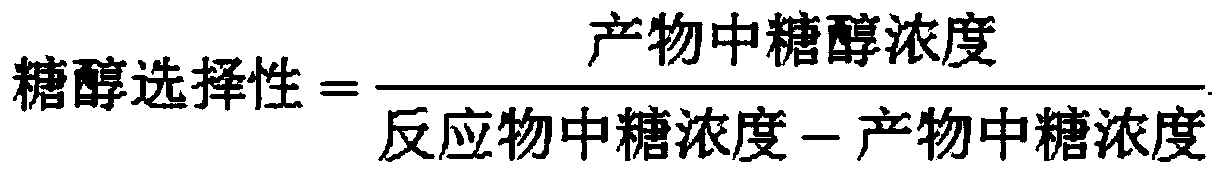
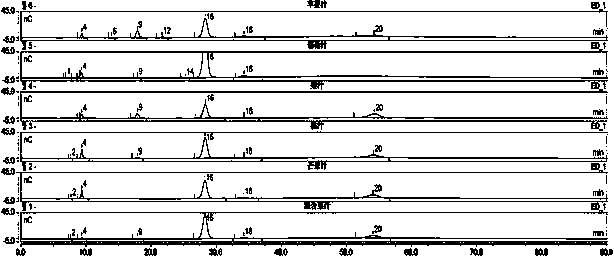
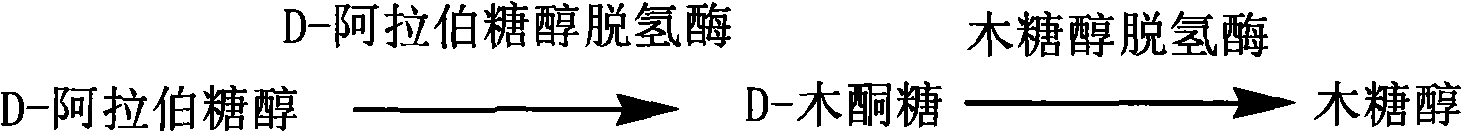Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "D-arabitol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
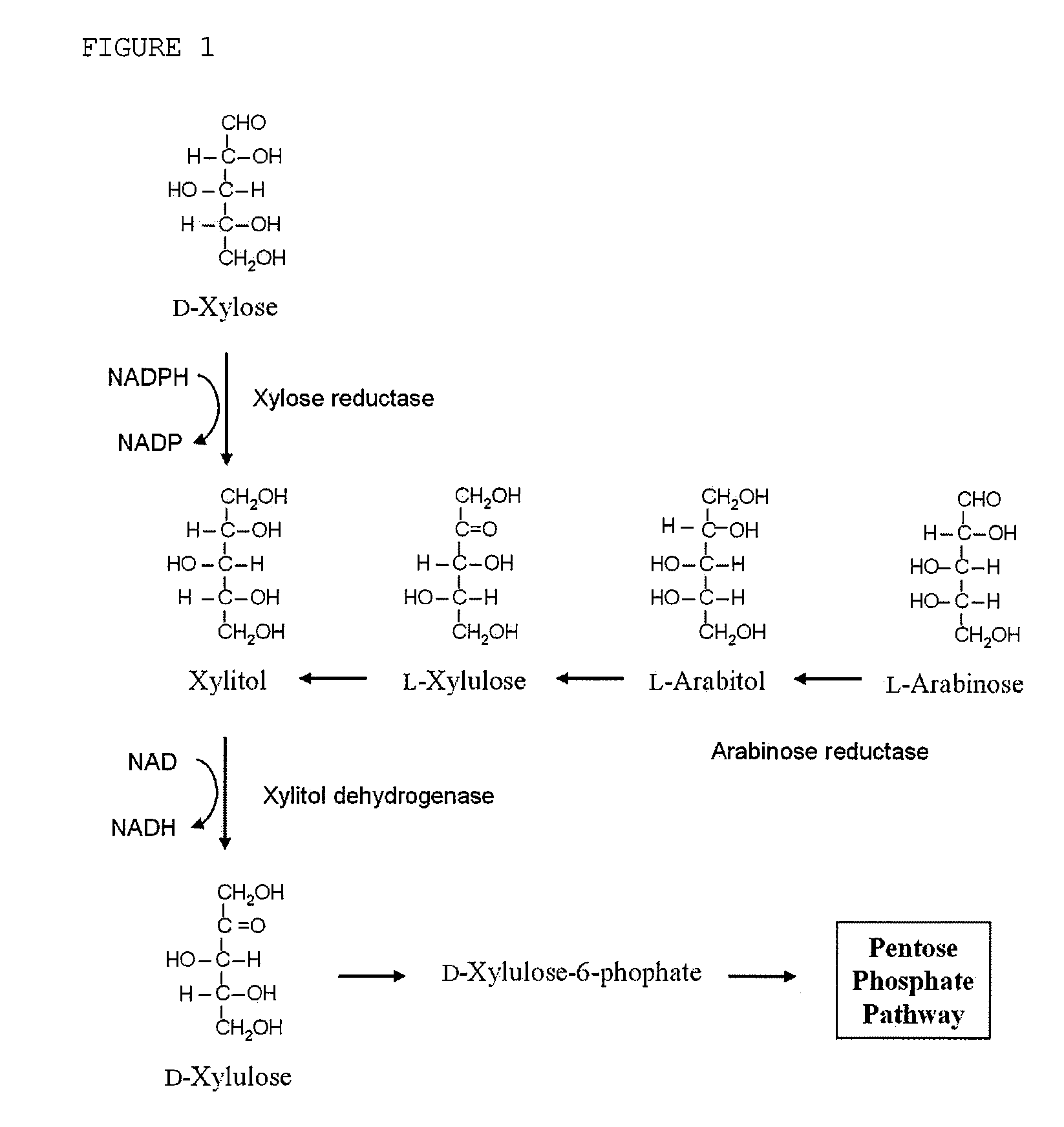
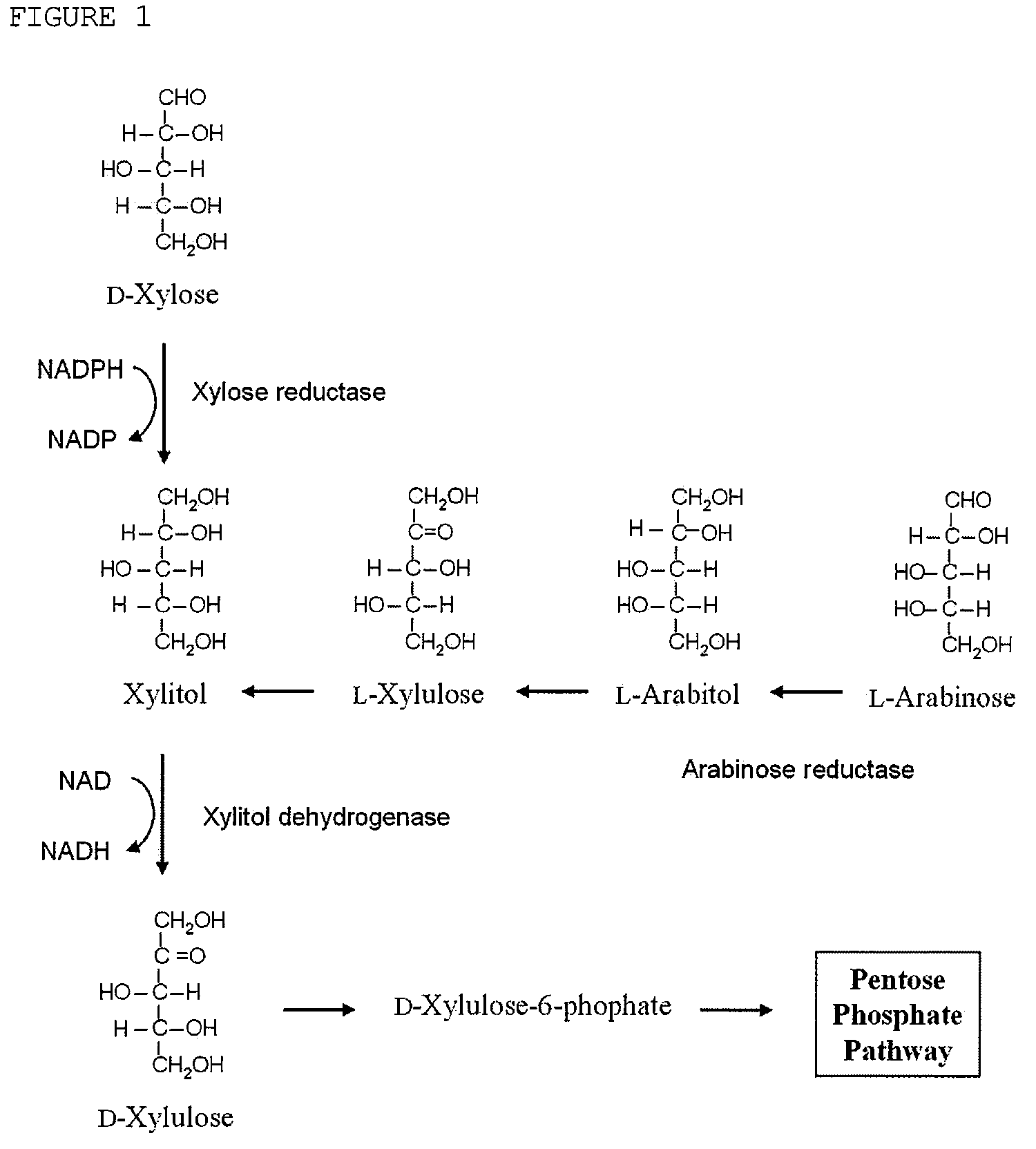
Arabitol, or arabinitol, is a sugar alcohol. It can be formed by the reduction of either arabinose or lyxose . Some organic acid tests check for the presence of D -arabitol, which may indicate overgrowth of intestinal microbes such as Candida albicans or other yeast / fungus species.
