Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Ionizing particles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
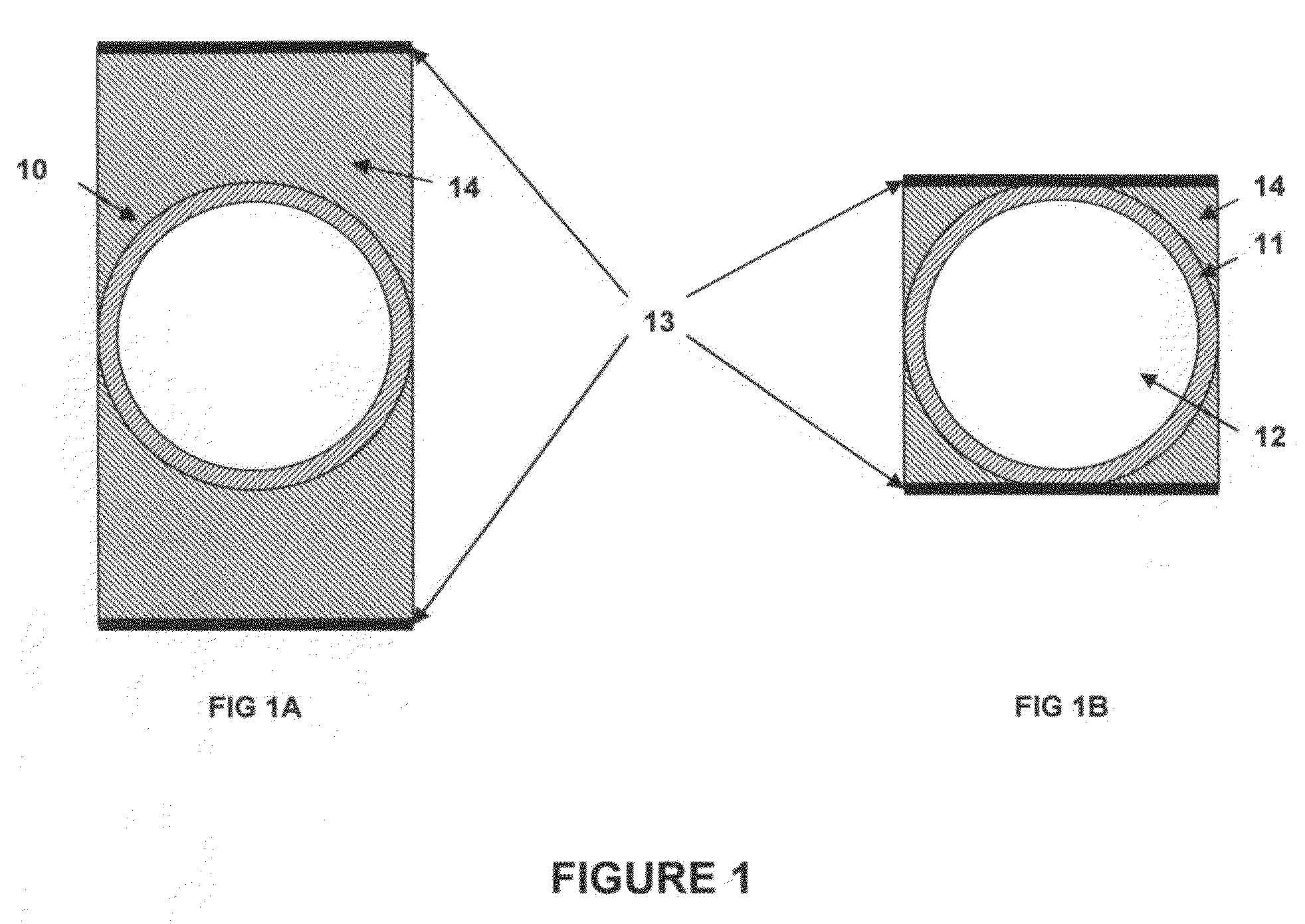
Directly ionizing particles are electrically charged particles that have sufficient kinetic energy to produce ionization by collision. These include, but are not limited to, electrons, protons, alpha particles (helium nucleus) and beta particles (high energy electrons).
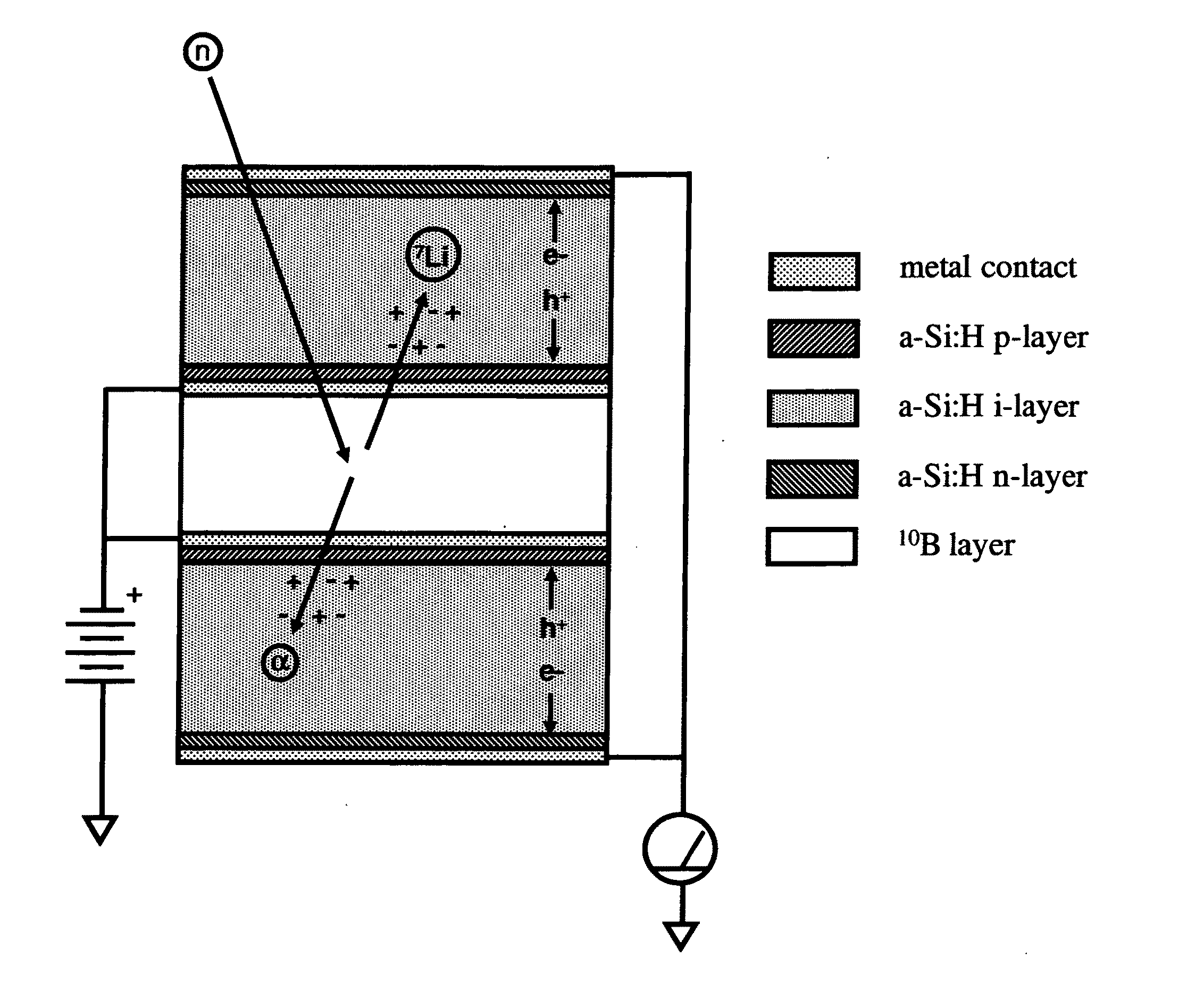
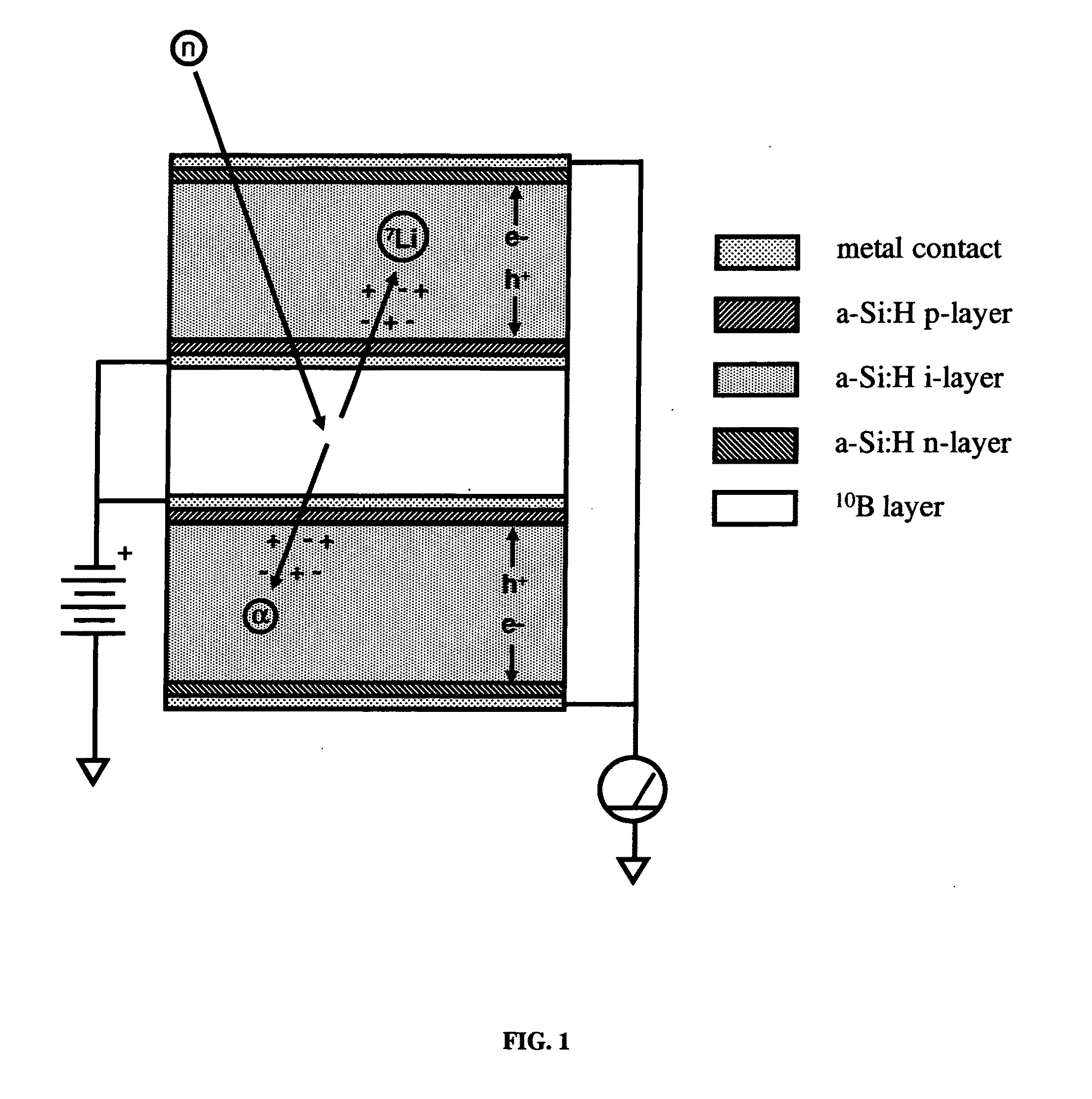
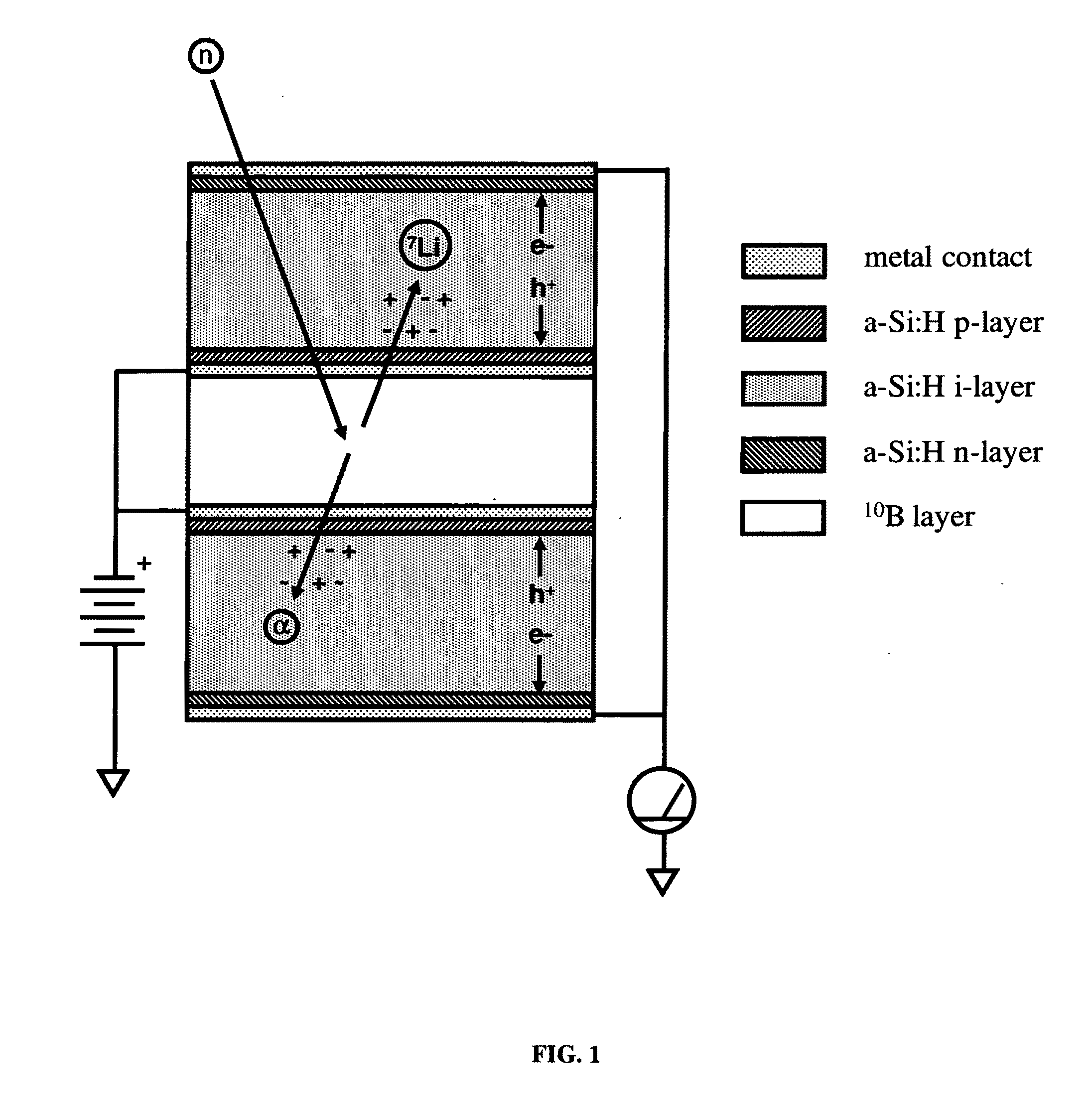
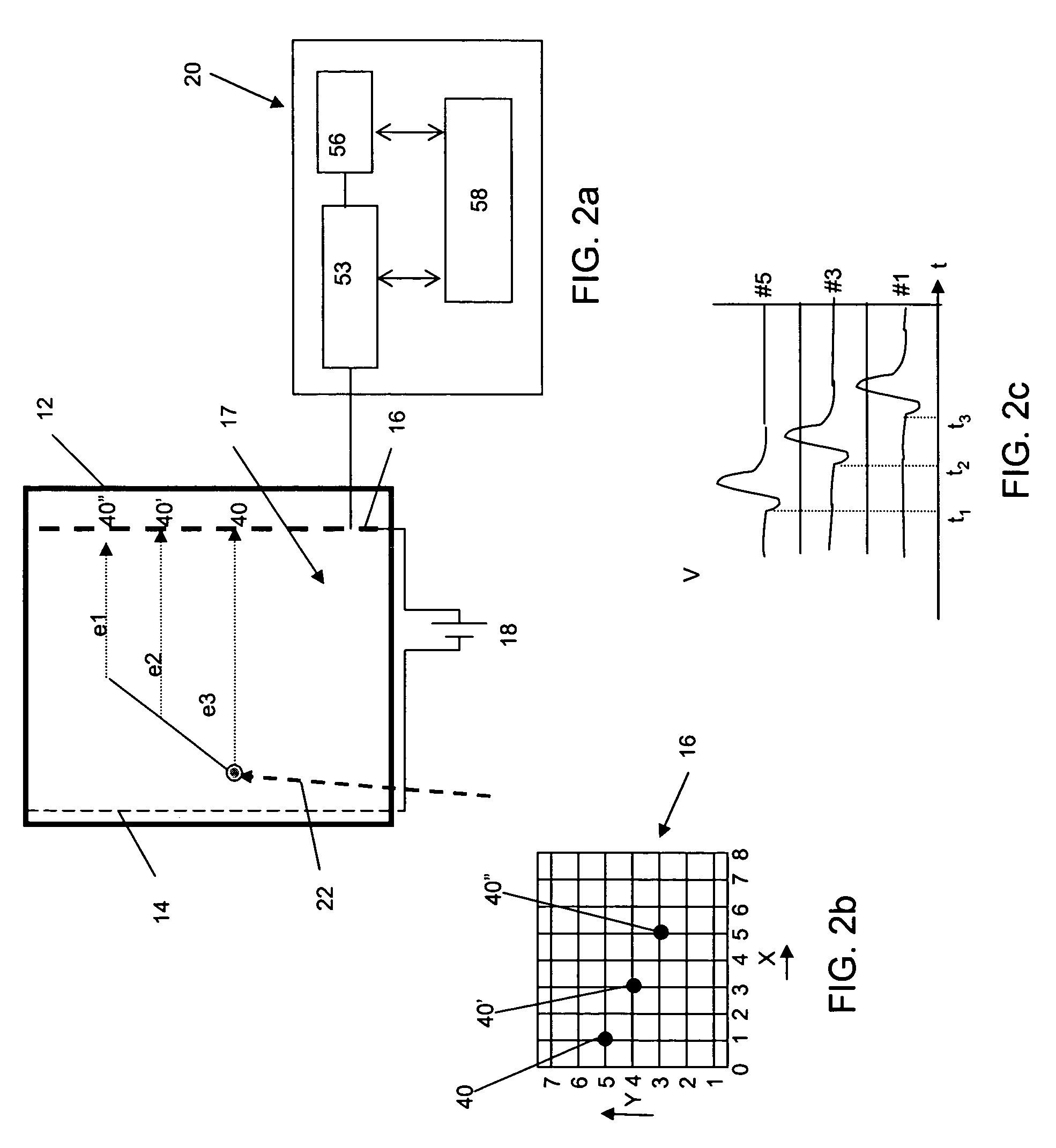
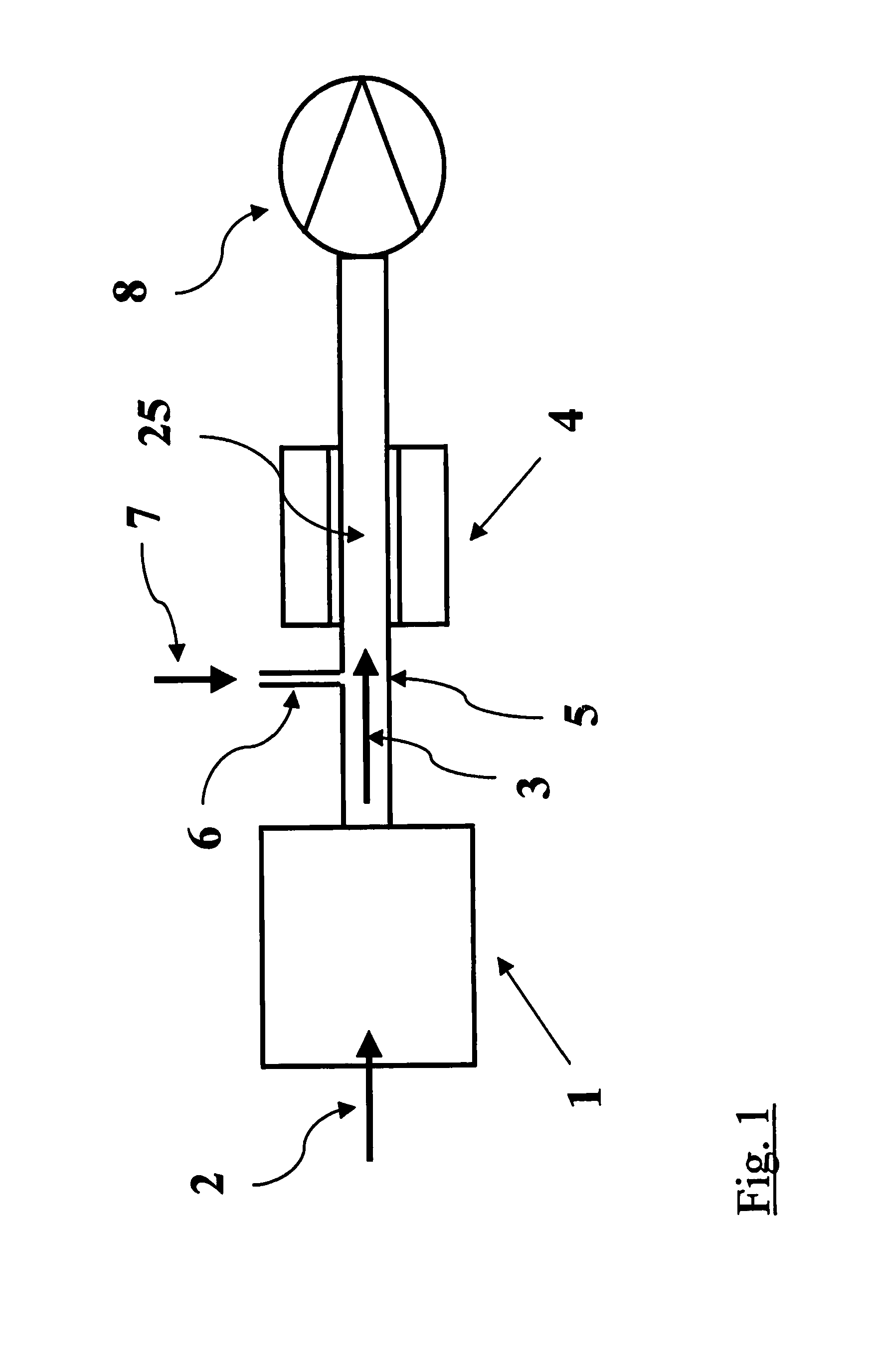
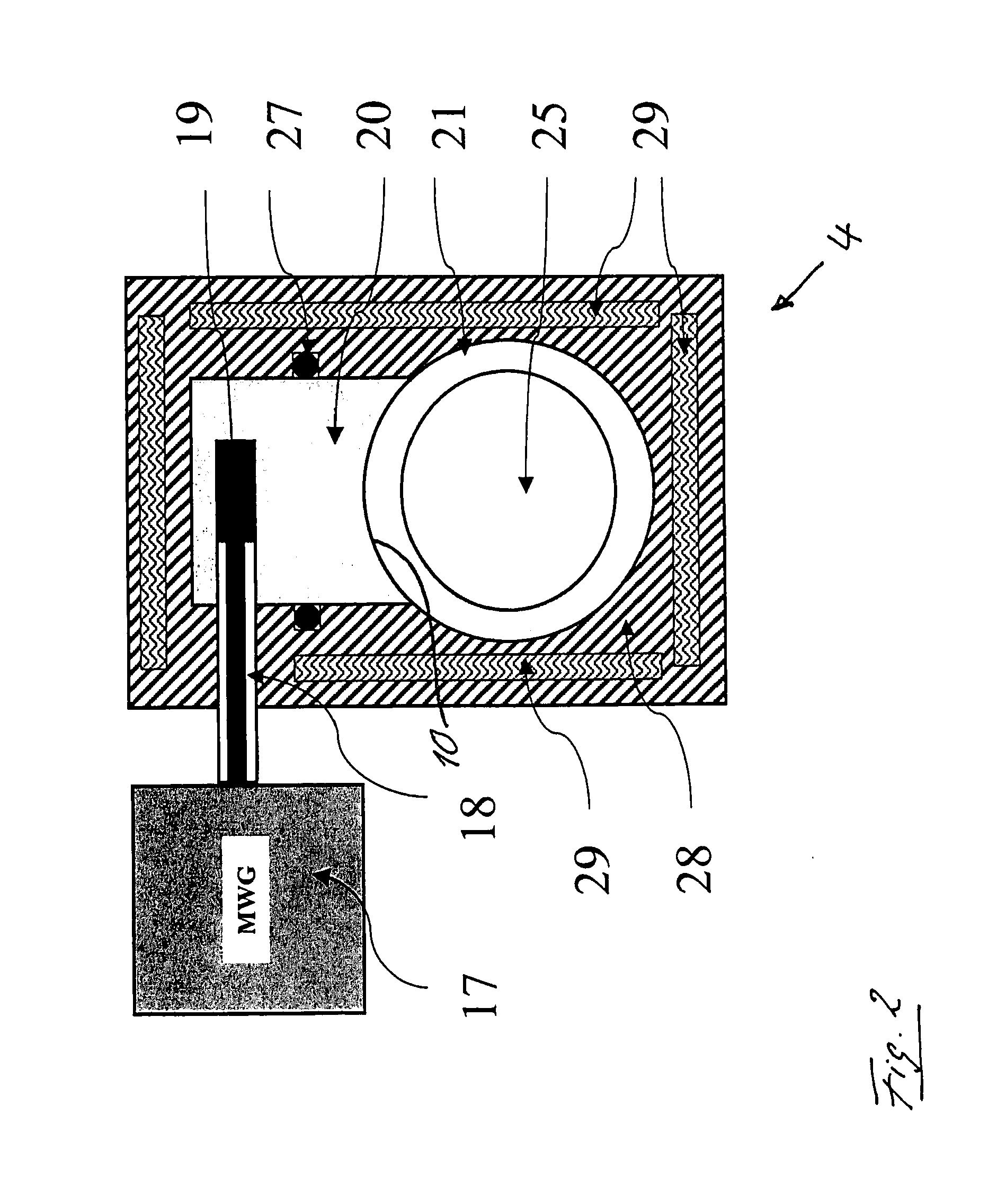
Solid state neutron detector
InactiveUS20110266643A1High neutron capture cross sectionLow costMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSemiconductor devicesElectron holeHigh absorption
A low-cost device for the detection of thermal neutrons. Thin layers of a material chosen for high absorption of neutrons with a corresponding release of ionizing particles are stacked in a multi-layer structure interleaved with thin layers of hydrogenated amorphous silicon PIN diodes. Some of the neutrons passing into the stack are absorbed in the neutron absorbing material producing neutron reactions with the release of high energy ionizing particles. These high-energy ionizing particles pass out of the neutron absorbing layers into the PIN diode layers creating electron-hole pairs in the intrinsic (I) layers of the diode layers; the electrons and holes are detected by the PIN diodes.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Mass spectrometer interface
ActiveUS20060186334A1Improve concentrationPromote liberationStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersThermal energyCompound (substance)
A mass spectrometer interface, having improved sensitivity and reduced chemical background, is disclosed. The mass spectrometer interface provides improved desolvation, chemical selectivity and ion transport. A flow of partially solvated ions is transported along a tortuous path into a region of disturbance of flow, where ions and neutral molecules collide and mix. Thermal energy is applied to the region of disturbance to promote liberation of at least some of the ionized particles from any attached impurities, thereby increasing the concentration of the ionized particles having the characteristic m / z ratios in the flow. Molecular reactions and low pressure ionization methods can also be performed for selective removal or enhancement of particular ions.
