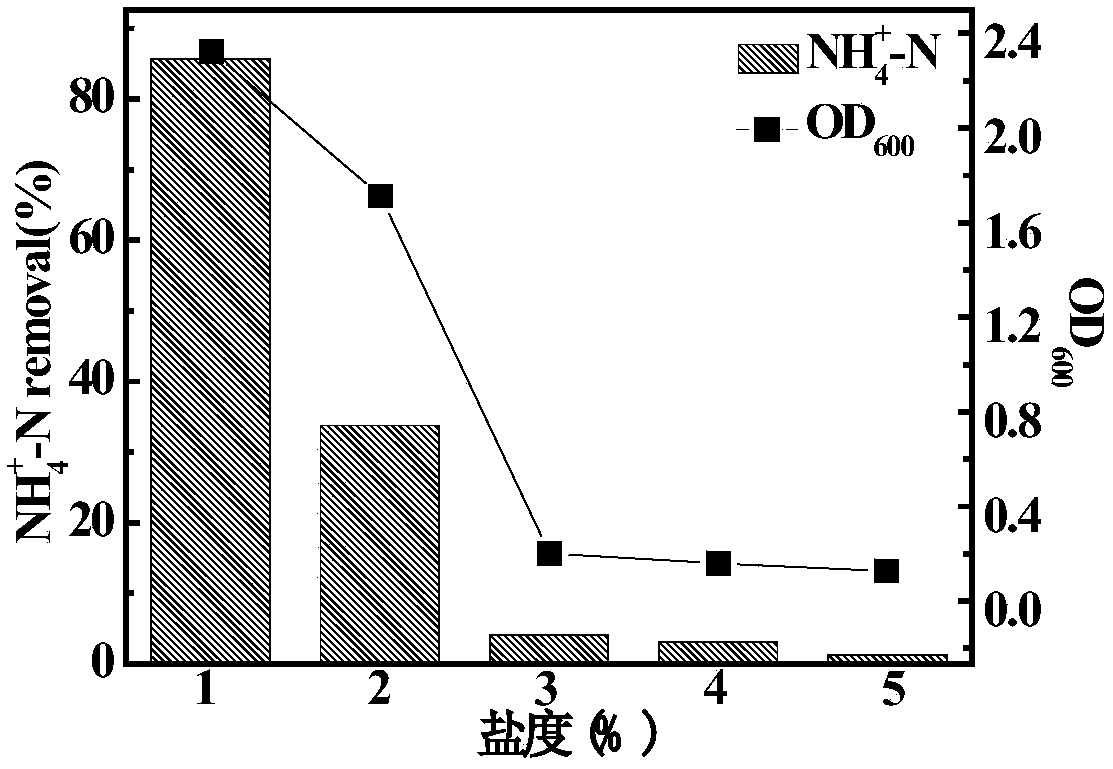
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Ochrobactrum species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ochrobactrum is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria in the Brucellaceae. The genus has been described by Holmes in 1988 and Ochrobactrum anthropi was proposed as the type species of the genus. Further work led to the recognition of 18 other species:
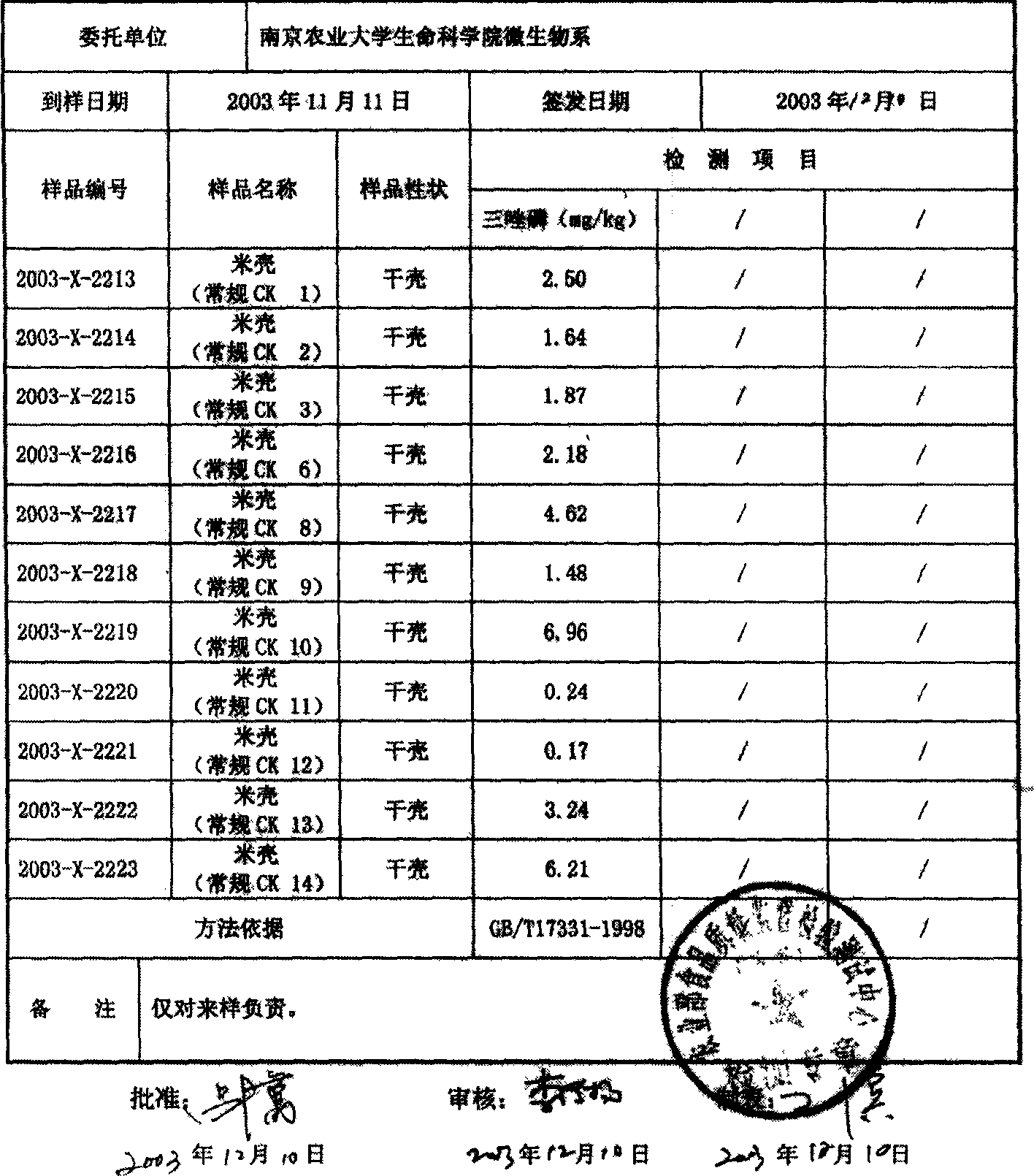
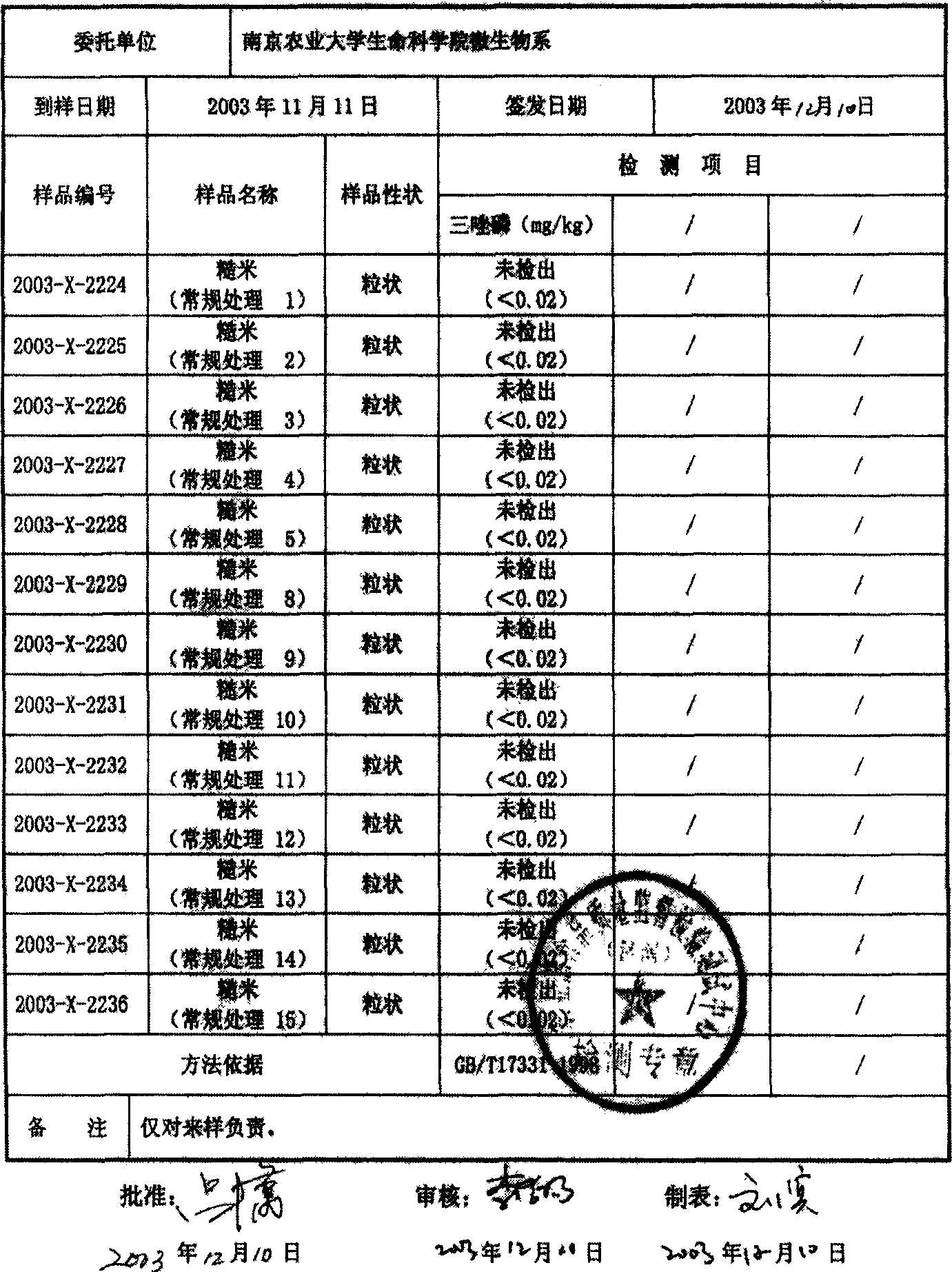
Immobilization method of salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain and application of immobilization method
ActiveCN104694525AWide variety of sourcesSimple methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTherapeutic effectNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses an immobilization method of a salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain and an application of the immobilization method. The immobilization method of the salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain comprises the following steps: firstly screening efficient anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria, denitrifying bacteria and petroleum-degrading bacteria, training salt tolerance and cold tolerance to respectively prepare trained Kuenenia. Anammoxidans, Ochrobactrum.spand Flavobacterium mizutaii; putting prepared biological carbon spheres into a salt-tolerant, cold-tolerant, efficient and compound degrading bacteria enrichment solution, culturing films for the biological carbon spheres and subsequently mixing the degrading bacteria enrichment solution with a salt-tolerant, cold-tolerant, efficient and compound degrading bacteria embedding compound solution, finally putting the biological carbon spheres in the mixed solution into a saturated borate solution and a 2%CaCl2 mixed solution one by one, then putting the biological carbon spheres into a refrigerator, crosslinking an washing to obtain salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain immobilization biological carbon spheres. The salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain is applied to purification of ammonia nitrogen and water polluted by petroleum hydrocarbon under the condition with low temperature and high salt, so that the strain is high in content of microbial biomass; obviously, the biological carbon spheres are used as carriers for immobilizing the salt-tolerant and cold-tolerant compound strain; the carriers are wide in material resources, simple to manufacture, suitable for industrialization, high in mechanical strength, excellent in treatment effect, low in cost and free of secondary pollution to the environment.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Mixed bactericide for restoring places polluted by polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, preparation method and application method
InactiveCN101735996AHigh activityLoose textureImmobilised enzymesWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonHigh activity
The invention provides a mixed bactericide for restoring places polluted by polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of environment pollution restoration engineering. The strains used by the bactericide are Bordetella, Ochrobactrum, Rhodococcus, Achcromobacter, Herbaspirillum and Microbacterium which are mixed according to the ratio of 21-101:40-200:22-102:20-100:1:2 for fermentation to obtain a bacterial liquid, and the bacterial liquid is mixed with solid carriers according to the mass ratio of 0.5-1:1 to obtain a solid bactericide which has the effective living bacteria count of 108-1011 / g. The mixed bactericide in the invention can effectively remove polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons polluting soils and water, and has the advantages of high activity, rapid growth and propagation, strong adaptability, no generation of secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Bacterial strains and variants thereof that can degrade polylactic acid, and uses of same
