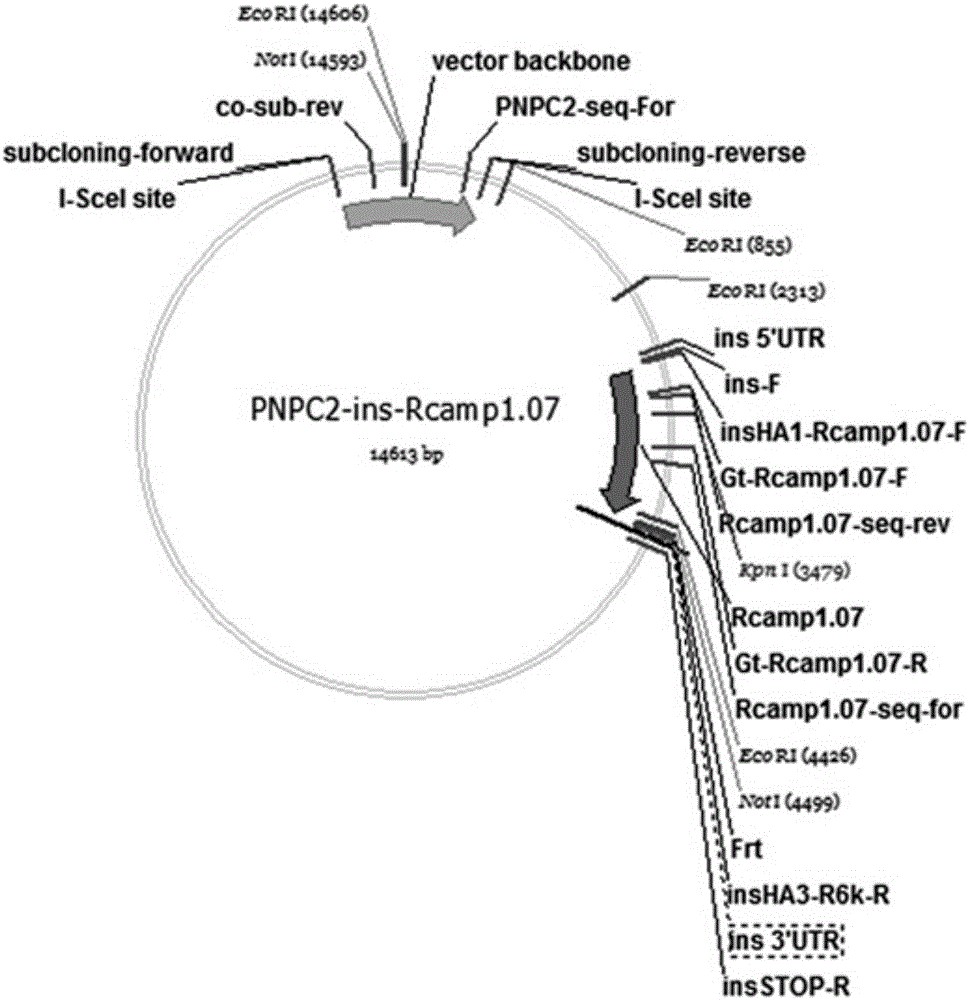
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Pancreatic stellate cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
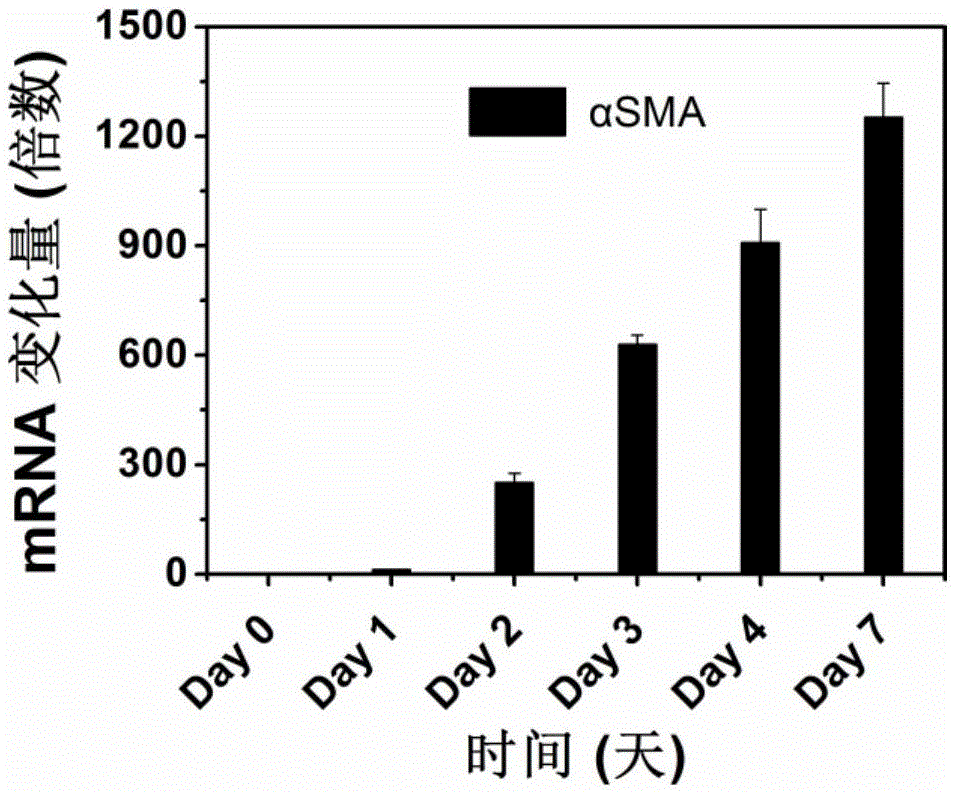
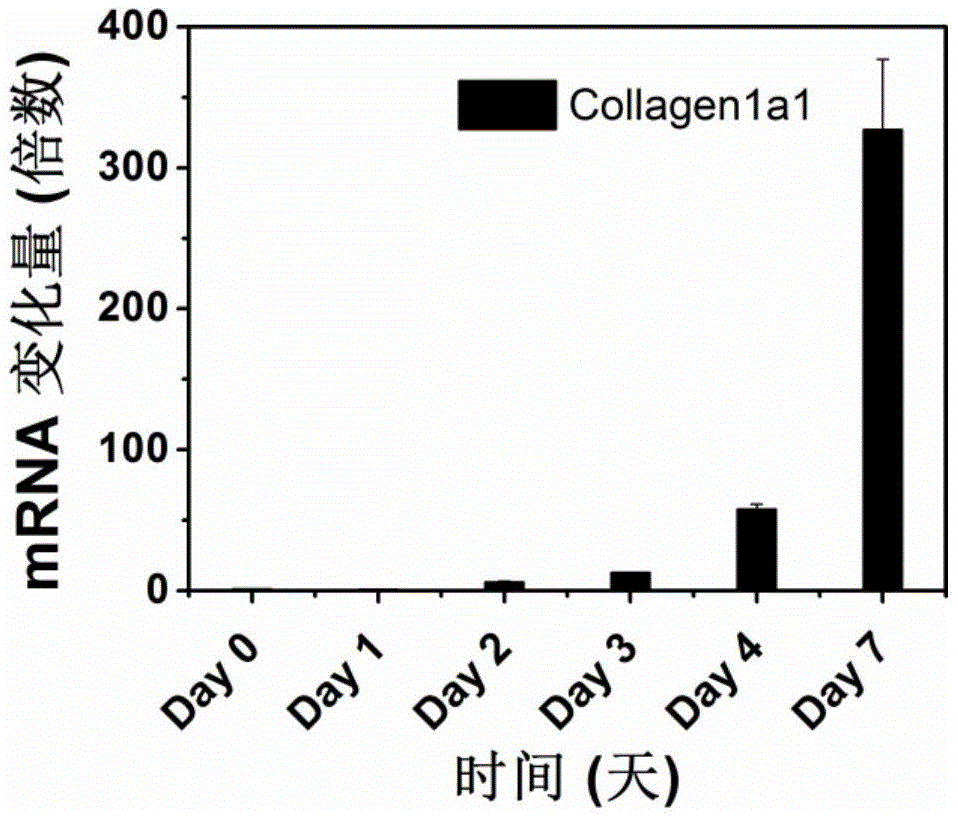
Pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are classified as myofibroblast-like cells that are located in exocrine regions of the pancreas. PaSCs are mediated by paracrine and autocrine stimuli and share similarities with the hepatic stellate cell. Pancreatic stellate cell activation and expression of matrix molecules constitute the complex process that induces pancreatic fibrosis. Synthesis, deposition, maturation and remodelling of the fibrous connective tissue can be protective, however when persistent it impedes regular pancreatic function.
Construction method for mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells and application
The invention discloses a construction method for a mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells and an application. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing a conditionally deleted Tmem30a gene homozygote mouse, wherein the two ends of one or more exon of the Tmem30a genes are inserted into homonymous arrayed loxP locus; mating the mouse with pancreatic beta cell specific transgenic mouse Ins2-Cre, thereby acquiring the mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells. The mouse with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells shows glucose intolerance and poor insulin sensitivity. The mouse model can be used as a diabetes research model.
Owner:成都基康医药科技有限公司
Co-transplantation of hepatic stellate cells and graft
InactiveUS20080145342A1Prevent graft rejectionPrevent rejectionBiocideHepatocytesCo transplantationMAMMAL LIVER
A method of inhibiting graft rejection includes isolating Hepatic Stellate Cells from a mammal liver, activating the isolated Hepatic Stellate Cells, and administering a combination of Hepatic Stellate cells and a graft to a mammal.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
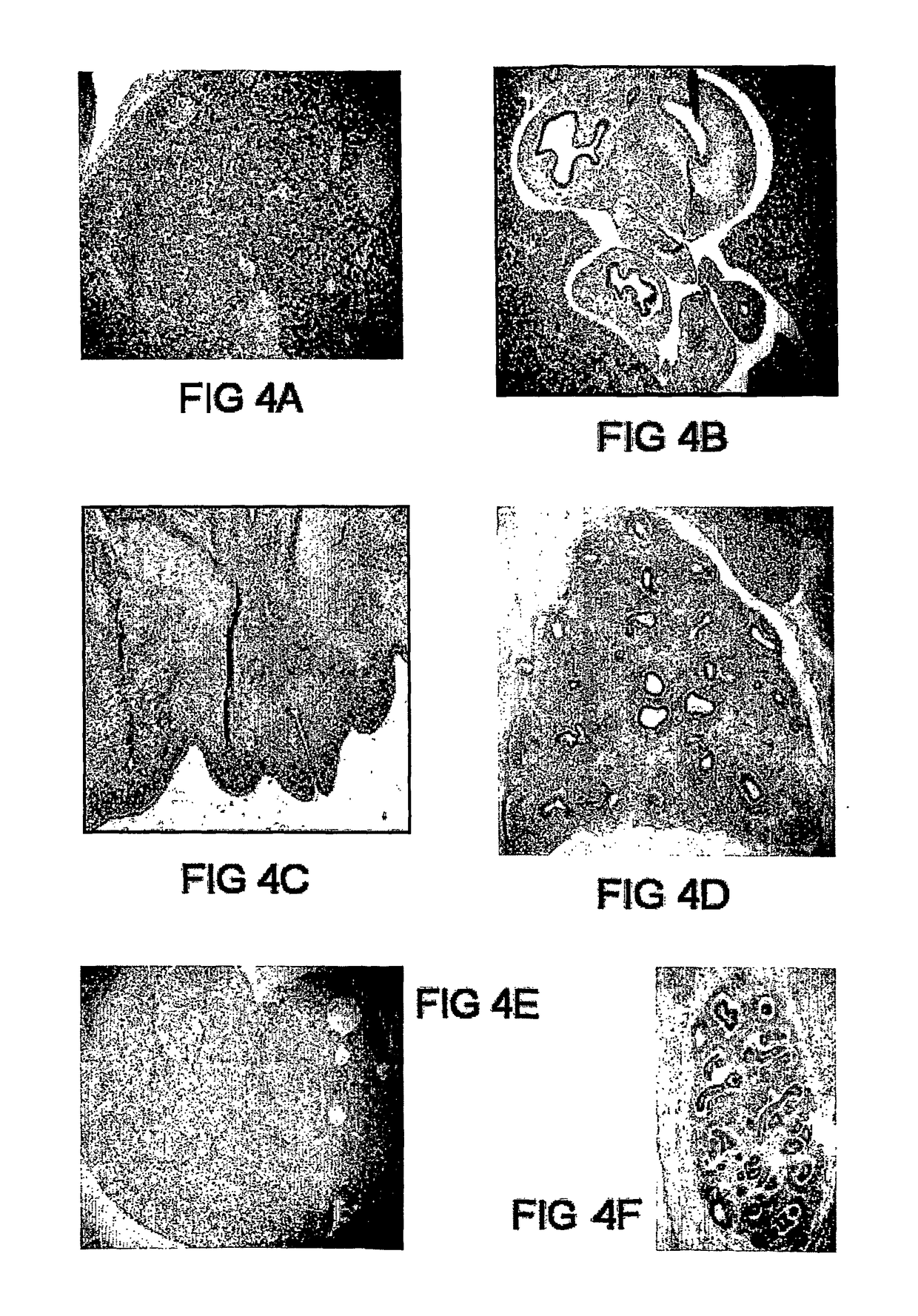
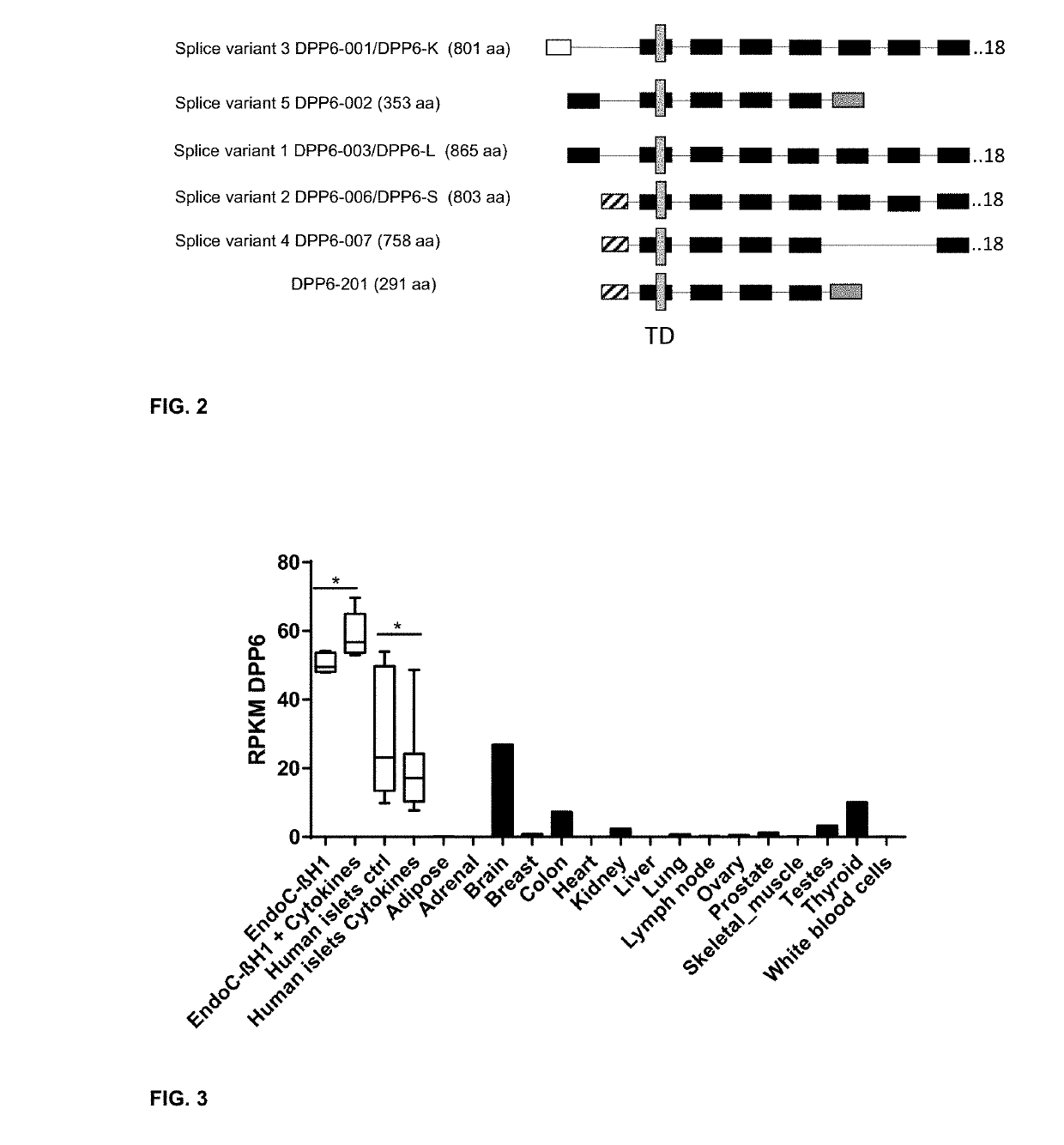
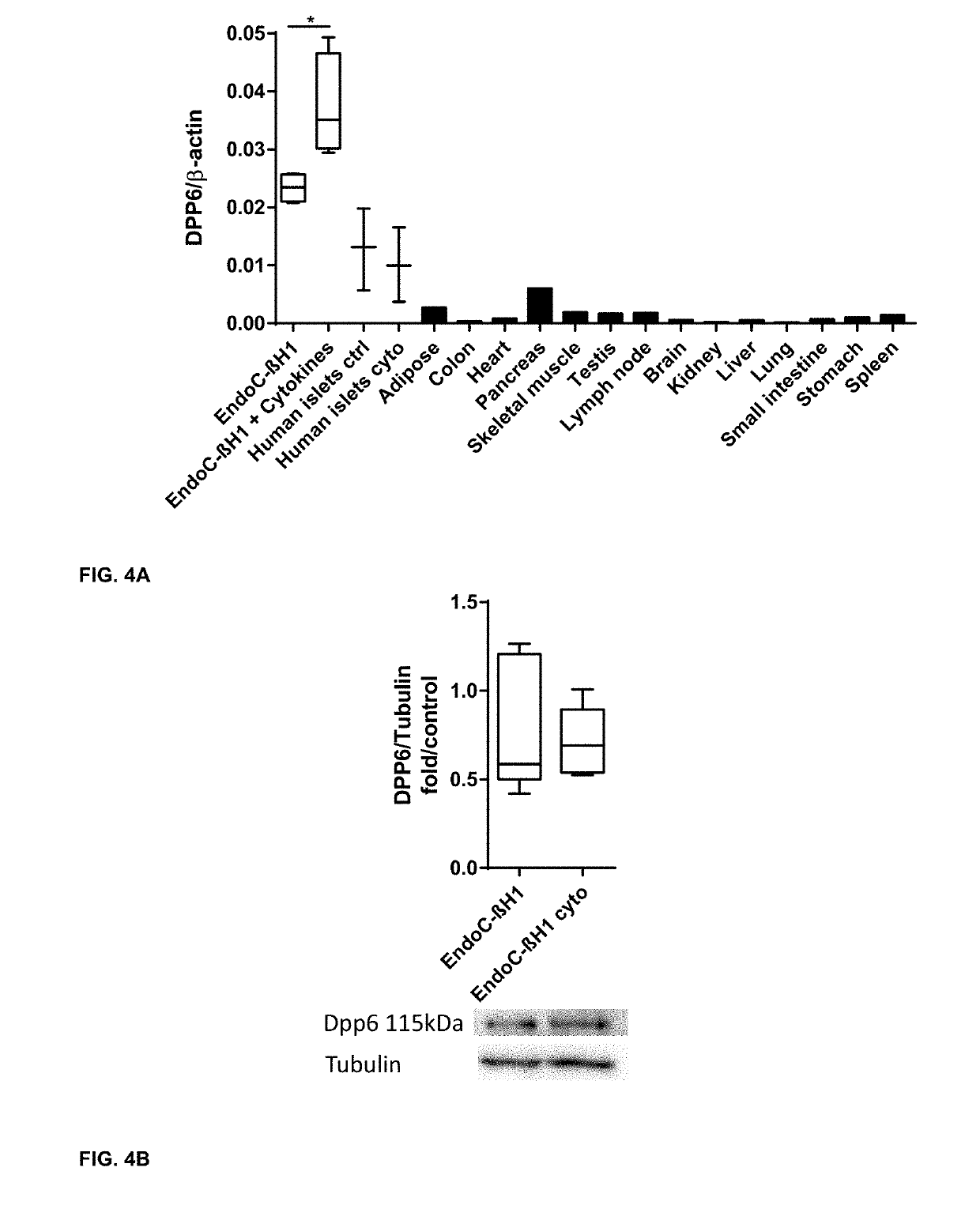
New plasma membrane biomarkers preferentially expressed in pancreatic beta cells useful in imaging or targeting beta cells
ActiveUS20100322850A1Evaluate effectivenessEarly detectionDisease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDendritic cell
The present invention is directed to the identification of a biomarker specifically located in the plasma membrane of pancreatic beta cells. It was selected by a Systems Biology approach on Massively Parallel Signal Sequencing datasets obtained in human islets and Affymetrix microarray datasets on human islets, purified rat primary beta and non beta cells and insulinoma cells. Based on a set of specific features the biomarker is a unique candidate for imaging and targeting strategies to study the pancreatic beta cell mass in health and disease (T1 