Owner:PERKINELMER SCI CANADA ULC
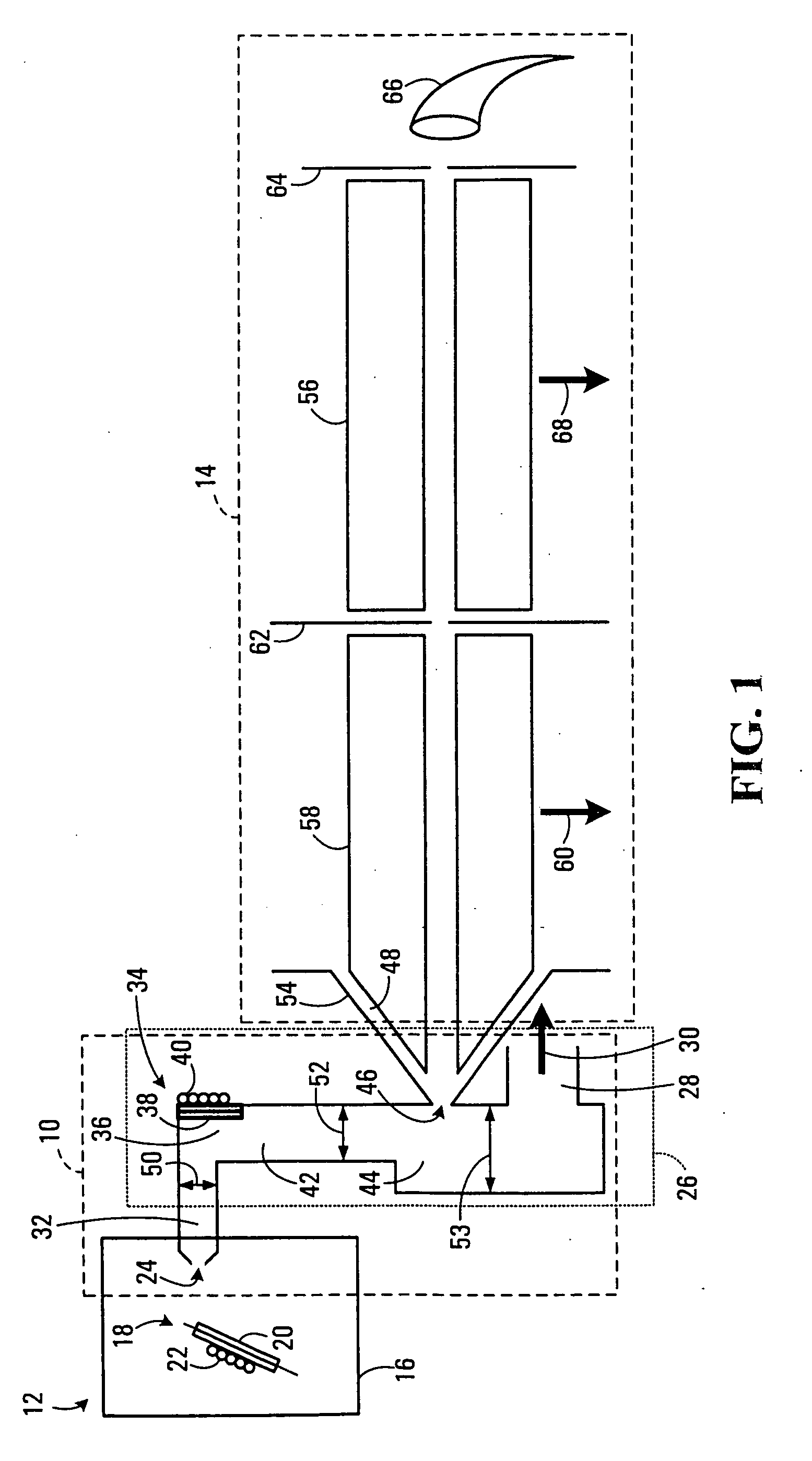
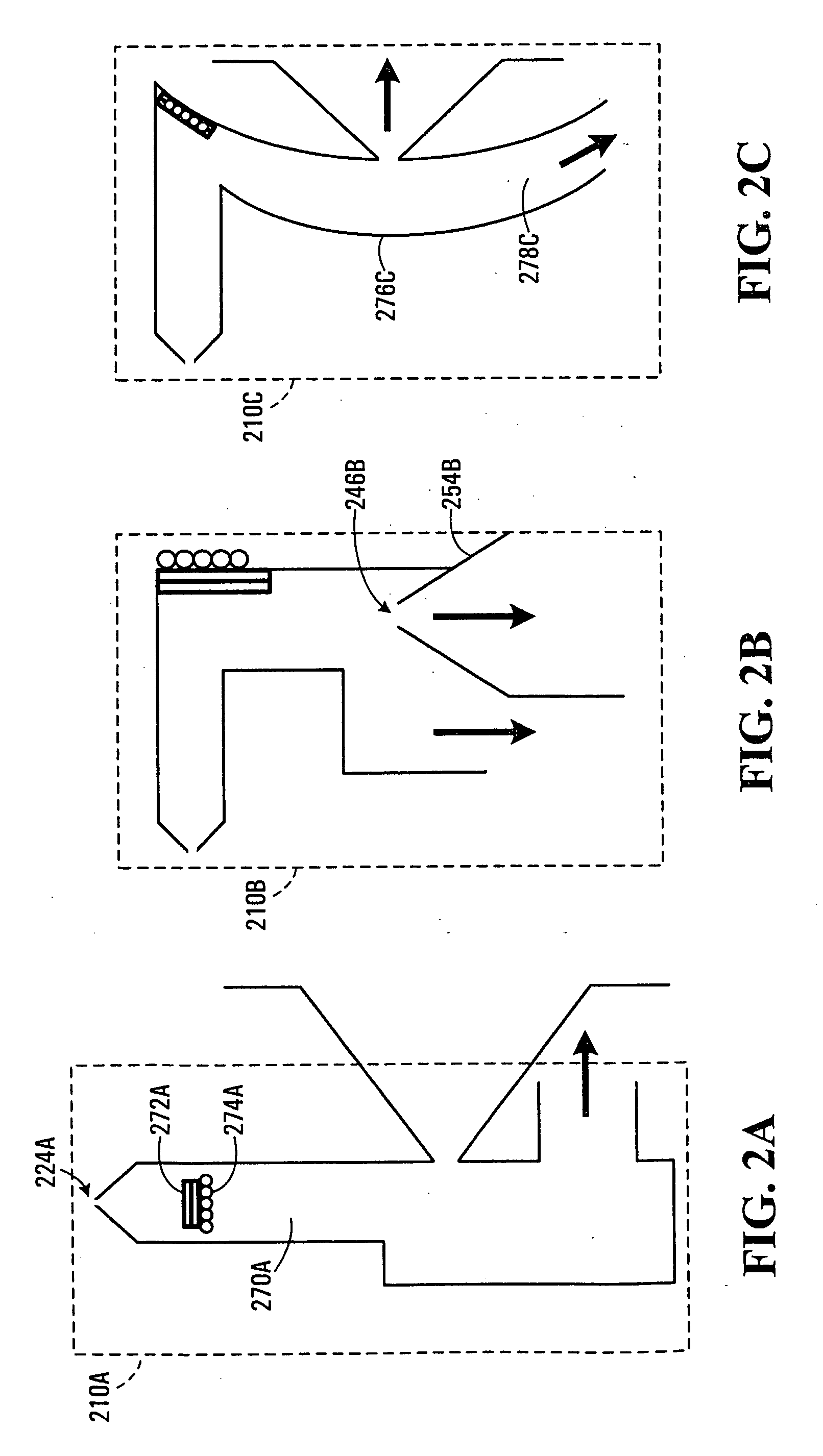
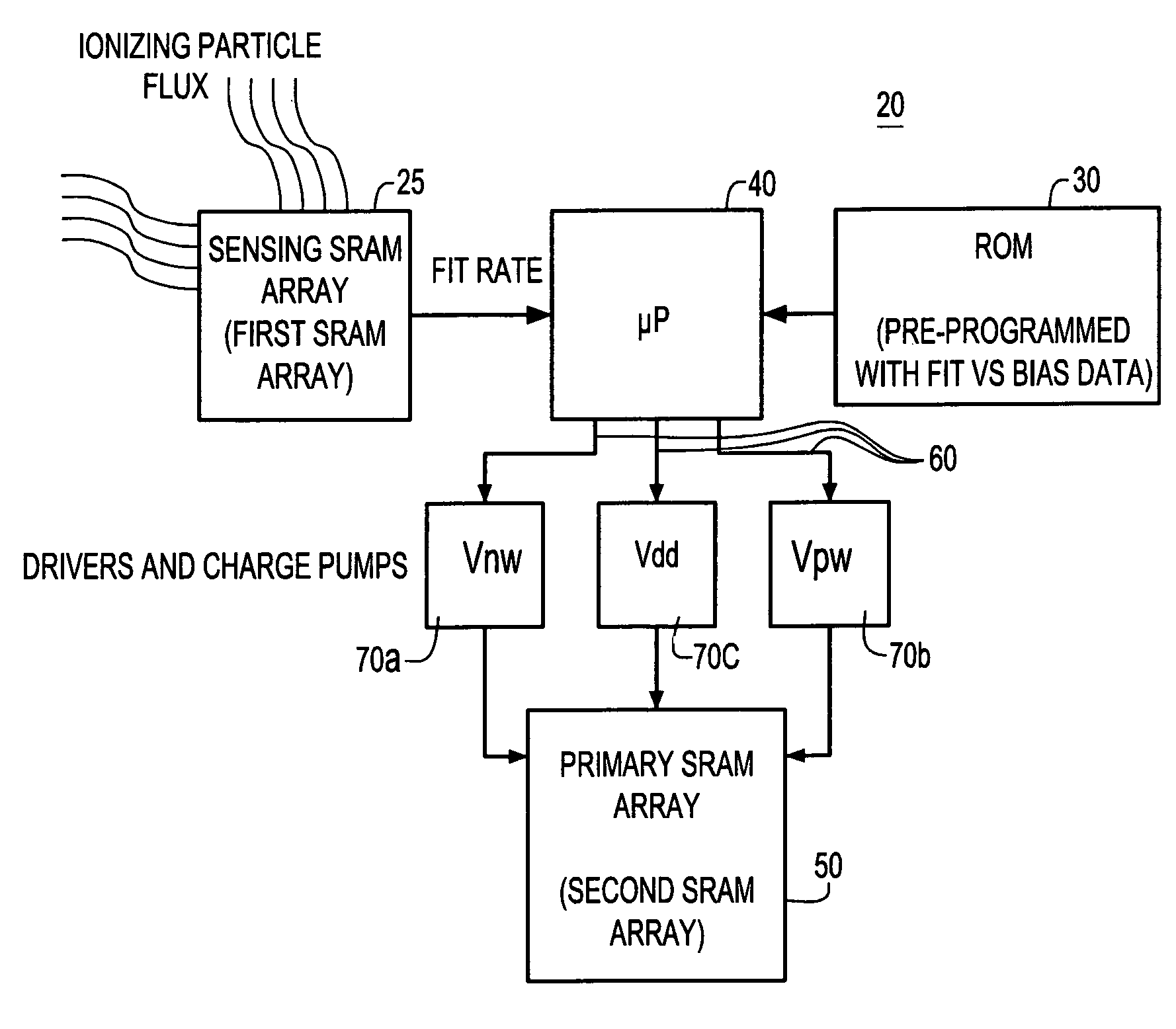
Real-time adaptive SRAM array for high SEU immunity
InactiveUS7283410B2Performance maximizationRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityOperating point
A system and method for automatically adjusting one or more electrical parameters in a memory device, e.g., SRAM arrays. The system and method implements an SRAM sensing sub-array for accelerated collection of fail rate data for use in determining the operating point for optimum tradeoff between single event upset immunity and performance of a primary SRAM array. The accelerated fail rate data is input to an algorithm implemented for setting the SEU sensitivity of a primary SRAM memory array to a predetermined fail rate in an ionizing particle environment. The predetermined fail rate is maintained on a real-time basis in order to provide immunity to SEU consistent with optimum performance.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Neutron source detection camera
InactiveUS20060017000A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionImaging equipment
A neutron imaging apparatus for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to the apparatus, the apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
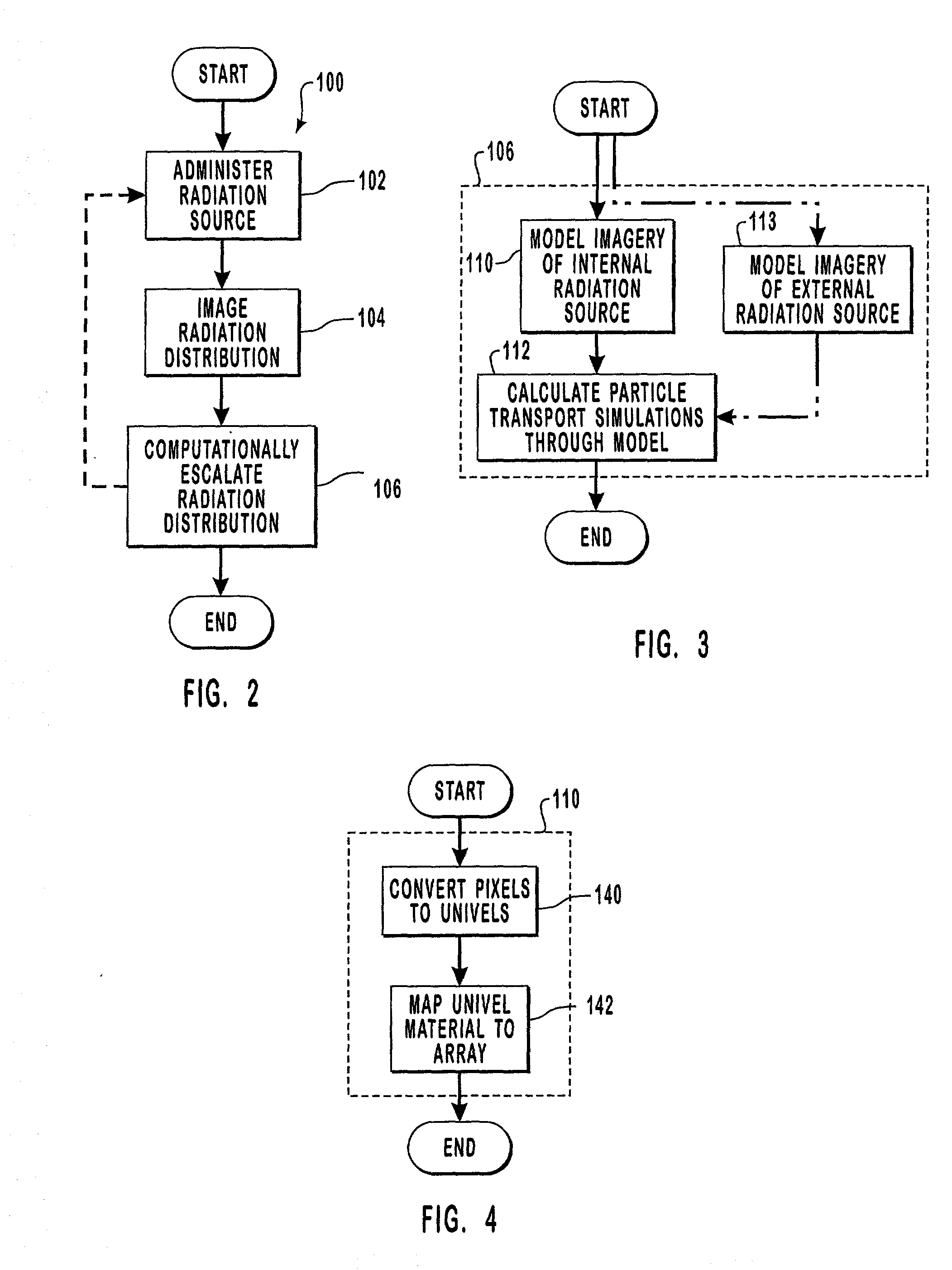
Methods and computer readable medium for improved radiotherapy dosimetry planning
InactiveUS20020046010A1Simple methodImprove calculation accuracyMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDosimetry radiationHigh energy
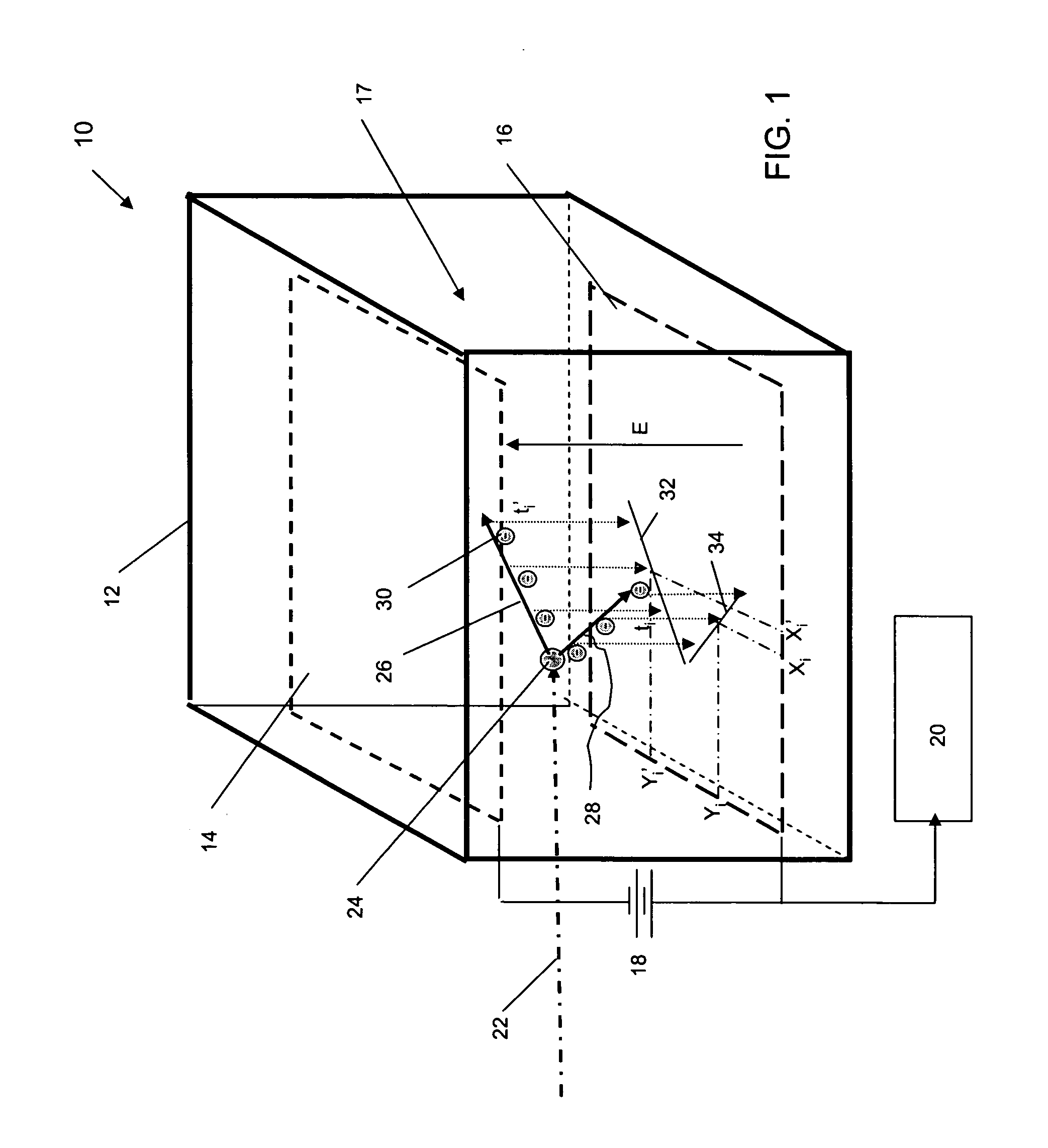
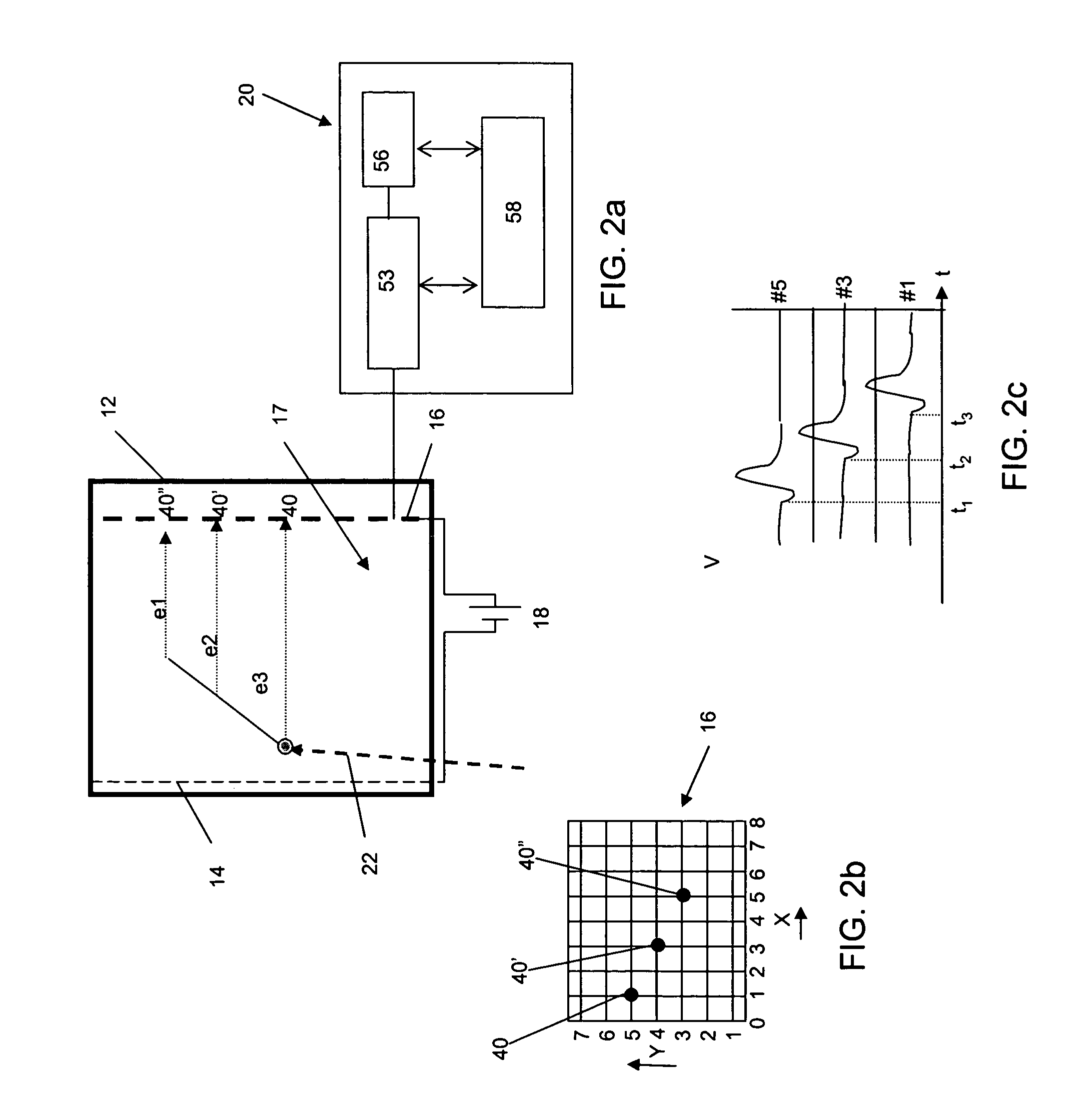
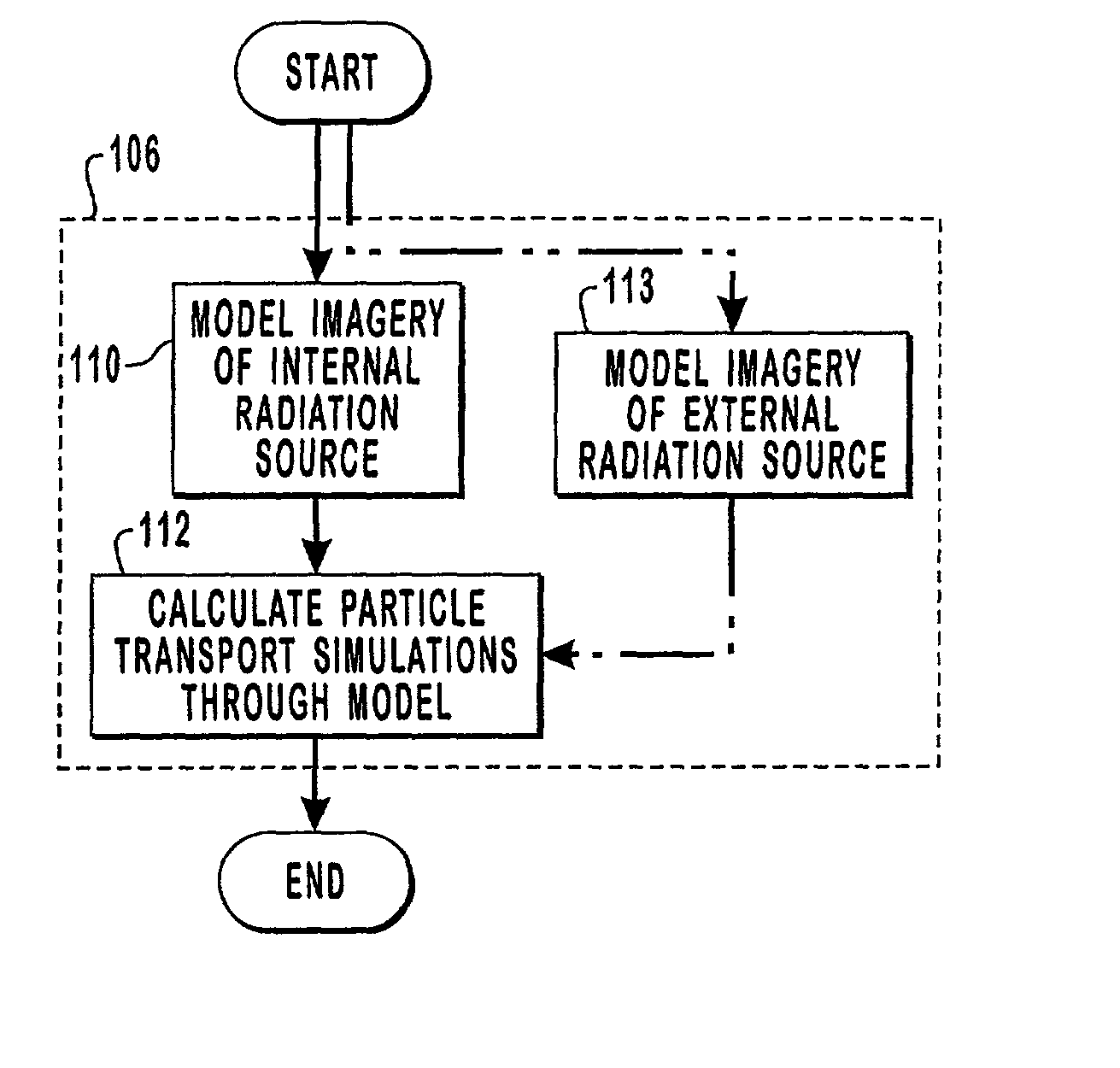
Methods and computer readable media are disclosed for ultimately developing a dosimetry plan for a treatment volume irradiated during radiation therapy with a radiation source concentrated internally within a patient or incident from an external beam. The dosimetry plan is available in near"real-time" because of the novel geometric model construction of the treatment volume which in turn allows for rapid calculations to be performed for simulated movements of particles along particle tracks therethrough. The particles are exemplary representations of alpha, beta or gamma emissions emanating from an internal radiation source during various radiotherapies, such as brachytherapy or targeted radionuclide therapy, or they are exemplary representations of high-energy photons, electrons, protons or other ionizing particles incident on the treatment volume from an external source. In a preferred embodiment, a medical image of a treatment volume irradiated during radiotherapy having a plurality of pixels of information is obtained.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Mass spectrometer interface
ActiveUS7091477B2Improve concentrationPromote liberationStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionThermal energyMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer interface, having improved sensitivity and reduced chemical background, is disclosed. The mass spectrometer interface provides improved desolvation, chemical selectivity and ion transport. A flow of partially solvated ions is transported along a tortuous path into a region of disturbance of flow, where ions and neutral molecules collide and mix. Thermal energy is applied to the region of disturbance to promote liberation of at least some of the ionized particles from any attached impurities, thereby increasing the concentration of the ionized particles having the characteristic m / z ratios in the flow. Molecular reactions and low pressure ionization methods can also be performed for selective removal or enhancement of particular ions.
