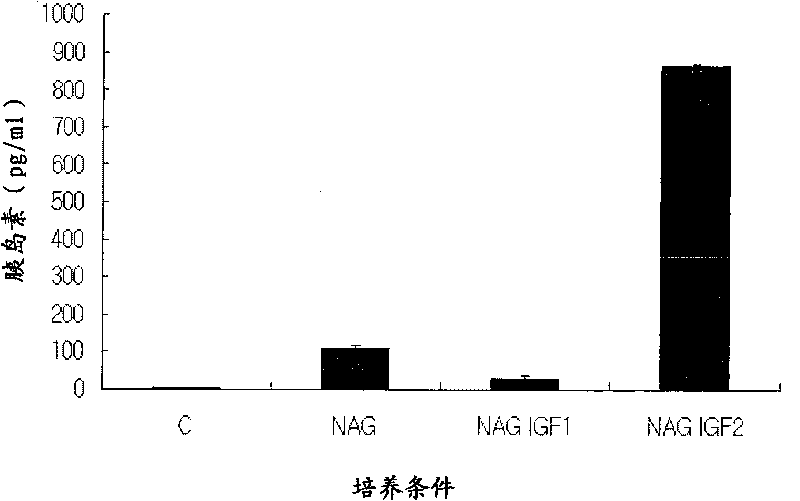
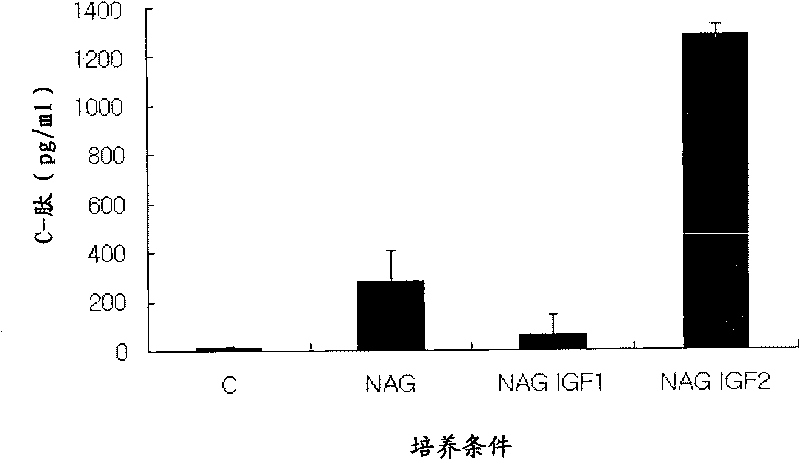
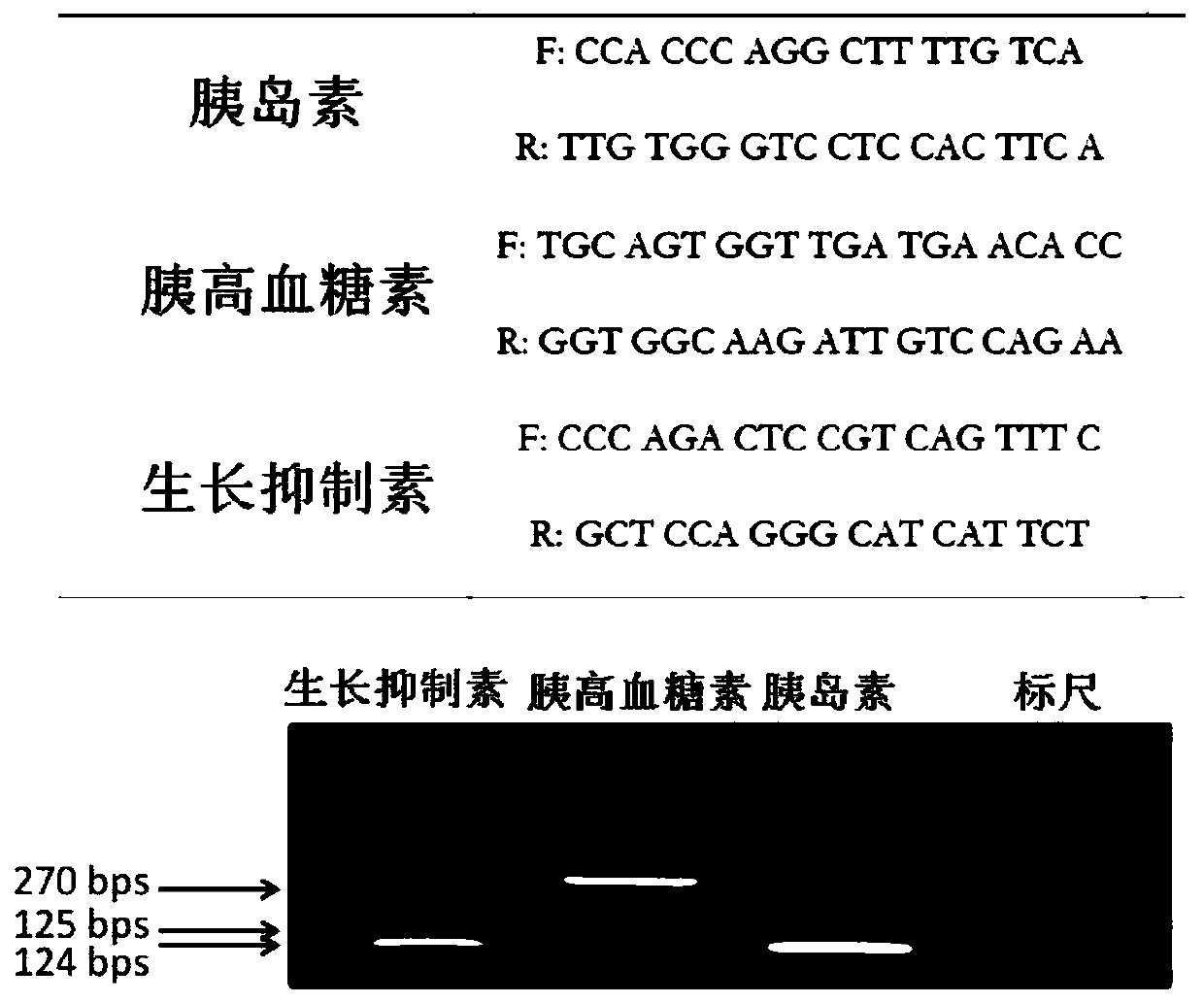
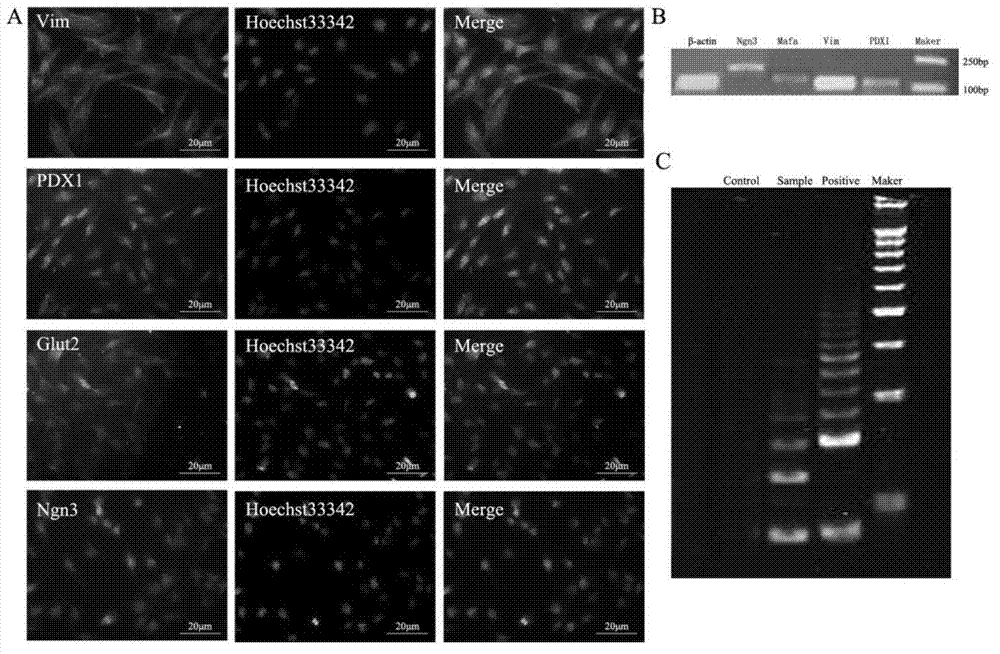
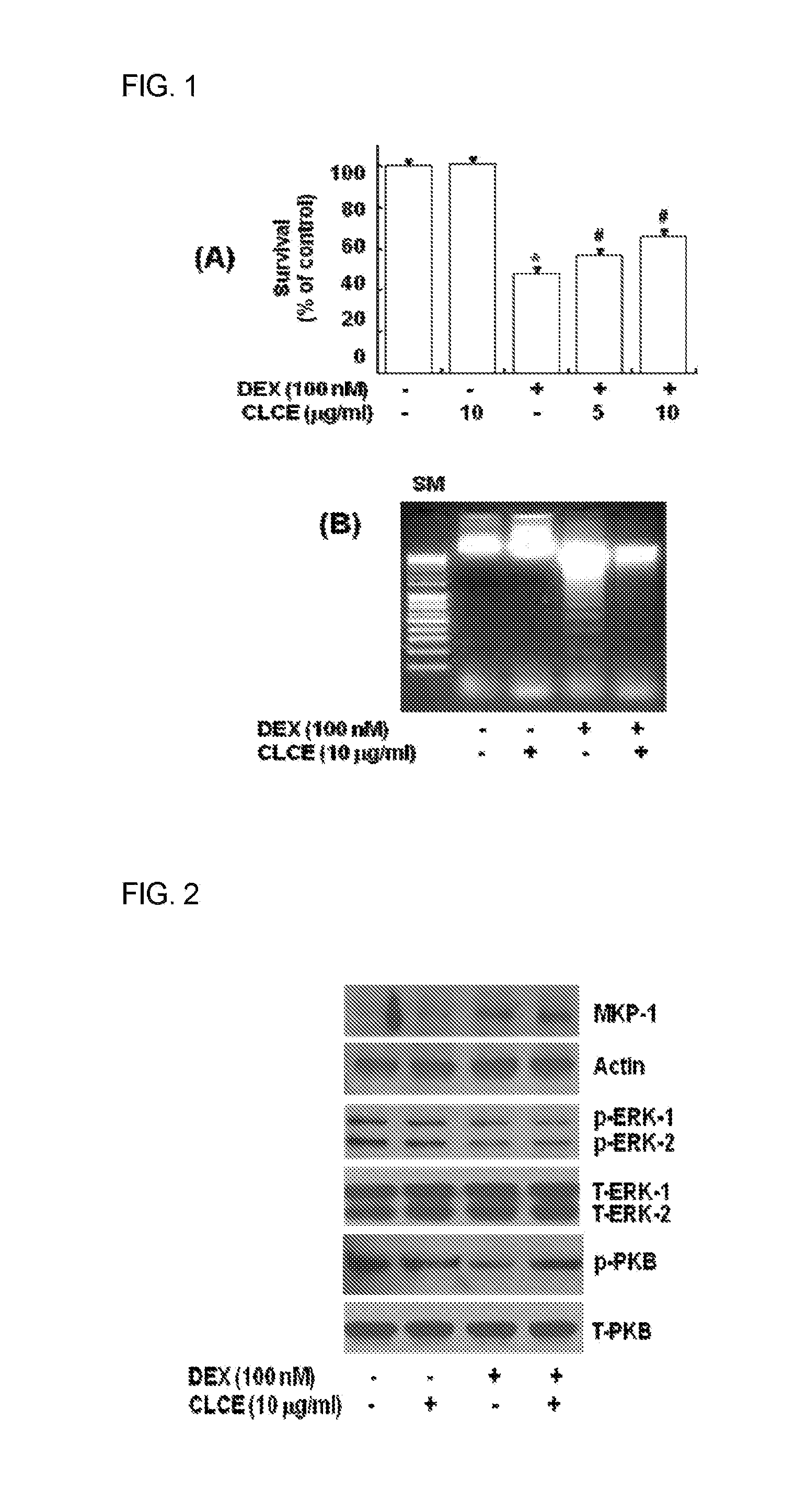
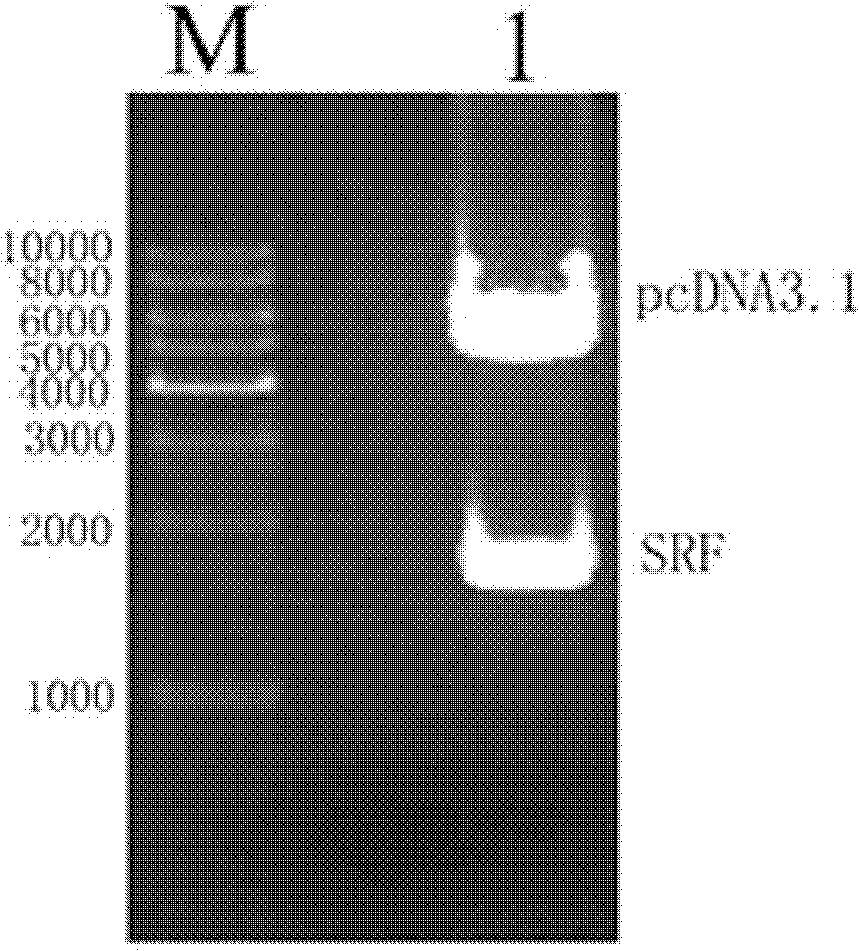Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Insulin Secreting Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment for diabetes
InactiveUS6558952B1Not prevent and decrease progressionMore complicatedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin Secreting CellEGF Receptors
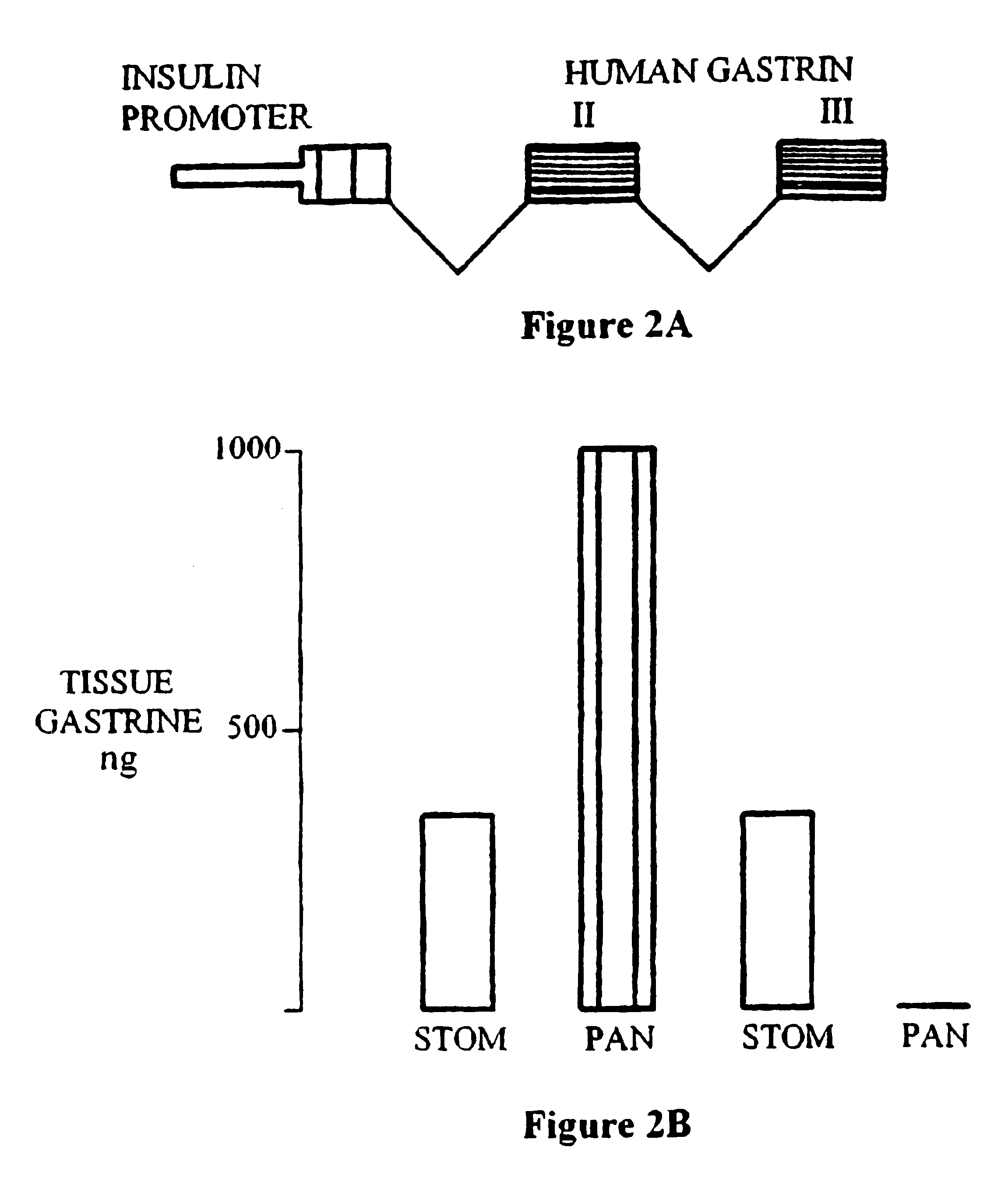
Methods and compositions for treating diabetes mellitus in a patient in need thereof are provided. The methods include administering to a patient a composition providing a gastrin / CCK receptor ligand, e.g., a gastrin, and / or an epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligand, e.g., TGF-alpha, in an amount sufficient to effect differentiation of pancreatic islet precursor cells to mature insulin-secreting cells. The composition can be administered systemically or expressed in situ by cells transgenically supplemented with one or both of a gastrin / CCK receptor ligand gene, e.g., a preprogastrin peptide precursor gene and an EGF receptor ligand gene, e.g., a TGF-alpha gene. The methods also include transplanting into a patient cultured pancreatic islets in which mature insulin-secreting beta cells are proliferated by exposure to a gastrin / CCK receptor ligand and an EGF receptor ligand.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Method of pre-inducing a state of immune tolerance before organ transplantation
InactiveUS6923959B2Delaying occurrenceReduce intensityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInsulin dependent diabetesDuctal cells
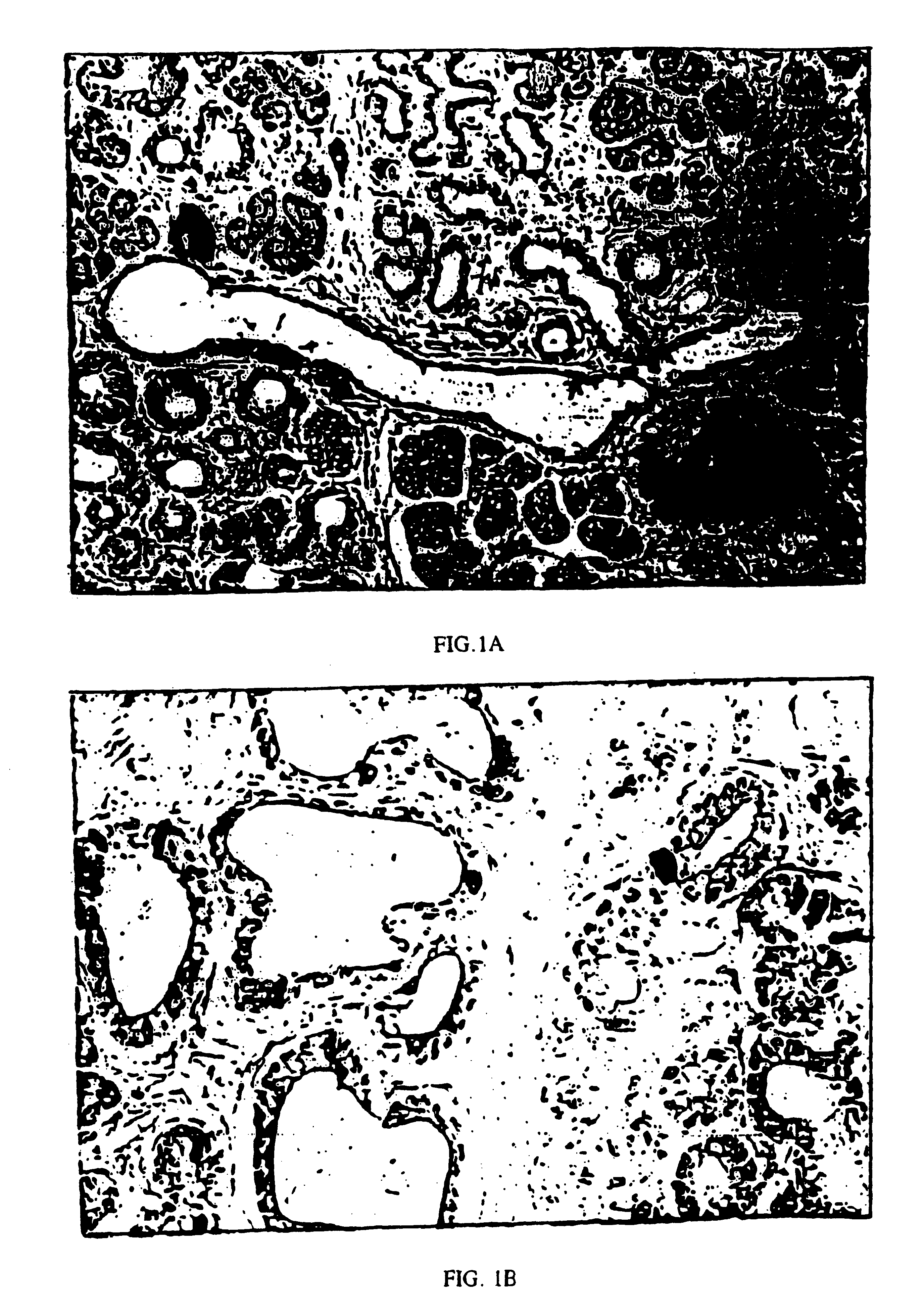
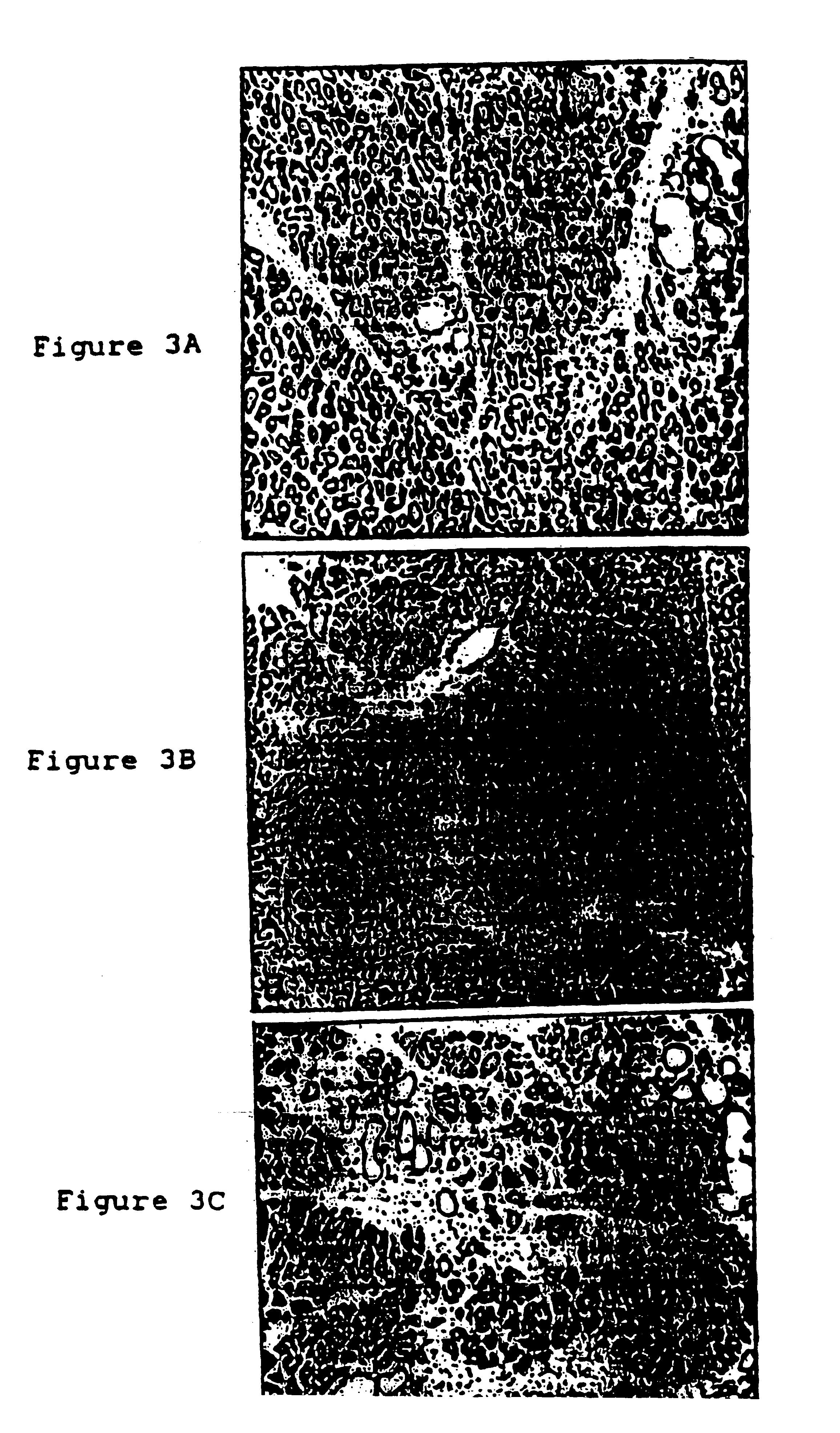
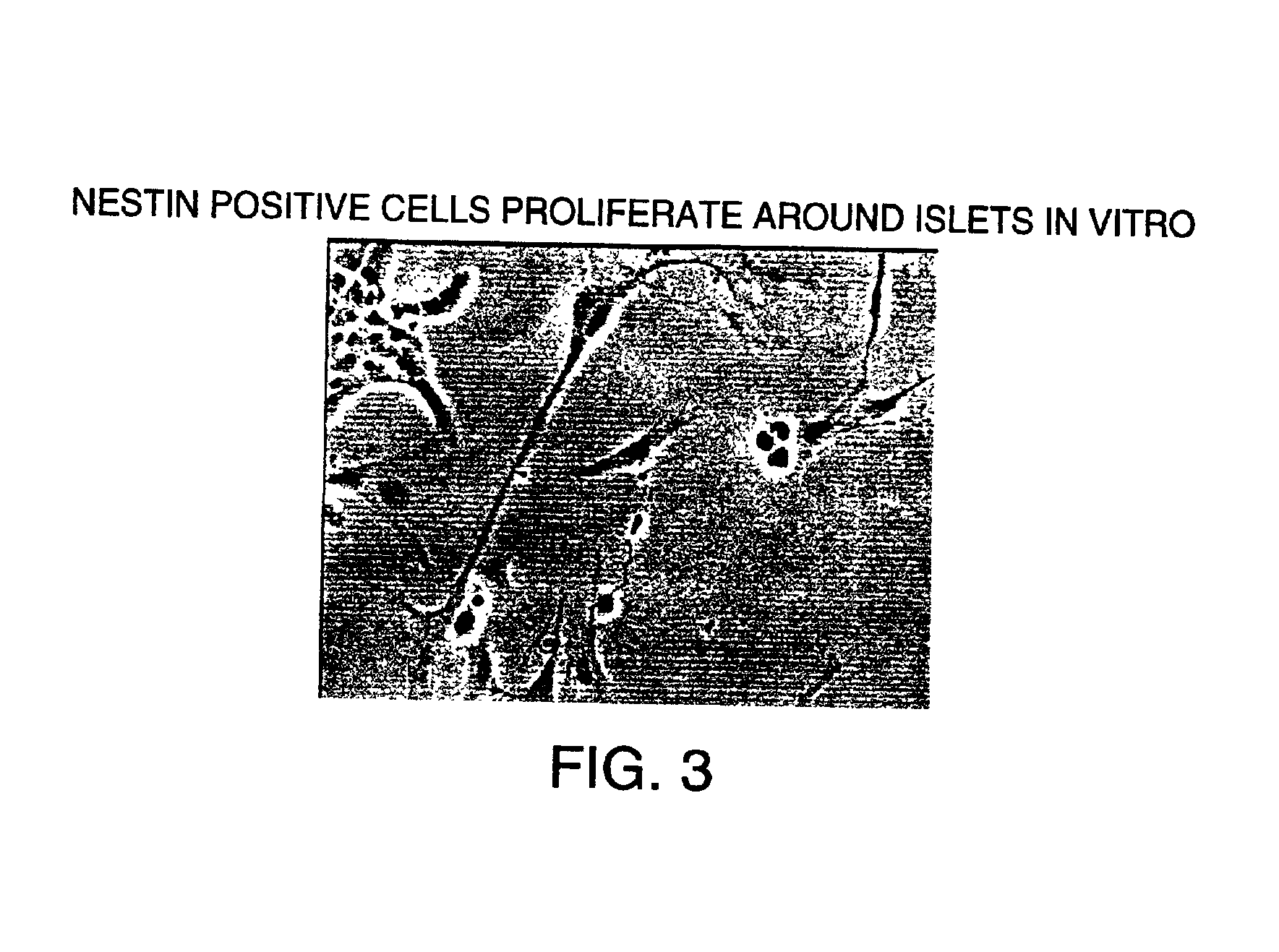
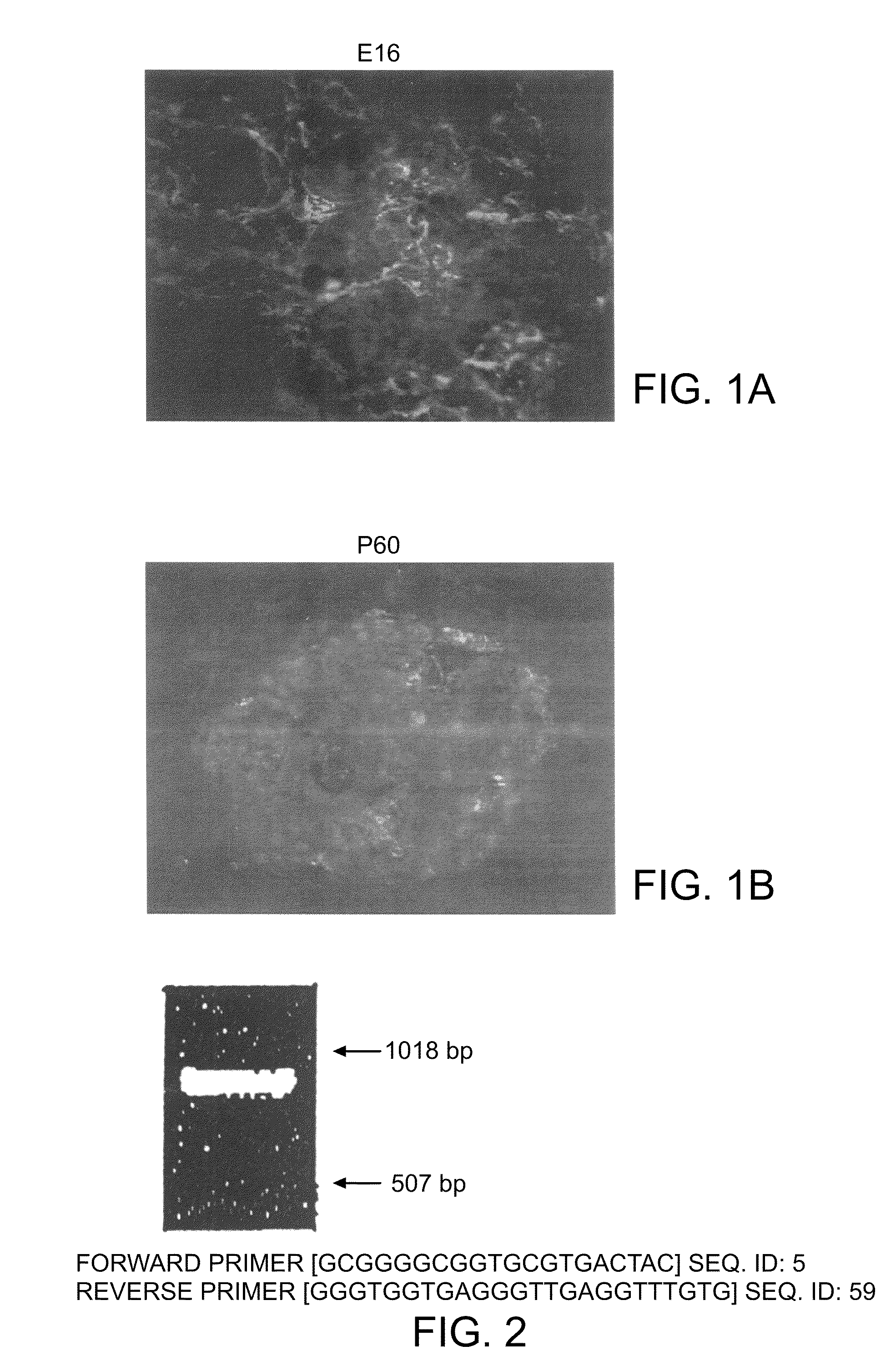
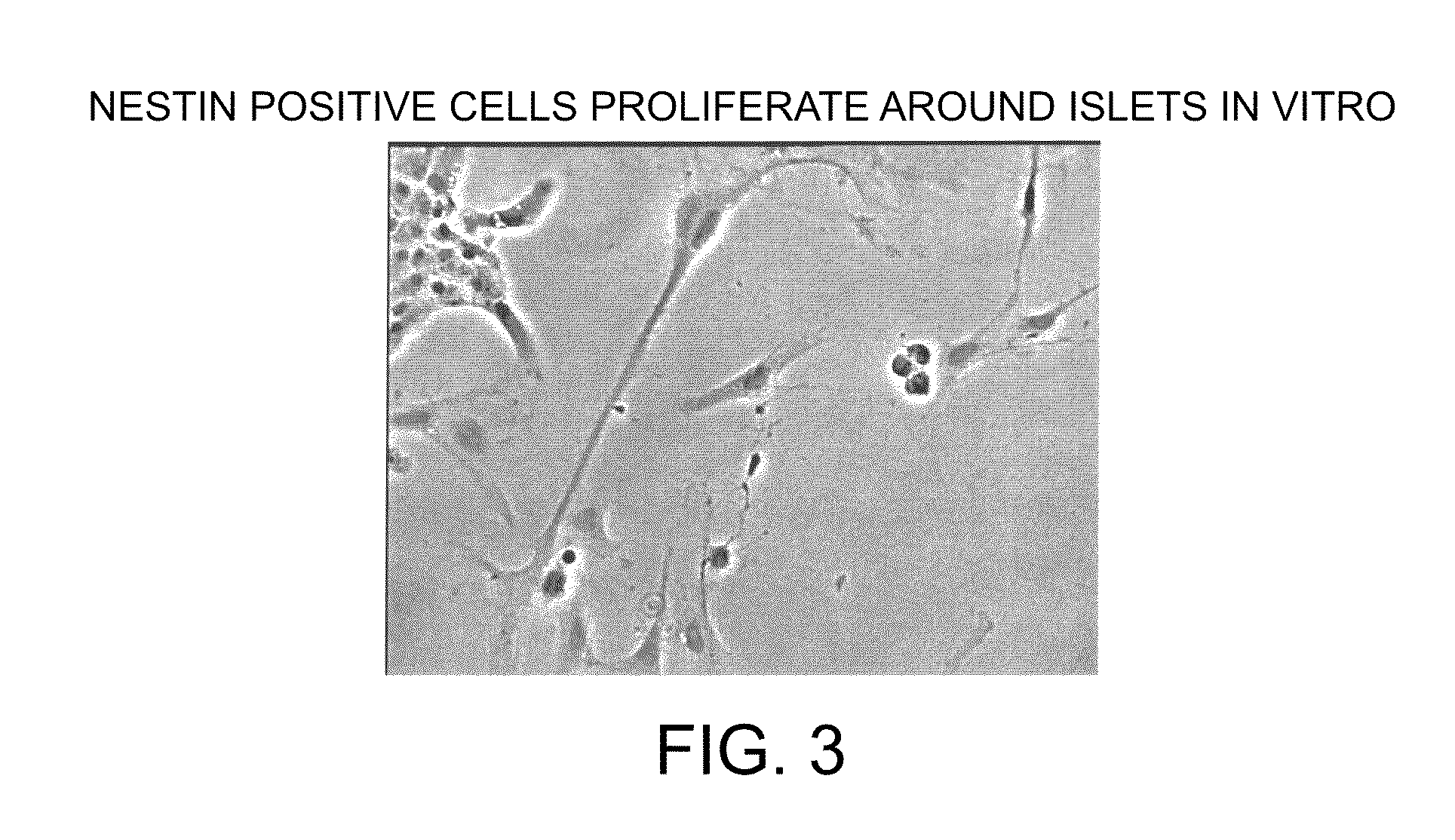
Methods and compositions are described for the treatment of type I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other conditions using newly identified stem cells that are capable of differentiation into a variety of pancreatic islet cells, including insulin-producing beta cells, as well as hepatocytes. Nestin has been identified as a molecular marker for pancreatic stem cells, while cytokeratin-19 serves as a marker for a distinct class of islet ductal cells. Methods are described whereby nestin-positive stem cells can be isolated from pancreatic islets and cultured to obtain further stem cells or pseudo-islet like structures. Methods for ex vivo differentiation of the pancreatic stem cells are disclosed. Methods are described whereby pancreatic stem cells can be isolated, expanded, and transplanted into a patient in need thereof, either allogeneically, isogeneically or xenogenically, to provide replacement for lost or damaged insulin-secreting cells or other cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods for generating insulin-secreting cells suitable for transplantation
