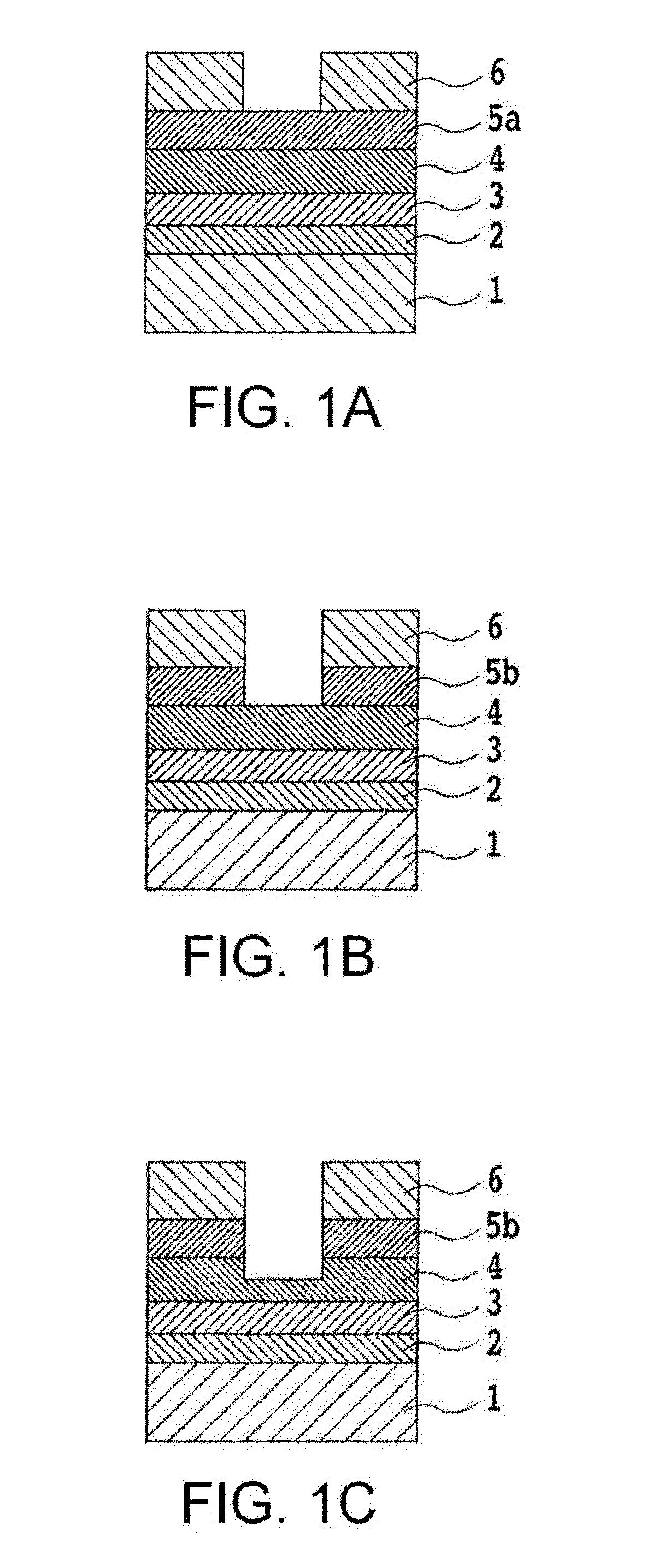
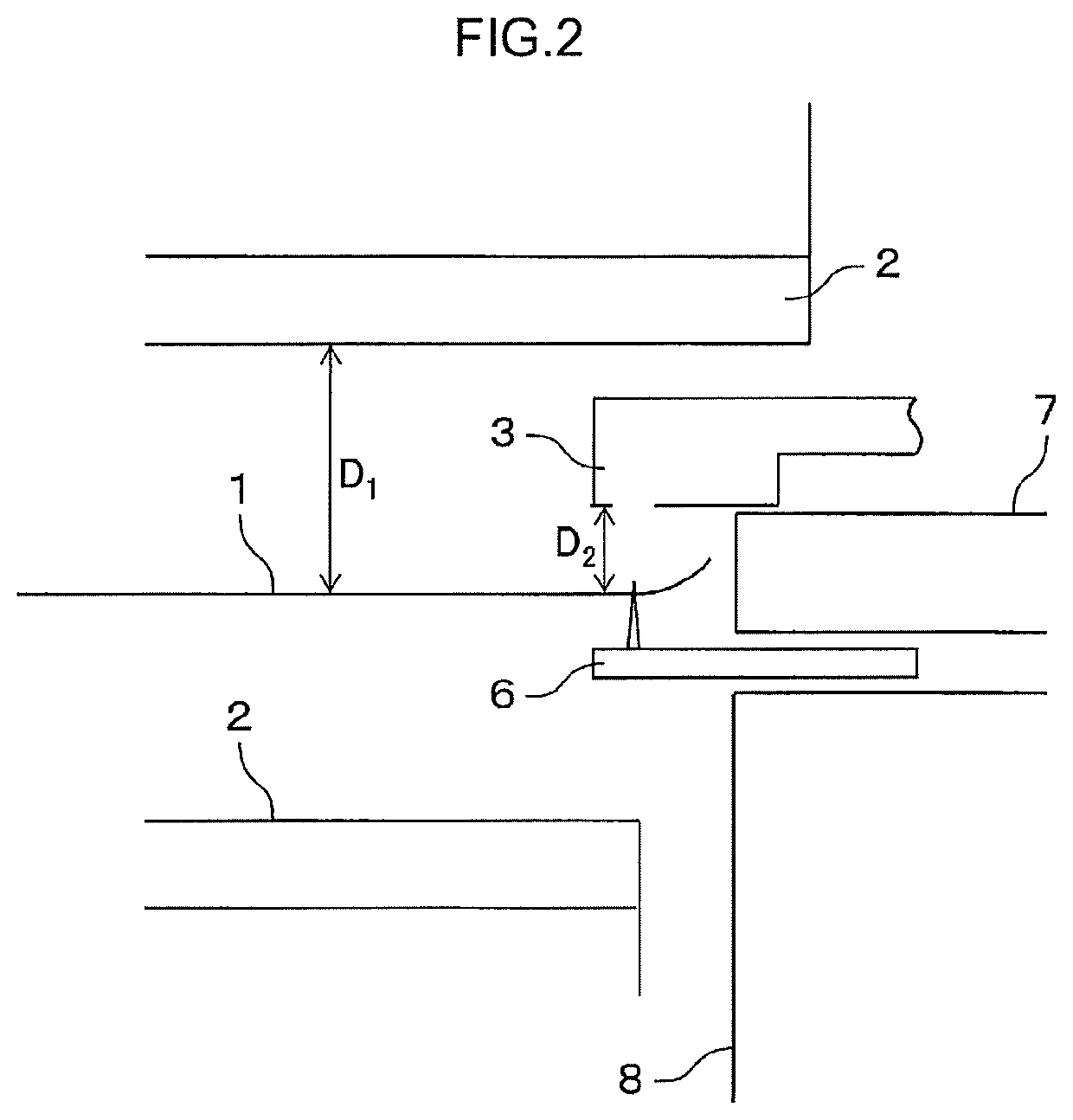
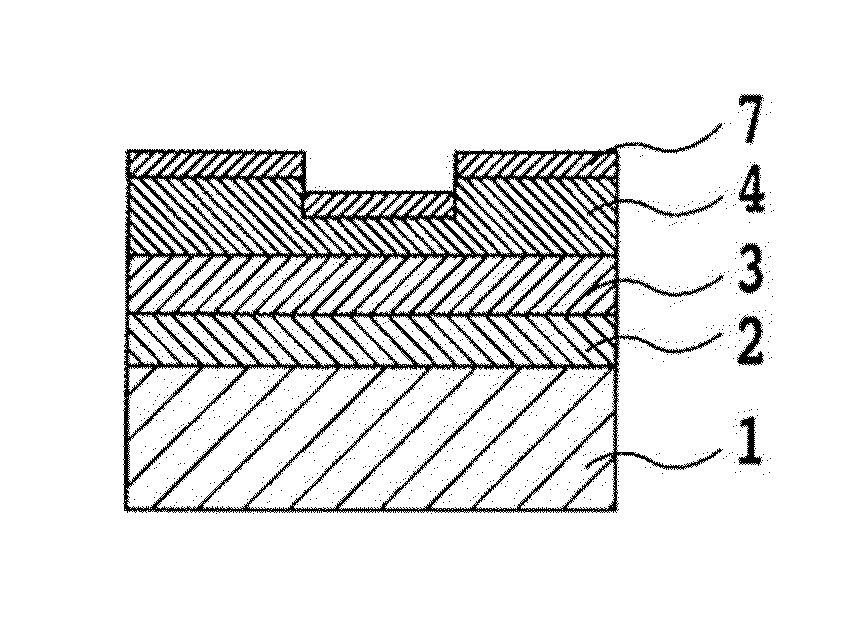
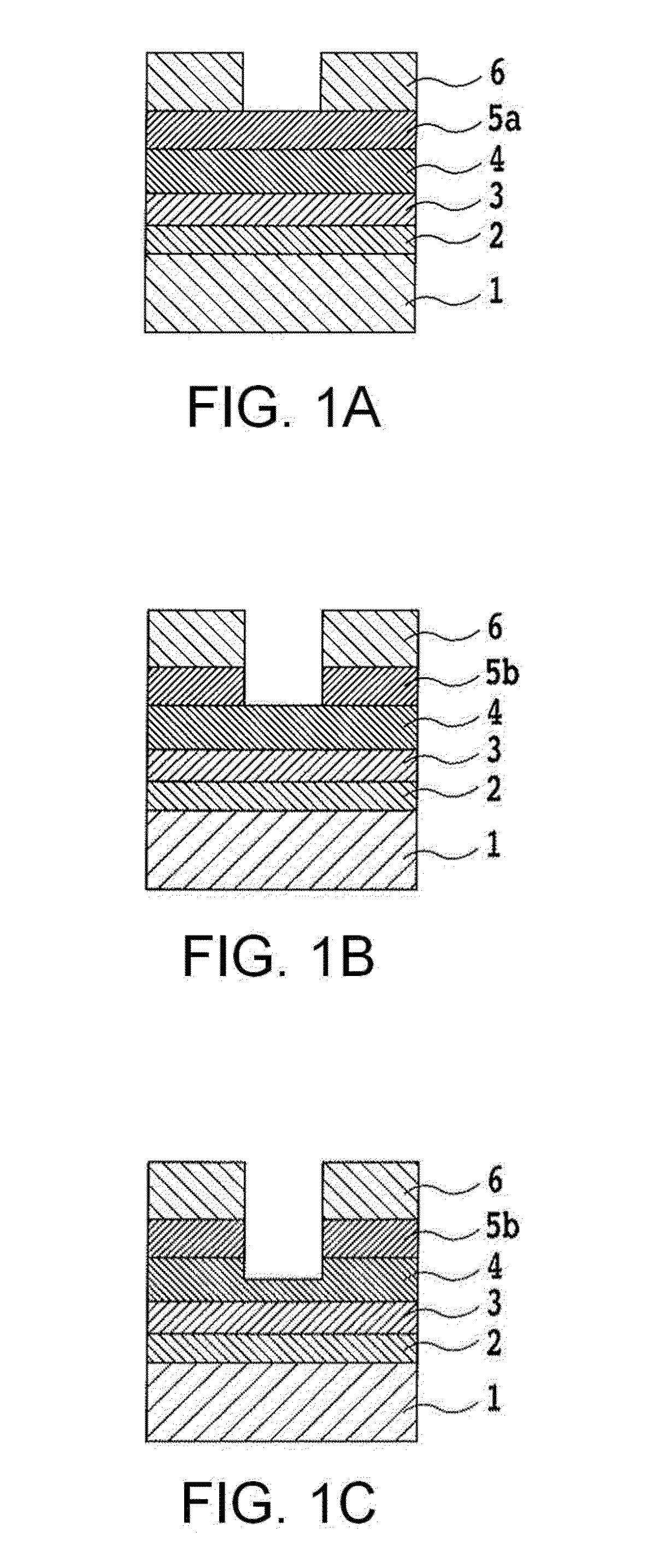
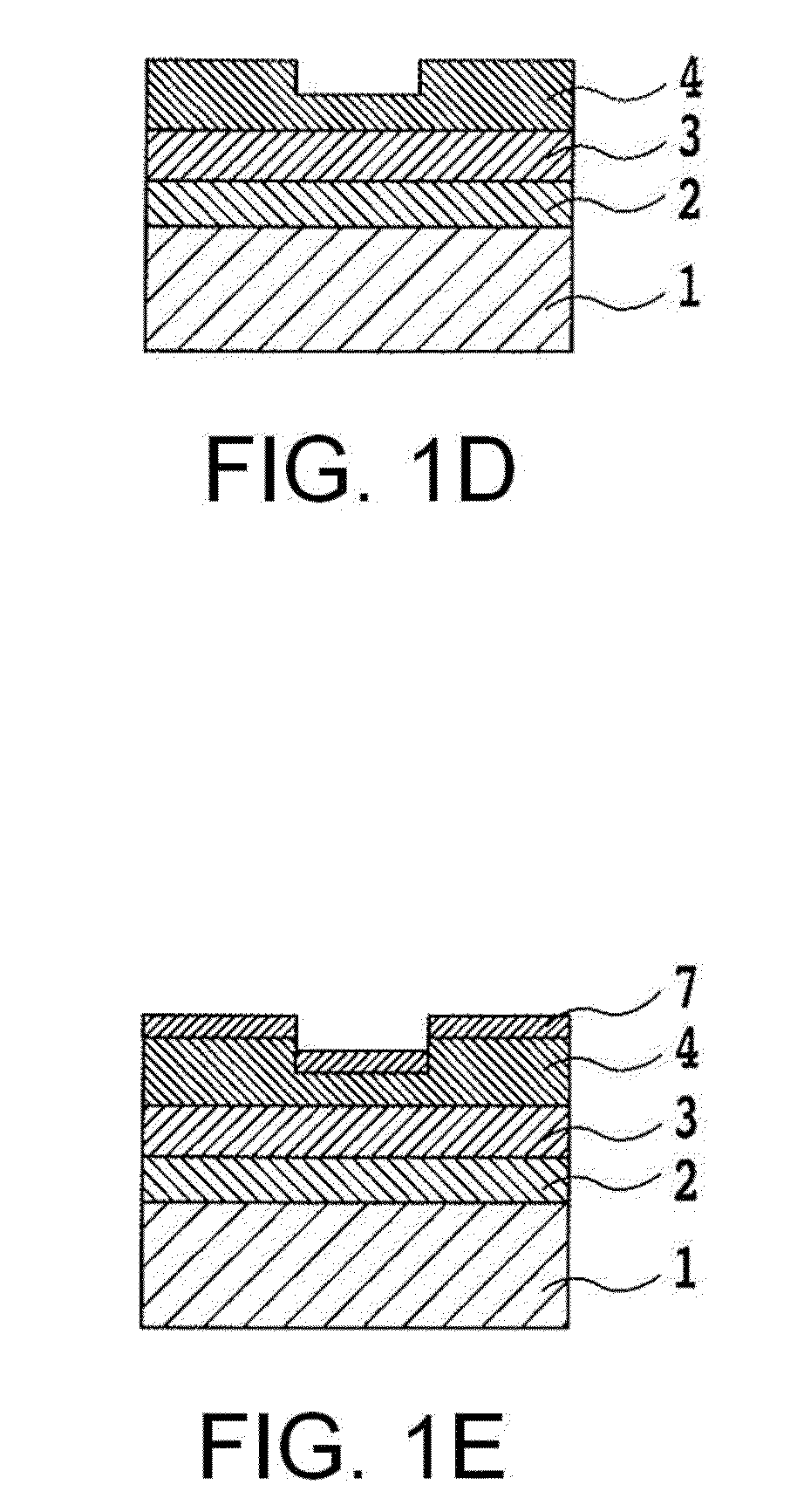
Rare earth magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20110000586A1Prevent oxidationMinimal hazardTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementRare-earth magnet
A rare earth magnet is prepared by disposing a R1-T-B sintered body comprising a R12T14B compound as a major phase in contact with an R2-M alloy powder and effecting heat treatment for causing R2 element to diffuse into the sintered body. The alloy powder is obtained by quenching a melt containing R2 and M. R1 and R2 are rare earth elements, T is Fe and / or Co, M is selected from B, C, P, Al, Si, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, Ge, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Hf, Ta, W, Pt, Au, Pb, and Bi.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20110036458A1Efficient productivityGood magnetic performancePermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRemanenceProduction rate
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared by disposing a powdered metal alloy containing at least 70 vol % of an intermetallic compound phase on a sintered body of R—Fe—B system, and heating the sintered body having the powder disposed on its surface below the sintering temperature of the sintered body in vacuum or in an inert gas for diffusion treatment. The advantages include efficient productivity, excellent magnetic performance, a minimal or zero amount of Tb or Dy used, an increased coercive force, and a minimized decline of remanence.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
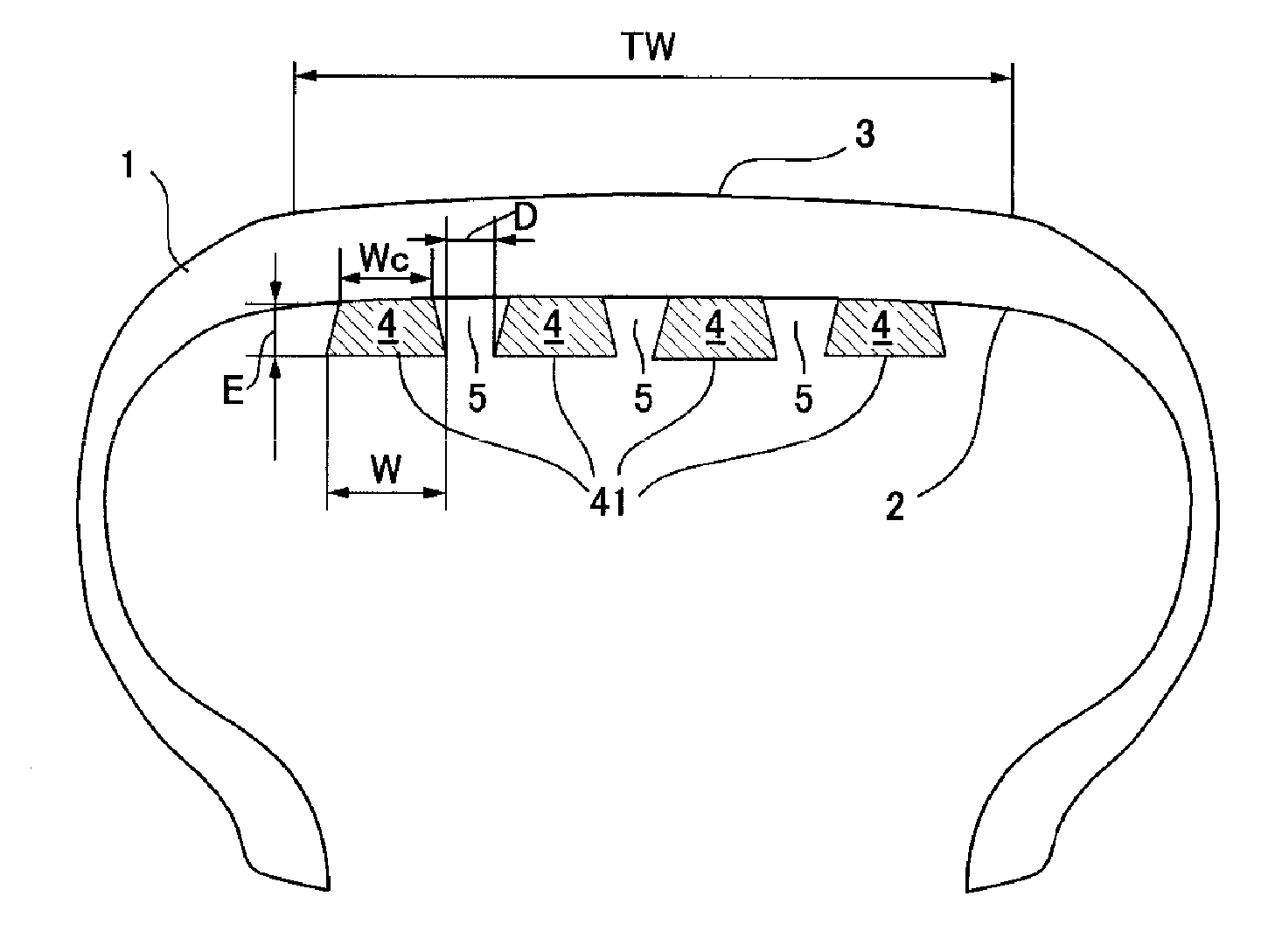
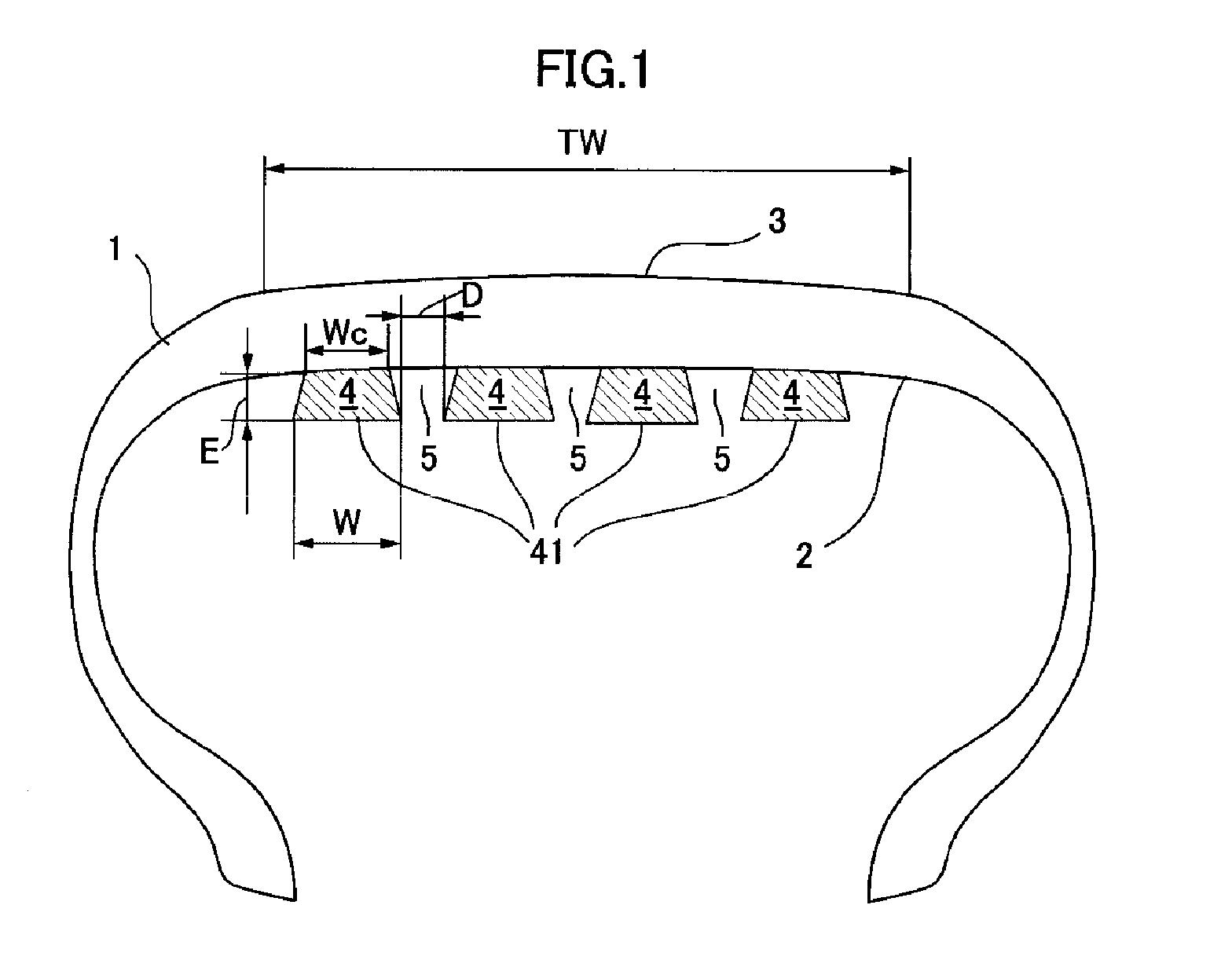
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20140020806A1Reduce cavity resonanceHigh-speed durabilityTyresInflatable tyresGround contactGroove width
A pneumatic tire provided with a noise damper in the tire cavity, which can maintain high-speed durability and productivity while also reducing cavity resonance, comprising a tread having a width TW in contact with the ground during travel, in which a noise damper made of a sound-absorbing material is attached to the tire internal surface in order to reduce cavity resonance, wherein the noise damper is at least one continuous ribbon made of a sound-absorbing material and having a width W and a thickness E, which is fixed over an attachment width Wc to the tire internal surface over a range of at least 30% of the inside of the tread in the radial direction, the start end and terminal end which are the two ends of the continuous ribbon are disposed in such a way as to be offset from each other in the axial direction, and the continuous ribbon forms, together with the tire internal surface, a continuous groove having a groove width D which is at least equal to 10% of the width W of the continuous ribbon.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN +1