Owner:PERKINELMER SCI CANADA ULC
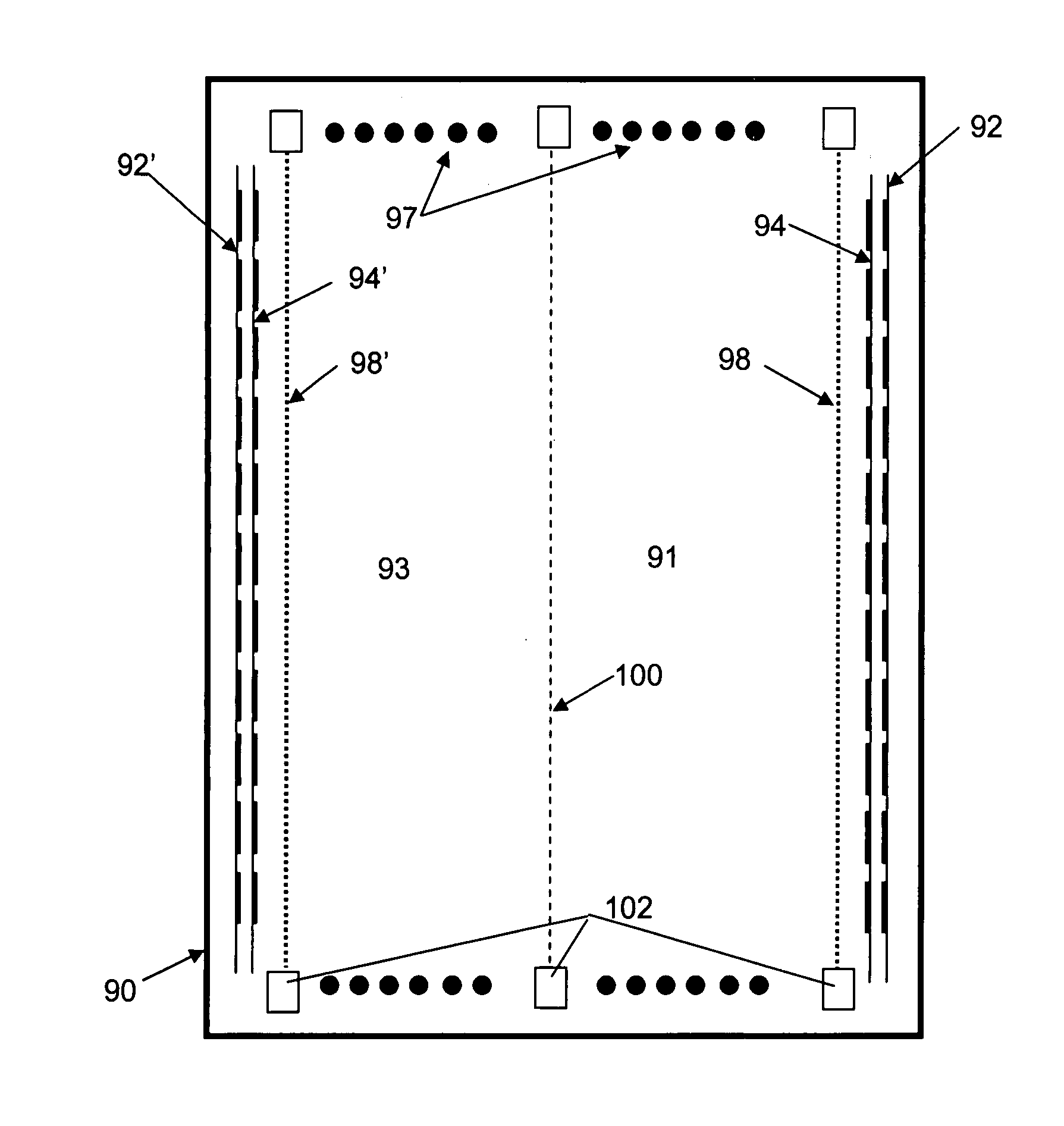
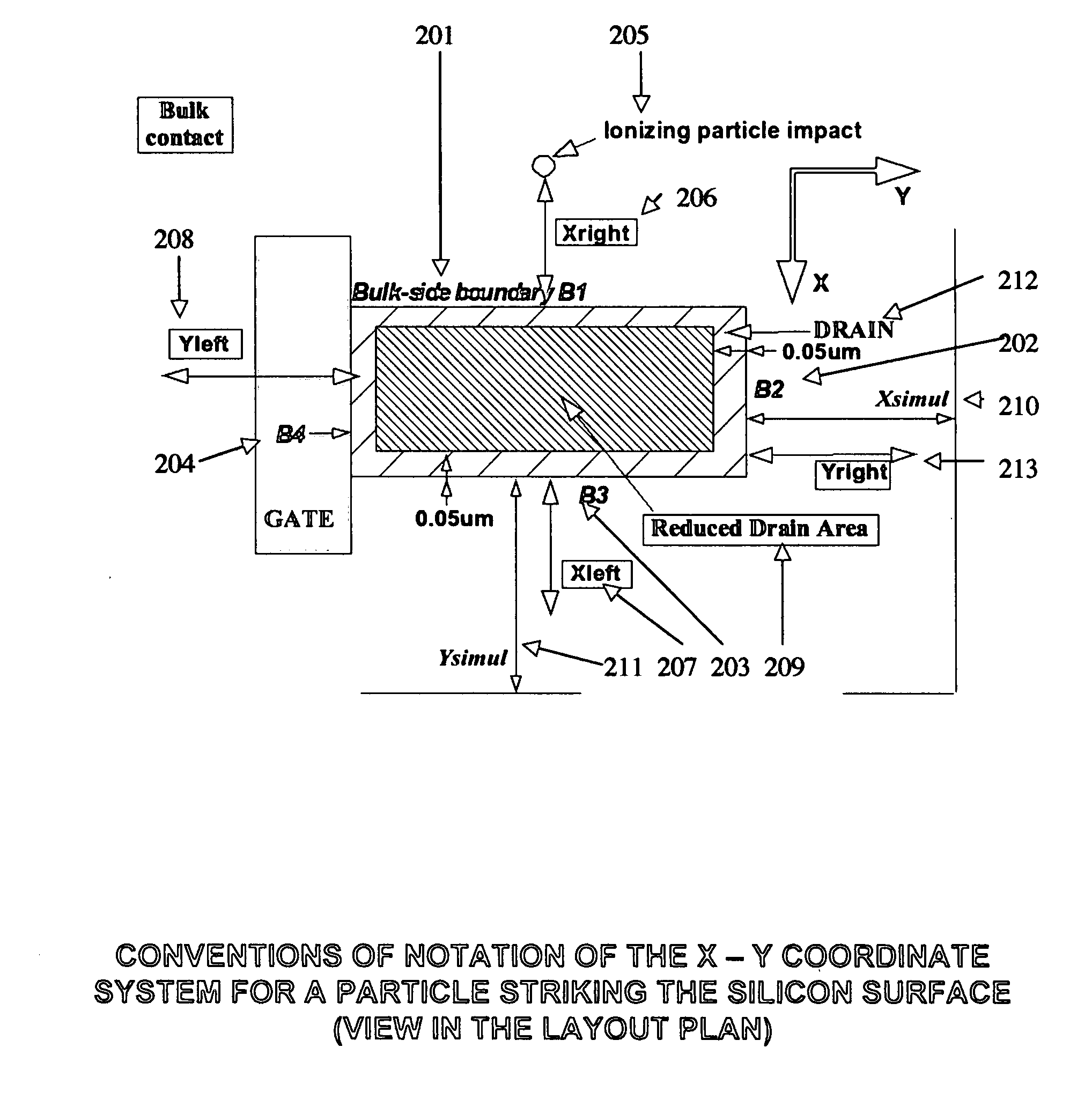
Apparatus and method for the determination of SEU and SET disruptions in a circuit caused by ionizing particle strikes
InactiveUS20080077376A1Accurate and fast simulation methodHigh speedAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationElectricityAlpha particle
This application discloses a new, and useful computer implemented method and apparatus that can be used for the determination of SEU and SET disruptions in a cell or circuit, caused by ionizing particle strikes, including those caused by neutrons (cosmic rays), alpha particles or heavy ions. The method of the present invention includes a fast simulation tool (“TFIT”), which calculates the electrical effect of a particle's impact to a cell, or a circuit. The method is used to predict the soft error rate (SER) calculations and the FIT (number of failures-in-time) performance of designated test cell's design, depending on the type of particle environment specified. The method is designed to simulate the response of the cell or circuit to the stimuli caused by a particle strike. These stimuli are modeled as a “current source” placed between the drain and the source of each struck transistor.
Owner:IROC TECH
Nuclear radiation shields, shielding systems and associated methods
InactiveUS20140151584A1Resistance to crackingImpart radioactivity-limiting element with flexibilityShieldingPortable shielded containersNuclear radiationRadiation shield
A radiation shield, which may attenuate nuclear radiation or ionizing particles, may include a non-toxic, radioactivity-attenuating material based on an element or an elemental species having an atomic number of 56 or more. Examples of such materials include barium sulfate and bismuth oxide. A radiation shield may include two or more different radioactivity-attenuating materials, which may attenuate different types of nuclear radiation or ionizing particles, or attenuate different energy ranges of nuclear radiation or ionizing particles. Different radioactivity-attenuating materials may be carried by different layers of the radiation shield. Radiation shields with at least partially superimposed layers are also disclosed. Adjacent layers of such a radiation shield may be able to move longitudinally relative to one another, or slide somewhat relative to each other. Any of these features may be incorporated into a blanket, a protective suit or other protective garment, tape or any other configuration of radiation shield. Pliable radiation shields that attenuate nuclear radiation or ionizing particles are also disclosed, as are methods for limiting exposure to nuclear radiation or ionizing particles.
Owner:BLOXR SOLUTIONS
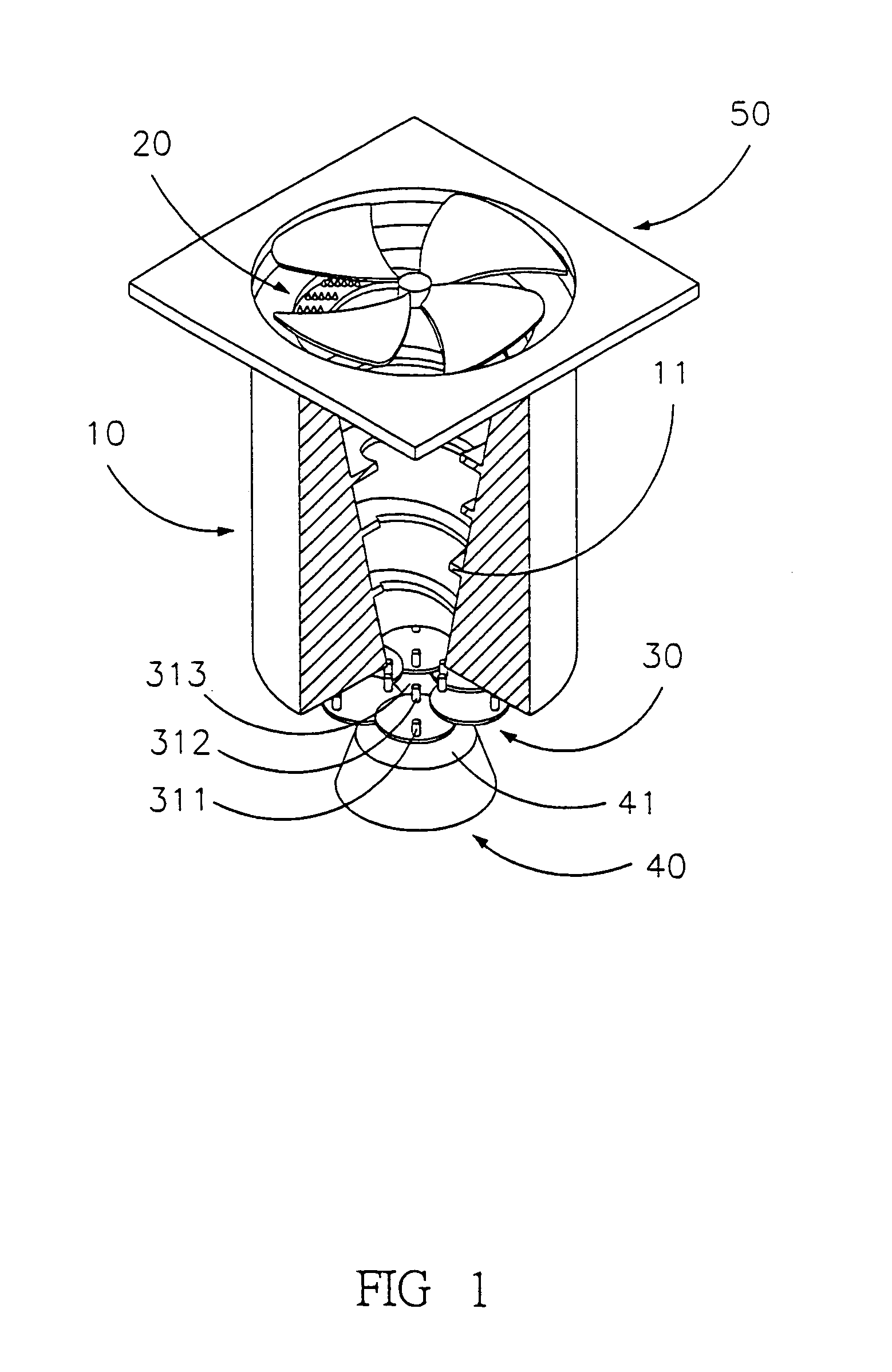
