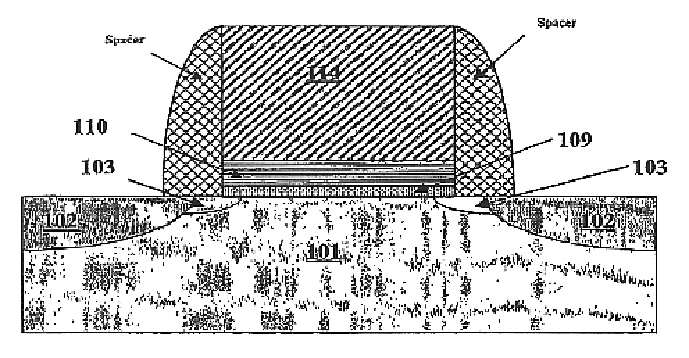
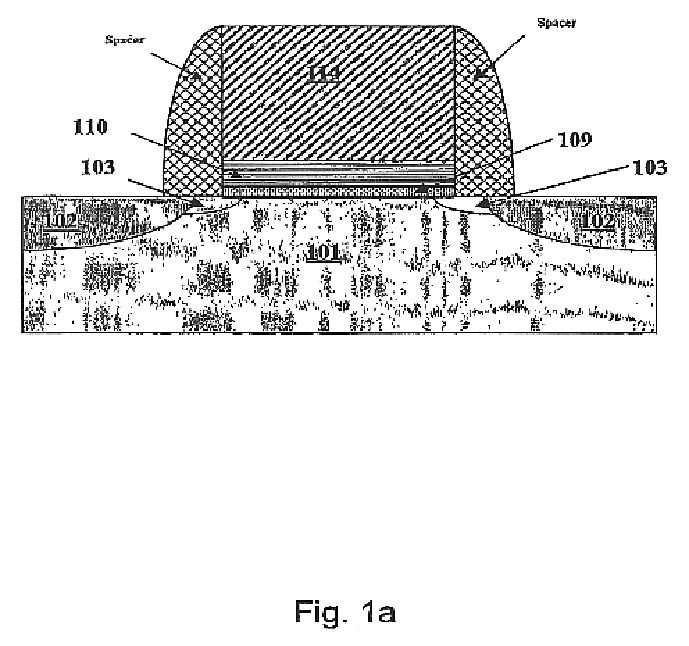
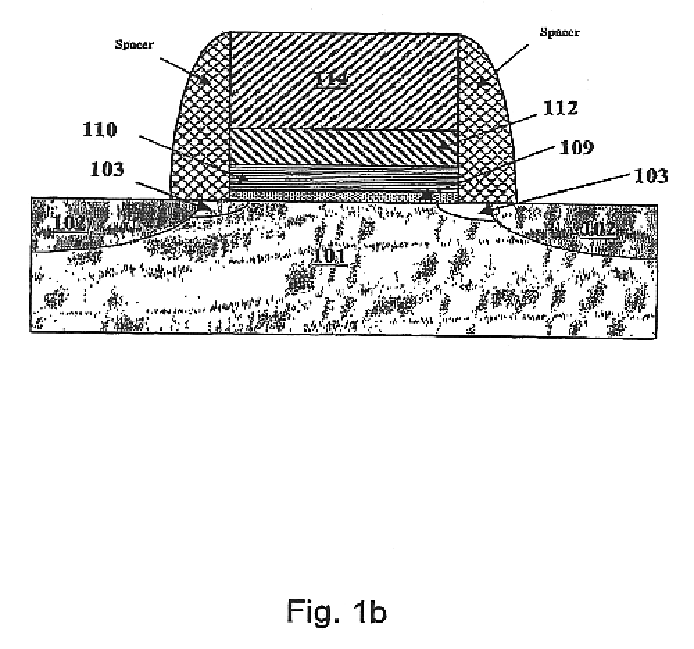
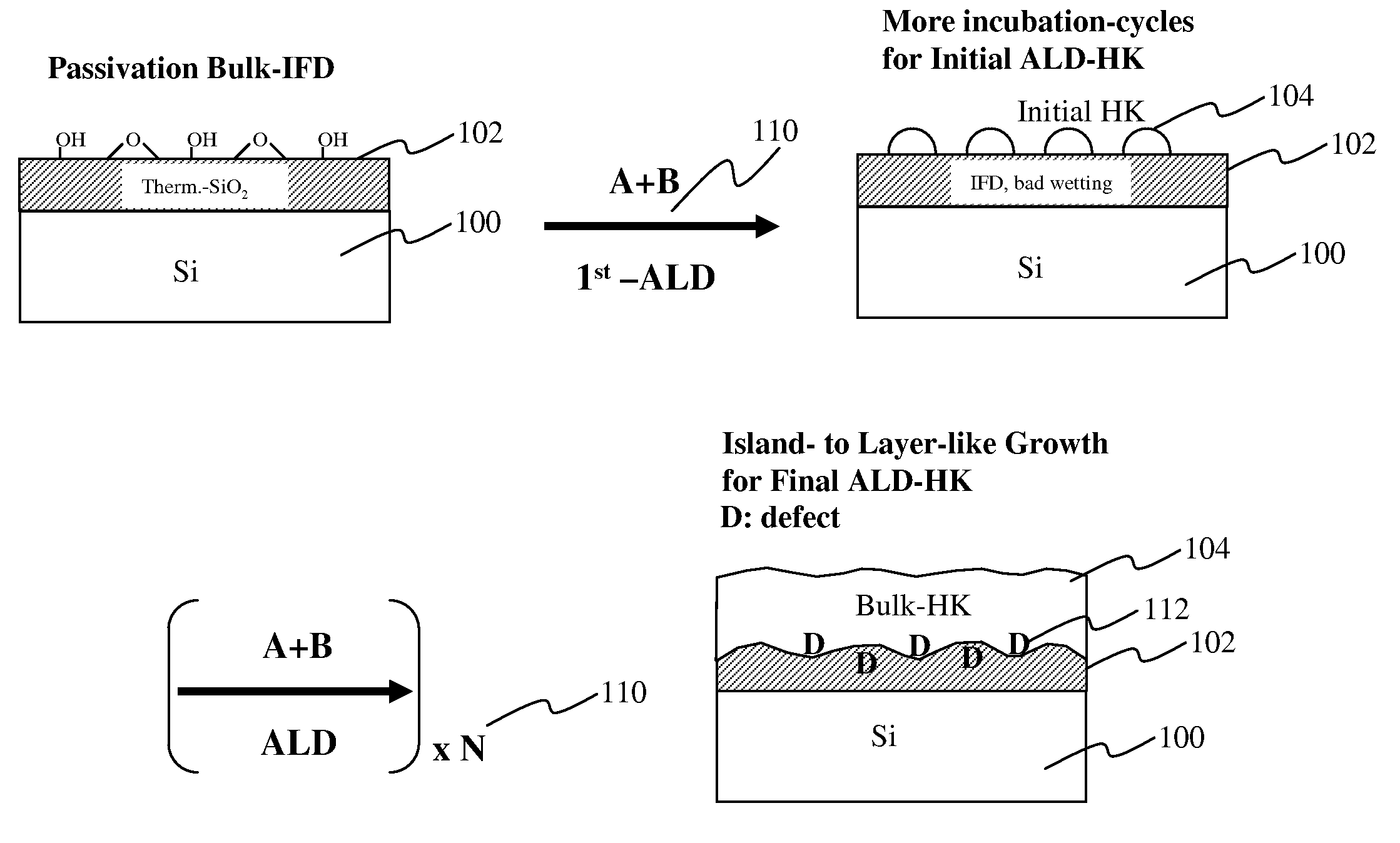
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
267 results about "Hydrogen radical" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
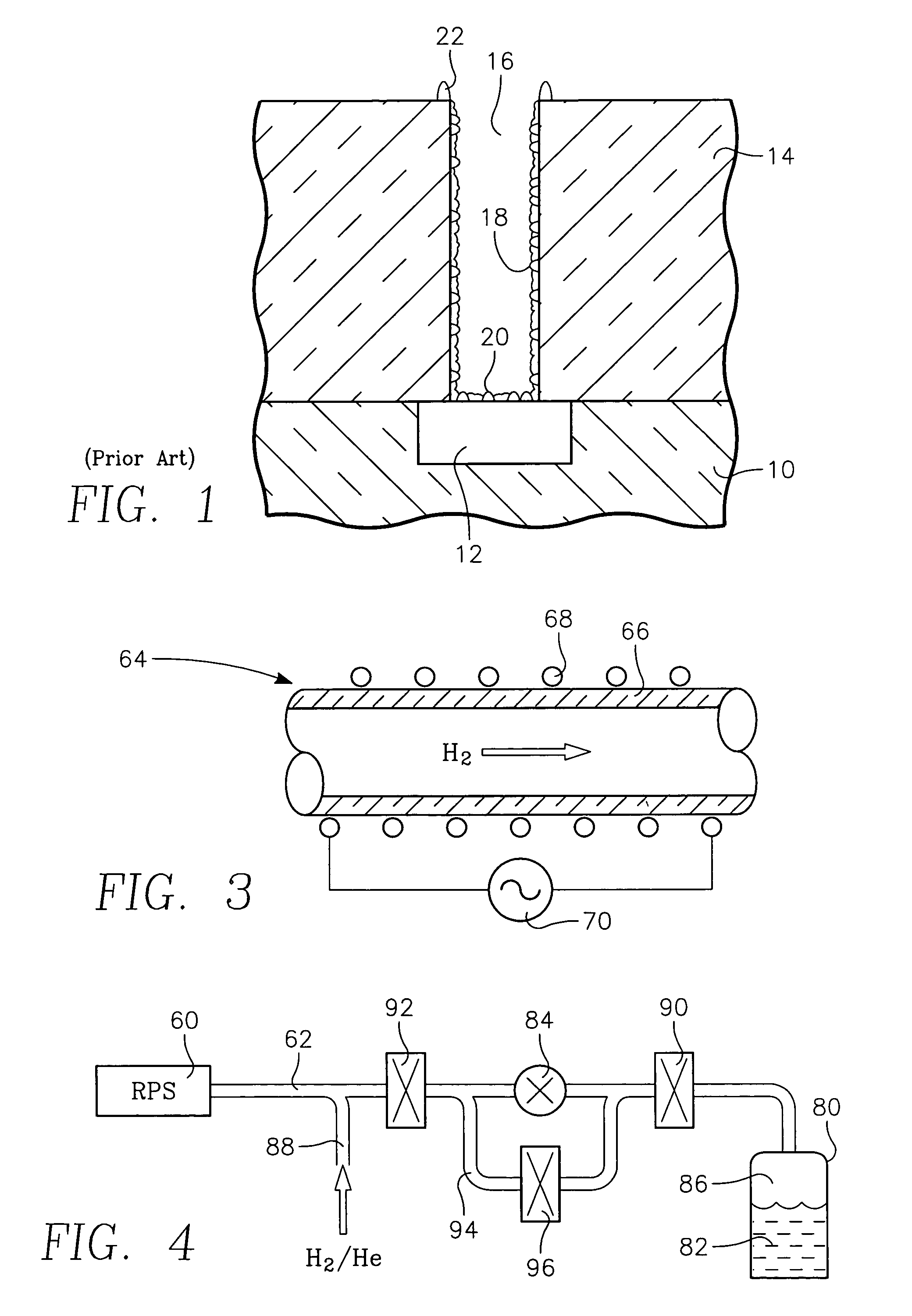
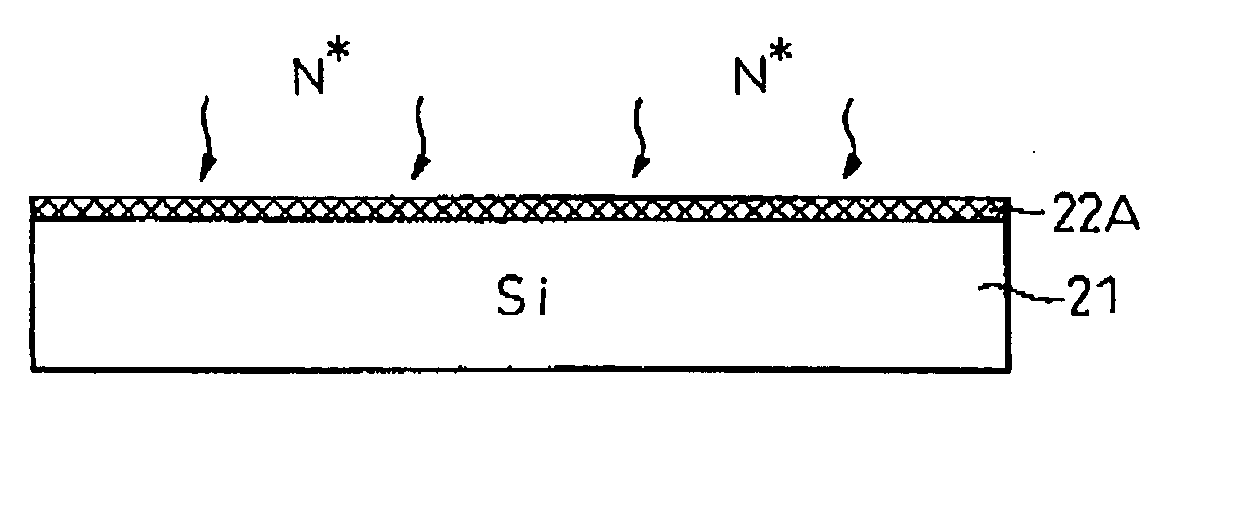
A hydrogen molecule has an electron pair, and therefore, it is not a free radical. When hydrogen gas is irritated with UV light in an isolated environment (without oxygen), a hydrogen molecule (H-H) may be broken evenly (homolytic cleavage) to give two hydrogen atoms or two free radicals:
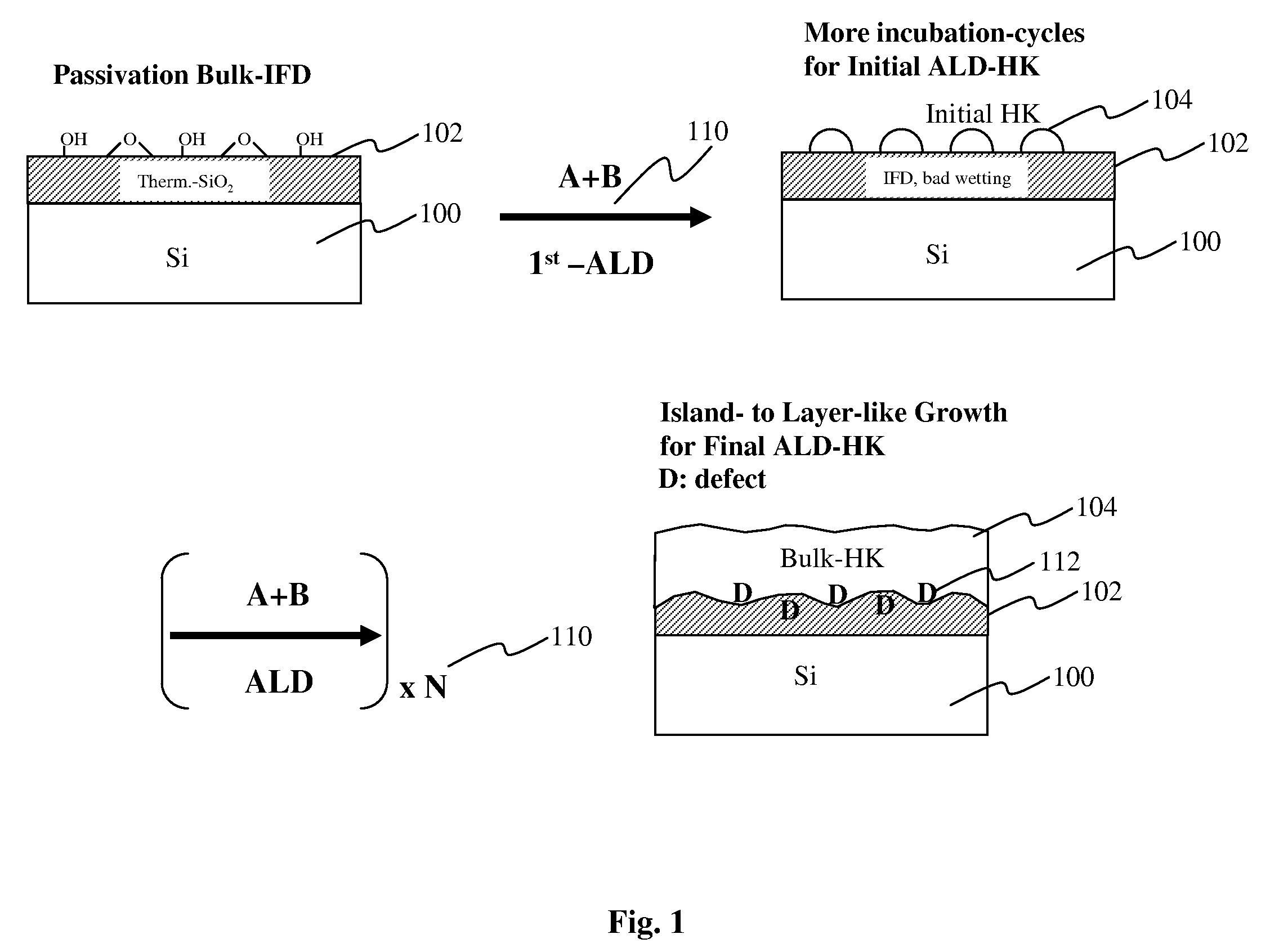
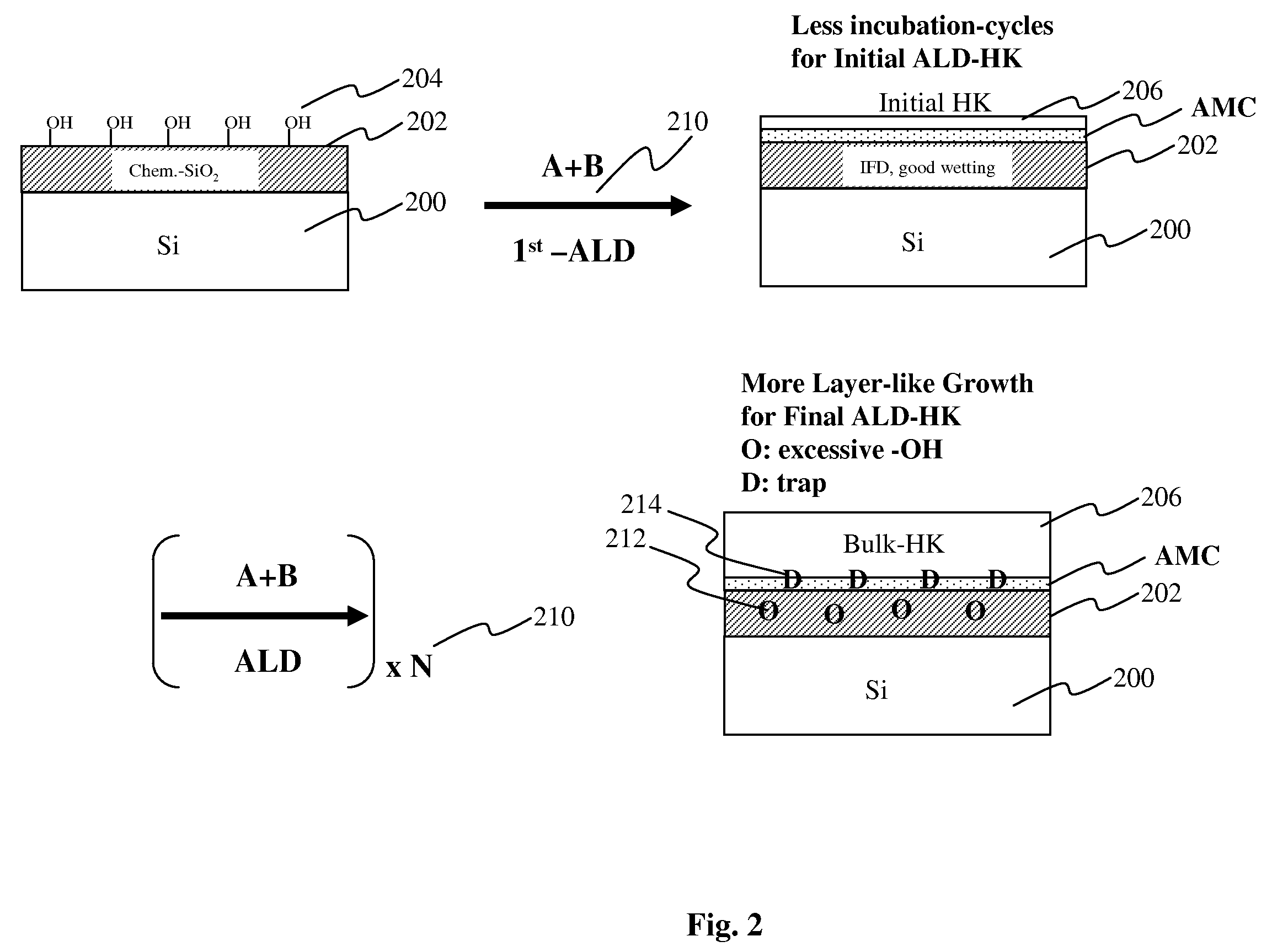
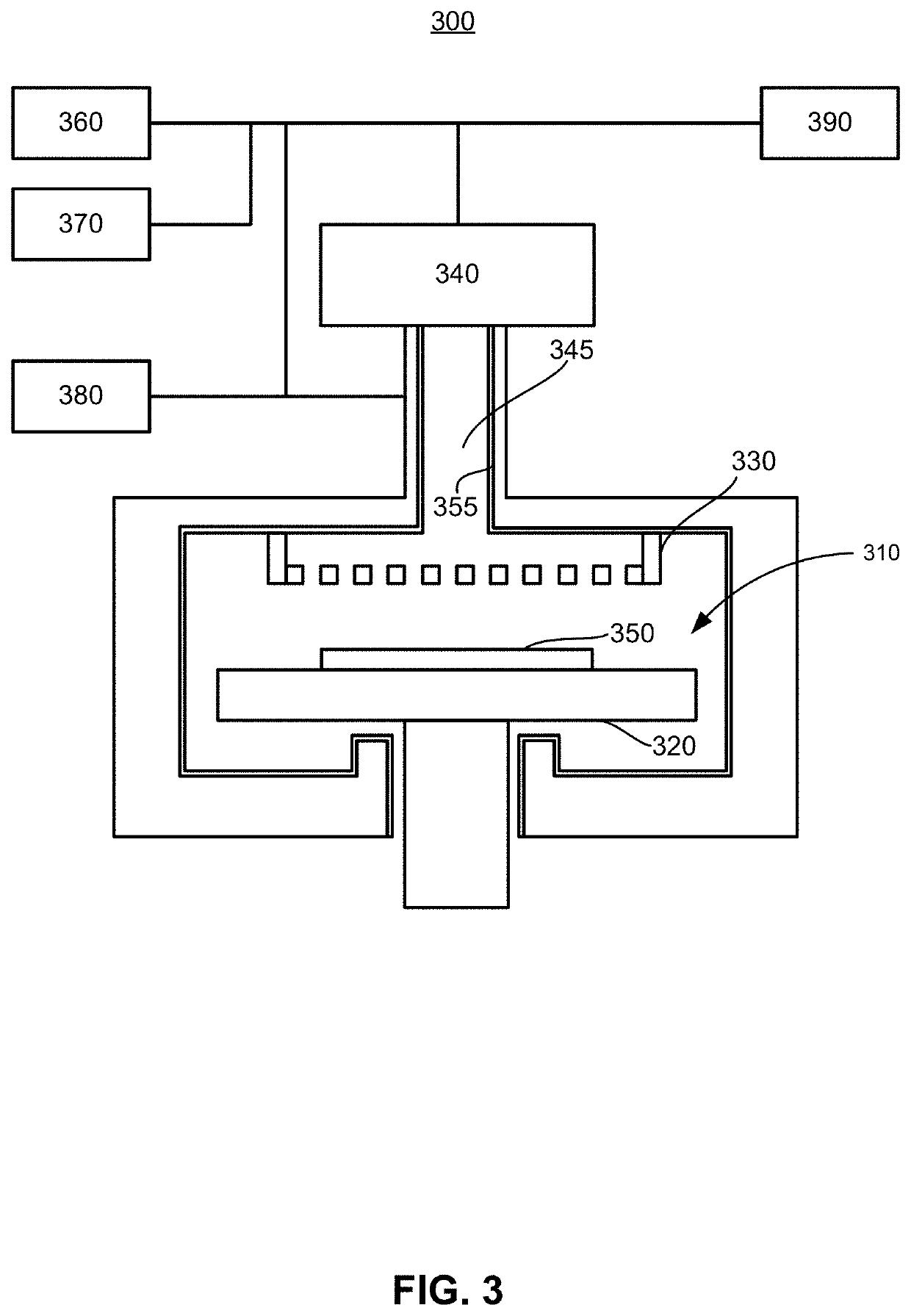
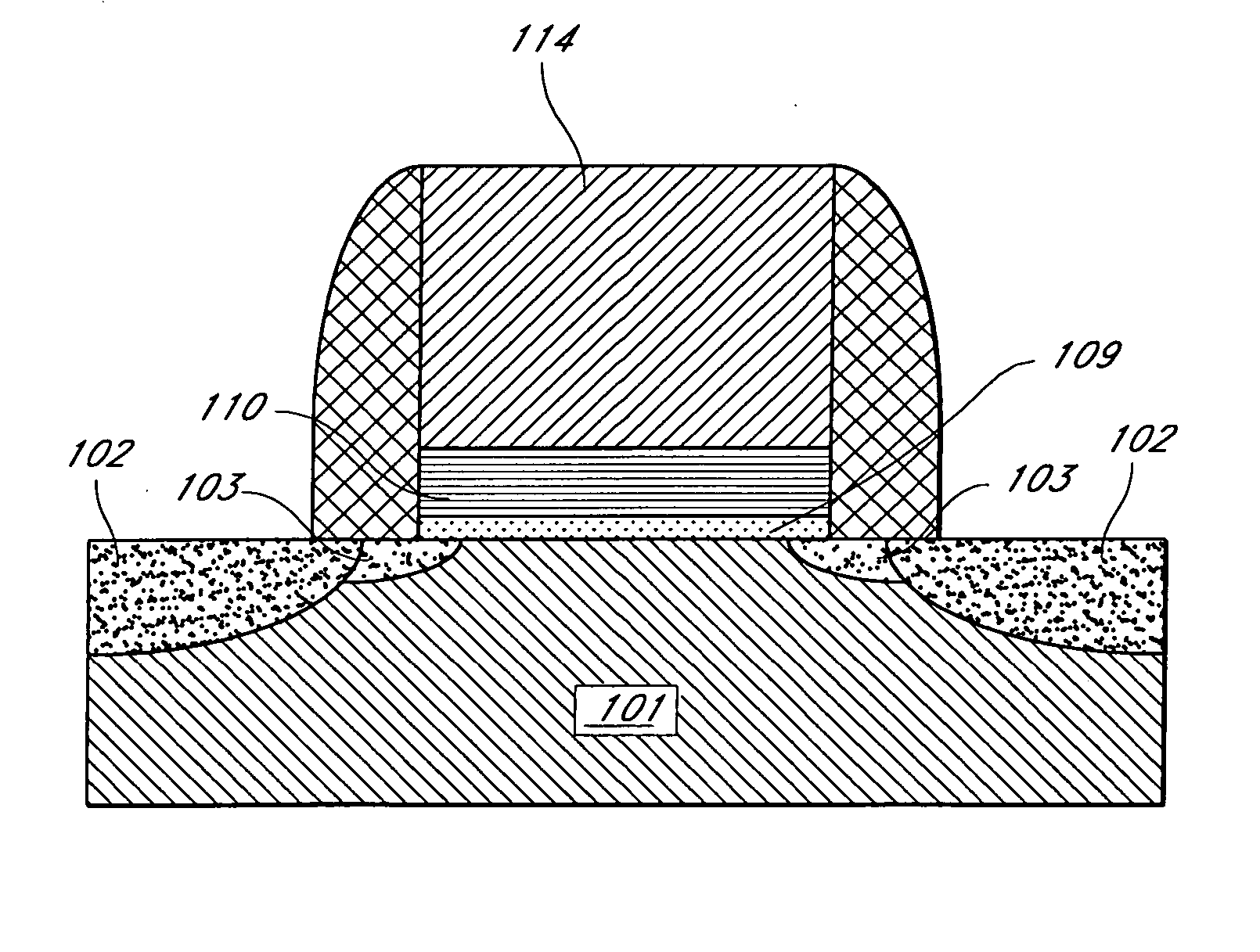
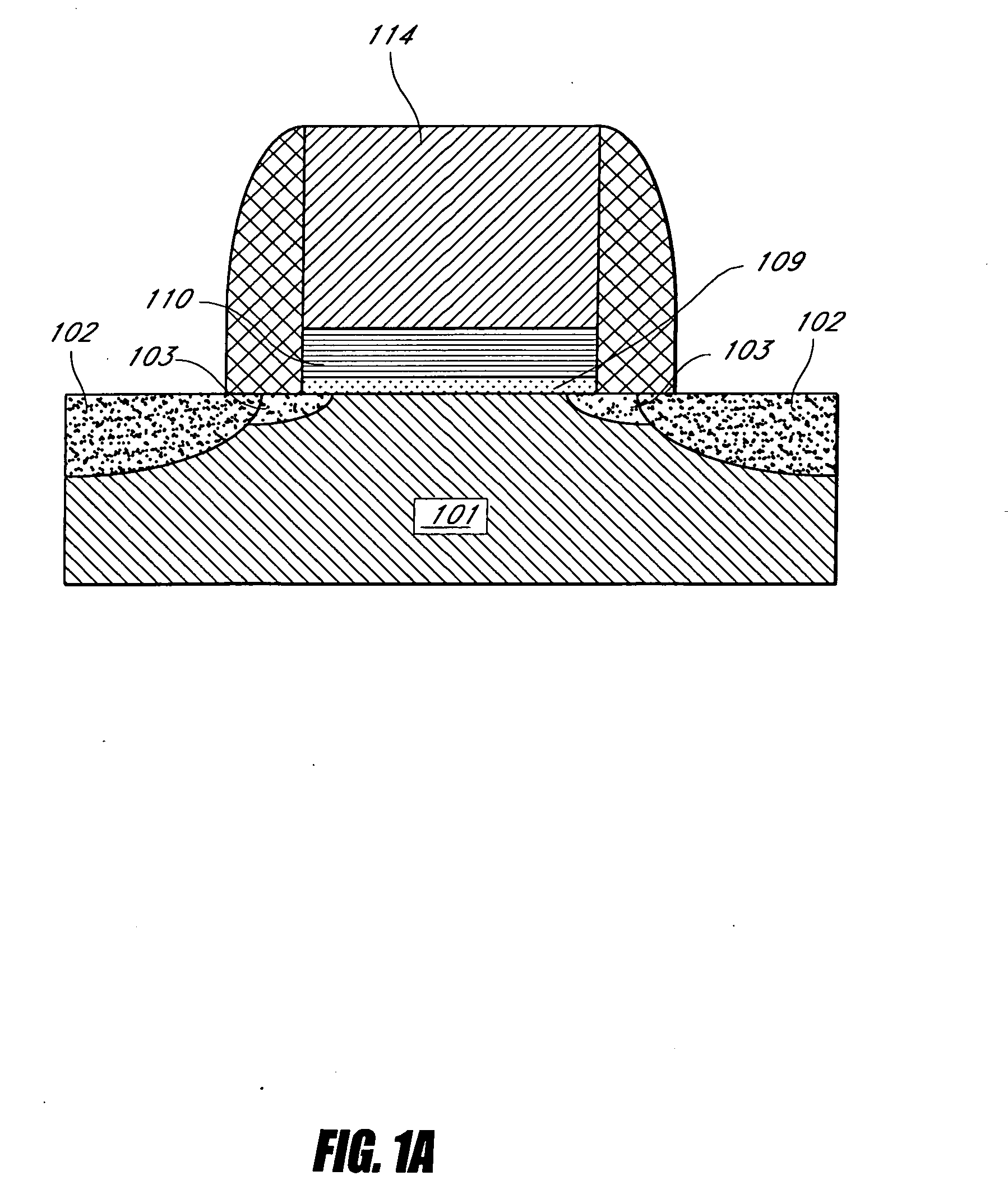
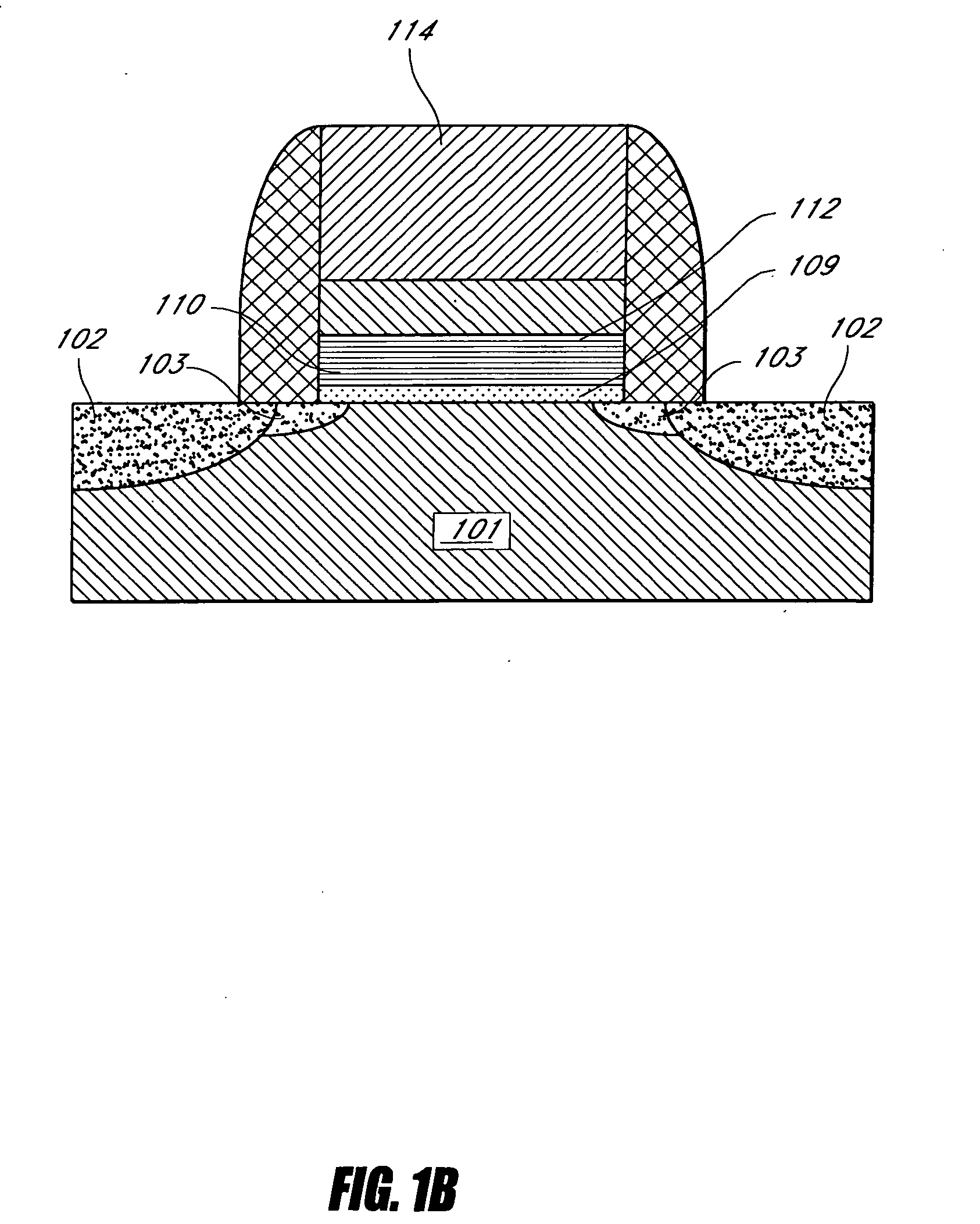
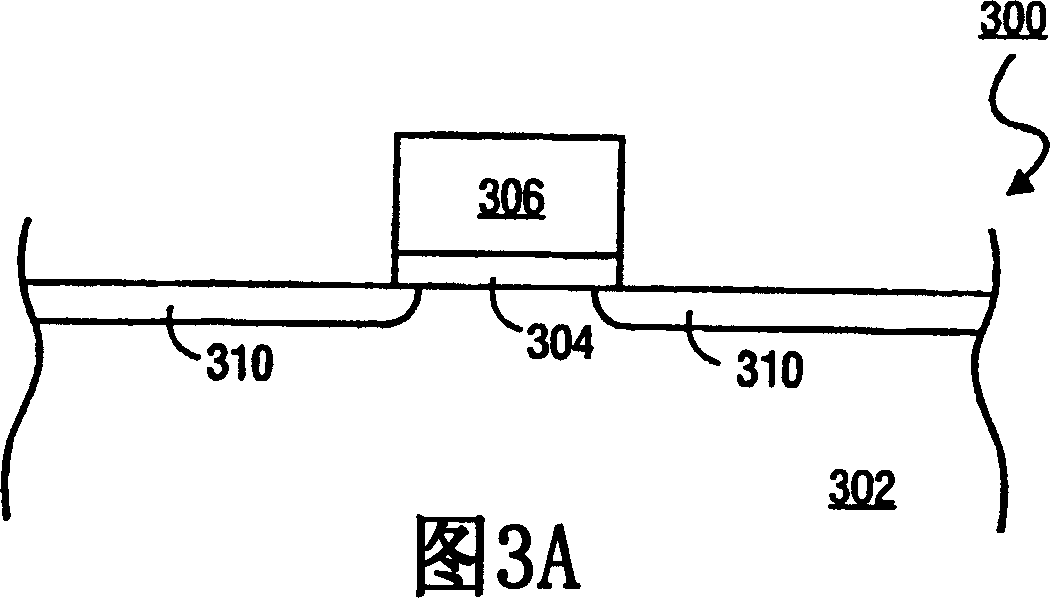
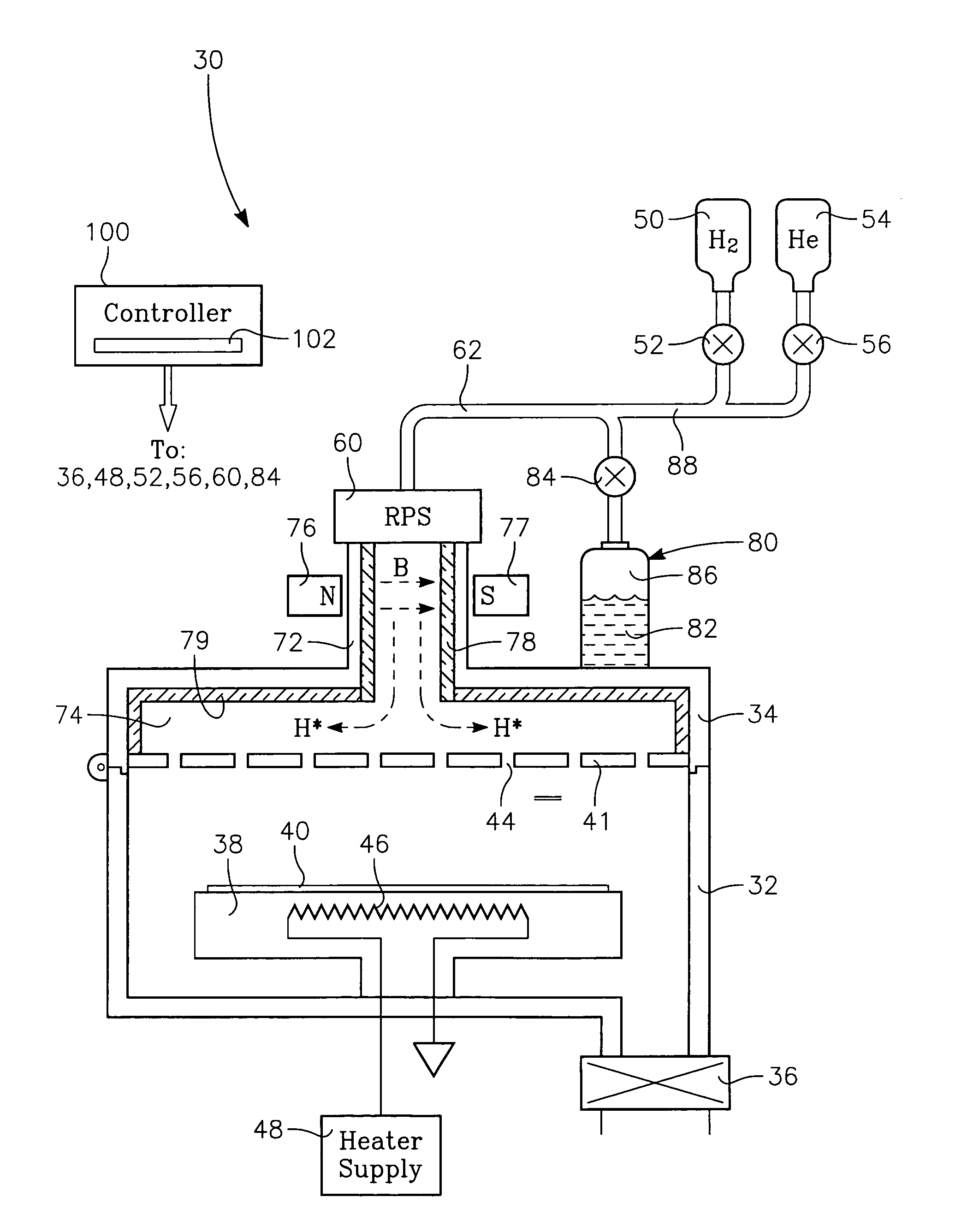
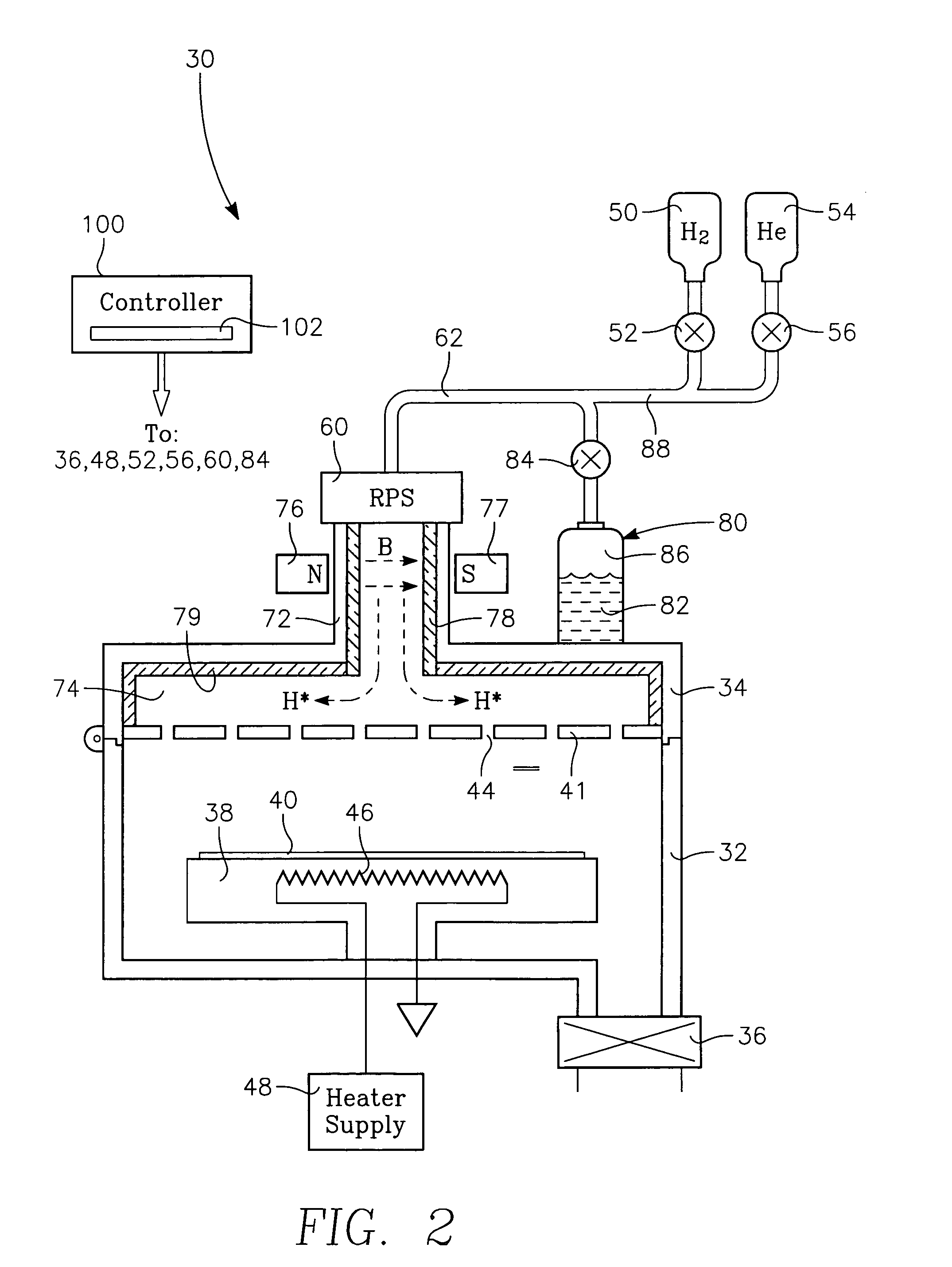
Method of depositing barrier layer for metal gates
InactiveUS6858524B2Eliminate the problemEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricRemote plasma
