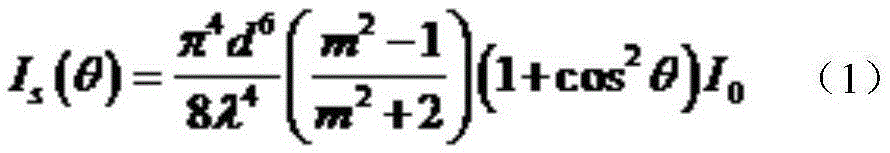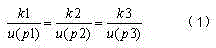Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Static light scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Static light scattering is a technique in physical chemistry that measures the intensity of the scattered light to obtain the average molecular weight Mw of a macromolecule like a polymer or a protein in solution. Measurement of the scattering intensity at many angles allows calculation of the root mean square radius, also called the radius of gyration Rg. By measuring the scattering intensity for many samples of various concentrations, the second virial coefficient A₂, can be calculated.
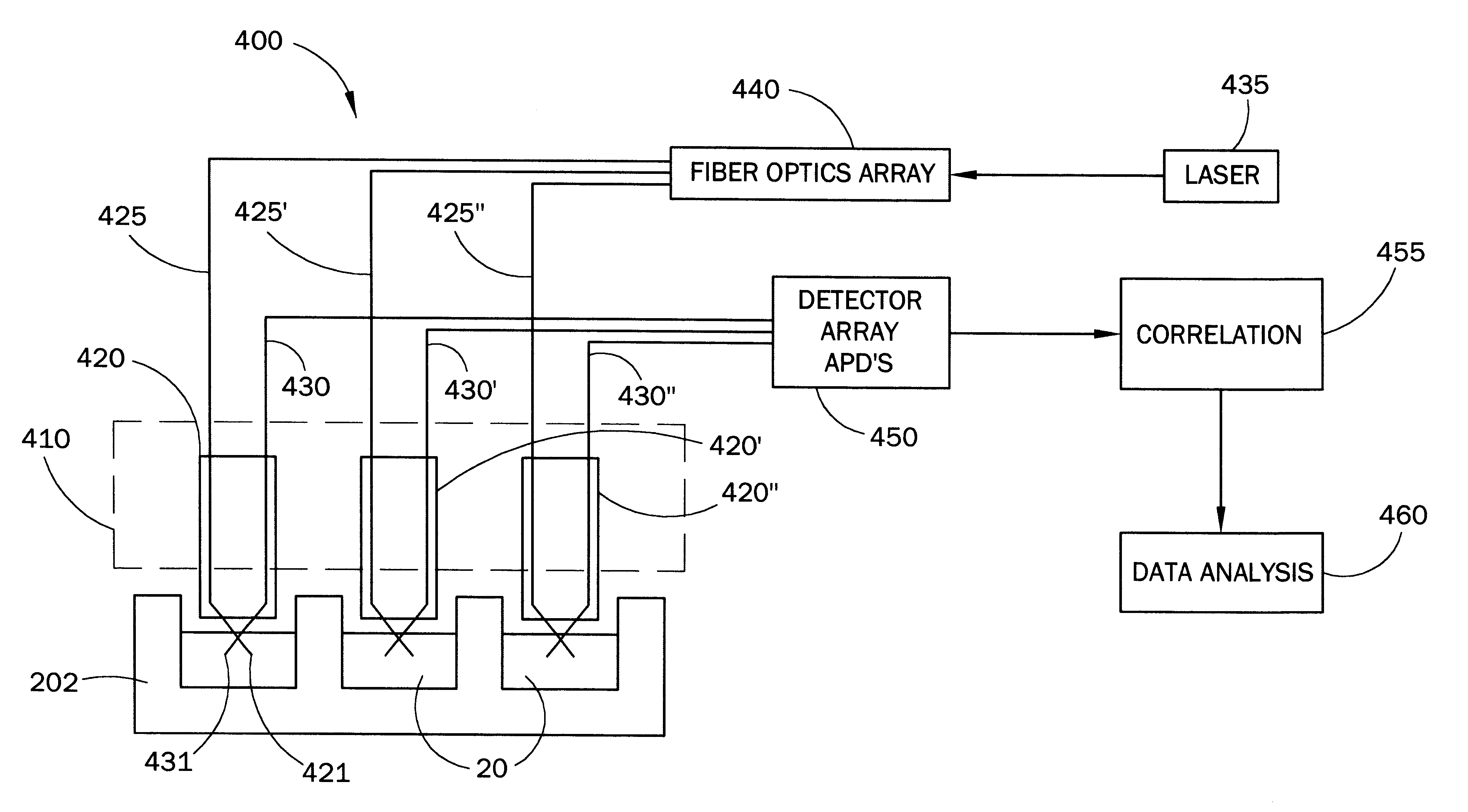
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
InactiveUS6519032B1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericEffectively and efficiently characterizingSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
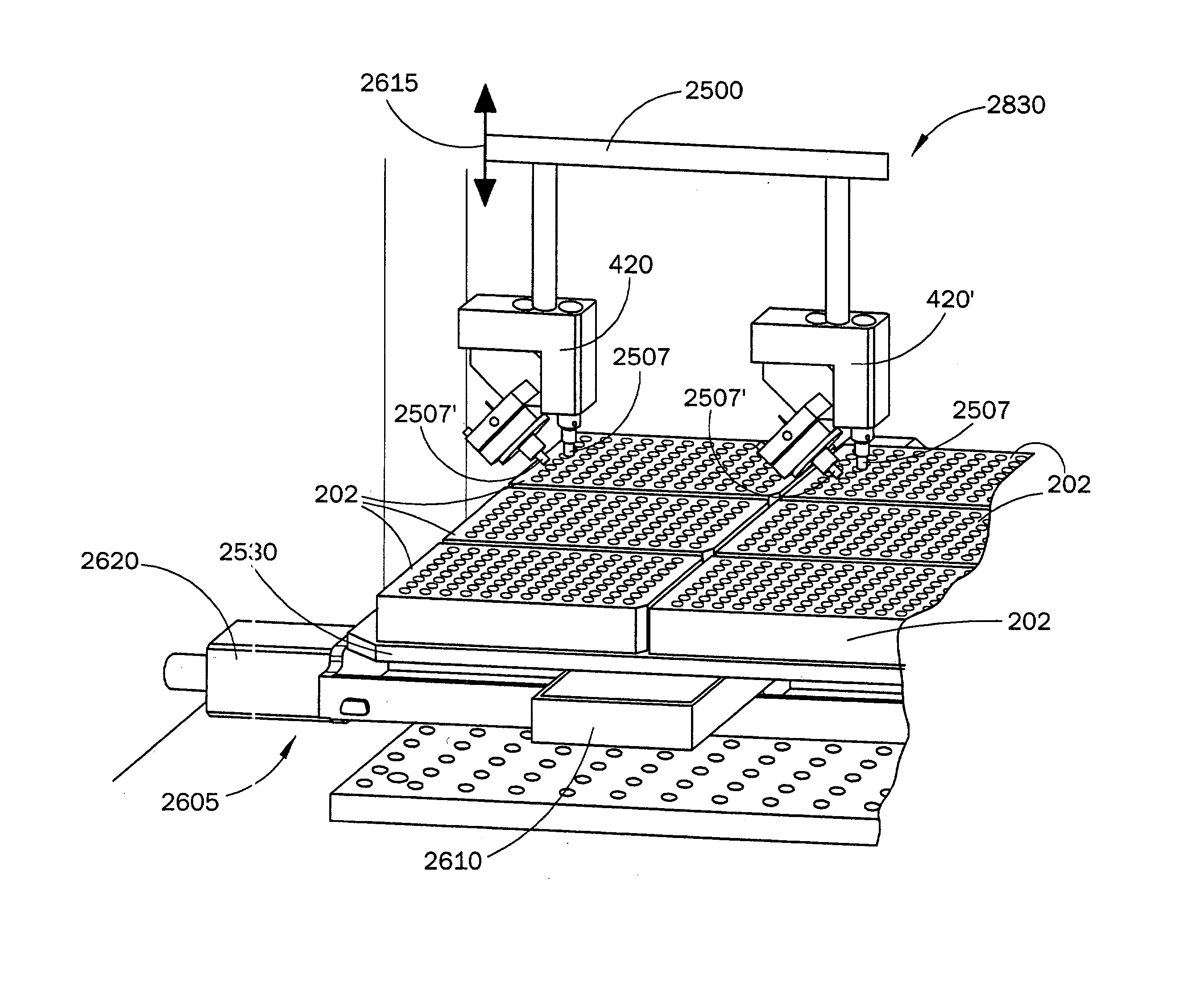
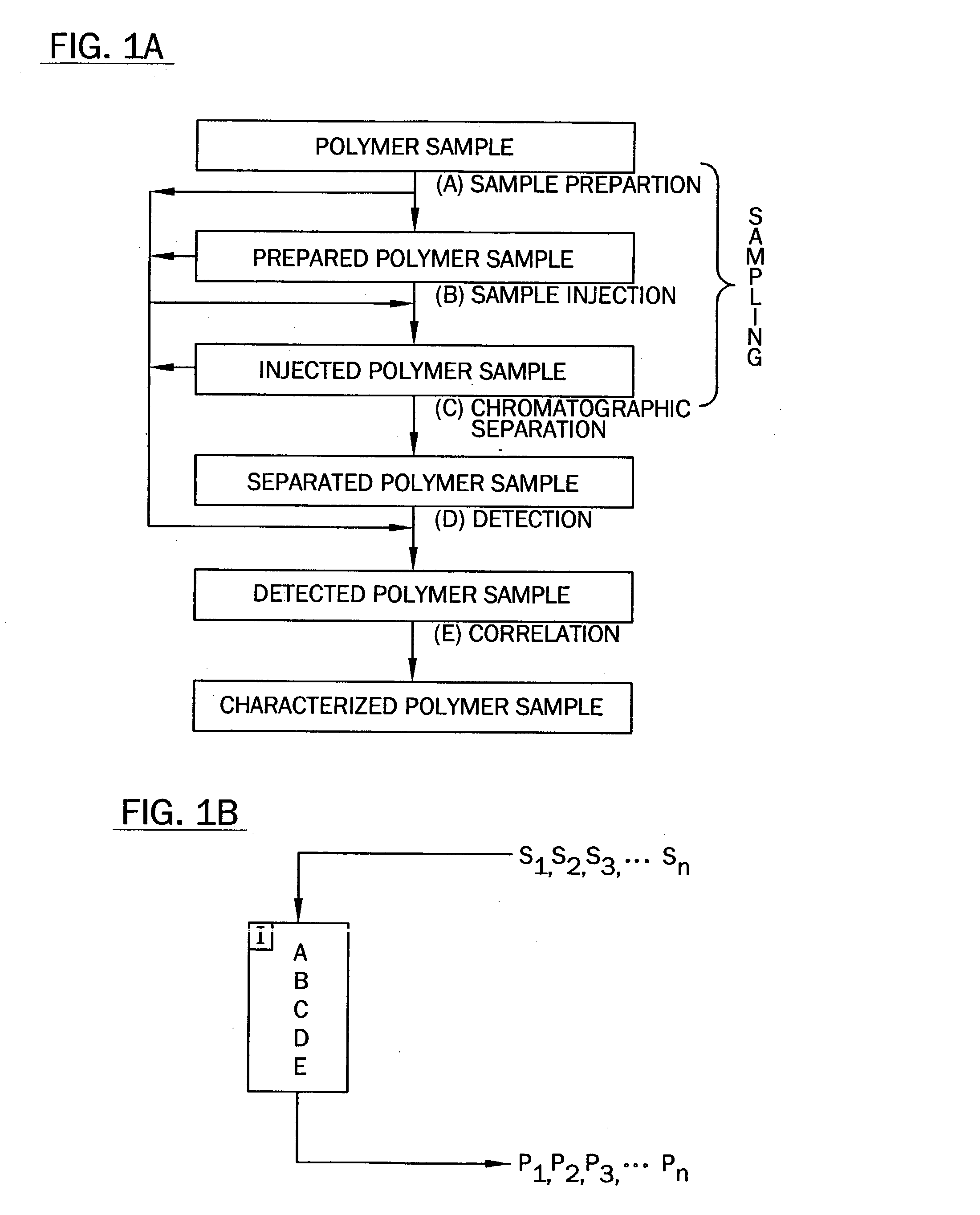
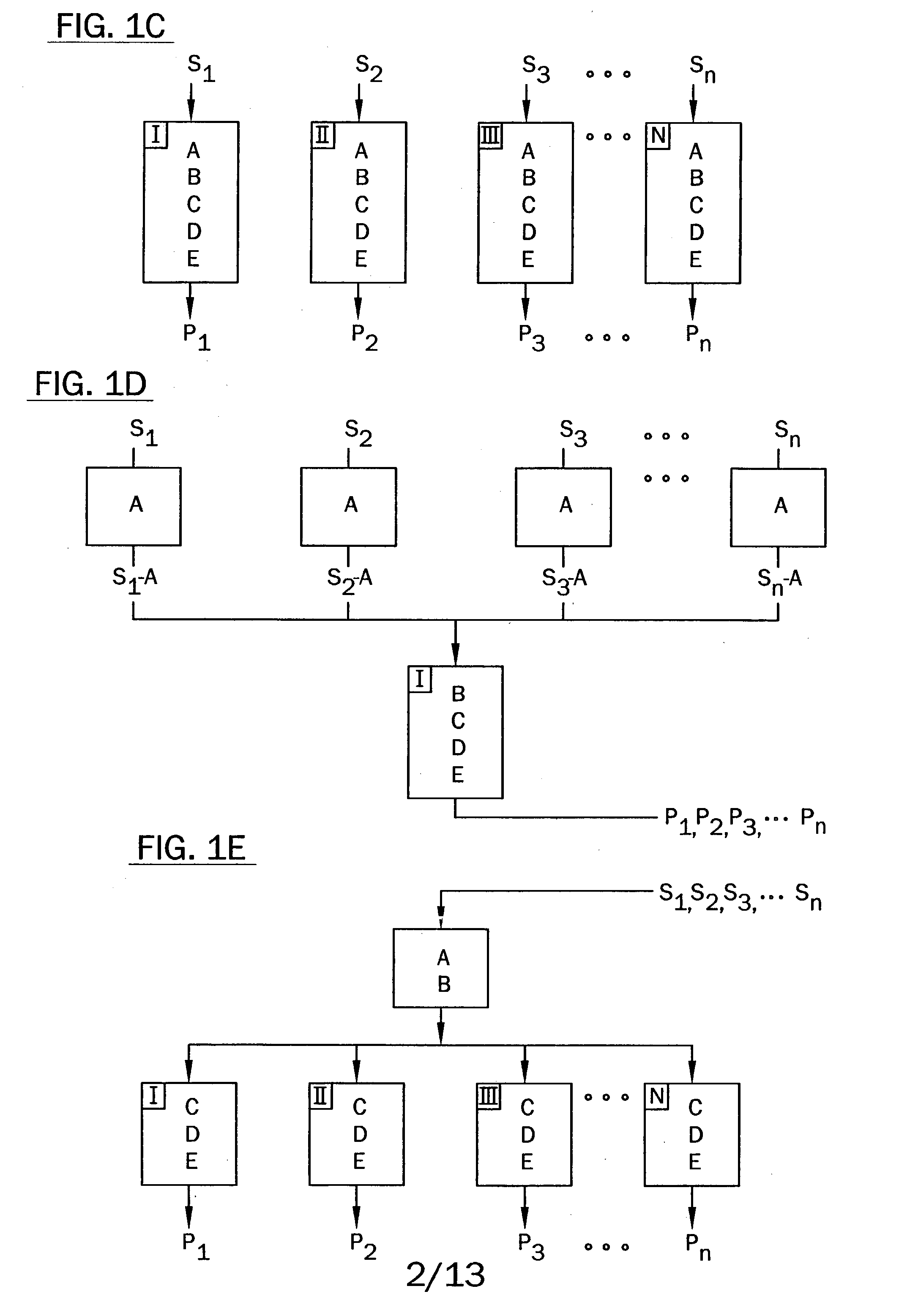
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
InactiveUS20030142309A1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
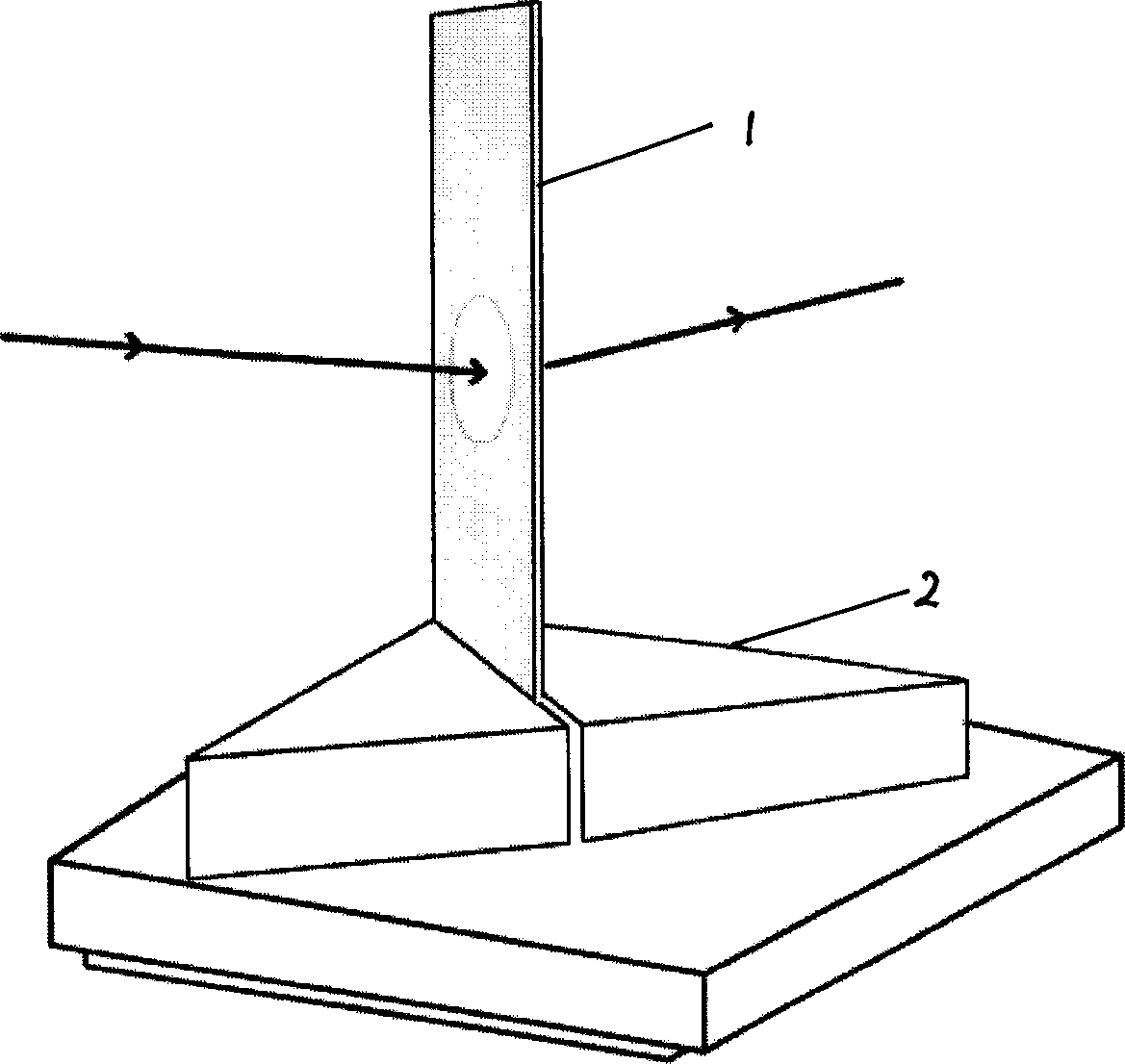
Light scattering detector
InactiveCN101118210AEasy to measureEliminates the problem of missed detectionsScattering properties measurementsMonitoring particle agglomerationChemical physicsBeam splitter
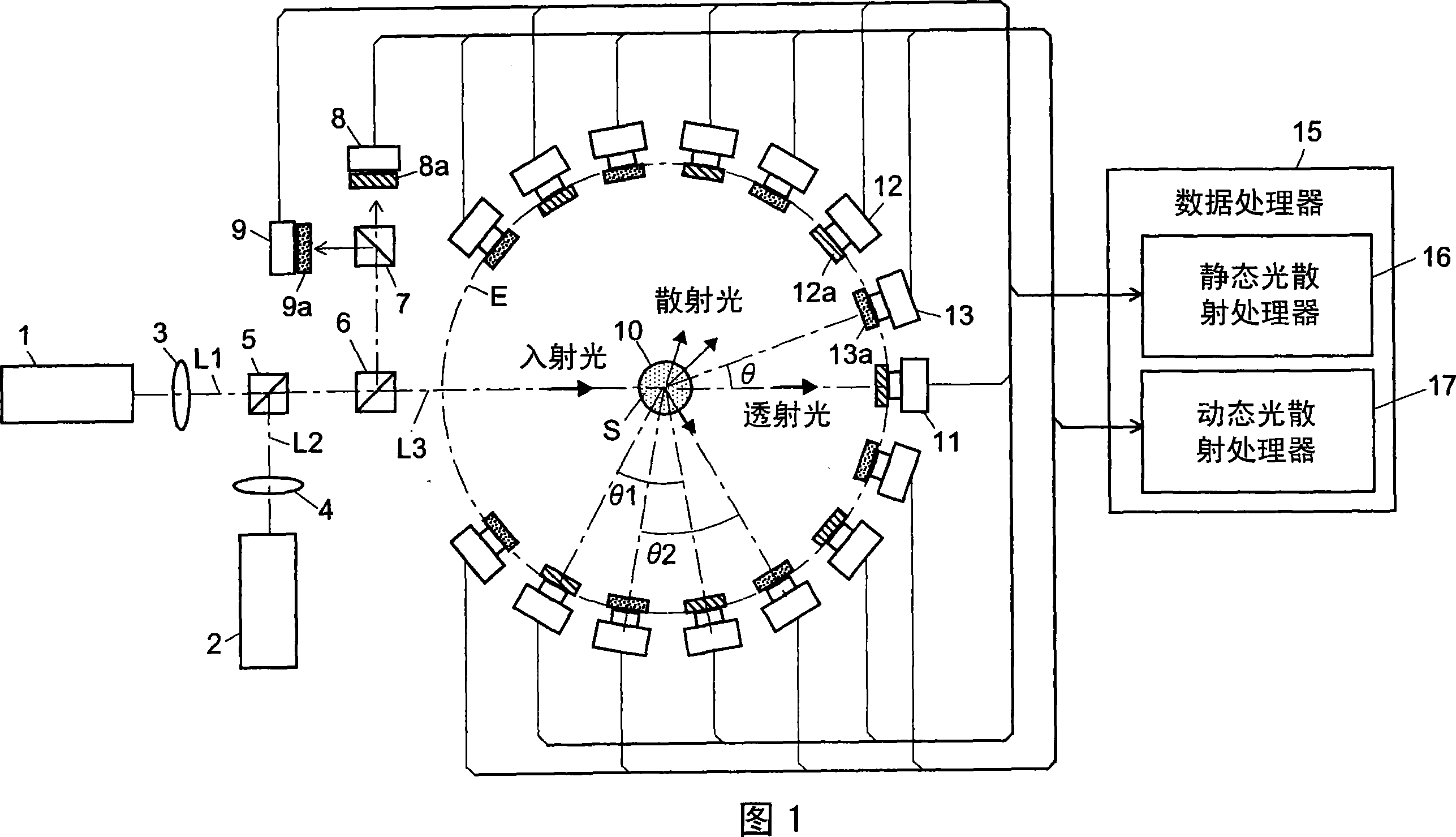
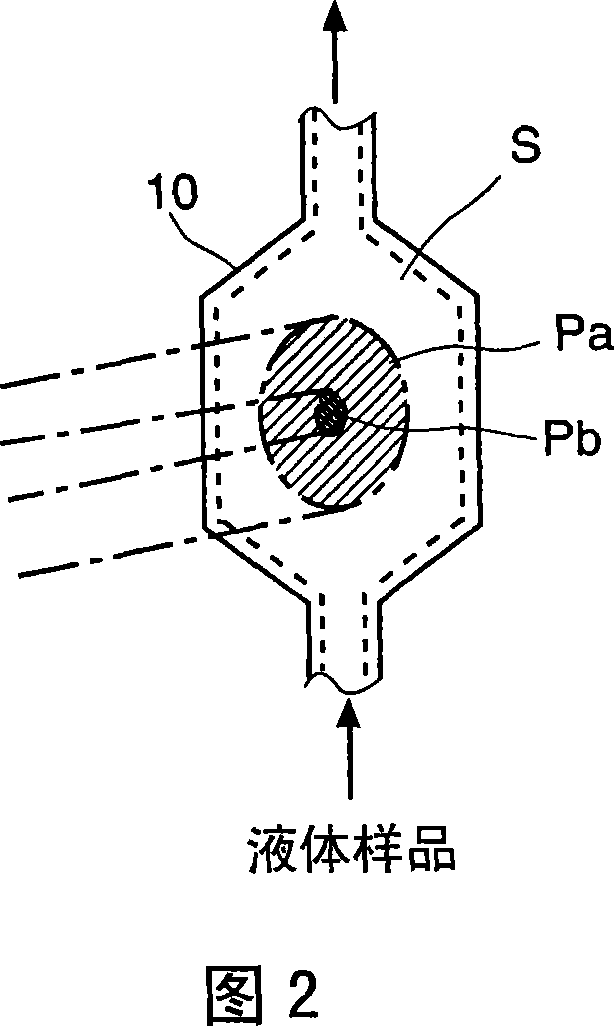
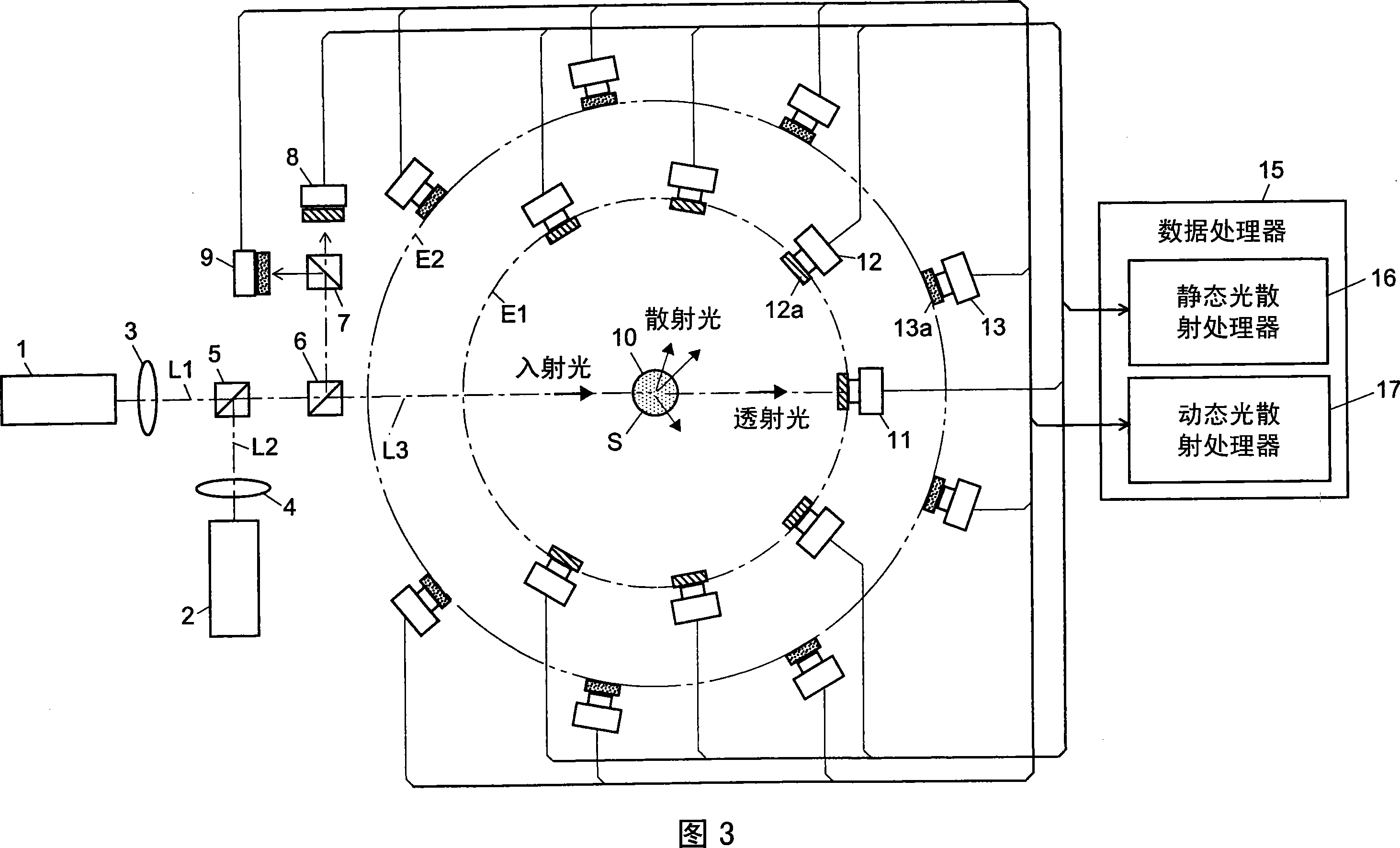
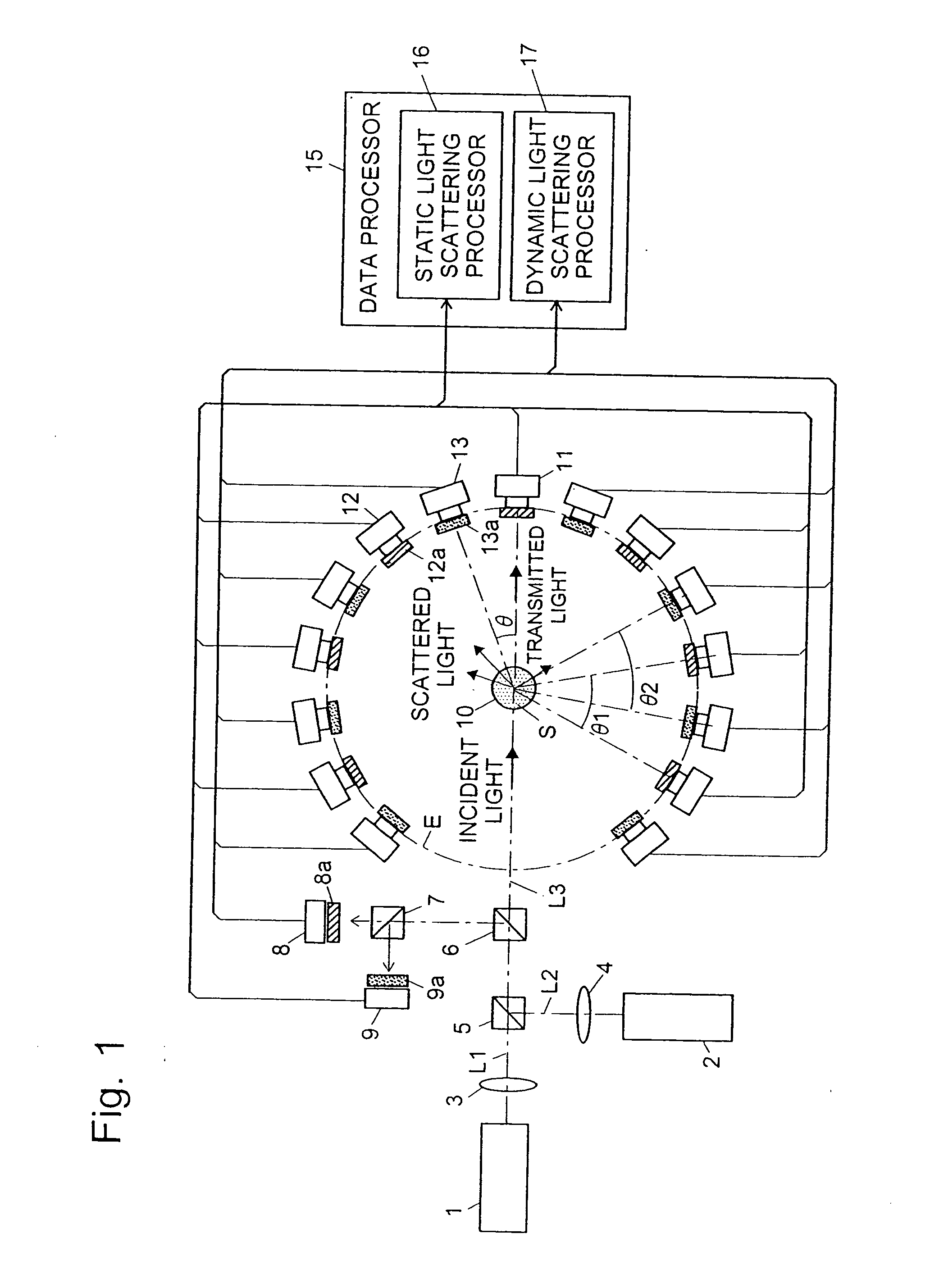
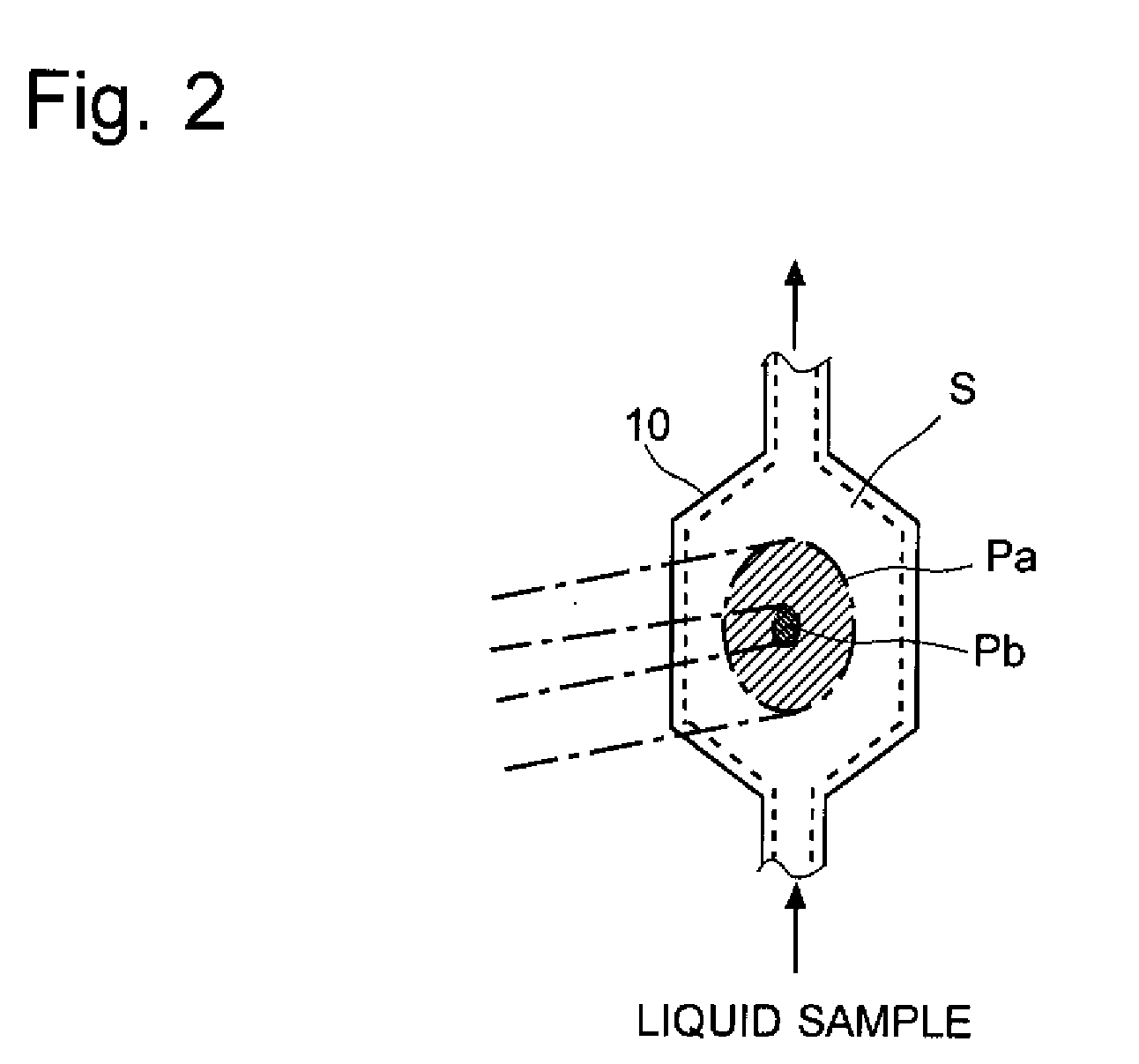
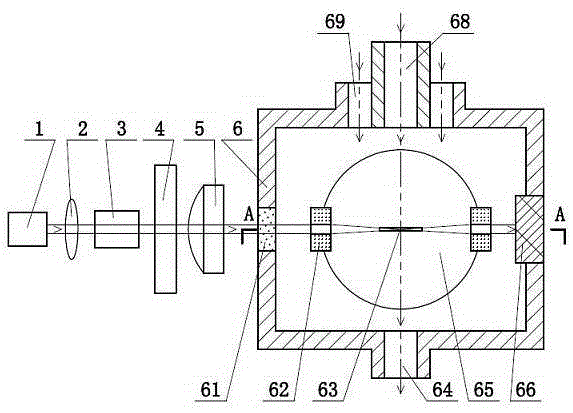
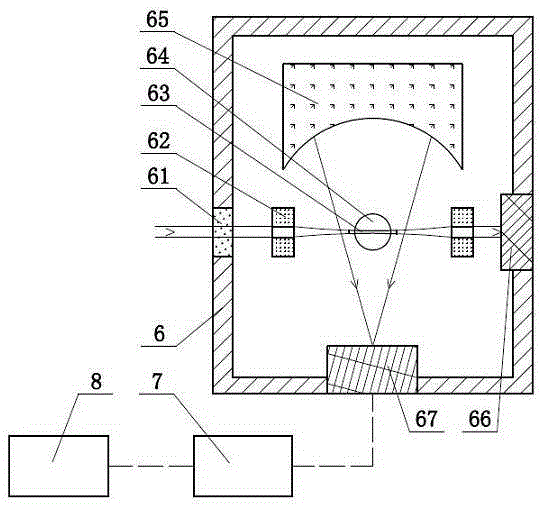
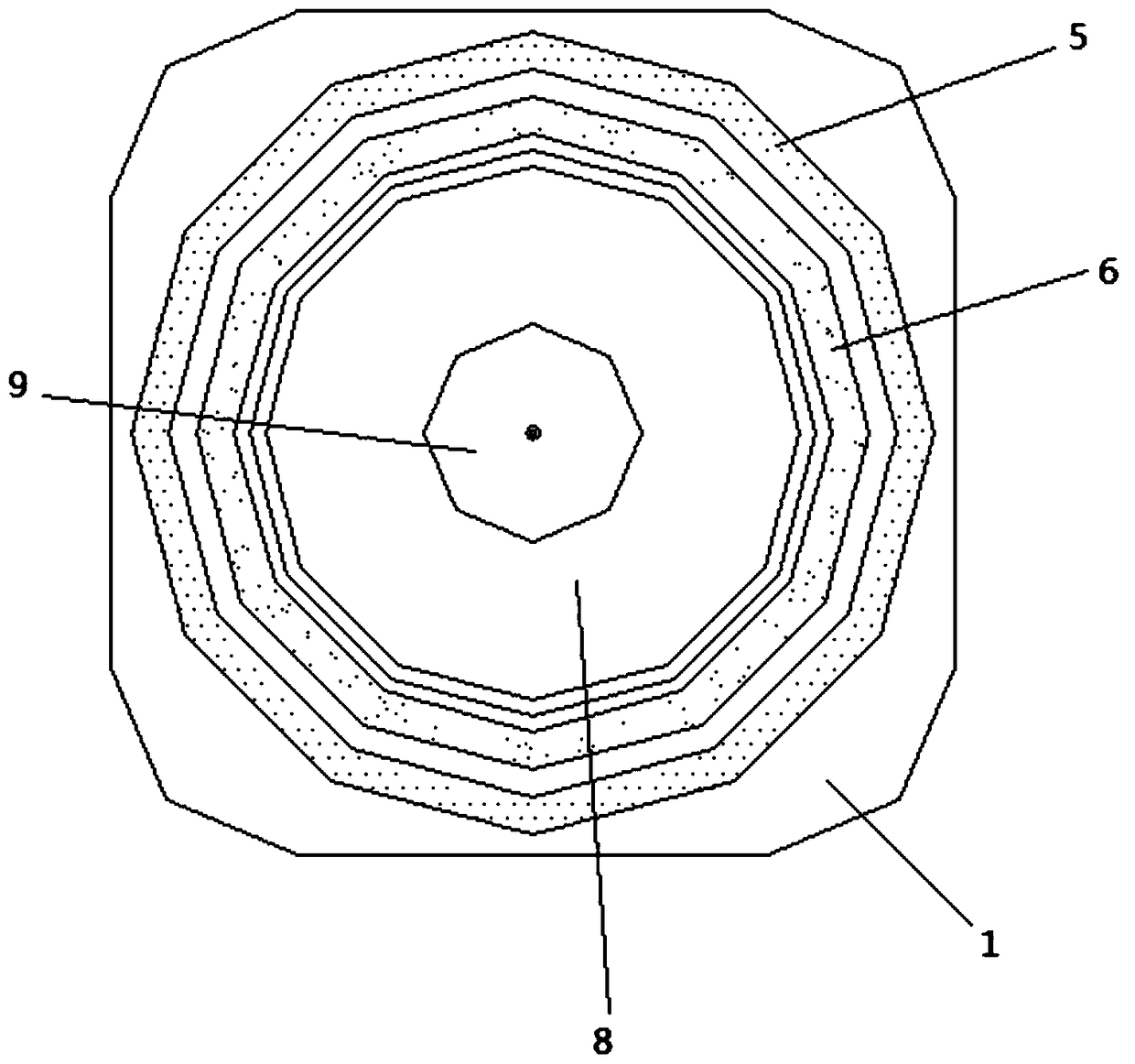
The light scattering detector according to the present invention aims at simultaneously measuring the molecular weight and size of particles having varieties of diameters. This detector facilitates the measurement operation and knowing how particles associate or dissociate as time progresses. In this detector, the emitted light (static light scattering measurement light) having a first wavelength by the first light source and the emitted light (dynamic light scattering measurement light) having a second wavelength which is different from the first wavelength by the second light source are combined by a beam splitter 5 and coaxially directed onto the sample sell 10 to which a liquid sample S is supplied. While the irradiated area by the static light scattering measurement light is large, the irradiated area by the dynamic light scattering measurement