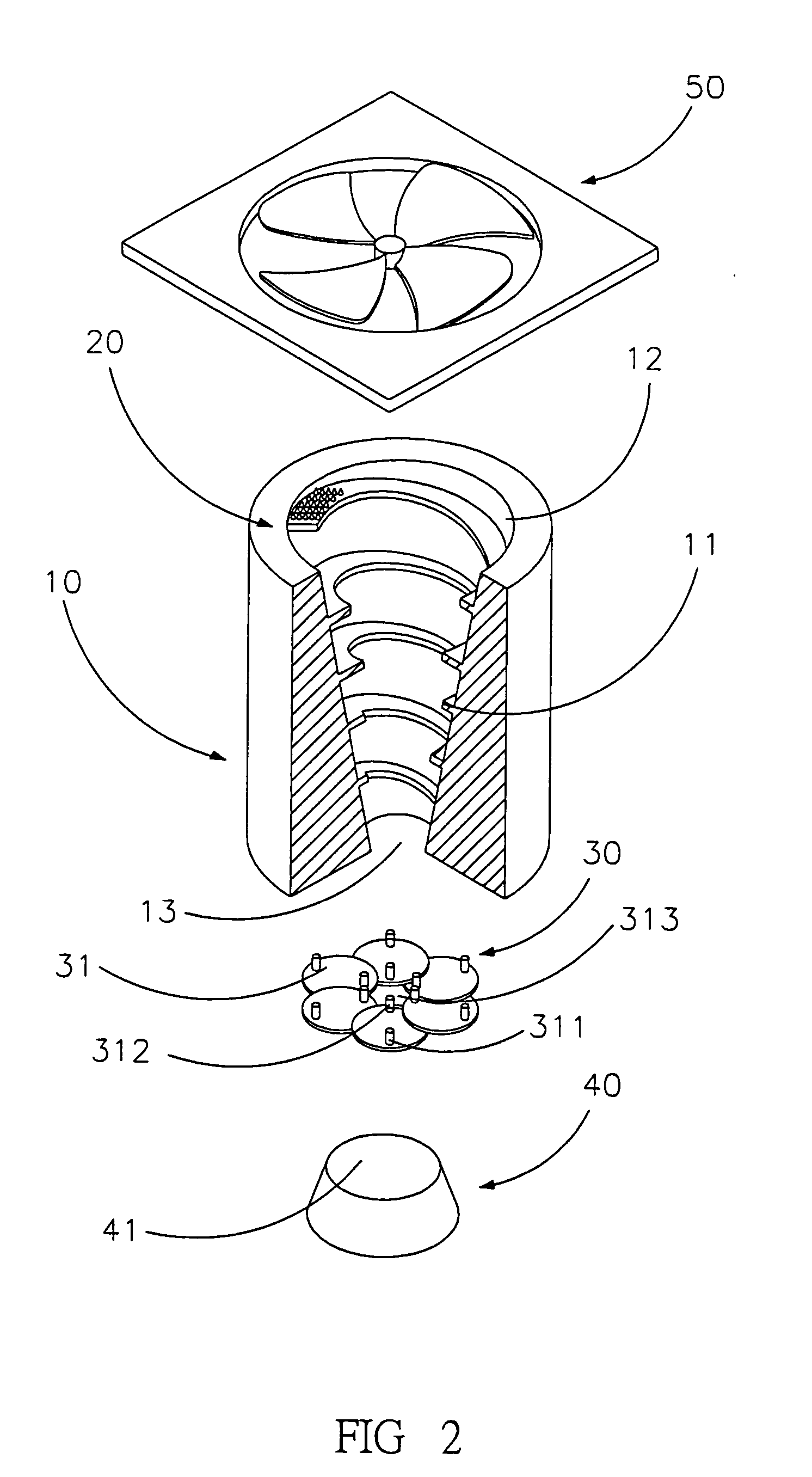
Adjustable eddy electrostatic precipitator
ActiveUS6962620B2Electrostatic separation housingExternal electric electrostatic seperatorInterior spaceEngineering
An adjustable eddy electrostatic precipitator, including a main body, an electrode array, an adjustable opening and a precipitating device. The main body has an inner space with an air guiding plate of helical shape, an entrance for air and an exit for air. The electrode array is placed close to the entrance, ionizing air as well as particles floating therein. The adjustable opening is located at the exit, having an adjustable aperture. The precipitating device is connected with a bias high voltage for adsorbing ionized particles. Air entering the main body through the entrance is ionized, ionizing particles floating therein. Ionized particles are driven towards a single zone and are collected depending on size and charge in an adjustable manner.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
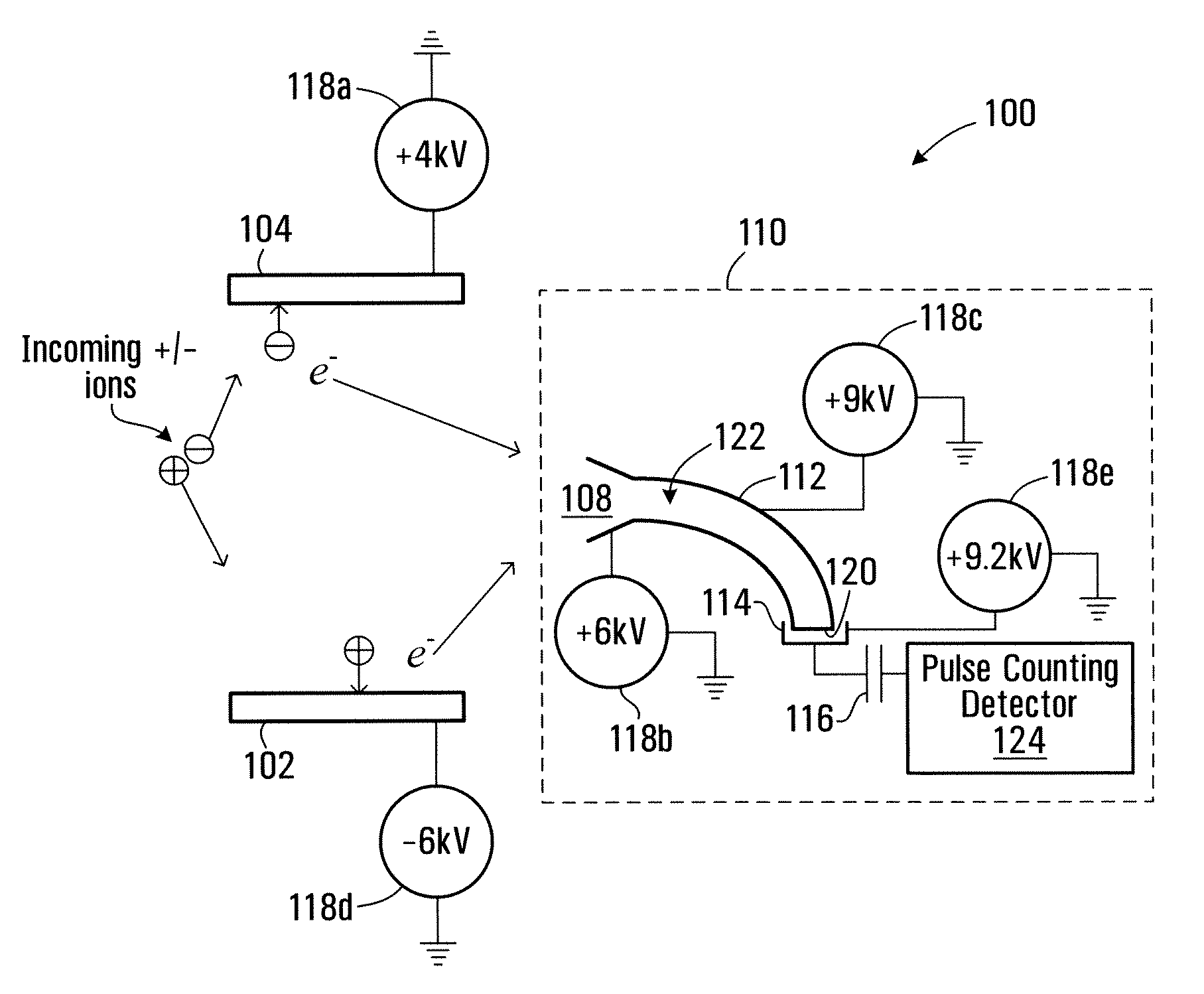
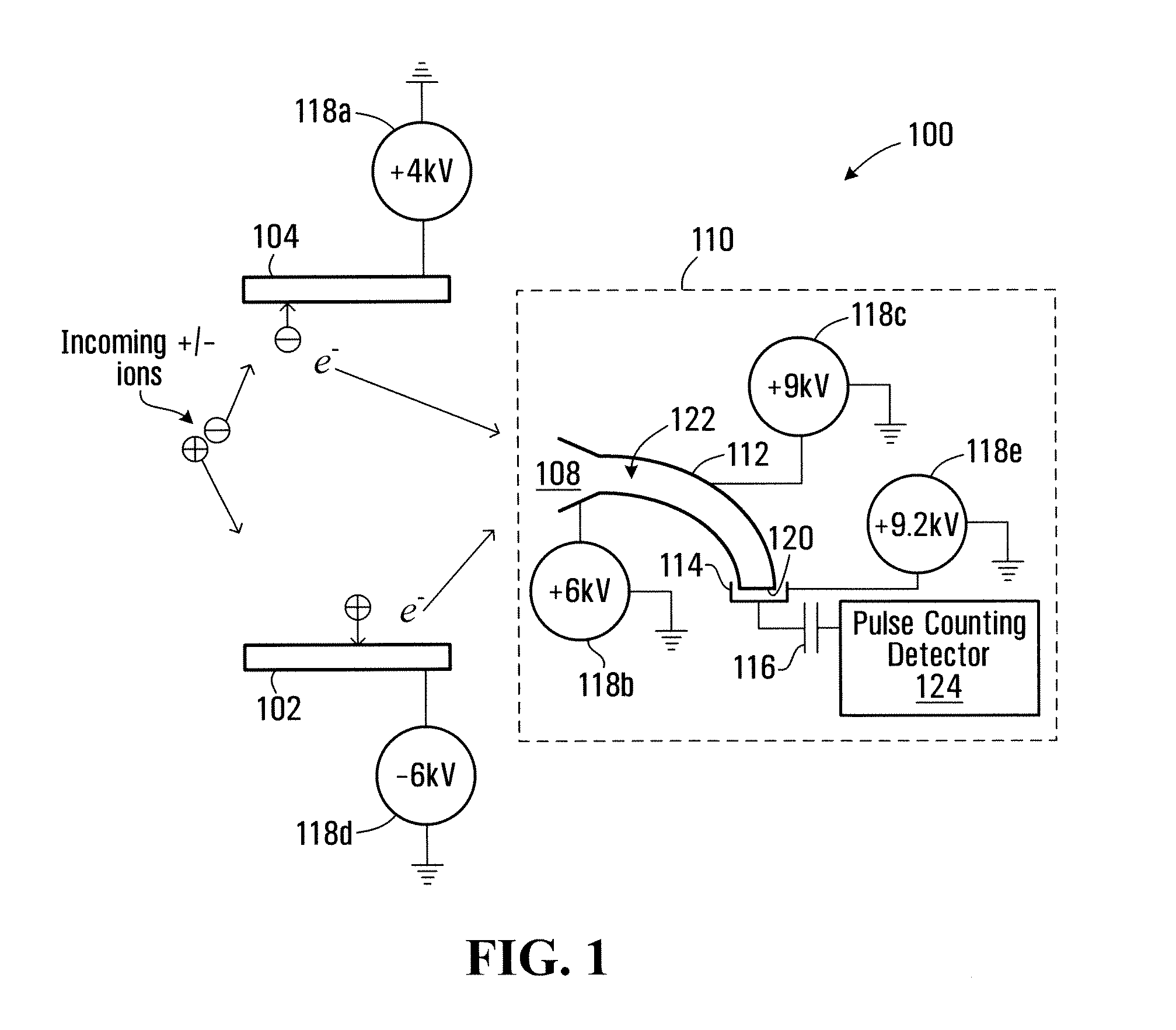
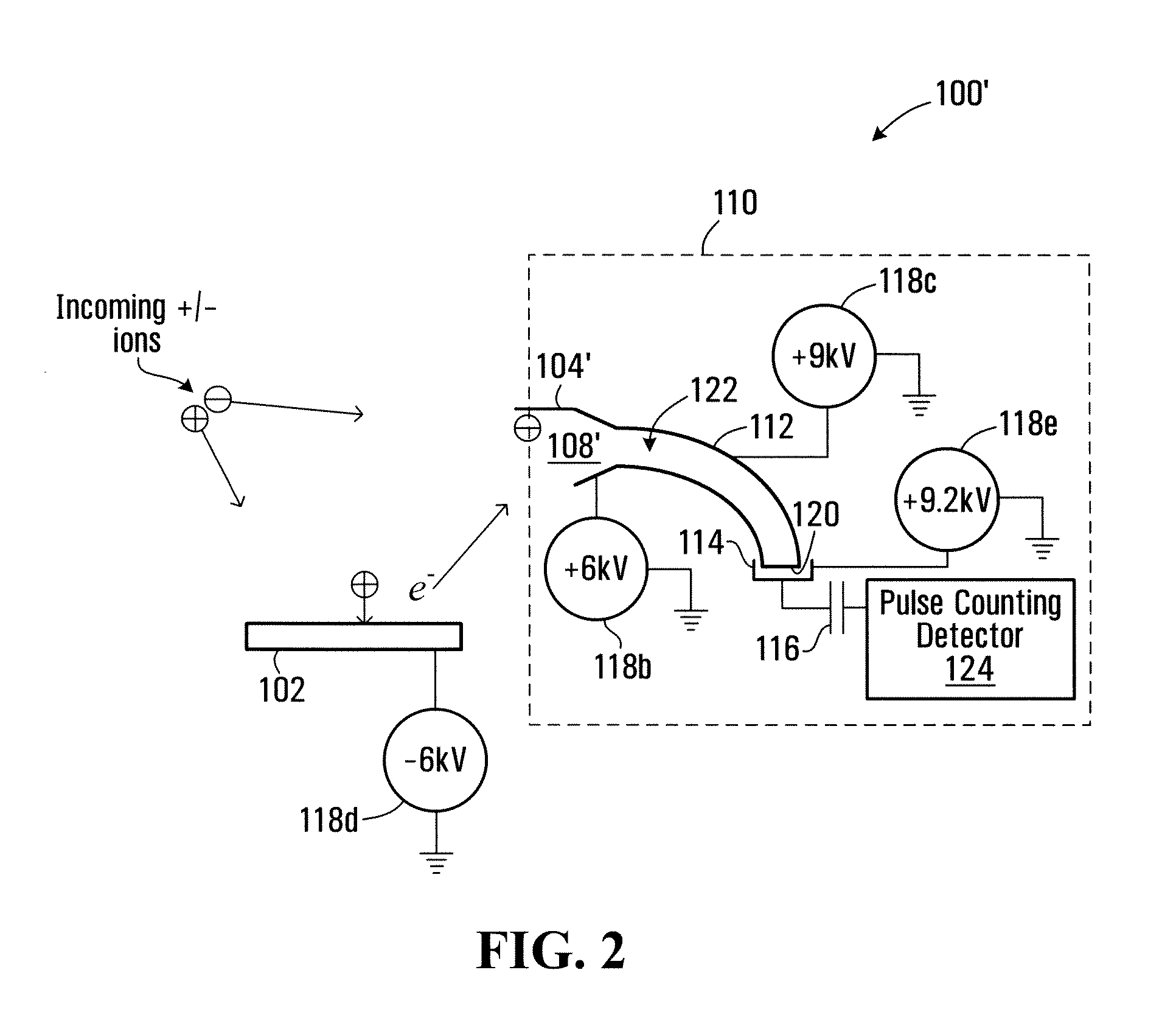
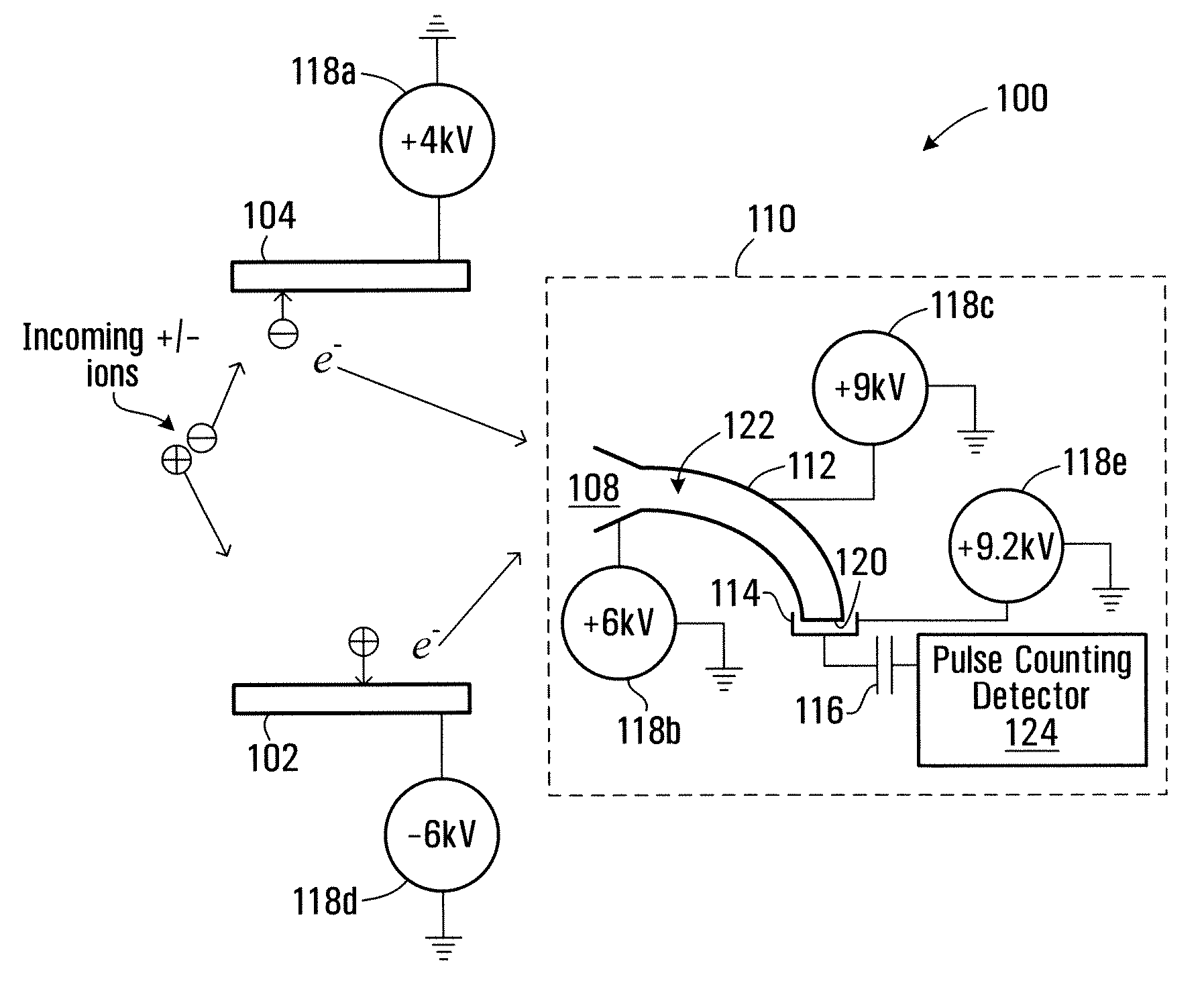
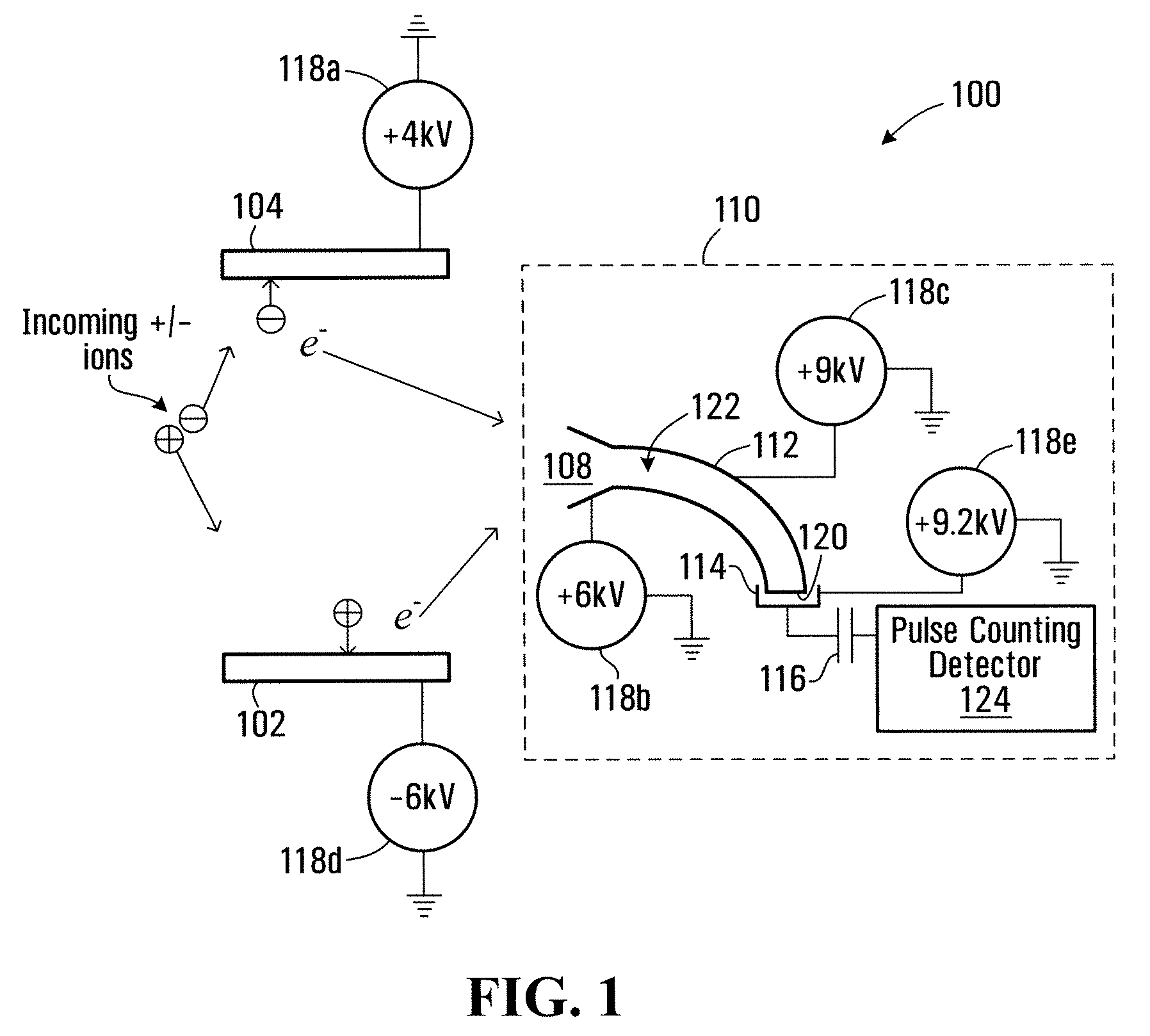
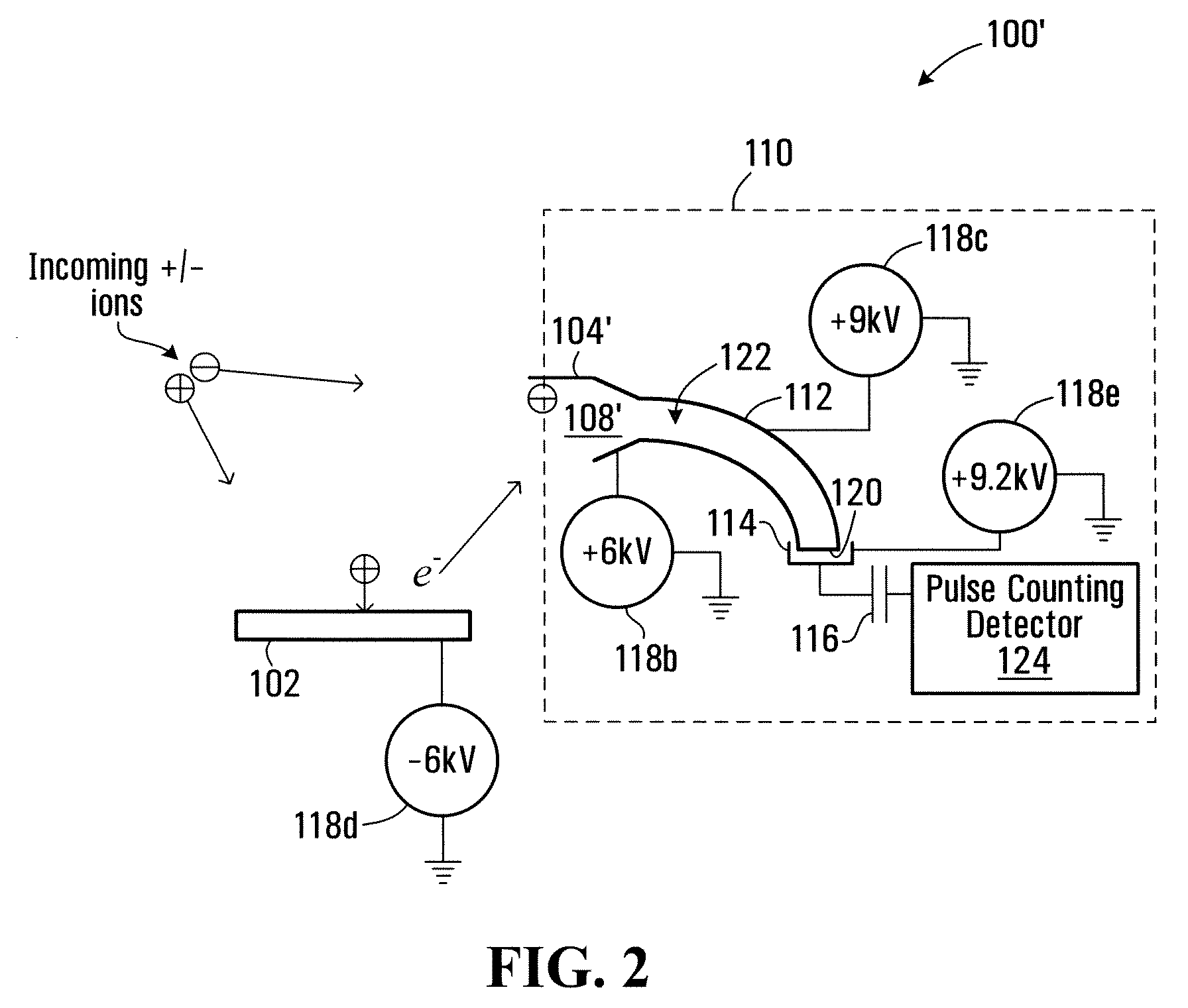
Method and apparatus for detecting positively charged and negatively charged ionized particles
ActiveUS20080073530A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationElectron multiplierSecondary electrons
An ion detector includes collision surfaces for converting both positively and negatively charged ions into emitted secondary electrons. Secondary electrons may be detected using an electron detector, than may, for example include an electron multiplier. Conveniently, secondary electrons (or electrons emitted by the multiplier) may be detected using an electron pulse counter.
Owner:PERKINELMER SCI CANADA ULC
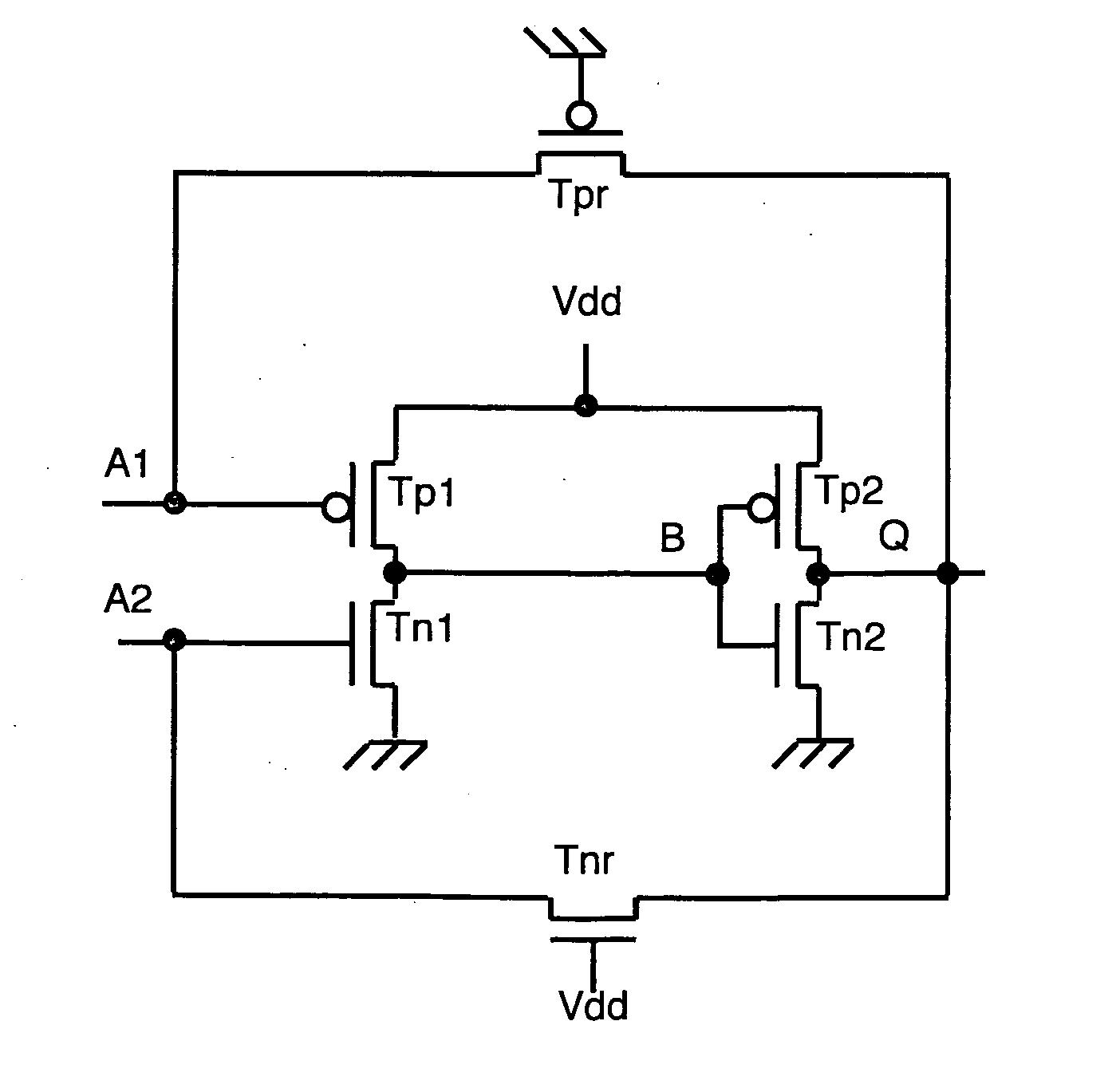
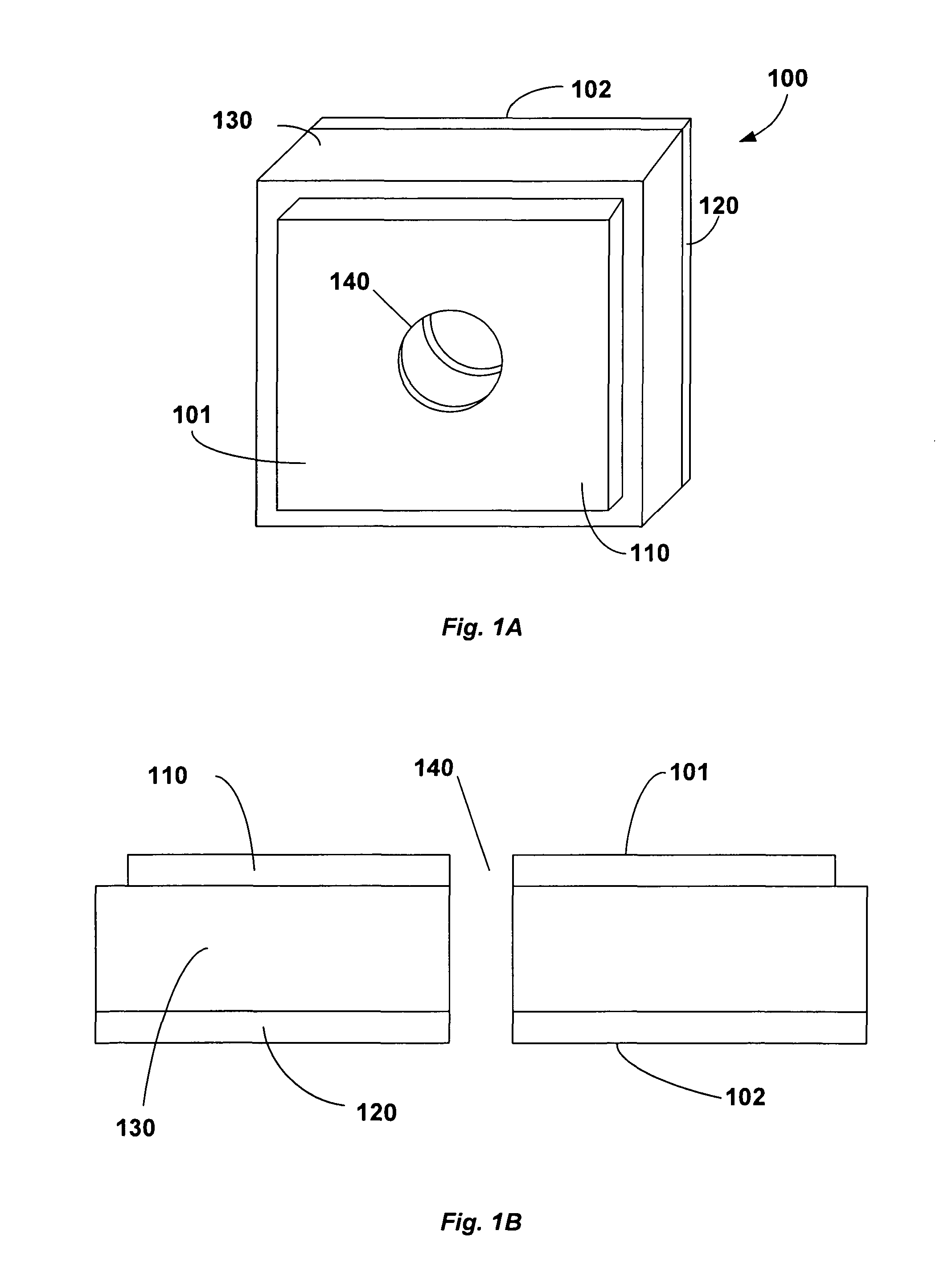
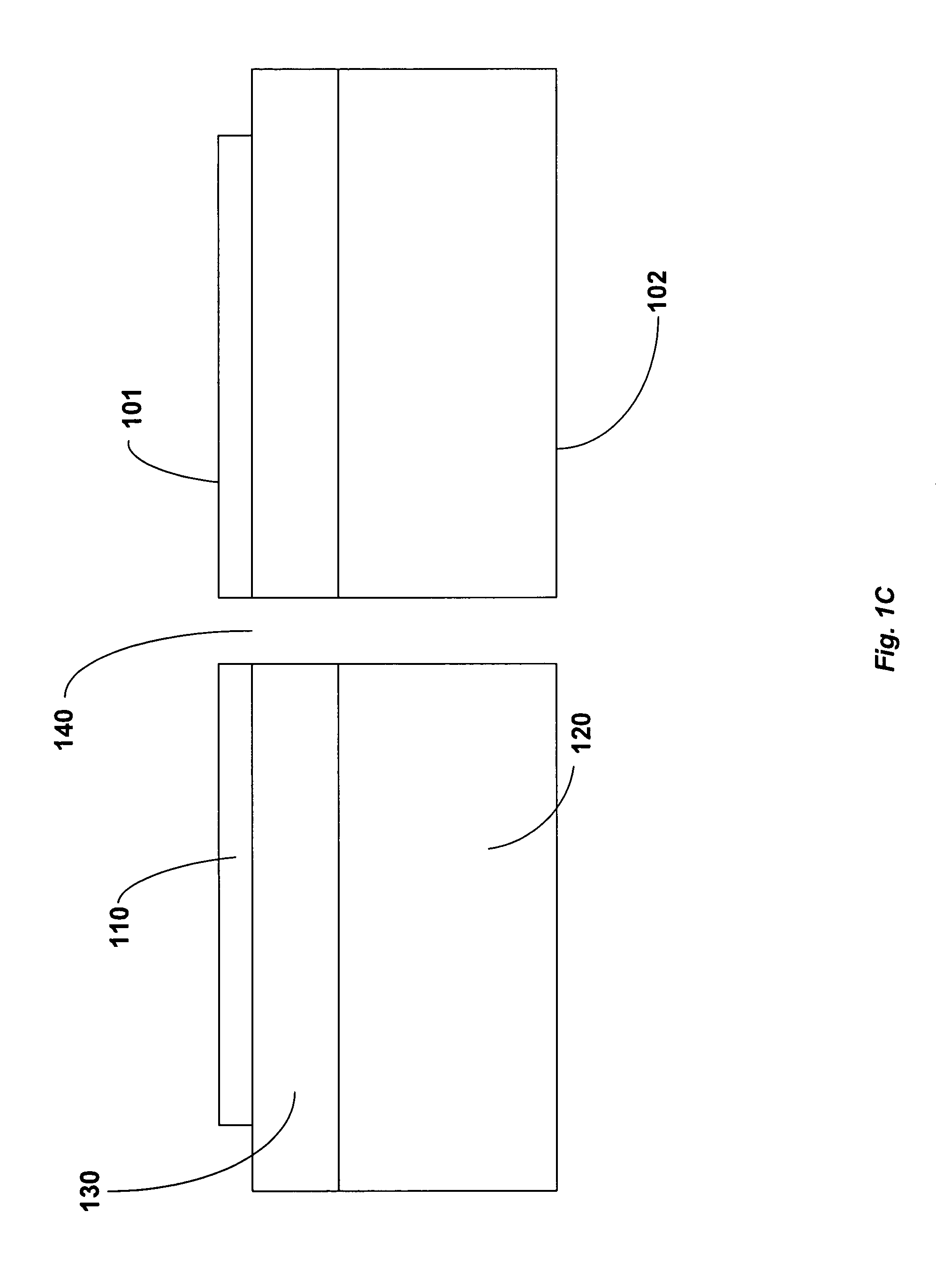
Hardened Memory Cell
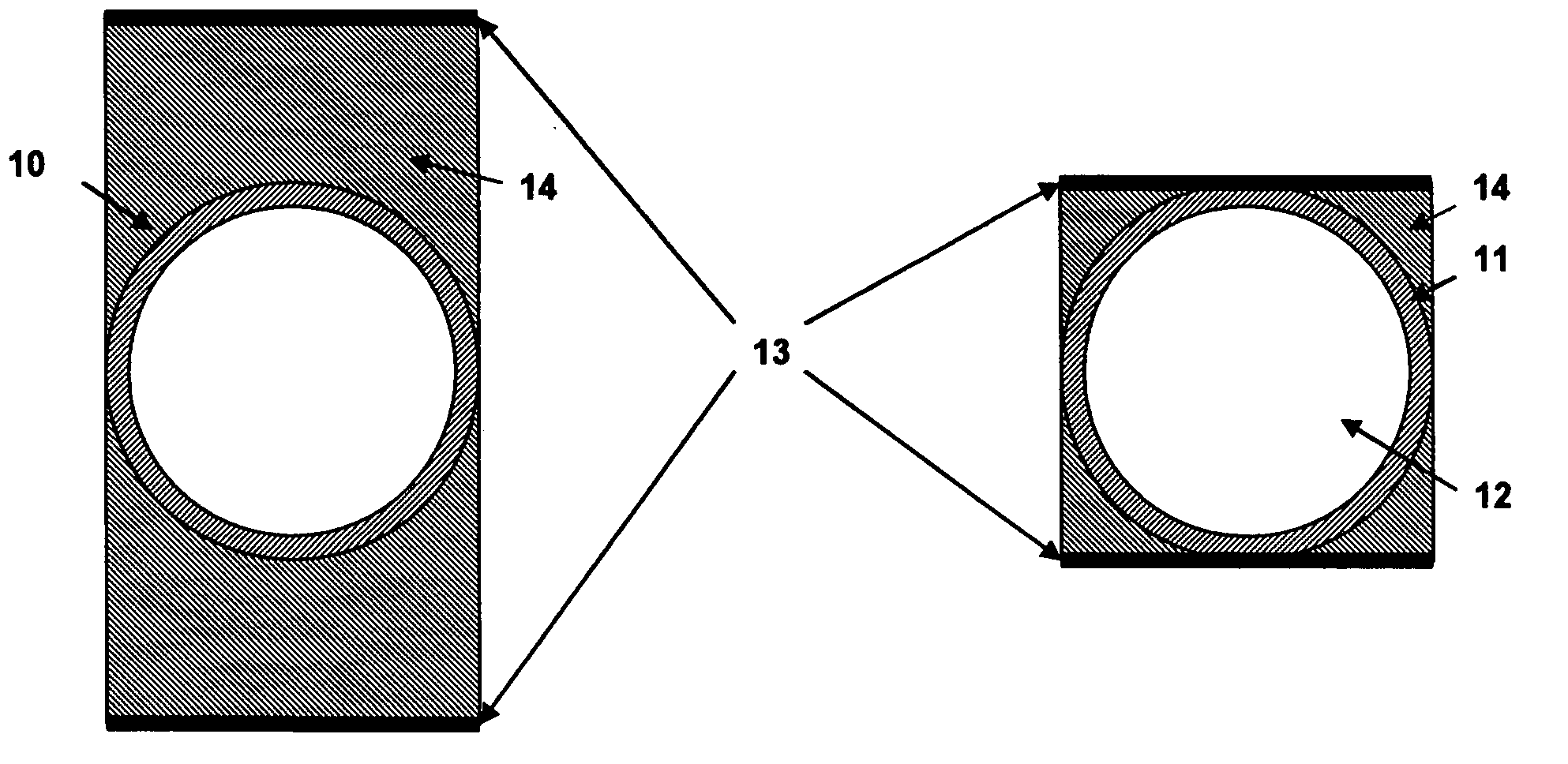
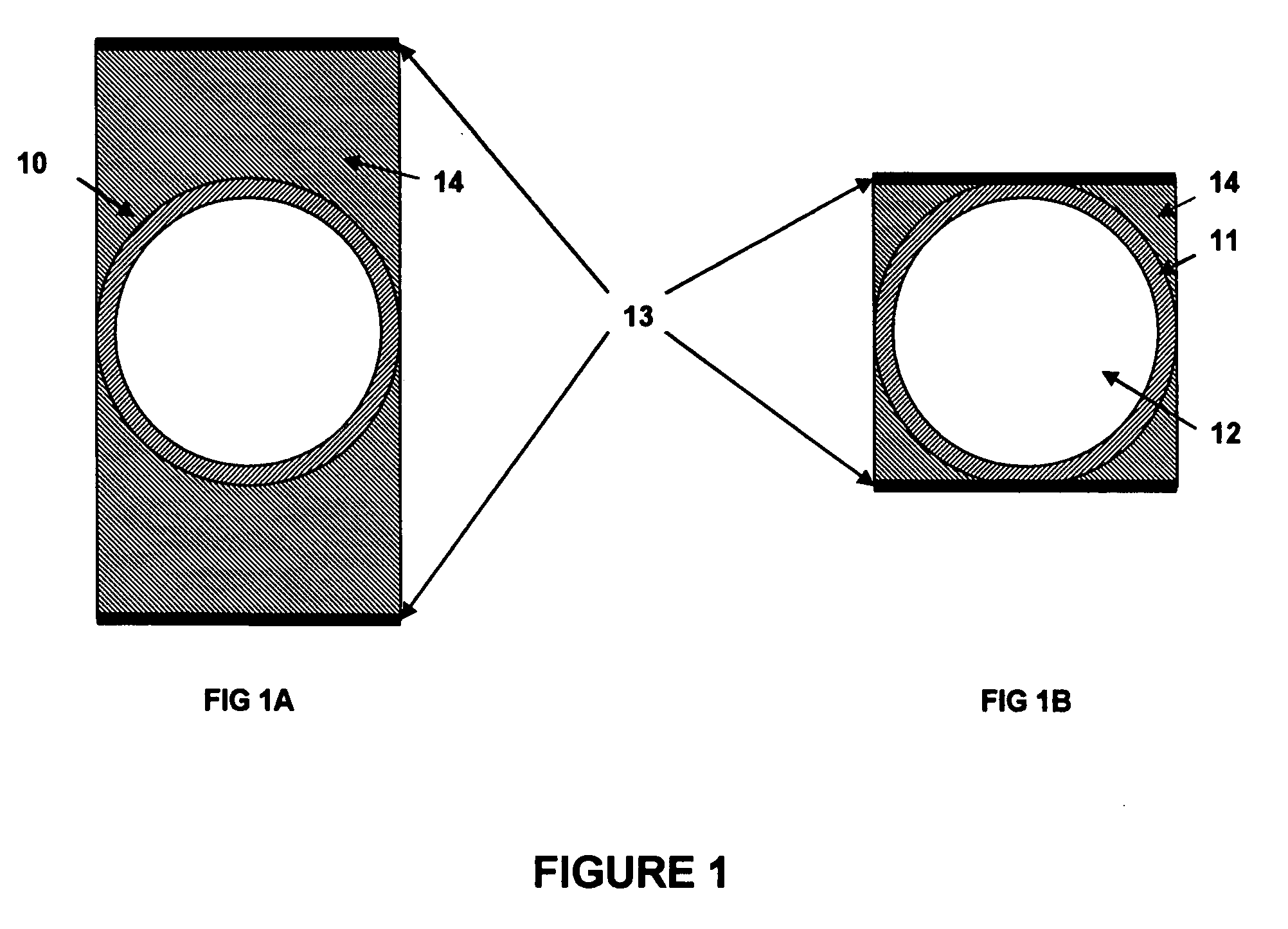
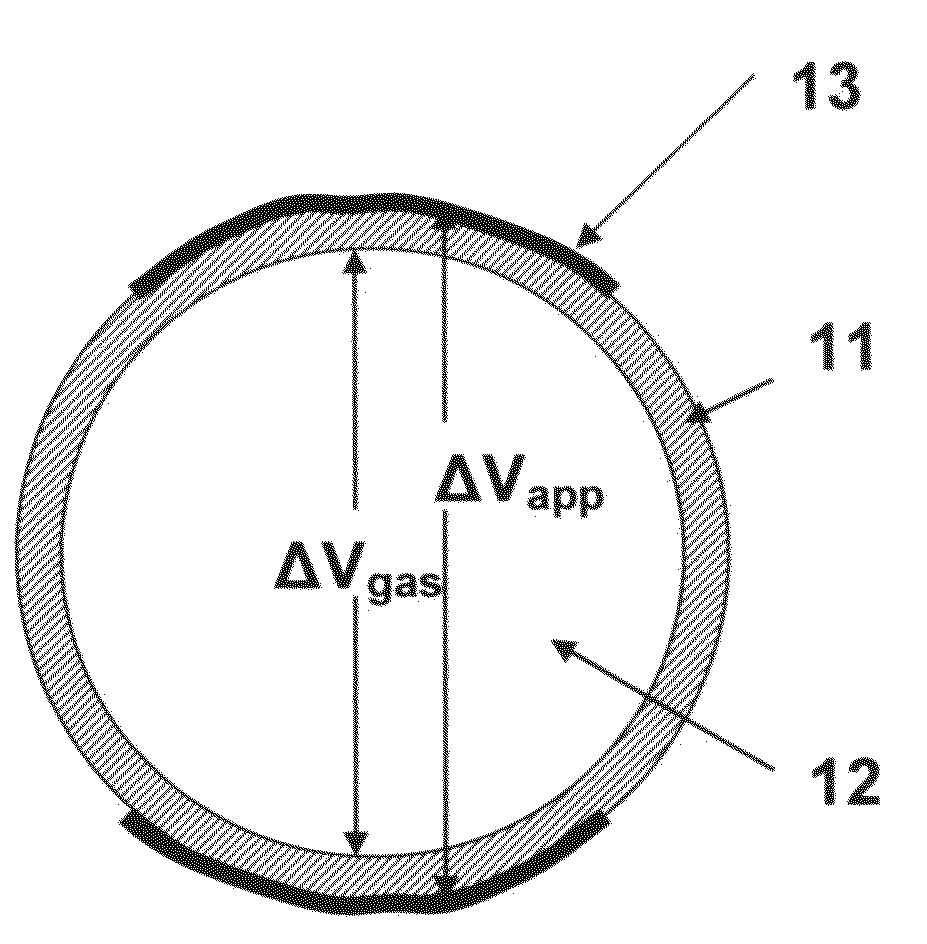
ActiveUS20080253180A1Low surface costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageIonizing particlesTransistor
The memory cell comprises first and second inverter circuits, connected in a loop. First and second decoupling transistors, normally turned off outside the write phases, are respectively connected between an output of the second inverter circuit and first and second inputs of the first inverter circuit. The memory cell is thereby protected against transient disturbances due to ionizing particles. The gates of the decoupling transistors are preferably respectively connected to a supply voltage for the P-type decoupling transistors and grounded for the N-type decoupling transistors.