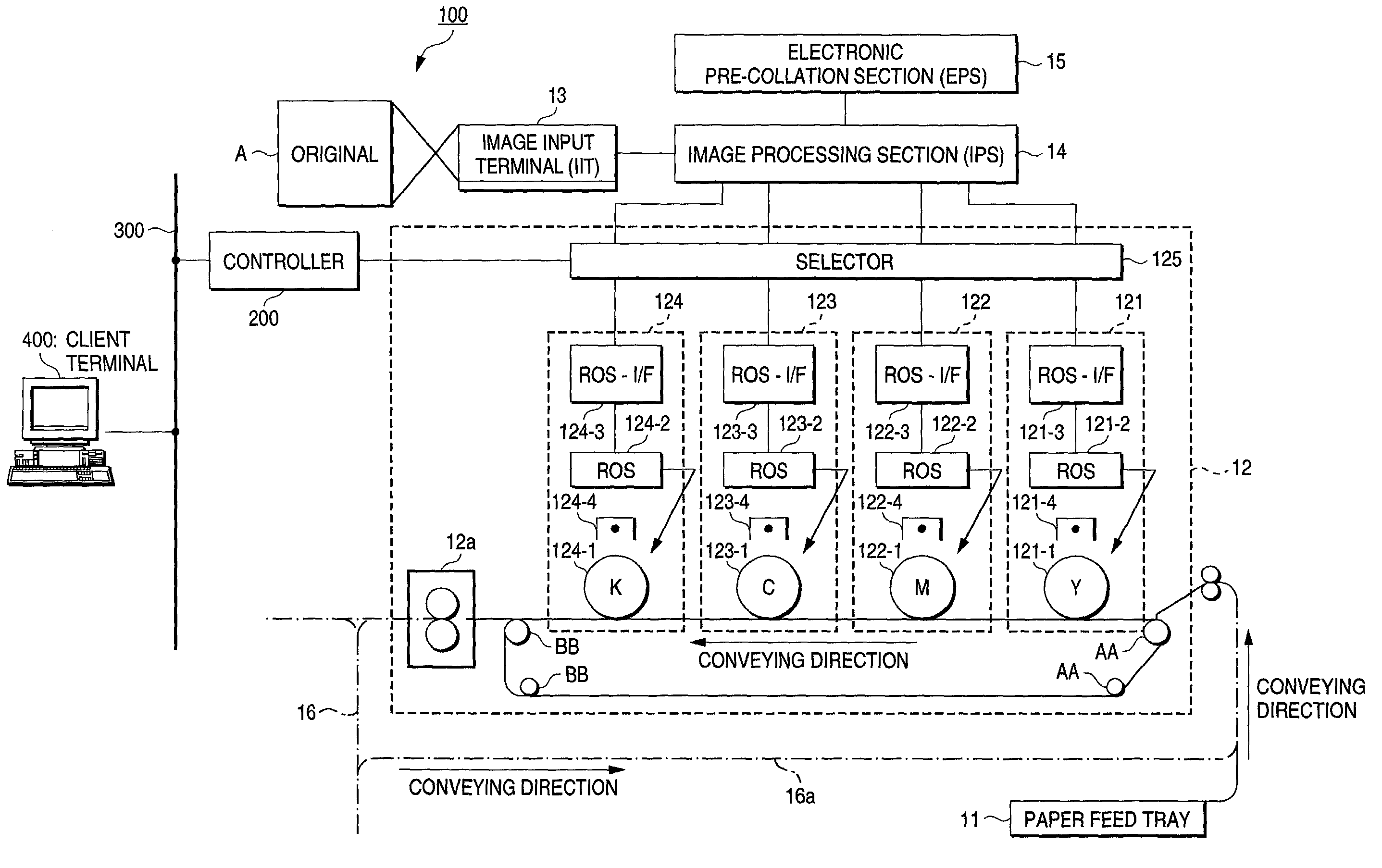
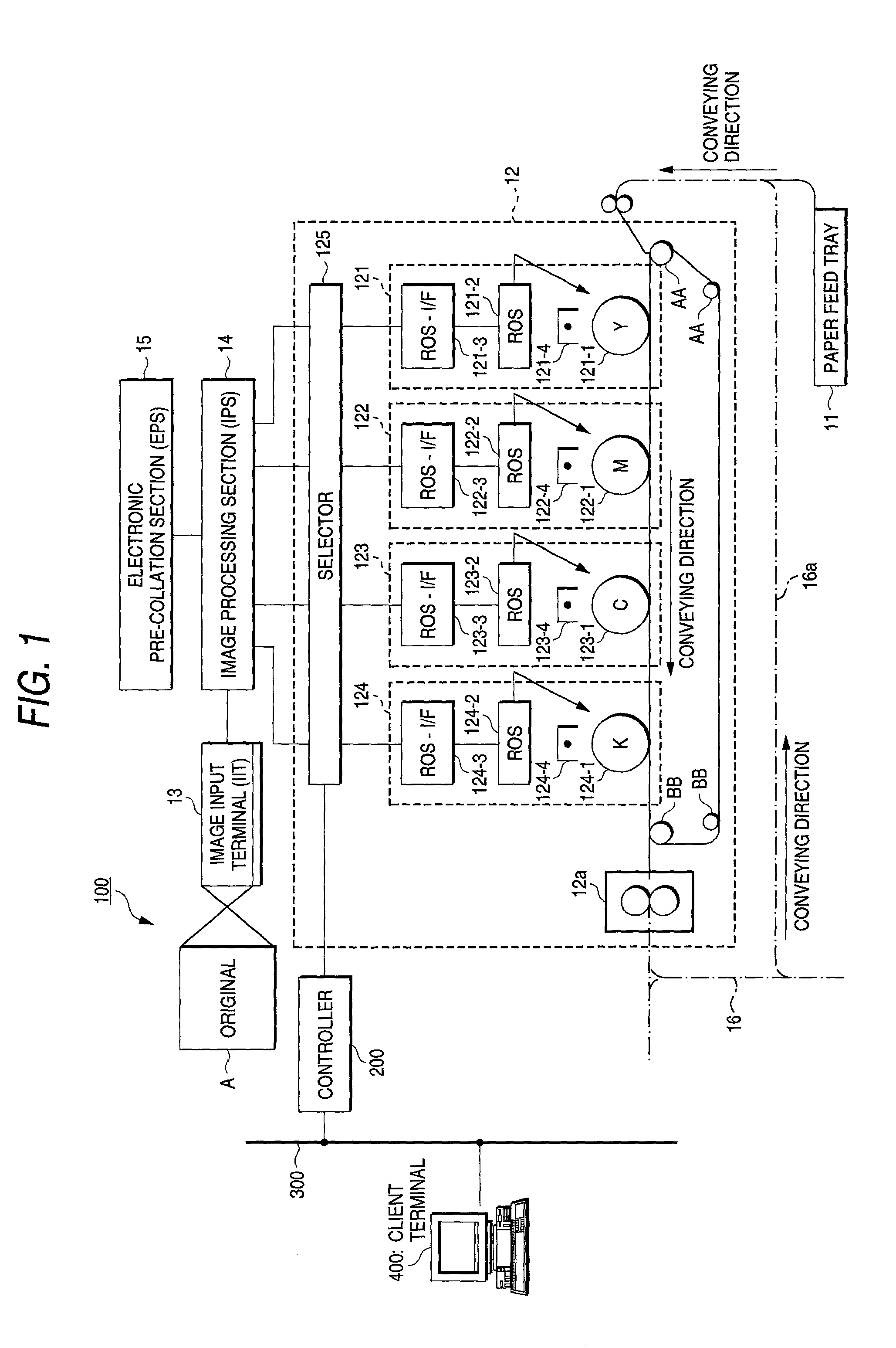
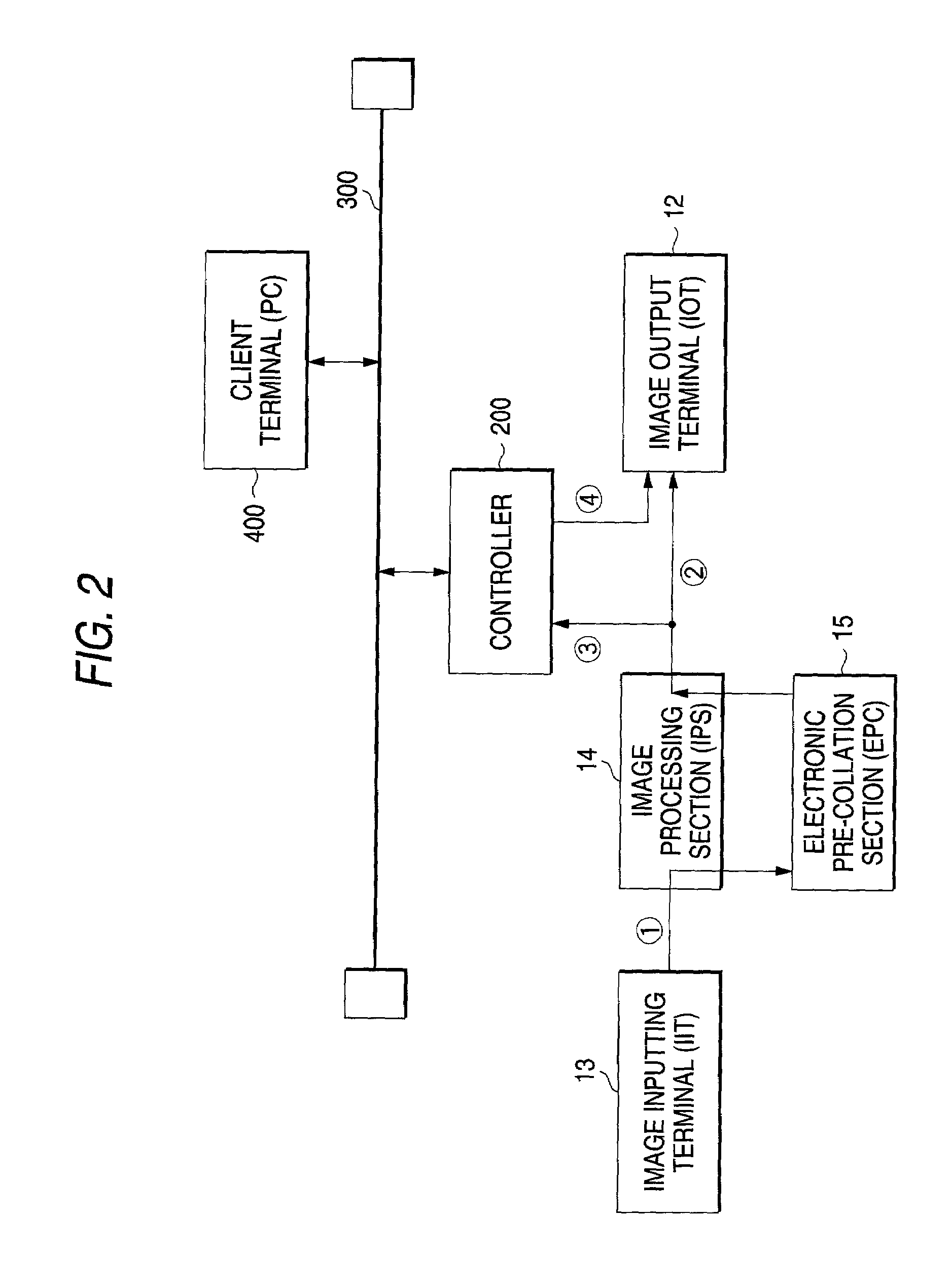
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7034961B2Increase memory capacityEfficient productivityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsData setComputer graphics (images)
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Rare earth permanent magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20110036457A1Efficient productivityGood magnetic performancePermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRemanenceProduction rate
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared by disposing a powdered metal alloy containing at least 70 vol % of an intermetallic compound phase on a sintered body of R—Fe—B system, and heating the sintered body having the powder disposed on its surface below the sintering temperature of the sintered body in vacuum or in an inert gas for diffusion treatment. The advantages include efficient productivity, excellent magnetic performance, a minimal or zero amount of Tb or Dy used, an increased coercive force, and a minimized decline of remanence.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20110036460A1Efficient productivityGood magnetic performancePermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRemanenceProduction rate
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared by disposing a powdered metal alloy containing at least 70 vol % of an intermetallic compound phase on a sintered body of R—Fe—B system, and heating the sintered body having the powder disposed on its surface below the sintering temperature of the sintered body in vacuum or in an inert gas for diffusion treatment. The advantages include efficient productivity, excellent magnetic performance, a minimal or zero amount of Tb or Dy used, an increased coercive force, and a minimized decline of remanence.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method and apparatus for forming an HSG-Si layer on a wafer
InactiveUS6838127B2Temperature regulationAvoid defectsTransistorElectric discharge tubesEngineeringMoisture
