Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
274 results about "Stencil printing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
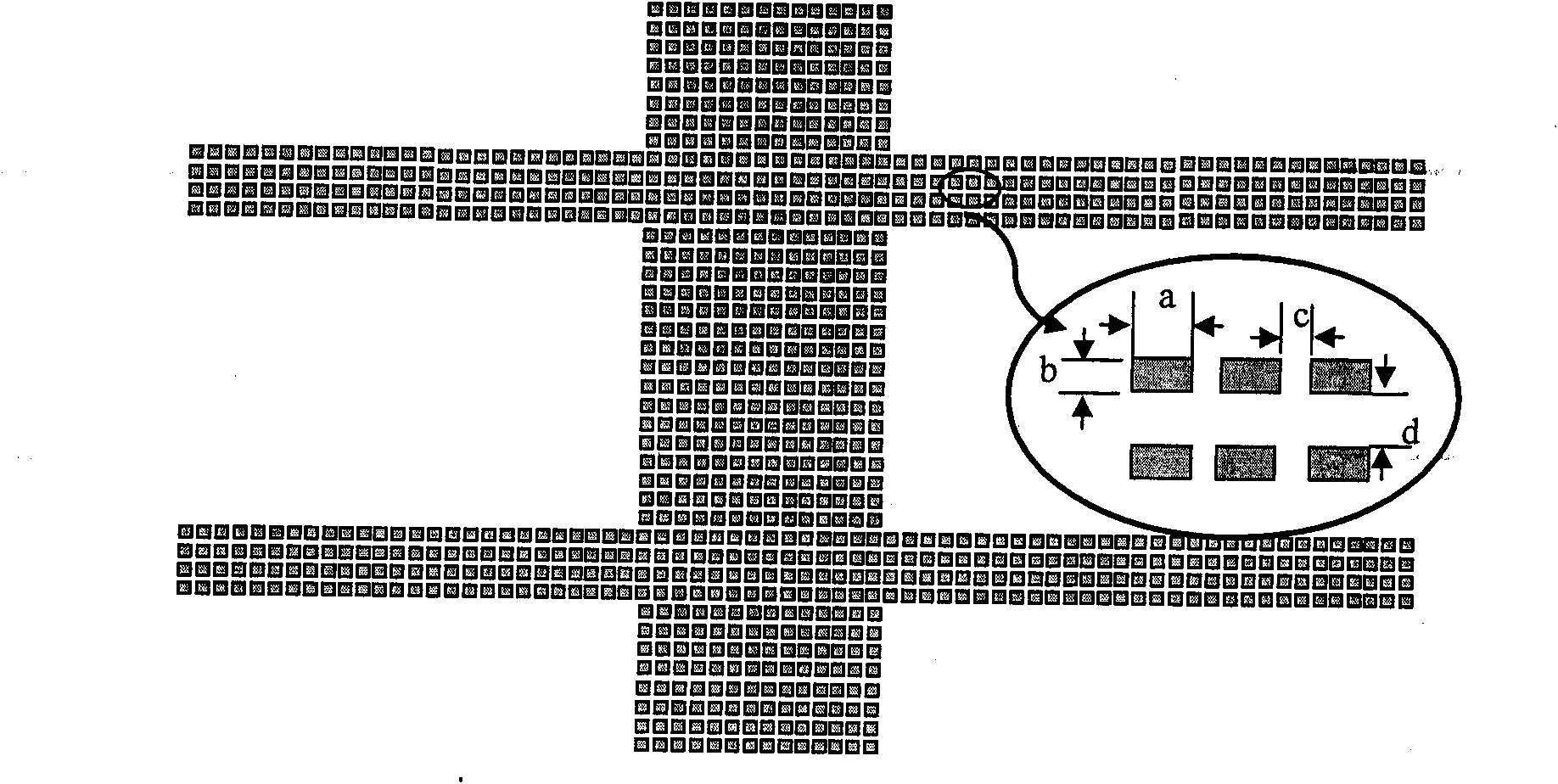
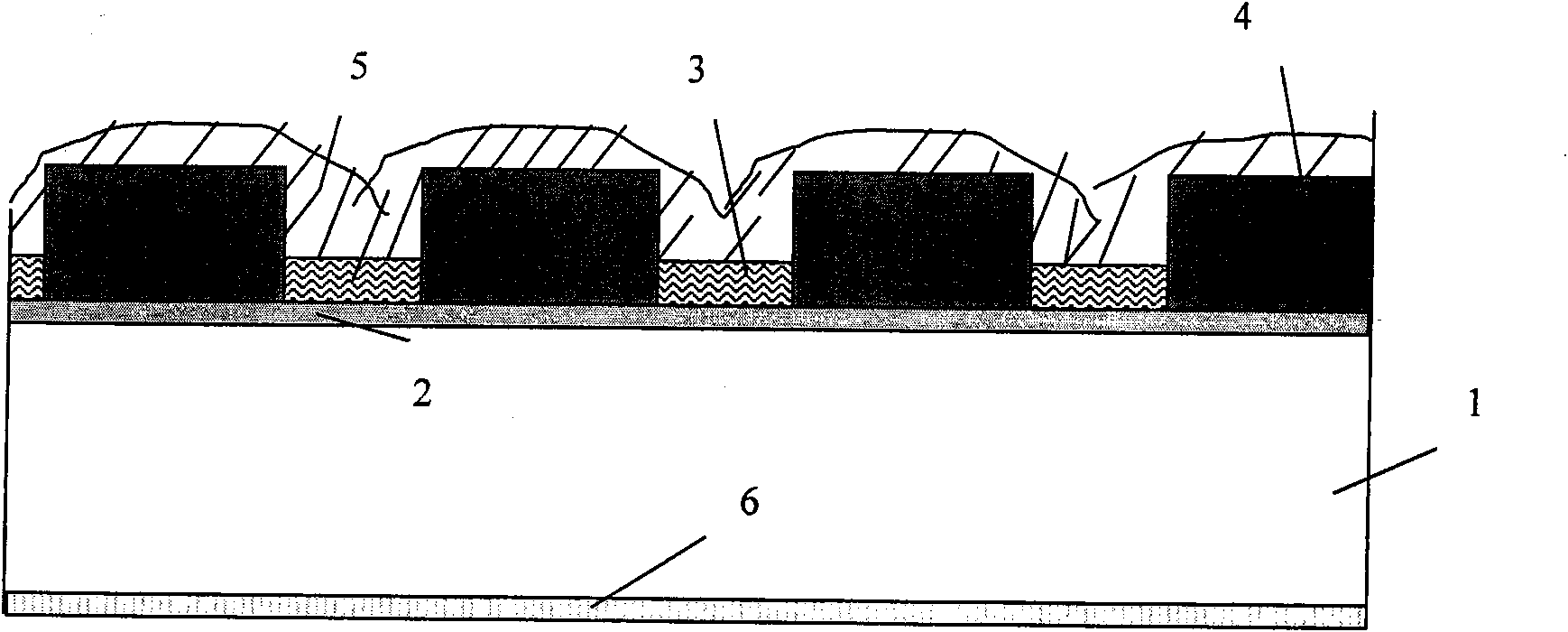
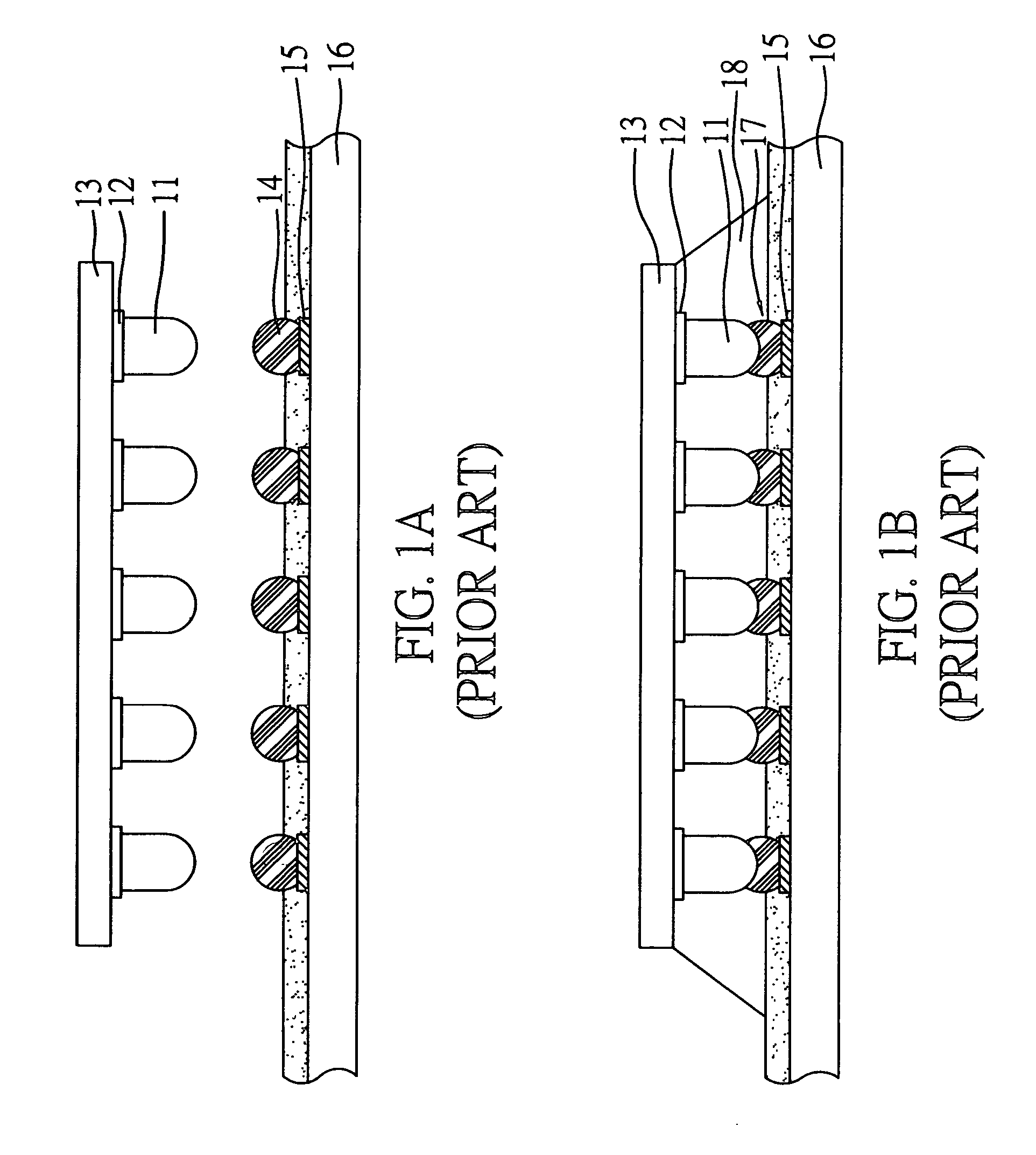
Stencil printing is the process of depositing solder paste on the printed wiring boards (PWBs) to establish electrical connections. It is immediately followed by the component placement stage. The equipment and materials used in this stage are a stencil, solder paste, and a printer.
