Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69results about How to "Avoid overetching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
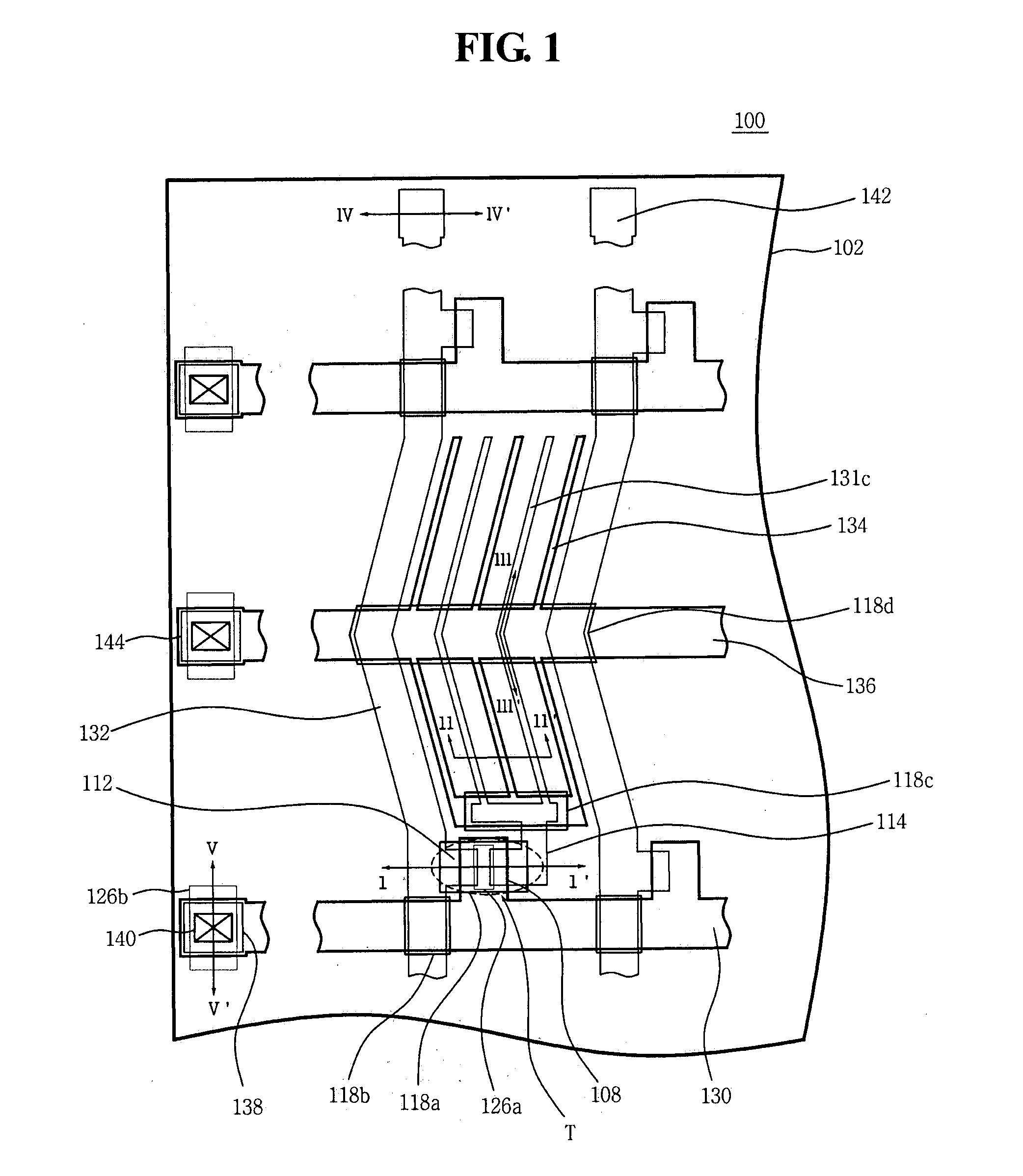
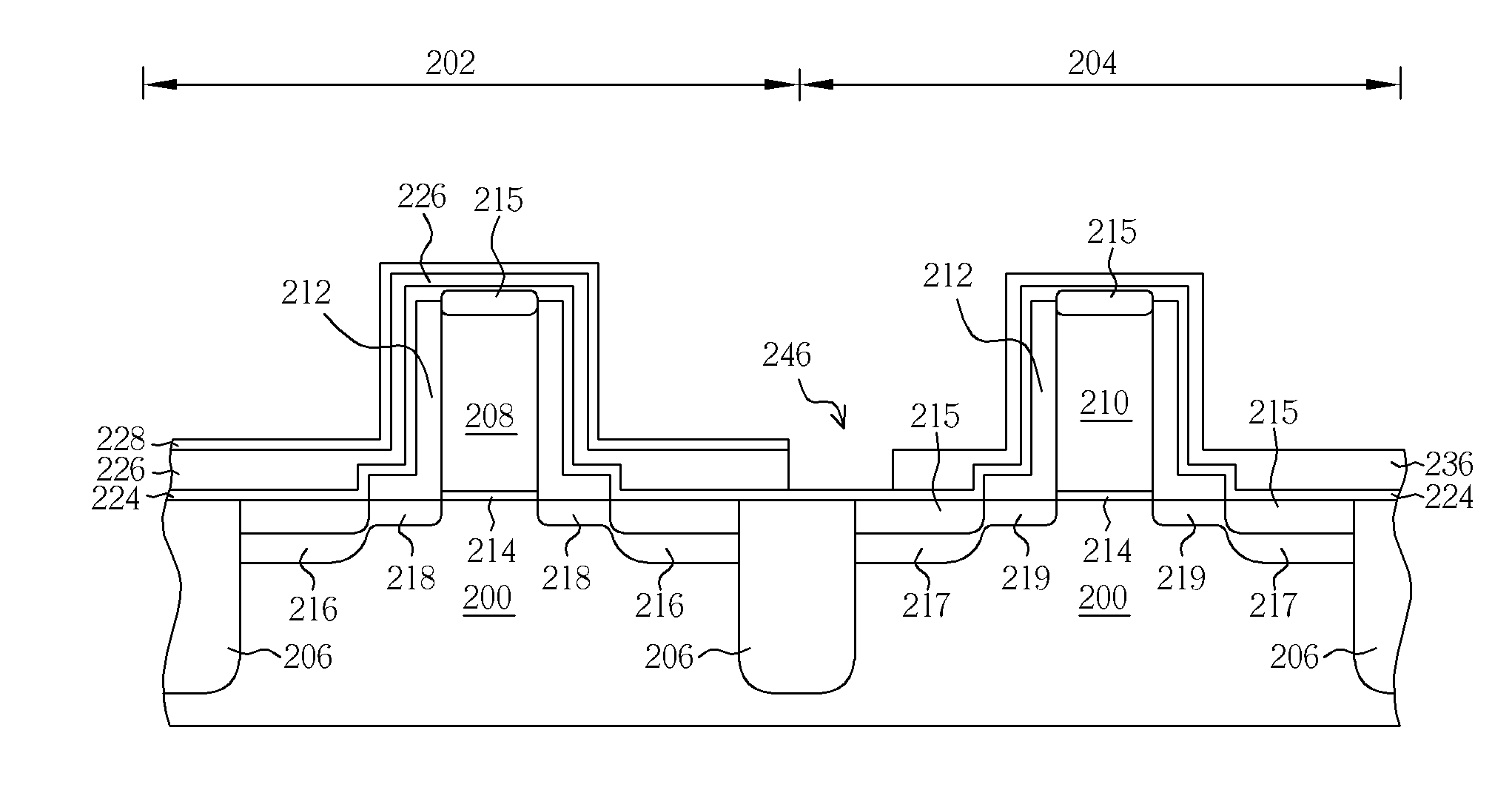
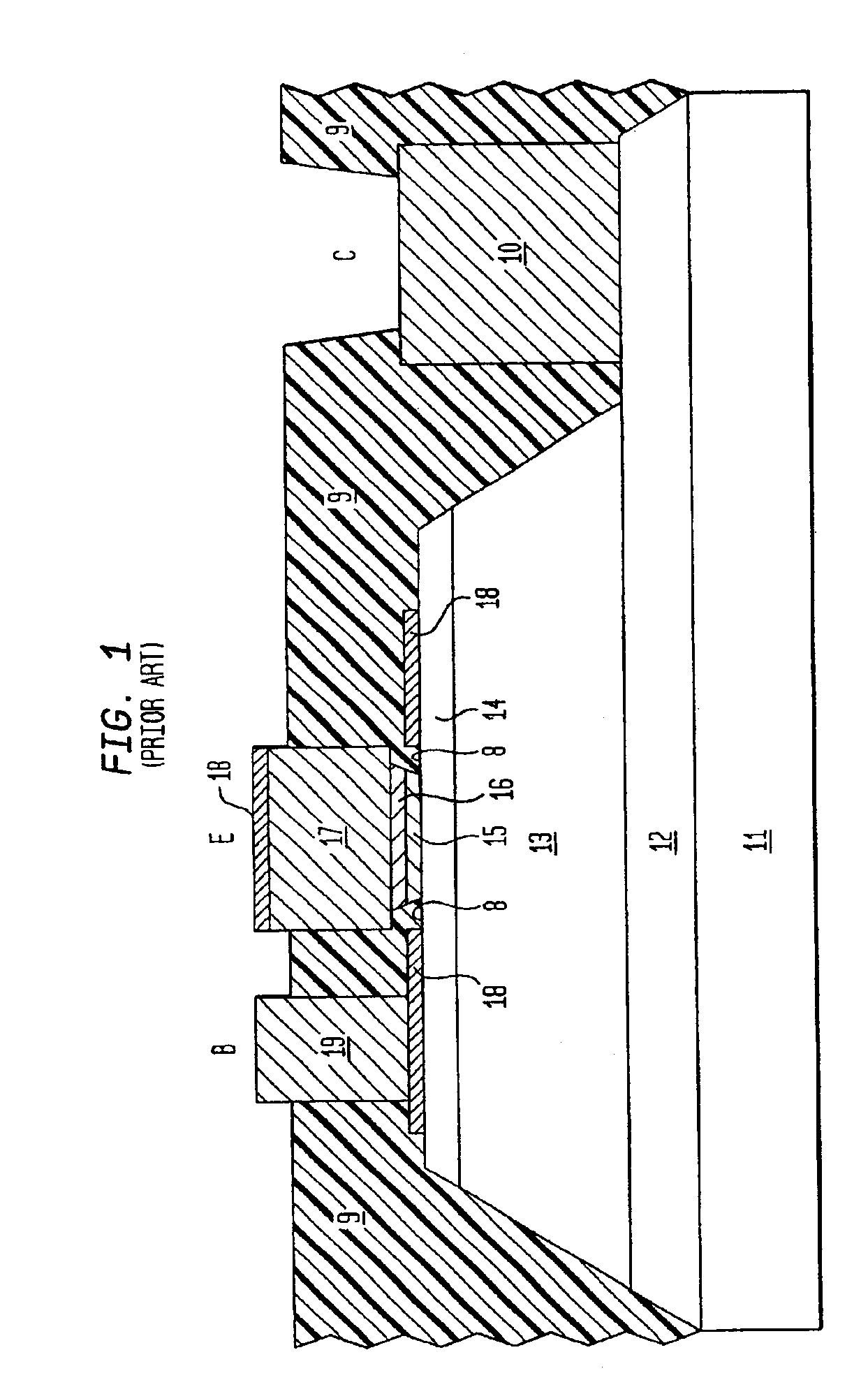
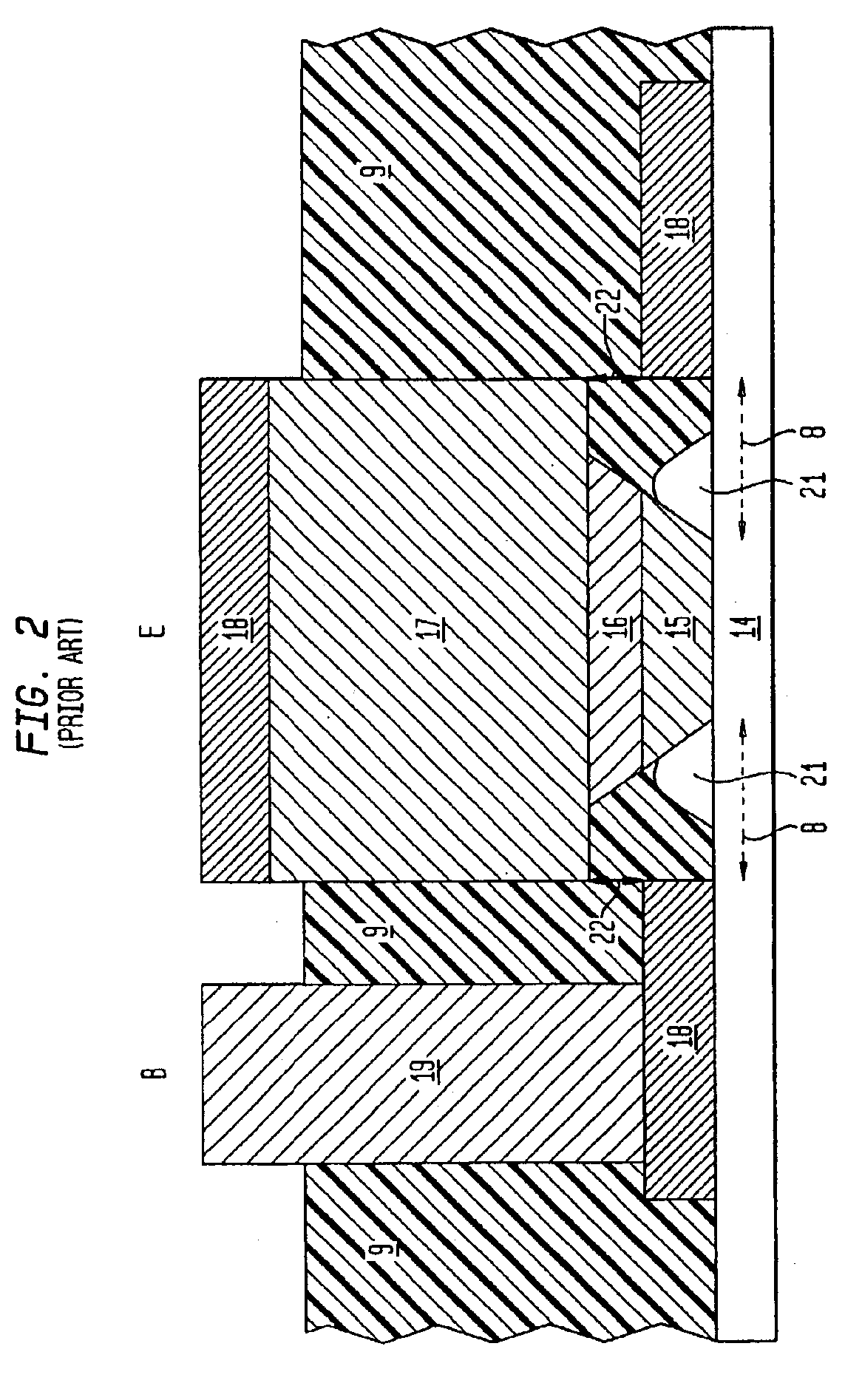
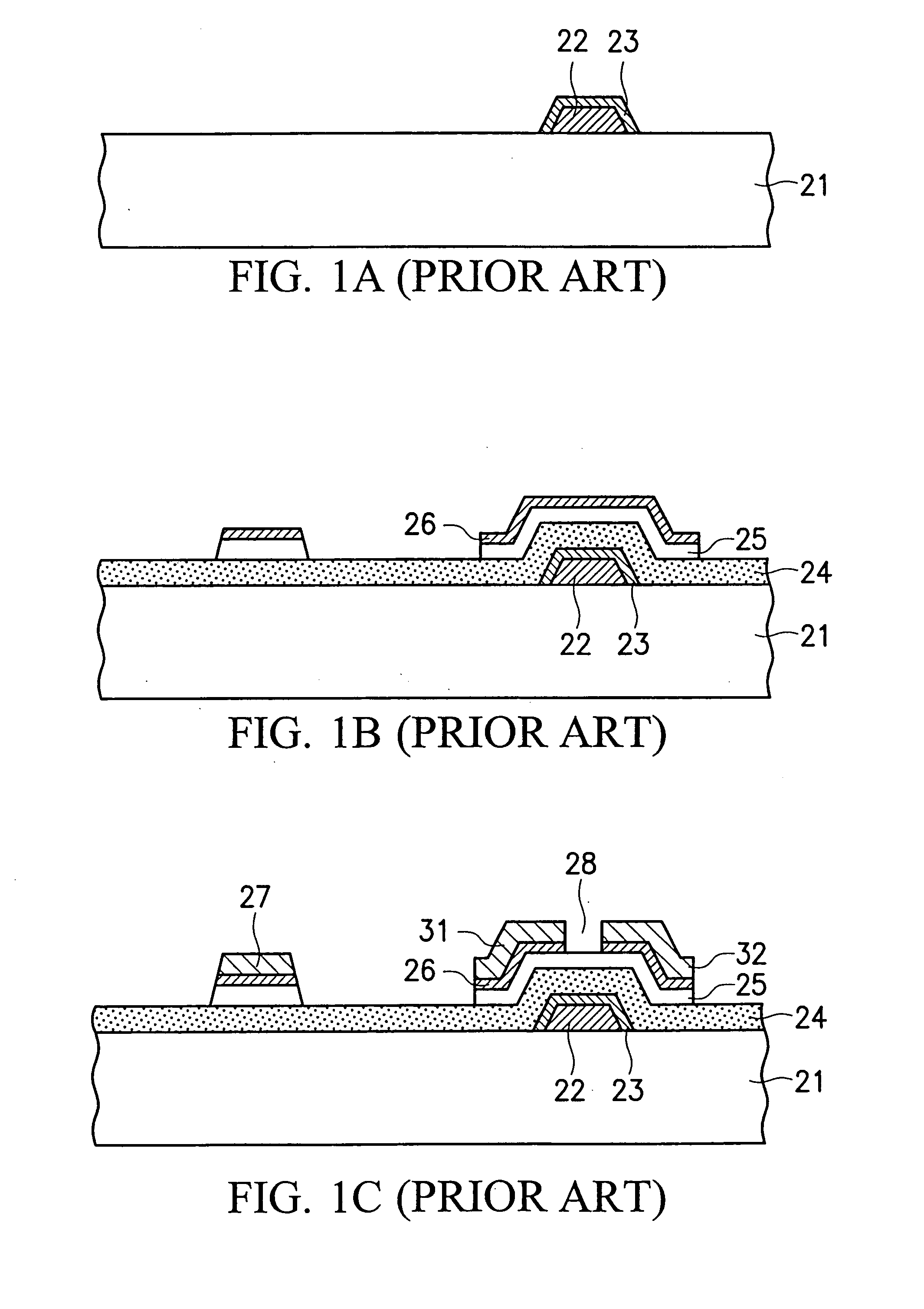
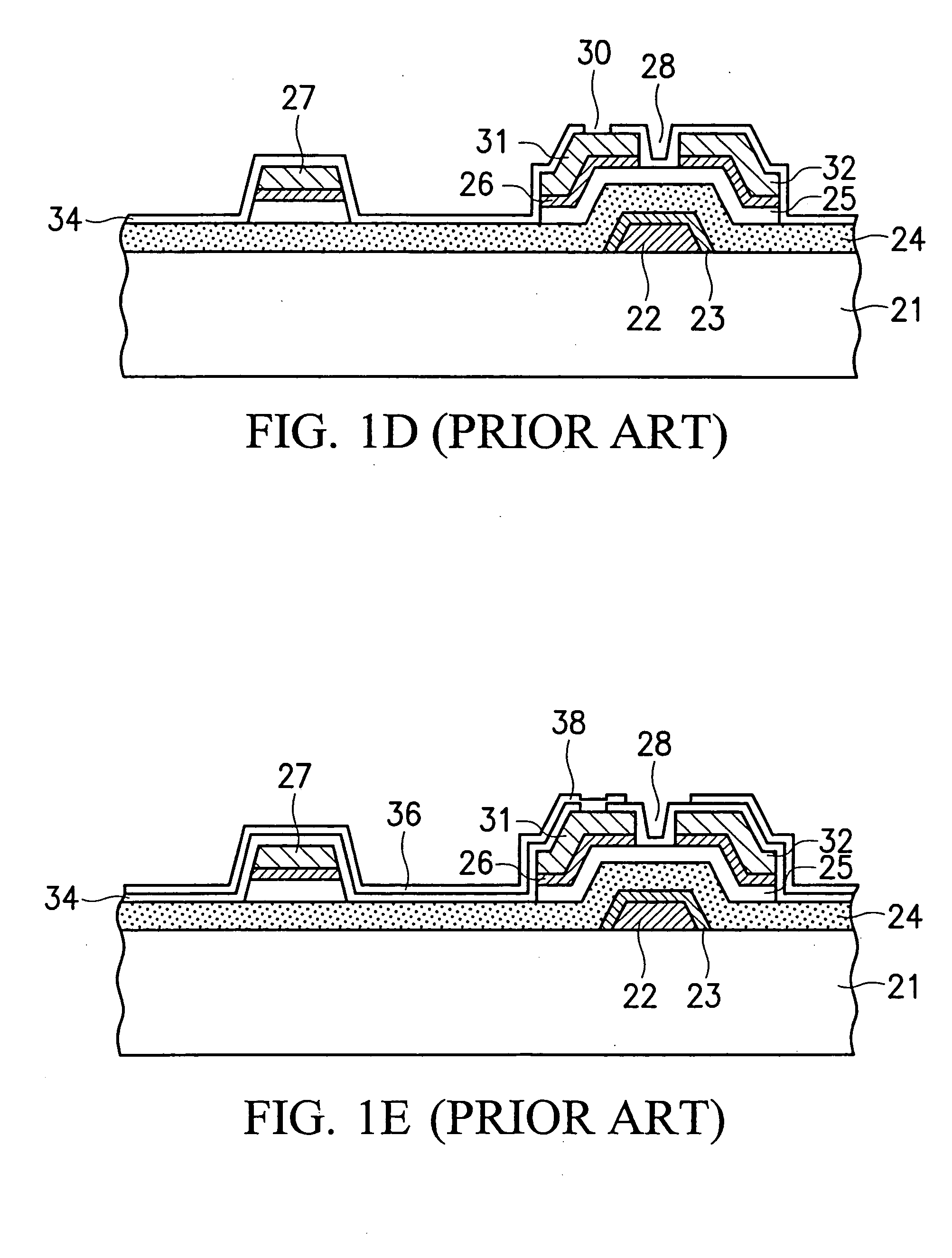
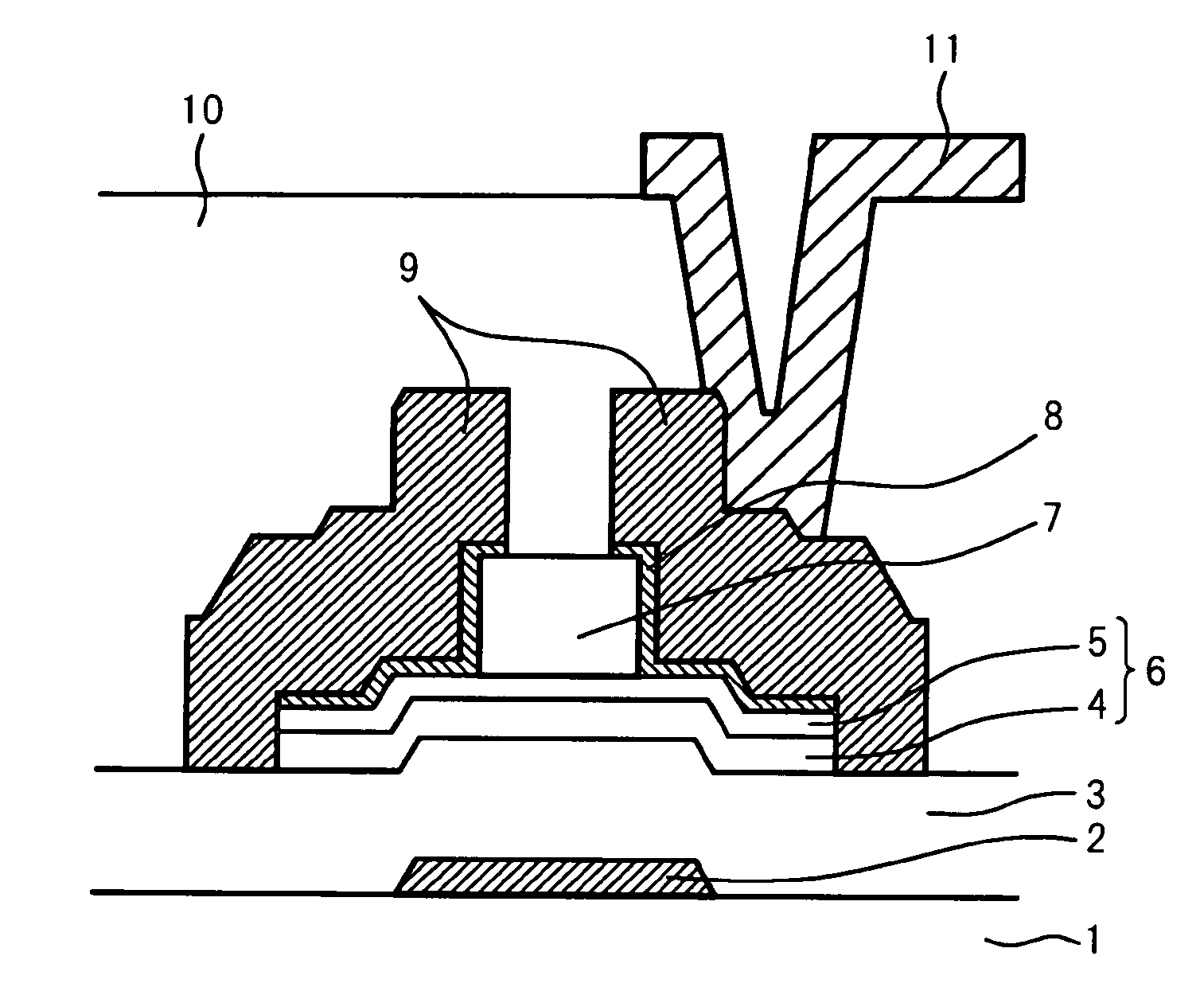
Organic light emitting diode display
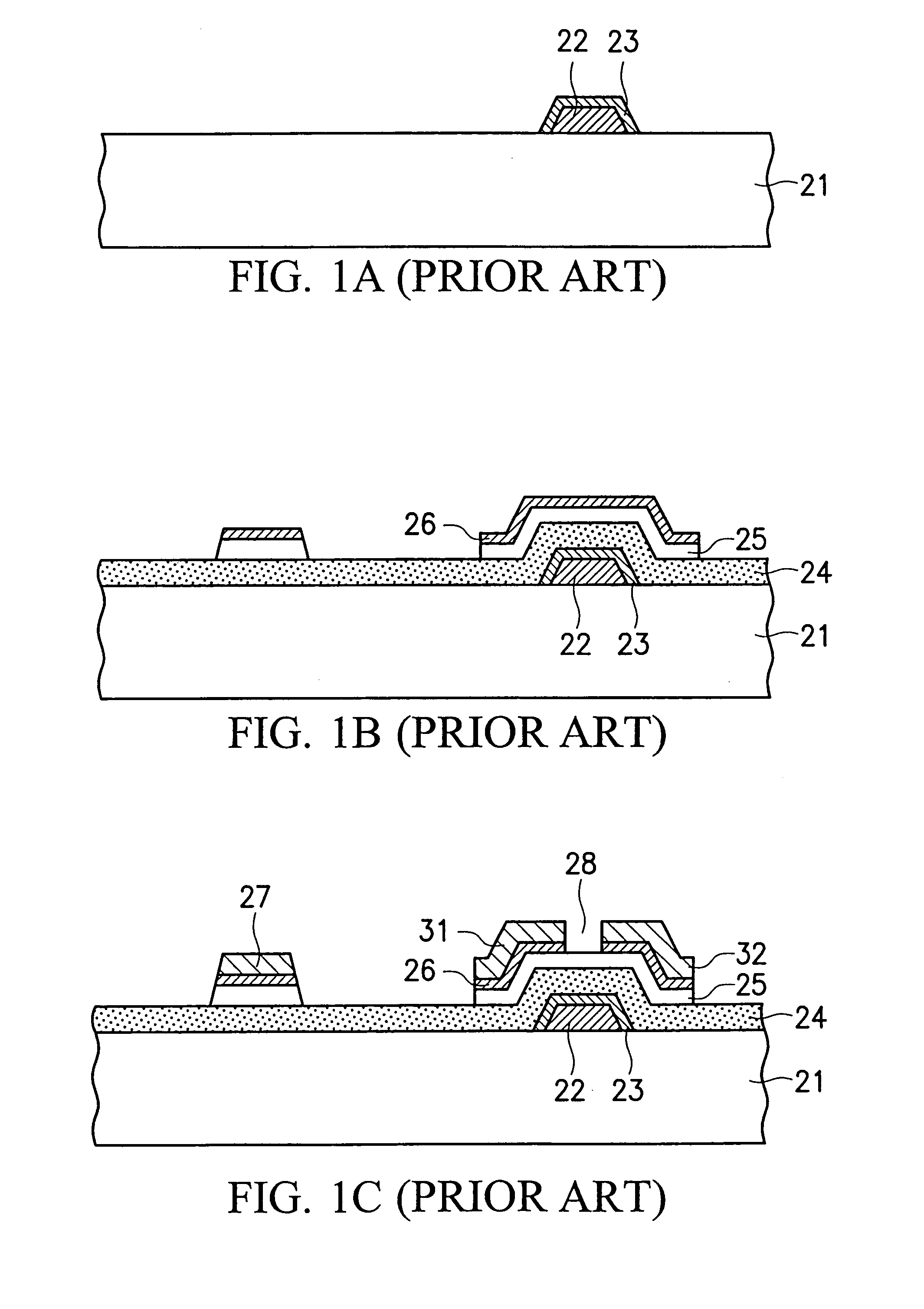
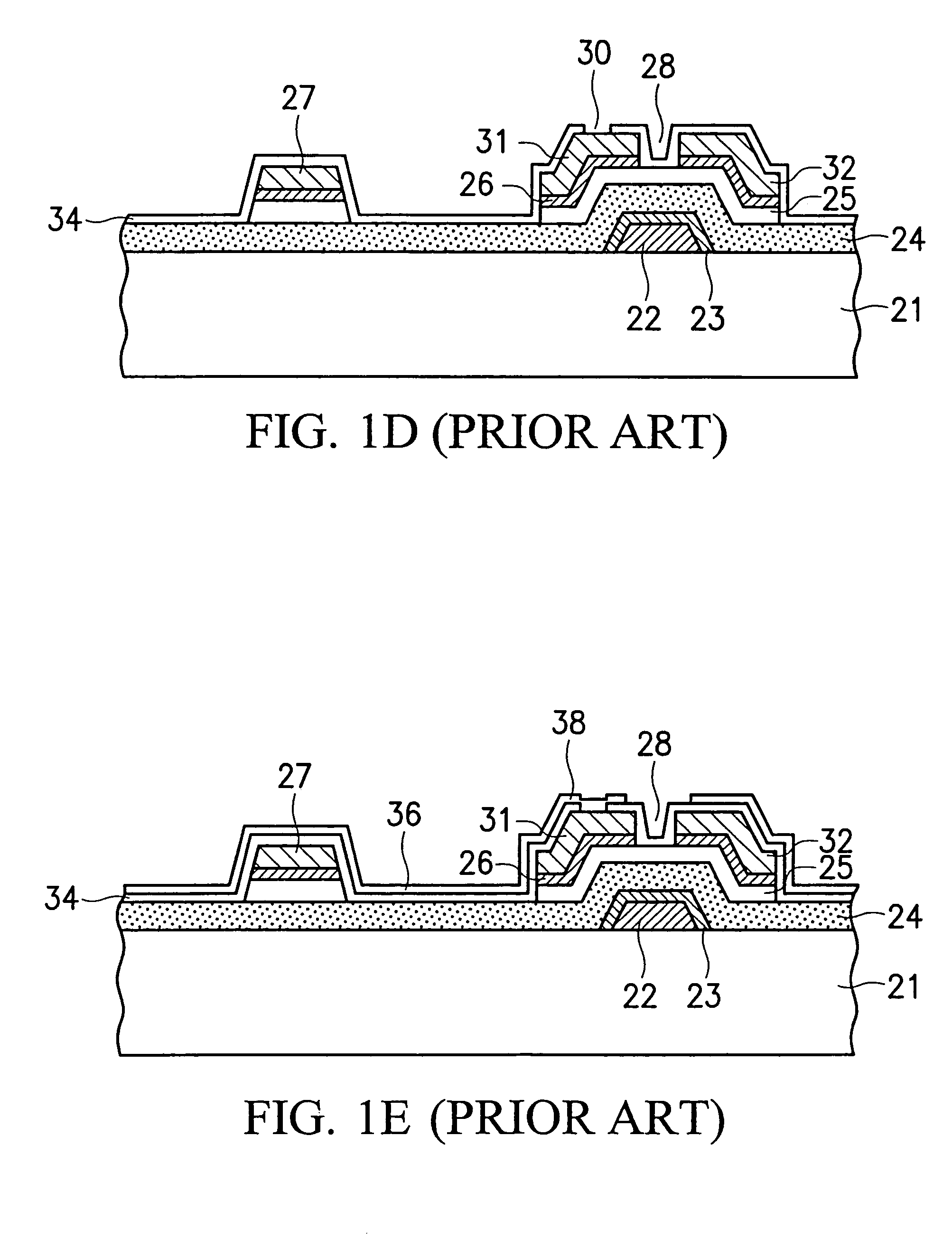
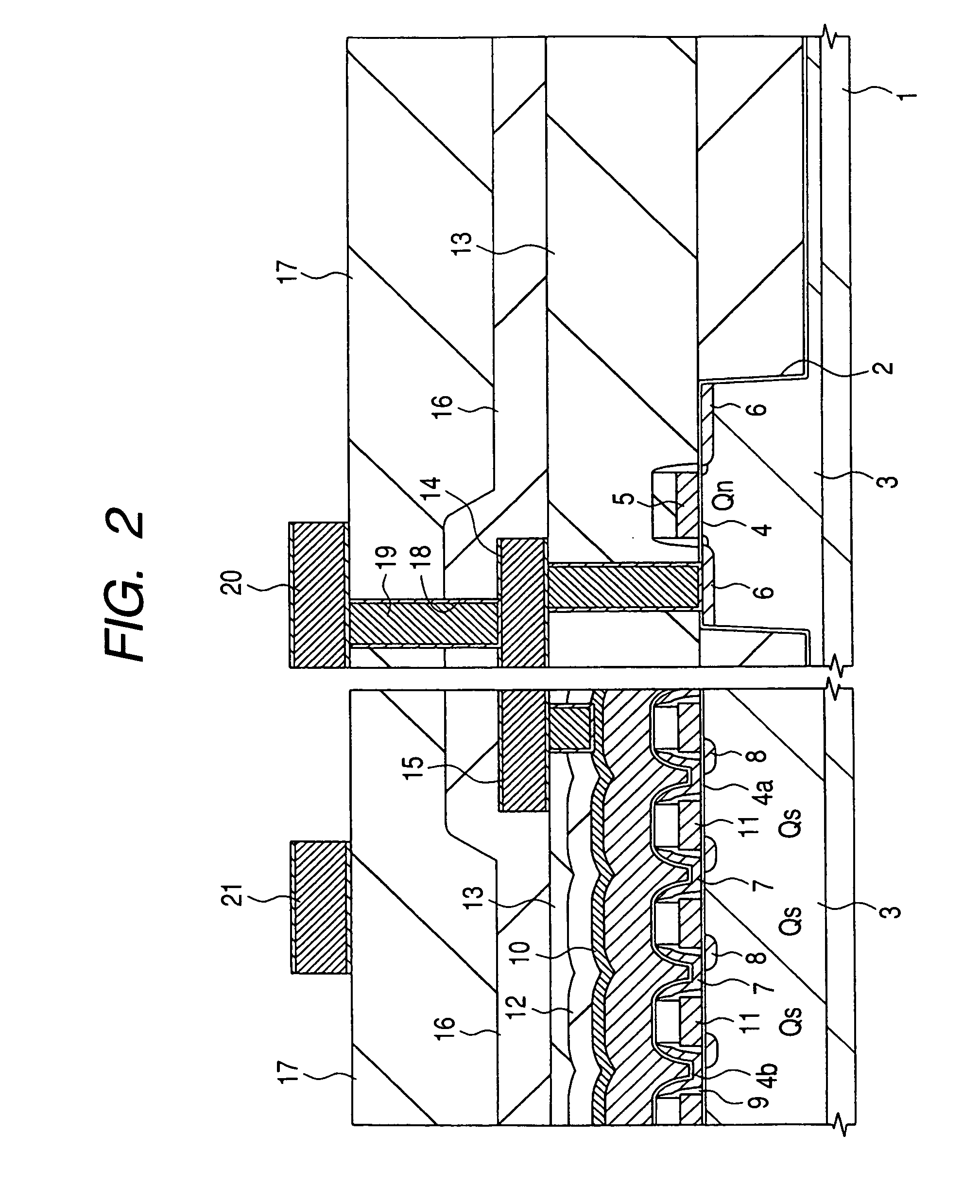
ActiveUS20110073863A1Improve featuresAvoid damageTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorOhmic contact
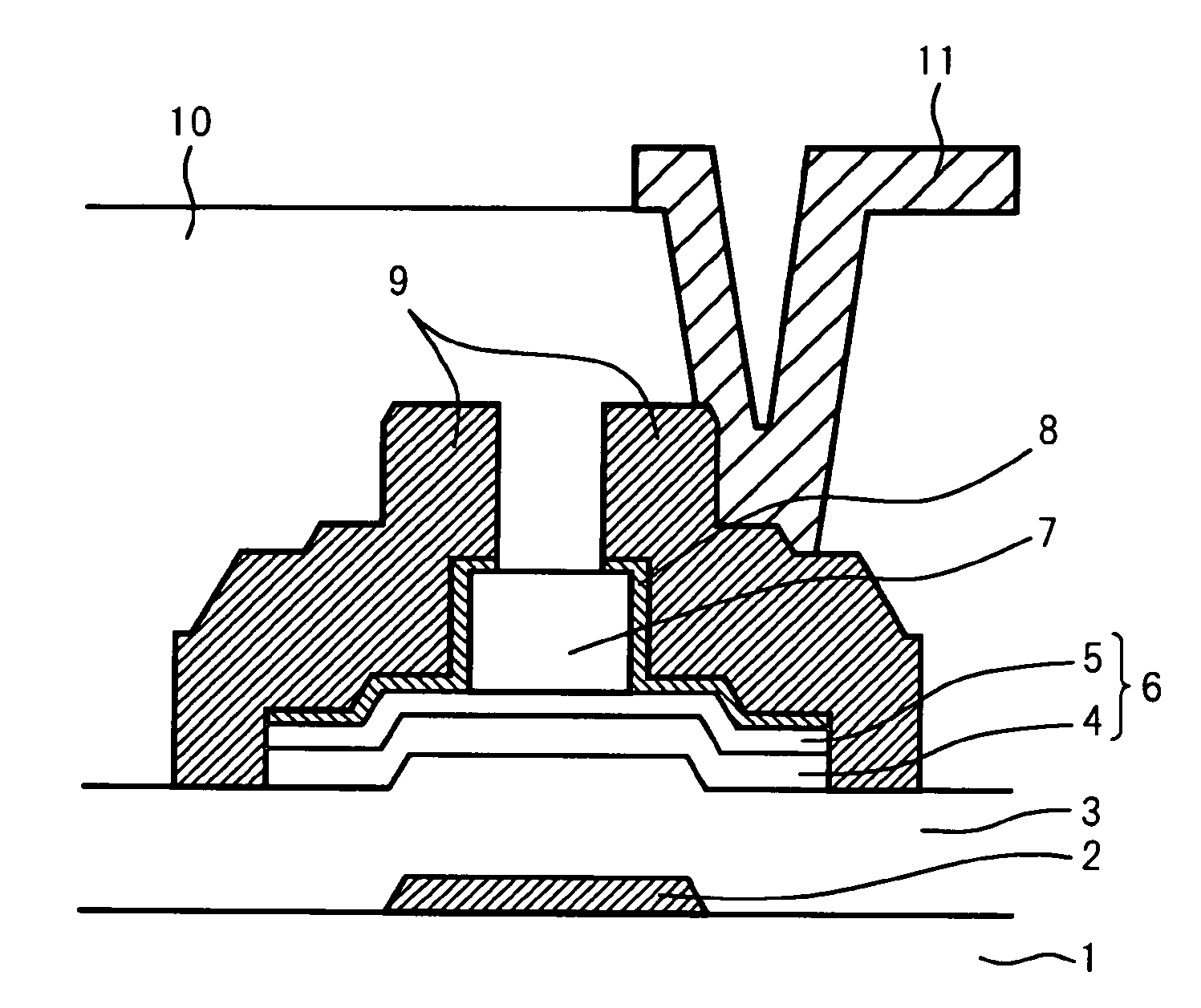
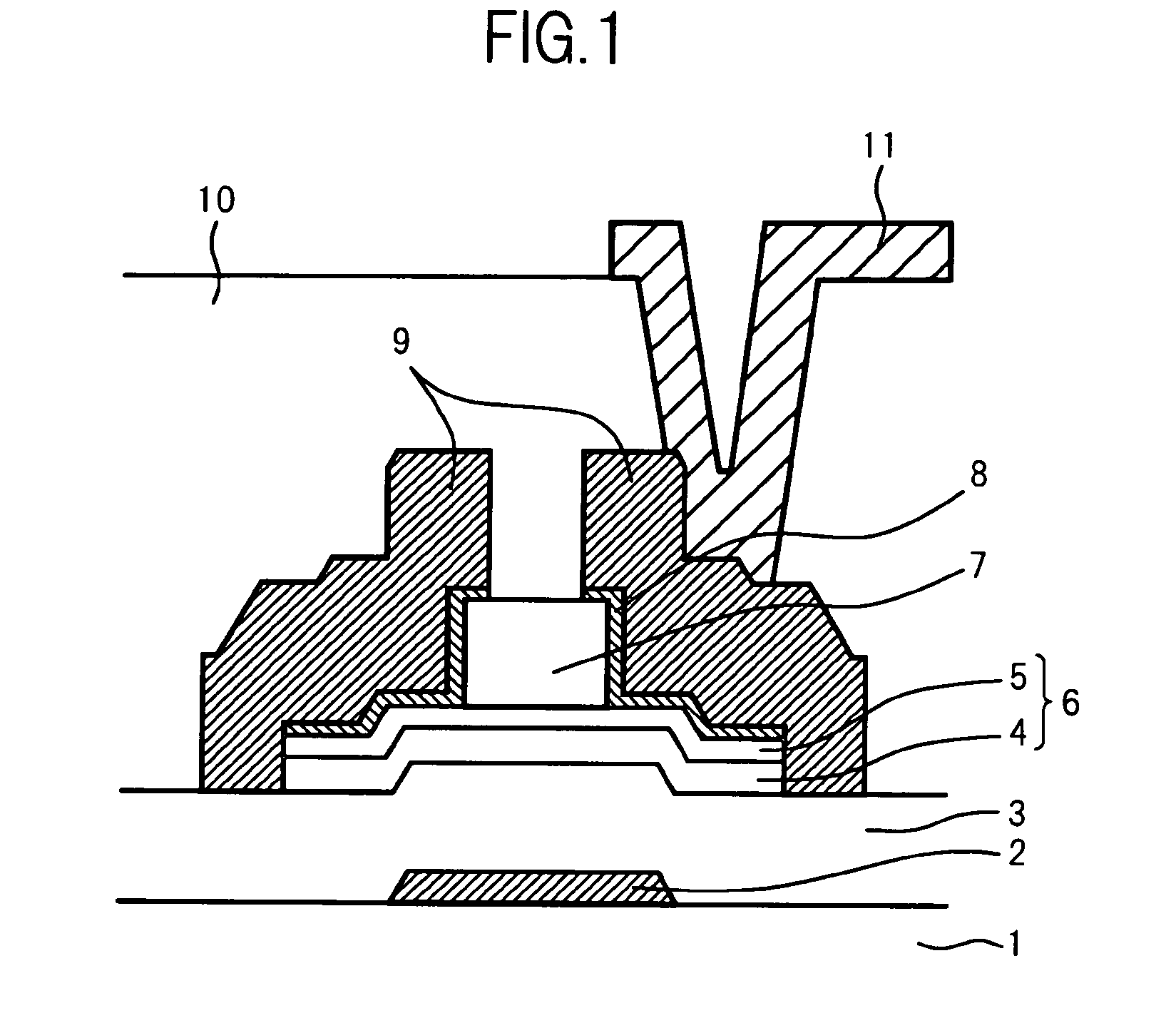
