Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "URA3" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
URA3 is a gene on chromosome V in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast). Its systematic name is YEL021W. URA3 is often used in yeast research as a "marker gene", that is, a gene to label chromosomes or plasmids. URA3 encodes Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase (ODCase), which is an enzyme that catalyzes one reaction in the synthesis of pyrimidine ribonucleotides (a component of RNA).
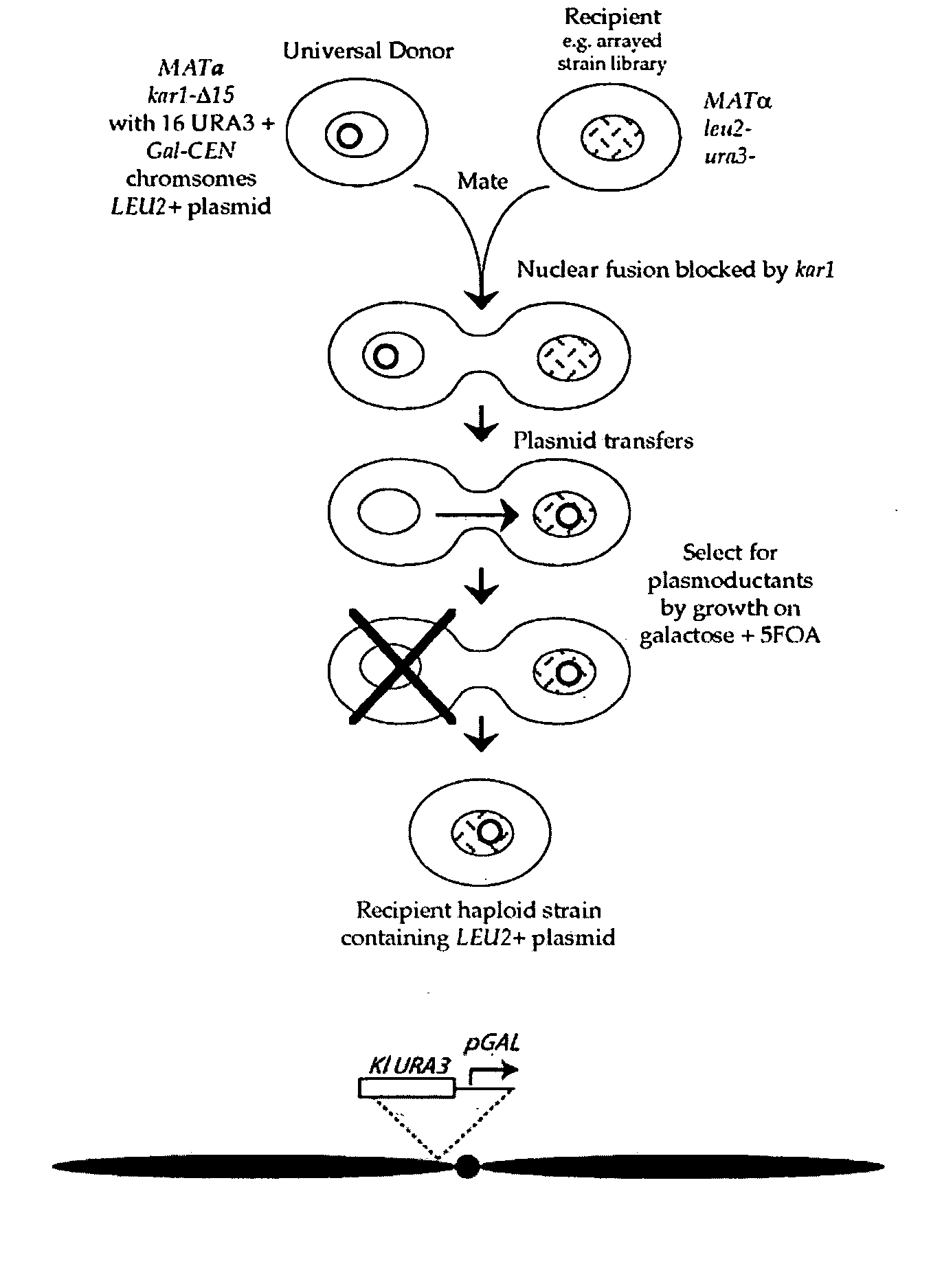
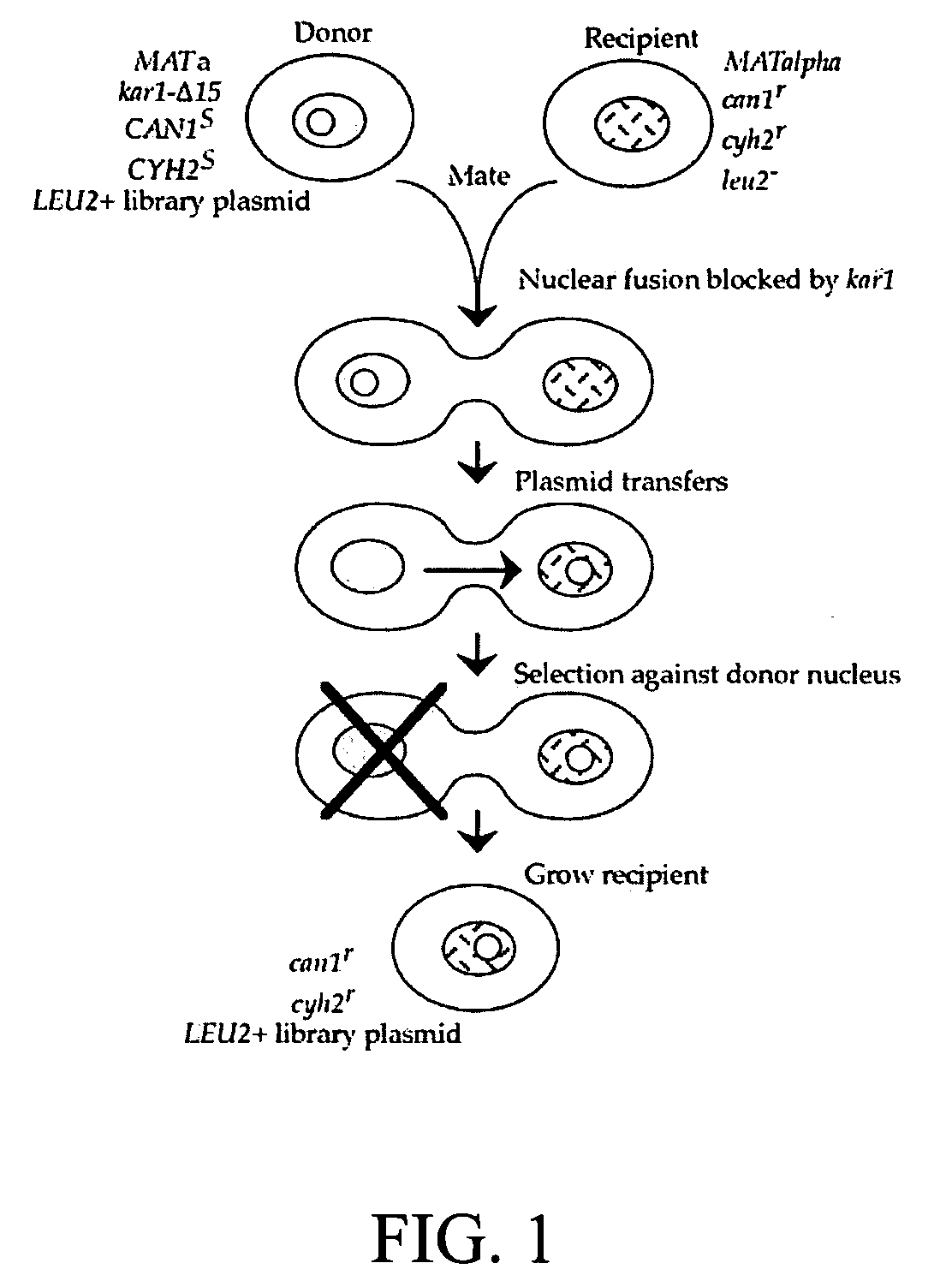
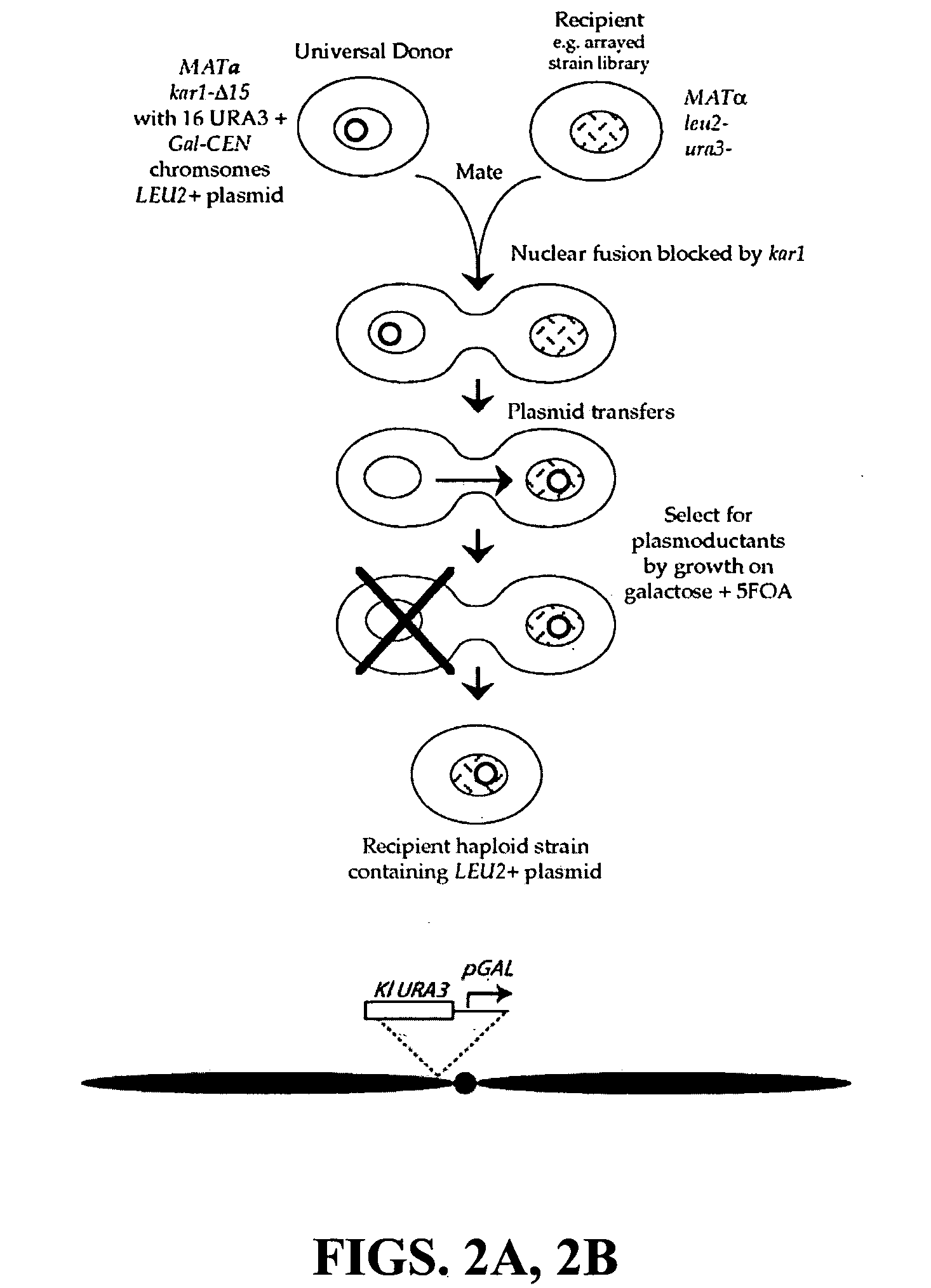
Donor yeast strain for transfer of genetic material
InactiveUS20060105361A1Reduce needSimple methodFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
The invention provides a universal yeast donor strain that contains a conditional centromere and a URA3 allele on every chromosome. This strain was constructed in four rounds of crosses of individual conditional chromosome strains using a novel tetrad-based screen to identify segregants in which all marked chromosomes were contained in the same spore. The invention also provides an improved high efficiency method to transfer extrachromosomal genetic material such as plasmid DNA into any Saccharomyces strain for use with the current gene disruption libraries. The method of transfer is mating-based method which uses a kar1 plasmid donor strain that can initiate mating but cannot form a diploid and allows plasmid transfer (plasmoduction) between nuclei in the heterokaryon. kar1 matings have been used to transfer YACs between yeast strains, but previous methods required specialized genetic backgrounds in the recipient strains and suffered from high rates of spurious chromosome transfer (Hugerat, Y., et al. 1994. Genomics 22:108). Plasmoduction with the universal donor strain only requires that the recipient strain be ura3, GAL+ and have another marker available for selection of the transferred plasmid. Counterselection against every donor chromosome also limits the amount of spurious allele transfer. The universal donor strain and the method of the invention are used to screen the yeast gene disruption library with plasmid-based dominant negative alleles of various genes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Genetically engineered bacterium for expressing human derived acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107815458AKeep aliveImprove stabilityFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationEnzyme GeneMicrobiology
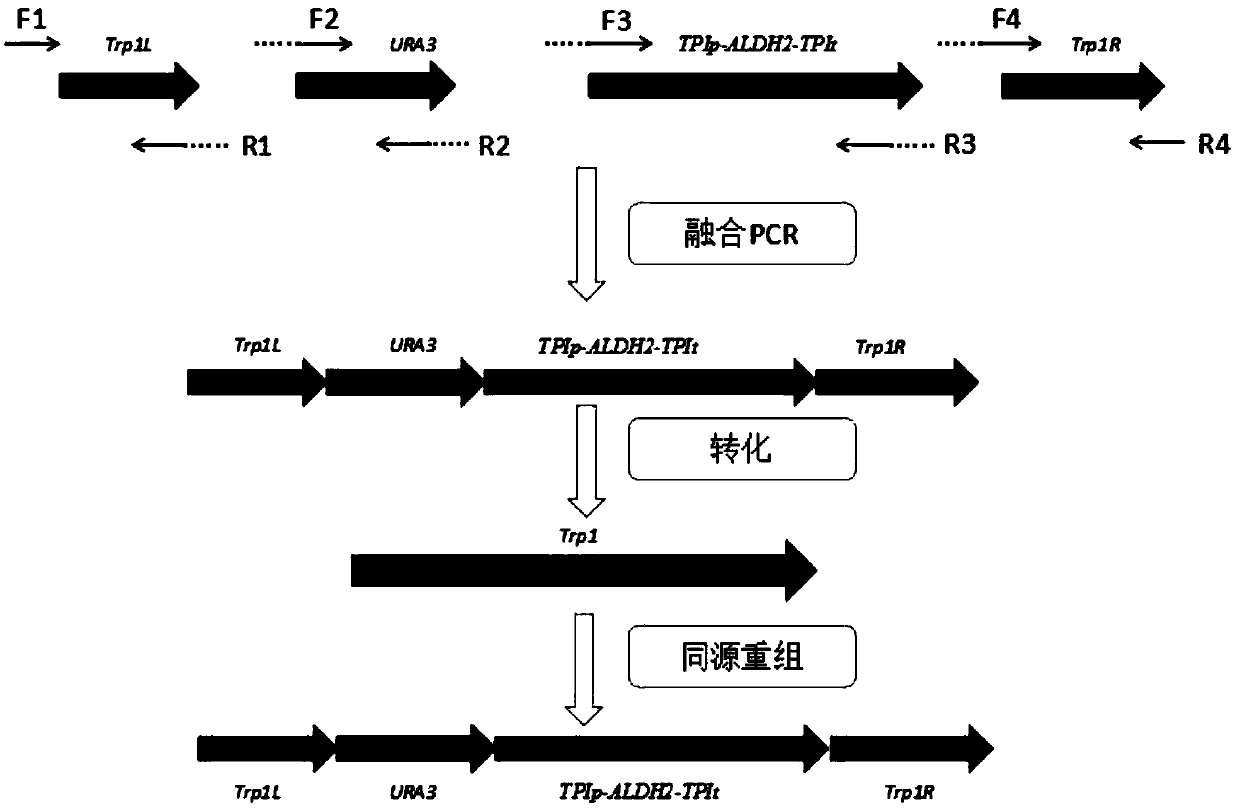
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for expressing a human derived acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme. The ALDH2 gene efficient expression component Trp1L-URA3-TPIp-ALDH2-TPIt-Trp1R is integrated into the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303-1A, the stability of gene expression is improved compared with free plasmid expression, a constitutive promoter is used, no induction agent is added during fermentation, and the product is relatively safe. When fermentation is performed for 96hours, the specific activity of producing acetaldehyde dehydrogenase reaches 0.97 U / mg. The specific activity of the producing acetaldehyde dehydrogenase reaches 6.256 U / mg in ethanol with the concentration of 250 mg / 100 mL, and the specific activity of the producing aldehyde dehydrogenase in a buffer with pH of 3 reaches 0.301 U / mg. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a host strain, on the one hand, the activity of the enzyme is kept, on the other hand, product safety is improved, and a new approach and a theoretical basis are provided for the research and development of antialcoholicdrugs.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV RUGAO FOOD BIOTECH RES INST
Glycerol channel protein gene deleted brewing microzyme strain capable of reducing glycerol output and increasing ethanol output and construction method thereof
ActiveCN1763175AGood physical propertiesIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlycerol
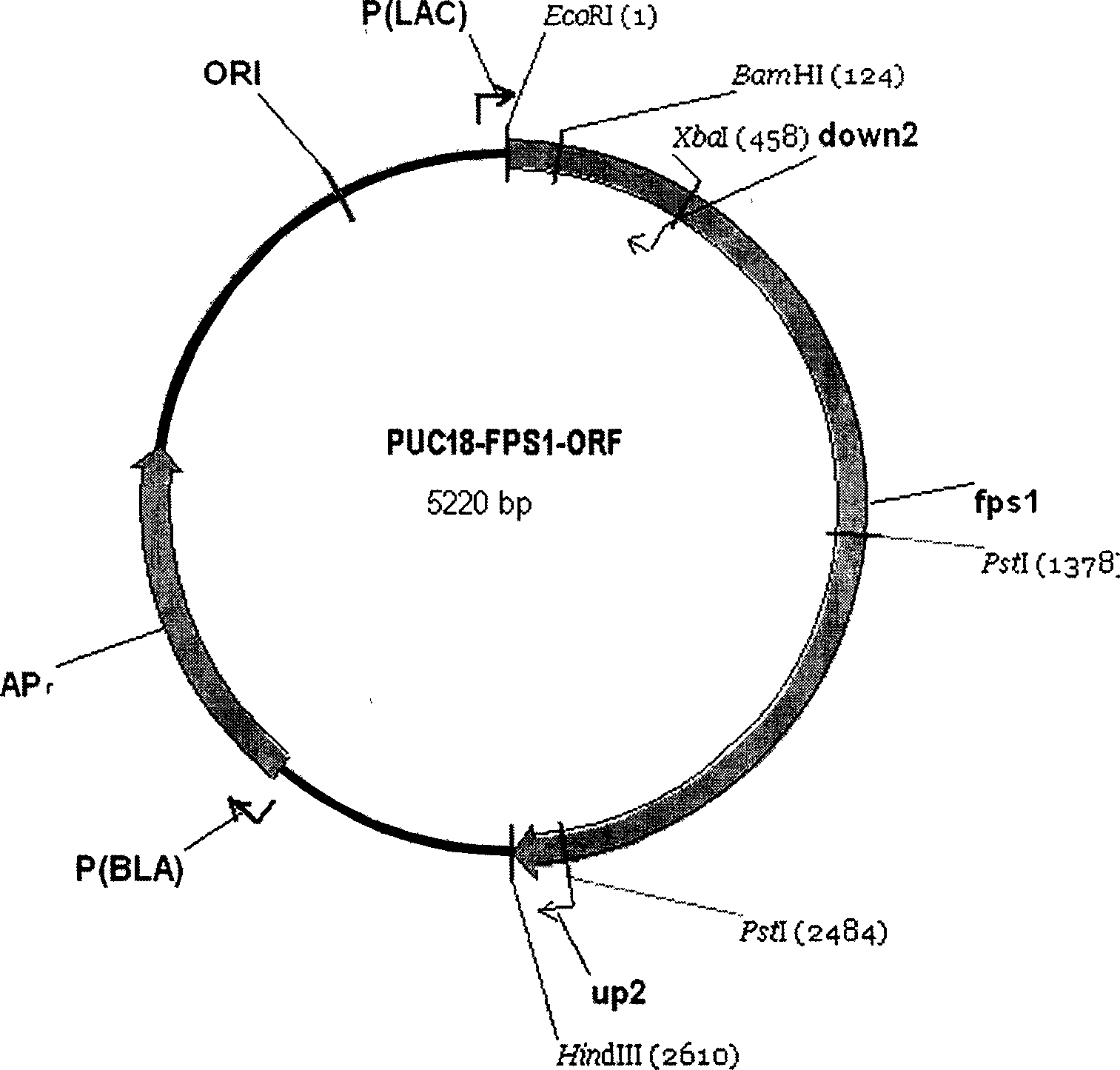