D, T2D, pancreatic cancers, obesity, islet transplantation, beta cell regeneration). The five specific features of the selected biomarkers are: 1) Preferentially expressed in pancreatic islets as compared to surrounding tissues; 2) Higher expression in pancreatic beta cells than in pancreatic alpha cells or than in other islet non-beta cells; 3) Expression levels in pancreatic beta cells are higher or comparable to glucokinase which is an enzyme specifically expressed in the pancreatic beta cell; 4) Located in the membrane and as such targetable with antibodies, peptides or small molecules which allows imaging, targeting and immunohistochemistry; and 5) Expression is not induced during the process of inflammation of the beta cell mass and the protein is not enriched in T-cells and dendritic cells or in other cells participating in the inflammation process.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +2
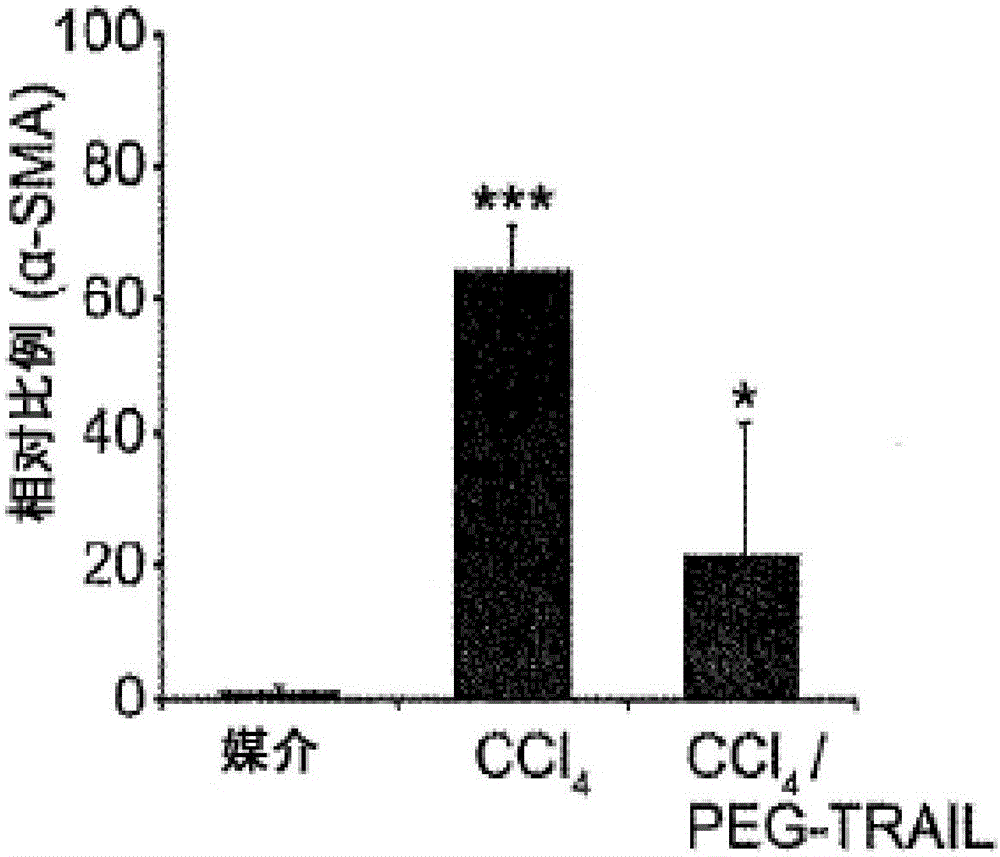
Trail receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic disease
ActiveUS20160022776A1Reduce the amount requiredUnwanted scarringPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTrail r1
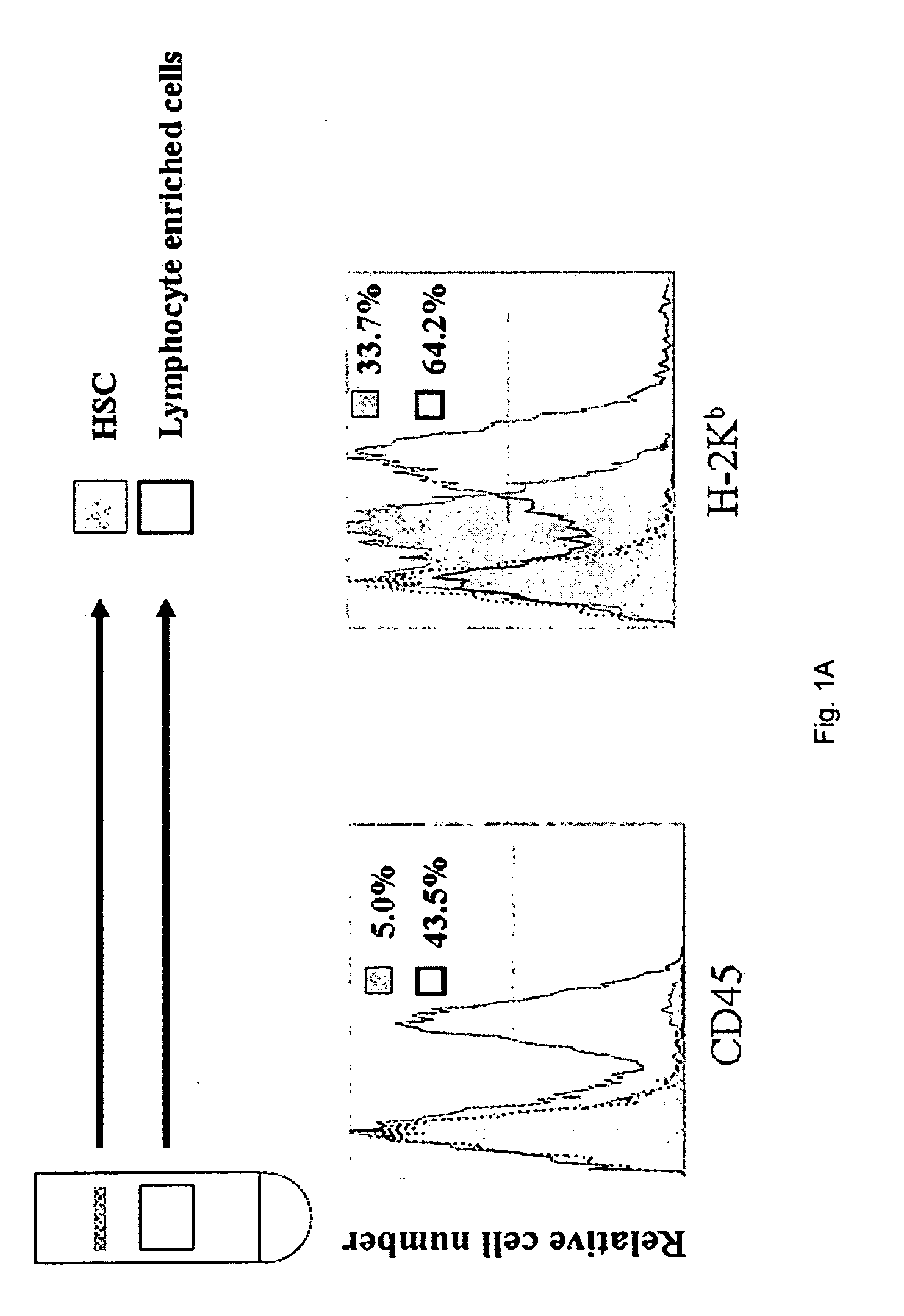
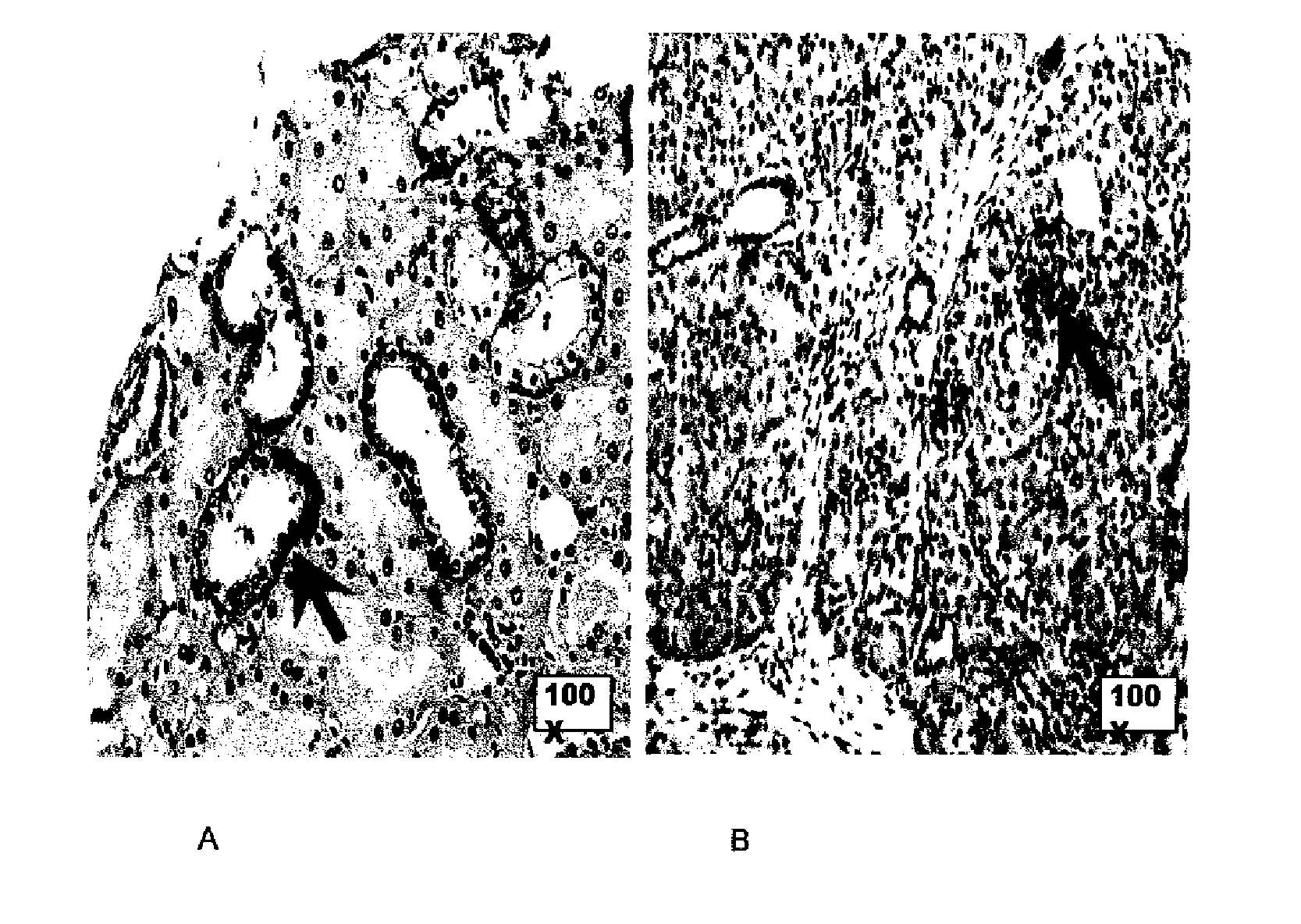
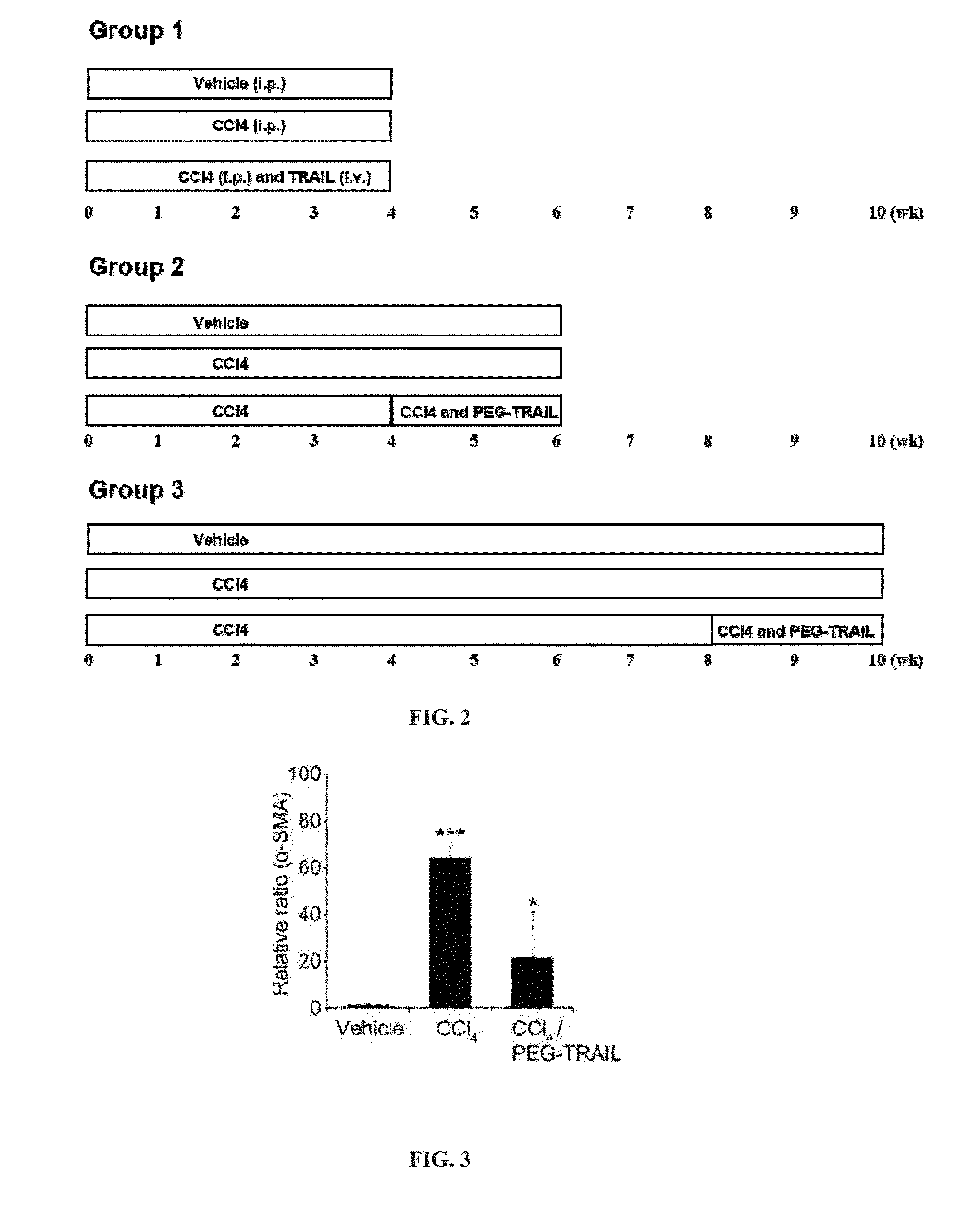
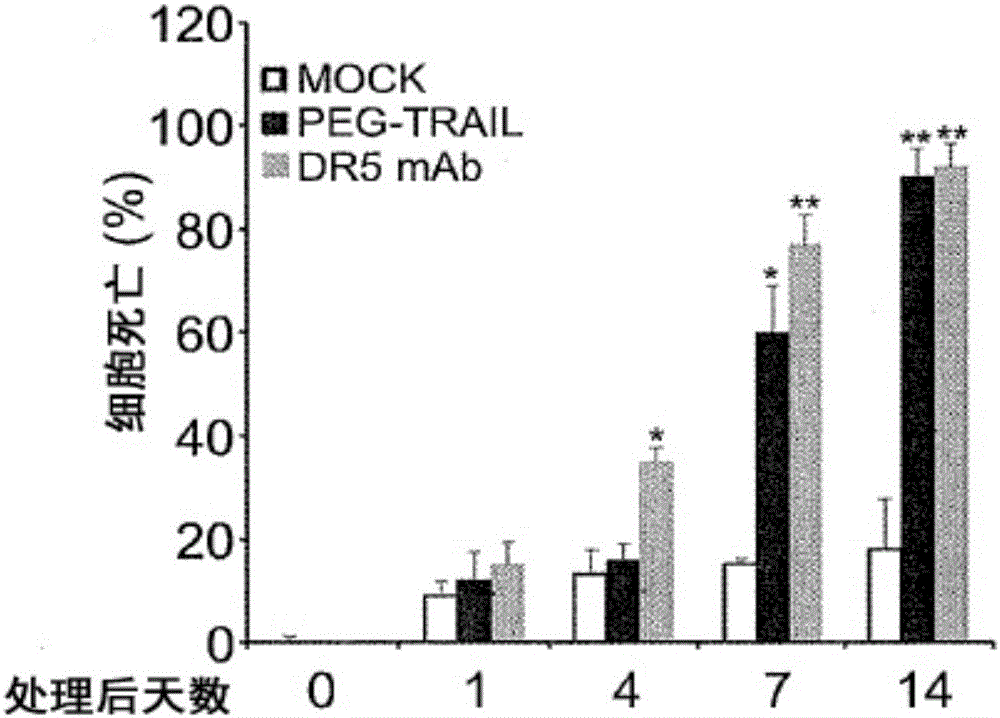
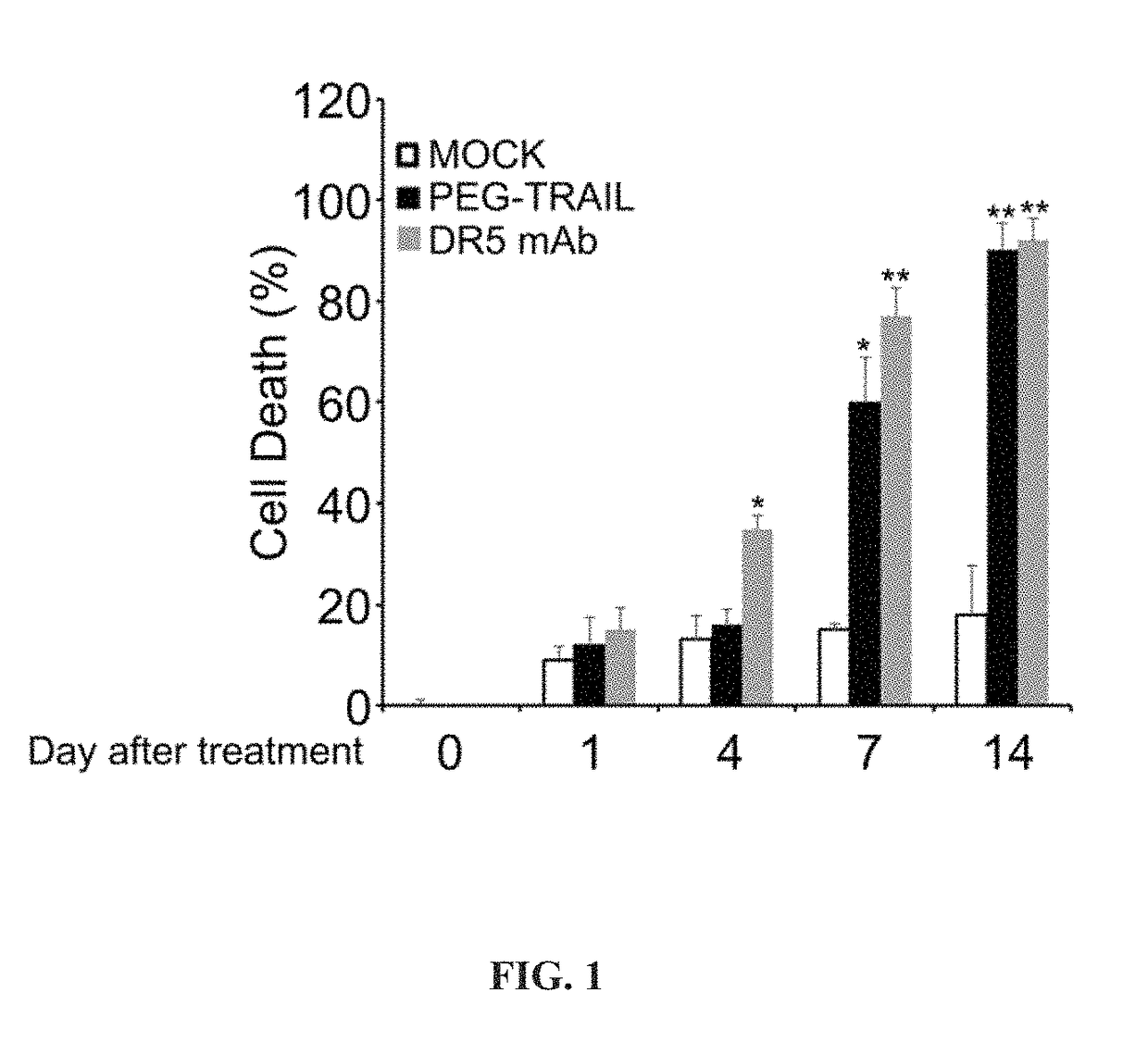
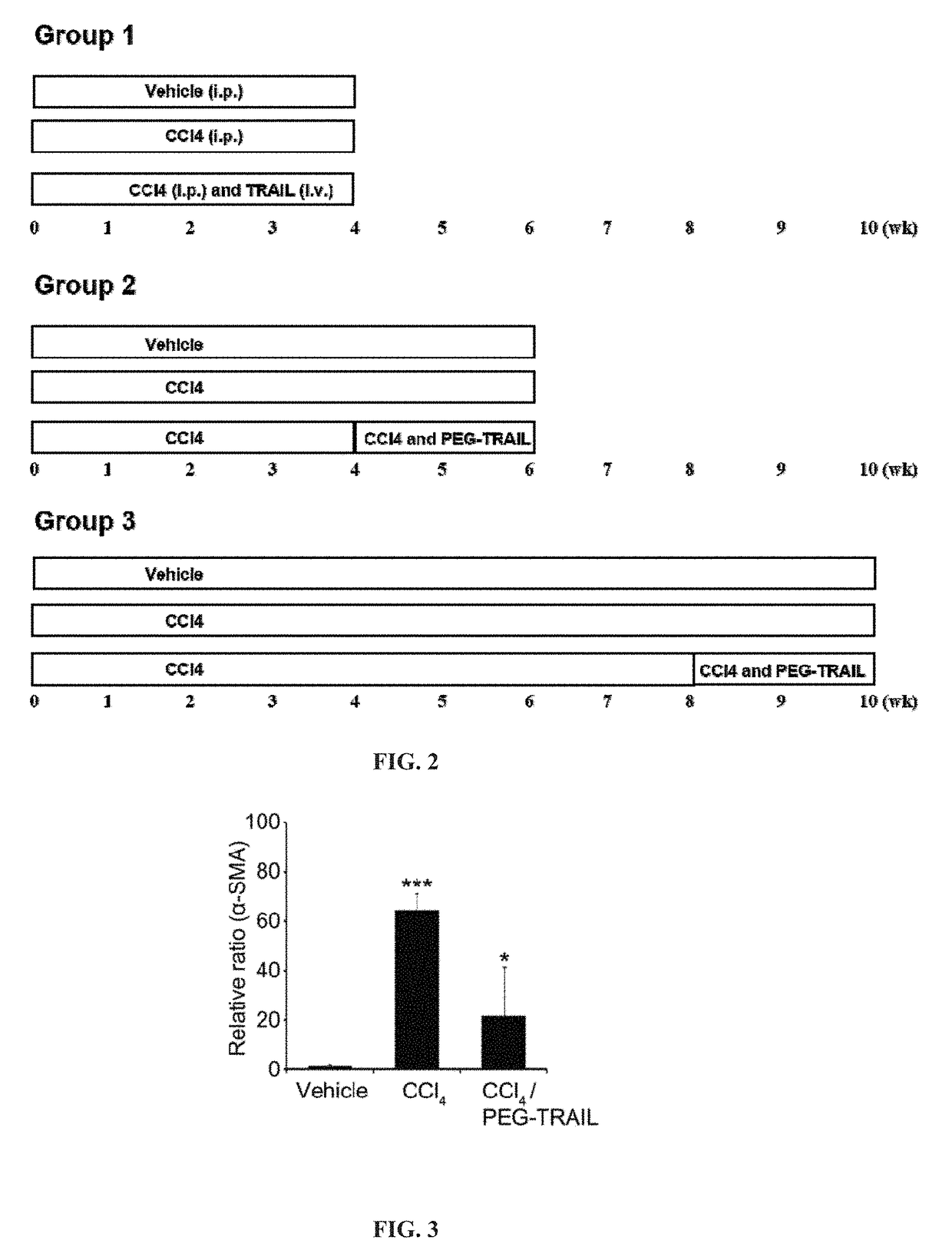
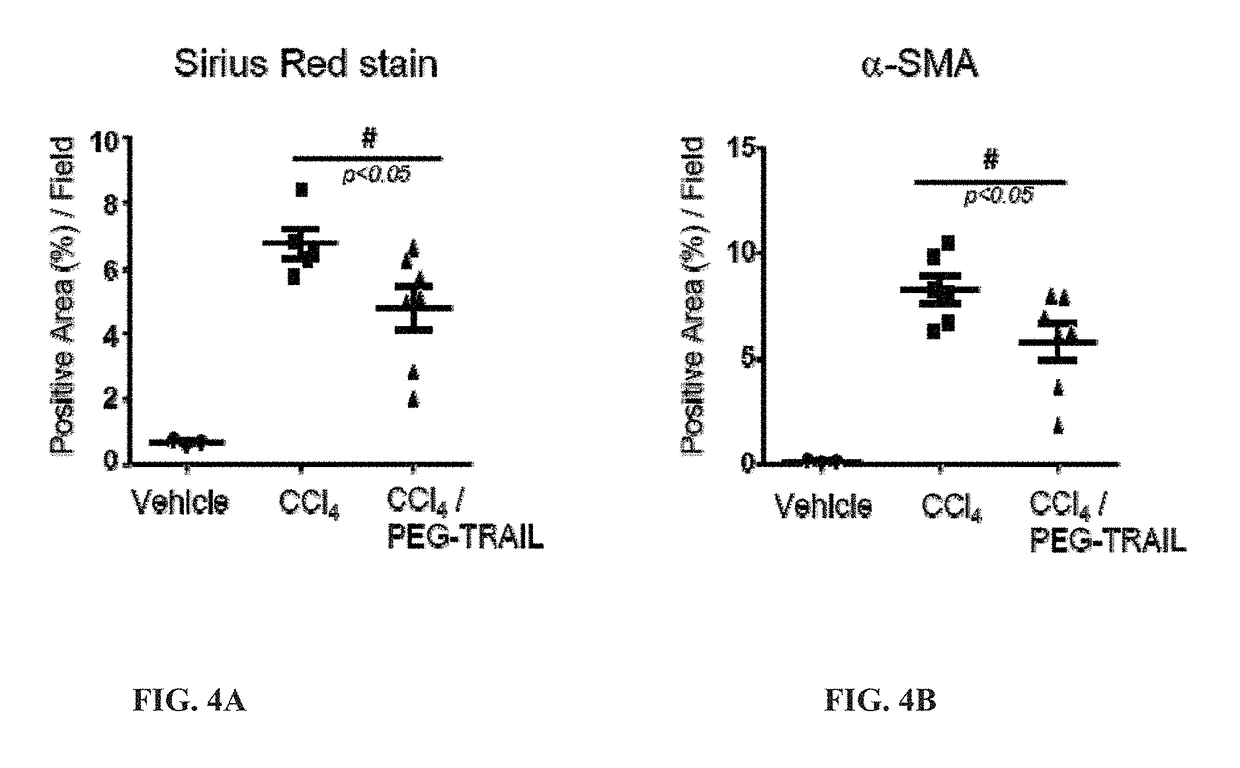
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:D&D PHARMATECH INC
TRAIL receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic diseases
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:B&L DELIPHARM CORP
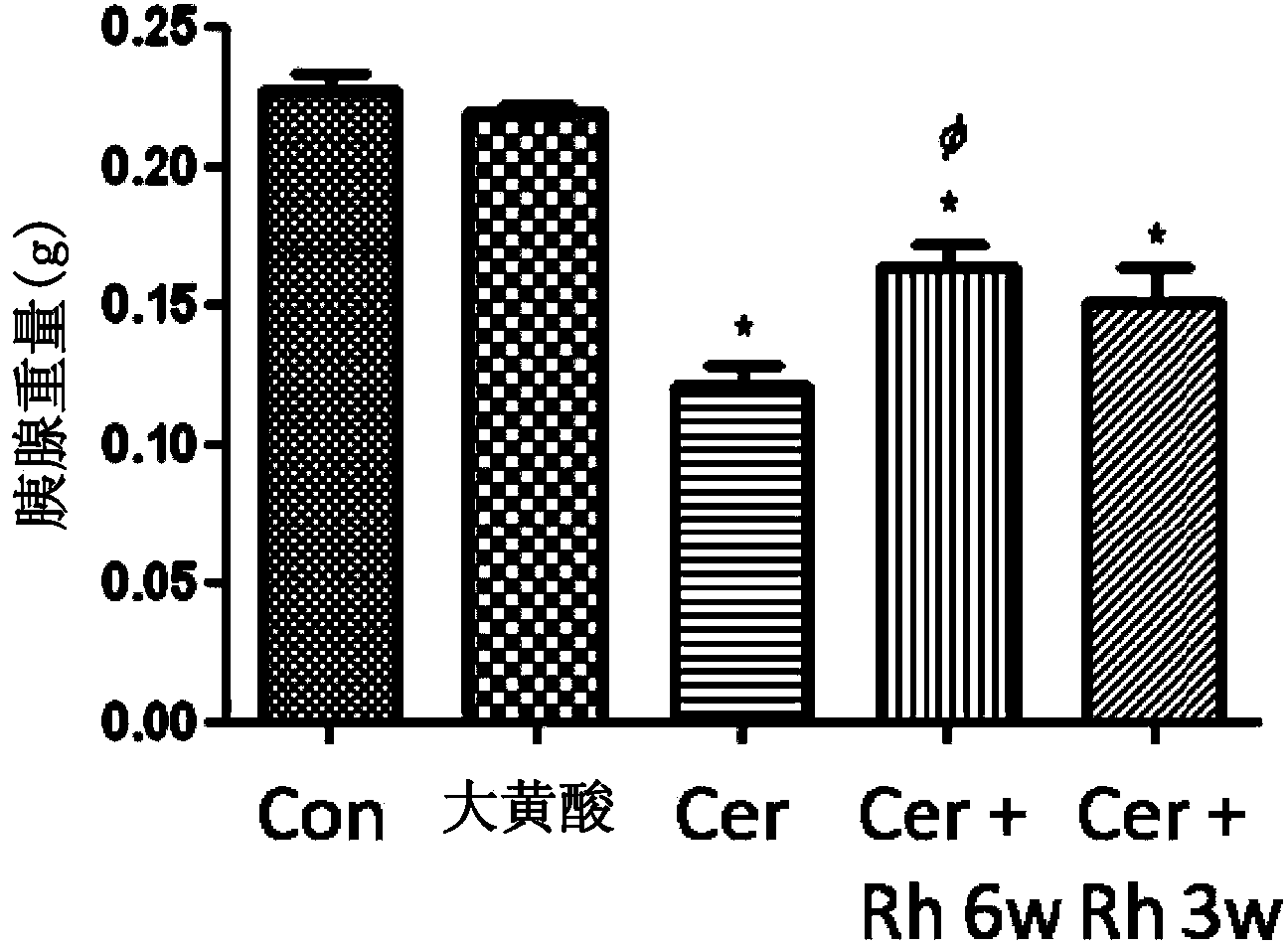
Method of using rhein for treating fibrotic conditions and tumors
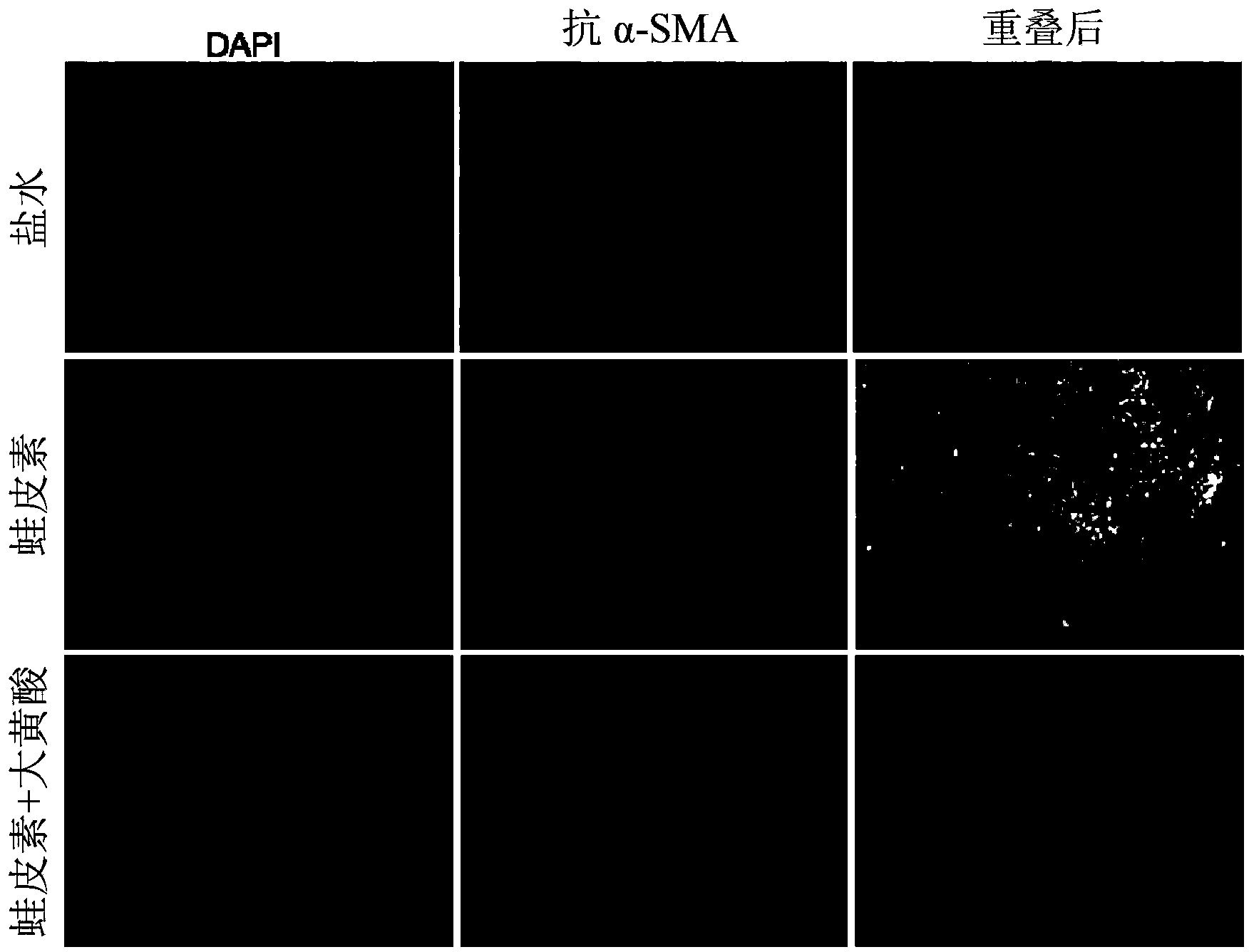
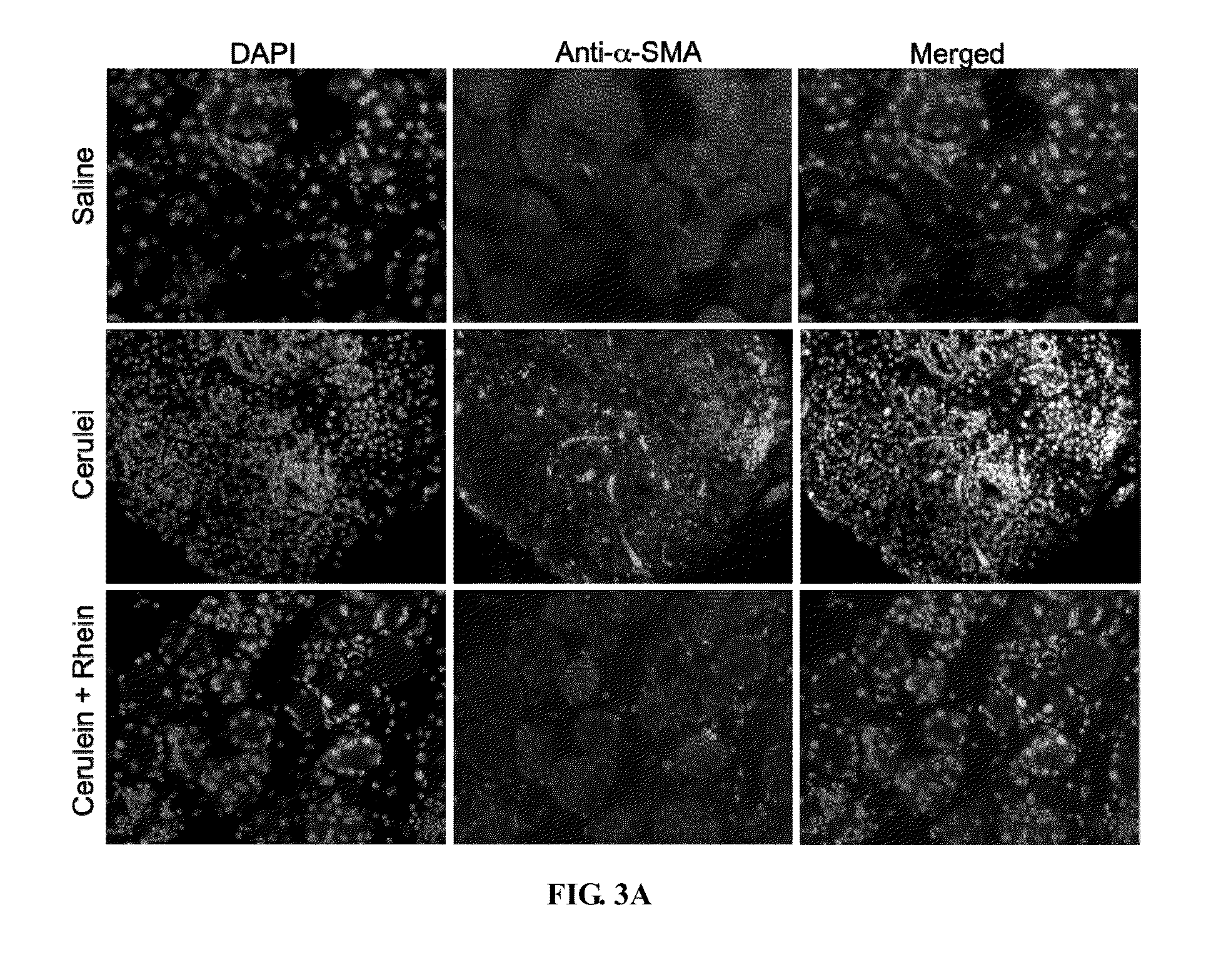
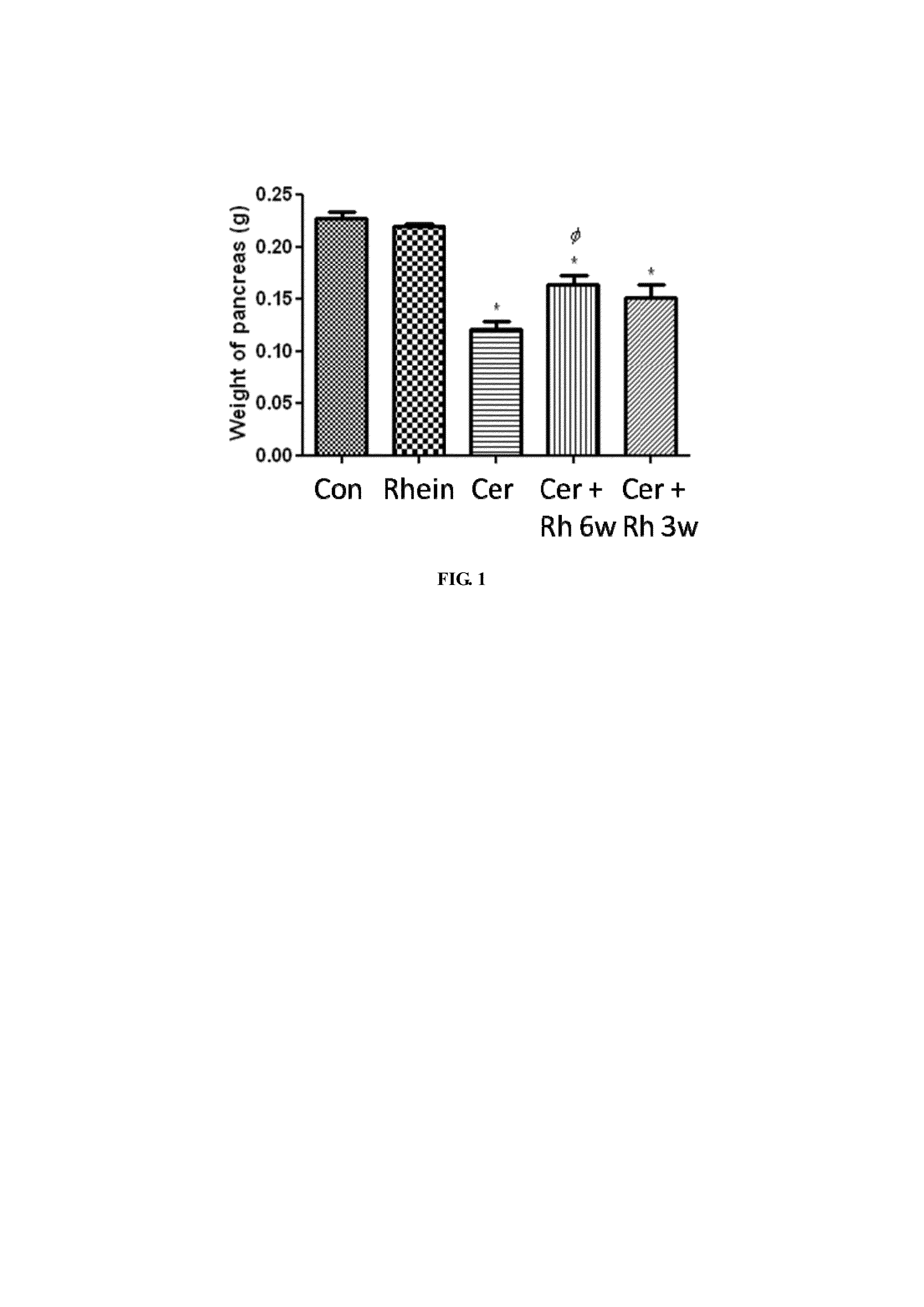
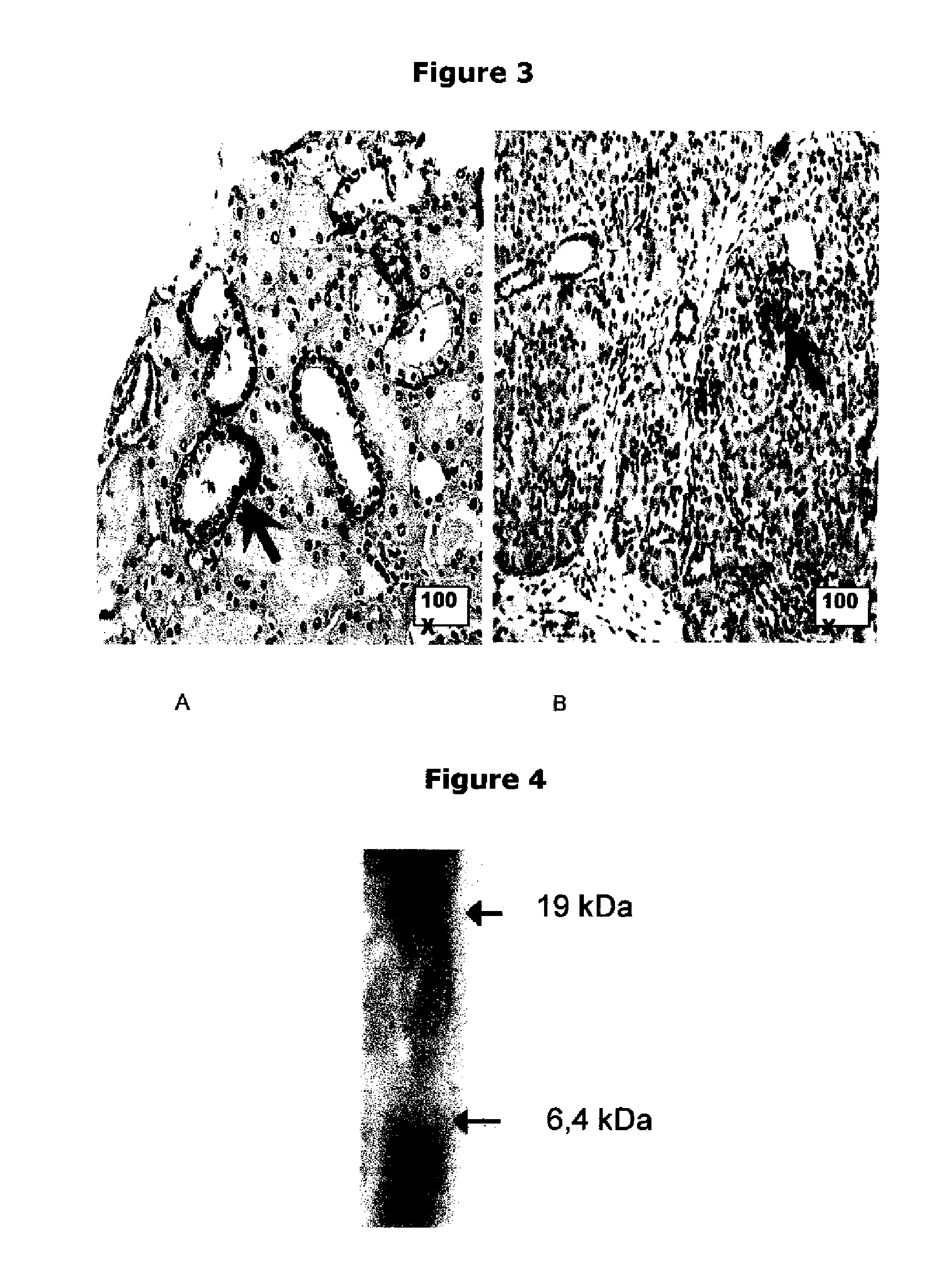
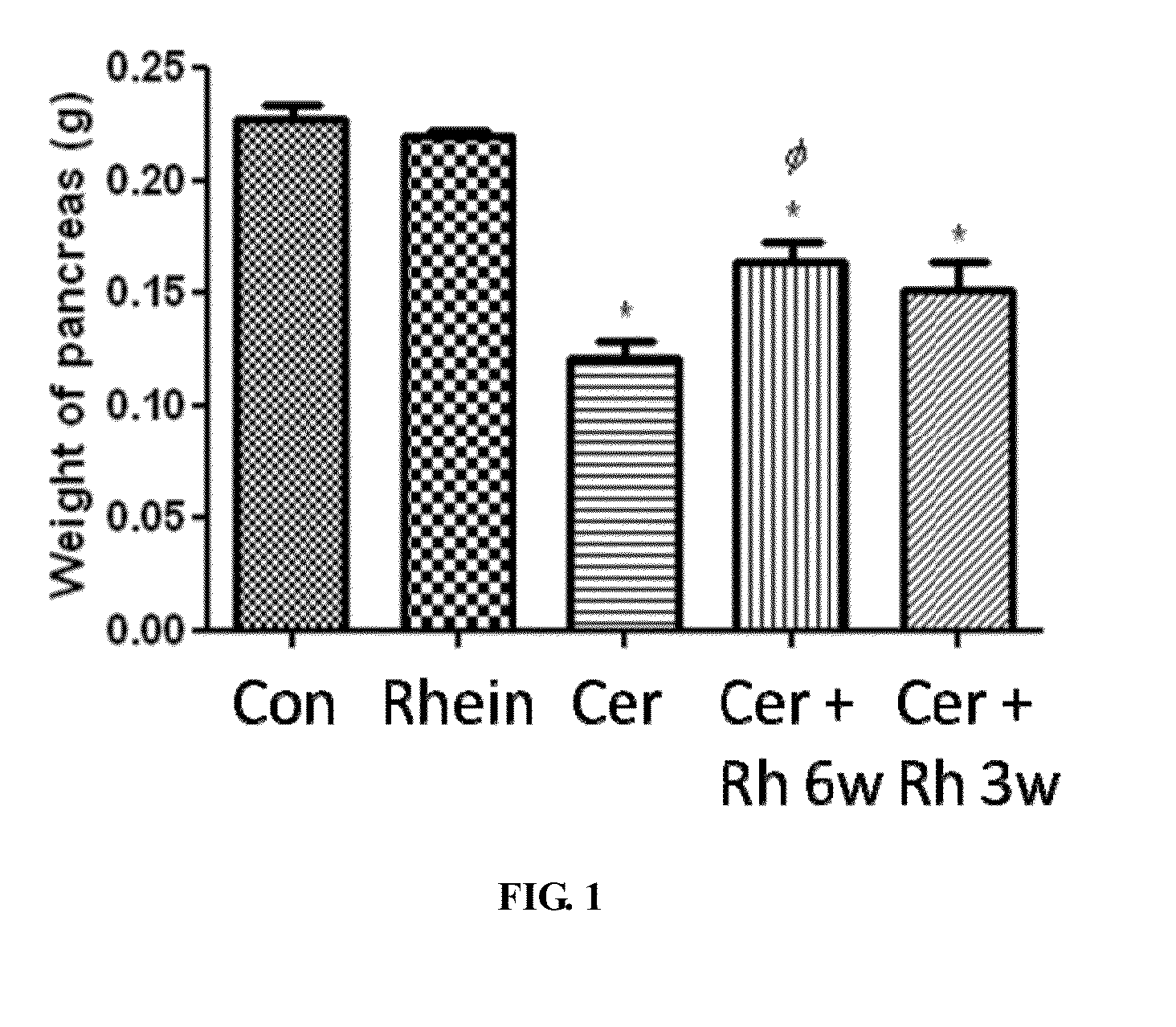
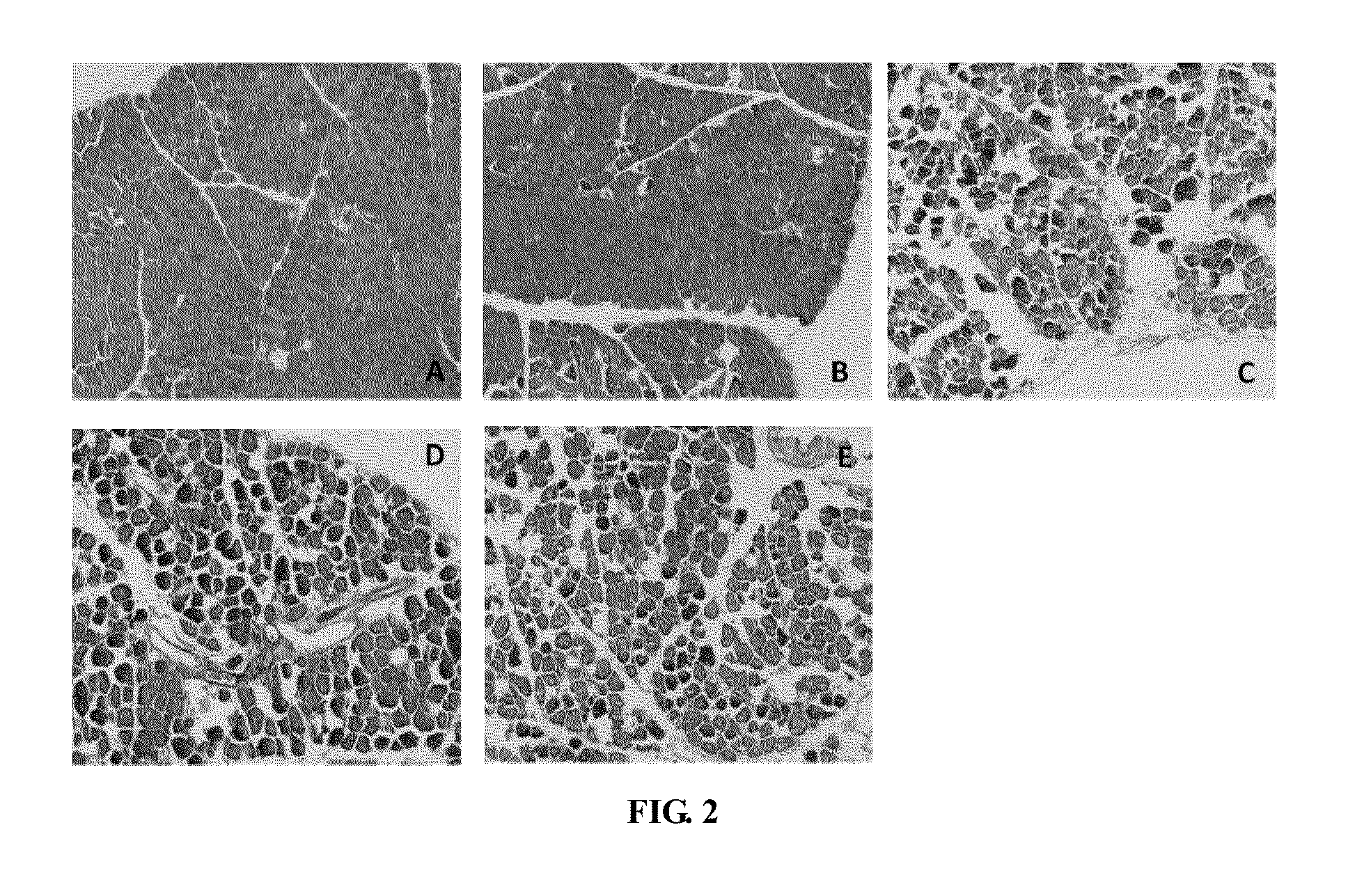
The present invention relates to a method of using an anthraquinone derivative namely 9,10-Dihyro-4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-2-anthracenecarboxylic acid, or known as Rhein, for treating chronic pancreatitis induced fibrosis of the pancreas. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of using Rhein, its derivatives and / or chemical variants as an anti-fibrotic agent. The present invention particularly relates to the suppression of pancreatic stellate cell activation for the management of chronic inflammatory, fibrotic and tumorigenic pathologies in the pancreas.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Methods for differentiating cells into hepatic stellate cells and hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, cells produced by the methods, and methods for using the cells