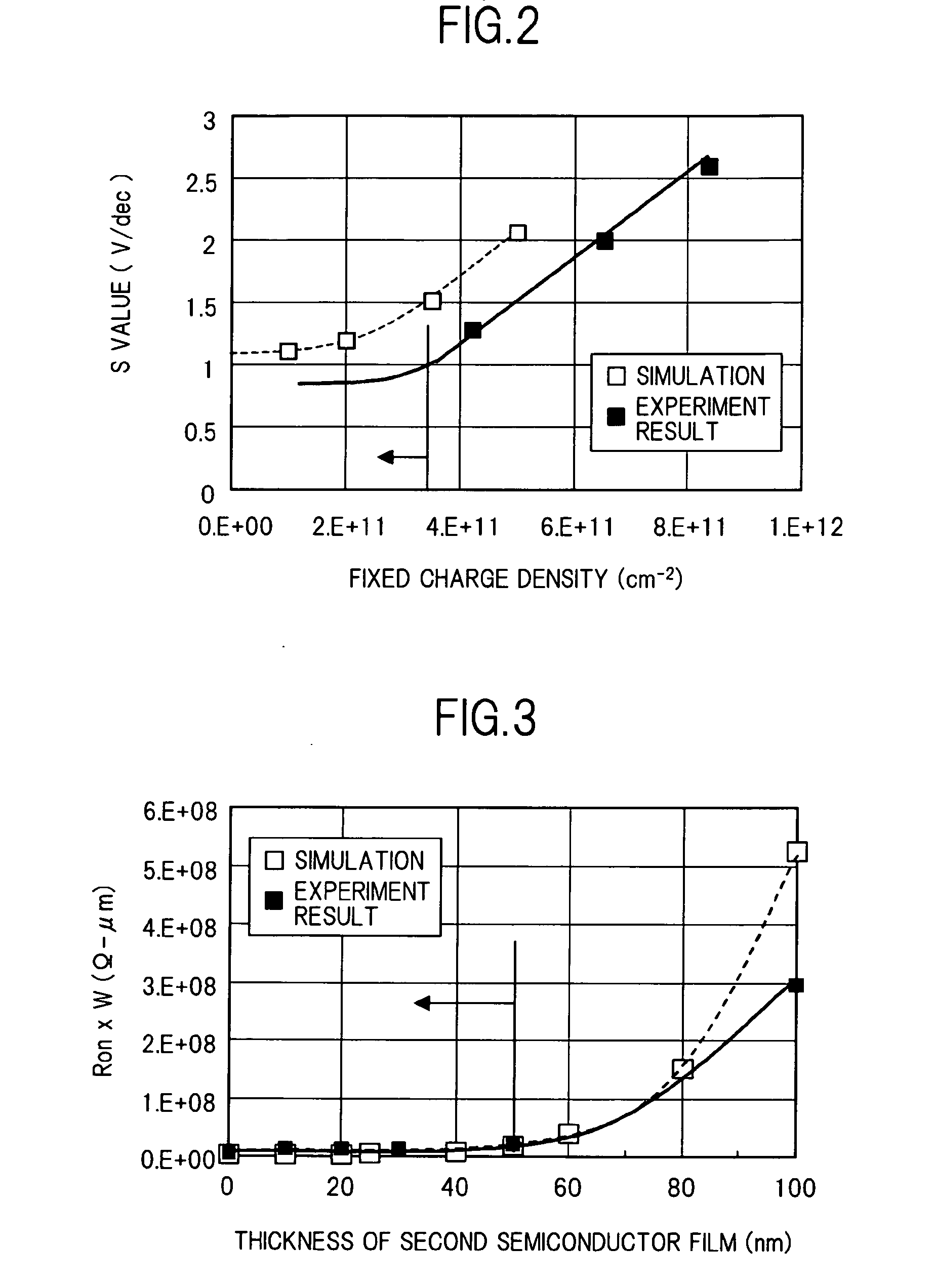
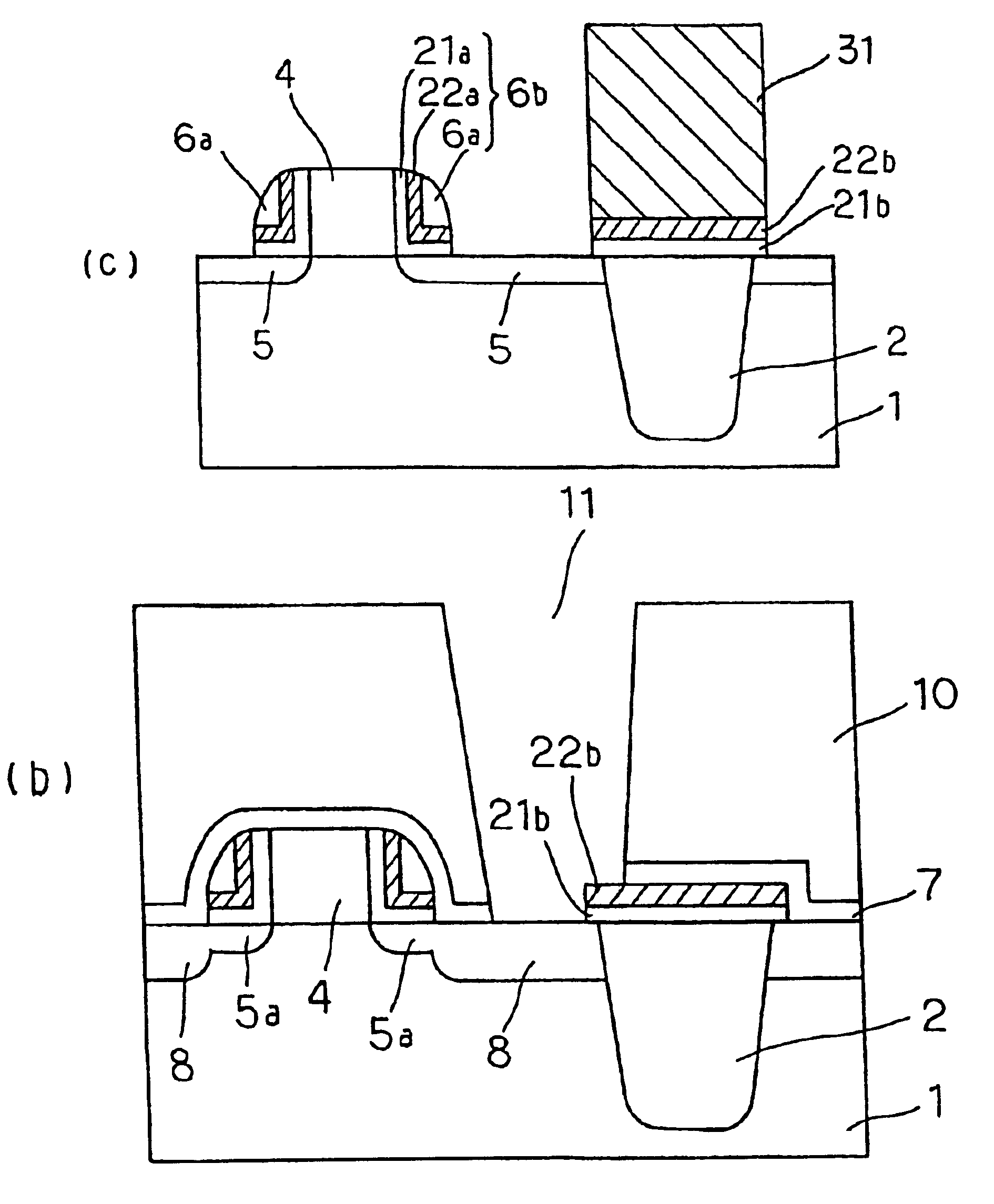
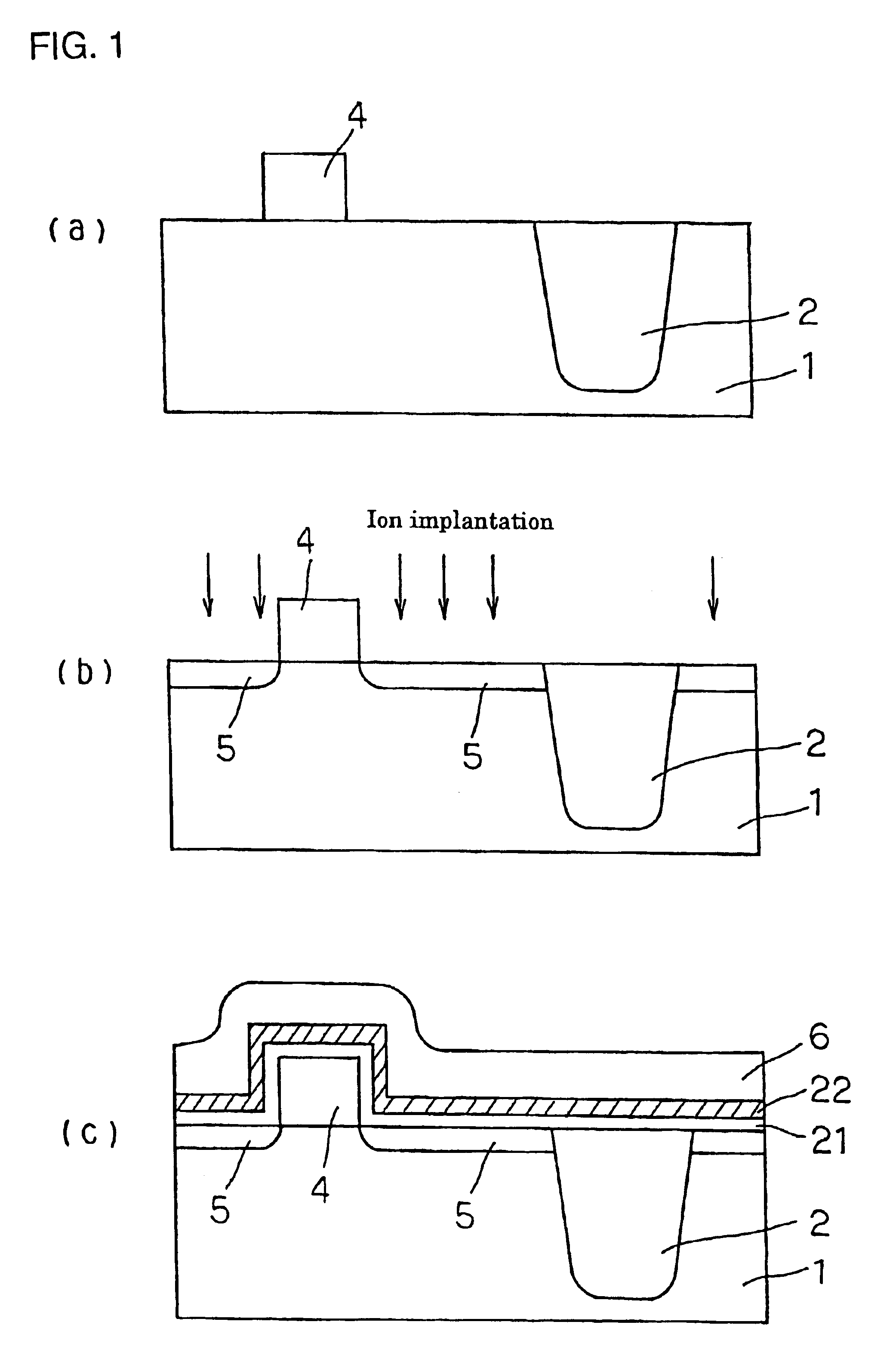
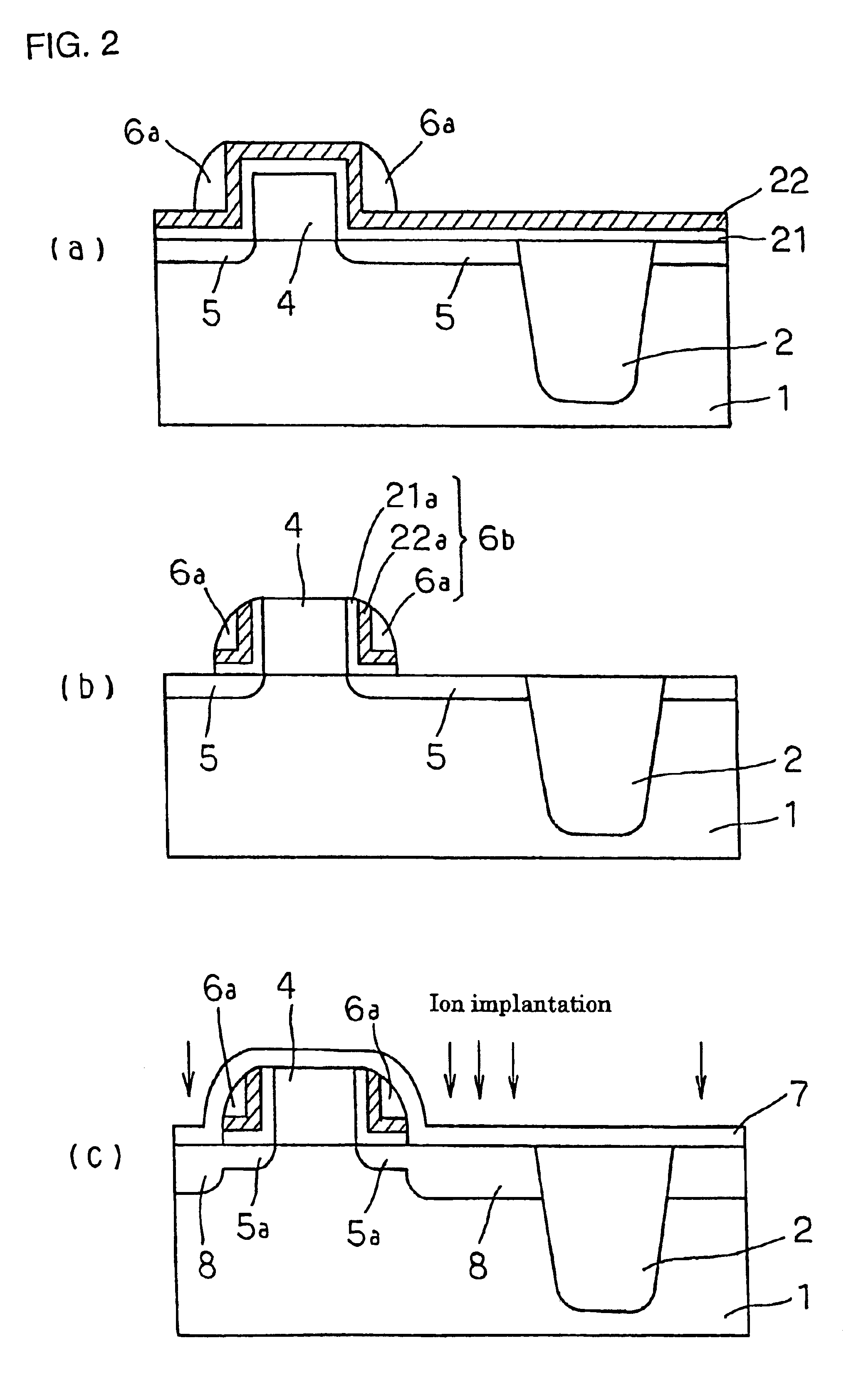
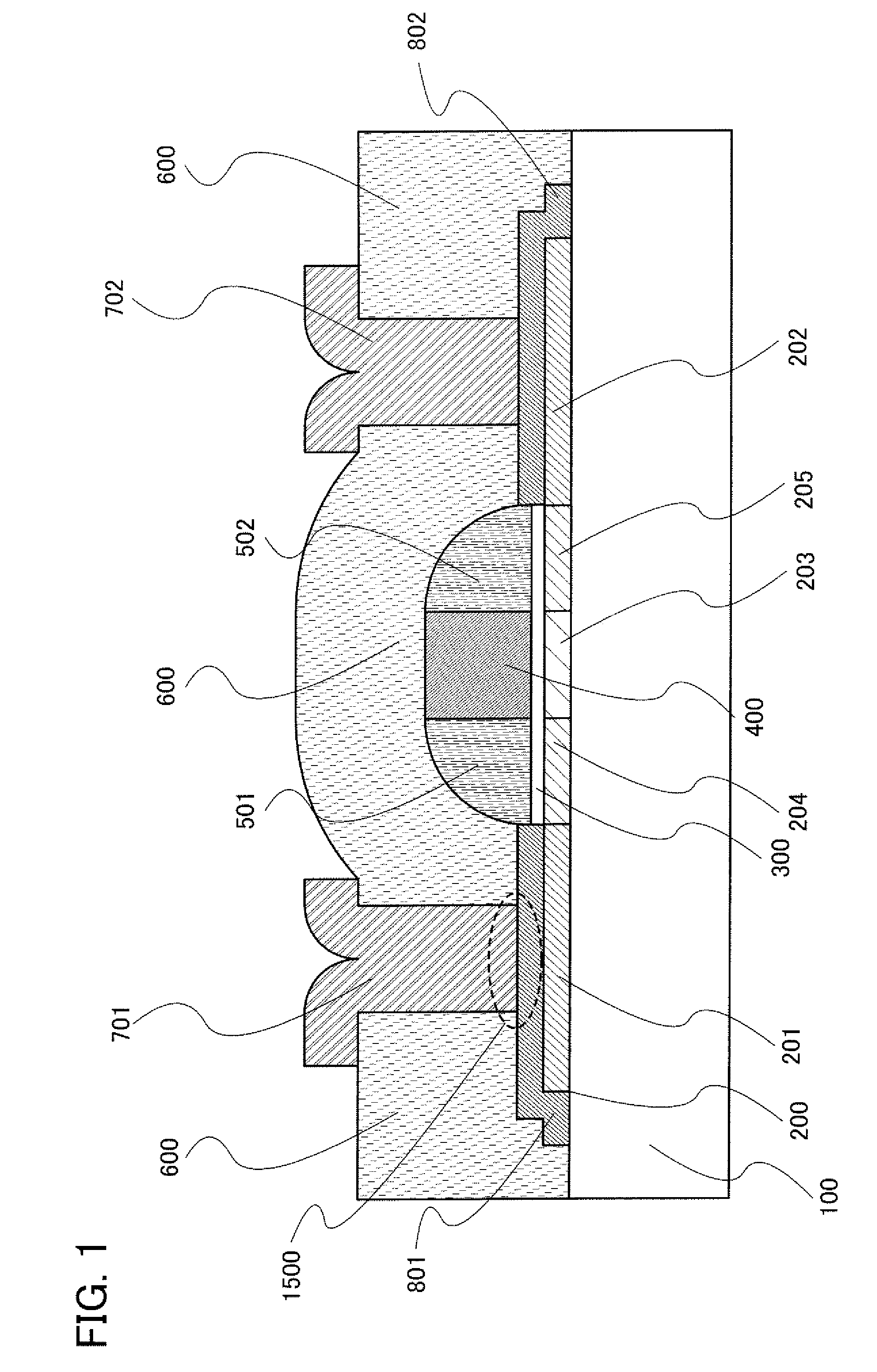
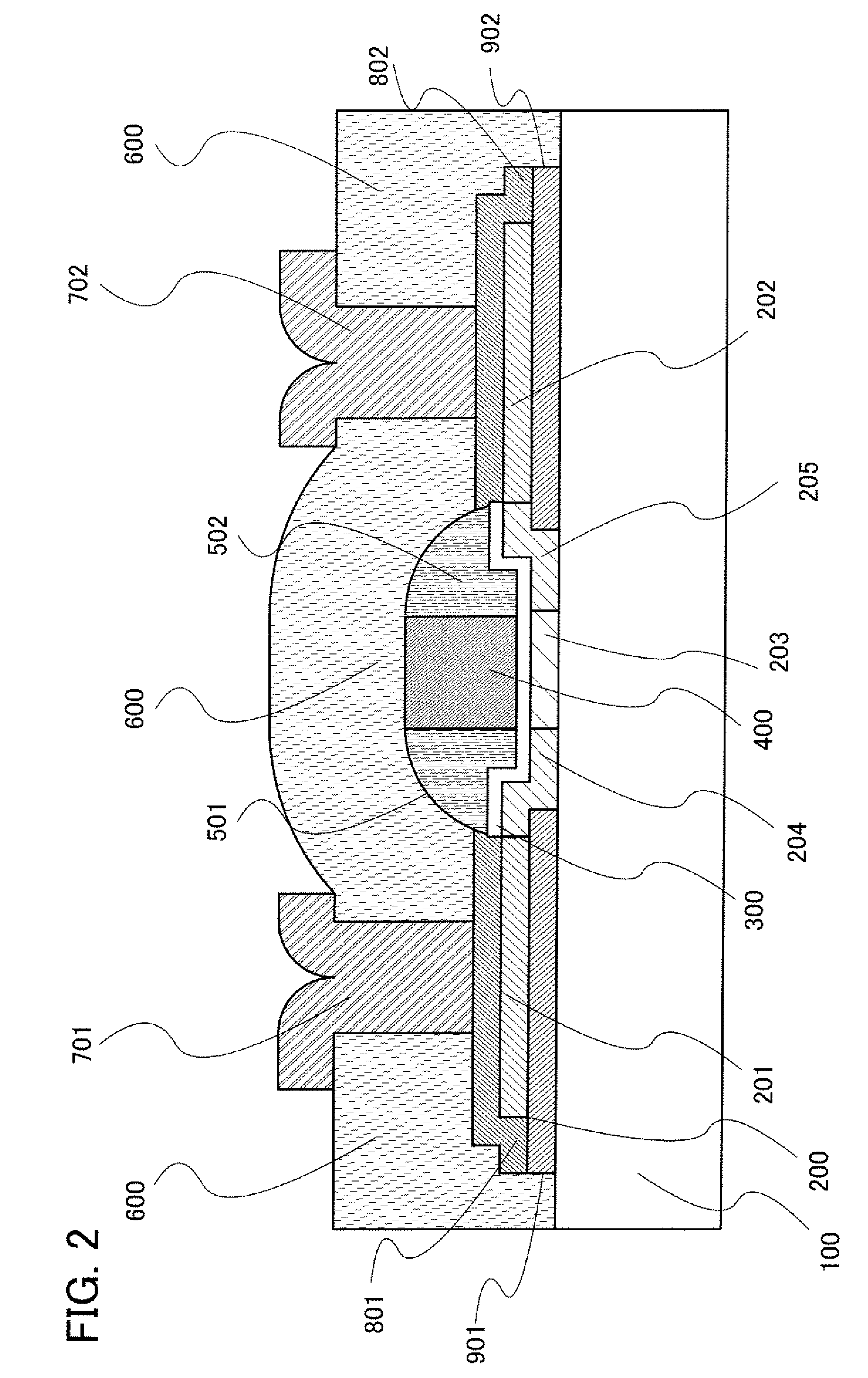
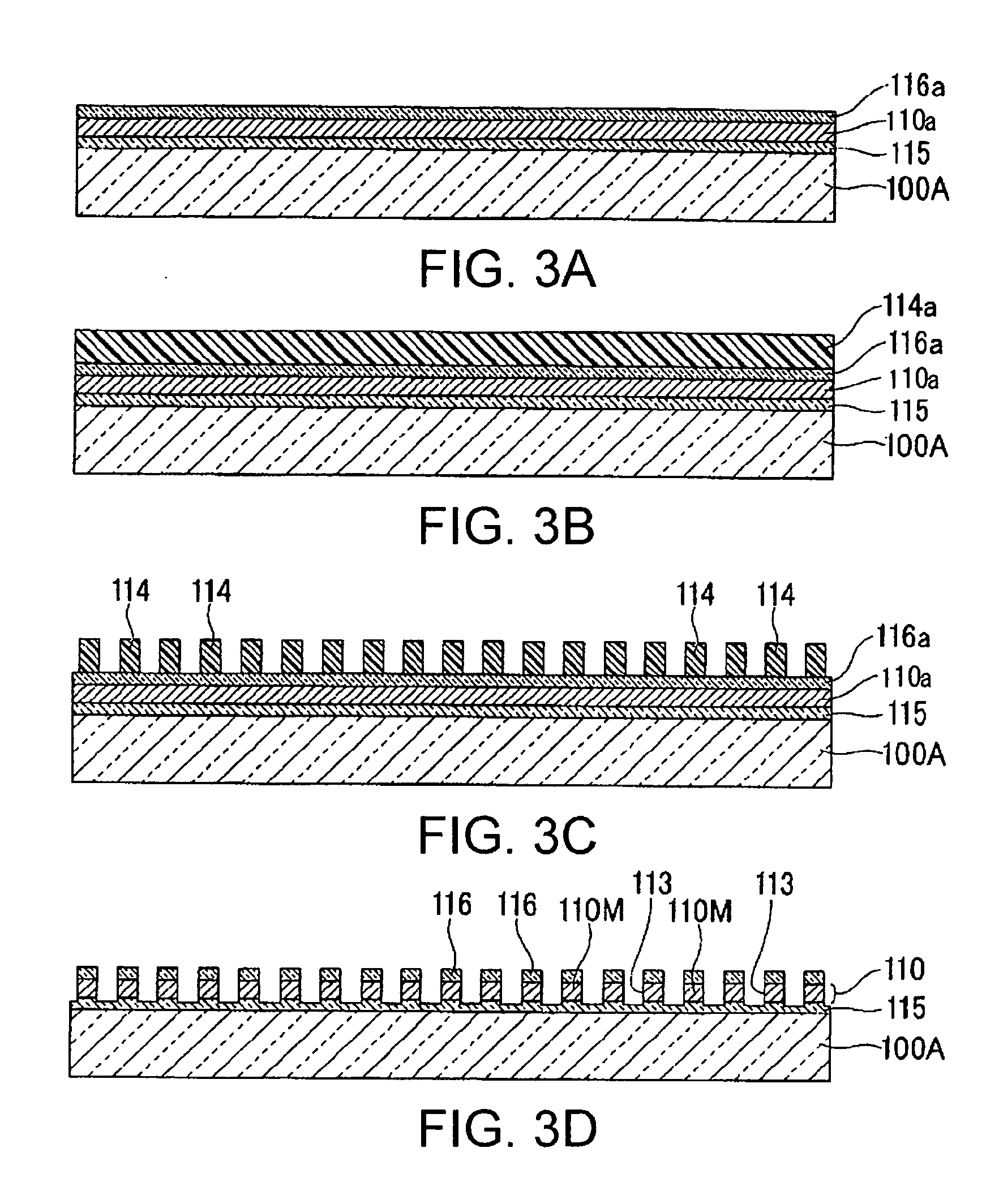
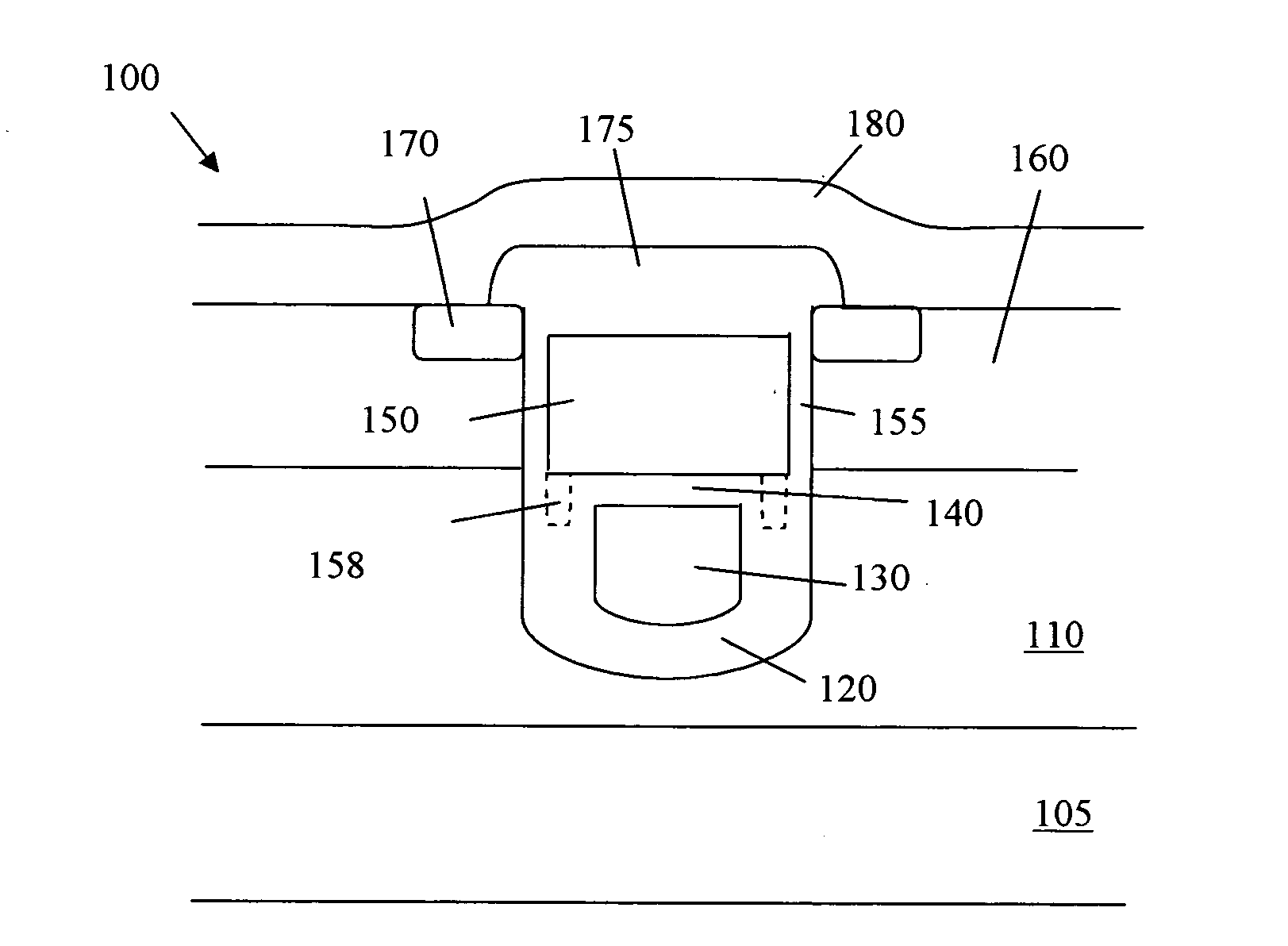
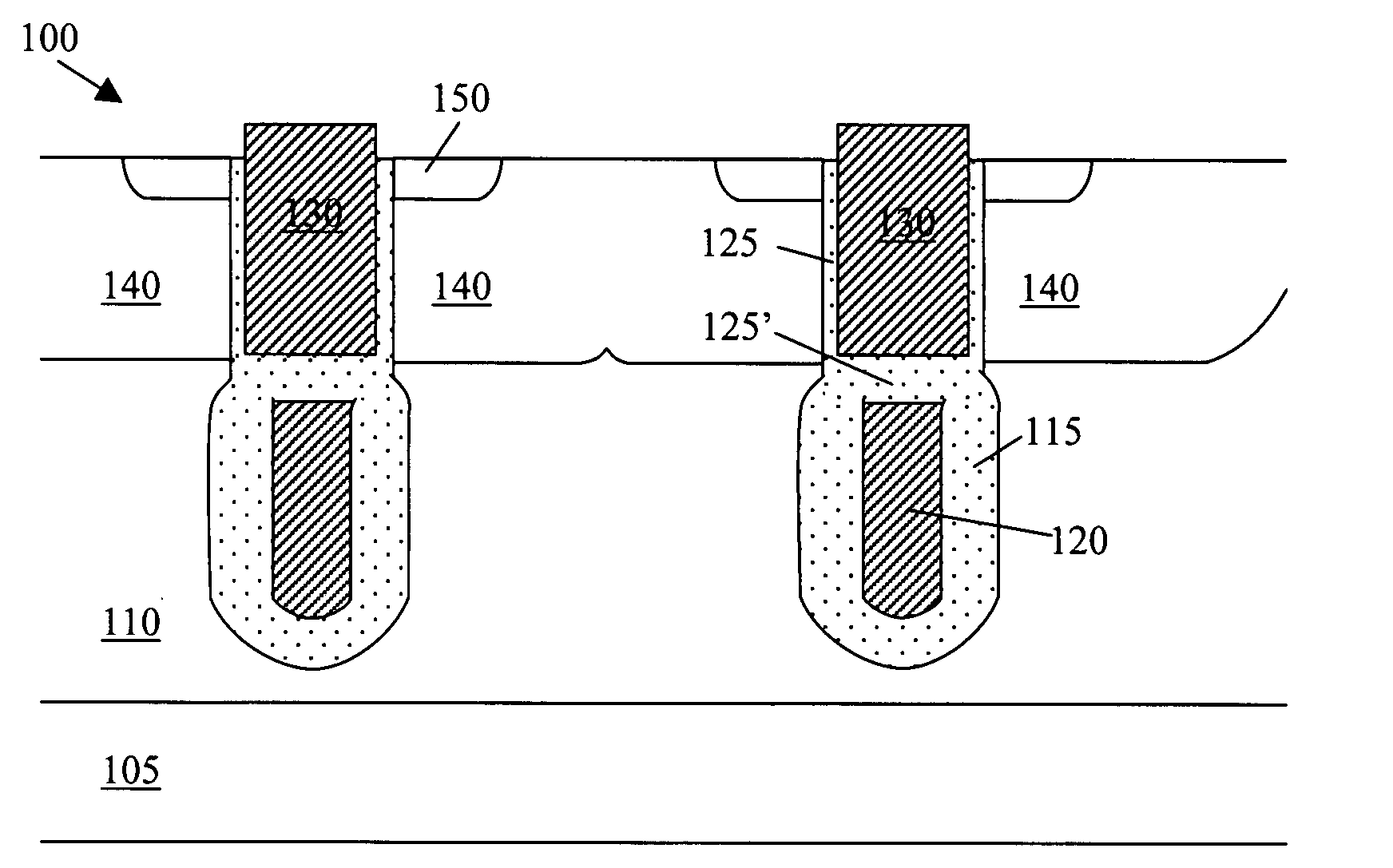
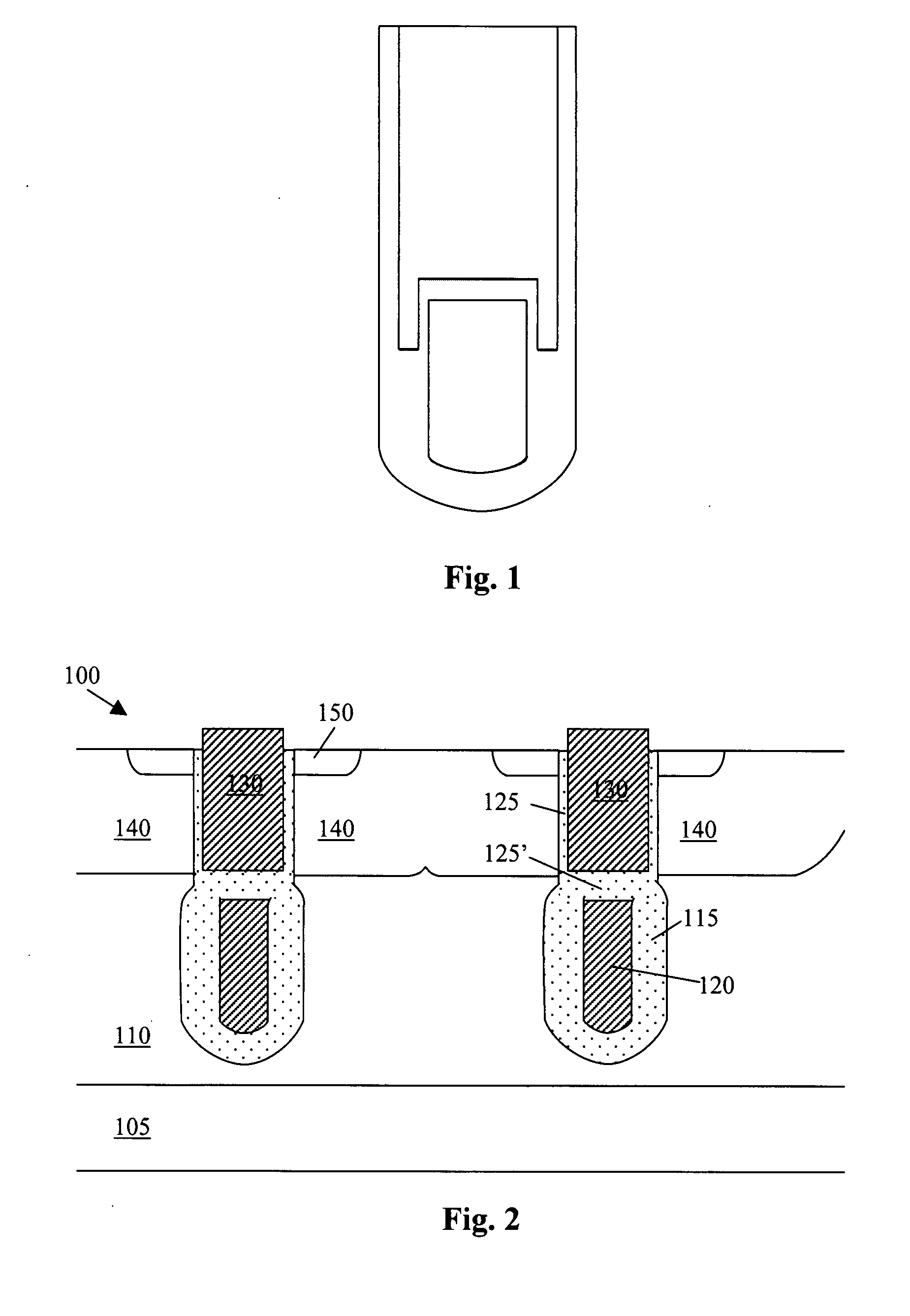
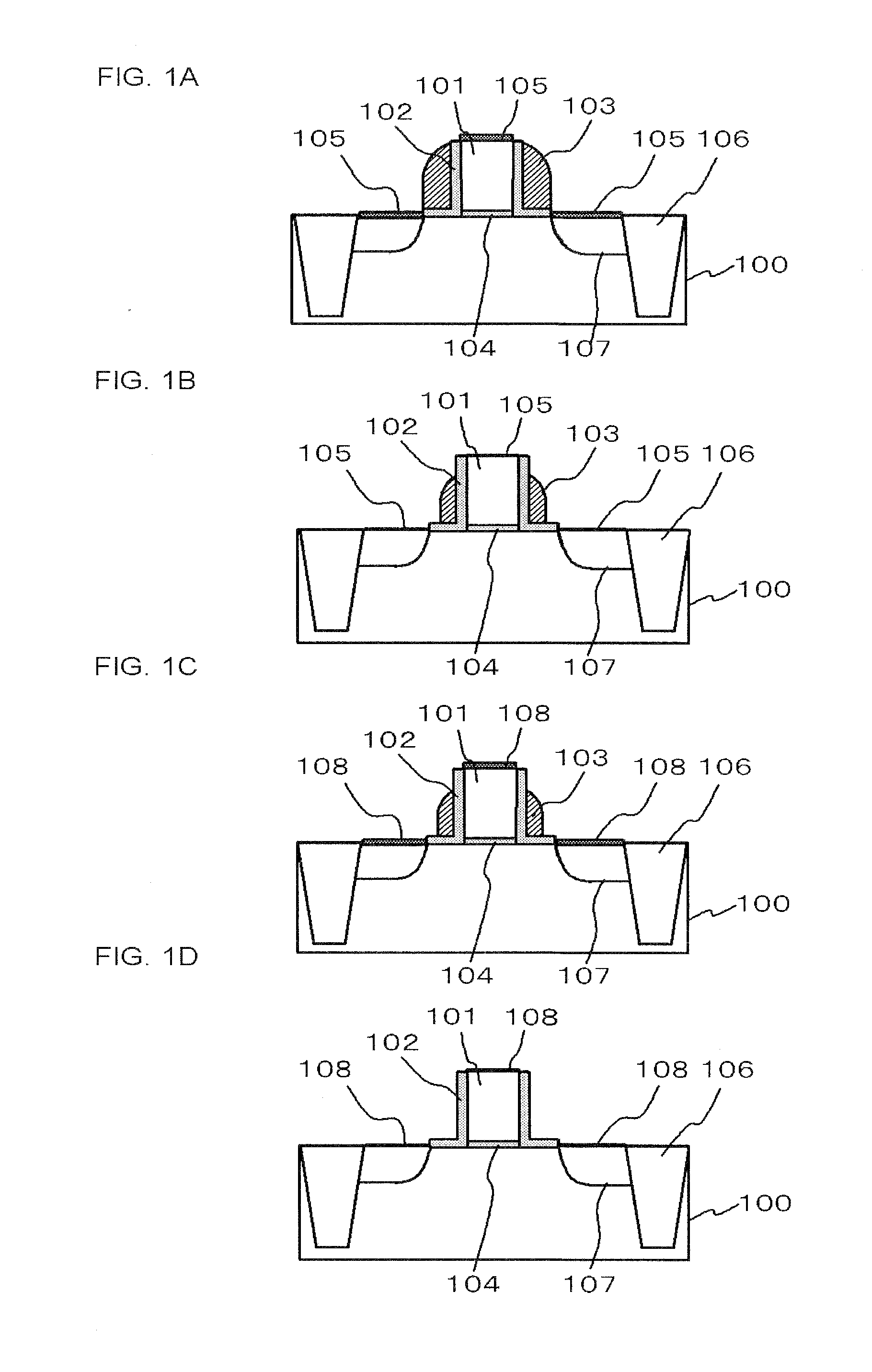
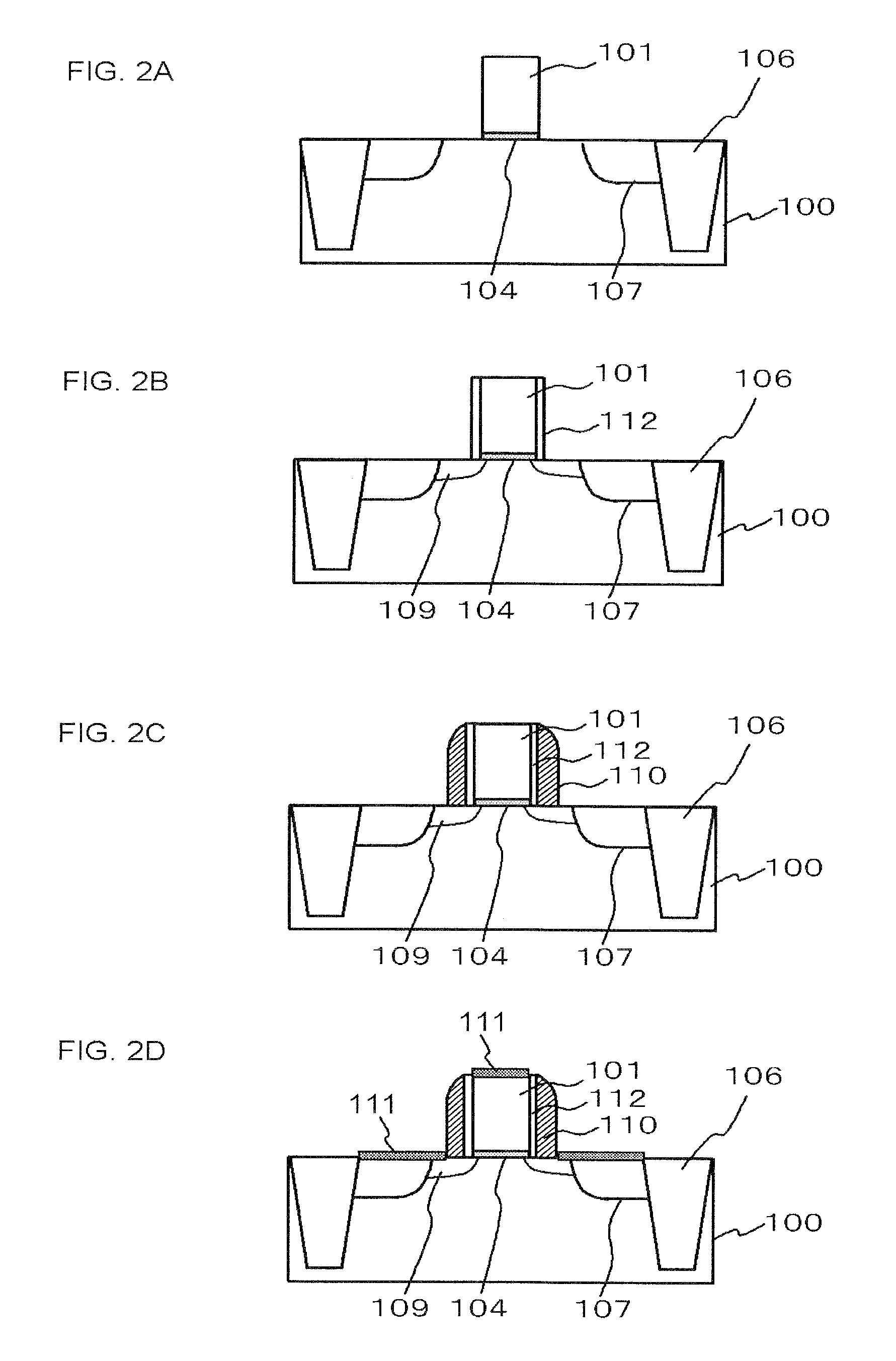
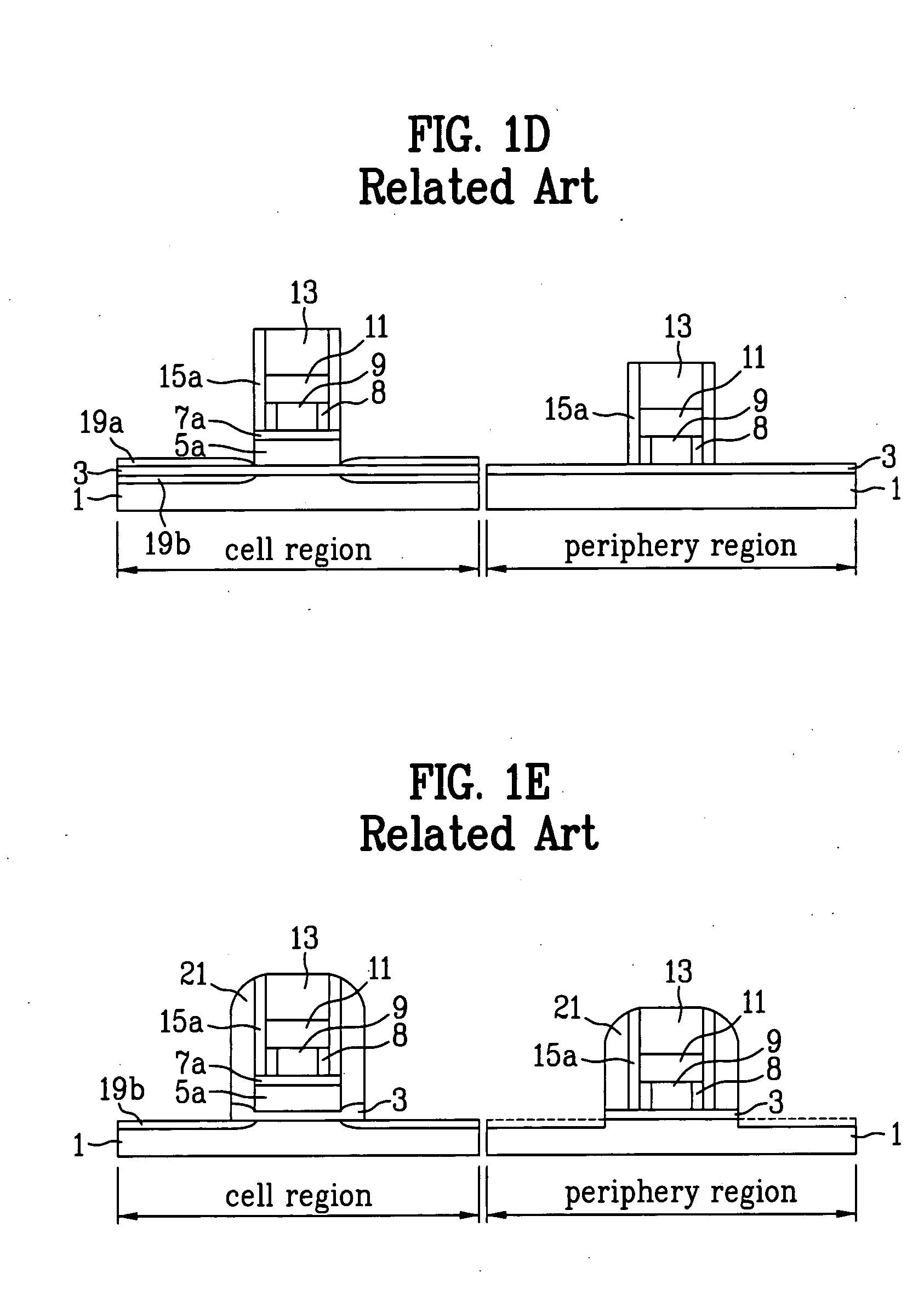
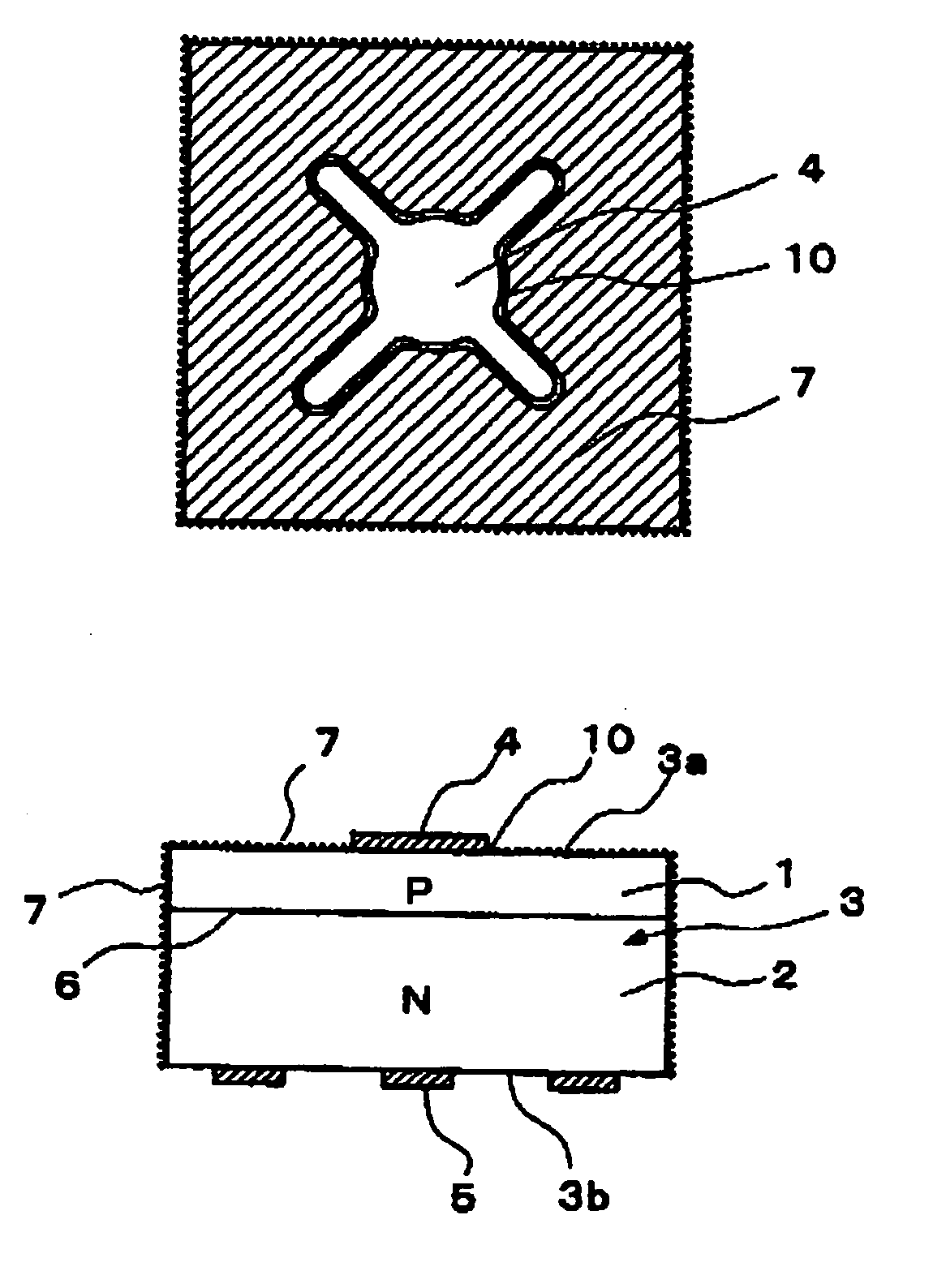
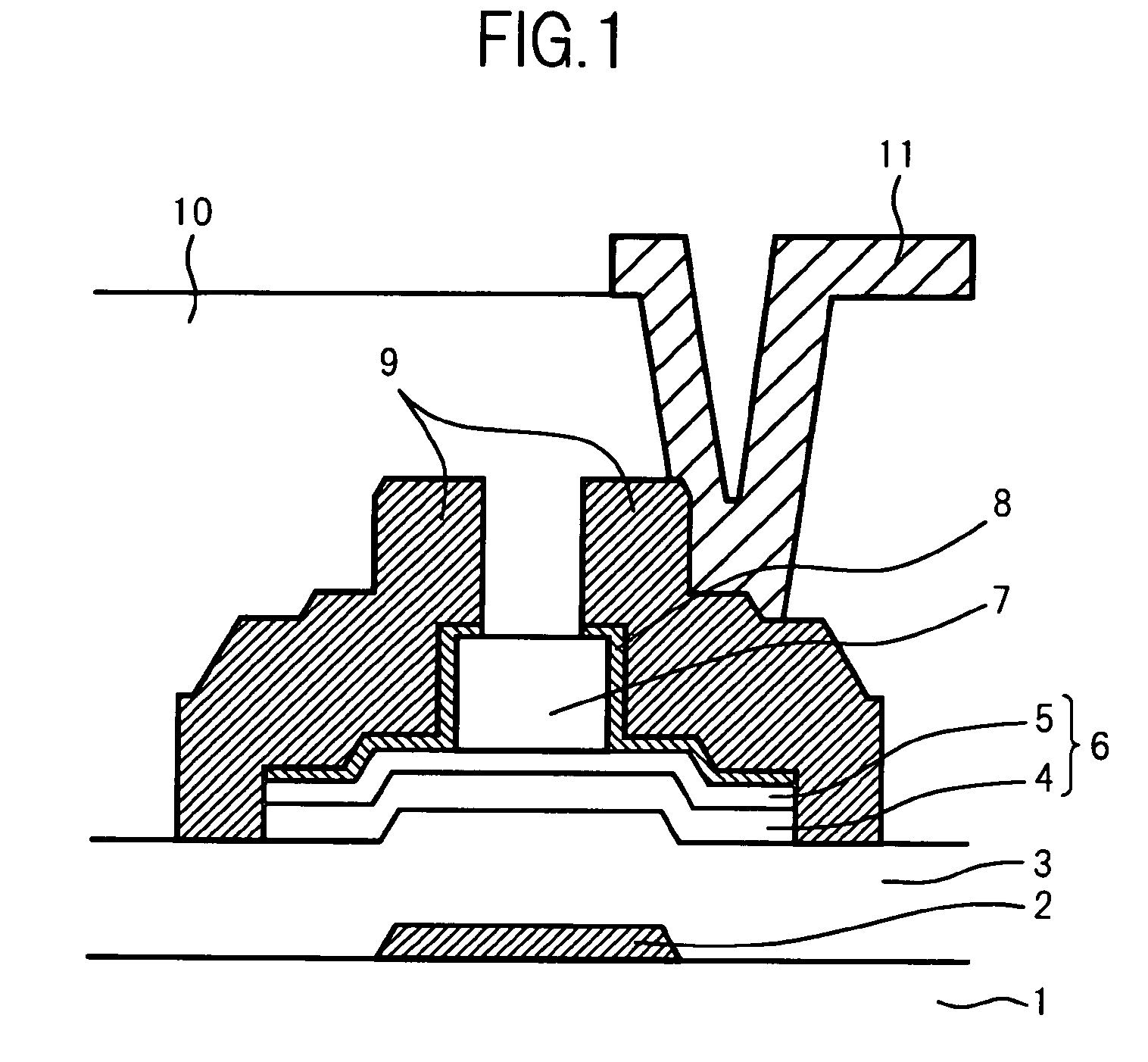
An organic light emitting diode display includes a thin film transistor on a substrate (1). The thin film transistor includes a gate electrode (2), a gate insulating film (3) that covers the gate electrode (2), a first semiconductor film (4) provided on the gate insulating film (3), a second semiconductor film (5) provided on the first semiconductor film (4), a back channel protection insulating film (7) and an ohmic contact film (8) provided on the second semiconductor film (5), and source / drain electrodes (9). A crystallinity of the first semiconductor film (4) is higher than that of the second semiconductor film (5). The back channel protection insulating film (7) is formed as one of an organic insulating film and an organic / inorganic hybrid insulating film. The thin film transistor has excellent off-state characteristics, swing characteristics, and saturation characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
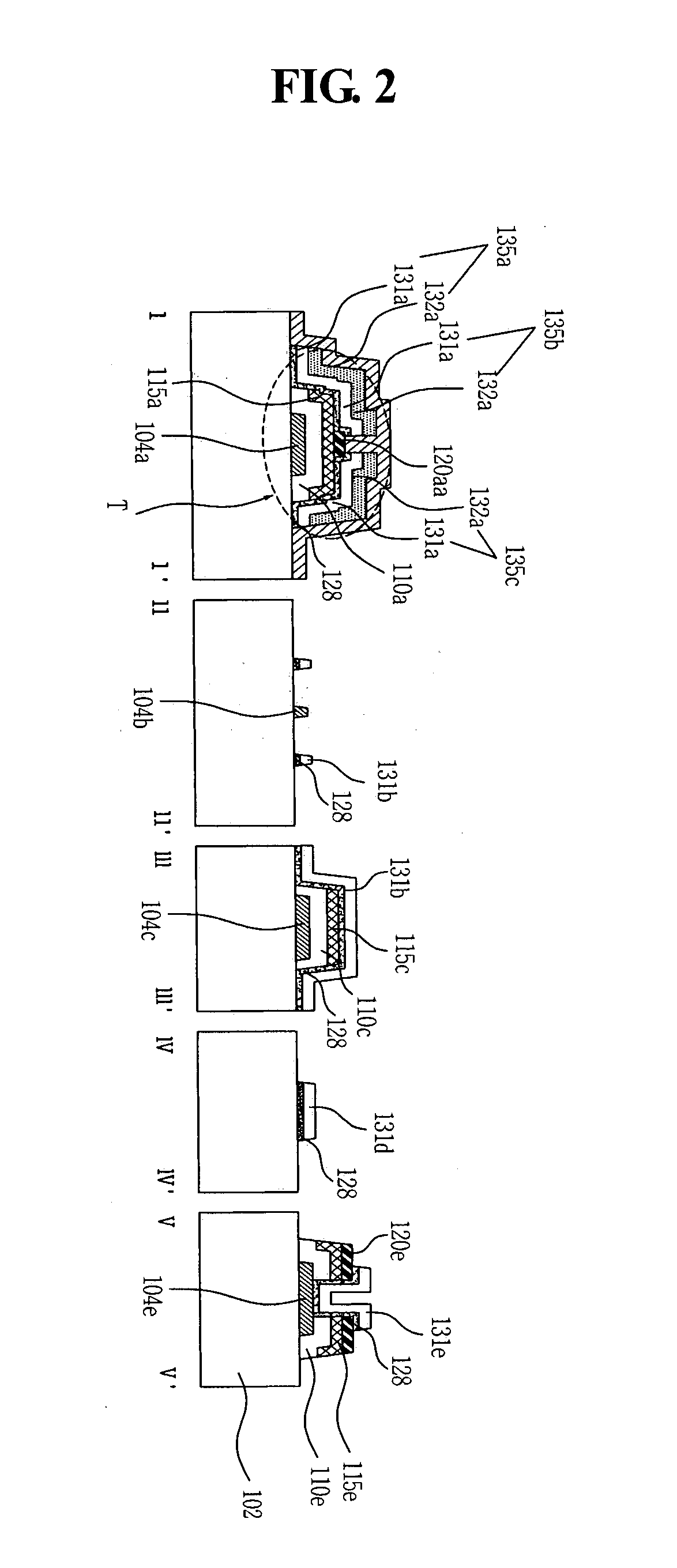