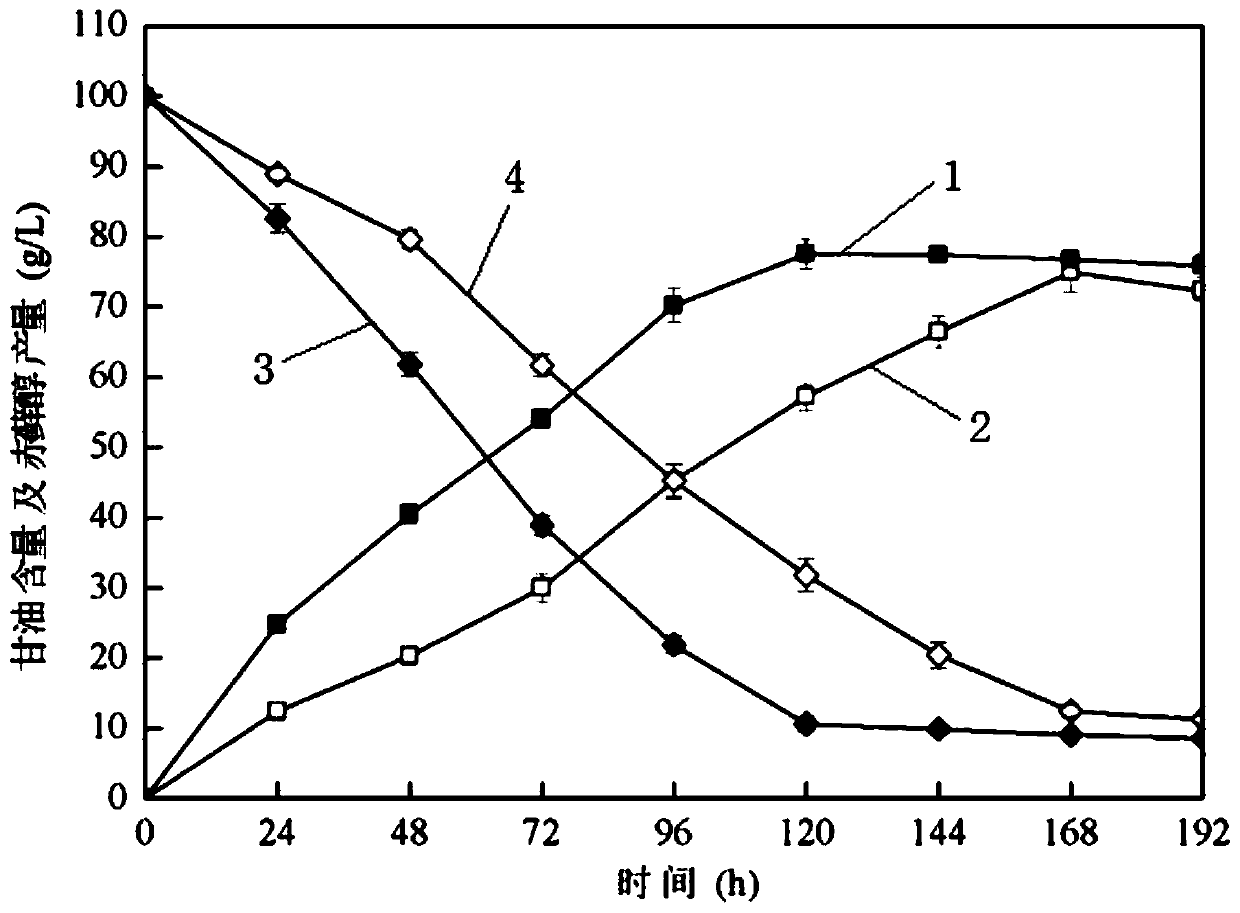
The present invention discloses one kind of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with glycerin passage protein gene deficiency and resulting in lowered glycerin generation and raised ethanol yield and its construction process. The construction process includes the following steps: 1. obtaining Saccharomyces cerevisiae monoploid and deleting of URA3 gene; 2. constructing PUC18-FPS1-ORF plasmid; 3. constructing PUC18-FUF plasmid; and 4. constructing KAM-21 strain. The present invention deletes glycerin passage protein FPS1 gene code embedded on cell membrane and loses the expression of FPS1 gene by means of gene engineering technology, so as to inhibit glycerin synthesizing way, convert from glycerin metabolism to ethanol metabolism, increase ethanol yield, and solve serial problems in ethanol production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation and application of OCH1 genetic flaw type P. pastoris X-33 bacterial strain
InactiveCN102120967AReduce in quantitySmall molecular weightFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastMicrobiology
The invention discloses preparation and application of an alpha-1,6 mannose transferase gene (och1) flaw type P. pastoris X-33 bacterial strain, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The engineering bacterial strain P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) is characterized in that a target gene knockout method by double-exchange homologous recombination is adopted, and a URA3 gene serves as a selective marker to knock out the alpha-1,6 mannose transferase gene (och1) of the P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) to obtain the P. pastoris X-33 (delta och1) bacterial strain with OCH1 gene knockout. The bacterial strain provides a P. pastoris expression system which modifies protein by virtue of low N-glycosylation modification and provides a favourable basis for further glycosylation modification. The bacterial strain has the advantage of great potential application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method
InactiveCN103774241AReduce masking effectLow costLibrary member identificationLibrary creationCDNA libraryGenome scale
The invention discloses a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method. The method takes a genome-grade cDNA as the bait to screen the genome-grade cDNA library. In the application process of the method, the cDNA library is subjected to a homogenization treatment so as to reduce the masking effect of the high-abundance interaction proteins to the low-abundance interaction proteins, and thus the screening efficiency is improved; and moreover the characteristic of yeast URA3 gene is utilized so as to automatically remove the sequences, which have the self-activating function, in bait cDNA. The invention establish a library versus library yeast two-hybrid massive interaction protein screening method, which has the advantages of high feasibility, low cost, low requirements on experiment conditions, and low workload; and successfully applies the method to a screening of pathogen-host plant interaction proteins.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Establishment and application of brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid
ActiveCN105400711ARealize accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseTrimeresurus flavoviridis
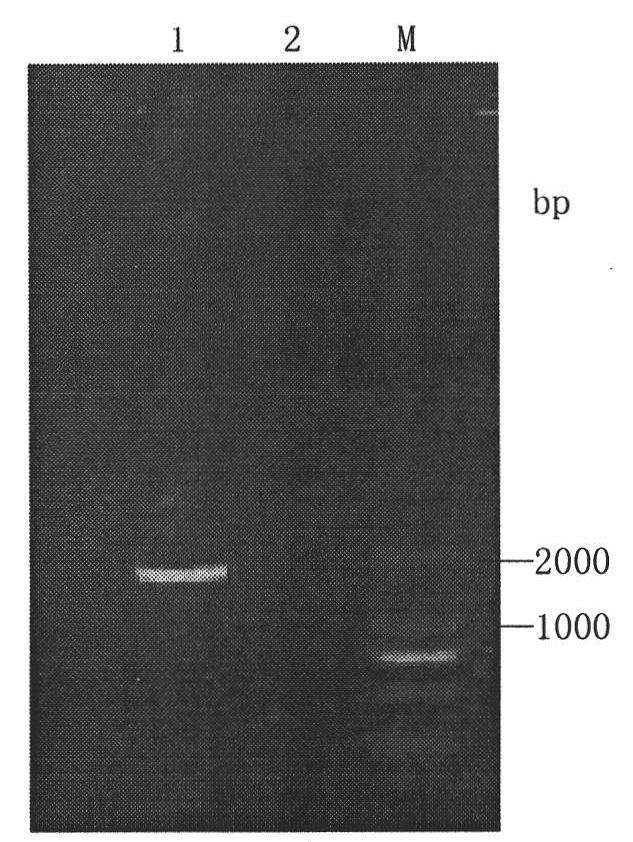
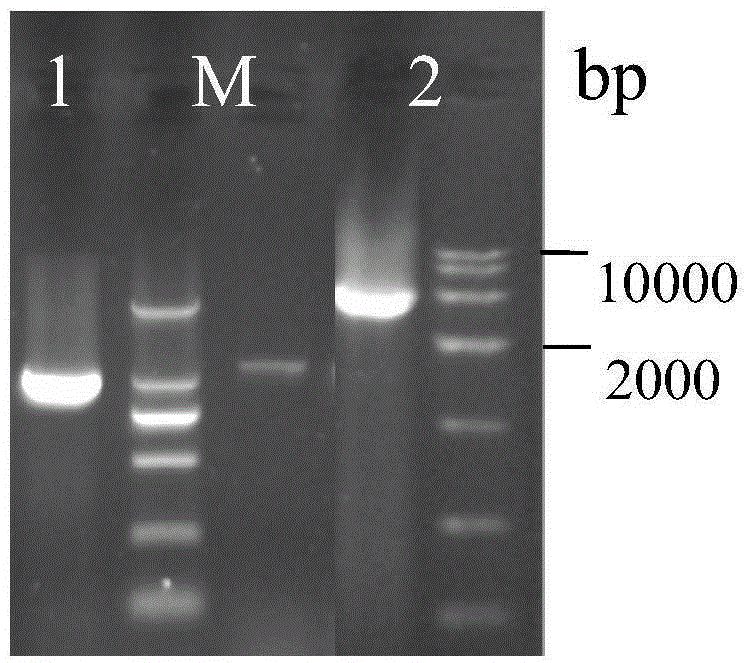
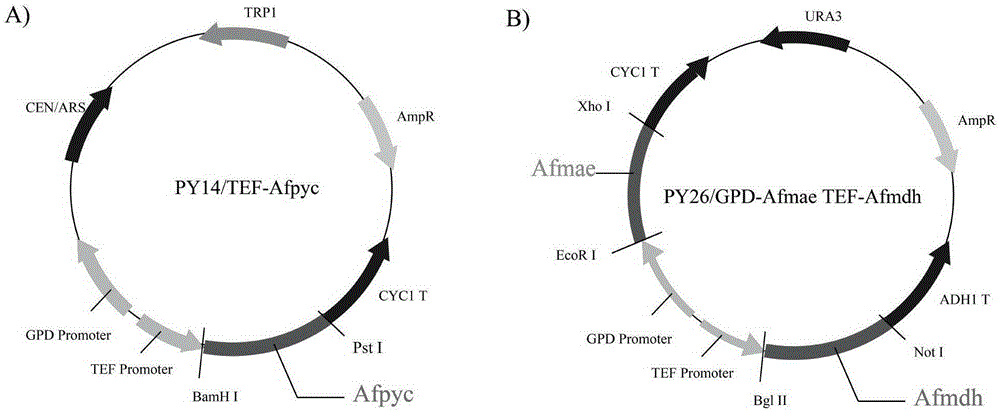
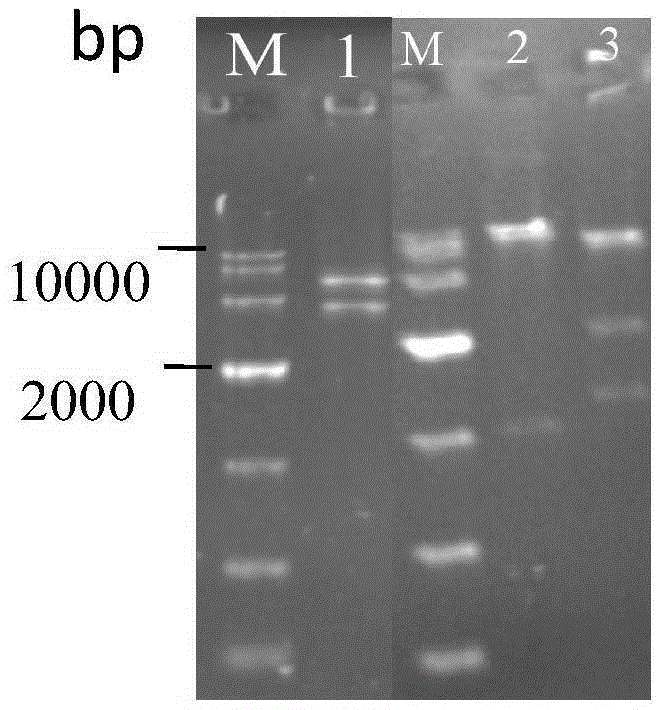
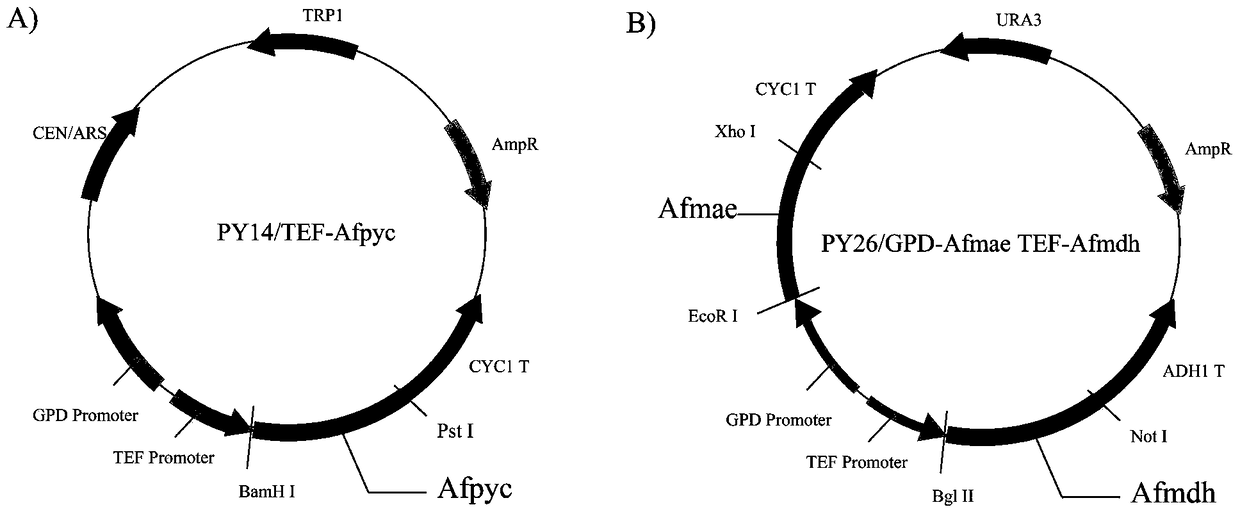