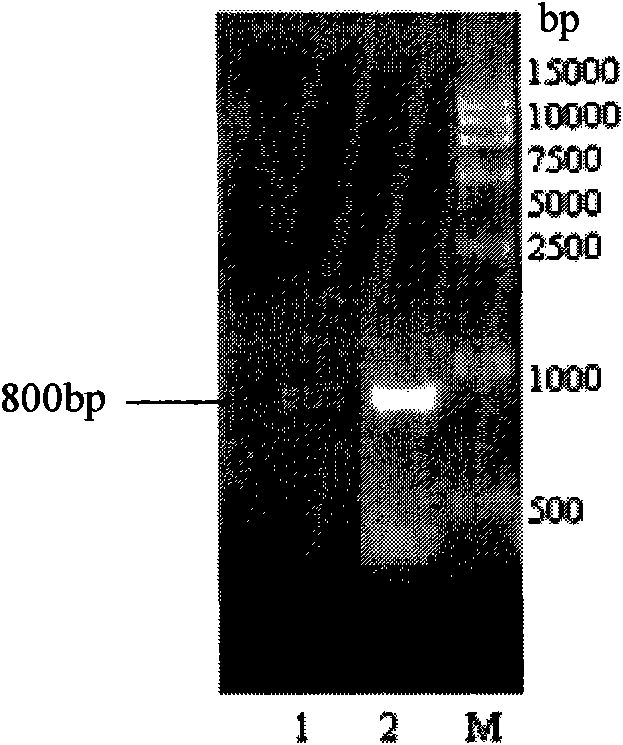
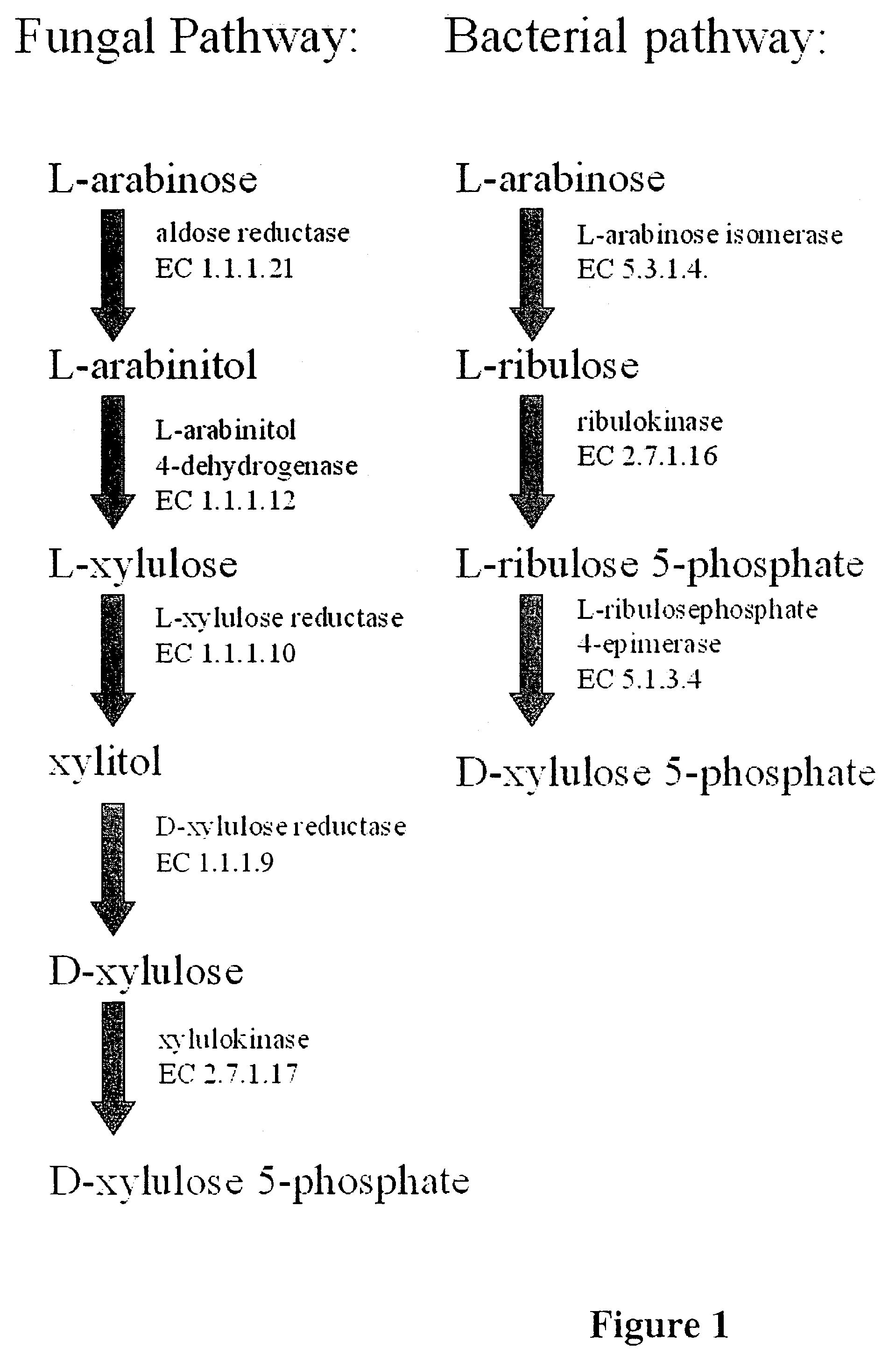
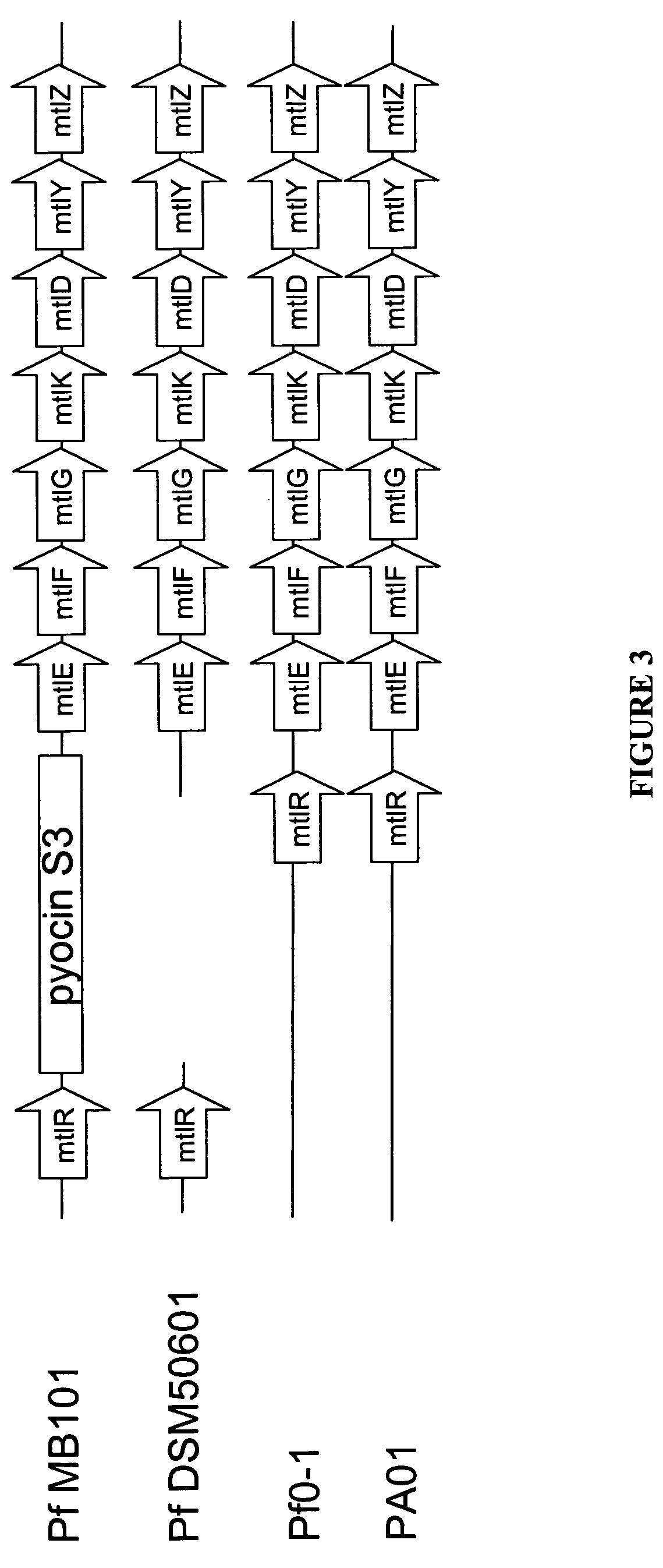
Engineering fungi for the utilisation of L-arabinose
A fungal microorganism can be engineered by means of genetic engineering to utilise L-arabinose. The genes of the L-arabinose pathway, which were unknown, i.e. L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase and L-xylulose reductase, were identified. These genes, together with the known genes of the L-arabinose pathway, form a functional pathway. This pathway can be introduced to a fungus, which is completely or partially lacking this pathway.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
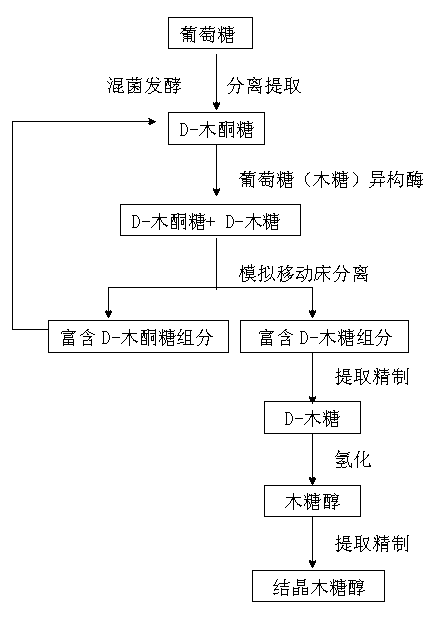
Method for producing xylitol and arabitol simultaneously by utilizing xylose mother liquid
ActiveCN101857523AValue expressionIncrease added valueOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationChromatographic separationArabitol
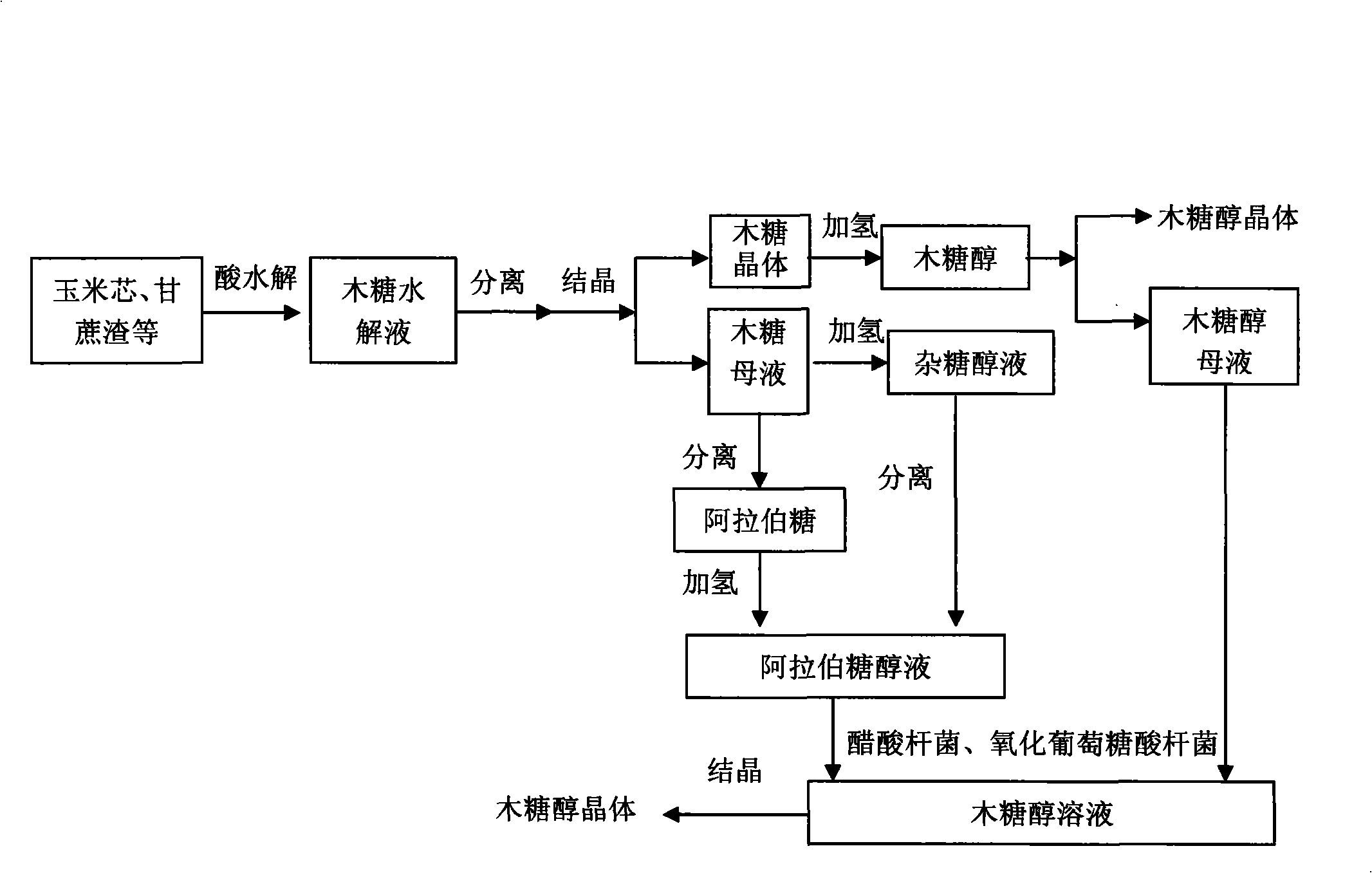
The invention discloses a method for producing xylitol and arabitol simultaneously by utilizing xylose mother liquid, which comprises the following steps: (1) diluting the xylose mother liquid, and obtaining a purifying liquid after decolorizing filtration and ion exchange; (2) adding nutrients into the purifying liquid, sterilizing, and then inoculating yeast and fermenting; (3) filtering and sterilizing the fermenting liquid, then carrying out the decolorizing filtration and the ion exchange, and carrying out initial concentration; (4) allowing the concentrated liquid to be prepared into mixed sugar alcohol by catalytic hydrogenation; (5) carrying out chromatographic separation for the mixed sugar alcohol after the decolorizing filtration and the ion exchange to obtain two fractions which are respectively a xylitol fraction and an arabitol fraction; and (6) carrying out evaporation concentration and crystallization for the two fractions so as to obtain xylitol crystals and arabitol crystals. The invention converts xylose and arabinose into xylitol and arabitol by hydrogenation, the conversion rate is higher compared with the method for producing xylitol by yeast fermentation.
Owner:山东绿健生物技术有限公司
Odor control absorbent article and method
A novel article and method are disclosed for reducing malodor in disposable products for the absorption of body fluids. An effective amount of pentitol is applied to a disposable absorbent material, prior to its use. In one aspect, the invention provides a water-swellable, water-insoluble, hydrogel-forming polymeric absorbent material. In one aspect, the pentitol is compositionally part of the absorbent structure or is coated on the absorbent material present in the absorbent structure. The pentitol preferably is located in the area of insult, i.e., that area of the absorbent product to be exposed to the body fluid intended to be absorbed. The pentitol in the novel article and method of the present invention is a compound selected from the group consisting of ribitol, D-arabinitol, L-arabinitol, and xylitol or a combination of one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of ribitol, D-arabinitol, L-arabinitol, and xylitol effective in preventing malodor.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Admixtures for mineral binders based on (oxidised) sugar and hydrogenated sugar, admixture-containing mineral binders, and a process for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20030010254A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove plasticityCosmetic preparationsSugar derivativesPhosphateArabitol
The invention relates to a novel admixture for mineral binders, composed of a composition containing at the same time a sugar or an oxidized sugar and a hydrogenated sugar. The oxidized sugar may consist, in particular, of gluconic acid or one of its salts or an oxidized starch hydrolysate. The hydrogenated sugar may consist in particular of maltitol, sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, arabitol, or a hydrogenated starch hydrolysate containing at least 40% by weight of maltitol. Within the admixture, this composition may be combined with conventional admixtures such as phosphates, borates, or amines. The combination of a sugar or an oxidized sugar and a hydrogenated sugar within this composition makes it possible to obtain synergistic effects, particularly in terms of plasticity and mechanical properties of the mineral binders. The admixtures claimed may be used equally well for admixing with cements, raw materials for cements as for admixing with mortars, slurries and concretes. They may also be used in other sectors such as, for example, the plaster industry, particularly as complexing agents or hydration or dehydration controllers.