Owner:IROC TECH
Method and apparatus for detecting positively charged and negatively charged ionized particles
An ion detector includes collision surfaces for converting both positively and negatively charged ions into emitted secondary electrons. Secondary electrons may be detected using an electron detector, than may, for example include an electron multiplier. Conveniently, secondary electrons (or electrons emitted by the multiplier) may be detected using an electron pulse counter.
Owner:PERKINELMER SCI CANADA ULC
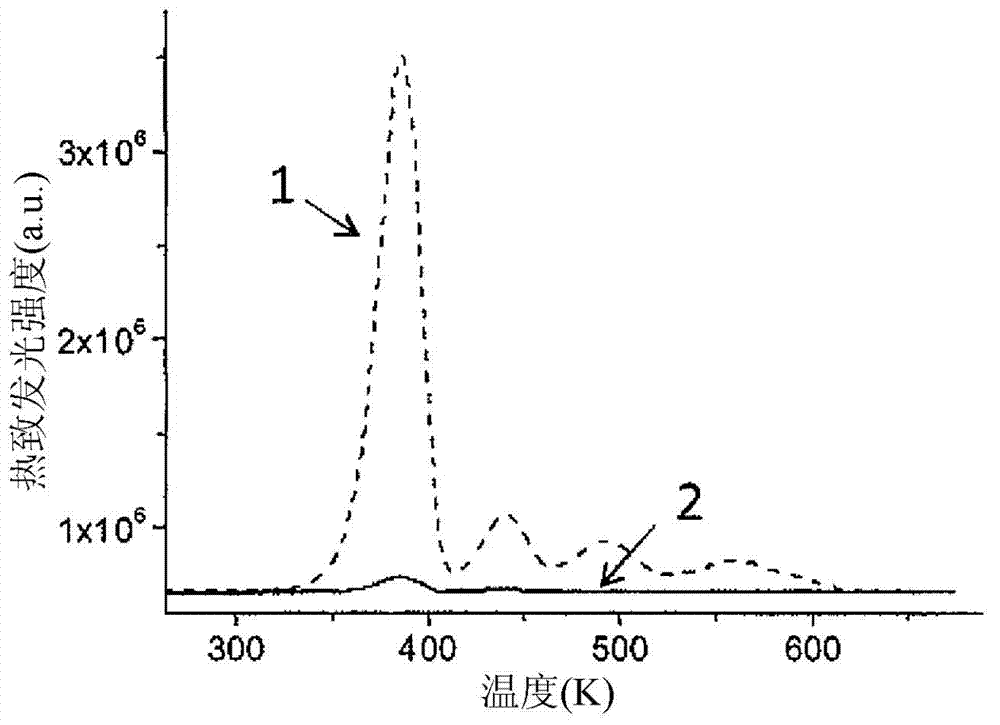
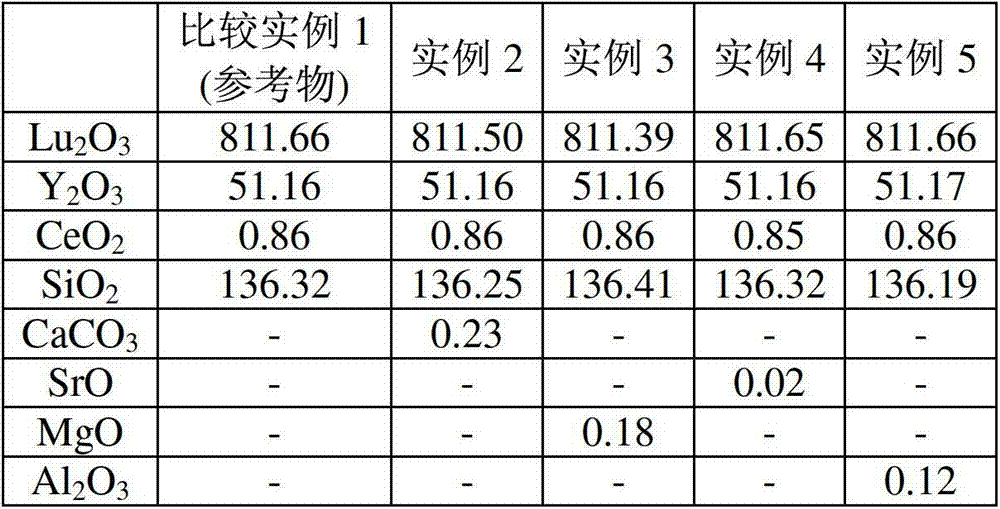
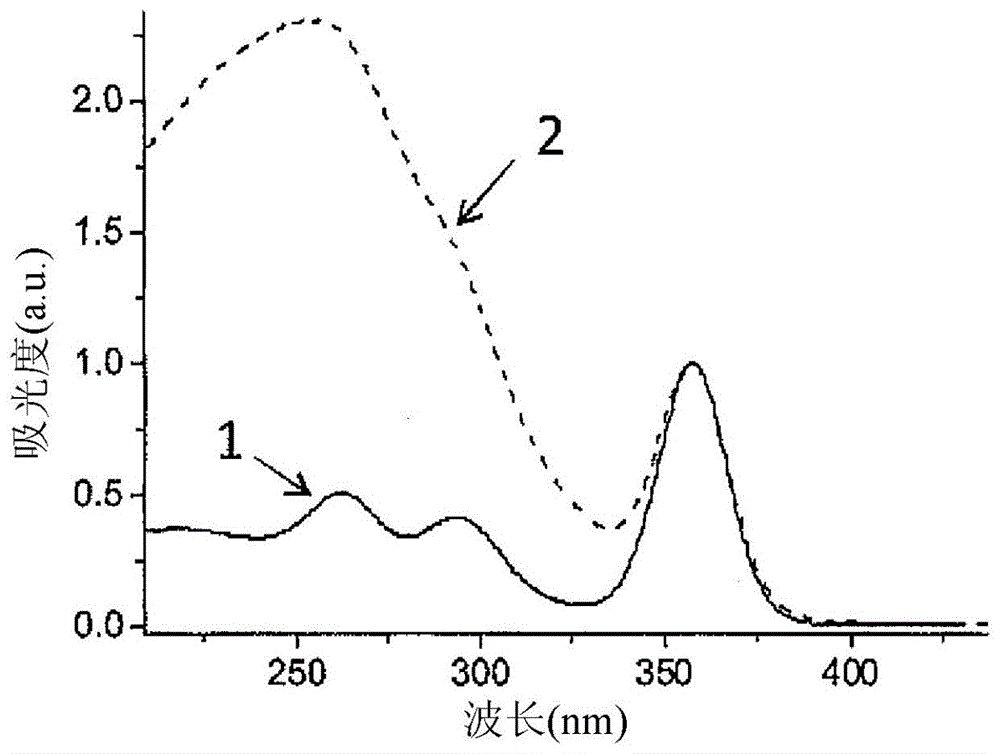
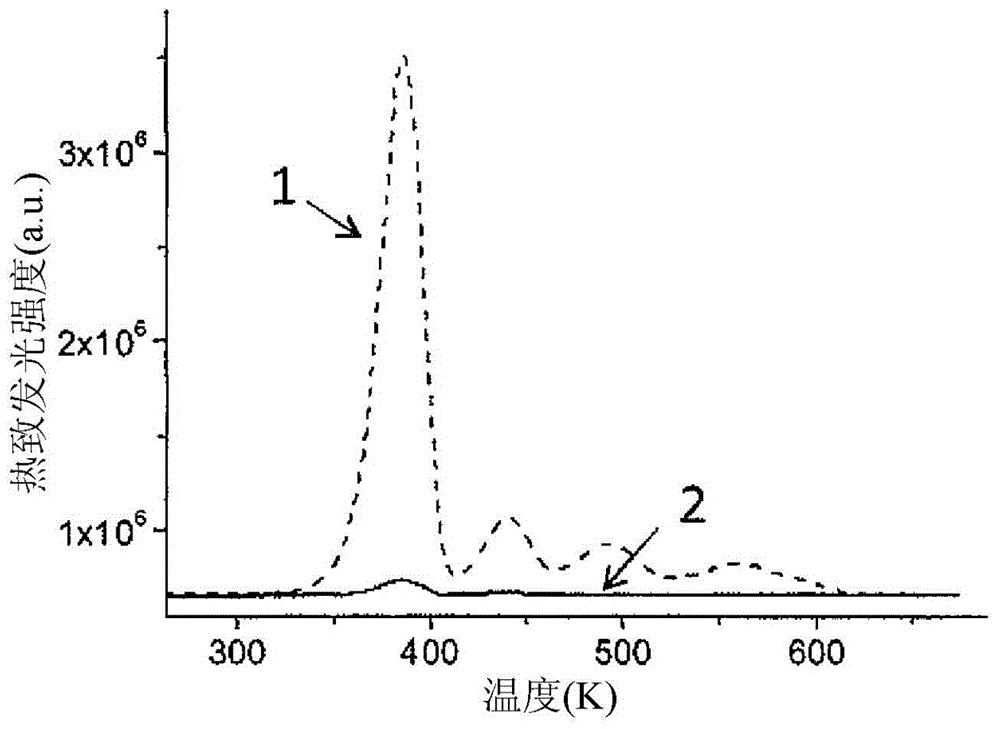
Luminescent material comprising a doped rare earth silicate
The invention relates to a material comprising a rare earth (Ln) silicate doped with an element B different from Ln, B being chosen among Ce, Pr, Tb, wherein B is at least partially in its 4+ oxidation state (B4+), the quantity of B4+ in said material being comprised between 0.0001 % and 0.1 % in mass. This material may be a scintillating material and may present an afterglow of generally less than 200 ppm after 100 ms relative to the intensity measured during an X-ray irradiation. It is preferably codoped. It may be obtained using an oxidizing annealing. It is particularly suited to integration in an ionizing particle detector that may be used in a medical imaging apparatus.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CRISTAUX & DETECTEURS
Neutron source detection camera
InactiveUS7049603B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionMomentum
A neutron imaging method for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to an apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
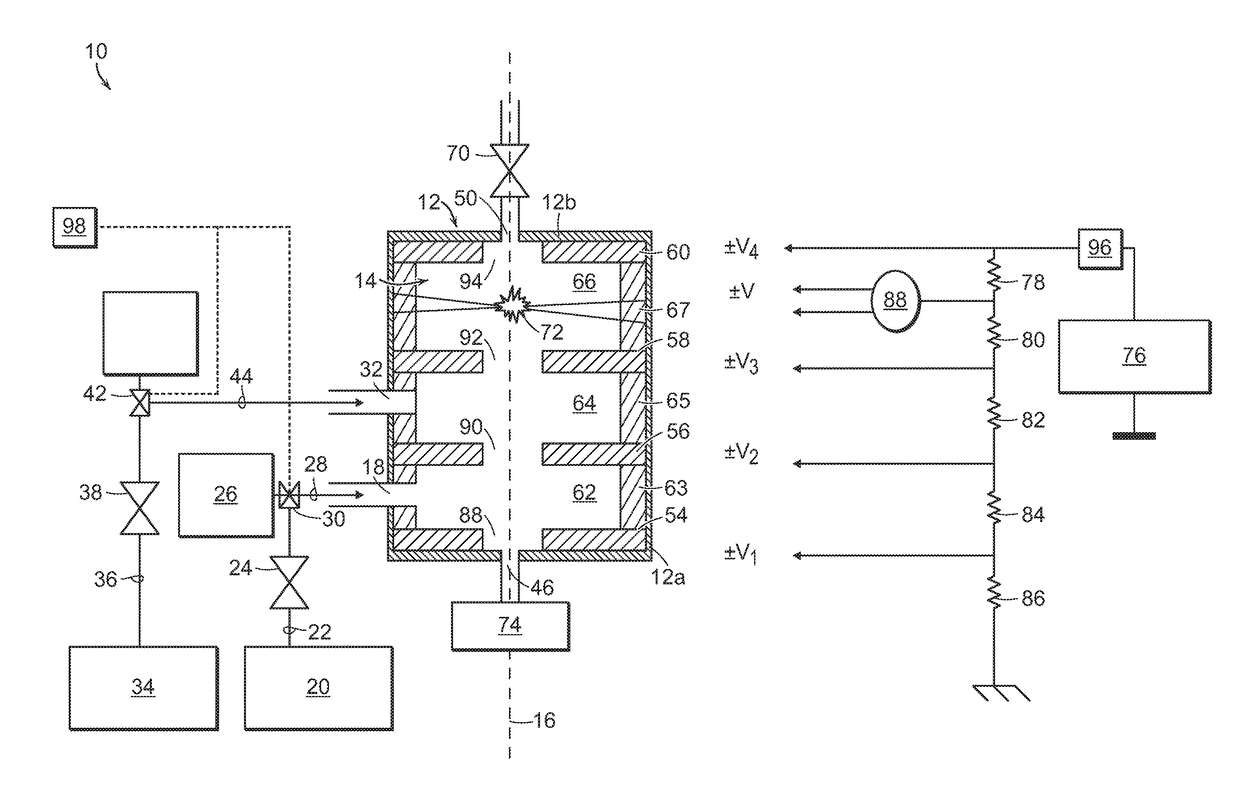
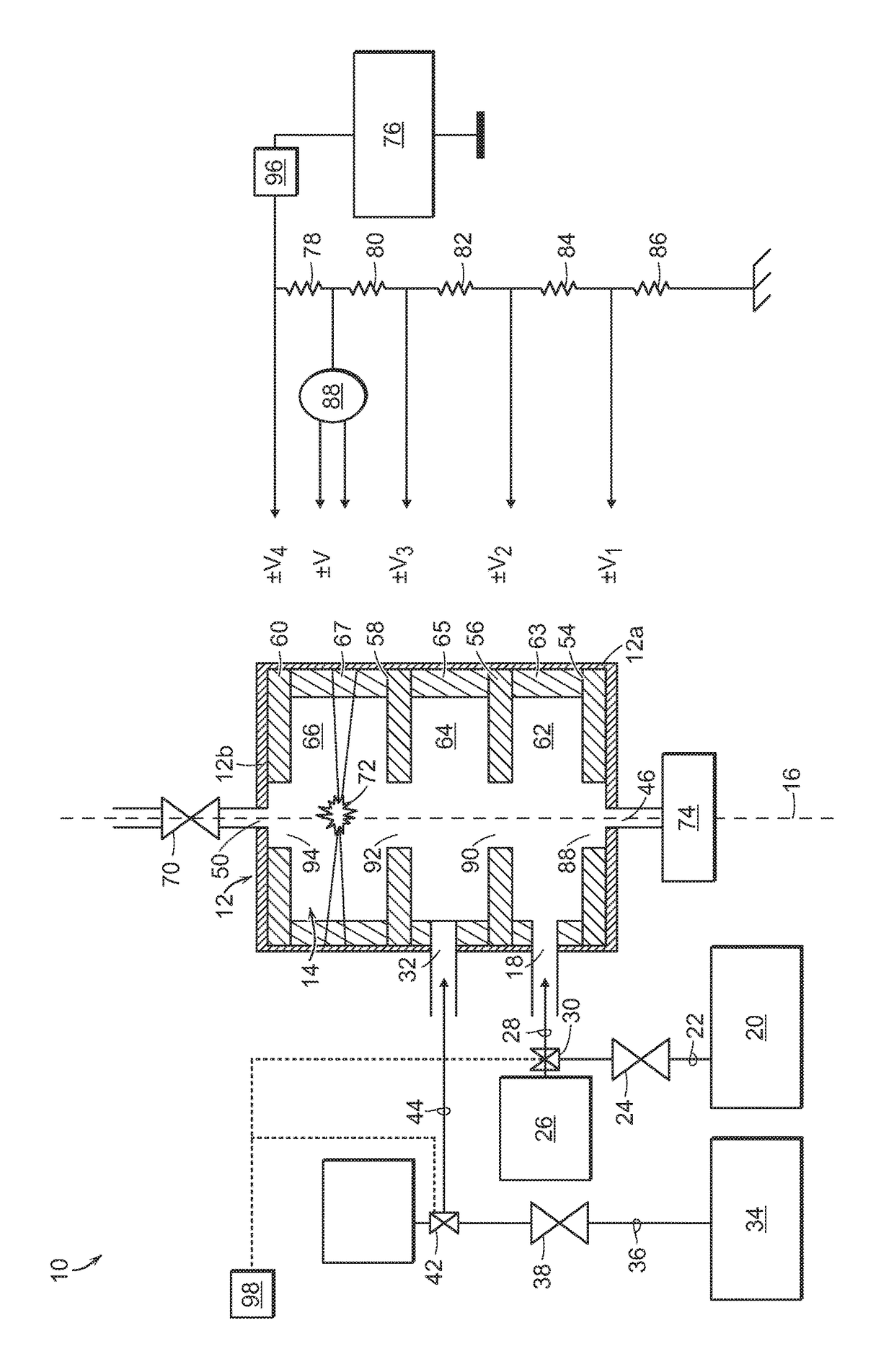
Optimisation of a method for calculating doses deposited by an ionising beam
InactiveUS20160346566A1Improve distributionQuick calculationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose gradientVoxel
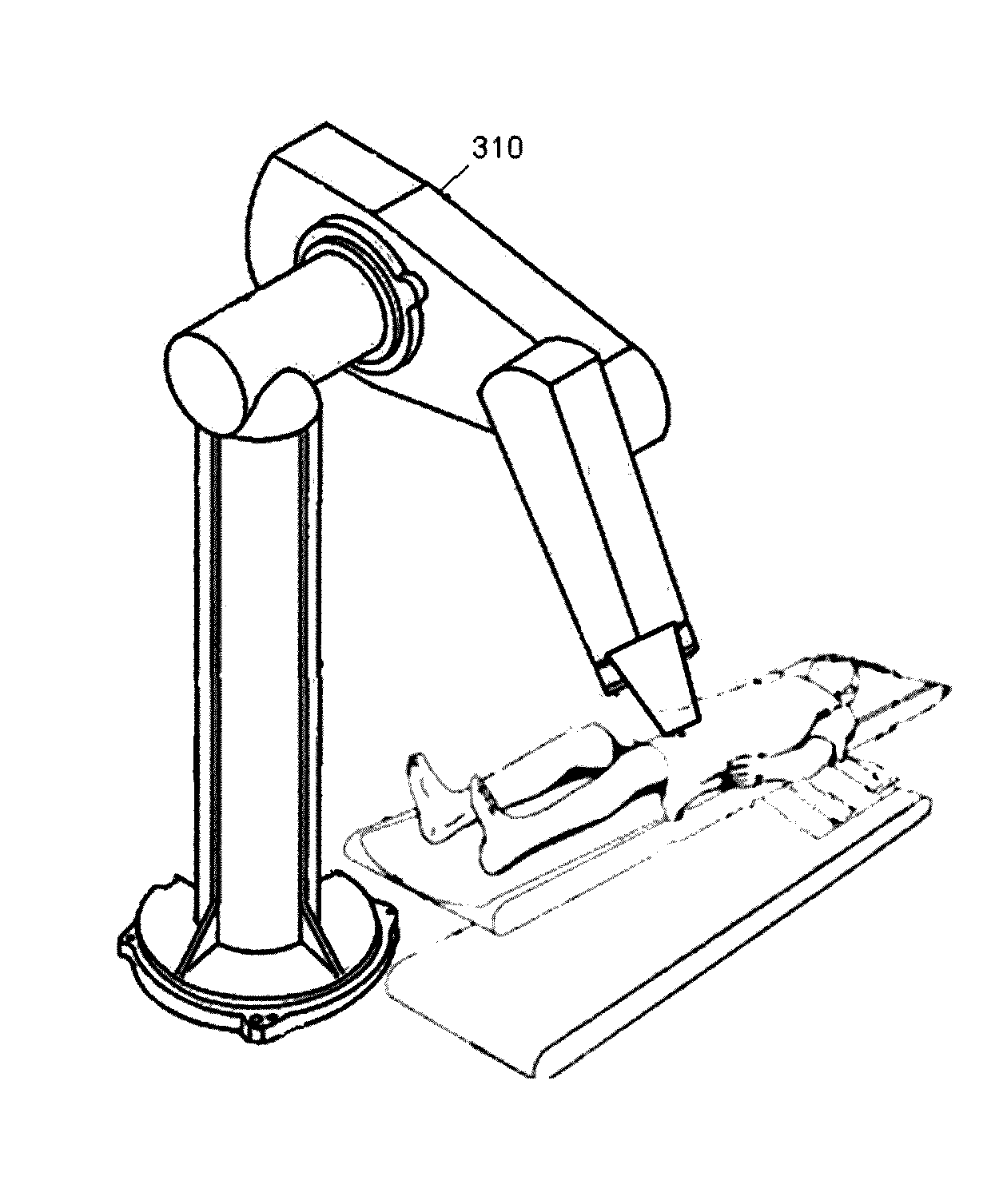
A method for estimating a dose gradient of the parameters of a beam of ionizing particles, the dose being deposited by the beam in a voxel of a meshed phantom of a patient, each mesh cell comprising voxels of one and the same material, the parameters of the beam comprising a fluence parameter and geometric parameters, the method comprises the determination of the analytic function for the gradient of the dose, deposited per mesh cell, of the parameters of the beam; and the determination of the estimation of the gradient of the dose in the voxel. Certain procedures for estimating the dose deposited are described. Developments deal with configurations having several independent of partially dependent irradiating beams, optimizations of the treatment plan using cost functions and the management of beams moving along trajectories. The use of servo-controlled robotic arms or of other mobile systems during irradiation is described.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Security inspection system for persons
ActiveUS20100072361A1Accurate detectionEffectively distinguish drugsTime-of-flight spectrometersGeological detection using milimetre wavesRadioactive agentIon-mobility spectrometry
The invention provides a security inspection system for inspecting persons, characterized in that it comprises: a passageway which provides an inspection space isolated or partially isolated from an ambient environment, in which at least one sub-passageway allowing persons to be inspected to pass is provided in the inspection space, and each of the sub-passageways is provided with at least one millimeter wave imaging device for millimeter wave imaging of persons being inspected; and an ion mobility spectrometer for ionizing particles of substance or gases that are released or volatilized from the inspected persons into the air in the passageway and then measuring a mobility rate thereof under the action of the electric field to effect identification of substances. At least one radioactive substance inspection device may also be provided in the passageway to detect whether the person being inspected carries radioactive substances.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD
System and method for spatially-resolved chemical analysis using microplasma desorption and ionization of a sample
ActiveUS8101923B2Damage to minimized eliminatedFragmentation and to minimized eliminatedParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansNoble gasDesorption
A method and system for desorbing and ionizing molecules from a sample for mass spectrometry using a microplasma device is disclosed. The system and method relies upon a microplasma device, or array of such devices, to partially ionize a gas to form a microplasma. The ionized gas can be a mixture of a noble gas, such as neon or argon, and hydrogen (H2). The ionized gas can form a effluent stream directed onto the surface of a sample to desorb molecules from the remainder of the sample. The desorbed molecules can be ionized by the effluent stream as they leave the surface of the sample. The ionization process can include: photoionization, penning ionization, chemical ionization (proton transfer), and electron impact ionization. The ionized particles from the sample can be directed to a mass spectrometer for analysis. This can produce spatially-resolved mass spectral data, and can be conducted concurrently with another imaging system, such as a microscope.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Non-radioactive, capacitive discharge plasma ion source and method
ActiveUS9607819B1Efficiently formedReduce operating costsSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapacitancePlanar electrode
A non-radioactive plasma ion source device includes at least four planar electrodes that define at least three chambers, including a discharger chamber and at least two additional chambers aligned along a major longitudinal axis of the housing. A discharger ionizes at least one of a transport gas and a discharge gas to form ions in the discharger chamber that are directed by a homogeneous electric field generated by the planar electrodes toward an analyte gas outlet. Ionized species of at least one of the transport gas and the discharge gas that are not entrained by a counterflow gas stream are discharged from the discharger chamber to form a stream of ionized particles that ionize a sample gas and thereby form a stream of ionized analyte particles of the same polarity. The ionized analyte particles are entrained with the stream of ionized particles and pass through an analyte gas outlet to an analyzer.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
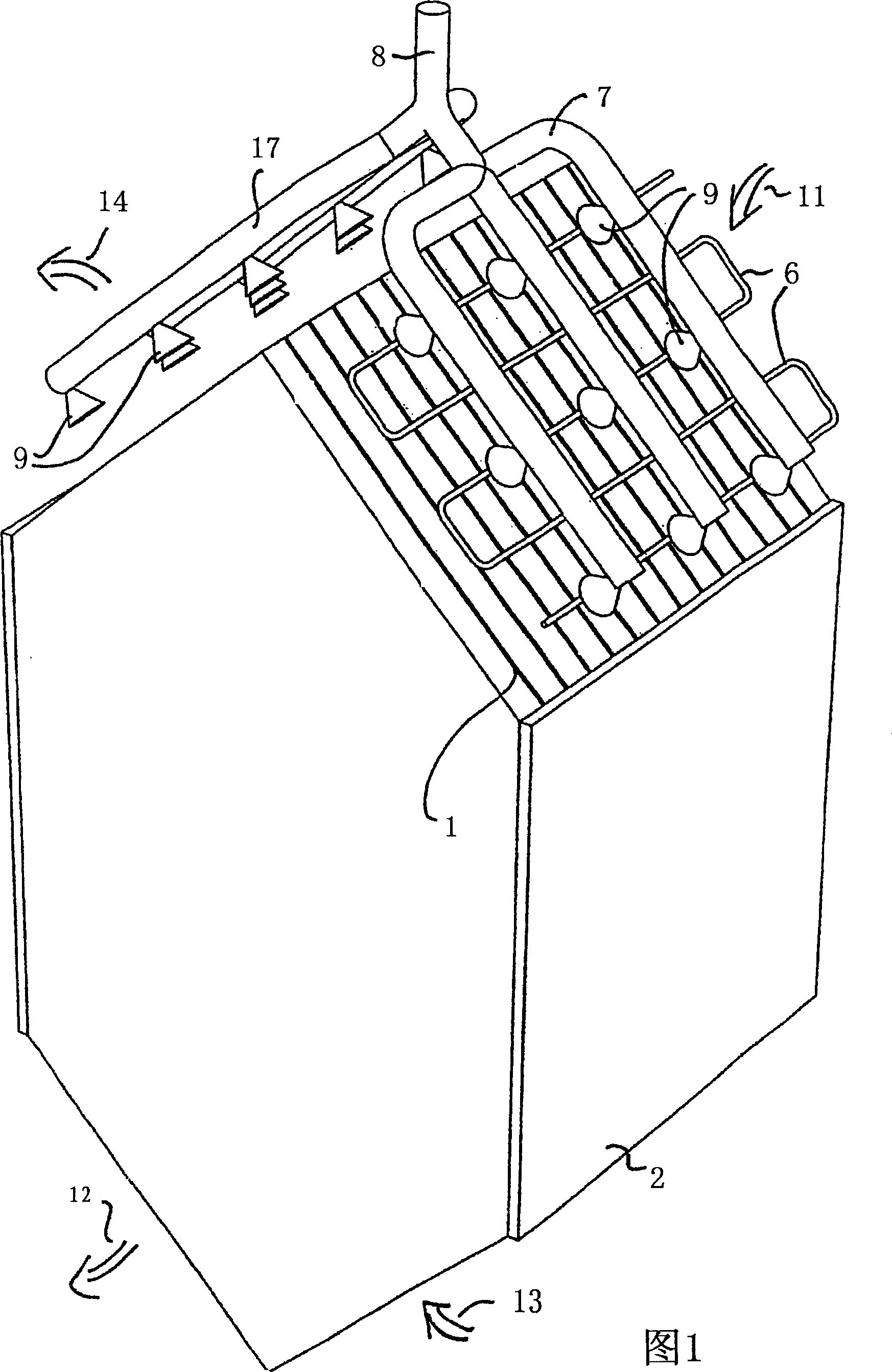
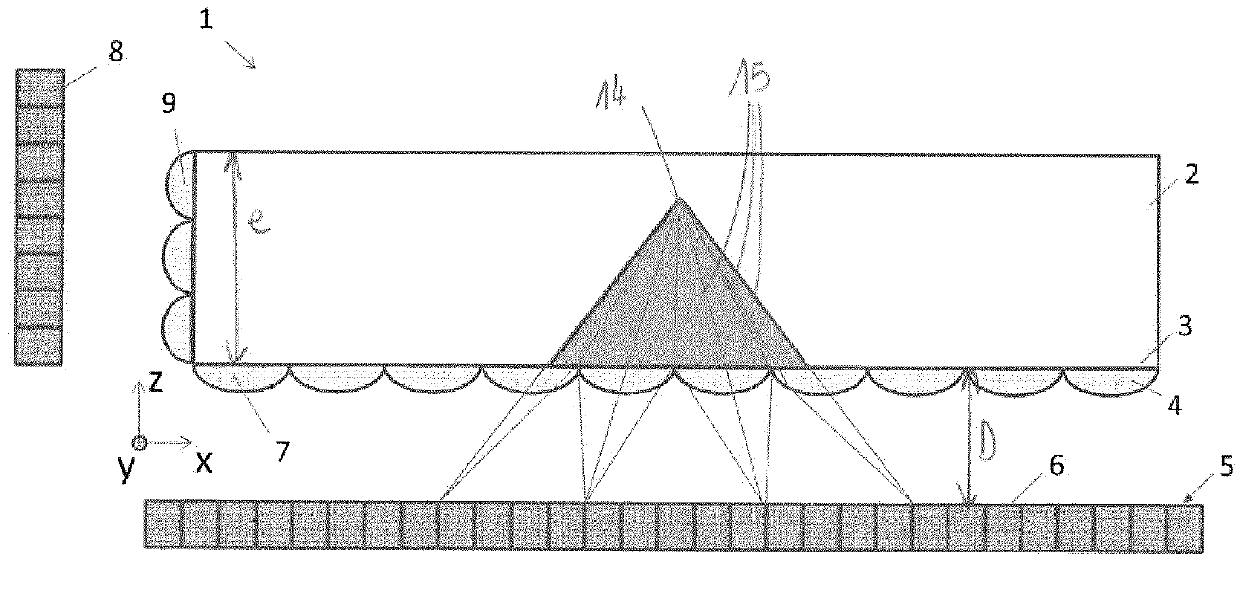
Device for ionizing particles carried in an airflow, for ventilation, heating, and/or air-conditioning system in particular
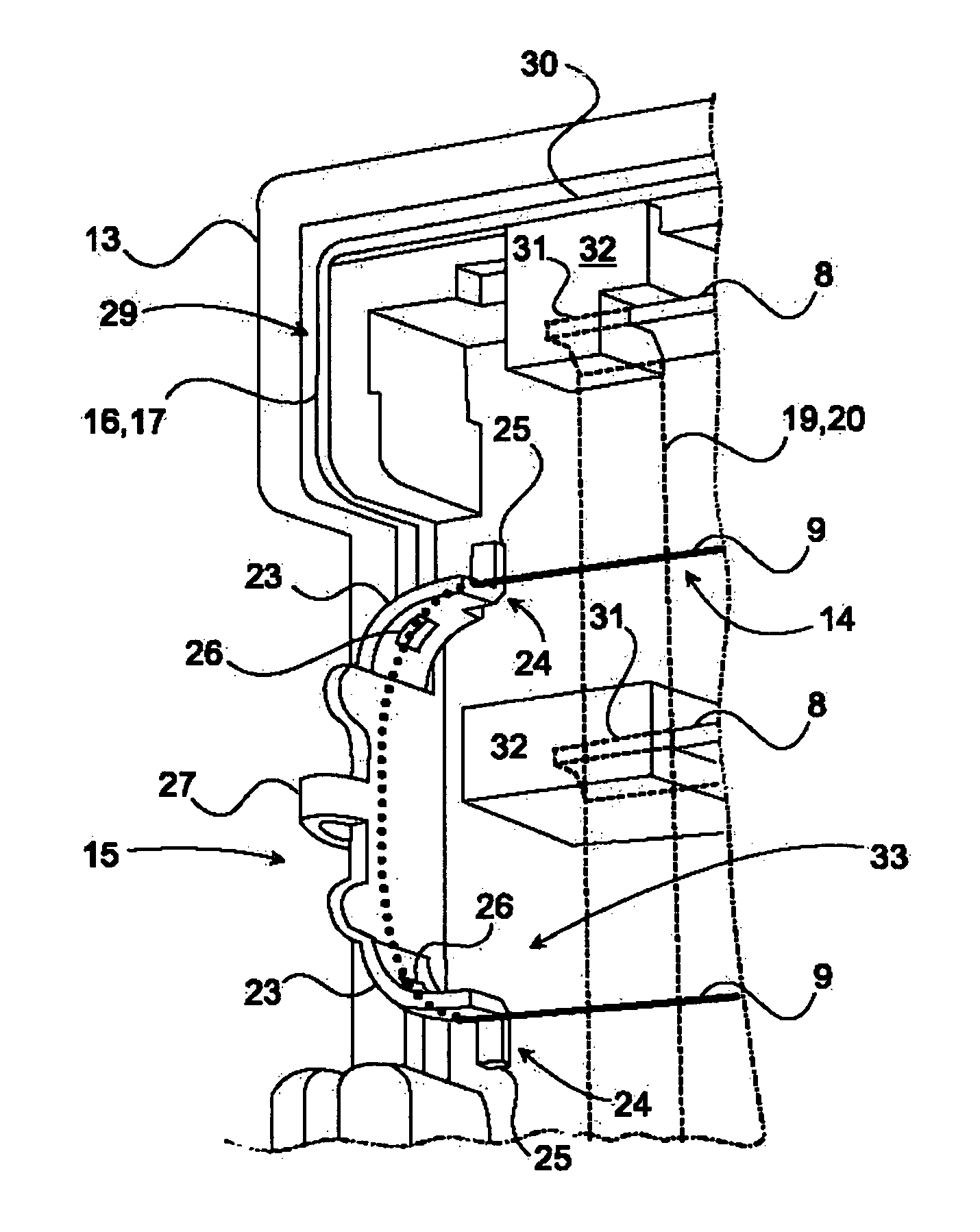
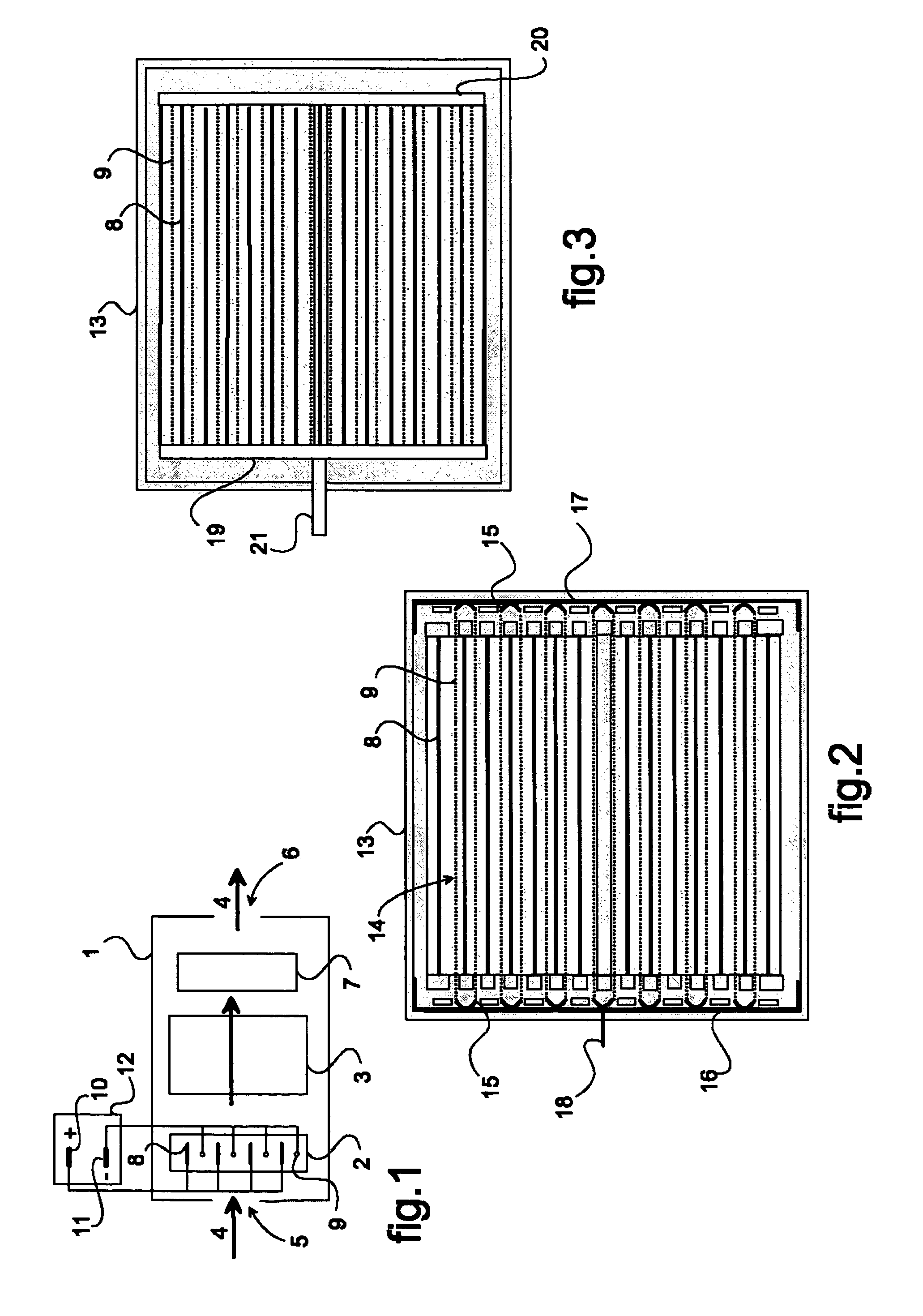