Thin film transistor substrate and method of manufacturing the same
A method of fabricating a liquid crystal display device includes forming a gate electrode; forming a gate insulator on the gate electrode, an active layer on the gate insulator, and an etch stopper on the active layer; depositing an ohmic contact layer, a first metal layer and a second metal layer on the substrate; etching the ohmic contact layer, and the first and second metal layers to form ohmic contact patterns, and first and second metal patterns including source, drain and pixel electrodes using a single photomask.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Double gate manufactured with locos techniques
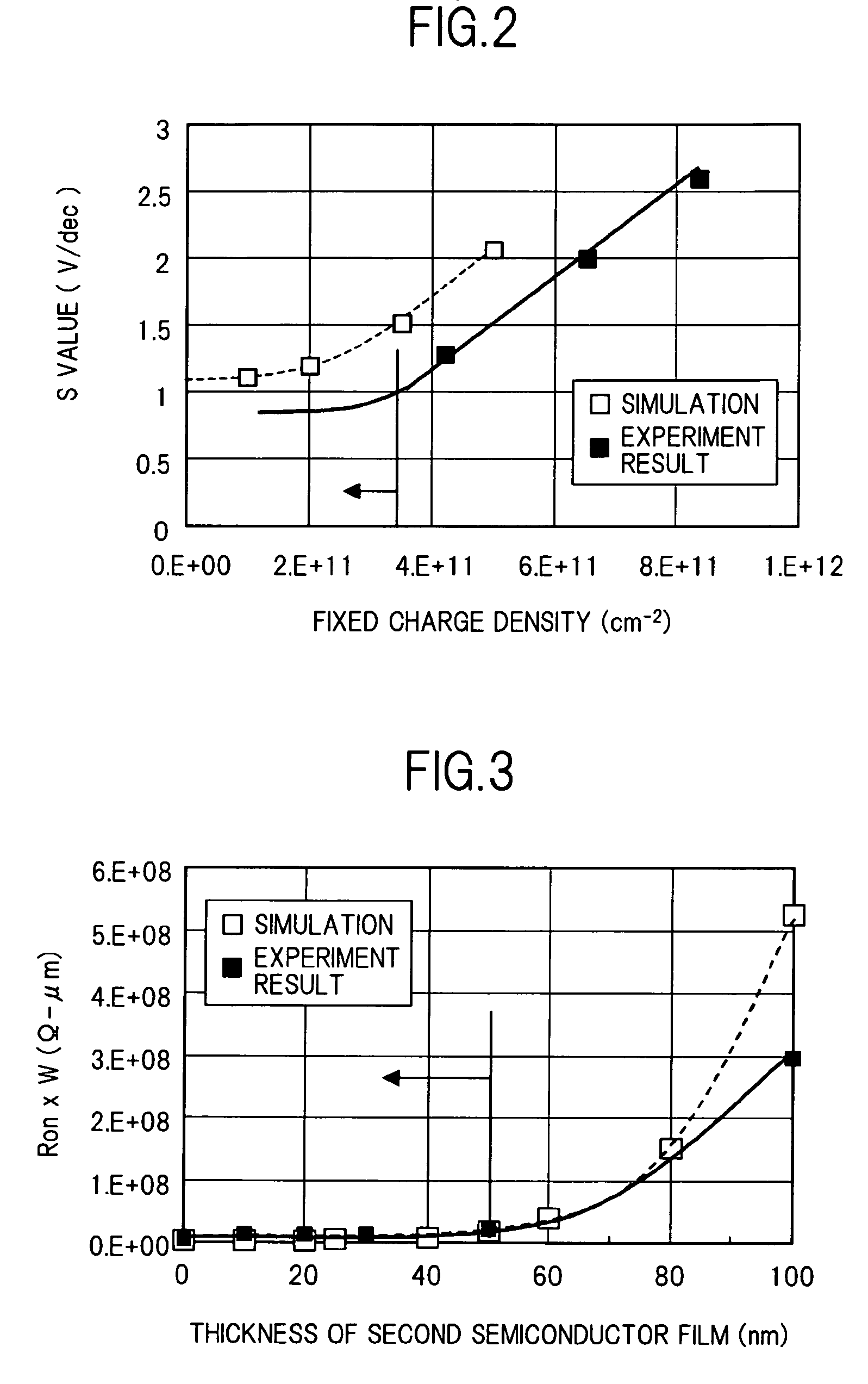
InactiveUS20100015770A1Avoid overetchingEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLOCOSInterface point