Owner:ROQUETTE FRERES SA
Technique for producing xylitol and dulcitol simultaneously
ActiveCN101775413ATake advantage ofMicroorganism based processesFermentationChromatographic separationArabitol
The invention discloses a technique for producing xylitol and dulcitol simultaneously, comprising the following steps: (1) diluting xylose mother liquor, carrying out chromatographic separation after decoloration, filtering and ion exchange and obtaining mixed liquor; (2) preparing the xylitol: adding nutritional components into the mixed liquor, inoculating yeast seed liquor after sterilization, carrying out fermentation and obtaining fermentation liquor; (3) filtering the fermentation liquor to remove the yeast, then carrying out decoloration, filtering and ion exchange, and then obtaining crystalline xylitol by evaporation, concentration and crystallization; (4) carrying out evaporation and concentration on the mixed liquor of galactose and arabitol obtained by chromatographic separation in the step (1), concentrating to the mass concentration of 35 to 45 percent, and then carrying out catalytic hydrogenation, thus obtaining the mixed liquor of the dulcitol and the arabitol; and (5) carrying out decoloration, filtering and ion exchange on the obtained mixed liquor, putting the mixed liquor into a crystallization kettle for evaporation till supersaturation, adding dulcitol seed crystal and seed crystal growth promoter, and carrying out crystallization to obtain crystalline dulcitol.
Owner:山东绿健生物技术有限公司
Gluconobacter oxydans and method for preparing ketoxylose using the same
ActiveCN101486984AConducive to industrialized continuous productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCollection management
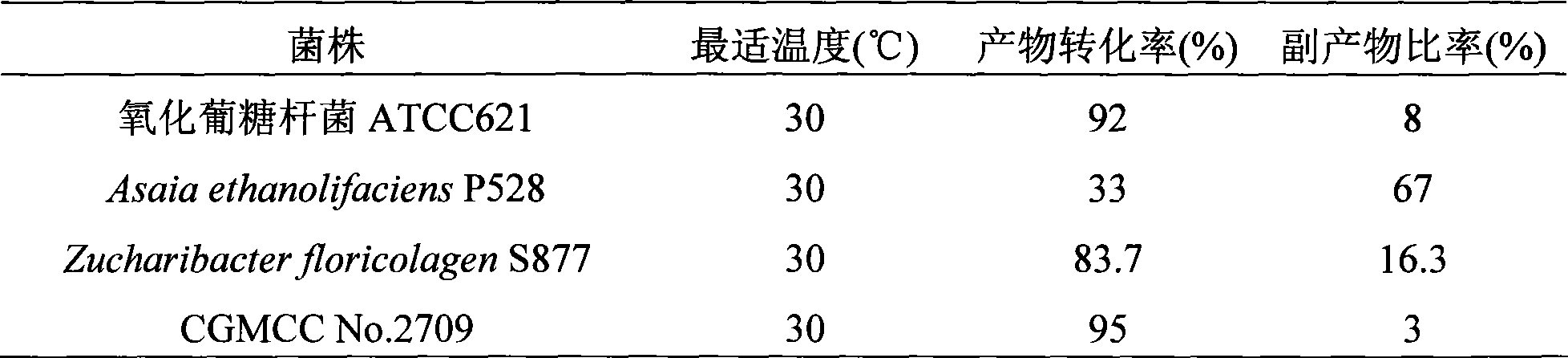
The invention discloses a Gluconobacter oxydans, which is classified and named as Gluconobacter oxydans NH-10, and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Center of Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2709. The invention further discloses a D-xylulose preparation method that uses the Gluconobacter oxydans. The strain obtained by screening can transform D-Arabitol so as to generate D-xylulose in high efficiency, the D-xylulose preparation method reaches the highest D-Arabitol transformation ratio of 99.5 percent (w / w) and the D-xylulose yield ratio of 95 percent, the D-xylulose concentration of a conversion fluid can reach 95g / L, and the conversion fluid hardly contains other ingredients.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANLI PHARMA
Odor control absorbent article and method
InactiveUS20030114806A1Controlling and reducing malodorEfficient and effectiveInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesD-arabitolWater insoluble
A novel article and method are disclosed for reducing malodor in disposable products for the absorption of body fluids. An effective amount of pentitol is applied to a disposable absorbent material, prior to its use. In one aspect, the invention provides a water-swellable, water-insoluble, hydrogel-forming polymeric absorbent material. In one aspect, the pentitol is compositionally part of the absorbent structure or is coated on the absorbent material present in the absorbent structure. The pentitol preferably is located in the area of insult, i.e., that area of the absorbent product to be exposed to the body fluid intended to be absorbed. The pentitol in the novel article and method of the present invention is a compound selected from the group consisting of ribitol, D-arabinitol, L-arabinitol, and xylitol or a combination of one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of ribitol, D-arabinitol, L-arabinitol, and xylitol effective in preventing malodor.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Activated carbon-loaded type ruthenium catalyst and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN109453765ALow costMild reaction conditionsSugar derivativesCatalyst activation/preparationD-arabitolMaltitol
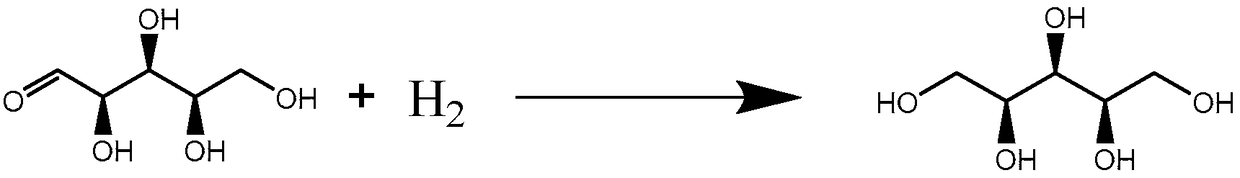