InactiveUS20030082810A1High degreeConvenient introductionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGlucose sensitivityInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention relates to methods for generating insulin secreting cells from precursor stem cells or from adult pancreatic exocrine cells. The methods of the invention are useful, for example, for generation of glucose sensitive insulin-secreting beta-cells suitable for transplantation, as well as for in situ development of insulin-secreting cells in a patient in need thereof. Further, the method of the invention relates to methods for preventing premature differentiation of precursor stem cells into insulin-secreting beta-cells. Still further, the invention relates to assay methods for identification of compounds that prevent or activate beta-cell differentiation.
Owner:SERUP PALLE +2
Induction culture medium and method for inducing human fat mesenchymal stem cells to generate insulin secreting cells
ActiveCN104263697AArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPentagastrin stimulation testInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention discloses an induction culture medium which comprises a solvent DMEM (dulbecco's modified eagle medium)-high sugar culture medium, platelets, all-trans vitamin A acid, activin A, glicetin I, a fibroblast growth factor, beta cytosine, an insuline-like growth factor, nicotinamide, polypeptide, pentagastrin and mercaptoethanol. Physical oscillation and collagenase / pancreatin dual digestion are performed to efficiently separate fat mesenchymal stem cells from human fat tissues. The fat mesenchymal stem cells are cultured for proliferation and subcultivation, and the induction culture medium is utilized to induce the fat mesenchymal stem cells to become insulin secreting cells, so that more than 40% of the fat stem cells are induced to differentiate into the insulin secreting cells.
Owner:胡振波
Insulin delivery system
Aspects of the disclosure generally relate to insulin delivery systems and compositions having a insulin secreting β cell line or insulin secreting recombinant non-β cells sequestered in a glucose-responsive material. The disclosed insulin delivery systems can be surgically implanted in a host and can provide a continuous source of insulin from the cells contained in the device. The combination of living cells with a glucose-responsive material provides a hybrid insulin delivery system that delivers physiologically relevant amounts of insulin in response to physiologically relevant glucose levels. In some aspects, the disclosed devices have a biphasic release of insulin in response to sudden increases in glucose concentrations in the fluids bathing the device.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method of transplanting in a mammal and treating diabetes mellitus by administering a pseudo-islet like aggregate differentiated from a nestin-positive pancreatic stem cell