light, which is coherent light, is narrow. Detectors 12 which selectively detect the first wavelength and detectors 13 which selectively detect the second wavelength are placed so as to encircle the sample cell 10. The detection signals by the detectors 11, 12 and the detection signals by the detectors 13 are separately mathematically-operated by a data processor 15 to calculate the molecule weight and size of the particles in the sample S.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20080285032A1Dynamic light scattering measurement result can be eliminatedEasy to operateScattering properties measurementsMonitoring particle agglomerationBeam splitterChemical physics
The light scattering detector according to the present invention aims at simultaneously measuring the molecular weight and size of particles having varieties of diameters. This detector facilitates the measurement operation and knowing how particles associate or dissociate as time progresses. In this detector, the emitted light (static light scattering measurement light) having a first wavelength by the first light source and the emitted light (dynamic light scattering measurement light) having a second wavelength which is different from the first wavelength by the second light source are combined by a beam splitter 5 and coaxially directed onto the sample sell 10 to which a liquid sample S is supplied. While the irradiated area by the static light scattering measurement light is large, the irradiated area by the dynamic light scattering measurement light, which is coherent light, is narrow. Detectors 12 which selectively detect the first wavelength and detectors 13 which selectively detect the second wavelength are placed so as to encircle the sample cell 10. The detection signals by the detectors 11, 12 and the detection signals by the detectors 13 are separately mathematically-operated by a data processor 15 to calculate the molecule weight and size of the particles in the sample S.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Process for producing cellulose acylate film
InactiveUS7470385B2Increase production capacityHigh mechanical strengthImpression capsPhotosensitive materialsCelluloseChemistry
A cellulose acylate film is produced by using a cellulose acylate solution and forming a film consisting of two or more layers by the co-casting method. The cellulose acylate to be used is selected so that the association molecular weight of cellulose acylate due to the static light scattering in the solution forming the outer layer becomes smaller than the association molecular weight of cellulose acylate due to the static light scattering in the solution forming the inner layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Laser granularity measurement instrument with combination of dynamic and static light scattering
