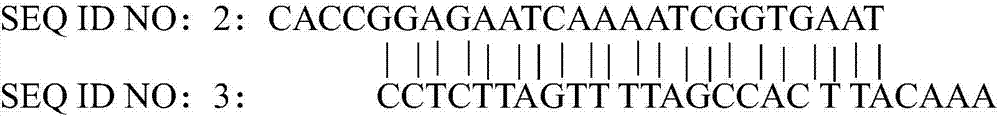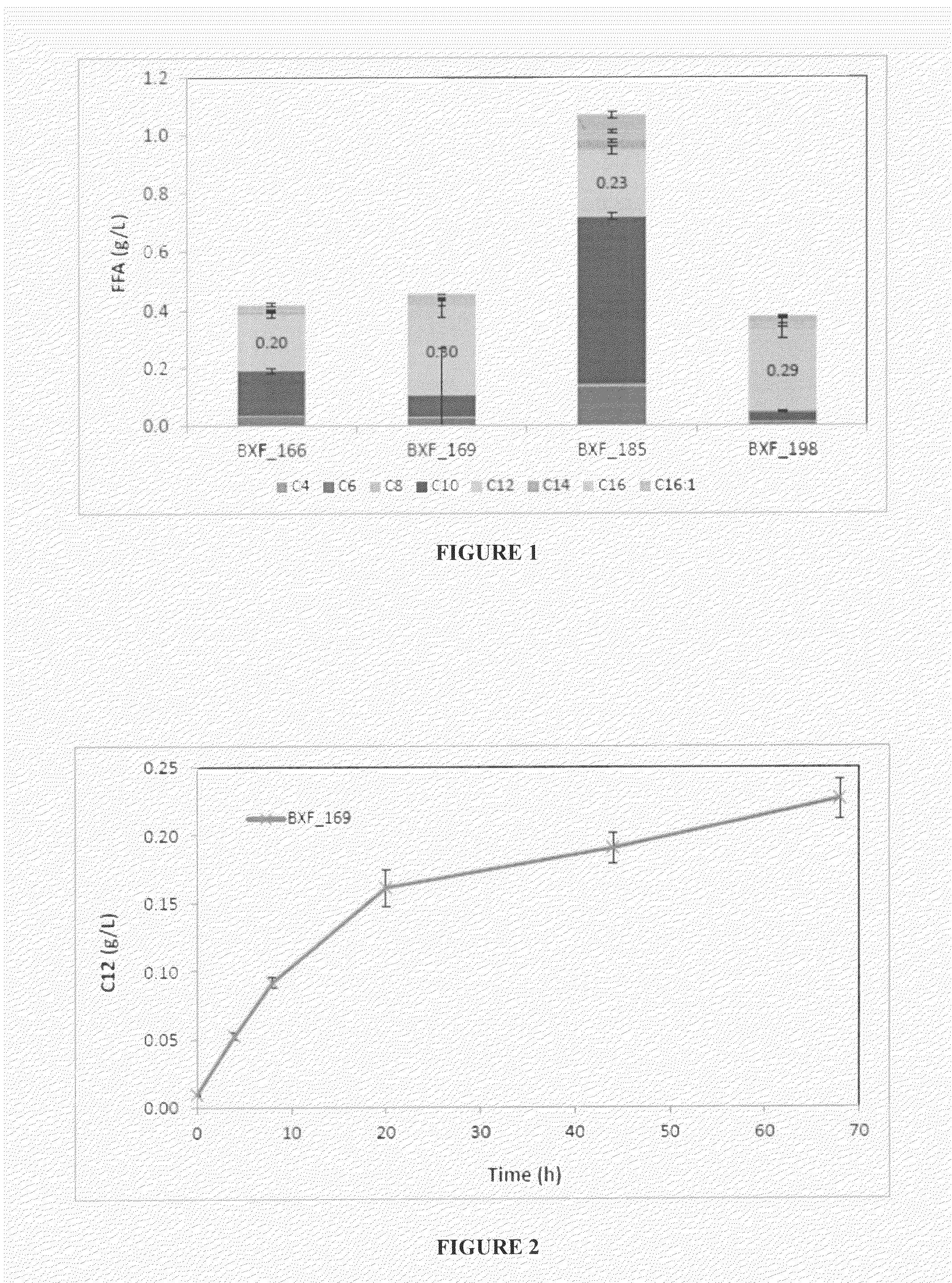Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Wild type cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wild type barm cells contain VRP1 cistron that encodes Verprolin protein. VRP1 protein is the barm ( S. cerevisiae ) ortholog of human Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein ( WASP ) -interacting protein ( WIP ) .
Methods for drug target screening
InactiveUS6165709AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyProtein targetProtein activity
The present invention provides methods for identifying targets of a drug in a cell by comparing (i) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell, (ii) the effects on a wild-type cell of modifications to a putative target of the drug, and (iii) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell which has had the putative target modified of the drug. In various embodiments, the effects on the cell can be determined by measuring gene expression, protein abundances, protein activities, or a combination of such measurements. In various embodiments, modifications to a putative target in the cell can be made by modifications to the genes encoding the target, modification to abundances of RNAs encoding the target, modifications to abundances of target proteins, or modifications to activities of the target proteins. The present invention also provides methods for drug development based on the methods for identifying drug targets.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
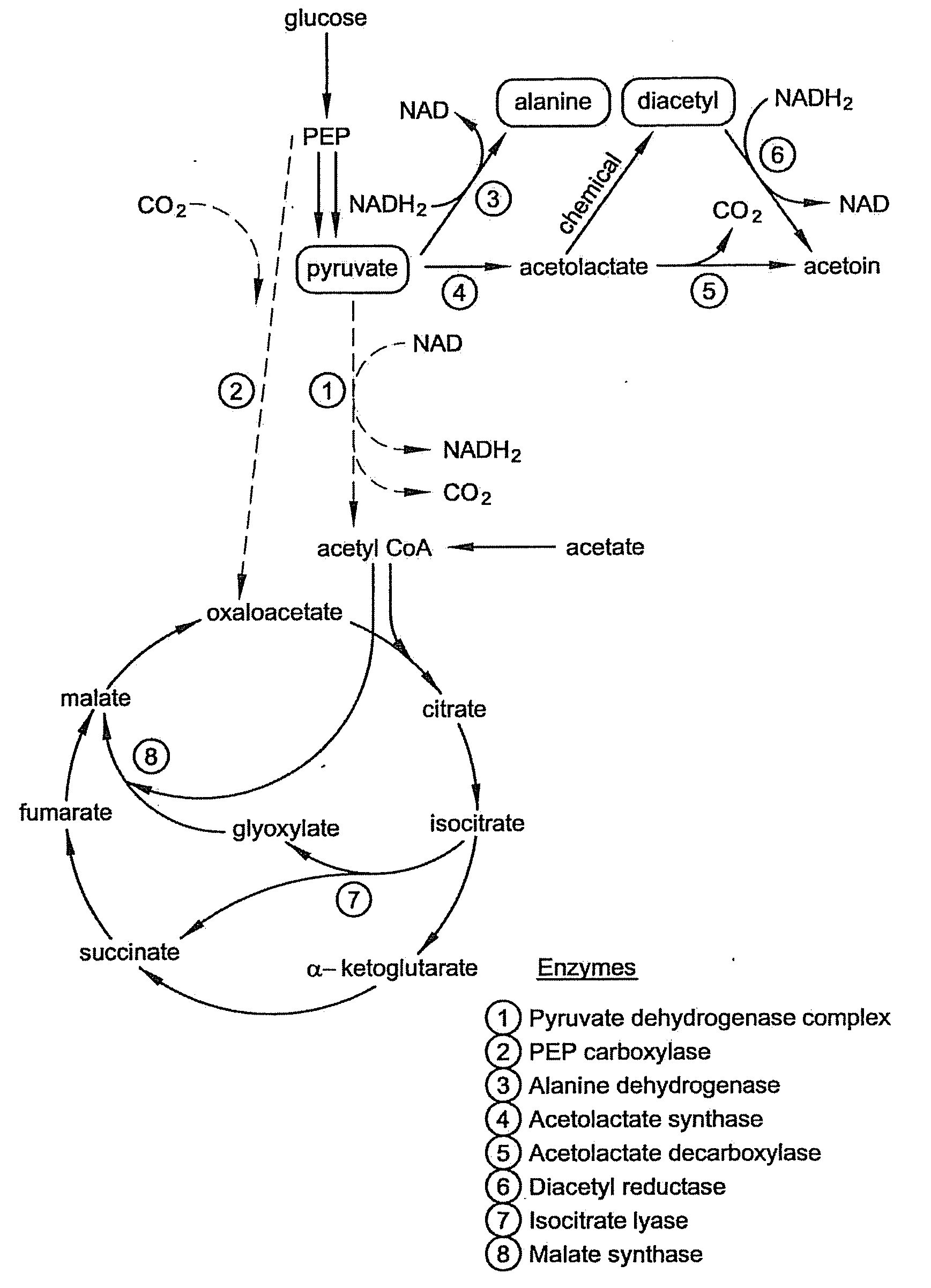
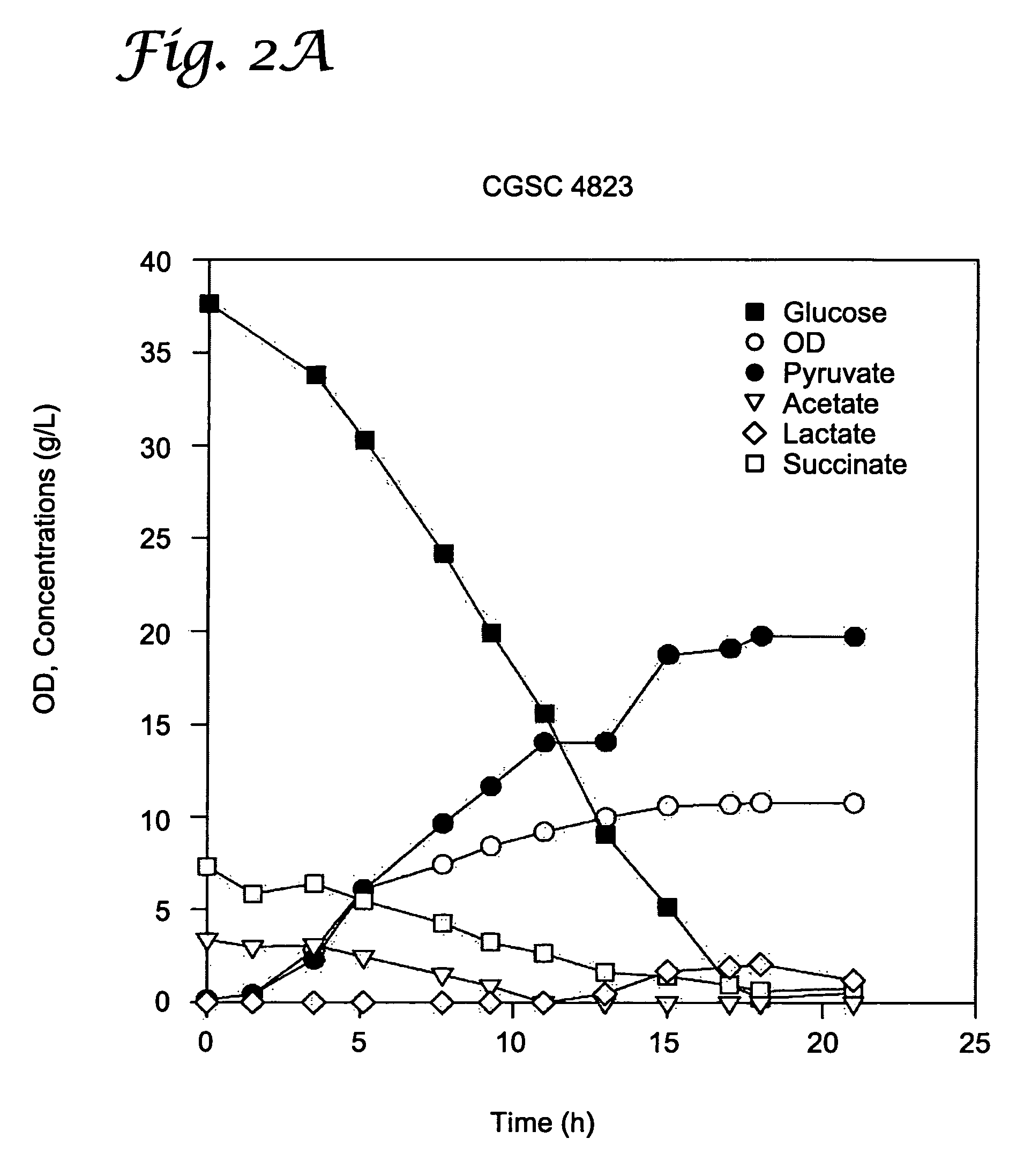
Microbial production of pyruvate and pyruvate derivatives
InactiveUS7749740B2Increase productionAdded and increased dehydrogenase activityBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismMetabolite
Microbial production of pyruvate and metabolites derived from pyruvate in cells exhibiting reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity compared to wild-type cells. Acetate and glucose are supplied as a carbon sources.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
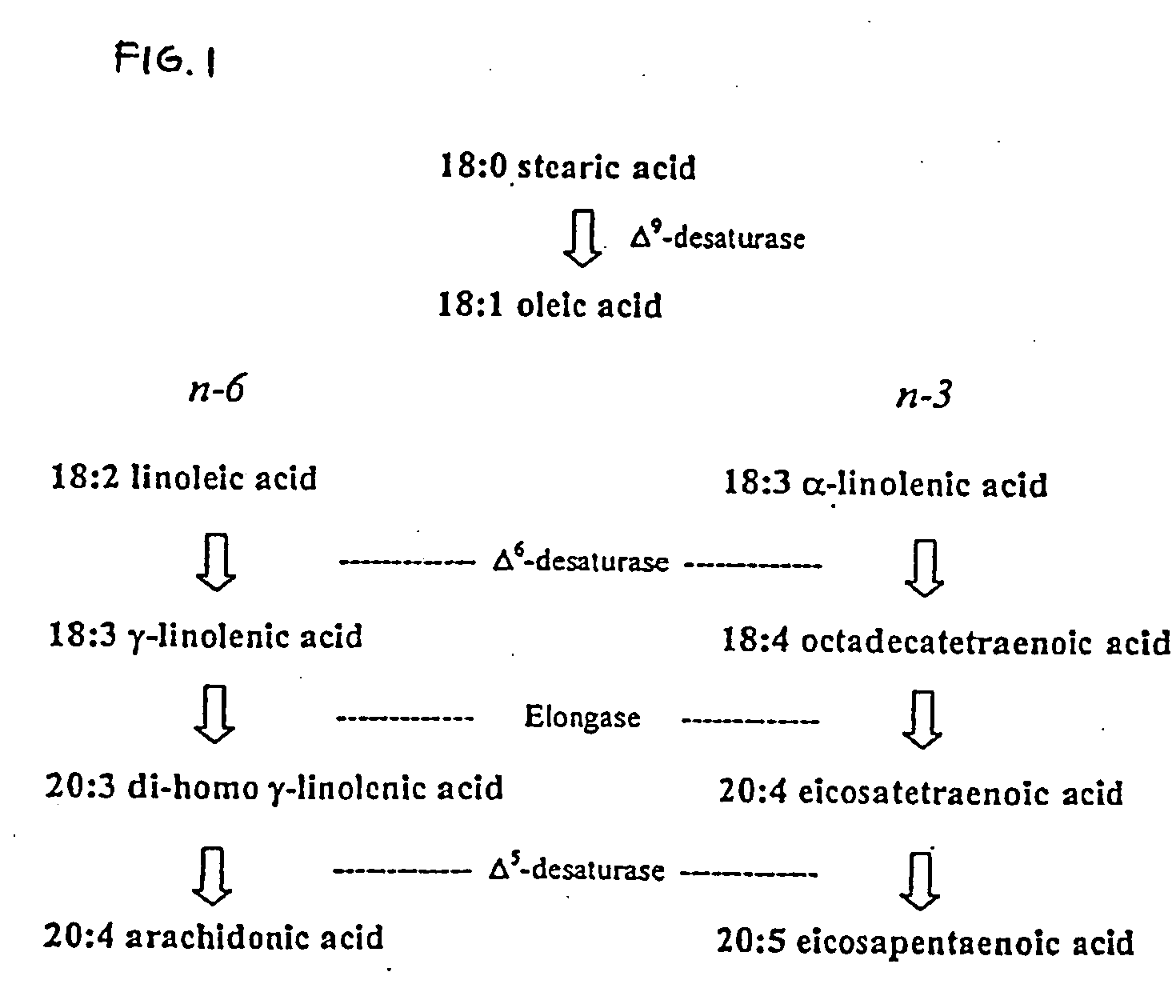
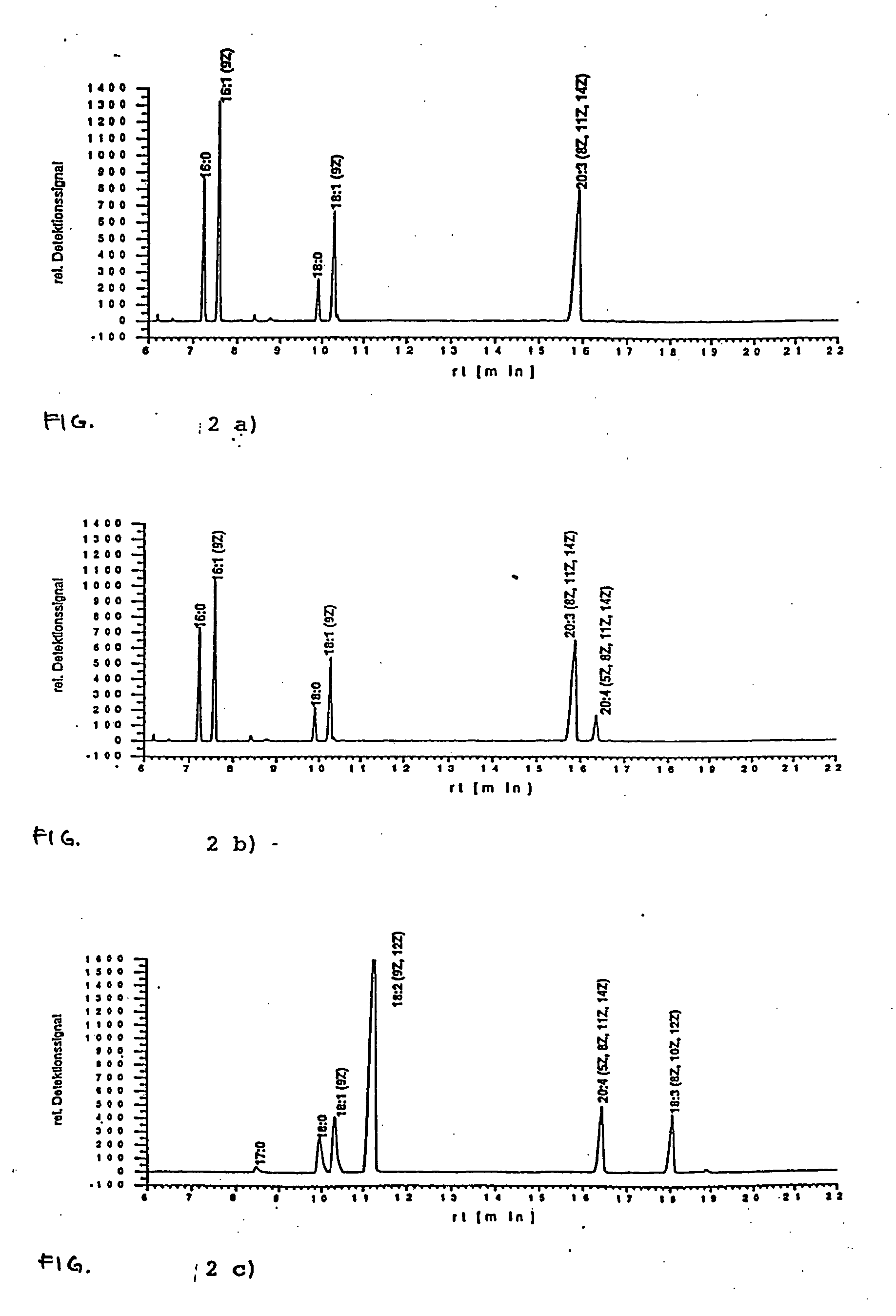
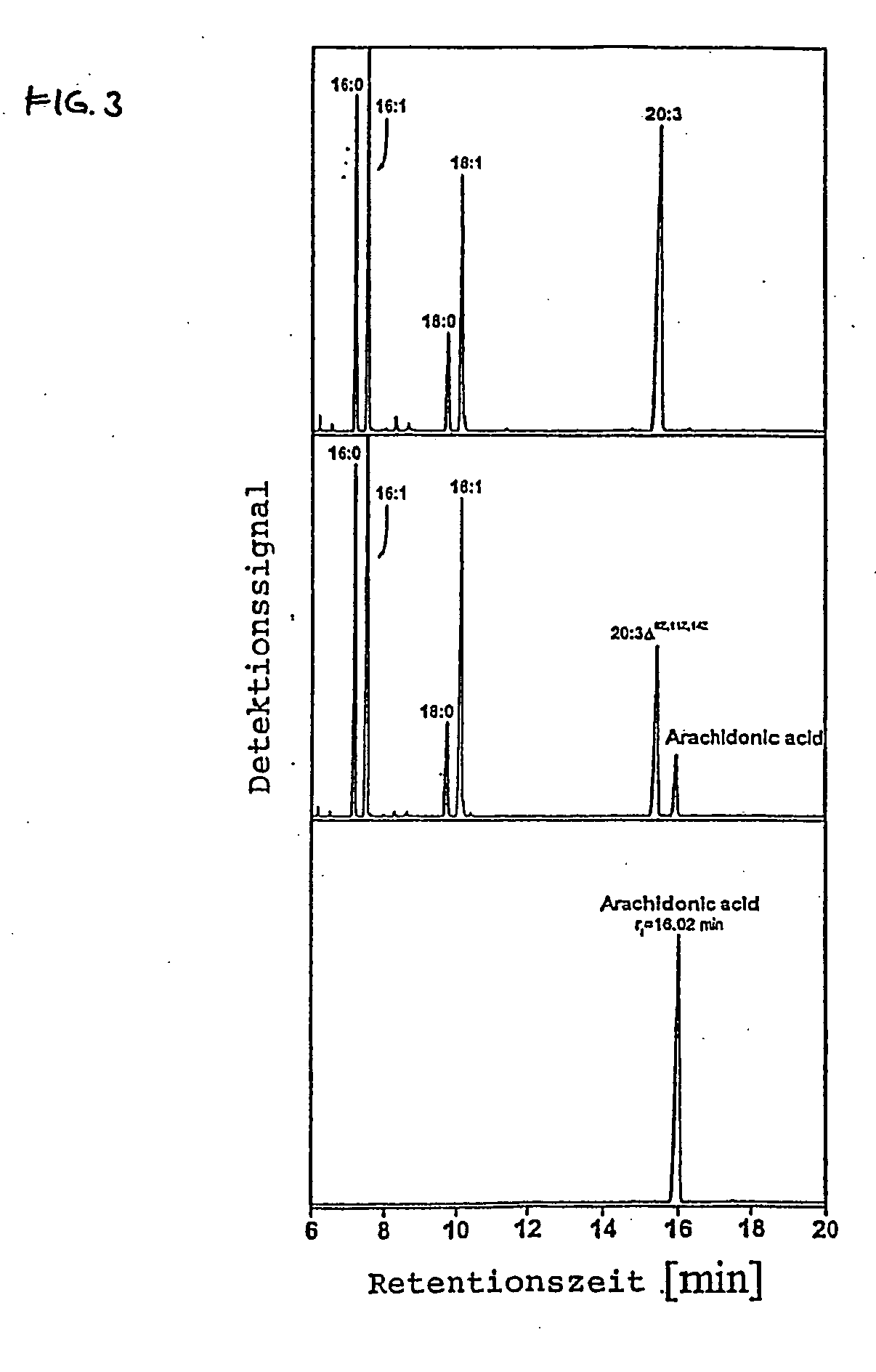
Method for producing arachidonic acid in transgenic organisms
InactiveUS20050089879A1Increase contentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant cellA-DNA
The invention relates to a method for the production of arachidonic acid in transgenic organisms, especially in transgenic plants and yeasts. The invention also relates to DNA sequences coding for a protein with enzymatic activity of a Δ5-desaturase from Phytophthera megasperma. The invention further relates to transgenic plants and plant cell and transgenic yeasts containing a nucleic acid molecule comprising a DNA sequence according to the present invention and having, on the basis thereof, an enhanced arachidonic acid synthesis in comparison with wild-type cells. The invention also relates to harvest products and propagating material of transgenic plants.
