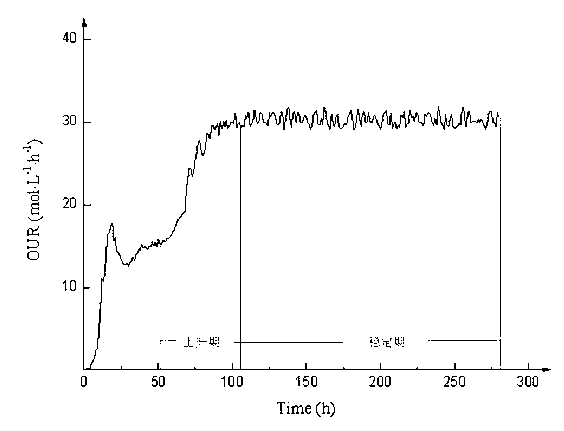
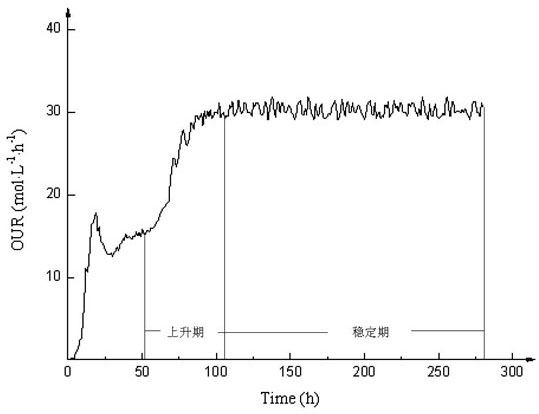
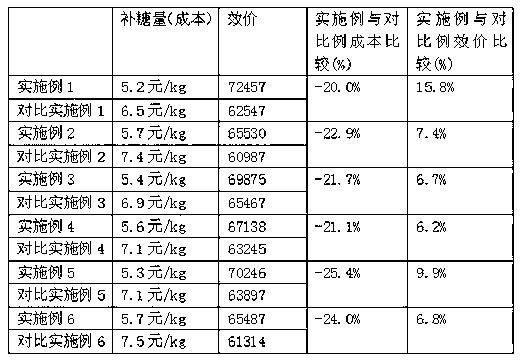
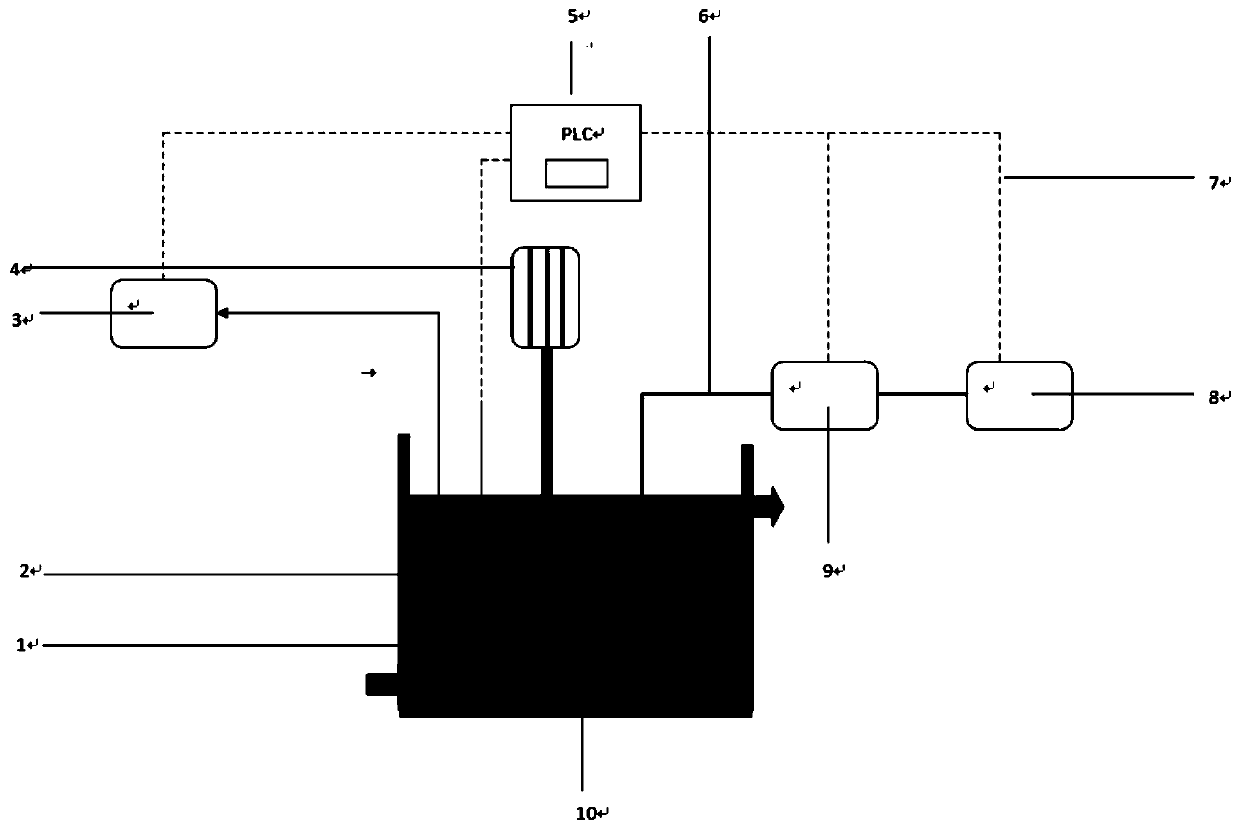
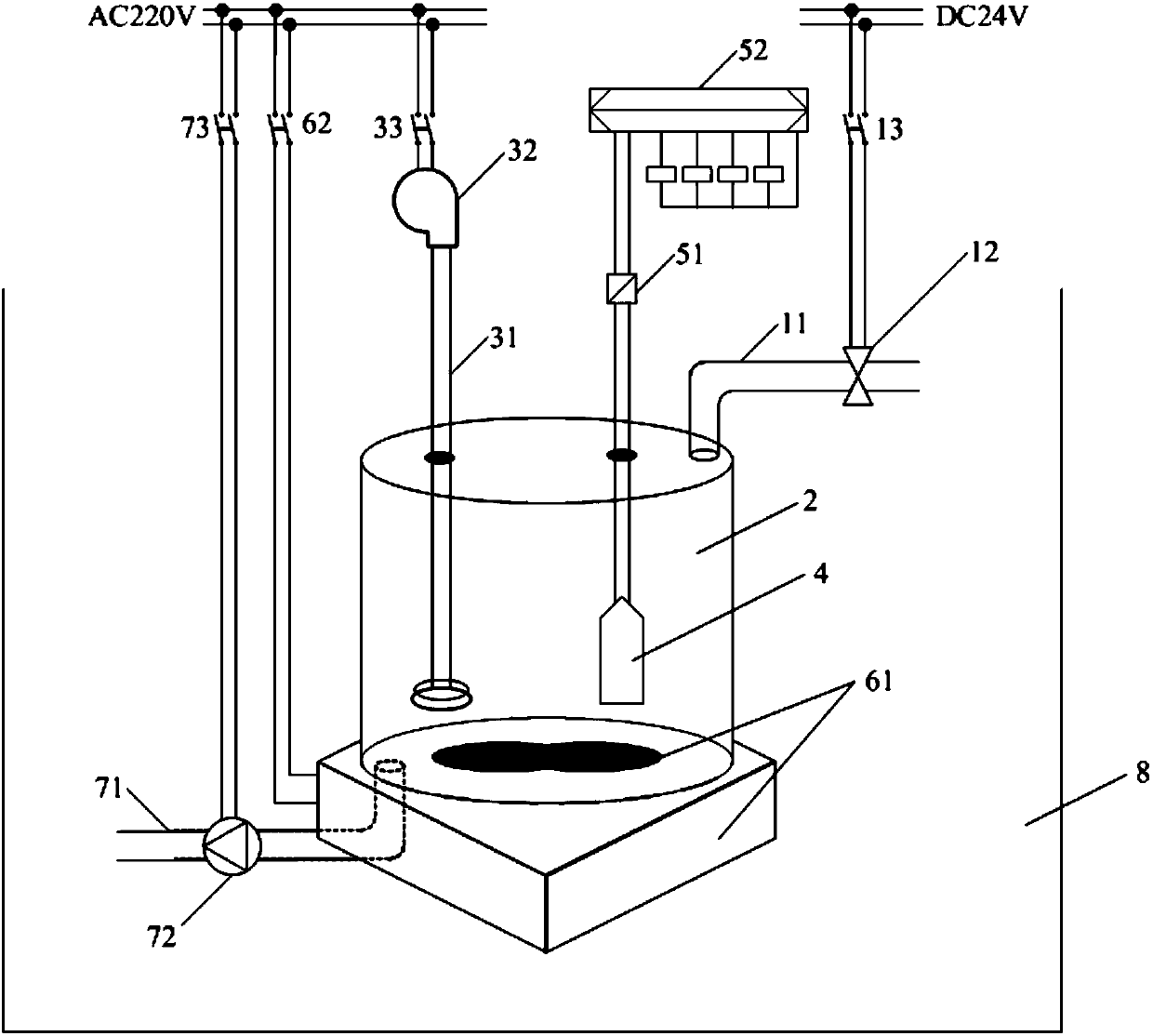
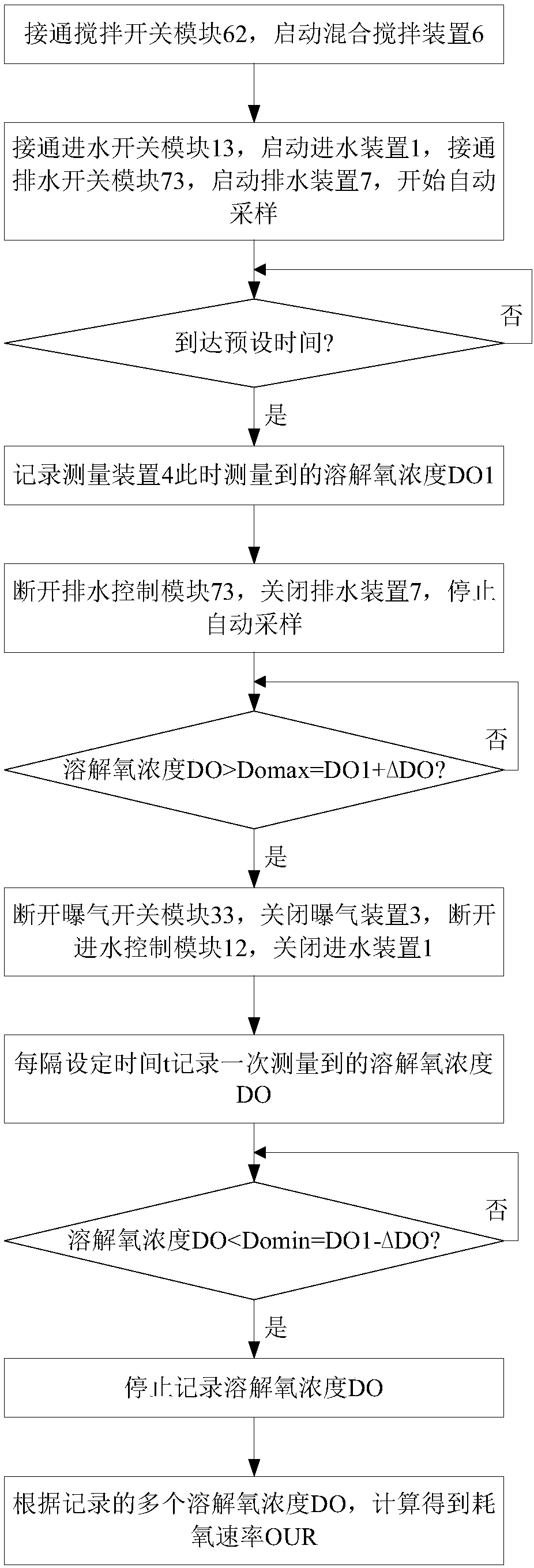
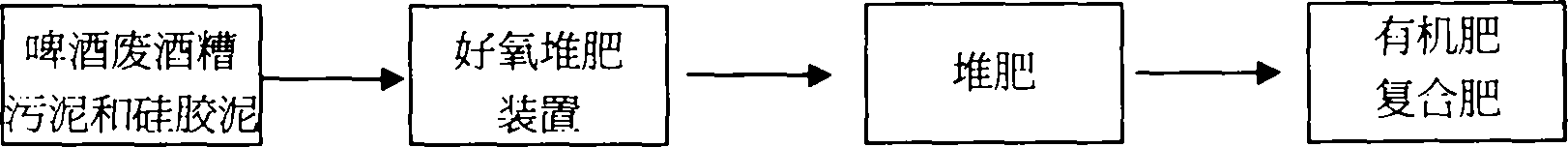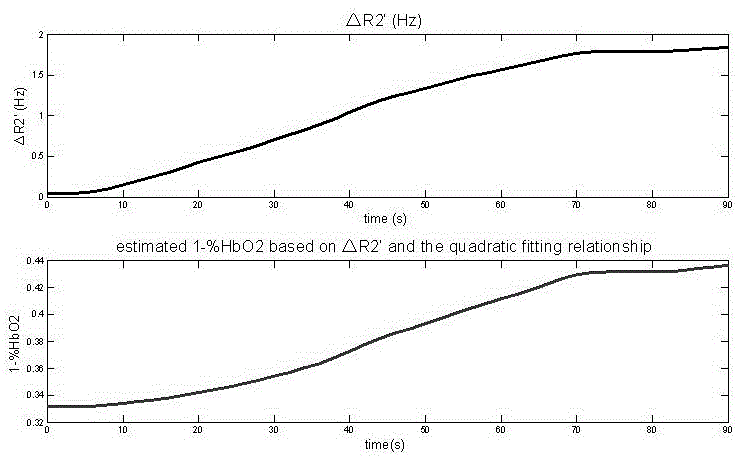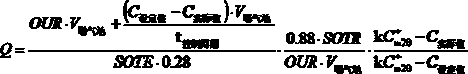Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Oxygen uptake rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxygen consumption the amount of oxygen consumed by the tissues of the body, usually measured as the oxygen uptake in the lung. The normal value is 250 ml/min (or 3.5 to 4.0 ml/kg/min), and it increases with increased metabolic rate.