InactiveCN105973772AIncrease rangeHigh measurement accuracyParticle size analysisRotary stageGranularity
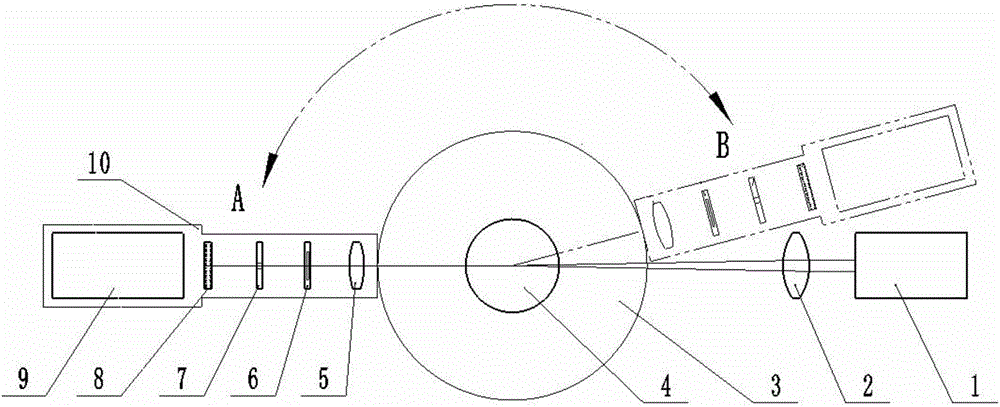
The invention relates to a laser particle size analyzer combining dynamic and static light scattering, which has a laser, a focusing lens, a sample pool, and a measuring optical path, wherein the measuring optical path is installed on a mechanical arm, and one end of the mechanical arm is connected to the outer edge of a rotating platform. The scattered light signal of the sample is received at different angles; the light emitted by the laser is directed to the sample pool through the focusing lens; the sample pool and the rotating platform are both circular, and the sample pool is set in the center of the rotating platform and does not rotate with the rotating platform. The invention installs the measurement optical path on the mechanical arm, and then drives the mechanical arm to rotate by controlling the rotating platform to realize the reception of scattered light signals at different angles, adopts dynamic light scattering to measure the particle size at a fixed angle, and continuously collects scattered signals at various angles when rotating. Scattering Mie theory to measure particle size, for wide distribution samples, both dynamic light scattering and static light scattering are used to measure, which greatly improves the measuring range and measurement accuracy of the instrument.
Owner:丹东百特仪器有限公司
Freeze indicator employing light scattering and method of making same
ActiveUS20140048010A1Simple configurationLow costThermometers using mean/integrated valuesThermometers using physical/chemical changesLiquid mediumColor changes
A freeze indicator including an indicator dispersion is described herein. Such an indicator dispersion can include: a liquid medium and particles of a colored indicator agent dispersed in the liquid medium. The colored indicator agent particles having an inherent color; wherein the indicator dispersion exhibits the inherent color of the colored indicator agent particles after freezing and is configured to have a less colored appearance before freezing and wherein light scattering masks the inherent color of the colored indicator agent particles before freezing. Some indicator dispersions can be free of color-changing chemical co-reactants. These freeze indicators can be small, have a low cost, and have a simple configuration.