The invention relates to strains of bacteria of the genus Ochrobactrum, that can degrade polylactic acid. The invention also relates to an enzyme that can degrade polylactic acid, characterized in that it is produced by said bacteria strains according to the invention. The invention also relates to the applications of said bacteria strains and said enzyme that can degrade polylactic acid.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
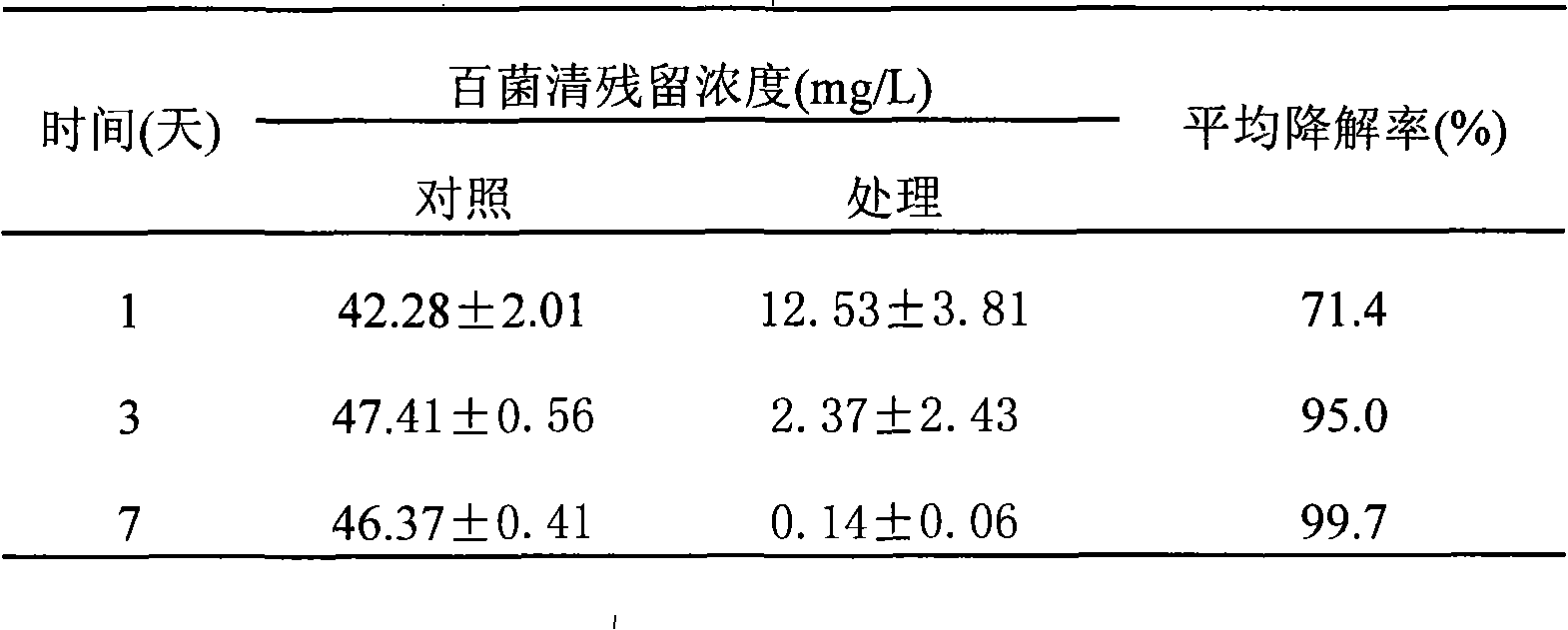
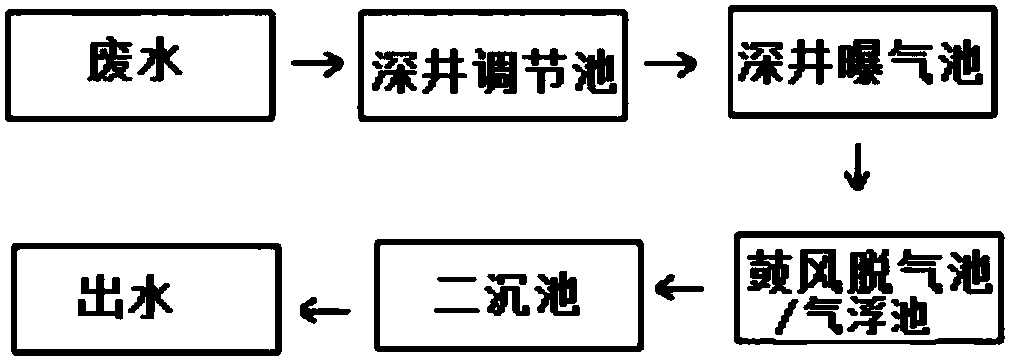
Degradation strain capable of high-efficiency degrading bactericide chlorothalonil and use thereof
InactiveCN101338284AEfficient degradation abilityAvoid secondary pollutionPigmenting treatmentBacteriaMicroorganismDisinfectant
The invention relates to a degrading bacteria which can effectively degrade a disinfectant of chlorothalonil. The classified name of the degrading bacteria is: Ochrobactrum lupine which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in June the 28th, 2007 and the preservation number thereof is CGMCC No.2098. The degrading bacteria is used to degrade the disinfectant of chlorothalonil and can be used for the biological purifying of water, soil or agricultural products polluted by the chlorothalonil.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High ammonia-nitrogen heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification resisting ochrobactrum and application thereof
ActiveCN109337832AStrong tolerance to high salinityEfficient nitrogen removal treatmentBacteriaWater contaminantsTotal nitrogenSalinity
The invention relates to a high ammonia-nitrogen heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification resisting ochrobactrum TAC-2 (Ochrobacterum sp.TAC-2) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2018028. The ochrobactrum can realize the process of synchronous nitrification and denitrification in an aerobic environment under the conditions of high ammonia nitrogen and high salinity and effectively removes total nitrogen from high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater and high-salinity wastewater; the ochrobactrum is especially suitable for removing ammonia-nitrogen from the high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater and has wide popularization significance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 capable of efficiently degrading chlorobenzene and application of ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1
ActiveCN109370945APollution efficientReduce pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsChlorobenzenePollution
The invention discloses ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 capable of efficiently degrading chlorobenzene and application of the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1. Organic pollutants include toluene, p-xylene, the chlorobenzene and 1, 2-dichlorobenzene or n-hexane. A method for applying the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 includes inoculating the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 into inorganic salt culture solution; adding the organic pollutants into the inorganic salt culture solution; carrying out degradation reaction under the conditions of the temperature of 25-35 DEG C, the rotational speed of 160 rpm and the pH (potential of hydrogen) of 6-8; degrading organic matters. The ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 and the application have the advantages that the chlorobenzene and other industrial common organic pollutants such as the toluene, the p-xylene, the 1, 2-dichlorobenzene and the n-hexane can be degraded by the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1; the chlorobenzene in industrial wastewater and waste gas can be efficiently purified by the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1, and the ochrobactrum ZJUTCB-1 is little in pollution, easy to popularize and low in purification cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for separating denitrification desulfurizing bacteria based on biodiversity information
InactiveCN104450592AEfficient Synchronized MetabolismImprove screening efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementThaueraSludge
The invention discloses a method for separating denitrification desulfurizing bacteria based on biodiversity information and relates to denitrification desulfurizing bacterium screening methods. The method comprises the steps of collecting sludge, conducting high-throughput sequencing on the sludge sample, analyzing the flora abundance fluctuation and space ecological distribution of the sludge sample, adopting different screening methods according to community composite and structure characteristics, conducting anaerobic culture on a target bacterial genus by means of an interlayer culture medium with different screening methods, selecting a single colony for isolated culture, and obtaining a single bacterial colony after repeated operation. Two kinds of denitrification desulfurizing bacterial strains, namely autotrophic denitrification desulfurizing bacteria which belong to Thiobacillus, and heterotrophic denitrification desulfurizing bacteria which belong to Thauera, Azoarcus, Arcobacter and Ochrobactrum are obtained through screening. Community structure information displayed by the strain screening result is consistent with that displayed by the high-throughput sequencing result, microbial resources are provided for improving biological treatment effectiveness of wastewater. Furthermore, the metabolic characteristics of the strains are identified.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Guangzhou pallor bacillus with high-efficiency degradation ability for pyridine
The invention provides Ochrobactrum guangzhouense P2 with high capacity in degrading pyridine. The strain as a novel species of Ochrobactrum genus is obtained by separating and purifying sludge of oil and gas factories, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number of CCTCC M 207191. The strain has higher capacity in degrading pyridine, and can effectively degrade pyridine in sludge, thus lowering the sludge processing cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Bacterium for degrading phoxim pesticide residue and produced bacterium formulation
The invention provides a degradation bacillus which can dispel the phoxime pesticide residue and its prodegradant. The used strain is Gram's staining reaction hysteroptosis X-12 which is Ochrobactrum.sp. The main biology characteristic is G-; the thaliana is the rod type whose size is (1.58-2.61)mu m*(0.79-1.23)mu m; it has flagellation around it and facultative anaerobes; the hydrogen peroxidase, oxidative enzyme, oxidation of ethanol and V.P. reaction is positive; the ketole reaction is negative; it can not be hydrolysed starched and oxide glucose to generate the acid so that the coagulate dydimic acid cow's milk; the Genbank landing number of the strain 16S rDNA is DQ093374.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
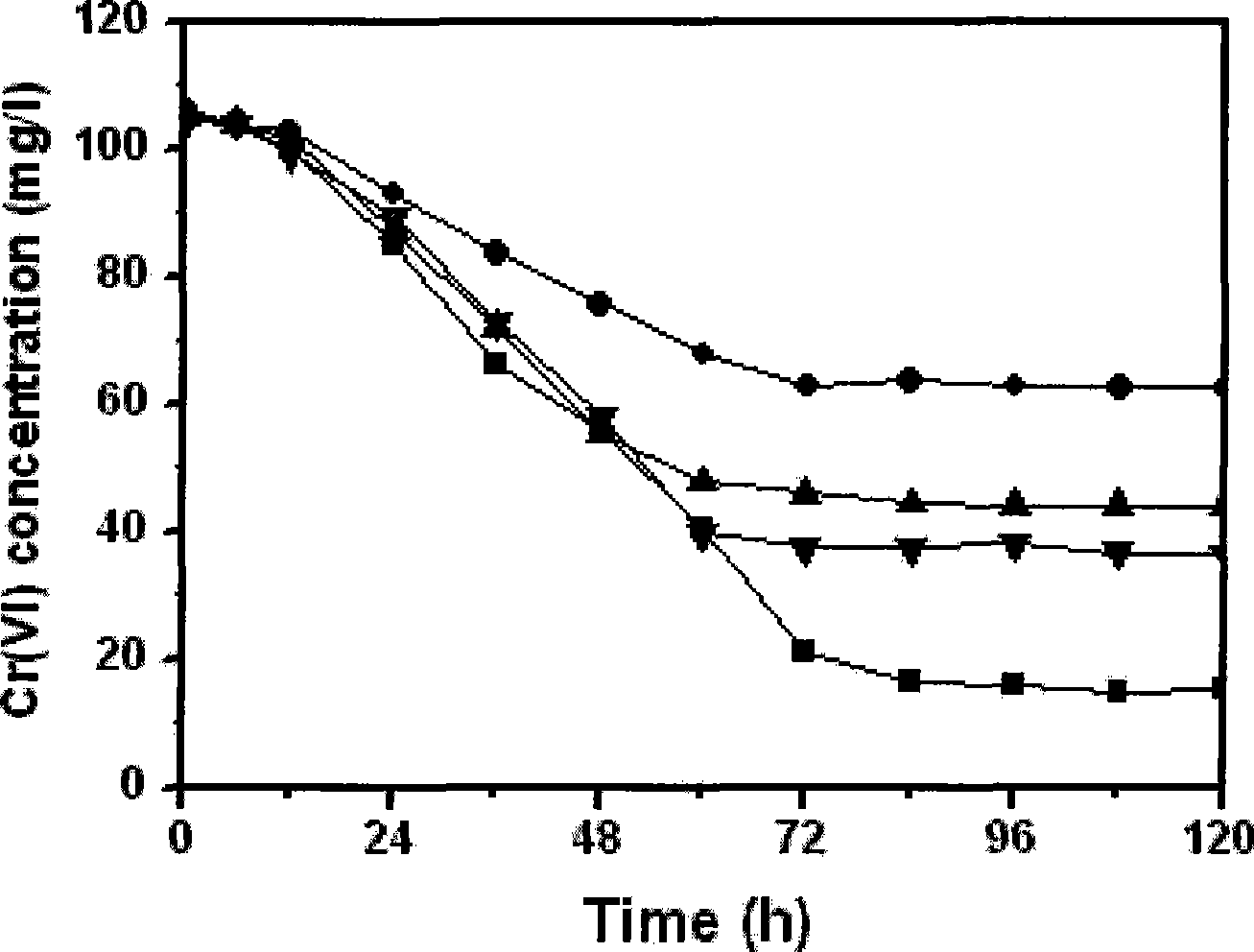
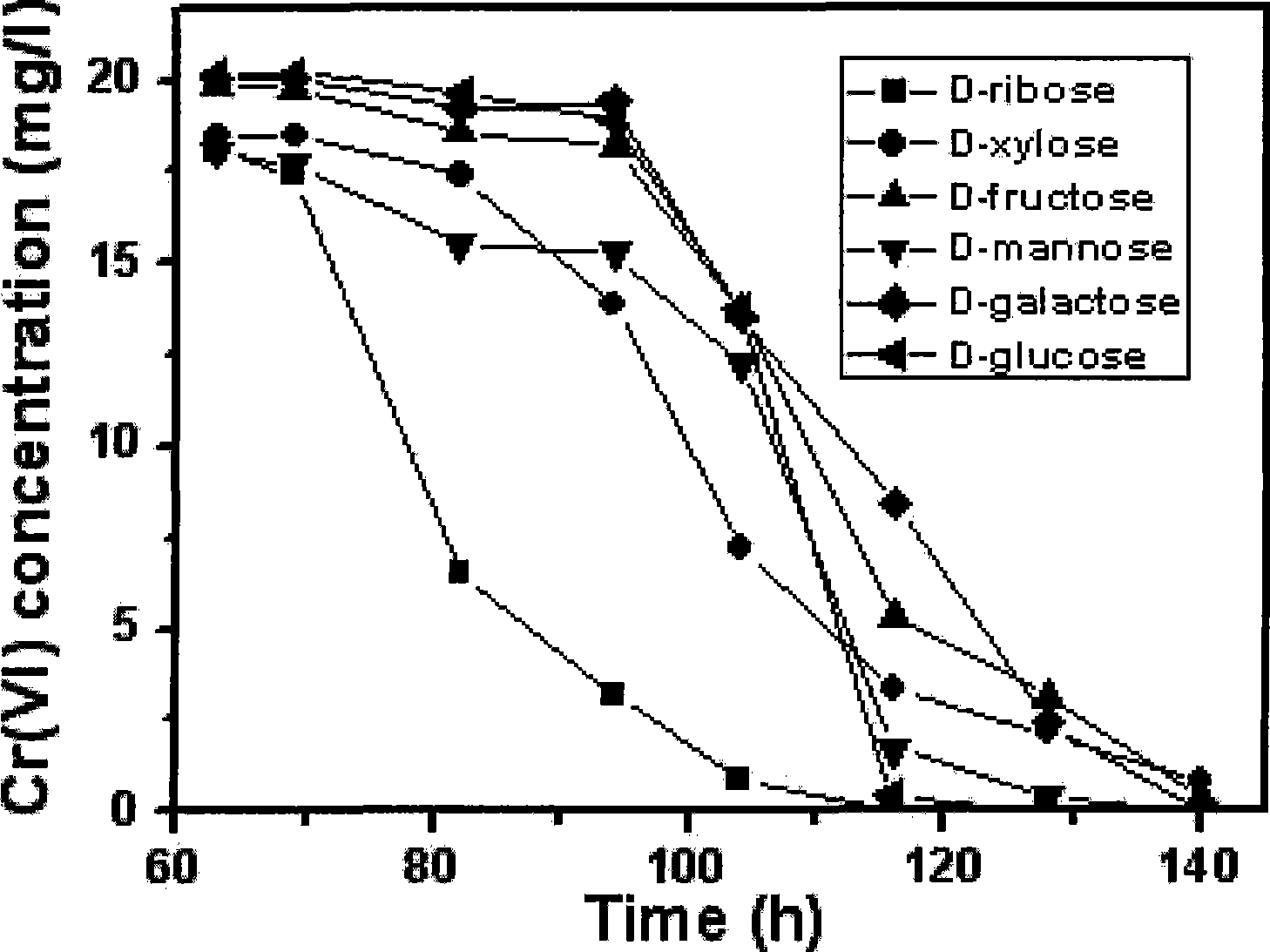
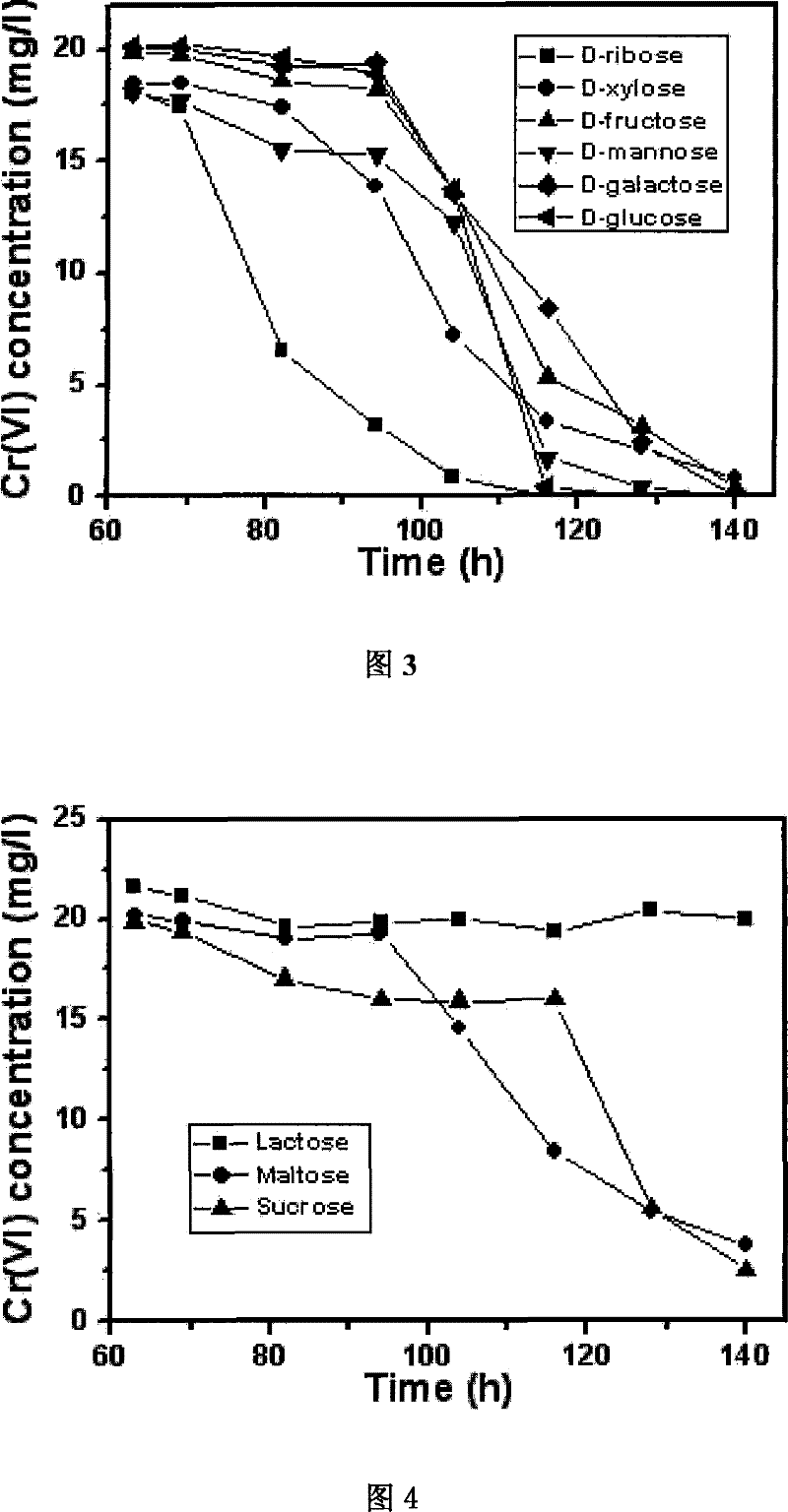
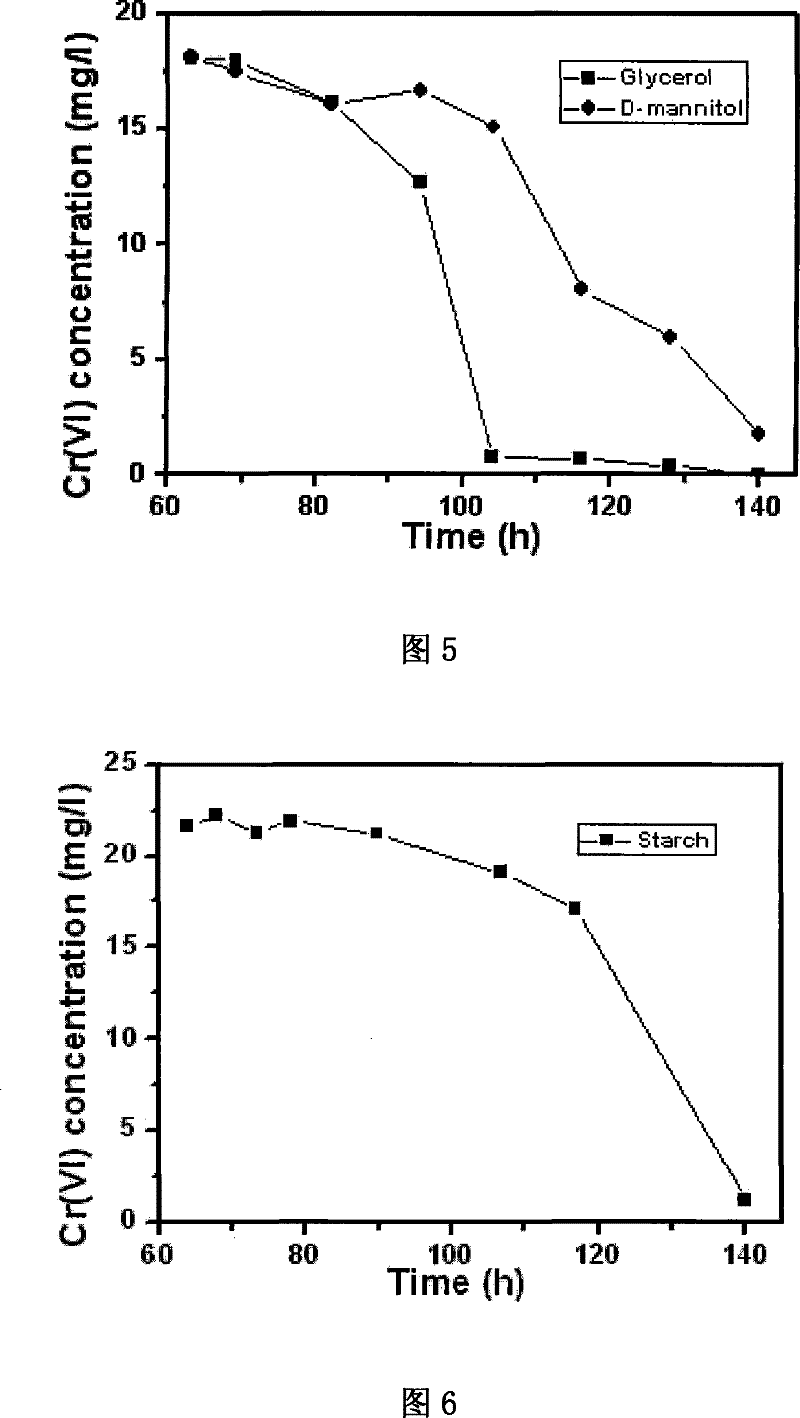
Ochrobactrum CTS-325 and culture method thereof and application thereof in reduction of hexavalent chromium
The invention discloses Ochrobactrum CTS-325 and a culturing method thereof as well as application to reducing hexavalent chromium, and relates to microbe and application thereof to efficiently and thoroughly reducing the hexavalent chromium under the aerobic condition as well as a culturing method thereof. The Ochrobactrum CTS-325 has a preserving number CGMCC1715. The strain can efficiently and thoroughly reduce the hexavalent chromium. The pH value is between 7 and 9 during reduction of the hexavalent chromium by the strain. The strain comprises one or combination of any few kinds of xylose, ribose, glucose, levulose, galactose, sucrose, maltose, starch, glycerin or mannite in an available culture medium on microbiology. When industrial waste water containing chromium and chromium slag leach liquor are treated by the Ochrobactrum CTS-325 in an optimized culture medium, the hexavalent chromium in the industrial waste water and the chromium slag leach liquor can be reduced to reach sewage discharge standard.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilizing method and application thereof