Resin composition and a multilayered container
InactiveUS20030018114A1Excellent gas barrier propertiesHigh transparencySynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialPolymer scienceDouble bond
The present invention provides a resin composition having an oxygen scavenging function. The resin composition comprises a gas barrier resin (A), a thermoplastic resin (B) other than the gas barrier resin (A), and a compatibilizer (C), wherein the gas barrier resin (A) has an oxygen transmission rate of 500 ml.20 mum / m2.days.atm (20° C., 65% RH) or less, the thermoplastic resin (B) has a carbon-carbon double bond, and an oxygen absorption rate of the resin composition is 0.001 m / m2.day or more.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Control device for fermenter
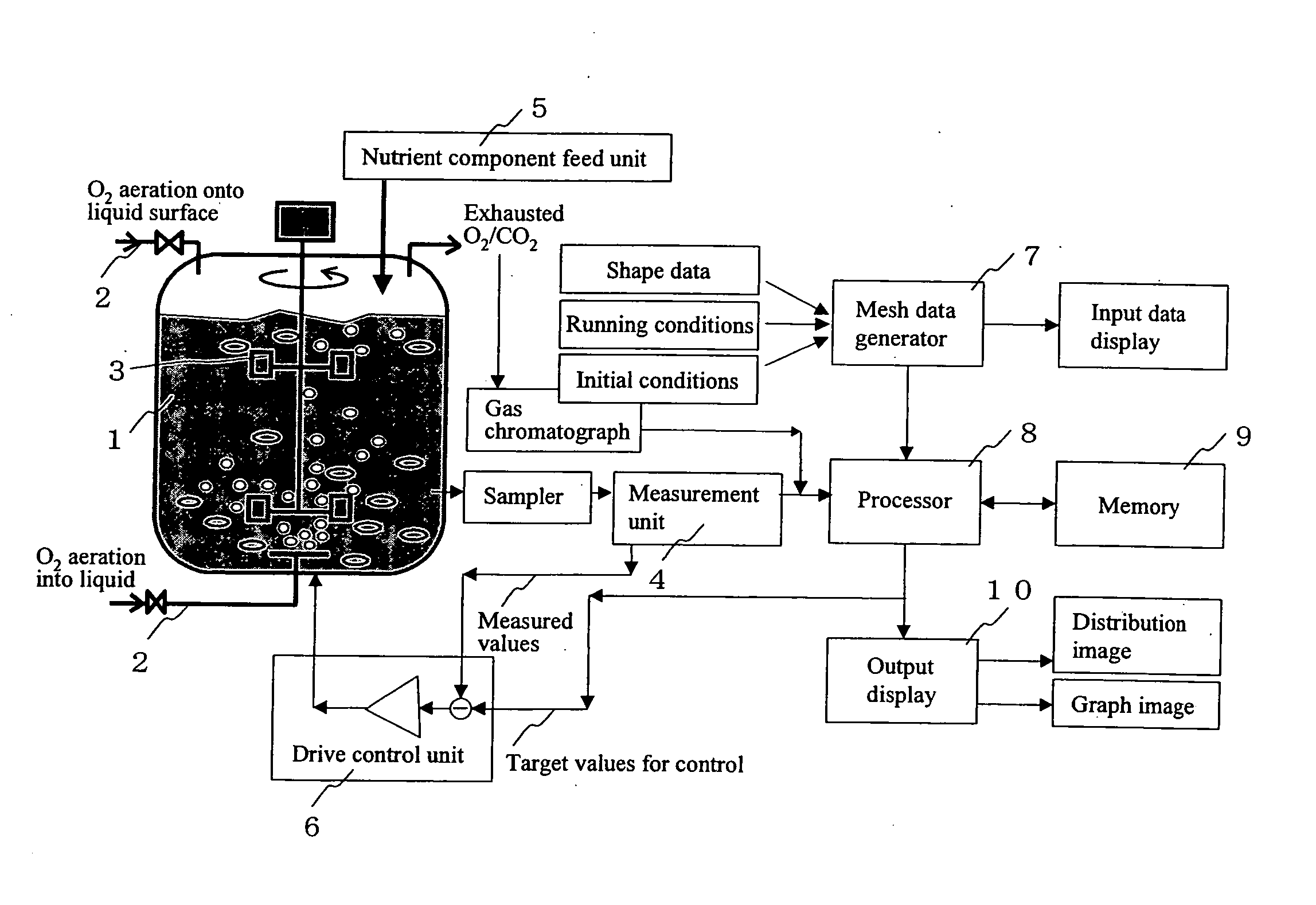
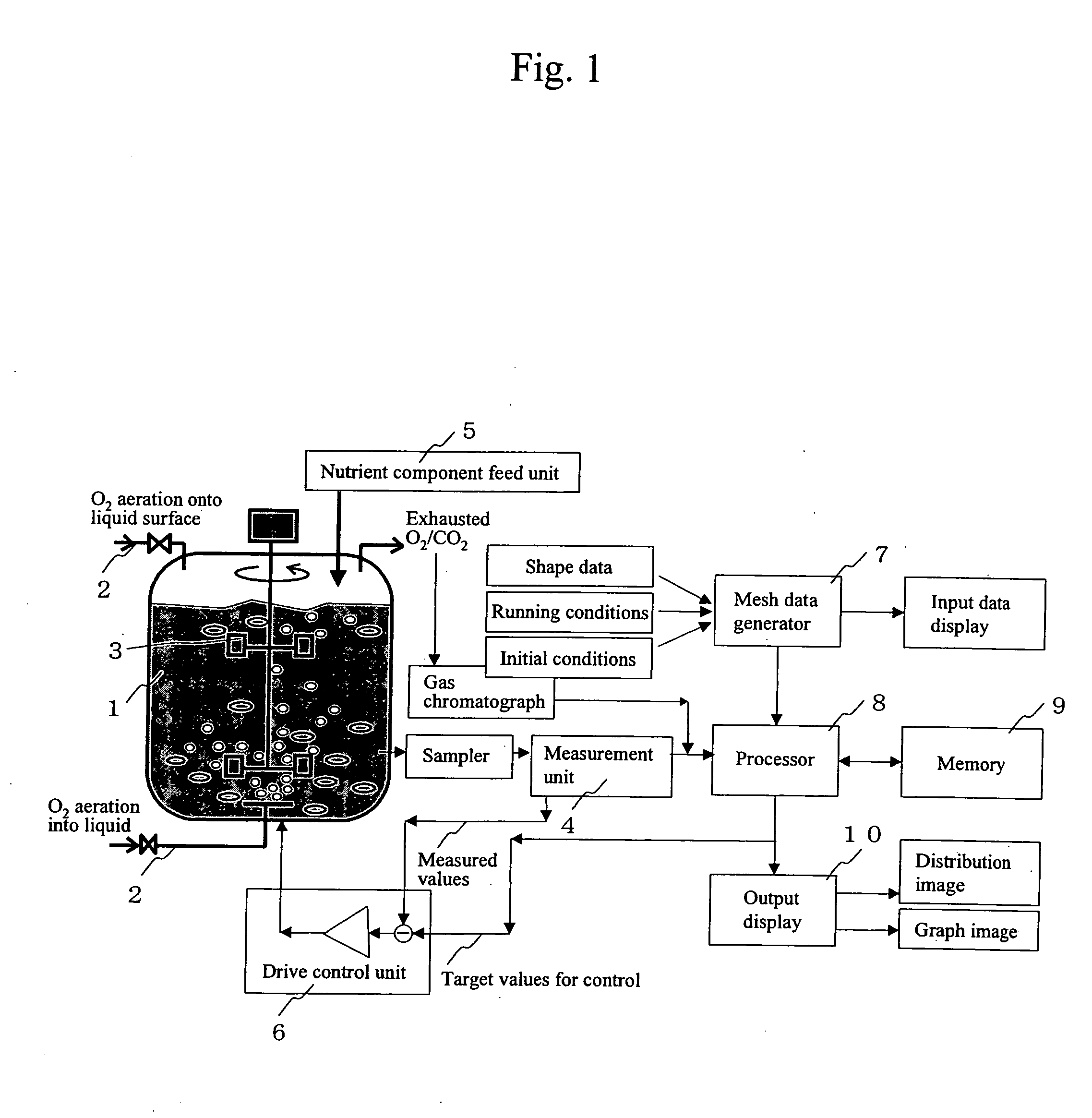
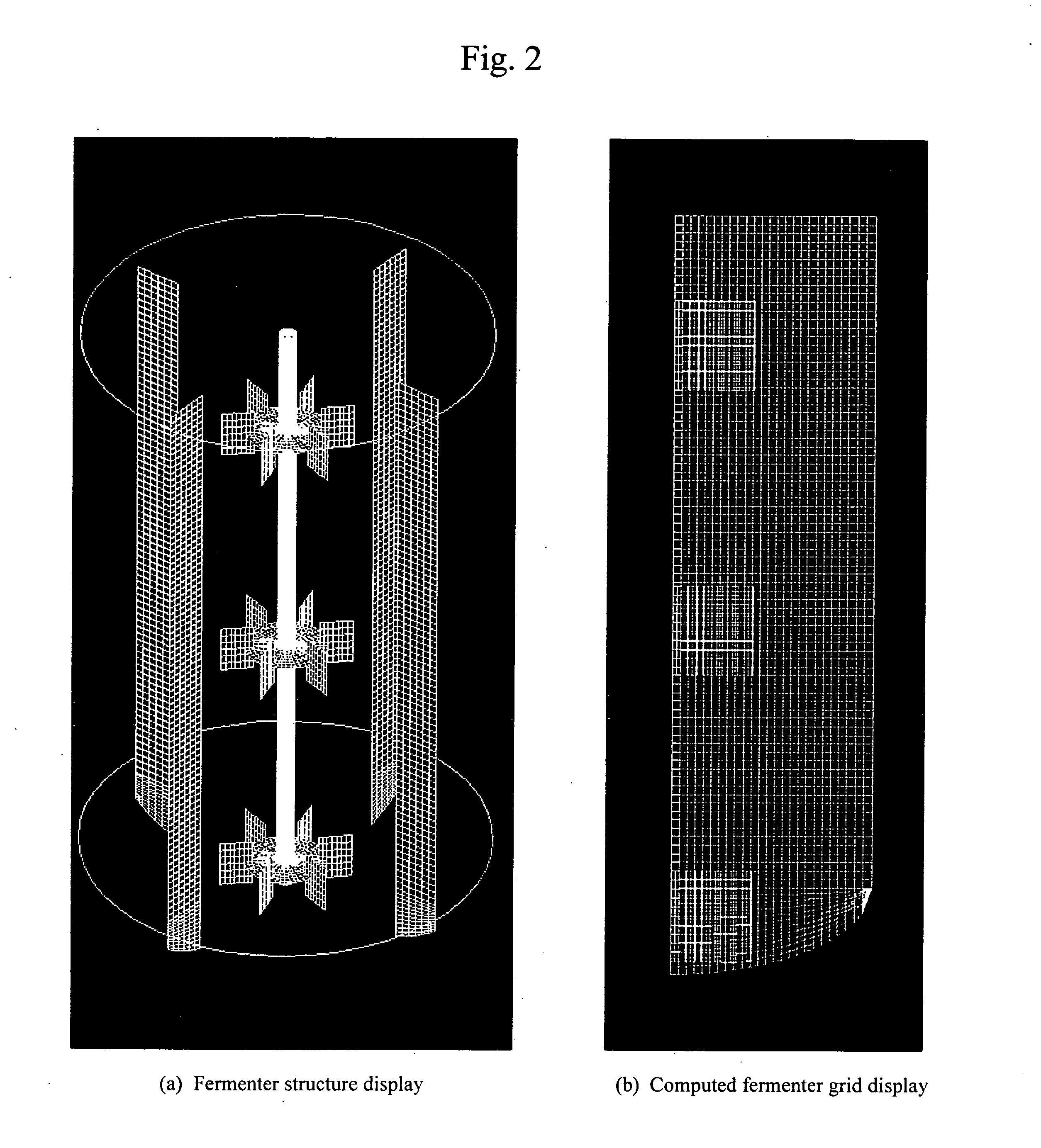
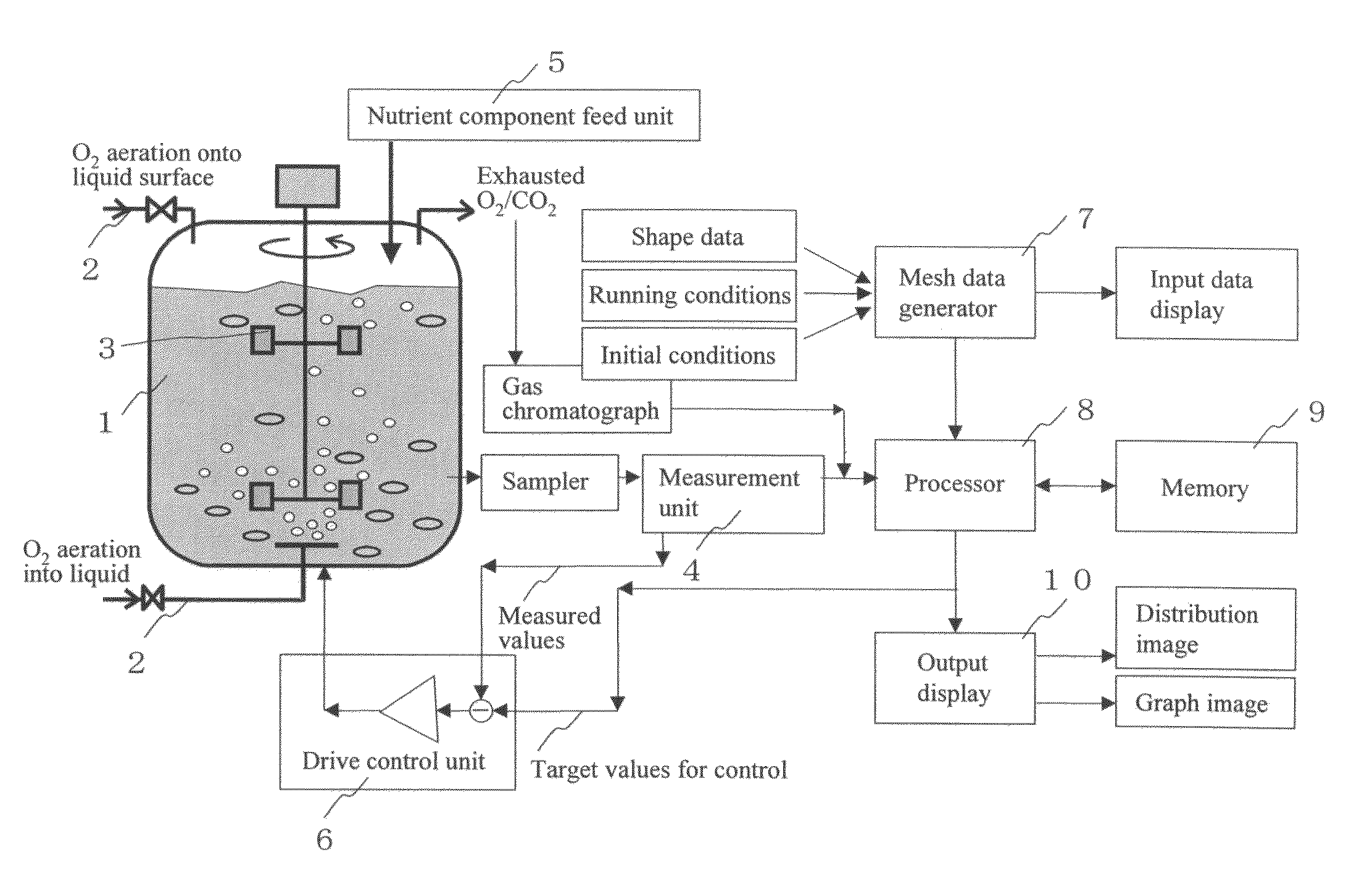
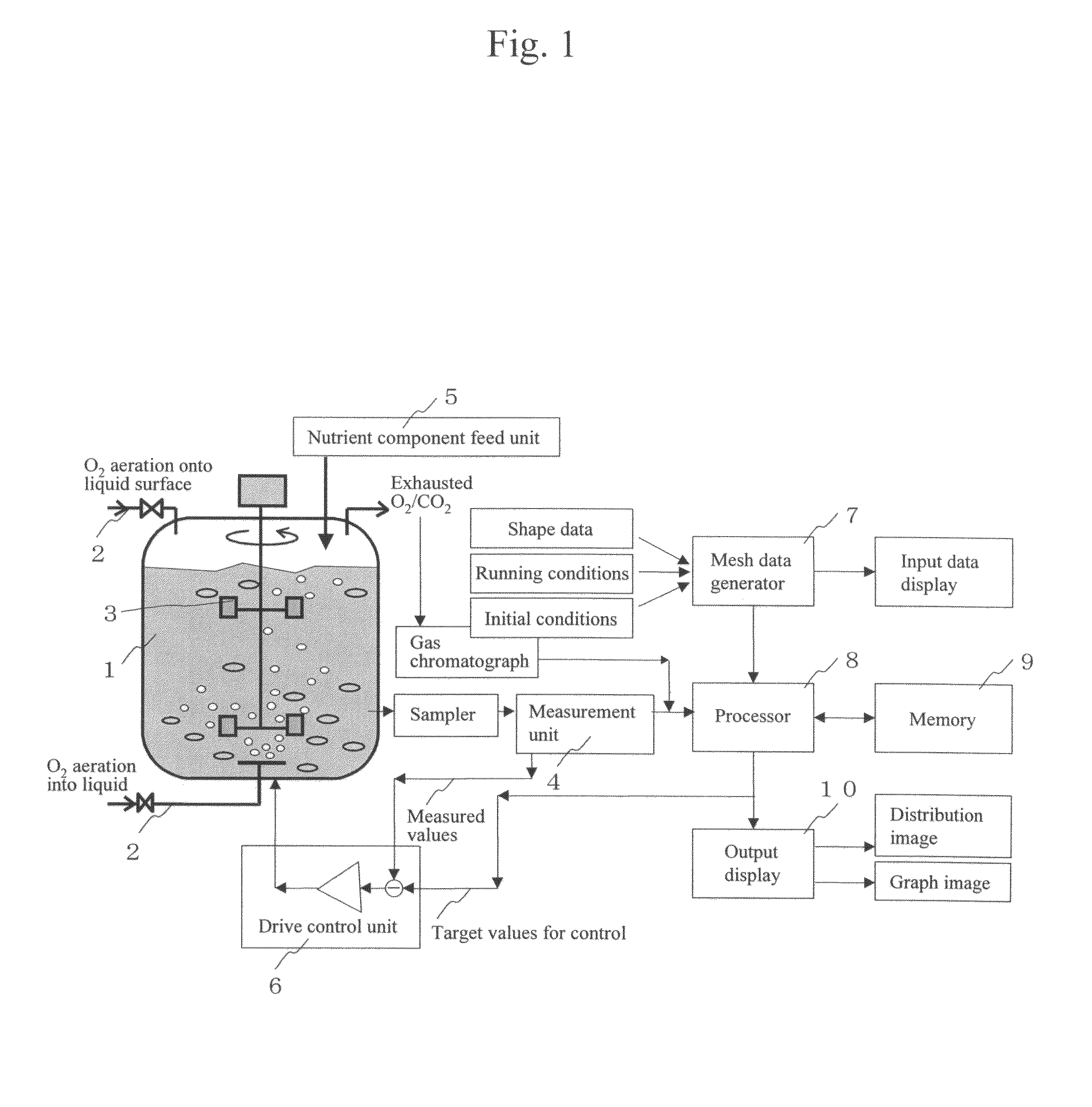
InactiveUS20060216818A1High yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSampled-variable control systemsDiffusionOxygen
The present invention allows biomass and / or biomass-produced components to be obtained at high yields by executing numeric simulation of flow to reasonably identify the running conditions suitable for a fermenter. The control device according to the present invention comprises an input means for entering measured data from a measurement means, which measures nutrient components, the concentrations of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and biomass in a culture medium; a computation means for calculating nutrient components uptake rate, oxygen uptake rate and carbon dioxide exhaust rate per unit amount of biomass from the measured data entered at the aforementioned input means, as well as volumetric mass transfer coefficient kLa from turbulent energy k and a turbulent energy dissipation rate e, both of which are calculated by a transport equation, as well as a diffusion coefficient D, followed by calculating the concentrations of the nutrient components, dissolved oxygen, and dissolved carbon dioxide in any area in the fermenter using an algorithm to numerically integrate a differential equation describing variations in medium components over time from the calculated nutrient components uptake rate, the calculated oxygen uptake rate, the calculated carbon dioxide exhaust rate, and the calculated volumetric mass transfer coefficient kLa; and a display means for displaying concentration distributions of the nutrient components, dissolved oxygen, and dissolved carbon dioxide in the fermenter based on the concentrations of the nutrient components, dissolved oxygen, and carbon dioxide in any area of the fermenter calculated at aforementioned computation means.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT SERVICES
Resin composition and a multilayered container
InactiveUS6822031B2Maintain good propertiesHigh transparencySynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialPolymer scienceDouble bond
The present invention provides a resin composition having an oxygen scavenging function. The resin composition comprises a gas barrier resin (A), a thermoplastic resin (B) other than the gas barrier resin (A), and a compatibilizer (C), wherein the gas barrier resin (A) has an oxygen transmission rate of 500 ml.20 mum / m<2>.days.atm (20° C., 65% RH) or less, the thermoplastic resin (B) has a carbon-carbon double bond, and an oxygen absorption rate of the resin composition is 0.001 m / m<2>.day or more.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
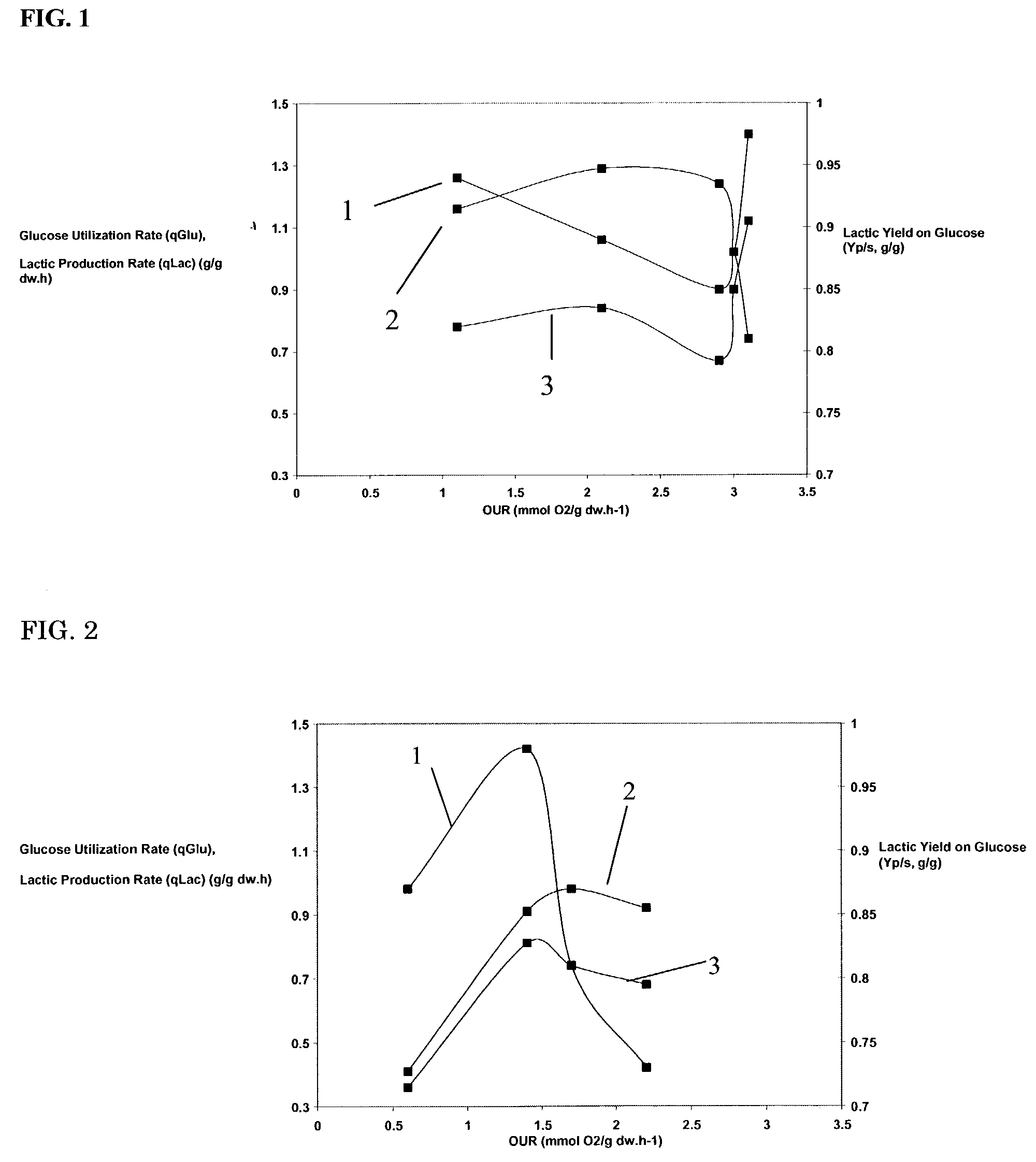
Fermentation process using specific oxygen uptake rates as a process control
Specific oxygen uptake (OUR) is used as a process control parameter in fermentation processes. OUR is determined during at least the production phase of a fermentation process, and process parameters are adjusted to maintain the OUR within desired ranges. The invention is particularly applicable when the fermentation is conducted using a microorganism having a natural PDC pathway that has been disrupted so that it no longer functions. Microorganisms of this sort often produce poorly under strictly anaerobic conditions. Microaeration controlled by monitoring OUR allows the performance of the microorganism to be optimized.