Owner:TEMPTIME CORP
Quick detection method for resonance light scattering of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in environmental water sample
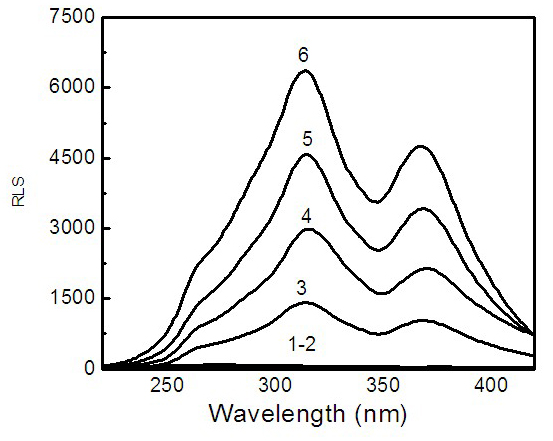
InactiveCN102183501AAnalysis method is simpleFast wayFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpectrofluorometerUltrapure water
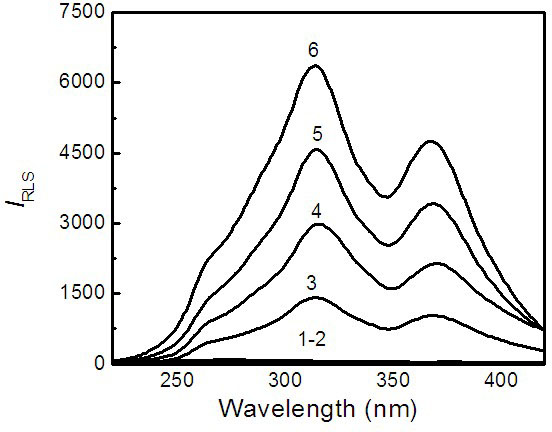
The invention discloses a quick detection method for resonance light scattering of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in an environmental water sample, and relates to the field of environmental analysis. A resonance light scattering analysis method is adopted in the method. The method comprises the following steps of: sequentially adding 0.40mL of 4.2*10<-4>mol / L rhodamine 6G solution and 1.0mL of butadiene rubber (BR) buffer solution with pH of 3.29 into a 10mL color comparison tube, swirling the solution uniformly, and adding the pretreated water sample to be detected; after uniform swirling mixing, fixing the volume to 10mL by using 18.2Momega ultrapure water, and immediately performing synchronous scanning on a fluorescence spectrophotometer in lambda ex=lambda em, wherein both the excitation slit and the emission slit are 5 nanometers, and the voltage is 400V; recording the scattered spectrum in a wavelength range of 220 to 420 nanometers; and performing preliminary qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis on whether the environmental water sample contains the PFOS according to the scattered signals at the wavelength of 313 nanometers. If the water sample contains the PFOS, the scattering intensity at the wavelength of 313 nanometers is enhanced; otherwise, the scattered signals at the wavelength of 313 nanometers are not changed. The invention is characterized in that: the method for detecting the PFOS in the environmental water sample is simple, quick and sensitive, and low in detection cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Pixel unit, production method thereof, array substrate and display device
ActiveCN105810719AAvoid mixing colorsImprove color mixingSolid-state devicesIdentification meansDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention provides a pixel unit.The pixel unit comprises a pixel limiting layer, a pixel electrode, a light-emitting layer and a common electrode.The pixel electrode comprises a bottom face and a side face, and the side face extends to the top of the sidewall of a second via hole along the sidewall of the second via hole.The light-emitting layer is formed on the pixel electrode and covers the pixel limiting layer, and the common electrode is formed on the light-emitting layer, covers the light-emitting layer and extends along the top face of the pixel limiting layer.The pixel unit enables the light-emitting layer to scatter much less light to the surrounding, so that color mixing among pixel units is improved greatly, the problem of color mixing caused by light scattering is solved effectively, light-emitting area of the pixel unit is increased greatly, overall brightness is enhanced, mask film cost is reduced to enable cost of the whole technology to be reduced substantially, production capacity is improved and light-emitting effect is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Light scattering-based monodisperse aerosol particle size and concentration measuring device
ActiveCN105334144AQuick detectionQuick checkParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisHigh concentrationSource tracing
The invention provides a light scattering-based monodisperse aerosol particle size and concentration measuring device, and belongs to the technical field of measuring. According to the light scattering-based monodisperse aerosol particle size and concentration measuring device, light beam emitted by a laser passes through an optical attenuator, a beam expander, a first diaphragm, and a scattering cavity, and enters into a light trap; the upper wall and the lower wall of the scattering cavity are provided with a gas inlet pipe and a gas outlet pipe; a photosensitive area is formed via cross of the connection line of the gas inlet pipe and the gas outlet pipe with the light beam; a spherical mirror is arranged in the scattering cavity; and the focus of the spherical mirror and the center of the photosensitive area are superposed. The light scattering-based monodisperse aerosol particle size and concentration measuring device is capable of solving a technical problem that simultaneous rapid detection on particle size and concentration of high concentration monodisperse aerosol generated by standard aerosol generators can not be realize using conventional instrument. Beneficial effects are that, light scattering principles are adopted, particle counting method of pulse detection and spectrophotometric method of direct-current level detection are combined, rapid detection of the particle size and concentration of monodisperse aerosol can be realized without using filter membranes and destroying aerosol particles . The light scattering-based monodisperse aerosol particle size and concentration measuring device is used for providing means for calibration and source tracing of aerosol particle size and concentration detection-related instrument.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEASUREMENT SCI RES INST