An HSG-Si layer is formed on a wafer under a uniform temperature condition. An apparatus for forming the HSG-Si layer includes a housing forming a process chamber, a first heater on which the wafer is positioned fixed in place at the bottom of the process chamber, a second heater at the top of the process chamber, and a thermal insulator which prevents the heat generated by the first heater from being transferred to the outside of the process chamber. A temperature control system regulates the temperature of the heaters. A method of forming the HSG layer includes steps of placing the wafer on the first heater, using the heaters to remove moisture from the wafer, injecting a source gas of the HSG-Si toward the upper surface of the wafer to form amorphous silicon on the wafer, and annealing the wafer for a predetermined period of time to transform the amorphous silicon into an HSG-Si layer. During the steps of forming the HSG-Si layer, the temperatures of the first and second heaters are regulated to maintain the surface temperature of the wafer constant.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rare earth magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20150093501A1Prevent oxidationMinimal hazardTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementRare-earth magnet
A rare earth magnet is prepared by disposing a R1-T-B sintered body comprising a R12T14B compound as a major phase in contact with an R2-M alloy powder and effecting heat treatment for causing R2 element to diffuse into the sintered body. The alloy powder is obtained by quenching a melt containing R2 and M. R1 and R2 are rare earth elements, T is Fe and / or Co, M is selected from B, C, P, Al, Si, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, Ge, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Hf, Ta, W, Pt, Au, Pb, and Bi.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
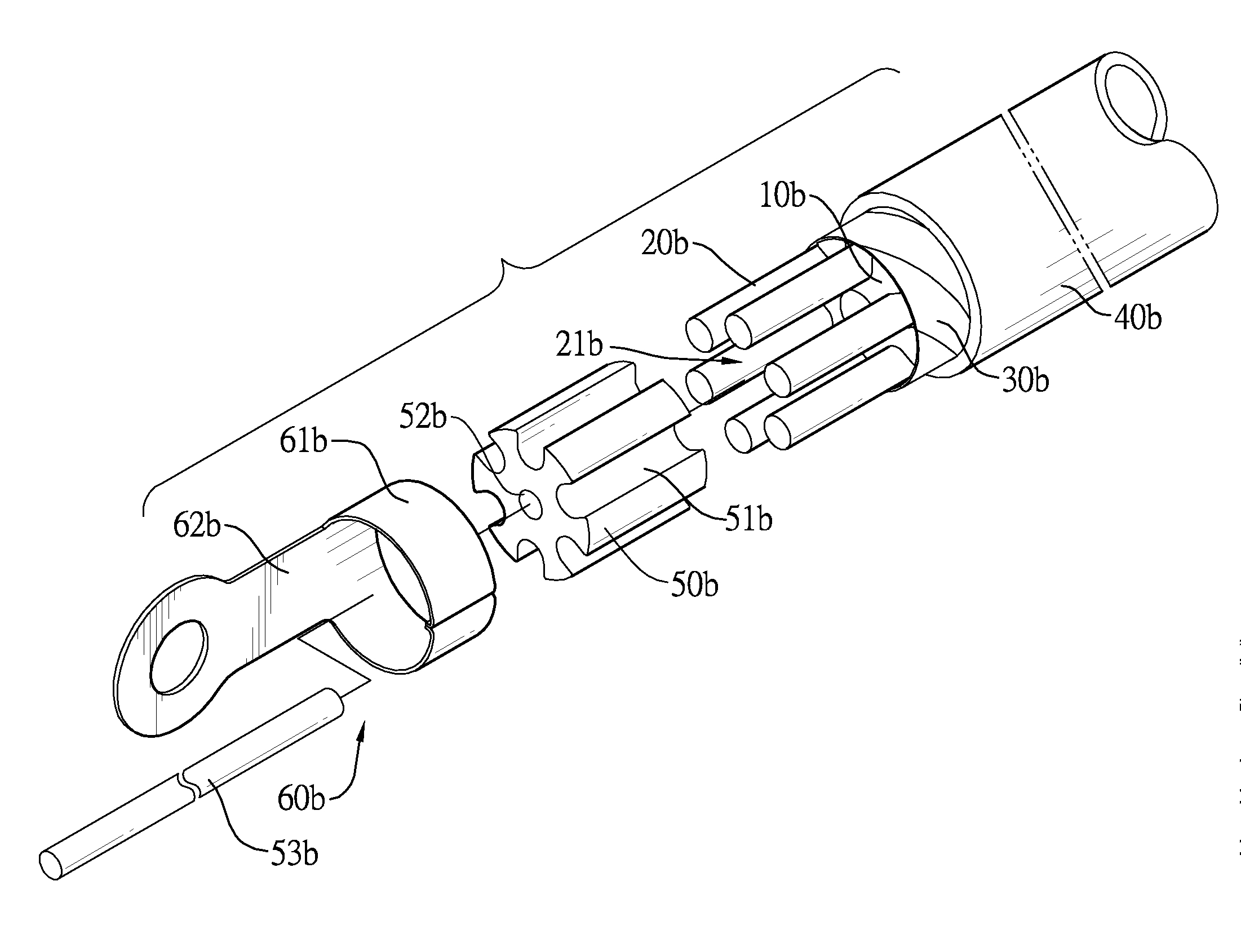
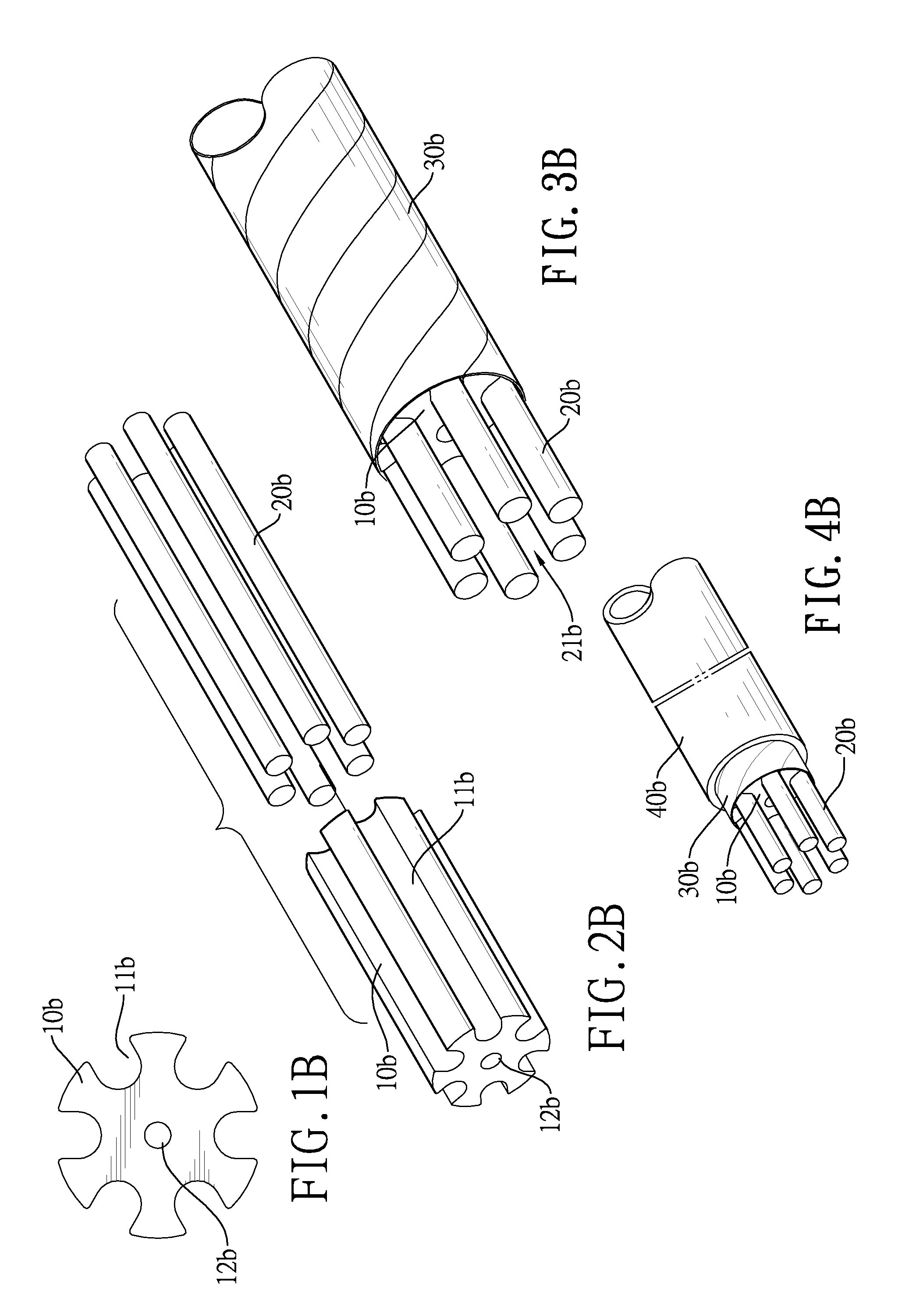
Parallel structure high conductibility cable with conductor keeper
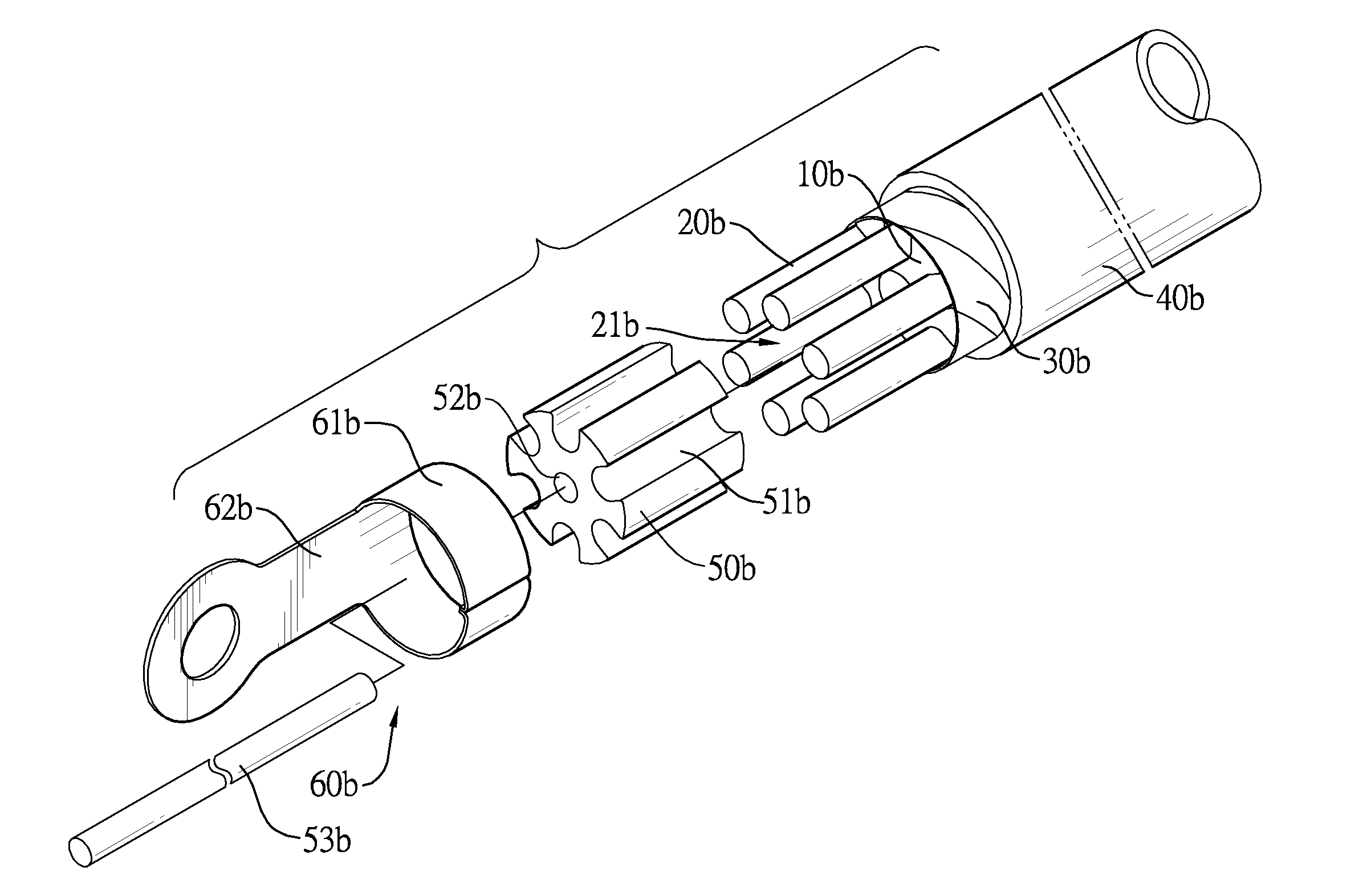
InactiveUS8586868B2Efficient productivityEnergy-savingSoldered/welded conductive connectionsConnections effected by permanent deformationElectrical conductorSkin effect
A cable has a conductor keeper, multiple bare conductors, a dielectric tape, a plastic jacket and two copper cylinders. The conductor keeper has multiple grooves. Each bare conductor is mounted in a corresponding groove of the conductor keeper and has a first end and a second end. The first end and second end of the bare conductor protrude out of the conductor keeper respectively so as to form two spaces. The dielectric tape is wrapped around the conductor keeper. The plastic jacket is coated around the dielectric tape. Two copper cylinders are mounted in the spaces of the bare conductors respectively to make the bare conductors surround the copper cylinders and the bare conductors connect to each other in parallel. Therefore, the skin effect is minimized and the bare conductors are efficient in that power consumption and emission of carbon dioxide during copper-smelting are significantly reduced.