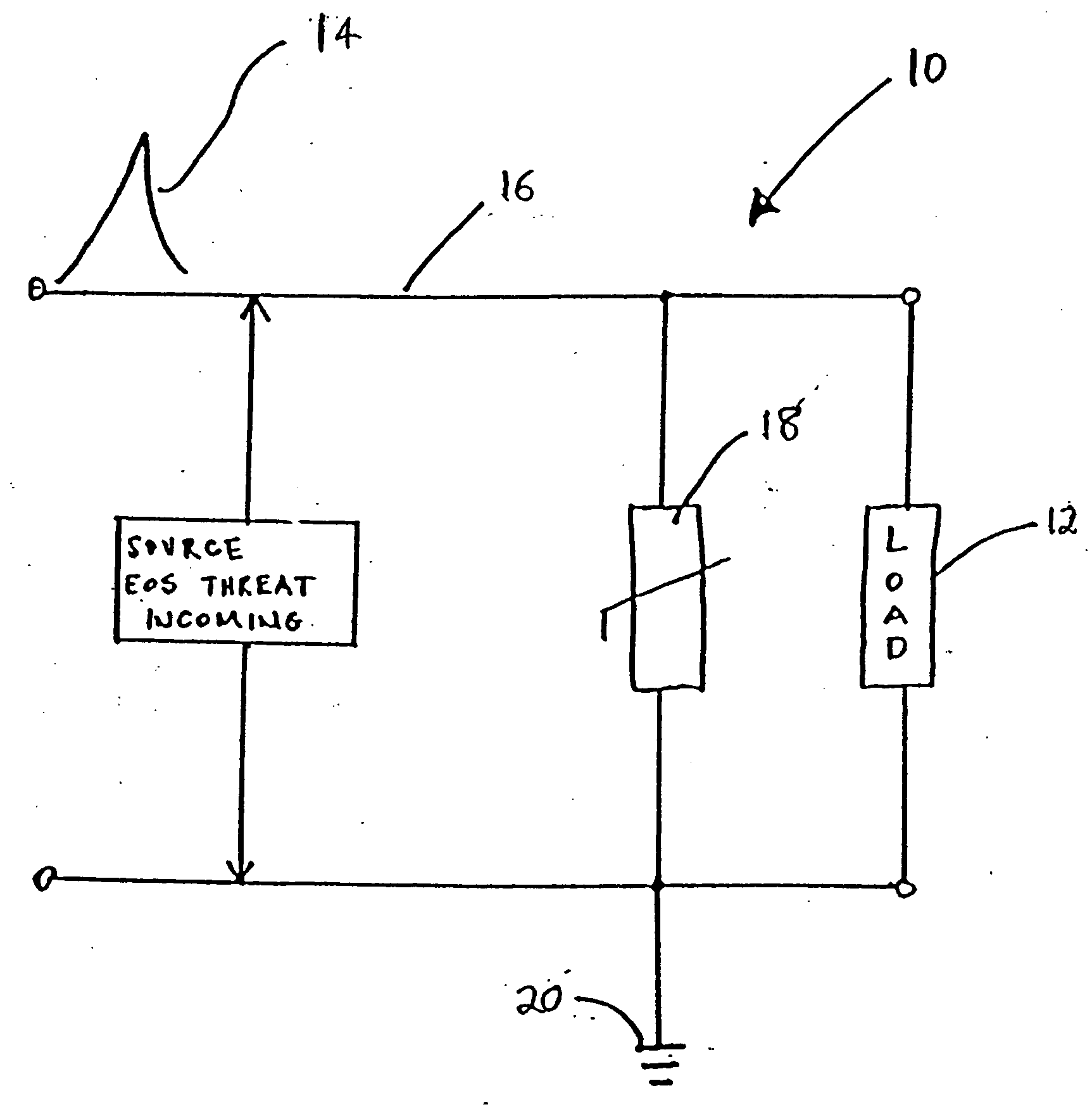
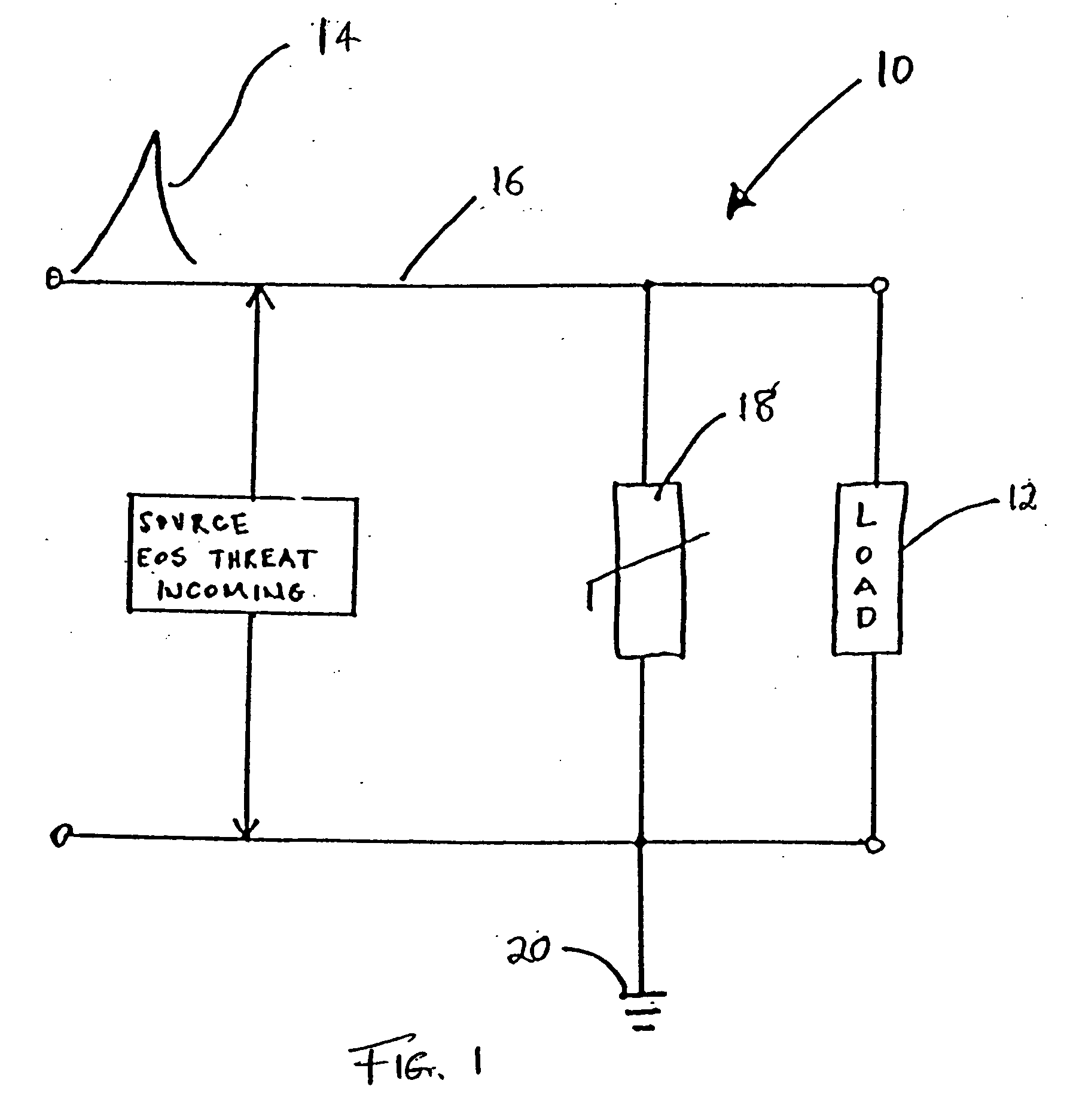
Direct application voltage variable material, devices employing same and methods of manufacturing such devices
ActiveUS20050057867A1Directly appliedCurrent responsive resistorsPrinted circuit aspectsStencil printingMechanical engineering
A voltage variable material (“VVM”) including an insulative binder that is formulated to intrinsically adhere to conductive and non-conductive surfaces is provided. The binder and thus the VVM is self-curable and applicable in a spreadable form that dries before use. The binder eliminates the need to place the VVM in a separate device or to provide separate printed circuit board pads on which to electrically connect the VVM. The binder and thus the VVM can be directly applied to many different types of substrates, such as a rigid FR-4 laminate, a polyimide, a polymer or a multilayer PCB via a process such as screen or stencil printing. In one embodiment, the VVM includes two types of conductive particles, one with a core and one without a core. The VVM can also have core-shell type semiconductive particles.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Combined stencil and digital printing system
InactiveUS20060249039A1Increase surface tensionScreen printersTypewritersStencil printingEngineering
A printing system comprising a stencil printing apparatus and a digital printing apparatus for high speed printing of images having details of high resolution, rich colors, or variability, optionally also comprising a wetting apparatus operative to wet at least a part of the printed object prior to the digital printing.