Owner:INST FUR PFLANZENGENETIK & KULTURPFLANZENFORSCHUNG
Cytochrome P450 oxygenases
ActiveUS7226768B2High activityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesCytochrome p450 enzymeAmino acid
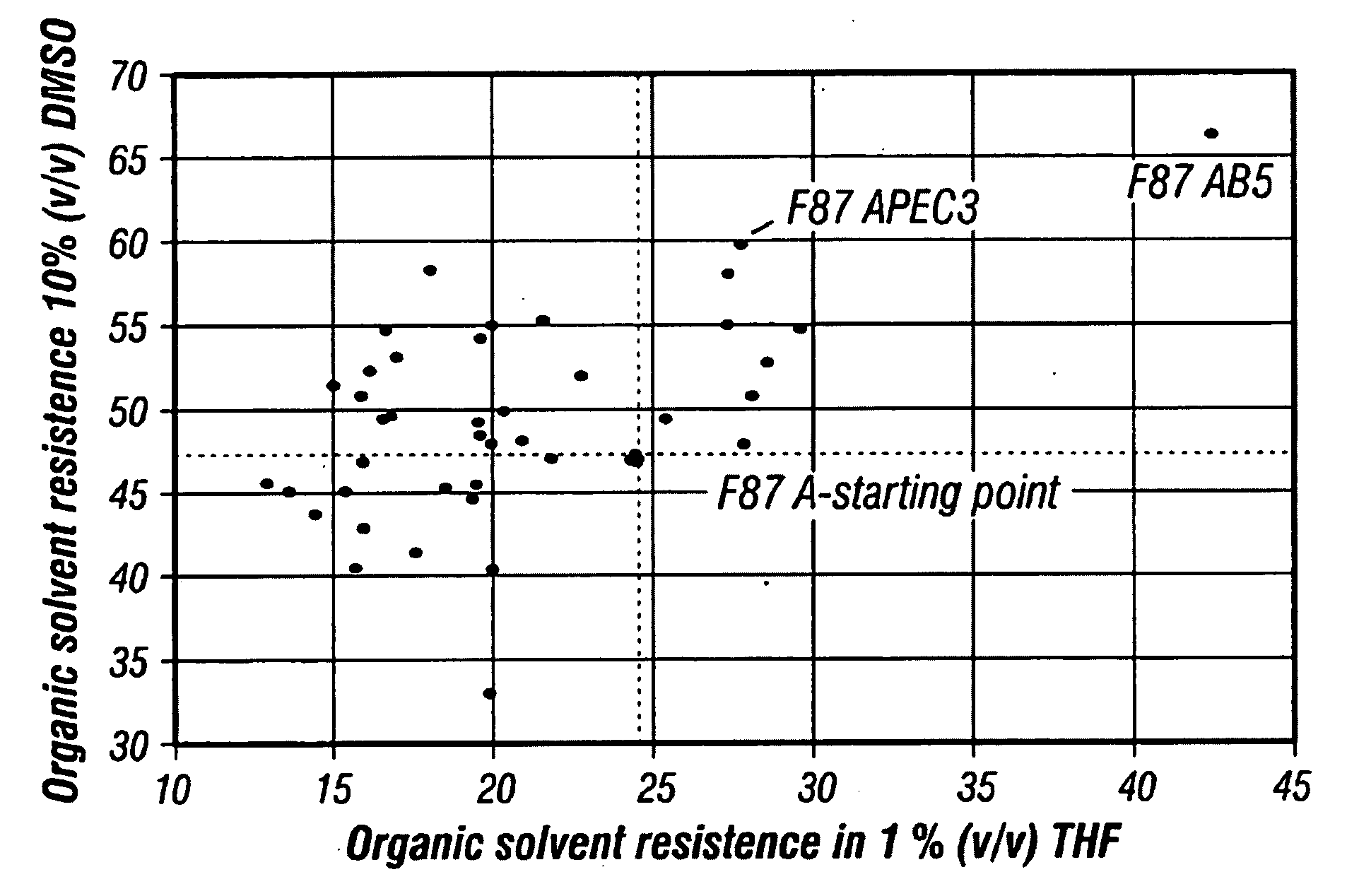
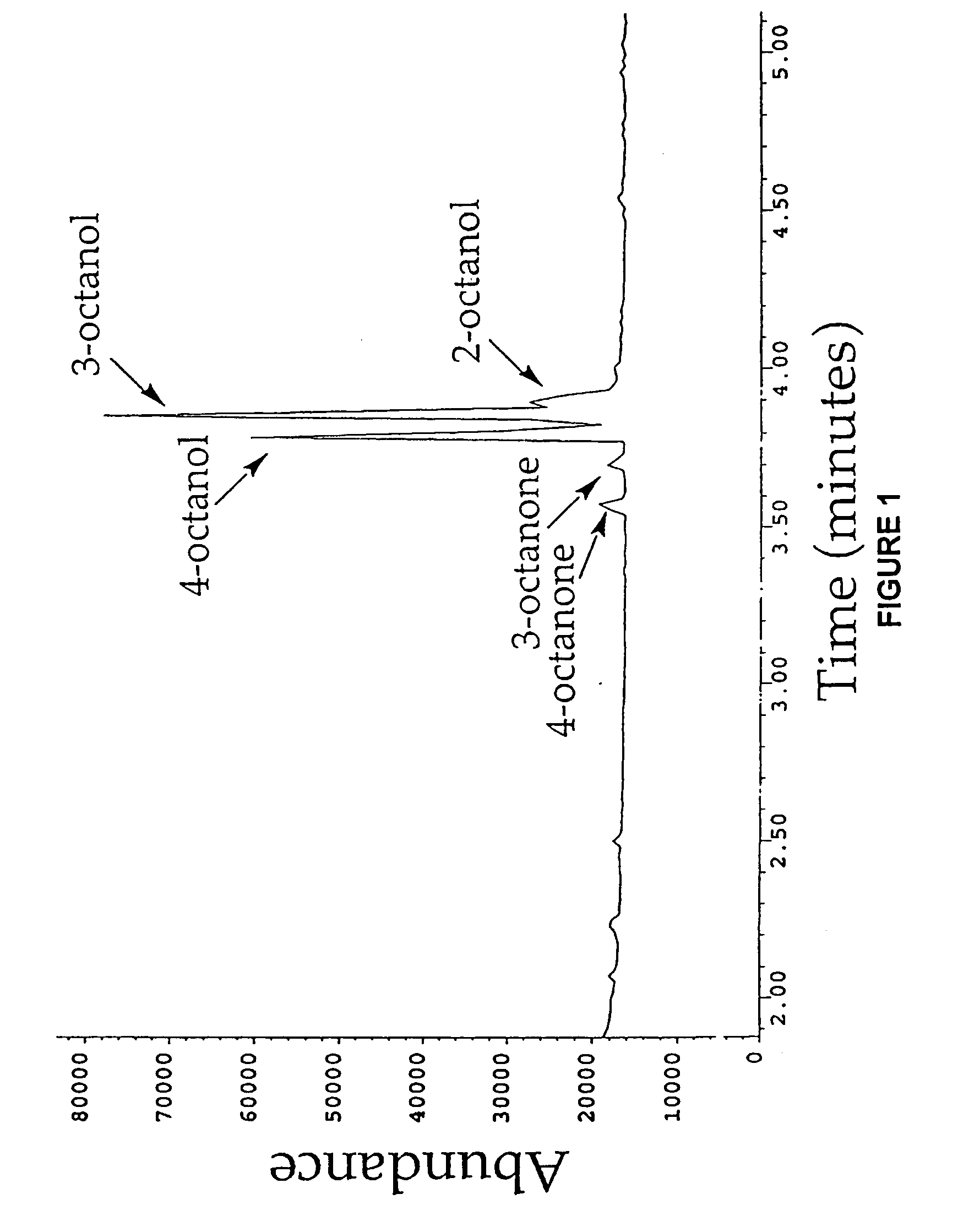
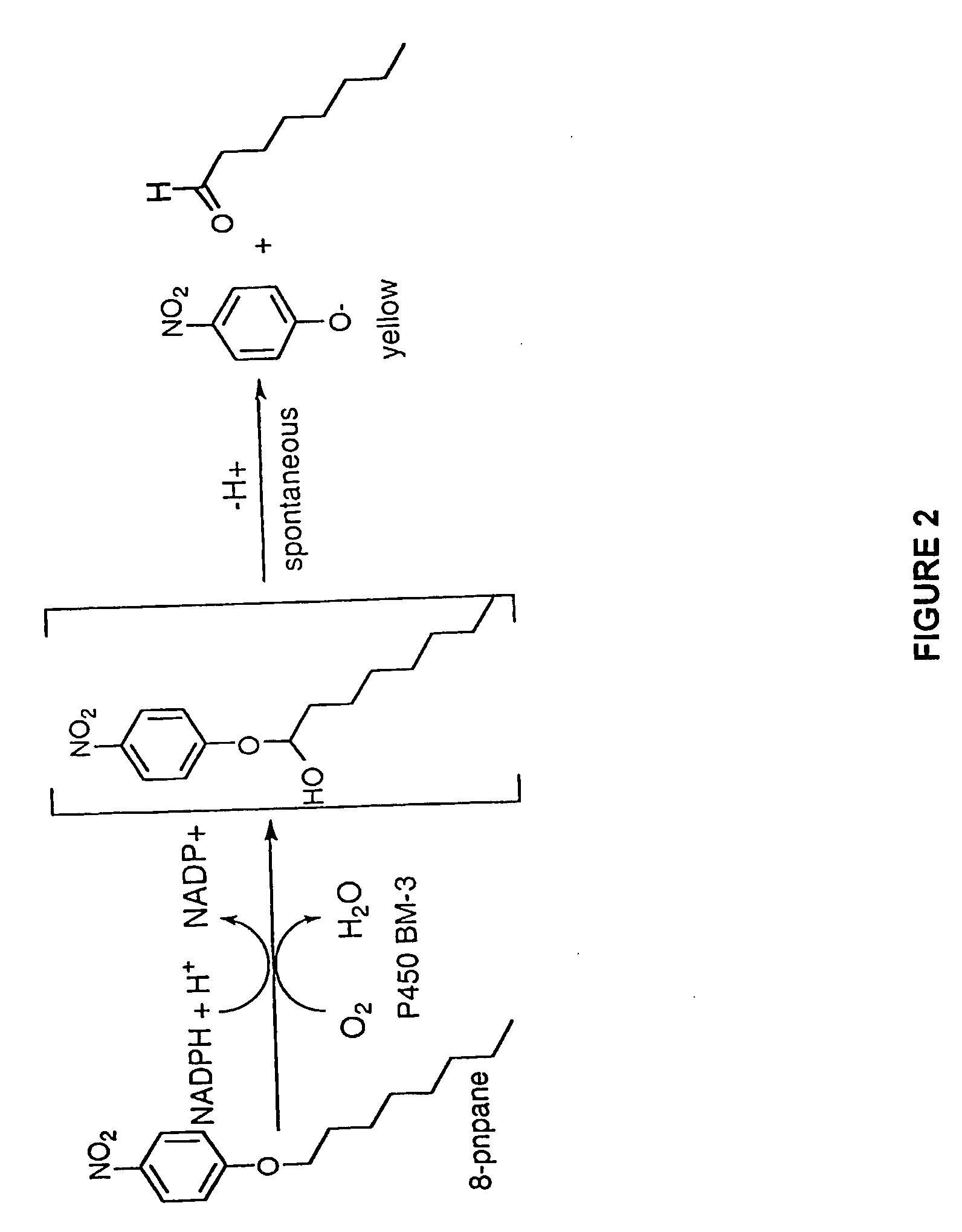
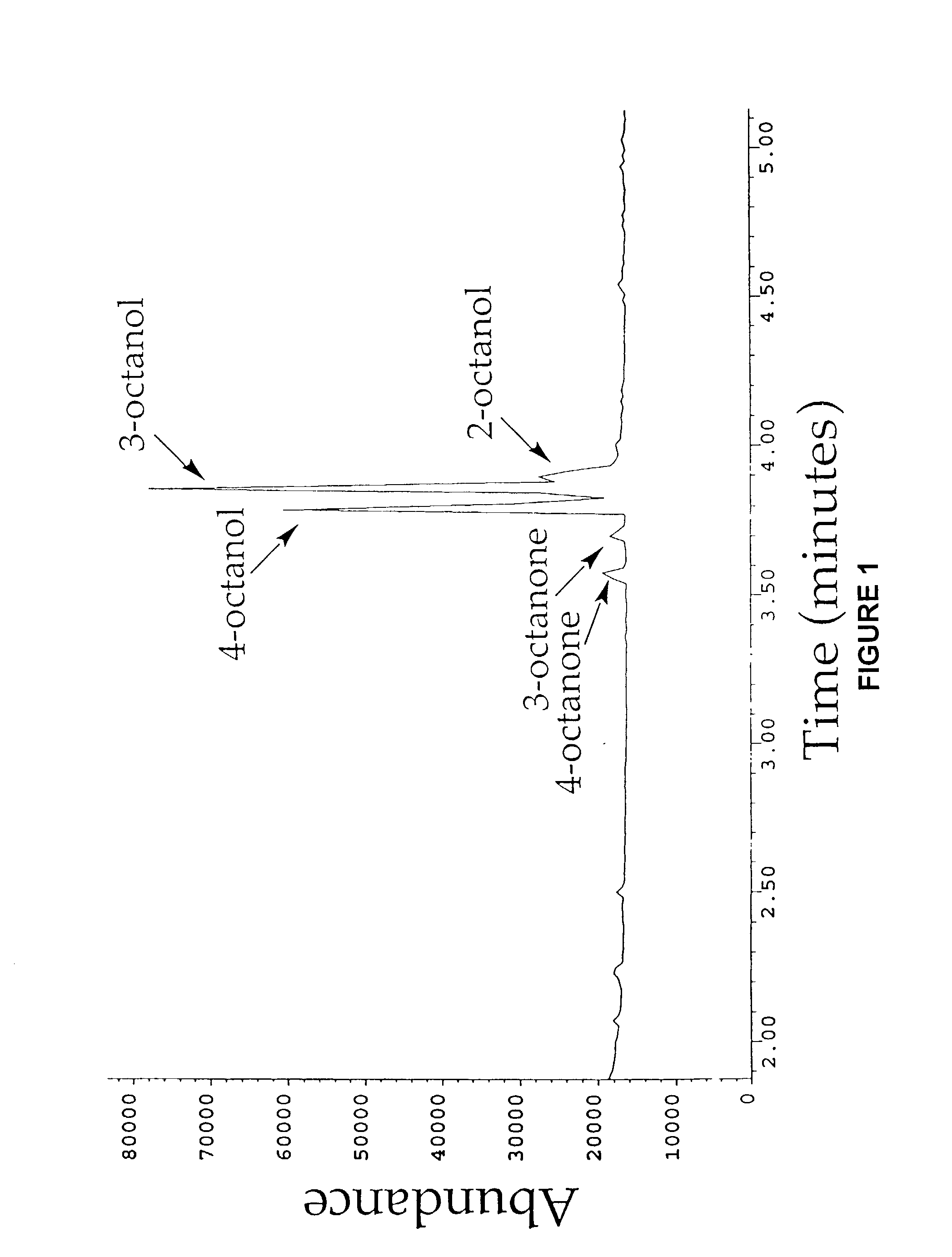
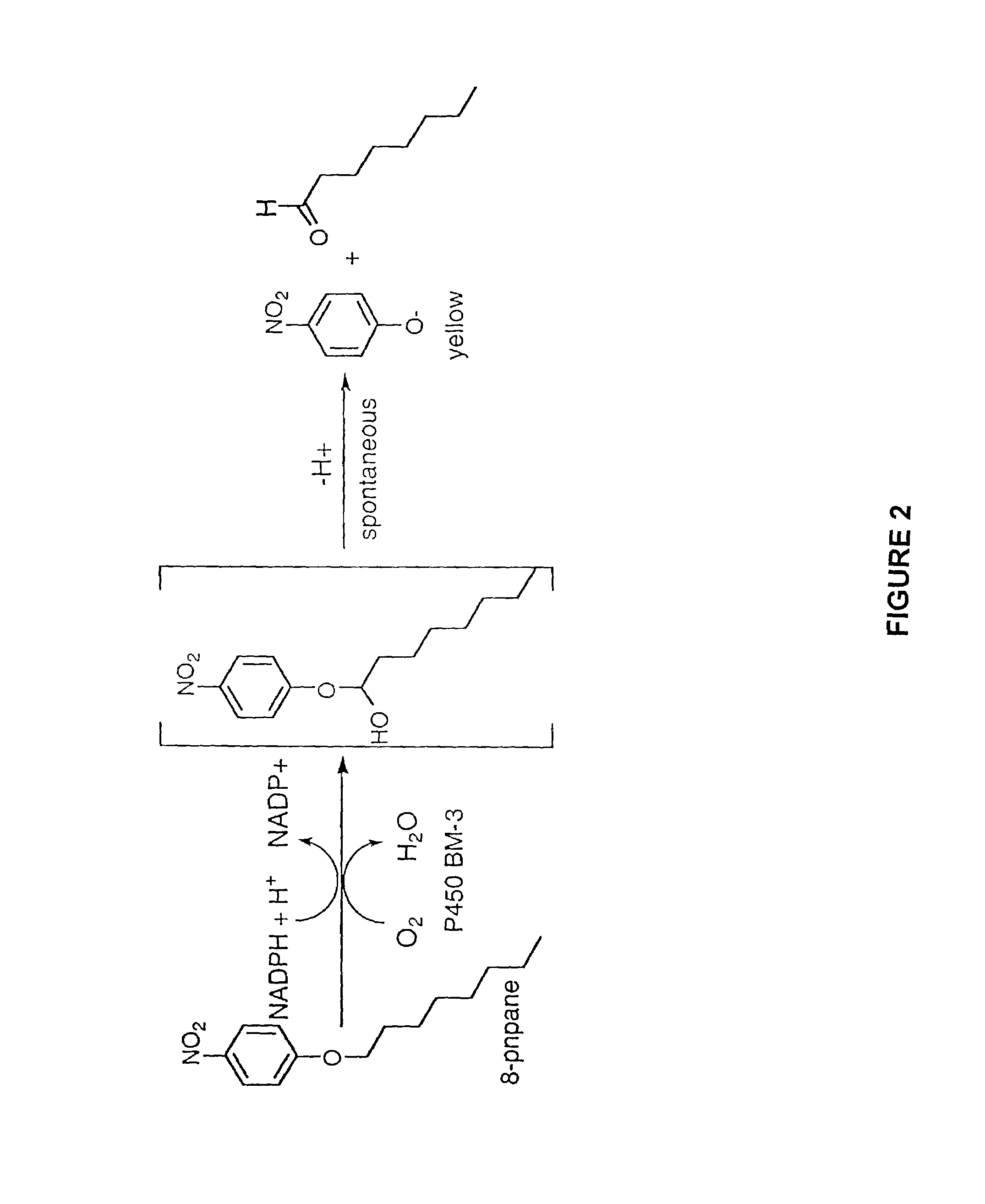
Nucleic acids encoding cytochrome P450 variants are provided. The cytochrome P450 variants of have a higher alkane-oxidation capability, alkene-oxidation capability, and / or a higher organic-solvent resistance than the corresponding wild-type or parent cytochrome P450 enzyme. A preferred wild-type cytochrome P450 is cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants include those having an improved capability to hydroxylate alkanes and epoxidate alkenes comprising less than 8 carbons, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to V78A, H236Q, and E252G of cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants also include those having an improved hydroxylation activity in solutions comprising co-solvents such as DMSO and THF, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to T235A, R471A, E494K, and S1024E of cytochrome P450 BM-3.