Owner:LIU LI WEN +1
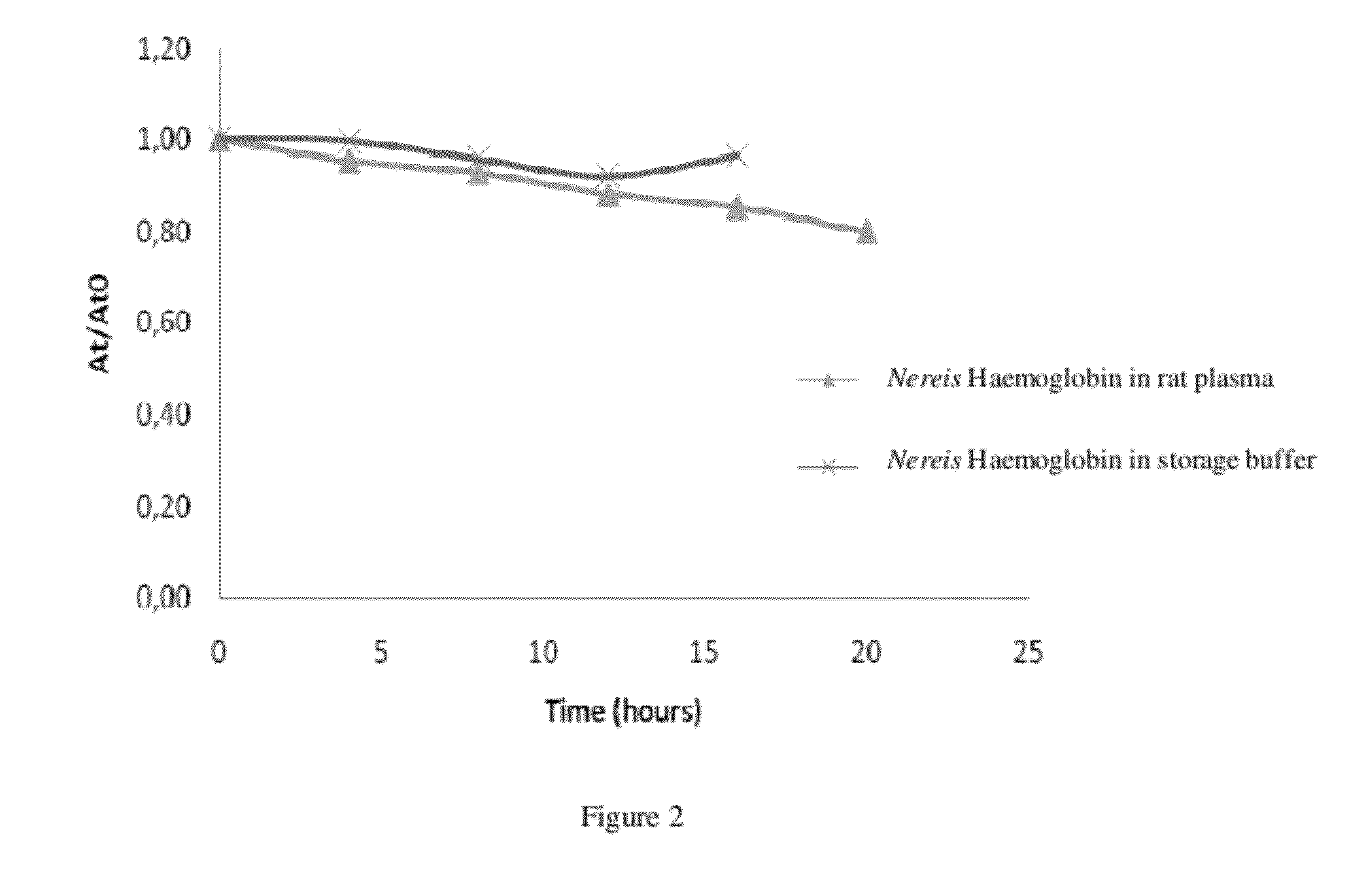
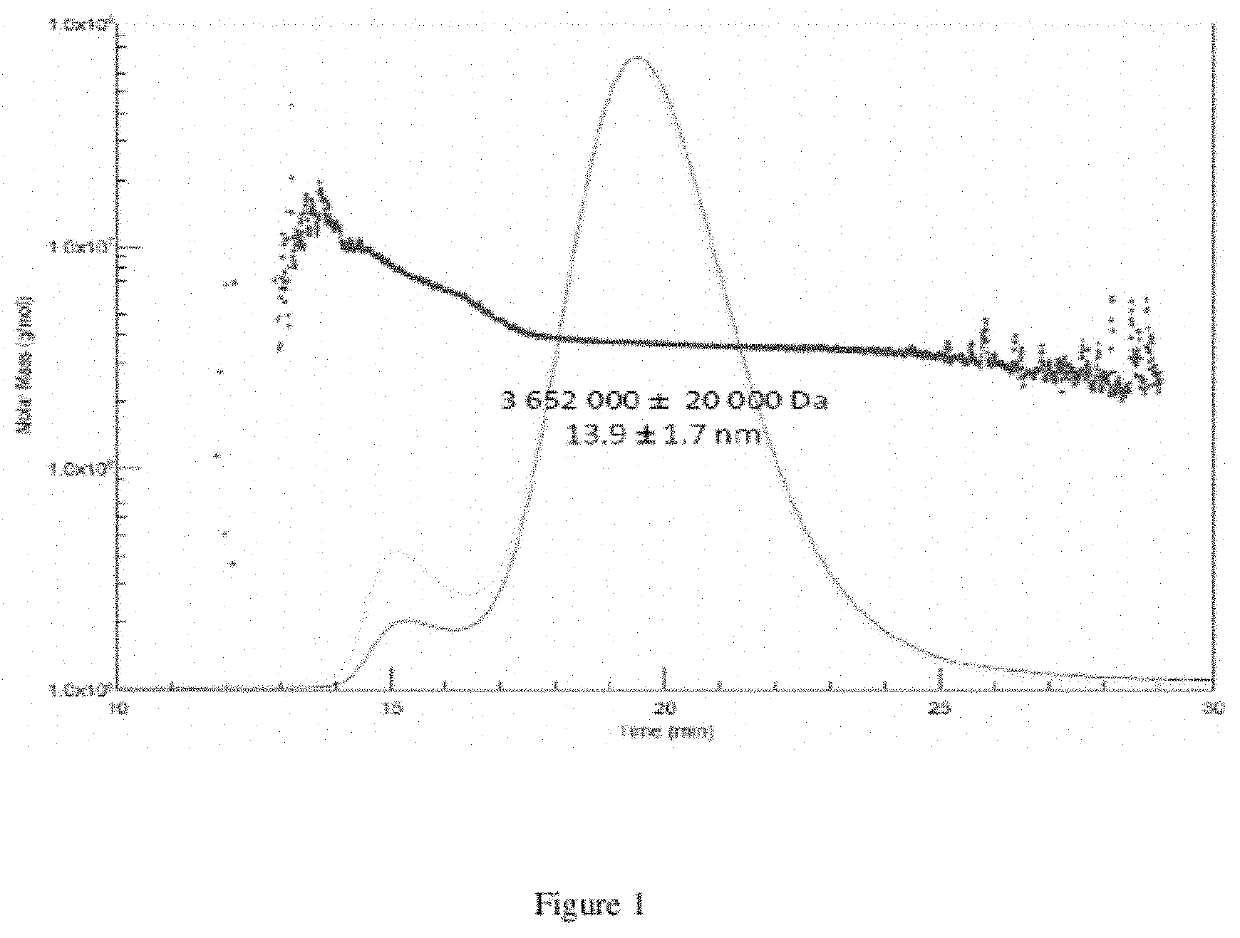
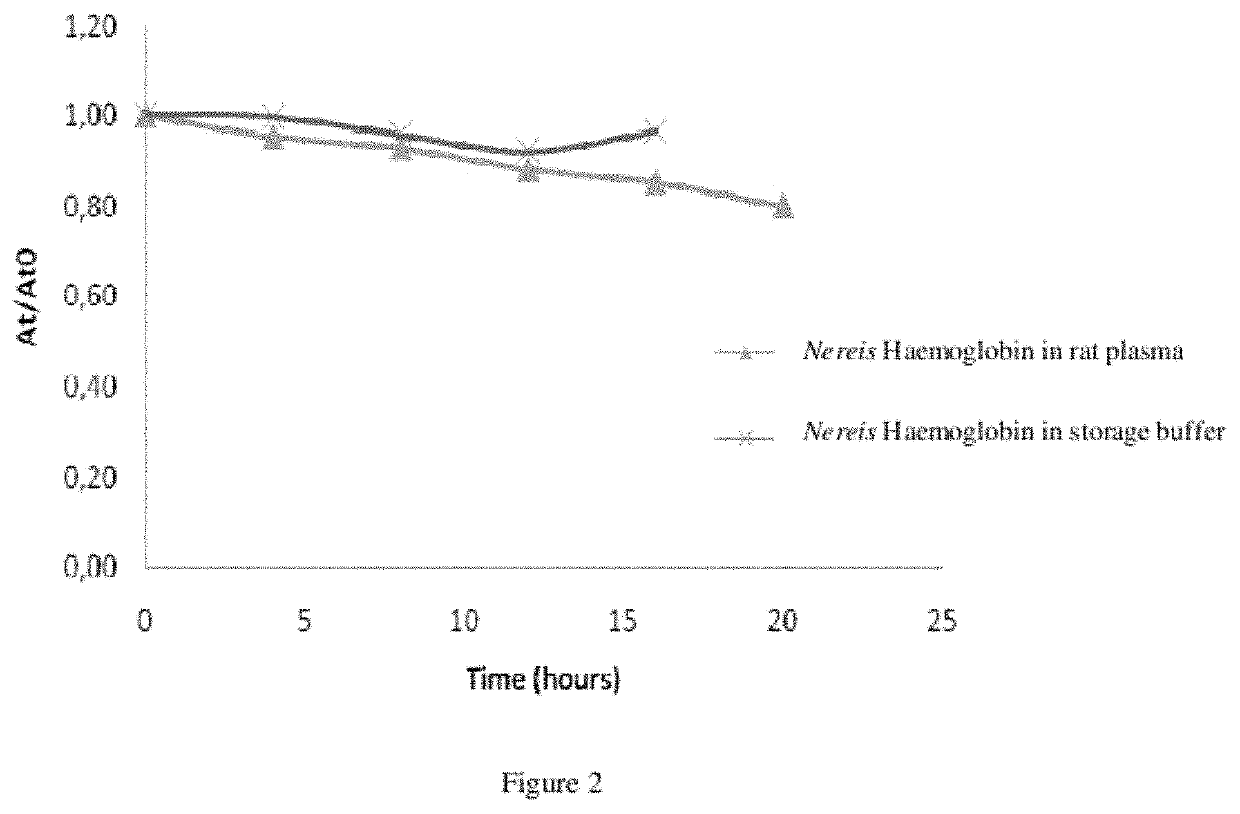
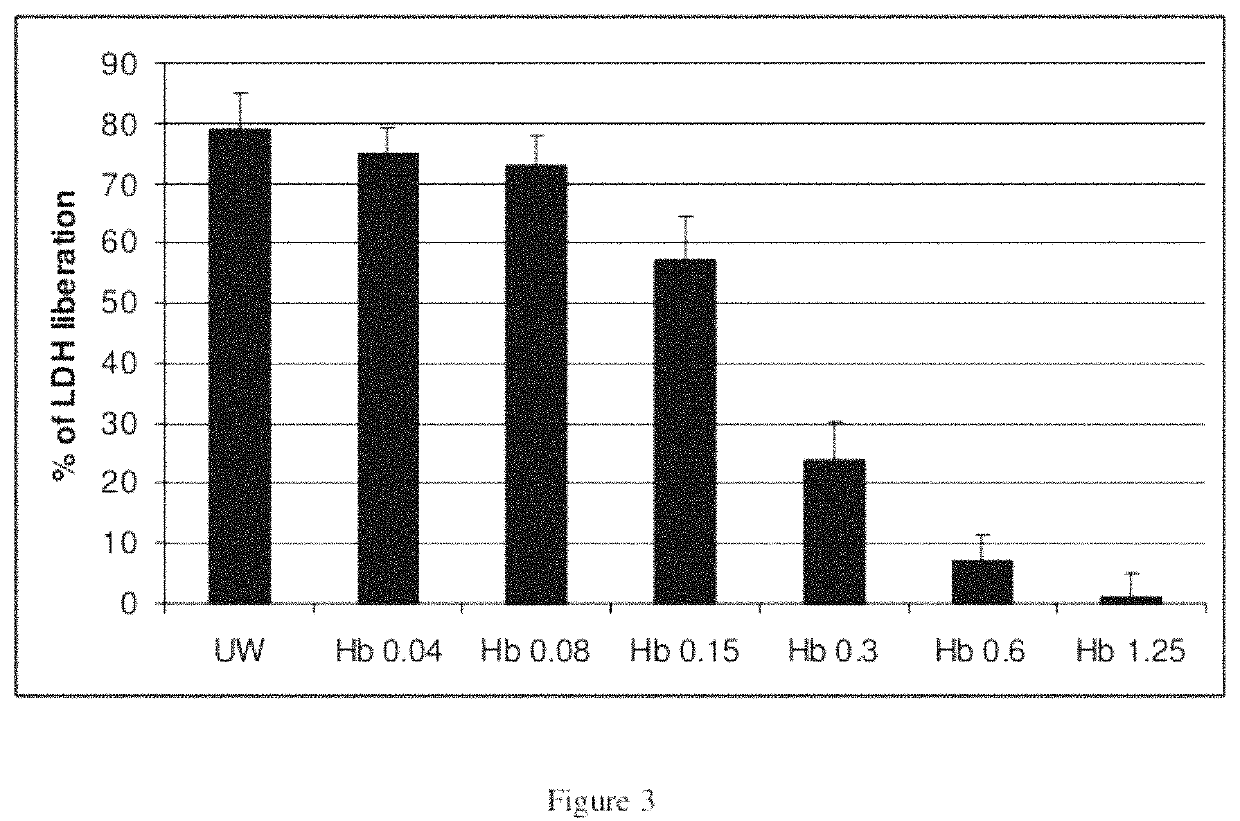
Novel heamoglobin and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120052136A1Reduce riskConvenient amountBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell culture mediaHemoglobin
The present invention relates to isolated haemoglobin from worms belonging to the Nereididae family and its use in cell culture medium, in preservation solutions and as artificial oxygen carrier for transfusion.
Owner:HEMARINA
Process for addition of haloalkanes to alkenes catalyzed by an organophosphite compound
InactiveUS6300532B1Improve productivityEfficient productivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsChemistryIodine atom
A process for catalytic addition of haloalkanes to alkenes involving the step of reacting the haloalkane with the alkene in the presence of a catalyst. The catalyst is an organophosphite compound represented by the following formula: P(ORa)(ORb)(ORc), where Ra, Rb, and Rc are each an alkyl group or an aralkyl group. The haloalkane is as follows: (i) CR1R2R3R4, wherein (a) each of R1, R2, R3 and R4 is selected from the group consisting of a chlorine atom, a bromine atom or an iodine atom; or (b) R1 is selected from the group consisting of a linear alkyl group; a halo-substituted linear alkyl group; an aralkyl group; an aralkyl group substituted with at least one of a halogen atom on the alkyl portion thereof or a halogen atom, alkyl group, alkoxy group or -CO2R10 wherein R10 is a C1-C4 alkyl group on the aryl portion thereof; an aryl group and an aryl group substituted with at least one of a chlorine atom, a fluorine atom, an alkoxy group or a -CO2R11 group, wherein R11 is a C1-C4 alkyl group; and R2, R3 and R4 are as follows: R2 is an iodine atom and R3 and R4 are each a halogen atom except R3 and R4 are not each a bromine atom or R2 and R3 are each a bromine atom and R4 is a halogen atom. The catalyzed addition of the haloalkane to the alkene proceeds without any other components present in an excess amount, by weight, of the combined amount of the haloalkane, alkene and organophosphite catalyst compound.
