Production of 3-hydroxybutyrate
A hydroxybutyric acid, wild-type technology, applied in the biological field of producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid and/or its variants, can solve the problems of energy consumption in the process required for extraction, not utilizing the photosynthetic potential of cyanobacteria, etc. Waste, no material loss, increased production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Generation of acetogens genetically modified to form 3HB via acetoacetate
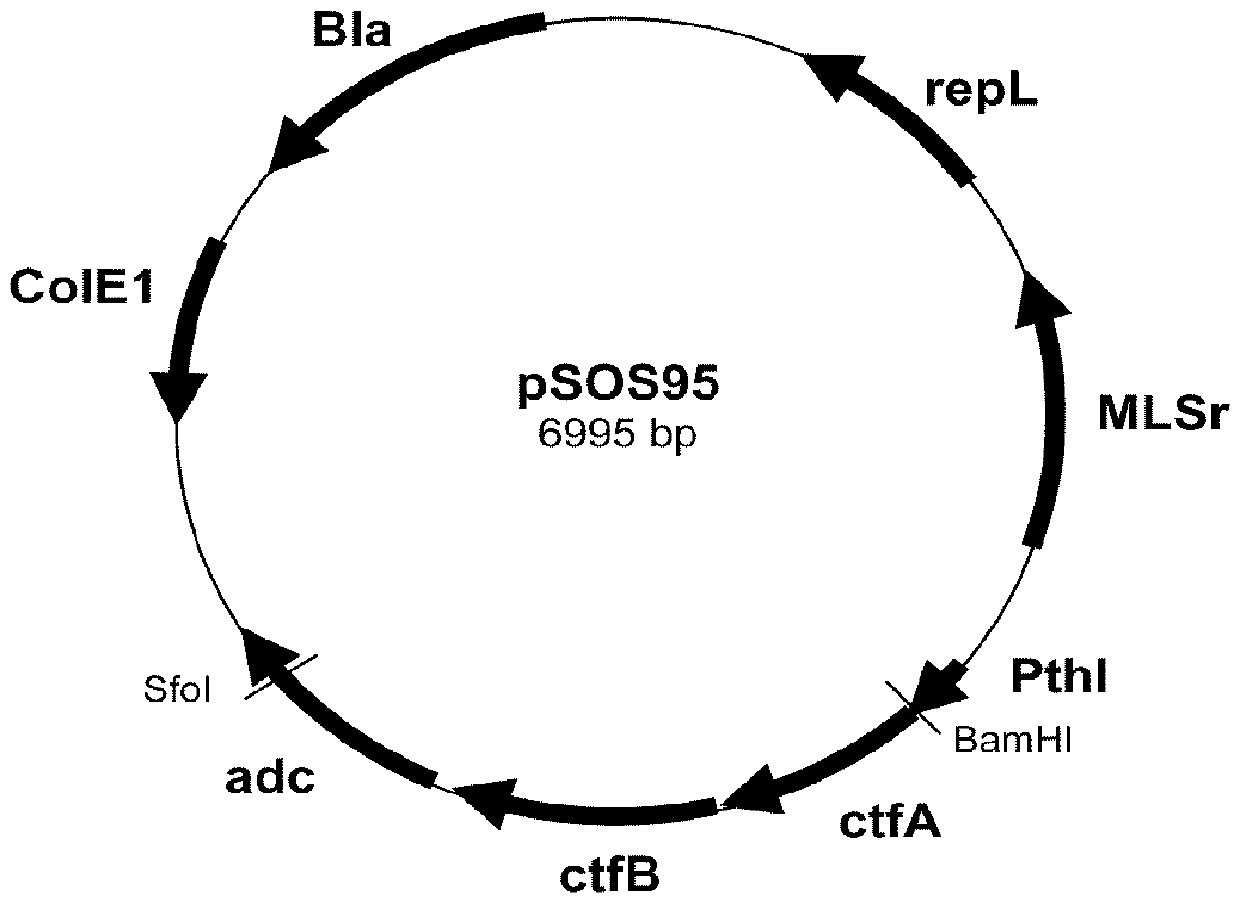
[0073] Thiolase (thl) from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATTC 824, acetoacetate transferase (ctfAB) from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATTC 824 and secondary alcohol dehydrogenase (sadh) from Clostridium beijerinckii DSM 6423 Gene insertion vector pEmpty. This plasmid is based on the plasmid backbone pSOS95 ( figure 1 ). To use pSOS95, it was digested with BamHI and Kasl. This removed the operon ctfA-ctfB-adc, but left the thl promoter and rho-independent terminator of adc. Clostridium ljungdahlii and C. autoethanogenum The transformation of was performed as described in Leang et al. 2013. The nucleotide sequences of the enzymes used are SEQ ID NO: 1, 3 (ctfA), 5 (ctfB) and 7, respectively. These sequences were transformed to be under the control of the thiolase promoter and integrated into the vector backbone as a single operator. The created vector was named pTCtS. The vector pTCts was...