ActiveCN104651342AEfficient removalEfficient removal effectWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesAquamicrobiumAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilizing method and an application thereof. The salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilizing method comprises the following steps: firstly screening out high-efficiency ammonia oxidizing bacteria, carrying out salt-tolerant and cold-resistant domestication on the high-efficiency ammonia oxidizing bacteria to obtain domesticated Ochrobactrum.sp and Aquamicrobium.sp, then putting prepared biological carbon balls into a salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacteria-enriched liquid for carrying out biofilm formation on the biological carbon balls, then mixing with salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium embedding mixed liquor, and finally putting the biological carbon balls in the mixed liquor into a saturated boric acid solution one by one, putting the biological carbon balls into a refrigerator, crosslinking, and cleaning, so that salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilized biological carbon balls are obtained. The salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilizing method has the advantages that the biological carbon balls are utilized as a carrier for immobilizing the salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacteria, a carrier material is local and available, a preparation method is simple, industrialization can be easily realized, the salt-tolerant cold-resistant ammonia oxidizing bacterium immobilized biological carbon balls can be applied to purification of low-temperature high-salt ammonia nitrogen polluted water, microbial biomass is high, mechanical strength is high, treatment effect is good, cost is low, recycling is not carried out, and no secondary pollution is produced to the environment.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Ochrobactrum and biological agent thereof, preparation method and application
ActiveCN105238729AEfficient degradationEasy to useBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses ochrobactrum and a biological agent thereof, a preparation method and application. The ochrobactrum is ochrobactrum intermedi. The biological agent with the ochrobactrum as an active ingredient is prepared by conducting test tube culture and liquid fermentation culture on the ochrobactrum intermedi. The preparing method of the biological agent with the ochrobactrum as the active ingredient comprises the steps of test tube culture and liquid fermentation culture. The application refers to the application of the biological agent with the ochrobactrum as the active ingredient in repairing polluted soil with thiophanate methyl residues and in degrading and removing the thiophanate methyl residues in crops. The thiophanate methyl residues degrading bacteria prepared through fermentation of strains TP206 can be widely used for eliminating thiophanate methyl residue pollution in the soil, can also be directly sprayed to the surface of the soil or surfaces of the crops in agricultural production, can effectively degrade and remove the thiophanate methyl residues and are convenient to use and low in cost.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
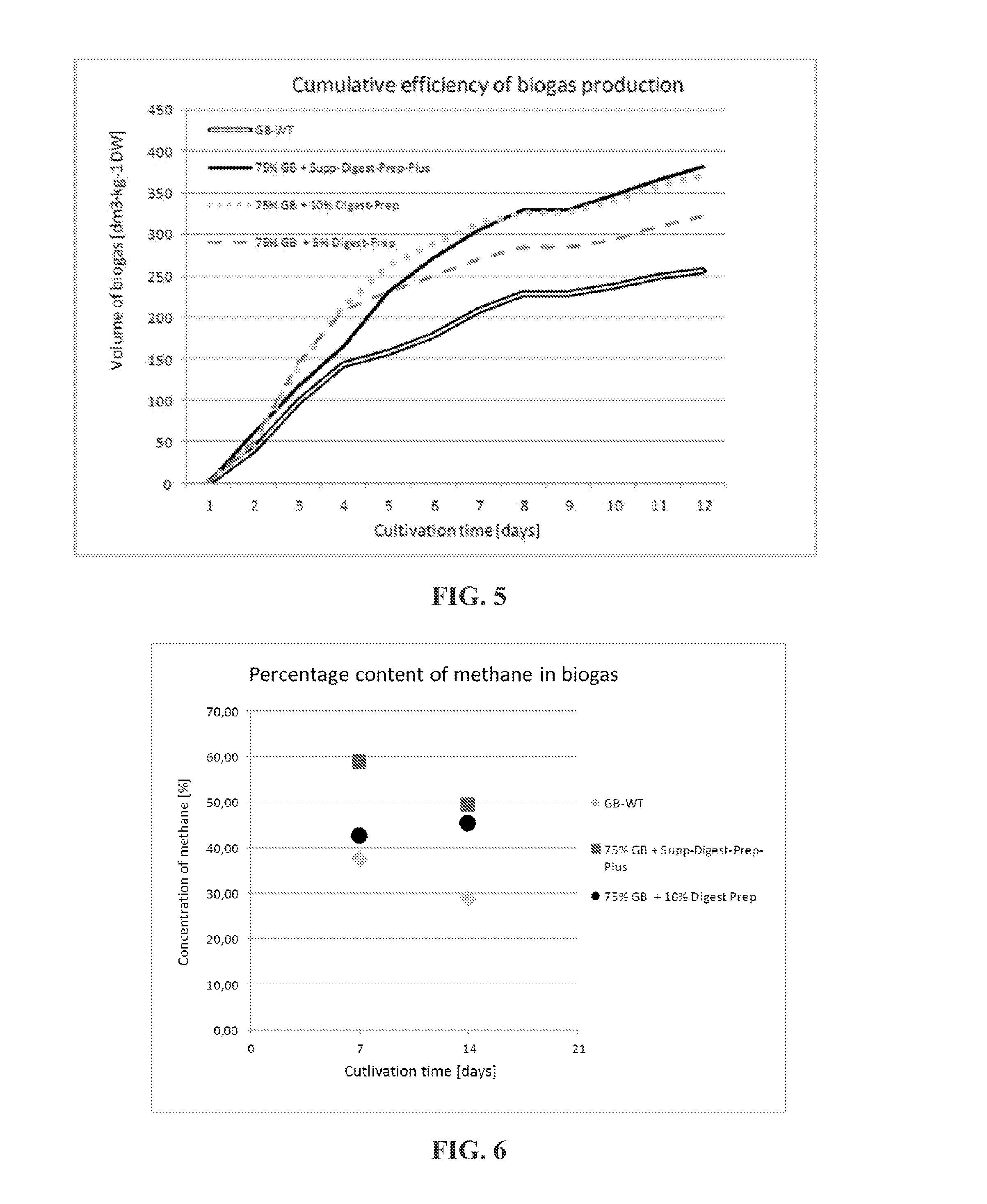
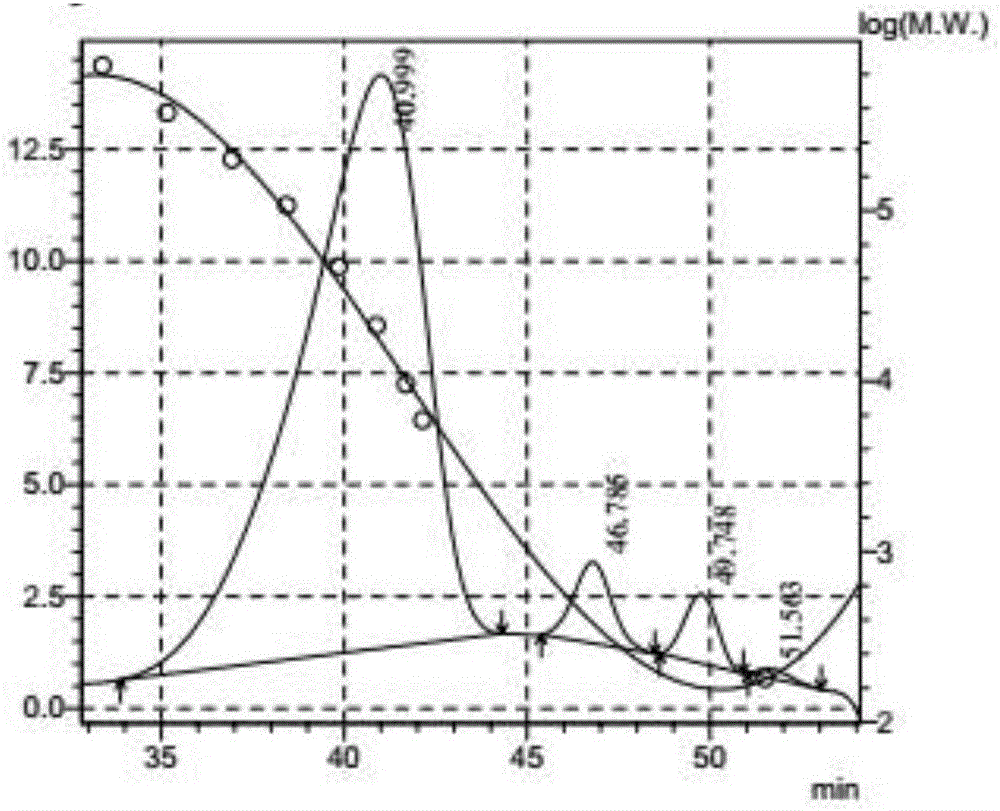
Consortium and preparation of microorganisms for catalyzing cellulose hydrolysis, preparation for methane fermentation supplementation, combination preparation, use thereof and method using the same
The invention relates to a consortium of microorganisms capable of hydrolyzing cellulose, preferably lignocellulosic biomass, which may comprise the following mixtures of bacterial strains: Bacillus sp. KP7, KP20 and Ochrobactrum sp. KP8 (the mixture deposited in PCM under the no. B / 00064), Providencia sp. KP14; Bacillus sp. KP6 and KP16 (the mixture deposited in PCM under the no. B / 00065), Bacillus sp. KP4, KP5, KP17 and KP22 (the mixture deposited in PCM under the no. B / 00066), Providencia sp. KP10; Bacillus sp. KP1 and KP19 (the mixture deposited in PCM under the no. B / 00067), Ochrobactrum sp. KP13; Bacillus sp. KP9 and KP12 (the mixture deposited in PCM under the no. B / 00068), as well as a preparation for hydrolyzing cellulose which may comprise this consortium, a supplement preparation, a combination preparation, and use and method of using the same.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI
Bacterial strain for high-producing bacterial polysaccharide and method thereof for preparing polysaccharide by fermenting traditional Chinese medicinal waste