The invention relates to an activated carbon-loaded type ruthenium catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof in preparation of sugar alcohols by catalytic hydrogenation of saccharides.The preparation method comprises the following steps of loading metal ruthenium onto the activated carbon by a simple impregnating reduction method, so as to prepare the loaded type Ru / C (ruthenium / carbon) catalyst with high dispersion degree; further applying the Ru / C catalyst into the hydrogenation process of a series of saccharides, such as xylose, arabinose, glucose, mannose and maltose, so as to prepare xylitol, arabitol, sorbitol, mannitol and maltitol at high efficiency. The activated carbon-loaded type ruthenium catalyst has the advantages that under certain reaction conditions, the high conversion rate of series saccharides and the high selectivity of sugar alcohols can be realized, the stability of the catalyst is good, the recycling is convenient, and the frequency of cyclic use is high; the preparation technology is simple, the production cost is low, the catalytic activity is high, and the preparation technology is suitable for preparing multiple types of sugar alcohols,has good universality and is suitable for being popularized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing xylitol and arabitol simultaneously by utilizing xylose mother liquid
ActiveCN101857523BValue expressionIncrease added valueOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationChromatographic separationD-arabitol
The invention discloses a method for producing xylitol and arabitol simultaneously by utilizing xylose mother liquid, which comprises the following steps: (1) diluting the xylose mother liquid, and obtaining a purifying liquid after decolorizing filtration and ion exchange; (2) adding nutrients into the purifying liquid, sterilizing, and then inoculating yeast and fermenting; (3) filtering and sterilizing the fermenting liquid, then carrying out the decolorizing filtration and the ion exchange, and carrying out initial concentration; (4) allowing the concentrated liquid to be prepared into mixed sugar alcohol by catalytic hydrogenation; (5) carrying out chromatographic separation for the mixed sugar alcohol after the decolorizing filtration and the ion exchange to obtain two fractions which are respectively a xylitol fraction and an arabitol fraction; and (6) carrying out evaporation concentration and crystallization for the two fractions so as to obtain xylitol crystals and arabitol crystals. The invention converts xylose and arabinose into xylitol and arabitol by hydrogenation, the conversion rate is higher compared with the method for producing xylitol by yeast fermentation.
Owner:山东绿健生物技术有限公司
Mannitol induced promoter systems in bacterial host cells
ActiveUS7476532B2Continuous and stable levelIncrease stringencyBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention provides methods for producing recombinant peptides in a bacterial host utilizing a mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol-inducible promoter, wherein the host bacterial cell that produces the peptide has been rendered incapable of degrading or metabolizing mannitol, arabitol, or glucitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention provides bacterial cells that have been genetically altered to inhibit the metabolism or degradation of mannitol, glucitol, or arabitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention utilizes mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol to induce expression of a target polypeptide from an inducible promoter, allowing for the use of an inexpensive and stable carbon source inducer in the fermentation processes for the production of recombinant peptides.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Xylose reductase mutant, genetically engineered bacteria and application in producing xylitol
ActiveCN105671013AHigh selectivityHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesD-arabitolArabinose
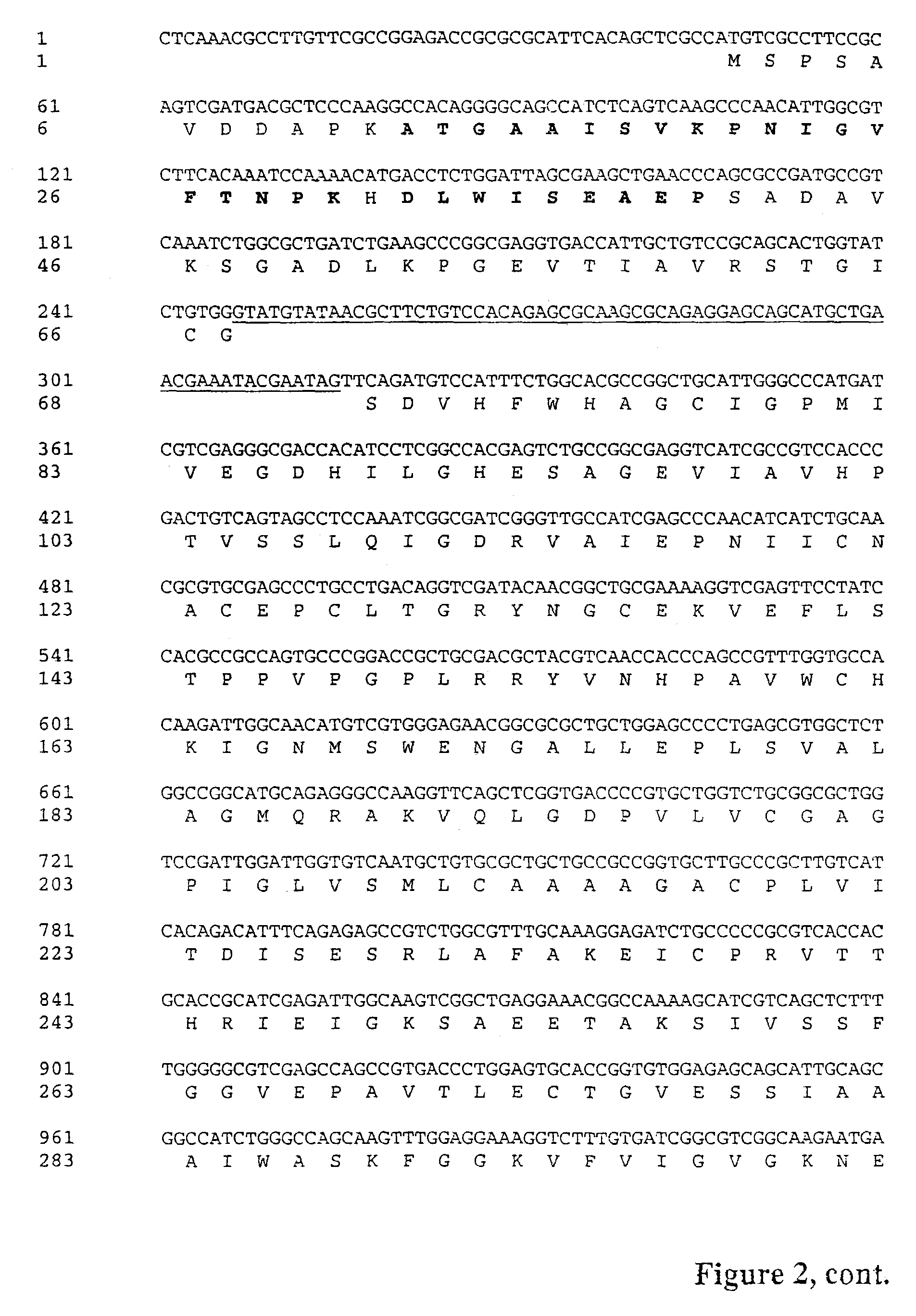
The invention discloses a xylose reductase mutant, genetically engineered bacteria and application in producing xylitol. The amino acid sequence of the xylose reductase mutant is shown in the SEQ ID No.1. Mutation of eight amino acid sites is carried out on xylose reductase, the activity of the xylose reductase mutant for catalyzing arabinose into arabitol is lowered, the selectivity of the xylose reductase mutant for converting xylitol is improved, and the by-product arabitol in the bioconversion product is not detected. The separation step of xylitol bioconversion production downstream can be simplified, the production cost is reduced, and the purity of the xylitol product is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
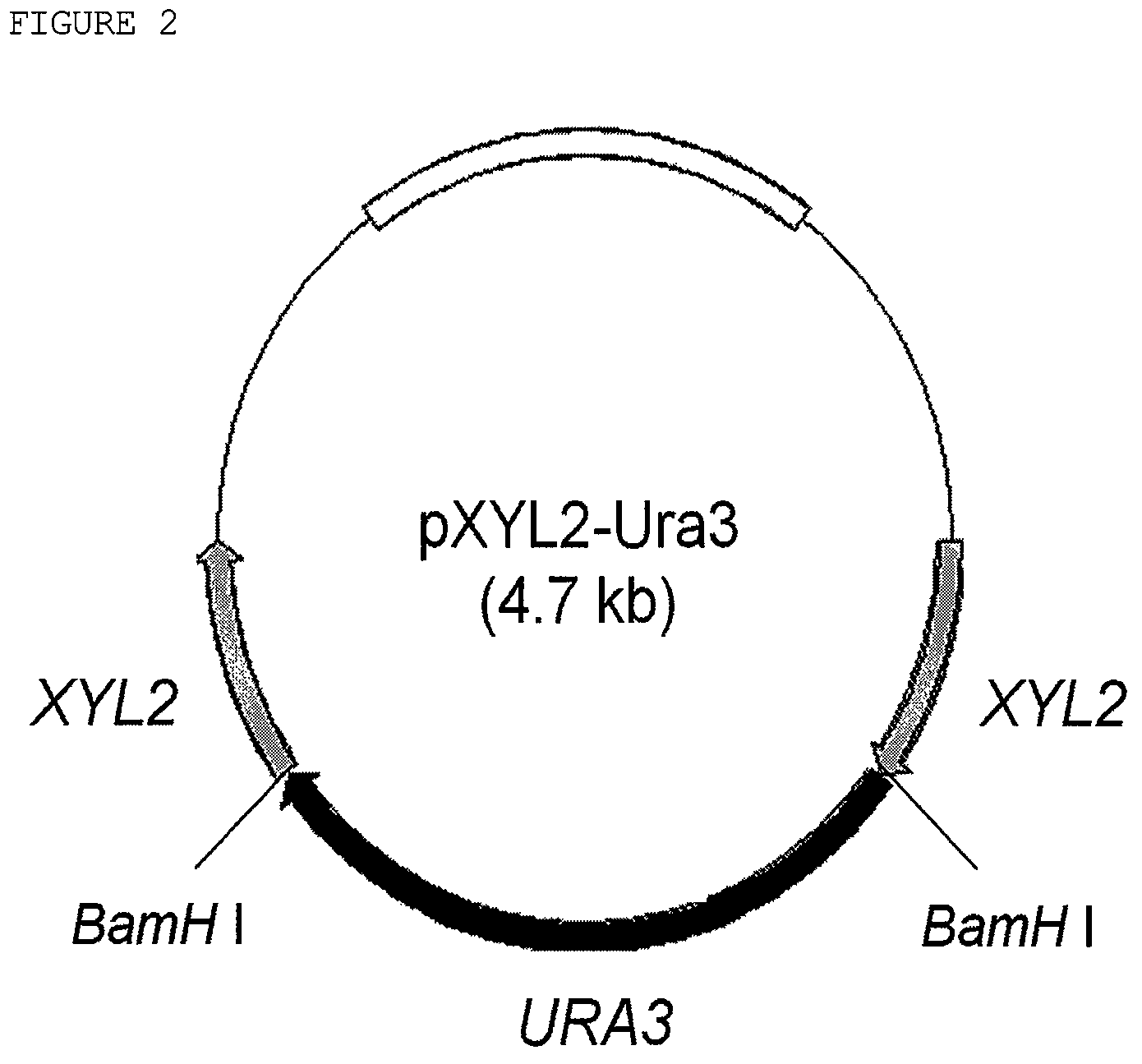
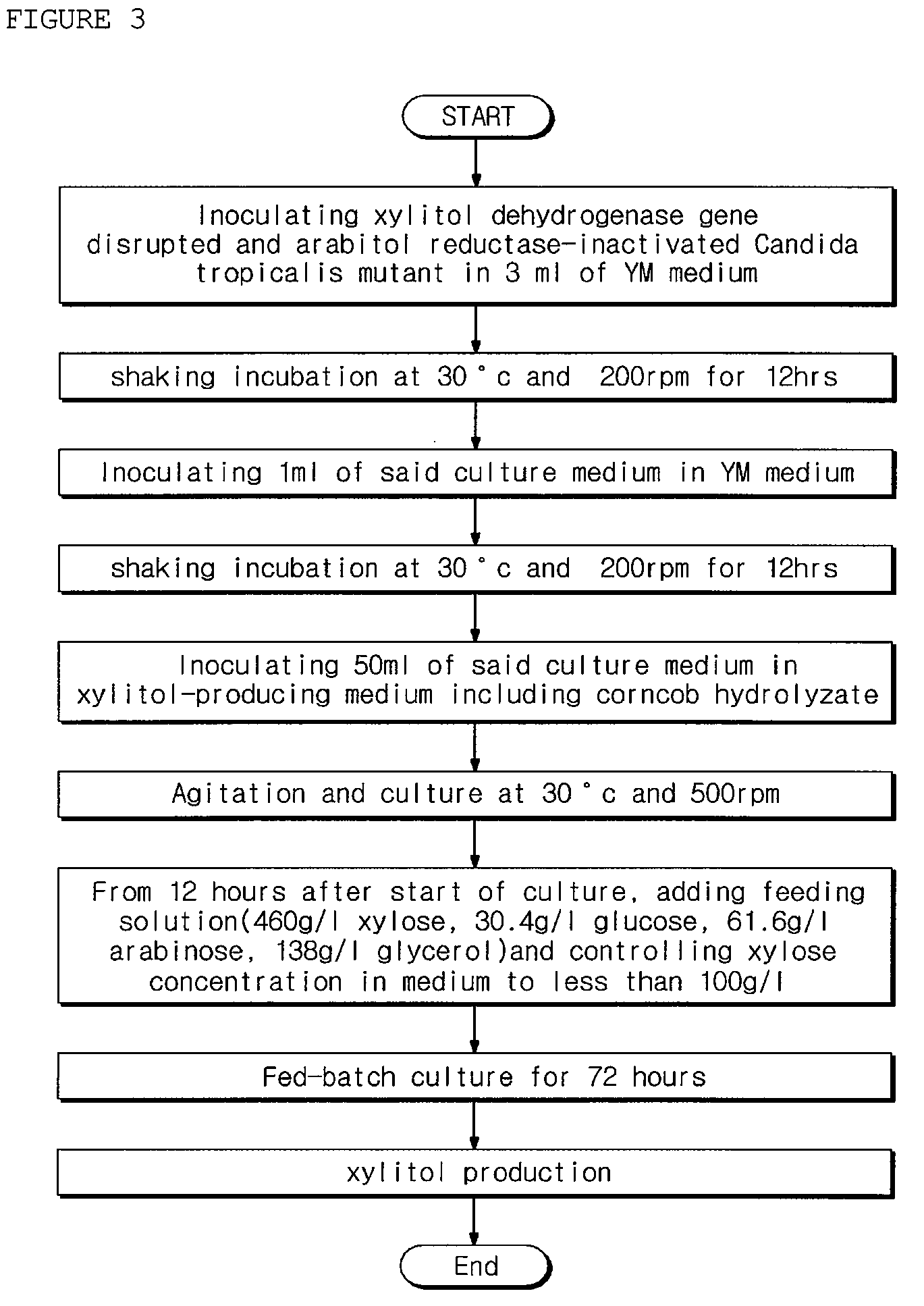
Xylitol dehydrogenase-inactivated and arabinose reductase-inhibited mutant of candida tropicalis, method of producing high-yield of xylitol using the same, and xylitol produced thereby