Molding composition with reduced light scattering
The present invention relates to a molding composition comprising(A) a copolymer containing at least one α,β-unsaturated monocarbonitrile and at least one aromatic vinyl monomer,(B) a graft rubber with an average particle size of from 100 to 280 nm, composed of at least one α,β-unsaturated monocarboxylic ester, and at least one graft shell composed of at least one aromatic vinyl monomer and of at least one α,β-unsaturated monocarbonitrile,(C) a graft rubber with an average particle size of from 410 to 1000 nm, composed of at least one α,β-unsaturated monocarboxylic ester, and at least one graft shell composed of at least one aromatic vinyl polymer and of at least one α,β-unsaturated monocarbonitrile, andwherein the ratio by weight of component (B) to component (C) is from 3:1 to 1:1. The invention also relates to the process of producing the molding composition and its use.
Owner:STYROLUTION EURO
Process for producing cellulose acylate film
InactiveUS20040188881A1High mechanical strengthSmall molecular weightPhotosensitive materialsSynthetic resin layered productsCelluloseStatic light scattering
A cellulose acylate film is produced by using a cellulose acylate solution and forming a film consisting of two or more layers by the co-casting method. The cellulose acylate to be used is selected so that the association molecular weight of cellulose acylate due to the static light scattering in the solution forming the outer layer becomes smaller than the association molecular weight of cellulose acylate due to the static light scattering in the solution forming the inner layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and device for measuring particulate matters by using dual wavelength polarized light scattering
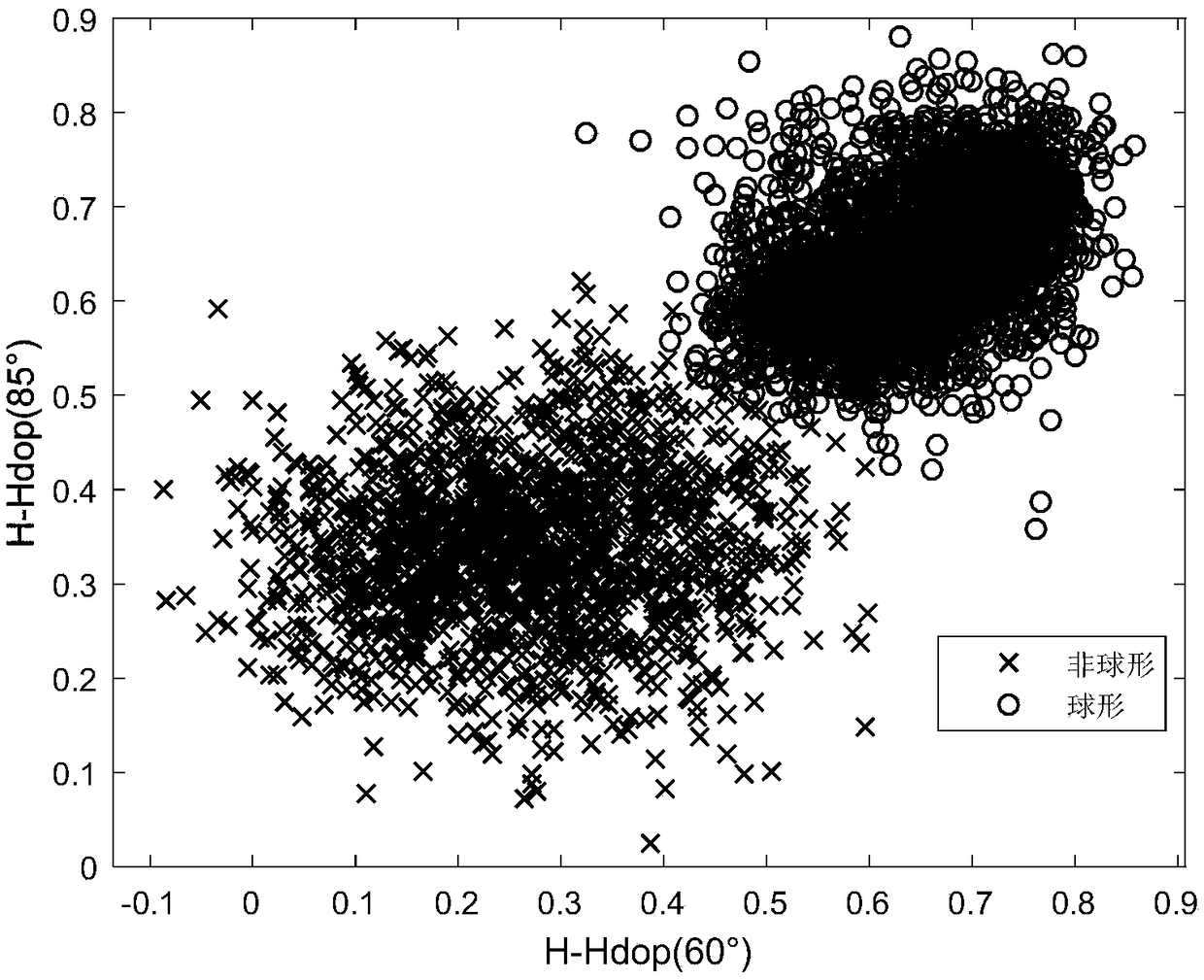
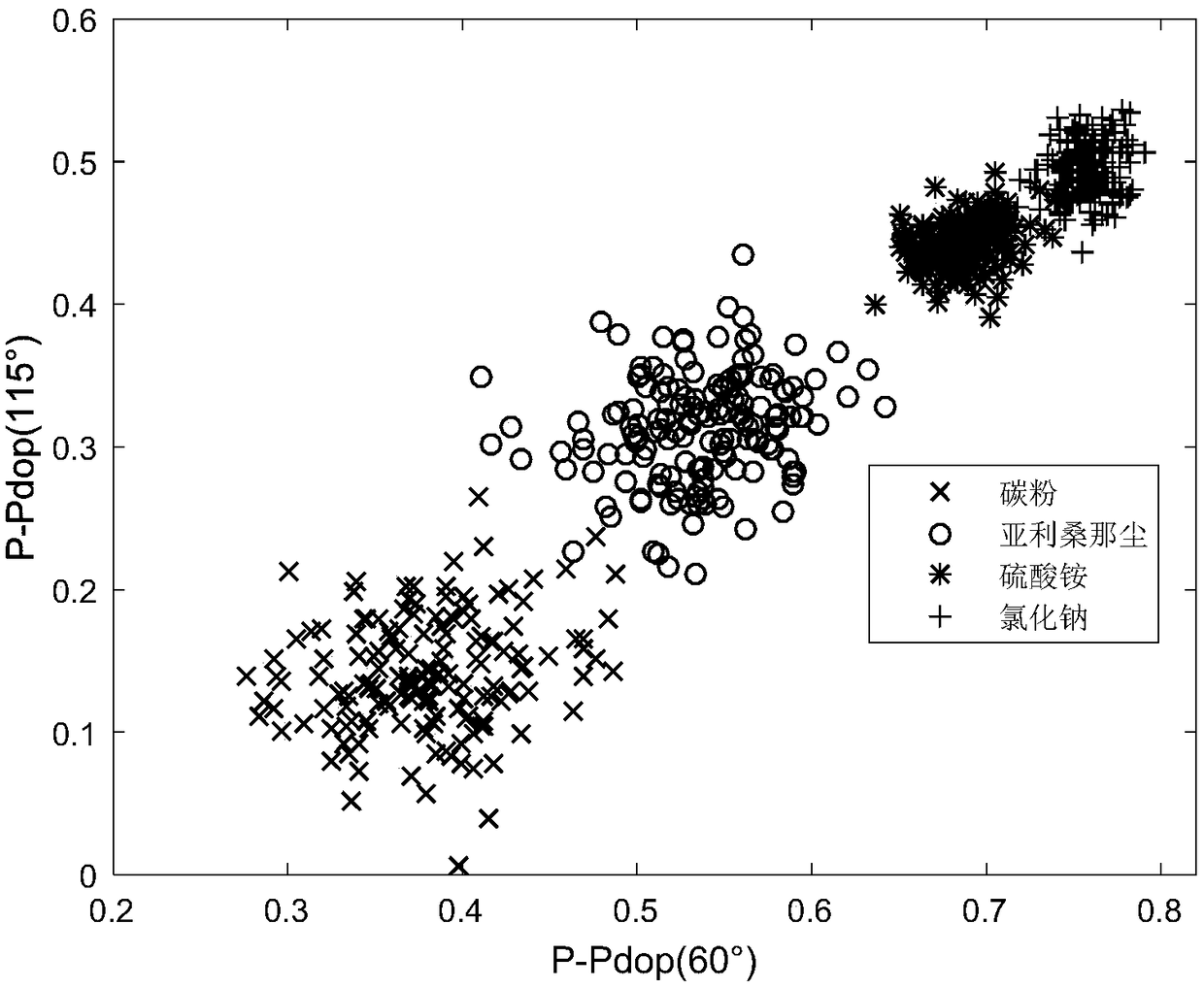
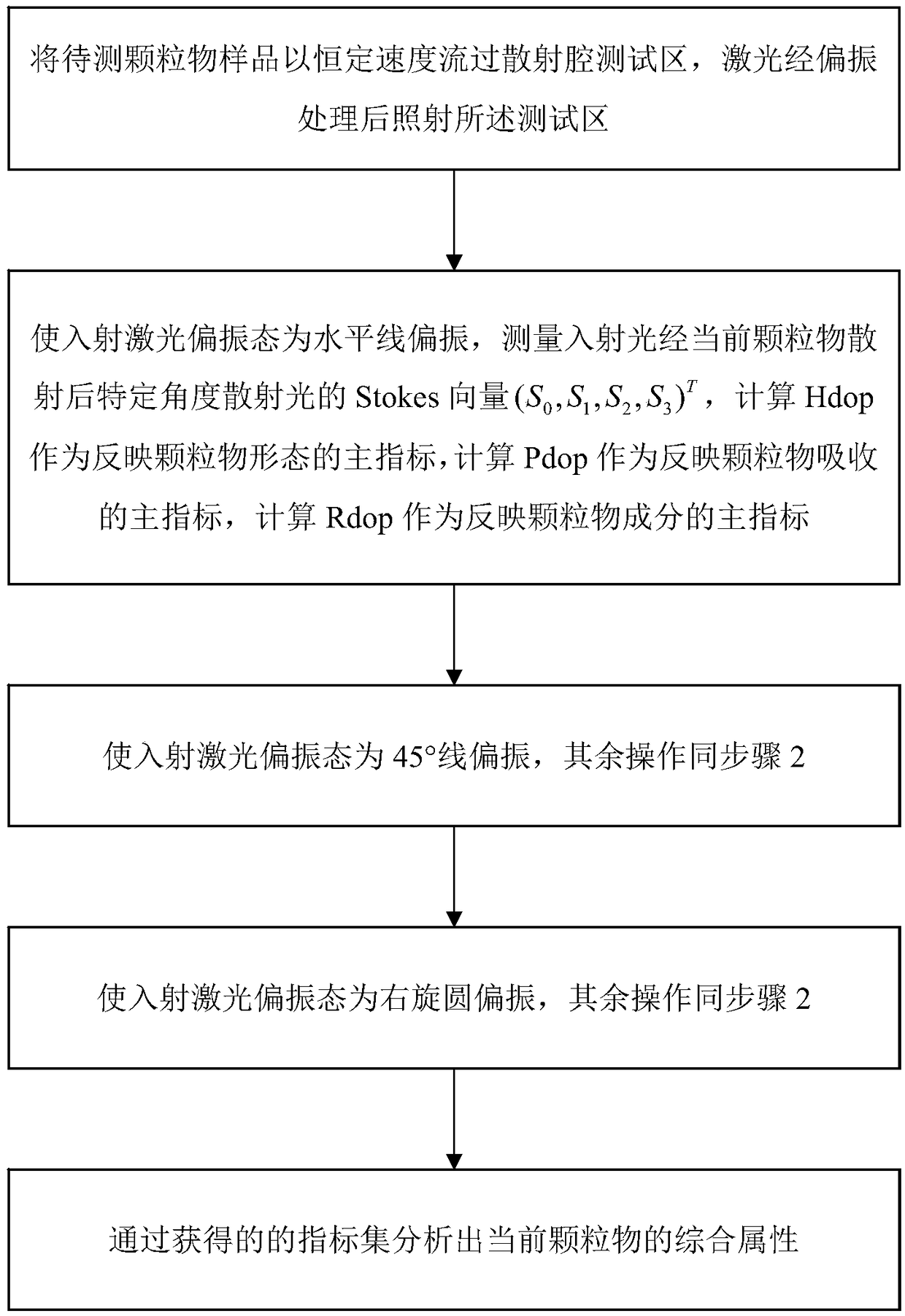
InactiveCN108844865AReduce in quantityLarge amount of informationParticle size analysisParticulatesLevel line
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring particulate matters by using dual wavelength polarized light scattering. The method includes the following steps: 1) letting a to-be-measuredparticulate matter sample flow through a scattering cavity test area with a constant speed, and irradiating the test area after a laser is processed through polarization; 2) making an incident laser polarization state horizontally polarized, measuring the Stokes vector (S0, S1, S2, S3)<T> of scattered light at a specific angle after incident light is scattered by current particulate matters, calculating Hdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter morphology, calculating Pdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter absorption, and calculating Rdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter components; 3) making the incident laser polarization state being 45 DEG linear polarization, the rest operation being the same with the step 2); 4) making the incident laser polarizationstate being right-hand circular polarization, the rest operation being the same with the step 2); and 5) analyzing the integration attribute of the current particulate matters through an obtained index set. The method can realize on-line rapid comprehensive analysis on the integration attribute of particulate matters. In addition, the device can maximumly reduce the number of detectors.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Device and method for detecting scattered light based on cooperation of ultrasonic modulation
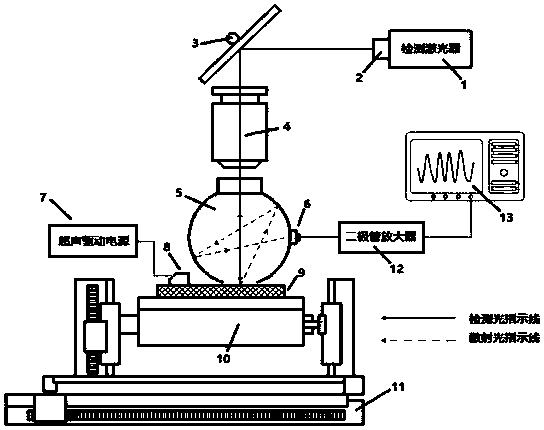
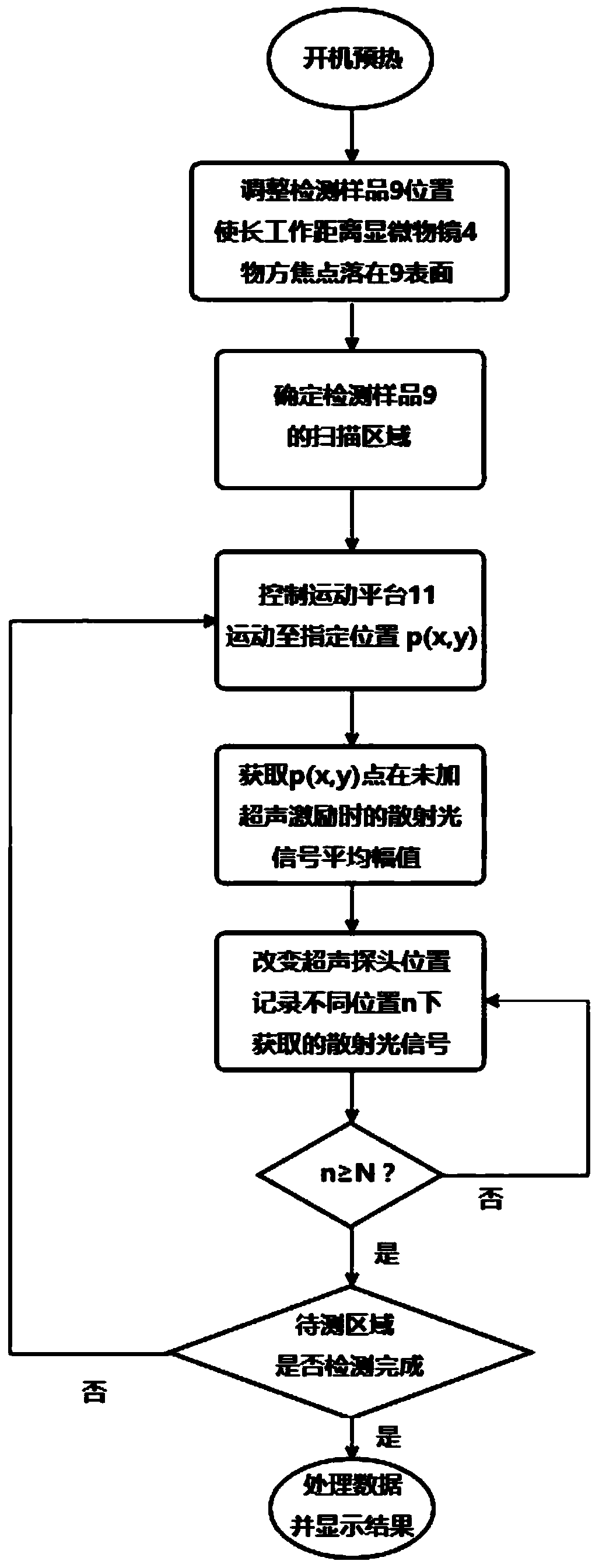
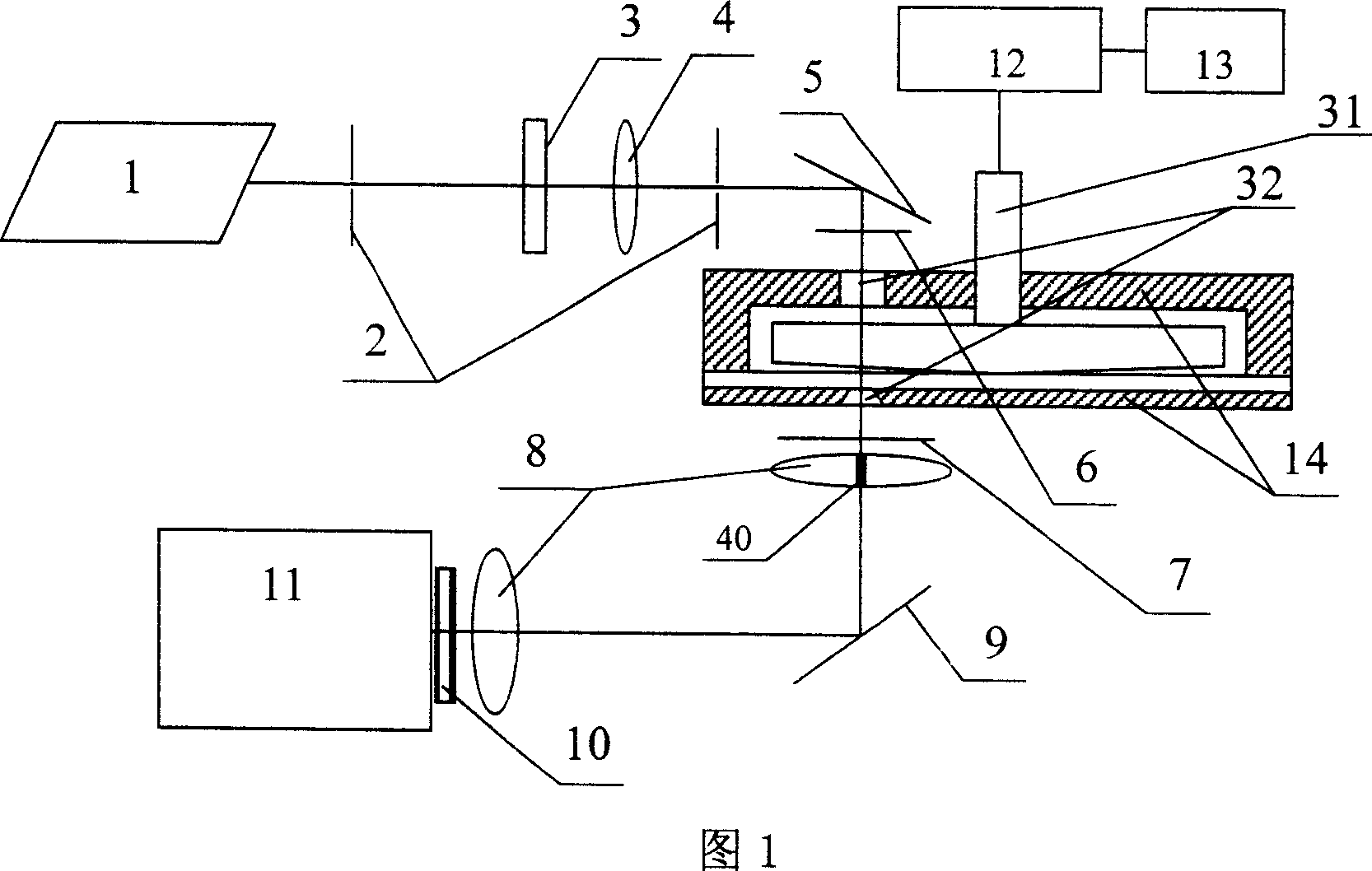
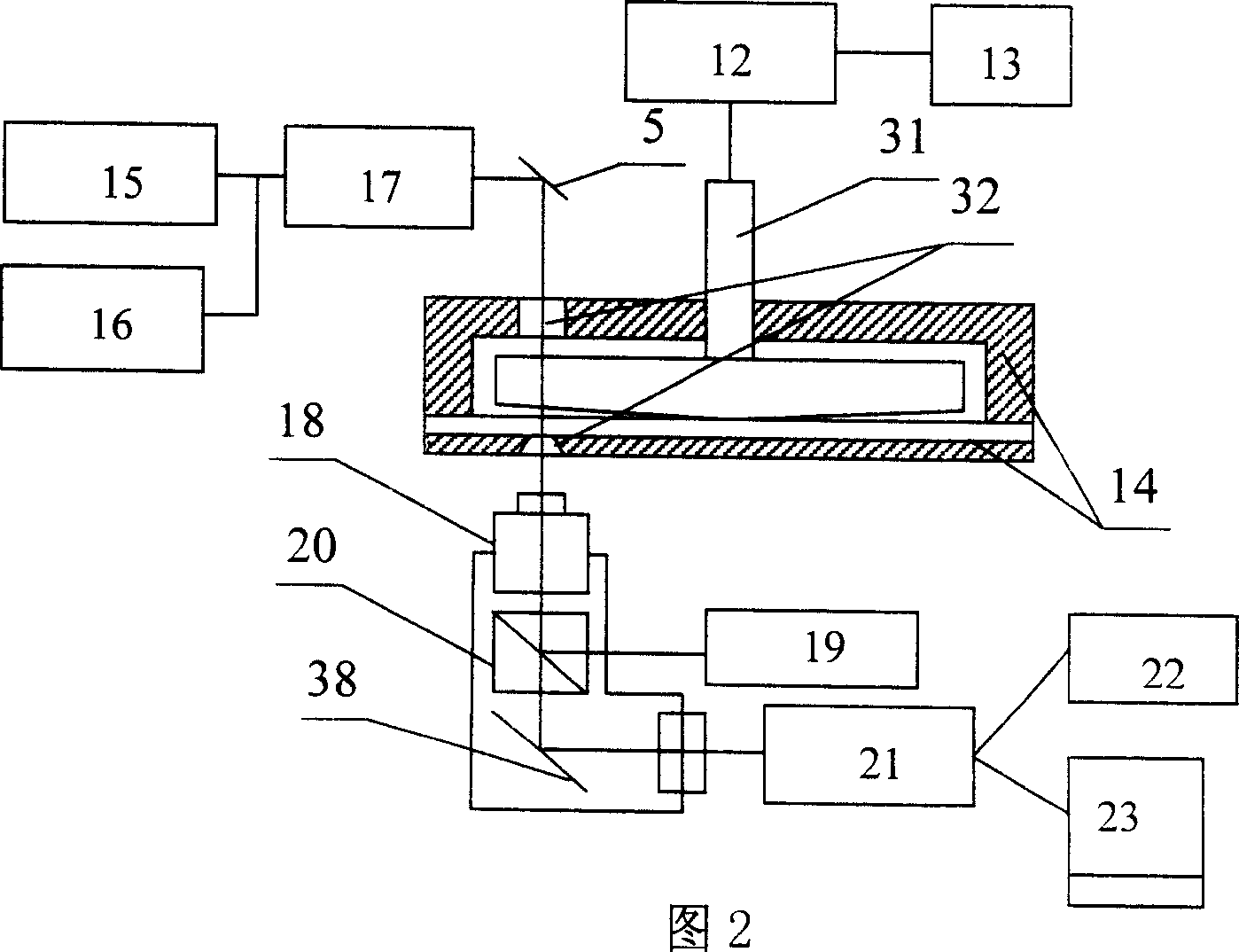
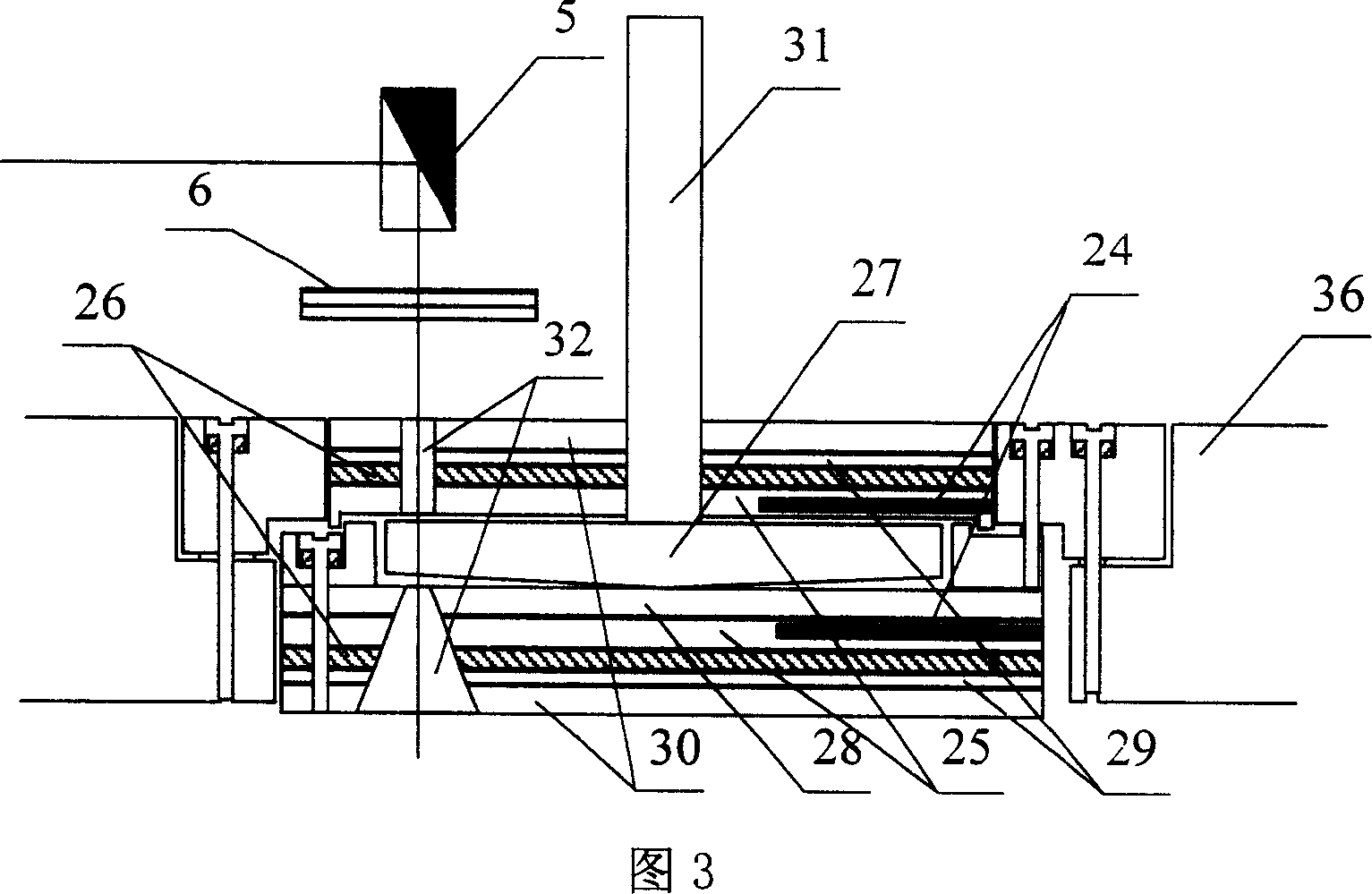
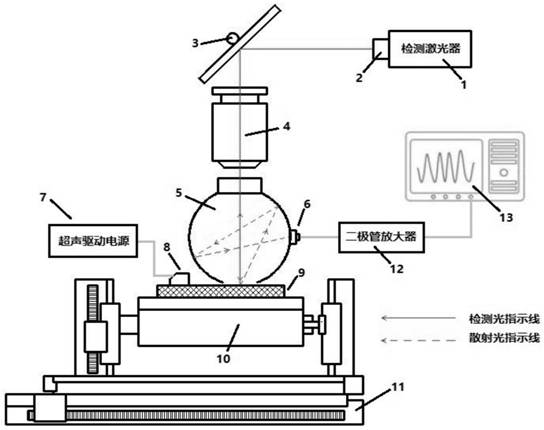
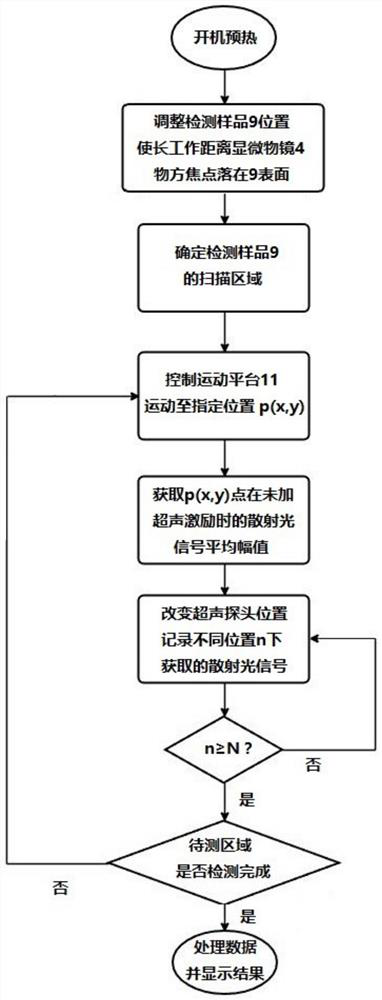
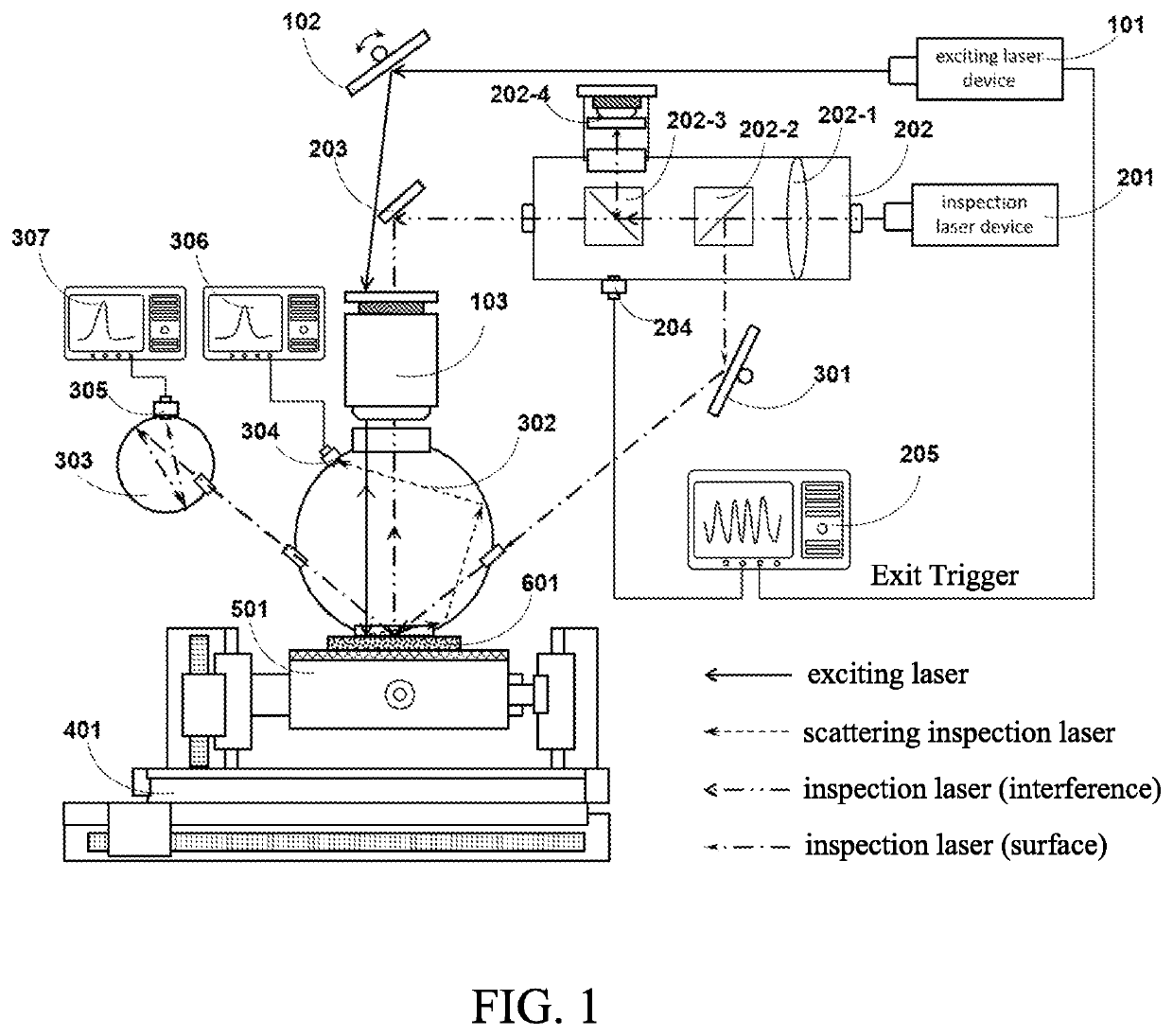
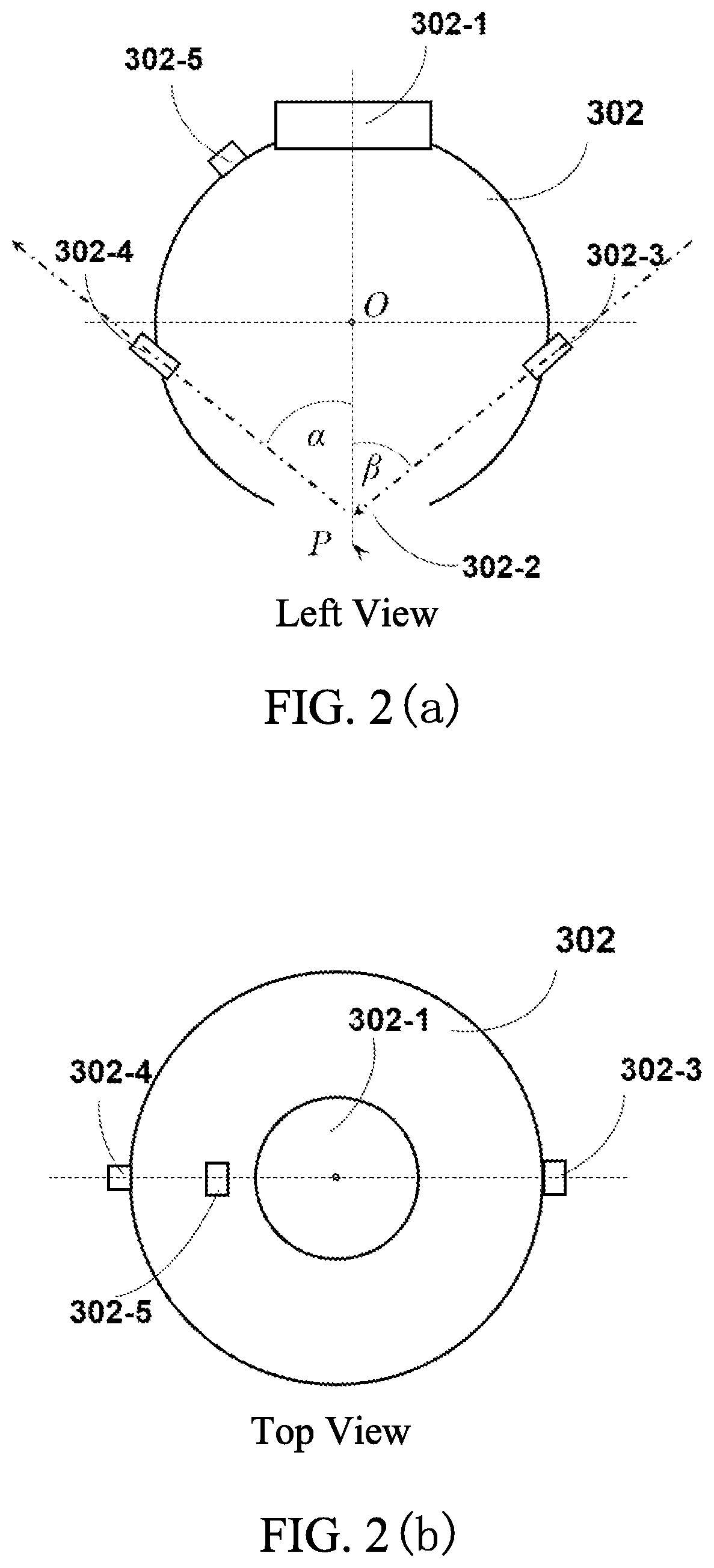
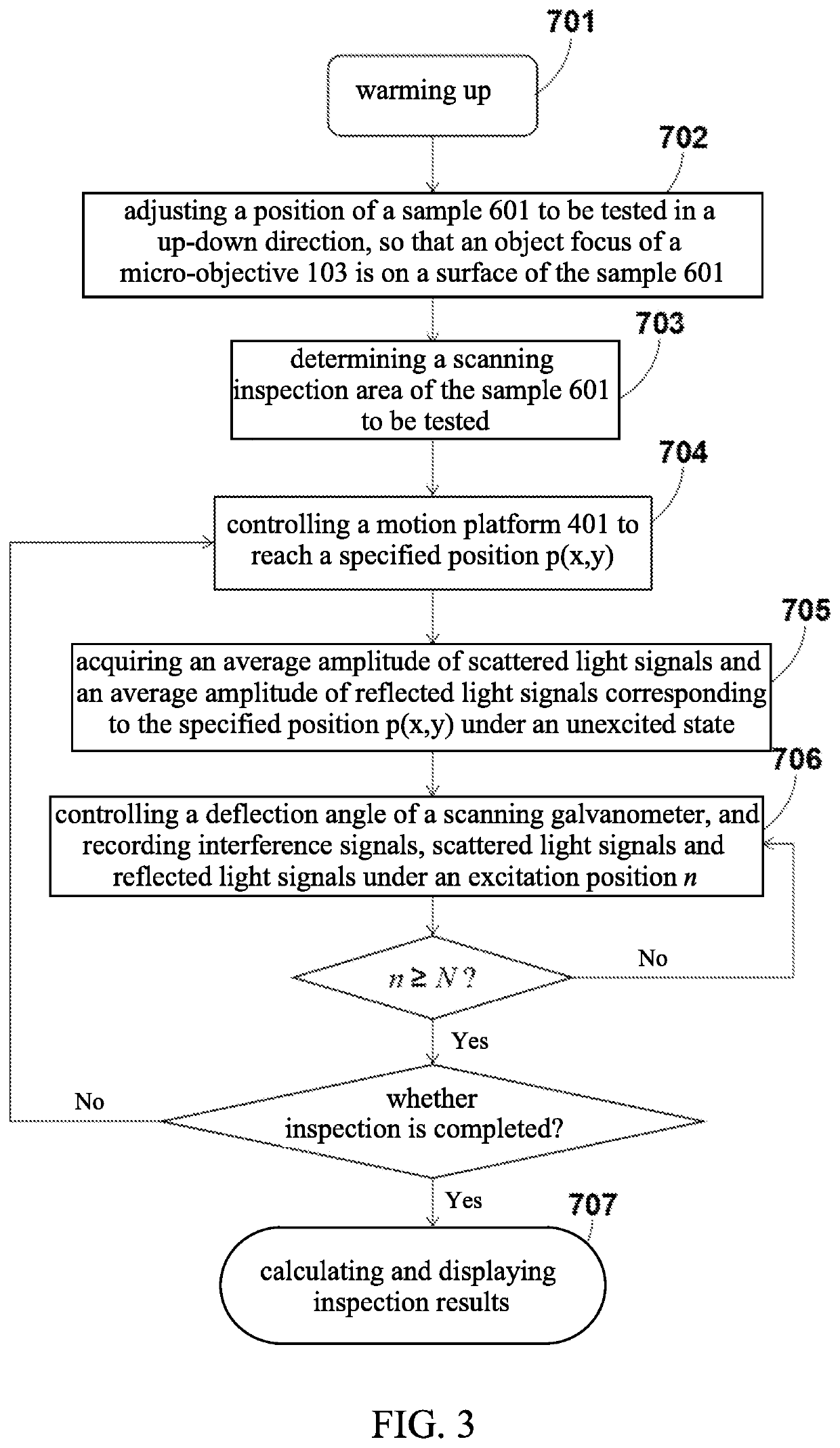
ActiveCN110779927AIntuitive defect distribution imageHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsMedicineLaser scattering