Owner:ALLIEDSIGNAL INC
Parallel structure high conductibility cable with conductor keeper
InactiveUS20110192647A1Efficient productivityEnergy-savingSoldered/welded conductive connectionsConnections effected by permanent deformationElectrical conductorSkin effect
A cable has a conductor keeper, multiple bare conductors, a dielectric tape, a plastic jacket and two copper cylinders. The conductor keeper has multiple grooves. Each bare conductor is mounted in a corresponding groove of the conductor keeper and has a first end and a second end. The first end and second end of the bare conductor protrude out of the conductor keeper respectively so as to form two spaces. The dielectric tape is wrapped around the conductor keeper. The plastic jacket is coated around the dielectric tape. Two copper cylinders are mounted in the spaces of the bare conductors respectively to make the bare conductors surround the copper cylinders and the bare conductors connect to each other in parallel. Therefore, the skin effect is minimized and the bare conductors are efficient in that power consumption and emission of carbon dioxide during copper-smelting are significantly reduced.
Owner:LIU LI WEN +1
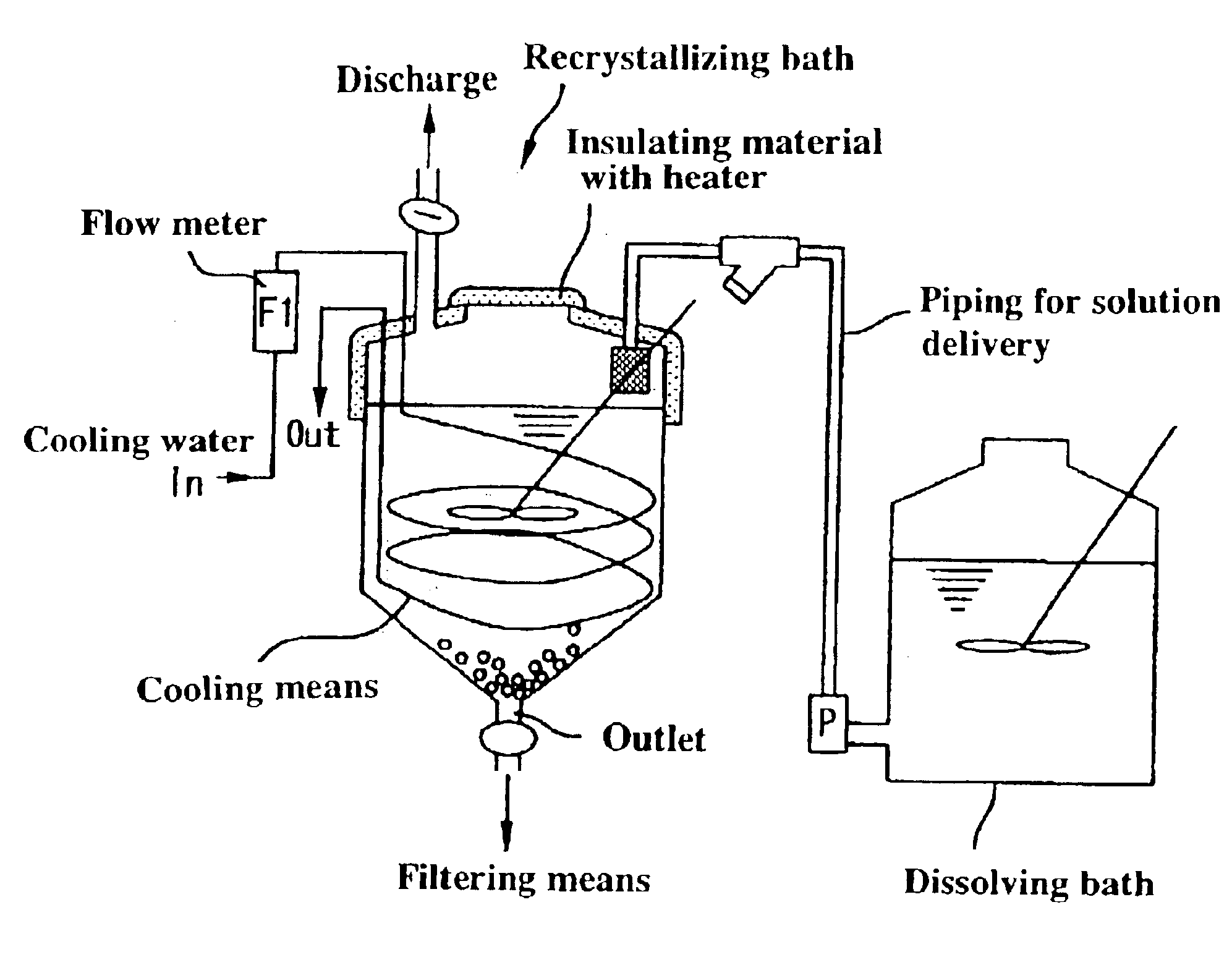
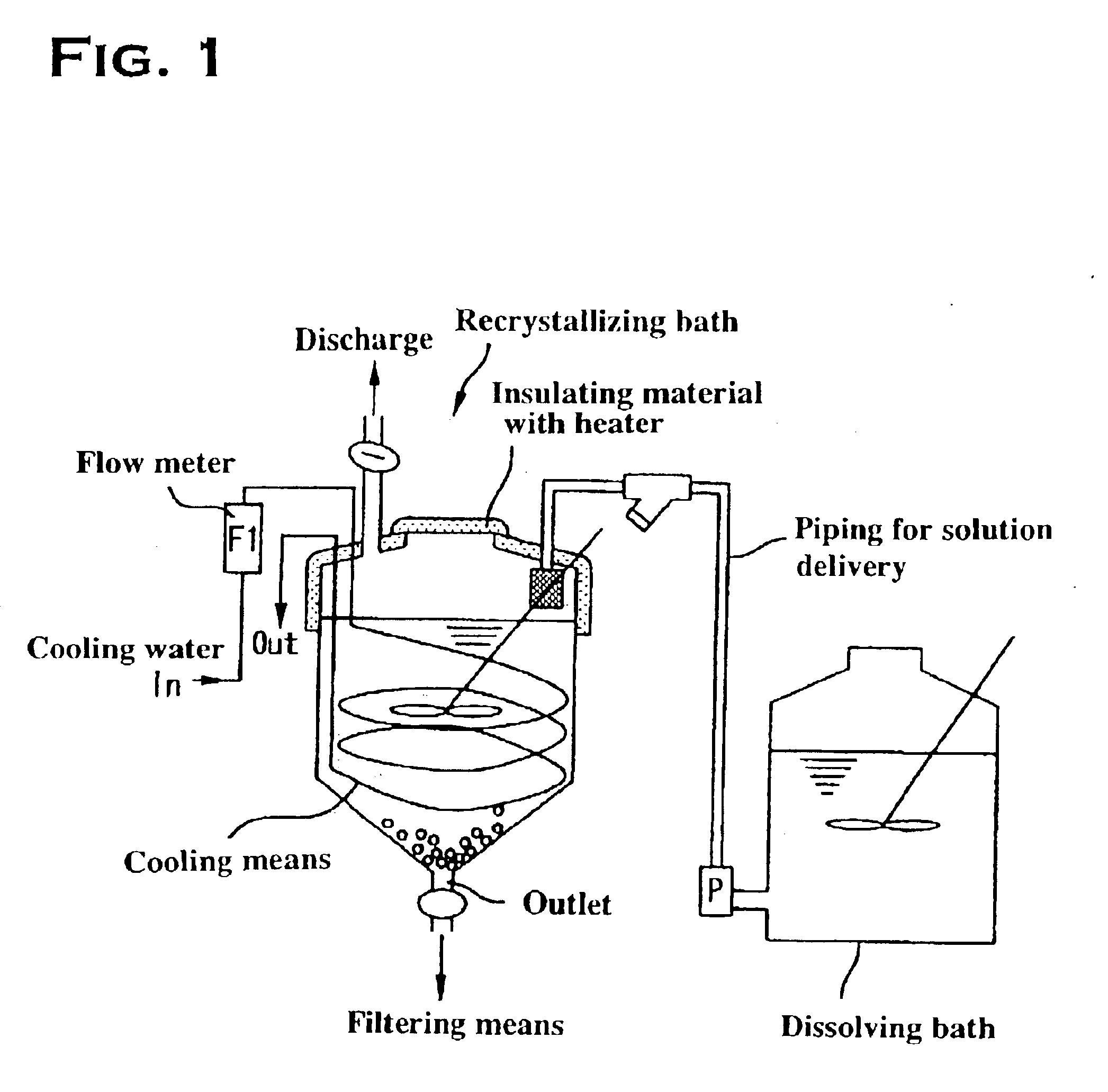
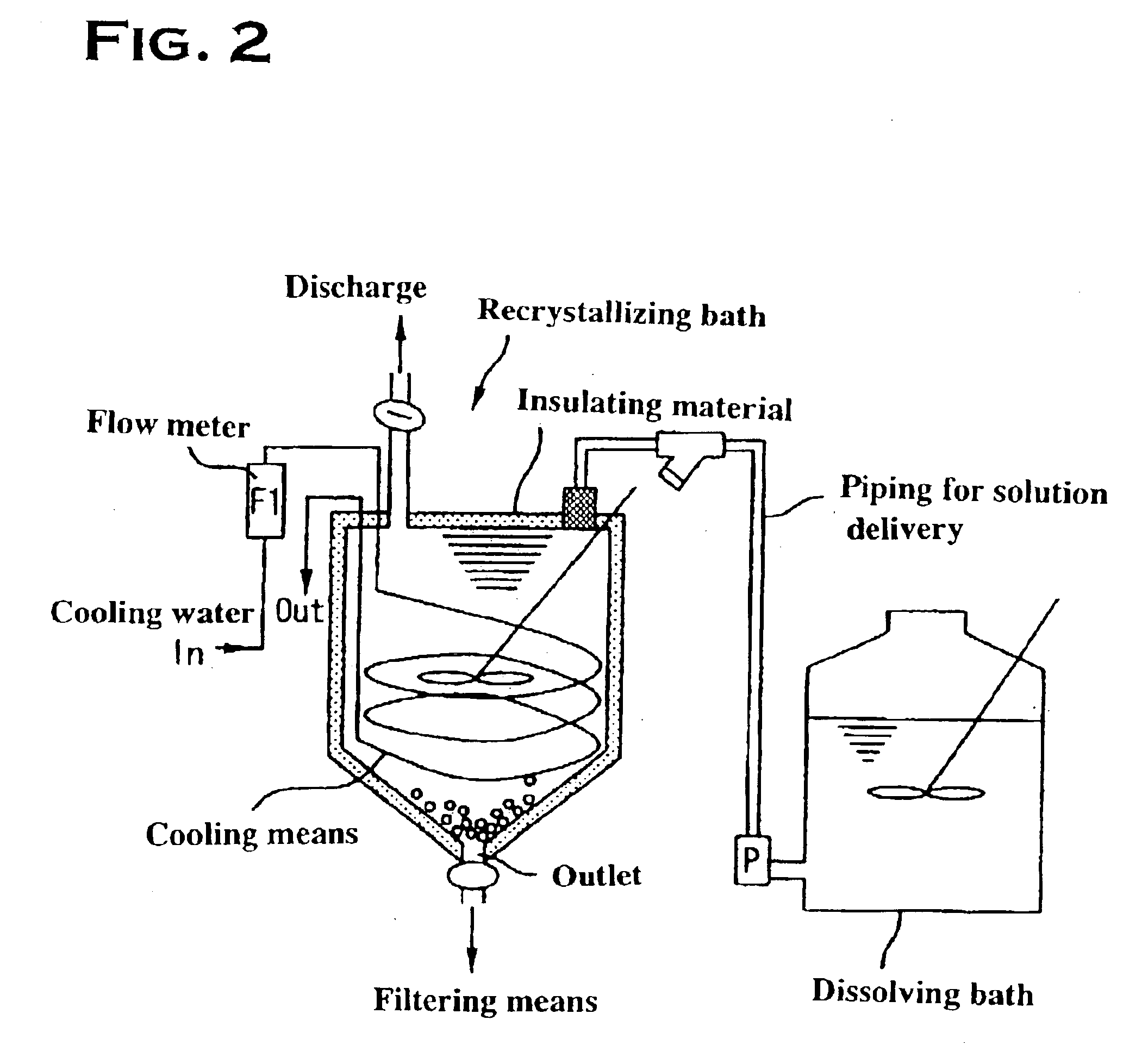
Method for manufacturing high-purity potassium fluoroniobate crystal, recrystallization bath used in manufacturing method thereof and high-purity potassium fluorotantalate crystal or high-purity potassium fluoroniobate crystal obtained by manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6860941B2Maintain good propertiesEfficient productivityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPotassium fluoridePotassium
It is an object to provide a product having a good crystal particle size distribution of a high-purity potassium fluorotantalate crystal or a high-purity potassium fluoroniobate crystal without using a physical method for particle classification. To that end, a method for manufacturing a high-purity potassium fluorotantalate crystal or a high-purity potassium fluoroniobate crystal is used, wherein the recrystallizing step comprising a first cooling process of cooling a saturated solution with a temperature of 60° C. to 90° C. obtained in the dissolving step at a cooling speed of T° C. / hour until the solution temperature of the saturated solution becomes a temperature of the range of 35 to 50° C., and a second cooling process of cooling the solution at a cooling speed of [T−18]° C. / hour to [T−1]° C. / hour from the end of the first cooling process to the solution temperature becoming a temperature of 10 to 20° C.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet and its preparation
ActiveUS20110036459A1Efficient productivityGood magnetic performancePermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRemanenceProduction rate
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared by disposing a powdered metal alloy containing at least 70 vol % of an intermetallic compound phase on a sintered body of R—Fe—B system, and heating the sintered body having the powder disposed on its surface below the sintering temperature of the sintered body in vacuum or in an inert gas for diffusion treatment. The advantages include efficient productivity, excellent magnetic performance, a minimal or zero amount of Tb or Dy used, an increased coercive force, and a minimized decline of remanence.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Heamoglobin and uses thereof
ActiveUS11224218B2Reduce riskConvenient amountBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyCell culture media
The present invention relates to isolated haemoglobin from worms belonging to the Nereididae family and its use in cell culture medium, in preservation solutions and as artificial oxygen carrier for transfusion.