InactiveUS20050244386A1Avoid immune responseReduce intensityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInsulin dependent diabetesDuctal cells
Methods and compositions are described for the treatment of type I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other conditions using newly identified stem cells that are capable of differentiation into a variety of pancreatic islet cells, including insulin-producing beta cells, as well as hepatocytes. Nestin has been identified as a molecular marker for pancreatic stem cells, while cytokeratin-19 serves as a marker for a distinct class of islet ductal cells. Methods are described whereby nestin-positive stem cells can be isolated from pancreatic islets and cultured to obtain further stem cells or pseudo-islet like structures. Methods for ex vivo differentiation of the pancreatic stem cells are disclosed. Methods are described whereby pancreatic stem cells can be isolated, expanded, and transplanted into a patient in need thereof, either allogeneically, isogeneically or xenogenically, to provide replacement for lost or damaged insulin-secreting cells or other cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Treatment for diabetes
InactiveUS20060234373A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsInsulin Secreting CellGastrin
Proliferating pancreatic islet cells obtained by the method of isolating a population of cells that preferably includes predominantly islet precursor cells that express one or more marker associated with an islet precursor cell and providing the precursor cells with one or more a pancreatic differentiation agent so that a population of cells is obtained that has a high proportion of cells with phenotypic characteristics of functional pancreatic islet β-cells. Optionally, the precursor cells are pretreated by providing them with one or more cell expansion agent to increase the number of cells in the population prior to differentiation. The pancreatic differentiation agent composition comprises a gastrin / CCK receptor ligand, e.g., a gastrin, in an amount sufficient to effect differentiation of pancreatic islet precursor cells to mature insulin-secreting cells. The cell expansion agent composition comprises one or more epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligand in an amount sufficient to stimulate proliferation of the precursor cells. The methods of treatment include transplanting either undifferentiated precursor cells and providing the pancreatic differentiation agent either alone or in combination with the cell expansion agent in situ, or transplanting the functional pancreatic islet β-cells into the patient. The pancreatic islet β-cells can be used for drug screening, and replenishing pancreatic function in the context of clinical treatment.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