The invention is directed to methods for culturing cells so that the cells are induced to differentiate into cells that express a hepatic stellate phenotype and cells that express a hepatic sinusoidal endothelial phenotype. The invention is also directed to cells produced by the methods of the invention. The cells are useful, among other things, for treatment of liver deficiency, liver metabolism studies, and liver toxicity studies.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
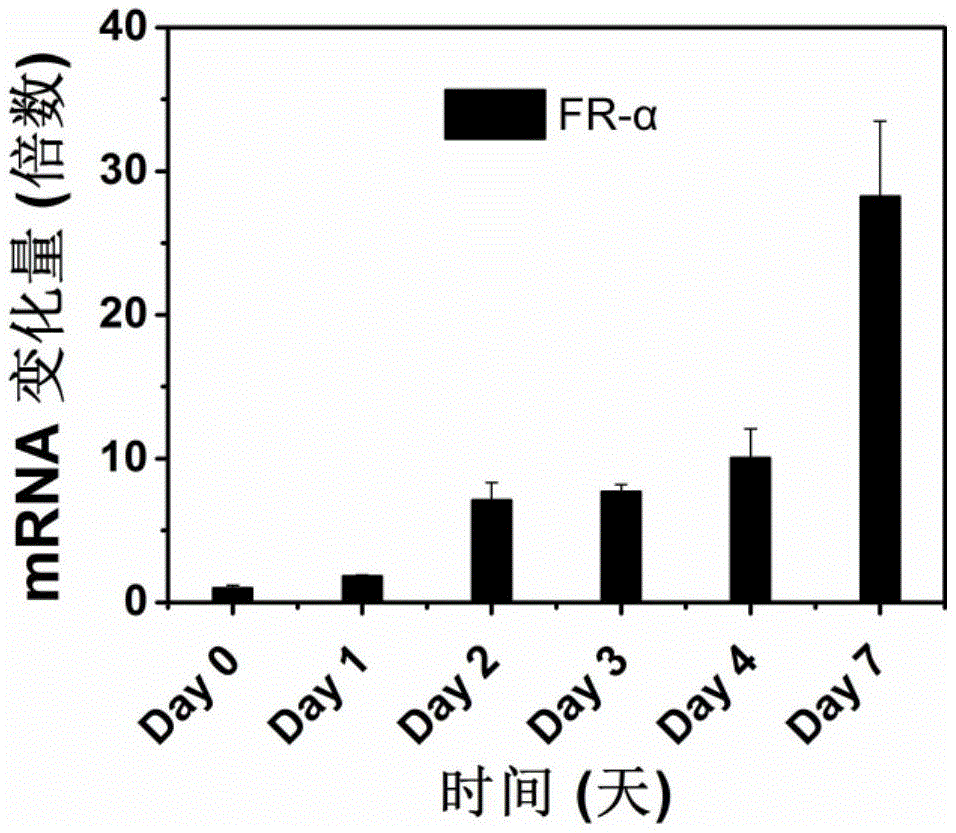
Polymer nano-carrier for folic acid specificity targeting of active hepatic stellate cell and medicinal application thereof
InactiveCN105560180AAchieve specific targetingIncrease profitDigestive systemPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFluorescencePolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a polymer nano-carrier for folic acid specificity targeting of an active hepatic stellate cell and medicinal application thereof. In the transformation process from a resting state to a muscle fibrosis sample active state, expression of an alpha type folate receptor in the hepatic stellate cell is remarkably enhanced. A folic acid-coupled polymer nano-micelle carrier is further prepared, and specificity targeting on the active primary rat hepatic stellate cell and cell strains of the polymer nano-micelle carrier is successfully achieved. According to a medicine nano-carrier system, polyethylene glycol is adopted as a material of a hydrophilic section, and resisting to protein adsorption and cell adhesion in blood circulation of the medicine nano-carrier system is ensured; polycaprolactone serves as a material of a hydrophobic section for nucleation, and loading of a plurality of hydrophobic anti-fibrosis medicines and fluorescent dye is facilitated. Folic acid coupled to a PEG shell guarantees that the carrier system conducts specificity recognition on folate receptors on the surface of the active hepatic stellate cell, finally, the utilization rate of the medicine is effectively increased, and the toxic and side effect of the medicine is lowered.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
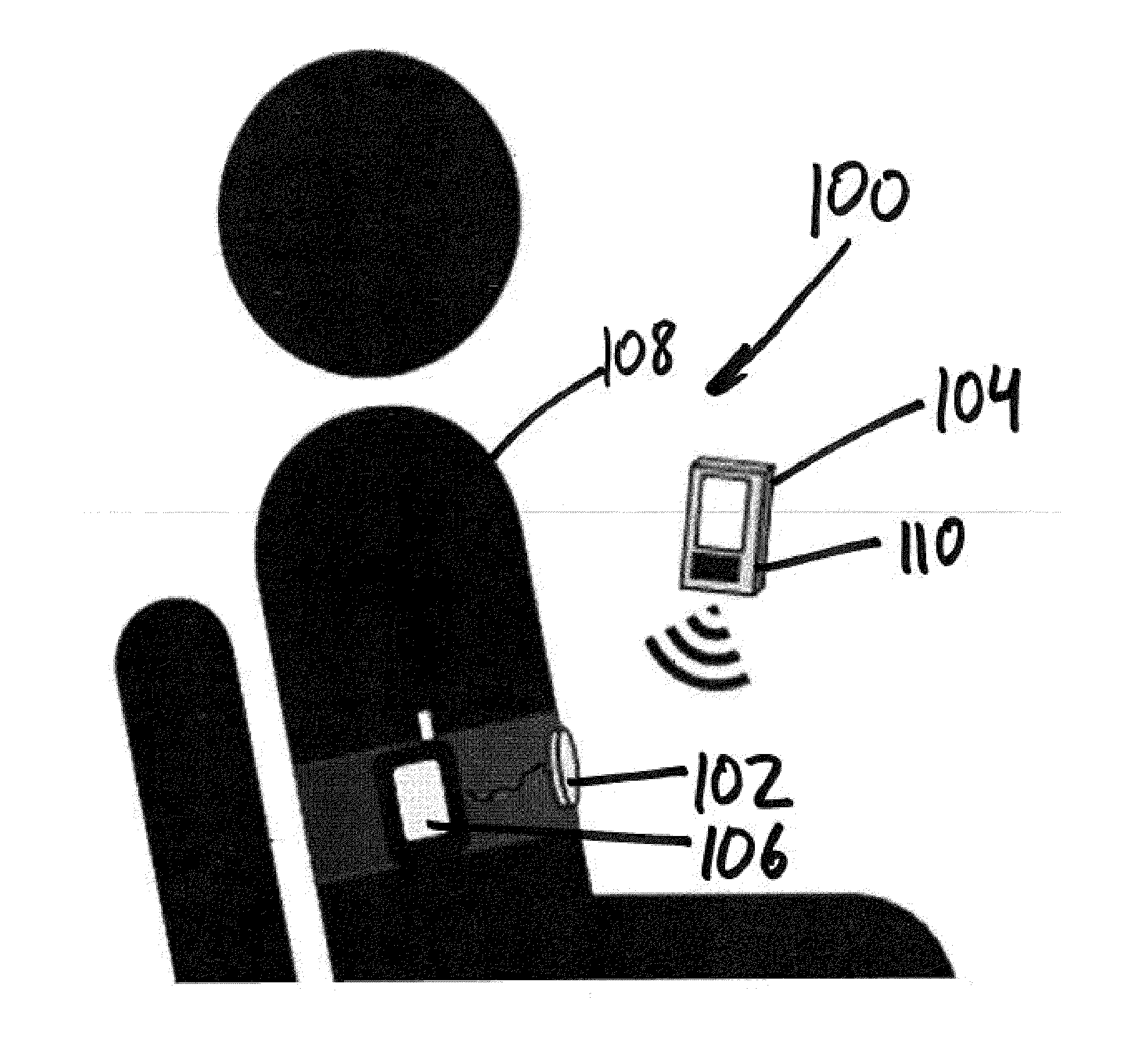
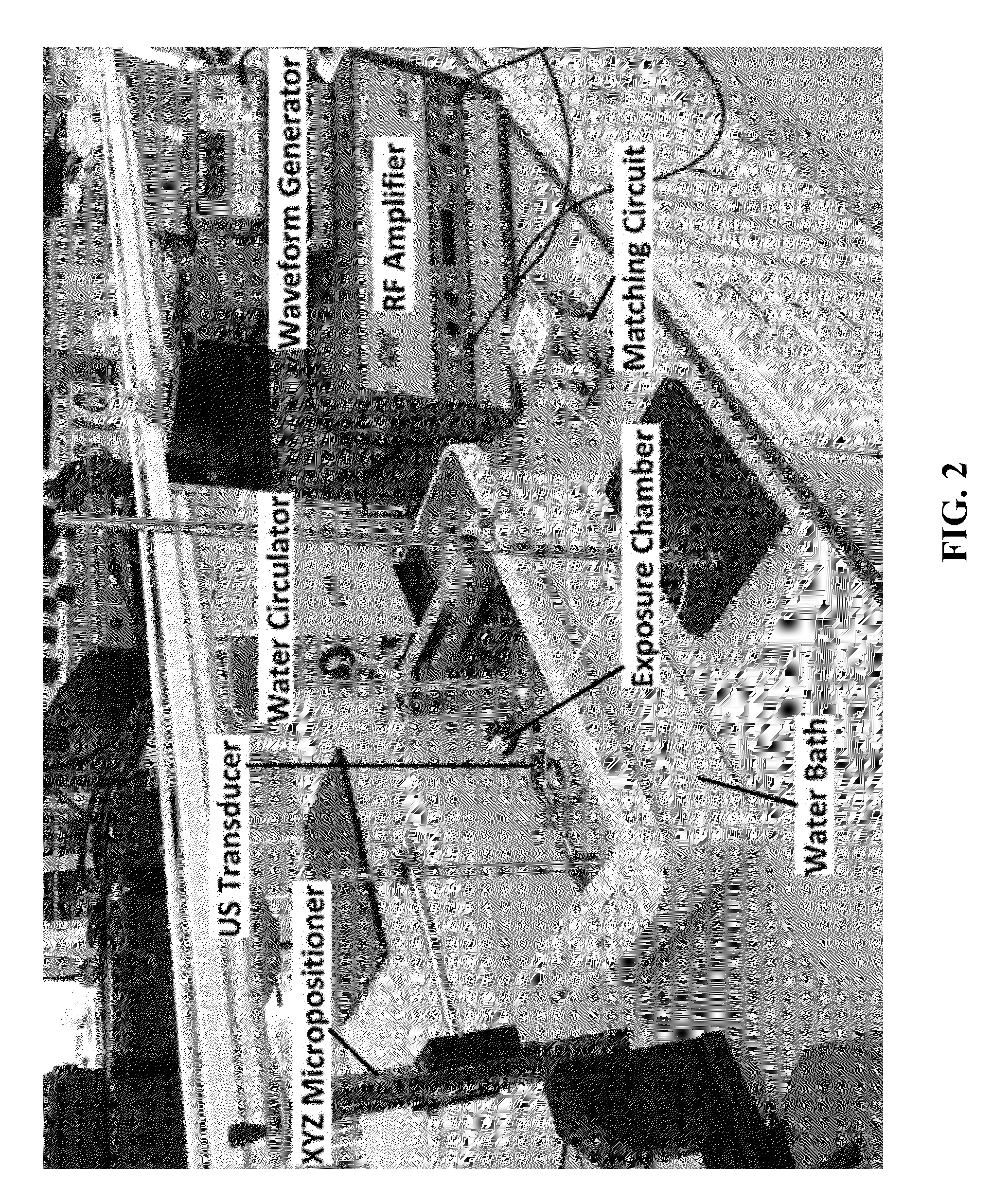
Ultrasound stimulation of pancreatic beta cells
A pancreatic beta cell stimulation system for stimulating release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells can include an ultrasonic transducer configured to be acoustically coupled to a body of a user; and an ultrasound controller configured to be in communication with the ultrasonic transducer so as to provide control signals to the ultrasonic transducer during operation. The ultrasound controller can be further configured to generate the control signals based on a planned amount of stimulation of pancreatic beta cells within the body of the user such that the control signals instruct the ultrasonic transducer to transmit ultrasound waves having selected intensity and frequency calculated to cause stimulation of the pancreatic beta cells.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
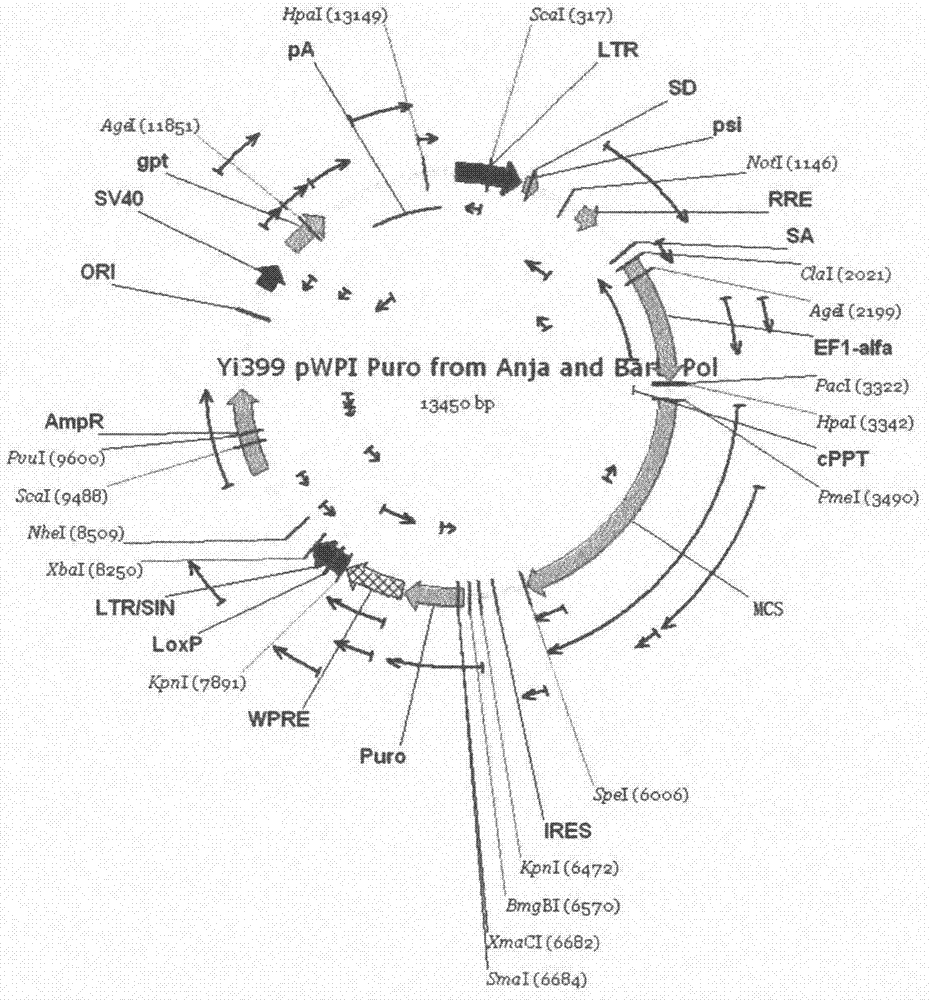
Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell line for stable expression of exogenous EX-4 gene
InactiveCN107502594APromote proliferationInhibit apoptosisPancreatic cellsCulture processEnzyme digestionT cell
The invention provides an MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) line for stable expression of EX-4. The MSCs line for stable expression of EX-4 is obtained by lentivirus infection. The lentivirus used by the invention is obtained by transfection of 293T cells with a PLVTH-pol-IRES-puro lentivirus overexpression system, and the lentivirus overexpression system comprises PLVTH-EX-4 expression plasmid, coating plasmid pMD2.G, and packaging plasmid p8.91. The PLVTH-EX-4 is obtained by double enzyme digestion of the lentivirus overexpression vector plasmid PLVTH-pol-IRES-puro and EX-4 target gene and then connection to T4 ligase. The cell line obtained by the invention on the one hand can enhance the anti anti-apoptosis ability, multiplication capacity and migration ability of MSCs itself, and on the other hand the EX-4 overexpressed MSCs group has better effects of inhibiting apoptosis and promoting proliferation on pancreatic beta cells than the MSCs group. Through the two aspects of effects, the cell line provided by the invention can recover the functions of pancreatic beta cells to a normal level, and improve the disadvantages of MSCs in treatment of diabetes.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Zebra fish model for screening medicine used for promoting function of pancreatic beta cell in vivo
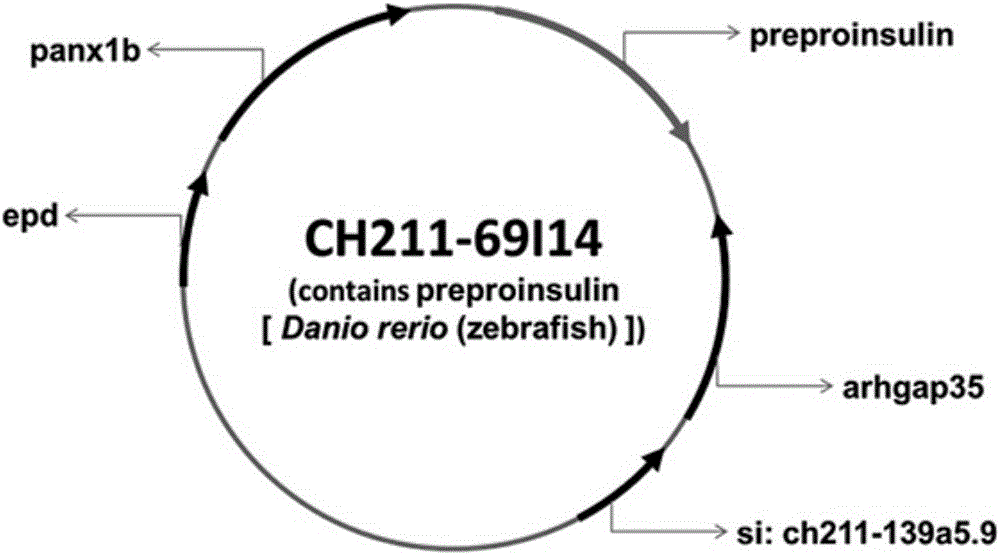
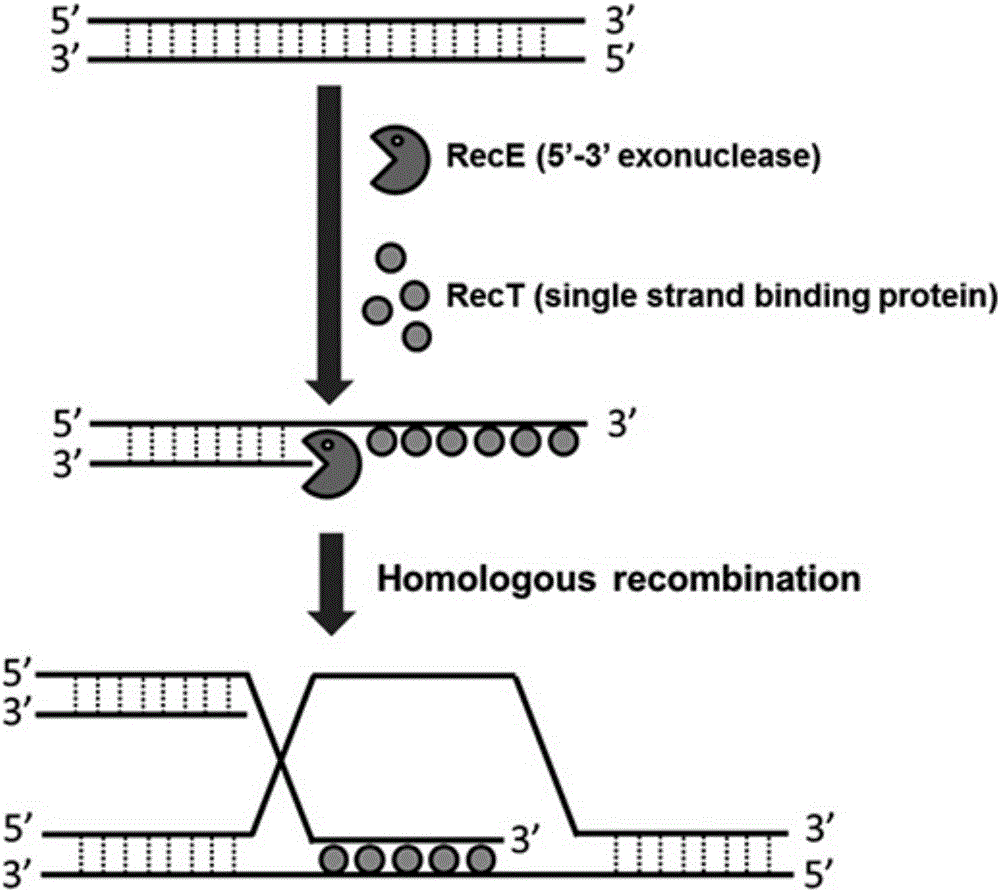
ActiveCN106755099AReport feature statusFacilitates high-throughput screeningVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsFluorescence
The invention discloses a zebra fish model for screening a medicine used for promoting the function of a pancreatic beta cell in vivo. The coded sequence of an ins gene on a gene BAC_CH211_69I14 of the zebra fish model is replaced by a fluorescent protein sequence, and a fluorescence signal is specifically expressed in the pancreatic beta cell to indicate the change of the calcium ion signal in the pancreatic beta cell in vivo. The invention creates the first animal model capable of indicating the function of the pancreatic beta cell in vivo. The change of the calcium signal in the pancreatic beta cell is observed in real time in vivo through a transgenic zebra fish system, and the state of the function of the pancreatic beta cell is intuitively and accurately reported. By using the transgenic zebra fish system, the functional characteristics of the pancreatic beta cell are conveniently automatically analyzed at high throughput on the in-vivo level, so that the zebra fish model has important practical significance and a broad application prospect for the high-throughput screening of the medicine used for promoting the function of the pancreatic beta cell.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for inducing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into pancreatic beta cells