Owner:NORO MOSELEY PARTNERS V +2
gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method
ActiveCN107354156AHigh knockout efficiencySimple manufacturing methodImmunoglobulin superfamilyStable introduction of DNAT cellCellular immunity
The invention discloses gRNA for knockout of a wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and a method. The sequence of the gRNA is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the gRNA and CRISPR / Cas9 jointly infect a T cell, the wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand is knocked out, and the T cell lacking the wild type TCR [beta] strand is constructed and used for CAR-T or TCR-T cellular immunotherapy. According to the gRNA for knockout of the wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and the method, the knockout efficiency is high, the preparation method is relatively simple and easy, and T cells lacking wild type TCR [beta] strands can be provided for clinic rapidly and efficiently.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
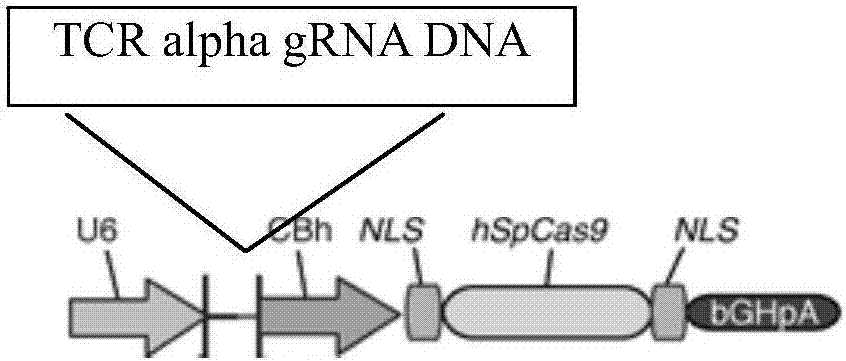
gRNA subjected to wild type T cell TCR alpha chain knockout and method
InactiveCN107236741AHigh gene knockout efficiencyEasy to prepareImmunoglobulin superfamilyStable introduction of DNAMolecular biologyT cell immunity
The invention discloses a gRNA subjected to wild type T cell TCR alpha chain knockout and a method. The sequence of the gRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. By using a CRISPR / Cas 9 technology, the gRNA and the CRISPR / Cas9 perform co-infection on T cells; the wild type T cell TCR alpha chain knockout is performed; the T cells lack of wild type T cell TCR alpha chains are built; the gRNA can be used for CAR-T or TCR-T cellular immunity treatment. The gRNA has high knockout rate; the preparation method is relatively simple and easy; the T cells lack of wild type T cell TCR alpha chains can be fast and efficiently provided for clinics.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Nonsymbiotic plant hemoglobins to maintain cell energy status
InactiveUS6936749B1Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesBacteriaSubstrate-level phosphorylationProgenitor
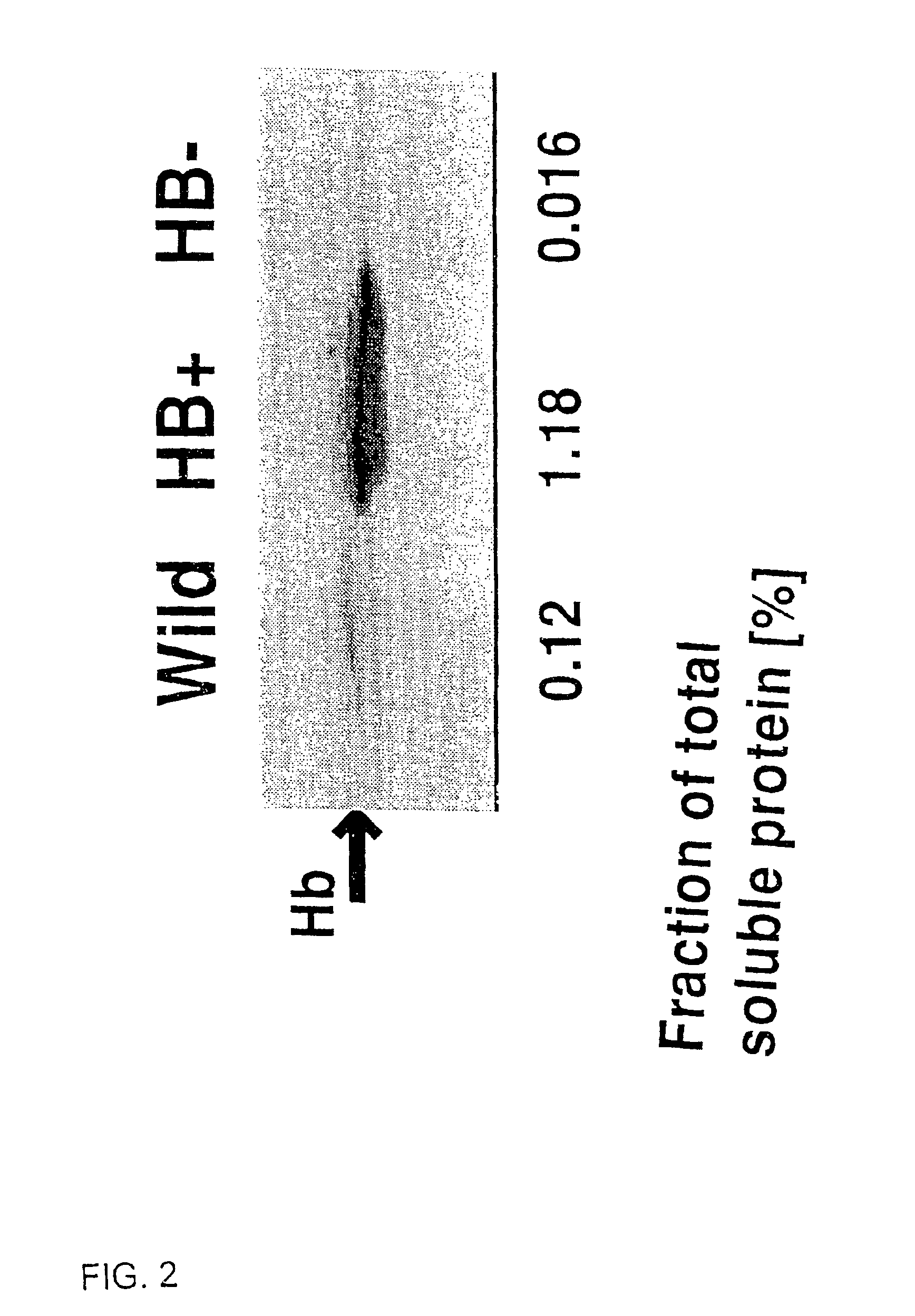
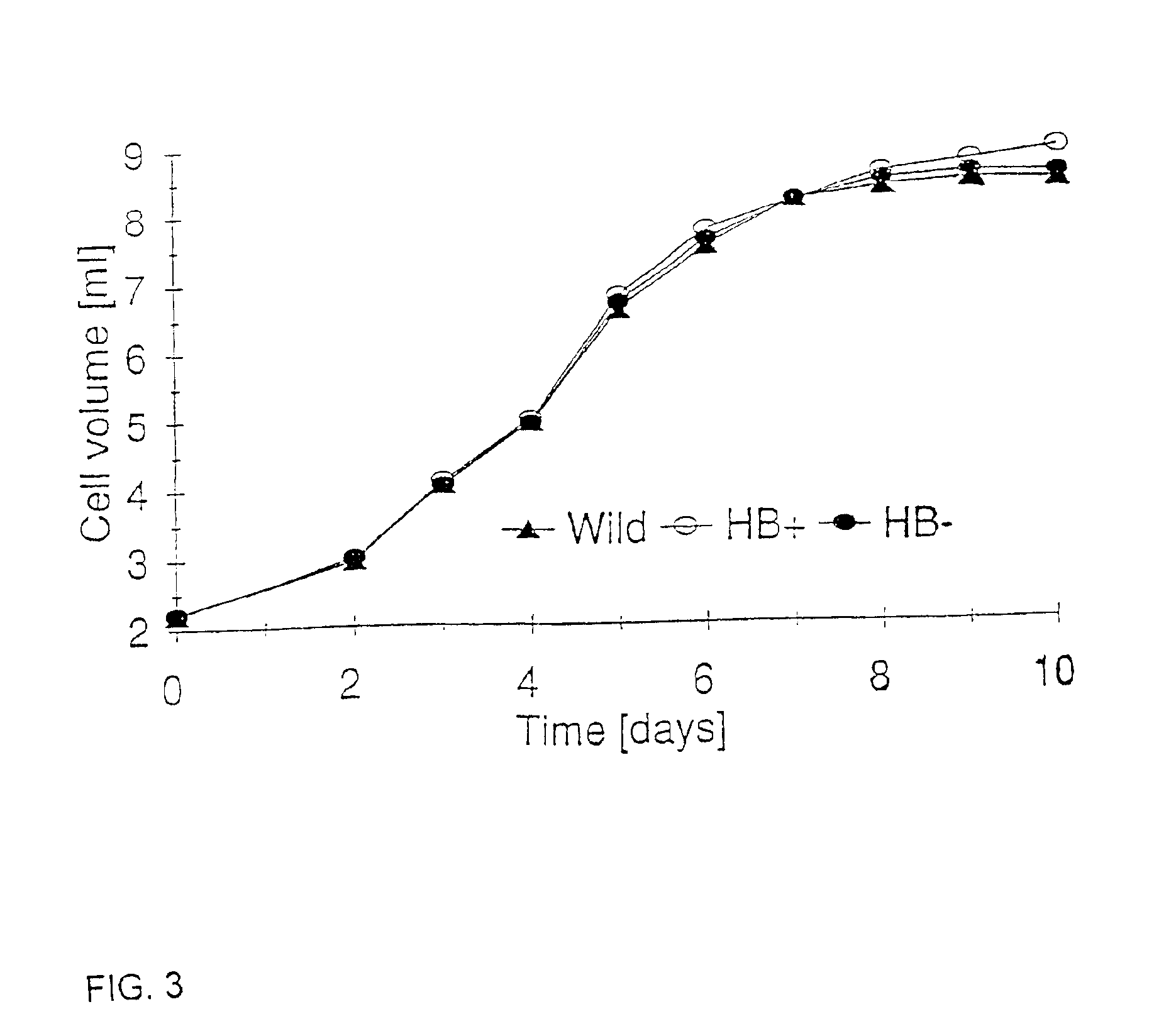
Nonsymbiotic hemoglobins are broadly present across evolution; however, the function of these proteins is unknown. Cultured maize cells have been transformed to constitutively express a barley hemoglobin gene in either the sense (HB+) or antisense (HB−) orientation. Hemoglobin protein in the transformed cell lines was correspondingly higher or lower than in wild type cells under normal atmospheric conditions. Limiting oxygen availability, by placing the cells in a nitrogen atmosphere for 12 hours, had little effect on the energy status of cells constitutively expressing hemoglobin, but had a pronounced effect on both wild type and HB− cells, where ATP levels declined by 27% and 61% respectively. Energy charge was relatively unaffected by the treatment in HB+ and wild type cells, but was reduced from 0.91 to 0.73 in HB− cells suggesting that the latter were incapable of maintaining their energy status under the low oxygen regime. Similar results were observed with P. aeruginosa cells transformed with an Hb expression vector. It is suggested that nonsymbiotic hemoglobins act to maintain the energy status of cells in low oxygen environments and that they accomplish this effect by promoting glycolytic flux through NADH oxidation, resulting in increased substrate level phosphorylation. Nonsymbiotic hemoglobins are likely ancestors of an early form of hemoglobin that sequestered oxygen in low oxygen environments, providing a source of oxygen to oxidize NADH to provide ATP for cell growth and development. This in turn suggests that cells containing increased levels of Hb protein will survive longer under low oxygen tension or high energy demand.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Process for reacting a carboxylic acid ester
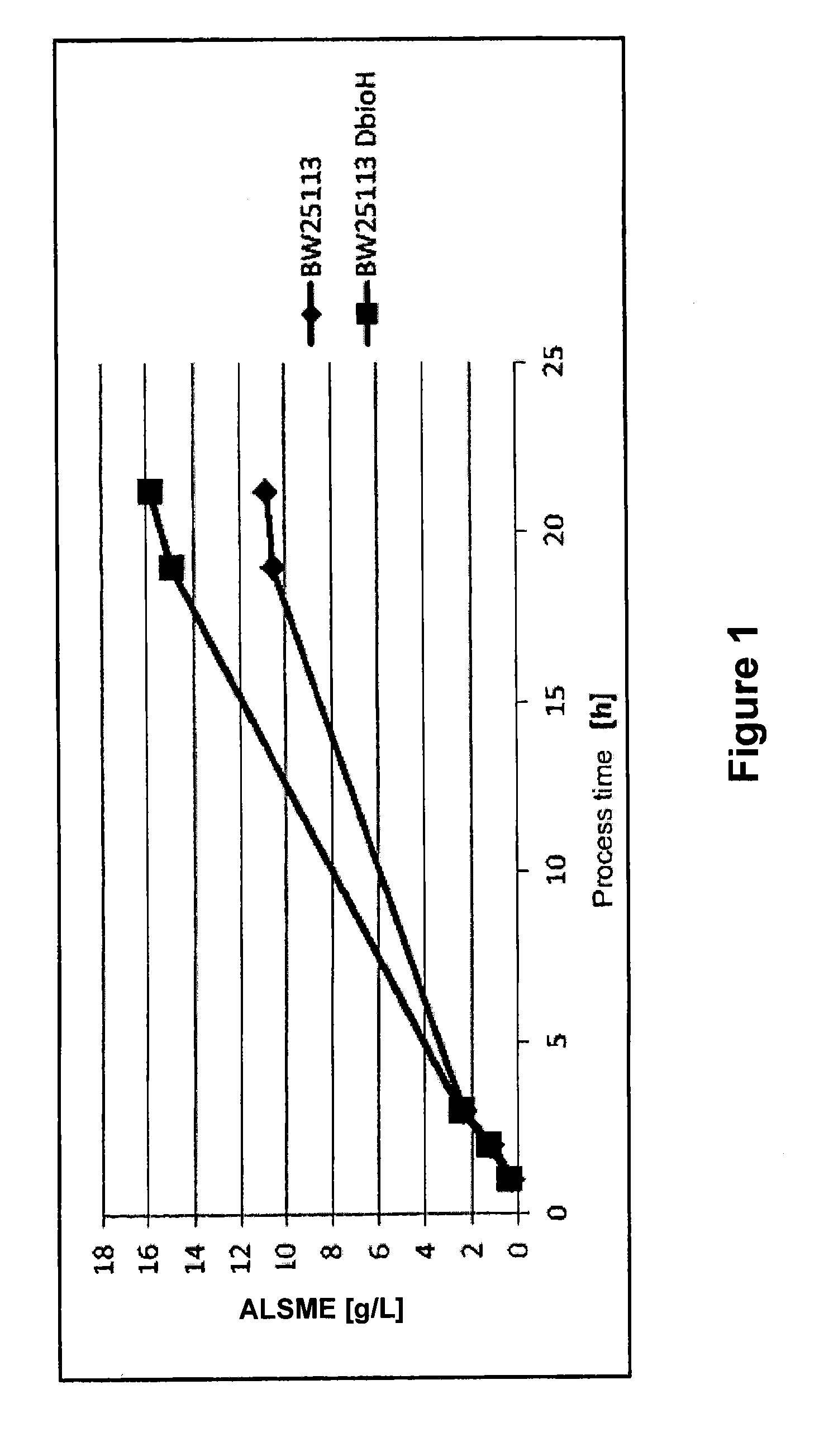
The invention provides a process for reacting a carboxylic acid ester of the formula (I)R1-A-COOR2 (I),wherein R1 is hydrogen, —CH2OH, —CHO, —COOR3, —CH2SH, —CH2OR3 or —CH2NH2, R2 is an alkyl group,R3 is hydrogen or an alkyl group, and A is a substituted, unsubstituted, linear, branched and / or cyclic alkylene, alkenylene, arylene or aralkylene radical having at least 4 carbons,in the presence of a cell. The process comprises a) contacting the cell with said carboxylic acid ester in an aqueous solution,wherein the cell is a recombinant cell which has reduced activity of a polypeptide comprising SEQ ID NO: 2 or a variant thereof over the wild-type cell.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Cell-based systems for producing influenza vaccines
ActiveUS20100021499A1Minimize and prevent virus infectionAvoid componentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsHemagglutininBinding site
The present invention relates to a cell-based method for producing influenza virus vaccines by enriching the population of surface-bound α2,6-sialic acid receptors on a cell surface, such as on a Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell surface. The host cell therefore presents numerous binding sites to which an influenza virus can bind via its hemagglutinin spike protein and infect the host cell. In contrast to wild-type CHO cells, the surface of the mutated CHO cells of the present invention contains an enriched population of α2,6-sialic acid receptors which makes the inventive CHO cells highly susceptible to viral infection, and therefore safe, effective, and highly efficient cells for rapidly producing influenza vaccines.