Owner:KORNIT DIGITAL TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Direct application voltage variable material, devices employing same and methods of manufacturing such devices
InactiveUS7183891B2Directly appliedCurrent responsive resistorsPrinted circuit aspectsScreen printingStencil printing
A voltage variable material (“VVM”) including an insulative binder that is formulated to intrinsically adhere to conductive and non-conductive surfaces is provided. The binder and thus the VVM is self-curable and applicable in a spreadable form that dries before use. The binder eliminates the need to place the VVM in a separate device or to provide separate printed circuit board pads on which to electrically connect the VVM. The binder and thus the VVM can be directly applied to many different types of substrates, such as a rigid FR-4 laminate, a polyimide, a polymer or a multilayer PCB via a process such as screen or stencil printing. In one embodiment, the VVM includes two types of conductive particles, one with a core and one without a core. The VVM can also have core-shell type semiconductive particles.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
System and methods for data-driven control of manufacturing processes
Systems and methods for implementing hybrid, closed-loop control that generates control values for processes defined by a limited number of function evaluations and large amounts of process and measurement noise. The described control system is applied to a stencil printing process for applying solder paste to an electronic medium such as a printed circuit board or semiconductor wafer. The control system is defined by a hybrid approach. A first, coarse algorithm is used to rapidly produce the value of a stencil printer control value resulting in a solder paste deposit having a volume within predetermined acceptable limits. After the coarse algorithm no longer produces solder paste deposits closer to a desired volume, a second, more refined estimator is used to fine tune the process. An additional transitional algorithm may be added between the coarse algorithm and refined estimator. The coarse algorithm may be implemented with a constrained-conjugated gradient search, and the refined search may be a implemented using a least-squares affine estimator or a quadratic estimator. The transitional algorithm may be implemented using a block version of a least-squares affine estimator.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for preparing front electrodes of solar cells
InactiveCN101562217AReduce surface recombinationHigh aspect ratioFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesStencil printingChemical plating
The invention relates to a method for preparing front electrodes of solar cells, which comprises the following steps: firstly preparing discontinuous dot electrodes; and then connecting the dot electrodes by electroplating technology to realize that the electrodes collect and transport current but dielectric films still exist between the dot electrodes to have the function of passivation. The discontinuous dot electrodes are prepared by photoetching, evaporation and dissection methods, or firstly printed by silkprint, stencil printing or ink jet printing and then prepared by a sintering method. The electroplating is photoinductive electroplating or chemical plating. The dot electrodes effectively reduce surface recombination; and the adopted electroplating technology not only simply and accurately realizes the connection of the dot electrodes, but also effectively reduces the width of grid lines, namely reduces electrode shading areas and further reduces the surface recombination so as to contribute to improving battery efficiency.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semi-aqueous solvent cleaning of paste processing residue from substrates
A process of cleaning of objects that relate to semiconductor fabrication processes, such as, for example, conductive paste screening in the production of multilayer ceramic substrates and composite solder paste by stencil printing in electronic circuit assembly. Specifically, the process removes a metal / polymer composite paste from screening masks and associated paste making and processing equipment used in printing conductive metal pattern onto ceramic green sheet in the fabrication of semiconductor packaging substrates. The process also cleans solder paste residue from stencil printing equipment used in electronic module assembly surface mount technology for SMT discretes, solder column attachment, and BGA (Ball Grid Array) attachment on ceramic chip carrier or for screening solder paste onto printed circuit board. More particularly, paste residue is cleaned from metal, ceramic, and plastic substrates by a non-alkaline semi-aqueous cleaning method employing high boiling propylene glycol alkyl ether or mixtures of propylene glycol alkyl ether and propylene glycol solvents.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Substrate for pre-soldering material and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS7112524B2Strengthen pre-soldering jointIncrease contact areaPrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesStencil printingResist
A substrate for a pre-soldering material and a fabrication method of the substrate are proposed. The substrate having at least one surface formed with a plurality of conductive pads is provided. An insulating layer is formed over the surface of the substrate in such a way that a top surface of each of the conductive pads is exposed. Next, a conductive film and a resist layer are formed in sequence on the insulating layer and the conductive pads, wherein a plurality of openings are formed in the resist layer to expose a part of the conductive film above the conductive pad. Then, a pre-soldering material is deposited over the conductive pad by stencil printing or electroplating process.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Substrate for pre-soldering material and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20050070084A1Strengthen pre-soldering jointIncrease contact areaPrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesResistStencil printing
A substrate for a pre-soldering material and a fabrication method of the substrate are proposed. The substrate having at least one surface formed with a plurality of conductive pads is provided. An insulating layer is formed over the surface of the substrate in such a way that a top surface of each of the conductive pads is exposed. Next, a conductive film and a resist layer are formed in sequence on the insulating layer and the conductive pads, wherein a plurality of openings are formed in the resist layer to expose a part of the conductive film above the conductive pad. Then, a pre-soldering material is deposited over the conductive pad by stencil printing or electroplating process.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Multi-layer paper peelable into at least two thin sheets