InactiveCN105462913ASimple methodEasy to operateArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell specificMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses a method for obtaining pancreatic beta cells through induced differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells through a gene transfer method. Pancreatic cell specific genes containing PDX1, MAFA, NGN3, FOXA2, NEUROD1 and FGF21 are used, adenovirus expression vectors of transmembrane singles are connected, various recombinant protein and small molecules are combined, and the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are induced to be directionally differentiated into the pancreatic beta cells. The inducing method is easy and convenient to implement, simple in operation and good in differentiation effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH +1
Method Of Using Rhein For Treating Fibrotic Conditions And Tumors
The present invention relates to a method of using an anthraquinone derivative namely 9,10-Dihyro-4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-2-anthracenecarboxylic acid, or known as Rhein, for treating chronic pancreatitis induced fibrosis of the pancreas. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of using Rhein, its derivatives and / or chemical variants as an anti-fibrotic agent. The present invention particularly relates to the suppression of pancreatic stellate cell activation for the management of chronic inflammatory, fibrotic and tumorigenic pathologies in the pancreas.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Trail receptor agonists for treatment of fibrotic disease
ActiveUS9901620B2Reduce the amount requiredUnwanted scarringPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseTrail r1
Pro-apoptotic agents such as ligands and agonists of agonistic TRAIL receptors can induce or increase apoptosis of cells that cause fibrosis and underlying diseases such as liver, pancreatic, lung and skin diseases characterized by fibrosis, cirrhosis, or complications thereof. The compositions and methods can be used to selectively remove activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the originators of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, and activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), the originators of pancreas fibrosis and pancreatitis, and can be effective to reduce or prevent further chronic fibrosis by simultaneously reducing multiple fibrosis-associated molecules secreted or induced by such activated stellate cells. The compositions are typically effective to target agonistic TRAIL receptors such as TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and TRAIL-R2 / DR5 that are selectively expressed in activated HSCs and PSCs in physiological conditions. Ligands and agonists that can be used to target agonistic TRAIL receptors include, but are not limited to, TRAIL-R1 / DR4 and / or TRAIL-R2 / DR5 agonists.