ActiveCN106754562AHigh purityLow nutritional requirements for fermentationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucroseSaccharum
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a bacterial strain for high-producing bacterial polysaccharide and a method thereof for preparing polysaccharide by fermenting traditional Chinese medicinal waste. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC); the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016273. A bacterial strain of intermediate ochrobactrum ZY03 is inoculated in a culture medium with a sucrose content of 10g / L; the yield of the polysaccharide can reach 6g / L at most; the conversion ratio can reach 67 percent at most.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Degradation strain capable of high-efficiency degrading bactericide chlorothalonil and use thereof
InactiveCN101338284BEfficient degradation abilityAvoid secondary pollutionPigmenting treatmentBacteriaMicroorganismDisinfectant
The invention relates to a degrading bacteria which can effectively degrade a disinfectant of chlorothalonil. The classified name of the degrading bacteria is: Ochrobactrum lupine which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in June the 28th, 2007 and the preservation number thereof is CGMCC No.2098. The degrading bacteria is used to degrade the disinfectant of chlorothalonil and can be used for the biological purifying of water, soil or agricultural products polluted by the chlorothalonil.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High efficient JM bacterium technology for processing high salt heavy metal degradation-resistant organic wastewater, killing bacteria and removing odor
ActiveCN108410754AActs as antibacterial and deodorantStable structureBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacillus licheniformisSide effect
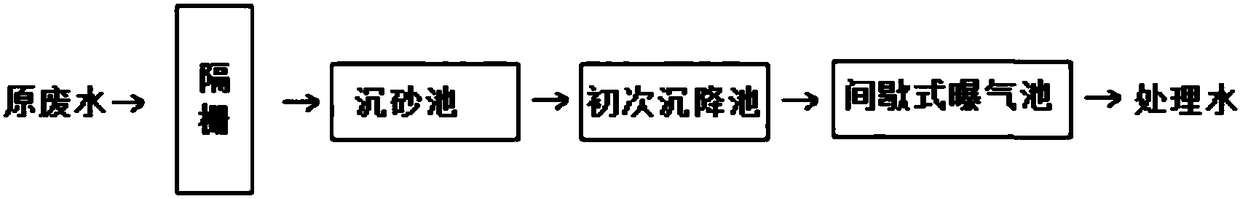
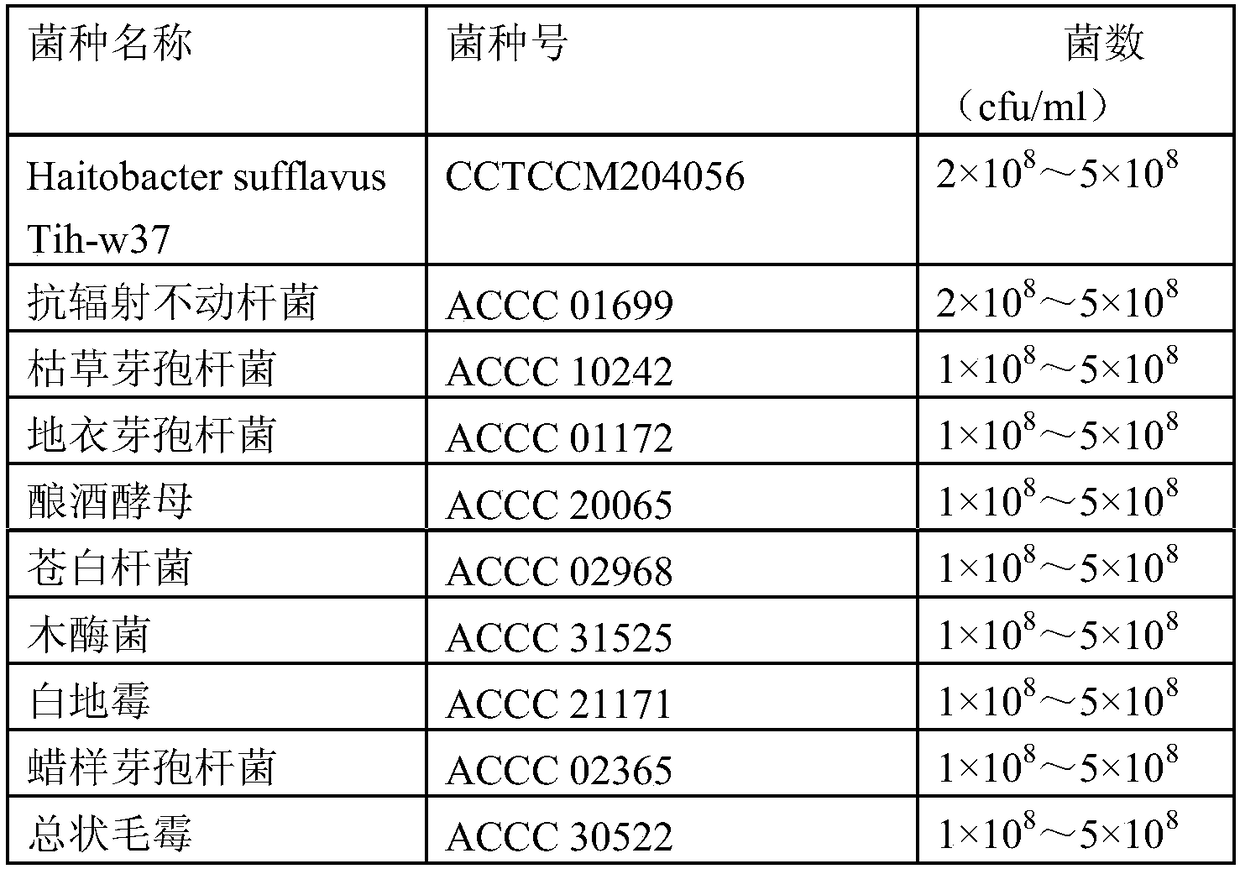
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiological wastewater processing, and specifically relates to a high efficient JM bacterium technology for processing high salt heavy metal degradation-resistant organic wastewater, killing bacteria and removing odor. The JM bacterium is a microbial composite inoculant, which comprises Haitobacter sufflavus Tih-w37, acinetobacter radioresistens,bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, brewer's yeast, trichoderma sp, ochrobactrum, cryytococcus neoformans, and bacillus cereus. The provided microbial composite inoculant has a stable structure and comprehensive functions, and does not have any side effect. The microbial flora can produce enzymes efficiently and proliferates quickly. Compared with EM bacteria, the JM bacteria are more efficient, more convenient, quicker, and more economic, and do have any toxicity or salt.
Owner:上海木良环保科技有限公司
Ochrobactrum-mediated transformation of plants
InactiveCN108513584ABacteria peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionOrigin of replicationVirulent characteristics
Methods and compositions for Ochrobactrum-mediated transformation of plants are provided. Methods include but are not limited to using an Ochrobactrum strain to transfer a polynucleotide of interest to a plant cell. These include VirD2-dependent methods. Compositions include an Ochrobactrum strain, transfer DNAs, constructs and / or plasmids. These include Ochrobactrum strains having a plasmid comprising one or more virulence gene(s), border region, and / or origin of replication. Plant cells, tissues, plants, and seeds comprising a polynucleotide of interest produced by the methods are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Compound microorganism bacterium agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN109517760AEasy accessWide variety of sourcesBacteriaWater contaminantsChemical oxygen demandSmeryngolaphria numitor
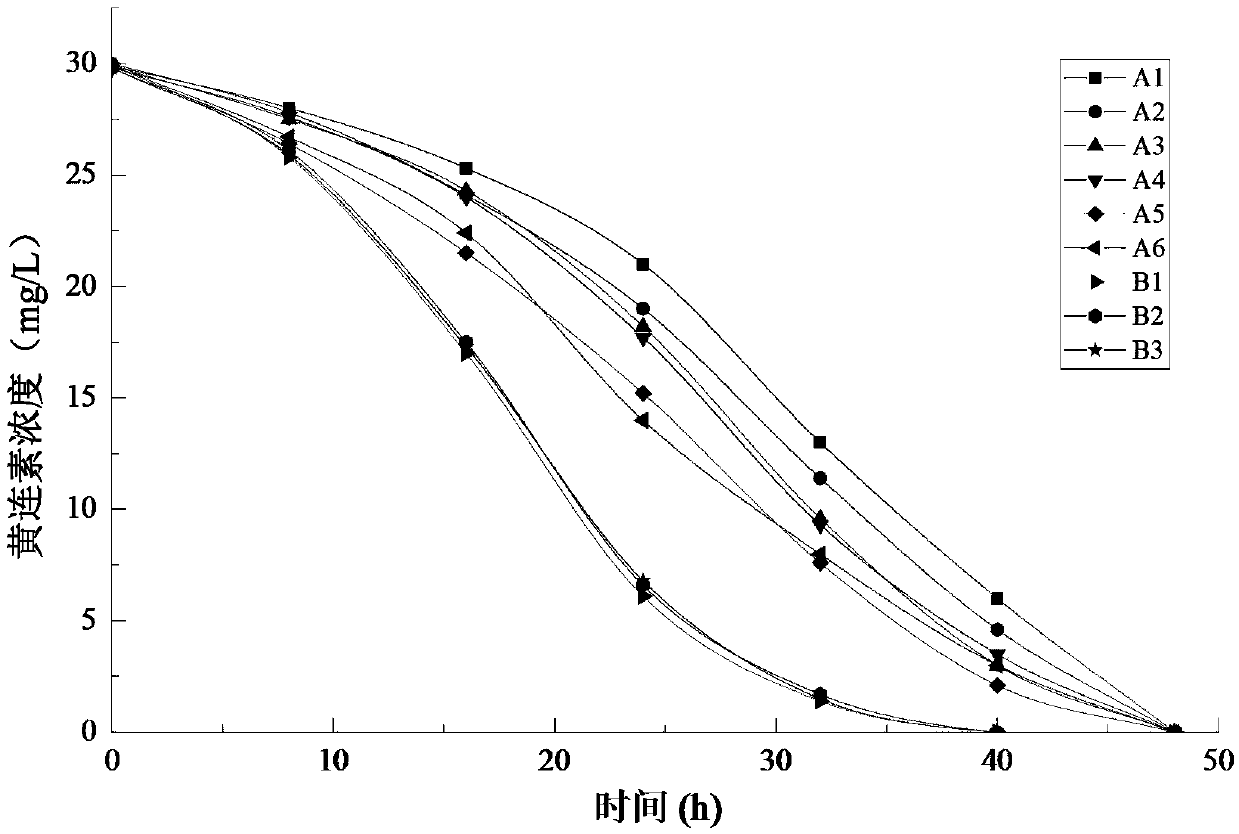
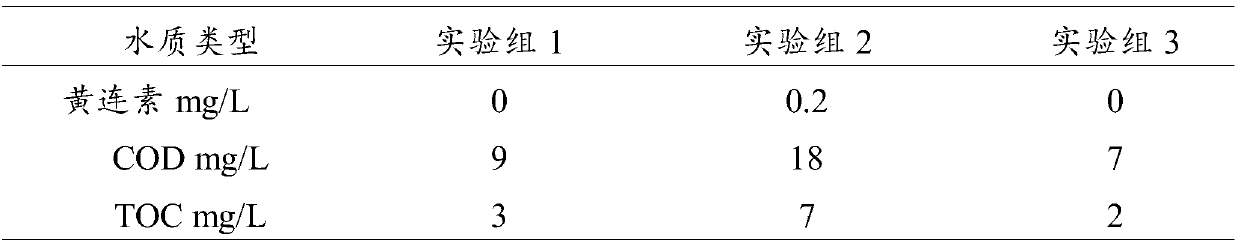
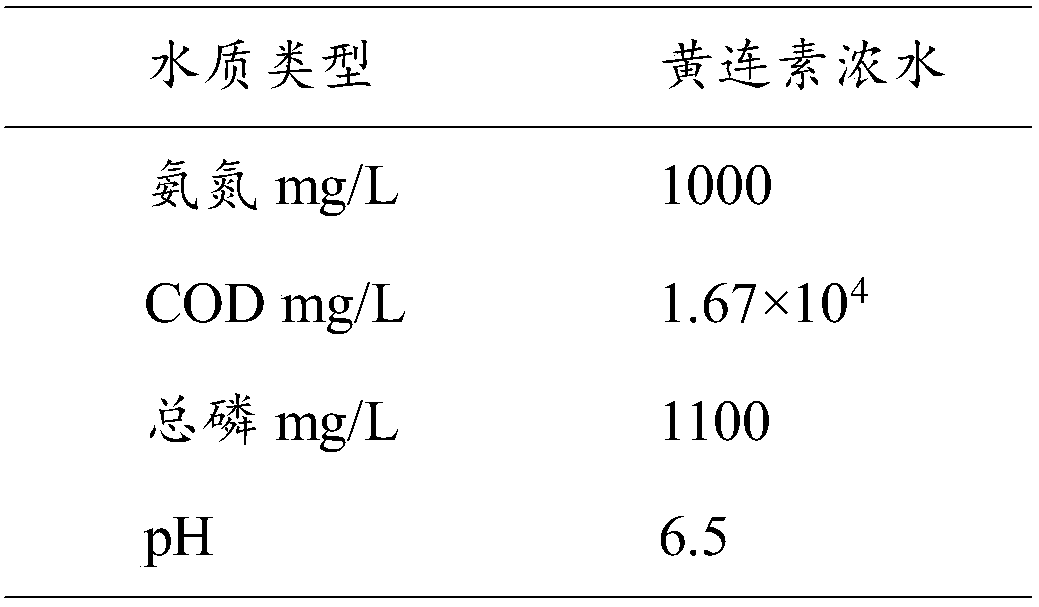