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
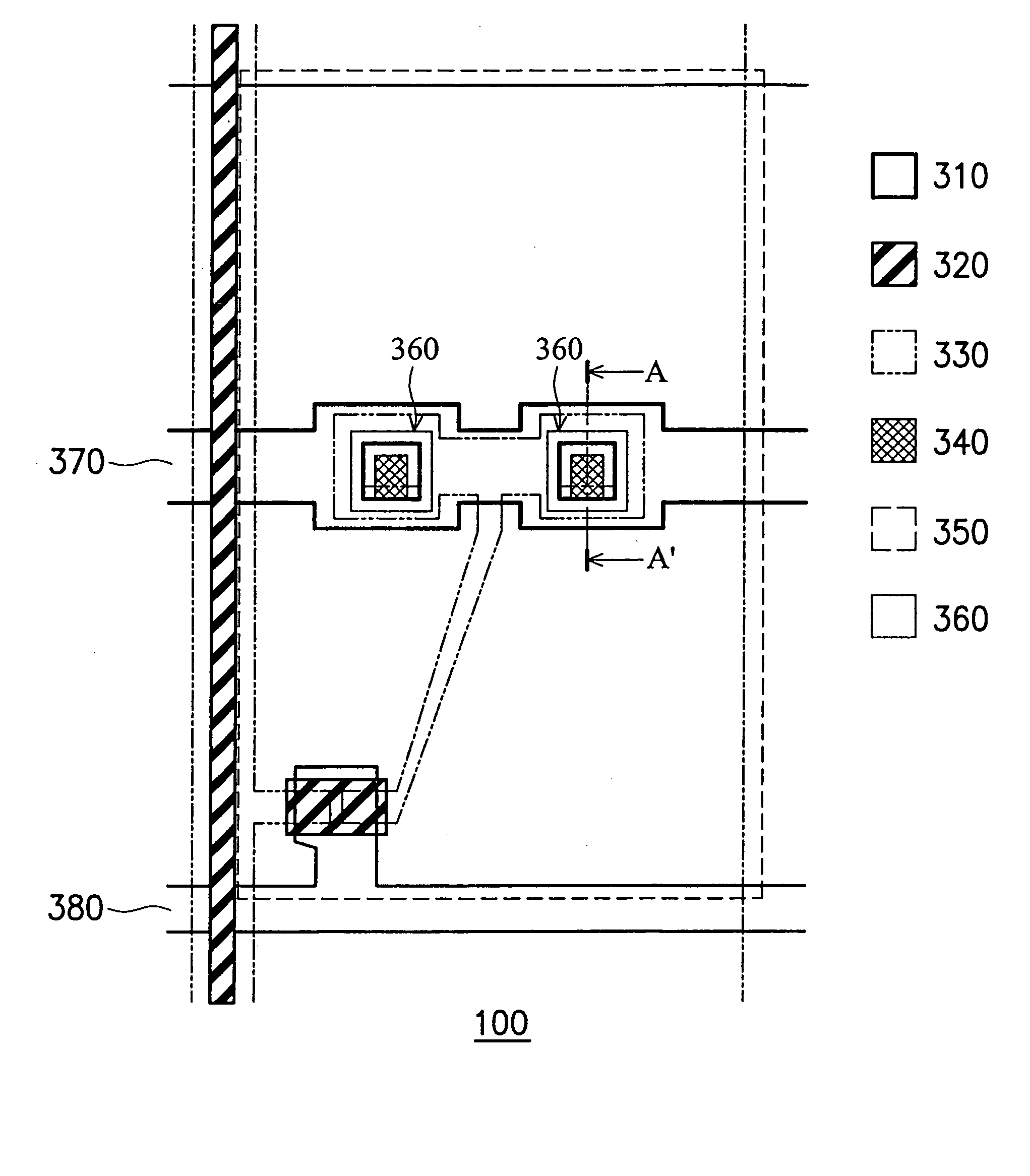
Display substrate and method of manufacturing the same
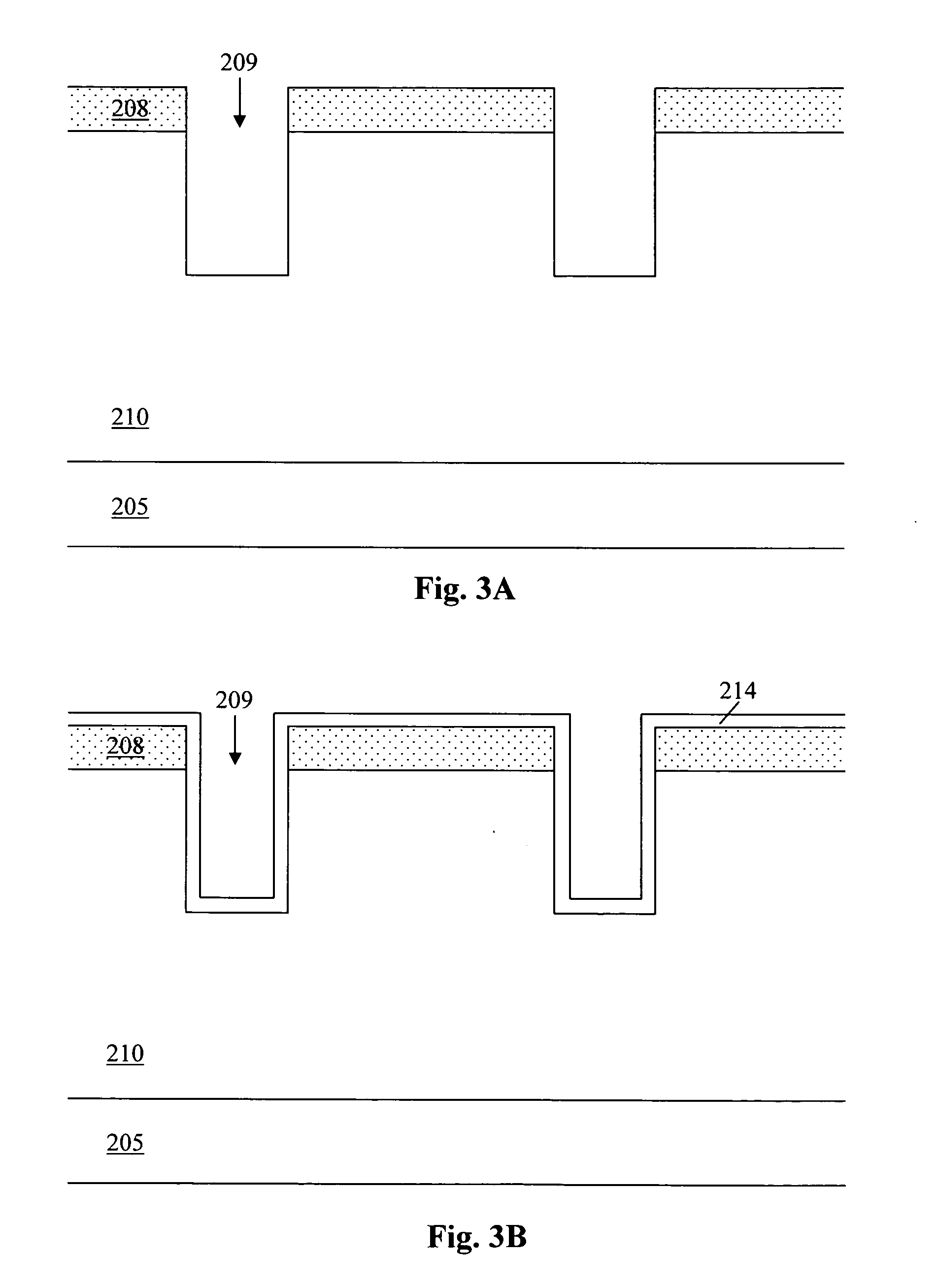
ActiveUS20130146902A1Improve productivityAvoid overetchingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarising elementsInsulation layerOptoelectronics
A display substrate includes a metal pattern, a first insulation layer pattern and a second insulation layer pattern. The metal pattern is on a base substrate. The first insulation pattern is on the metal pattern and includes one of a silicon nitride (SiNx) and a silicon oxide (SiOx). The second insulation pattern is on the first insulation pattern and includes a remaining one of the silicon nitride (SiNx) and the silicon oxide (SiOx).