Method for constructing tissue engineering islet by adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells and obtained tissue engineering islet
InactiveCN104789520AWide variety of sourcesImprove adsorption capacityArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell adhesionAdhesion process
The invention discloses a method for constructing tissue engineering islet by adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells and the obtained tissue engineering islet. The method employs adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells with extensive sources to perform culture on islet acellular matrix, so that the acellular matrix can provide a three-dimensional space suitable for growth to adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells so as to promote cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation, and formation of a three-dimensional structure engineering islet tissue able to stably secrete insulin. The method realizes gathering of insulin secreting cells, enhances cell utilization and is expected to promote the effect of repairing islet injury by tissue engineering method.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Inducer for inducing human adipose derived stromal cells into insulin-secretion cells, induction medium and method
InactiveCN103756954AGenetic change noNo riskArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin Secreting CellRHODIOLA ROSEA ROOT
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and relates to an inducer for inducing human adipose derived stromal cells into insulin-secretion cells, an induction medium and a method. The inducer for inducing human adipose derived stromal cells into insulin-secretion cells consists of the following components: a rhodiola rosea injection, nicotinamide, taurine and GLP-1. Every 1,000ml of the induction medium containing the inducer comprises 20-40g of the rhodiola rosea injection, 0.97-1.47g of the nicotinamide, 0.25-0.50g of the taurine, 26.84-40.27mg of the GLP-1 and the balance being a human adipose derived stromal cell serum-free medium, which are mixed uniformly, filtered and degermed. According to the inducer for inducing human adipose derived stromal cells into insulin-secretion cells, the induction medium and the method, differentiation of the human adipose derived stromal cells into the insulin-secretion cells is induced by using the injection of a traditional Chinese medicine, namely, rhodiola rosea, and each component is safe and nontoxic. The method has few steps and is short in time and high in the inducing efficiency.