Disclosed herein are Xylitol dehydrogenase-inactivated and arabinose reductase-inhibited mutant of Candida tropicalis, a method of producing a high yield of xylitol using the same, and xylitol produced by the method. More specifically, disclosed are a method for producing a high yield of xylitol, in which a high concentration of xylose contained in a biomass hydrolyzate is converted to xylitol using xylitol dehydrogenase-inactivated mutant of Candida tropicalis, without controlling dissolved oxygen to a low level, as well as xylitol produced according to the method. Also disclosed are a xylitol production method, in which the production of byproduct arabitol, which is produced when using a biomass as a substrate and adversely affects the yield of xylitol, is significantly reduced through the use of Candida tropicalis mutant ara-89 (KCTC 11136bp) having an inhibited activity of arabinose reductase converting arabinose to arabitol, thus increasing xylitol productivity, as well as xylitol produced by the method.
Owner:LPBIO +1
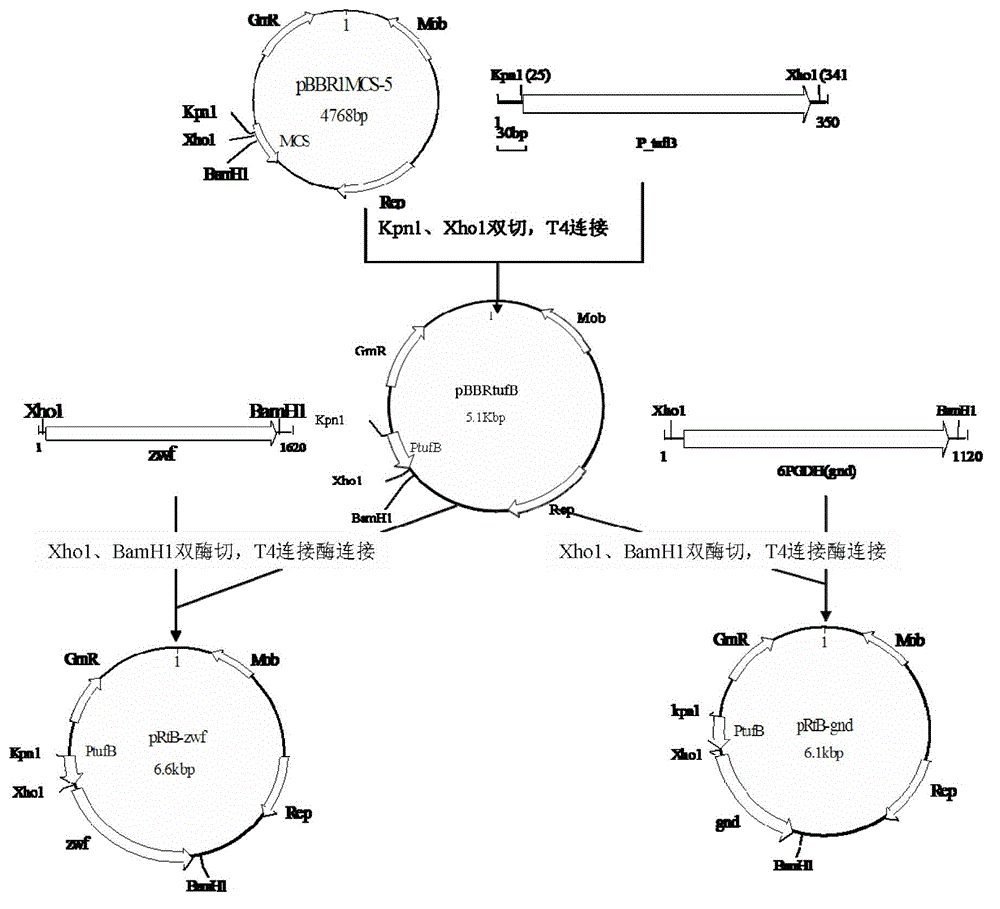
Gluconobater oxydans genetic engineering strain and construction method thereof
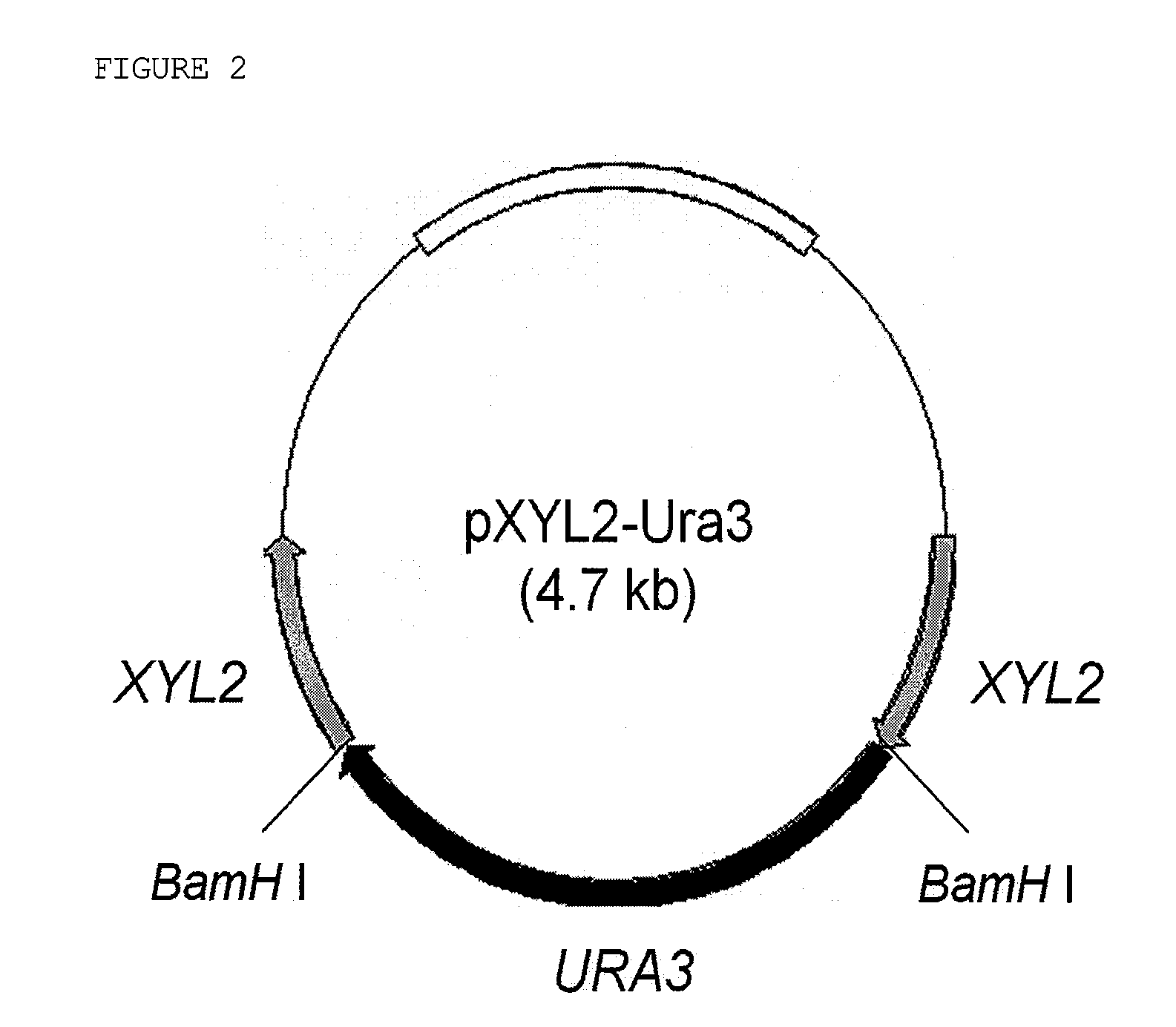
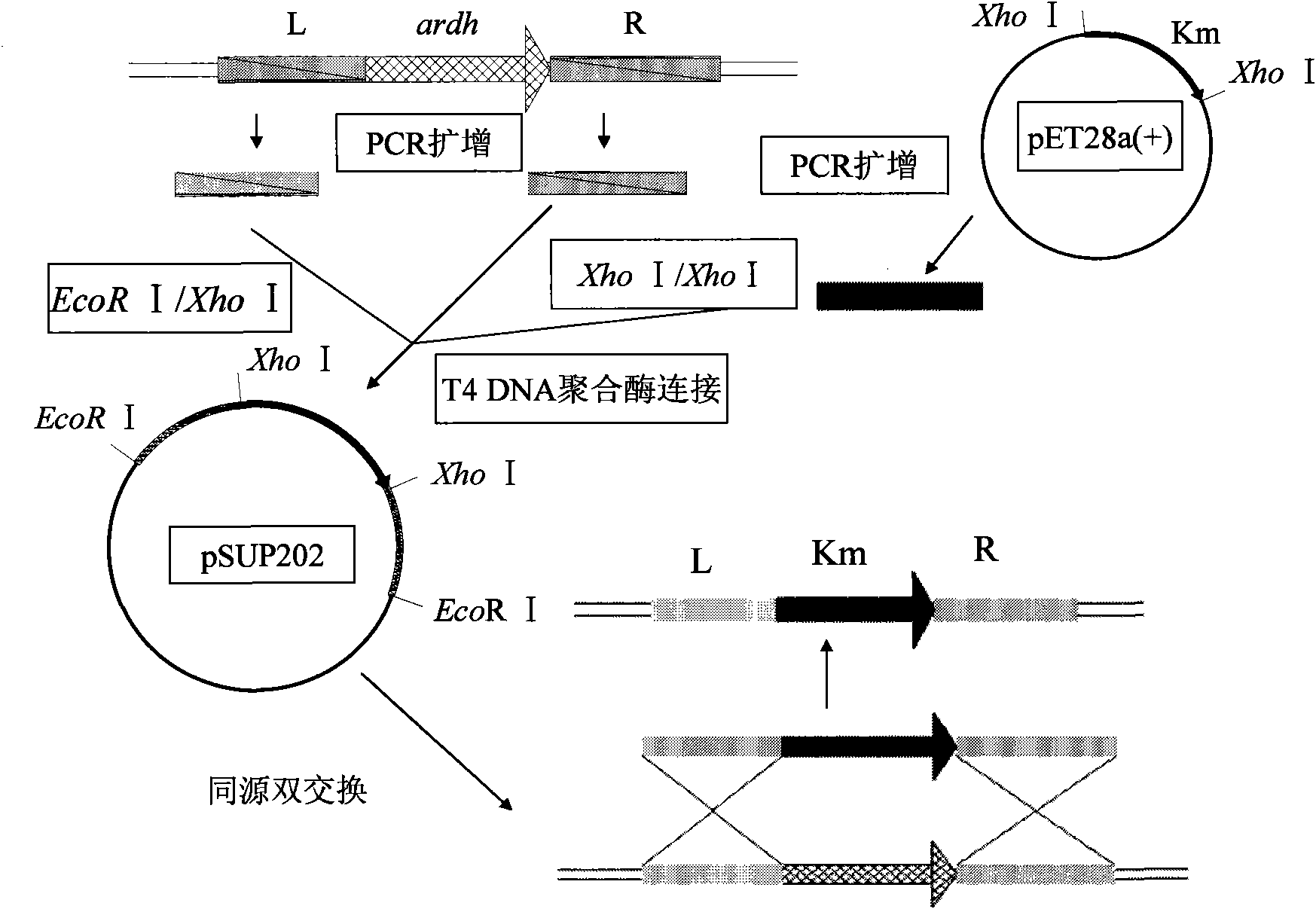
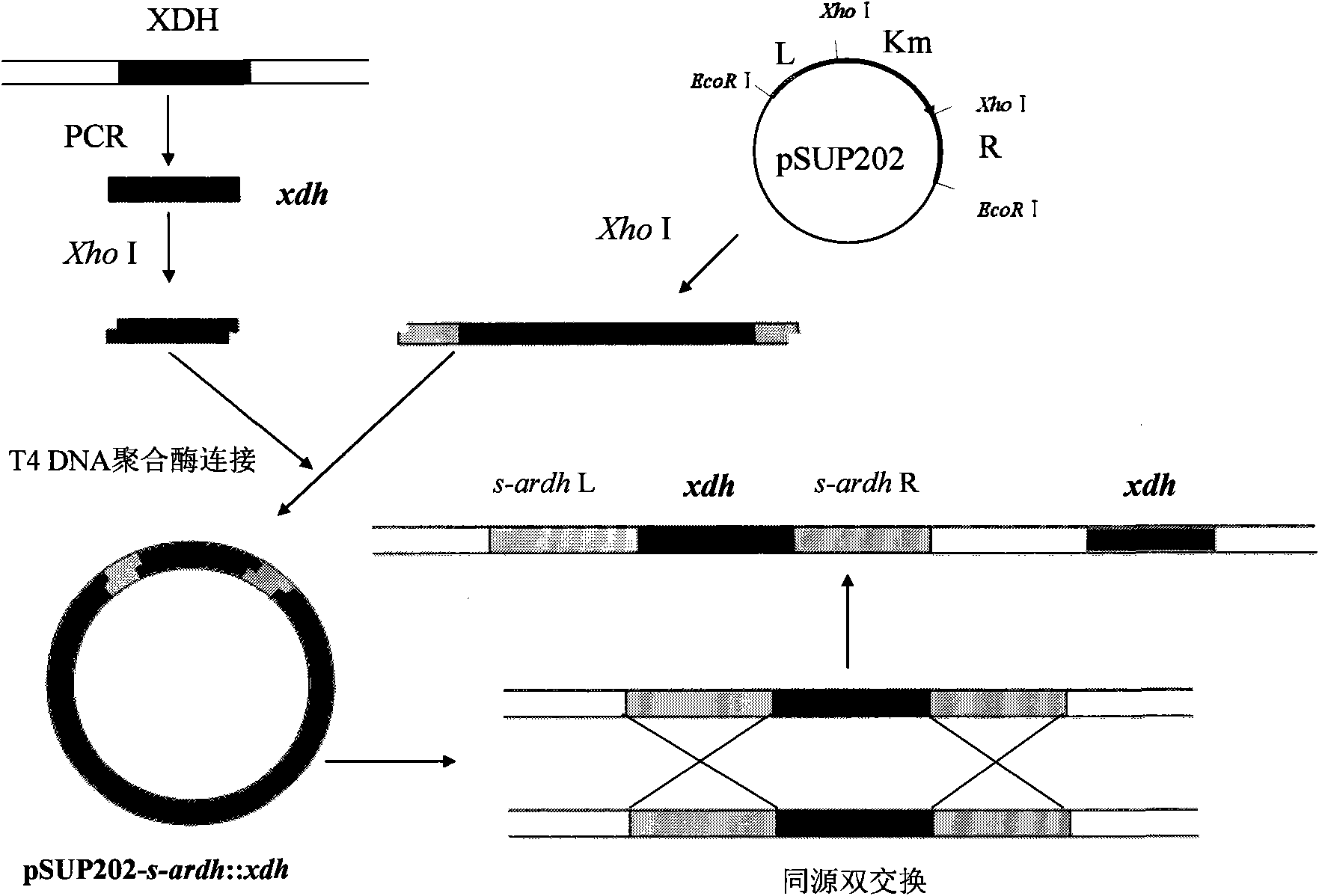
InactiveCN101880643AHigh yieldSolve accompanying problemsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesD-arabitolGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a gluconobater oxydans genetic engineering strain, which is s-ArDH gene deletion gluconobater oxydans. The invention also discloses a gluconobater oxydans genetic engineering strain, which has the s-ArDH gene deletion and is reinforced by XDH genes in the positions of s-ArDH genes. The invention simultaneously discloses a construction method of the two kinds of genetic engineering strains. The gluconobater oxydans genetic engineering strain of the invention can interdict the generation of D-arabite in xylulose reverse reaction in the xylitol preparation process through converting the D-arabite by a biological method, so the problem of byproduct concomitance in the xylitol production process can be fundamentally solved. In addition, an XDH reinforced strain improves the activity xylitol dehydrogenase, and improves the conversion rate of the xylitol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing eutrit by waste xylose mother liquor or eutrit mother liquor in production process of eutrit
InactiveCN101285082AUtilization of Xylose Mother Liquor and Xylitol Mother LiquorTake advantage ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesD-arabitolD-Arabinitol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for producing xylitol through using xylose mother liquor or xylitol mother liquor depleted during the production of xylitol. The method comprises the following: 1 a step of adding hydrogen into arabinose separated from the xylose mother liquor to obtain D-arabitol or separating after adding hydrogen to obtain the D-arabitol; 2 a step of converting the D-arabitol obtained during the step 1 or the D-arabitol in the xylitol mother liquor into xylitol through making use of a strain simultaneously containing D-arabitol dehydrogenase and xylitol dehydrogenase; 3 a step of concentrating and crystallizing the xylitol conversion liquor obtained during the step 2 to obtain an xylitol product after removing thallus cells. The method which makes full use of the xylose mother liquor and xylitol mother liquor produced by a traditional method with simple and reasonable process can improve the utilization factor of raw materials such as corn cob and bagasse by about 9 to 14 percent, thereby greatly reducing the total production cost and consequently improving the economic efficiency of xylitol production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Xylitol as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101619327AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldOrganic chemistryTobacco treatmentProduction rateArabitol
The invention relates to a method for preparing xylitol by a complex enzyme method, the obtained xylitol and the application of the xylitol. The method is as follows: arabitol oxidizing dehydrogenase, xylitol reductase and inductive agent xylitol are added into d-arabitol, calcium carbonate and sugar so as to prepare the xylitol. The method has strong continuous operability, low equipment investment and operation cost, easy operation and industrialization realization and very high conversion rate and production rate of the xylitol. The xylitol prepared by the method can be used for tobacco products.