Owner:FLUGEN
Cytochrom P450 oxygenases
InactiveUS20080293928A1High activityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesCytochrome p450 enzymeAmino acid
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Algal mutants with increased lipid productivity
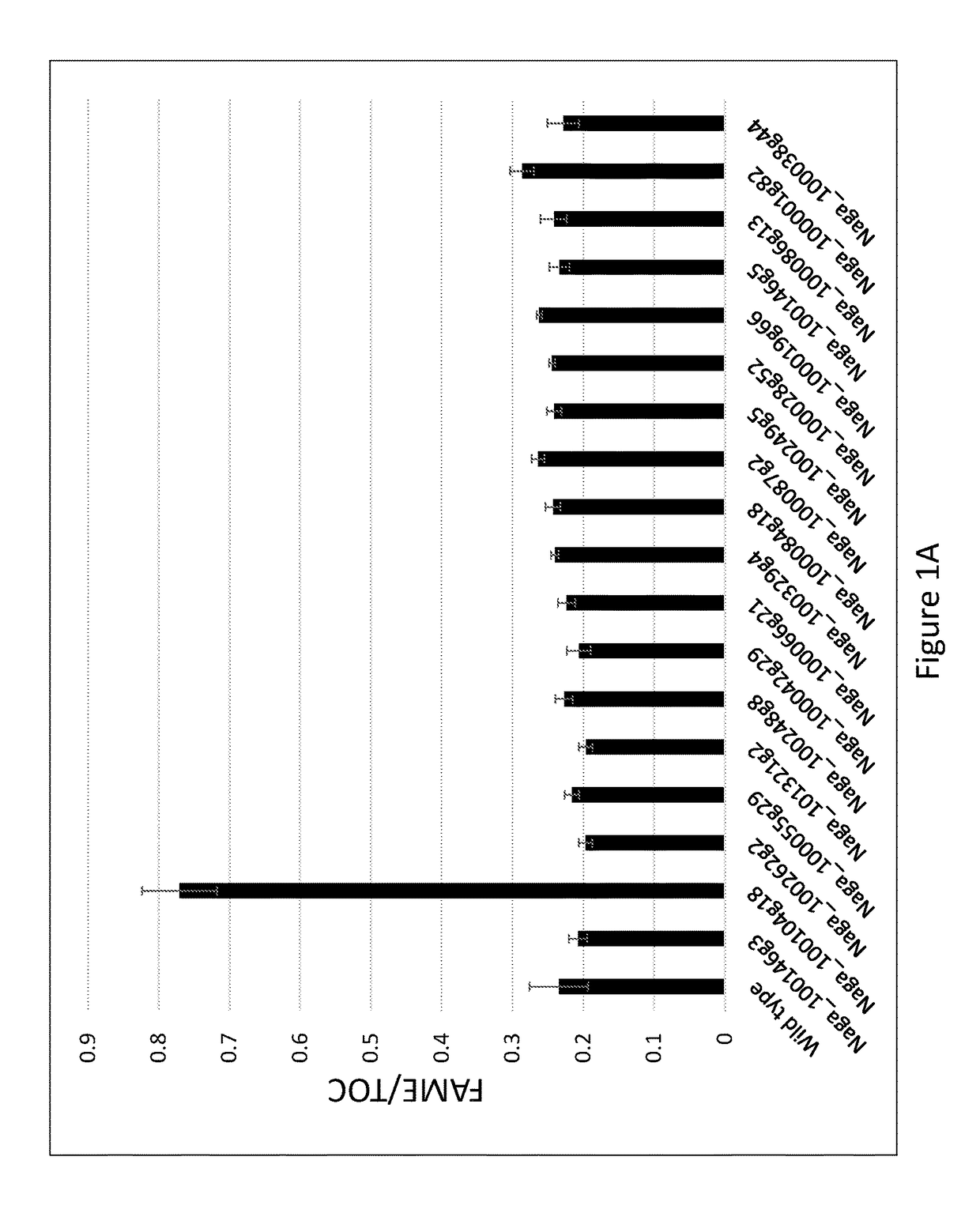
The present invention provides mutant microorganism that have higher lipid productivity than the wild type microorganisms from which they are derived while producing biomass at levels that are at least 45% of wild type biomass productivity under nitrogen replete conditions. Particular mutants produce at least 50% as much FAME lipid as wild type while producing at least the amount of biomass produced by wild type cells under nitrogen replete conditions. Also provided are methods of producing lipid using the mutant strains.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
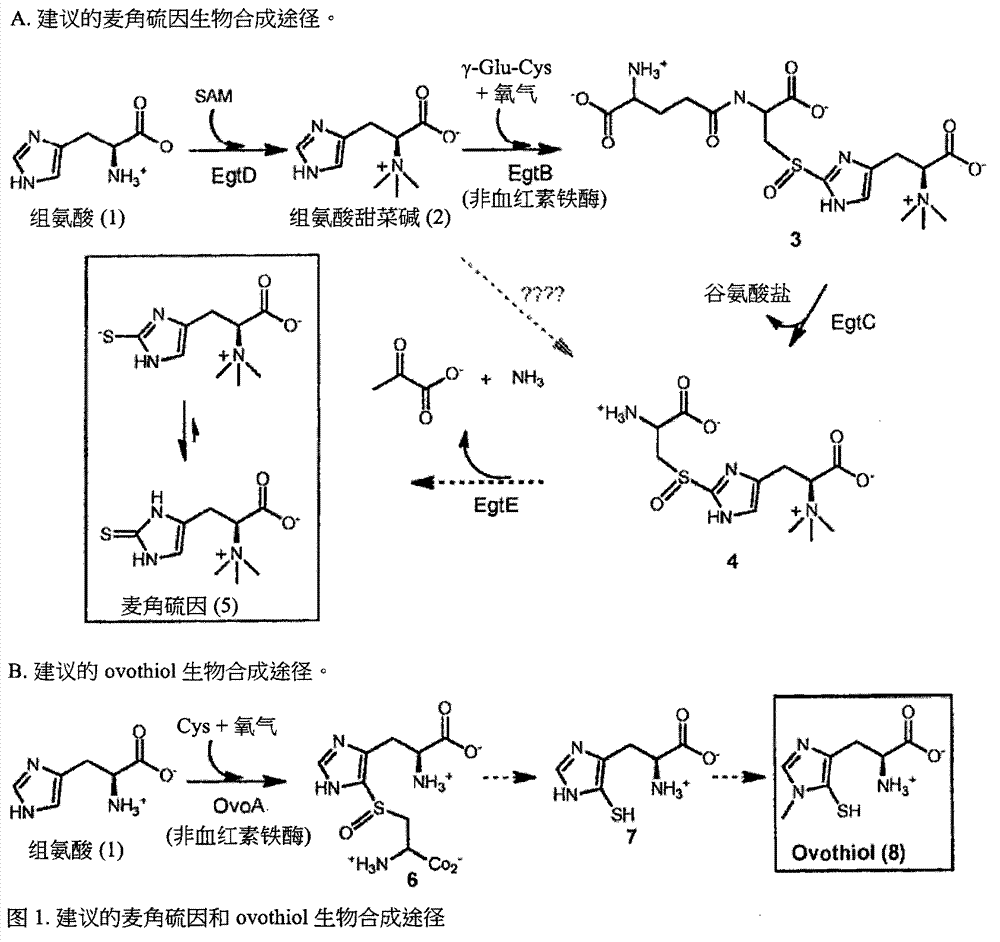
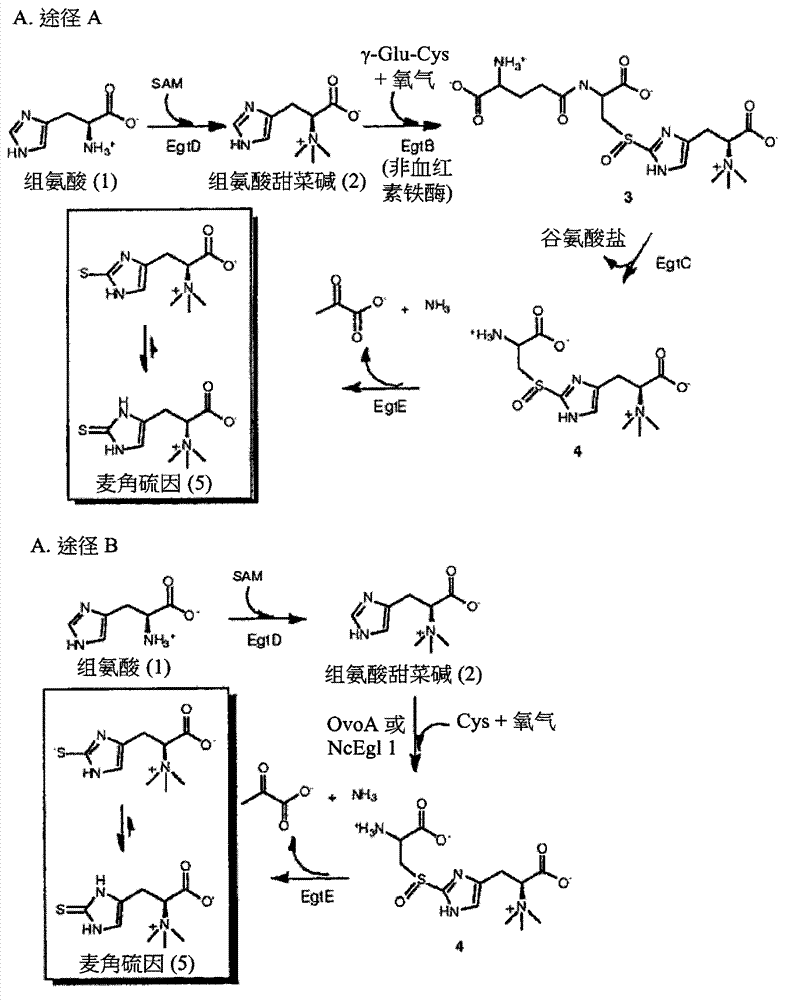
Ergothioneine production through metabolic engineering
The present disclosure relates to the production of ergothioneine through either in vitro enzymatic transformations or fermentations using microbials created by metabolic engineering. Also disclosed are transformed cells useful in such methods and ergothioneine produced by such methods. Transformed cells of the disclosure are capable of converting histidine and cysteine or hercynine and cysteine into ergothioneine in greater efficiency than the untransformed wild-type cells.
Owner:刘平华 +2
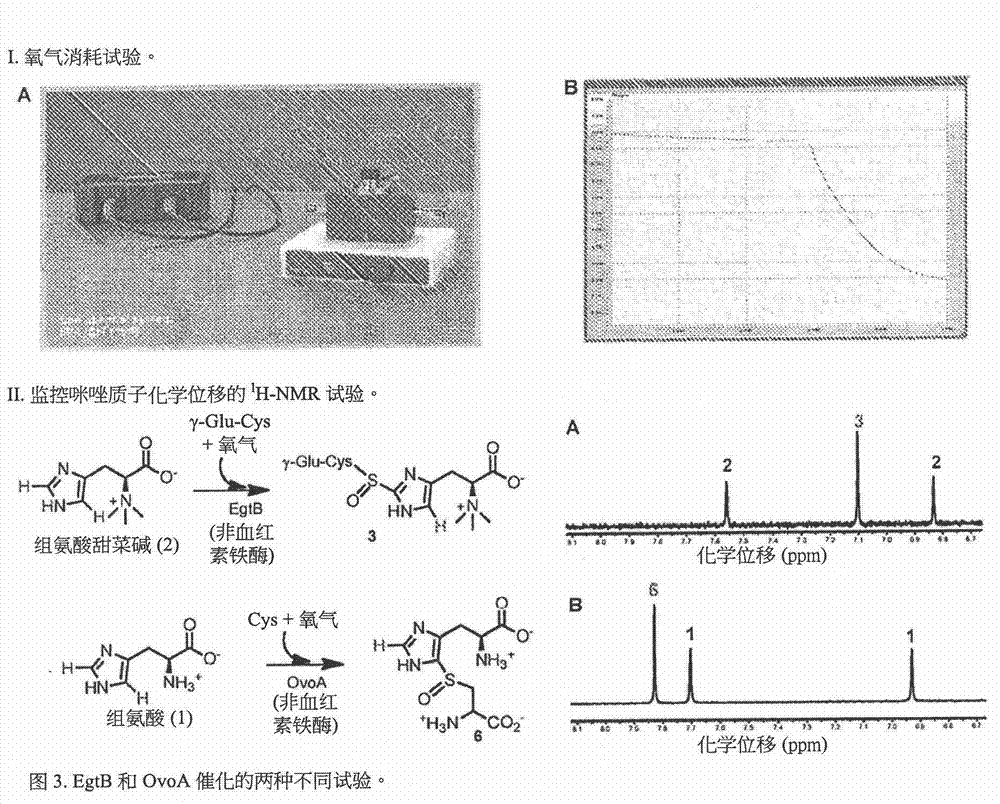
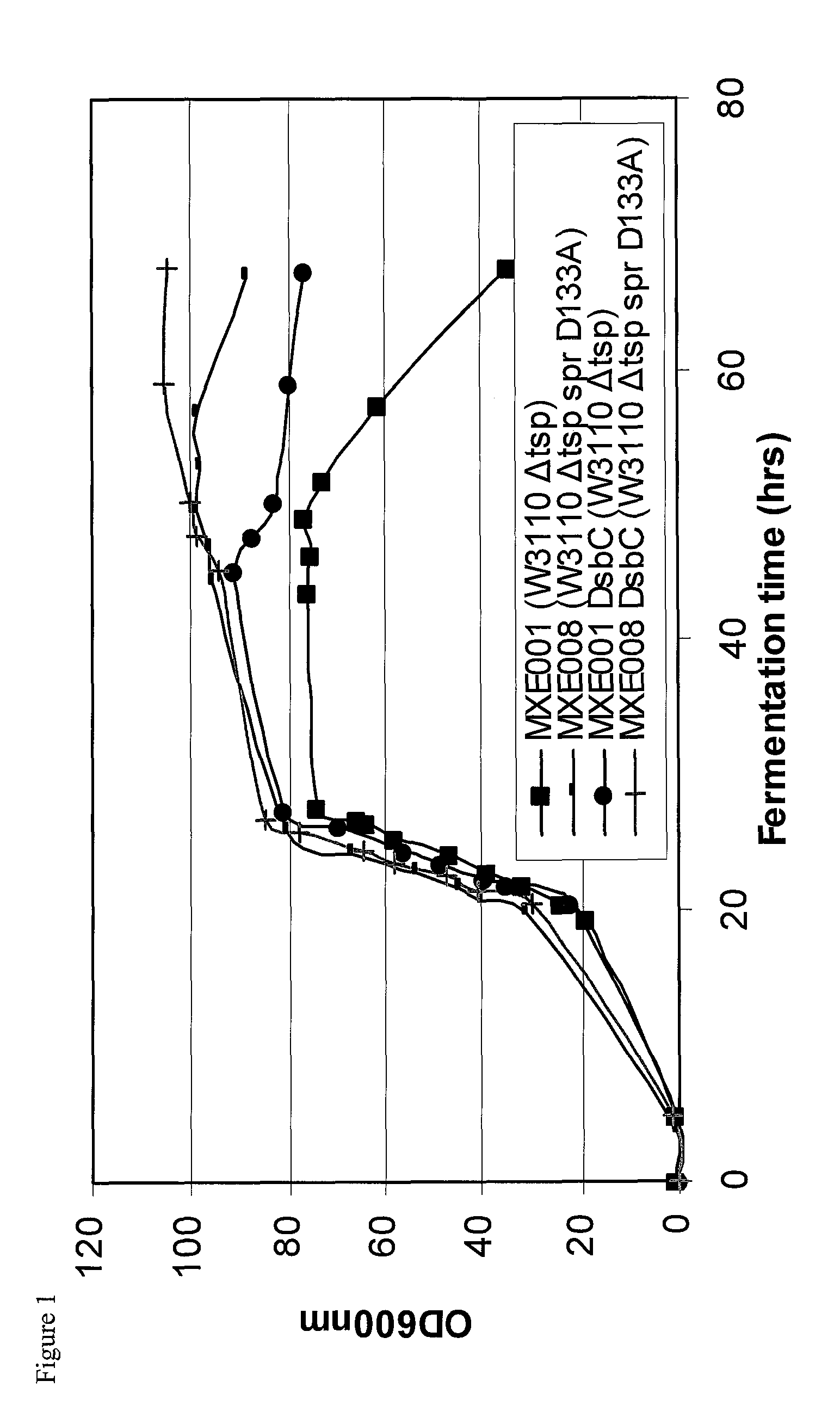
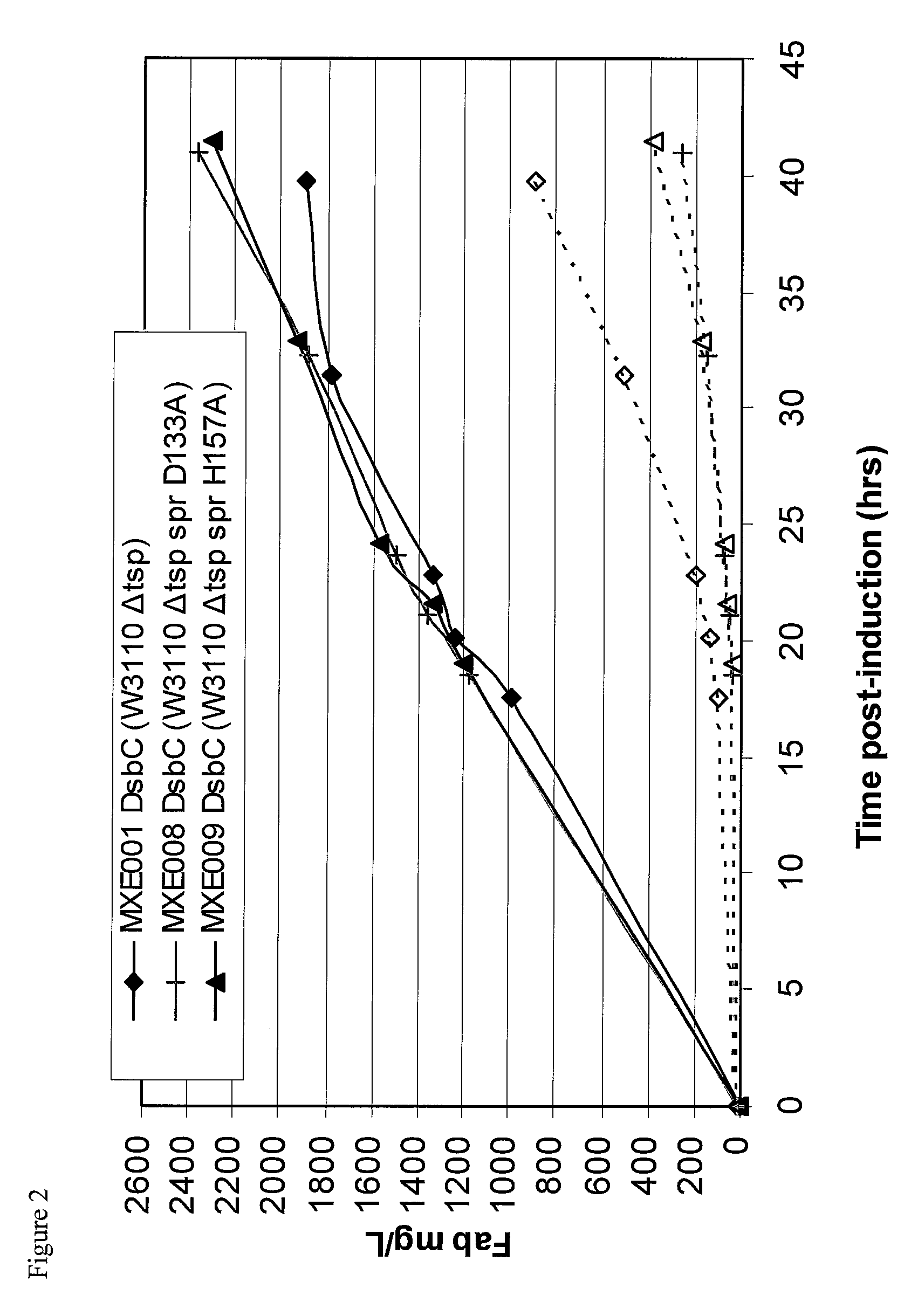
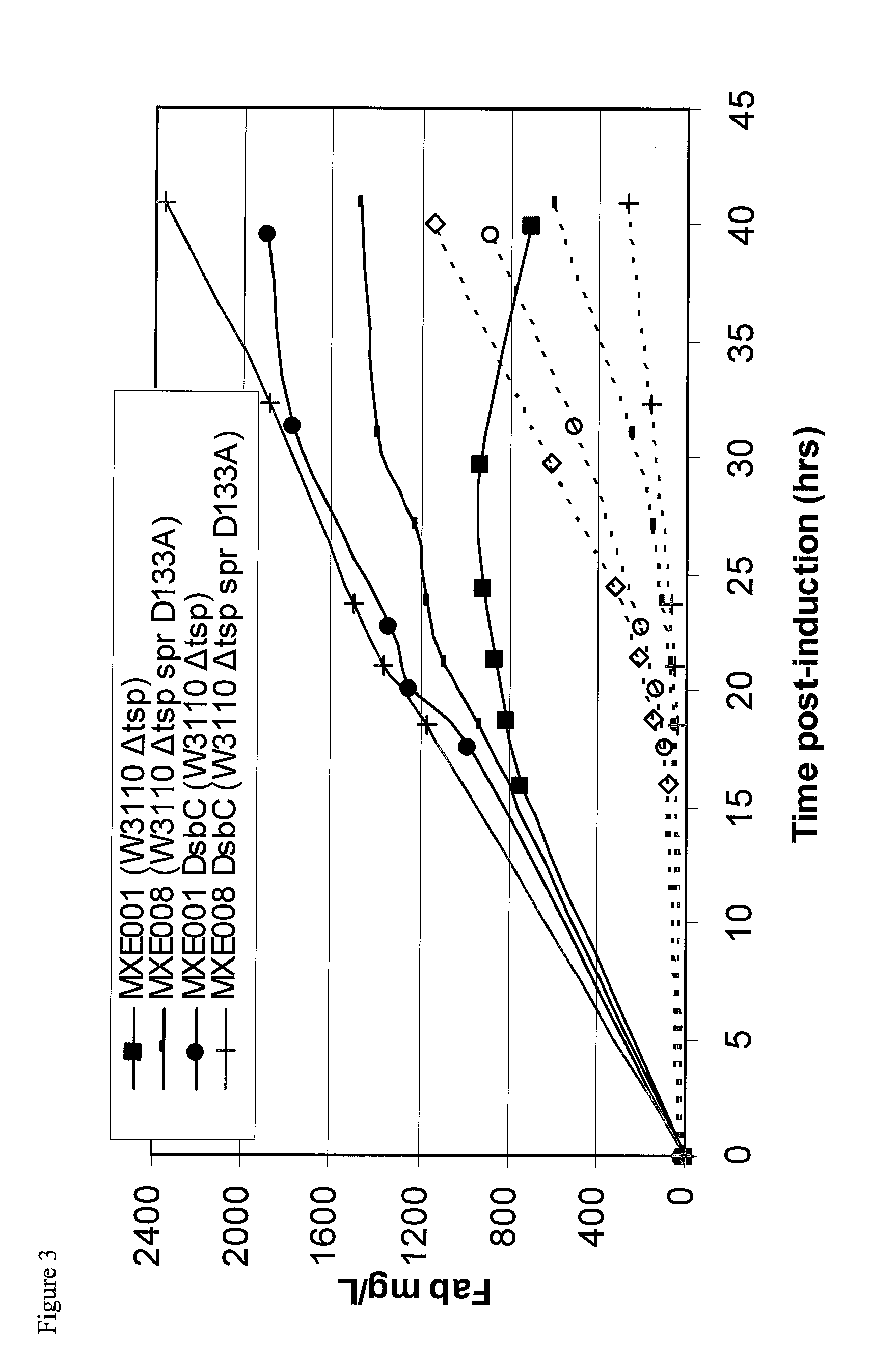
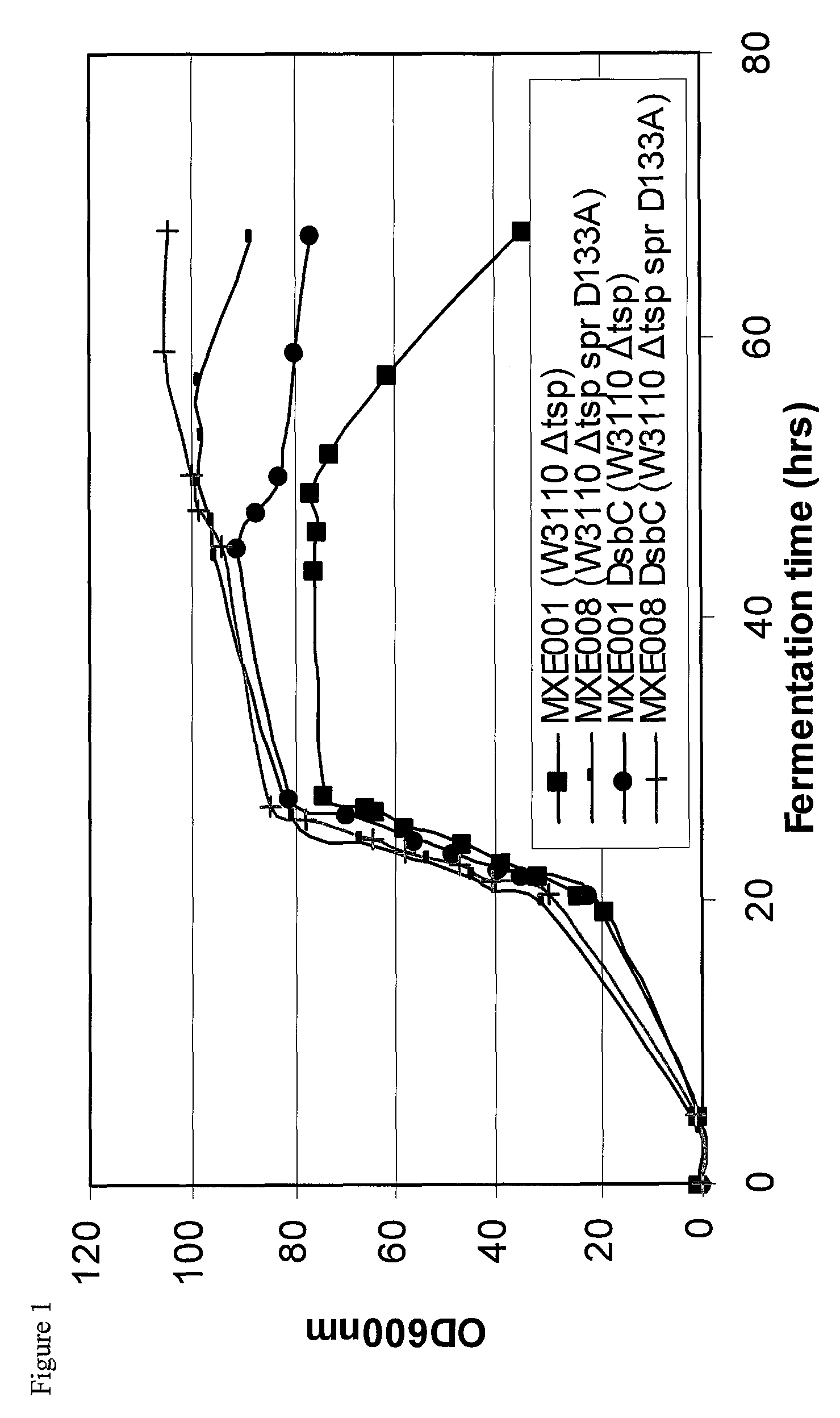
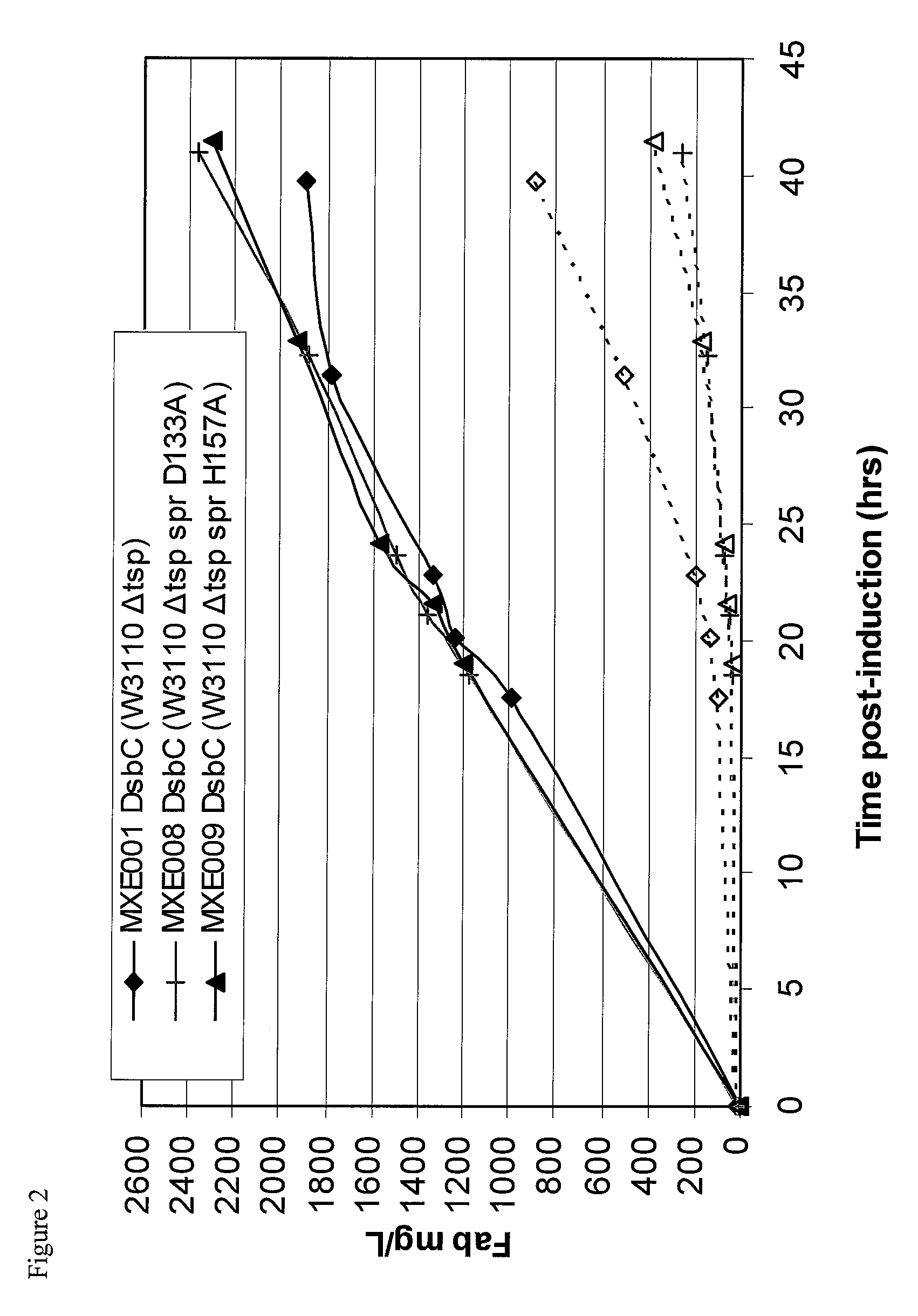
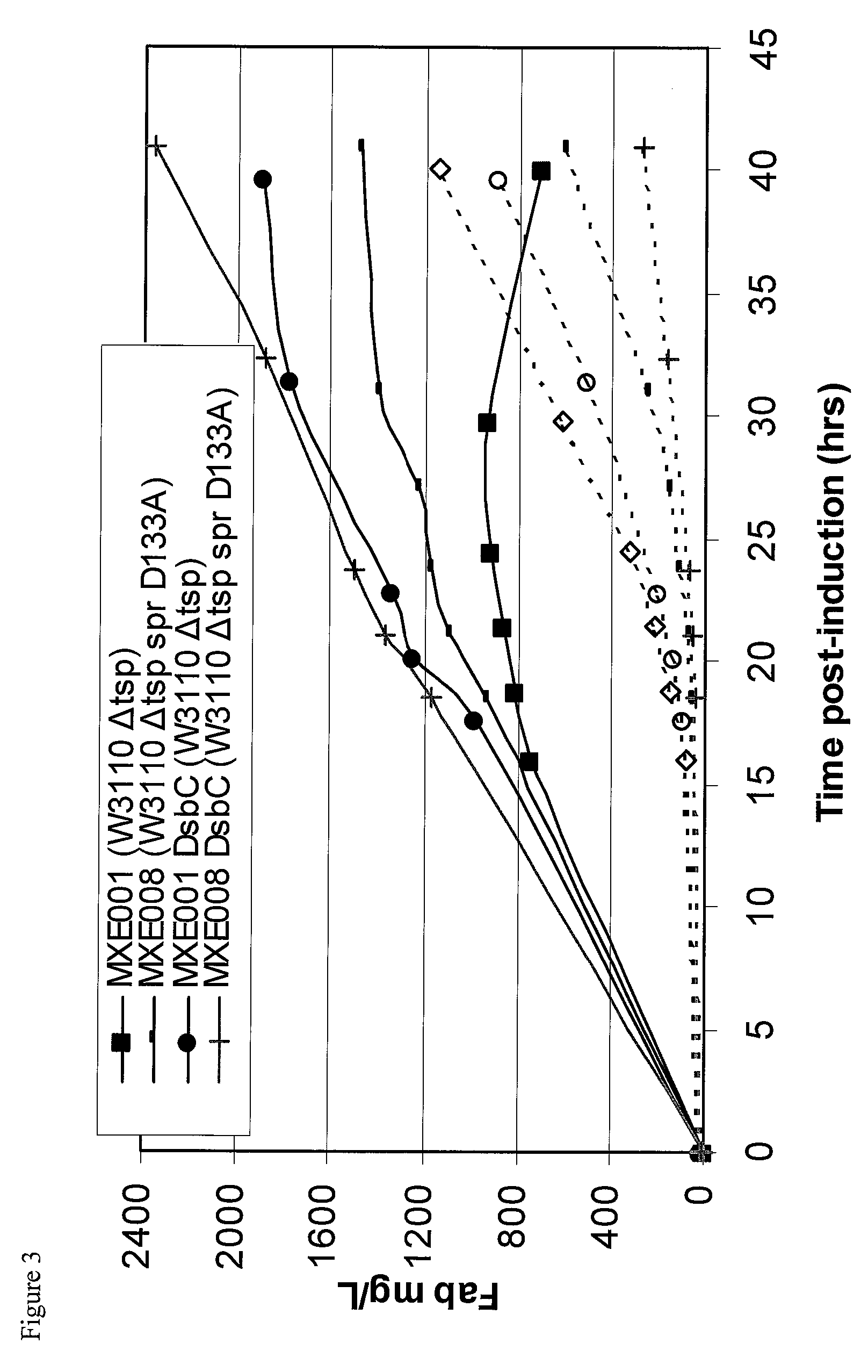
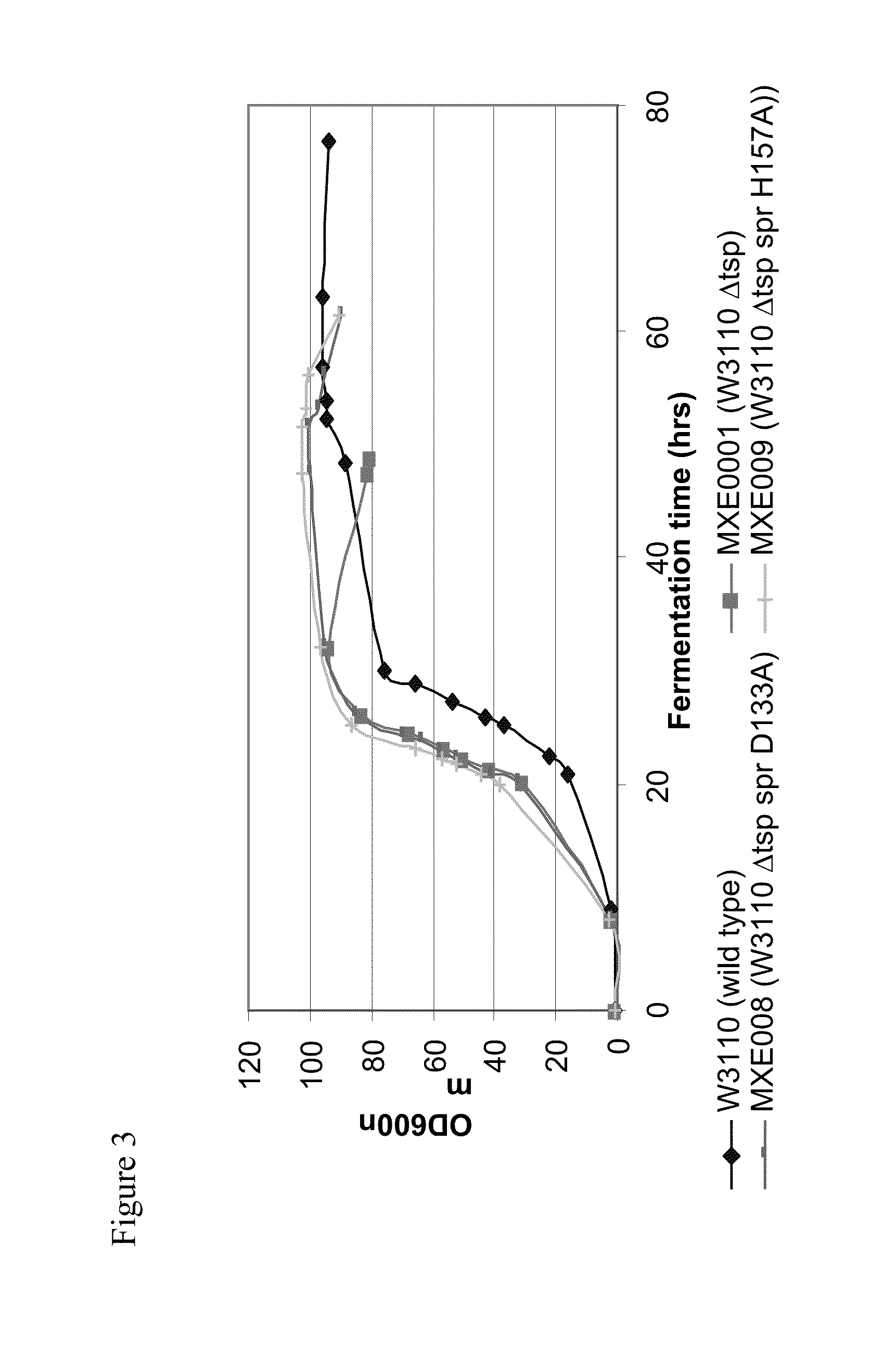
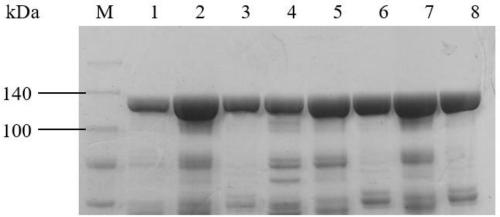
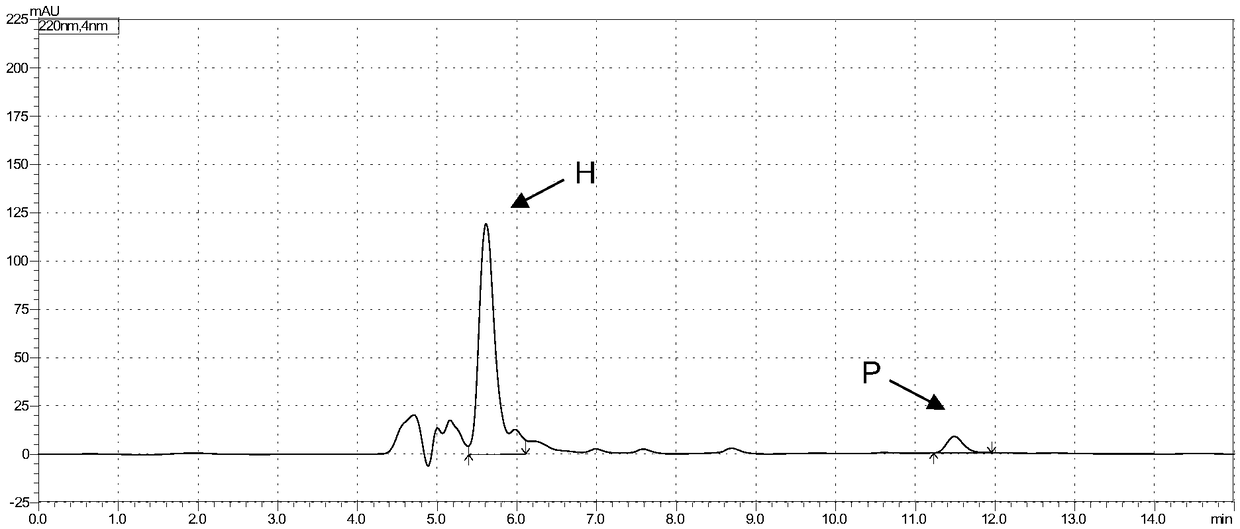
Bacterial host strain comprising a mutant SPR gene and having reduced TSP activity
ActiveUS8969039B2Advantageous growth and protein production phenotypeBacteriaHydrolasesProtein activityAmino acid
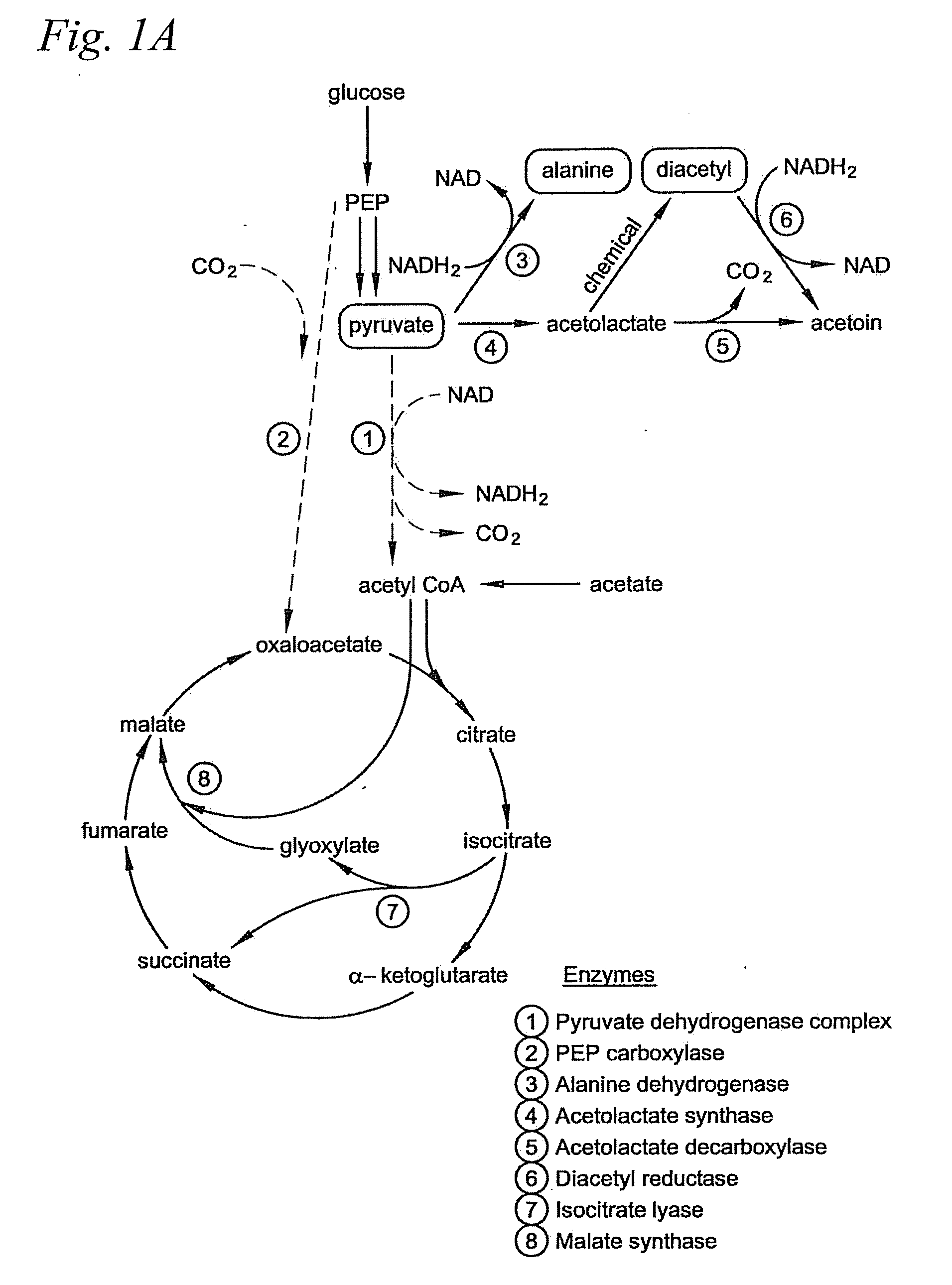
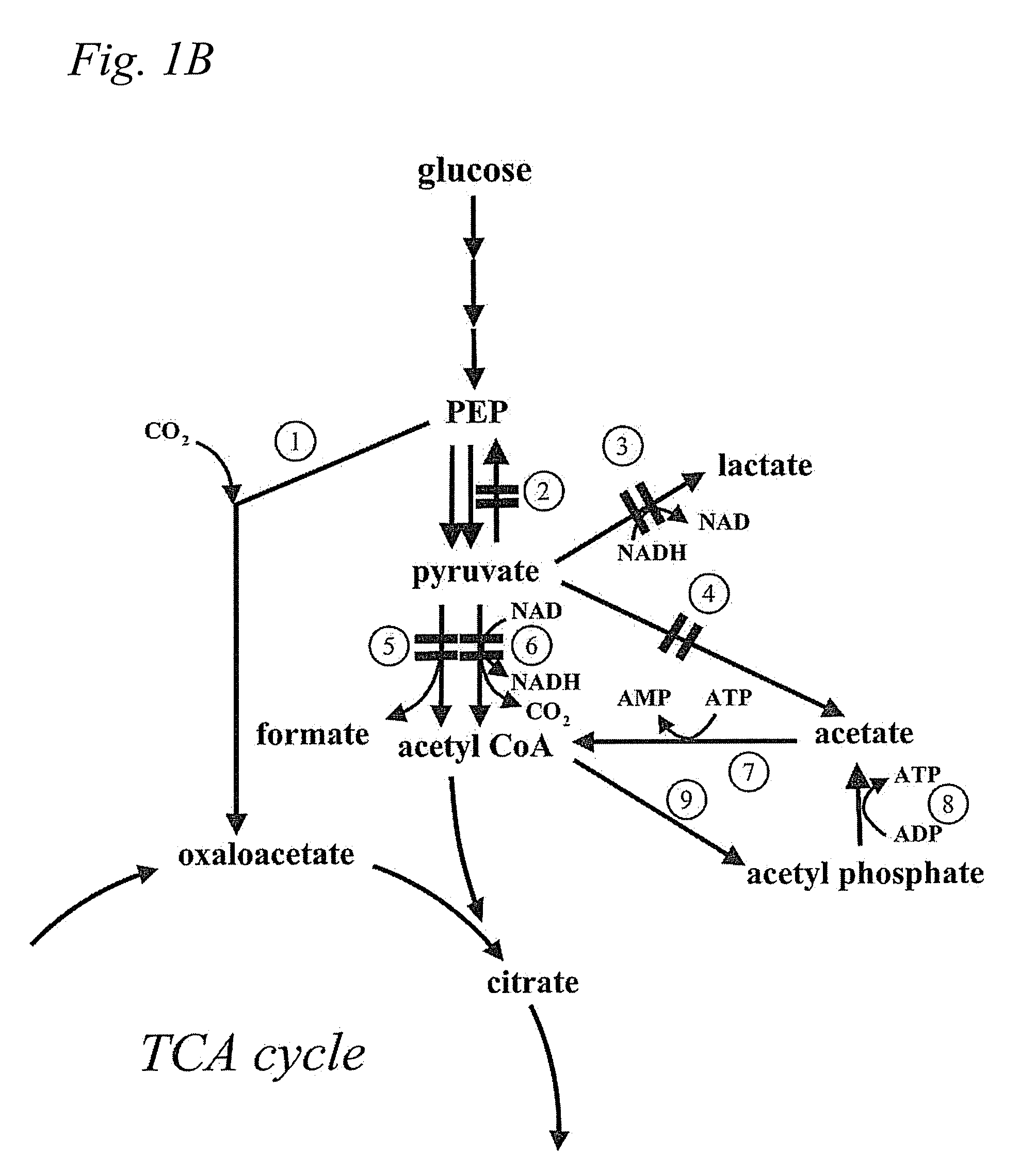
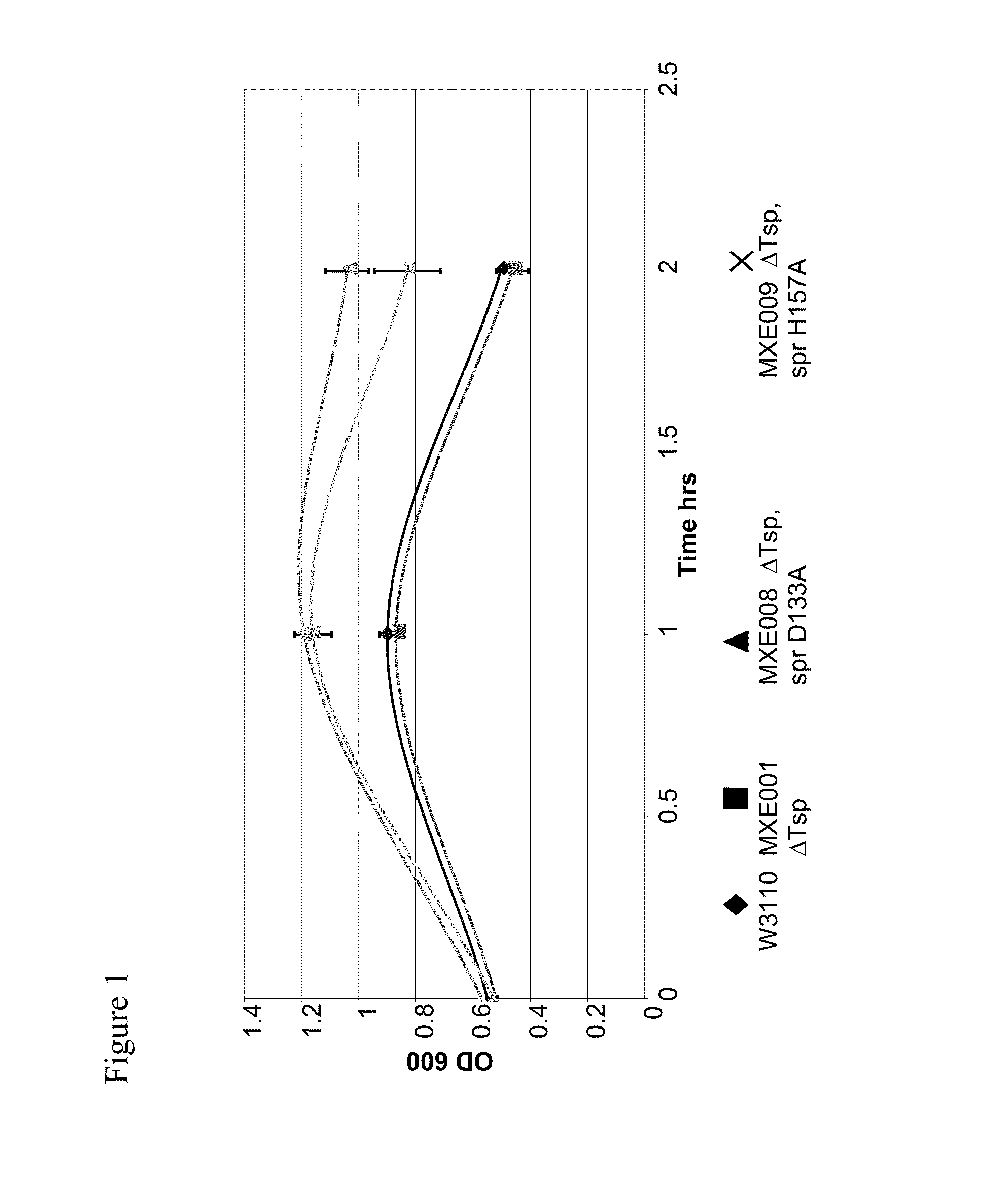
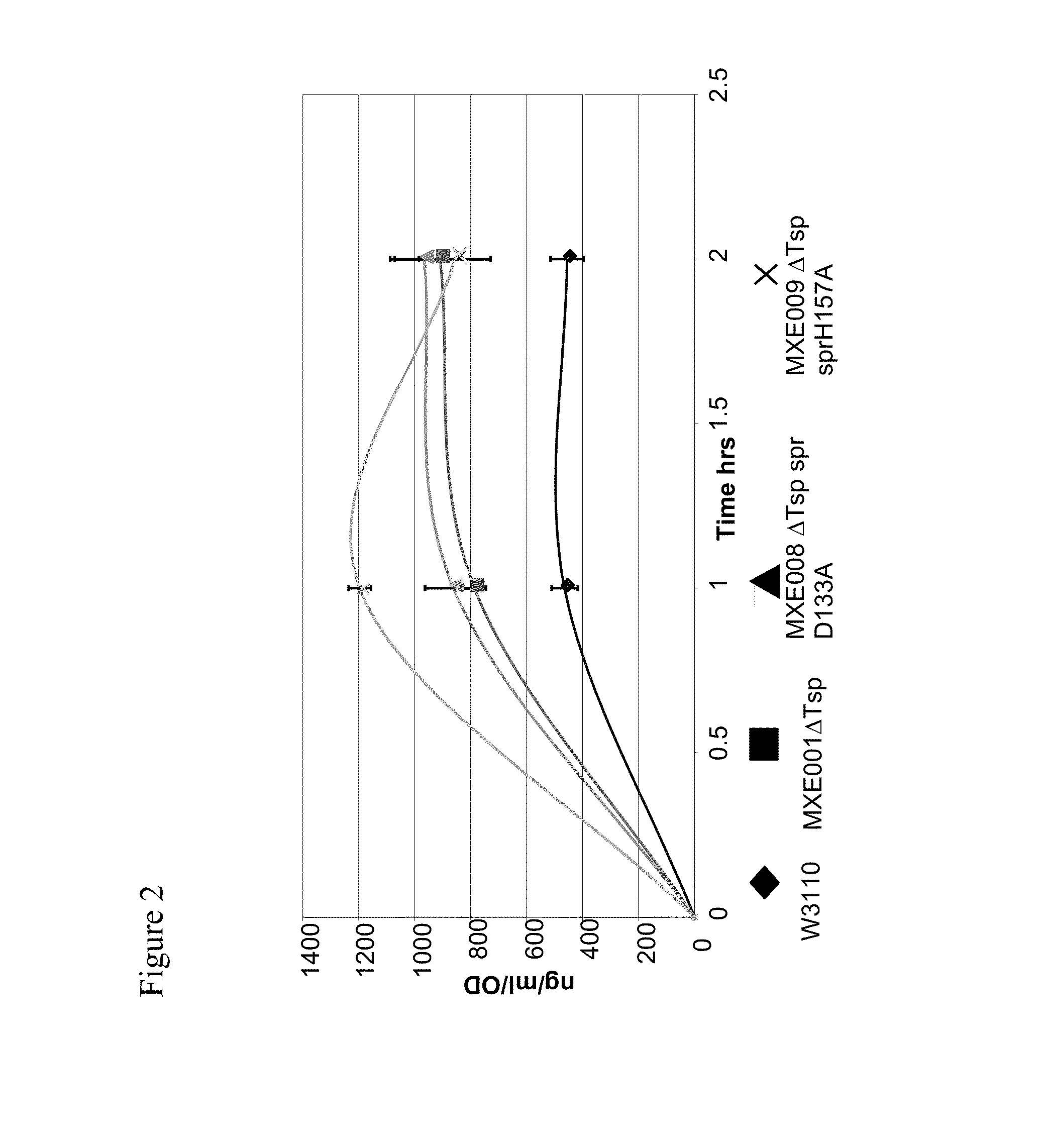
The present invention provides a recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising a mutant spr gene encoding a spr protein having a mutation at one or more amino acids selected from D133, H145, H157, N31, R62, I70, Q73, C94, S95, V98, Q99, R100, L108, Y115, V135, L136, G140, R144 and G147 and wherein the cell has reduced Tsp protein activity compared to a wild-type cell.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Bacterial host strain expressing recombinant dsbc and having reduced tsp activity
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Bacterial host strain expressing recombinant DsbC and having reduced Tsp activity
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
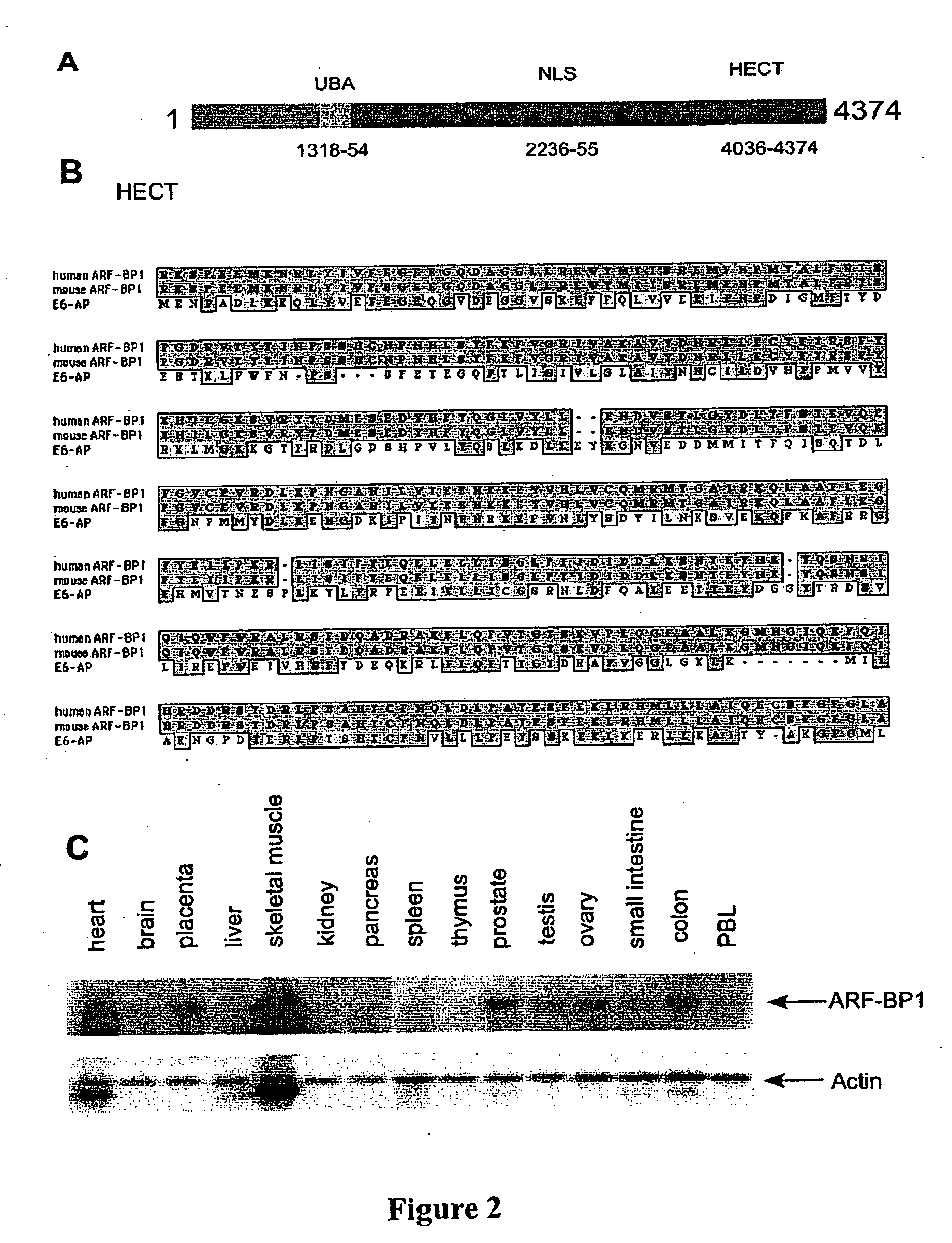
ARF-BP1 as mediator of p53-dependent and independent tumor suppression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060088847A1Assessing abilityAvoid interactionHydrolasesTissue cultureUbiquitin ligaseSomatic cell