Owner:CARGILL INC
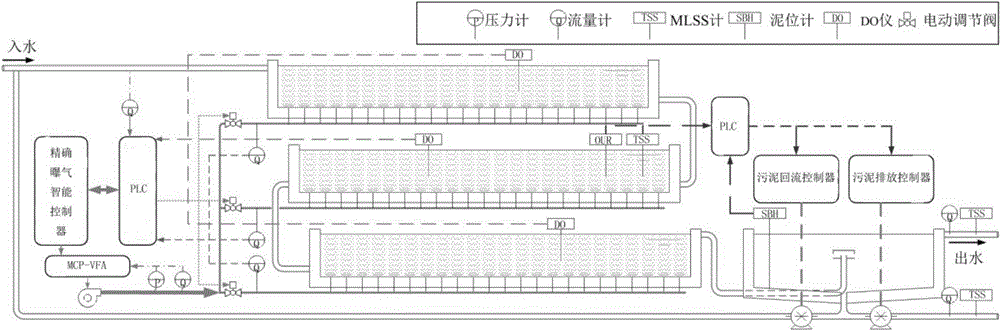
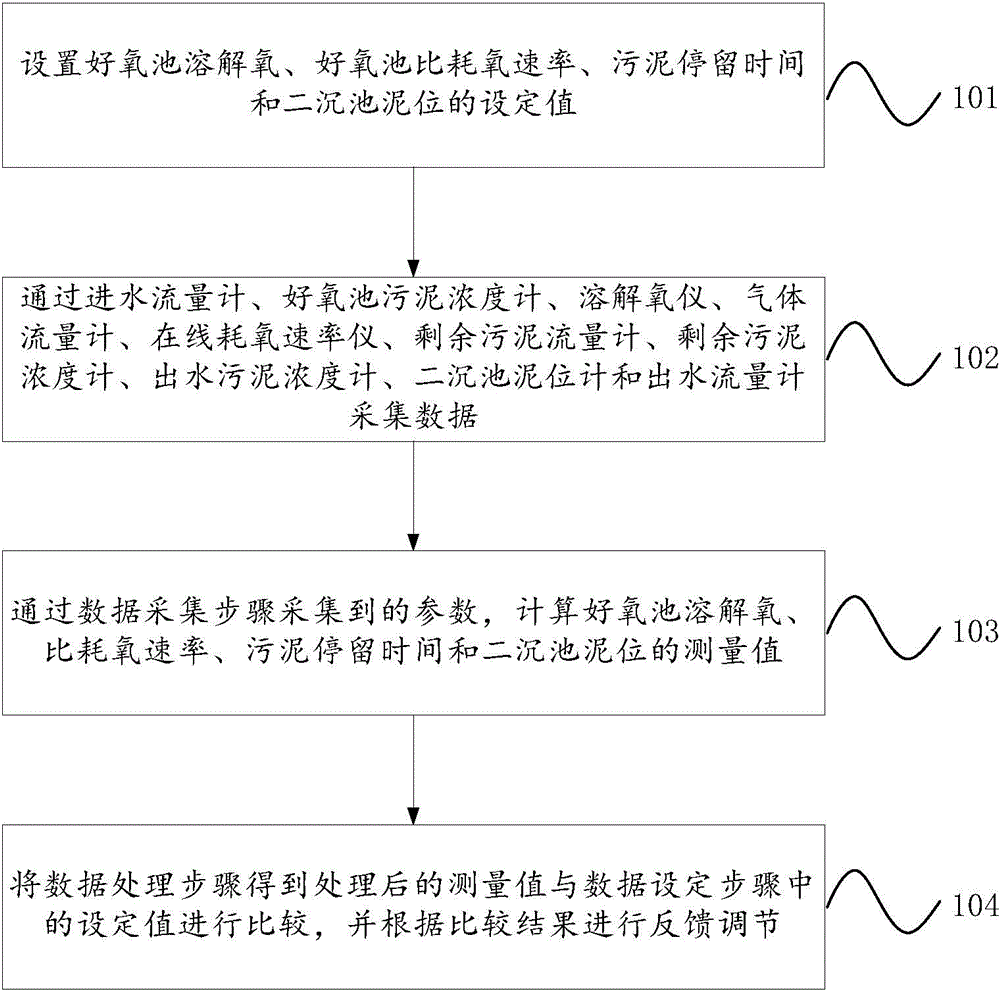
Method for automatically controlling dissolved oxygen, sludge load and sludge age in real time in sewage plant
ActiveCN104090488ARealize automatic operationImprove effluent qualityTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentWater volumeSludge
The invention provides a method for automatically controlling dissolved oxygen, the sludge load and the sludge age in real time in a sewage plant. The method includes the following steps: setting data, wherein parameter setting is carried out on the aerobiotic pool dissolved oxygen, the aerobiotic pool specific oxygen uptake rate, the sludge age and the secondary sedimentation tank sludge position in a system; collecting the data, wherein system parameters are collected by instruments installed at all positions of the system; processing the data, wherein actual values of the aerobiotic pool dissolved oxygen, the specific oxygen uptake rate, the sludge age and the secondary sedimentation tank sludge position are calculated according to the collected system parameters; adjusting the system, wherein the actual values after processing are compared with a set parameter value, and automatic feedback adjustment is carried out on the system according to a comparative result. By means of the method, inlet water quality and volume changes can be monitored on line in real time, impact of inlet water quality and the inlet water volume to the system are automatically controlled, adjusted and restrained through the system, the sludge load is basically stabilized by stabilizing the specific oxygen uptake rate, and meanwhile the sludge age and the aerobiotic pool dissolved oxygen can be stabilized to accordingly stabilize the outlet water quality of the system.
Owner:北京清控人居环境研究院有限公司
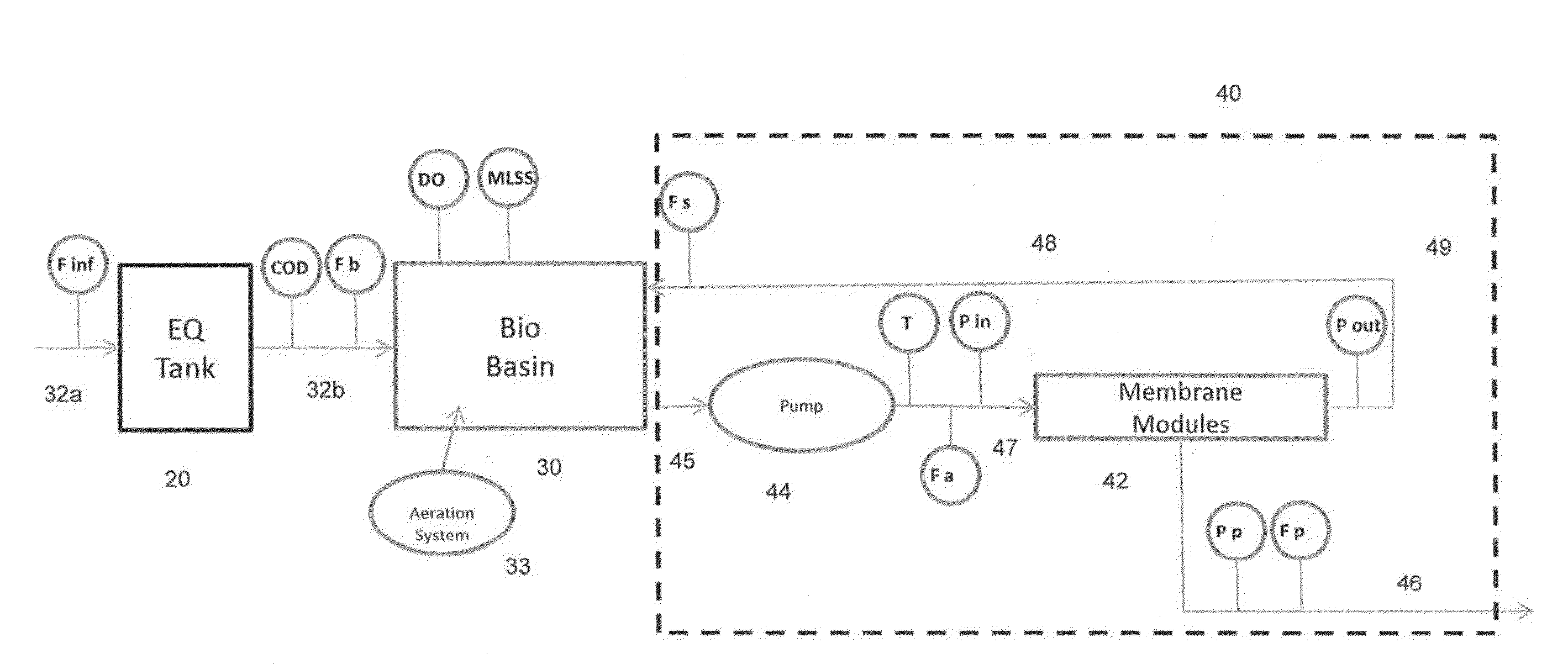
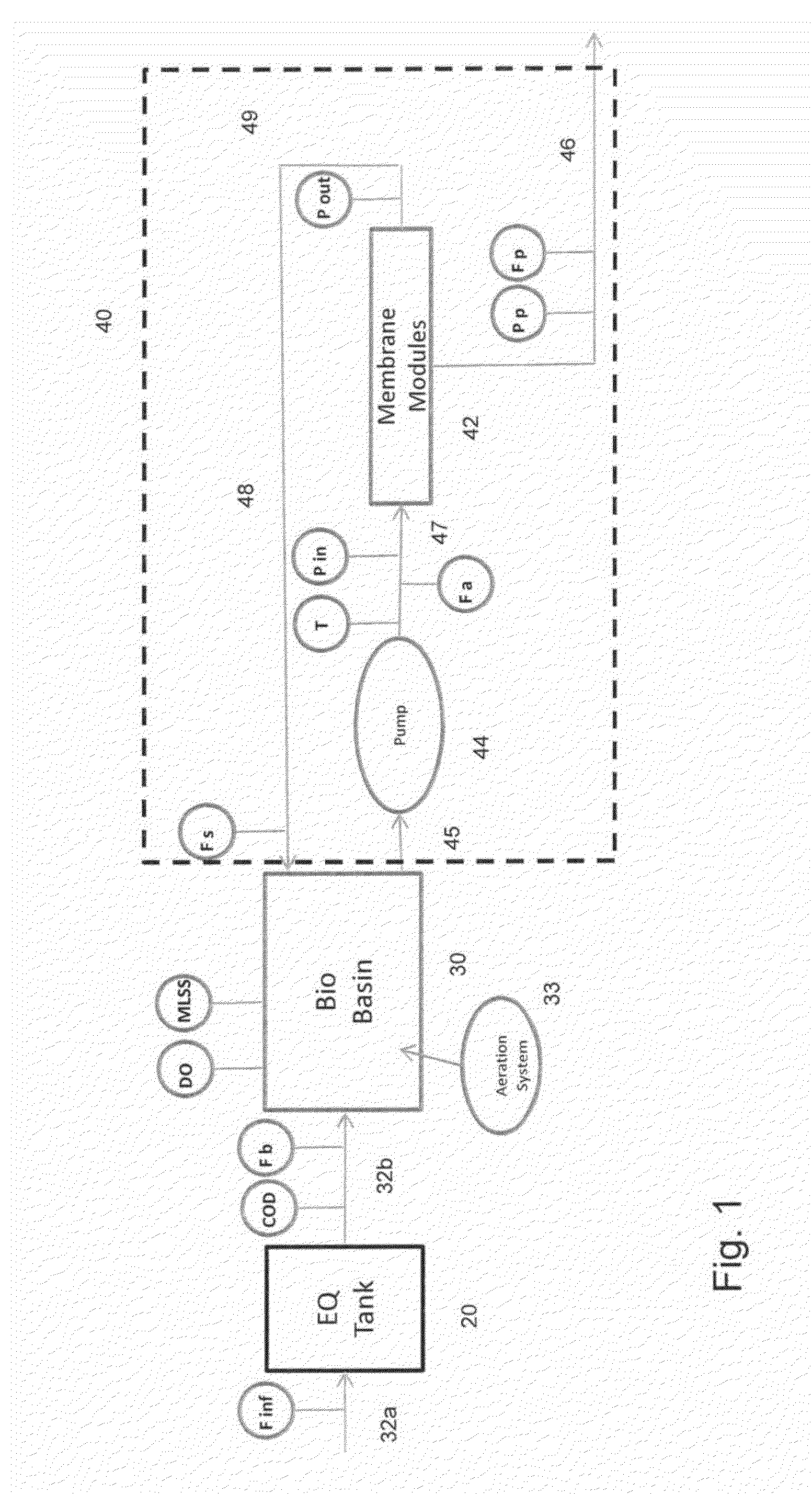
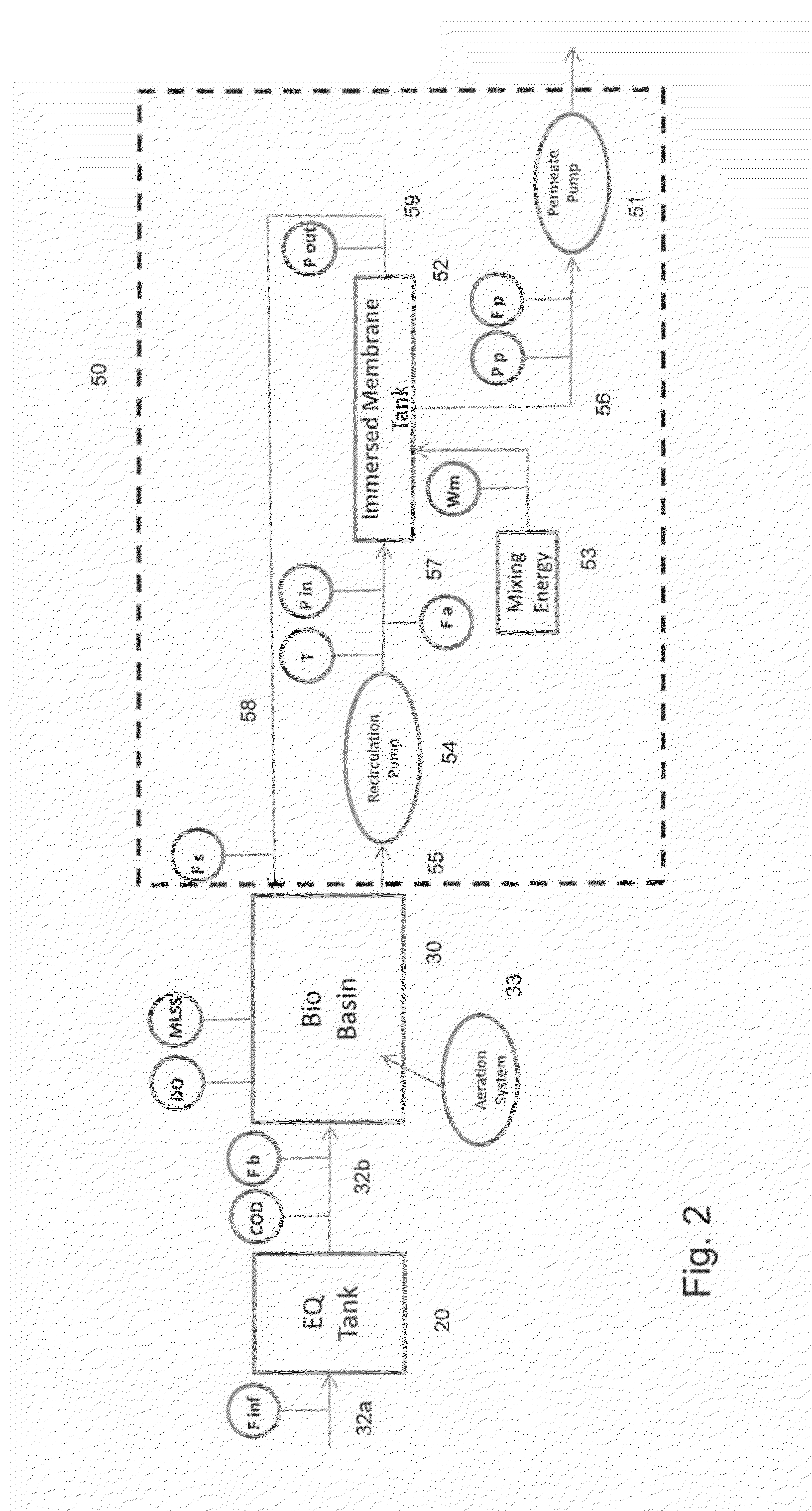
Advanced control system for wastewater treatment plants with membrane bioreactors
InactiveUS20130001142A1Semi-permeable membranesWater treatment parameter controlControl systemMembrane bioreactor
An advanced control system for a membrane bioreactor based wastewater treatment plant is disclosed. The disclosed control system comprises a membrane bioreactor (MBR) system and a microprocessor based controller that receives signals corresponding to selected measured MBR parameters and calculates or estimates one or more MBR calculated parameters including Membrane Conductivity (Fxc); and / or Oxygen Uptake Rate (OUR). The microprocessor based controller compares one or more calculated or estimated MBR parameters to prescribed setpoints or desired ranges and governs one or more pumps and valves in the MBR system to adjust the cleaning cycle the MBR system, the MBR flows in the MBR system, or the influent flow to the biological basin in response thereto.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
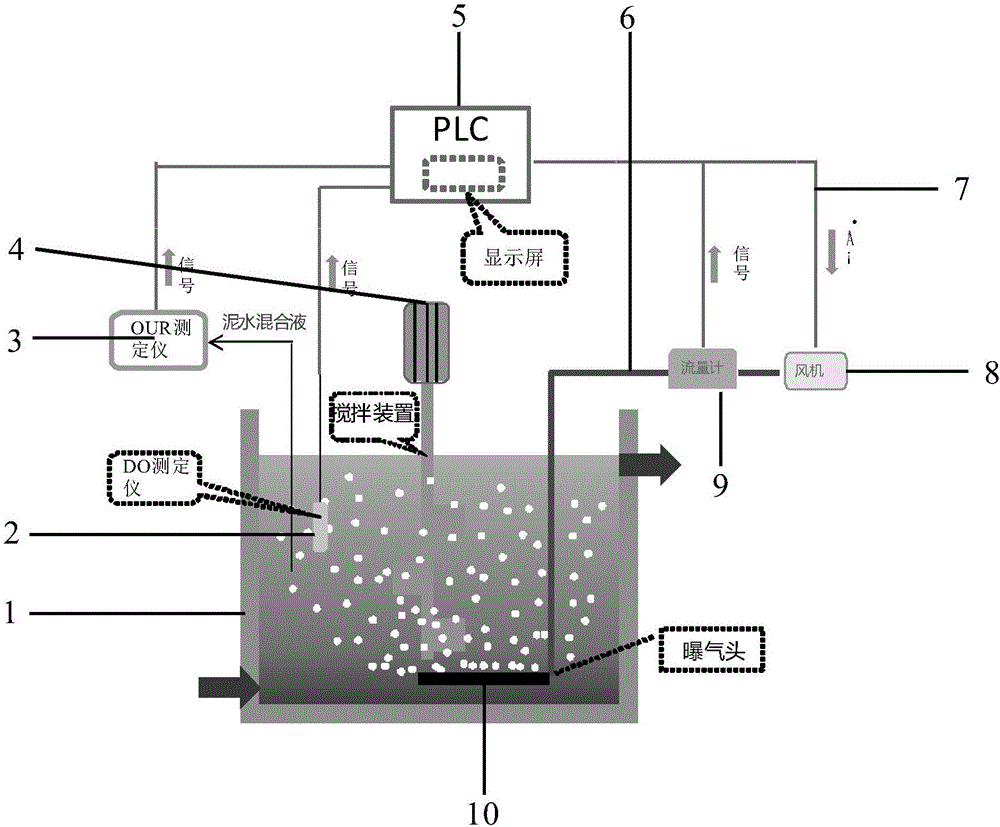
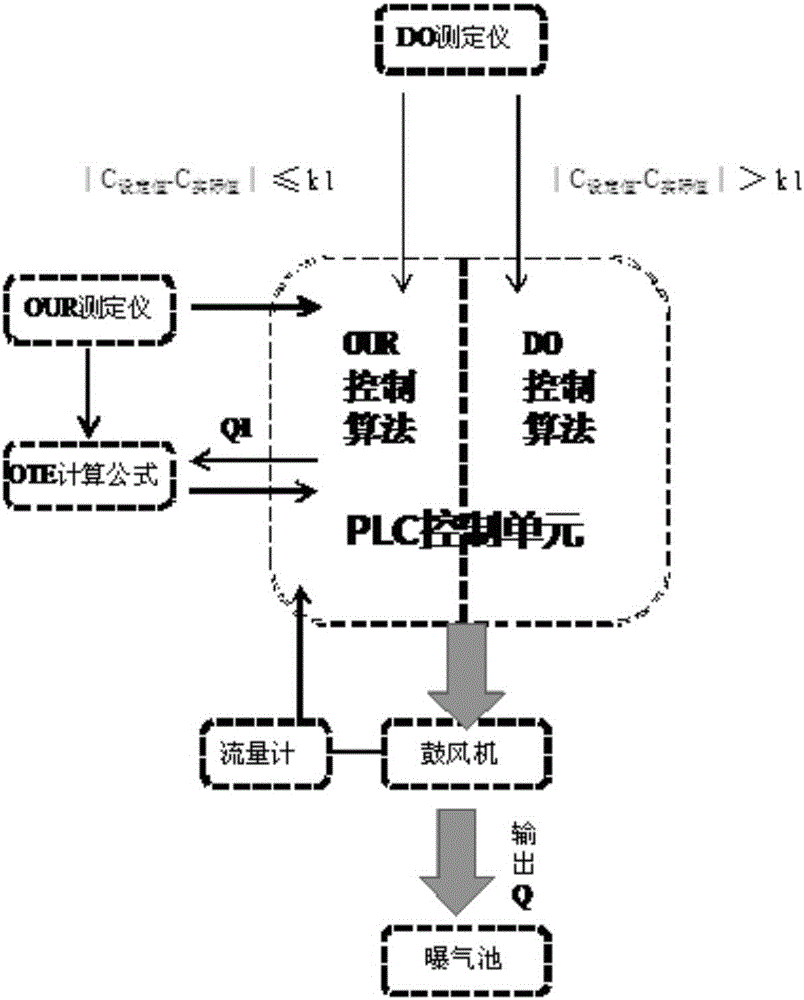
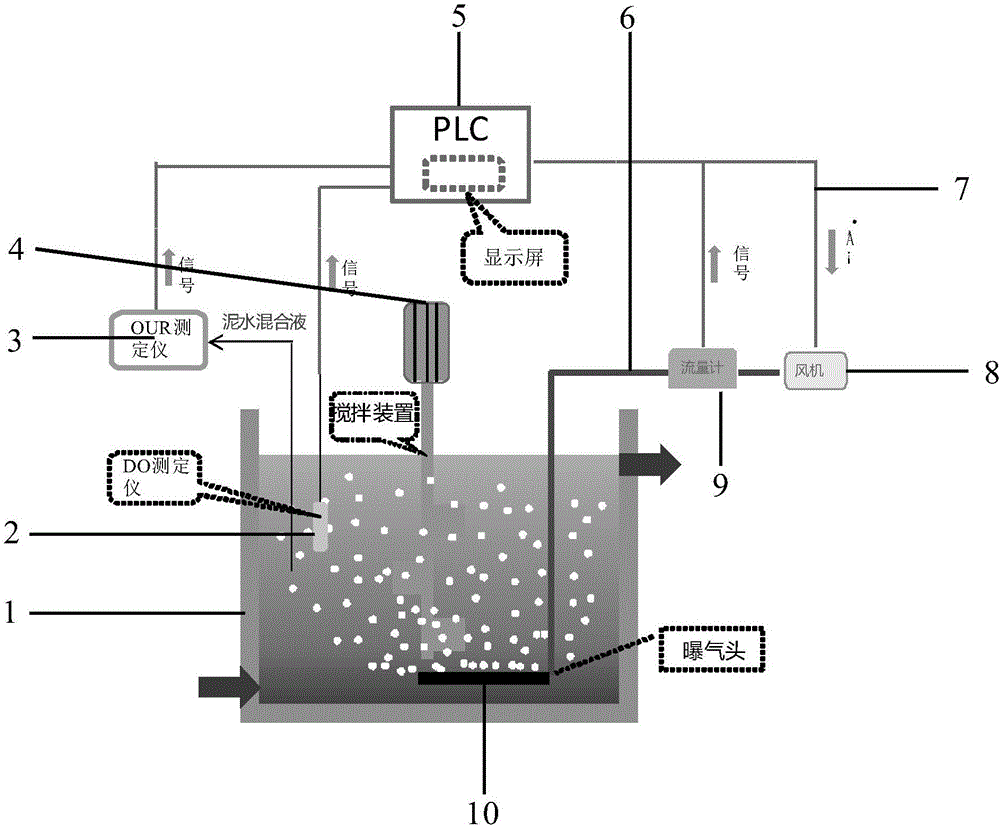
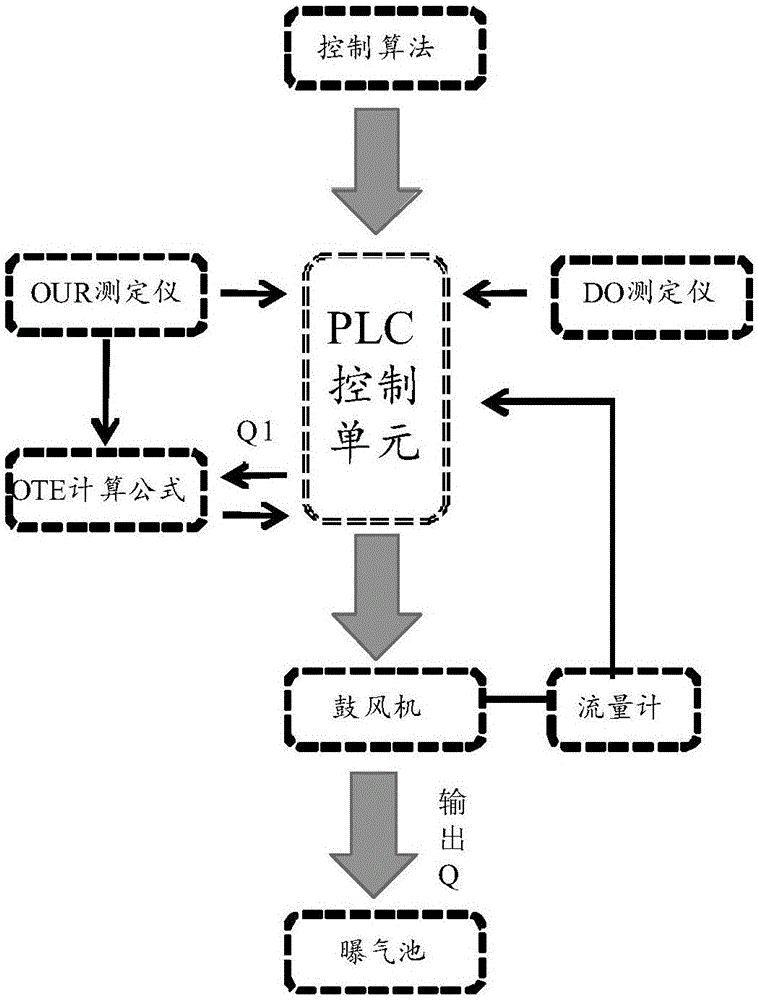
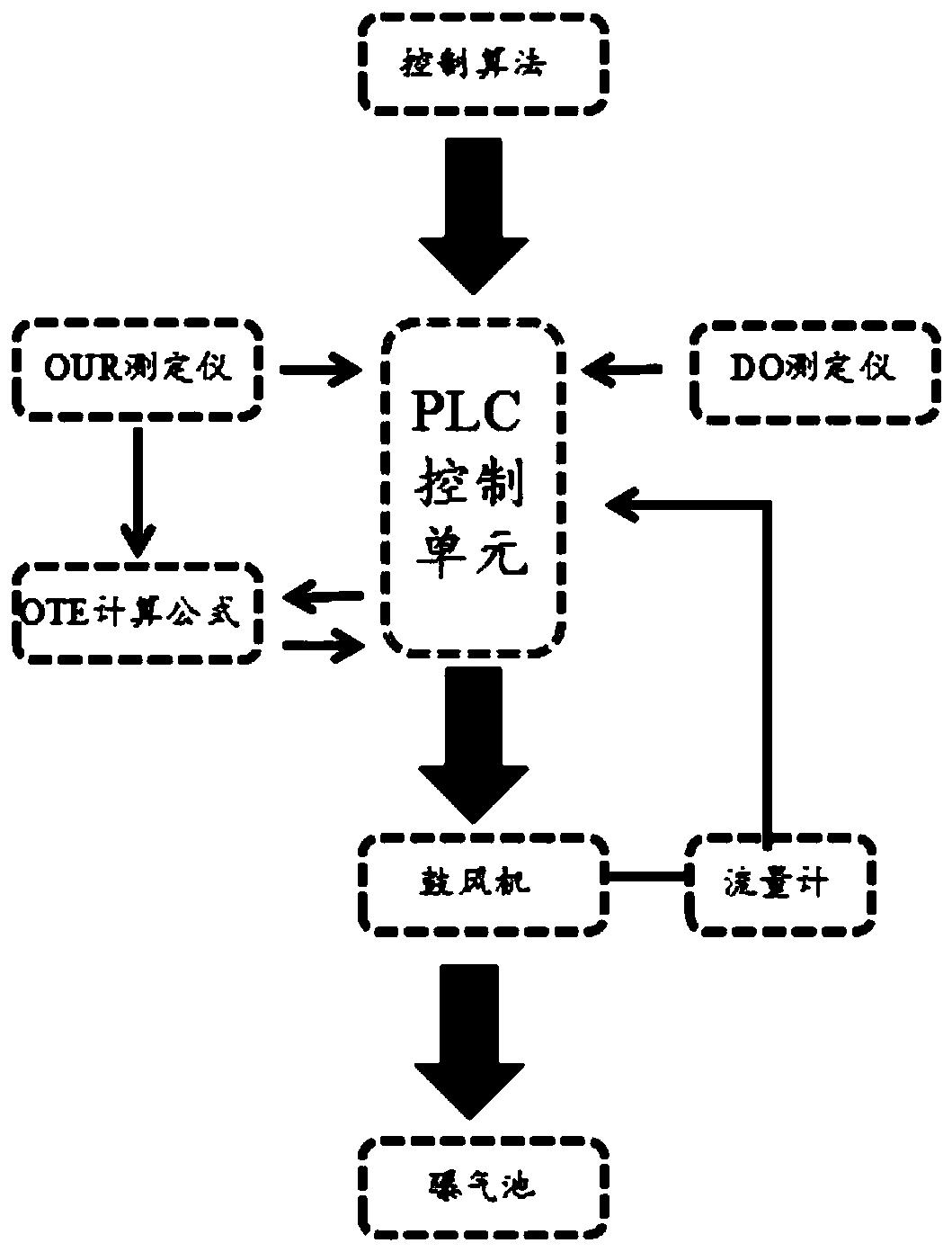
Aeration control system based on oxygen uptake rate tester and method of aeration control system
InactiveCN106277299ASmall adjustmentPrecision AerationWater treatment parameter controlSustainable biological treatmentSludgeWater quality
The invention discloses an aeration control system based on an oxygen uptake rate tester. The aeration control system comprises a data collection unit, a PLC control unit and an aeration unit, wherein the data collection unit comprises an OUR tester and a DO tester; the aeration unit comprises an air blower, a micro-hole aeration head and a flow meter; and the PLC control unit comprises hardware including a control cabinet, a display screen and the like as well as control software, the control software comprises a control unit and a DO feedback protecting unit, and the control unit is mainly based on an OUR value, an OTE value and a dissolved oxygen value. The invention further provides a method for carrying out aeration control by virtue of the aeration control system. According to the method, a precise aeration algorithm based on OUR and a DO feedback protecting module are combined, so that the sludge activity can be accurately monitored, the aeration quantity can be precisely controlled, the long-term over-high or over-low dissolved oxygen caused when the system malfunctions can be solved, and the purposes of long-term and stable effluent quality, energy saving and consumption reduction are achieved.
Owner:尚川(北京)水务有限公司
System and method for monitoring municipal saprobia inhibitive ability in real time based on oxygen uptake rate (OUR)
ActiveCN102520016AGuaranteed to be airtightEliminate distracting factorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSiphonProgrammable logic controller
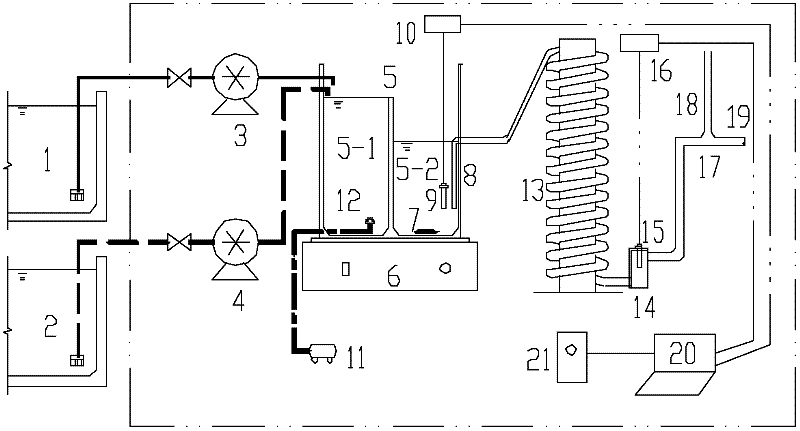
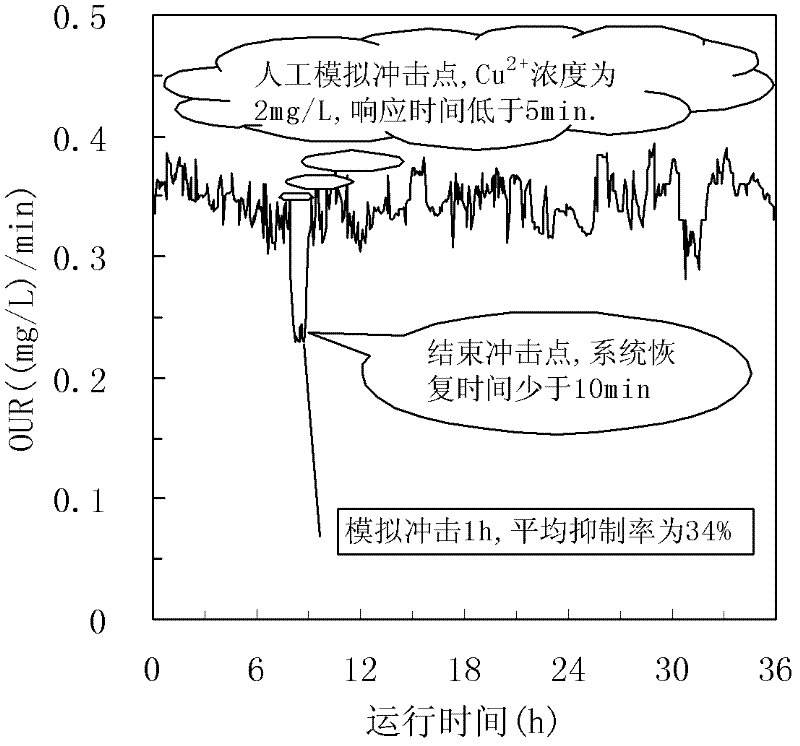
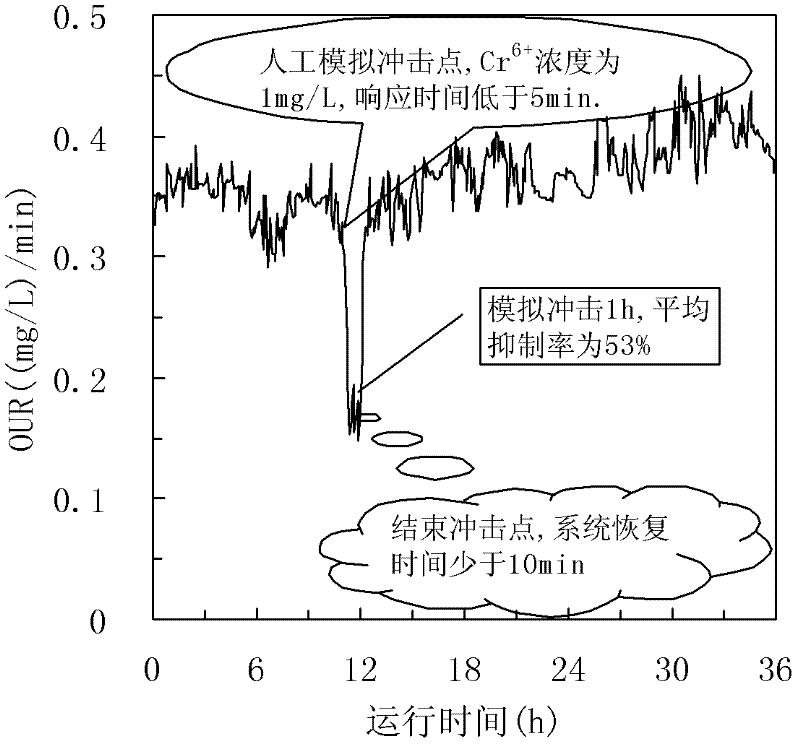