InactiveUS6977111B2Low densityLose weightNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperWood veneerStencil printing
Disclosed is a multi-layer paper suitable as a material for preparing heat-sensitive stencil printing masters. The multi-layer paper is produced by combining a plurality of thin paper layers by paper making. The multi-layer paper has a peel strength of 10 N / m or less and may be delaminated into at least two tissue sheets.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
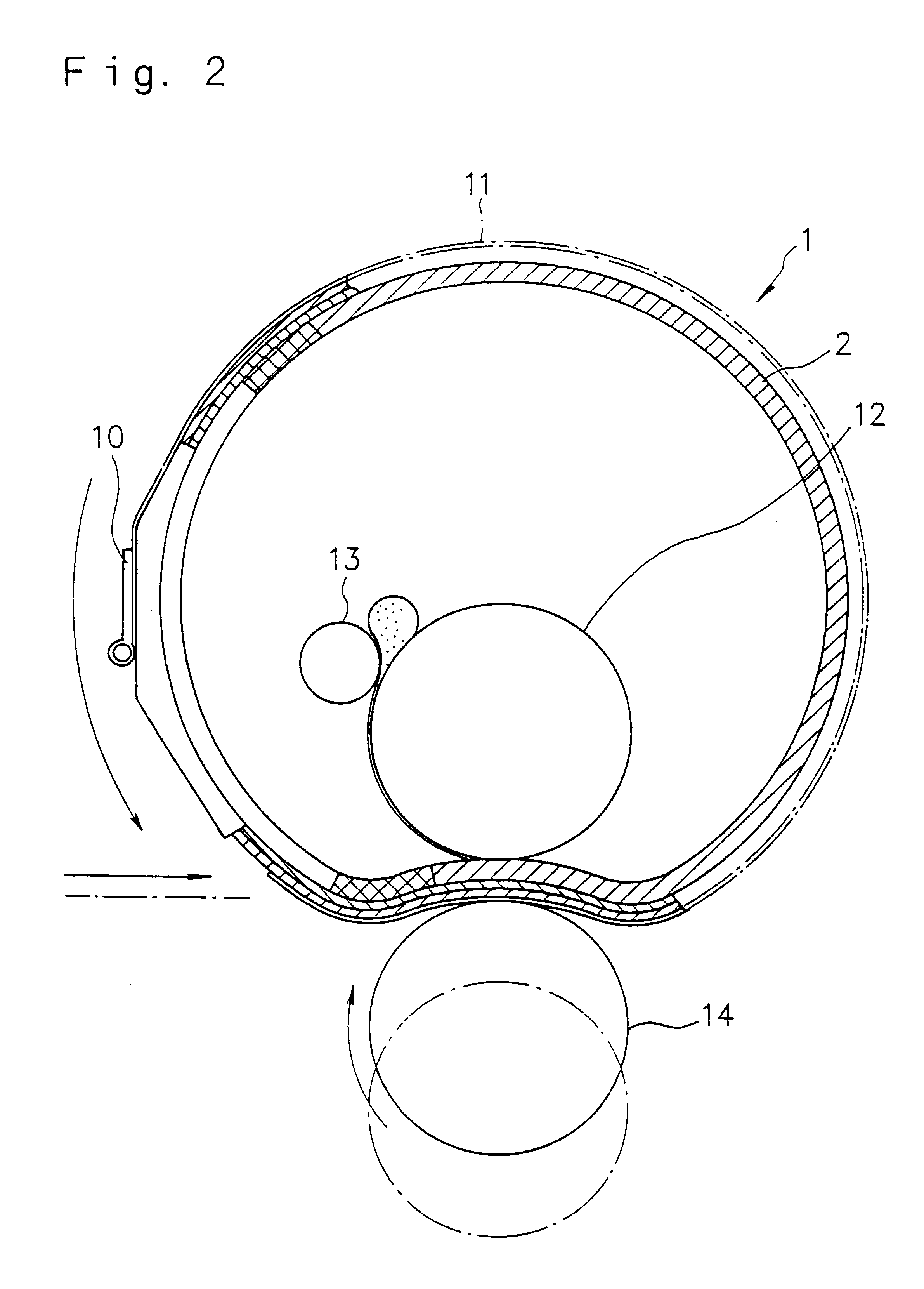
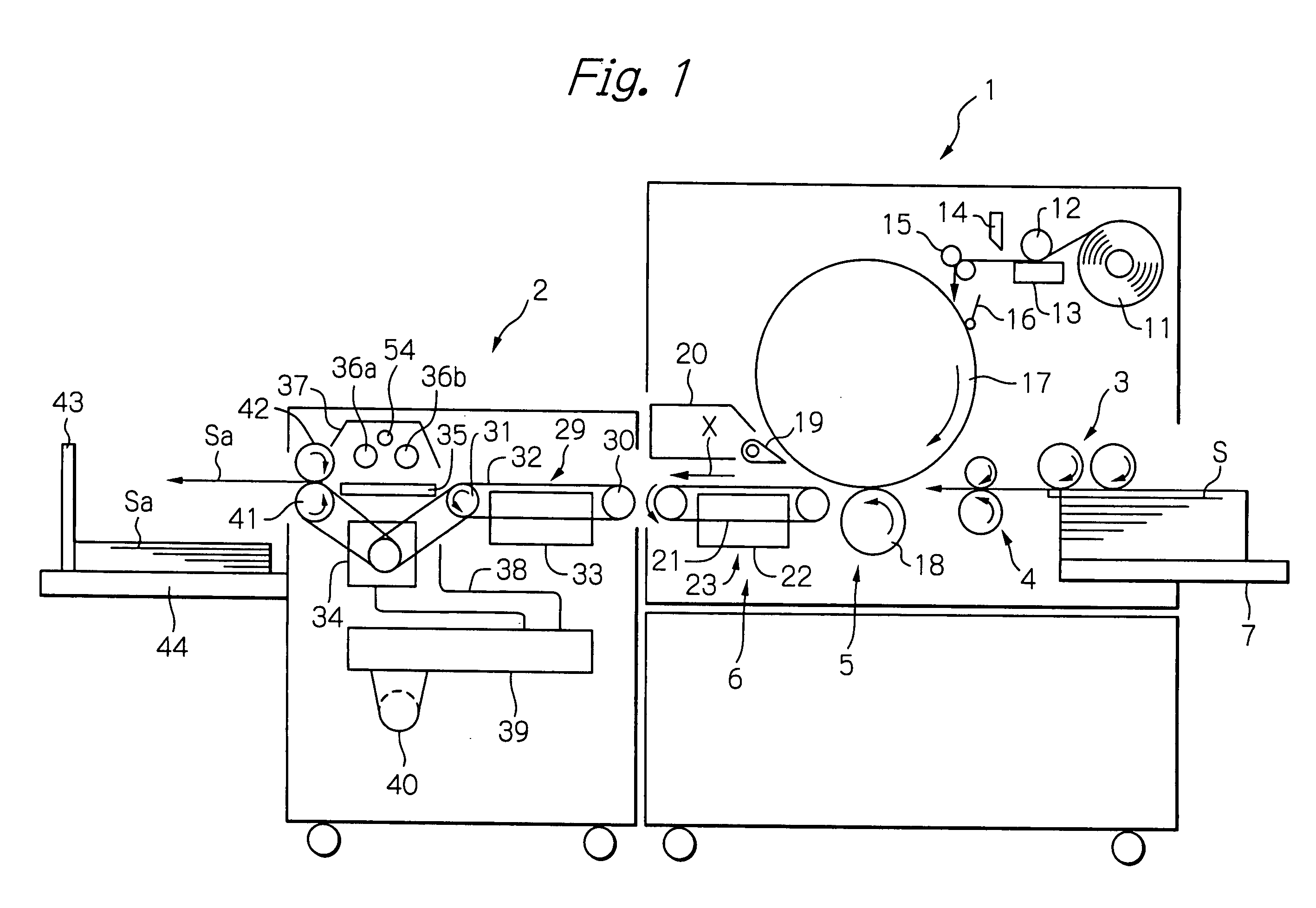
Stencil printing machine and stencil printing drum
A stencil printing machine has a printing drum having a cylindrical circumferential wall adapted to receive a perforated stencil sheet wrapped on an outer circumferential surface thereof and driven to rotate around a central axis thereof the circumferential wall having an opening portion with many through holes formed therein, a non-opening portion formed around the opening portion, and at least one recessed portion formed in at least one part of the opening portion adjacent to the non-opening portion in an axial direction of the circumferential wall; an ink supplying roller situated in the printing drum for supplying ink to an inner circumferential surface of the cylindrical circumferential wall of the printing drum; and a press roller situated adjacent to the printing drum and being urged against the outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical circumferential wall of the printing drum.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
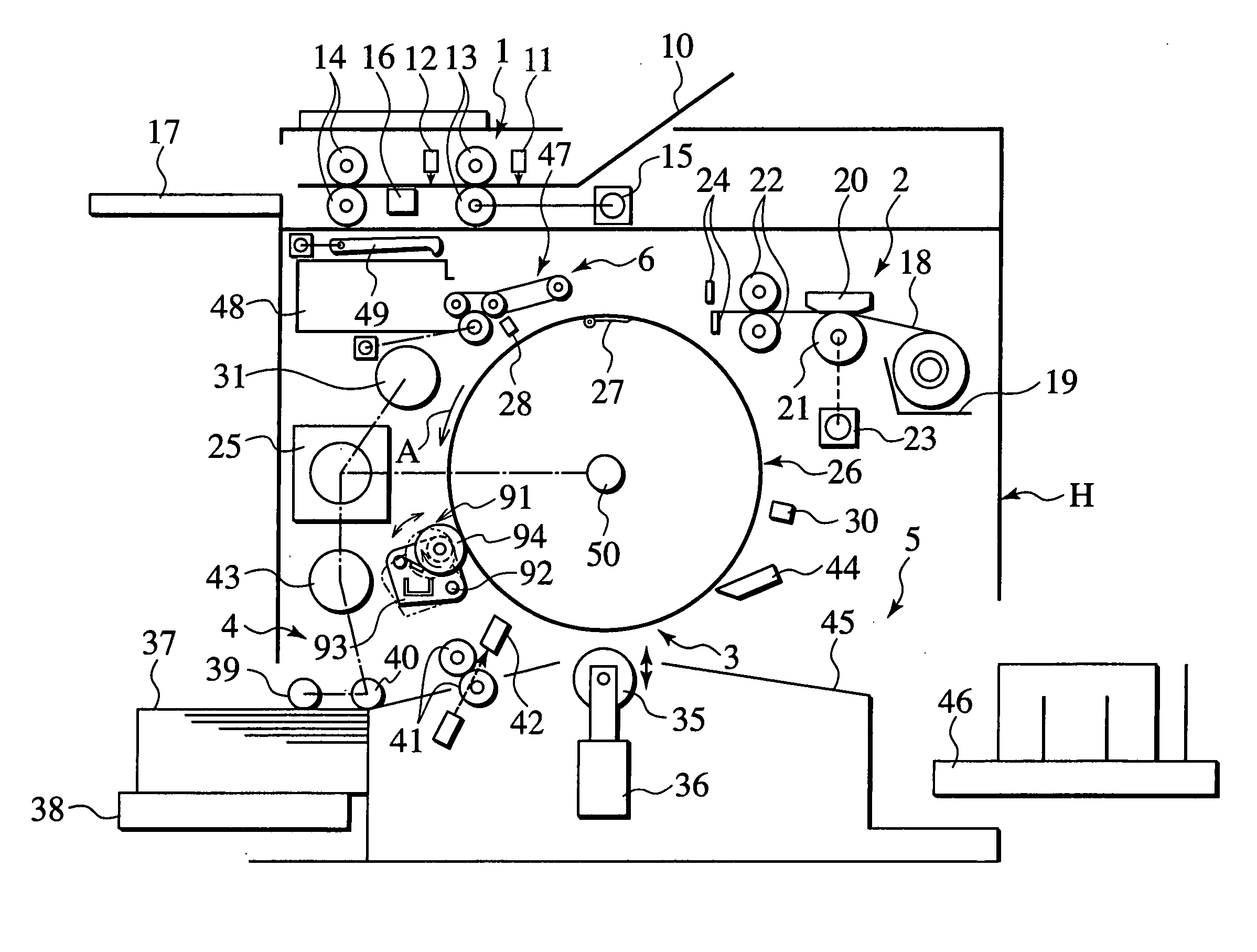
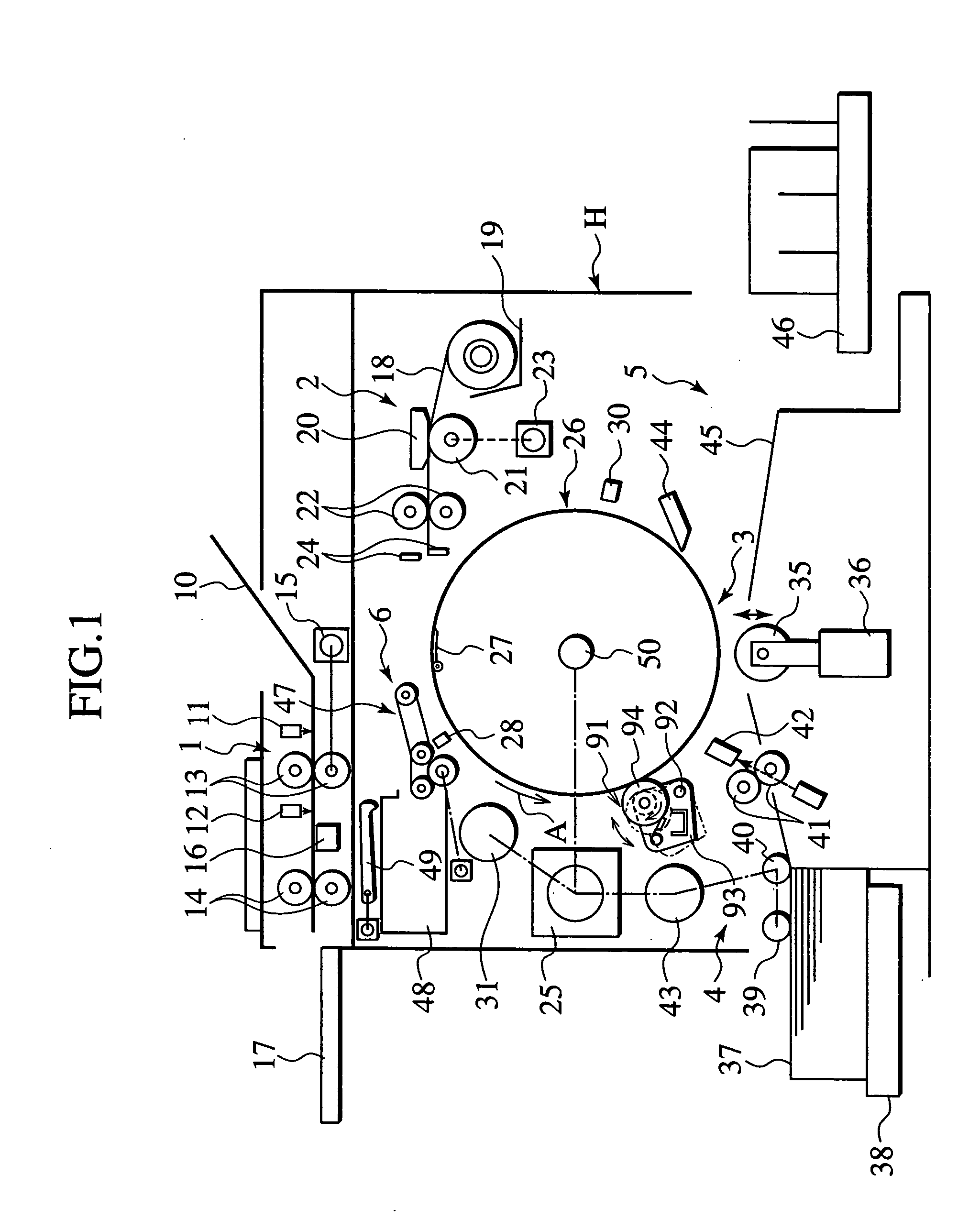
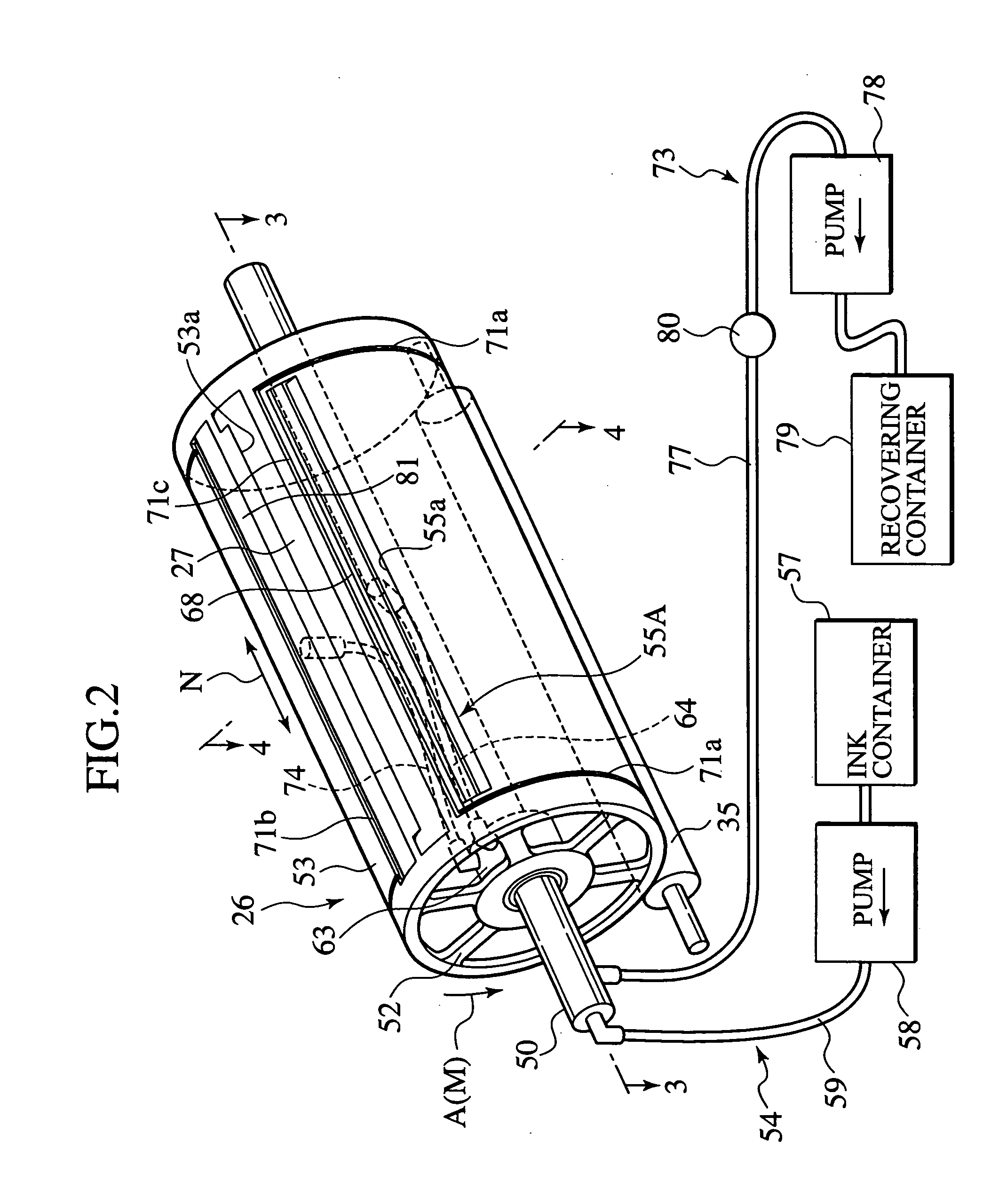
Stencil printing machine, ink recovering method, image unevenness preventing method, and ink adapting method
InactiveUS20050056169A1Simple configurationRaise the ratioInking apparatusStencilling apparatusStencil printingRecovery method
A stencil printing machine has a rotatable printing drum including an outer peripheral wall of ink impermeable material. A stencil paper is mounted on the surface of the outer peripheral wall. An ink supplying mechanism includes an ink supplying unit in the outer peripheral wall of the printing drum. The ink supplying mechanism supplies ink from the ink supplying unit to the surface of the outer peripheral wall. A pressure roller presses a fed print sheet against the outer peripheral wall. An ink recovering mechanism recovers ink which has flown out of a maximum printing area of the outer peripheral wall of the printing drum. A pressing mechanism presses the stencil paper against the outer peripheral wall of the printing drum.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Method for attaching dice to a package and arrangement of dice in a package
InactiveUS20060270104A1Improve productivityAvoid damage to the structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStencil printingEngineering
The invention relates to a method and arrangement for assembling and packaging single and multiple semiconductor dice with an intermediate arranged interposer. The interposer is arranged onto the backside of a die within the wafer composite and thereby during the wafer level process. Preferably the interposer is printed by a stencil printing process.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Method of applying an encapsulant material to an ink jet printhead
A stencil printed encapsulant material is provided for use in protecting electrical components in thermal ink jet printhead cartridges. A method of applying an encapsulant material to an ink jet print cartridge by stencil printing is also provided. The method includes providing a stencil having at least one aperture, providing an ink jet cartridge and stencil printing an encapsulant material onto a portion of the ink jet print cartridge thereby forming a layer of encapsulant material to protect electrical components or other printhead components.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Reflow process welding method
ActiveCN103920956ANo pollutionCreate pollutionPrinted circuit assemblingSoldering apparatusStencil printingAlloy
Owner:WUXI CHINA RESOURCE MICRO ASSEMBLY TECH
Method for forming heightened solder bumps on circuit boards
InactiveUS6979636B1Quality improvementAchieve height demandPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStencil printingResist
The present invention relates a method for forming heightened solder bumps on a circuit board, which has a surface formed with a plurality of pads and a solder resist thereon and the pads are exposed from the solder resist. The steps of the method mainly are: firstly, applying a first stencil printing and a first reflow process to the circuit board so that a plurality of first solder bumps form on the pads respectively. Then, apply a second stencil printing and a second reflow process to the circuit board so as to have solder paste formed on the first solder bumps and to have the solder paste integrated with the first solder bumps respectively to form the heightened solder bumps on the pads.
Owner:COMPEQ MFG
Water-in-oil type emulson ink for stencil printing
A water-in-oil type emulsion ink composed of 10–90% by weight of an oil phase and 90–10% by weight of an aqueous phase. The oil phase contains an esterified vegetable oil (an esterified vegetable oil obtained by recycling and esterifying edible waste oil such as soybean methyl ester, soybean butyl ester, or tall oil butyl ester).
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for Fabricating Circuit Board with Conductive Structure
InactiveUS20070186412A1Reduce connectivityImprove connectivityPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted electric component incorporationStencil printingResist