The present invention relates to the mechanism of ARF-mediated cell growth suppression. ARF-BP1 is identified as a novel ubiquitin ligase, and a major component of ARF-containing nuclear complexes in human cells. The present invention discloses a novel mechanism of ARF-mediated p53 activation and that ARF-BP1 is a critical mediator of both p53-independent and p53-dependent tumor suppression functions of ARF. Inactivation of ARF-BP1 in normal cells stabilizes p53 and induces p53-dependent apoptosis. Inactivation of ARF-BP1, but not Mdm2, in p53-wildtype cells promotes cell growth inhibition in a manner reminiscent of ARF induction. ARF-BP1 directly binds and ubiquitinates p53 and inactivation of endogenous ARF-BP1 is crucial for ARF-mediated p53 stabilization in Mdm2-null cells. ARF-BP1 is advantageous over Mdm2 as a target for suppressing tumor cell growth regardless of p53 status.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
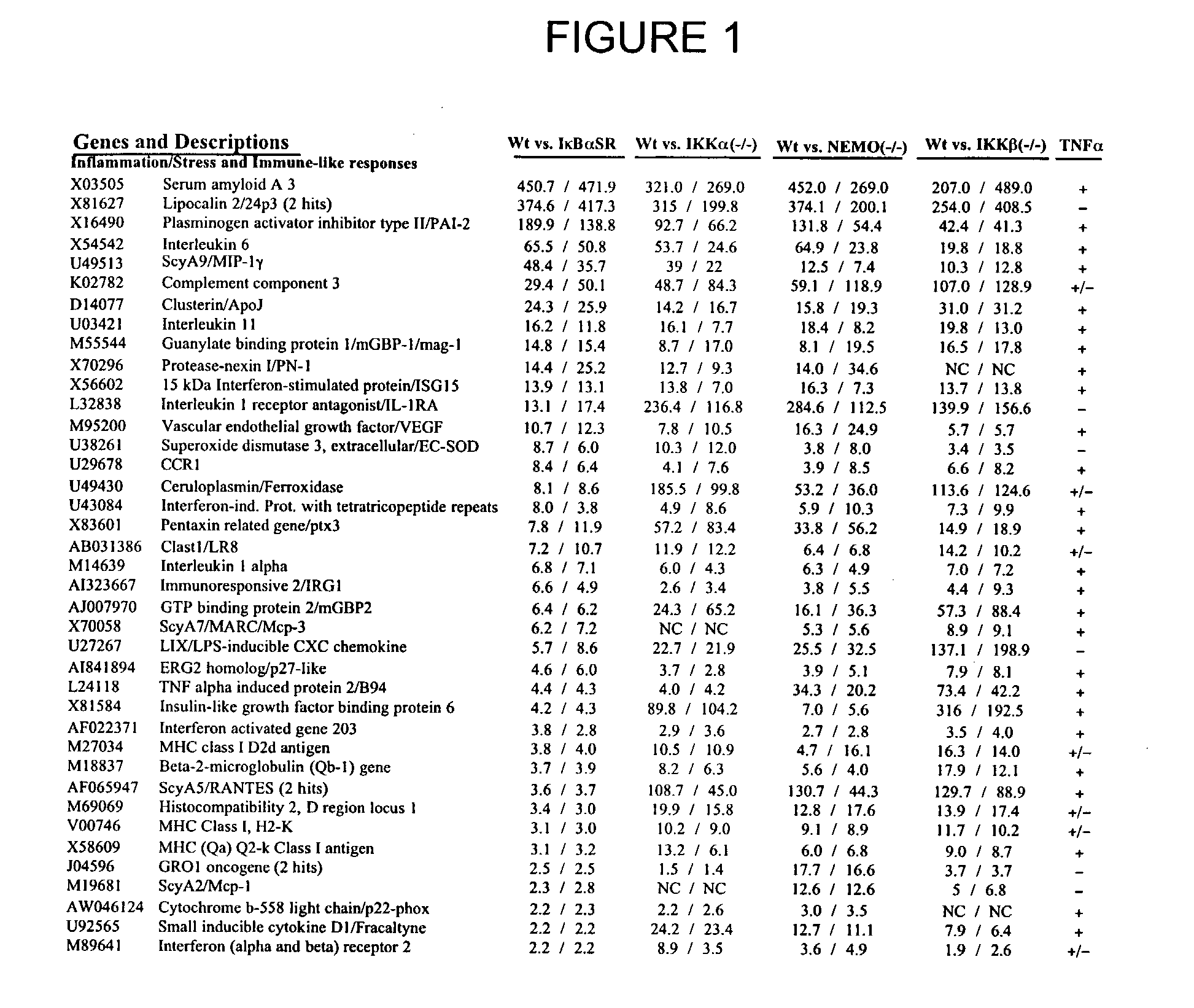
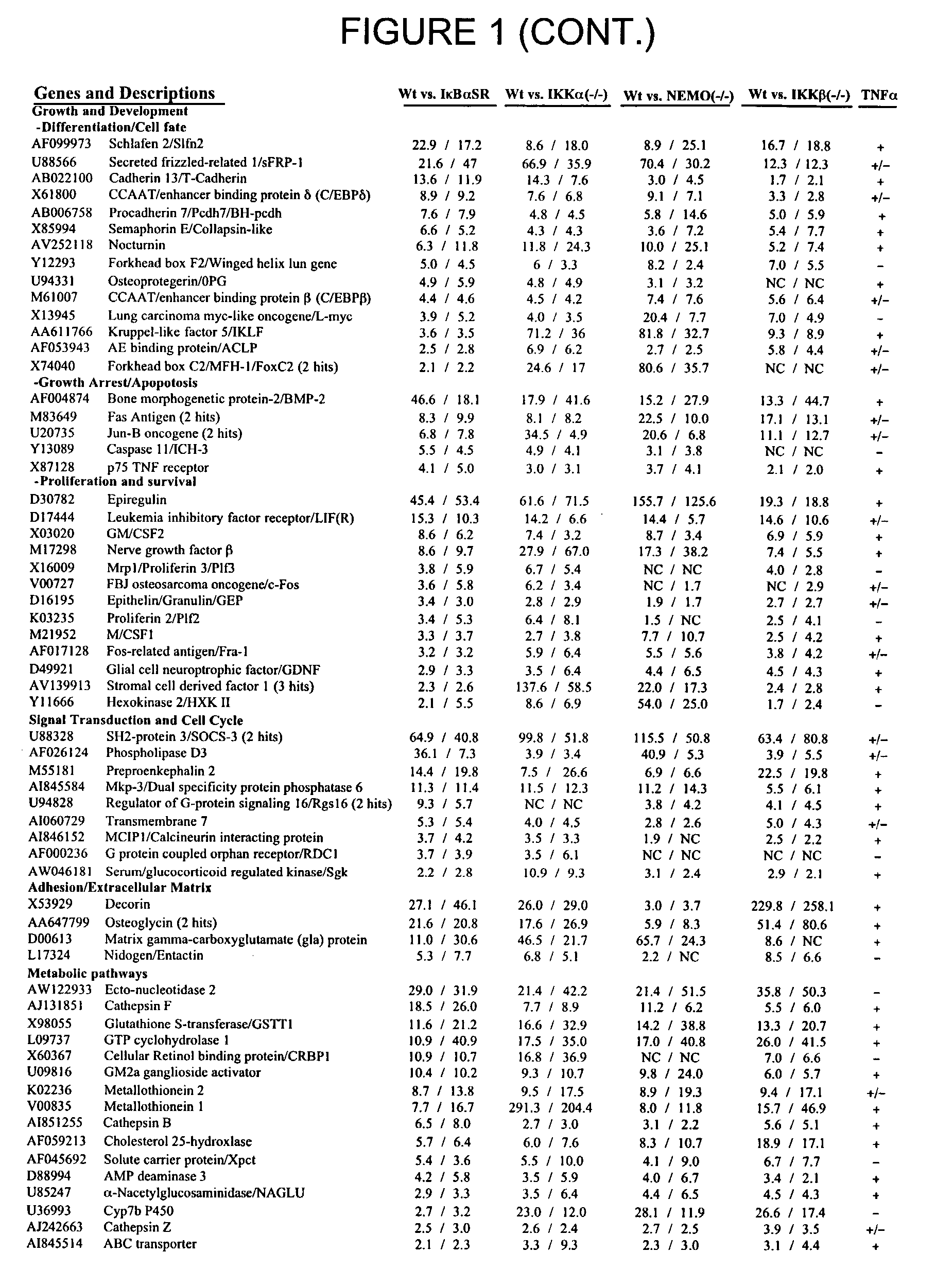
Methods for the Identification of IKKalpha Function and other Genes Useful for Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
InactiveUS20070128648A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological pathwayGene expression level
The invention provides a method for identifying genes involved in the NF-κB pathway comprised of the steps of determining the level of expression of a gene in an experimental sample obtained from the cells having deficient levels of a component of the NF-κB pathway; determining the level of expression of said gene in a control sample obtained from wild type cells having levels of a component of a biological pathway; selecting genes having a level of expression that are modulated in said experimental sample relative to said wild type sample. The invention also provides a method of treating inflammatory related diseases by modulating the activity of IKKα.
Owner:LI JUN +5
Methods for the identification of IKKalpha function and other genes useful for treatment of imflammatory diseases
The invention provides a method for identifying genes involved in the NF-kappaB pathway comprised of the steps of determining the level of expression of a gene in an experimental sample obtained from the cells having deficient levels of a component of the NF-kappaB pathway; determining the level of expression of said gene in a control sample obtained from wild type cells having levels of a component of a biological pathway; selecting genes having a level of expression that are modulated in said experimental sample relative to said wild type sample. The invention also provides a method of treating inflammatory related diseases by modulating the activity of IKKalpha.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
Production of fatty acids esters
A microbial cell is used for producing at least one fatty acid ester, wherein the cell is genetically modified to contain (i) at least one first genetic mutation that enables the cell to produce at least one fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A (CoA) thereof by increased enzymatic activity in the cell relative to the wild type cell of malonyl-CoA dependent and malonyl-ACP independent fatty acyl-CoA metabolic pathway, wherein the fatty acid contains at least 5 carbon atoms; and (ii) a second genetic mutation that increases the activity of at least one wax ester synthase in the cell relative to the wild type cell and the wax ester synthase has sequence identity of at least 50% to a polypeptide of SEQ ID NO: 1-8 and combinations thereof or to a functional fragment of any of the polypeptides for catalyzing the conversion of fatty acid and / or acyl coenzyme A thereof to the fatty acid ester.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Microbial production of pyruvate and pyruvate derivatives