Owner:D&D PHARMATECH INC
Culture medium for separating and inducing human adipose stem cells into pancreatic beta cells and use method of culture medium
InactiveCN104862268AGenetic change noNo riskVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsInsulin Secreting CellGene Modification
The invention provides a culture medium for separating and inducing human adipose stem cells into pancreatic beta cells and a use method of the culture medium. The optimal culture medium is designed; gene transfection is not required, so that the risk of gene modification and cancers is avoided, few induction steps are used, the use is simple, and the induction time is short and is shortened by 30% in comparison with the prior art; the culture medium is safe, nontoxic and high in success rate of induction. Moreover, after autogenous adipose mesenchymal stem cells are induced and differentiated into insulin-secreting cells, rejection and ethical problems are avoided after autotransplantation, and the safety is high, so that the clinical application prospect is wide. The culture medium is simple, feasible, low in cost and good in use effect.
Owner:GUIZHOU BEIKE FACTORR BIOTECH CO LTD
Application of mTORC1 in medicines for regulating and controlling functions and conversion of pancreatic beta cells
InactiveCN107684622AFunction increaseMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaPancreatic islets
The invention discloses application of mTORC1 in medicines for regulating and controlling the functions and conversion of pancreatic beta cells; and the functions of pancreatic beta cells are improvedby regulating the activity or regulation bypass of mTORC1 passages and / or the pancreatic non-beta cells are converted into new pancreatic beta cells. The conversion is gene recording without a differentiation process. The invention discloses that the mTORC1 passages are of an important role in identity maintenance of beta cells. The specific Raptor knockout of the beta cells can cause functionaldisorders and cell immaturity of the beta cells as well as hyperglycemia since metabolic requirements cannot be met, and simultaneously causes expression increase of MafB, so that transdifferentiationis caused. The activity of the mTORC1 passages is adjusted, or regulation bypasses of the mTORC1 passages can serve as a new target spot for beta cell therapy, and the functions of the beta cells areimproved, or new beta cells are generated by non-beta cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR ENDOCRINE & METABOLIC DISEASES +1
Method for establishing Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation model and method for separating hepatic stellate cells
InactiveCN105941329AIncrease productionHigh activityCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsIntraperitoneal routeClawed Jird
The invention discloses a method for establishing a Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation model and a method for separating hepatic stellate cells. The method for establishing the Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation model comprises the steps that a donor is narcotized, and a grafted liver is cut and taken out of the donor; a receptor is narcotized, the liver is cut out, the grafted liver is implanted into the receptor with the liver cut out; the survival rate of the Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation model is calculated. Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation is executed, changes of the Mongolian gerbil orthotopic liver transplantation model are observed, and the survival rate is calculated. The method for separating the hepatic stellate cells of Mongolian gerbil comprises the steps that chloral hydrate is used for intraperitoneal injection to narcotize the male Mongolian gerbil, or the male Mongolian gerbil which dead just now is selected, and the grafted liver is cut and taken out of the donor; the hepatic stellate cells are separated out of the grafted liver and obtained. According to the method for separating the hepatic stellate cells, the yield and survival rate of the hepatic stellate cells can be increased, and the purity of HSCs can be guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
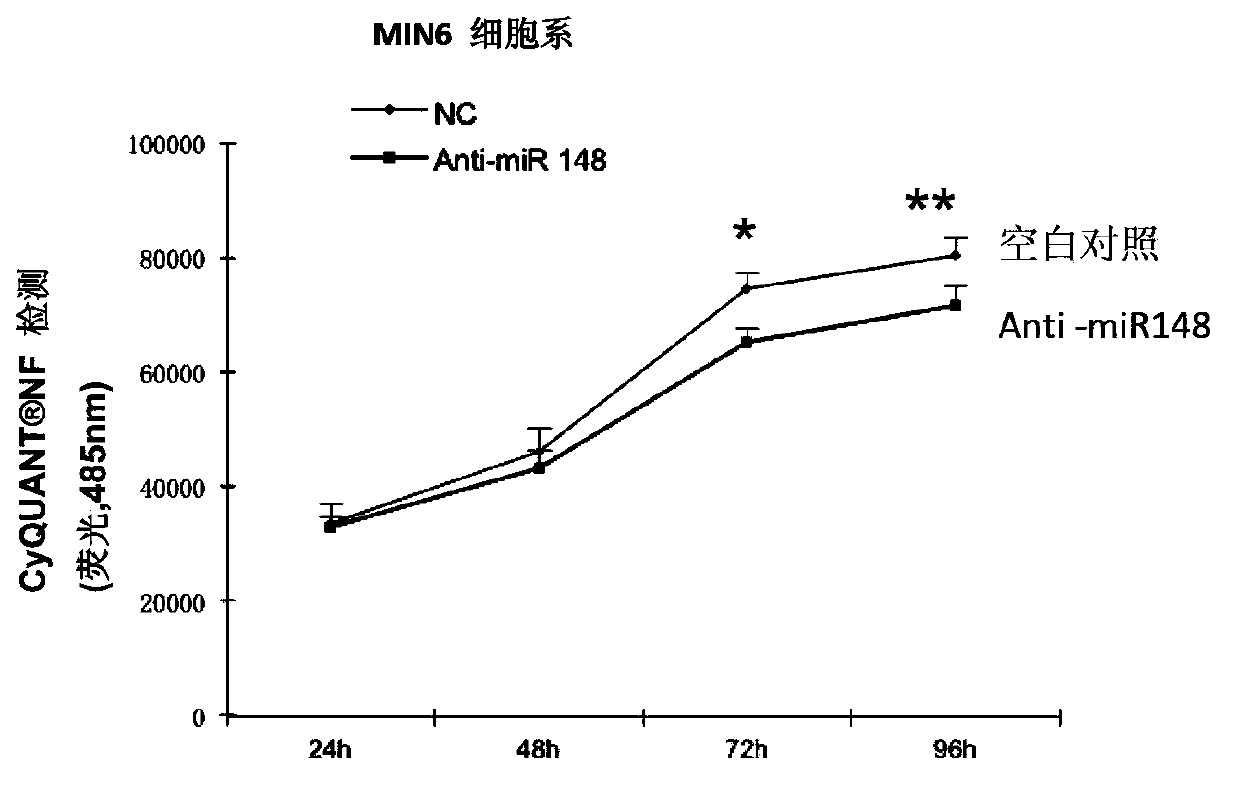
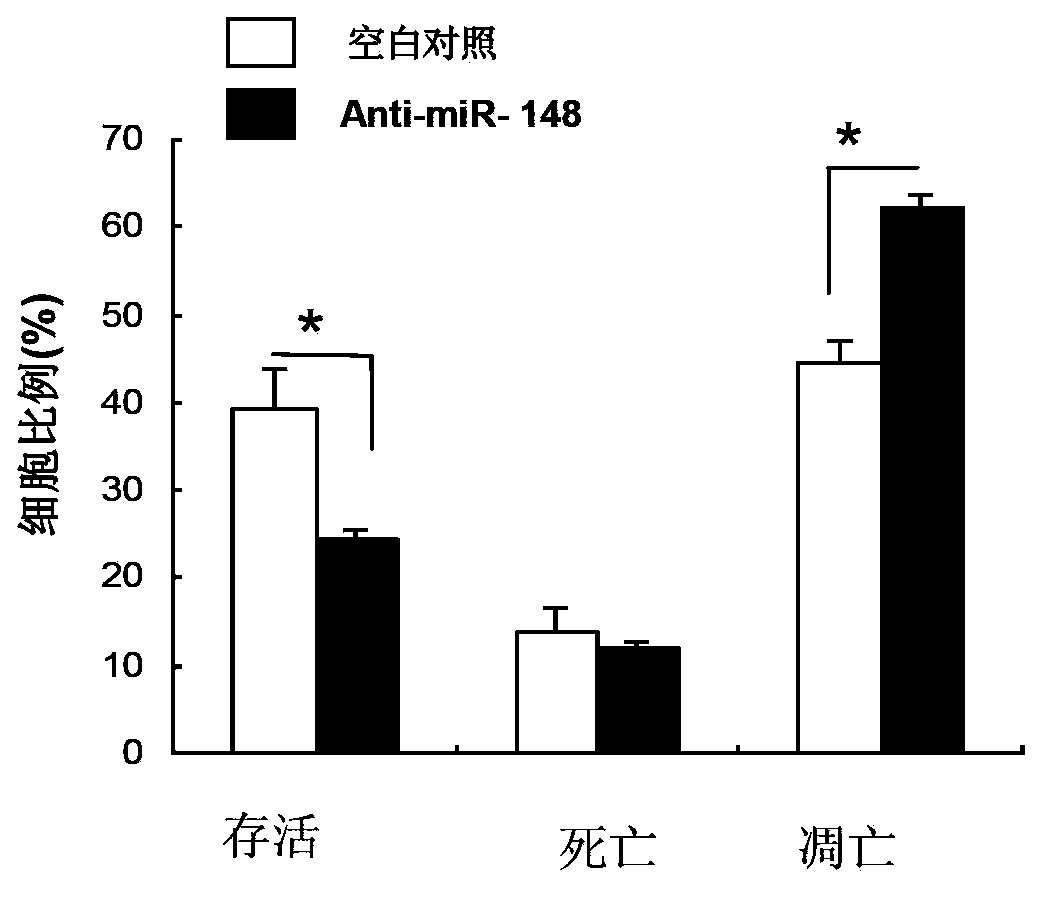
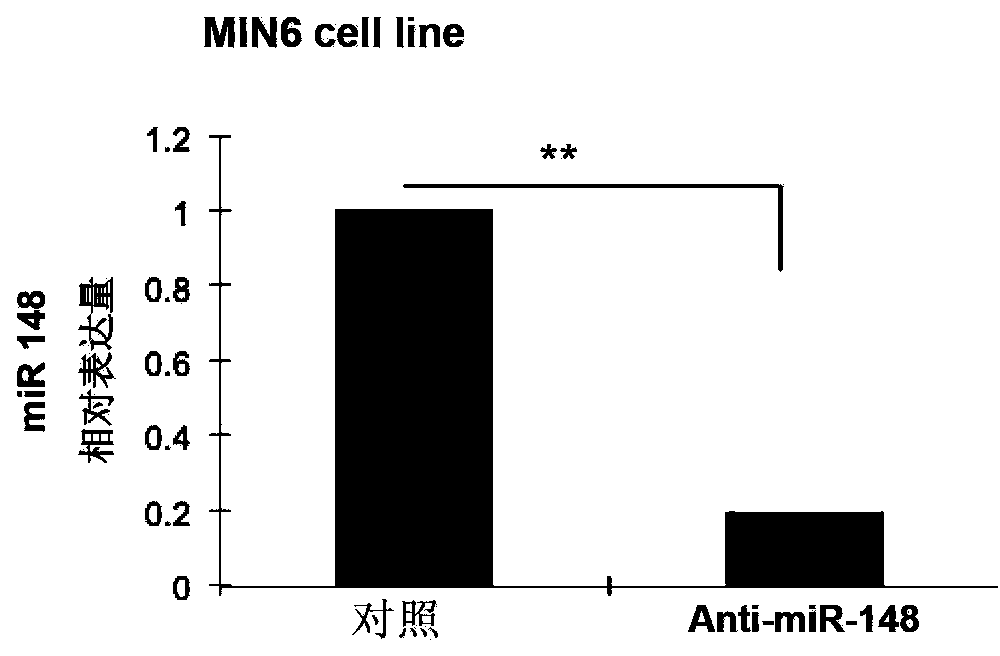
Application of miR-148 to proliferation of pancreatic beta cells
ActiveCN103417987APromote proliferationPro-apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderApoptosisDiabetes treatment
The invention relates to the field of biology and medical drugs, and discloses the function of miR-148 on proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells, which provides a new target spot for diabetes treatment as well as preparation or screening of drugs for curing 2-type diabetes. According to the invention, miR-148 can be applied to the preparation or screening of drugs for controlling pancreatic beta cells, and preparation or screening of drugs for controlling apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells, or preparation or screening of drugs for curing 2-type diabetes.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
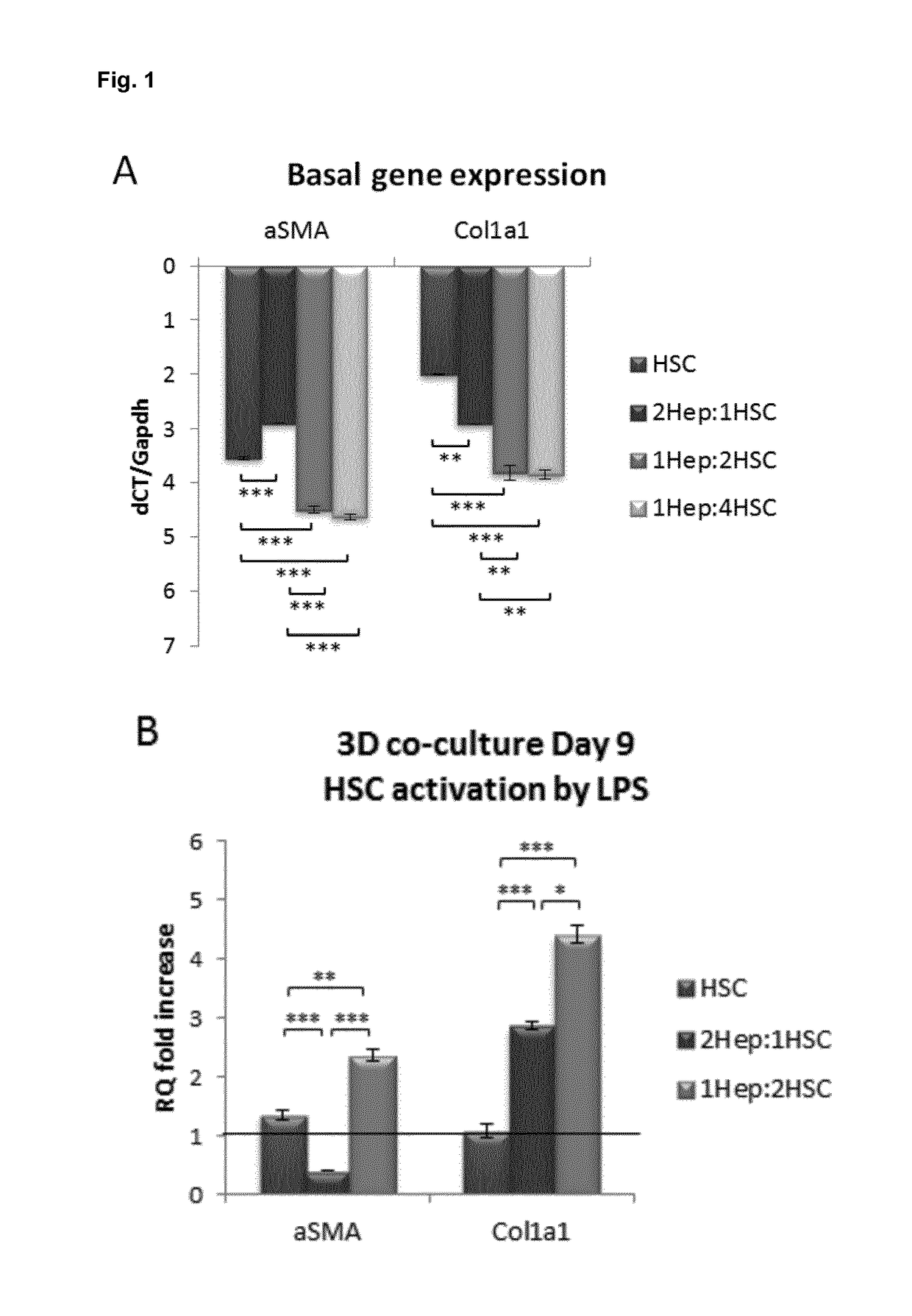
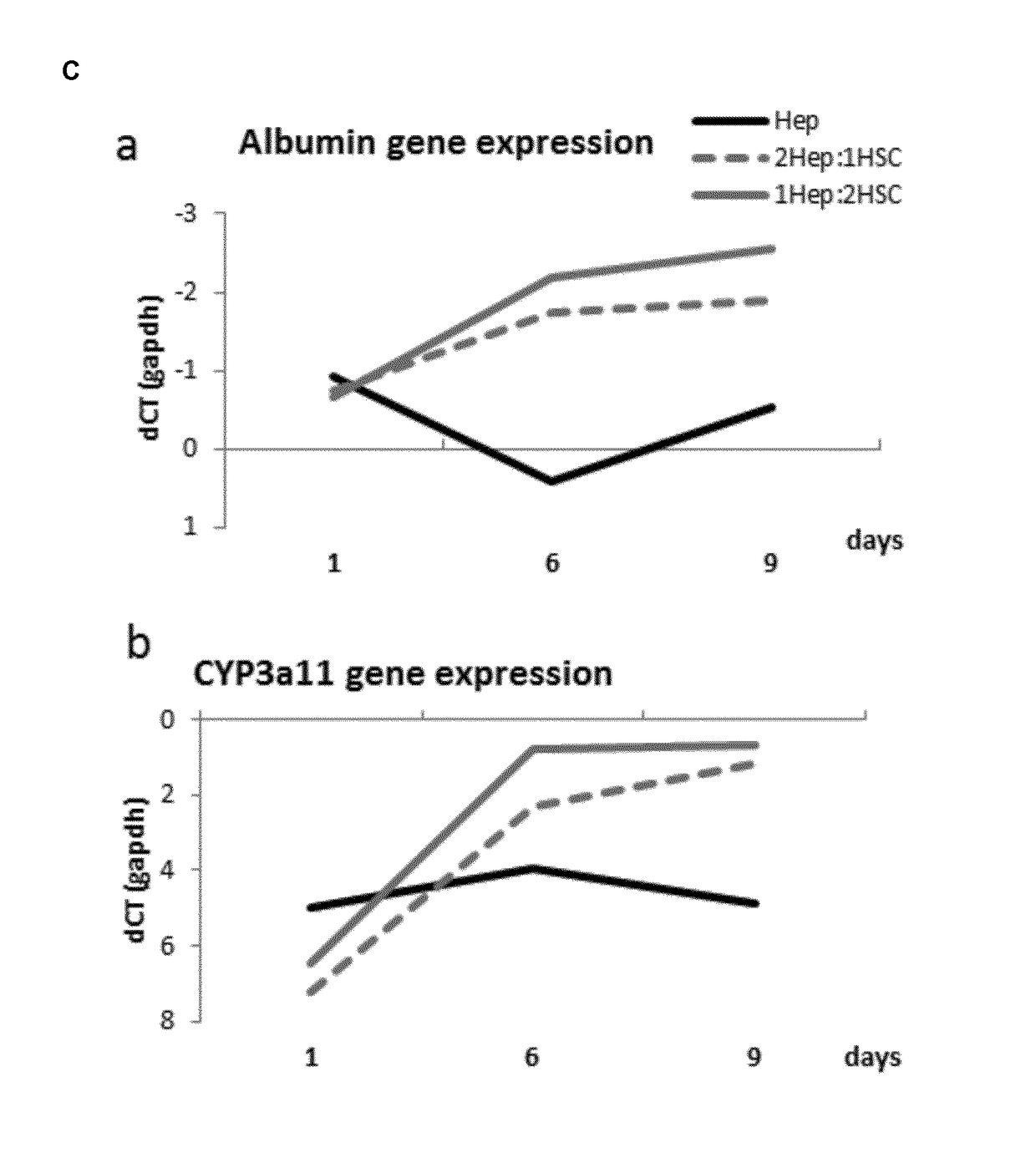
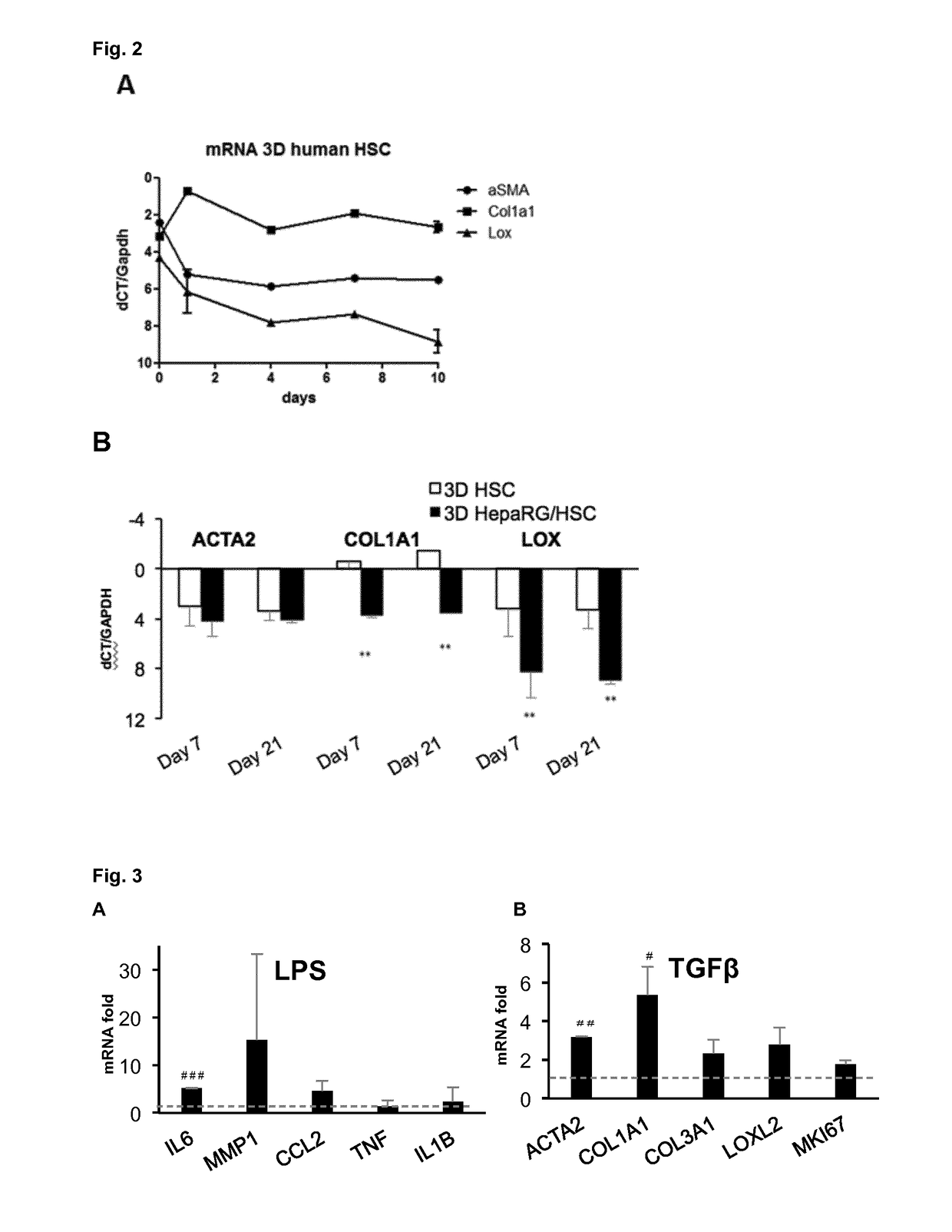
Human hepatic 3D co-culture model and uses thereof