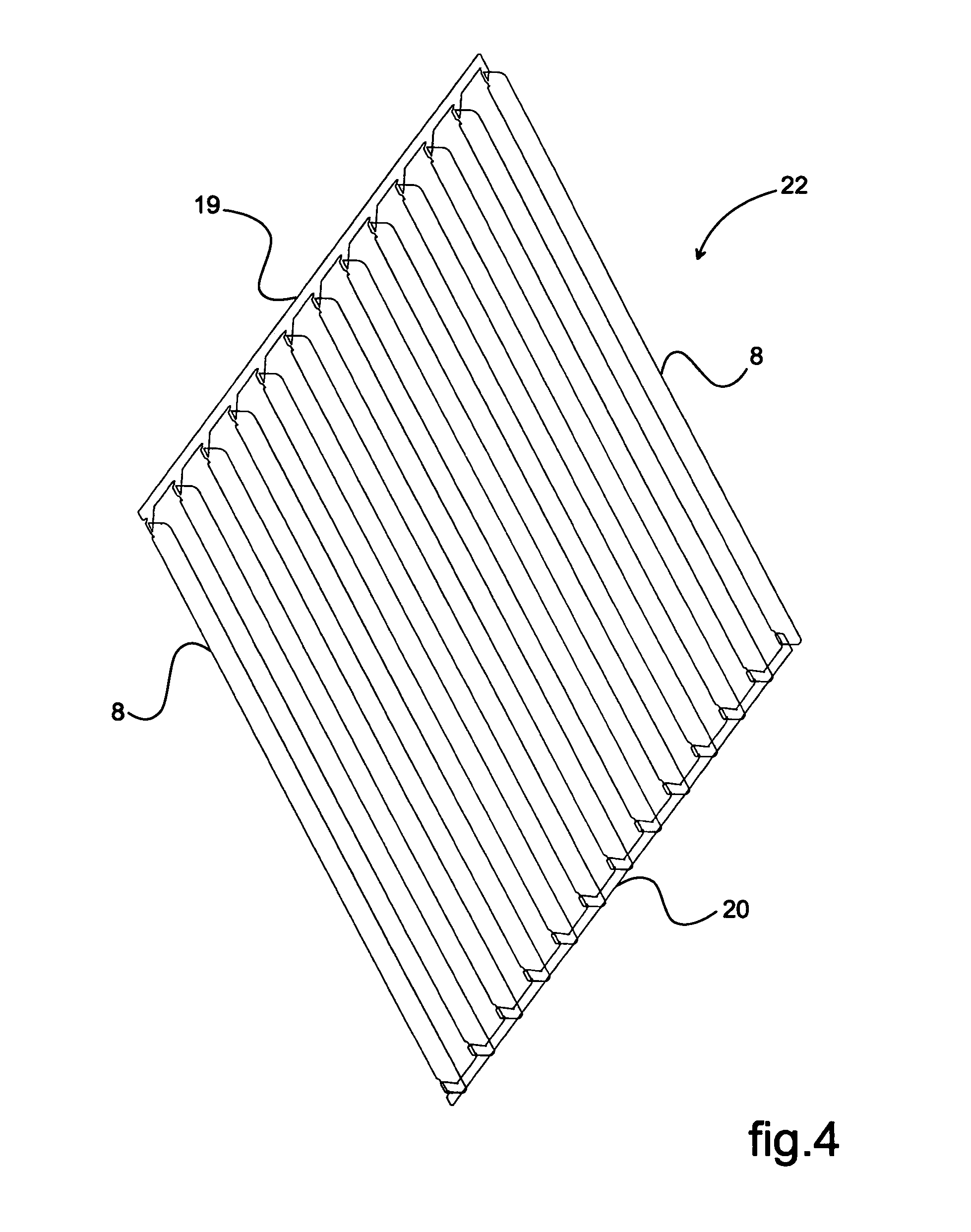
InactiveUS7540903B2Easy to operateEasy to produceElectrode carrying meansElectrode constructionsElectrical conductorEngineering
The object of the invention is a device for ionizing (2) particles carried in an airflow (4) circulating inside a system, this device (2) including at least two electrodes (8, 9) held by a chassis (13) and connected, respectively, to the corresponding terminals (10, 11) of a polarized electrical power supply. Two adjacent first electrodes (8) are arranged on either side of a second electrode (9), which is formed from at least one conductor cable (14). The latter (14) is hooked onto fingers (15) that are designed as an elastic part for tensioning the conductor cable (14) and that are held by the chassis (13).
Owner:VALEO SYST THERMIQUES
Method and Device for Ionizing Particles of a Sample Gas Flow
ActiveUS20160126079A1Eliminate wall effectReduce concentrationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansIon clustersIonizing particles
A device for ionizing sample particles of a sample gas flow comprises a first flow tube for providing the sample gas flow, and an introducing means for providing H2SO4 molecules to an interaction region. In addition the device comprises a generator for producing reagent primary ions from particles of candidate reagent gas flow essentially in a primary ion production region. The device is configured to introduce said reagent primary ions with H2SO4 molecules in said interaction region in order to arrange interaction between the reagent primary ions and the H2SO4 molecules, thereby producing HSO4− ions and again to produce HSO4− ion clusters comprising HSO4− ions and at least two H2SO4 molecules via interactions of HSO4− with other H2SO4 molecules in said interaction region. Furthermore the device is configured to introduce said HSO4− ion clusters with the sample particles of the sample gas flow in order to provide reactions between said HSO4− ion clusters and the sample particles, and thereby provide a sample cluster comprising the HSO4− ion clusters and said base sample to be determined.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI
Method and device for ionizing particles of a sample gas flow
InactiveCN105247653AEasy to openSo as not to damageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsSoft x raySoft X-rays
A device for ionizing particles (molecules or clusters) of a sample gas flow comprises a first flow tube for providing the sample gas flow, and a generator for producing reagent primary ions from particles of candidate reagent gas flow at a primary ion production region. The device also has an interaction region for introducing the reagent ions into the sample gas flow in order to arrange interaction between the reagent primary ions and the particles of the sample gas flow, thereby producing sample gas ions to be delivered to a detector. The generator for producing reagent primary ions is a non-radioactive soft X-ray radiation source.
Owner:AIRMODUS +1
Air purification device and method
InactiveCN106705247AIonization achievedAchieve ionizationSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses an air purification device. The air purification device comprises a shell, a high-voltage electrostatic dust removal unit and an air blower; the dust removal unit comprises an ionization unit and a dust collecting unit located at a downstream position of the ionization unit; a first gap and a first working voltage are set between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the ionization unit, wherein the first working voltage is set to be capable of ionizing particles in air passing through the ionization unit, and the first gap is set to be not less than the insulation distance of the air and enable the ionized particles to pass through the ionization unit; and a second gap smaller than the first gap and a second working voltage smaller than the first working voltage are set between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the dust collecting unit, wherein the second gap and the second working voltage are set to enable the ionized particles to be adsorbed on the electrodes of the dust collecting unit so as to achieve the dust removal function. According to the air purification device, the purification efficiency can be ensured, and the generation amount of ozone can be minimized. The invention further discloses an air purification method.
Owner:刘希威
Neutron detector
InactiveUS20080315108A1Efficient discriminationImproved signal characteristicTube/lamp screens manufactureElectric discharge tubesDielectricPulse height analyzer
A neutron detector comprises a gas-filled dielectric shell, preferably a glass balloon, having opposite electrodes. An electric field is established whereby ionizing particles may be detected via ionization and current flow in the gas, using a pulse height analyzer or other conventional means. The dielectric shell preferably has low gas permeability and a bulk resistivity in the range of 108 to 1017 Ω-m, and is preferably in the millimeter to centimeter size range. Multiple balloons may be arranged in parallel or may be individually addressable by the detector electronics.
Owner:MATERIALS INNOVATION INC +1
Neutron detector
InactiveUS7923698B2Line/current collector detailsElectric discharge tubesDielectricPulse height analyzer
A neutron detector comprises a gas-filled dielectric shell, preferably a glass balloon, having opposite electrodes. An electric field is established whereby ionizing particles may be detected via ionization and current flow in the gas, using a pulse height analyzer or other conventional means. The dielectric shell preferably has low gas permeability and a bulk resistivity in the range of 108 to 1017 Ω-m, and is preferably in the millimeter to centimeter size range. Multiple balloons may be arranged in parallel or may be individually addressable by the detector electronics.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
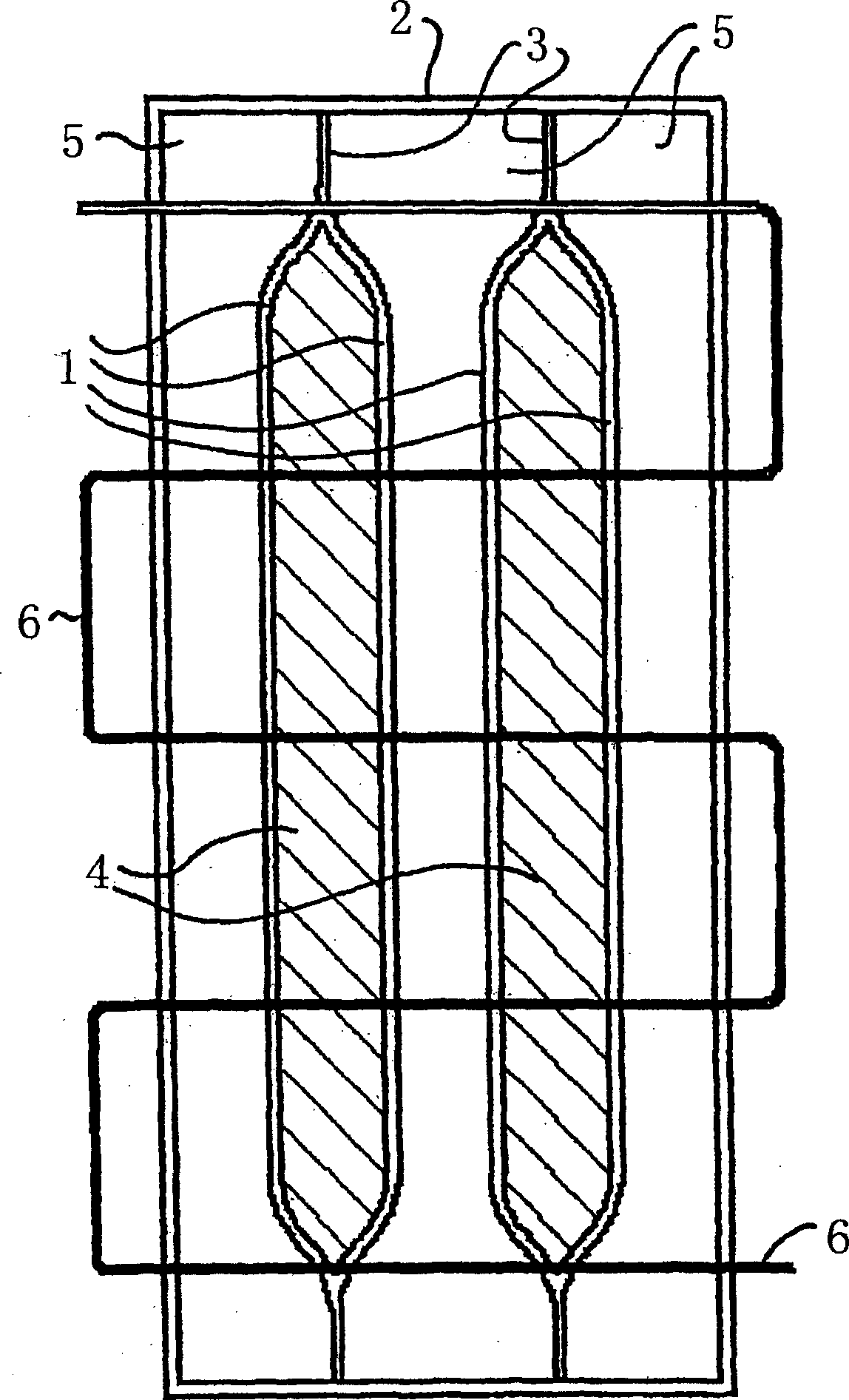
Plate heat exchanger
InactiveCN1759289ASimple structureEasy maintenanceEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsPlate heat exchangerDistribution system
A plate heat exchanger for exchanging heat between a first air stream and a second air stream includes a plurality of plates limiting first and second exchange chambers which are serially arranged in a transversal direction with respect to the plates. A first air stream of outside air passes through the first exchange chambers, a second air stream originating from ventilated rooms passes through the second exchange chambers. The heat exchanger further includes an ionization device for ionizing particles entrained in the first air stream so that the particles deposit at conductive plates of the first exchange spaces, a water distribution system for periodically discharging water into the first exchange spaces for cleaning the plates of the heat exchanger from deposited particles, and a water collection device for discharging collected water.