InactiveUS20100304450A1Redox balancedIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismMetabolite
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Bacterial host strain comprising a mutant spr gene and having reduced tsp activity
ActiveUS20150132828A1Advantageous growth and protein production phenotypeBacteriaHydrolasesMutated proteinMicrobiology
The present invention provides a recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising a mutant spr gene encoding a spr protein having a mutation at one or more amino acids selected from D133, H145, H157, N31, R62, I70, Q73, C94, S95, V98, Q99, R100, L108, Y115, V135, L136, G140, R144 and G147 and wherein the cell has reduced Tsp protein activity compared to a wild-type cell.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
P450BM3 mutant, and application of P450BM3 mutant in hydroquinone synthesis using benzene or phenol as substrate
ActiveCN109136203AHigh catalytic activityReduce manufacturing costOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringPhenolHigh activity
The invention provides a mutation site remarkably associated with the specific enzyme activity of a cytochrome P450BM3 monooxygenase, a cytochrome P450BM3 monooxygenase mutant, a coding gene of the mutant, a recombinant plasmid containing the cytochrome P450BM3 monooxygenase mutant gene, a recombinant transformant containing the cytochrome P450BM3 monooxygenase mutant gene, a preparation method ofthe mutant, and application of the mutant in hydroquinone synthesis using benzene or phenol as a substrate. Compared with a wild cytochrome P450BM3 monooxygenase, the P450BM3 mutant provided by the invention shows high activity and extremely high regioselectivity; and through the mutant, pure hydroquinone can be more effectively prepared, and the production cost can be greatly reduced, so that higher applicability for industrial hydroquinone production is achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
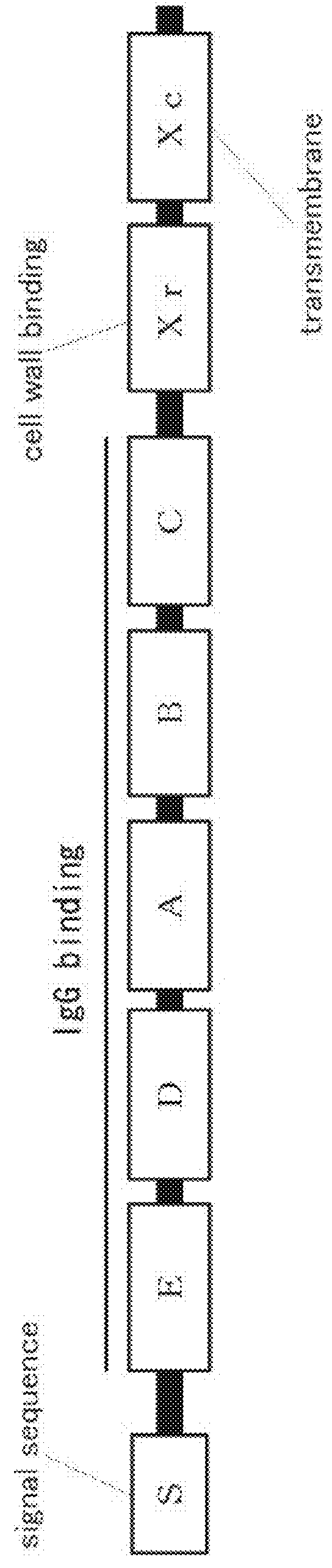
Mutated protein of protein A having reduced affinity in acidic region and antibody-capturing agent
ActiveUS9382297B2Reduced ability to bindEasy to eluteAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesSequence analysisMutated protein
A modified protein of an extracellular domain of protein A, which has the reduced ability to bind to immunoglobulin in an acidic region, compared with the wild-type extracellular domain of protein A, without impairing a selective antibody-binding activity in a neutral region. On the basis of three-dimensional structure coordinate data on a complex of the extracellular domain of protein A bound with the Fc region of immunoglobulin G, the modified protein is obtained by the substitution of amino acid residues that are located within the range of 10 angstroms from the Fc region and have a 20% or more ratio of exposed surface area, by histidine residues. Preferably, the modified protein is obtained by the substitution of amino acid residues at sites identified from the analysis of sequences selected from a library constituted by the protein group, by histidine residues. These substitutions may be combined.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Recombinant Bacterial Host Cell for Protein Expression