The invention discloses establishment and application of a brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. Genes of pyruvic carboxylase (Afpyc), malic dehydrogenase (Afmdh) and malic acid transport protein (Afmae) coming from Aspergillus flavus ATCC13697 are excessively and dissociatively expressed in the bacterium strain S.cerevisiae tTAM(delta)ura3(delta)trpl high in pyruvic acid yield, the malic acid accumulation path is established, and the bacterium W1101 is obtained. The bacterium strain is used for producing L-malic acid through fermentation; after fermentation is conducted for 84 h, the malic acid yield is 27.3 g / L; an original starting bacterium strain does not accumulate malic acid, the metabolism path of aspergillus flavus of the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain is successfully applied to brewing yeast, and a new strategy is provided for establishing the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Industrial rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacteria with low-yield urea and building method thereof
InactiveCN103710278AHigh biosecurityReduce contentFungiVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyBiology
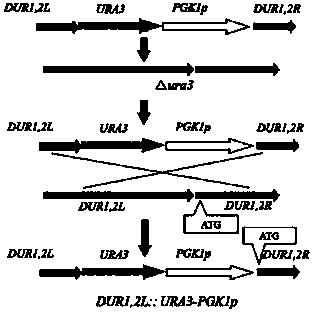
The invention discloses industrial rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacteria with low-yield urea. The building method of the engineering bacteria comprises the following steps: building URA3 gene knockout component, respectively transforming a-type and alpha-type haploid rice wine yeasts, so as to obtain a uracil defect type strain; building a strong promoter containing PGK1p and a high-expression component of a URA3 gene; respectively transforming the a-type and alpha-type haploid rice wine yeasts; integrating into a strain genome by homologous recombination; inserting the PGK1p strong promoter before an initiation codon of a DUR1,2 gene to obtain a prototrophic haploid engineering strain for high expression of the DUR1,2 gene; fusing into diploid again, so as to obtain the industrial rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacteria with low-yield urea. The engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention are prototrophic, the growth and fermentation abilities are very nearly the same as those of a parent strain, the content of urea and EC in a fermentation liquor can be obviously reduced, and no exogenous gene is led in. Therefore, the industrial rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacteria are high in biosecurity and have good industrial application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Yeast for dietary therapy of diabetes and construction method thereof
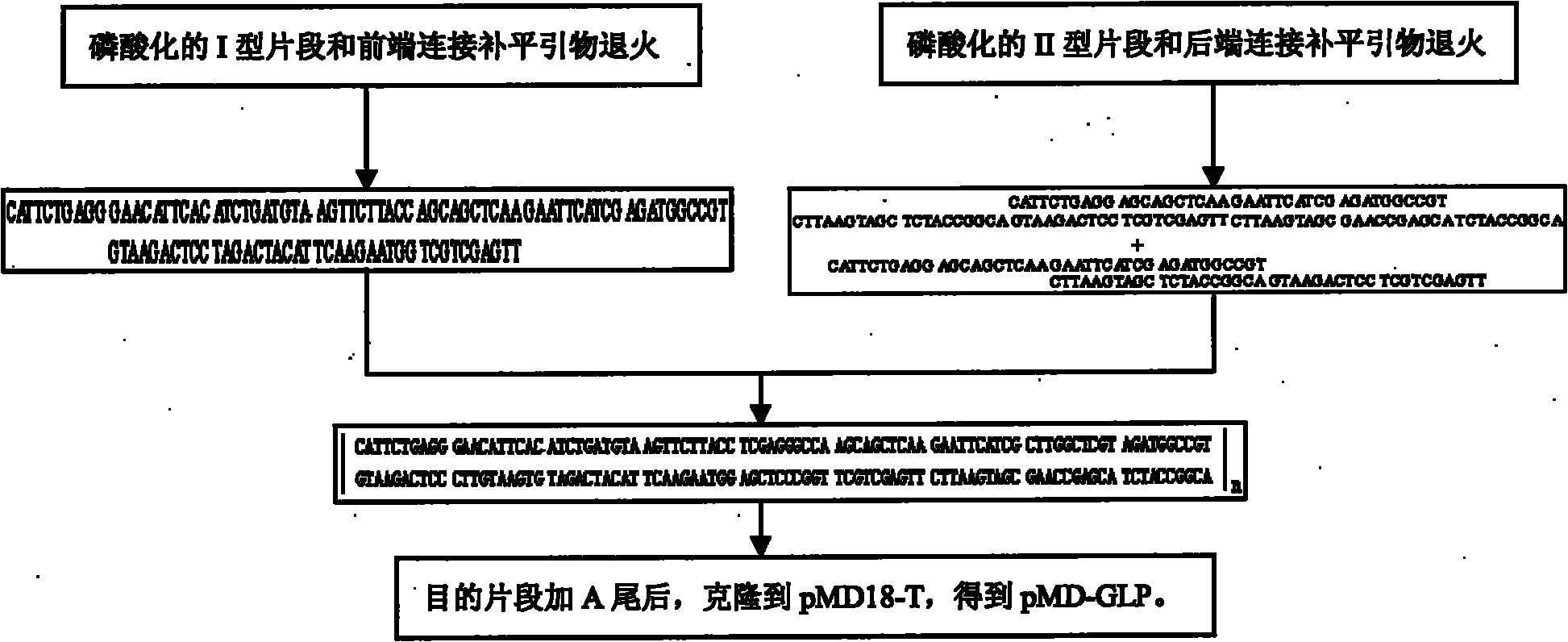
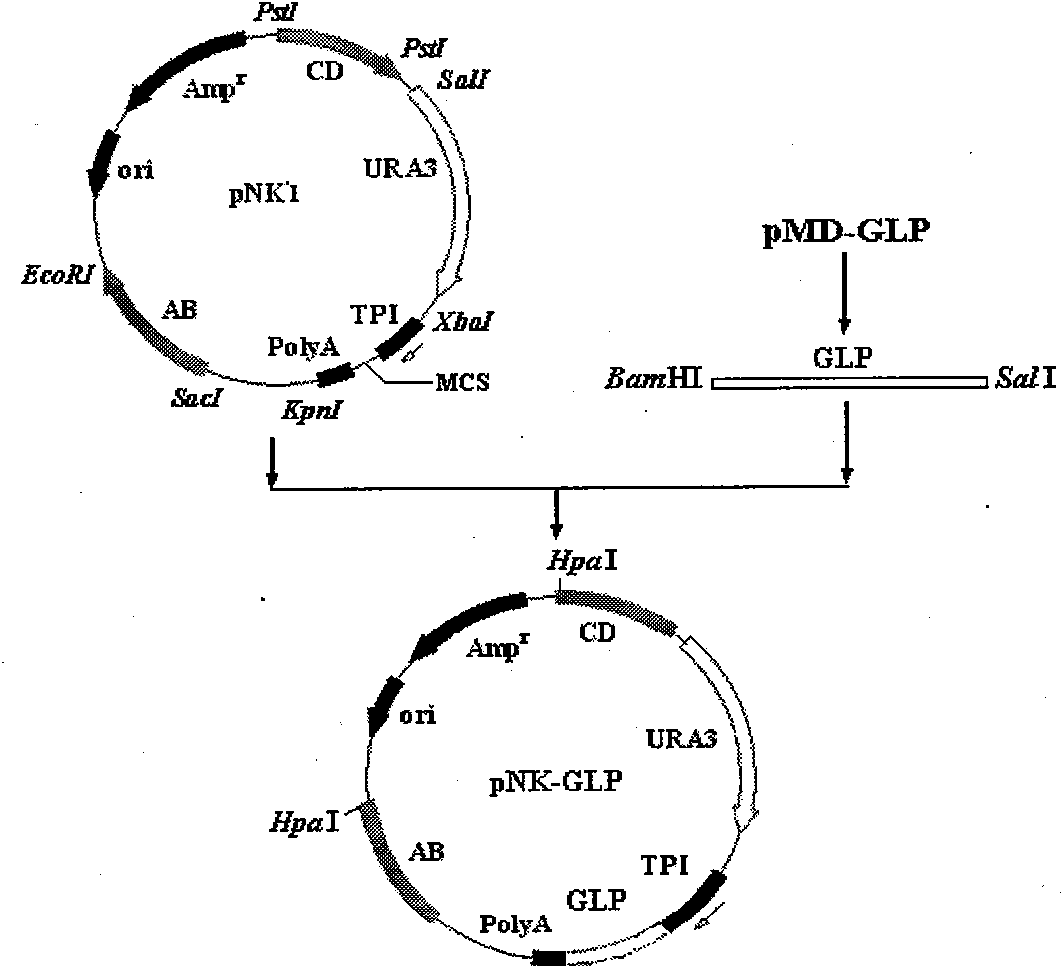
InactiveCN101824388AReduce biological activityImprove bioavailabilityFungiMetabolism disorderYeast chromosomeRestriction site
The invention describes a yeast for the dietary therapy of diabetes and a construction method thereof. A saccharomyces cerevisiae genome DNA as a template is used for amplifying two sections of rDNA sequences; pYX212 as a template is used for amplifying a nutritional marker gene URA3 and an expression cassette segment driven by a triosephosphate isomerase promoter; the four amplified products are respectively cloned at corresponding loci of pUC18, and thereby an integrating vector pNK1 is obtained. A DNA synthesization point mutation technique is then utilized to remove the restriction sites of dipeptidase VI and trypsin in the natural GLP-1 molecule, so that type I primer segments, type II primer segments and left and right connected filling primer segments are synthesized, and a ten-repeat tandem rolGLP-1 sequence is obtained by the method of step-by-step annealing and one-step connection, and is cloned in the pNK1, so that pNK-GLP is obtained. The pNK-GLP is then linearized, saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ2407 is transformed, and after screening, recombinant yeast SG2 is obtained. Because the rolGLP-1 gene is integrated in yeast chromosome, the recombinant strain can stably and efficiently express the characteristics of the rolGLP-1 and reduce the blood sugar level of a rat with hyperglycaemia, and can be used in the development of yeast biomedicine for treating diabetes.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
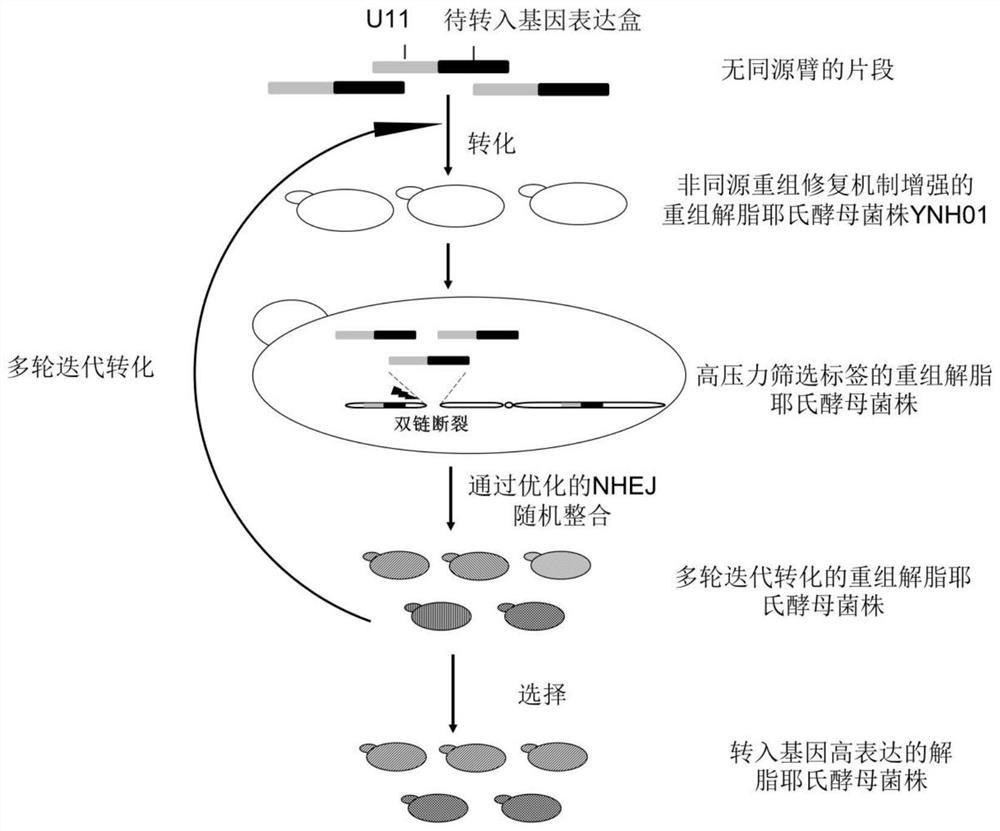
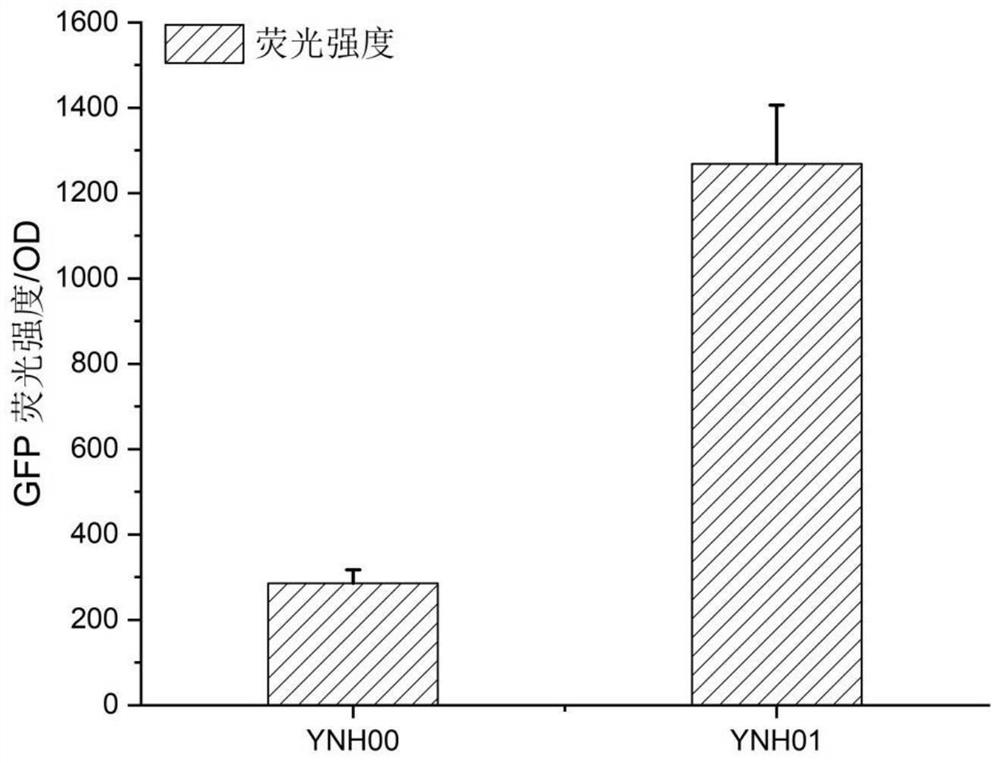
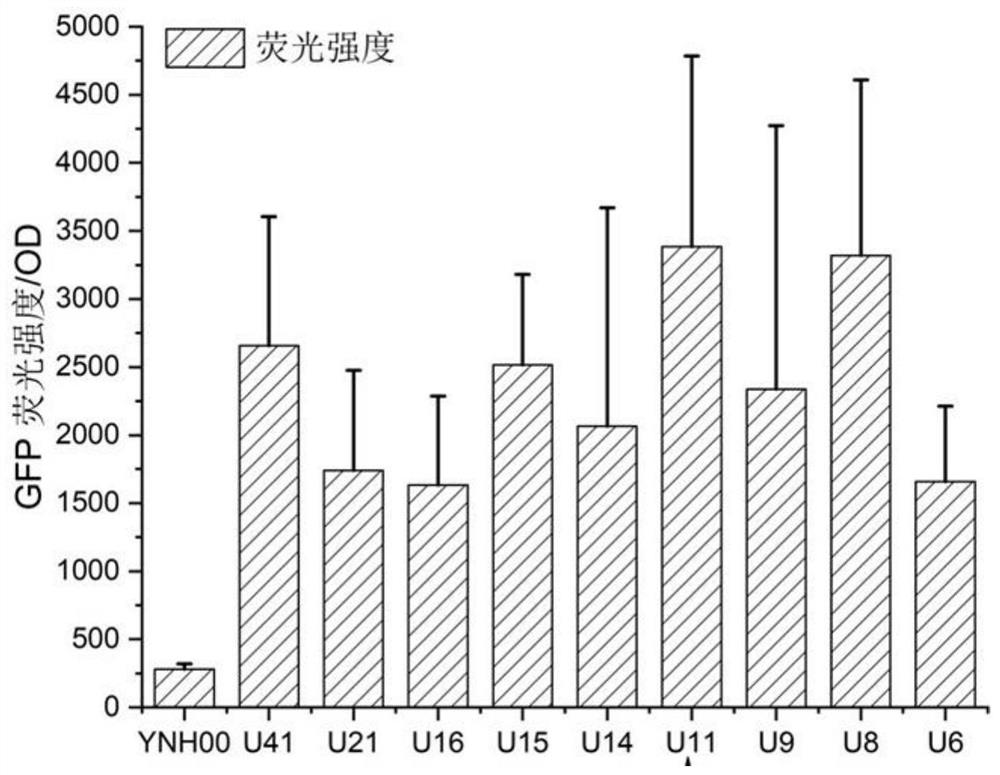
Method for integrating yarrowia lipolytica genome based on non-homologous end-linking mechanism
ActiveCN112251458ASignificant difference in yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationNutritionPromoter
The invention discloses a method for integrating a yarrowia lipolytica genome based on a non-homologous end-linking mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: integrating yarrowia lipolytica endogenous genes DL4 and XRCC4 and an exogenous wisdom gene PAXX into a genome rDNA site of a yarrowia lipolytica ATCC201249 strain in an rDNA site integration manner, so as to obtain a recombinant strain YNH01; linking a to-be-transferred gene expression cassette with a URA3 nutrition tag U11 truncated to 11bp by a promoter, and transforming an obtained linking fragment into the strain YNH01,so as to obtain a high-pressure screening tag strain; transforming the linking fragment into the high-pressure screening tag strain, so as to obtain a recombinant strain subjected to two-round transformation; and transforming the linking fragment into the recombinant strain subjected to two-round transformation again, so as to obtain a transferred gene high-expression strain. According to the method, a large number of diversified strains are obtained within a short time, and the efficient application of an NHEJ integration technology in microbial synthesis of natural products is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Double-fluorescence screening method for fungal gene knockout
ActiveCN110117609AReduce workloadOmit the verification link of southern blot (blot hybridization)Stable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesCompetent cellFungal gene
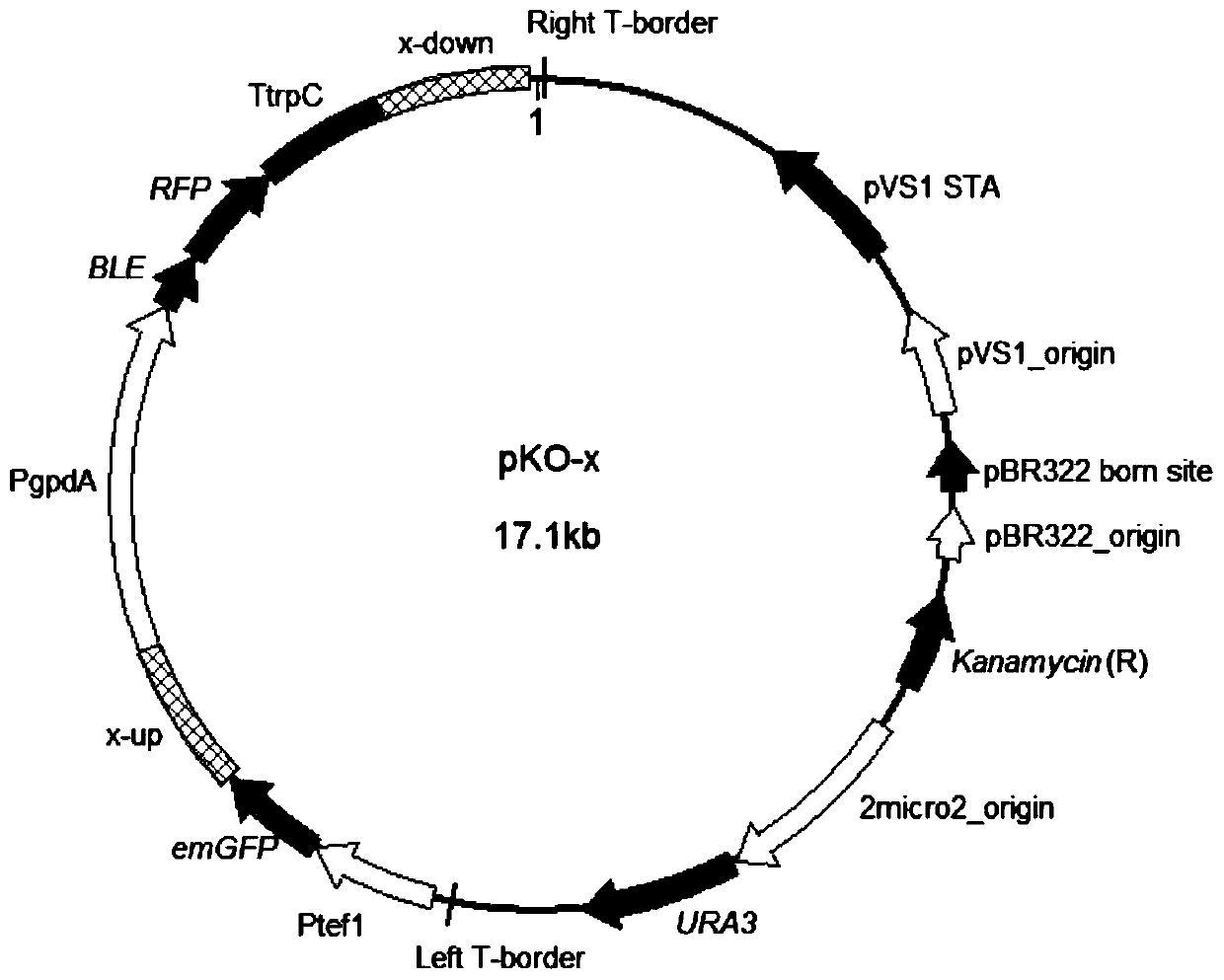
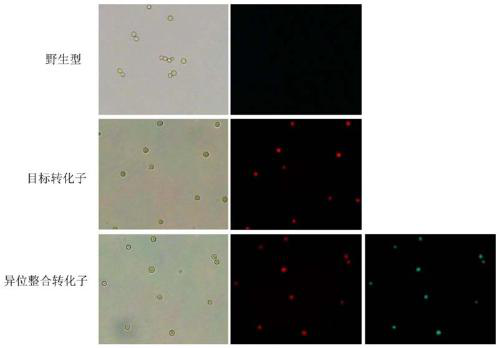
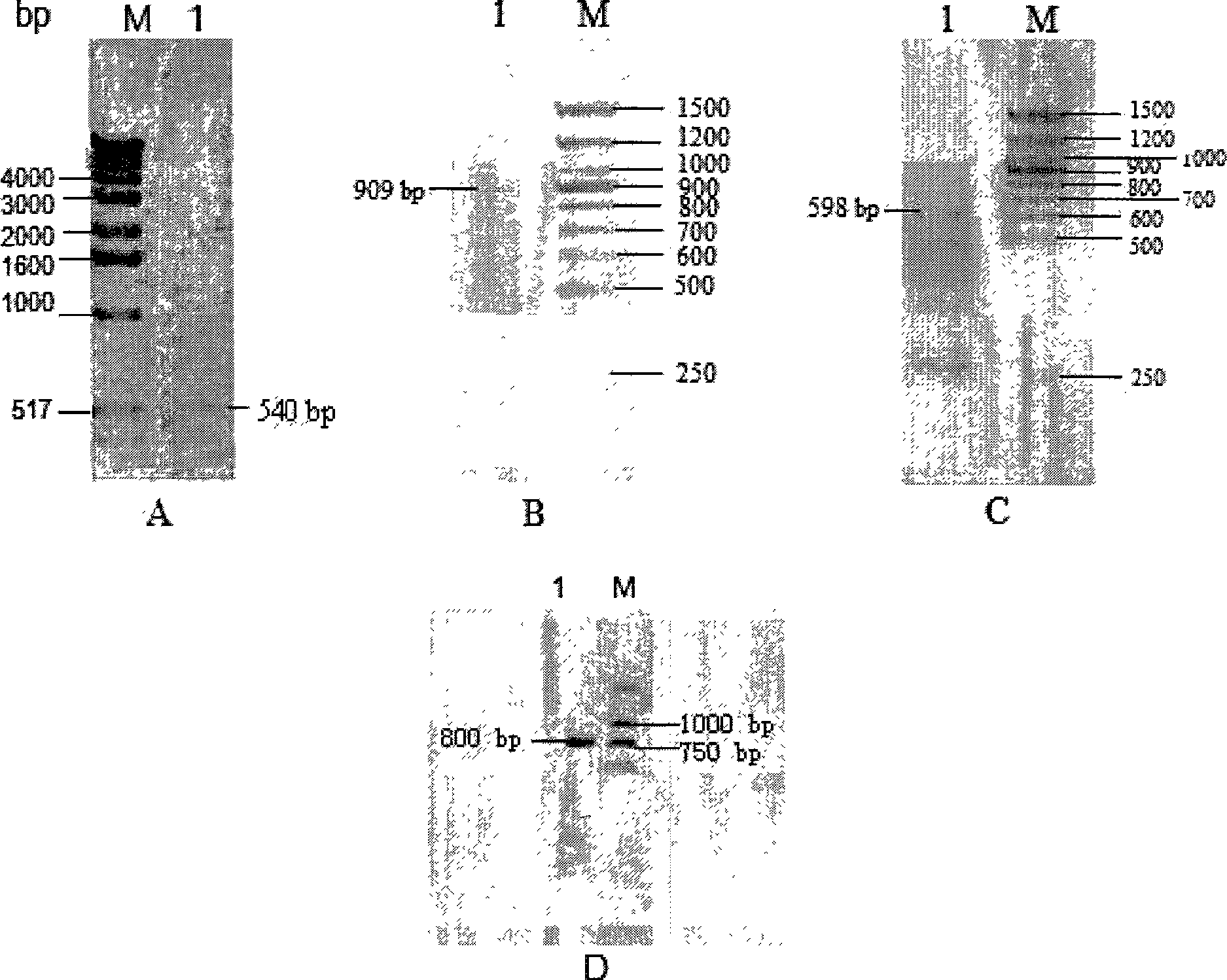
The invention discloses a double-fluorescence screening method for fungal gene knockout, and relates to the technical field of fungal gene knockout. The method comprises the steps that a 2.9-kb URA3-2micro2_origin fragment in a pYES2 carrier DNA template is amplified, the fragment is inserted into a pCAMBIA1300 carrier, and a pUM carrier is obtained; then, a tef1 promoter, an eGFP gene, a PgpdA promoter, a ble resistance gene, an RFP gene, a TtrpC terminator, an upstream homologous arm of a target gene x and a downstream homologous arm of the target gene x are amplified respectively; finally,a knockout carrier pKO-x of the target gene x is established; the pKO-x is transformed into agrobacterium competent cells, fungi is transformed through an agrobacterium mediated method, antibiotic screening is carried out to obtain a resistance transformant, then fluorescence microscope detection is carried out on the resistance transformant, the resistance transformant is a target transformant ifonly red fluorescence is emitted, the resistance transformant is an ectopic integration transformant if both green fluorescence and red fluorescence exist, and the transformant is a wild type if no fluorescence is emitted. The method can be used for effectively distinguishing the target transformant from the ectopic integration transformant.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic reference material for gene detection of alpha-thalassemia and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111893178AEasy to countEasy to calculateFungiHaemoglobins/myoglobinsHereditary MutationThalassemia
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a genetic reference material for gene detection of alpha-thalassemia and a preparation method thereof. The genetic reference material of the invention is to insert yeast cells of a genetic reference material gene required for gene detection of the alpha-thalassemia into a URA3 gene. The invention selects the yeastcells as the background and carriers of genetic mutation, utilizes the advantages that the yeast cells are convenient to storage and culture, simple in genetic operation, high in homologous recombination efficiency, convenient to count and the genome DNA copy number is convenient to calculate and the like, and combines a CRISPR / Cas9 technology to target the URA3 gene to prepare the genetic reference material for gene detection of the alpha-thalassemia, and consistency with human cell sample treatment operations can be achieved through protoplast formation.