A method of manufacturing a high performance MOS device and transistor gate stacks comprises forming a gate dielectric layer over a semiconductor substrate; forming a barrier layer over the gate dielectric layer by an ALD type process; and forming a gate electrode layer over the barrier layer. The method enables the use of hydrogen plasma, high energy hydrogen radicals and ions, other reactive radicals, reactive oxygen and oxygen containing precursors in the processing steps subsequent to the deposition of the gate dielectric layer of the device. The ALD process for forming the barrier layer is performed essentially in the absence of plasma and reactive hydrogen radials and ions. This invention makes it possible to use oxygen as a precursor in the deposition of the metal gates. The barrier film also allows the use of hydrogen plasma in the form of either direct or remote plasma in the deposition of the gate electrode. Furthermore, the barrier film prevents the electrode material from reacting with the gate dielectric material. The barrier layer is ultra thin and, at the same time, it forms a uniform cover over the entire surface of the gate dielectric.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method of Fabricating a Gate Dielectric for High-K Metal Gate Devices
ActiveUS20100075507A1Facilitate formation of the high-k dielectric layerImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricSulfur
The present disclosure provides a method of fabricating a semiconductor device. The method includes providing a substrate, forming an interfacial layer on the substrate by treating the substrate with radicals, and forming a high-k dielectric layer on the interfacial layer. The radicals are selected from the group consisting of hydrous radicals, nitrogen / hydrogen radicals, and sulfur / hydrogen radicals.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