A method for fabricating a circuit board having a conductive structure is disclosed. The method includes: forming first and second insulating protective layers respectively on first and second surfaces of a circuit board; forming a conductive layer on the first insulating protective layer and the openings; forming first and second resist layers on the conductive layer and the second insulating protective layer respectively; forming first electrically connecting structures by electroplating on the exposed conductive layer over a plurality of first and second electrically connecting pads in openings of the first resist layer; removing the first and the second resist layers and the conductive layer covered by the first resist layer; and forming second electrically connecting structures by stencil printing on the conductive layer over the second electrically connecting pads on the first surface and on a plurality of third electrically connecting pads of the second surface of the circuit board.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Printing apparatus
ActiveCN1846994AAdjustable clamping pressureAdjust clamping pressurePrinted circuit assemblingScreen printersStencil printingEngineering
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Printing control apparatus having printing order information producing function
InactiveUS20020029703A1High operating requirementsAddressographsLiquid surface applicatorsStencil printingEngineering
A printing control apparatus for controlling a stencil printing machine (50, 100), wherein a stencil sheet, which is made on the basis of image data, is wound around a printing drum (25; 125, 126) with which a print sheet (34; 141) is held in pressured contact to perform a stencil printing operation, provides the stencil printing machine with image data representative of an image to be reproduced as an object, and printing order information representative of a page order in which the printing operation is performed using image data, an ink color for the printing drum to be used, and a timing in which one printing drum is replaced with another one. In accordance with the printing order information, the ink color contained in image data is detected and an order for each page to be printed is determined on the basis of a user's print request to execute the printing operation according to the page order and to reduce the number of times the printing drum is replaced with.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Semi-aqueous solvent cleaning of paste processing residue from substrates
InactiveUS20030066540A1Eliminate residueElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStencil printingSolvent
The present invention relates generally to a new process of cleaning of objects that relate to semiconductor fabrication processes, such as, for example, conductive paste screening in the production of multilayer ceramic substrates and composite solder paste by stencil printing in electronic circuit assembly. Specifically, this invention is concerned with removing a metal / polymer composite paste from screening masks and associated paste making and processing equipment used in printing conductive metal pattern onto ceramic green sheet in the fabrication of semiconductor packaging substrates. This invention is also concerned with cleaning of solder paste residue from stencil printing equipment used in electronic module assembly surface mount technology for SMT discretes, solder column attachment, and BGA (Ball Grid Array) attachment on ceramic chip carrier or for screening solder paste onto printed circuit board. More particularly, this invention is concerned with cleaning of paste residue from metal, ceramic, and plastic substrates by a non-alkaline semi-aqueous cleaning method employing high boiling propylene glycol alkyl ether or mixtures of propylene glycol alkyl ether and propylene glycol solvents.
Owner:IBM CORP
Combined stencil and digital printing system
A carousel and station-based printing system for textiles comprises one or more stations with a digital printing apparatus and optionally other stations with a stencil printing apparatus. The system allows for high speed printing of images having details of high resolution, rich colors, or variability, optionally also comprising a wetting apparatus operative to wet at least a part of the printed object prior to the digital printing.
Owner:KORNIT DIGITAL LTD
Process for producing catalyst-coated membranes and membrane-electrode assemblies for fuel cells
ActiveUS7285307B2High positioning accuracyPromote stratificationDielectric heatingSolid electrolytesStencil printingCoated membrane
The present invention provides a continuous process for producing catalyst-coated polymeric electrolyte membranes and membrane electrode assemblies for fuel cells. The process of the invention uses an ionomer membrane having a polymeric backing film on the back side. After the first coating step, the membrane is dried, during which the residual solvent may be almost completely removed. After this, the polymeric backing film is removed and the back side of the membrane is coated in a second step. The front and back sides of the membrane can be coated by various methods, such as screen printing or stencil printing. Two gas distribution layers are applied to the two sides of the catalyst-coated membrane to produce a 5-layer membrane electrode assembly. The membrane electrode assemblies are used in polymeric electrolyte membrane fuel cells and in direct methanol fuel cells.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Apparatus and method for cleaning stencils employed in a screen printing apparatus
InactiveUS20070295231A1Simple methodConductive pattern polishing/cleaningOffice printingLeading edgeScreen printing
A stencil printing method and apparatus for printing paste material in a given pattern on a substrate from a paste dispenser through a stencil to define the stencil pattern on a substrate. The apparatus is provided with a cleaning module that can be moved against the printing face of the stencil and moved, along a given path beneath the stencil, for cleaning the printing face of the stencil. The cleaning module includes a blade assembly mounted there on transverse to the path of movement of the cleaning module. The print apparatus further including selectively operable means for actuating the blade assembly during a select cleaning cycle to engage the leading end of its blade with the underside of the stencil as the cleaning module is passed beneath said stencil whereby the leading edge of the blade scrapes debris from the underside of said stencil. The stencil printing and cleaning method of the invention uses the steps of: dispensing a paste material through a stencil onto a substrate surface to define a given pattern thereon; and passing a cleaning module, provided with a scraping blade that can be extended above the module to contact the lower surface of the stencil to clean the underside thereof when the leading edge of the blade is in contact with the underside of the stencil.