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for fabricating strained-silicon CMOS transistor
First, a semiconductor substrate having a first active region and a second active region is provided. The first active region includes a first transistor and the second active region includes a second transistor. A first etching stop layer, a stress layer, and a second etching stop layer are disposed on the first transistor, the second transistor and the isolation structure. A first etching process is performed by using a patterned photoresist disposed on the first active region as a mask to remove the second etching stop layer and a portion of the stress layer from the second active region. The patterned photoresist is removed, and a second etching process is performed by using the second etching stop layer of the first active region as a mask to remove the remaining stress layer and a portion of the first etching stop layer from the second active region.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device with bump electrodes
InactiveUS6861749B2Avoid overetchingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact padDevice material
A semiconductor device comprises a substrate having contact pads each covered by under bump metallurgy and a plurality of bump electrodes respectively provided on the under bump metallurgy covering the contact pads. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the semiconductor device is characterized by having at least one contact pad (e.g., a test contact pad) which is not provided with any bump electrode but still has under bump metallurgy provided thereon. According to another embodiment of the present invention, the semiconductor device is characterized by having at least a conductive line formed of the same material as the under bump metallurgy for interconnecting at least two of the contact pads. The present invention further provides methods of manufacturing the semiconductor devices.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100151599A1Avoid overetchingMinimizing damageLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDevice materialEngineering
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes depositing material on a wafer in a process chamber to form a thin film on the wafer, a by-product layer being simultaneously formed on an inner part of the process chamber, monitoring a change in thickness or mass of the by-product layer on the inner part of the process chamber during a process in the process chamber by using a QCM installed in the process chamber, and determining an end point of the process in the process chamber based on the monitored change in thickness or mass of the by-product layer in the process chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having an isolation region, a trench formed on a semiconductor substrate and an insulating film buried within the trench; includes: forming a gate electrode in an active region adjacent to the isolation region; applying an ion implantation onto the substrate to form a first dopant diffusion region; forming a first and a second insulating film, on the entire surface of the substrate; performing an etch back, to form a first sidewall of the second insulating film on a lateral face of the gate electrode; etching the first insulating film to form a second sidewall of the first insulating film on the lateral face of; making another ion implantation to form a second dopant diffusion region; forming an interlayer insulating film; and forming a contact hole to reach the second dopant diffusion region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
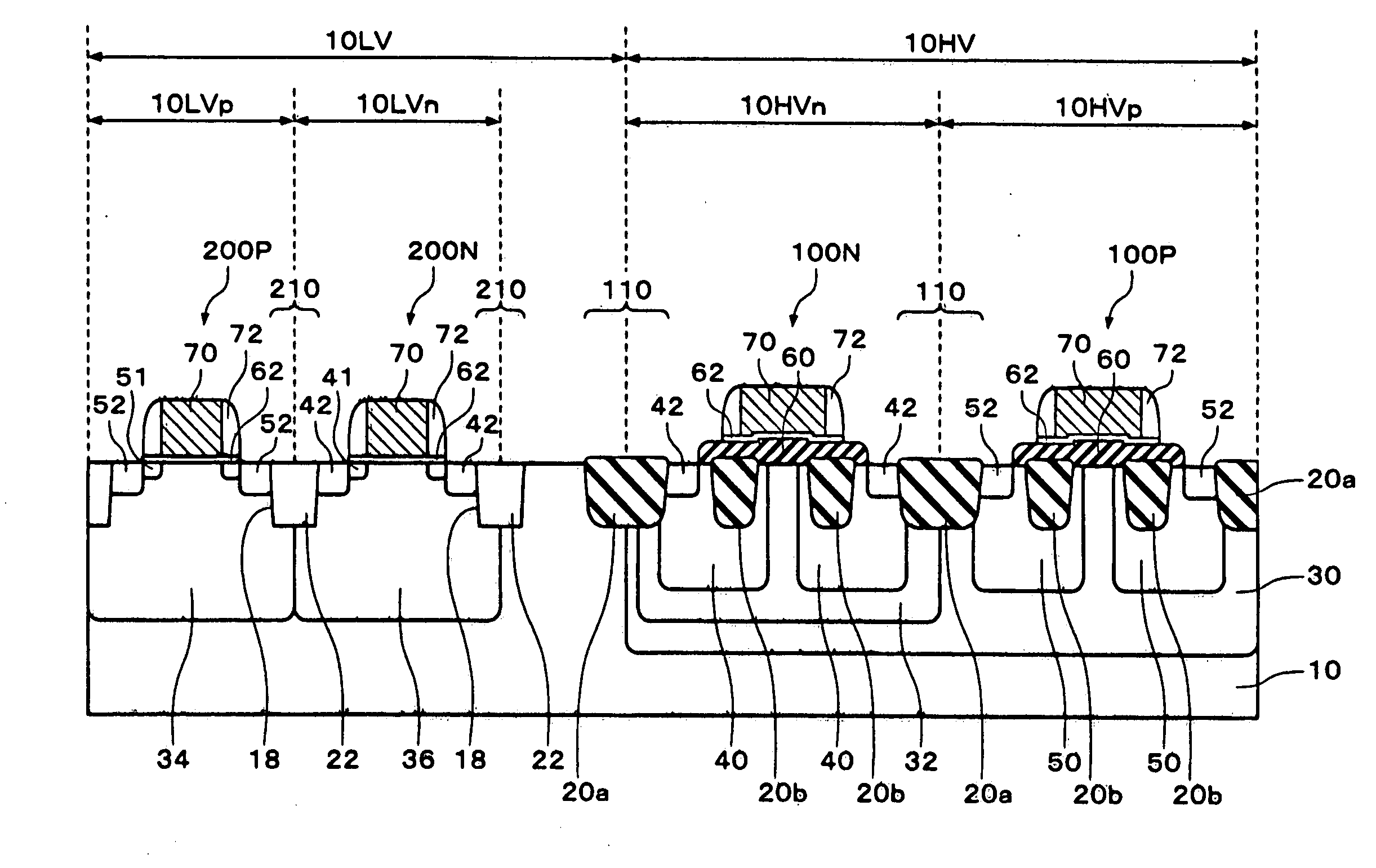
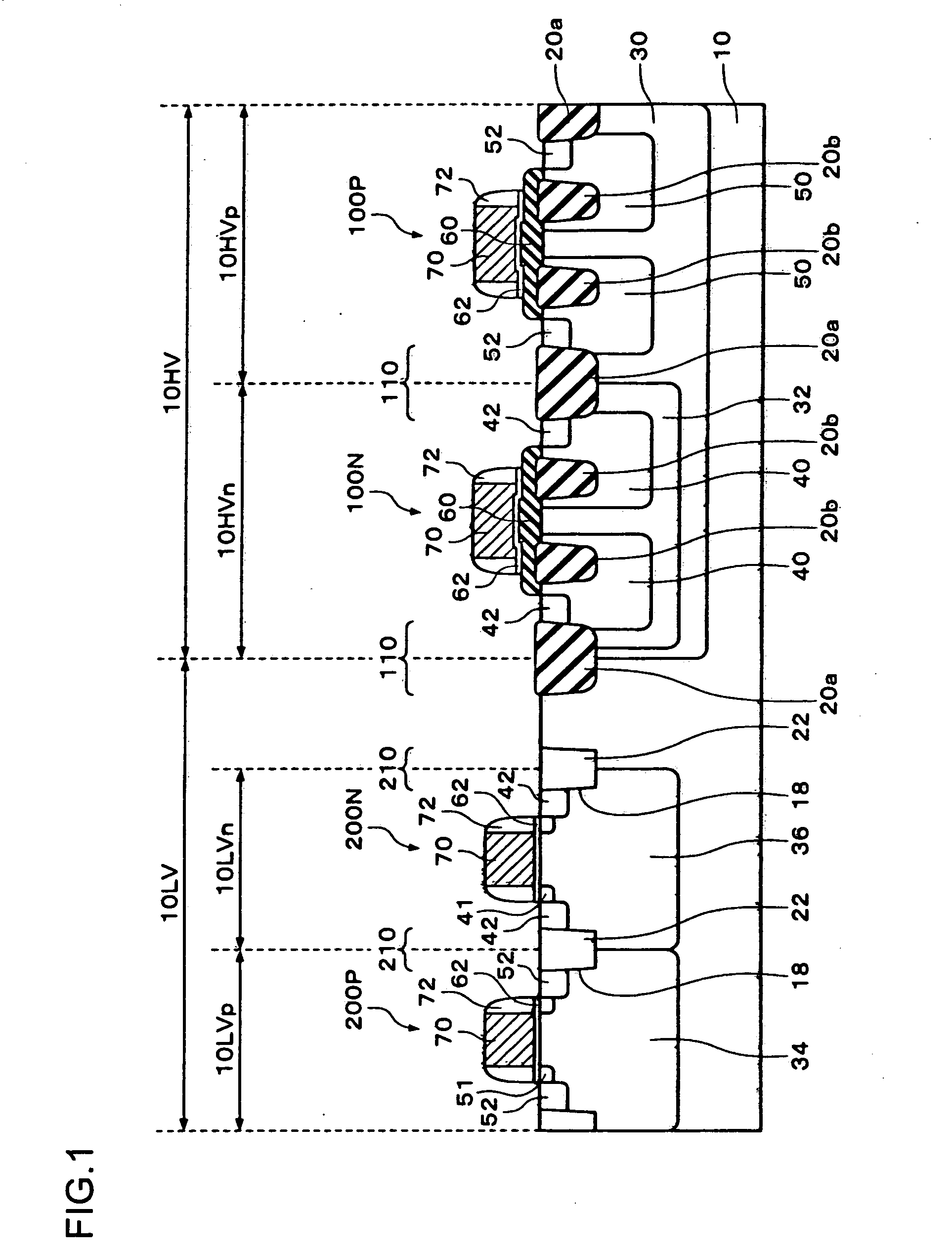
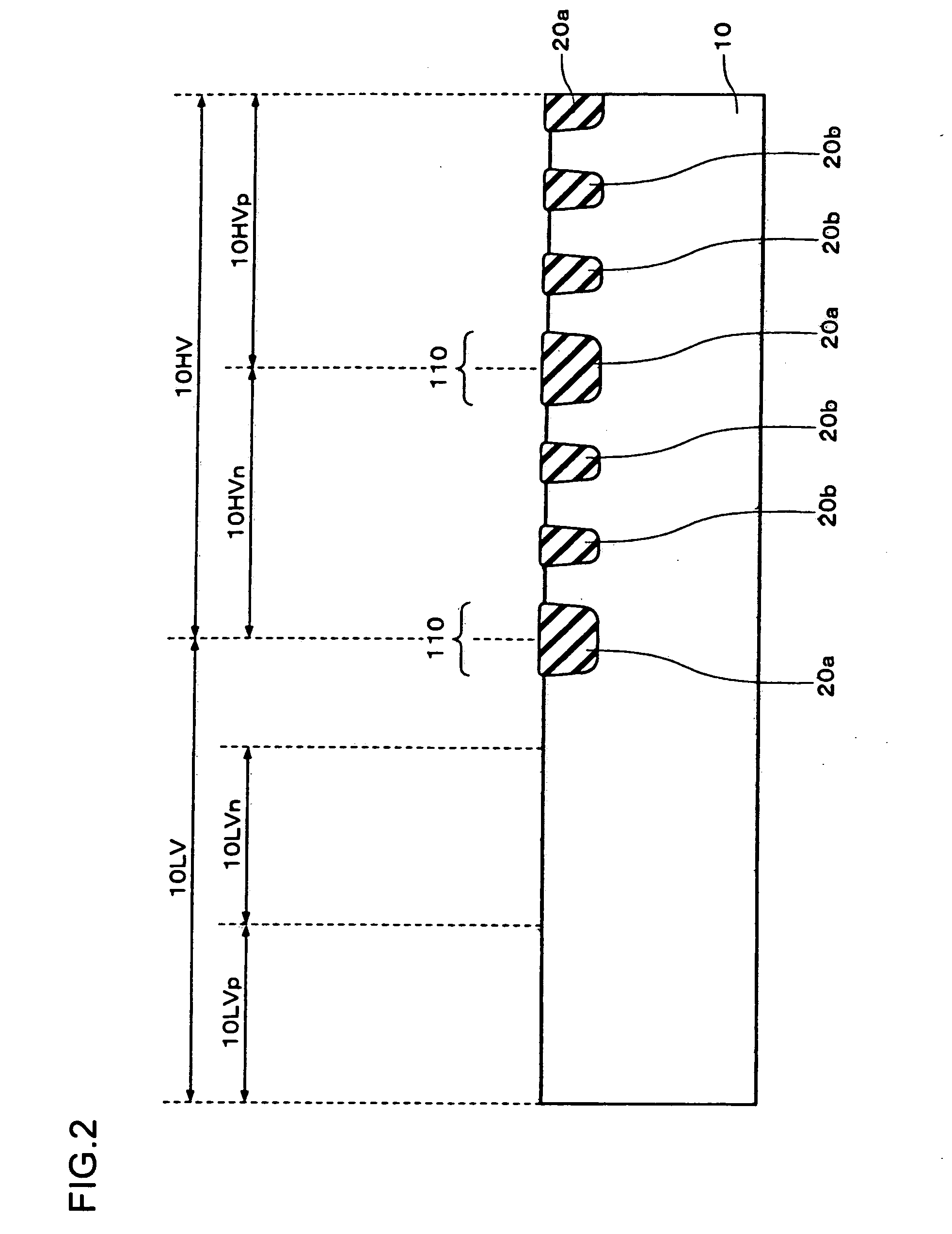
ActiveUS8253252B2Increase contact resistanceAvoid overetchingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationEngineering
It is an object to provide an element structure of a semiconductor device for having a sufficient contact area between an electrode in contact with a source region or a drain region and the source region or the drain region, and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device with the element structure. An upper electrode is formed over a high-concentration impurity region (the source region or the drain region). A contact hole passing through an interlayer insulating film is formed overlapping with a region where the upper electrode and the high-concentration impurity region are stacked.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Polarizing device, method for manufacturing the same, liquid crystal device, and projection display device
ActiveUS20080303987A1Simple structureHigh aspect ratio structurePolarising elementsColor television detailsProjection displayMetal
A polarizing device includes: a polarizing device unit composed of a metallic film formed on a base, the metallic film having a plurality of slit-shaped openings; and an etching sacrifice layer provided between the base and the polarizing device unit, so that the etching sacrifice layer is partly etched together with the metallic film during the etching of the polarizing device unit; wherein the etching sacrifice layer is composed of a material that has an etching rate equal to or greater than that of the metallic film.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method to manufacture split gate with high density plasma oxide layer as inter-polysilicon insulation layer
ActiveUS20100099230A1Improve configurationReduce gate-to-drain capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh densityInsulation layer
This invention discloses a method of manufacturing a trenched semiconductor power device with split gate filling a trench opened in a semiconductor substrate wherein the split gate is separated by an inter-poly insulation layer disposed between a top and a bottom gate segments. The method further includes a step of forming the inter-poly layer by applying a RTP process after a HDP oxide deposition process to bring an etch rate of the HDP oxide layer close to an etch rate of a thermal oxide.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Double gate manufactured with locos techniques
InactiveUS20080296673A1Avoid overetchingEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInsulation layerLOCOS
This invention discloses a trenched semiconductor power device that includes a trenched gate surrounded by a source region encompassed in a body region above a drain region disposed on a bottom surface of a substrate. The trenched gate further includes at least two mutually insulated trench-filling segments with a bottom insulation layer surrounding a bottom trench-filling segment having a bird-beak shaped layer on a top portion of the bottom insulation attached to sidewalls of the trench extending above a top surface of the bottom trench-filling segment.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080206947A1Rapid thermal oxidationQuality improvementTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical solution
A method of manufacturing the semiconductor device is provided, which provides a prevention for a “dug” of a silicon substrate caused by the etching in regions except a region for forming a film during a removal of the film with a chemical solution. A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes forming a first silicon oxide film on a surface of a silicon substrate or on a surface of a gate electrode when a silicon nitride film for a dummy side wall is etched off, to provide a protection for such surfaces, and then etching a portion of the silicon nitride film with a chemical solution, and then a second oxide film for supplementing a simultaneously-etched portion of the first silicon oxide film is formed, and eventually performing an etching for completely removing the silicon nitride film for the dummy side wall.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method of fabricating a flash memory device
InactiveUS20060148171A1Improve isolationAvoid overetchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDouble gate
A method of fabricating a flash memory device, having a double gate structure, including an oxide / nitride / oxide (ONO) layer, provides more stable operation by using a dummy pattern upon forming the ONO layer and using a control gate after forming a floating gate. The method includes steps of forming a floating gate on a semiconductor substrate; forming a dummy pattern on the floating gate; etching the floating gate using the dummy pattern as a hard mask; forming an insulating layer flush with an upper surface of the dummy pattern; removing the dummy pattern to leave a space for an ONO layer and control gate formation; and sequentially forming an ONO layer and a control gate in the space left by removing the dummy pattern.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
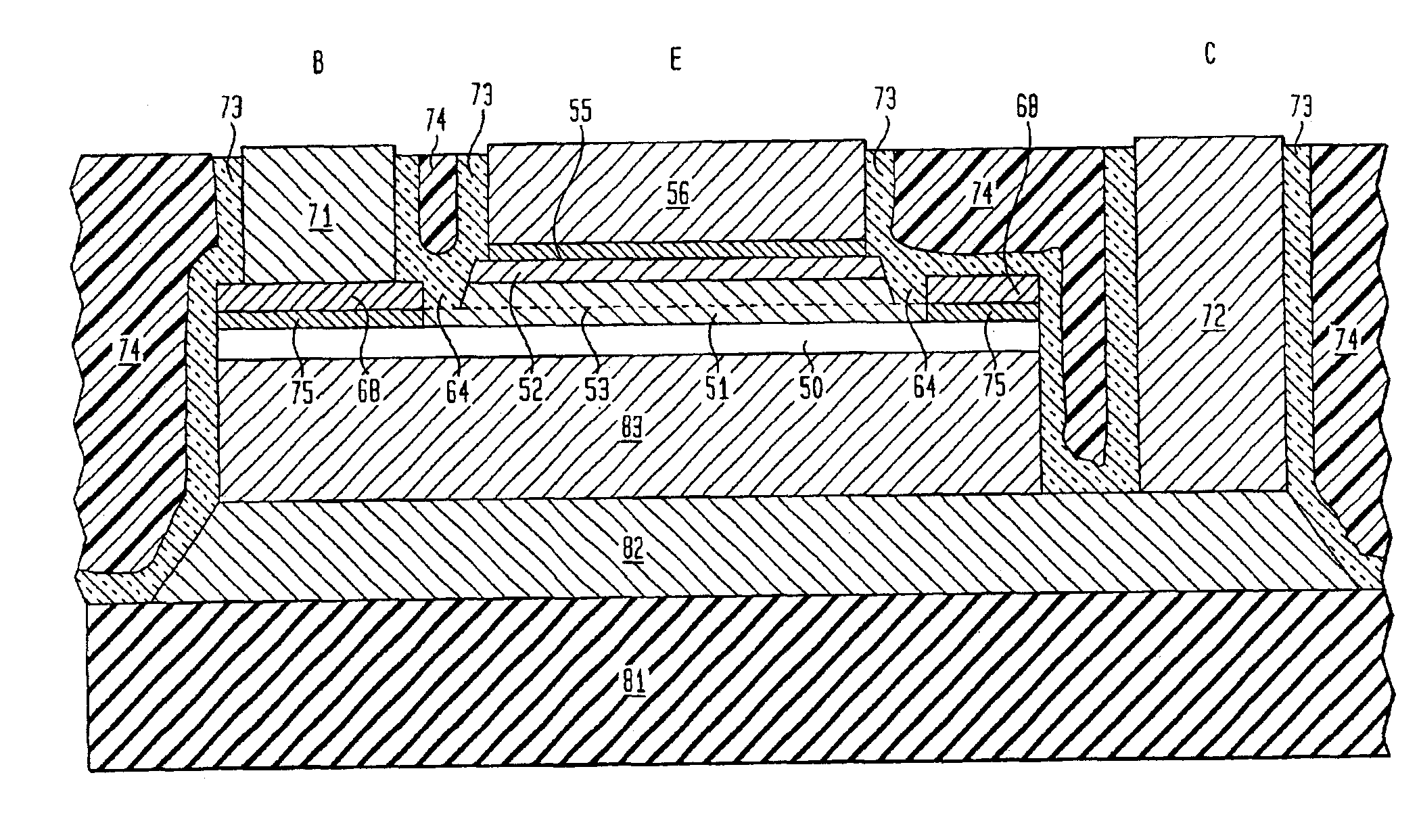
Semiconductor structure and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20180269252A1Avoid damageAvoid problemsTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureFloating diffusion
A semiconductor structure and a fabrication method are provided. The fabrication method includes: providing a substrate, containing first doping ions and including a pixel region for forming a pixel structure; forming a deeply doped region, in the photosensitive region of the substrate and containing second doping ions; forming a floating diffusion area in the floating diffusion region of the substrate and containing third doping ions; forming a gate structure on the substrate at the junction of the photosensitive region and the floating diffusion region; forming a sidewall film covering the gate structure and the substrate; forming a sidewall spacer; forming a first doped region in the floating diffusion region on one side of the gate structure; forming a metal connection layer on the first doped region; forming an interlayer dielectric layer on the substrate; and forming a source / drain contact plug in the interlayer dielectric layer.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Method and apparatus for a self-aligned heterojunction bipolar transistor using dielectric assisted metal liftoff process
InactiveUS6894362B2Improved etch controlEliminates etchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionDielectric
Disclosed is a manufacturing method to fabricate Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors (HBTs) that enables self-alignment of emitter and base metal contact layers with precise sub-micron spacing using a dielectric-assisted metal lift-off process. Such an HBT process relies on the formation of an “H-shaped” dielectric (i.e., Si3N4 / SiO2) mask conformally deposited on top of the emitter contact metallization that is used to remove excess base metal through lift-off by a wet chemical HF-based etch. This HBT process also uses a thin selective etch-stop layer buried within the emitter layer to prevent wet chemical over-etching to the base and improves HBT reliability by forming a non-conducting, depleted ledge above the extrinsic base layer. The geometry of the self-aligned emitter and base metal contacts in the HBT insures conformal coverage of dielectric encapsulation films, preferably Si3N4 and / or SiO2, for reliable HBT emitter p-n junction passivation. Thus, the disclosed HBT process enables scaling of narrow emitter stripe widths down to sub-micron dimensions producing transistors with cut-off frequencies in the range of several hundred GigaHertz.