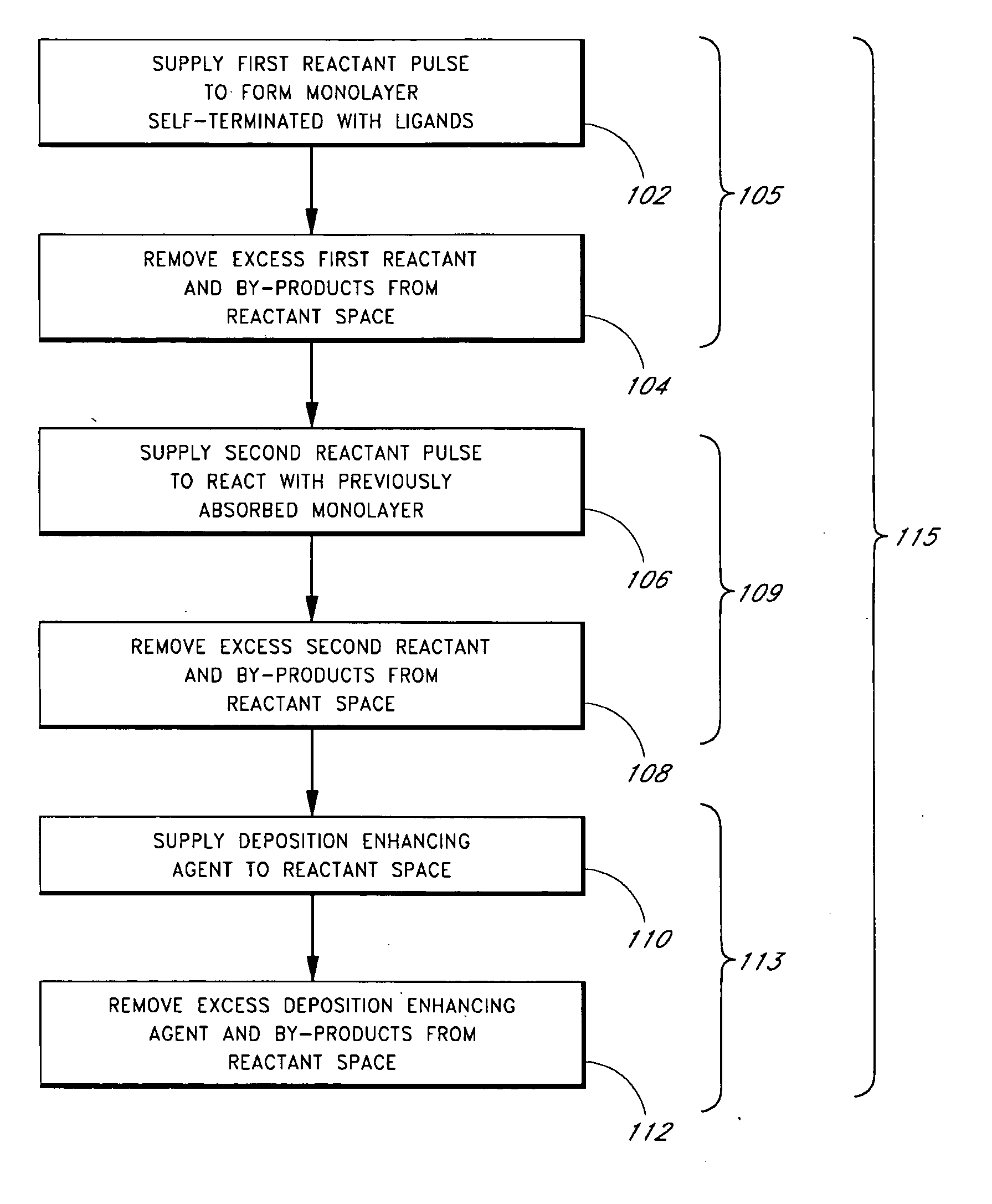
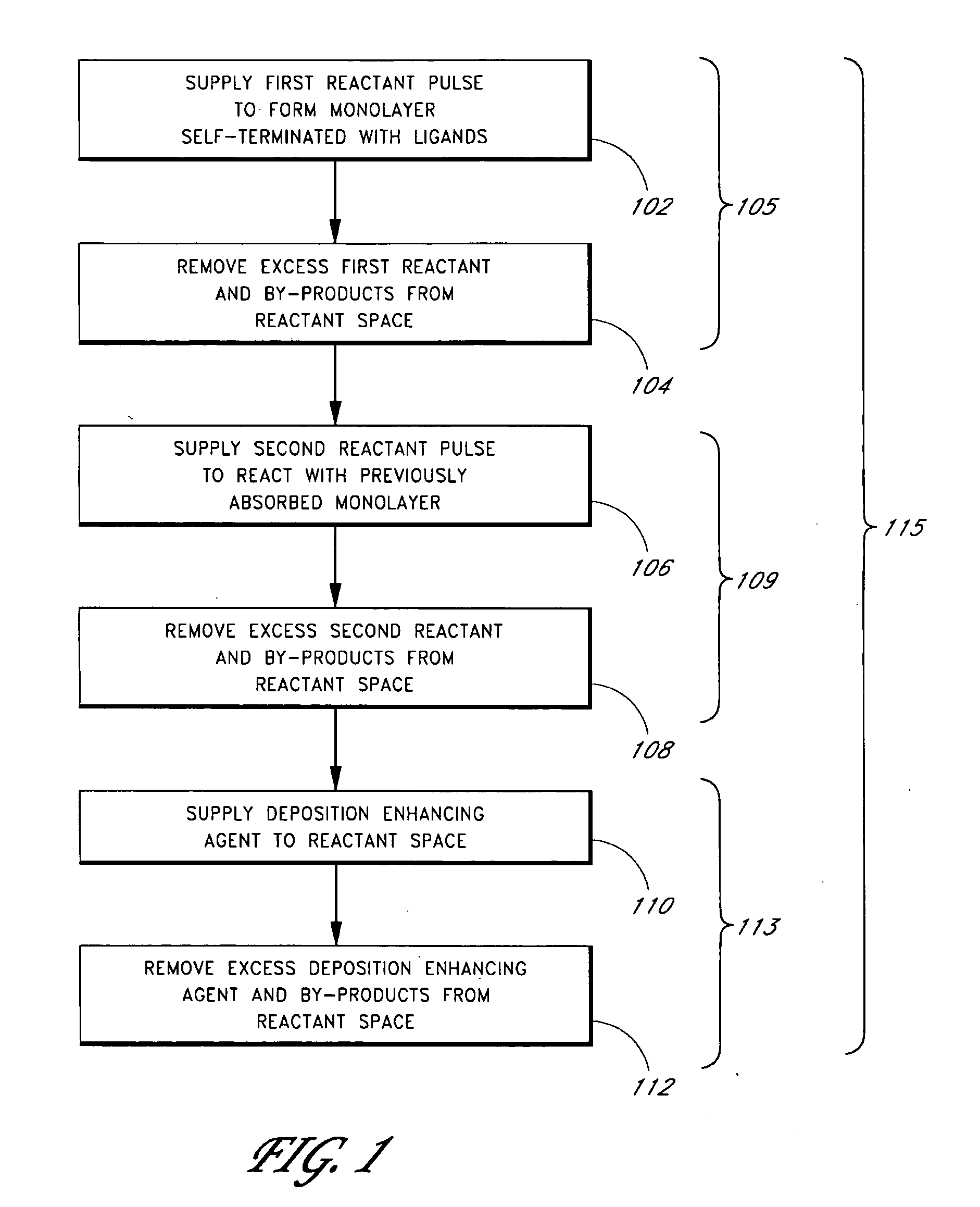
Enhanced thin film deposition
ActiveUS20070148350A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanesNitrogen
Methods of producing metal-containing thin films with low impurity contents on a substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD) are provided. The methods preferably comprise contacting a substrate with alternating and sequential pulses of a metal source chemical, a second source chemical and a deposition