Owner:IBM CORP
Emulsion ink for stencil printing
A W / O emulsion ink for stencil printing contains, in its water phase, a material which reacts with oxygen dissolved in the water phase and reduces the amount of oxygen dissolved in the water phase.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Material for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) antenna conductive pattern
PendingCN108084799ARich in mineralsLower resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingStencil printingPrinting ink
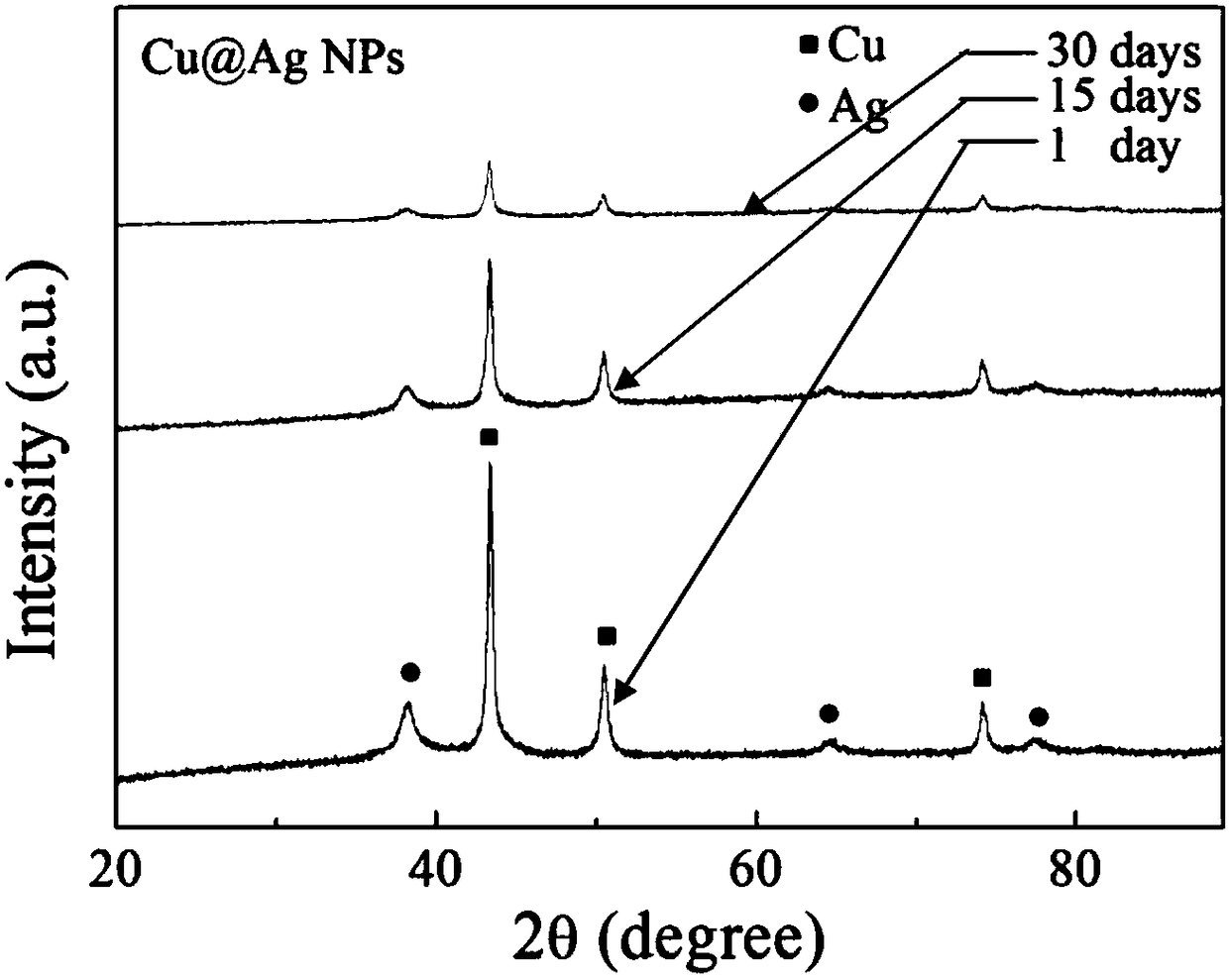
The invention provides a material for an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) antenna conductive pattern. The material for the RFID antenna conductive pattern has the following specific characteristics that the material is metal nano-particles which are of core-shell structures, wherein the inner cores are Cu particles of about 50 nm, and an Ag layer coats the surfaces of Cu through a composite method of displacement and chemical deposition; Cu@Ag nano-particles, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water are mixed to prepare conductive printing ink with the solid content of about 70 percent;the material is obtained through metal stencil printing and sintering. Antenna patterns with different thicknesses can be manufactured by the material by adopting metal stencil printing so as to meetdifferent impedance requirements of antennae of various frequency bands. The Cu@Ag nano-particles have the characteristics of low impedance, high conductivity, controllable Ag layer thickness and thelike; compared with Cu conductive printing ink, the Cu@Ag nano-particles have high oxidation resistance; compared with pure Ag or Au conductive printing ink, the cost is greatly reduced; optimal sintering performance can be realized by controlling the thickness of the Ag layer; moreover, a preparation process of the material is simple and convenient; a printing ink solvent is environment-friendlyand renewable, and has a very great application prospect in the field of conductive printing ink for the RFID antenna.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Printer driver for setting stencil printing machine printing condition items and the like
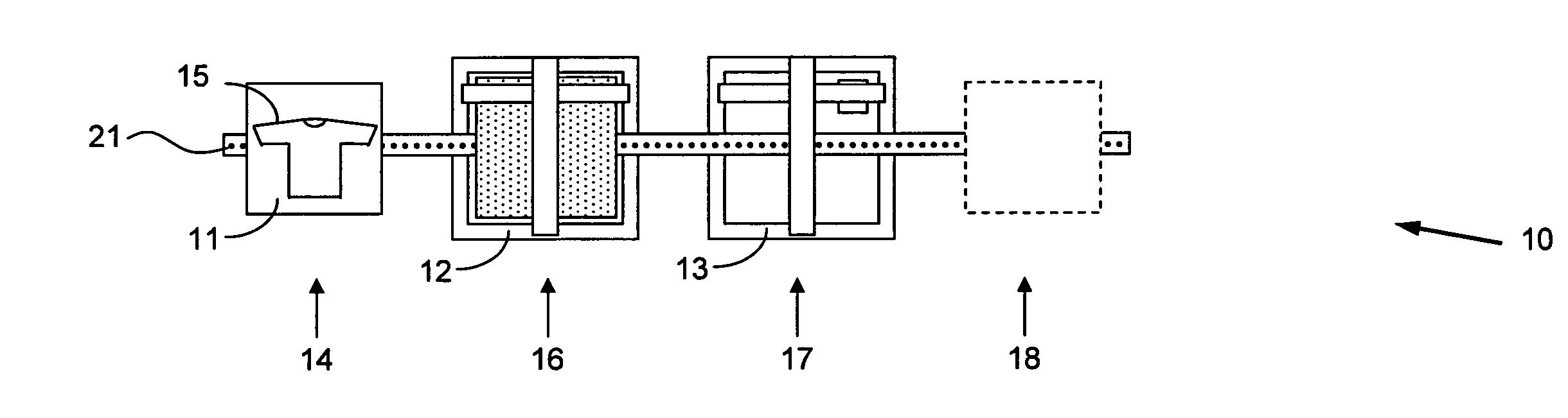
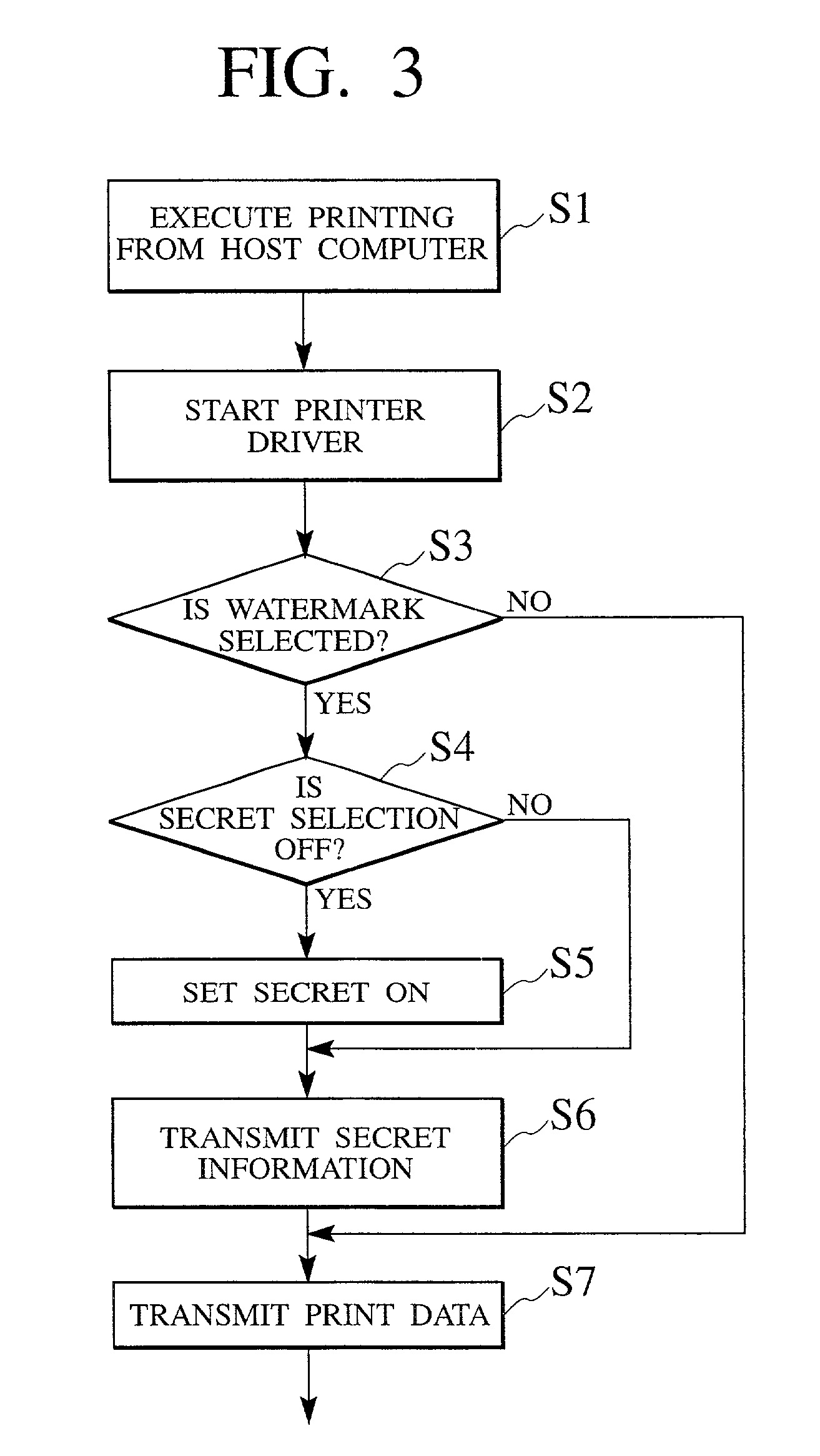
In the disclosed invention, when watermark print is set during printing, the printer driver makes a secret operation setting for holding the secret of print data accordingly, and transmits this print data to the stencil printing machine. Therefore, even if the printing of the stencil printing machine is remotely operated, it is possible to prevent an inadvertent failure to set a secret operation and to keep the secret of print data.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Printing device and ultraviolet irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20060219106A1Easy to operateStencilling apparatusForme preparationStencil printingUltraviolet