The invention provides a compound microorganism bacterium agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof and relates to the technical field of microorganism bacterium agents. An activecomponent of the compound microorganism bacterium agent comprises a compound microorganism; the compound microorganism comprises: bacillus circulans, bacillus, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, bacillus cereus, sphingomonas and ochrobactrum; the total amount of microorganisms in the compound microorganism bacterium agent is not lower than 1*10<7> cfu / mL. The compound microorganism bacterium agent canbe used for treating berberine production wastewater; the adding amount of the compound microorganism bacterium agent is 2 percent, the removal rate of berberine is 100 percent, the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal rate is 75 to 94 percent, the TOC (Total Organic Carbon) removal rate is 83 to 95 percent, the NH3-N removal rate is 89 to 92 percent and the TP (Total Phosphorus) removal rate is 73 to 100 percent.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Azoxystrobin degrading bacterium and microbial inoculum produced by using degrading bacterium and applications of degrading bacterium
ActiveCN104593287ASolve pollutionSolve the problem of excessive pesticide residuesBacteriaWater contaminantsEcological environmentPesticide residue
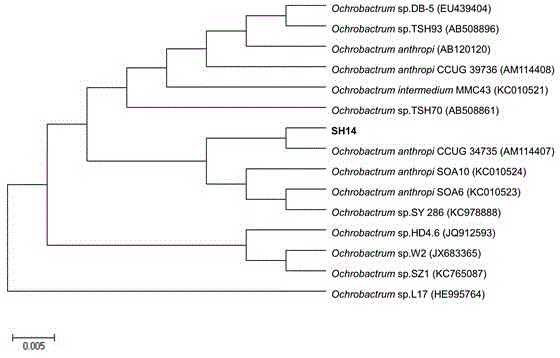
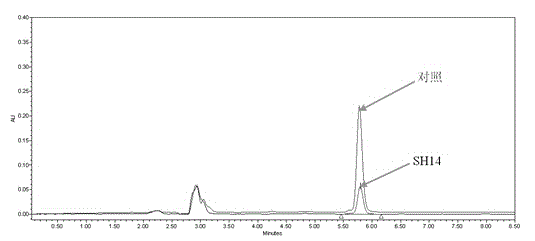
The invention discloses an azoxystrobin degrading bacterium and a microbial inoculum produced by using the degrading bacterium and applications of the degrading bacterium. The strain is ochrobactrum anthropi (Ochrobactrum (anthropi) SH14, the strain is preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection on December 20, 2013, and the Preservation Number is CCTCC NO: M 2013681. The strain can effectively degrade azoxystrobin pesticide residues in a short time, so that the strain can be used for restoring natural environments such as water and soil and the like polluted by azoxystrobin. A preparation prepared by using the strain has the advantages of low production cost, easiness for use, good removal effect, and the like. By using the microbial inoculum, the residual quantity of azoxystrobin in water and soil can be reduced by over 85% in a short period of time, so that natural environments polluted by azoxystrobin are effectively restored, and the excessive pesticide residue problem and the environmental pollution problem in agricultural production are solved, thereby protecting the ecological environment and the human health.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pesticide carbendazim degrading microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107011912BProtection securityPromote greenAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaAgricultural sciencePesticide residue
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
A method for efficiently degrading azoxystrobin by using Pallidum pallidus
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly discloses a method for efficiently degrading azoxystrobin by utilizing ochrobactrum anthropic. Ochrobactrum anthropic SH14 is used for degrading the azoxystrobin under the condition that the temperature is 30.2 DEG C, the pH is 7.9 and the inoculum size is 0.2g / L, and the degradation rate of the ochrobactrum anthropic SH14 on 50mg / L of azoxystrobin is above 85%; the method disclosed by the invention provides theoretical practice basis for future large-scale industrial production and application of the ochrobactrum anthropic SH14 and has wide signification.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Triazoline pesticide residual degrading strain and strain therefrom
InactiveCN1584017AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaBiological propertyPesticide residue
A triazophosphorus pesticide residual degrading bacteria and bacteria preparation produced from it are disclosed, the strain is Gram's chromatic reacting negative bacteria strain MP-4, which belongs to ochrobactrum.sp. Its characteristics are G-, nemaline, 1.58X0.79mum; reaction of oxidase, glycolic oxidation and V.P is positive; indole reaction is negative; Genbank number of the strain 16S rDNA is AY331578. Its advantages include decrement of pesticide residual amount, atoxic and innoxious green agricultural product.
Owner:南京农大环境生物工程有限公司
Ochrobactrum sp. for degrading tetrabromobisphenol-a (TBBPA) and its application