Owner:重庆市人口和计划生育科学技术研究院 +1
Orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase gene, and protein and use thereof
ActiveCN101440375AIncrease production intensityImprove utilizationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTotal rna
The invention relates to an orotidine-5'-phosphoric acid decarboxylase gene separated from rhodosporidum toruloides and coding albumen and a recombined vector thereof. The rhodosporidum toruloides AS2.0389 total RNA is taken as a template, the degeneracy PCR and RACE methods are used, Rt-ura3 and cDNA sequences which are as shown in SEQ ID No:1 are obtained by separation, a genome DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No:3, and an amino acid sequence of the coding albumen is as shown in SEQ ID No:2. The obtained vector pYES2 / CT-Rt-ura3 can be used for compensating biosynthesis way of pyrimidine of auxotroph distillers yeast BY4741, and makes constructed engineering strain normally grow in a culture medium without containing uracil. When the Rt-ura3 gene is used as auxotroph marker gene or counter selection marker gene, a new yeast genetic operation system and a new recombined engineering strain can be constructed.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain for secreting and expressing cellulase and building method thereof
ActiveCN108624613AReduce manufacturing costImprove the efficiency of hydrolyzing celluloseFungiStable introduction of DNAGene expressionURA3
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain for secreting and expressing cellulase and a building method thereof. The building method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining host bacteria Kalpha by culturing raw spores by using Angel wine-brewing high-activity dry yeast, screening to obtain a haploid strain with a mating type being an alpha type, and carrying out reverse selection by using a 5-fluororotic acid flat plate to obtain the host bacteria Kalpha; (2) building site-directed integration plasmids of cellulase gene expression boxes; and (3) transforming andscreening the yeasts. The method is capable of achieving site-specific integration, expression and secretion of various cellulase genes in derivative strains of the saccharomyces cerevisiae industrialstrain by repeatedly using the URA3 screening mark; the recombinant strain is capable of effectively improving the efficiency for hydrolyzing cellulose through commercial cellulase; the production cost of the cellulase is reduced; the lignocellulose resource can be efficiently transformed to produce alcohol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Chick pea kluyveromyces expression system and its use
The present invention provides auxotrophic chick pea Kluyveromyces capable of being used in gene engineering host bacillus, polynucleotides carrier constituted with the URA3 of the strain, chemical and electric transforming method to transform foreign gene into host bacillus, and the obtained gene engineering chick pea Kluyveromyces strain with specific foreign gene.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
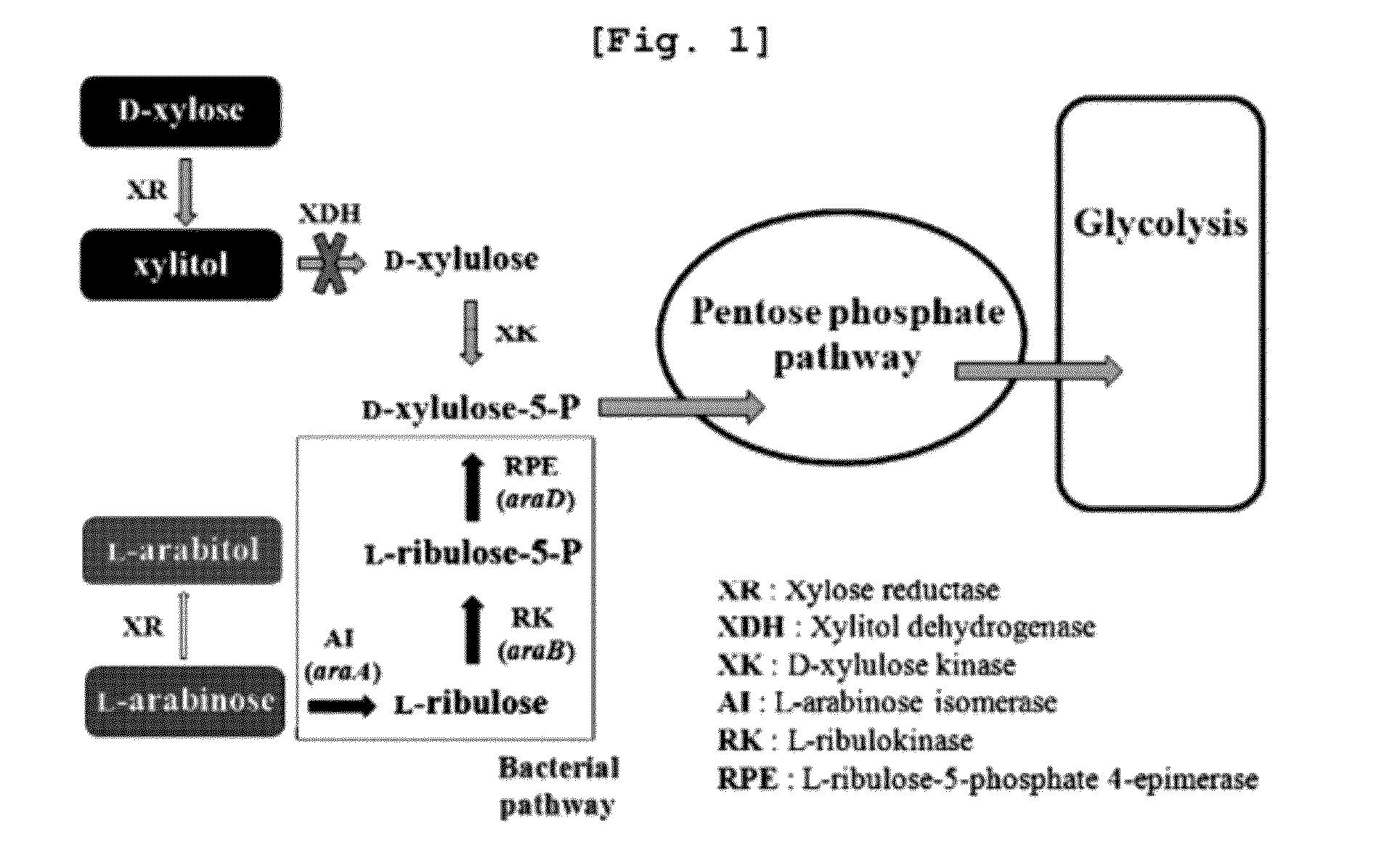
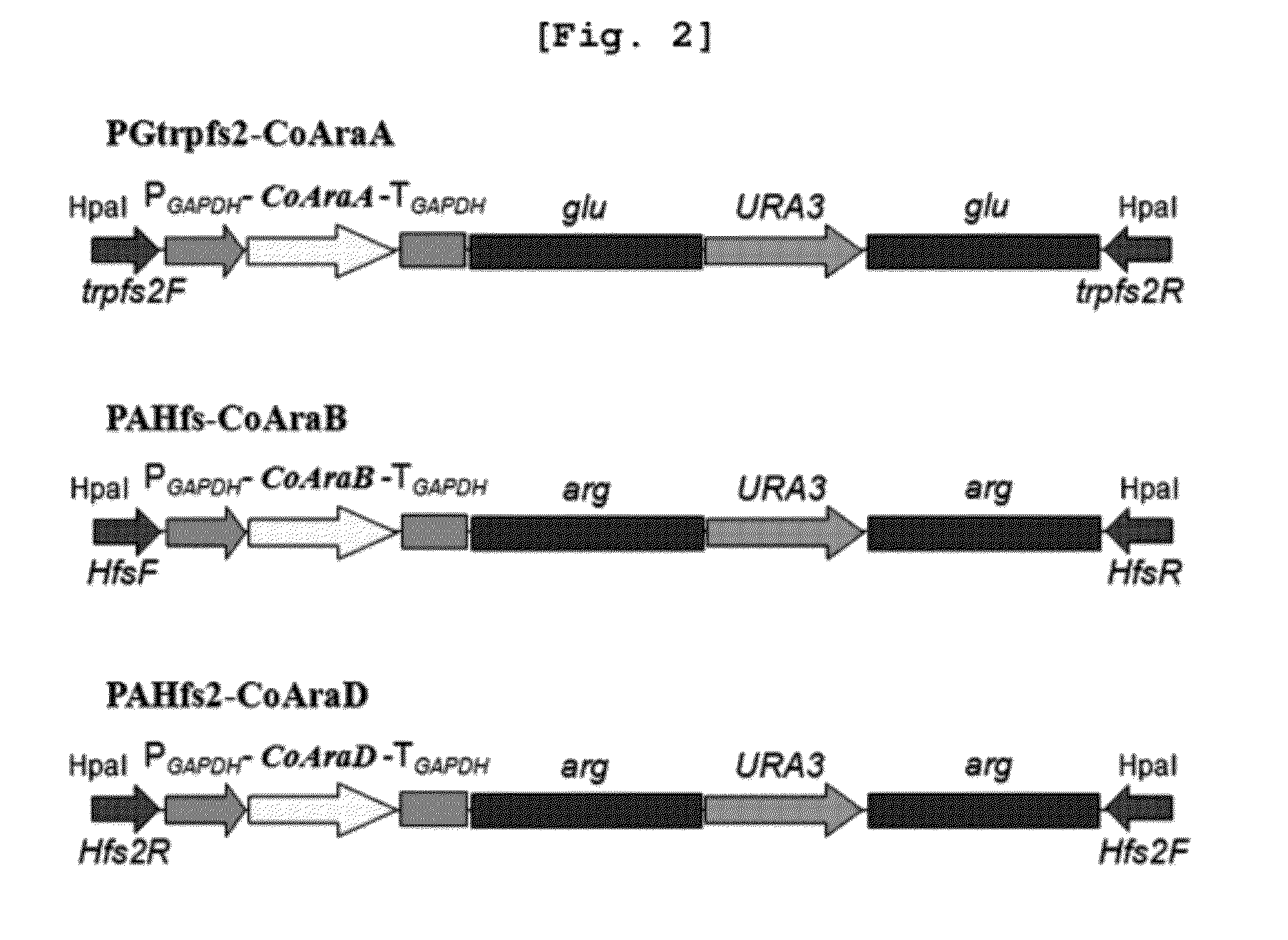
Xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway and production method of xylitol using the same
ActiveUS8343736B2Easy to useImprove productivityMicroorganismsRecombinant DNA-technology[Candida] apicolaArabitol
The present invention relates to an efficient production method of xylitol by using the xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway to inhibit the production of arabitol, the byproduct, and instead to use arabinose only for cell metabolism in xylose / arabinose mixed medium. More precisely, to express efficiently L-arabinose isomerase (araA), L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Candida tropicalis, codon optimization was performed. Then, each gene was inserted in the gene expression cassette containing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and the selection marker URA3, which was introduced into Candida sp. microorganism. As a result, arabitol, the byproduct interrupting the purification and crystallization of xylitol could be inhibited, making the production method of xylitol of the present invention more efficient. The xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway of the present invention can be effectively used for the production of xylitol with high productivity by inhibiting the generation of arabitol.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering bacterium with low yield of citrulline
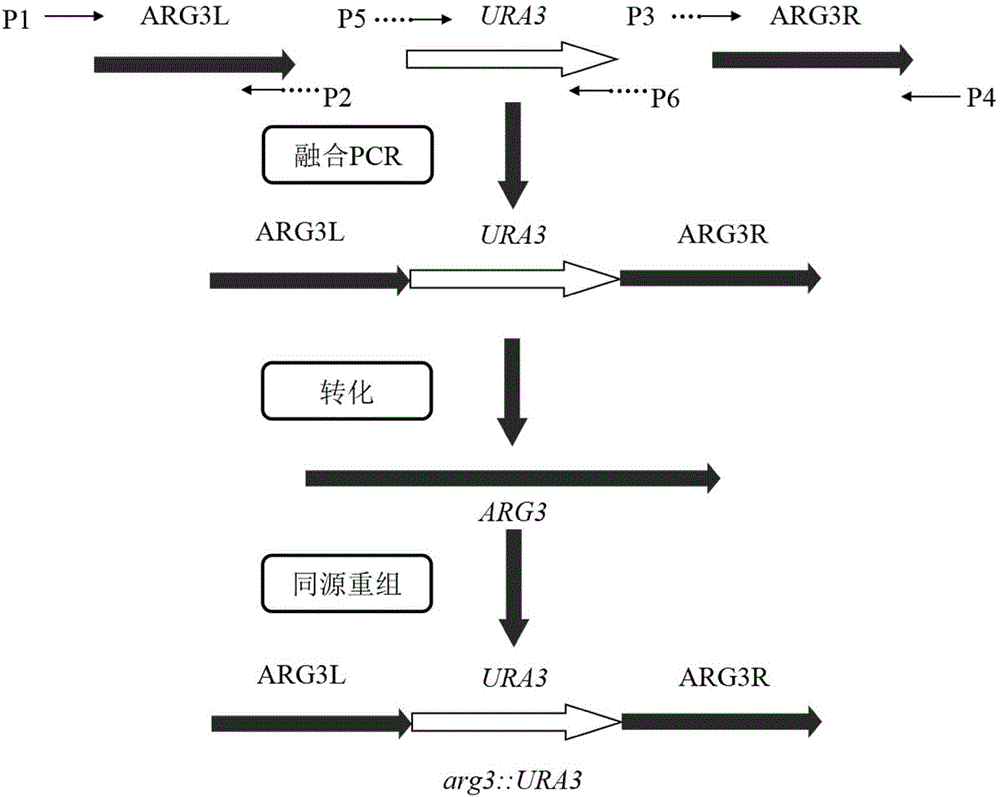
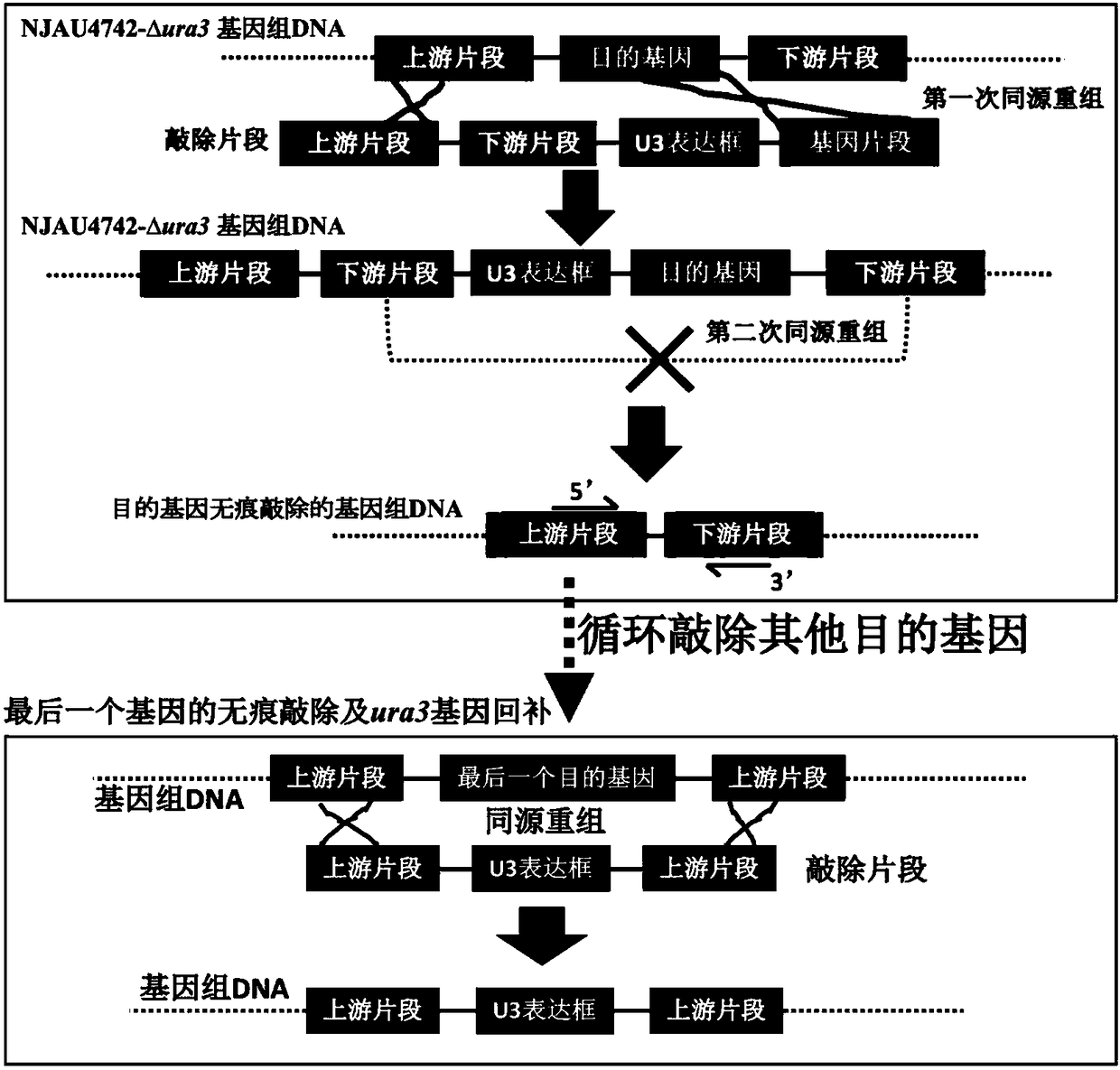
The invention discloses an industrial saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering bacterium with a low yield of citrulline and belongs to the technical field of fermentation and biotechnology. A method comprises the following steps: taking saccharomyces cerevisiae uracil auxotroph recovery as a screening marker for constructing a gene deletion ARG3L-URA3-ARG3R of an encoding gene ARG3 of ornithine carbamoyl transferase; converting into a uracil auxotroph haploid; and inserting a complete saccharomyces cerevisiae URA3 gene into an opening reading frame of the saccharomyces cerevisiae genome ARG3 through homologous recombination, thereby acquiring the haploid engineering bacterium without the ARG3 gene. The yeast engineering bacterium acquired according to the method is a prototrophy bacterial strain, contains no exogenous gene and has bio-security; the growth and fermentation properties of the engineering bacterium are similar to those of the original strain in a rice juice fermentation process, but the content of citrulline is reduced by 39.0%; and a new idea for reducing the EC content in industrial production is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi
ActiveCN108384797ASolve scientific research problems that are extremely difficult to operateRealize traceless recyclable operationFungiStable introduction of DNAHygromycin BGene Position
The invention relates to a traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi. According to the method, the traceless knockout mutant of the trichoderma guizhouense ura3 gene is obtained through twotimes of homologous recombination events and in combination with the resistance screening strategy of hygromycin B and the lethal strategy of 5-FOA; based on the mutant, the knockout fragment containing the ura3 gene expression cassette is inserted at the position of the target gene through the homologous recombination method, and the mutant having the first-time homologous recombination is screened by utilizing the nutrition defect feature of the ura3 traceless mutant; after the second-time homologous recombination, the ura3 gene and the target gene are removed through recombination, at the time, inverse screening is carried out by utilizing the lethal feature of 5-FOA, and thus the traceless mutant with the target gene completely deleted is obtained. The system is optimized sufficiently,the homologous recombination ratio is 15% or above, the single-gene traceless operating period is shortened to be within 15 days, meanwhile, the traceless overexpression of the target gene can be realized, and no exogenous fragments are introduced during the process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Construction and application of URA3 defective P. pastoris X-33 strain
The invention discloses construction and application of an orotidine-5'- phosphate decarboxylase (ura3) defective P. pastoris X-33 strain, belonging to the technical field of biologic engineering. The engineering strain P. pastoris X-33 (delta ura3) is obtained by a homologous recombination target gene knockout method. The strain can use the ura3 gene as a selected marker for constructing different kinds of engineering strains, and when the engineering strains are constructed, the carried ura3 genes are not required to be from the same microbial population. Simultaneously, the invention provides a better platform strain for performing subsequent engineering reconstruction such as glycosylation reconstruction on the X33, thus having great potential application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant yeast strain for fermenting erythritol under high nitrogen condition, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110129381AImprove filtration efficiencyAddressing Fermentation DelaysMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain for fermenting erythritol under high nitrogen condition, a construction method and an application thereof. The recombinant strain is constructed by:obtaining the SNF1 gene in the whole genome of Yarrowia lipolytica, using the Yarrowia lipolytica genome as a template to separately amplify the upstream and downstream fragments of the SNF1 gene andthe URA3 fragment by PCR reaction, ligating the upstream and downstream fragments of the SNF1 gene to the upstream and downstream of the URA3 fragments by an overlap extension PCR method to obtain aSNF1 gene knockout component, transferring the SNF1 gene knockout module to the selected uracil-deficient Yarrowia lipolytica strain, and screening to obtain the Yarrowia lipolytica recombinant strainin which the SNF1 gene was knocked out. The strain eliminates the coupling between nitrogen hunger stress and erythritol synthesis by knocking out the SNF1 gene of Snf1 protein. The recombinant yeaststrain of the invention can synthesize erythritol under high nitrogen conditions, and the fermentation efficiency is obviously improved, which solves the problem of delayed fermentation and low yieldin industrial production of erythritol.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Construction and application of an engineered strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing l-malic acid
ActiveCN105400711BRealize accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseAspergillus flavus
The invention discloses establishment and application of a brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. Genes of pyruvic carboxylase (Afpyc), malic dehydrogenase (Afmdh) and malic acid transport protein (Afmae) coming from Aspergillus flavus ATCC13697 are excessively and dissociatively expressed in the bacterium strain S.cerevisiae tTAM(delta)ura3(delta)trpl high in pyruvic acid yield, the malic acid accumulation path is established, and the bacterium W1101 is obtained. The bacterium strain is used for producing L-malic acid through fermentation; after fermentation is conducted for 84 h, the malic acid yield is 27.3 g / L; an original starting bacterium strain does not accumulate malic acid, the metabolism path of aspergillus flavus of the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain is successfully applied to brewing yeast, and a new strategy is provided for establishing the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pichia pastoris efficient gene knockout method
InactiveCN109082444AEfficient enrichmentStrong specificityFungiStable introduction of DNAPichia pastorisYeast