Owner:HEMARINA
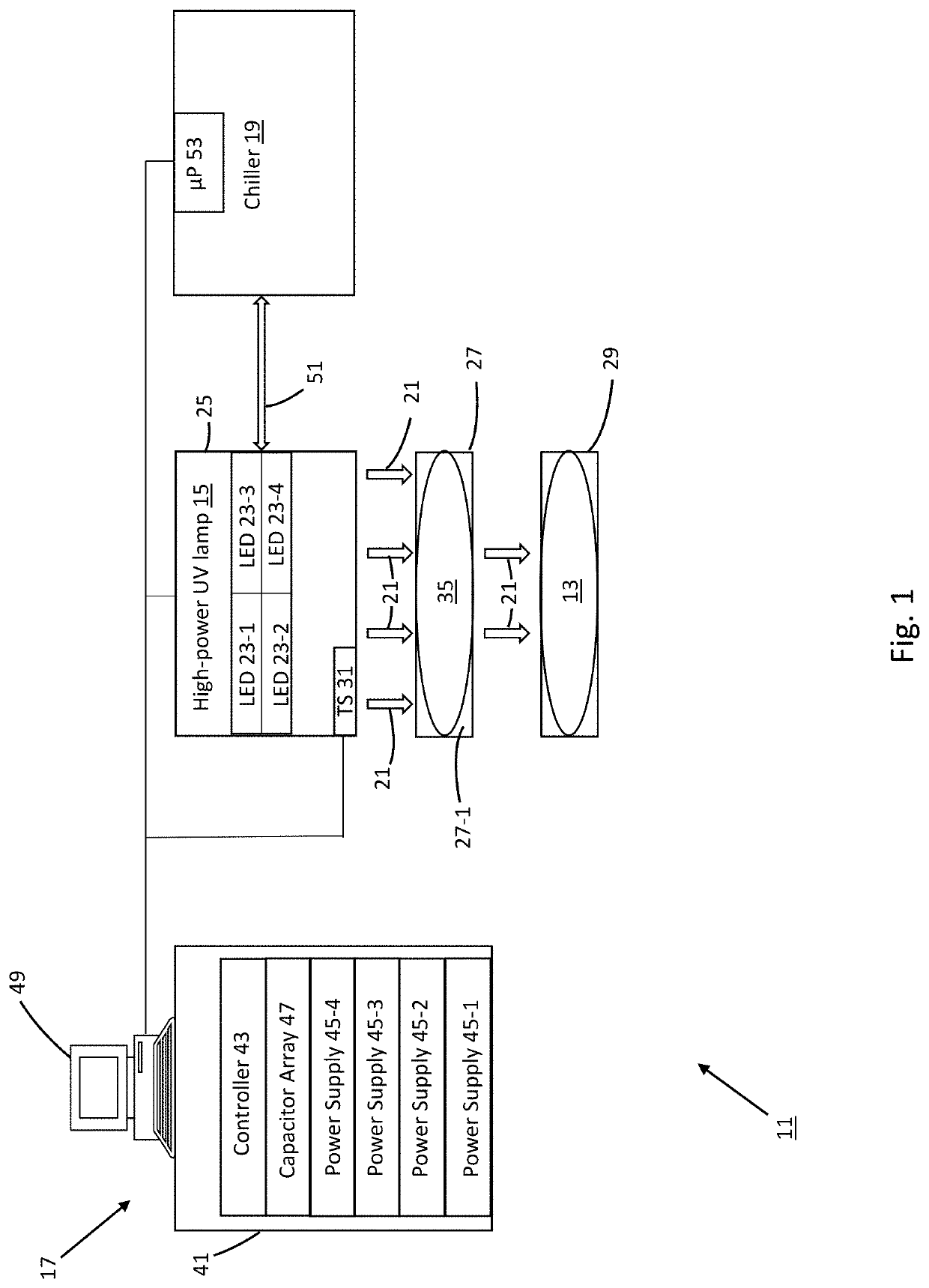
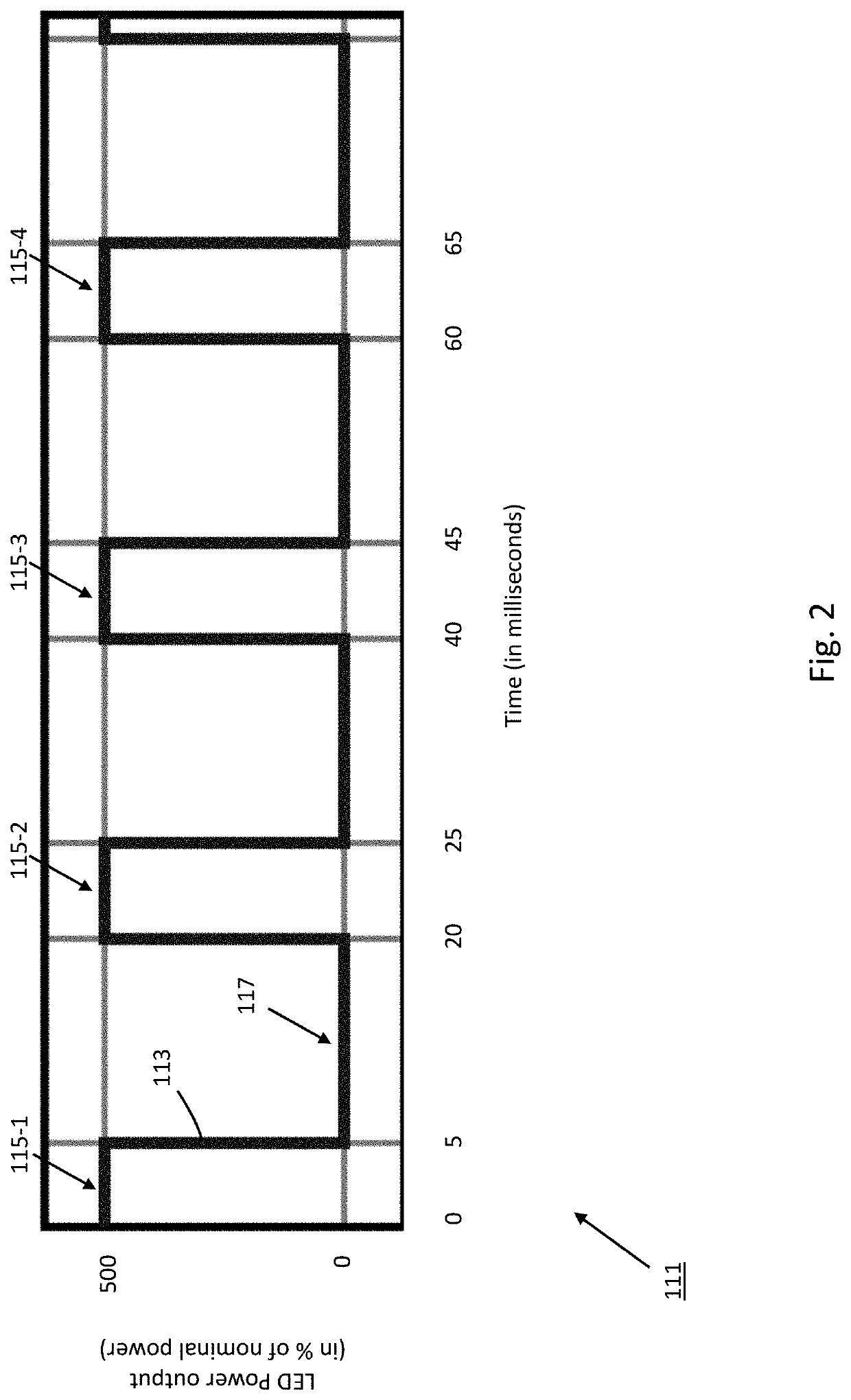
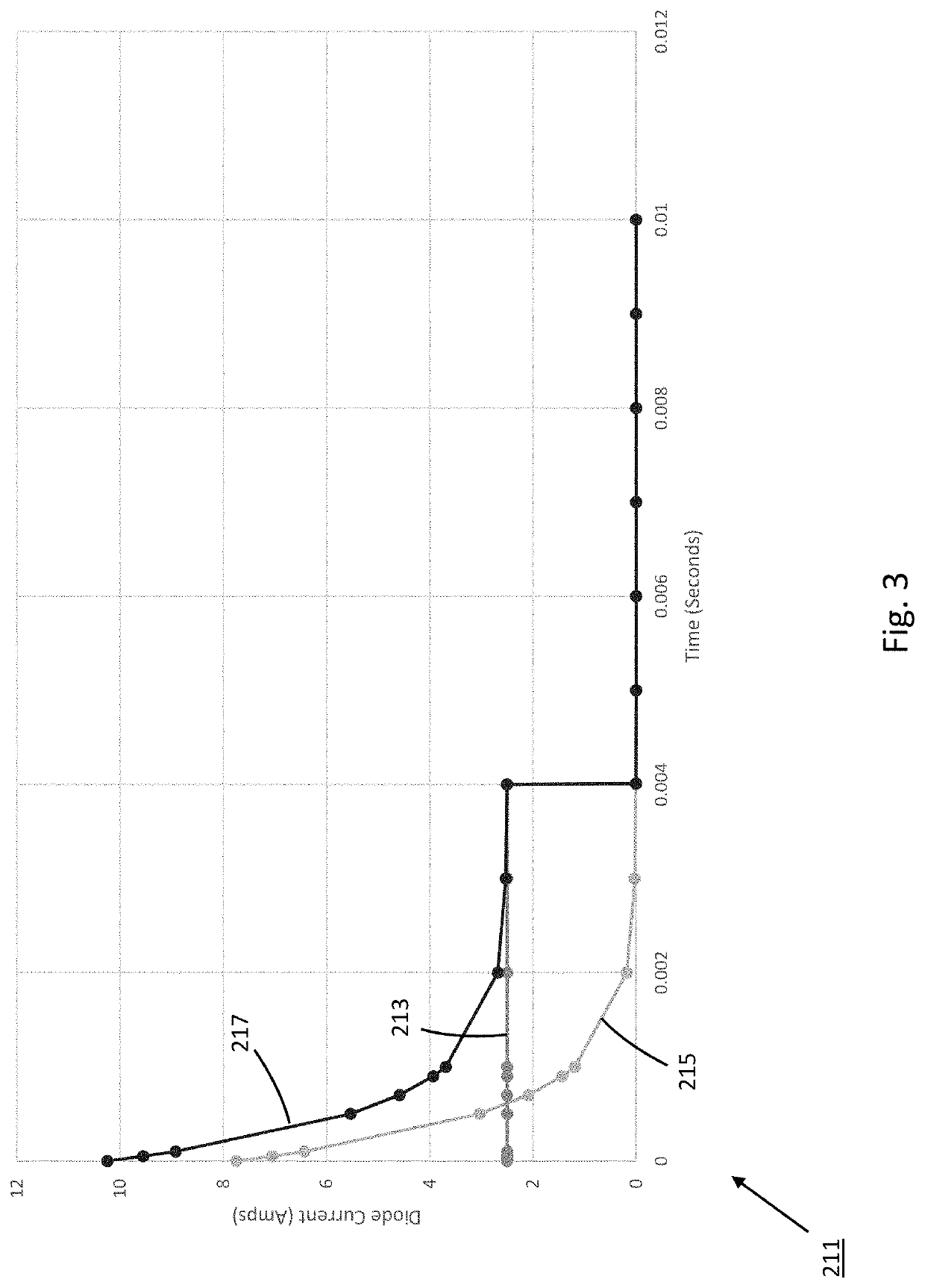
High-power light system
ActiveUS20200253014A1Maximize productionLightweight productionElectrical apparatusComputational physicsLighting system
A high-power light system includes a lamp for producing light within a designated wavelength range, a chiller for maintaining the lamp below a defined temperature threshold, and a control module for regulating operation of both the lamp and the chiller. The lamp includes a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) arranged into independently-operable modules. In use, the control module selectively overdrives the LEDs to yield high-power light within the designated wavelength range. To prevent overheating within the lamp, the control module restricts the lamp to a pulse-based operational cycle, whereby each period of LED activation is of limited duration and is immediately followed by a period of deactivation at least three times as long in duration as the period of activation. Additionally, one or more temperature sensors are disposed within the lamp and enable the control module to temporarily suspend LED activation when measured temperature levels exceed the defined threshold.
Owner:CARPE DIEM TECH
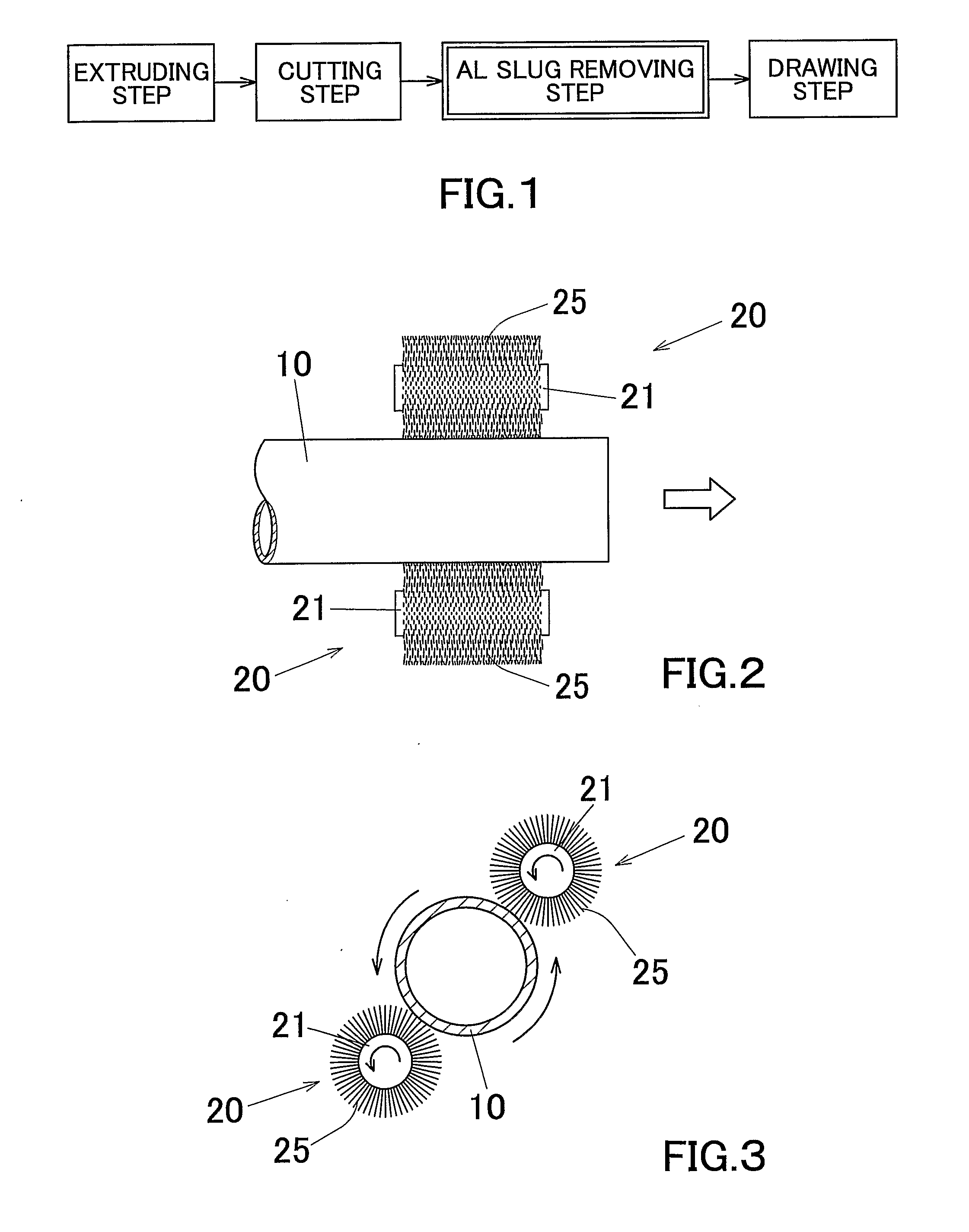
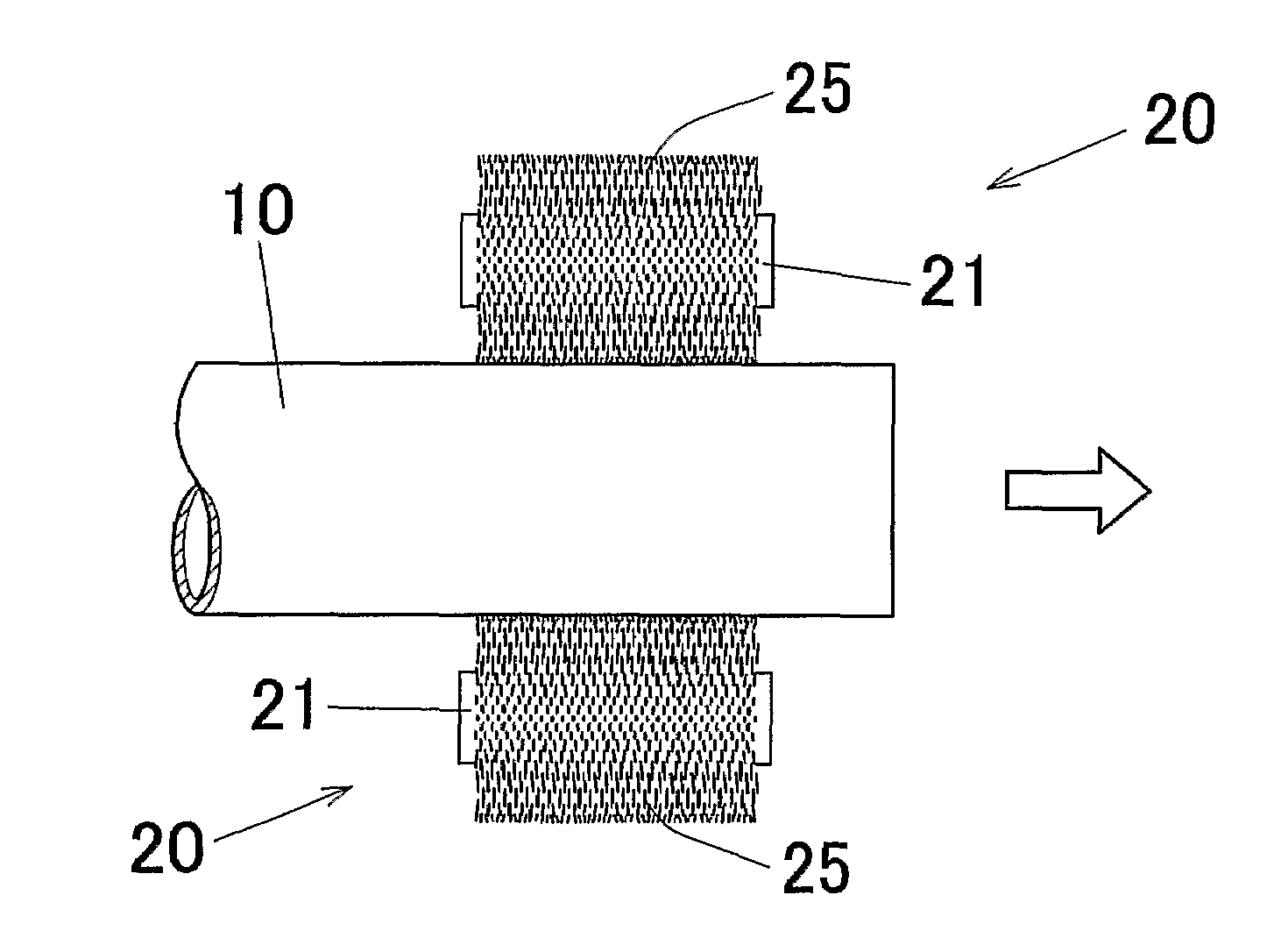
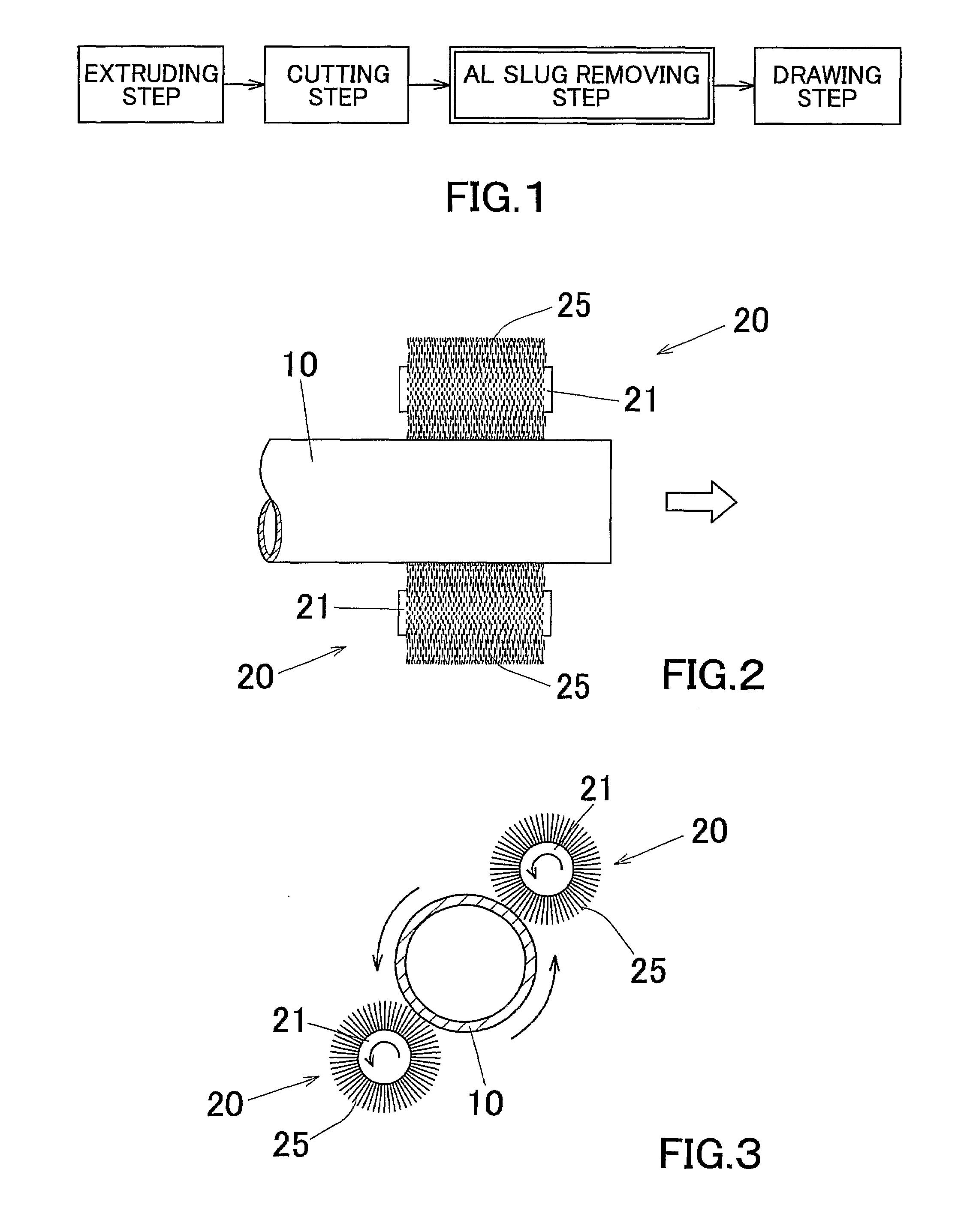
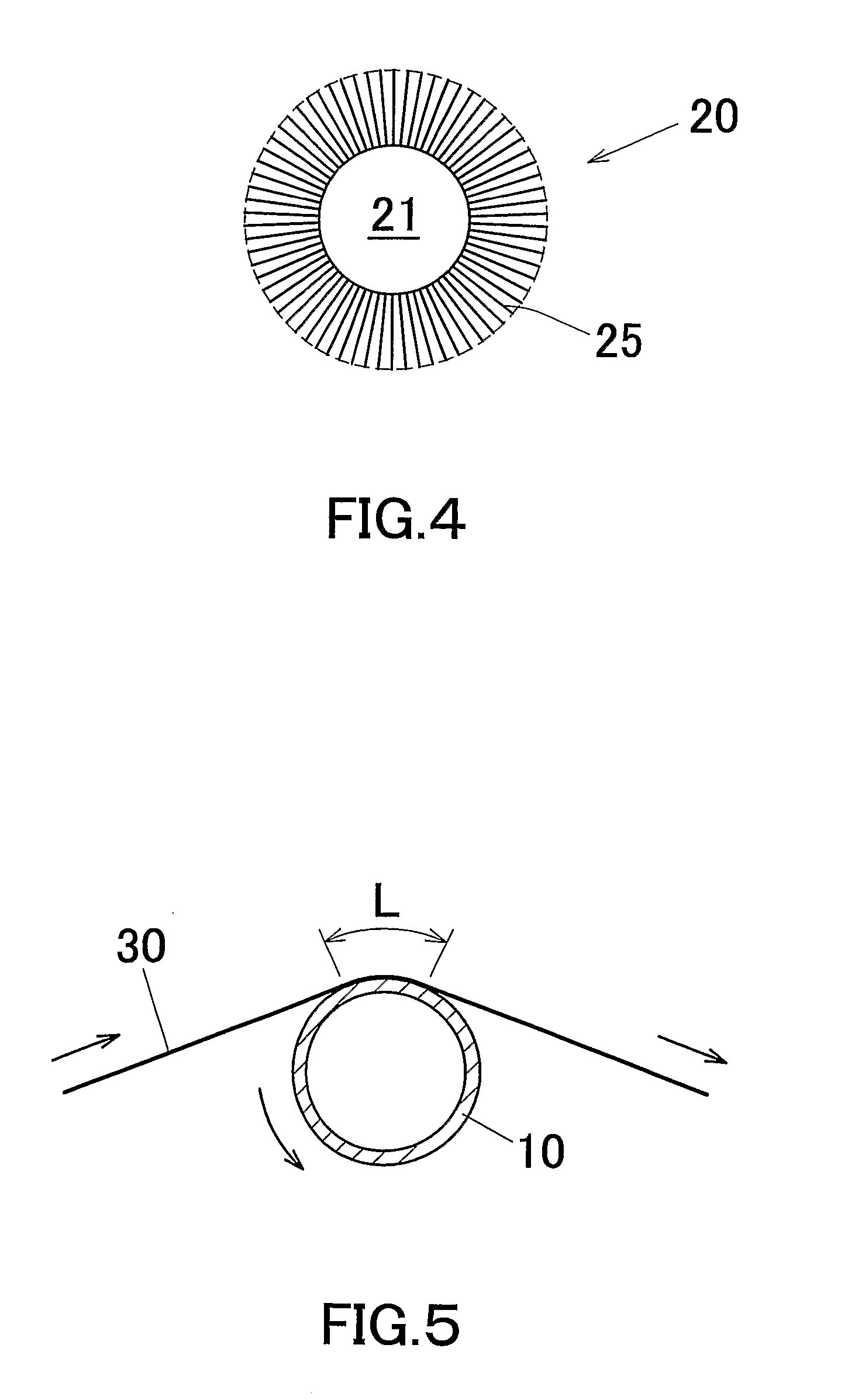
Aluminum Pipe Production Method
InactiveUS20070277580A1Quality improvementEfficient productivityPhotosensitive materialsRolling equipment maintainenceProduction rateMethods of production
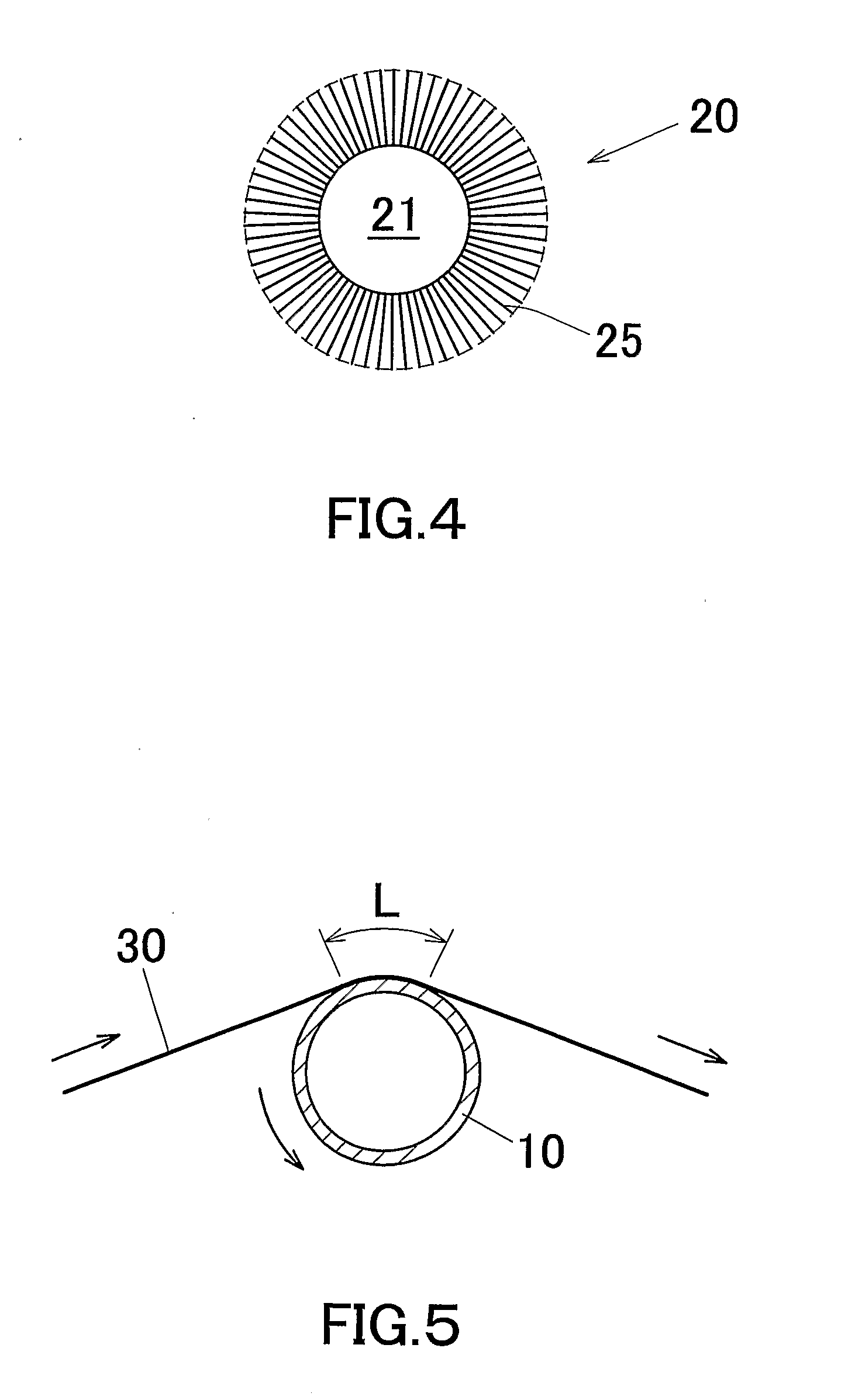
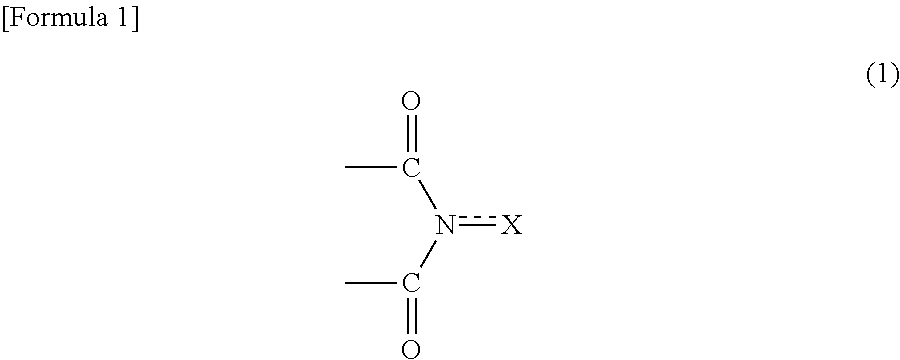
The invention is directed to a aluminum pipe production method comprising an extrusion step for obtaining an aluminum raw pipe (10) and a drawing step for executing a drawing process of the aluminum raw pipe (10). Before executing the drawing step a slug removing step for removing aluminum slugs (1) adhering to a surface of the aluminum raw pipe (10) is executed by rubbing off the aluminum slugs (1). This can provide an aluminum pipe production method capable of preventing generation of defect protrusions while improving the productivity.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Process for producing aromatic carboxylic acid
InactiveUS9242921B2High catalytic activityEfficient productionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by oxidationReaction intermediateManganese
A process for allowing an oxidation reaction efficiently to produce an object aromatic carboxylic acid with an efficient productivity by improving a catalyst activity even in the presence of a relatively small amount of a catalyst is provided.The process comprises oxygen-oxidizing an aromatic compound having an alkyl group and / or an alkylene group as a substrate in the presence of a catalyst containing a cyclic imino unit having an N—OR group (wherein R