Owner:RJM SEMICON
Thin film transistor liquid crystal display and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS7112459B2Reduce in quantityReduce stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayThin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display
A thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) and fabrication method thereof. The fabrication method includes depositing a first metal layer on a transparent substrate, patterning the first metal layer to form at least two adjacent gate electrodes, forming a gate insulating layer on the gate electrodes, forming a semiconductor layer on the insulating layer, patterning the semiconductor layer into a predetermined shape, depositing a second metal layer on the transparent substrate, patterning the second metal layer to form a source / drain electrode layer, and depositing an insulating layer on the transparent substrate. A contact hole is defined via the insulating layer, source / drain electrode layer, and gate insulating layer, exposing a part of the surface of transparent substrate between the adjacent gate electrodes. A transparent conductive layer is deposited on the transparent substrate, and a light-shielding matrix is formed directly above the contact hole.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050151259A1Good control over etchingIncreasing the thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A silicon-rich oxide (SRO) film is arranged over an uppermost third-level wiring in a semiconductor device. Then, a silicon oxide film and a silicon nitride film lying over the third-level wiring are dry-etched to expose part of the third-level wiring to thereby form a bonding pad and to form an opening over the fuse. In this procedure, the SRO film serves as an etch stopper. This optimizes the thickness of the dielectric films lying over the fuse.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050112825A1Prevent removalRelieve stressTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh voltage transistorsSilicon
A semiconductor device manufacturing method includes: forming a first isolation region for setting a high-voltage-proof transistor forming region in a semiconductor layer; forming a second isolation region for setting a low-voltage-driven transistor forming region in the semiconductor layer by shallow-trench-isolation processing; and forming an offset insulating layer for electric field relaxation of high-voltage-proof transistors in the semiconductor layer by local-oxidation-of-silicon processing. The second step including: forming a trench in the semiconductor layer; forming an insulating layer filling up the trench and covering the entire upper surface of the semiconductor layer; removing part of the exposed insulating layer with a mask covering the insulating layer above a the offset insulating layer forming region and the trench forming region; removing at least the insulating layer in the high-voltage-proof transistor forming region by chemical-mechanical-polishing; and removing the insulating layer in the offset insulating layer forming region.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Integrated circuit structure including fuse and method thereof
ActiveUS20160049367A1Control thicknessAvoid overetchingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric layerIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit structure includes a fuse. The integrated circuit structure further includes a first dielectric layer and a patterned dummy. The fuse is disposed on a substrate. The first dielectric layer covers the fuse. The patterned dummy is disposed on the first dielectric layer and the patterned dummy has a first recess exposing a part of the first dielectric layer directly above the fuse. A method of forming the integrated circuit structure including a fuse is also provided.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method
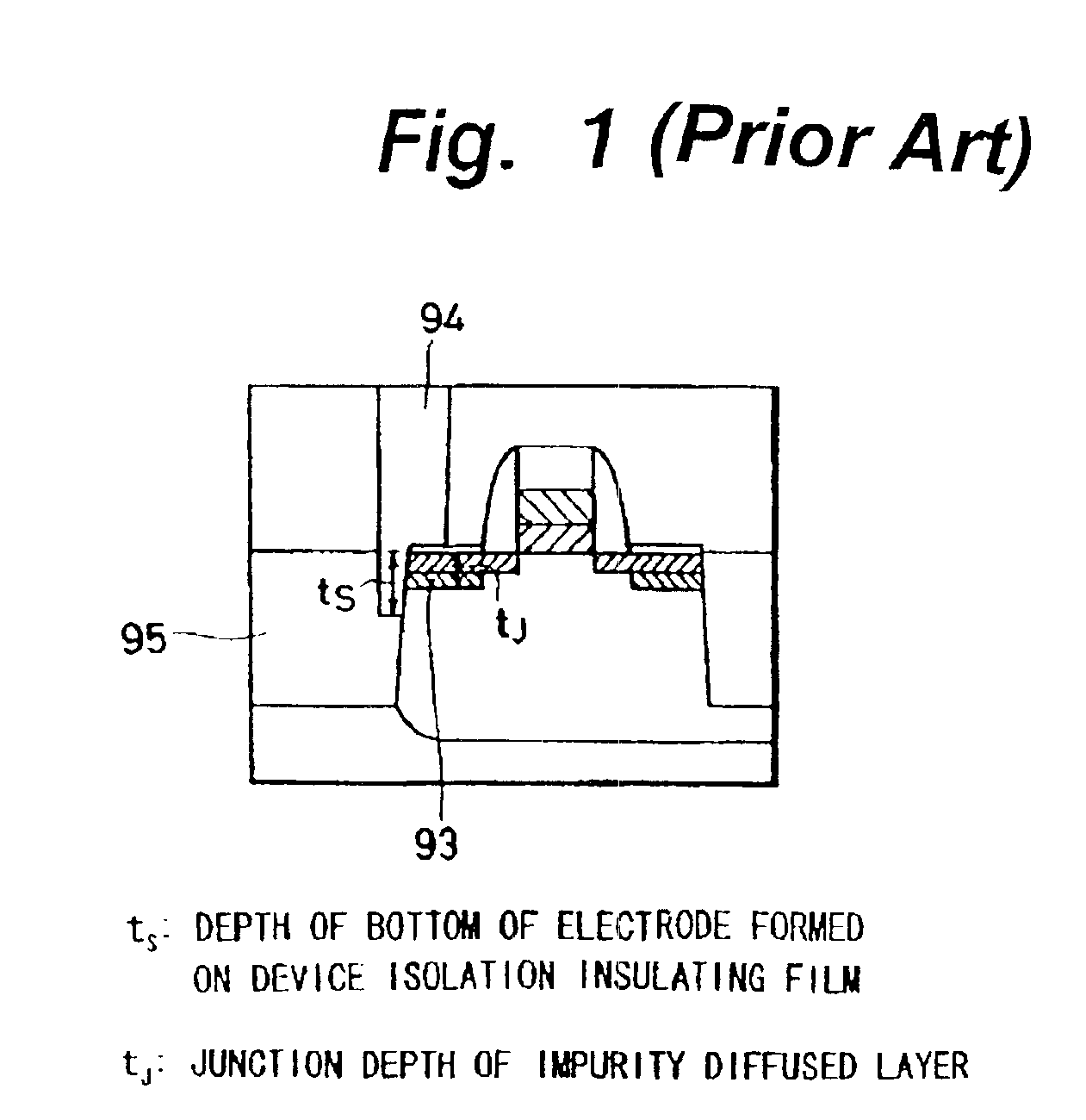
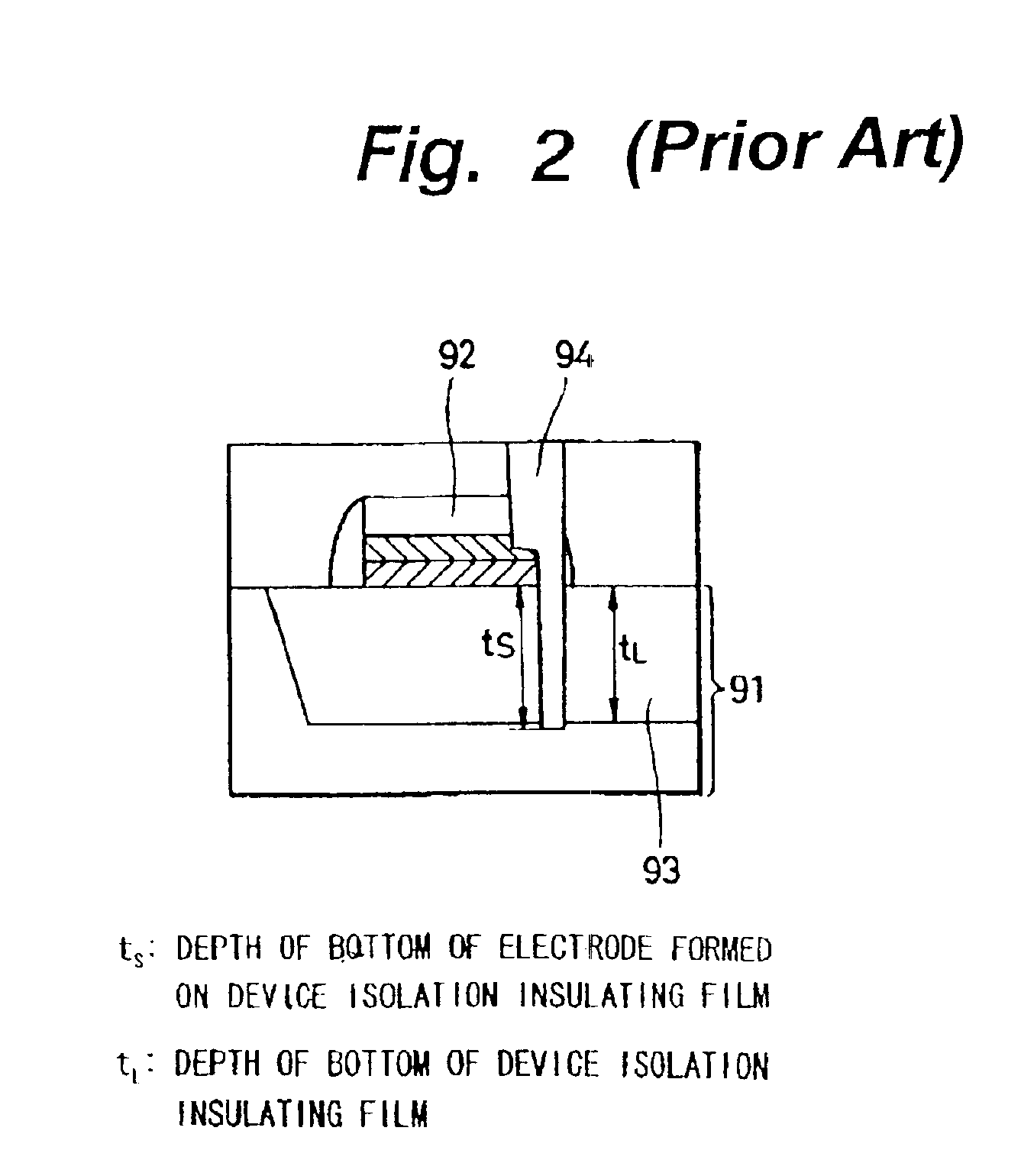
InactiveUS6909132B2Blocking can be undesirablePrevent junction leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpurity diffusionJunction leakage
In a contact structure having a large aspect ratio in a LSI device incorporating DRAM cells and logics, for the purpose of preventing over-etching of a device isolation insulating film and an impurity diffusion layer and thereby minimizing junction leakage, a first etching stopper layer covering a peripheral MOS transistor and a second etching stopper layer overlying a capacitor section of a DRAM memory cell are formed. An impurity diffusion layer of the peripheral MOS transistor is connected to a metal wiring layer formed in an upper level of the capacitor section by an electrode layer extending through the first and second etching stopper layers. At least one of such impurity diffusion layers is connected to the electrode layer at its boundary with the device isolation insulating film, and depth of the bottom of the electrode layer formed on the device isolation insulating film from the surface of the impurity diffusion layer is shorter than the junction depth of the impurity diffusion layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting element and manufacturing method thereof
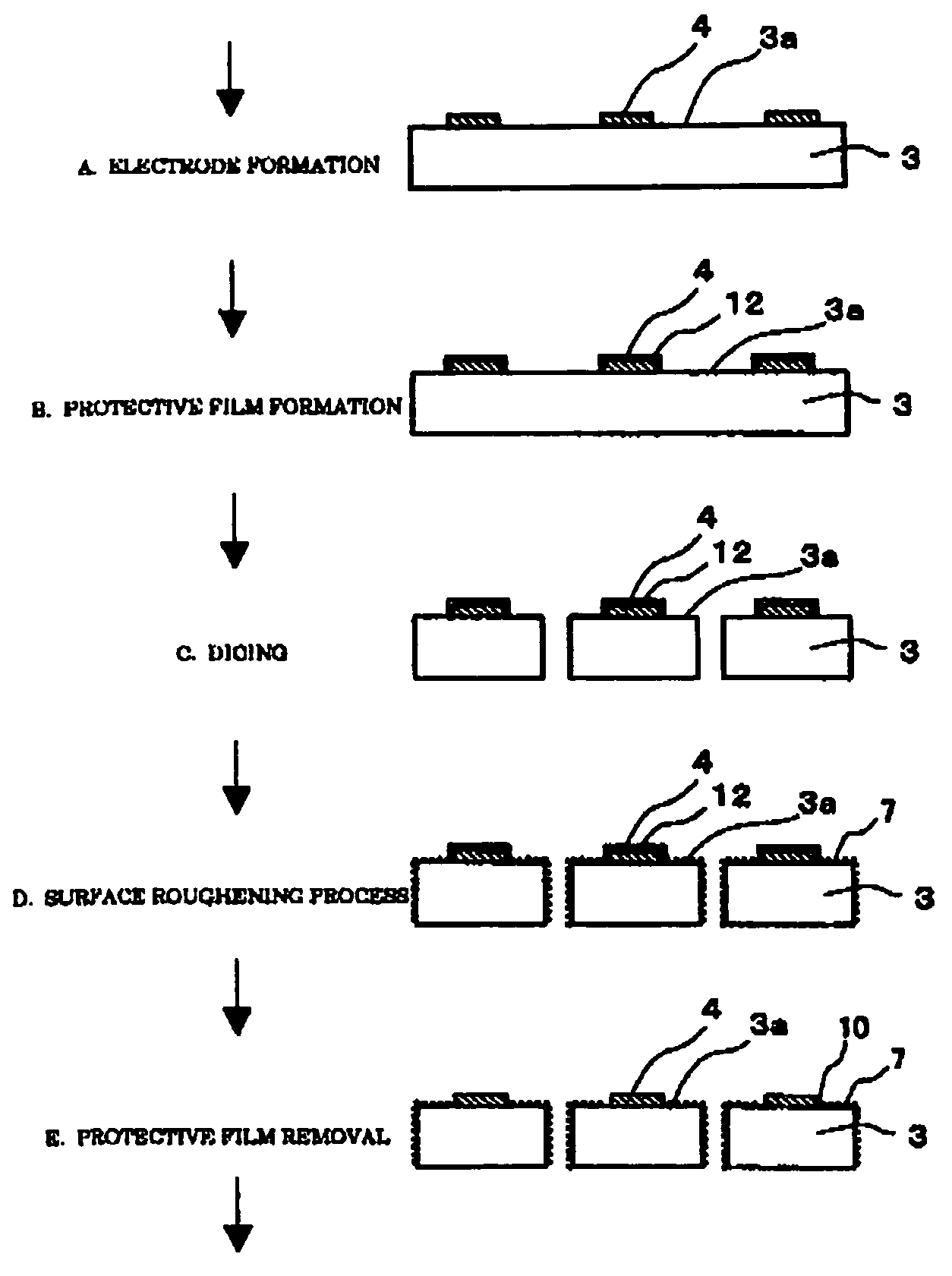
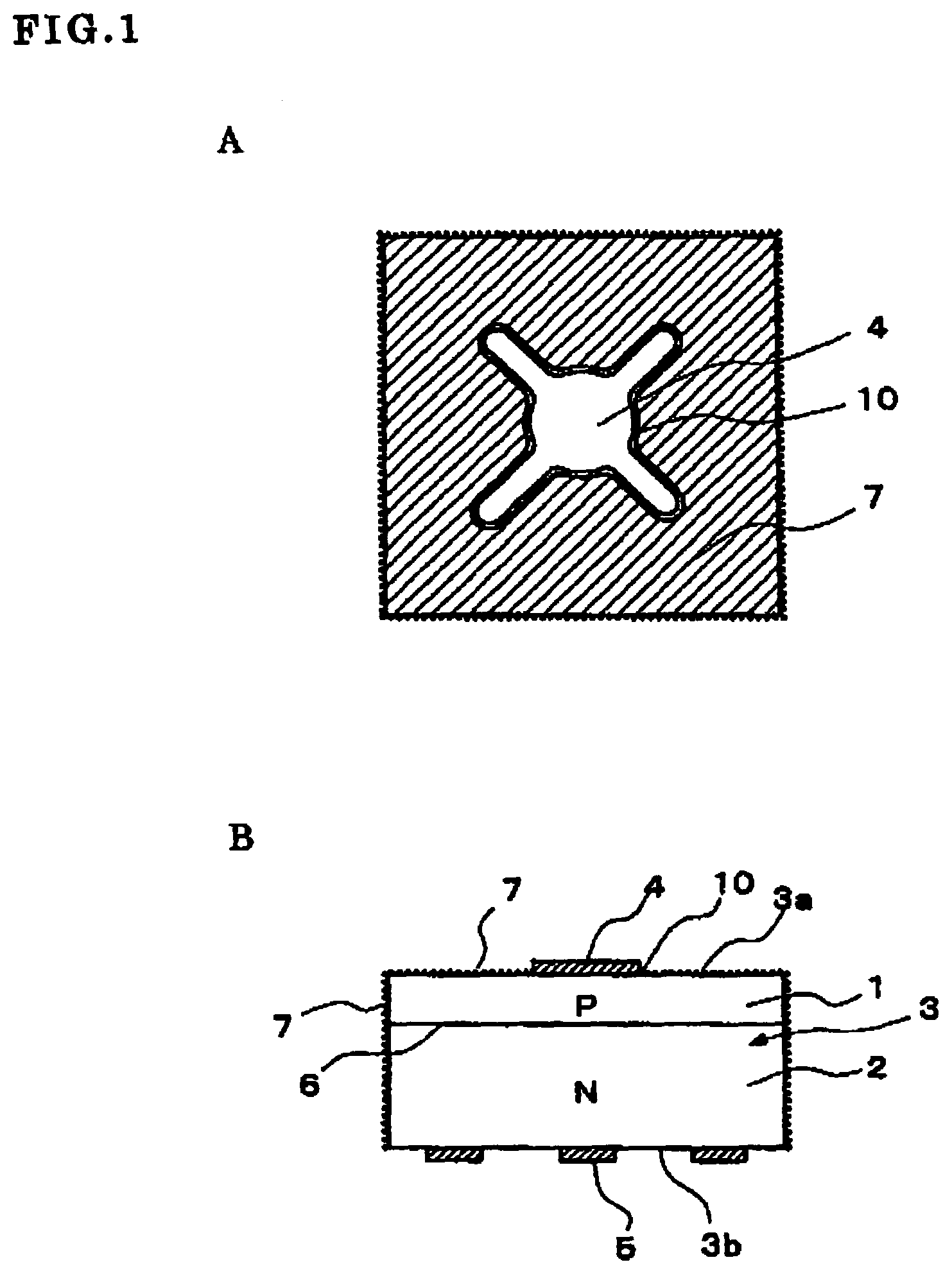
ActiveUS7211834B2Improve reliabilityAvoid overetchingSemiconductor devicesChemical treatmentEngineering
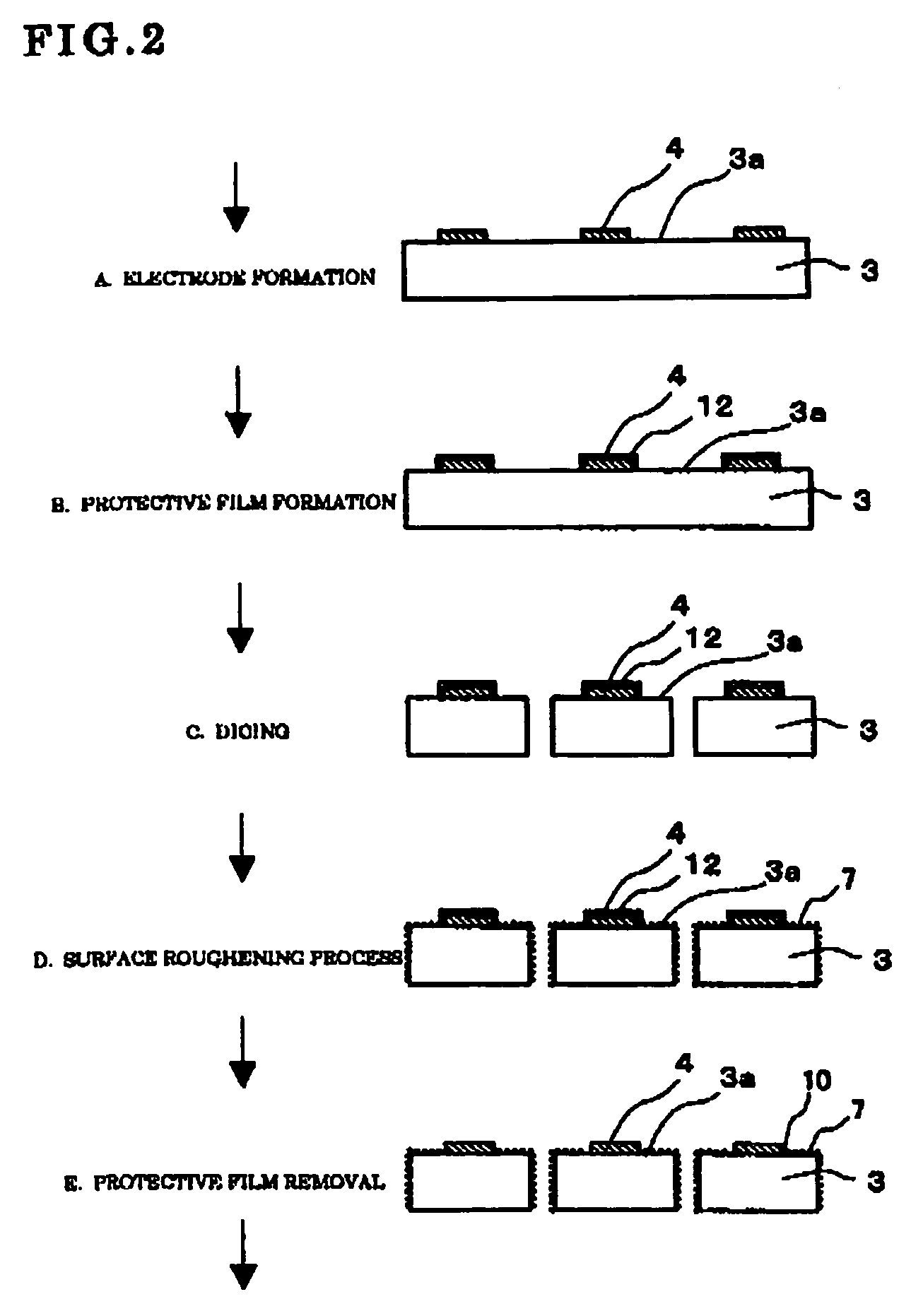
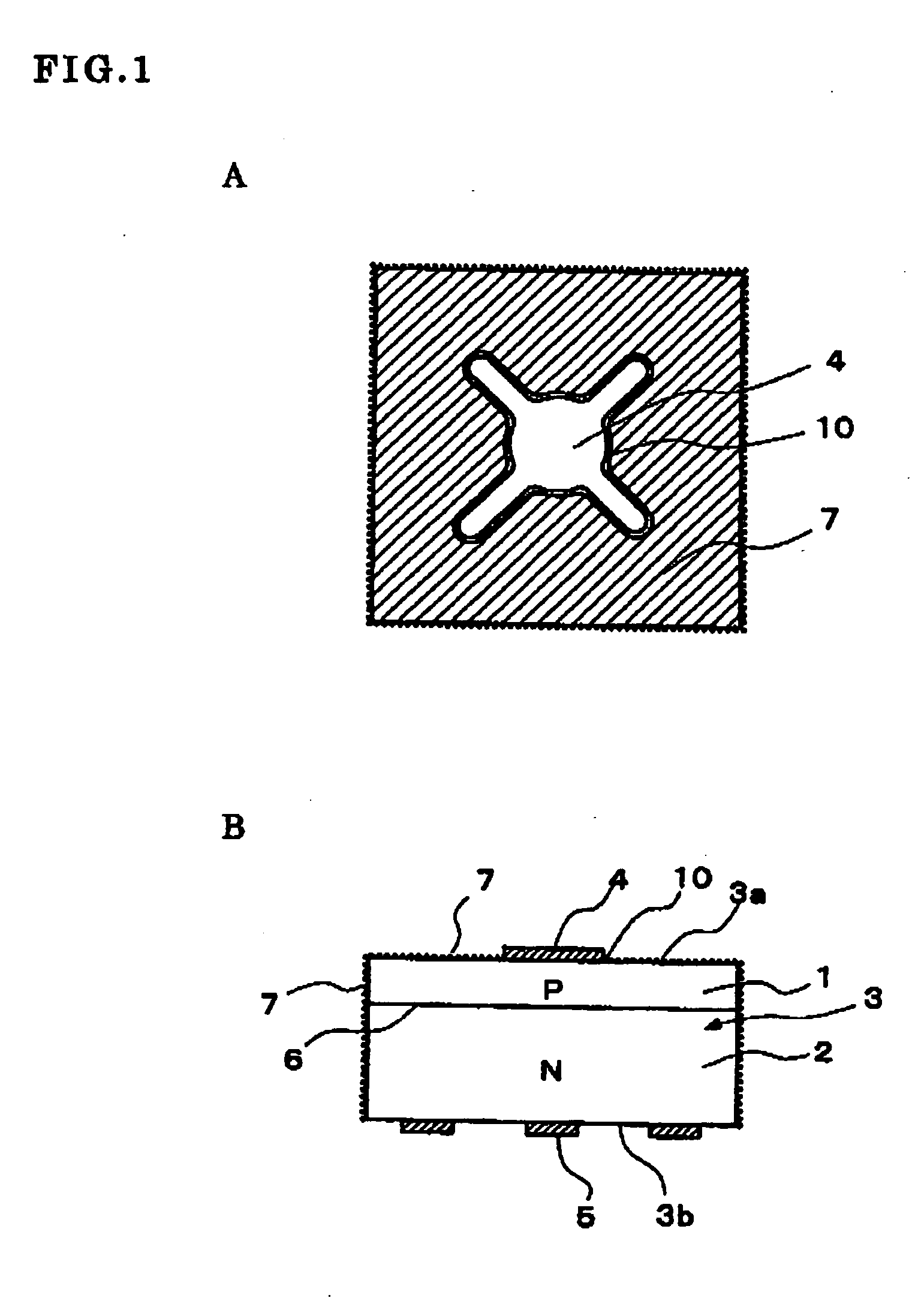
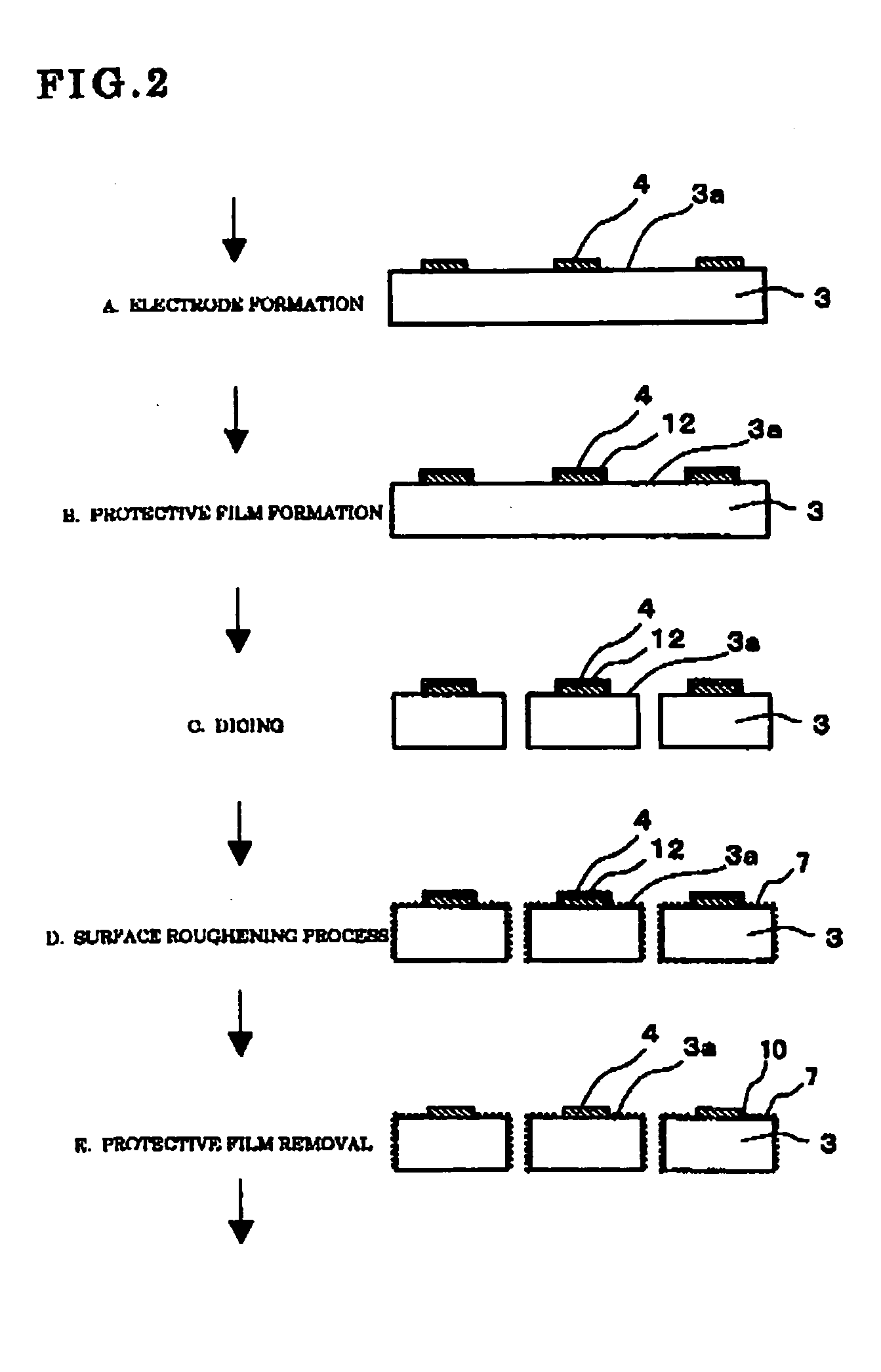
An improvement in electrode reliability is realized by preventing over-etching on a peripheral lower portion of an electrode while maintaining the flow of steps of roughening a surface after forming the electrode on a semiconductor substrate. After a P-side electrode 4 is formed on a main surface 3a of a semiconductor substrate 3, a surface of the P-side electrode 4 is selectively covered with a protective film 12, after the semiconductor substrate 3 is cut into chips, the surface is roughened from above the protective film 12, the main surface 3a around the P-side electrode 4 and a side surface are roughened with a non-chemical treatment region 10 which is a non-roughened surface region being left in a peripheral portion of the P-side electrode 4 covered with the protective film 12, and thereafter the protective film 12 is removed.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
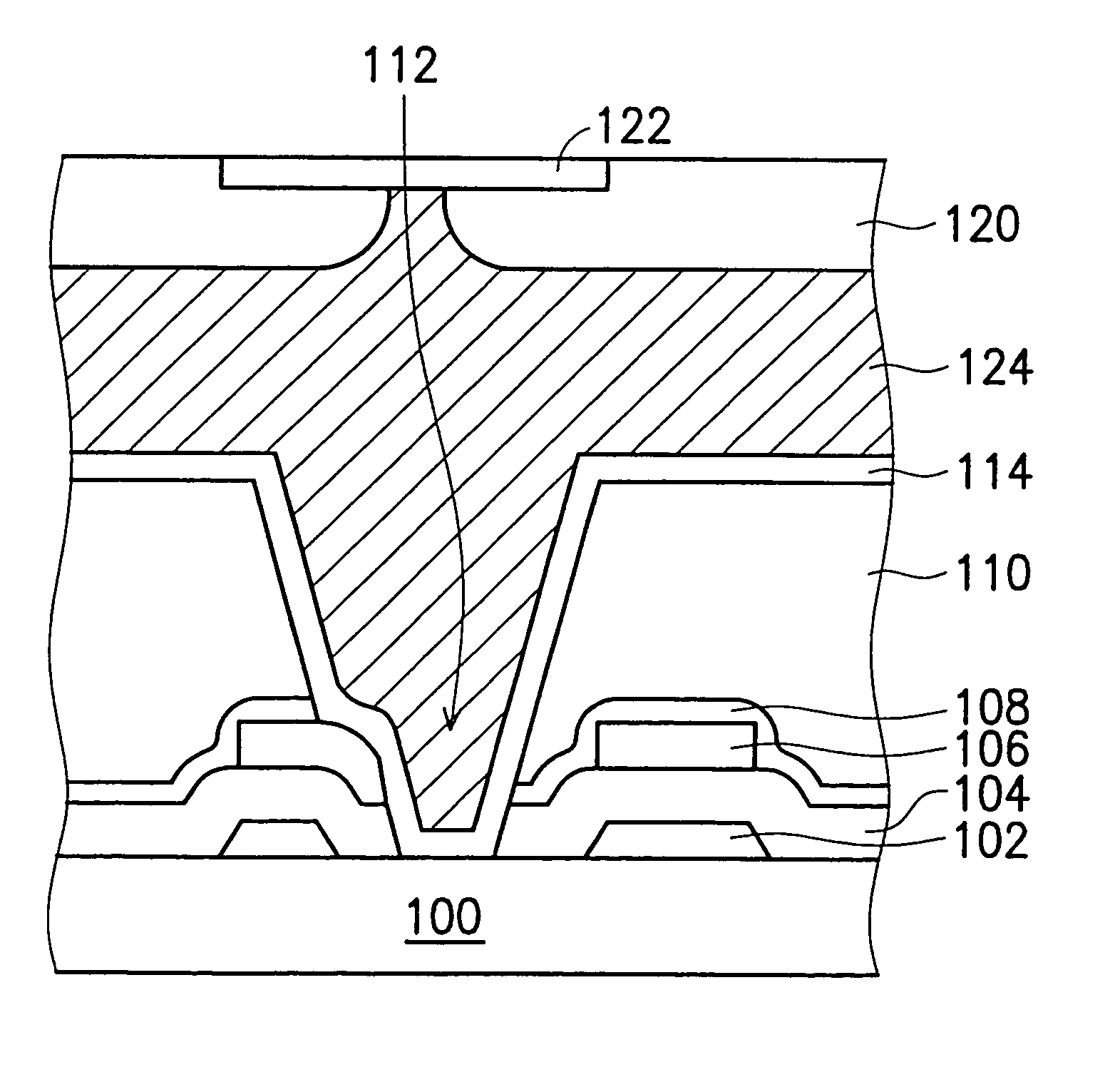
Metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor including a planarized material layer and method of fabricating the same
A method of fabricating a MOS transistor, and the MOS transistor fabricated by the method, includes providing a substrate, forming a predetermined layer having a non-planar surface on the substrate, the predetermined layer including at least one active region, forming a gate electrode material layer on the non-planar, predetermined layer, forming a material layer and a hard mask layer on an entire surface of the gate electrode material layer, and planarizing a top surface of the material layer to form a planarized material layer, forming a photoresist pattern on the planarized material layer and the hard mask layer to pattern the gate electrode material layer, forming a hard mask pattern by etching the hard mask layer using the photoresist pattern as an etching mask, and forming a predetermined pattern by etching the planarized material layer and the gate electrode material layer according to a shape of the hard mask pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