The invention in general relates to human hepatic 3D co-culture models, more in particular 3D spheroid co-cultures of human hepatocyte-like cells and hepatic stellate cells. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for obtaining such co-cultures, as well as the use of said co-cultures in the identification of pro-fibrotic and / or anti-fibrotic compounds.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Hepatic stellate cell targeted hyaluronic acid nano-micelle, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107854431AImprove targetingStrong specificityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseHepatic fibrosis
The invention provides a hepatic stellate cell targeted hyaluronic acid nano-micelle, a preparation method and application thereof. The nano-micelle can encapsulate antifibrosis drugs and treat hepatic stellate cell lesion caused liver diseases, like hepatic fibrosis, liver cirrhosis and the like, has the advantages of small particle size (less than 100nm), good specificity, high hepatic stellatecell targeting efficiency, obvious anti-hepatic fibrosis function in vivo and in vivo and the like, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
15-methylene-14-deoxy-11,12-dehydro-andrographolide derivative and drug application thereof
ActiveCN109824654AClear activityAnti-hepatic enhancementOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryRenal cortexDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and relates to a 15-methylene-14-deoxy-11,12-dehydro-andrographolide derivative. Experiments prove that the compounds obviously inhibit the migration and activation of hepatic stellate cells, obviously inhibit the mesenchymal transition of TGF-beta 1-induced human alveolar type II epithelial cells A549, obviously inhibit the mesenchymal transition of human renal cortex proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells HK-2, and obviously inhibit the migration of angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced primary human cardiac fibroblasts HCFB. The compound is taken as an active ingredient for preparing anti-fibrosis drugs, has high efficiency and low toxicity, provides a new drug route for the treatment and prevention of fibrosis-related diseases, and thus the selectable range of clinical drugs is expanded, so that the derivative has a good application and development prospect.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Plasma membrane biomarkers preferentially expressed in pancreatic beta cells useful in imaging or targeting beta cells
ActiveUS8425878B2Evaluate effectivenessEarly detectionAnimal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiseaseInflammation Process
The present invention is directed to the identification of a biomarker specifically located in the plasma membrane of pancreatic beta cells. It was selected by a Systems Biology approach on Massively Parallel Signal Sequencing datasets obtained in human islets and Affymetrix microarray datasets on human islets, purified rat primary beta and non beta cells and insulinoma cells. Based on a set of specific features the biomarker is a unique candidate for imaging and targeting strategies to study the pancreatic beta cell mass in health and disease (T1 D, T2D, pancreatic cancers, obesity, islet transplantation, beta cell regeneration). The five specific features of the selected biomarkers are: 1) Preferentially expressed in pancreatic islets as compared to surrounding tissues; 2) Higher expression in pancreatic beta cells than in pancreatic alpha cells or than in other islet non-beta cells; 3) Expression levels in pancreatic beta cells are higher or comparable to glucokinase which is an enzyme specifically expressed in the pancreatic beta cell; 4) Located in the membrane and as such targetable with antibodies, peptides or small molecules which allows imaging, targeting and immunohistochemistry; and 5) Expression is not induced during the process of inflammation of the beta cell mass and the protein is not enriched in T-cells and dendritic cells or in other cells participating in the inflammation process.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +2
Method of using rhein for treating fibrotic conditions and tumors
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
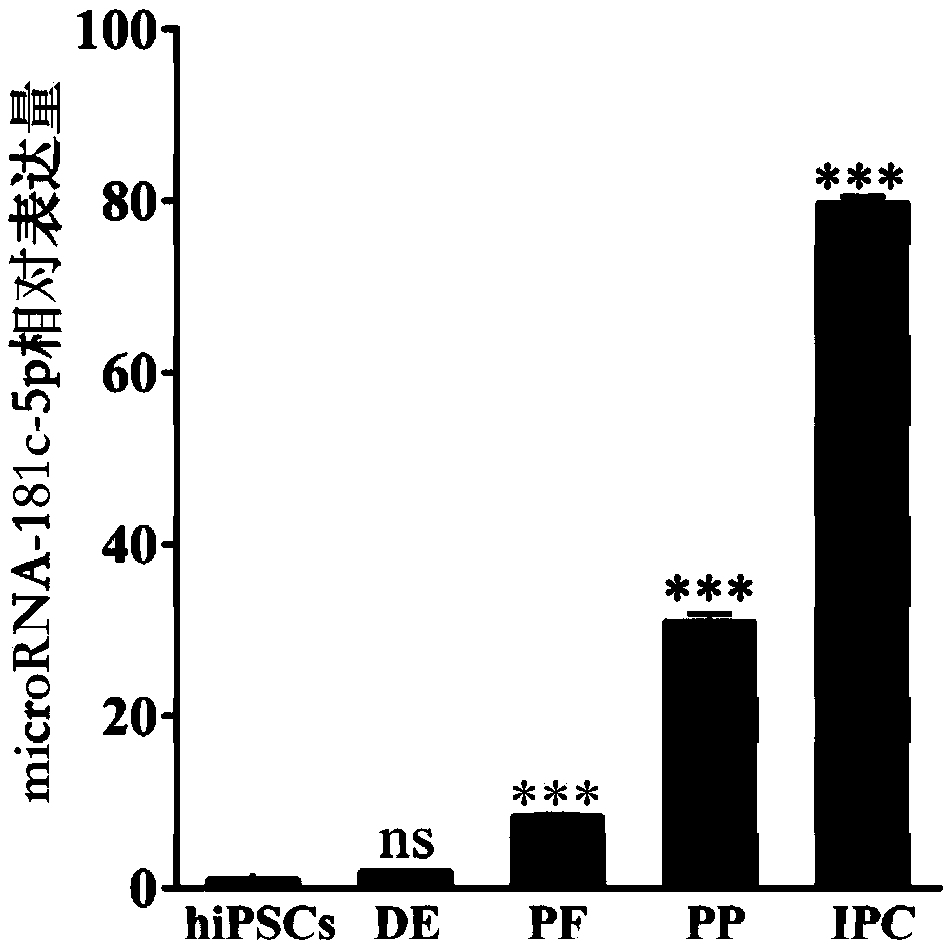
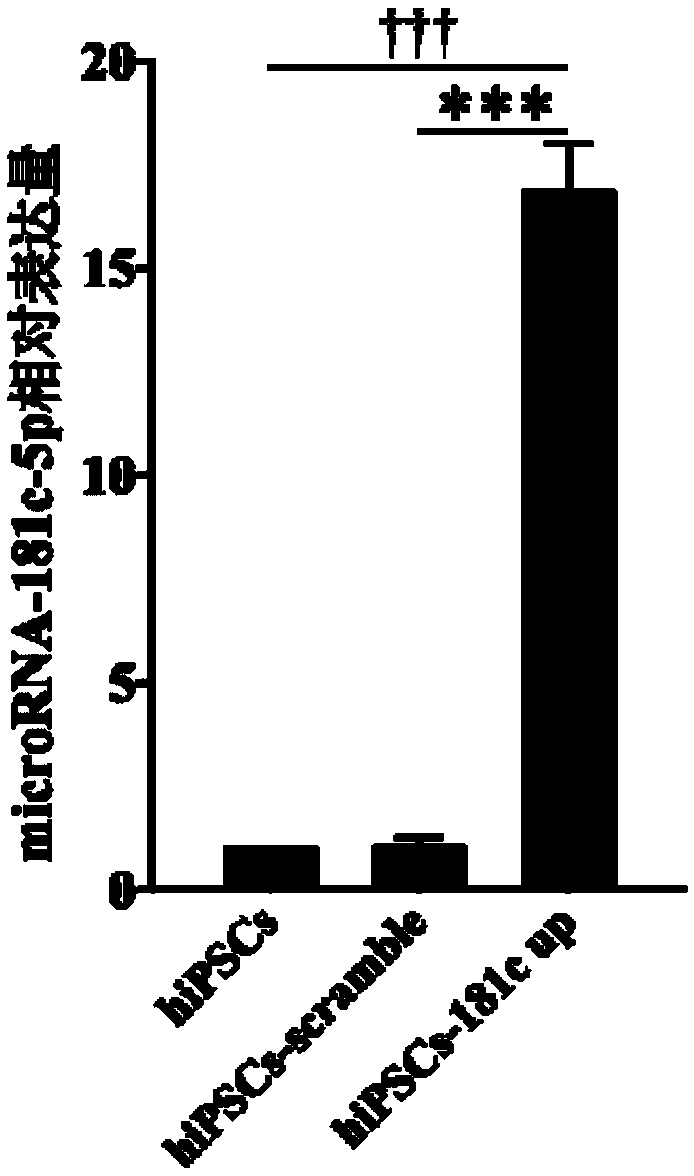
Method for promoting human iPS to be directionally differentiated into pancreatic Beta cells through microRNA-181c-5p
ActiveCN109486770AHigh differentiation efficiencyPromotePancreatic cellsCulture processMicroRNAPancreatic islets
The invention discloses a method for promoting human iPS to be directionally differentiated into pancreatic Beta cells through microRNA-181c-5p, and provides an application of the microRNA-181c-5p, oran encoding gene thereof, or a recombinant vector for expressing the encoding gene, a recombinant virus or a transgenic cell for promoting a stem cell to be directionally differentiated into the pancreatic Beta cells, and further provides an application of the microRNA-181c-5p, or the encoding gene thereof, or the recombinant vector for expressing the encoding gene, the recombinant virus or the transgenic cell for preparing a product of promoting the stem cell to be directionally differentiated into the pancreatic Beta cells. The method is capable of, through using a mode of the overexpression microRNA-181c-5p, greatly improving efficiency of in-vitro directionally inducing human iPS differentiation. Differentiation efficiency of the pancreatic Beta cells in the method reaches 35.8%.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
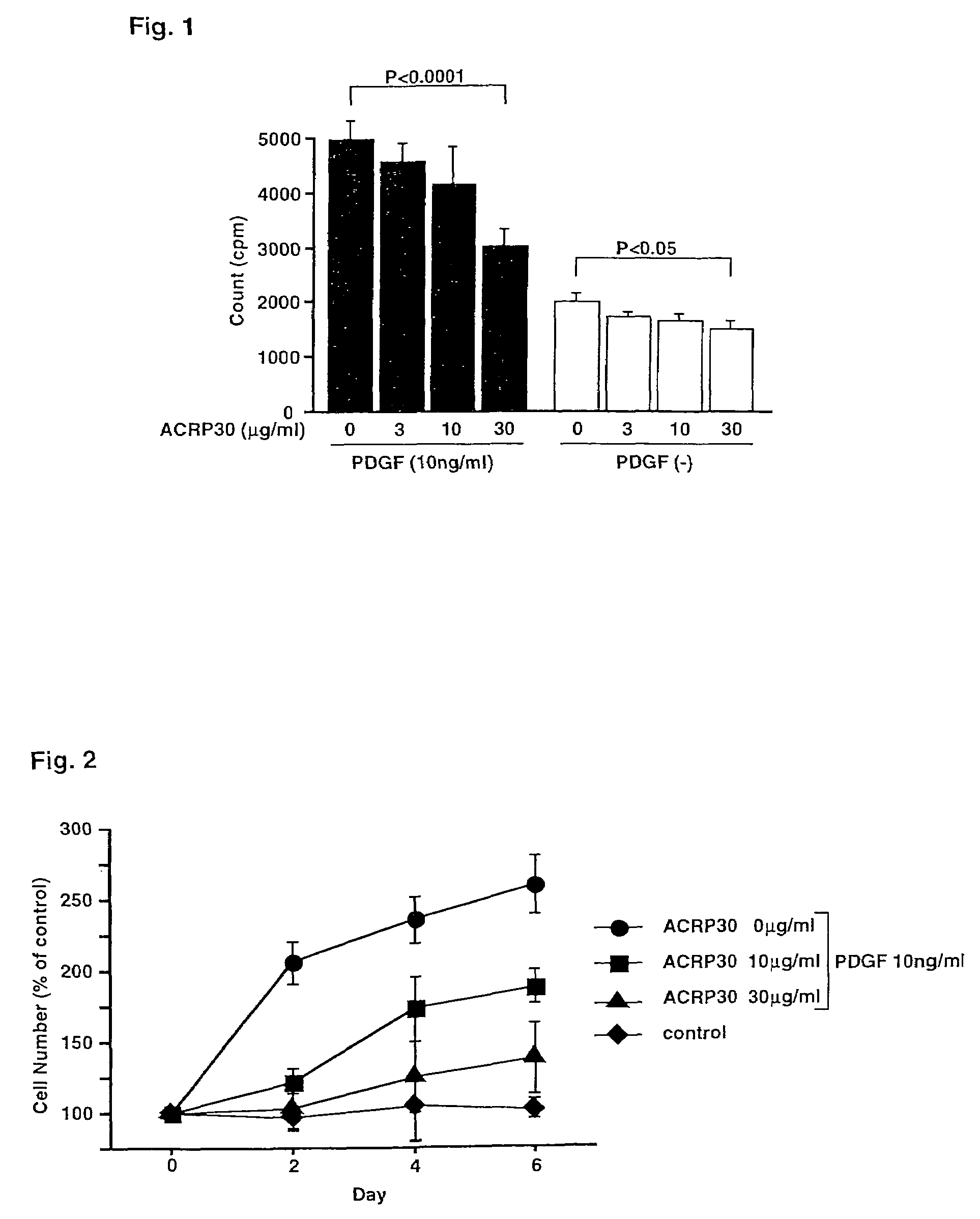
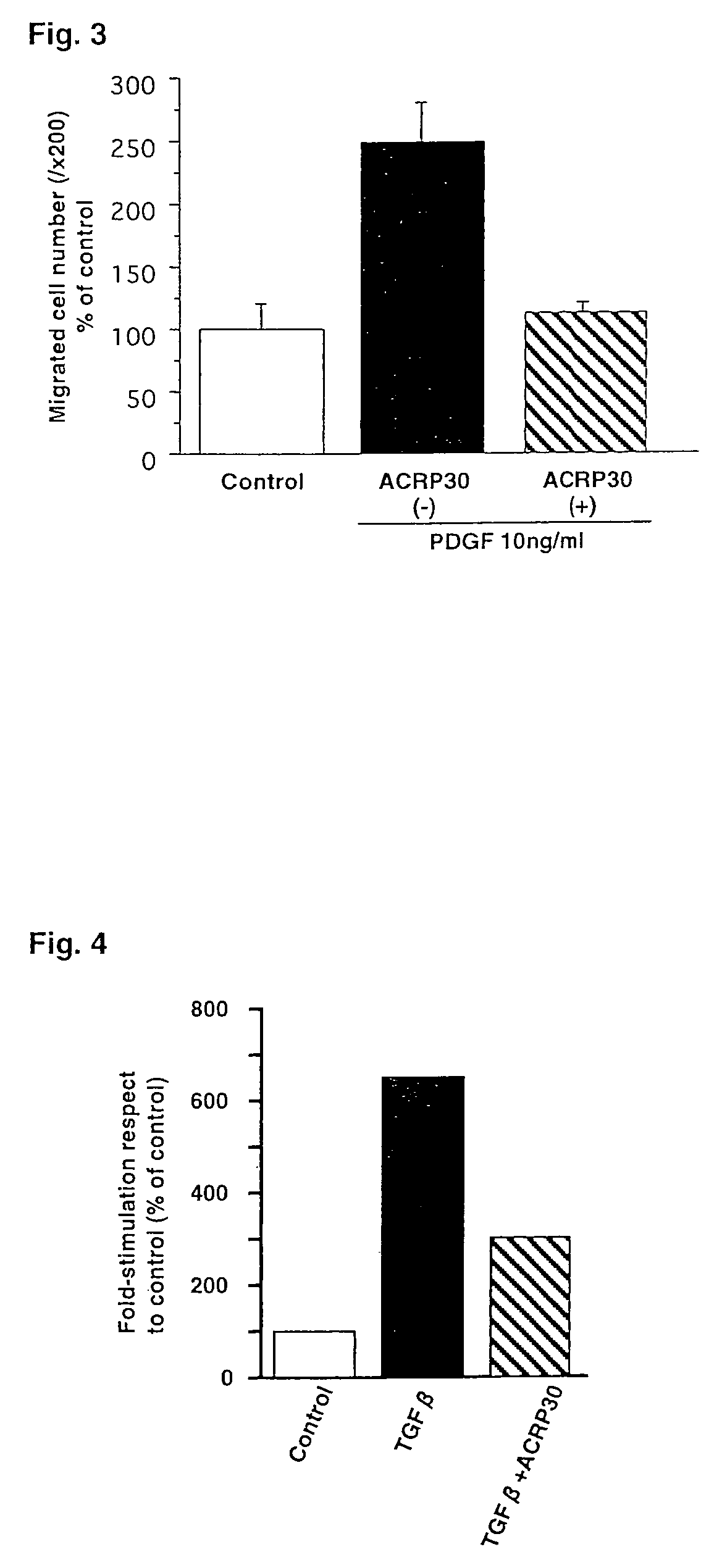
Liver generation promoter