The invention provides a device and method for detecting scattered light based on cooperation of ultrasonic modulation. The device comprises an ultrasonic excitation device, a laser scattering detection device, a motion platform, a sample table, a photodiode, a diode amplifier and a digital oscilloscope. After combination of the ultrasonic modulation technology with the laser scattering defect detection technology, ultrasonic modulation is carried out on the surface of a detected sample; with introduction of dynamic changes of defect characteristics in a moving state, a static light scatteringeffect of defects in the state is observed and analyzed; and the amplitude and phase changes of the scattered light intensity are analyzed to realize defect detection. According to the invention, ultrasonic modulation is added in scattering detection and two defect detection results are provided; and a visual defect distribution image is provided in a scanning manner. The device and method for detecting scattered light based on cooperation of ultrasonic modulation can be applied to defect detection of precision optical elements and are particularly suitable for finished product detection of ultra-precision optical elements with strict requirements on sub-surface defects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
In-situ observation system combining laser light scattering and microscope under the shear field
InactiveCN1967254AEasy accessHigh precisionScattering properties measurementsMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesObservation systemLiquid crystal
The invention relates to original location observation system under the shear field with laser light scattering and microscopy, and the system can also be used to liquid-crystal, emulsion, and other system's research under the shear field. The system includes laser light scattering and microscopy system, and the two systems share the sample pool with the heater on a platform, and precision controllable shear field imposed devices and total reflection coating mirror. The invention can precisely impose fixed or variable rate shear field to precise temperature experimental samples (polymer melt or solution, polymer blends alloy, etc.). Using stable output laser as light scattering source, through the lens group and CCD array detector to obtain the reflection form of reciprocal space and scattering patterns of structure, and meanwhile, in the same experimental conditions, switched to the microscope optical path, to obtain the shape and structure of real space, and comparing the obtained microscope pattern after FFT transfer with the corresponding scattering pattern, to verify generated concrete shape and structure under the shear field.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Freeze indicator employing light scattering and method of making same
ActiveUS9297706B2Low costSimple configurationThermometers using mean/integrated valuesThermometers using physical/chemical changesLiquid mediumColor changes
A freeze indicator including an indicator dispersion is described herein. Such an indicator dispersion can include: a liquid medium and particles of a colored indicator agent dispersed in the liquid medium. The colored indicator agent particles having an inherent color; wherein the indicator dispersion exhibits the inherent color of the colored indicator agent particles after freezing and is configured to have a less colored appearance before freezing and wherein light scattering masks the inherent color of the colored indicator agent particles before freezing. Some indicator dispersions can be free of color-changing chemical co-reactants. These freeze indicators can be small, have a low cost, and have a simple configuration.
Owner:TEMPTIME CORP
Reflective lens for ultrathin backlight module group
PendingCN108873120AIncrease the light output angleUniform light outputMirrorsNon-linear opticsOptoelectronicsSurface structure
The invention discloses a reflective lens for an ultrathin backlight module group, and the reflective lens comprises a loading edge, a support column, a transmission cylinder, a central cylinder, a first light scattering groove, and a second light scattering groove. The lens is of a double-layer cylindrical surface structure. The lower surface of the lens is provided with a light source cavity, and the lower surface of the lens around the light source cavity is provided with the support column. A side edge of the lens is provided with the loading edge. The upper surface of the lens is providedwith the first light scattering groove, and the second light scattering groove is disposed below the first light scattering groove. The upper surface of the lens at an outer side of the first light scattering groove is provided with a light scattering and diffusion groove. The first light scattering groove, the second light scattering groove and the light scattering and diffusion groove enable the upper surface of the lens to be segmented into the central cylinder and the transmission cylinder. The central cylinder is located at the center of the transmission cylinder, and a central axis of the central cylinder is coaxial with the central axis of the transmission cylinder. The lens is large in light outgoing angle, is uniform in outgoing light, and reduces the thickness of the backlight module group.