A system for monitoring municipal saprobia inhibitive ability in real time based on oxygen uptake rate (OUR) comprises an aeration siphon device communicated with a sewage supplying system and a sludge supplying system. The aeration siphon device is composed of an aeration groove and a siphon groove in adjoining mode, the wall of the aeration groove is higher than that of the siphon groove, the aeration groove is communicated with the sewage supplying system and the sludge supplying system, and the siphon groove is communicated with an inlet of a closed coiler flow-pushing type bioreactor through a siphon tube. A dissolved oxygen (DO) detection system detects DO values of the inlet and an outlet of the closed coiler flow-pushing type bioreactor, and the signal output end of the DO detection system is connected onto a programmable logic controller (PLC) control system which is connected with an alarm system. The core part of system for monitoring municipal saprobia inhibitive ability in real time adopts the closed coiler flow-pushing type bioreactor so as to monitor the DO value of the inlet and the DO of the outlet in real time, automatically calculate mutation condition of activated sludge OUR, determines OUR mutation rate with different inhibition degree through plenty of experiments, and judge inhibitable degree of the saprobia by comparing automatically calculated OUR mutation rate with a preset value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for determining activated sludge treatment capacity
ActiveCN105699601AQuick judgmentMake up for the lack of processing power that is difficult to assessWater treatment parameter controlSustainable biological treatmentEngineeringSewage
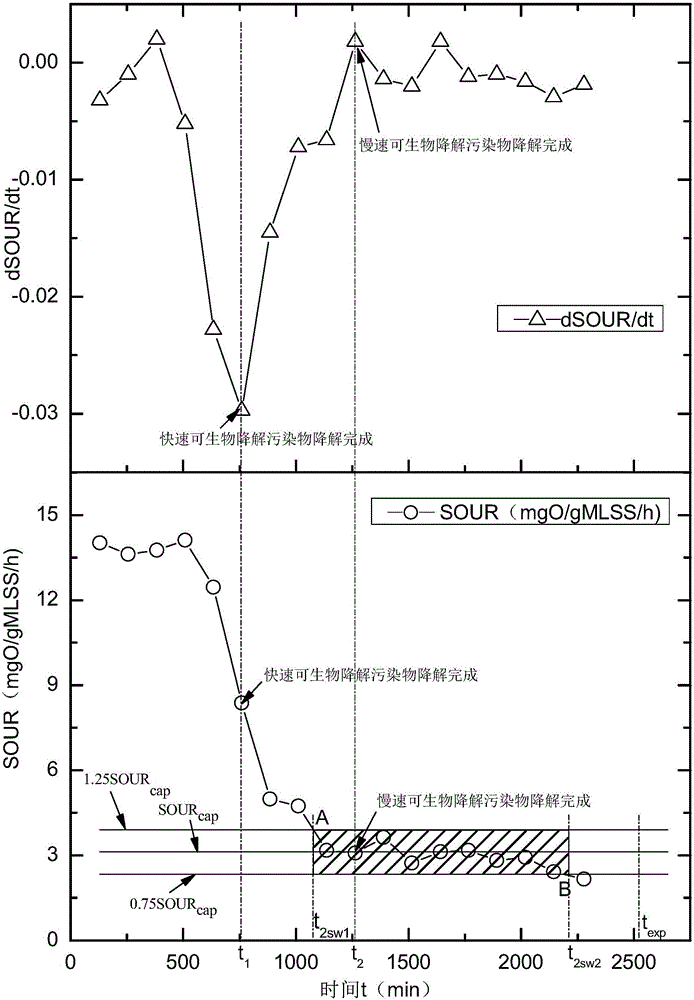
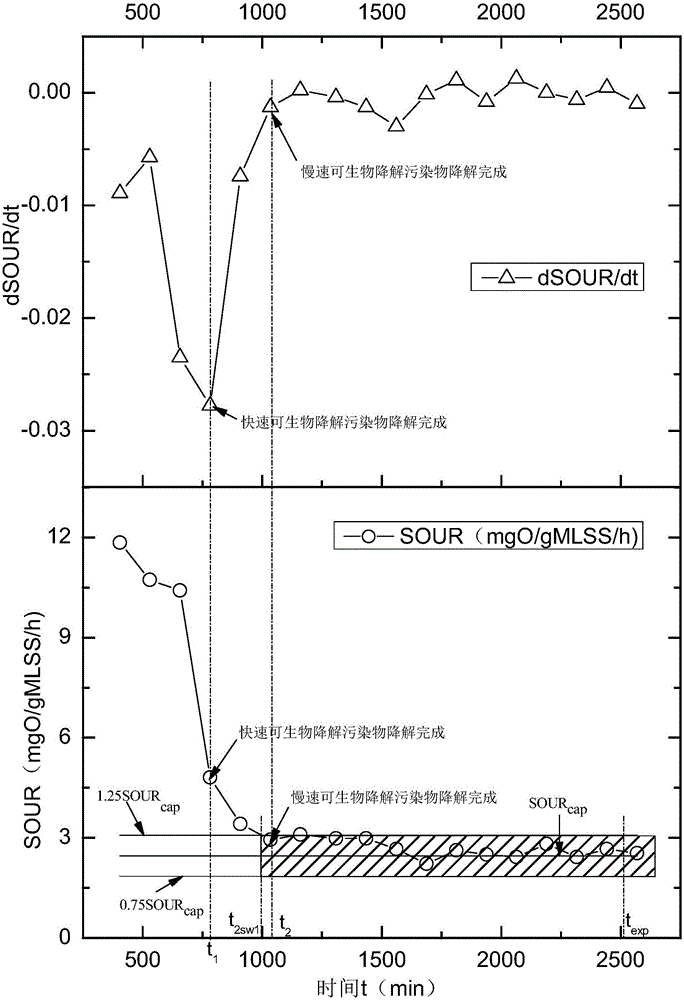
The invention discloses a method for determining activated sludge treatment capacity. The method comprises the steps that 1, respiration map analysis is conducted on activated sludge of an aeration tank of a sewage plant, and the oxygen uptake rate (OUR) value is determined; 2, the activated sludge of the aeration tank of the sewage plant is mixed with raw water for an aeration test; 3, the value of sludge concentration of the aeration tank of the sewage plant is tested, all the oxygen uptake rates (OUR) are divided by the sludge concentration MLSS, and the specific oxygen uptake rate (SOUR) is obtained; 4, an SOUR curve obtained through the aeration test is drawn, and two time points t1 and t2 are obtained according to derivative change characteristic points; 5, if t2 is in a defined safe area, effluent of a sludge treatment system can reach the standard safely. According to the method for determining the activated sludge treatment capacity, the activated sludge treatment capacity can be analyzed and determined according to an activated sludge respiration map and aeration test data. By means of the method, technical staff of the sewage plant can understand the treatment capacity of current activated sludge treatment, operating parameters are adjusted in time, and guiding suggestions are provided for reasonable operation, energy saving and consumption reduction of the sludge plant.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
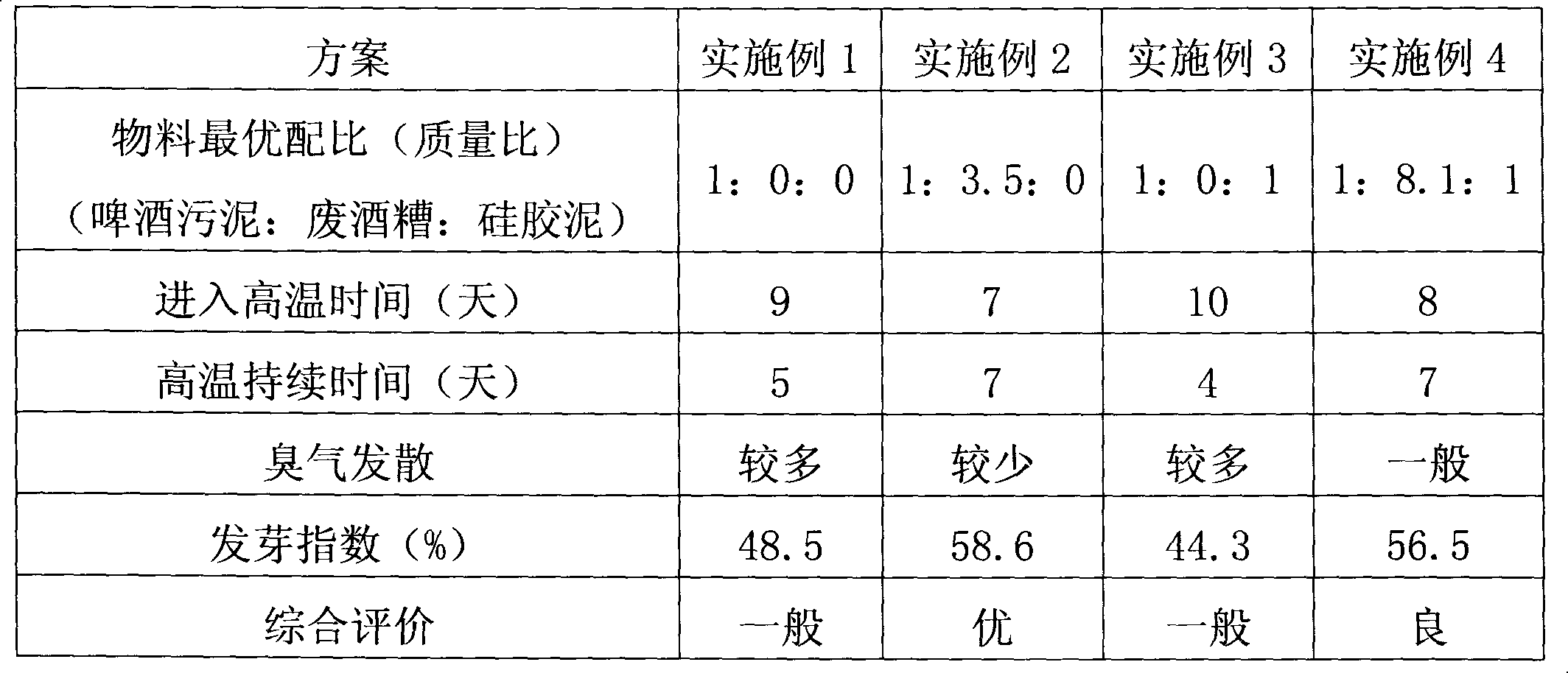
Method for producing compost by using beer production waste
ActiveCN102936159AAchieve recyclingEfficient recyclingBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationInorganic compoundSilica gel
The invention discloses a method for producing compost by using beer production waste. The method includes preparing raw materials: according to a weight ratio, mixing one or more of dewatered sludge, waste lees and silica gel sludge which are discharged through beer production, determining pH of the materials to be 7-7.5 and regulating a water content to be 55-60%; composting: adding the prepared raw materials in to a compost reactor, feeding in air continuously, guaranteeing that the reactor operates under an aerobic state, stacking for 13-17 days to finish the composting, during the stacking process, turning the stack once every 2-3 days, and detecting pH, temperature, oxygen uptake rate and humification coefficient of the stack; analyzing a compost product: measuring content of various elements of an end product compost, screening and grinding the compost after stabilizing and drying, and applying directly to an organic fertilizer or an organic or inorganic compound fertilizer. The method is simple in operation, low in operation cost, free of secondary pollution and convenient to manage.
Owner:QINGDAO LILIHUI BIOTECH
Aeration control system and method based on OUR (oxygen uptake rate) tester
ActiveCN106277383APrecision AerationTo achieve the purpose of saving energy and reducing consumptionWater treatment parameter controlWater aerationAutomatic controlWater quality
The invention discloses an aeration control system. The system comprises a data acquisition unit, a PLC (programmable logic controller) control unit and an aeration unit, wherein the data acquisition unit comprises an OUR (oxygen uptake rate) tester and a DO (dissolved oxygen) tester, and the aeration unit comprises an air blower, a micropore aeration head and a flowmeter. The invention further provides an aeration control method adopting the aeration control system. System automatic control software calculates the aeration quantity required to be supplied in combination with the OUR value and DO value automatically acquired by an online tester as well as the OTE value calculated according to the OUR value and the aeration quantity by inputting an automatic control algorithm, a signal is output to change the flow of air blowing, the DO is stabilized at the set value, the deviation doesn't exceed 0.5 mg / L, dynamic balance of supply and demand of oxygen is realized, the problem of poorer effluent quality due to insufficient oxygen supply can be solved completely, besides, energy waste caused by excessive aeration can also be reduced, and the function of evaluating the performance of the aeration system is realized.
Owner:尚川(北京)水务有限公司
Method for monitoring biological treatment oxygen uptake rate of sewage and controlling aeration quantity
ActiveCN103922461AContinuous measurementGood control effectTreatment using aerobic processesFlow control using electric meansSludgeSewage