InactiveUS20110281332A1Lower capability requirementsPromote degradationBacteriaSolid waste disposalTetrabromobisphenol ASludge
The invention discloses an Ochrobactrum sp. for degrading TBBPA and its application in environmental remediation. An Ochrobactrum sp. for degrading TBBPA was isolated from the sludge in a high risk area of electronic waste in the invention. The strain is named as Ochrobactrum sp. T, which has been deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on Oct. 28, 2009 with an accession number of CCTCC M209246. Ochrobactrum sp. T obtained in the invention has high degradation capability to TBBPA in environment. The degradation efficiency of the strain achieves 96.2%. The strain could be applied to degrading TBBPA in environmental remediation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
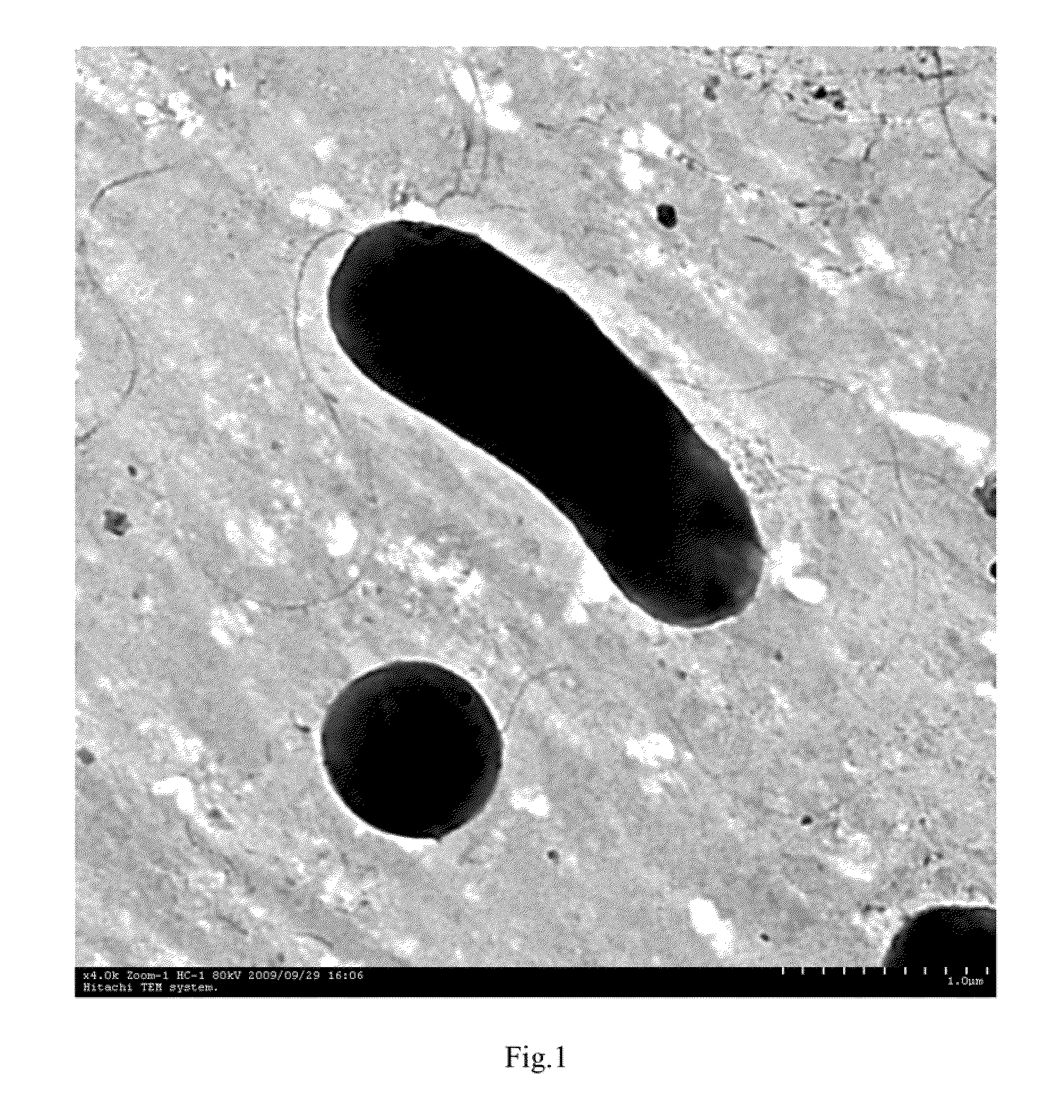
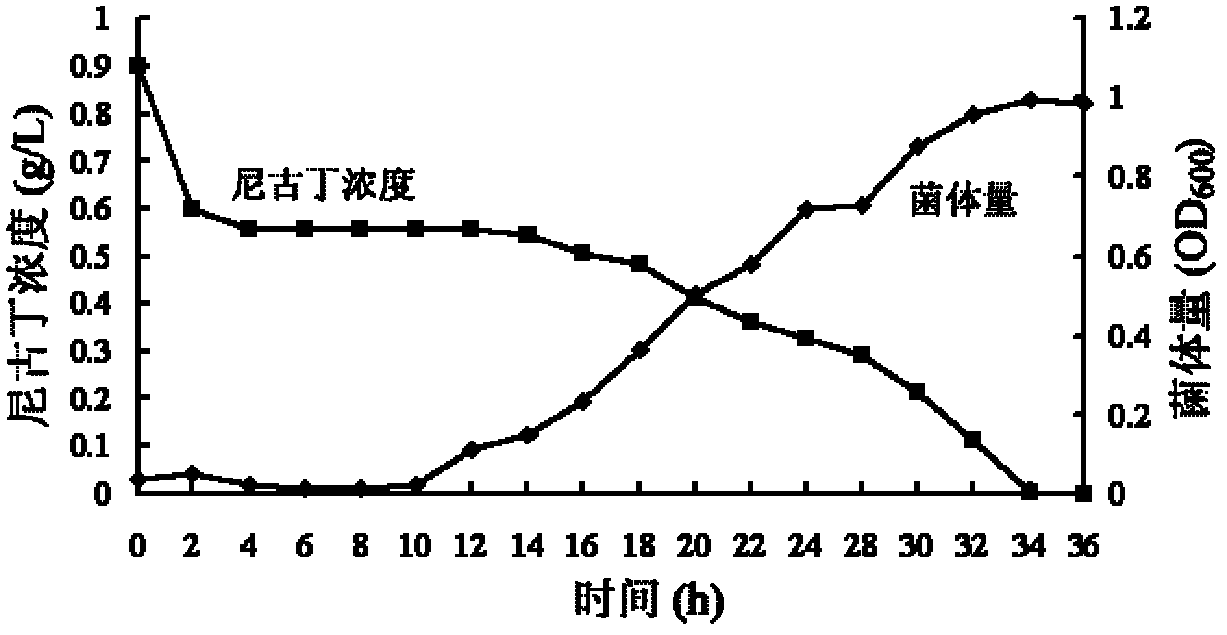
Ochrobactrum and application thereof
InactiveCN102433275AImprove qualityReduce pollutionBacteriaTobacco treatmentOchrobactrum sp.Microorganism
The invention relates to ochrobactrum and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 disclosed by the invention was preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) on 3rd, November, 2011 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5442. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 has the capability of metabolizing nicotine and can growat the concentration of the nicotine as high as 4.5g / L. By culturing the ochrobactrum sp.4-40 in a large amount, a biocatalyst using a complete cell of the strain is used for completely degrading pure nicotine and can be used for reducing the content of the nicotine in tobacco leaves simultaneously. The ochrobactrum sp.4-40 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nicotine in tobacco and tobacco wastes can be degraded and the harm of cigarettes on a human body and the pollution to the environment are reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Ochrobactrum CTS-325 and culture method thereof and application thereof in reduction of hexavalent chromium
ActiveCN101418266BEfficient reductionEfficient and thorough restorationBacteriaIndustrial waste waterSlag
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of Pallidus tritici capable of degrading lincomycin
ActiveCN104962495BReduce adverse effectsEfficient treatment methodBacteriaSolid waste disposalBacillus licheniformisMicroorganism
The invention discloses wheat ochrobactrum of degradable lincomycin. The wheat ochrobactrum is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center as the preservation number CGMCC No.10665. The wheat ochrobactrum of the degradable lincomycin can use the lincomycin as an exclusive carbon source to grow, and the degradation capacity of the strain for the lincomycin can reach 100 percent in 24 hours. The strain can be used for harmlessly treating fermented fungi residue in the industrial production of the lincomycin, the treatment method is effective, environment-friendly, capable of saving the resource, low in treatment cost and capable of thoroughly eliminating adverse impact of lincomycin waste hypha on the environment.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Triazophos pesticide residual degrading strain and strain therefrom
InactiveCN1257264CEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaBiological propertyPesticide residue
The invention provides a triazophos pesticide residue degrading bacterium and the bacterial agent produced therefrom. The used bacterial strain is Gram staining negative bacterial strain MP-4, which is identified as Ochrobactrum.sp. The main biological characteristic is G - , the bacteria are rod-shaped, about 1.58×0.79μm in size, with periosteum flagella, facultative anaerobic; catalase, oxidase, ethanol oxidation and V.P. reactions are positive; indole reaction is negative; starch cannot be hydrolyzed, glucose is oxidized Produce acid to coagulate litmus lactic acid. The Genbank accession number of the strain 16S rDNA is AY331578. The direct application of degrading bacteria products can reduce the amount of pesticide residues in crops by more than 90%, solve the problem of excessive pesticide residues in agricultural production, and produce non-toxic and pollution-free green agricultural products.