enhancing agent. The deposition enhancing agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, hydrogen plasma, hydrogen radicals, silanes, germanium compounds, nitrogen compounds, and boron compounds. In some embodiments, the deposition-enhancing agent reacts with halide contaminants in the growing thin film, improving film properties.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
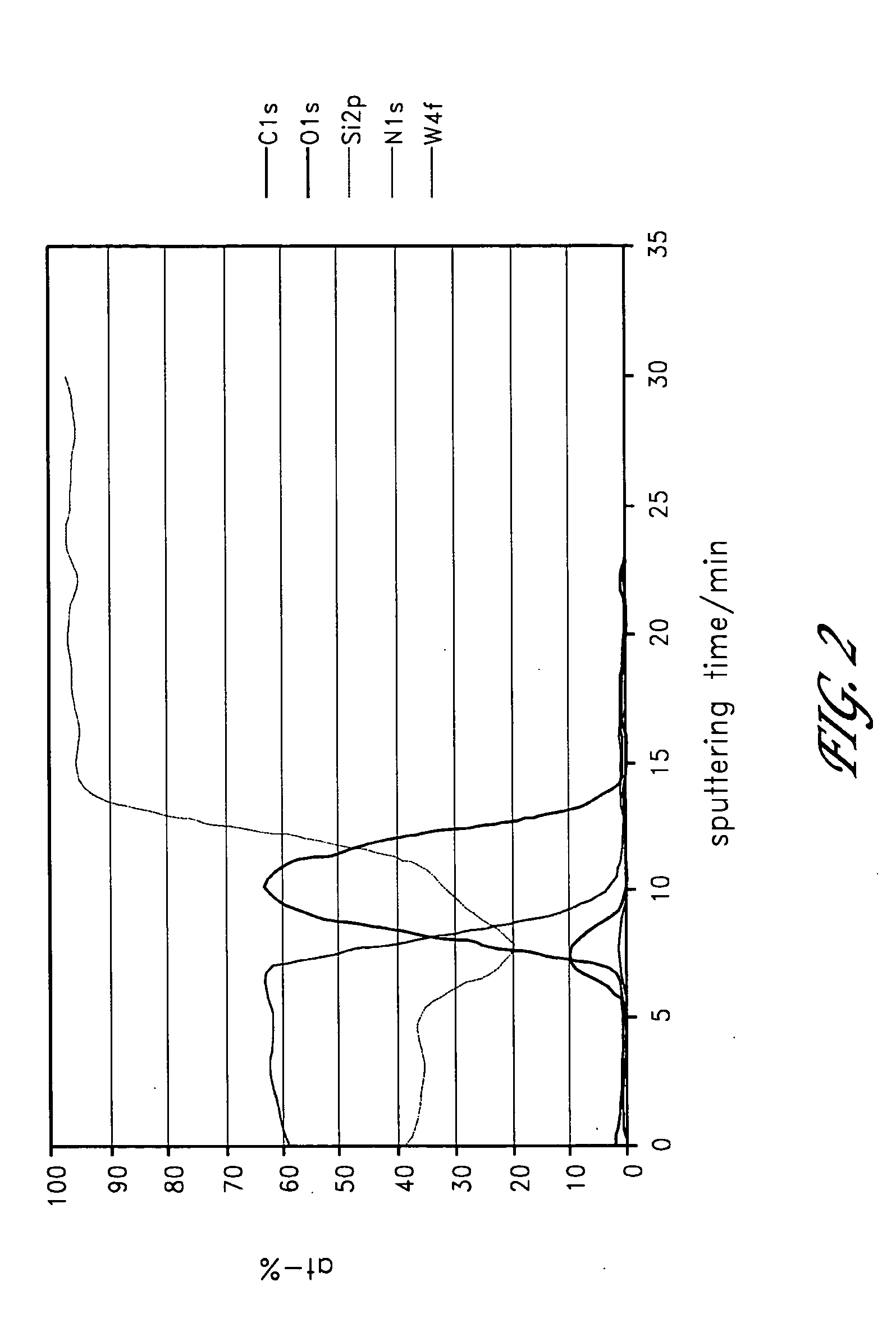
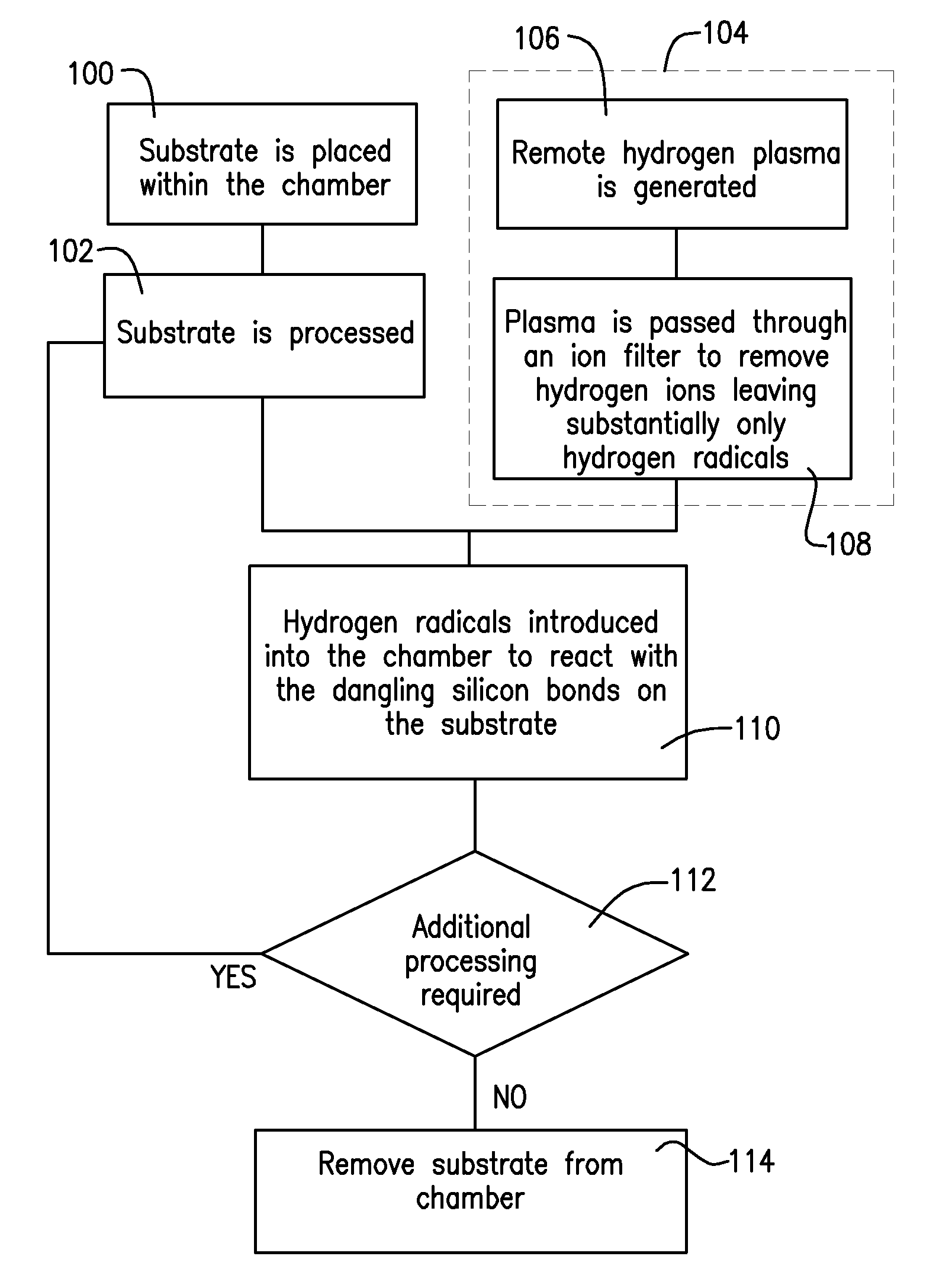
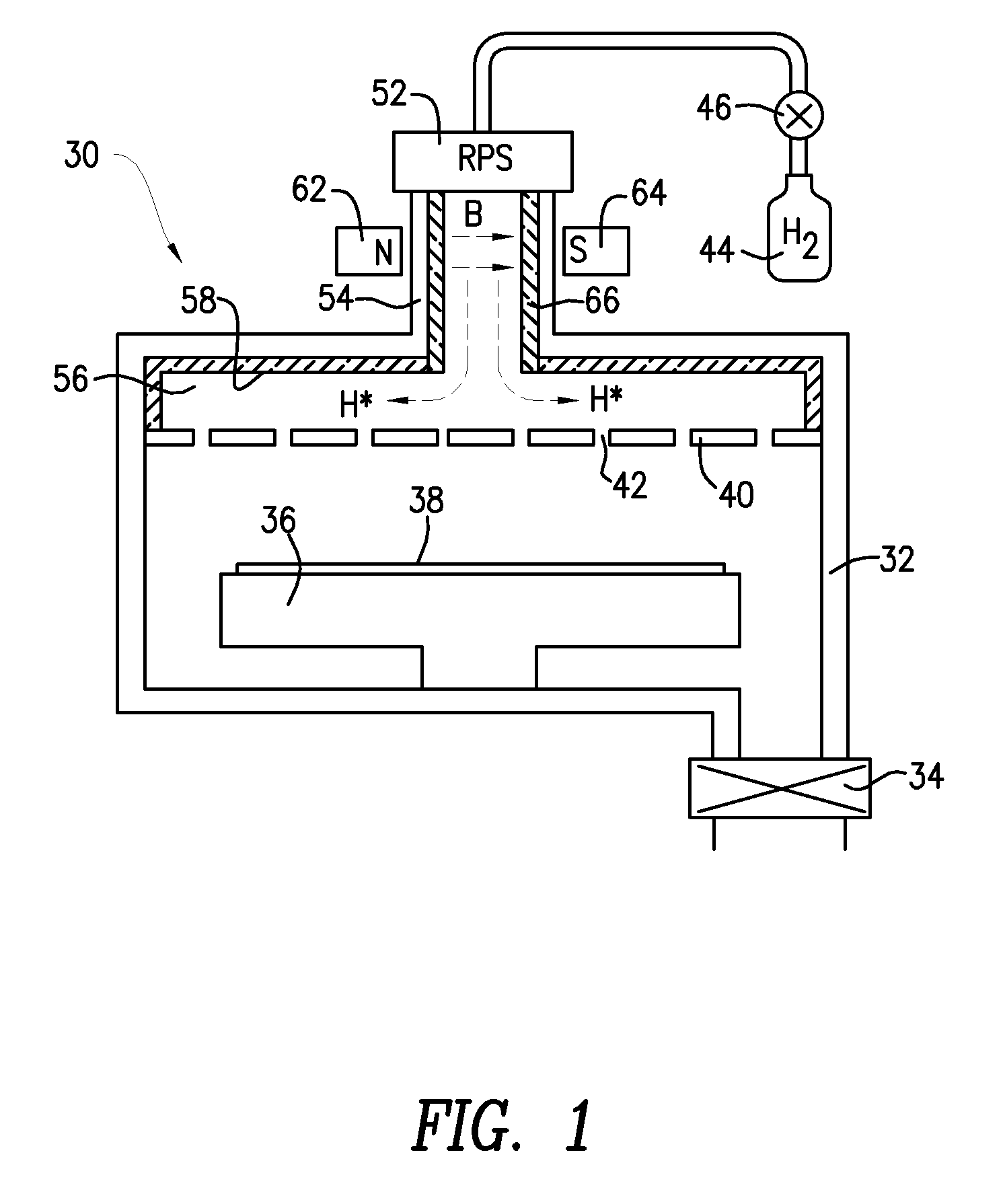
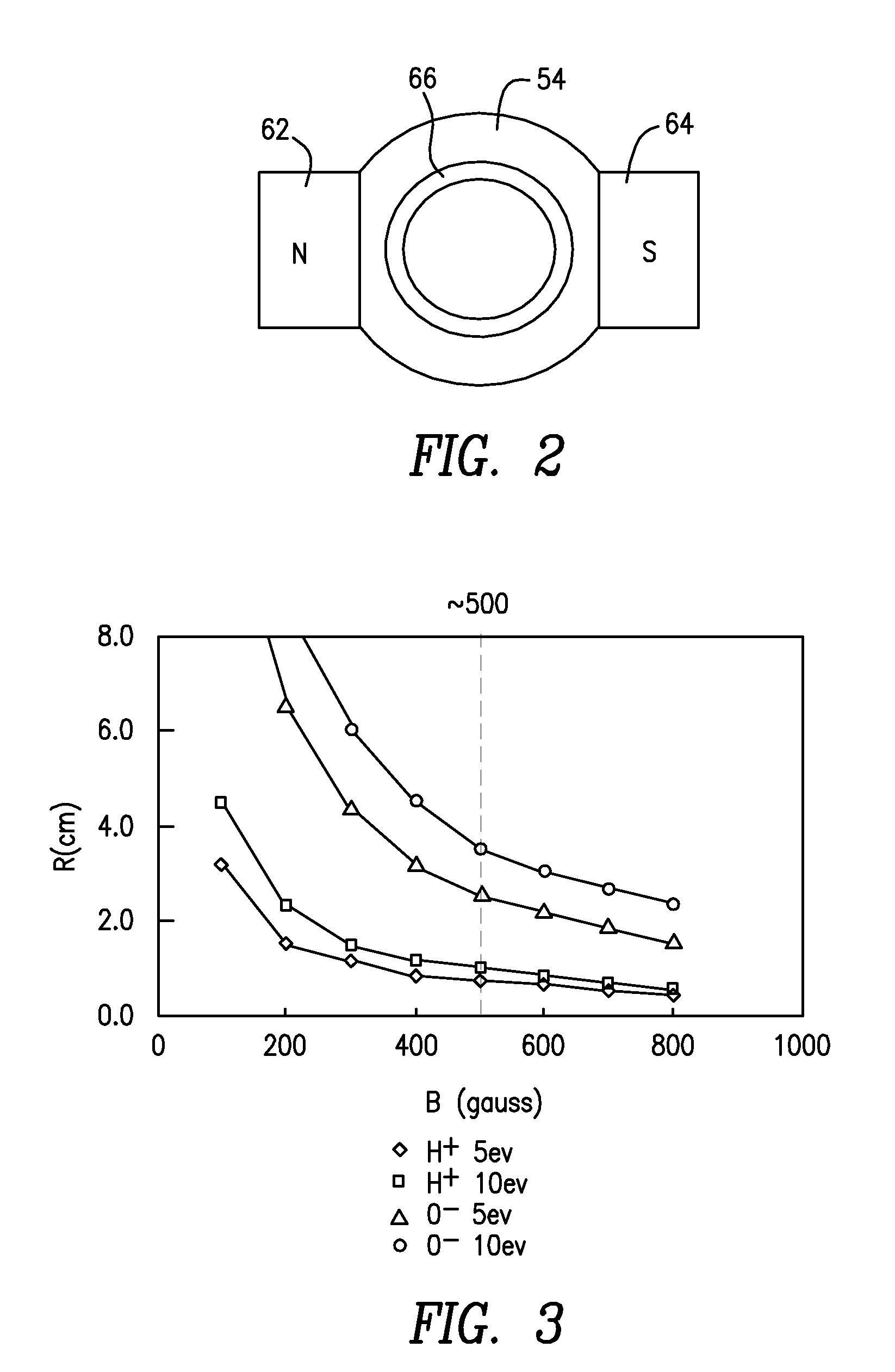
Remote Hydrogen Plasma With Ion Filter for Terminating Silicon Dangling Bonds