represents a hydrogen atom or a protecting group for a hydroxyl group) and a transition metal co-catalyst (a cobalt compound, a manganese compound, and a zirconium compound) to produce the aromatic carboxylic acid corresponding to the aromatic compound. The oxidation reaction is carried out with feeding a mixture of the catalyst and at least one member selected from the group consisting of the substrate, a reaction intermediate (e.g., a ketone and an aldehyde), and a reaction product (e.g., water and an aromatic carboxylic acid) successively or continuously to the oxidation reaction system. The oxidation reaction may usually be carried out in the absence of a reaction solvent. The reaction may be conducted with removing water produced by the reaction from the reaction system.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Aluminum pipe production method
InactiveUS7631530B2Quality improvementEfficient productivityPhotosensitive materialsRolling equipment maintainenceProduction rateHigh productivity
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Process for producing polymer film
ActiveUS20180171085A1Improve productivityEfficient productivityCoatingsProduction ratePolymer thin films
The present invention provides a process for producing a polymer film at high productivity: during a process for drying gripped portions of both edges of a gel film, a first heat treatment is performed by blowing hot air in the film width direction and a second heat treatment is performed by blowing hot air at gripped portions of both edges of the gel film in a direction parallel to the film running direction.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Calibration device and calibration method for display panel brightness uniformity
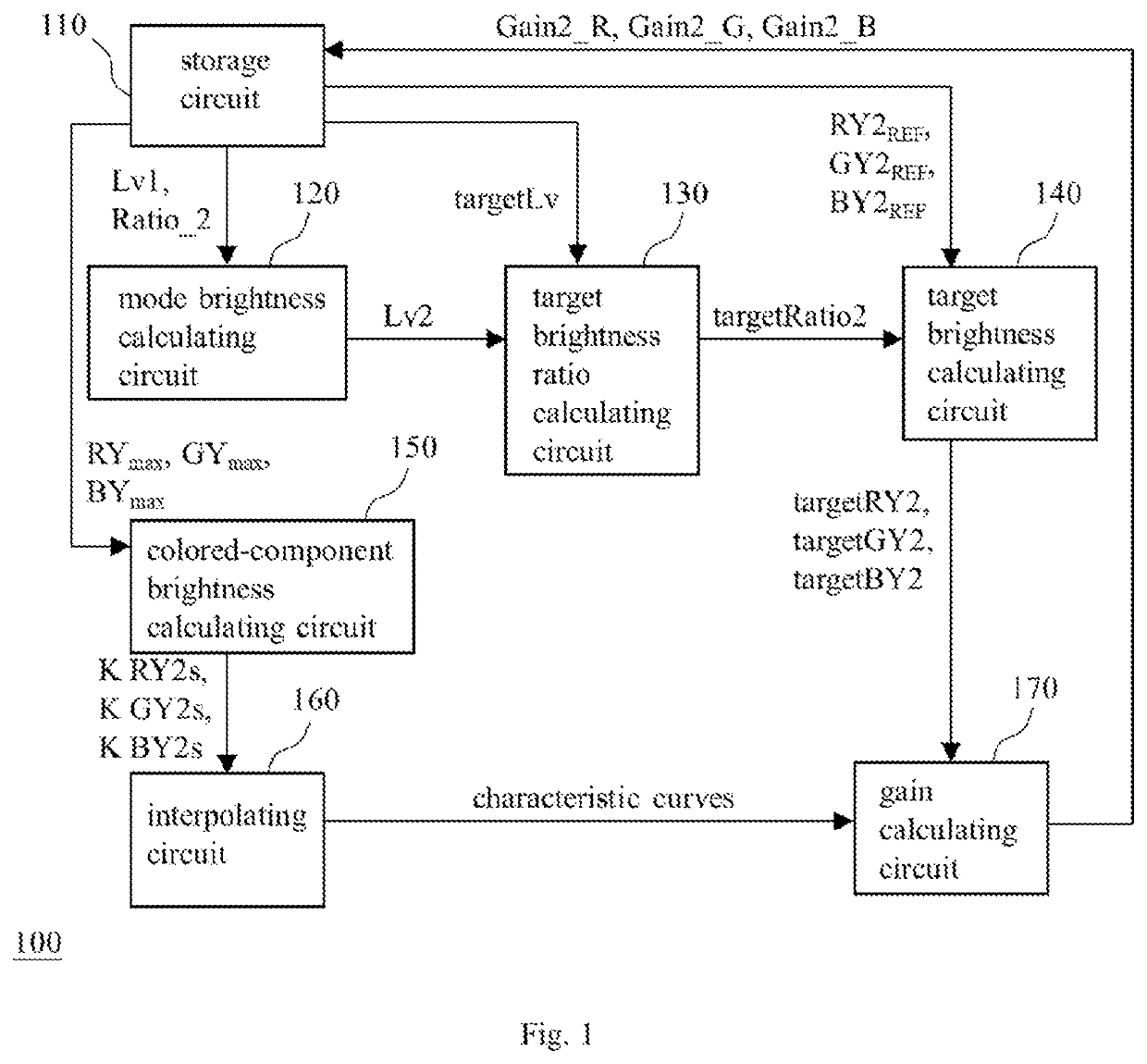
Disclosed is a calibration device and calibration method for display panel brightness-uniformity. The method includes: storing a first-mode measured brightness-value, K sets of maximum brightness-values of a display region, a set of second-mode brightness-reference-values, and a second ratio of a second-mode measured brightness-value to the first-mode measured brightness-value; calculating a second-mode brightness-value according to the first-mode measured brightness-value and the second ratio; calculating a second-mode target brightness ratio according to a target brightness setting and the second-mode brightness-value; calculating X second-mode target brightness-value(s) according to the set of second-mode brightness-reference-values and the second-mode target brightness ratio; calculating K sets of second-mode colored-component brightness-values according to the K sets of maximum brightness-values; generating X second-mode brightness curve(s) according to the K sets of second-mode colored-component brightness-values; and calculating X second-mode brightness-gain(s) for second-mode calibration according to the X second-mode target brightness-value(s) and the X second-mode brightness curve(s).