Owner:ANHUI COREACH TECH
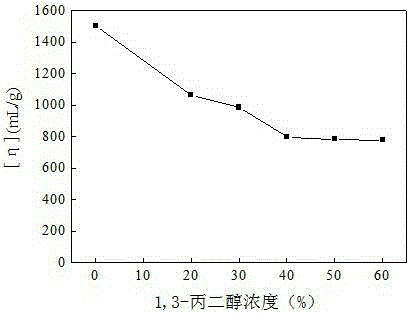
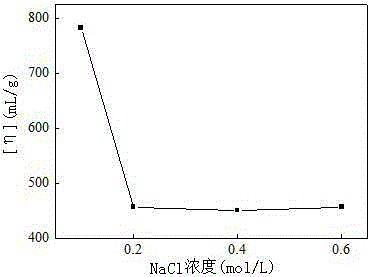
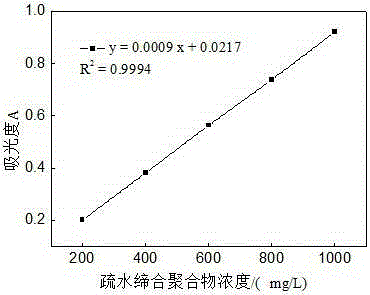
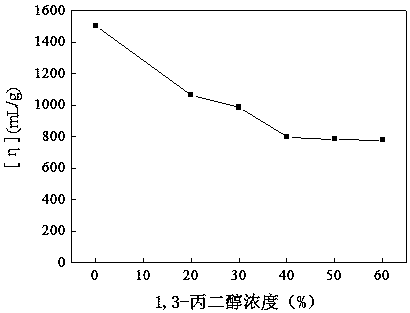
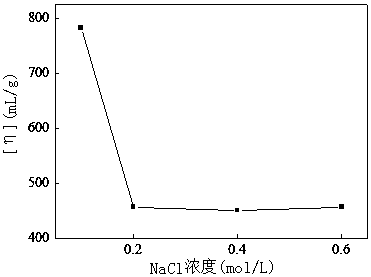
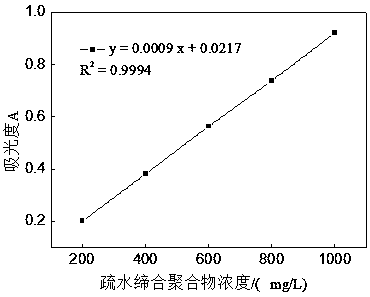
Hydrophobic associated polymer molecular weight distribution curve testing method
InactiveCN105203482ALow molecular weightCumulative percentage data is scarceColor/spectral properties measurementsPolymer scienceFiltration
The invention provides a hydrophobic associated polymer molecular weight distribution curve testing method. According to the method, hydrophobic association in a hydrophobic associated polymer solution is eliminated firstly under a proper solvent condition, polyelectrolyte effect is shielded, so that macromolecules are in a unimolecular dispersion state in a weak solution, then millipore filter membranes with different pore diameters are selected based on the membrane pore size separation principle, and a hydrophobic associated polymer is graded by means of a millipore filter membrane flow test device so that polymers with different molecular weights are separated; fitting of a percolate mass and filtration time relation curve is conducted with a quadratic equation so as to obtain the mass of a polymer solution in any grade, the concentration of the polymer solution in any grade is measured with the spectrophotometric method, and then the accumulated percentage composition of each grade is calculated. The molecular weight of the hydrophobic associated polymer in any grade is measured accurately with the static light scattering and viscosity method, and a molecular weight integral distribution curve or differential distribution curve is obtained according to the molecular weight of each grade and the accumulated percentage composition.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
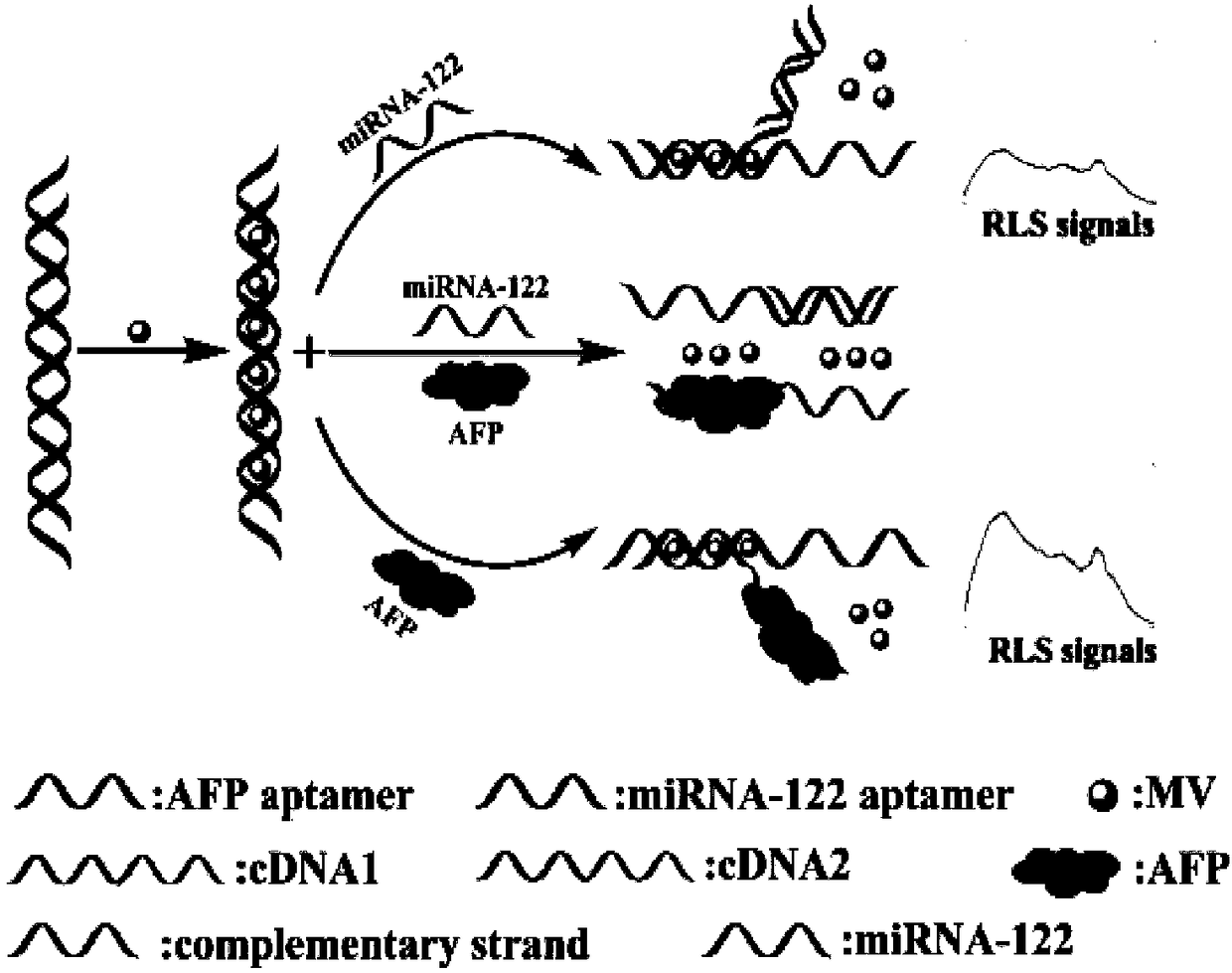
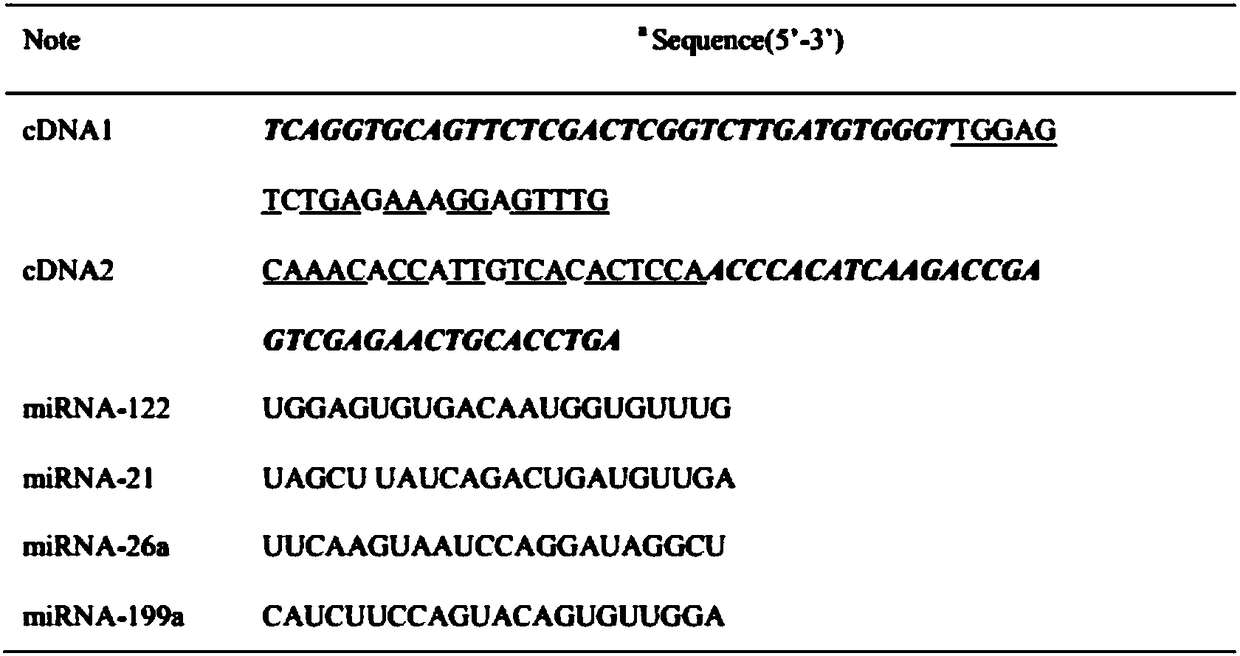
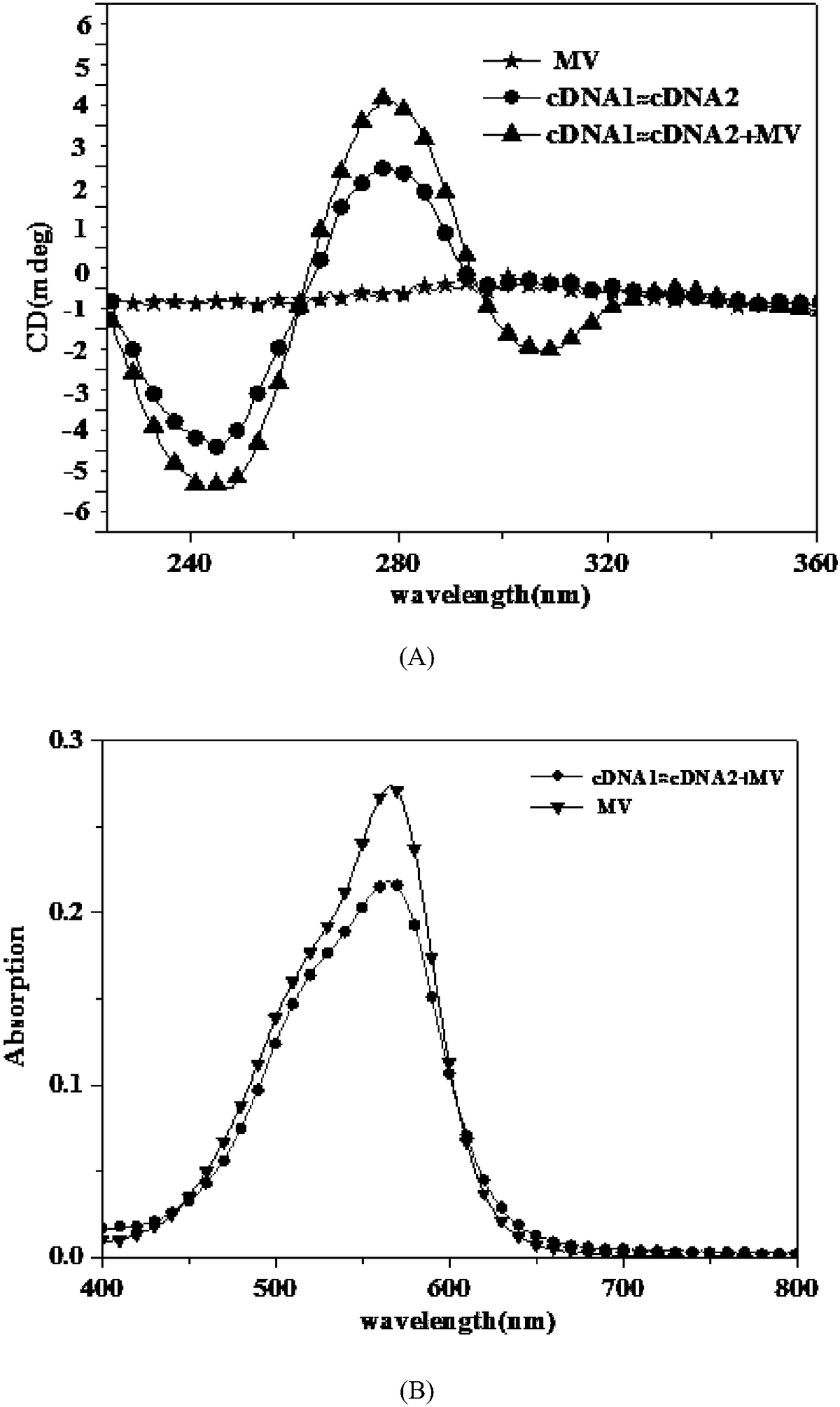
Biosensor for simultaneously detecting AFP (Alpha Fetoprotein) and miRNA-122 through resonance light scattering and preparation method of biosensor
InactiveCN108489944ALow costGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsMethyl violetMethyl purple
The invention discloses a biosensor for simultaneously detecting AFP (Alpha Fetoprotein) and miRNA-122 through resonance light scattering and a preparation method of the biosensor. The biosensor is composed of hybridized double chains cDNA1 and cDNA2 and methyl violet (MV), wherein the methyl violet is embedded into the hybridized double chains; cDNA1 comprises an AFP aptamer fragment; and cDNA2 comprises a miRNA-122 aptamer fragment. Under mutual actions of electrons of methyl violet (MV) and dsDNA, amplified resonance light scattering signals can be generated, a double-function label-free probe sensor has detection limits of 0.94mu g and 98mP upon AFP and miRNA-122 respectively, a relatively efficient, rapid and low tumor marker detection technique is established, and the technique has potential application in clinical screening of early-stage liver cancer.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
A subsurface defect detection device and method based on ultrasonic modulation
ActiveCN110779927BIntuitive defect distribution imageHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsLaser scatteringPhotodiode
The invention provides a device and method for detecting scattered light based on cooperation of ultrasonic modulation. The device comprises an ultrasonic excitation device, a laser scattering detection device, a motion platform, a sample table, a photodiode, a diode amplifier and a digital oscilloscope. After combination of the ultrasonic modulation technology with the laser scattering defect detection technology, ultrasonic modulation is carried out on the surface of a detected sample; with introduction of dynamic changes of defect characteristics in a moving state, a static light scatteringeffect of defects in the state is observed and analyzed; and the amplitude and phase changes of the scattered light intensity are analyzed to realize defect detection. According to the invention, ultrasonic modulation is added in scattering detection and two defect detection results are provided; and a visual defect distribution image is provided in a scanning manner. The device and method for detecting scattered light based on cooperation of ultrasonic modulation can be applied to defect detection of precision optical elements and are particularly suitable for finished product detection of ultra-precision optical elements with strict requirements on sub-surface defects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device and method for simultaneously inspecting defects of surface and subsurface of optical element
ActiveUS20210055230A1Image defectHigh sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase-affecting property measurementsLaser scatteringEngineering
A device and a method for simultaneously inspecting defects of a surface and a subsurface of an optical element are provided. Combined with laser-induced ultrasound and laser scattering inspection technologies, through generating acoustic sound waves on the surface and the subsurface of the optical element to be tested by lasers, a static light scattering effect of subsurface defects under modulation of the acoustic sound wave is observed and analyzed; through analyzing amplitude and phase changes of scattered light intensity and reflected light intensity, inspection for the defects of the surface and the subsurface of the optical element is realized. The present invention can be applied in quality inspection of precise optical elements, especially in finished product inspection of ultra-precise optical elements having strict requirements on the subsurface defects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical bonding member and touch display device
The invention discloses an optical bonding member and a touch display device. The optical bonding member is used for bonding the display device and the touch device together. The optical bonding member comprises: a cystic structure filled with a liquid optical adhesive and an adhesive annular sheet structure around the cystic structure; wherein the refractive index of the liquid optical adhesive is 90%-110% of that of a substrate of the touch device. The touch display device composed of the optical adhesive member provided by the present invention can effectively suppress light scattering caused by air gap and does not increase the process steps. The touch display device has reworkability, and can effectively reduce production costs.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVIC OPTOELECTRONICS
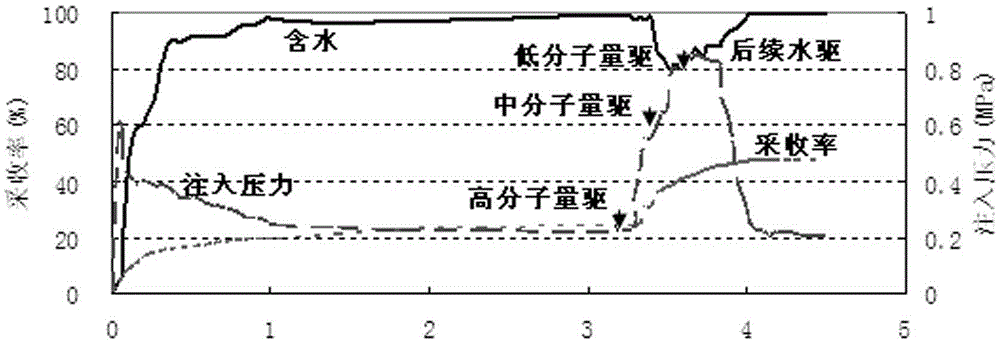
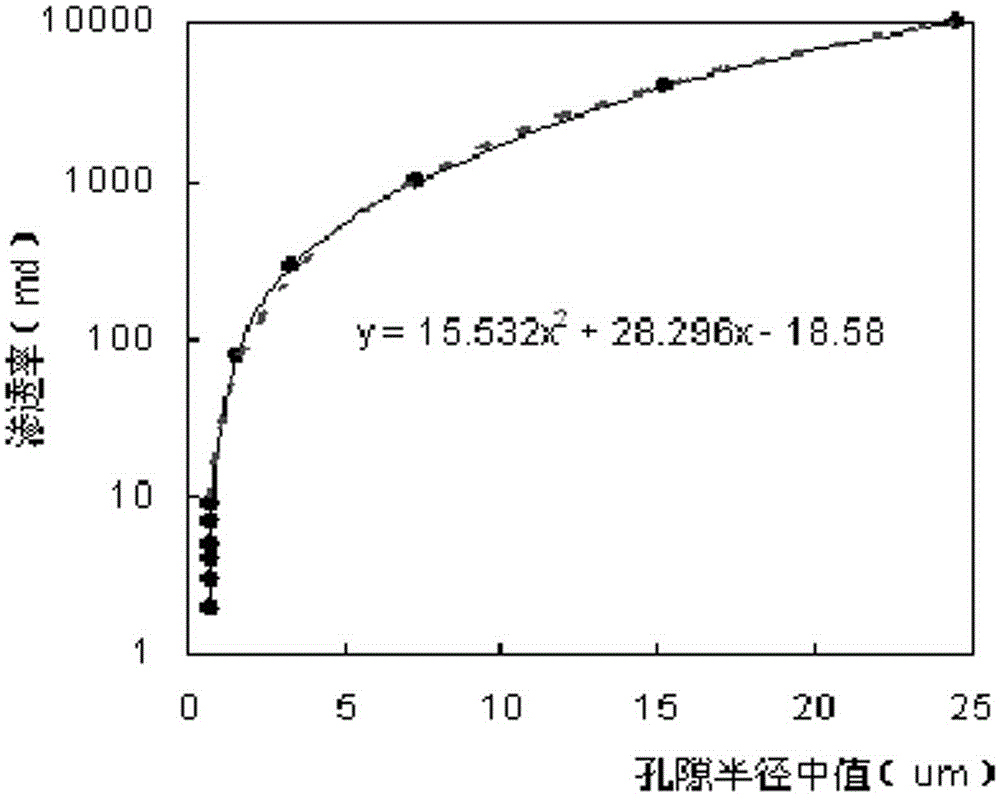
Low-permeability oilfield energy-gathering equi-fluidity oil displacement method
InactiveCN105317412AImprove oil displacement efficiencyIncrease productionFluid removalScatterometerReservoir engineering
The invention discloses a low-permeability oilfield energy-gathering equi-fluidity oil displacement method and relates to the technical field of reservoir engineering. The method comprises the following steps: step I, counting and classifying permeabilities: classifying and counting the longitudinal permeabilities of an oil reservoir according to 10-50, 50-100, and greater than 100*10<-3> um<2>, and calculating the averaged permeability of each oil reservoir and the corresponding effective thickness; step II, selecting the molecular weight of polyacrylamide: according to the rule that k1, k2 and k3 are matched with the polyacrylamide P1, P2 and P3 with proper molecular weight respectively, wherein the molecular turning radius of polyacrylamide is smaller than 1 / 10 of the mid-value of a channel and can be measured by a BI-200 SM type wide angle dynamic / static light scatterometer system produced by BIC.