Owner:青岛瑞思科生物科技有限公司
Enhancement of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by cells through induction of cellular senescence
InactiveUS20170196913A1Improve glucose homeostasisIncrease secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic cellsInsulin Secreting CellD-Glucose
Methods for increasing glucose induced insulin secretion in an insulin secreting cell by inducing senescence in the cell are provided. Further, methods for treating diabetes, by providing cells with increased glucose induced insulin secretion to a subject, as well as a population of modified insulin secreting cells are provided.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Stem cells of the islets of langerhans and their use in treating diabetes
InactiveCN1589330AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin dependent diabetesDisease
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Stem cells of the islets of langerhans and their use in treating diabetes mellitus
Methods and compositions are described for the treatment of type I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other conditions using newly identified stem cells that are capable of differentiation into a variety of pancreatic islet cells, including insulin-producing beta cells, as well as hepatocytes. Nestin and ABCG2 have been identified as molecular markers for pancreatic stem cells, while cytokeratin-19 serves as a marker for a distinct class of islet ductal cells. Methods are described whereby nestin and / or ABCG2-positive stem cells can be isolated from pancreatic islets and cultured to obtain further stem cells or pseudo-islet like structures. Methods for ex vivo differentiation of the pancreatic stem cells are disclosed. Methods are described whereby pancreatic stem cells can be isolated, expanded, and transplanted into a patient in need thereof, either allogeneically, isogeneically or xenogenically, to provide replacement for lost or damaged insulin-secreting cells or other cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation process for insulin-secreting cells and special medium composition used therein
InactiveCN103184186ANo importEasy to operateArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsINSULIN USEInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention discloses a medium composition for inducing mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. The medium composition comprises a medium A, a medium B and a medium C. The medium A comprises the following solutes: a fetal calf serum with a concentration of 4.75 to 5.25 ml / L and activin A with a concentration of 4.75 to 5.25ng / mL. The medium B comprises the following solutes: retinoic acid with a concentration of 0.95 * 10<-5> to 1.05 * 10<-5> mol / L, EGF with a concentration of 19 to 21ng / ml, bFGF with a concentration of 19 to 21ng / ml, glutamine with a concentration of 1.9 to 2.1 mmol / L, 0.95 to 1.05% of non-essential amino acids and 1.9 to 2.1% of B27. The medium C comprises the following solutes: a fetal bovine serum with a concentration of 4.5 to 5.5 ml / L, exendin-4 with a concentration of 19 to 21 ng / ml, activin A with a concentration of 9.5 to 10.5 ng / ml, nicotinamide with a concentration of 9.5 to 10.5 mmol / L, 1.9 to 2.1% of B27 and 0.95 to 1.05% of N2. An induction culture method provided by the invention is applicable to a variety of tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and has the advantages of no introduction of viruses, easy operation and high efficiency.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for inducing placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into islet-like cells
InactiveCN105132360AWide variety of sourcesNo painArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin Secreting CellMesenchymal stem cell
The invention relates to a method for inducing placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into islet-like cells. According to the method, placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells are induced to be differentiated to islet-like cells and are identified by using cytokines, such as basic fibroblast growth factors (bFGF), hexadecadrol and beta-mercaptoethanol. The method lies in further investigating the differentiation potential of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells, discussing and studying optimum conditions of in-vitro separation, culture and differentiation of the placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells, studying the possibility and the feasibility of inducing the placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into the islet-like cells, seeking an optimum inducing system of inducing differentiation in vitro and further finding a method for inducing the placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated to insulin-producing cells (IPCs). Therefore, the method provides a foundational research basis for clinical application of the placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the insulin-producing cells.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW MEDICINE RES INST OF INTEGRATED WESTERN MEDICINE & TCM CO LTD
Stem cell preparation for treating diabetes mellitus and preparation method of stem cell preparation
InactiveCN103845362AImprove stabilityGood curative effectMetabolism disorderArtificial cell constructsInsulin Secreting CellBlood sugar
The invention provides a stem cell preparation for treating diabetes mellitus. The stem cell preparation comprises: stem cells separated and extracted from human blood or tissues and organs and / or islet-like cells induced and differentiated from the stem cells and a cell preservation solution containing 0.5% of heparin calcium, wherein the cell content is 1*10<5> to 5*10<7> / ml. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the stem cell preparation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) separation and purification of the stem cell; (2) in vitro culture of the stem cells or in vitro induction and differentiation of the stem cells to form islet-like cells; (3) diluting the cell obtained in the step (2) by using the cell preservation solution to prepare a stem cell preparation; (4) quality detection of the stem cell preparation. The stem preparation is transplanted into the body and can be differentiated into insulin-secreting cells to secret insulin, and the blood sugar concentration of a person with diabetes is effectively reduced. Thus, a new way is provided for overcoming treatment of the diabetes dependent on the insulin and curing the diabetes once and for all.
Owner:上海坤爱生物科技股份有限公司
Method for in vitro induction of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) differentiated into insulin-secreting cells (ISCs)
The invention discloses a method for the in vitro induction of hAMSCs differentiated into ISCs. According to the method, the extracted hAMSCs are cultured for 7 days by a serum-free high sugar-DMEM induction medium containing niacinamide of 10mmol / L and an N2 supplement. The hAMSCs induced by the method of the invention express insulin gene mRNA and PDX-1 gene mRNA, and the content of insulin in the supernatant of the culture reaches above 330muIU / ml; and the method of the invention allows the in vitro induction of the hAMSCs differentiated into the ISCs to be realized.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
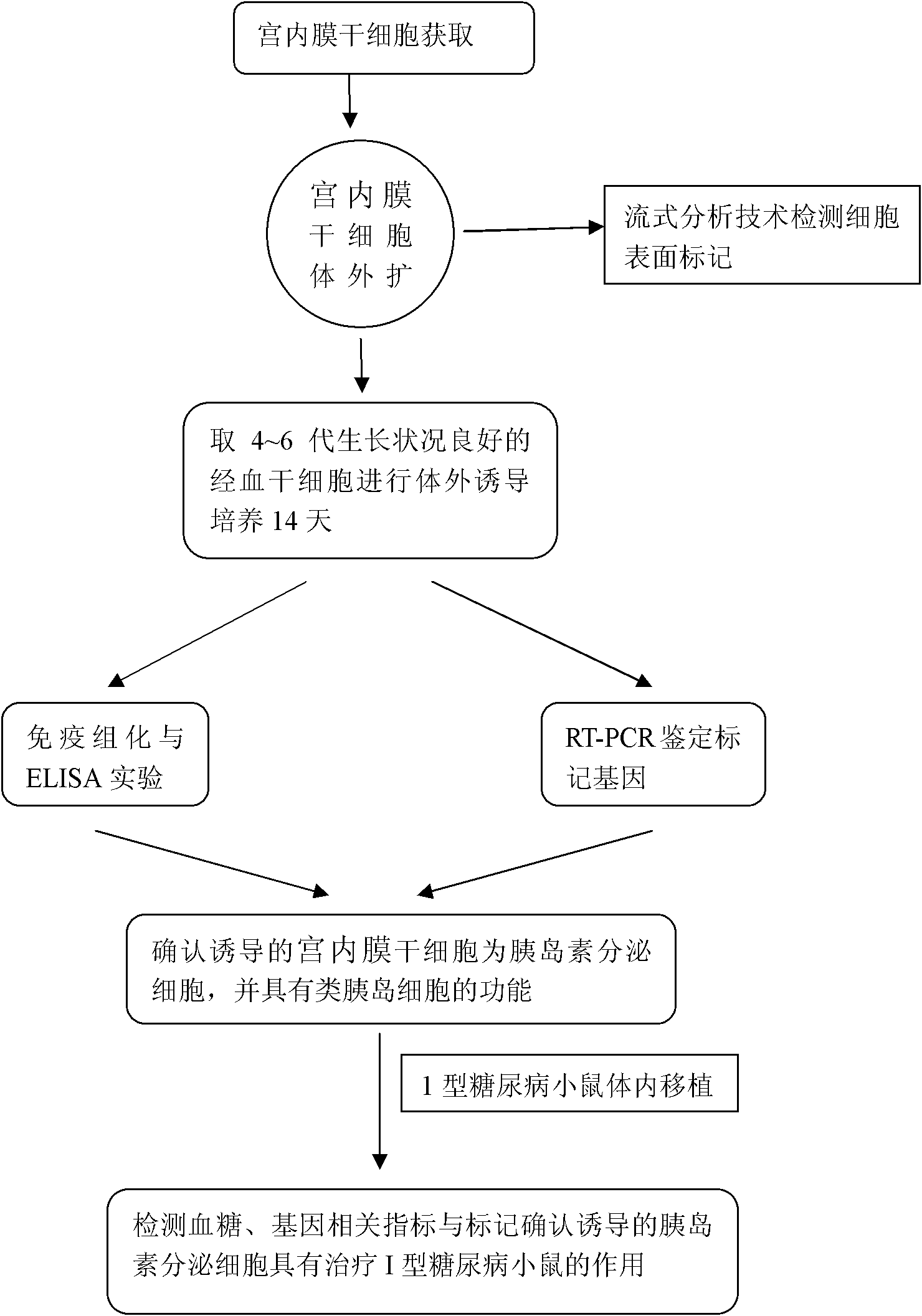
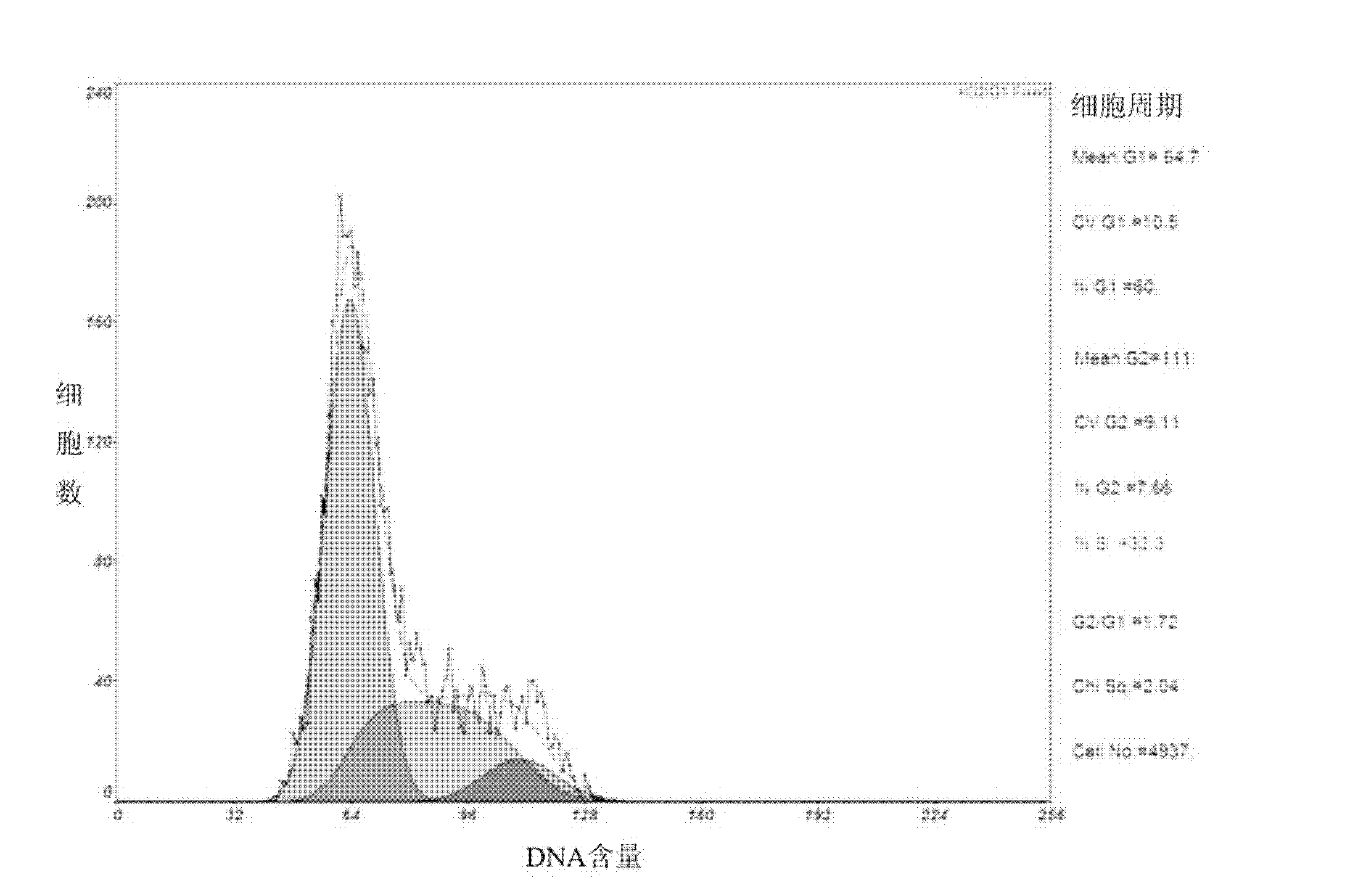
Method for directionally inducing insulin-secreting cells by endometrial stem cells
InactiveCN102154203AImprove induction efficiencyImprove symptoms of hyperglycemiaSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPhosphateInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention discloses a method for directionally inducing insulin-secreting cells by endometrial stem cells, which comprises the following steps of: 1, separation culture and amplification of the endometrial stem cells; and 2, in vitro inducing differentiation. The step of in vitro inducing differentiation comprises the following specific steps of: digesting the fourth to sixth generation of cells with good growth conditions, which are obtained in the step 1, by pancreatic enzymes; when the cells are observed under a microscope to be changed into single circles, stopping digesting by a DMEM(dulbecco's modified eagle medium) culture medium containing fetal calf serum with the volume concentration of 13 to 17 percent; centrifuging and washing the obtained cell precipitates by a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution); adding an inducing culture medium into the cells washed by the PBS; placing the obtained cells into an incubator with the concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 of 4 to 6 percent,the saturated humidity of 94 to 96 percent and the temperature of 36 to 38 DEG C for culturing; and culturing the cells for 13 to 15 days to obtain the insulin-secreting cells. The obtained insulin-secreting cells are used for treating diabetes mellitus so as to provide a novel seed resource for stem cell therapy.