ActiveUS20150111249A1Reduced Tsp protein activityPromote growthBacteriaHydrolasesGeneticsProtein folding
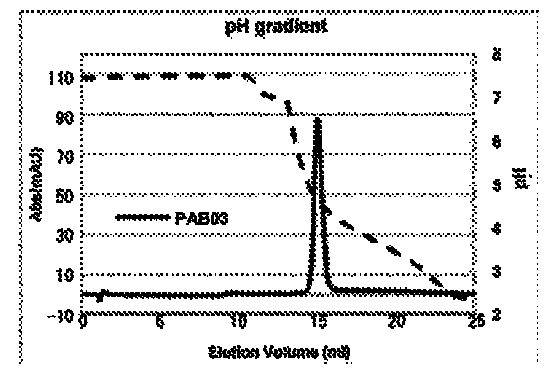
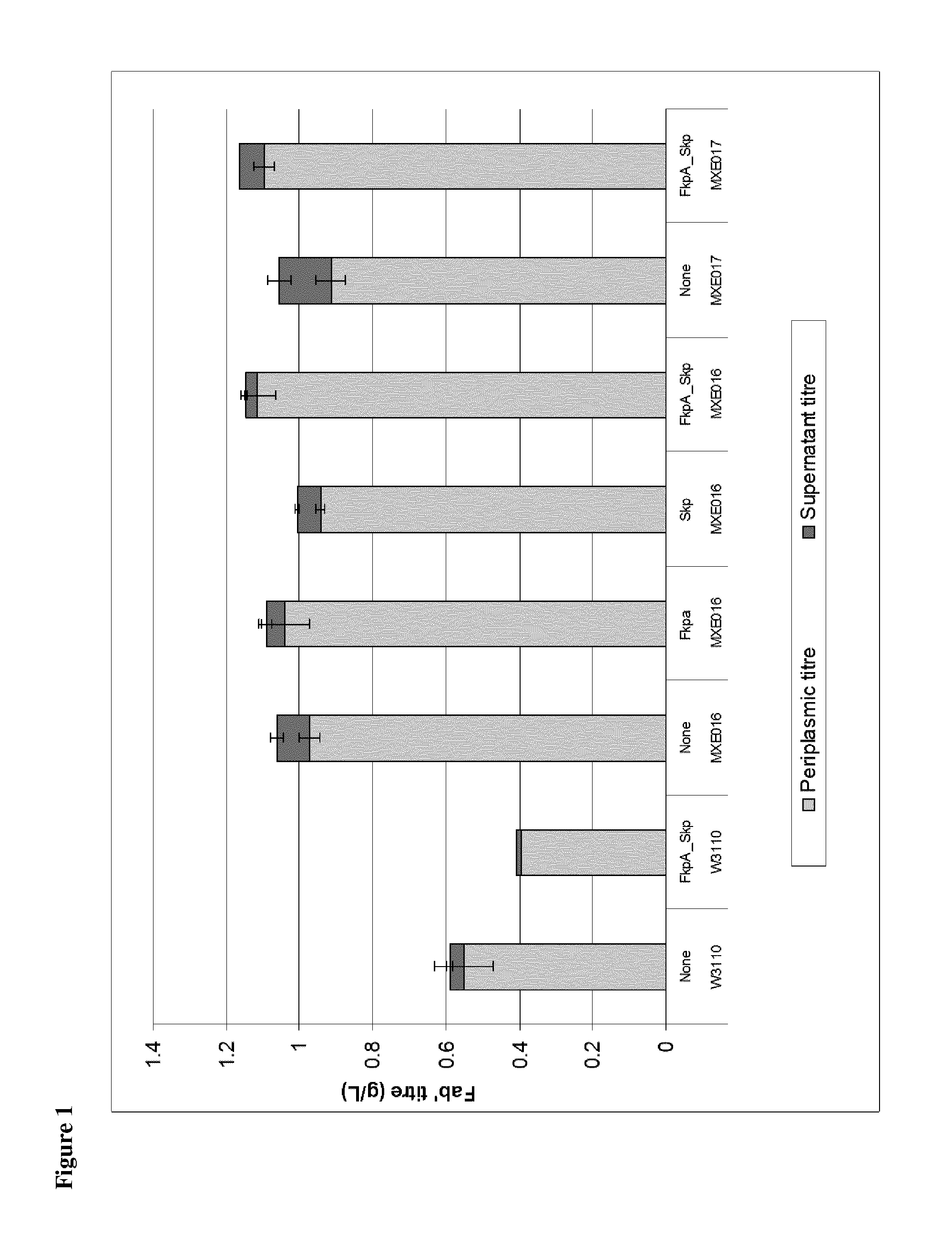
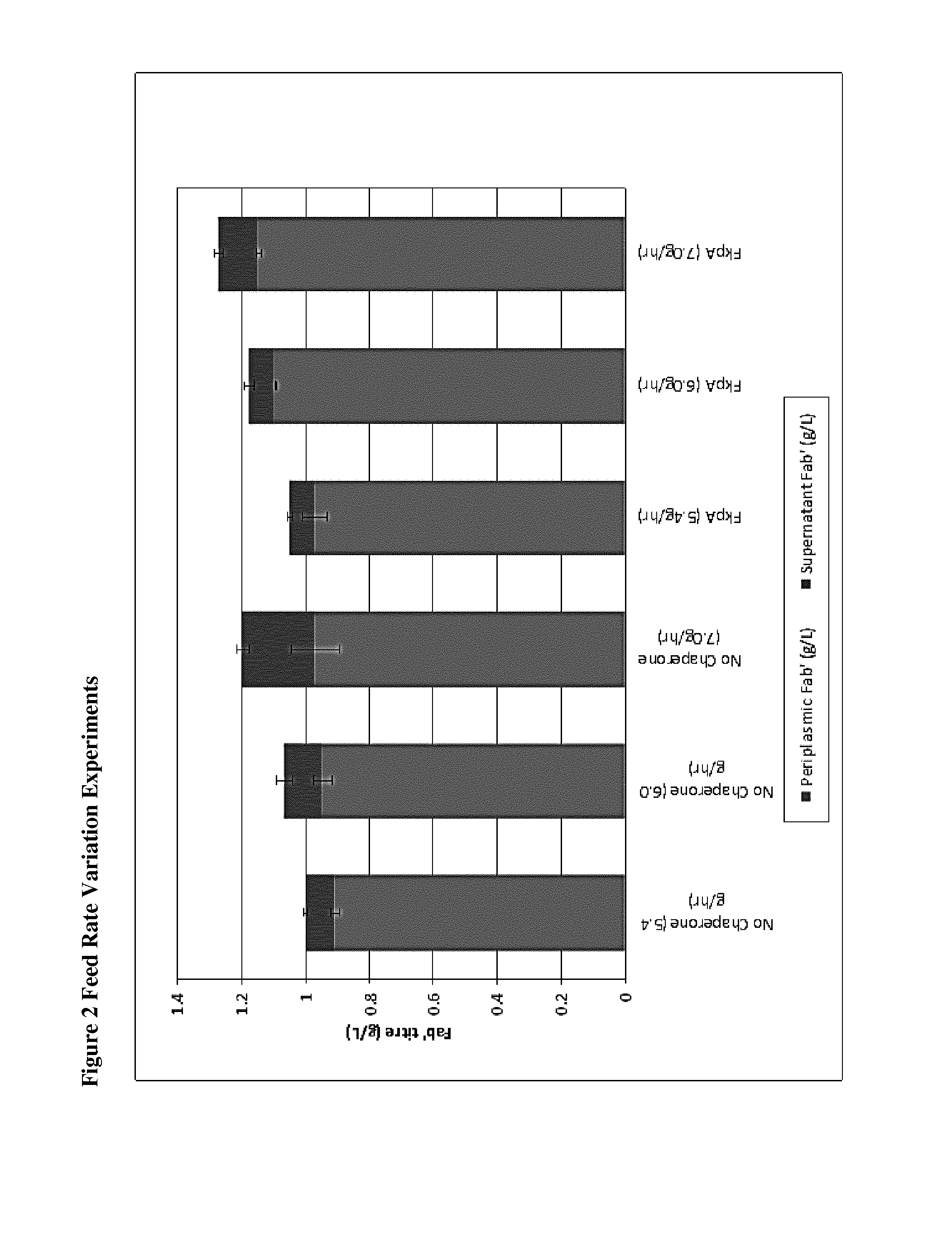
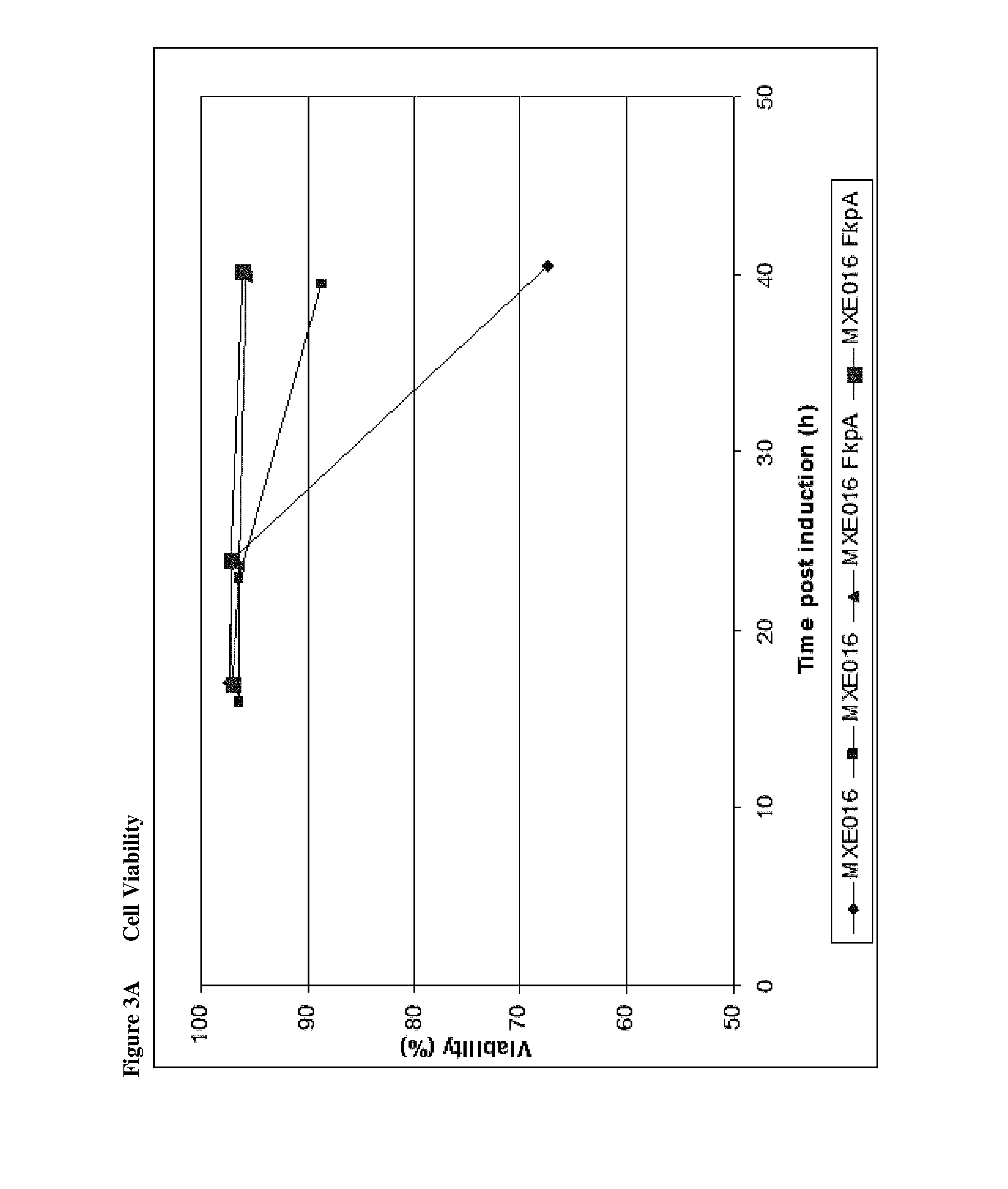
The present disclosure relates to a recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising: a.) a mutant spr gene encoding a spr protein having a mutation at one or more amino acids selected from D133, H145, H157, N31, R62, I70, Q73, C94, S95, V98, Q99, R100, L108, Y115, V135, L136, G140, R144 and G147 and b.) a gene capable of expressing or overexpressing one or more proteins capable of facilitating protein folding, such as FkpA, Skp, SurA, PPiA and PPiD, wherein the cell has reduced Tsp protein activity compared to a wild-type cell, methods employing the cells, use of the cells in the expression of proteins in particular antibodies, such as anti Fc Rn antibodies and proteins made by the methods described herein.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SRL
Production of 3-hydroxybutyrate
There is provided amicrobial cell which is capable of producing acetoacetate, 3-hydroxybutyrate and / or 3-hydroxybutyrate variants, wherein the cell is genetically modified to comprise an increased expression relative to its wild type cell of: - an enzyme E1 capable of catalysing the conversion of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA; - an enzyme E2 capable of catalysing the conversion of acetoacetyl-CoAto acetoacetate; and -an enzyme E3 capable of catalysing the conversion of acetoacetate to 3-hydroxybutyrate and / or variants thereof.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
EGFR inhibitor for targetedly treating cancer and preparation method and application thereof
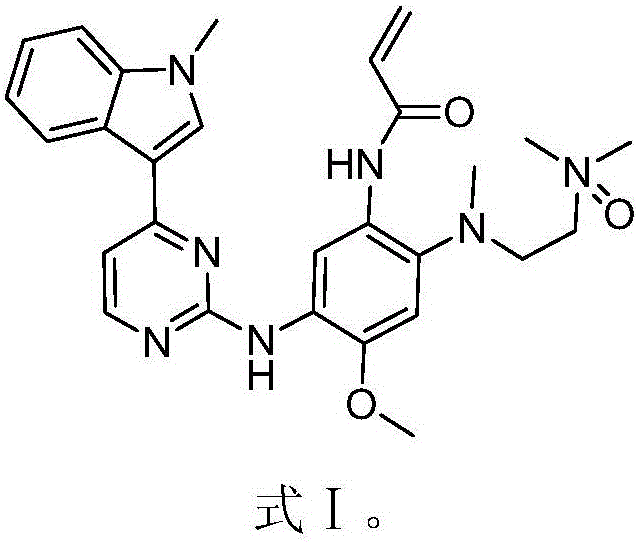
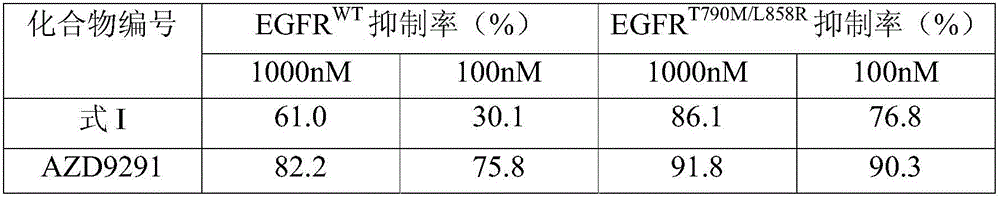
ActiveCN105777716ALittle side effectsOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSide effectDouble mutation
The invention discloses an EGFR inhibitor for targetedly treating a cancer and a preparation method and application thereof.The structural formula of the EGFR inhibitor is shown in the formula I.The EGFR inhibitor can be used for preventing and / or treating the cancer such as a human skin caner or a lung cancer.The EGFR inhibitor can selectively inhibit cell lines of EGFR double mutation (EGFRT790M and L858R), and the inhibitory activity to EGFR wild type cells is weak; therefore, the EGFR inhibitor can be used for treating lung cancer patients with EGFRT790M and L858R mutation, and the side effects are fewer, wherein the side effects are caused by inhibiting wild type EGFR, for example, Afatinib.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
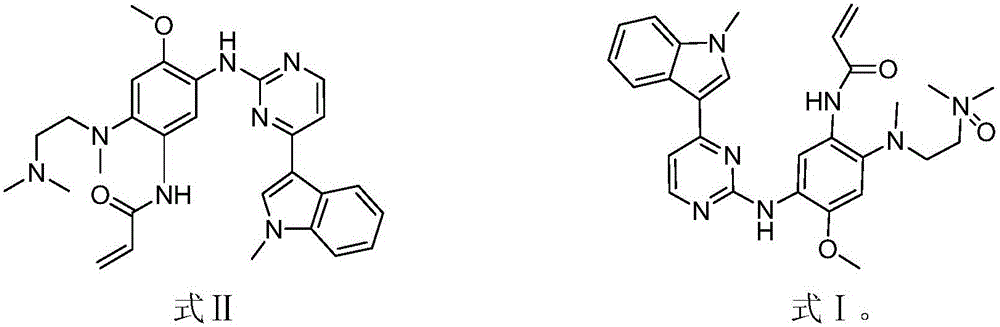
EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) inhibitor for targeted therapy of cancers, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105585557ANovel chemical structureLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical structureSide effect