Owner:HUABAO FLAVOURS & FRAGRANCES CO LTD +1
Method for producing D-arabitol from Hansenula polymorpha mutant strain and Hansenula polymorpha
ActiveCN104195059AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceD-arabitol
The invention provides a method for producing D-arabitol from Hansenula polymorpha mutant strain and Hansenula polymorpha. A gene engineering technique is mainly utilized to obtain a D-arabitol high-yield mutant strain by establishing a Hansenula polymorpha acid phosphatase gene mutant strain. The method has the advantages of low cost and short production cycle, is easy to operate, and provides a new way for solving the problem of shortage of D-arabitol sources. The mutant strain is supplemented by batches through glucose to perform biotransformation so as to produce the D-arabitol; and the conversion rate of the substrate glucose is 51.2%, which is obviously higher than the conversion rate of the substrate glucose when the initial strain is supplemented by batches through glucose to perform biotransformation so as to produce the D-arabitol.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
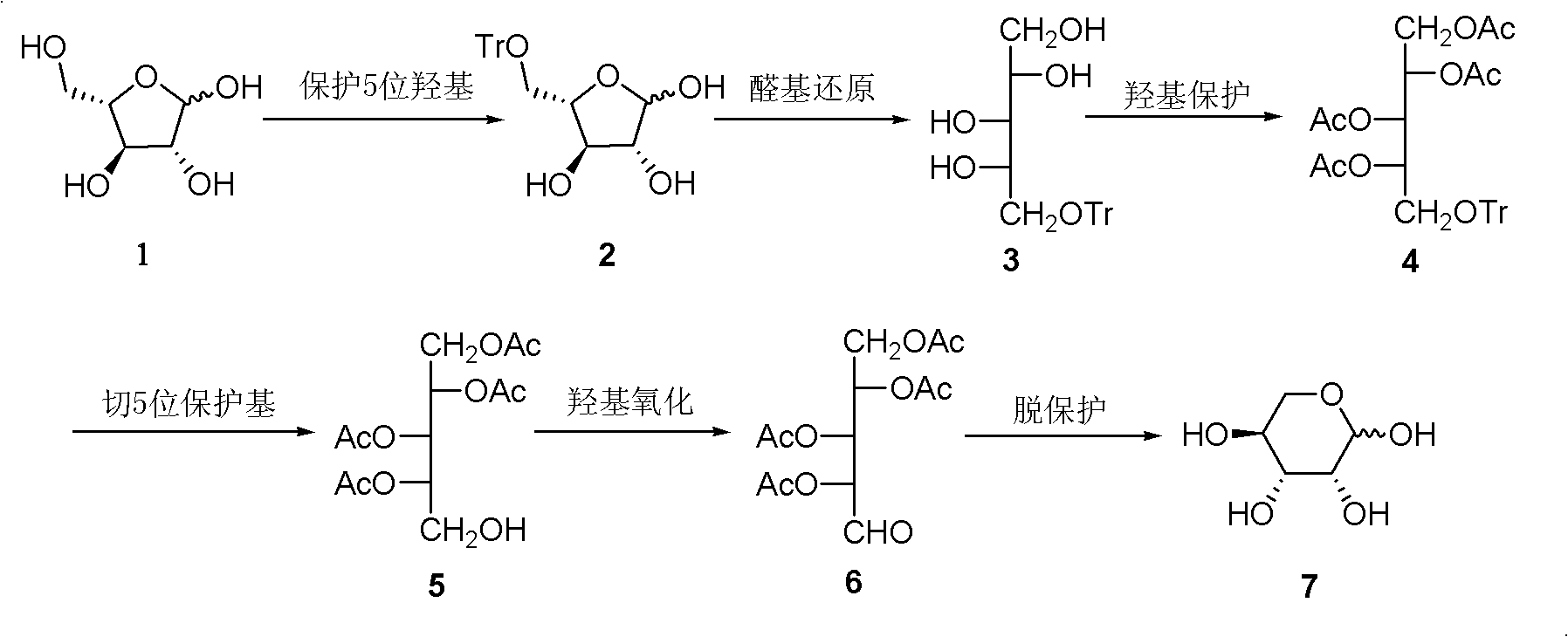
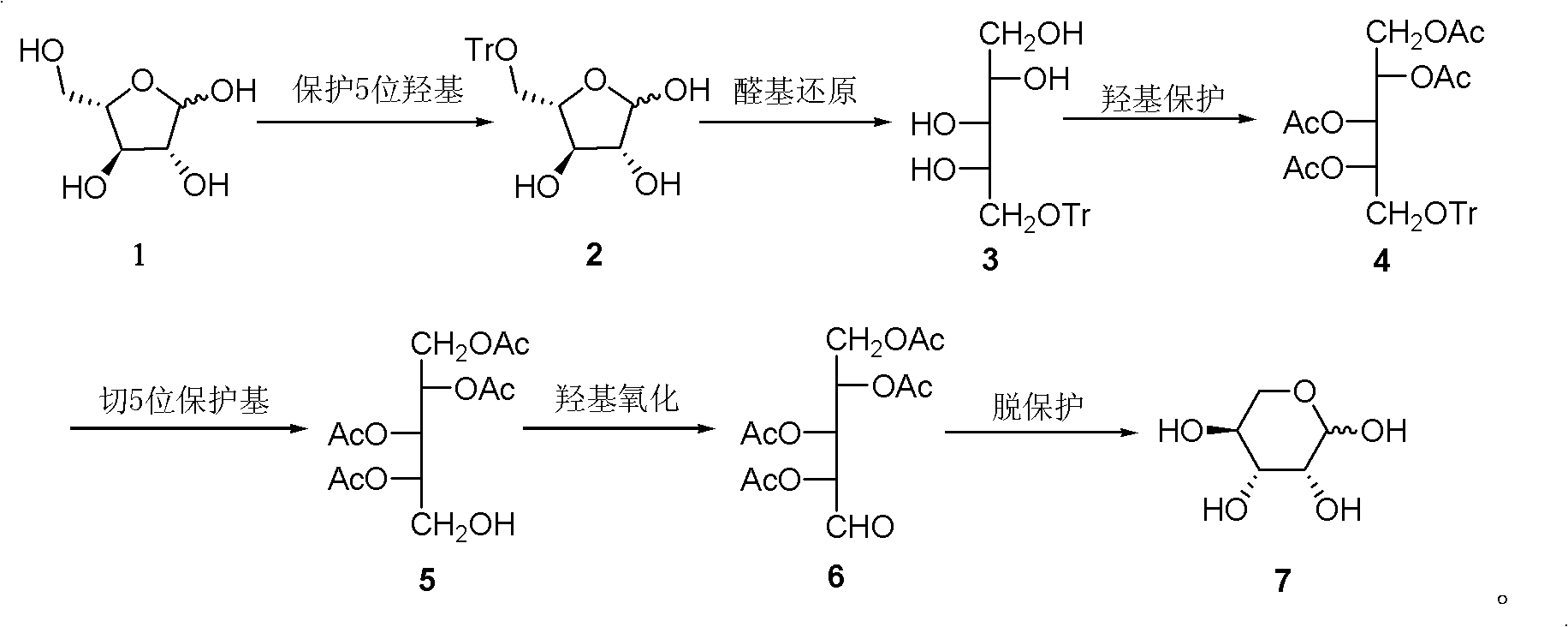
A kind of preparation method of L-lyxose
InactiveCN102286030AHigh purityRaw materials are cheap and easy to getSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAcetic acidSwern oxidation
The invention relates to a preparation method of L-lyxose and relates to a five-carbon sugar. The invention provides a preparation method of L-lyxose and the method has cheap and easily available raw materials, fewer reagents and simple process. The technical scheme of the preparation method uses L-arabinose as a raw material; L-arabinose is subjected to hydroxyl protection and is reduced into a sugar alcohol, then the molecular configuration is changed under Swern oxidation condition, and finally the product L-lyxose with mirror symmetry conversion is obtained. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing 5-O-triphenylmethyl-L-arabinose (2); synthesizing 5-O-triphenylmethyl-L-arabitol (3); synthesizing 5-O-triphenylmethyl-1,2,3,4-tetraacetylarabitol (4); synthesizing L-arabitol-1,2,3,4-tetraacetate (5); synthesizing L-lyxose-2,3,4,5-tetraacetate (6); and synthesizing L-lyxose (7).
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for catalyzing sugar and sugar alcohol hydrocracking reaction through nickel-based catalyst
ActiveCN104557451AImprove catalytic performanceIncrease productivityOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsD-arabitolArabitol
The invention relates to a method for catalyzing sugar and sugar alcohol hydrocracking reaction through a nickel-based catalyst. Under the action of the nickel-based catalyst, the aqueous solution of xylose, glucose, fructose, arabinose, xylitol, sorbitol, arabitol and other carbon-rich sugar and sugar alcohol is adopted as the raw material, the raw material is subjected to the hydrogenation dehydration and decomposed into low-carbon alcohols in a highly selective manner, and the low-carbon alcohols mainly comprise ethanediol, 1,2-propylene glycol and 1,3-propylene glycol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for simultaneous rapid detection of various sugars, sugar alcohols and alcohols in beer
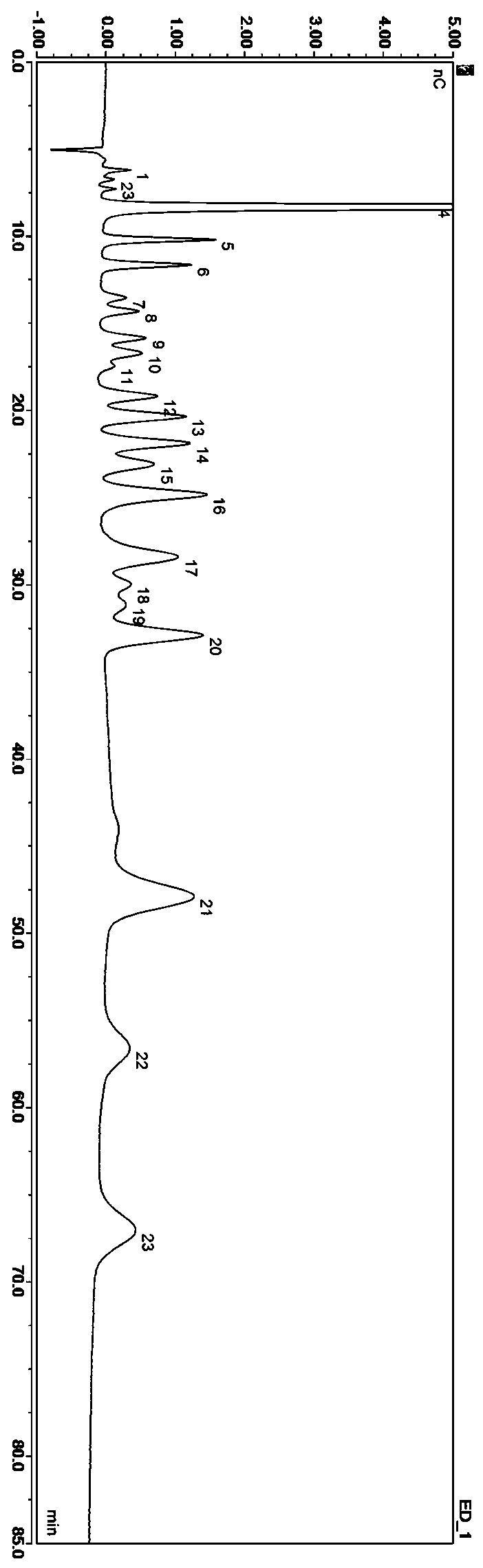
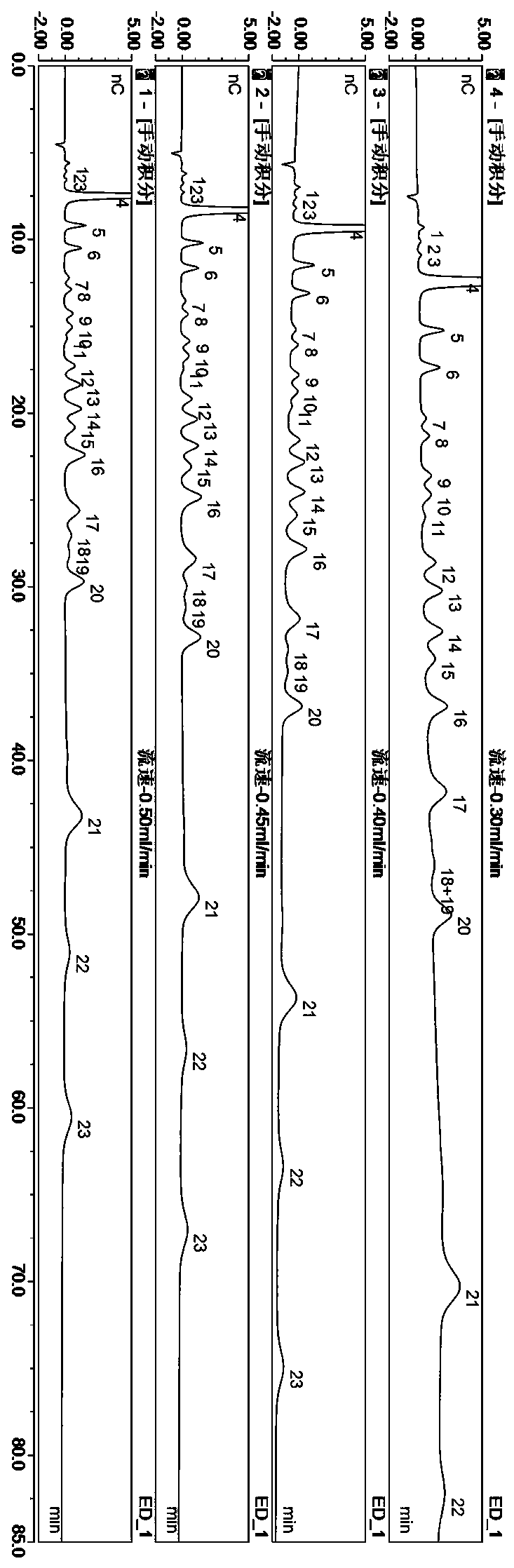
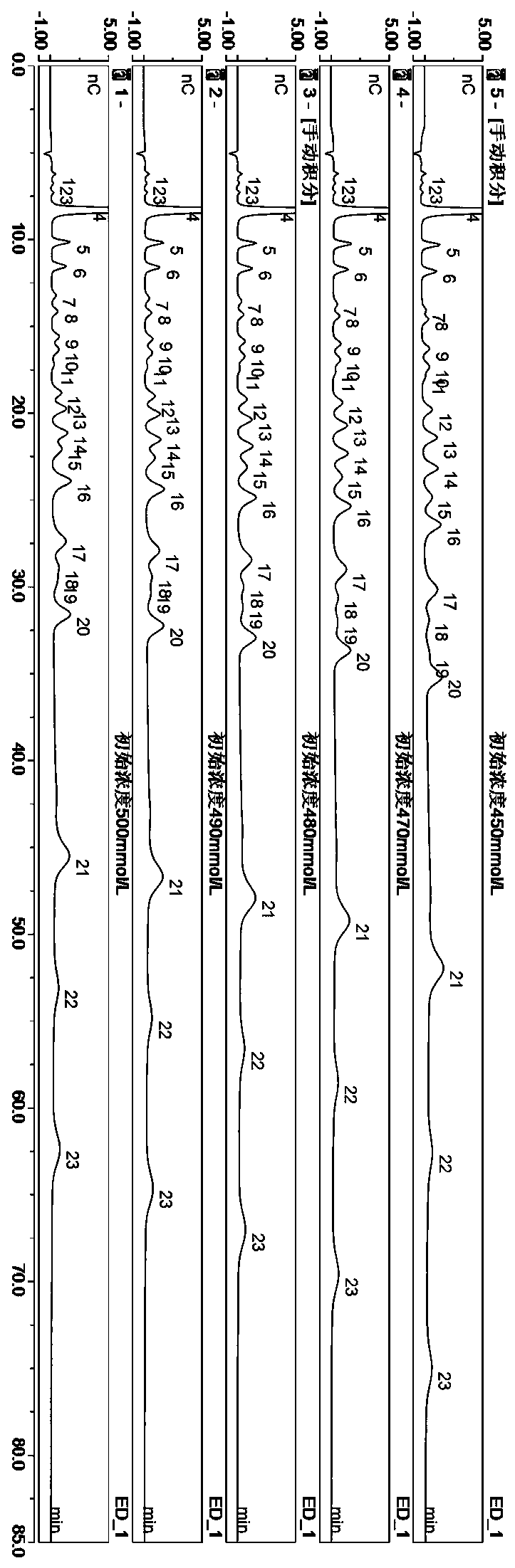
ActiveCN110514777AImprove detection efficiencyReduce the cost of testing manpower and material resourcesComponent separationIon chromatographyArabitol
Owner:日照海关综合技术服务中心
Gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacteria and preparation method and application thereof in preparing xylitol
InactiveCN102978148ASolve the problem of low conversion rate and low concentration of xylitolSimple and fast operationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesD-arabitolGluconobacter oxydans
The invention discloses a preparation method of gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacteria, which performs over-expression of the key restriction enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) for controlling the phosphopentose path to increase the metabolic flux of the path so as to realize cyclic regeneration of coenzyme NADH. The invention also discloses a fermentation technology of the engineering bacteria and application thereof in converting and preparing xylitol. According to the invention, the effect of the engineering bacteria in converting D-arabitol to generate xylitol is obviously superior to that of an original strain; and the conversion rate of xylitol against D-arabitol can reach 60-90%. The technology solves the problems of low conversion rate and low xylitol concentration of a bioconversion method for preparing xylitol to a certain degree, and has the advantages of economy and practicability, simplicity and convenience in operation and energy conservation and environmental protection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for simultaneously detecting 22 sugars, sugar alcohol and alcohol in fruit juice
ActiveCN110514778ASolve the technical problems of low efficiency in component determinationSolve low-efficiency technical problemsComponent separationIon chromatographyArabitol
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting 22 sugars, sugar alcohol and alcohol in fruit juice, and belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. The method adopts an integral impulse ampere-ion chromatography to research experiment factors affecting component separation via a processing method before optimization; and the method for simultaneously detecting the 22 sugars, the sugar alcohol and the alcohol (2,3-butanediol, propylene glycol, methyl alcohol, glycerin, erythritol, xylitol, rhamnose, arabitol, sorbitol, trehalose, galactitol, mannitol, 2-deoxidized-D-glucose, arabinose, melibiose, glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose, saccharose, raffinose and maltose) at a time is built. The technical difficulty of accurately analyzing the plurality of components, sugars, sugar alcohol and alcohol, in the fruit juice is solved; the method is fast, accurate and sensitive, achieves simultaneous analysis of the plurality of categories and the plurality of components, and makes an important contribution to component detection of the fruit juice.