Owner:项桂法
Method for constructing pancreatic stem cell line from human insulin and differentiating to insulin secretion cell
InactiveCN102433300APromote growthImprove survival rateMetabolism disorderNervous system cellsInsulin Secreting CellStem cell line
The invention discloses a method for constructing and differentiating a pancreatic stem cell line from human insulin. The pancreatic stem cell line is a pancreatic stem cell amplified from human insulin mass and has a multi-lineage differentiation potential. The induced pancreatic stem cell line can be differentiated to form nerve-like cells, fat-like cells, bone-like cells and functional insulin-like cell mass. The functional insulin-like cell mass is transplanted to a body of a nude mouse model suffered from diabetes, so that the blood sugar concentration of the nude mouse model can be reduced and normal blood sugar level can be maintained within one month.
Owner:厚朴生物科技(苏州)有限公司
Method for inducing human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in vitro
InactiveCN102618500AHigh transfection efficiencyImprove securityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsProgenitorInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a method for inducing human mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in vitro, which includes, according to the technical scheme, constructing recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmids of SRF (serum response factor) gene; preliminarily inducing human mesenchymal stem cells into nestin cells first; further inducing the nestin cells into pancreatic progenitor cells; transfecting an eukaryotic expression vector containing the SRF gene to the cells above; and finally inducing the cells into insulin-secreting cells, wherein the eukaryotic expression vector comprises pEGFP (plasmid enhanced green florescence protein), pcDNA or pCMV. By the method, new seed cell sources for cell therapy of diabetes mellitus are provided, new theoretical and experimental basis is provided for directed induction of mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into insulin-secreting cells and clinical application of the insulin-secreting cells, and new models for drug development and screening related to the insulin-secreting cells are provided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stem cells of the islets of langerhans and their use in treating diabetes mellitus
Methods and compositions are described for the treatment of type I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other conditions using newly identified stem cells that are capable of differentiation into a variety of pancreatic islet cells, including insulin-producing beta cells, as well as hepatocytes. Nestin and ABCG2 have been identified as molecular markers for pancreatic stem cells, while cytokeratin-19 serves as a marker for a distinct class of islet ductal cells. Methods are described whereby nestin and / or ABCG2-positive stem cells can be isolated from pancreatic islets and cultured to obtain further stem cells or pseudo-islet like structures. Methods for ex vivo differentiation of the pancreatic stem cells are disclosed. Methods are described whereby pancreatic stem cells can be isolated, expanded, and transplanted into a patient in need thereof, either allogeneically, isogeneically or xenogenically, to provide replacement for lost or damaged insulin-secreting cells or other cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for induced differentiation of human amniotic mesenchyme cells in vitro into insulin-secreting cells
InactiveCN106011048AImprove induction conversion rateArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin Secreting CellPrimary cell
The invention provides a method for induced differentiation of human amniotic mesenchyme cells in vitro into insulin-secreting cells. The steps include: isolation culture of primary cells; purification of primary cells; primary cell identification by a flow cytometer; 2-mercaptoethanol, B27, bFGF, and nicotinamide induction; and cell morphology and function identification after induction. The method for induced differentiation of human amniotic mesenchyme cells in vitro into insulin-secreting cells provided by the invention induces human amniotic mesenchymal cells to differentiate into nestin positive cells, induces nestin positive cell amplification and differentiation into precursor cells, and induces insulin-secreting cell maturation, confirms that amniotic mesenchyme cells have the possibility of transformation into insulin-secreting cells in specific environment, amniotic mesenchyme cells have wide sources, and no ethical obstacle exists, therefore the method provides a new idea for clinical stem cell transplantation.