The invention discloses an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) inhibitor for targeted therapy of cancers, and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the EGFR inhibitor is disclosed as Formula I, wherein R is H, OH, NR', C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 alkenyl, aryl or heterocycle, and R' is C1-C3 alkyl. The EGFR inhibitor can be used for preventing and / or treating cancers, such as human skin squamous carcinoma or lung cancer. Compared with the existing inhibitors (such as AZD9291, afatinib and the like), the EGFR inhibitor disclosed by the invention has novel chemical structure. The EGFR inhibitor can selectively inhibit cell lines of EGFR double mutants (EGFRT790M / L858R), and has lower inhibition activities for EGFR wild type cells. Therefore, the EGFR inhibitor disclosed by the invention can be used for treating the patient with lung cancer with EGFRT790M / L858R mutants, and has lower side effect (caused by the inhibition of the wild type EGFR, such as afatinib).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biosynthetic production of acyl amino acids
InactiveCN107075463ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Microbial production of pyruvate and other metabolites
InactiveUS20050255572A1Redox balancedIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaAcetic acidMicroorganism
Microbial production of pyruvate and metabolites derived from pyruvate in cells exhibiting reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity compared to wild-type cells. Acetate and glucose are supplied as a carbon sources.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
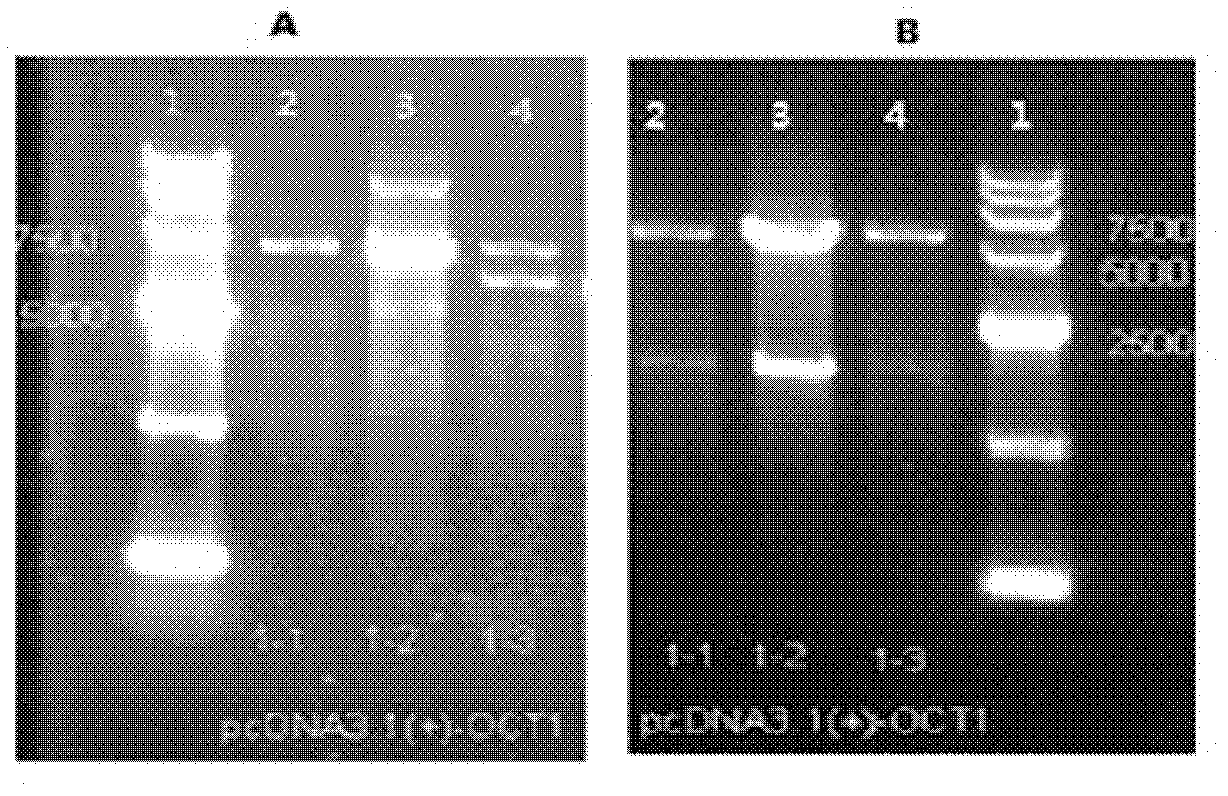
Construction and applications of cell model expressing human organic cation transporter-1
ActiveCN102181449ATransshipment predictionPredict interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCanine kidneyHuman body
The invention provides a construction method and applications of a cell model expressing human organic cation transporter-1. A hOCT1 wild-type gene segment is obtained from a hepatic tissue; two mutant gene segments P341L and M420del can be obtained by specific point mutation; the two segments are connected with a plasmid vector; darby canine kidney cells (MDCK) are transfected; G418 resistance screening is carried out to obtain wild-type cells expressing hOCT1 and cells of two mutants; mRNA level verification is carried out on the cells; and functional verification is carried out by utilizing a hOCT1 substrate and an inhibitor. The cell model provided by the invention can be used for screening the hOCT1 classic substrate and the inhibitor, and predicting the transportation of medicament in human bodies and medicament interaction which possibly happen; and by utilizing the cell model, the influence of gene polymorphism of the transporter on the medicament transportation function can be predicted; and the cell model provides a standard for clinical reasonable medicament administration and individualized medicament administration, and has reasonable design and good repetitiveness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6f8b222e-5a7b-41ca-b86a-4b04c7497be5/DEST_PATH_HDA0001417539750000011.png)
![gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6f8b222e-5a7b-41ca-b86a-4b04c7497be5/DEST_PATH_HDA0001417539750000012.png)
![gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method gRNA for knockout of wild type T cell TCR [beta] strand and method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6f8b222e-5a7b-41ca-b86a-4b04c7497be5/DEST_PATH_HDA0001417539750000013.png)