A printing device comprising a stencil printing device which is excellent in operativity, in which a print drum with UV ink and non-UV ink can be used in a single stencil printing device. The printing device has a stencil printing control device and UV irradiation control device in which a drum unit ink type identifying sensor, which detects whether the print drum attached to the stencil printing device main body is a print drum unit for UV ink or a drum unit for non-UV ink, is used to operate at least a UV lamp, of the UV lamp and a UV auxiliary lamp, and to irradiate UV light when attachment of the drum unit for UV ink is detected, or to stop the operation of the UV lamp and UV auxiliary lamp when attachment of the print drum unit for non-UV ink is detected.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Peelable stenciling ink and method of using
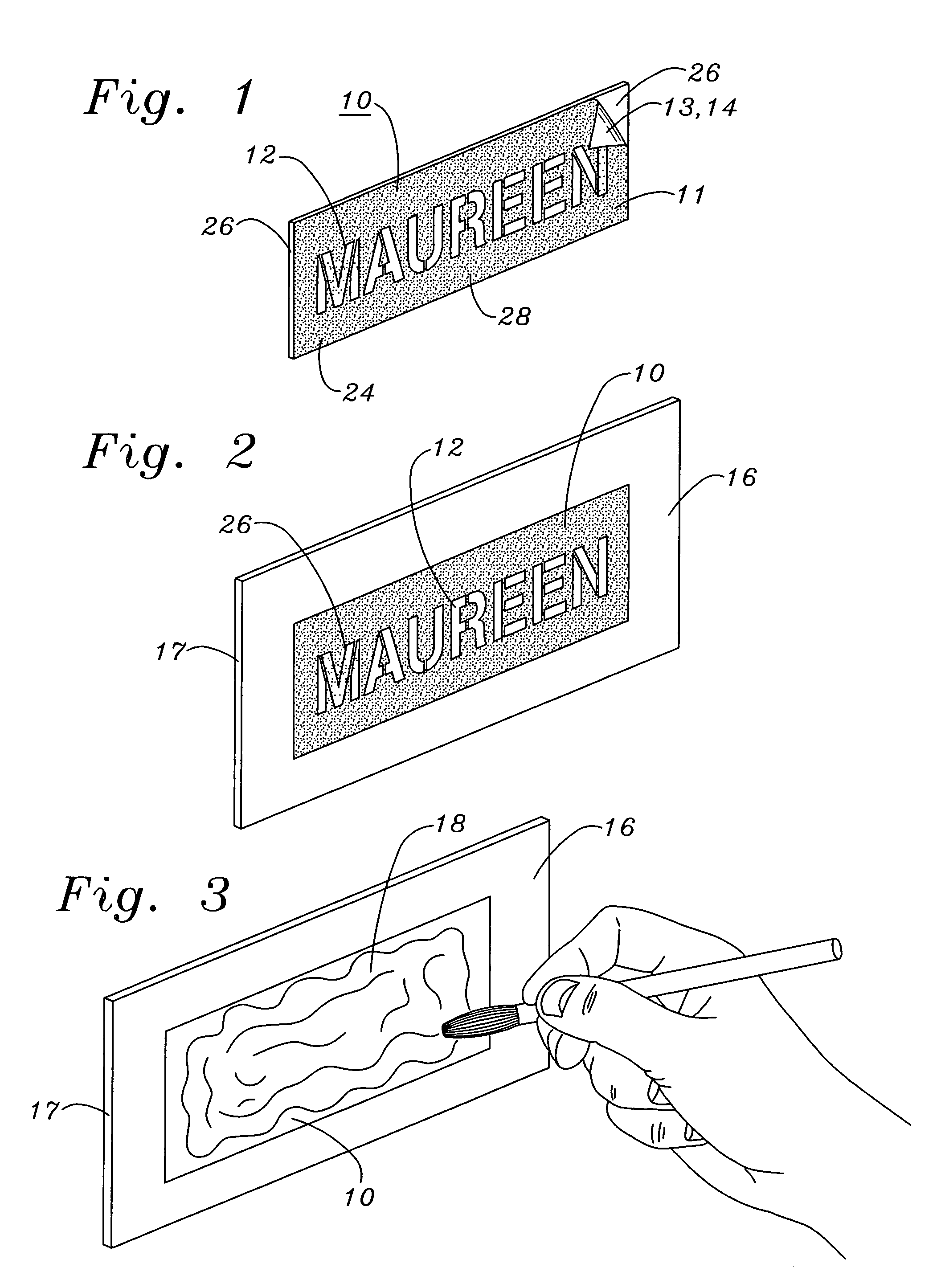
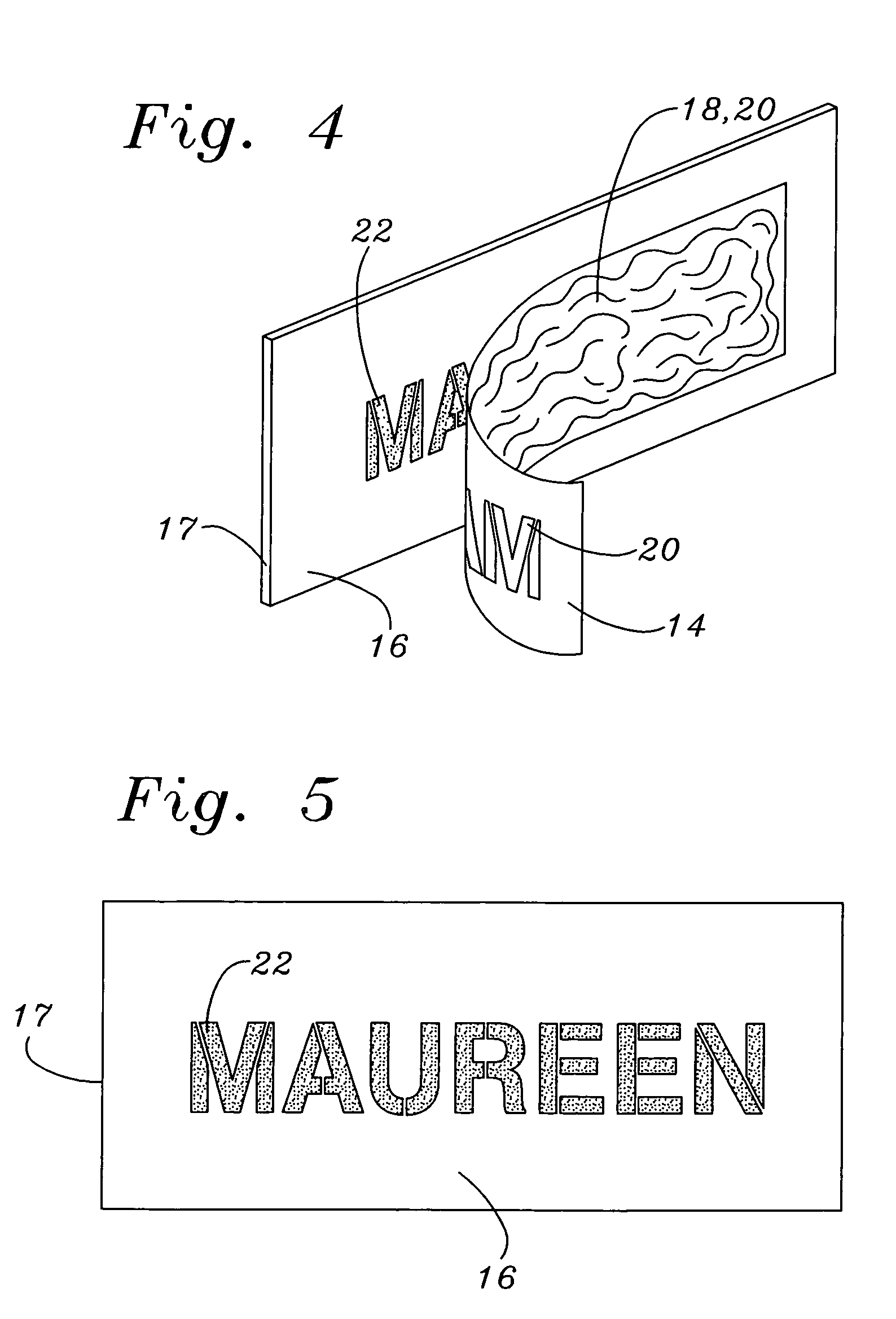
InactiveUS7169219B1Easily imprintedAbrasion resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsInksStencil printingEvaporation
A peelable stenciling ink for imprinting indicia such as letters, numbers and symbols on a surface of an article such as a sport ball made of leather or a synthetic polymer, e.g., a thermoplastic material, consists of a solvent, a dye dispersed in the solvent, and a film-forming polymer soluble in the dye-solvent solution to form a thick paste and hardenable into a solid, flexible film upon evaporation of the solvent from a thin layer of ink applied to an article surface. A method of using the ink comprises the steps of temporarily adhering a stencil sheet in fluid-tight contact to an article surface by a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, smearing a layer of the ink on the obverse surface area of the stencil sheet through indicia-shaped openings through the sheet onto the article surface, allowing sufficient time for dye in the ink to penetrate the article surface, and for the solvent to evaporate and cause the film-forming substance to harden into a solid film peelable from the article surface, and peeling the stencil sheet and solid film off the article surface, thereby leaving indicia markings imprinted on and dye-penetrated beneath the article surface, thus making the markings resistant to obliteration by scuffing or abrasion.