The invention provides a pichia pastoris efficient gene knockout method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a knockout plasmid pGE1203-ADE-URA3 through a plasmid pYES2; S2, enabling the knockout plasmid to be knocked-in the upstream and the downstream of a target gene och1 in a pichia pastoris group; and S3, identifying a protein with plasmid knockout activity, shearing a nucleotide sequence, and knocking-out the target gene och1, to obtain pichia pastoris in which the target gene och1 is knocked-out. The method is capable of effectively improving galactosylated modification of the pichia pastoris to the protein, solving a problem of fused protein hyperglyeosylation, and efficiently knocking-out the och1 gene of the pichia pastoris.
Owner:惠州卫生职业技术学院
Method for introducing site-specific mutagenesis rapidly and efficiently
InactiveCN103589748AAvoid spreadingEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
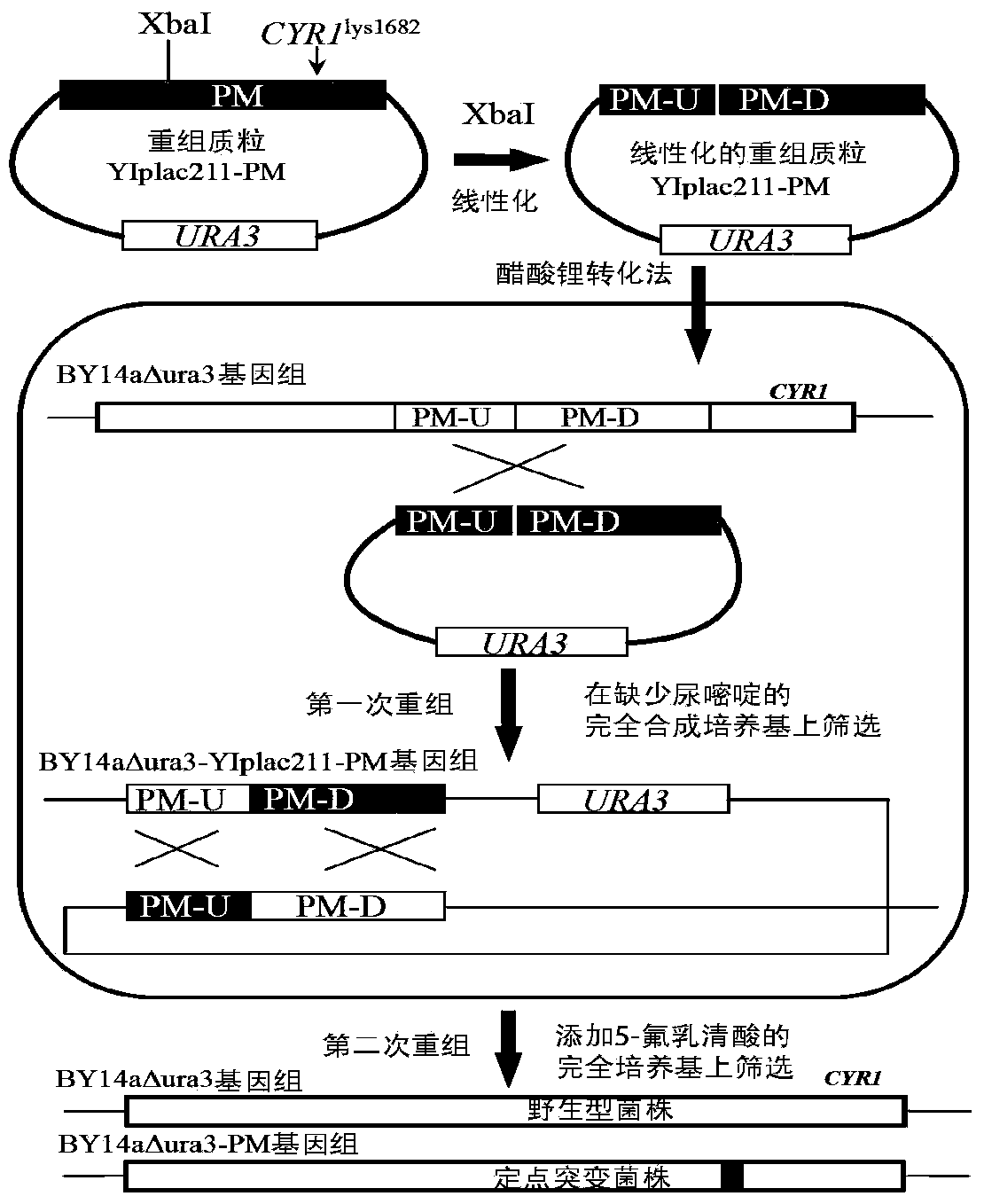
The invention discloses a method for introducing site-specific mutagenesis rapidly and efficiently. The method provided by the invention can realize the introduction of site-specific mutagenesis by using an integrated plasmid YIplac211 as the carrier, selecting URA3 gene carried by the integrated plasmid as selection marker, and carrying out homologous recombination of direct repeats twice. According to the invention, no exogenous gene remains during the introduction of site-specific mutagenesis so as to ensure the safety of strains. Additionally, the method provided by the invention can also use other industrial strains besides yeast.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Xylitol Producing Microorganism Introduced with Arabinose Metabolic Pathway and Production Method of Xylitol Using the Same
ActiveUS20120171739A1Easy to useImprove productivityFungiRecombinant DNA-technologyD-arabitolCandida tropicalis
The present invention relates to an efficient production method of xylitol by using the xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway to inhibit the production of arabitol, the byproduct, and instead to use arabinose only for cell metabolism in xylose / arabinose mixed medium. More precisely, to express efficiently L-arabinose isomerase (araA), L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Candida tropicalis, codon optimization was performed. Then, each gene was inserted in the gene expression cassette containing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and the selection marker URA3, which was introduced into Candida sp. microorganism. As a result, arabitol, the byproduct interrupting the purification and crystallization of xylitol could be inhibited, making the production method of xylitol of the present invention more efficient. The xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway of the present invention can be effectively used for the production of xylitol with high productivity by inhibiting the generation of arabitol.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
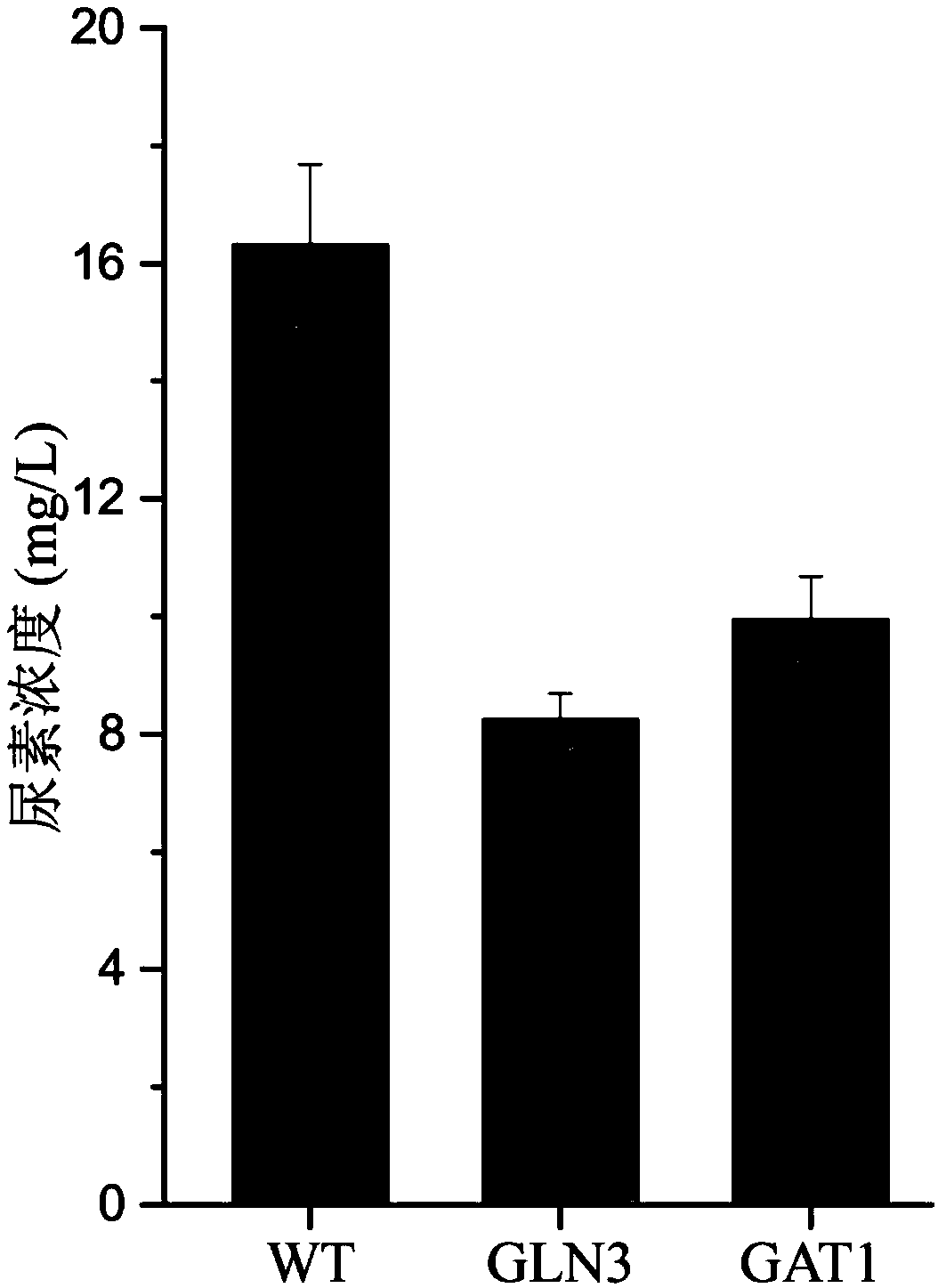
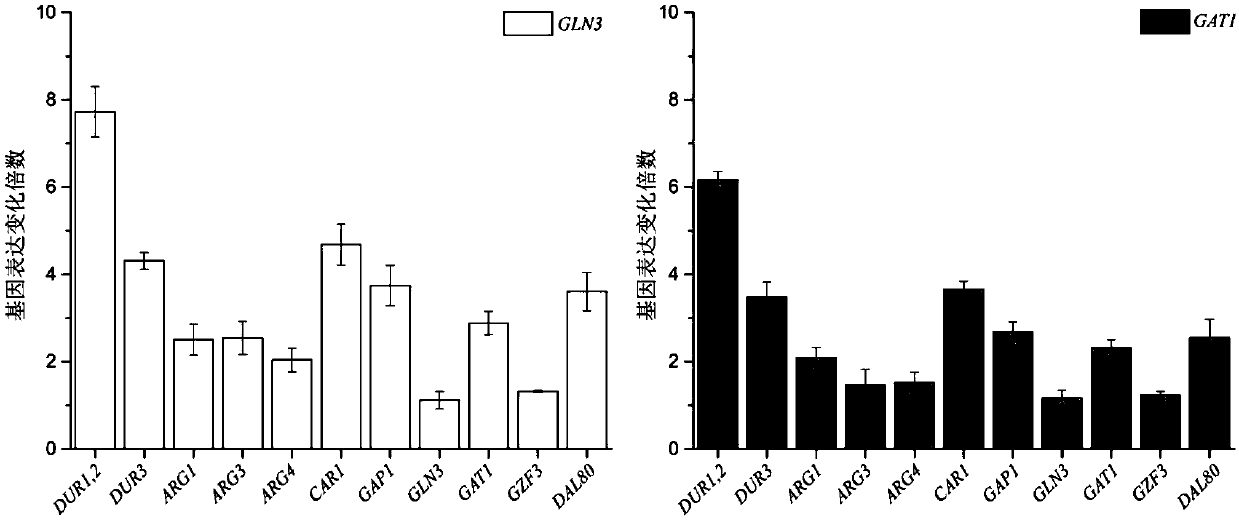
Method for reducing yellow wine yeast urea accumulation by regulating and controlling activating transcription factors
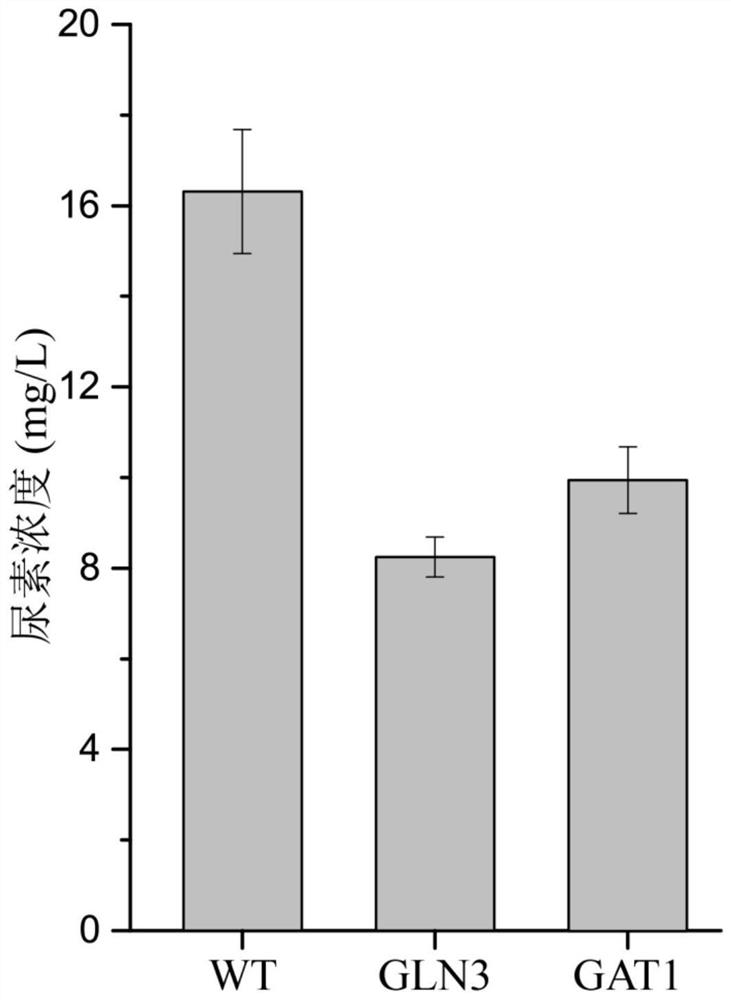
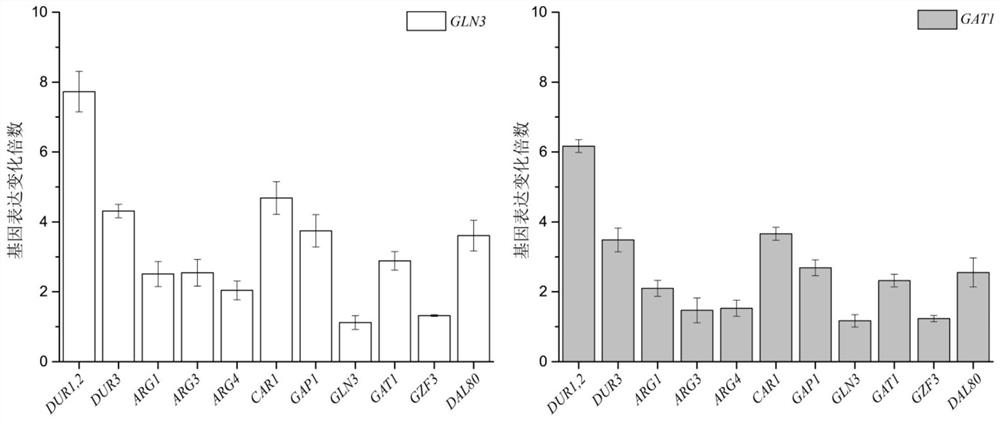
The invention discloses a method for reducing yellow wine yeast urea accumulation by regulating and controlling activating transcription factors, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Recombinant yellow wine yeast JNZ01 (MATa, delta ura3, delta trp1,TOR1S1972R, delta fpr1) are used as original strains; GLN3, FKBP12, GAT1 or FKBP12 is subjected to fusion expression on a genome; SPT15 andFRB are subjected to fusion expression on plasmid; by adding rapamycin, FKBP12 and FRB are combined. On the basis, Gln3 and Gat1 are transferred to the cell nucleus under the effect of cell nucleus location protein Spt15; activation urea uses related gene transcription, so that the urea accumulation in the fermentation process is respectively reduced by 49.45 percent and 38.98 percent and is respectively reduced to 8.25 mg / L and 9.95mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
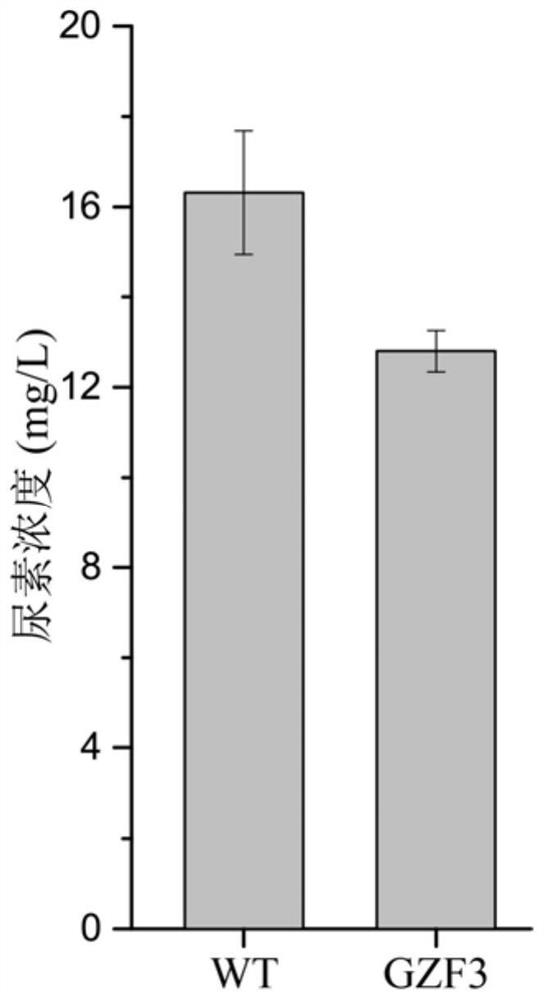
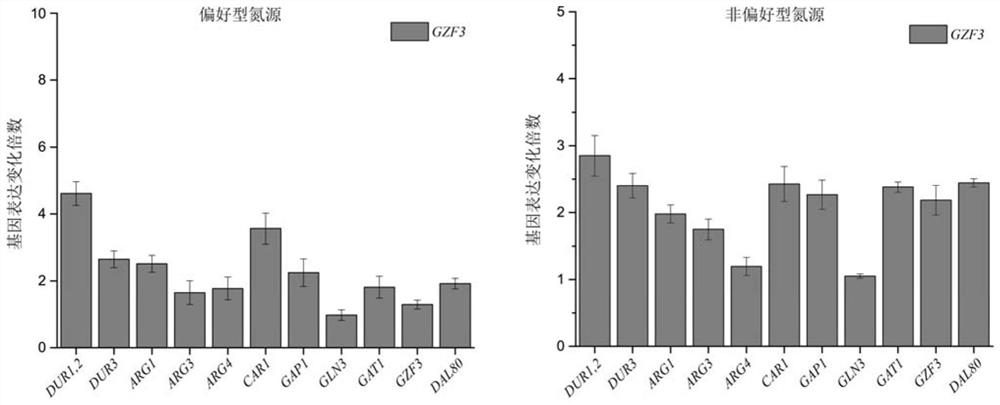
A method to localize gzf3 to the cytoplasm to reduce urea accumulation in rice wine yeast
The invention discloses a method for positioning Gzf3 on cytoplasm to reduce urea accumulation of yellow rice wine yeast and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the method, recombinant yellow rice wine yeast JNZ01 (MATa, delta ura3, delta trp1, TOR1S1972R and delta fpr1) is used as a starting strain, GZF3 and FKBP12 are fused and expressed on a genome, and RPL13A and FRB arefused and expressed on a plasmid; rapamycin is added to combine the FKBP12 and the FRB. On the basis, the Gzf3 is transferred to the cytoplasm under the action of cytoplasm positioning protein Rpl13Aand urea is activated; related genes are transcribed to reduce the accumulation of the urea in a fermentation process is reduced by 21.51 percent and the accumulation of the urea is reduced to 12.80 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Expression vector based on URA3 gene and construction method thereof
PendingCN111850017ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCloning Site