Owner:MENTUS HLDG AG
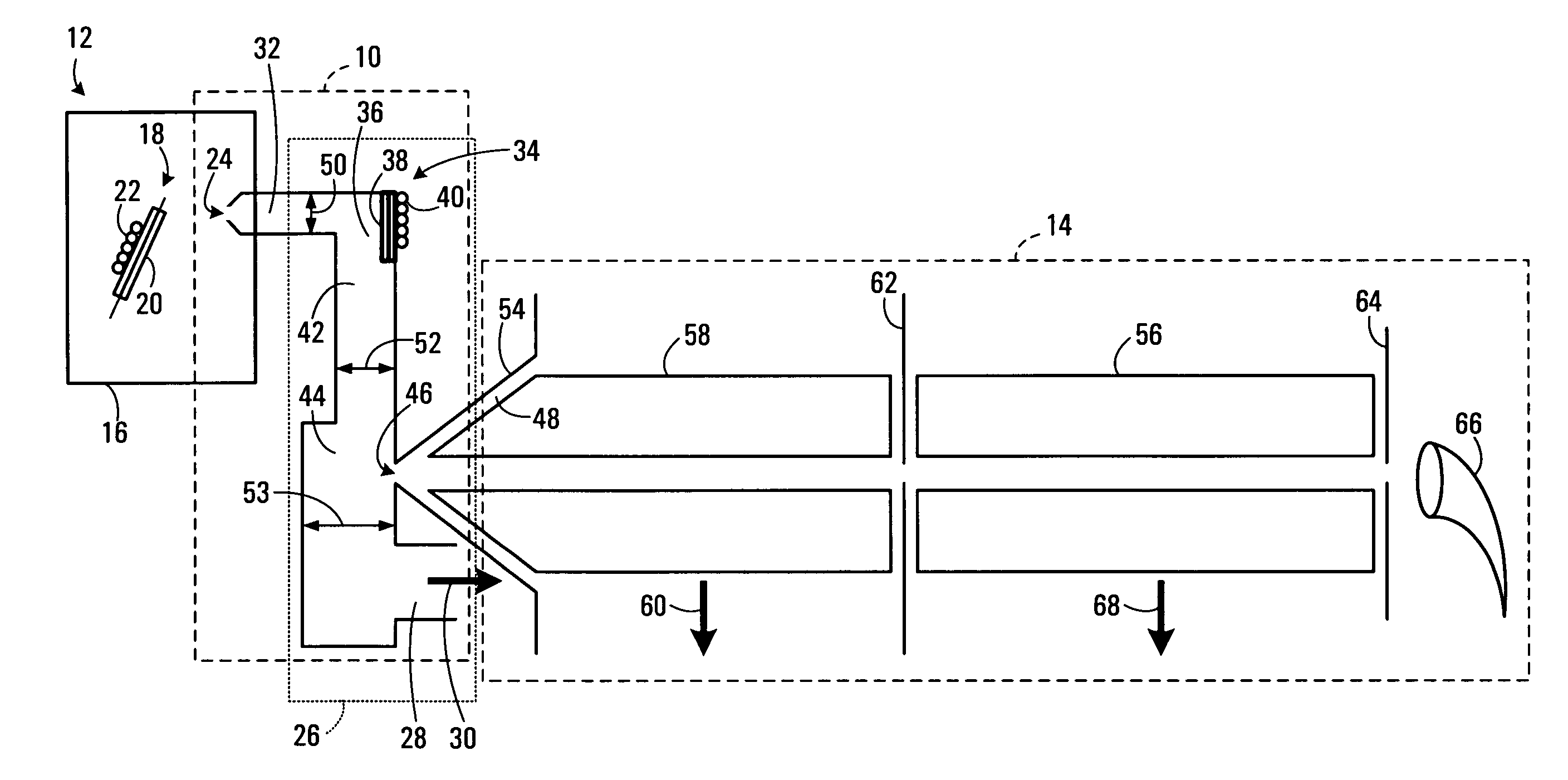
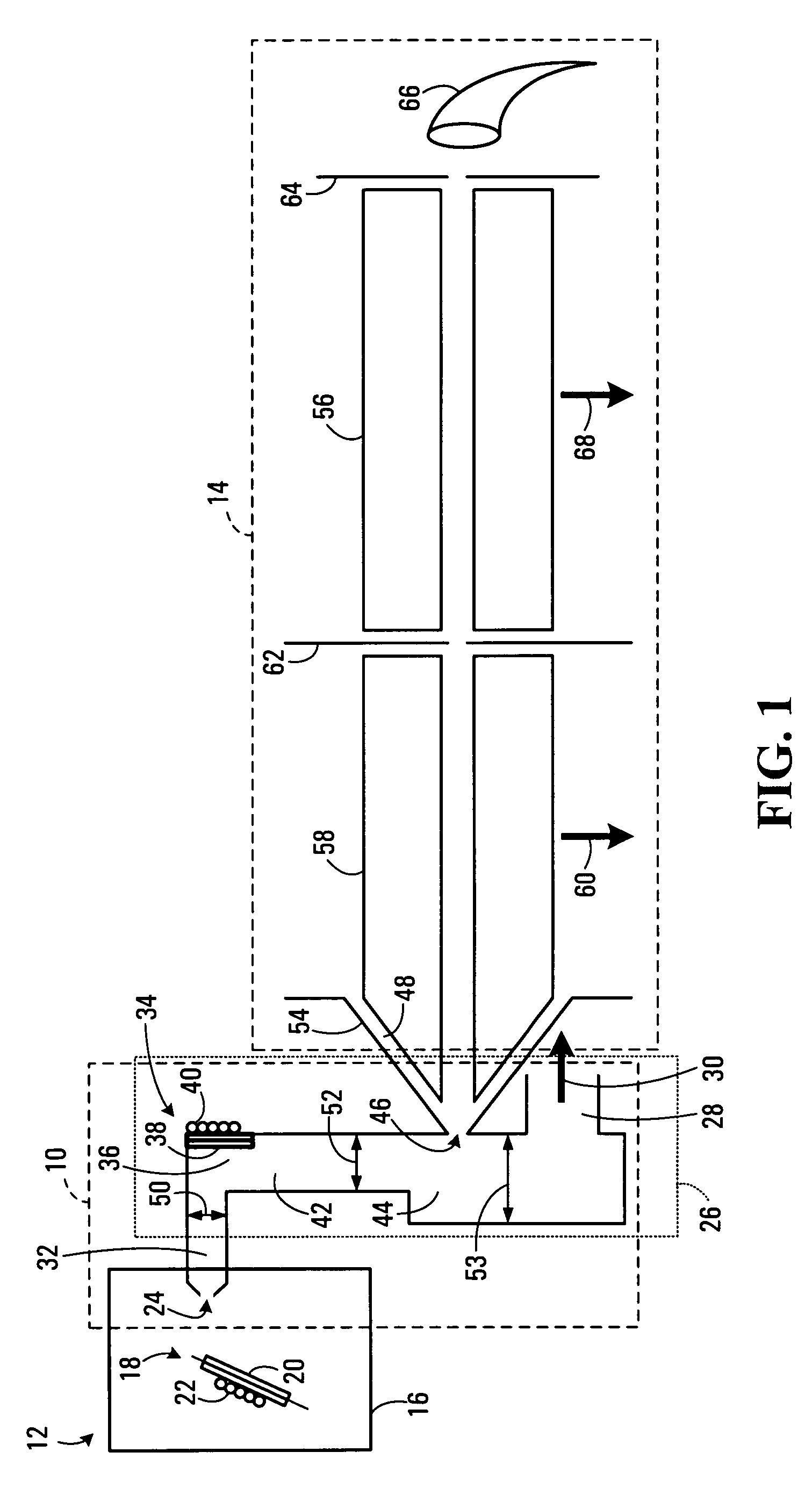
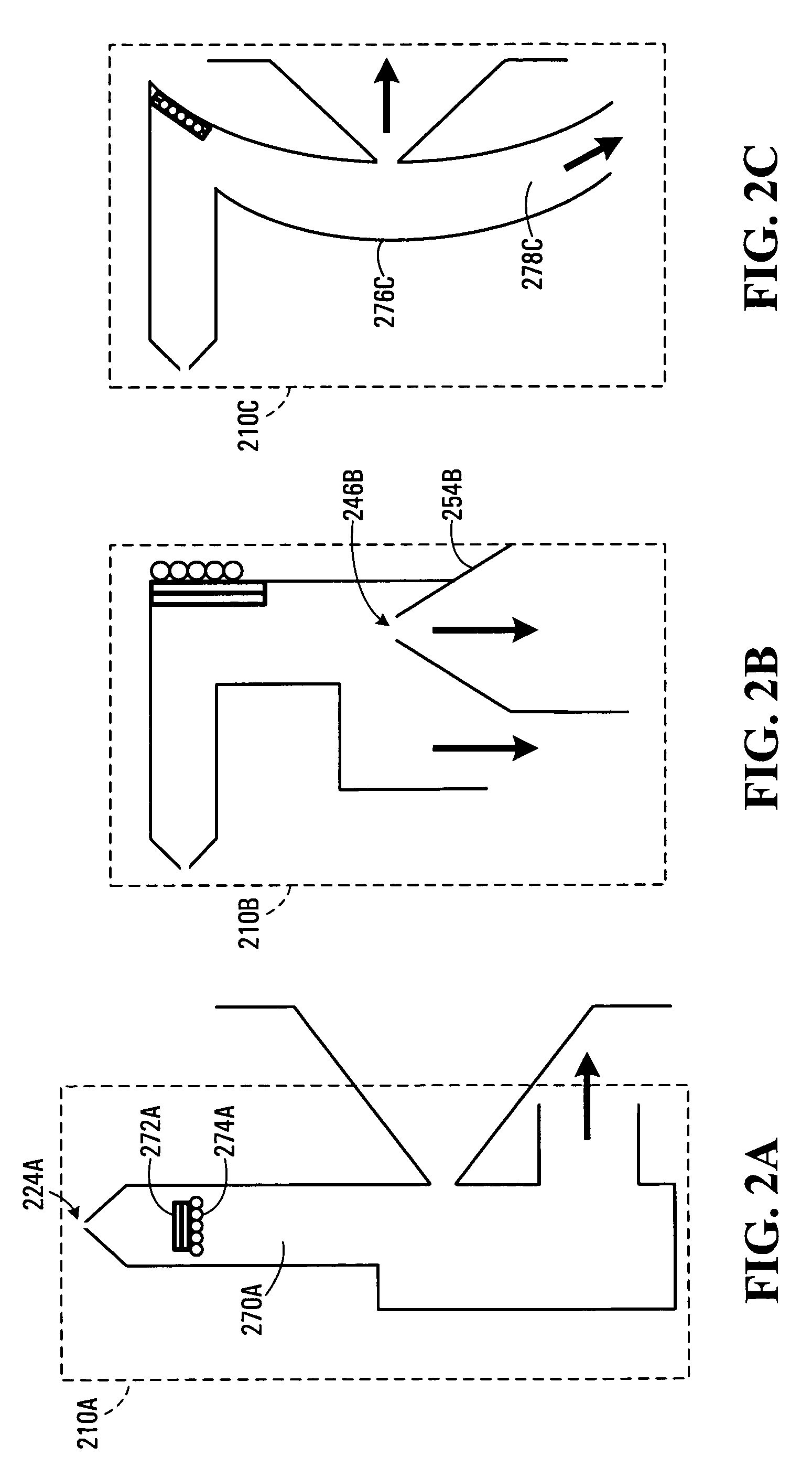
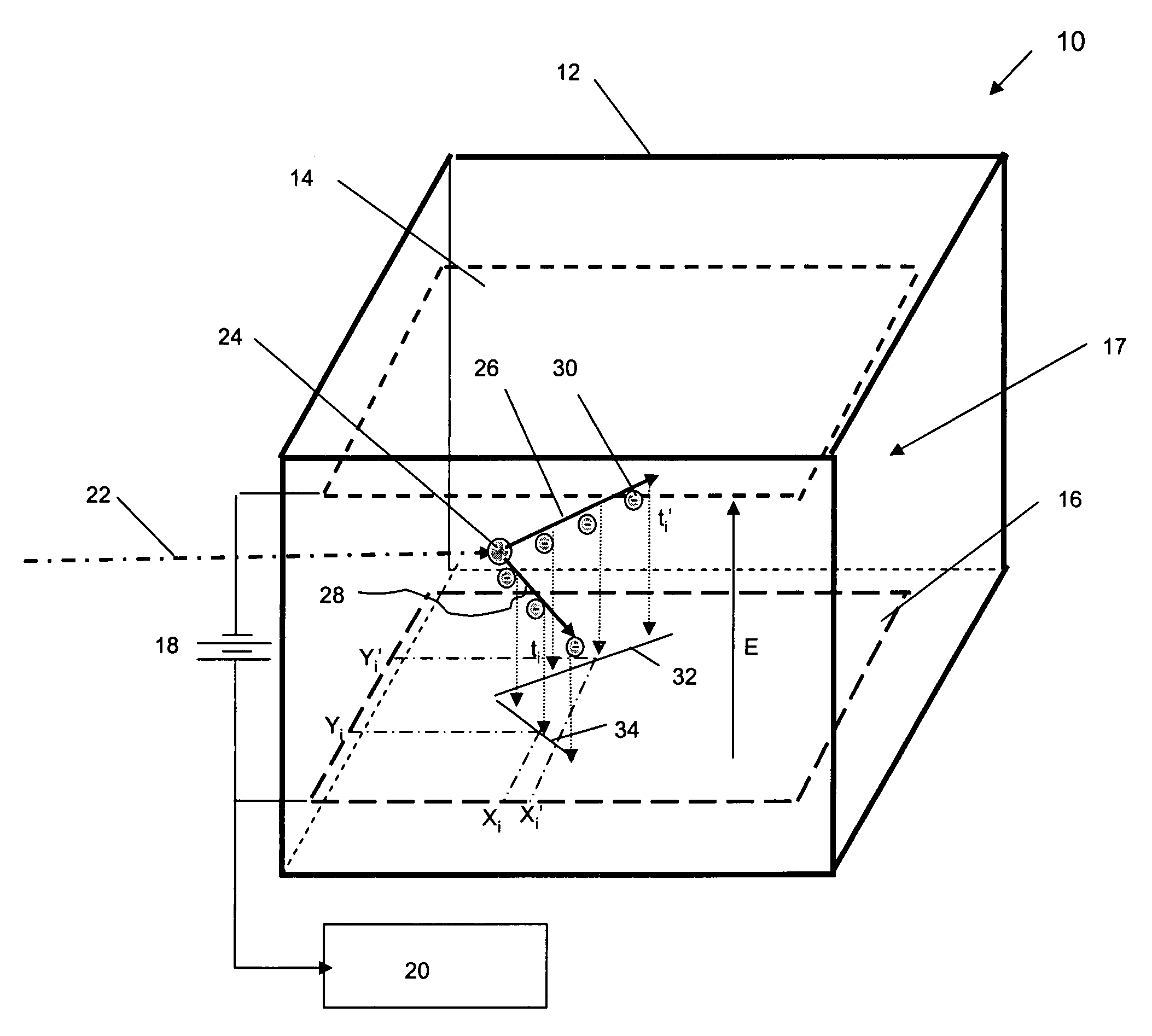
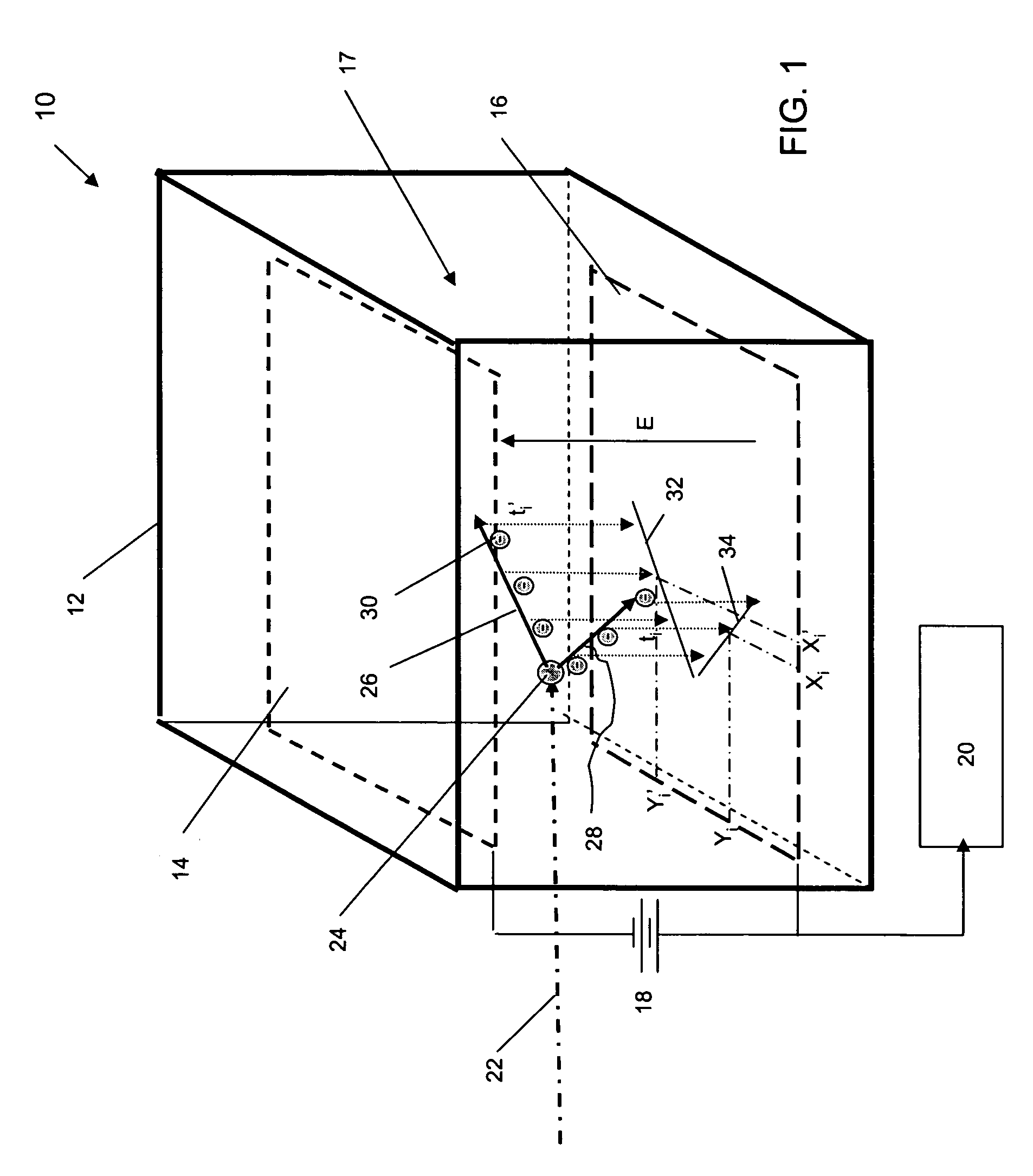
Apparatus for registration of photons and ionizing particles with simultaneous directional definition, for each photon or ionizing particle, of a point of origin in a fluid-filled conduit
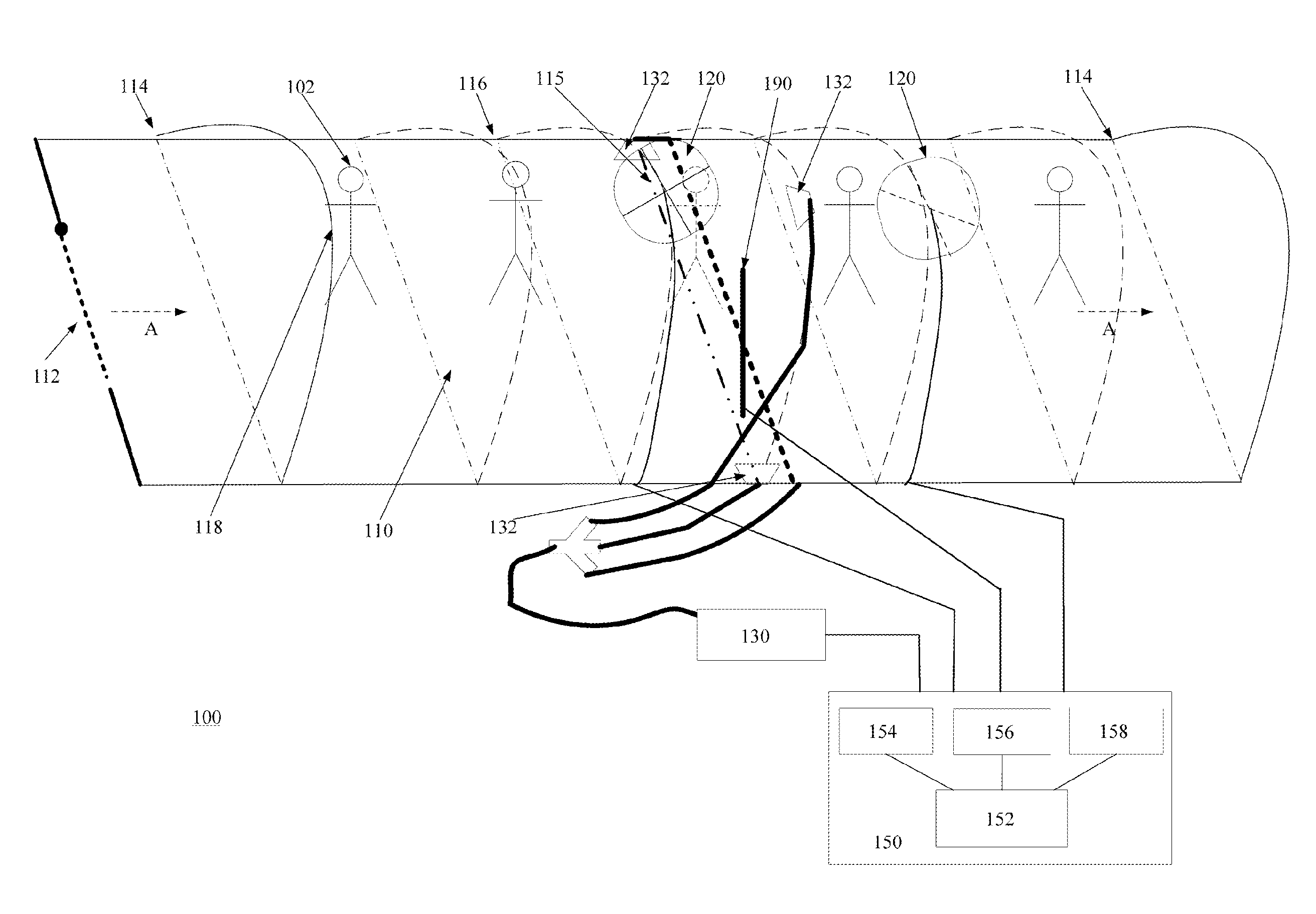
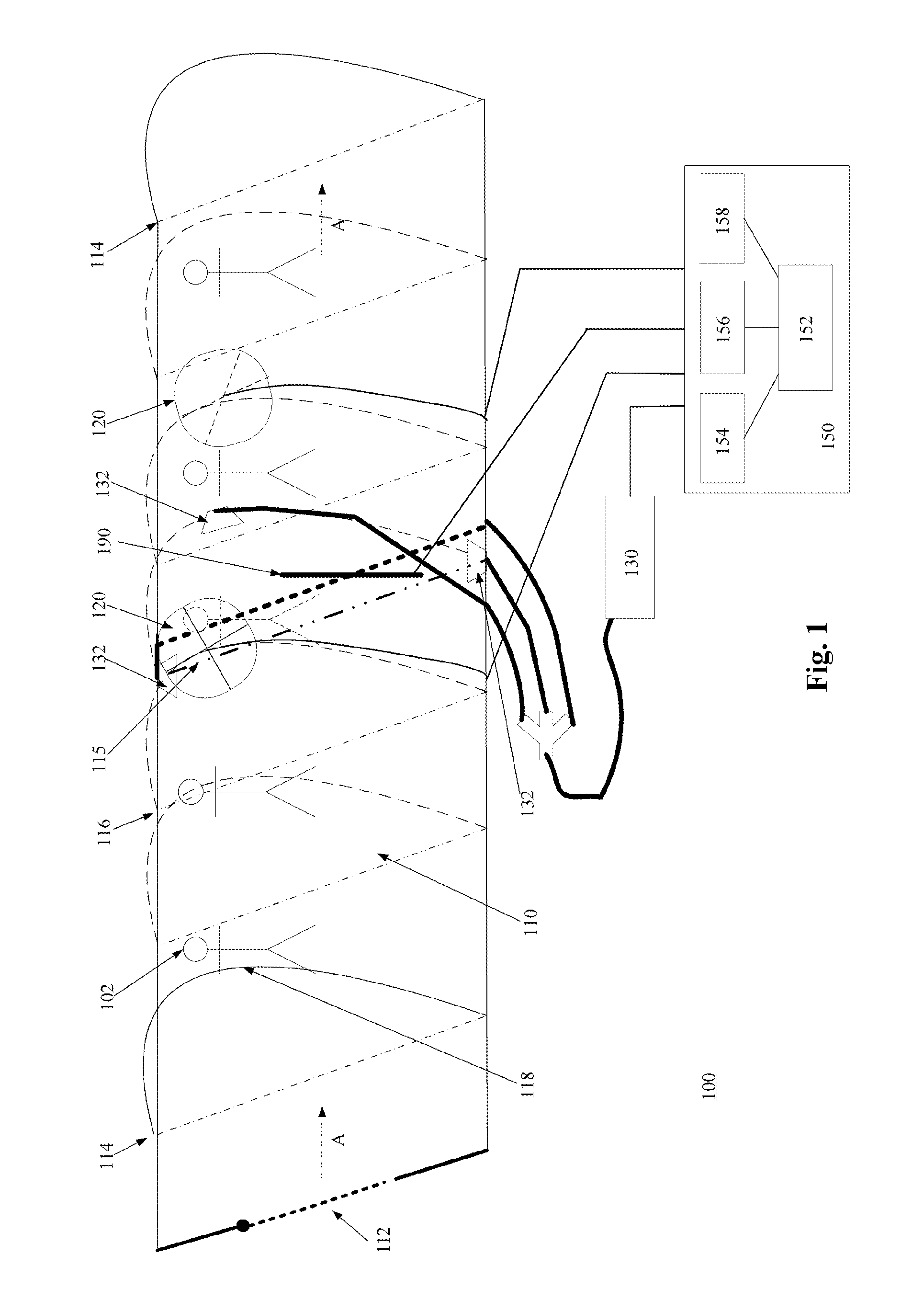
ActiveUS8466412B2Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorIonizing particles
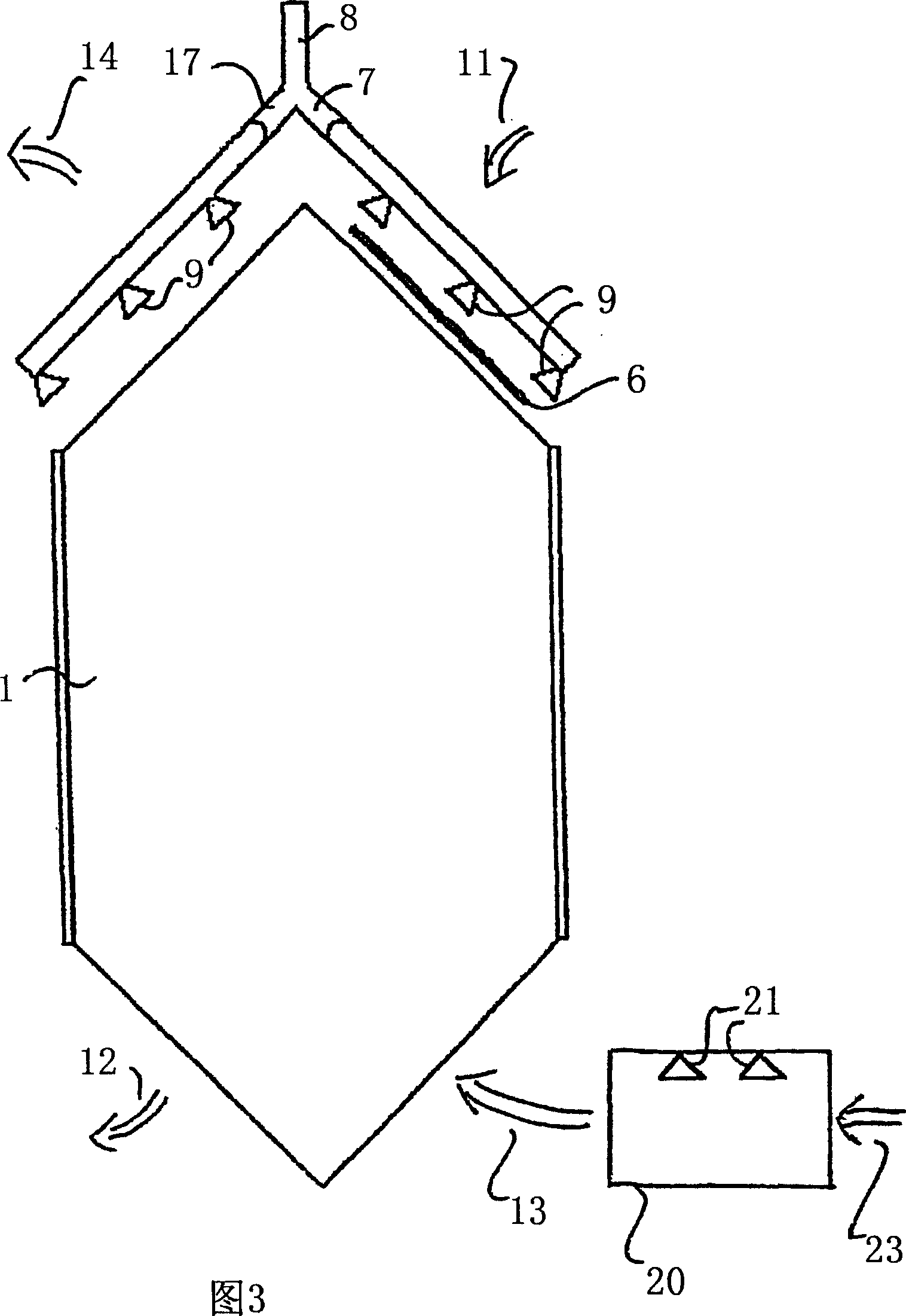
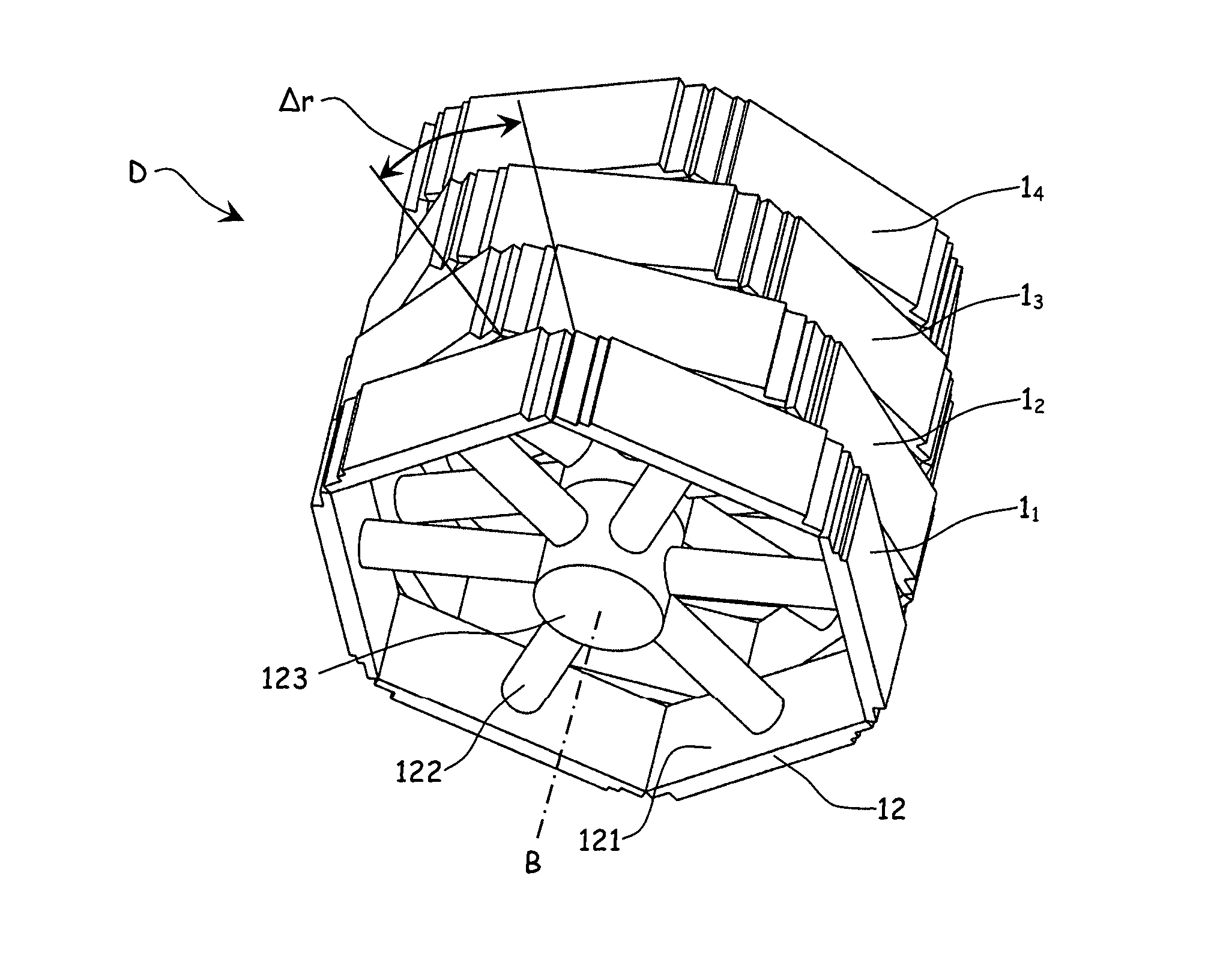
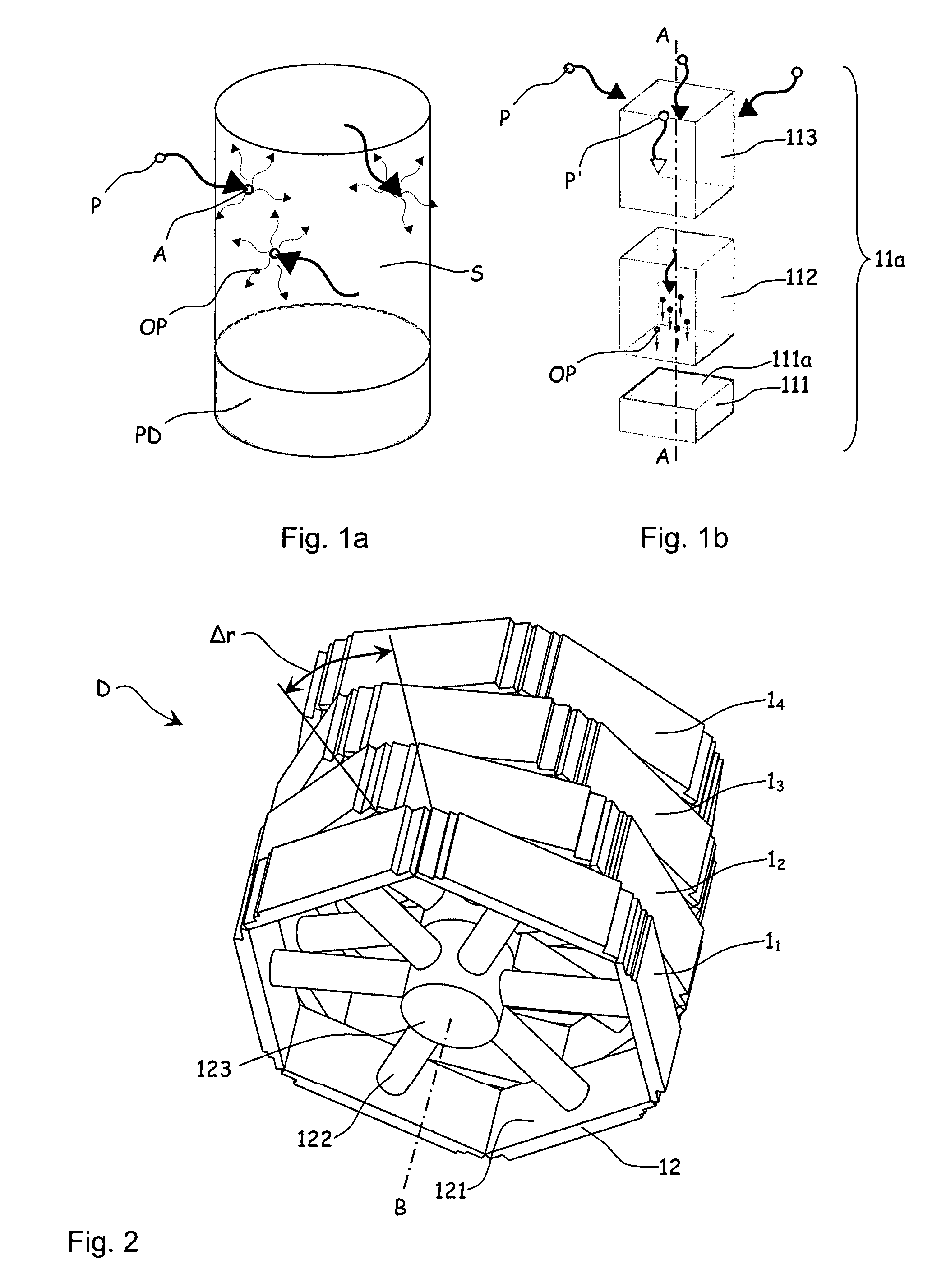
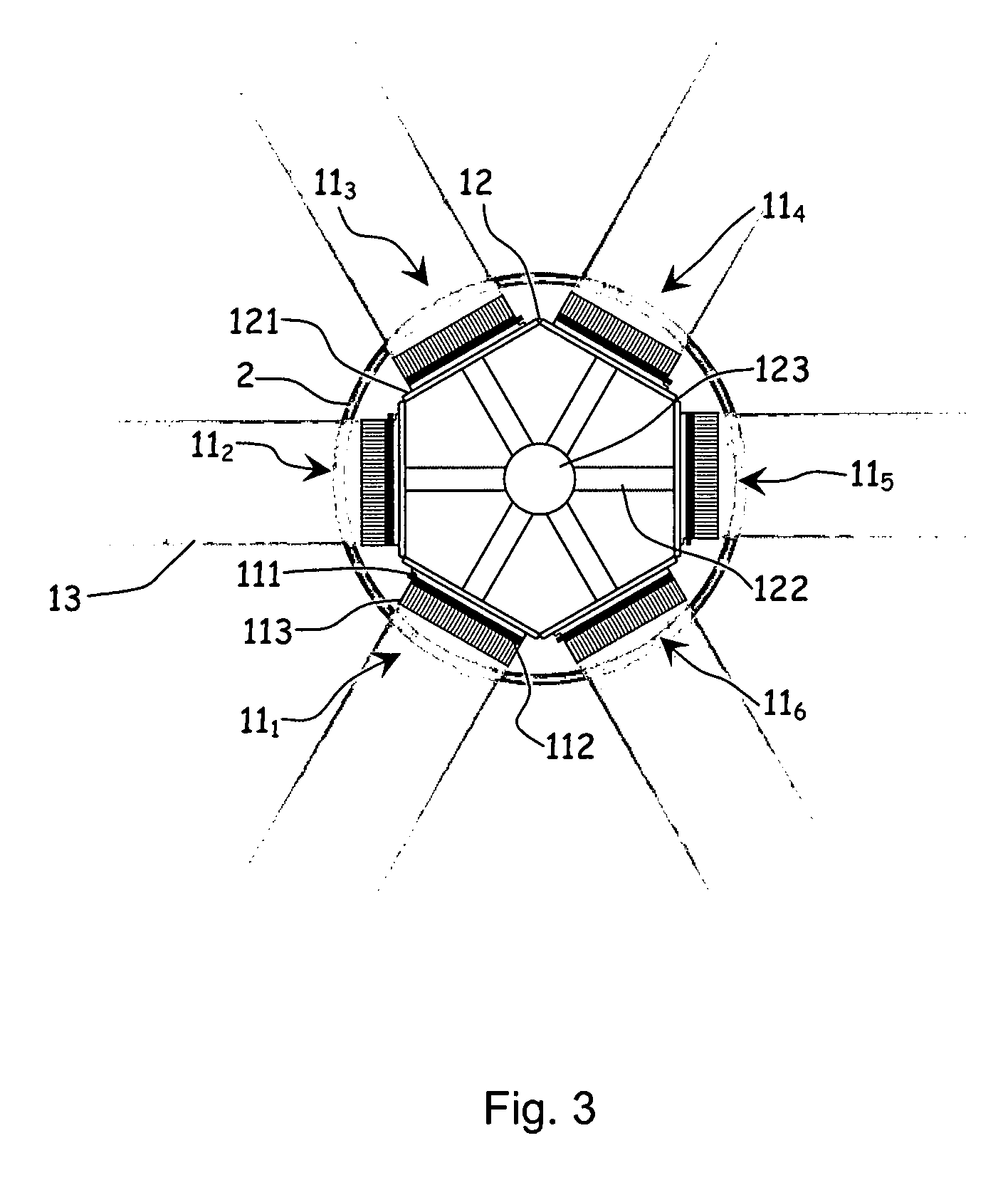
A detection apparatus (D) for photons or ionizing particles (P) is described, in which a detector system (11) is provided with several detecting units (11a), each including a scintillator (112) connected to a reader surface (111a) on an electronic charge reader (111), the scintillator (112) being arranged to generate cellular charges on the reader surface (111a) when capturing the photons or the ionizing particles (P), there being a collimator (113) arranged, connected to the scintillator (112) opposite the electronic charge reader (111), the collimator (113) being arranged to capture photons or ionizing particles (P′) exhibiting a direction of motion coinciding with a longitudinal axis (A) of the collimator (113), and to reject photons or ionizing particles (P′) exhibiting a direction of motion deviating from the direction of the longitudinal axis (A) of the collimator (113).