Owner:DALIAN HUAO SHENGFENG OILFIELD TECH SERVICECO LTD
Biomolecule interaction analyzing method based on solid phase surface intensified light scattering
InactiveCN1811384AAvoid interferenceHigh selectivityPreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsAssay sensitivitySpectrofluorometer
The present invention relates to an analysis method capable of utilizing interaction produced by bioprobe molecule and biotarget molecule on the slide surface to intensify light-scattering signal to implement qualitative and quantitative determinations and intermolecular interaction character analysis. Said method includes the following processes: pretreatment of concave slide, fixation of probe molecule, combination of bioprobe and biotarget molecule, adopting synchronous scanning mode on the general spectrofluorometer to obtain scattering spectrum, utilizing said scattering spectrum to make qualitative and quantitative determinations of biotarget molecule and analysis of intermolecular intraction character and regeneration of bioprobe.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Low-emission fibre-matrix material curable thermally by radical polymerization
Fibre-matrix material curable thermally by radical polymerization, comprising (A) a polymeric matrix curable thermally by radical polymerization, (B) at least one kind of reinforcing fibres and (C) at least one particulate initiator of the radical polymerization, having an average particle size of 5 nm to 500 μm, as measured by static light scattering, and selected from the group consisting of benzpinacol and substituted benzpinacols; processes for producing it, and its use for producing fibre-reinforced thermoset mouldings.
Owner:ELANTAS +1
Method for Determination of Molecular Weight Distribution Curve of Hydrophobically Associating Polymers
InactiveCN105203482BAvoid difficultiesColor/spectral properties measurementsPolymer scienceFiltration
The invention provides a method for determining the molecular weight distribution curve of a hydrophobically associative polymer: firstly, under suitable solvent conditions, the hydrophobic association in a solution of the hydrophobically associative polymer is eliminated, the polyelectrolyte effect is shielded, and the macromolecules are dissolved in a dilute solution. Then, using the principle of membrane pore size separation, microporous membranes with different pore sizes were selected, and the hydrophobically associative polymers were classified by the microporous membrane flow experimental device to separate polymers with different molecular weights. Use quadratic equation to fit the relationship between filtrate mass and filtration time to obtain the mass of each fraction of polymer solution, measure the concentration of each fraction of polymer solution by spectrophotometry, and then calculate the cumulative percentage of each fraction . Combined with static light scattering and viscosity method, the molecular weight of each fraction of the hydrophobically associative polymer is accurately determined, and the molecular weight integral distribution curve or differential distribution curve is obtained according to the molecular weight and cumulative percentage of each fraction.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
A laser particle size analyzer and measurement method for realizing all-round measurement
ActiveCN112255150BRaise the lower limit of measurementAchieve continuous seamless receptionParticle size analysisParticle Size AnalyzerSample pool
This disclosure proposes a laser particle size analyzer and a measurement method for realizing all-round measurement. The laser particle size analyzer includes a rotating laser transmitter receiver and a sample pool. The circle, the rotating laser transmitting receiver includes a rotating device and a measuring device arranged on the rotating device, the measuring device is used to emit a laser signal to the sample cell and detect an echo signal. The disclosed laser particle size analyzer and its measurement method can realize continuous and seamless reception of scattered light from 0° to 180°, and further expand the measurement lower limit of the laser particle size analyzer. The measured results are in good agreement with the nominal values, and the lower limit of measurement is close to the theoretical limit of the static light scattering method. And by using the rotating laser transmitter receiver for multi-angle measurement, and then measure the size of irregular particles at different angles.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Concentrating photoelectric conversion device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveCN104868835BEasy to manufacturePrevent proliferationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaicsEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
The present invention aims to provide a concentrator photovoltaic conversion device having the advantages of no need for redesigning a band gap, using existing solar cells obtained from non-solar cell manufacturers, easy manufacturing, easy thermal design, and capacity of suppressing reduction of conversion efficiency even in the case of improved concentrating efficiency. In order to solve the problems, the present invention provides the concentrator photovoltaic conversion device, comprising a concentrating mirror and a photovoltaic conversion element arranged opposite to the concentrating mirror, wherein the photovoltaic conversion element comprises a light scattering-used solar cell having a through hole, and a concentrating-used solar cell arranged in the through hole of the light scattering-used solar cell, in addition, the concentrating mirror is formed by transparent thermosetting resin, and the photovoltaic conversion element is carried on an external connection substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
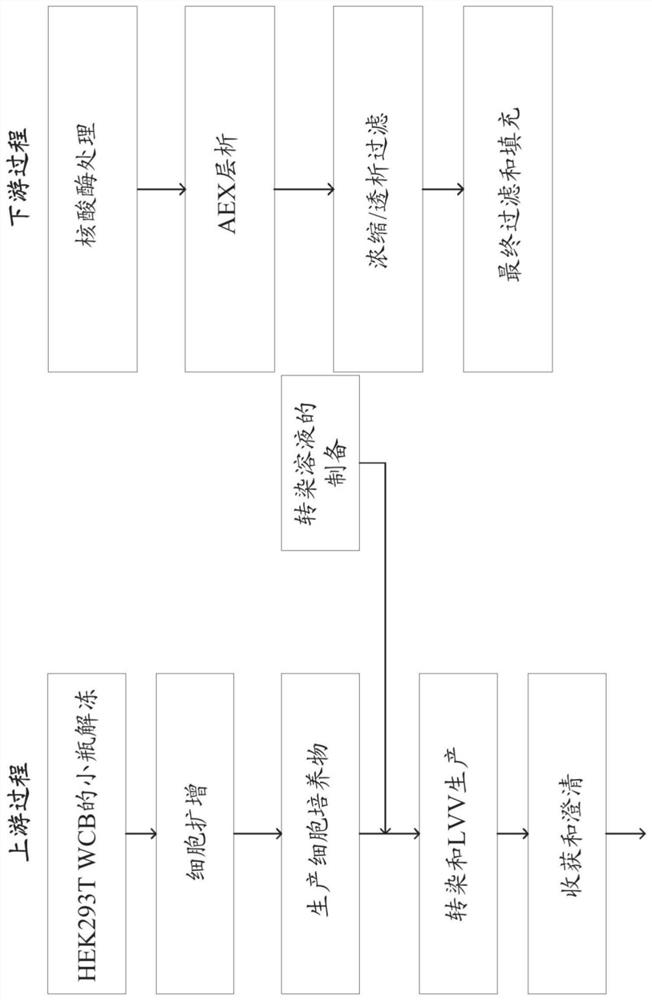
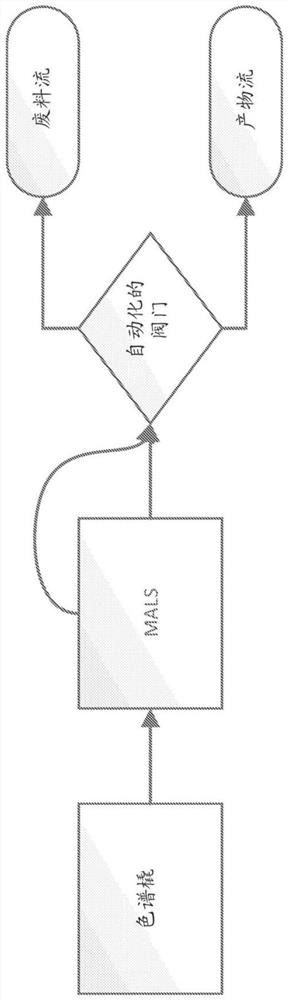
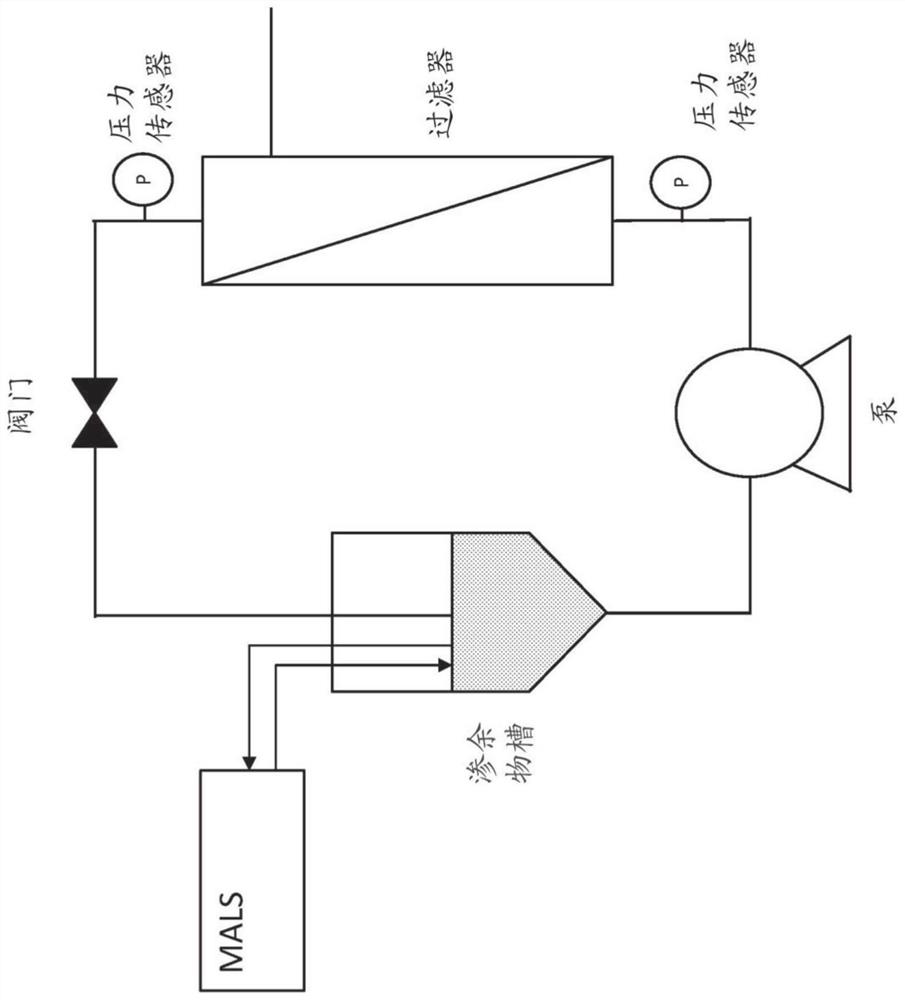
Methods and systems for manufacturing viral vectors
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for manufacturing viral vectors (e.g., lentiviral vectors) using a static light scattering device in series with the manufacturing process.
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
Concentrator photovoltaic conversion device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104868835AEasy to manufacturePrevent proliferationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaicsEngineeringEnergy conversion efficiency
The present invention aims to provide a concentrator photovoltaic conversion device having the advantages of no need for redesigning a band gap, using existing solar cells obtained from non-solar cell manufacturers, easy manufacturing, easy thermal design, and capacity of suppressing reduction of conversion efficiency even in the case of improved concentrating efficiency. In order to solve the problems, the present invention provides the concentrator photovoltaic conversion device, comprising a concentrating mirror and a photovoltaic conversion element arranged opposite to the concentrating mirror, wherein the photovoltaic conversion element comprises a light scattering-used solar cell having a through hole, and a concentrating-used solar cell arranged in the through hole of the light scattering-used solar cell, in addition, the concentrating mirror is formed by transparent thermosetting resin, and the photovoltaic conversion element is carried on an external connection substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com