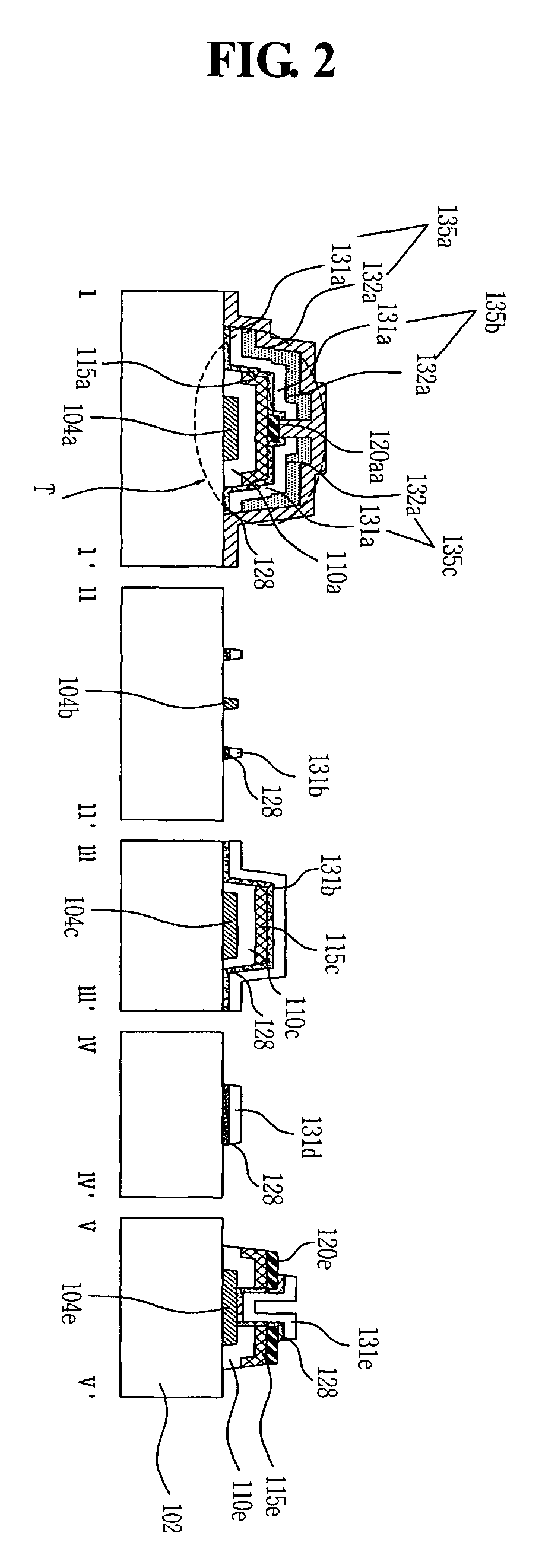
Flexible touch screen panel and method of manufacturing the same
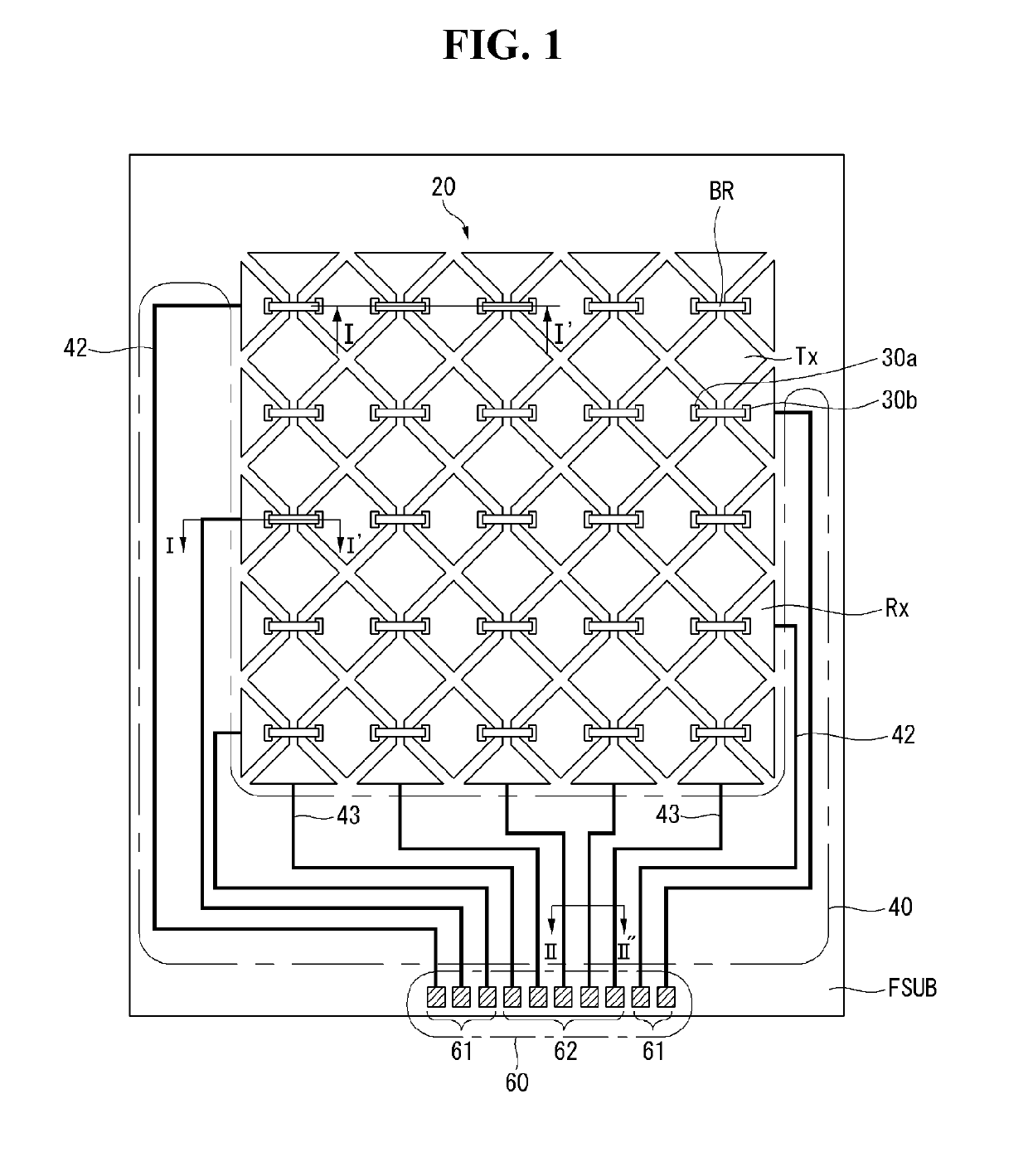
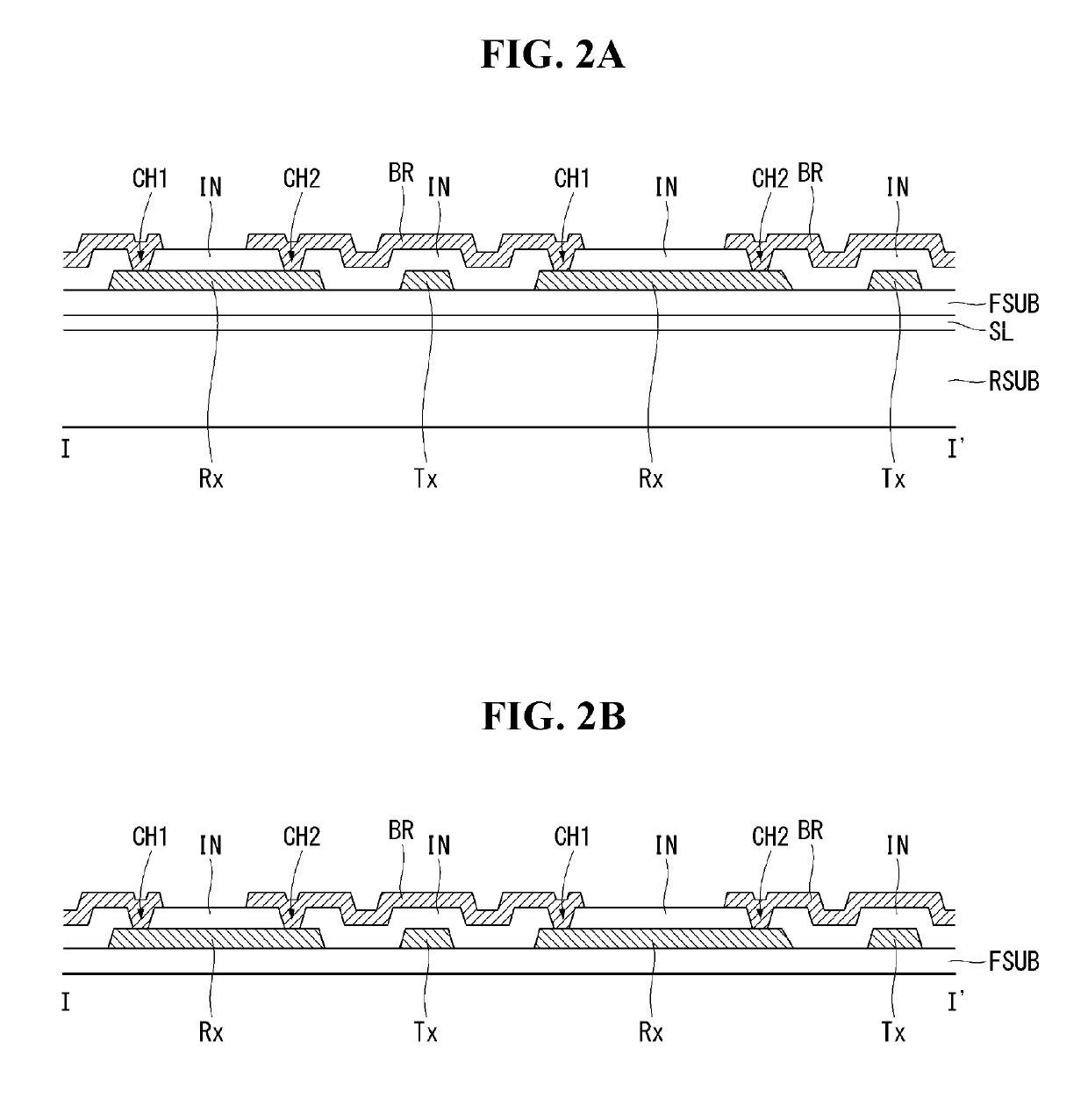
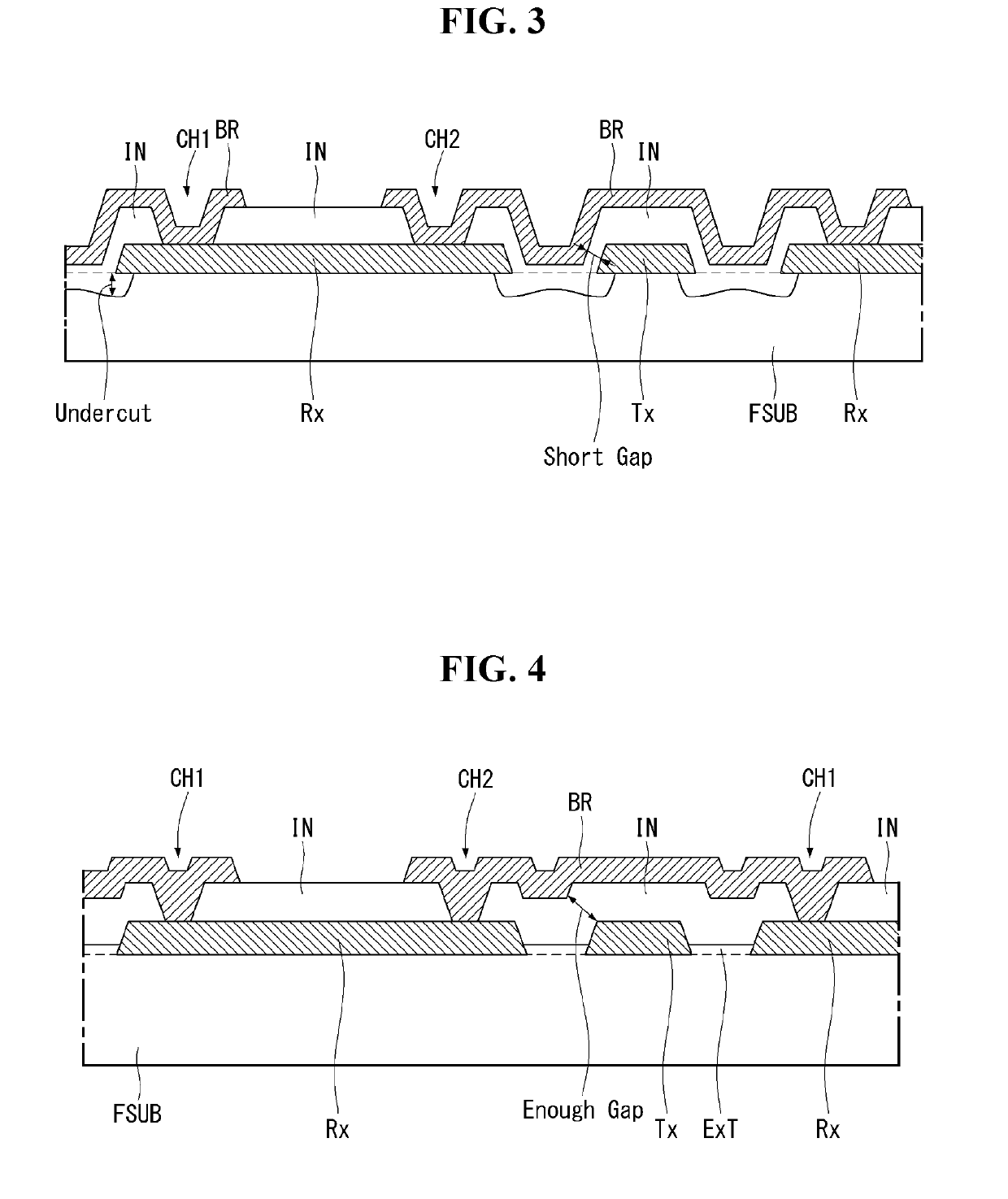
ActiveUS20190179441A1Avoid overetchingAvoid undercutInput/output processes for data processingContact holeElectrical and Electronics engineering
A flexible touch screen panel can include a flexible substrate including a plurality of trenches; first electrodes and second electrodes disposed in the plurality of trenches in the flexible substrate; an insulating film covering the first electrodes and the second electrodes; a contact hole in the insulating film to expose at least one of the first electrodes; and a bridge disposed on the insulating film, the bridge electrically connecting two of the first electrodes to each other through the contact hole.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor light-emitting element and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060011934A1Improve reliabilityAvoid overetchingSemiconductor devicesChemical treatmentEngineering
An improvement in electrode reliability is realized by preventing over-etching on a peripheral lower portion of an electrode while maintaining the flow of steps of roughening a surface after forming the electrode on a semiconductor substrate. After a P-side electrode 4 is formed on a main surface 3a of a semiconductor substrate 3, a surface of the P-side electrode 4 is selectively covered with a protective film 12, after the semiconductor substrate 3 is cut into chips, the surface is roughened from above the protective film 12, the main surface 3a around the P-side electrode 4 and a side surface are roughened with a non-chemical treatment region 10 which is a non-roughened surface region being left in a peripheral portion of the P-side electrode 4 covered with the protective film 12, and thereafter the protective film 12 is removed.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Thin film transistor substrate and method of manufacturing the same
A method of fabricating a liquid crystal display device includes forming a gate electrode; forming a gate insulator on the gate electrode, an active layer on the gate insulator, and an etch stopper on the active layer; depositing an ohmic contact layer, a first metal layer and a second metal layer on the substrate; etching the ohmic contact layer, and the first and second metal layers to form ohmic contact patterns, and first and second metal patterns including source, drain and pixel electrodes using a single photomask.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Producing method of suspension board with circuit
ActiveCN104703400AAvoid overetchingReduced connection reliabilityArm with actuatorsPrinted circuit secondary treatmentElectrolysisElectrical conductor
A method for producing a suspension board with circuit includes the steps of (7) removing a first electroless plating layer corresponding to a first terminal and / or a second electroless plating layer corresponding to a second terminal by etching, (8) removing a metal supporting board in contact with the lower surface of a first conductive layer filling the inside of a first opening portion, and (9) providing an electrolytic plating layer on the surface of the first terminal with the first electroless plating layer removed and / or the surface of the second terminal with the second electroless plating layer removed and the lower surface of the first conductive layer exposed from the inside of the first opening portion by electrolytic plating supplying electricity from the metal supporting board.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Thin film transistor liquid crystal display and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20050037528A1Reduce in quantityReduce stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayThin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display
A thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) and fabrication method thereof. The fabrication method includes depositing a first metal layer on a transparent substrate, patterning the first metal layer to form at least two adjacent gate electrodes, forming a gate insulating layer on the gate electrodes, forming a semiconductor layer on the insulating layer, patterning the semiconductor layer into a predetermined shape, depositing a second metal layer on the transparent substrate, patterning the second metal layer to form a source / drain electrode layer, and depositing an insulating layer on the transparent substrate. A contact hole is defined via the insulating layer, source / drain electrode layer, and gate insulating layer, exposing a part of the surface of transparent substrate between the adjacent gate electrodes. A transparent conductive layer is deposited on the transparent substrate, and a light-shielding matrix is formed directly above the contact hole.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Organic light emitting diode display
ActiveUS8278665B2Avoid damageAvoid overetchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorOhmic contact
An organic light emitting diode display includes a thin film transistor on a substrate (1). The thin film transistor includes a gate electrode (2), a gate insulating film (3) that covers the gate electrode (2), a first semiconductor film (4) provided on the gate insulating film (3), a second semiconductor film (5) provided on the first semiconductor film (4), a back channel protection insulating film (7) and an ohmic contact film (8) provided on the second semiconductor film (5), and source / drain electrodes (9). A crystallinity of the first semiconductor film (4) is higher than that of the second semiconductor film (5). The back channel protection insulating film (7) is formed as one of an organic insulating film and an organic / inorganic hybrid insulating film. The thin film transistor has excellent off-state characteristics, swing characteristics, and saturation characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Methods for making internal die filters with multiple passageways which are fluidically in parallel
InactiveUS20050133480A1Avoid overetchingAvoid underetchingPaper/cardboard articlesPrintingElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
An internal filter includes a lower substrate and an upper substrate. Fluid passages are formed by etching grooves into the surface(s) of the upper and / or lower substrates, and / or in one or more intermediate layers. The filter pores extending between the fluid passages are formed by etching second grooves that fluidly connect the fluid passages. Two or more sets of the one or two intermediate layers can be implemented to provide additional filter passages and / or pores. Each set can be connected to a separate fluid source and / or a separate microfluidic device. In another internal filter, the inlet and outlet passages and the filter pores are formed on the same upper or lower substrate. The inlet and outlet passages are partially formed in a first step. In a second step, the inlet and outlet passages are completed at the same time that the filter pores are formed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com