Owner:吴卫江
Method of generating islet beta-cells from exocrine pancreatic cells
InactiveUS7604991B2Metabolism disorderPancreatic cellsPancreatic islet transplantationInsulin Secreting Cell
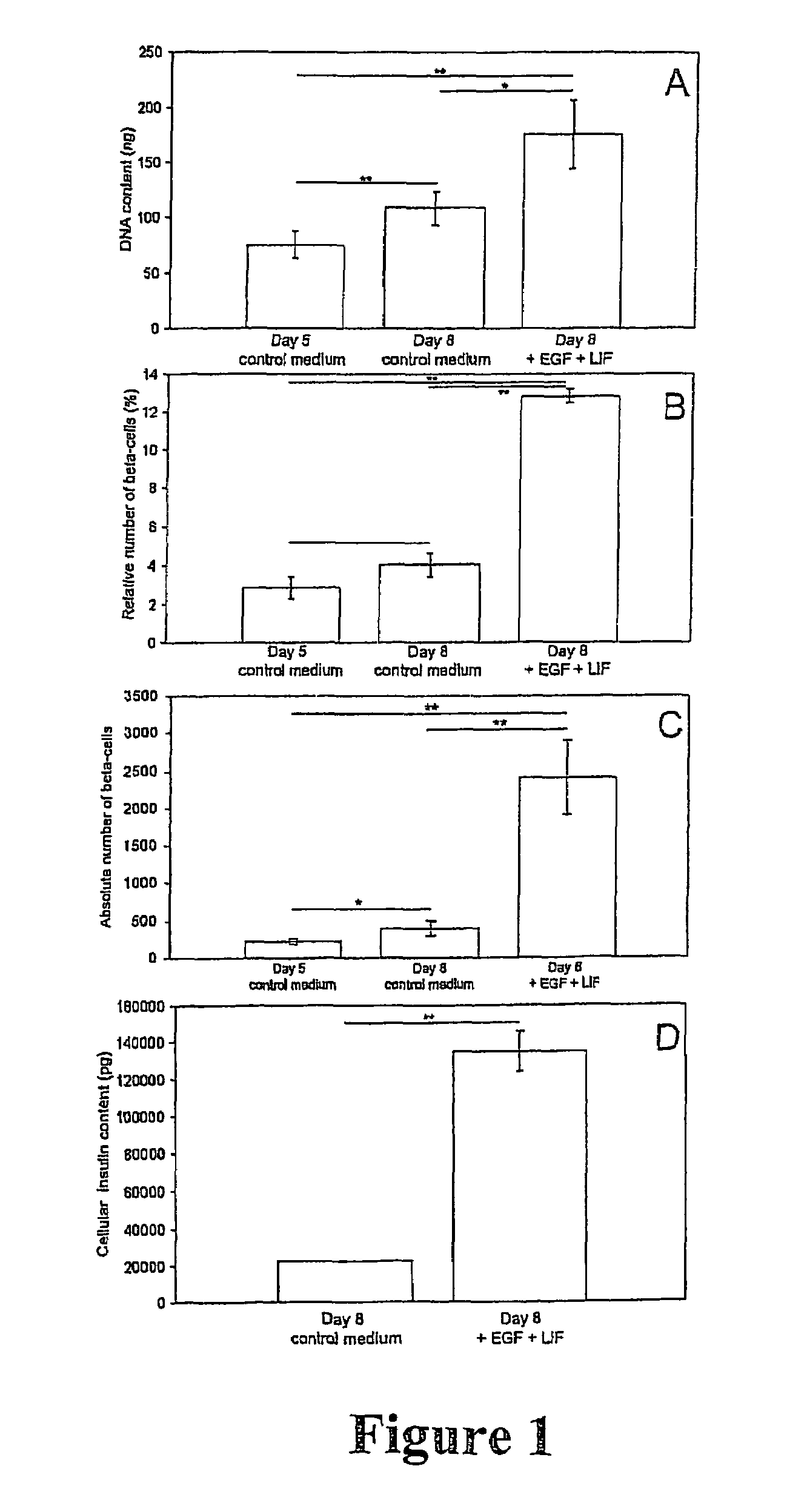
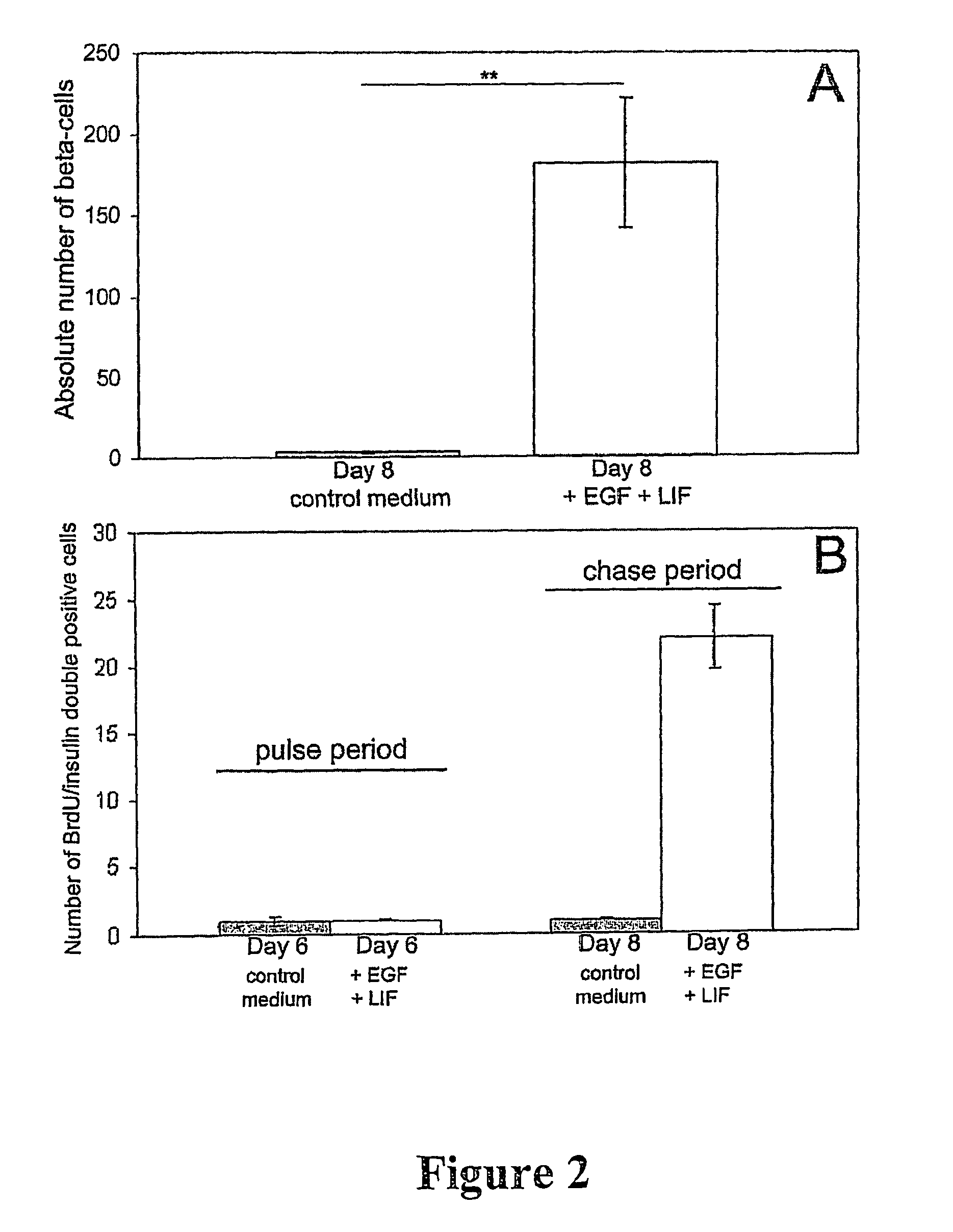
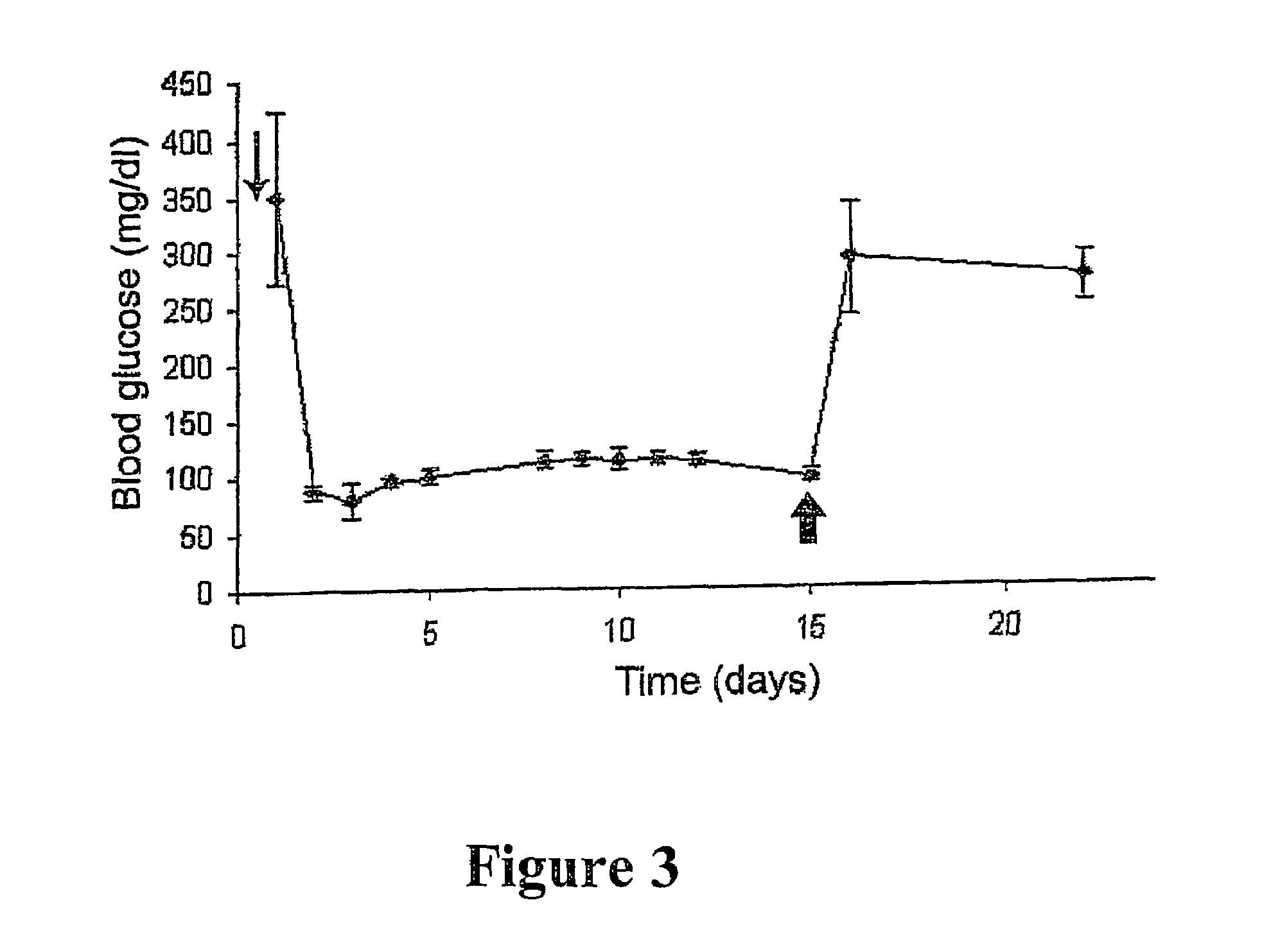
The present invention discloses an in vitro method wherein mammalian beta-cell differentiation can be induced in dedifferentiated exocrine pancreatic cells in a medium comprising ligands of the EGF receptor and the GP130 receptor, such as EGF and LIF. Insulin secreting cells, obtainable by this method, provide a means for the treatment of diabetes by islet transplantation.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL +1
Method for the differentiation of human adult stem cells into insulin-secreting cells
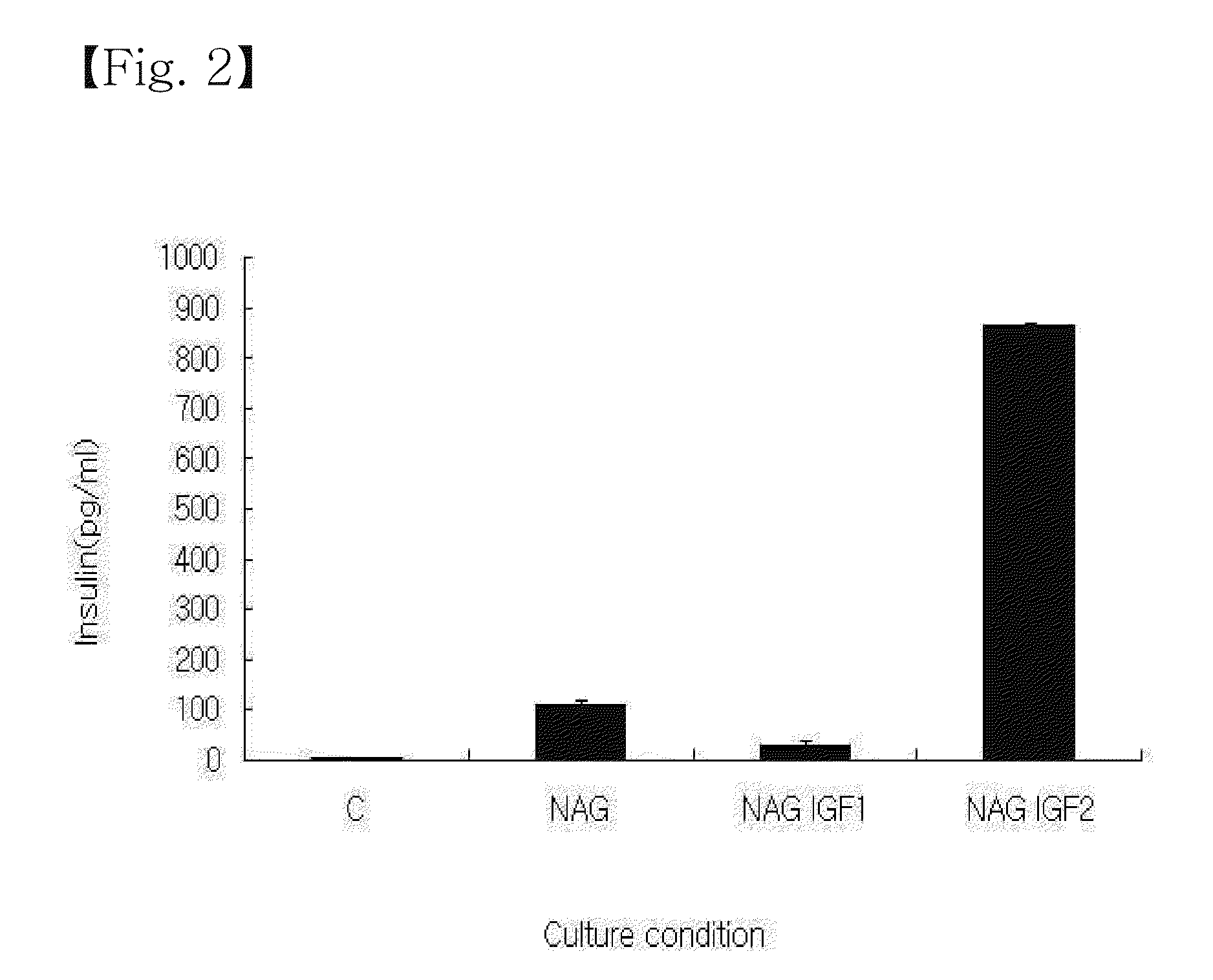
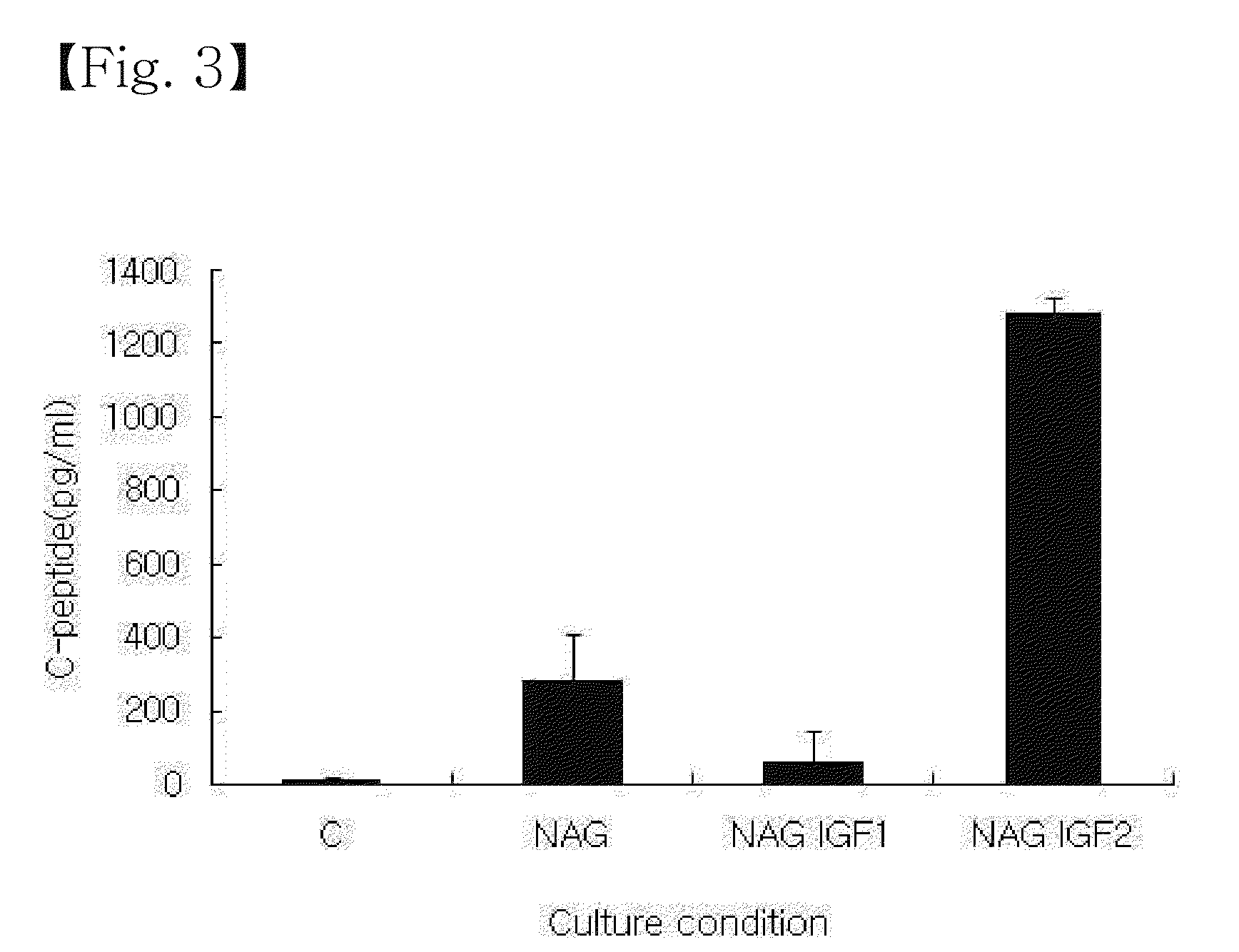
Disclosed is a method for differentiating human adult stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. Human adult stem cells, isolated from the subcutaneous adipose tissues around the eyes, are induced to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in a medium in the presence of cytokines and growth factors including B27 supplement, fibroblast growth factor-2, epidermal growth factor, nicotinamide, glucagon-like peptide-1, activin A, insulin-like growth factor, betacellulin, etc., with a glucose shift from a high concentration to a low concentration. Having the ability to producing insulin and C-peptide at high levels, the insulin-secreting cells can be excellent curatives for type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Owner:孔喜淑
Artificial islet or artificial pancreas and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110464880AEffective analog structureEffectively simulate physiological functionsProsthesisInsulin Secreting CellBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an artificial islet or artificial pancreas and a preparation method thereof. The artificial islet or artificial pancreas includes a supporting body with a porous structure andcells capable of secreting insulin and growing in the porous structure of the supporting body. The preparation method of the artificial islet or artificial pancreas comprises the steps that a PLGA porous sphere supporting body is prepared; the cells capable of secreting the insulin are planted in the PLGA porous sphere supporting body, and the cells planted in the PLGA porous sphere supporting body are detected. The construction of the artificial islet or artificial pancreas is based on the porous structure of PLGA or a polylactic acid polymer sphere and the good biodegradability and biocompatibility thereof, and effectively simulating the structure and physiological function of an islet is facilitated. The insulin secretory cells are set in the constructed artificial islet or artificial pancreas porous sphere, the cell morphology is good, the overall morphology and size are similar to normal mouse islets, and an effective solution is provided for solving the shortage of donors in clinical islet transplantation.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for constructing human islet-derived pancreatic stem cell line and method for differentiation of human islet-derived pancreatic stem cell line into insulin-producing cells
ActiveCN102899288APromote growthImprove survival rateMetabolism disorderNervous system cellsNeural cellInsulin Secreting Cell
The invention discloses a method for constructing a human islet-derived pancreatic stem cell line and a method for differentiation of the human islet-derived pancreatic stem cell line into insulin-producing cells. The pancreatic stem cell line is obtained by amplifying pancreatic stem cells in human pancreatic clusters, and is a potential source for multidirectional differentiation. When induced, the pancreatic stem cell line can differentiate to form neuron-like cells, adipose-like cells, osteoblast-like cells and functional islet-like cell clusters. By transplanting the functional islet-like cell clusters into a body of a diabetic nude mouse model, the blood glucose concentration of the nude mouse model can be reduced and reach a normal level within 24 days.
Owner:苏州厚朴惠康生物医药科技有限公司
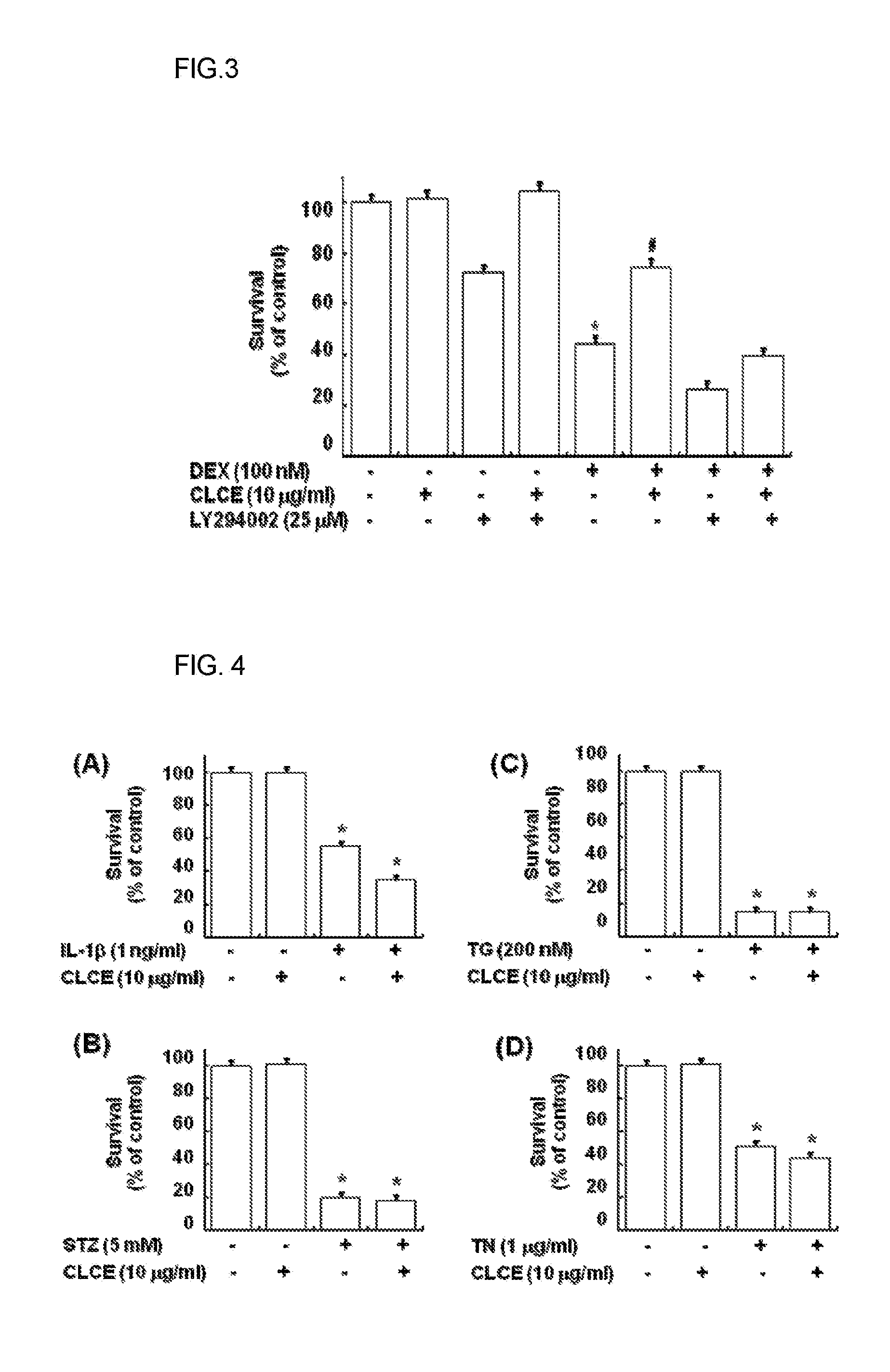
Pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of steroid-induced diabetes and health functional food
A pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating steroid-induced diabetes (SID) and a health functional food, and more particularly to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating SID and a health functional food, contain a Ceriporia lacerata culture extract as an active ingredient. The pharmaceutical composition and the health functional composition have the effect of protecting INS-1 insulin-secreting cells by blocking the steroid-mediated proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction of INS-1 insulin-secreting cells. Thus, the pharmaceutical composition and the health functional composition can be developed as the active ingredient of pharmaceutical or functional food compositions serving to protect or regenerate β-cells by blocking the steroid-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis of β-cells.
Owner:KIM BYOUNG CHEON
Method for induced differentiation of amnion epithelial stem cells into functional pancreatic beta cells as well as application of induced differentiation
PendingCN110423720ARich sourcesImprove hyperglycemiaMetabolism disorderPancreatic cellsInsulin Secreting CellIn vivo
The invention discloses a method for induced differentiation of amnion epithelial stem cells into pancreatic beta cells with biological functions. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) separation, culture, amplification and identification of amnion epithelial stem cells; 2) induced differentiation in vitro: the second-third generation of amnion epithelial stem cells are selected for experiments and subjected to induced differentiation by a culture medium containing nicotinamide. Insulin secretion cells which can express specific markers of pancreatic beta cells and have functions of normal pancreatic beta cells are obtained by 14 days of differentiation in vitro; and 3) in vivo transplantation: insulin secretion cells produced by induction are transplanted into type-1 diabetes miceand can obviously relive the hyperglycemia state of mice.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Culture medium for separating and inducing human adipose stem cells into pancreatic beta cells and use method of culture medium
InactiveCN104862268AGenetic change noNo riskVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsInsulin Secreting CellGene Modification
The invention provides a culture medium for separating and inducing human adipose stem cells into pancreatic beta cells and a use method of the culture medium. The optimal culture medium is designed; gene transfection is not required, so that the risk of gene modification and cancers is avoided, few induction steps are used, the use is simple, and the induction time is short and is shortened by 30% in comparison with the prior art; the culture medium is safe, nontoxic and high in success rate of induction. Moreover, after autogenous adipose mesenchymal stem cells are induced and differentiated into insulin-secreting cells, rejection and ethical problems are avoided after autotransplantation, and the safety is high, so that the clinical application prospect is wide. The culture medium is simple, feasible, low in cost and good in use effect.
Owner:GUIZHOU BEIKE FACTORR BIOTECH CO LTD
Process for preserving insulin-secreting cells intended to be transplanted in a patient
InactiveUS20090286315A1Reduce riskMaintain capacityMetabolism disorderDead animal preservationInsulin Secreting CellMicrobiology
Process for preserving insulin secreting cells intended to be transplanted, including the following steps: introducing an initial volume of culture medium and insulin-secreting cells into a culture container, providing a culture medium source, and replacing, at time intervals below 8 hours, the culture medium in the culture container with culture medium from the source so as to renew the culture medium contained in the container.
Owner:MACO PHARMA SA +2
Method for the differentiation of human adult stem cells into insulin-secreting cells
InactiveUS20100190251A1Improve efficiencyMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh concentrationInsulin-like growth factor
Disclosed is a method for differentiating human adult stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. Human adult stem cells, isolated from the subcutaneous adipose tissues around the eyes, are induced to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells in a medium in the presence of cytokines and growth factors including B27 supplement, fibroblast growth factor-2, epidermal growth factor, nicotinamide, glucagon-like peptide-1, activin A, insulin-like growth factor, betacellulin, etc., with a glucose shift from a high concentration to a low concentration. Having the ability to producing insulin and C-peptide at high levels, the insulin-secreting cells can be excellent curatives for type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Owner:KONG HEESUK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com