Owner:WYNNE JOHN H
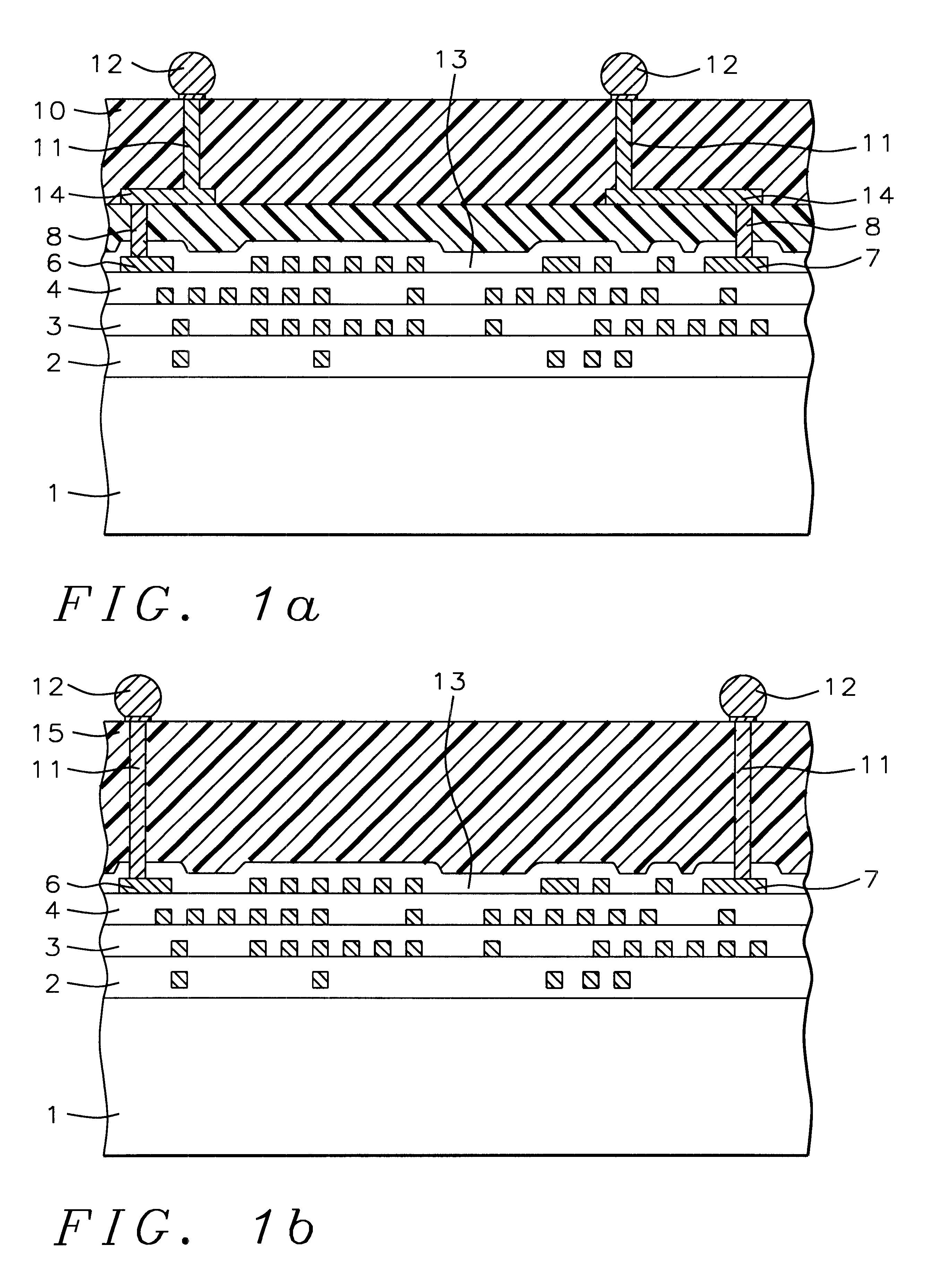
Wafer scale packaging scheme
InactiveUS6486563B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStencil printingWafer dicing
A process and a package for achieving wafer scale packaging is described. A layer of a polymeric material, such as polyimide, silicone elastomer, or benzocyclobutene is deposited on the surface of a chip. Via holes through this layer connect to the top surfaces of the studs that pass through the passivating layer of the chip. In one embodiment, the polymeric layer covers a redistribution network on a previously planarized surface of the chip. Individual chip-level networks are connected together in the kerf so that conductive posts may be formed inside the via holes through electroplating. After the formation of solder bumps, the wafer is diced into individual chips thereby isolating the individual redistribution networks. In a second embodiment, no redistribution network is present so electroless plating is used to form the posts. In a third embodiment, there is also no redistribution network but electroplating is made possible by using a contacting layer. Solder bumps attached to the posts are then formed by means of electroless plating, screen or stencil printing.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power module manufacturing method for connecting nano-silver soldering paste with bare DBC
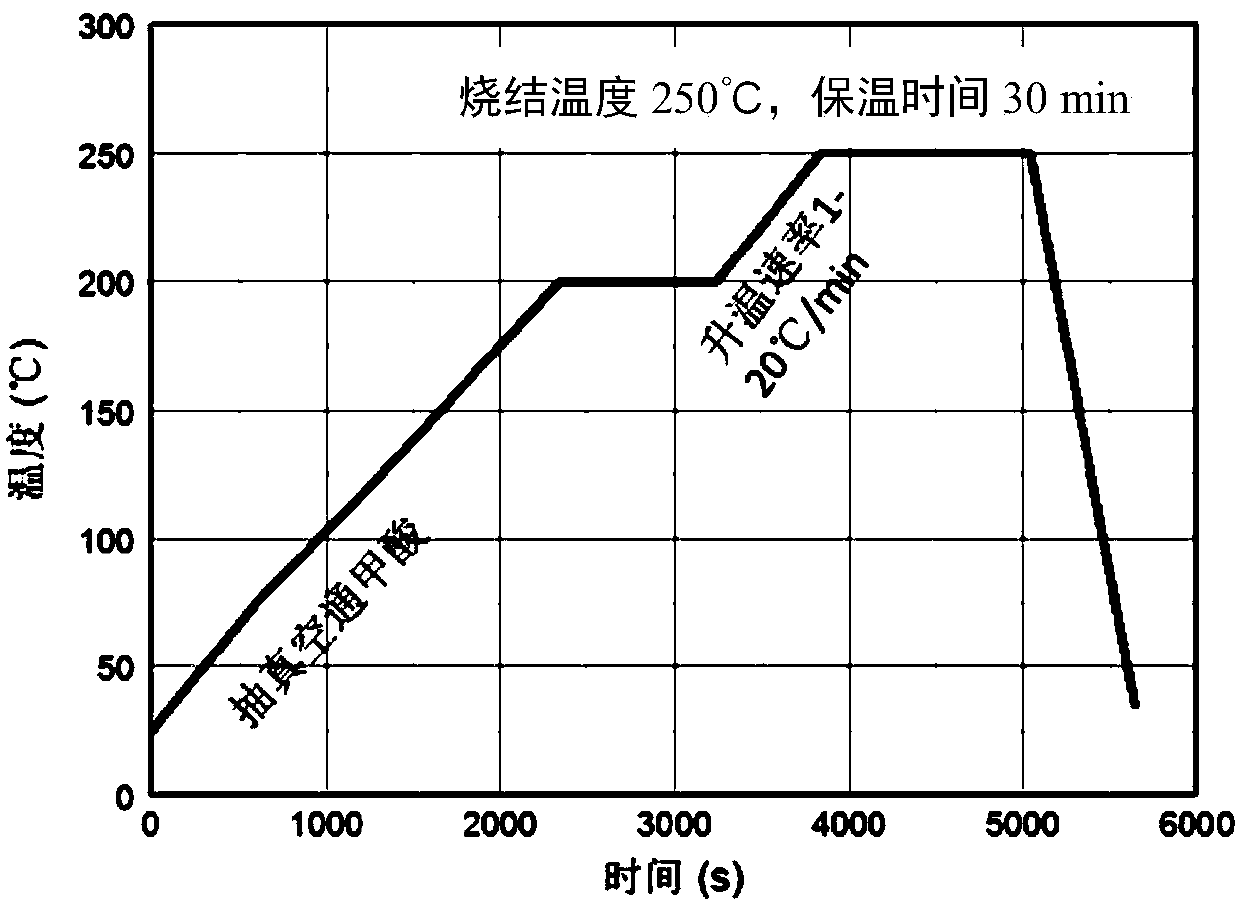
ActiveCN107871675AImprove connection strengthImprove connection reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStencil printingDBc
The invention relates to a power module manufacturing method for connecting nano-silver soldering paste with bare DBC (Direct Bonding Copper). The method comprises a cleaning process, a soldering paste printing process, a chip mounting process and a sintering process. In the cleaning process, the bare DBC is cleaned by adopting ultrasonic oscillation. In the soldering paste printing process, the nano-silver soldering paste is printed by adopting metal stencil printing, and nano-silver is printed twice. In the chip mounting process, chip mounting is performed by adopting a chip mounter. In thesintering process, sintering is performed by adopting a vacuum reflow furnace to obtain an oxygen-free atmosphere of formic acid, and a sintering temperature and a heating rate are controlled. The dense connection between the nano-silver soldering paste and the bare DBC can be realized and the bare DBC can be prevented from being oxidized. No special equipment is required; the treatment process isconvenient and easy; the process is simple; a power chip can be connected with a bare copper substrate or a copper-clad substrate through the nano-silver soldering paste; the reliability of subsequent lead bonding is ensured; the reliability of a power module is improved; and the application of the nano-silver soldering paste to the power semiconductor module packaging is greatly facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com