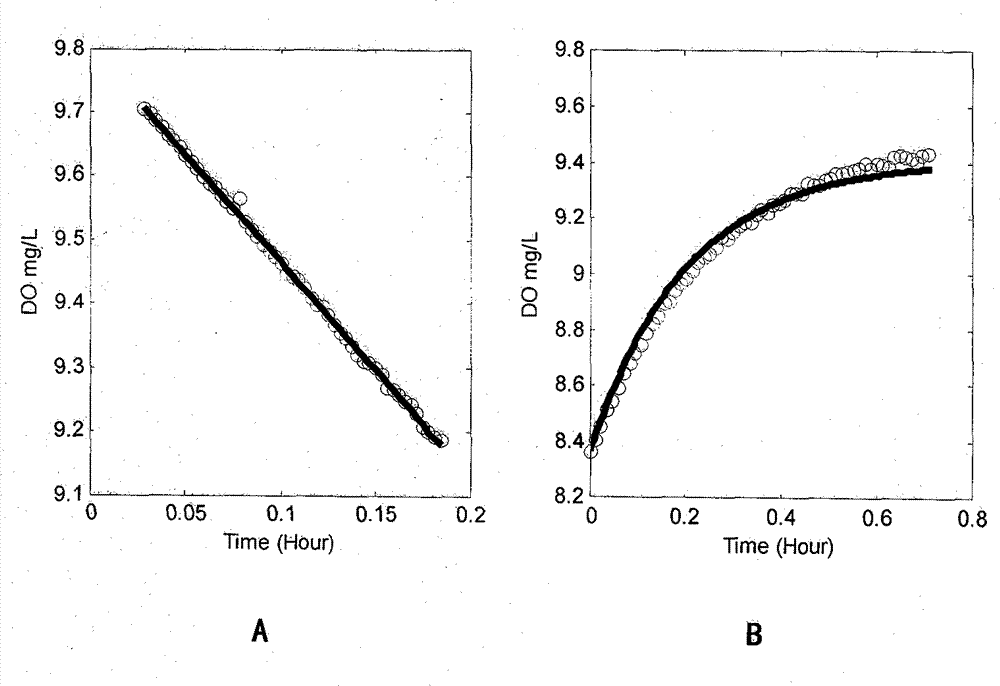
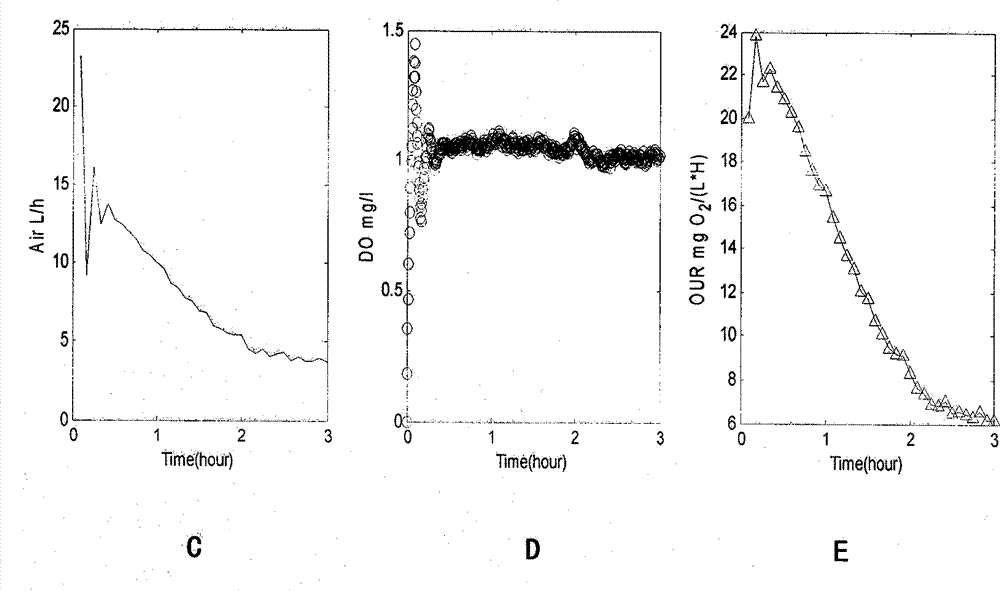
The invention relates to a method for monitoring the biological treatment oxygen uptake rate of sewage and controlling the aeration quantity. The method comprises the following steps: determining the oxygen transfer coefficient KLa(d<-1>) of aeration oxygenation and the saturated dissolved oxygen concentration mg / L under different air flow q, temperature and preset sludge concentration conditions, finding relation of the oxygen transfer coefficient KLa to the air supply amount q and the temperature T, fitting the dissolved oxygen change curve within a period of time under the preset oxygen transfer coefficient KLa(d<-1>) and dissolved oxygen concentration conditions in order to find the oxygen uptake rate within the period of time, utilizing the oxygen uptake rate of a last period of time as the possible oxygen uptake rate of a next period of time, finding the lowest aeration quantity q of the next period time for reaching the preset dissolved oxygen concentration, applying the above found air quantity q into a reactor within a following period of time, determining the dissolved oxygen change curve of the following period of time, and finding the oxygen uptake rate within the following period of time. The method overcomes the defects of large equipment investment, complex construction, low test frequency and the like existing in the prior art. The method enables OUR (oxygen uptake rate) to be continuously monitored only through using a dissolved oxygen probe without an extra auxiliary reactor, an extra dissolved oxygen probe or a sewage transmission device.
Owner:江苏美景时代环保科技有限公司
Bacterial cultivation system for growth of substrate specific micro-organisms for use in industrial wastewater remediation
ActiveUS8052873B1Adequate air introductionWater treatment compoundsMultistage water/sewage treatmentCell massWaste treatment
A waste treatment method includes the concentration of selected strains of bacteria in a selected medium in the presence of nutrients and water, under aerobic conditions. This concentrated batch is thereafter discharged for downstream applications in wastewater remediation. The present invention employs a cultivation chamber having inlet ports and a circular vent port that allows for adequate air introduction and heat release. Aeration is achieved by recirculation of the fluid medium from the top of the apparatus through a pipe that runs the length of the inner wall and is specially configured at the top to minimize cell damage. Fluid can be routed tangentially in both the clockwise and counterclockwise directions within the chamber. The conical bottom also has an orifice allowing for recirculation of the fluid medium tangentially to the sidewalls. Upon completion of the batch cultivation, the medium and bacteria are discharged for downstream applications in wastewater remediation of paper mill, chemical plant, oil refinery, and other industrial effluents. The aeration and circulation of the fluids is designed to limit cells shearing and damage yet achieve critical cell mass (e.g. between 107 and 1010 cfu (colony forming units) per milliliter (ml)) and dissolved oxygen uptake rates (e.g. between about 50 and 1500) during cultivation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL BUSINESS SPECIALISTS
Hemoglobin Overexpression in Fungal Fermentations
InactiveUS20080193969A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleotideFermentation
The present invention relates to fungal host cells that are transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fungal oxygen-binding proteins or fragments thereof that comprise the oxygen-binding domain. Upon transformation of the host cell with the construct, the oxygen-binding protein confers to the host cell improved fermentation characteristics as compared to untransformed host cells. These characteristics include e.g. increases in oxygen uptake rates, biomass densities, volumetric productivities and / or product yields. The invention further relates to fermentation processes in which the host cells are used and to fungal oxygen binding proteins, in particular fungal flavohemoglobins and hemoglobin domains, and to nucleotides sequences encoding these proteins.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
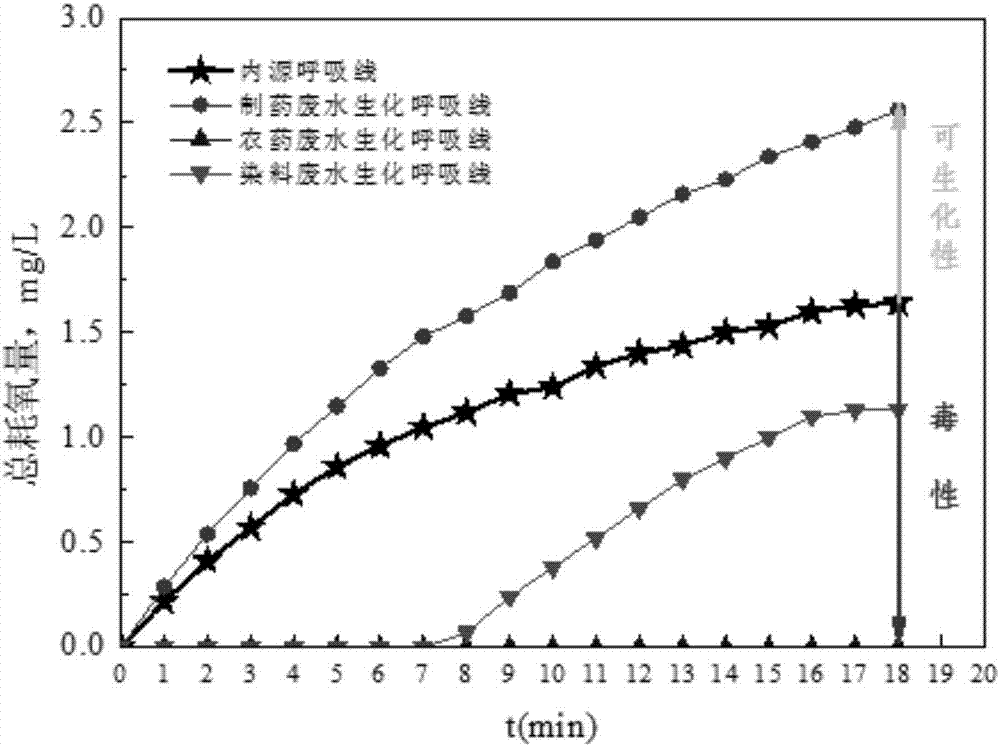
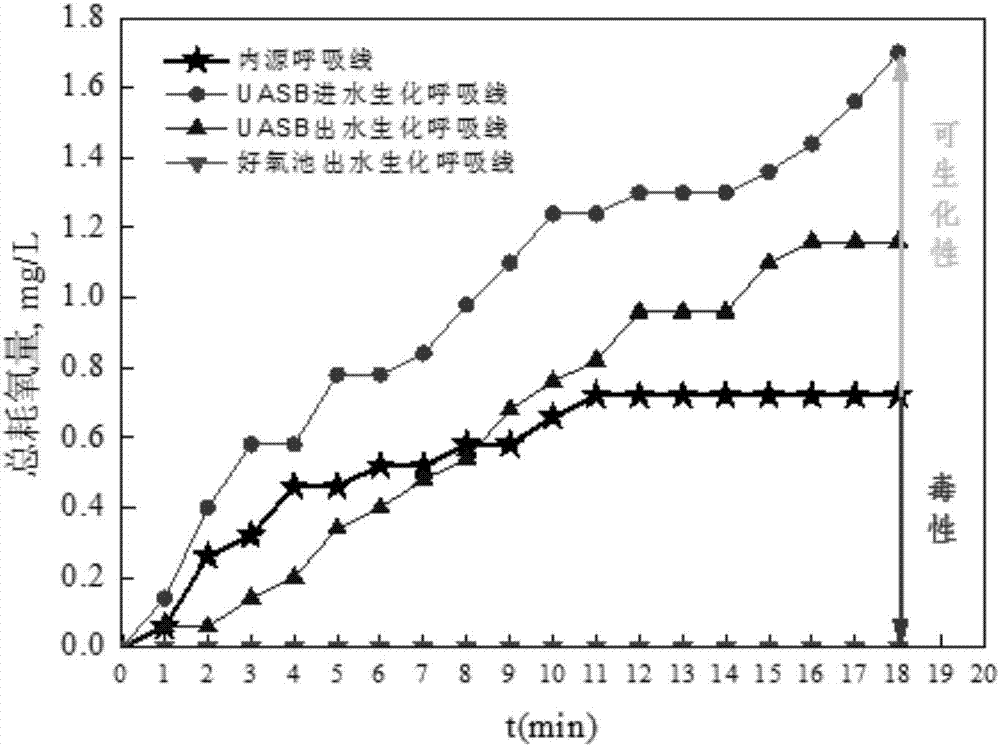
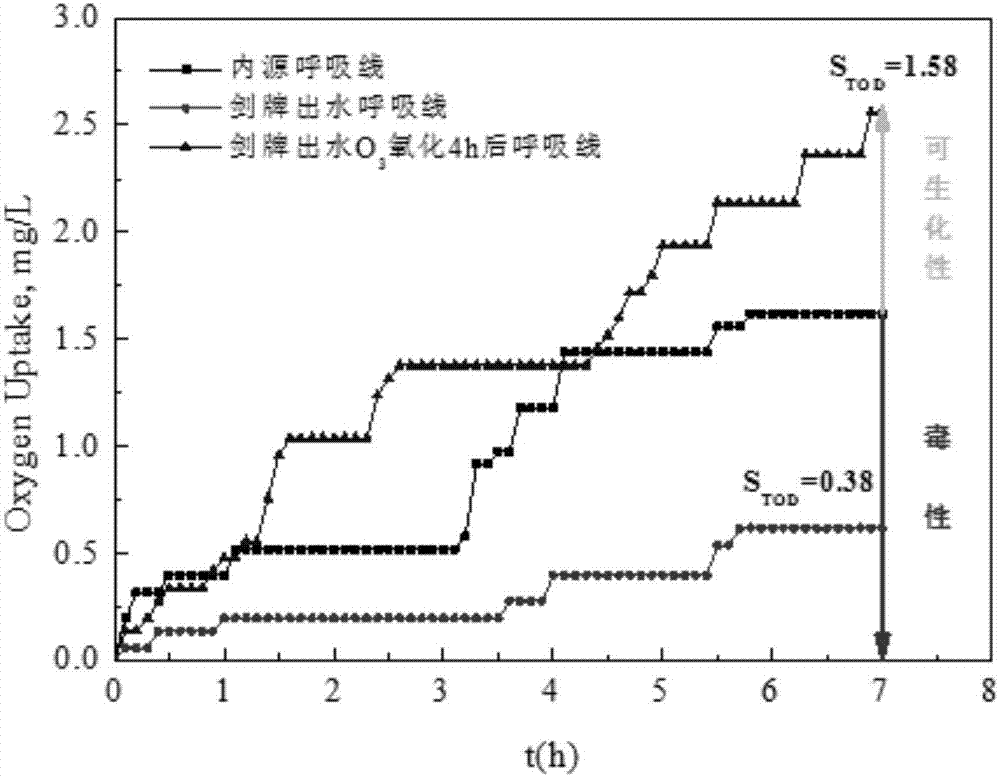
Method for evaluating toxicity and biodegradability of chemical wastewater
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the toxicity and the biodegradability of chemical wastewater and belongs to the field of water pollution control. Relative oxygen consumption is adopted to evaluate the biodegradability and the toxicity of chemical wastewater: (1) if STOD of a water sample to be detected is larger than 1, a matrix in wastewater has no toxicity and is biodegradable, and the larger the STOD value is, the better the biodegradability is; (2) if STOD of the water sample to be detected is equal to 1, the matrix in wastewater has no toxicity but is non-degradable; and (3) if STOD of the water sample to be detected is smaller than 1, the matrix in wastewater has toxicity and is non-degradable, and the smaller the STOD value is, the stronger the toxicity is. A method for measuring the oxygen consumption and the oxygen uptake rate of microbes in real time is adopted, so that errors caused by adopting a dilution multiple method to measure BOD5 are avoided, the problem that BOD5 cannot evaluate the toxicity of wastewater is solved, and the method provided by the invention is convenient and quick and can acquire measurement results within 20 min.