InactiveUS7074756B2Prevent and inhibitPromote regenerationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHepatic fibrosisBiological activation
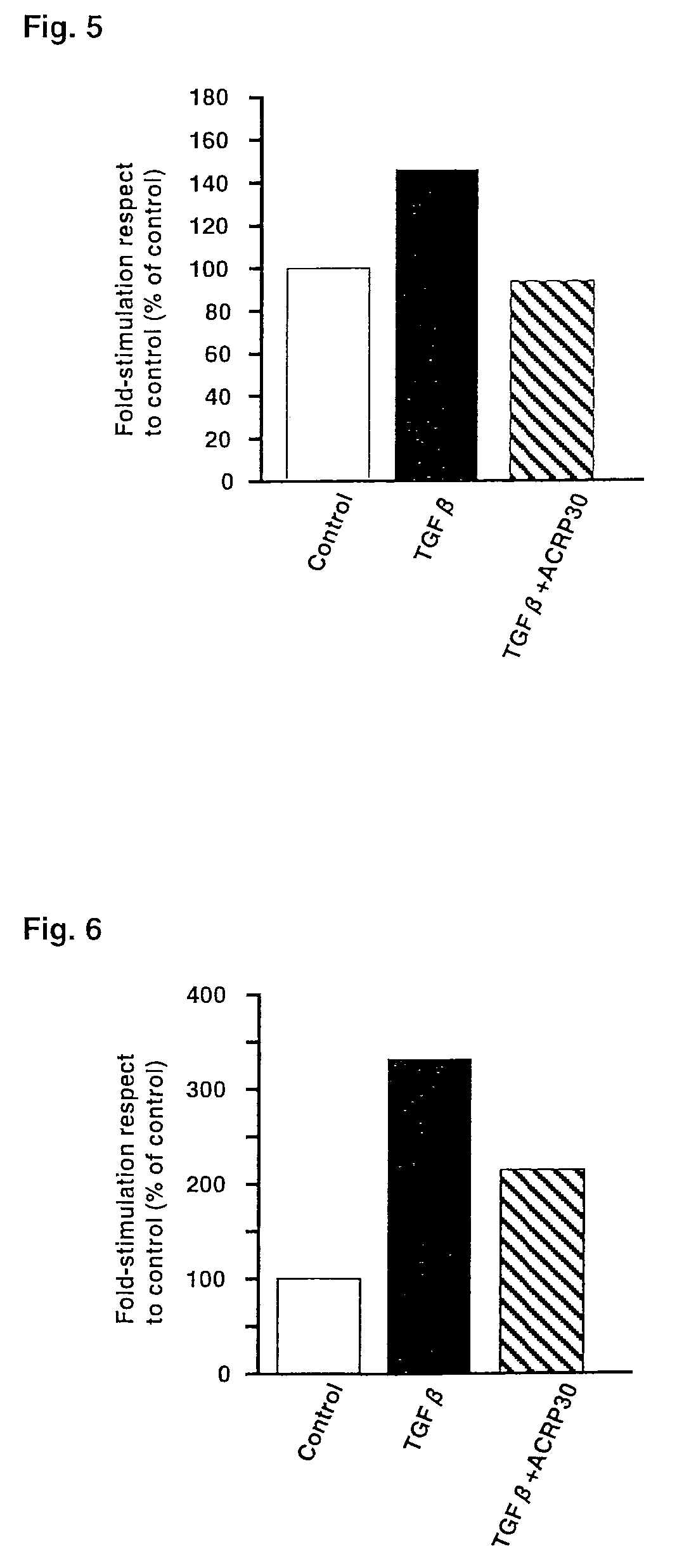
Although it is known that adiponectin, which is adipose-specific protein, has effects of suppressing the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle, an effect against arteriosclerosis, an effect of inhibiting the activation of monocytes and macrophages and an anti-inflammatory effect, its action on hepatic stellate cells has never been known hitherto. The present invention has elucidated that adiponectin inhibits the actions of TGFB and PDGF on hepatic stellate cells and thereby exerts effects of suppressing hepatic fibrosis and promoting the proliferation of normal hepatocytes.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Method for expanding pancreatic beta cell in vitro
ActiveCN103305457AReduce separation and purification stepsLow costArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell culture mediaIn vivo
The invention discloses a method for expanding pancreatic beta cells in vitro. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing expression supernatant of Reg Ialpha protein; (2) separating and purifying pancreas conduit epithelial cells, and carrying out induced differentiation to obtain pancreatic beta cells; and (3) adding the expression supernatant of the Reg Ialpha protein prepared in the step (1) into a cell culture medium, and inoculating the pancreatic beta cells to culture. The method for expanding pancreatic beta cells in vitro can be used for establishing an expansion model of the in-vitro expanded pancreatic beta cells, is helpful for screening pancreatic beta cell expansion prompting medicines in large scale and obtaining medicines for expanding the pancreatic beta cells in vivo and in vitro effectively, in particular Chinese patent medicines, so that pancreatic beta cells are enriched through in-vitro expansion to provide donorcells for diabetes treatment, or the pancreatic beta cell expansion condition is improved under the conditioning of the Chinese patent medicines.
Owner:吉林省合众生物科技有限公司
New application of guava leaves and total flavones of guava leaves
ActiveCN108619245ASimple extraction methodThe detection method is simpleDigestive systemPlant ingredientsSide effectActive component
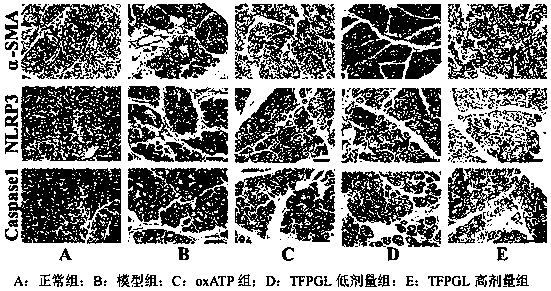
The invention relates to application of total flavones of guava leaves in preparation of drugs for prevention and treatment of pancreatitis. The invention further provides a pharmaceutical compositionfor prevention and treatment of pancreatitis. The pharmaceutical composition comprises an effective therapeutic dose of total flavones of guava leaves as an active component and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Animal experiments show that the total flavones of the guava leaves can inhibit the excessive proliferation of pancreatic stellate cells and alleviate the degree of pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of the P2X7R-mediated NLRP3 inflammation signal pathway, have good effects on prevention and treatment of pancreatitis, have no toxic and side effects and can be used for preparing drugs for prevention and treatment of pancreatitis.
Owner:天津市医药科学研究所
Application of artesunate in preparation of medicine used for inhibiting migration of hepatic stellate cells
InactiveCN102988343AInhibit migrationInterfering with or mitigating the processOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemMedicineHepatic stellate cell
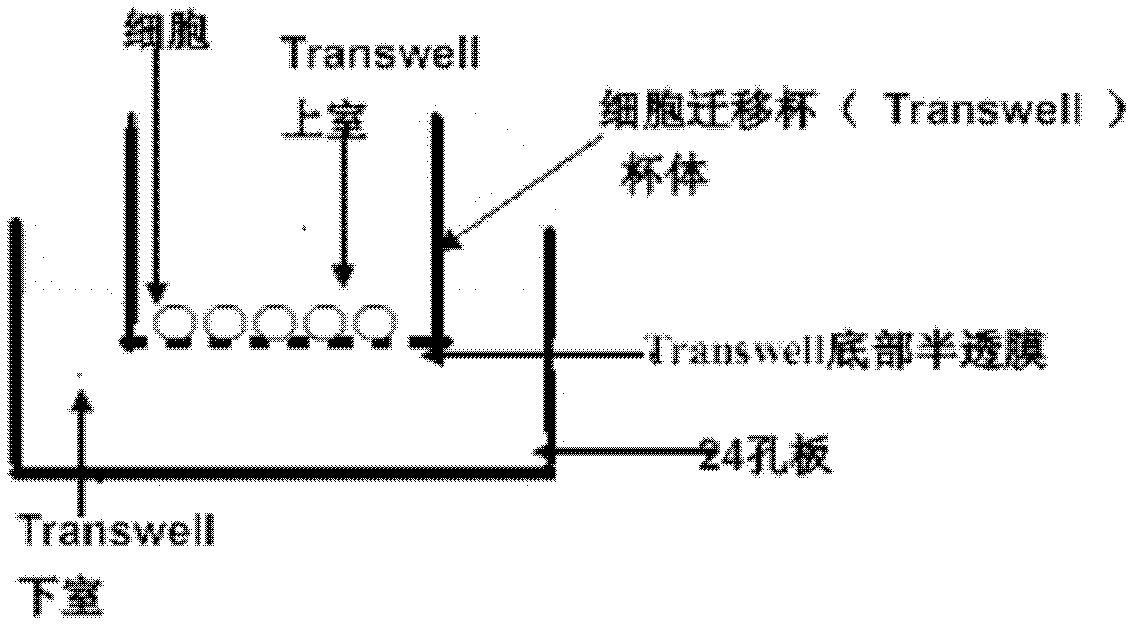
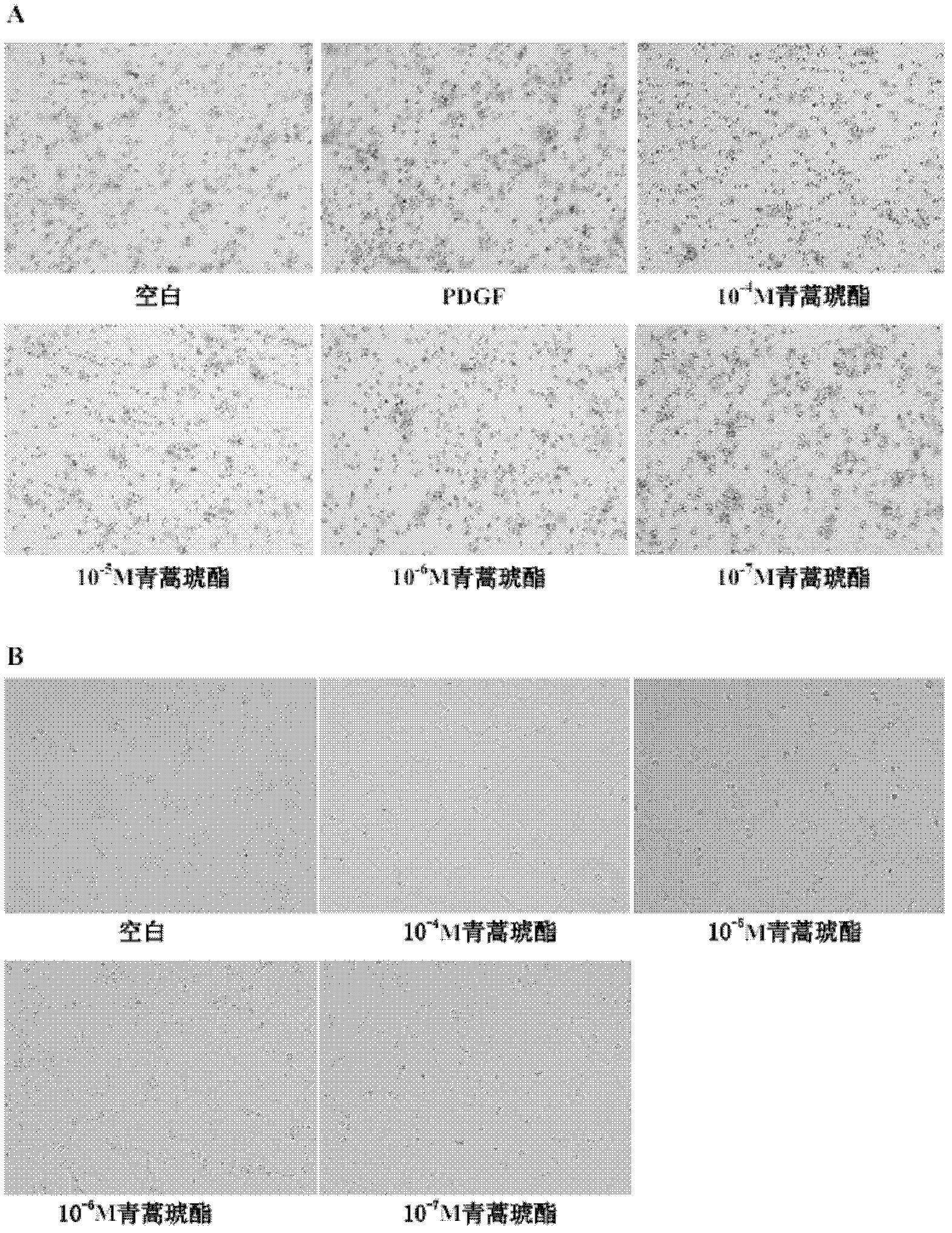
The invention discloses an application of artesunate in preparation of medicine used for inhibiting migration of hepatic stellate cells. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a PDGF (platelet derived growth factor)-induced human hepatic stellate cell strain (LX-2) migration screening platform is designed, and the fact that artesunate with the concentration of being 10<-4>-10<-7>mol / L can inhibit migration of PDGF-induced hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is found.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
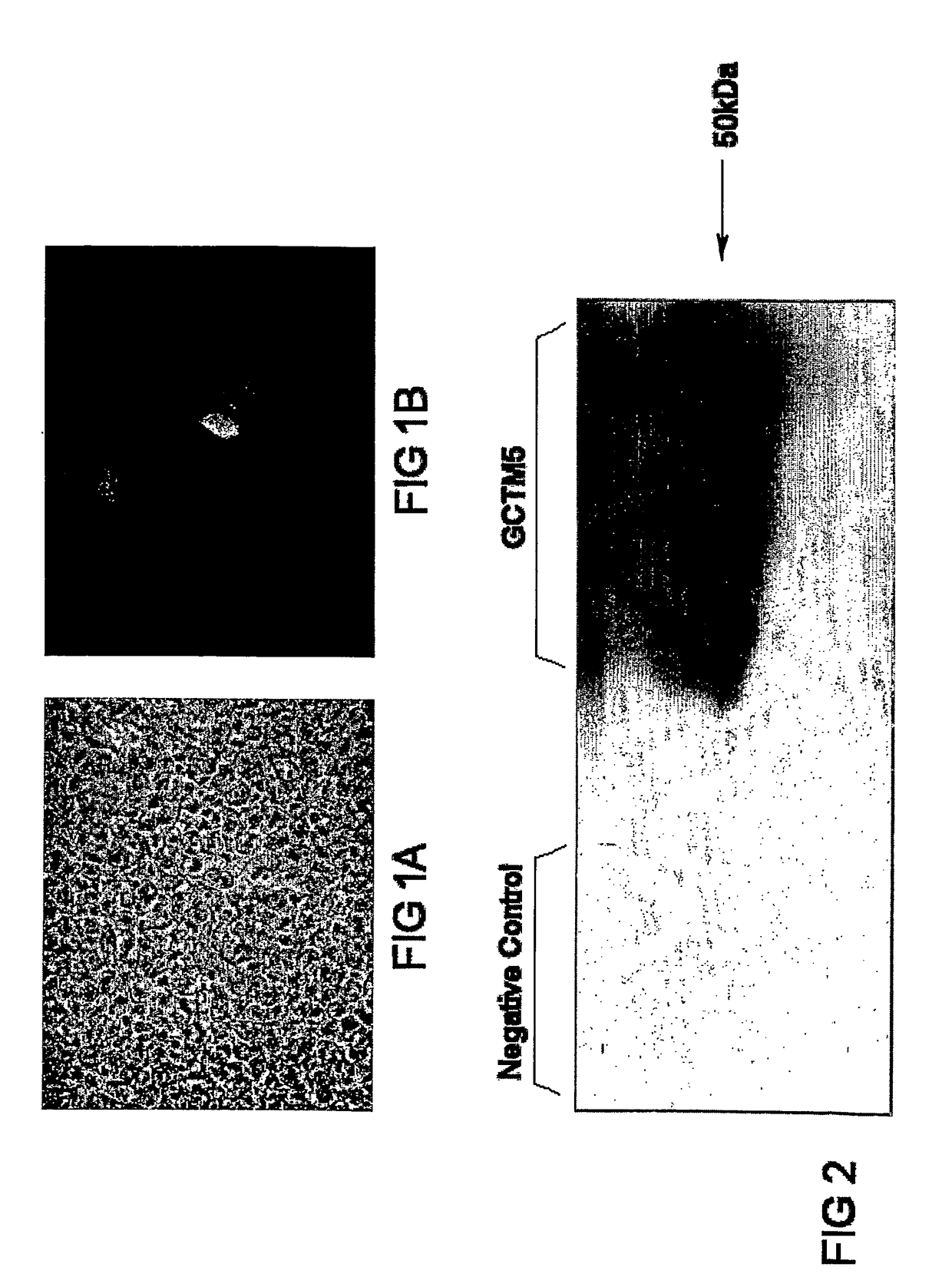
Cell marker for hepatic and pancreatic stem cells and progenitor cells
The present invention provides a cell marker that is characterized by binding to a GCTM-5 antibody of active fragment. The cell marker identifies a unique sub-population of stem cells that show characteristics of hepatic or pancreatic stem cells or hepatic or pancreatic progenitor cells. More specifically the marker is an early liver marker, which could prove a useful tool for the isolation and identification of liver and pancreatic progenitors for both diseased adult liver and differentiating human embryonic stem cells.
Owner:MONASH UNIV +2
A new biomarker expressed in pancreatic beta cells useful in imaging or targeting beta cells
ActiveUS20190145987A1Early detectionEvaluate effectivenessSolid sorbent liquid separationDisease diagnosisCytoplasmBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention is directed to the identification of a biomarker specifically located in the plasma membrane of pancreatic beta cells. Based on a set of specific features the biomarker is a unique candidate for imaging and targeting strategies to study the pancreatic beta cell mass in health and disease (T1D, T2D, pancreatic cancers, obesity, islet transplantation, beta cell regeneration).
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com