Owner:日照海关综合技术服务中心
Hyphopichia burtonii strain and applications thereof
The invention discloses a hyphopichia burtonii strain and applications of the hyphopichia burtonii strain. The hyphopichia burtonii strain has the following morphological characteristics: the strain is inoculated to a PDA culture medium through a streak inoculation method, culturing is carried out for 2d at 28 DEG C, the diameter of the bacterial colony is 5-8 mm, the bacterial colony is round-jellyfish-shaped, is milk white in color, has the butyrous texture, and is non-transparent, and the edge of the bacterial colony is blanket-shaped. The hyphopichia burtonii strain can be used for producing arabitol in Maotai-flavor baijiu.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Screening method of D-arabitol high-yield yeast mutant strain
PendingCN104164415AImprove reliabilityStable Screening EfficiencyMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesD-arabitolScreening method
The invention provides a screening method of a D-arabitol high-yield yeast mutant strain. By using a mutant strain obtained by carrying out mutagenesis on Kluyveromyces lactis by a low-energy N+ ion implantation technique as a screening object, a high-flux screening method, which is implemented by primary screening based on a high-sugar solid culture medium and secondary screening based on paper chromatography / high-performance liquid chromatography combination, is established. The method has the advantages of high screening efficiency, low cost, short screening period and the like, is easy to operate, and provides a new method for efficiently screening the D-arabitol high-yield strain by modifying the yeast with low-energy ion implantation.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing arabitol by flammulina velutipes
InactiveCN102875330AIncrease added valueLess investmentHydroxy compound separation/purificationHigh concentrationReflux extraction
The invention relates to a method for preparing arabitol by flammulina velutipes, which utilizes the characteristic that flammulina velutipes sporocarp contains rich arabitol to prepare the low-cost and environment-friendly arabitol by taking the flammulina velutipes sporocarp as a raw material; and the product can be taken as natural sweetener and functional food raw material. The method comprises the steps of: drying the fresh flammulina velutipes sporocarp, and then using high-concentration alcohol to soak or carry out reflux extraction on the dried flammulina velutipes sporocarp; carrying out vacuum concentration on the leach liquor to recover ethanol; putting the concentrated solution in the environment of 0-10 DEG C; separating out the arabitol by crystallization; filtering or centrifuging while the arabitol is cool to obtain arabitol crystal; then, carrying out recrystallization on the arabitol crystal by methanol; continuously carrying out vacuum concentration on the separated mother liquor of the crystal to recover ethanol; and repeating the operation of crystallization and recrystallization to improve the yield of the arabitol. In order to save the cost, the method is more suitable for taking defective flammulina velutipes sporocarp or the head cut from the flammulina velutipes sporocarp as raw material. The technology has the characteristics of being simple in equipment, saving the cost and protecting the environment, thus improving the economic benefit of the flammulina velutipes industry.
Owner:SERICULTURE & AGRI FOOD RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Novel oils having antibacterial activity
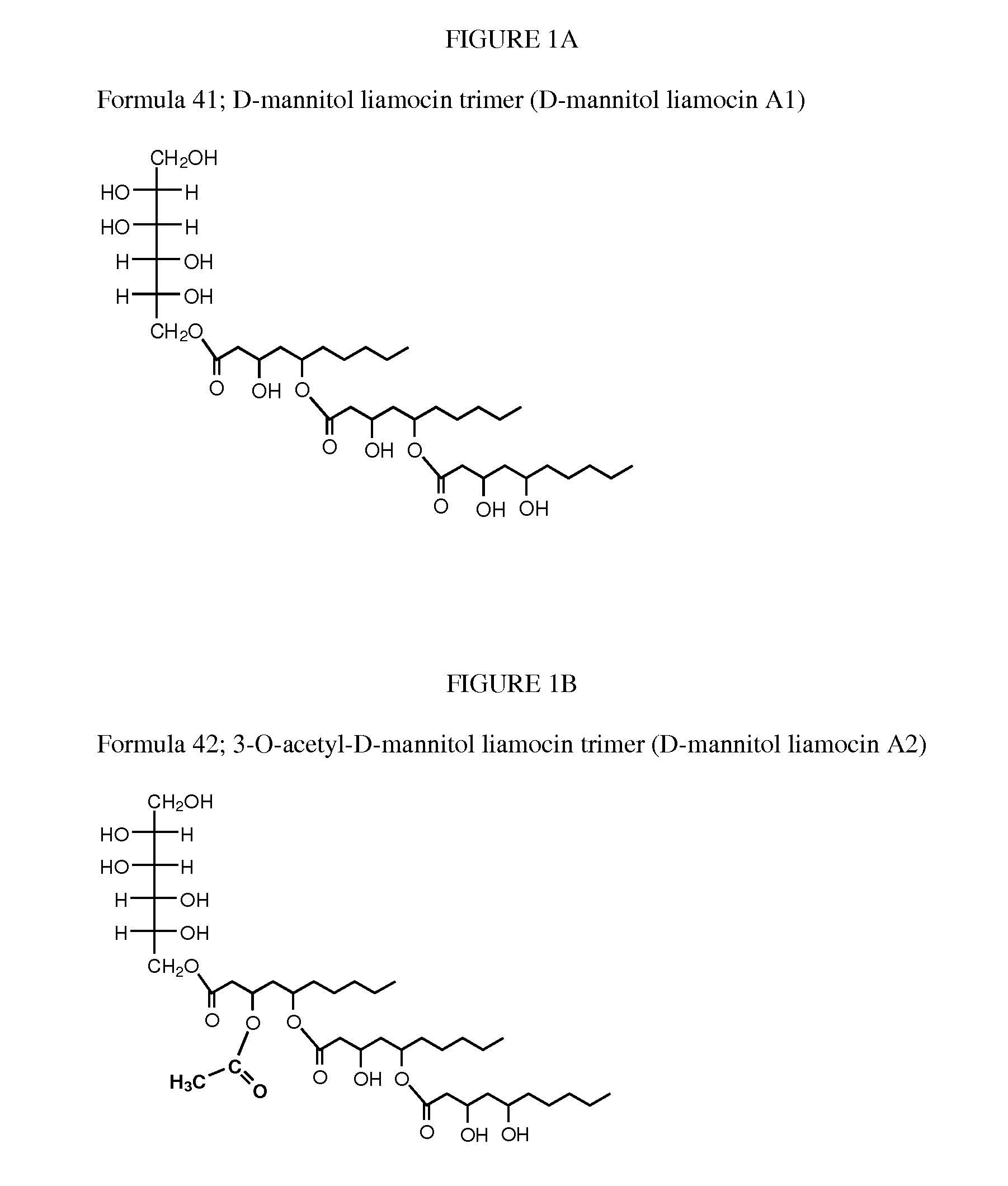
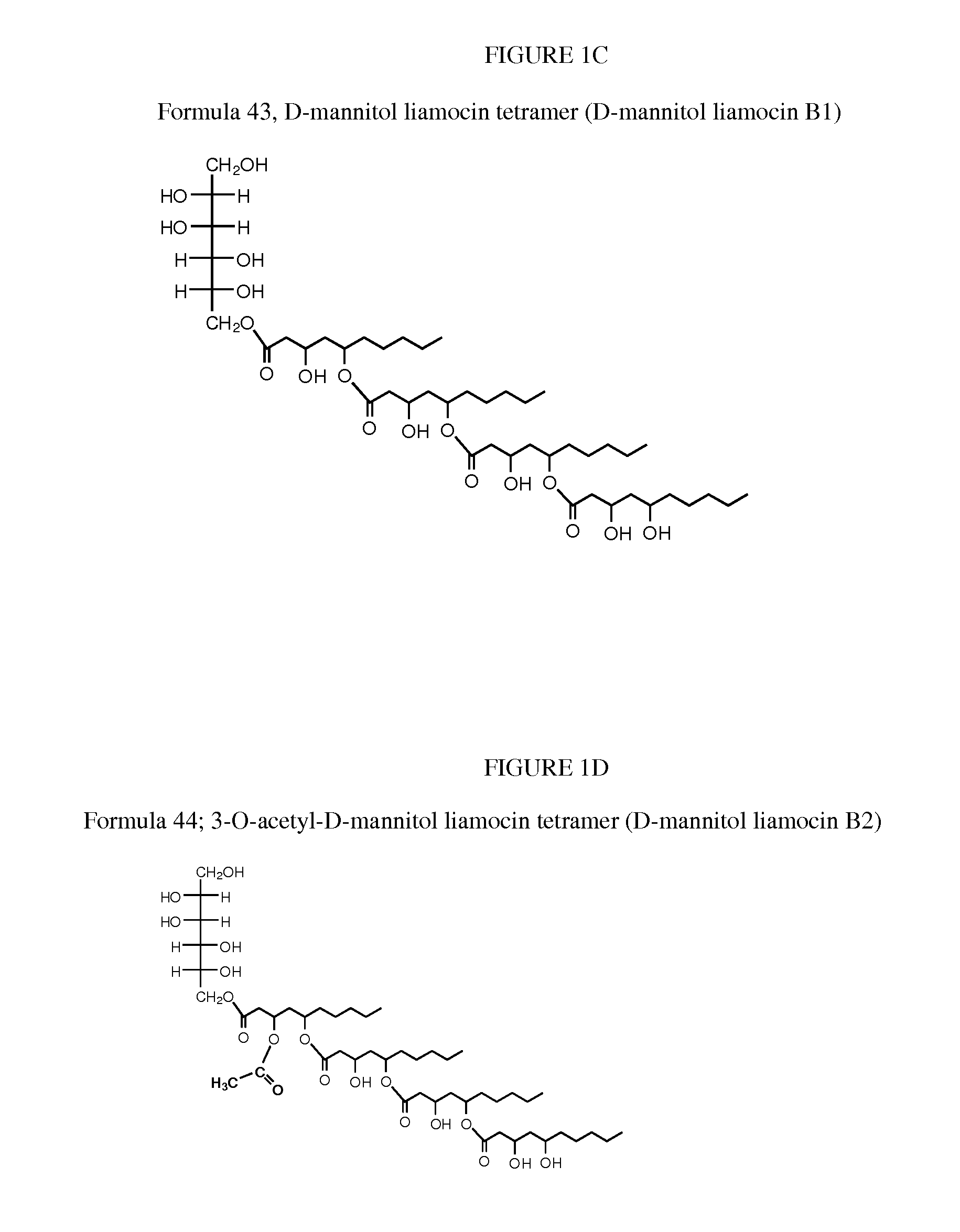
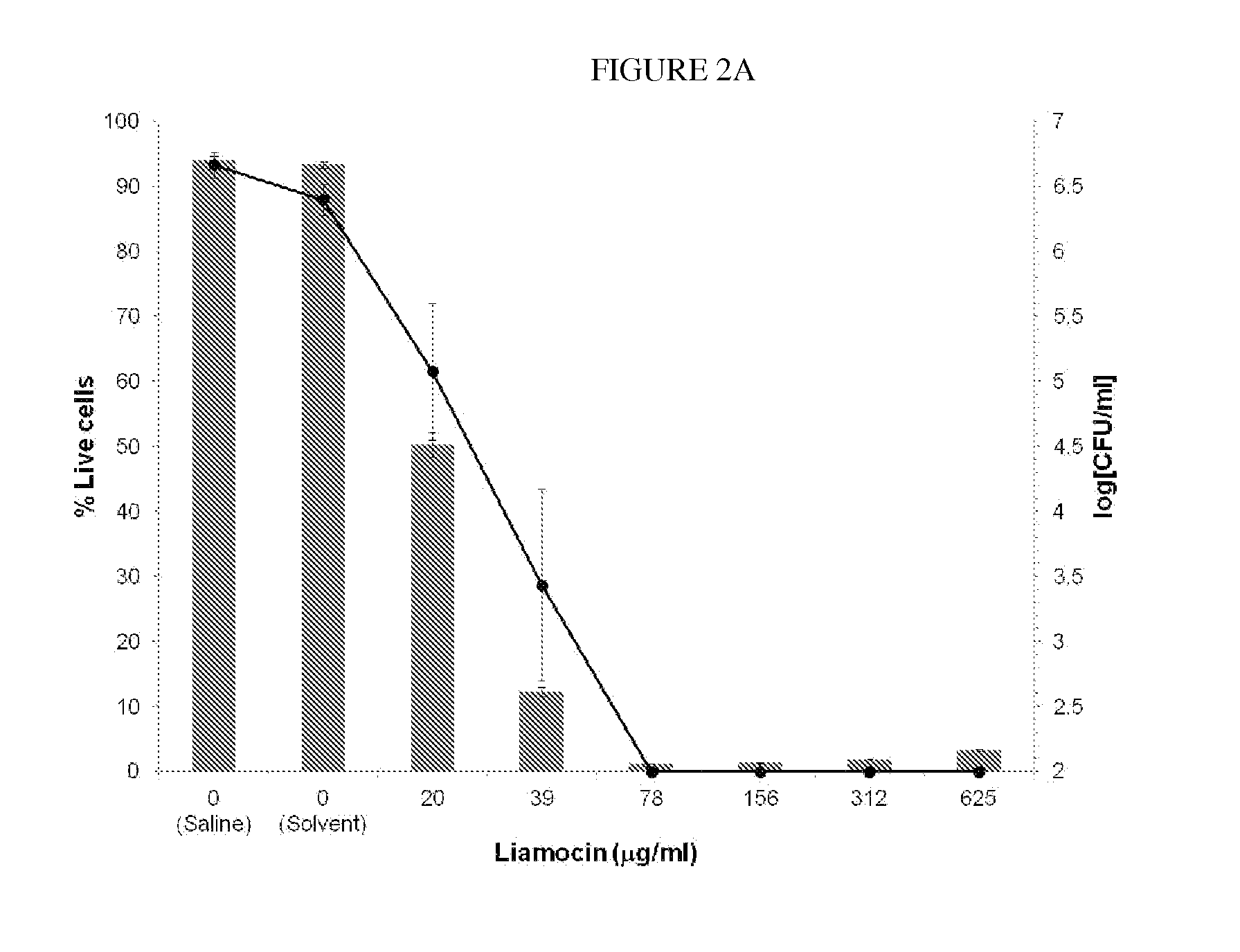
Novel compounds, called liamocins from Aureobasidium pullulans, having the general structure in Formula 1 are disclosed.where R1 is either COCH3 or H; and R2 is between two to ten O-linked 3,5-dihydroxydecanoate; and R3 can be a polyol (e.g., L- or D-glycerol, L- or D-threitol, L- or D-erythritol, L- or D-arabitol, L- or D-xylitol, L- or D-lyxitol, L- or D-ribitol, L- or D-allitol, L- or D-altritol, L- or D-mannitol, L- or D-iditol, L- or D-gulitol, L- or D-glucitol (also called sorbitol), L- or D-galactitol (also called dulcitol), and L- or D-talitol), 2-amino-D-mannitol, 2N-acetylamino-D-mannitol, L-rhamnitol, or D-fucitol; except when R3 is D-mannitol, R2 is not 2 nor 3 O-linked 3,5-dihydroxydecanoate chains. These liamocins described above in addition to D-mannitol liamocin A1, D-mannitol liamocin A2, D-mannitol liamocin B1, and D-mannitol liamocin B2, alone or in combination with each other, can be used to kill certain bacteria and to treat certain bacterial infections.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway and production method of xylitol using the same