Owner:NANJING UNIV YANCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH & ENG RES INST
Control device for fermenter
InactiveUS7771988B2High yieldSampled-variable control systemsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDiffusionDisplay device
The control device according to the present invention includes an input device for entering measured data from a measurement unit, which measures nutrient components, the concentrations of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and biomass in a culture medium; a processor for calculating nutrient components uptake rate, oxygen uptake rate and carbon dioxide exhaust rate per unit amount of biomass from the measured data entered in the aforementioned input device, as well as volumetric mass transfer coefficient kLa from turbulent energy k and a turbulent energy dissipation rate e, both of which are calculated by a transport equation, as well as a diffusion coefficient D, followed by calculating the concentrations of the nutrient components, dissolved oxygen and dissolved carbon dioxide in any area in the fermenter; and a display for displaying concentration distribution of the nutrient components, dissolved oxygen, and dissolved carbon dioxide in the fermenter.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT SERVICES
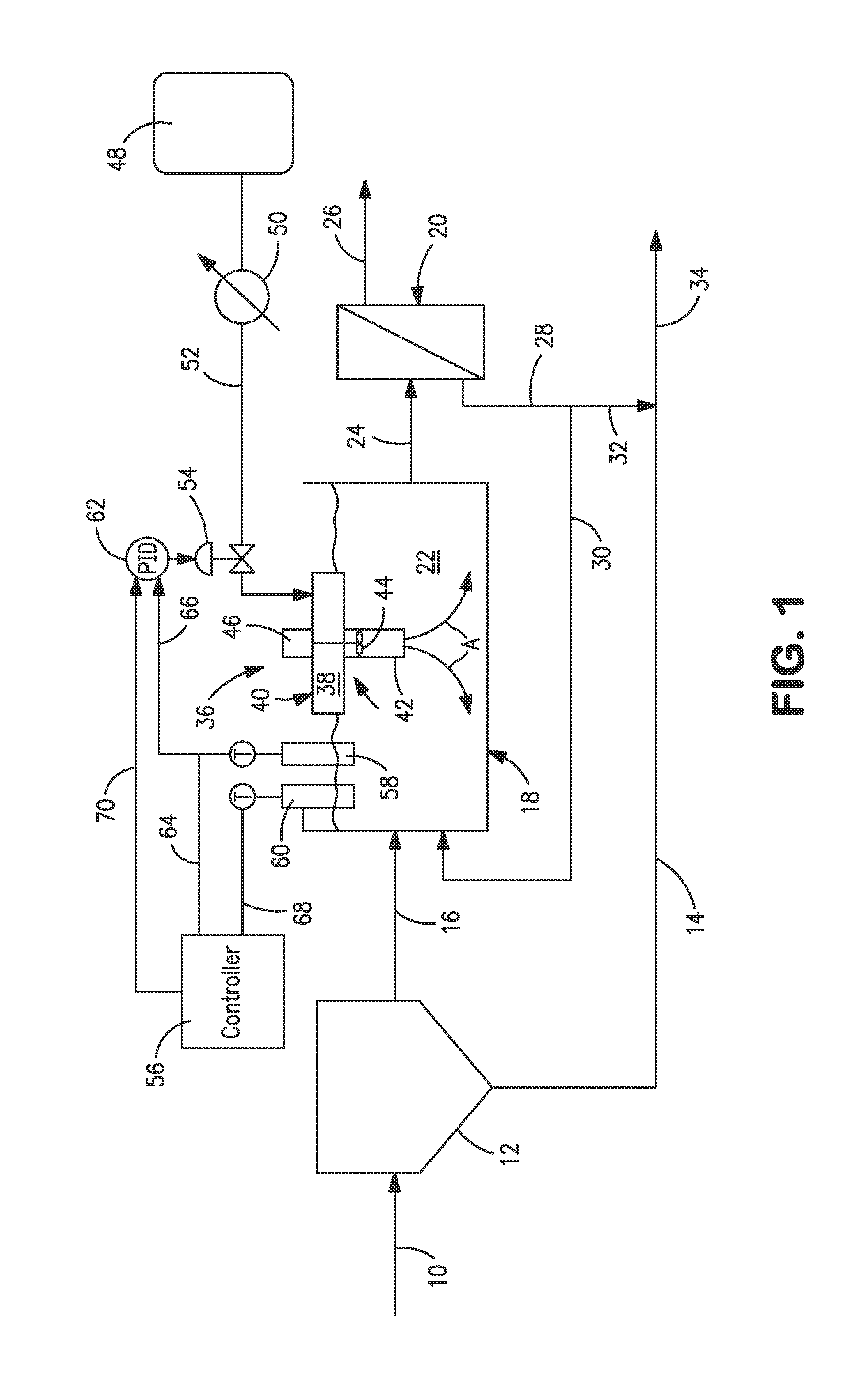
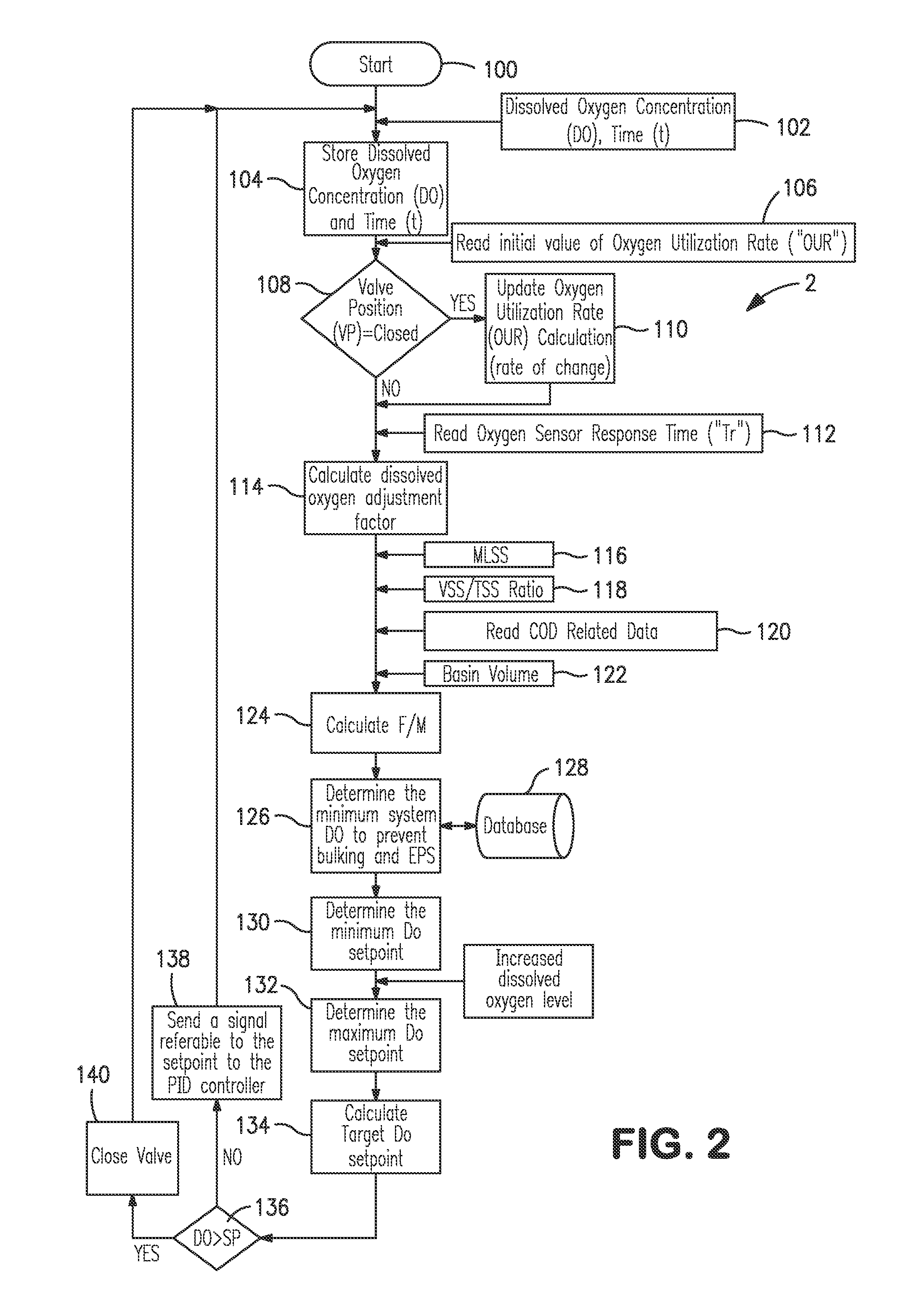
Oxygen control for wastewater treatment
InactiveUS20140332464A1Mitigation of membrane foulingMinimize bulking and generationSemi-permeable membranesWater treatment parameter controlPOLYMER SUBSTANCEMixed liquor suspended solids
A method and system for controlling dissolved oxygen levels in a secondary treatment system of a wastewater treatment facility that can employ a membrane bioreactor in which oxygen introduction into mixed liquor is controlled to prevent bulking and minimize generation of extra cellular polymeric substances. The control is exercised by insuring that dissolved oxygen levels within the mixed liquor do not fall below a minimum system level at which microorganism stress would occur. This is done by setting a minimum dissolved oxygen level control point equal to a sum of the minimum system level and an adjustment factor determined on the basis of oxygen uptake rate and time delays inherent in sensing oxygen levels and changes thereof within the mixed liquor. The minimum system dissolved oxygen level can be continually calculated on the basis of an inferred food to mass ratio that would vary with sensed mixed liquor suspended solids.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method and device for optimizing and scaling up vitamin B12 fermentation process
InactiveCN101775424AIncrease productionFermentation process optimization and scale-upBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteVitamin B12
The invention provides a method for optimizing and scaling up the fermentation process using a bioreactor device. The method comprises the following steps: 1. measuring physiological parameters and the related characteristics or combined characteristics of the physiological parameters of the fermentation process of the bioreactor device, wherein the physiological parameters are selected from the following parameters: dissolved oxygen, oxygen uptake rate, pH, carbon dioxide excretion rate, respiratory quotient, living cell rate or cell shape, consumption of measured metabolic product or matrix or combined characteristics; and 2. comparing the physiological parameters and the related characteristics or combined characteristics which are measured in the step 2, with preset physiological parameters and the related characteristics or combined characteristics; selecting a bioreactor device of which data are most similar to the preset values; and determining the optimized and scaled-up bioreactor device, wherein the physiological parameters are shown in the step 1.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fermentation production method of rifamycin SV based on oxygen uptake rate OUR used as control parameter
ActiveCN103642870APromote growthEasy to synthesizeMicroorganism based processesFermentationThree levelPure culture
The invention discloses a fermentation production method of rifamycin SV based on oxygen uptake rate OUR used as a control parameter. By using nocardia intermedien as an original strain, rifamycin SV is produced by virtue of pure culture and three-level fermentation. In the fermentation preparation process, the stirring rotation speed of a fermentation tank and ventilation flow in the fermentation process are controlled to reach different oxygen supply levels; the oxygen uptake rate OUR of a fermentation system at high level is kept to be between 18 and 20mmol / L / h in 70-75 hours in the earlier stage of the fermentation process, so that hypha is quickly grown and the titer is quickly increased; after 70-75 hours in the earlier stage of the fermentation process, the stirring rotation speed of the fermentation tank and the ventilation flow are reduced, and the oxygen uptake rate OUR is controlled to be between 13 and 15mmol / L / h until the tank is put at the end. According to the method, the thallus growth and the synthesis of the rifamycin SV are increased, the conversion rate is increased, the production period is shortened, the fermentation production level is stably improved, and the yield of the rifamycin SV is improved.
Owner:HEBEI XINGANG PHARMA +1
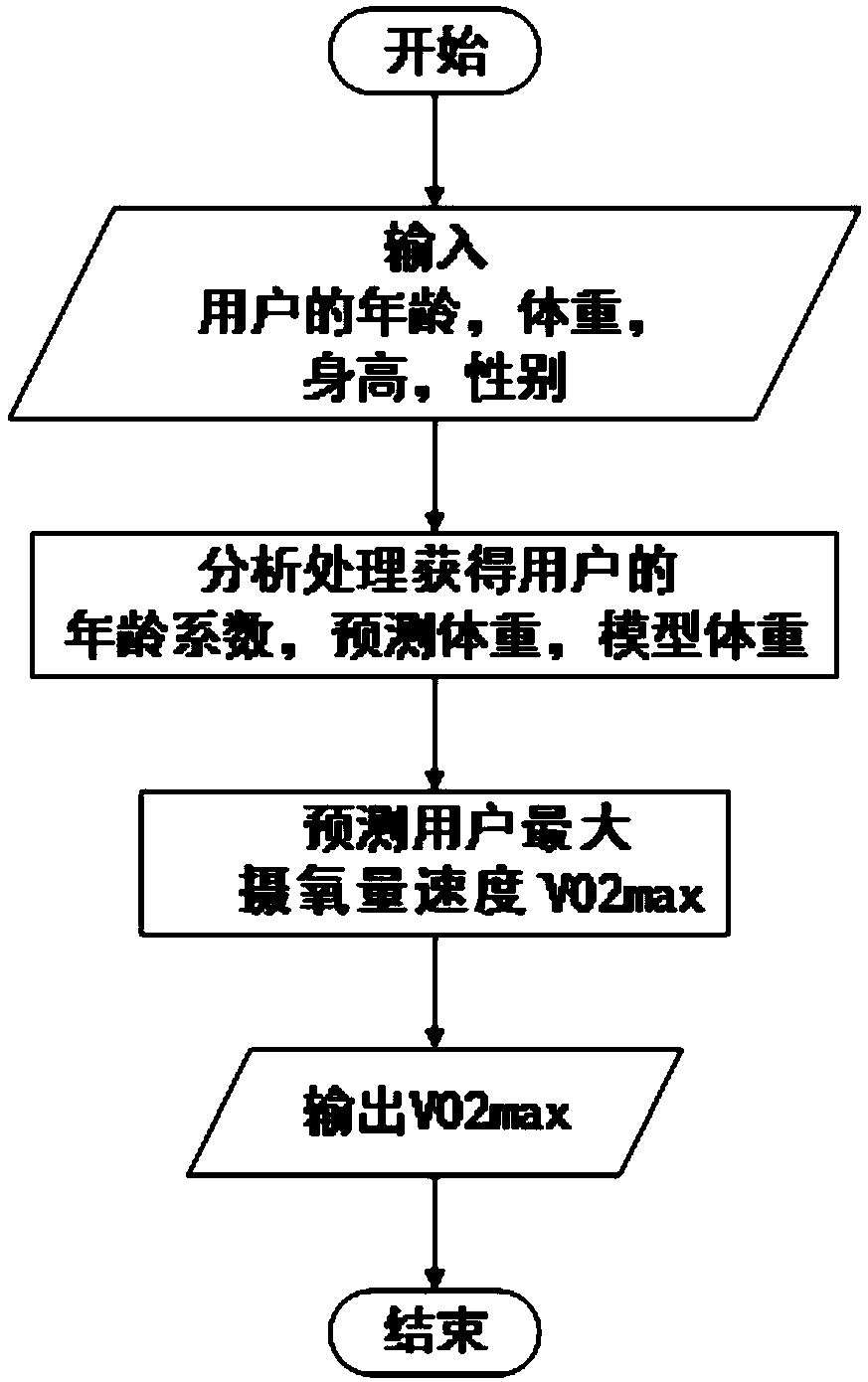
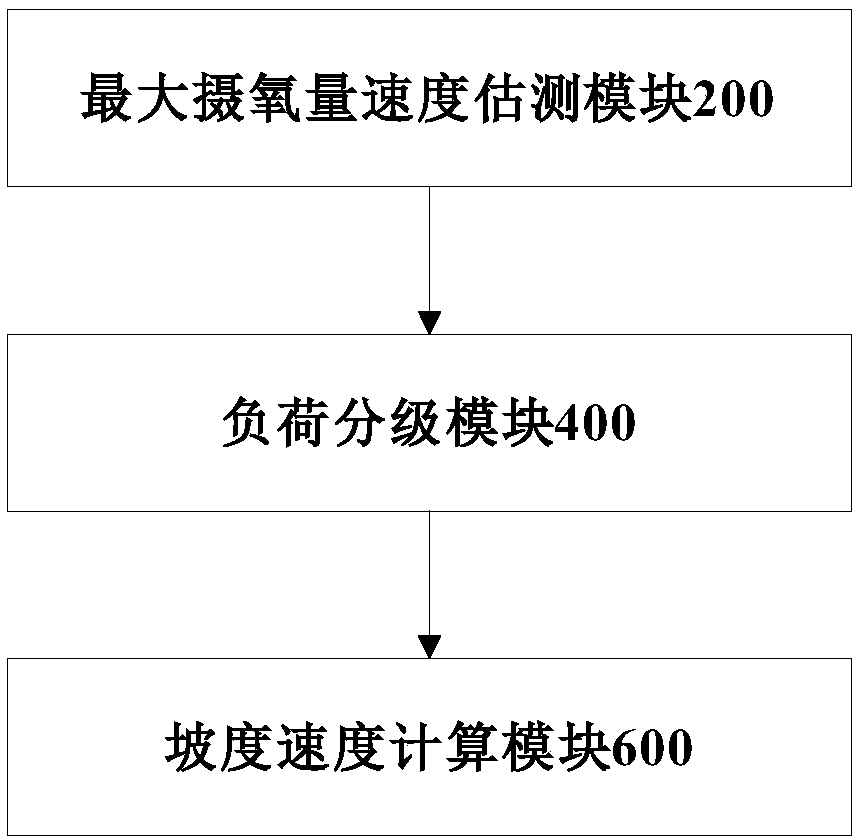
Testing method and device for submaximal cardiorespiratory fitness based on slope and speed of treadmill
ActiveCN110477920AAvoidance of cardiovascular eventsFast test speedRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsThree levelExercise state
The present application discloses an adjustment method and adjustment device for a slope and speed of a treadmill based on cardiorespiratory fitness. The method comprises the following steps: estimating the maximum oxygen uptake rate of a user based on basic information of the user; classifying the exercise risk and age of the user based on the basic information of the user, and obtaining initialvalues of three-level load of the user in a submaximal test mode based on the exercise risk, age and maximum oxygen uptake rate of the user; and obtaining a load value of the submaximal test of the user based on the maximum oxygen uptake rate, comparing a load value with a set threshold value of each-level load to determine the exercise state, and obtaining the speed and slope of the treadmill test under each-level load according to the relationship of each-level load value and the speed and the slope in different exercise states. The method provided by the present application can classify thetest load in a personalized manner based on the exercise risk and age, and facilitates avoiding the occurrence of cardiovascular events due to irrational intensity during the test; and meanwhile, themethod can quickly obtain the test speed and slope value.