Owner:VISURAY TECH
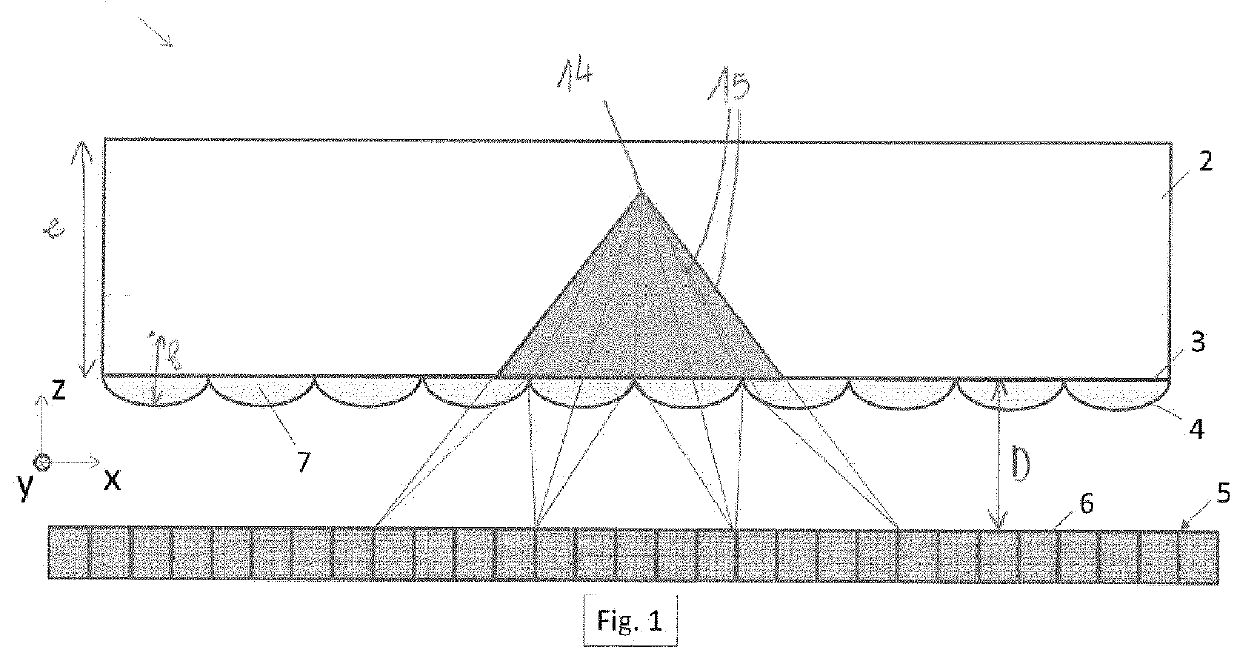
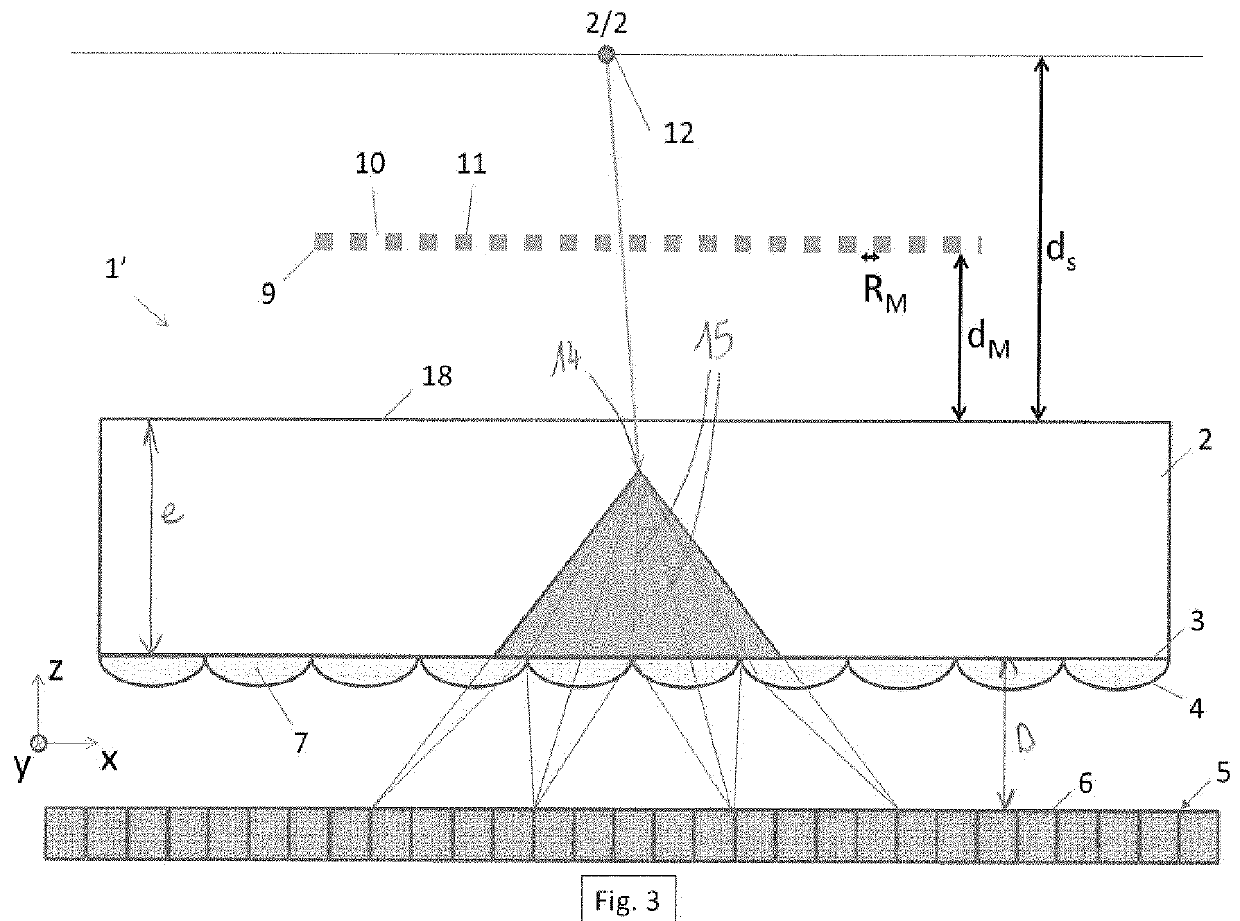
Detector for detecting the traces of ionizing particles
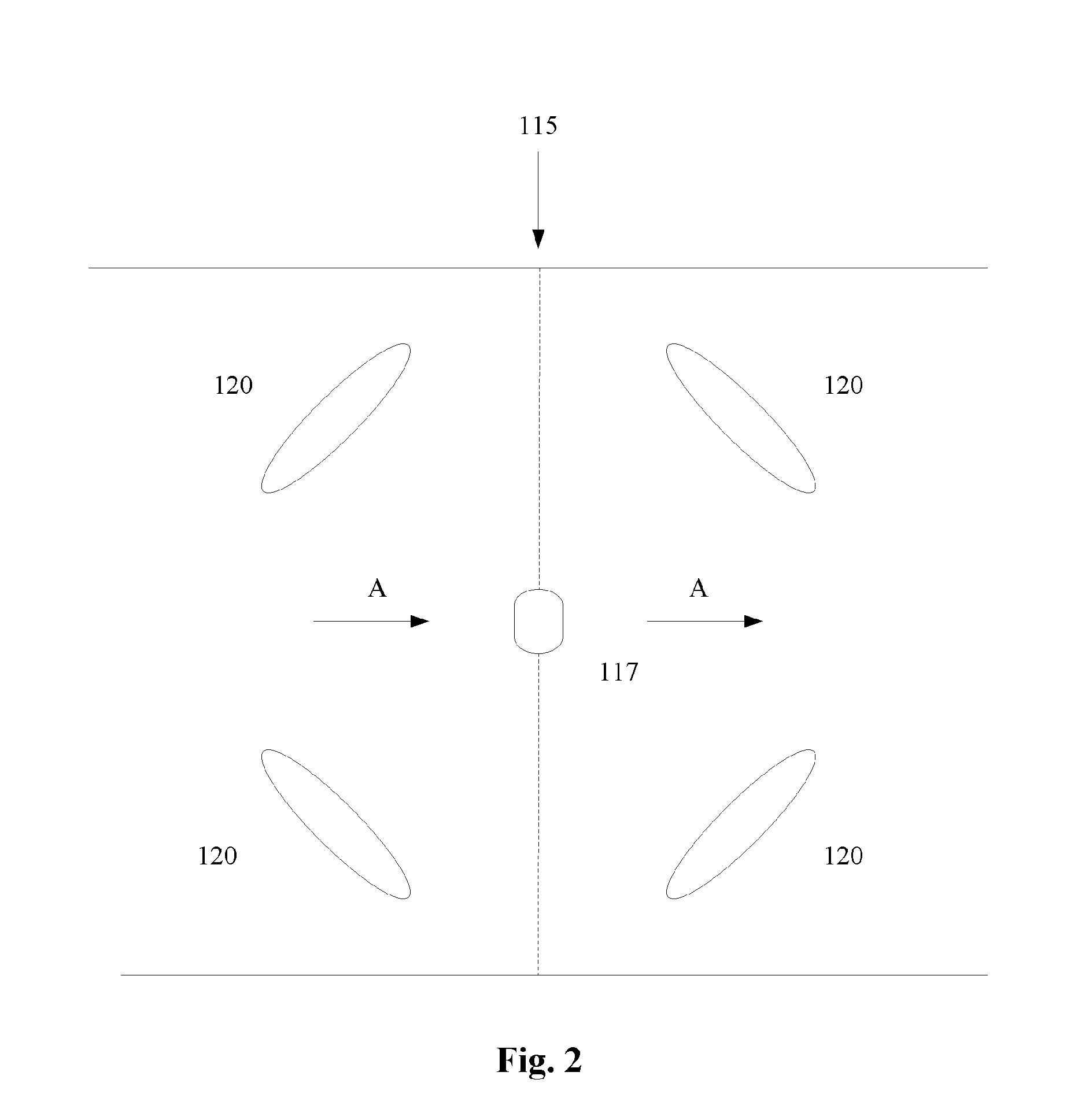
ActiveUS20160054456A1High sensitivityImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorMicro lens array
A detector for detecting the traces of ionizing particles includes a scintillator capable of emitting photons when ionizing particles pass therethrough; a first imager capable of detecting each photon emitted by the scintillator, and a first microlens array, each microlens of the first microlens array being arranged such as to produce an image of the trace of the particles by focusing the photons emitted in the scintillator on the first imager.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
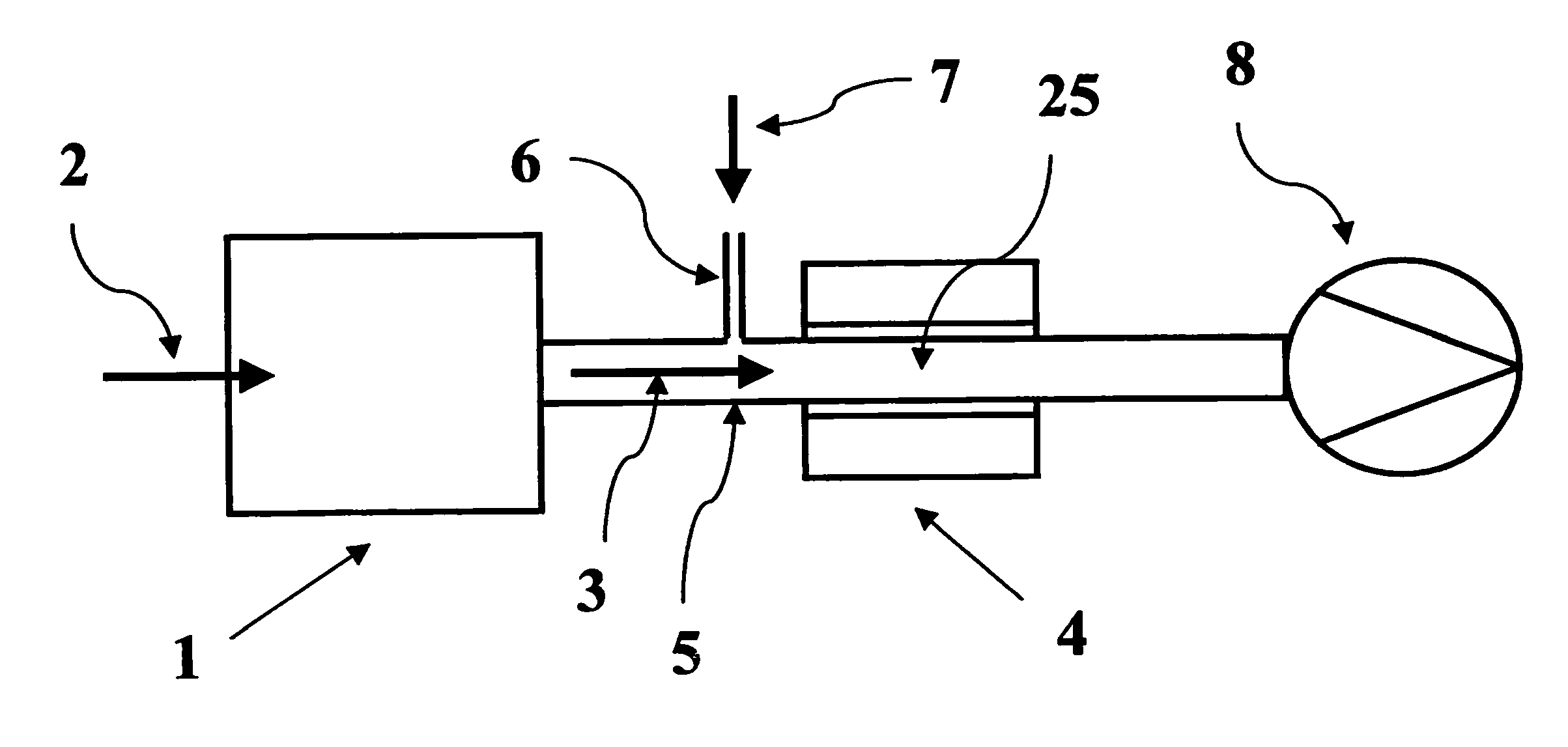
Method and device for cleaning the waste gases of a processing system
InactiveUS20100322827A1Minimizes condensationMinimizes precipitationCombination devicesGas treatmentExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
In order to clean the waste gases from a processing system (1), in which a process using non-metal halide is carried out, the waste gas (3) is mixed with a gas (7) that prevents recombination of ionized particles formed from the non-metal fluoride. In a gas discharge chamber (25), the waste gas (3, 7) is then converted into a plasma in which the non-metal halide, present in the waste gas (3, 7), is ionized. The ionized particles, that have been saturated with the gas, prevent the recombination thereof and can then be removed from the waste gas.
Owner:CS CLEAN SYST AG +1
Luminescent material comprising doped rare earth silicate
Owner:LUXIUM SOLUTIONS LLC
A method and device for protecting reliability of an electronic device when ionizing particles are bombarded
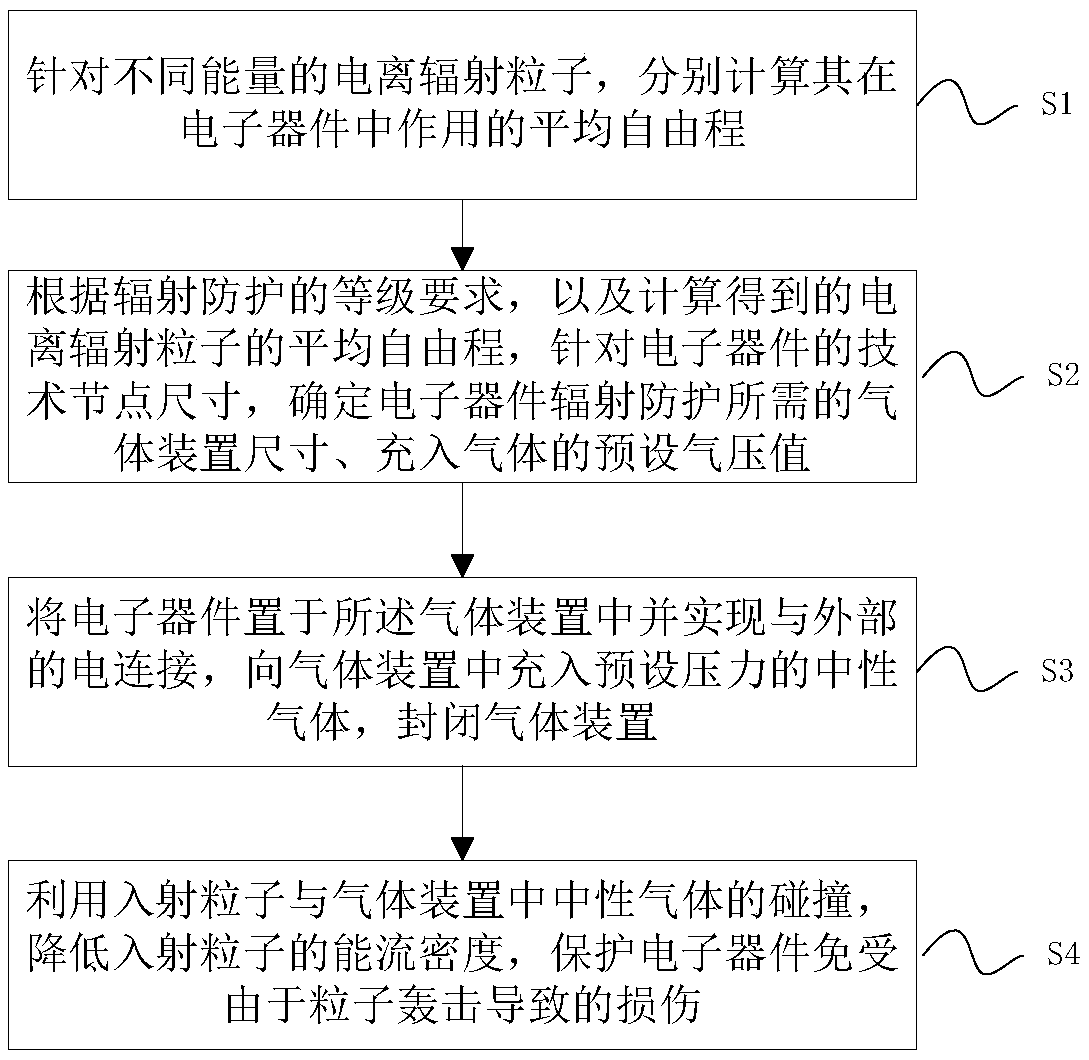
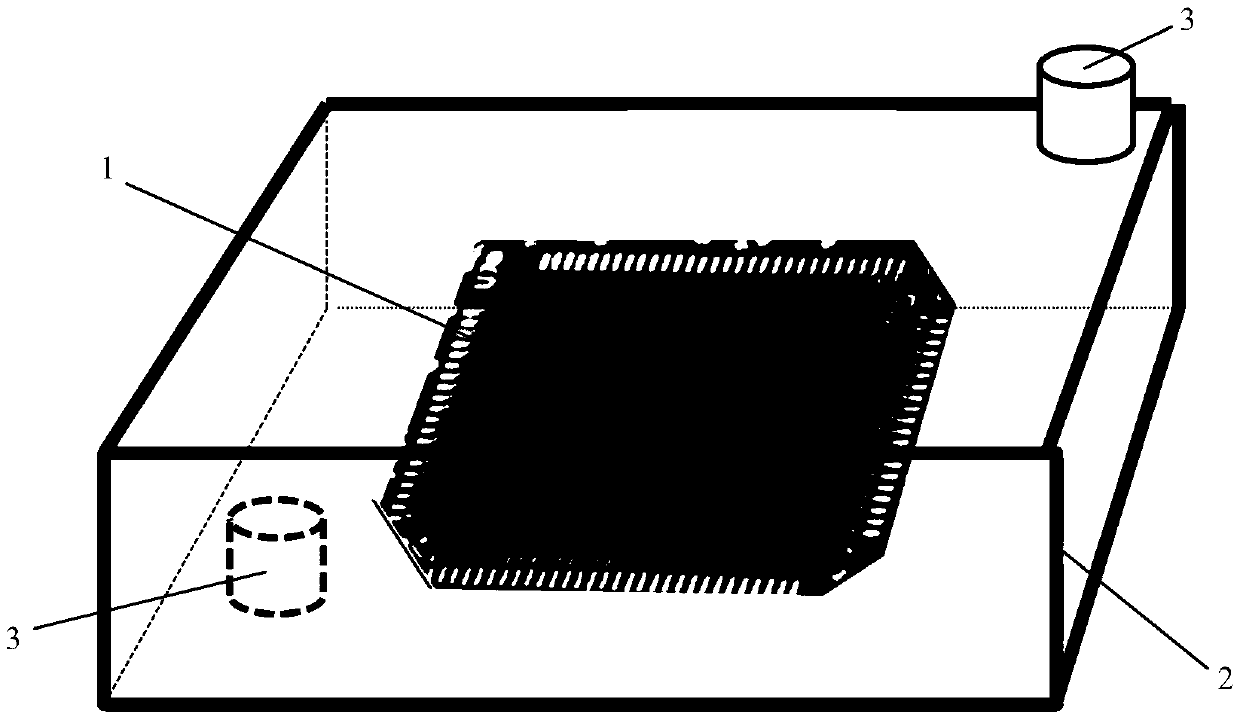
ActiveCN109041554AReduce energy flux densityFree from damageMagnetic/electric field screeningSpecial data processing applicationsMean free pathIonizing particles
The invention discloses a method and device for protecting the reliability of an electronic device when ionizing particles are bombarded. The method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating theaverage free path of ionizing radiation particles with different energies acting in the electronic device; S2, according to the grade requirement of the radiation protection and the average free pathof the ionizing radiation particles, determining the size and the air pressure value of the gas device required for radiation protection of the electronic device according to the technical node size of the electronic device; S3, placing the electronic device in the gas device and filling neutral gas with preset pressure; S4, reducing the energy flow density of the incident particles by the collision of the incident particles with the neutral gas in the gas device, and protecting the electronic device from damage caused by particle bombardment. Considering that the main external factor of damaging the electronic device is the strength of the ion energy flow, the invention reduces the energy flow density of the incident particles through the arrangement of the gas device and is combined withthe reliability circuit design, thereby protecting the electronic device from the damage caused by the particle bombardment and improving the reliability thereof.
Owner:ETOWNIP MICROELECTRONICS BEIJING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com