Owner:南京农大环境生物工程有限公司
A functional protein capable of degrading*
InactiveCN104673763BEffective catalytic degradationMicroorganism based processesBacteria peptidesPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonReaction temperature
The invention provides functional protein capable of degrading chrysene. The functional protein capable of catalyzing and degrading the chrysene is obtained by extracting and purifying a bacterium liquid of Ochrobactrum anthropic DW1 with the strain preservation number of CGMCC NO.8621. When the functional protein catalyzes and degrades the chrysene, the proper pH value ranges from 6.0 to 8.0, the most proper pH value is 7.0, the functional protein can be deactivated and denaturized easily when the pH value is smaller than 4 or larger than 10, the proper reaction temperature ranges from 30 DEG C to 45 DEG C, the most proper reaction temperature is 35 DEG C, the functional protein can be deactivated and denaturized easily when the temperature is higher than 50 DEG C, and Cu<2+>, Ni<2+> and Hg<2+> ions with the concentration of 1 mmol / L have stronger inhibition effects on the activity of the functional protein. The functional protein can effectively catalyze and degrade the chrysene and has the application potential for soil and water polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon chrysene.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Plasmid containing functional gene capable of degrading benzo [ghi] perylene
InactiveCN104711258APromote degradationMicroorganism based processesDNA preparationVitamin CBacterial strain
The invention provides a plasmid containing a functional gene capable of degrading benzo [ghi] perylene. The plasmid containing the functional gene capable of degrading benzo [ghi] perylene is obtained by extracting and purifying bacterium liquid of bacterial strain of lupin Ochrobactrum lupine DW3. The preparation method of the plasmid comprises the following steps: inoculating the lupin Ochrobactrum lupine DW3 in a glass bottle which is filled with benzo [ghi] perylene, a basal culture medium, trace metal liquid ad a vitamin C solution; culturing for 20 days to obtain bacterium liquid; extracting and purifying the bacterium liquid to obtain the plasmid containing the functional gene capable of degrading benzo [ghi] perylene. The plasmid containing the functional gene capable of degrading benzo [ghi] perylene has the ability of constructing bacterial strains with degrading function for benzo [ghi] perylene, improving the biodegradation effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants represented by the benzo [ghi] perylene and having application potential for the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon benzo [ghi] perylene polluted soil and water.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Functional protein capable of degrading chrysene
InactiveCN104673763AEffective catalytic degradationMicroorganism based processesBacteria peptidesPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonReaction temperature
The invention provides functional protein capable of degrading chrysene. The functional protein capable of catalyzing and degrading the chrysene is obtained by extracting and purifying a bacterium liquid of Ochrobactrum anthropic DW1 with the strain preservation number of CGMCC NO.8621. When the functional protein catalyzes and degrades the chrysene, the proper pH value ranges from 6.0 to 8.0, the most proper pH value is 7.0, the functional protein can be deactivated and denaturized easily when the pH value is smaller than 4 or larger than 10, the proper reaction temperature ranges from 30 DEG C to 45 DEG C, the most proper reaction temperature is 35 DEG C, the functional protein can be deactivated and denaturized easily when the temperature is higher than 50 DEG C, and Cu<2+>, Ni<2+> and Hg<2+> ions with the concentration of 1 mmol / L have stronger inhibition effects on the activity of the functional protein. The functional protein can effectively catalyze and degrade the chrysene and has the application potential for soil and water polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon chrysene.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com