Owner:北京动亮健康科技有限公司
Preparation method for composite inhibitor used for preventing and handling serf-combustion of coal
InactiveCN107033924AGood dispersionEffective prevention and control of spontaneous combustionDust removalFire preventionIon exchangeOxygen
The invention specifically relates to a preparation method for a composite inhibitor used for preventing and handling serf-combustion of coal, belonging the technical field of prevention of serf-combustion of coal. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with sodium-based montmorillonite as a raw material, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion and then subjecting the dispersed sodium-based montmorillonite to ion exchange with ferric trichloride; then with cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide as an intercalator, preparing high-dispersibility modified iron-based montmorillonite; subjecting reduced iron powder, graphite and copper powder to ball milling and alloyage and carrying out physical combination under the action of pressure to form a short-circuit corrosion microbattery together so as to improve an oxygen uptake rate; then loading modified iron-based montmorillonite with magnesium chloride; and then carrying out compounding with carboxymethyl cellulose, ethyl acetate, gelatin and the like so as to obtain the composite inhibitor used for preventing and handling serf-combustion of coal. The composite inhibitor used for preventing and handling serf-combustion of coal can deeply enter the pores of coal, consumes oxygen in a surrounding environment, reduces the temperature of coal due to its water absorption performance, decreases contact between coal and oxygen and lowers the possibility of serf-combustion of coal.
Owner:CHANGZHOU C PE PHOTO ELECTRICITY SCI & TECHN
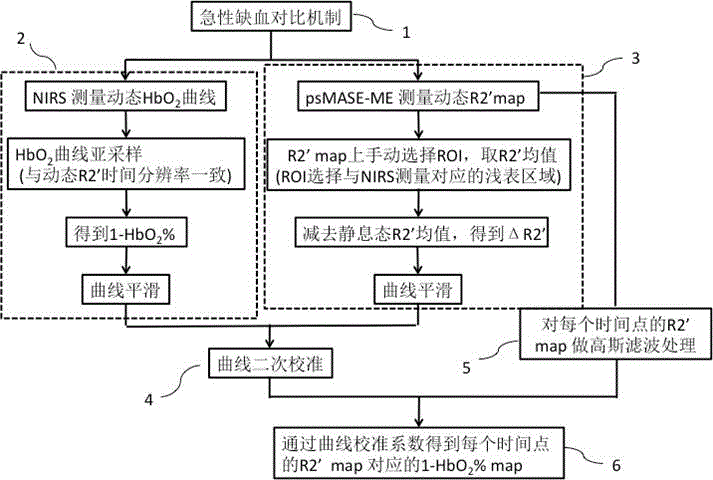
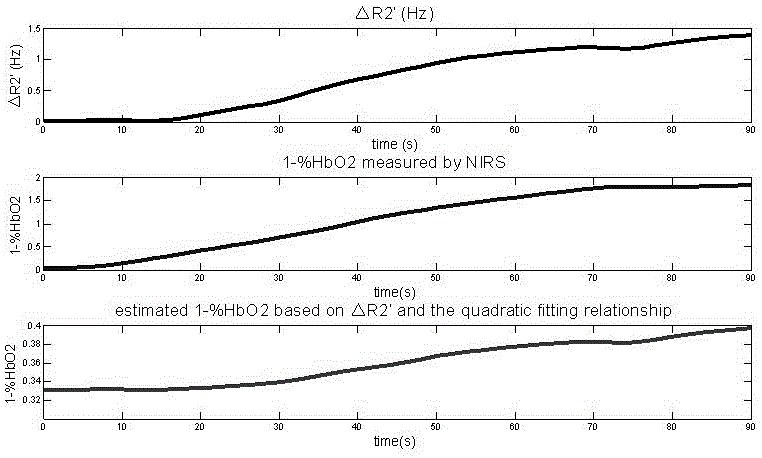
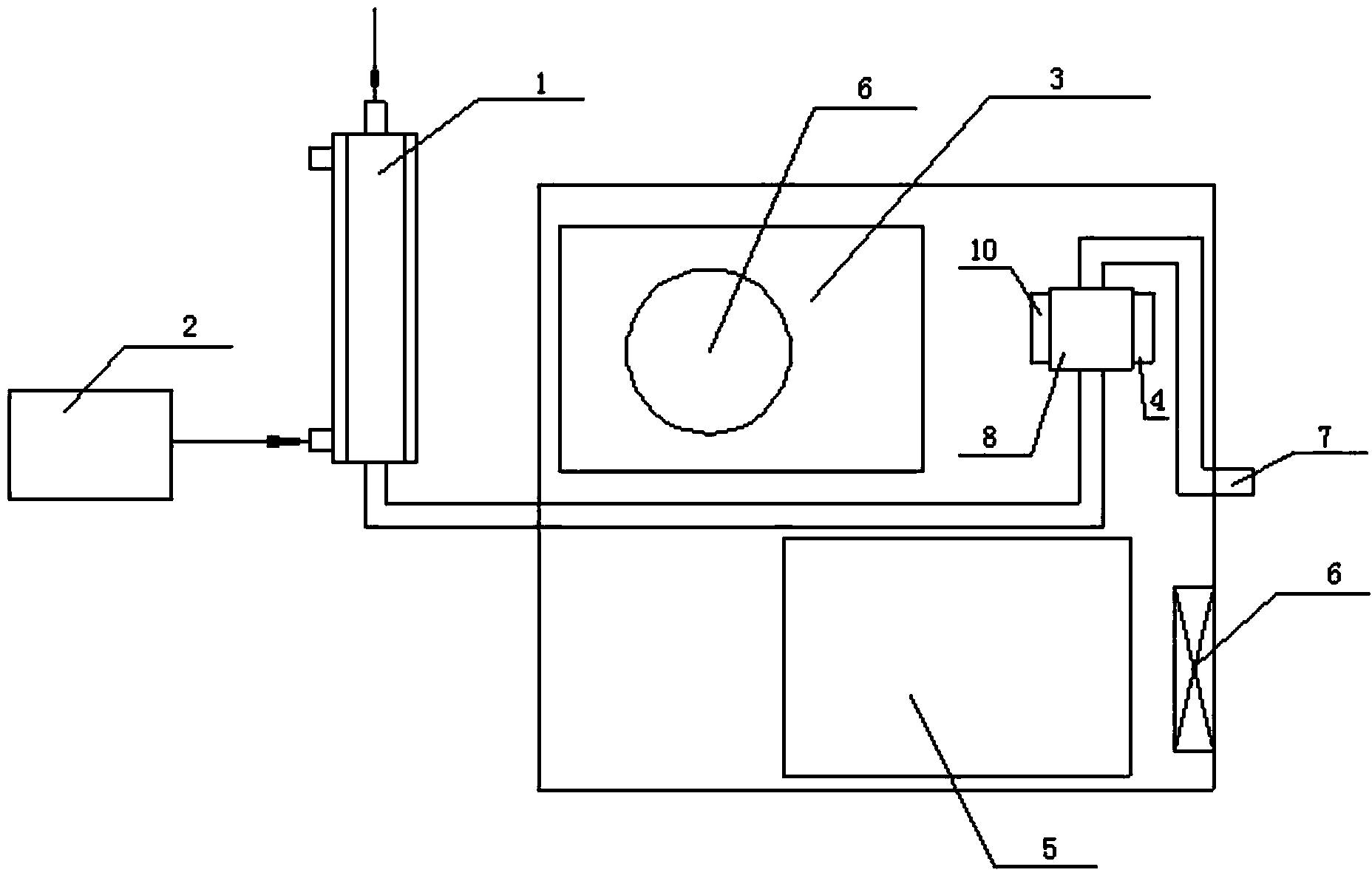
A noninvasive dynamic muscle oxygen uptake rate measuring method based on magnetic resonance imaging
The invention provides a method of estimating the distribution diagram of the dynamic oxygen uptake rates of whole muscular tissue by using the imaging results of noninvasive quantitative dynamic magnetic resonance R2' and the results of the oxygen uptake rates of superficial muscle tissue measured by an NIRS. The method comprises the step of firstly, dynamically obtaining the R2' distribution diagram of the whole muscle tissue according to an improved multiple-echo asymmetrical spin echo (ps MASE) sequence of pulses periodically moving for 180 degrees and a moving window estimation (ME) strategy; secondly, obtaining the %HbO2 change curve of superficial muscles by using the NIRS and performing sampling to the time resolution the same as that of dynamic R2' measurement; thirdly, fitting the R2' and the %HbO2 via a secondary empirical equation and calculating the dynamic 1-%HbO2 change process of the whole diagram via a coefficient obtained after fitting.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Device and method for online detecting oxygen and carbon dioxide in biological fermentation tail gas
InactiveCN103869091AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicrocontrollerFermentation
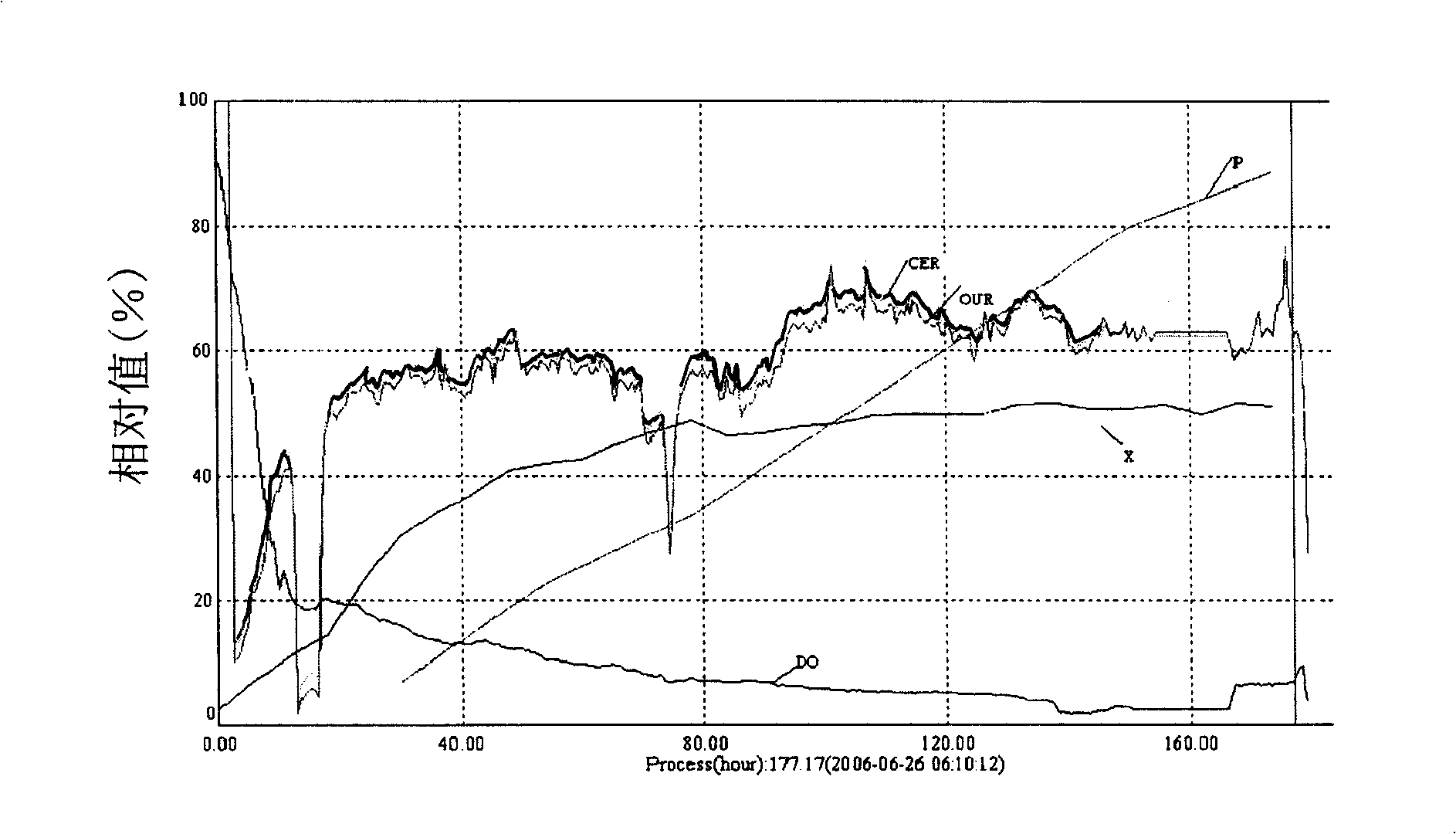
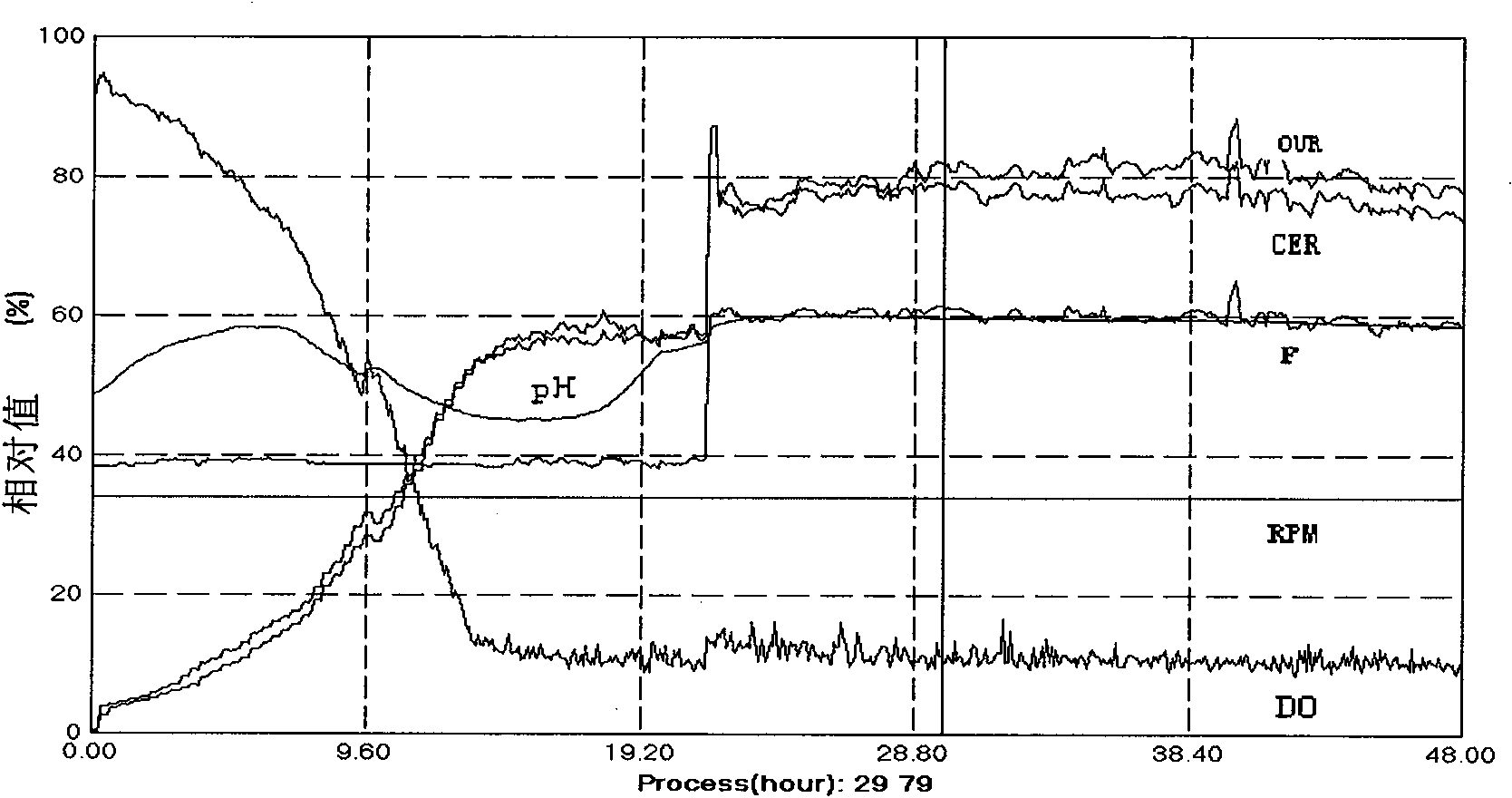
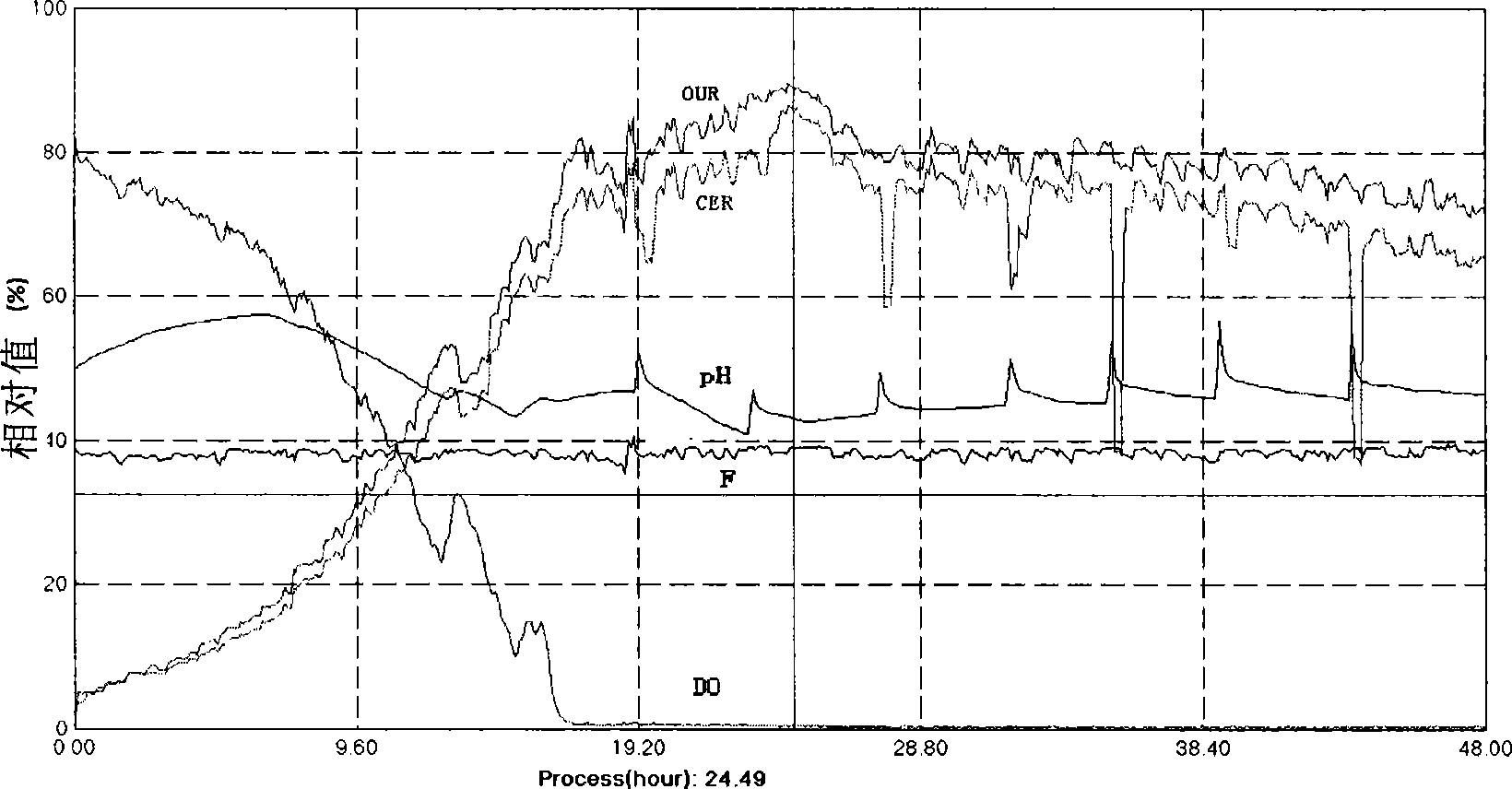
The invention discloses a device and method for online detecting oxygen and carbon dioxide in a biological fermentation tail gas. The device comprises a water removing device, a gas detecting chamber, a singlechip, a heat radiating fan, a power supply and a PC (Personal Computer) terminal, wherein the gas detecting chamber comprises a gas inlet end and a gas outlet end, the gas inlet end is connected with a gas outlet, the gas detecting chamber is internally provided with an oxygen sensor and a carbon dioxide sensor, the singlechip is connected with the oxygen sensor and the carbon dioxide sensor, the power supply is connected with the oxygen sensor, the carbon dioxide sensor and the heat radiating fan, and the PC terminal is connected with the singlechip. The invention further provides a method for online detecting the oxygen and the carbon dioxide in the biological fermentation tail gas. The device is simple in structure, strong in practicability, low in manufacturing cost, capable of continuously online operating for a long time, and capable of simultaneously completing online detection of contents of oxygen and carbon dioxide; the influence of the water in the tail gas is eliminated, and thus important respiratory metabolism parameters such as CER (Carbon dioxide Evolution Rate), OUR (Oxygen Uptake Rate) and RQ (Respiratory Quotient) in a fermentation process are obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
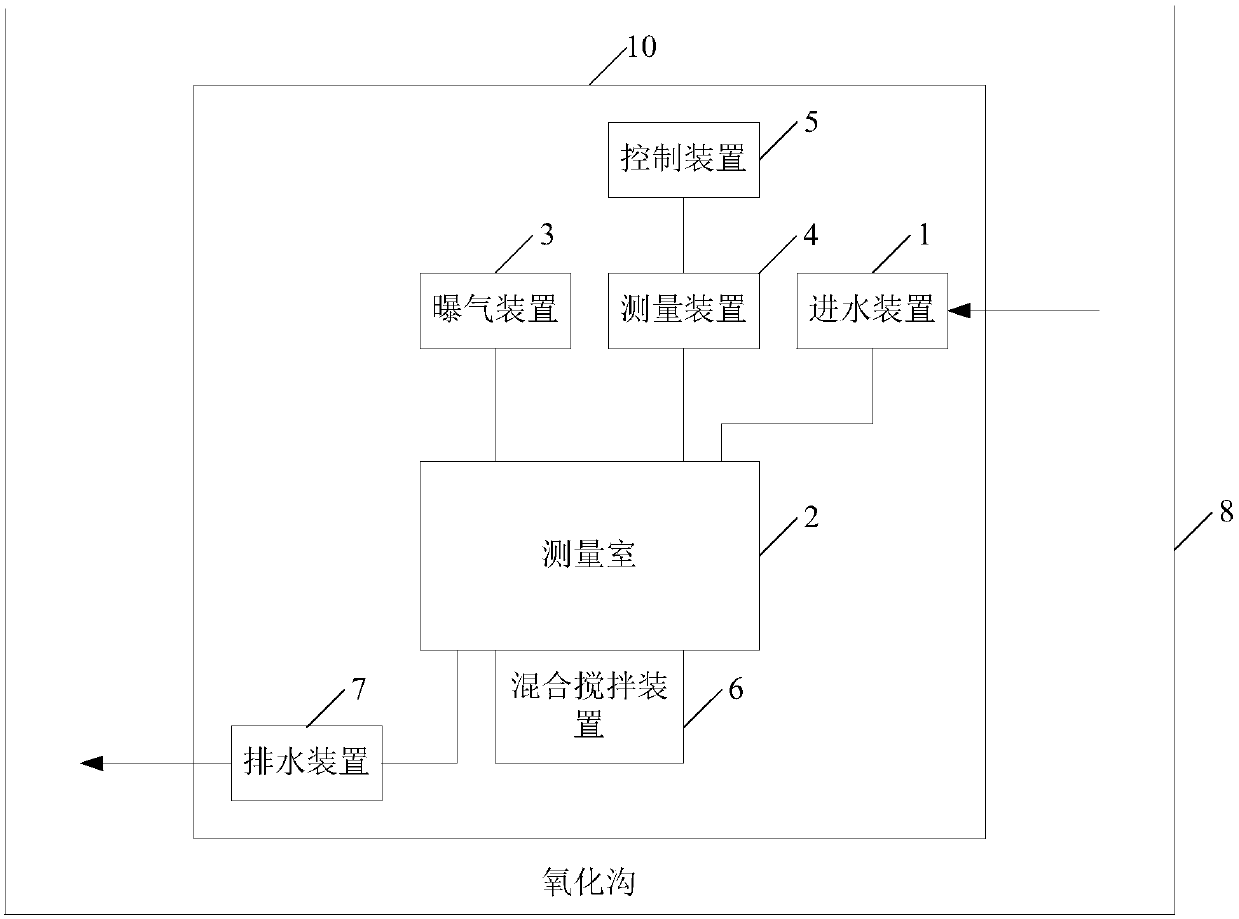
Online measuring device and method for specific oxygen uptake rate (SOUR) of activated sludge in sewage treatment system
ActiveCN103278495AAccurate measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceData acquisitionVolatile suspended solids
The invention provides an online measuring device for specific oxygen uptake rate (SOUR) of activated sludge in a sewage treatment system. The online measuring device is characterized by comprising a pre-aeration unit, an SOUR metering unit, a biomass metering unit, and a data control and calculation unit, wherein the pre-aeration unit comprises a first electric control valve, a first water pump, a second water pump, a pre-aeration tank and an aeration system, wherein the SOUR metering unit comprises a second electric control valve, a third electric control valve, an airtight breathing chamber, a dissolved oxygen meter and an electromagnetic stirrer, the biomass metering unit comprises a fourth electric control valve, a fifth electric control valve and an active micro-biomass online detection system, and the data control and calculation unit comprises a data acquisition card, a computer and a software program system. According to the online measuring device, the total active micro-biomass in the activated sludge system is adopted for replacing mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) or mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) in a conventional SOUR calculation method so as to accurately measure the SOUR of the activated sludge.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
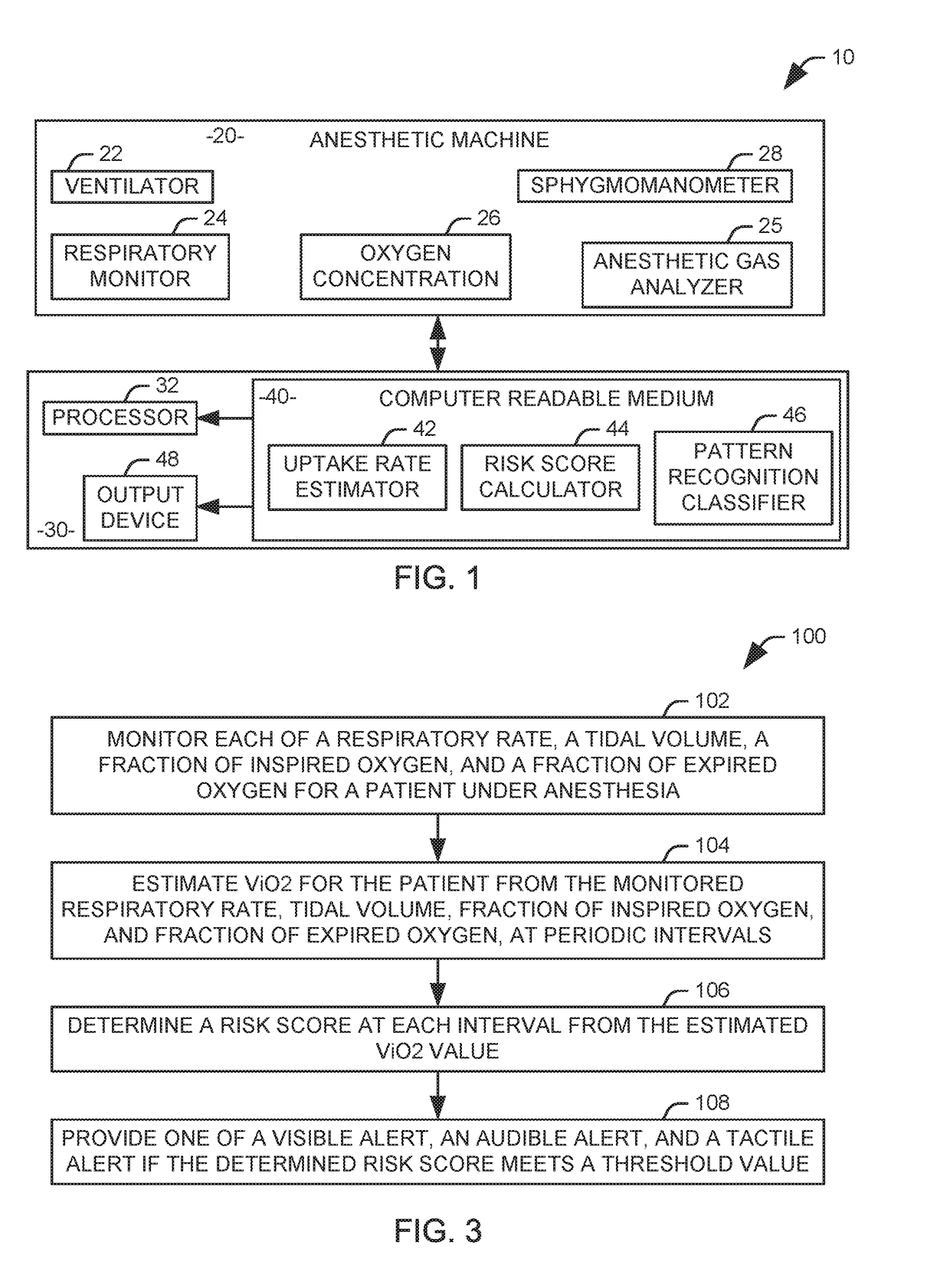
Monitoring oxygen uptake of a patient under anesthesia