ActiveUS8343736B2Easy to useImprove productivityMicroorganismsRecombinant DNA-technology[Candida] apicolaArabitol
The present invention relates to an efficient production method of xylitol by using the xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway to inhibit the production of arabitol, the byproduct, and instead to use arabinose only for cell metabolism in xylose / arabinose mixed medium. More precisely, to express efficiently L-arabinose isomerase (araA), L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Candida tropicalis, codon optimization was performed. Then, each gene was inserted in the gene expression cassette containing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and the selection marker URA3, which was introduced into Candida sp. microorganism. As a result, arabitol, the byproduct interrupting the purification and crystallization of xylitol could be inhibited, making the production method of xylitol of the present invention more efficient. The xylitol producing microorganism introduced with arabinose metabolic pathway of the present invention can be effectively used for the production of xylitol with high productivity by inhibiting the generation of arabitol.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing xylitol and its intermediate D-xylosone by microbial transformation of glucose and strain used in the same
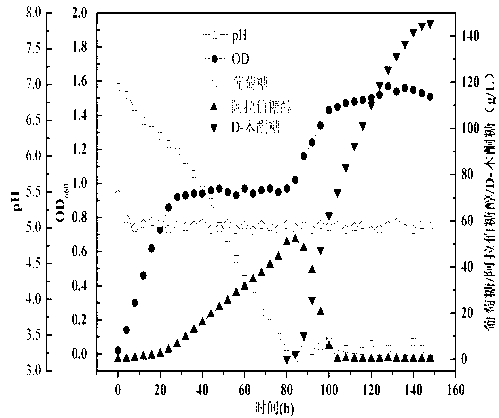
ActiveCN102796797AHigh yieldRelease feedback inhibitionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyArabitol
The invention discloses a method for preparing D-xylosone by microbial transformation of glucose, comprising the following steps: firstly, respectively preparing an osmophilic yeast seed liquid and a gluconobacter oxydans seed liquid by using glucose as a raw material, then inoculating the osmophilic yeast seed liquid to conduct arabitol fermentation, and then in middle and later stage inoculating the gluconobacter oxydans seed liquid to conduct mixed culture fermentation, simultaneously controlling the glucose content in the broth to be 5-10g / L, and converting arabitol into D-xylosone. According to the method, the feedback inhibition of arabitol is removed, and the efficiency of preparing D-xylosone from glucose is raised. The invention further discloses a method for preparing xylitol by microbial transformation of glucose, comprising the following steps: firstly converting glucose into D-xylosone by the above method, then converting D-xylosone into D-xylose by isomerization of enzyme, extracting and refining, and conducting catalytic hydrogenation to obtain xylitol. According to the method, the production efficiency of xylitol is raised, and the cost of preparing xylitol by biological method is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANLI PHARMA
Dry compositions and methods for gel electrophoresis
ActiveUS20120160684A1Easy resuspensionHigh resolutionElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementD-arabitolChemistry
The invention provides dry compositions for preparing and loading a sample on a gel for electrophoretic separation. The dry compositions preferably include a tracking dye and a sedimenting agent selected from a five-carbon polyol (e.g., ribitol, arabitol, or xylitol), iso-erythritol, maltitol, and saccharine. Methods for making and using, as well as kits comprising the disclosed compositions, are also provided.
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC
Candida bacterial strain and method for producing D-arabitol
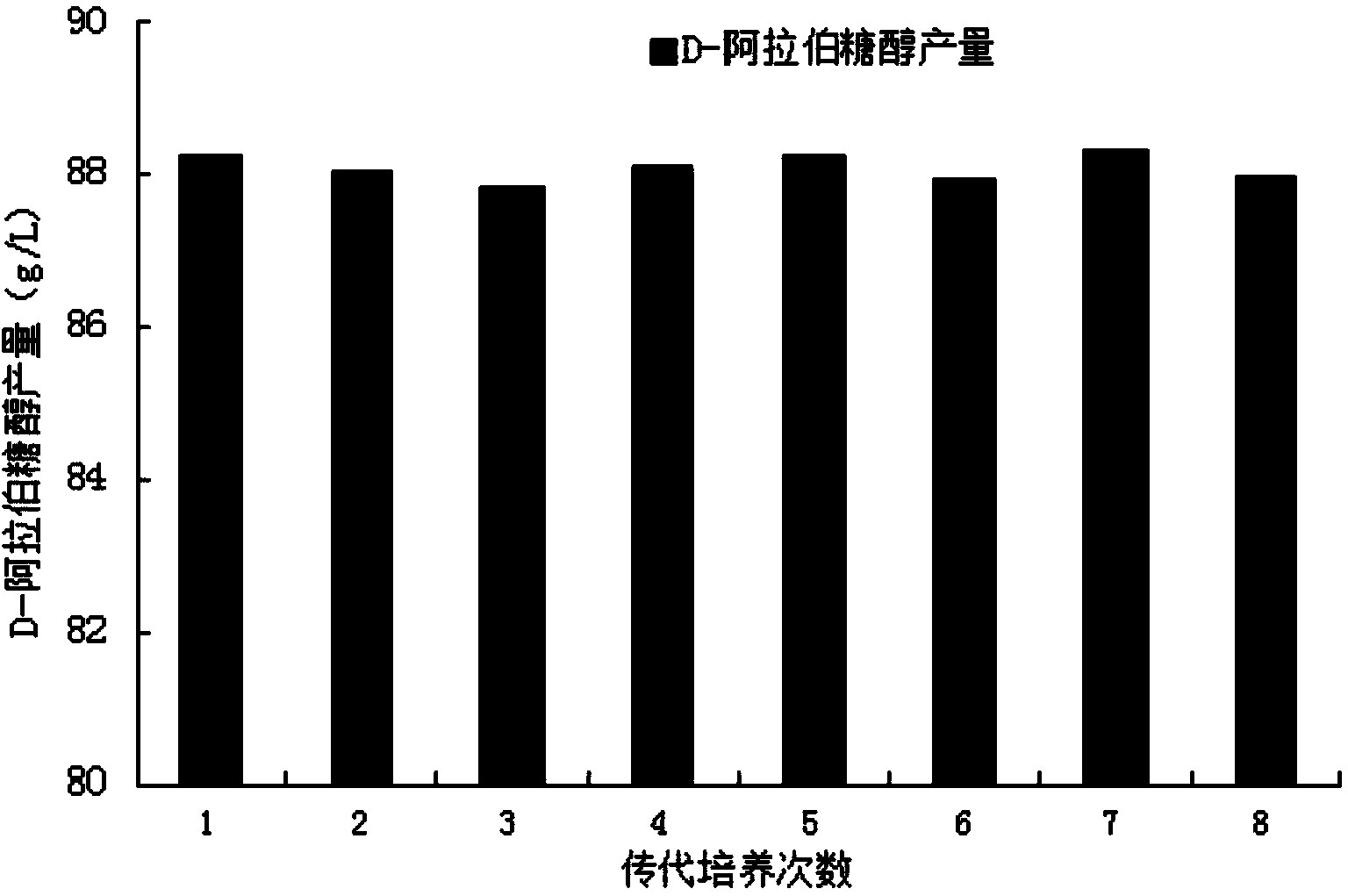
The invention discloses a Candida bacterial strain and a method for producing D-arabitol. The Candida sp.H2 has the preservation number of CGMCC No.3255 in China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms (CCCCM), and the 26S rDNA D1 / D2 region sequence of the bacterial strain is displayed in SEQ IC NO:1. In the invention, the method using the Candida bacterial strain to produce D-arabitol is as follow: cultivating the Candida bacterial strain in a seed liquid culture medium containing glucose and yeast extracts to obtain the inoculum of Candida; then inoculating the inoculum of Candida to the seed liquid culture medium containing glucose and yeast extracts to ferment and produce D-arabitol. Compared with the prior art, the invention provides a new Candida bacterial strain which can be used for producing D-arabitol. The D-arabitol produced with the Candida sp.H2 of the invention has higher yield, and the accumulation amount can reach the high level of 86.55g.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com