The invention provides an expression vector based on a URA3 gene and a construction method of the expression vector. The vector sequentially comprises a URA3 homologous arm, a strong promoter, multiple cloning sites, a terminator, a URA3 homologous arm or a URA3 promoter or a URA3 terminator. The construction method comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA of a target species; designing aprimer for amplification to obtain a URA3 homologous arm, a strong promoter, a terminator, a URA3 homologous arm or a URA3 promoter element or a URA3 terminator element; obtaining other elements; andconnecting the recombinase with a plurality of elements to obtain the complete vector in one step.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAZHEN PHARM CO LTD
A method of regulating transcriptional activators to reduce urea accumulation in rice wine yeast
The invention discloses a method for reducing yellow wine yeast urea accumulation by regulating and controlling activating transcription factors, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Recombinant yellow wine yeast JNZ01 (MATa, delta ura3, delta trp1,TOR1S1972R, delta fpr1) are used as original strains; GLN3, FKBP12, GAT1 or FKBP12 is subjected to fusion expression on a genome; SPT15 andFRB are subjected to fusion expression on plasmid; by adding rapamycin, FKBP12 and FRB are combined. On the basis, Gln3 and Gat1 are transferred to the cell nucleus under the effect of cell nucleus location protein Spt15; activation urea uses related gene transcription, so that the urea accumulation in the fermentation process is respectively reduced by 49.45 percent and 38.98 percent and is respectively reduced to 8.25 mg / L and 9.95mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
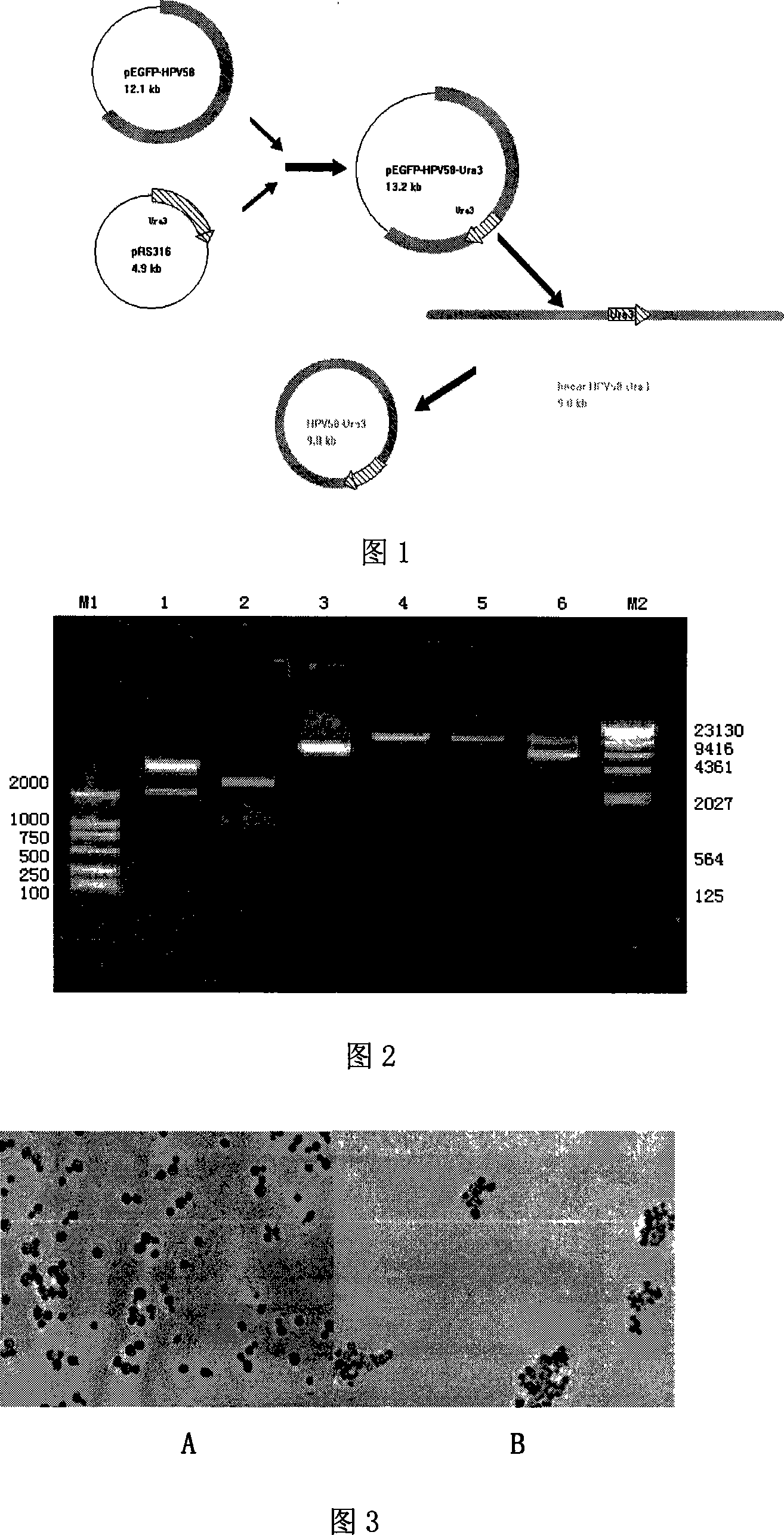
Yeast proliferation model of human papilloma virus as well as constructing method and uses
InactiveCN101200696AReduce distractionsImprove cyclization efficiencyFungiVector-based foreign material introductionForeign proteinHPV vaccines
The present invention discloses a human papilloma virus cerevisiae proliferation model and a preparation method, which is the saccharomyces cerevisiae cell Y303 ATCC No.96659 or saccharomyces cerevisiae cell YPH500 ATCC No.76626 of a HPV genome containing a cerevisiae nutrition defect screening mark Ura3. The model of the present invention can be used for researching on the function of HPV gene, or a cerevisiae RNA interfere technology is used for researching on the functions of different genes, or a cerevisiae expression vector is introduced again to express interested foreign protein in cells, so as to research on the effect of the cerevisiae expression vector in virus living period, or virus main capsid protein L1 expression vector is introduced for packing infective virus granules to be used for the experiment or research on HPV bacterin.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for fermentation production of D-tagatose by saccharomyces cerevisiae
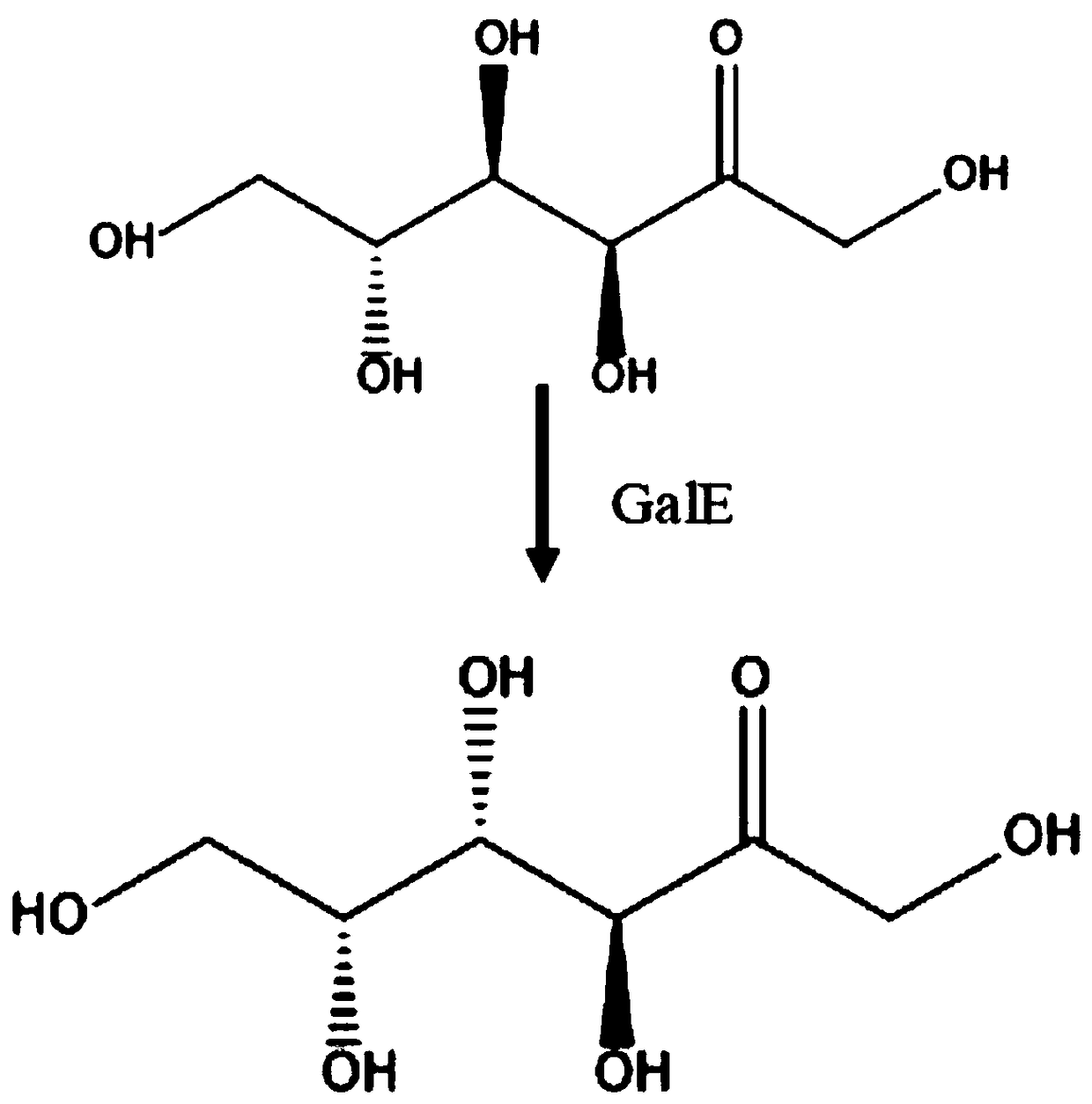
InactiveCN108774636ALow costFriendly and easy to controlMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliBiotechnology
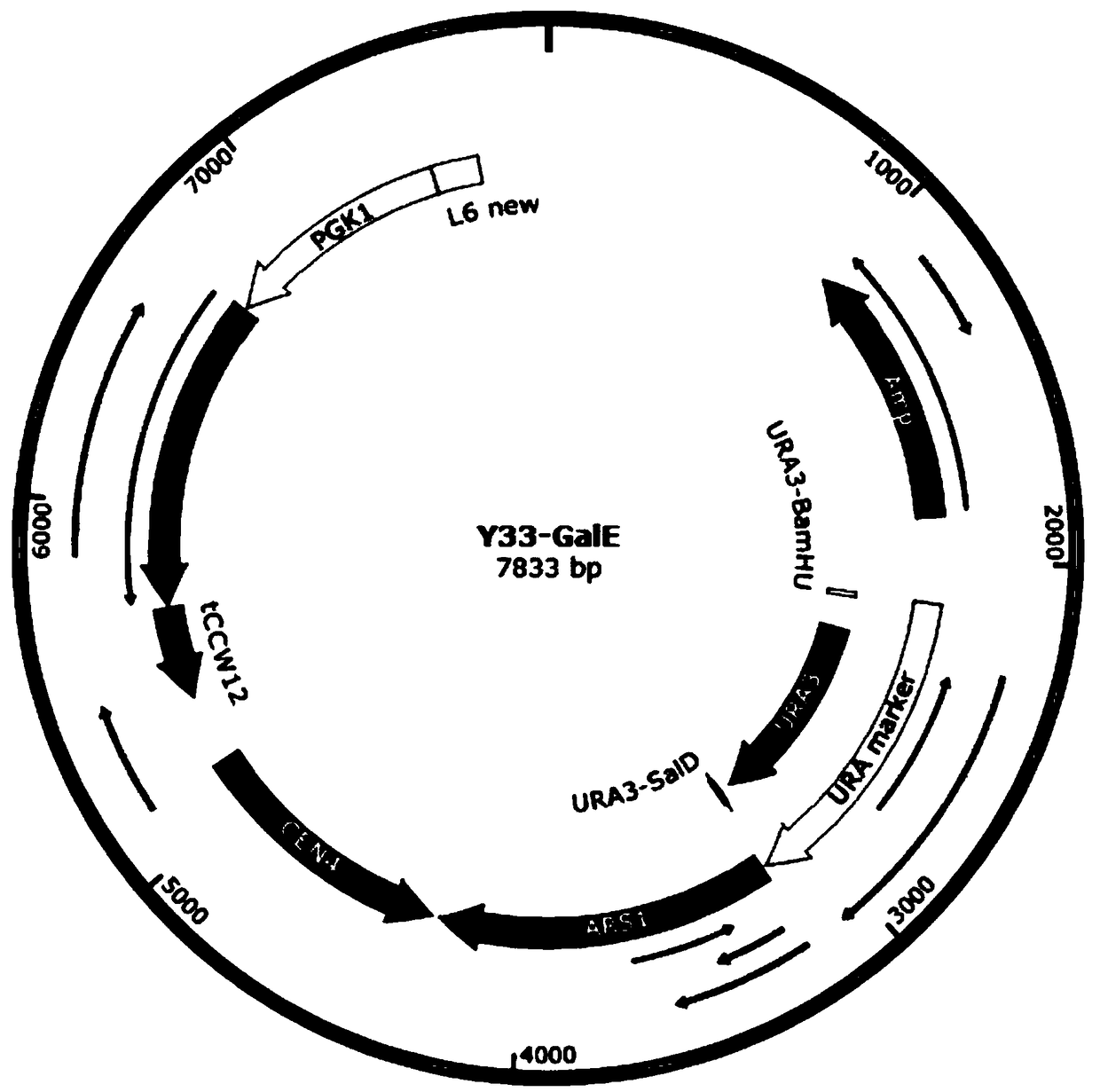
The invention relates to a method for fermentation production of D-tagatose by saccharomyces cerevisiae including the following steps: codons for optimizing gene GalE according to codon preference ofsaccharomyces cerevisiae are built in the saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector YCplac33 to produce a vector 1, wherein, the expression vector YCplac33 carries ampicillin resistance gene of escherichia coli and a selection marker URA3 gene of saccharomyces cerevisiae; the above recombined carrier 1 is transferred to a wild type saccharomyces cerevisiae W303, wherein, positive monoclonal genesare selected pursuant to the selection marker URA3 of the saccharomyces cerevisiae and the positive monoclonal genes are cultured for extraction of a genome of the yeast to be further verified by PCRto produce a final fermentation strain; the fermentation strain is cultured under a certain condition till bacteria hits a certain concentration; corresponding substrate fructose is added to the strain for a 5-day reaction under 35-36 DEG C and 220-250 rpm to produce D-tagatose, and the D-tagatose is collected, separated and purified. The process has separation and purification procedures only inthe final step of production, and the product purification process is simple.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
Method for replacing essential gene promoter in yeast genome
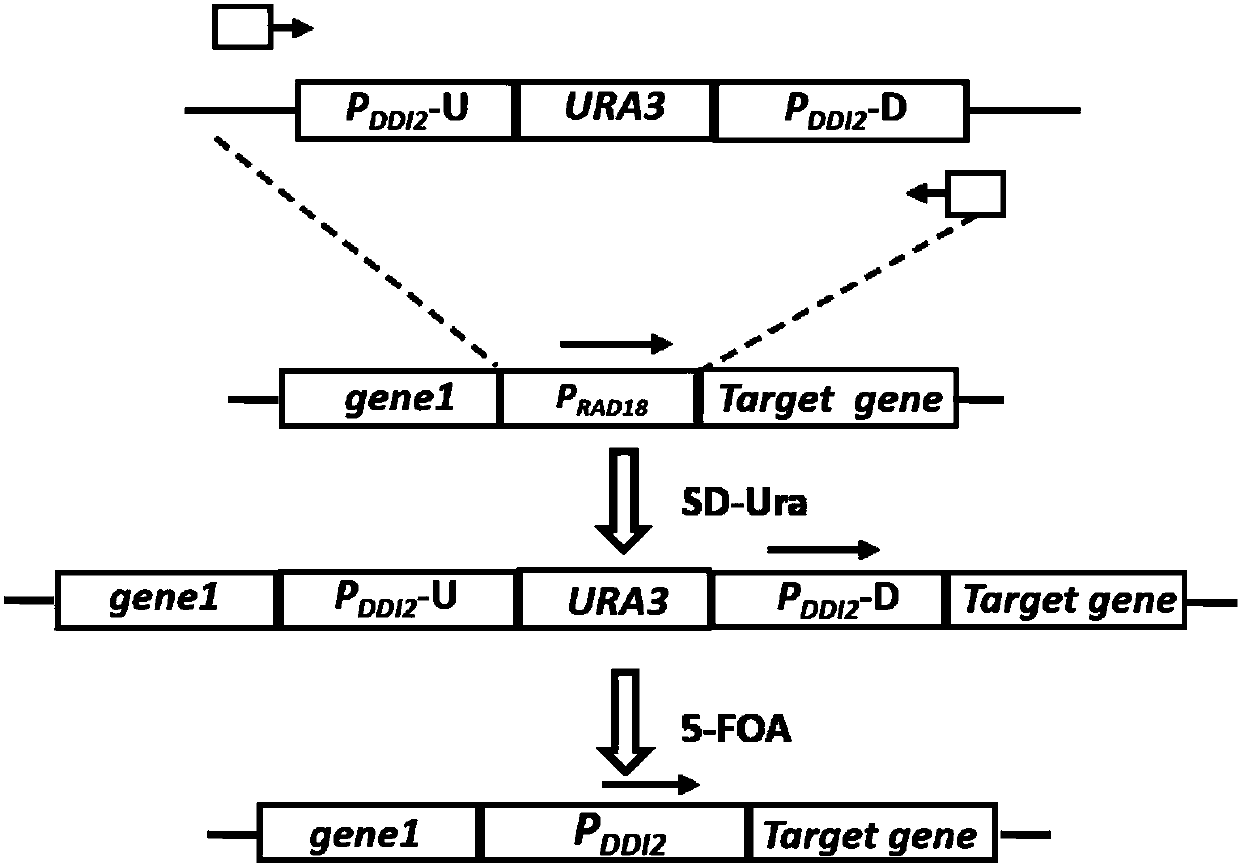
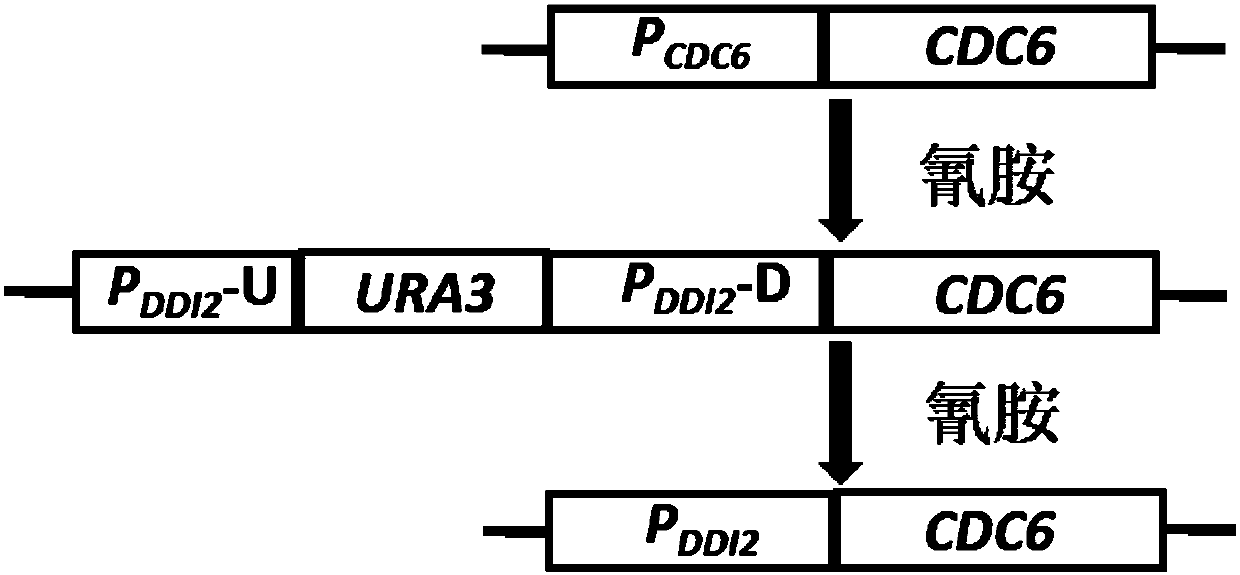
InactiveCN107557377AGuaranteed survivalAvoid residueFungiVector-based foreign material introductionYeastYeast genome
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a method for replacing an essential gene promoter in a yeast genome. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, a DDI2-URA3-DDI2 fragment is prepared; S2, the DDI2-URA3-DDI2 fragment is transformed into the yeast genome, and a transformant is obtained; S3, the transformant is cultured in a YPD culture medium containing cyanamide, pop-out URA3 and a DDI2 promoter are obtained through screening by 5-FOA, and the essential gene promoter is replaced with a yeast strain of the DDI2 promoter. On the basis of a pop-in / pop-outmethod, a new genome integration strategy is developed for replacement of the essential gene promoter in yeast, so that recycling of marker genes is realized, and no traces of repetitive sequences remain in the yeast genome.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com