Systems and method are provided for monitoring a patient during surgery. An anesthetic machine includes a ventilator configured to provide breathable gas to a patient, an oxygen concentration sensor configured to monitor the concentration of oxygen in gas inhaled and exhaled by the patient, and a respiratory monitor configured to monitor a respiratory rate and a tidal volume of the patient. An uptake rate estimator is configured to estimate a pulmonary oxygen uptake rate (ViO2) for the patient from the concentration of oxygen in gas inhaled and exhaled by the patient and a minute volume of the patient. A risk score calculator is configured to determine a risk score for the patient at each interval as a function of the estimated ViO2 value. An output device is configured to provide the determined risk score to a human operator.
Owner:STAPELFELDT WOLF H
Efficient production method for cellulase
PendingCN105255848ABest carbon to nitrogen ratioPrevent autophagyGlycosylasesPenicillium bilaiaeBiotechnology
The invention relates to an efficient production method for cellulase, and particularly discloses a method for controlling cellulase fermentation through the oxygen uptake rate. Through optimal screening of culture media and optimal controlling over oxygen uptake rate conditions, the stable fermentation method is determined, and the enzyme activity of a produced cellulase preparation is improved by more than 50 percent; the technology can be widely applied to cellulase production through filamentous fungi such as penicillium and aspergillus.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
Process for producing salinomycin by glucose supplement and fermentation based on metabolic parameter OUR (oxygen uptake rate)
ActiveCN102703540AWeaken the "glucose effect"High potencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationStationary phaseMature technology
The invention discloses an optimization method of a fermentation process of salinomycin, and particularly relates to a process for producing salinomycin by glucose supplement and fermentation based on a metabolic parameter OUR (oxygen uptake rate). The fluid glucose supplement is processed when fermentation enters a thalli metabolism stationary phase, namely OUR stationary phase after sugar oil conversion is finished so as to reduce the 'glucose effect', so the valence of the product is improved, and the production cost is reduced at the same time. The process disclosed by the invention has a mature technology and is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:内蒙古拜克生物有限公司
An aeration control system and method based on an oxygen consumption rate measuring instrument
ActiveCN106277383BPrecision AerationTo achieve the purpose of saving energy and reducing consumptionWater treatment parameter controlWater aerationAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention discloses an aeration control system. The system comprises a data acquisition unit, a PLC (programmable logic controller) control unit and an aeration unit, wherein the data acquisition unit comprises an OUR (oxygen uptake rate) tester and a DO (dissolved oxygen) tester, and the aeration unit comprises an air blower, a micropore aeration head and a flowmeter. The invention further provides an aeration control method adopting the aeration control system. System automatic control software calculates the aeration quantity required to be supplied in combination with the OUR value and DO value automatically acquired by an online tester as well as the OTE value calculated according to the OUR value and the aeration quantity by inputting an automatic control algorithm, a signal is output to change the flow of air blowing, the DO is stabilized at the set value, the deviation doesn't exceed 0.5 mg / L, dynamic balance of supply and demand of oxygen is realized, the problem of poorer effluent quality due to insufficient oxygen supply can be solved completely, besides, energy waste caused by excessive aeration can also be reduced, and the function of evaluating the performance of the aeration system is realized.
Owner:尚川(北京)水务有限公司 +1
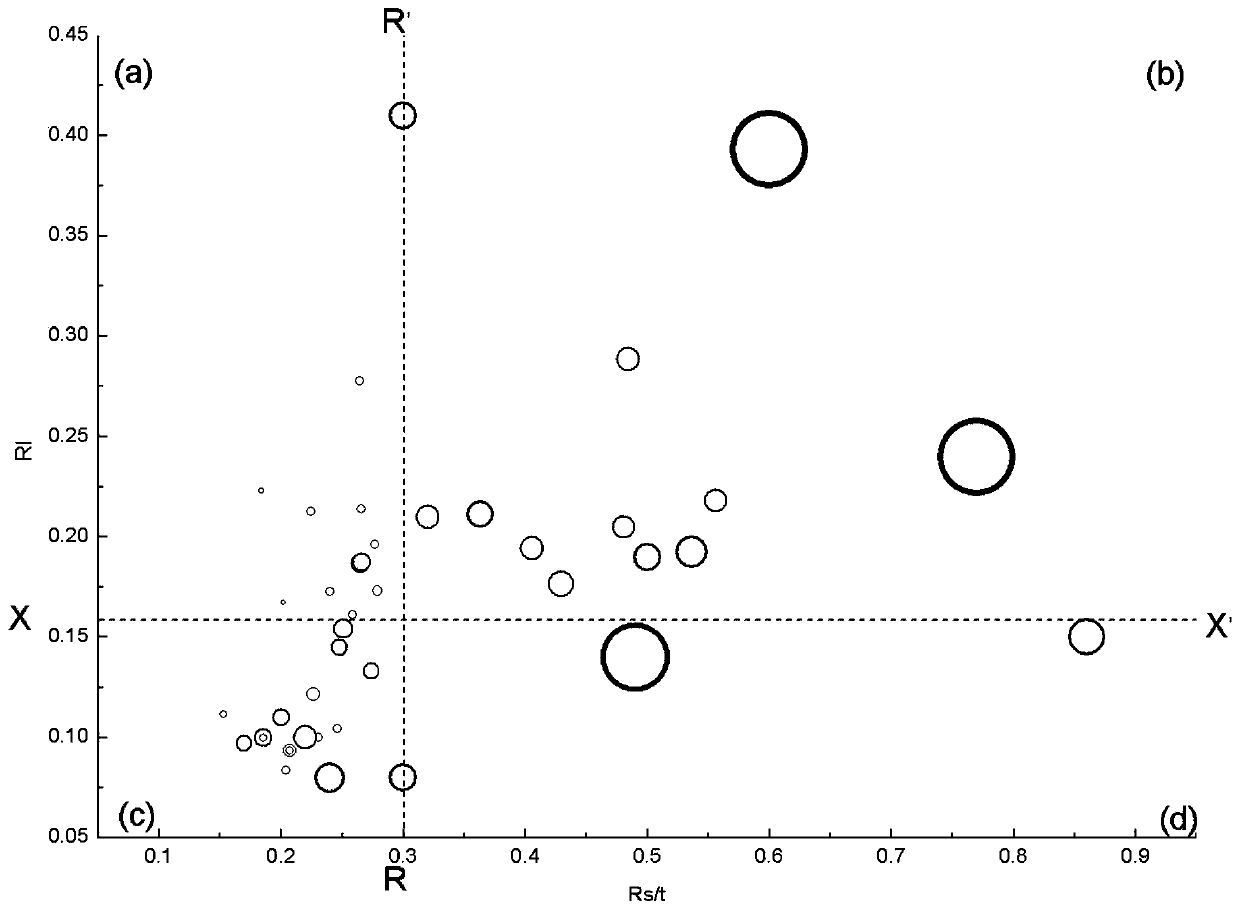
Method of judging state of river microorganisms and selecting purification measures
The invention discloses a method of judging the state of river microorganisms and selecting purification measures, which comprises steps: the suspension of a river representative section is taken to be subjected to respiratory atlas analysis, and an oxygen uptake rate (OUR) is measured; a three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of a dissolved organic matter in each representative section is measured; the three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum is divided to five regions according to peak positions, and a peak T characterizing plastein, a site respiratory ratio OURs / OURt and an endogenous respiratory ratio OURe / OURt are selected; and a bubble diagram is drawn, the plane of the bubble diagram is divided to four regions, and different regions correspond to different microorganism health states, different contamination degrees and different enhanced purification measures. The invention discloses a method of judging the state of river microorganisms and selecting purification measures. A comprehensive evaluation method for the river microorganism state, the pollution state and the enhanced purification measures is built, and a theoretical basis and a technical support are provided for enhancing ecological management of the river.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Oxygen exposure control method and device in sewage treatment
ActiveCN109775845AGuaranteed processing efficiencyEasy to controlSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentAeration rateOrganic matter
The embodiment of the invention provides an oxygen exposure control method and device in sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps: collecting actual dissolved oxygen concentration inan aerobic tank, and computing the oxygen uptake rate OUR when the microorganism in the aerobic tank degrades an organic matter in the aerobic tank based on the actual dissolved oxygen concentration;computing the given aeration rate based on the OUR and the preset given dissolved oxygen concentration, wherein the given aeration rate is the aeration rate required by the microorganism in the aerobic tank to maintain the organic matter degradation in OUR and ensure that the dissolved oxygen concentration in the aerobic tank is maintained at the given dissolved oxygen concentration; and adjusting the current actual aeration rate as the given aeration rate. Through the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the aeration rate can be precisely given into the aerobic tank, thereby maintaining the dissolved oxygen concentration in the aerobic tank as the given value, and then guaranteeing the sewage treatment efficiency and realizing precise control.
Owner:BEIJING ETECHWIN ELECTRIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com