Embodiment 2
[0075] 3HB strain in H 2 and CO 2 Upper fermentation showing acetoacetate and 3HB production
[0076] For cell culture of Clostridium ljungdahlii pTCts, grow 5 mL of culture anaerobically in a medium with approximately 400 mg / L L-cysteine hydrochloride and 400 mg / L Na 2 S×9H 2 O, 100 mg / L erythromycin in 500 ml medium (ATCC1754 medium: pH 6.0; 20 g / L MES; 1 g / L yeast extract, 0.8 g / L NaCl, 1 g / L NH 4 Cl, 0.1 g / L KCl, 0.1 g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 0.2 g / L MgSO 4 ×7H 2 O; 0.02 g / L CaCl 2 ×2H 2 O; 20 mg / L nitrilotriacetic acid 10 mg / LMnSO 4 ×H 2 O; 8 mg / L (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 ×6H 2 O; 2 mg / L CoCl 2 ×6H 2 O; 2 mg / L ZnSO 4 ×7H 2 O; 0.2mg / L CuCl 2 ×2H 2 O; 0.2 mg / L Na 2 MoO 4 ×2H 2 O; 0.2 mg / L NiCl 2 ×6H 2 O; 0.2 mg / / L Na 2 SeO 4 ; 0.2 mg / L Na 2 WO 4 ×2H 2 O; 20 μg / L d-biotin, 20 μg / L folic acid, 100 g / L pyridoxine-HCl; 50 μg / L thiamine-HCl × H 2 O; 50 μg / L riboflavin; 50 μg / L niacin, 50 μg / L calcium pantothenate, 1 μg / L vitamin B12; 50 μg / L p-amin...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Fermentation of the vector control strain did not produce acetoacetate or 3HB
[0080] For cell culture of Clostridium ljungdahlii pEmpty, grow a 5 mL culture anaerobically in a medium with approximately 400 mg / L L-cysteine hydrochloride and 400 mg / L Na 2 S×9H 2 O, 100 mg / L erythromycin in 500 ml medium (ATCC1754 medium: pH 6.0; 20 g / L MES; 1 g / L yeast extract, 0.8 g / L NaCl, 1 g / L NH 4 Cl, 0.1 g / L KCl, 0.1 g / L KH2 PO 4 , 0.2 g / L MgSO 4 ×7H 2 O; 0.02 g / L CaCl 2 ×2H 2 O; 20 mg / L nitrilotriacetic acid 10 mg / LMnSO 4 ×H 2 O; 8 mg / L (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 ×6H 2 O; 2 mg / L CoCl 2 ×6H 2 O; 2 mg / L ZnSO 4 ×7H 2 O; 0.2mg / L CuCl 2 ×2H 2 O; 0.2 mg / L Na 2 MoO 4 ×2H 2 O; 0.2 mg / L NiCl 2 ×6H 2 O; 0.2 mg / / L Na 2 SeO 4 ; 0.2 mg / L Na 2 WO 4 ×2H 2 O; 20 μg / L d-biotin, 20 μg / L folic acid, 100 g / L pyridoxine-HCl; 50 μg / L thiamine-HCl × H 2 O; 50 μg / L riboflavin; 50 μg / L niacin, 50 μg / L calcium pantothenate, 1 μg / L vitamin B12; 50 μg / L p-aminobenzoate; 50 μg / L l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com