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Process Stream Decontamination Systems and Methods with Atomization Optimization
InactiveUS20140286823A1Optimizes amountConvenient timeProcess control/regulationLavatory sanitoryInjection pressureProcess engineering
A decontamination system for decontaminating at least one contaminant in a process stream. Decontaminant liquid is dispersed into the process stream sing atomization. Differential injection pressure and / or injection flow rate are monitored to help ensure that the atomization process is optimized.
Owner:ENERGY FAB SOLUTIONS
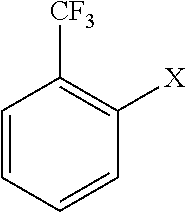
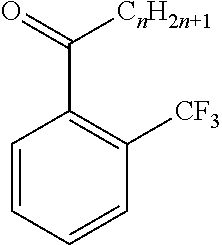
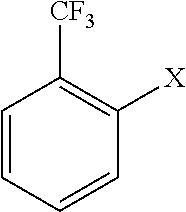
Method of producing 2'-trifluoromethyl group-substituted aromatic ketone
ActiveUS20170088499A1Efficient productivitySimple methodOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by hydrolysisGrignard reagentAromatic ketones
A method produces a 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone and includes reacting a 2-halogen-substituted benzotrifluoride compound with magnesium metal to convert the compound to a Grignard reagent; and reacting the Grignard reagent with an acid anhydride; and then hydrolyzing the resultant to produce a 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone. The method of producing a 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone enables 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone to be produced without using expensive raw materials by generating a Grignard reagent as an intermediate and reacting this Grignard reagent with an acid anhydride in an efficient productivity. The 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone that is produced by the method of producing a 2′-trifluoromethyl-substituted aromatic ketone can be used as fine chemicals, raw materials for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, raw materials for resins and plastics, electronics and information related materials, optical materials, and the like.
Owner:TORAY FINE CHEMICALS CO LTD
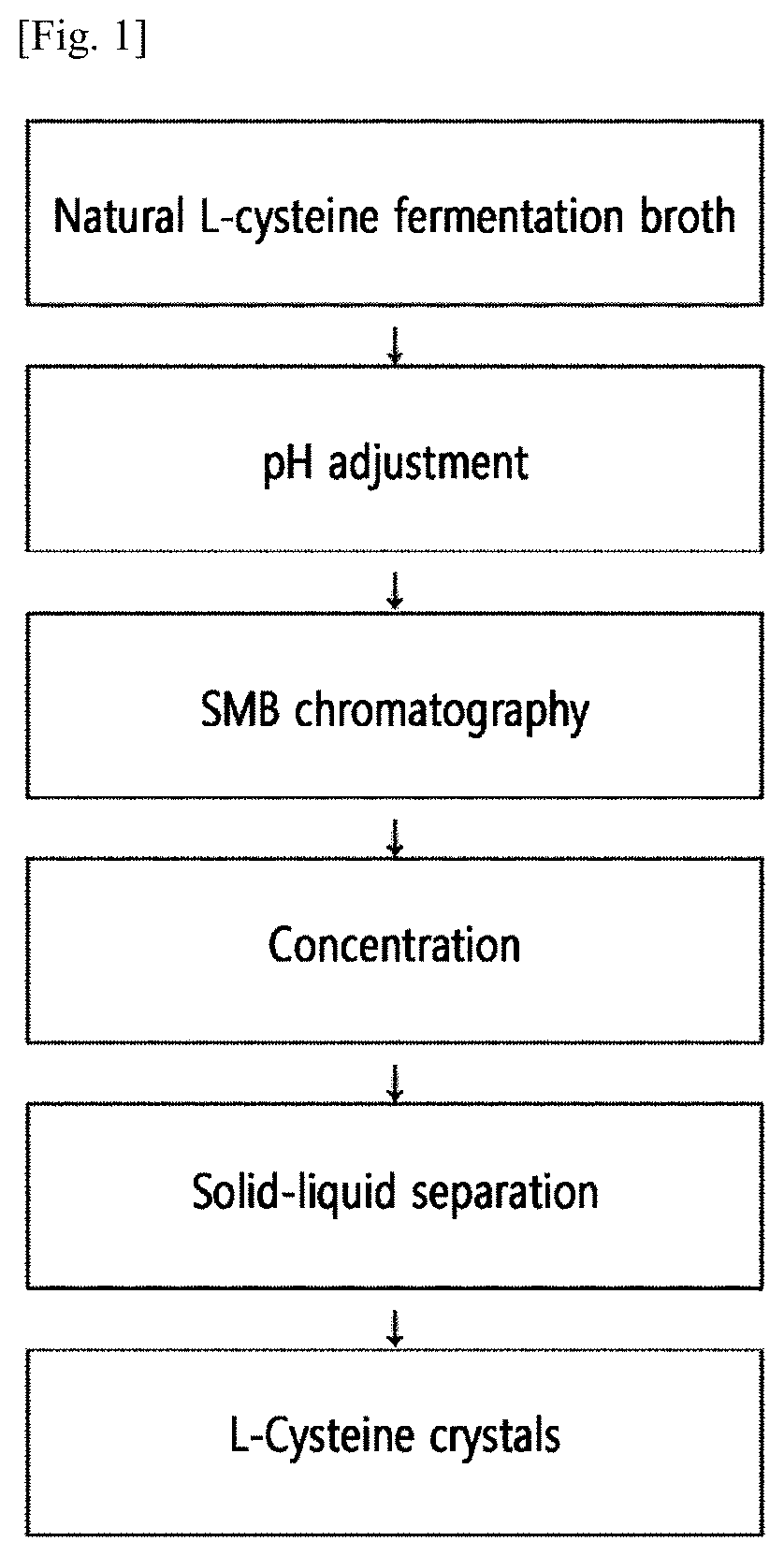
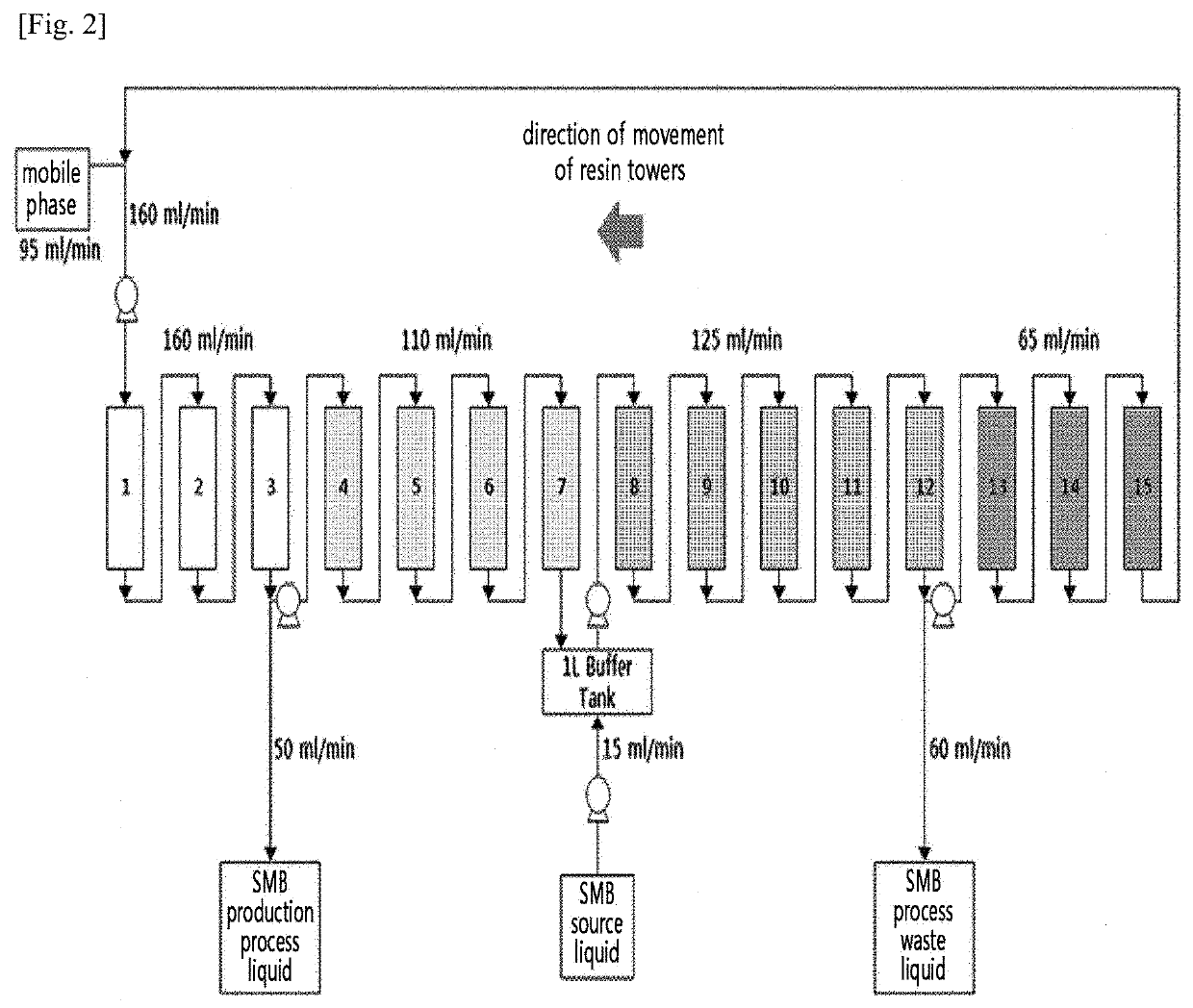
Method for preparing natural l-cysteine crystals by continuous chromatography
ActiveUS20210054424A1High purityHigh rateCation exchanger materialsOrganic chemistryChemical reactionChemical compound
The present disclosure relates to a method for preparing L-cysteine crystals, and L-cysteine crystals prepared by the method. Through the method for preparing L-cysteine crystals of the present disclosure, L-cysteine crystals can be obtained from a natural L-cysteine fermentation broth with a high recovery rate and / or purity without a chemical reaction or the use of an artificial synthetic compound.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
LED lamp forming material and light-pervious waterproof LED lamp
ActiveUS10001271B2Improves UV resistanceLow temperature resistanceElectric circuit arrangementsProtective devices for lightingWeather resistanceEngineering
The present invention relates to an LED lamp forming material with an outstanding weather resistance performance and a reliable seal performance, and also relates to a light-pervious waterproof LED lamp manufactured by the LED lamp forming material. A lamp forming mold is prepared according to a shape of the light-pervious waterproof damp required by a user, a circuit board including a driving circuit and an LED light source is suspended within a molding cavity of the LED lamp forming mold, a PVC paste or a modified PVC paste is injected into the molding cavity, heating is performed for 15 to 30 minutes, the PVC paste or the modified PVC paste within the molding cavity of the LED lamp is solidified, the solidified LED waterproof lamp is taken out of the molding cavity, so as to obtain the light-pervious waterproof LED lamp.
Owner:XU SONGYAN
Method of Manufacturing a Magnetic Recording Medium
InactiveUS20100133229A1Improve performanceSimple processDecorative surface effectsCoating part of support with magnetic layerResistAtmosphere
A method of manufacturing a magnetic recording medium avoiding degradation of magnetic performance due to a manufacturing process, including forming a mask protective film on a magnetic layer; forming a resist with a predetermined pattern on the mask protective film; forming a protective mask by etching the mask protective film using the resist as a mask; forming protrusions and recesses on a magnetic layer by etching the magnetic layer using the resist and the protective mask as masks; removing the protective mask; and forming a protective layer on the magnetic layer having the protrusions and recesses; where the magnetic recording medium is not exposed to the atmosphere during a period of time at least from the step of removing the protective mask to the step of forming the protective layer.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Process stream decontamination systems and methods with atomization optimization
InactiveUS8968650B2Optimizes amountConvenient timeProcess control/regulationSamplingInjection pressureProcess engineering
Owner:ENERGY FAB SOLUTIONS
Process for producing polymer film
The present invention provides a process for producing a polymer film at high productivity: during a process for drying gripped portions of both edges of a gel film, a first heat treatment is performed by blowing hot air in the film width direction and a second heat treatment is performed by blowing hot air at gripped portions of both edges of the gel film in a direction parallel to the film running direction.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
High-power light system
ActiveUS11497093B2Maximize productionLightweight productionElectrical apparatusEngineeringComputational physics
A high-power light system includes a lamp for producing light within a designated wavelength range, a chiller for maintaining the lamp below a defined temperature threshold, and a control module for regulating operation of both the lamp and the chiller. The lamp includes a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) arranged into independently-operable modules. In use, the control module selectively overdrives the LEDs to yield high-power light within the designated wavelength range. To prevent overheating within the lamp, the control module restricts the lamp to a pulse-based operational cycle, whereby each period of LED activation is of limited duration and is immediately followed by a period of deactivation at least three times as long in duration as the period of activation. Additionally, one or more temperature sensors are disposed within the lamp and enable the control module to temporarily suspend LED activation when measured temperature levels exceed the defined threshold.
Owner:CARPE DIEM TECH
Method of manufacturing a magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS8663486B2Improve performanceSimple processDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingResistUltraviolet lights
A method of manufacturing a magnetic recording medium, includes, in the order recited, the steps of forming a mask protective film composed of carbon on a magnetic layer; forming a resist with a predetermined pattern on the mask protective film; forming a protective mask by etching the mask protective film using the resist as a mask; forming protrusions and recesses on a magnetic layer by etching the magnetic layer using the resist and the protective mask as masks; removing the protective mask, including removing the mask protective film comprised of carbon, using ultraviolet light with a principal wavelength not longer than 340 nm; and forming a protective layer on the magnetic layer having the protrusions and recesses formed thereon.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com