InactiveUS20110008950A1Avoid damageElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureDangling bondSemiconductor
Apparatus and methods for repairing silicon dangling bonds resulting from semiconductor processing are disclosed. The silicon dangling bonds can be repaired by introducing hydrogen radicals with substantially no hydrogen ions into the processing chamber to react with the silicon dangling bonds, eliminating them.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
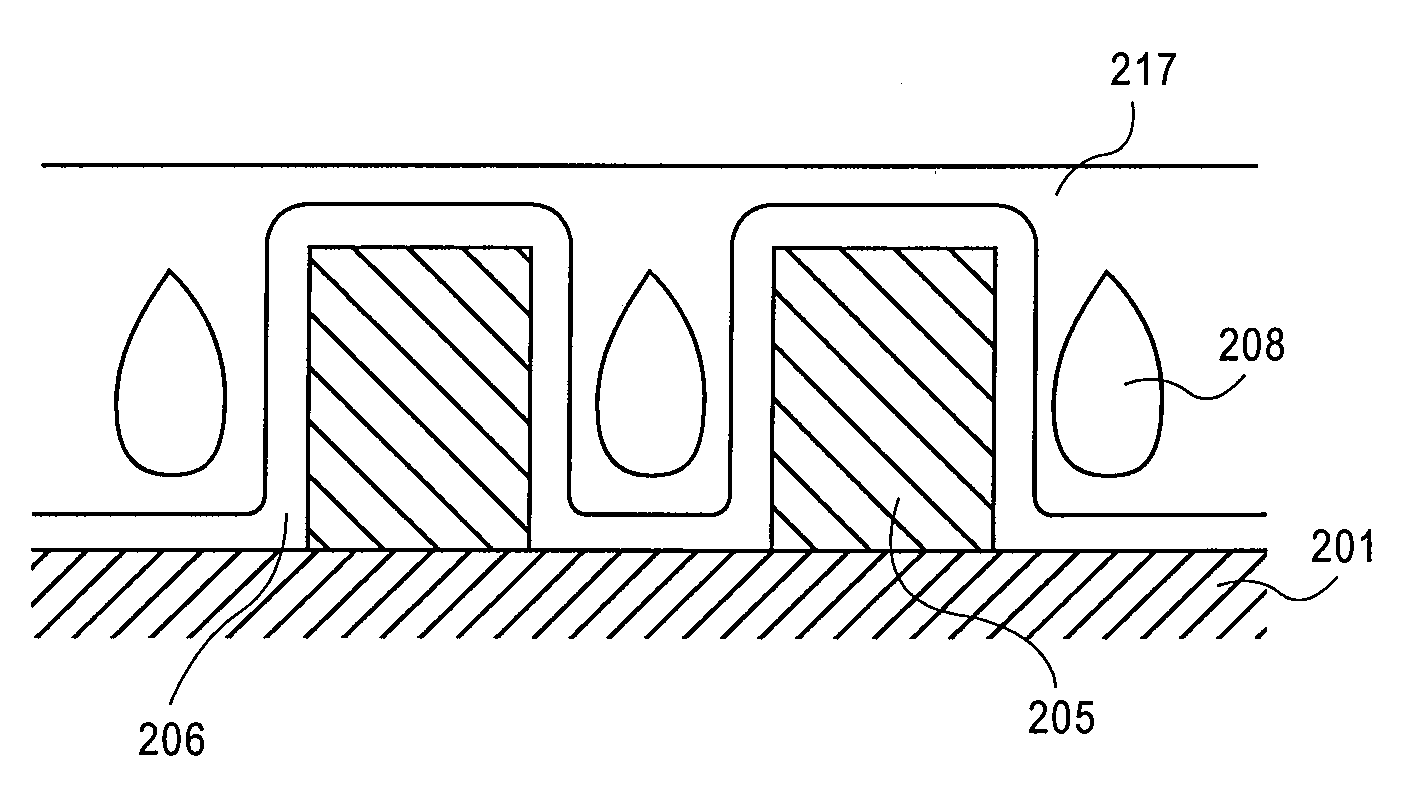
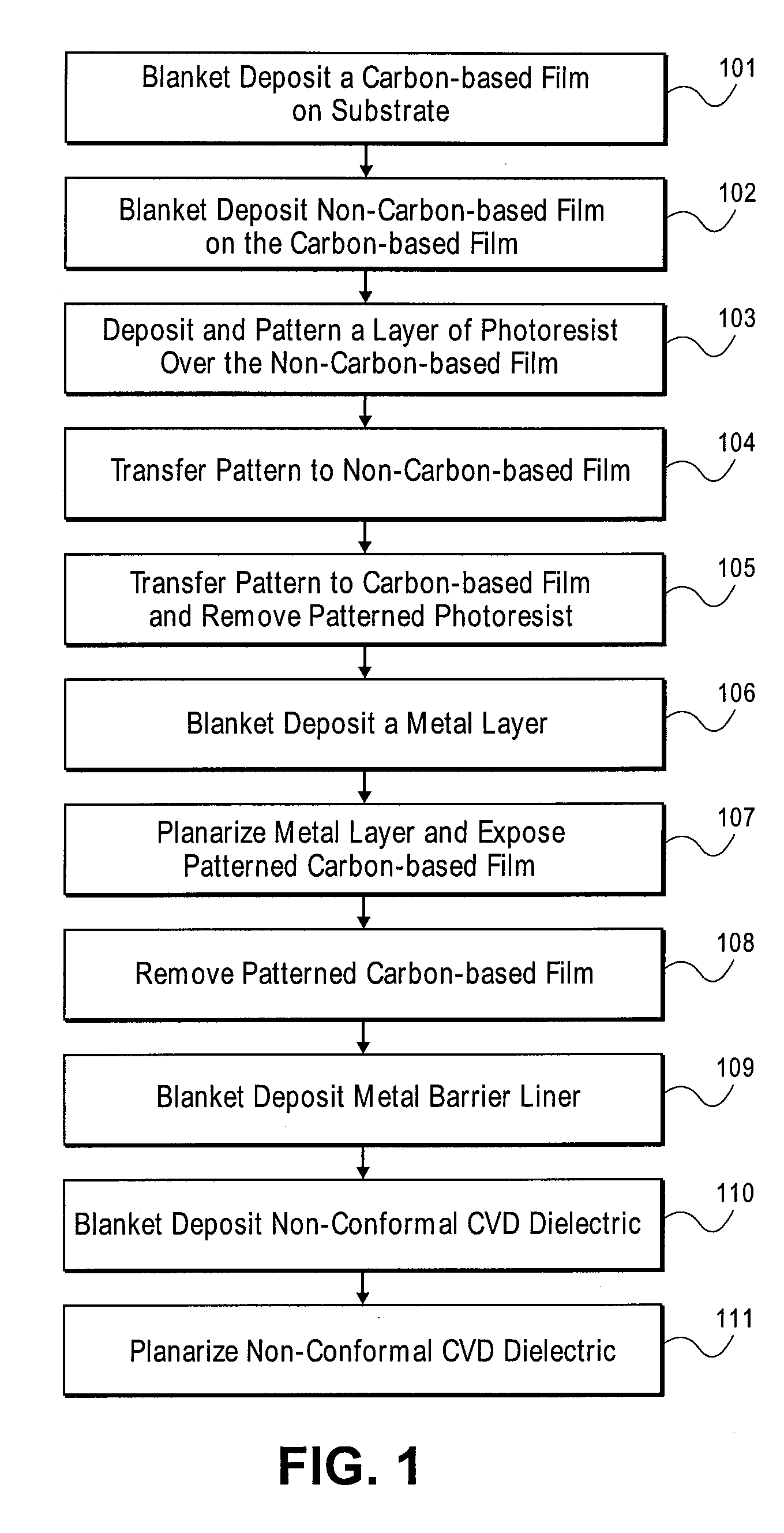
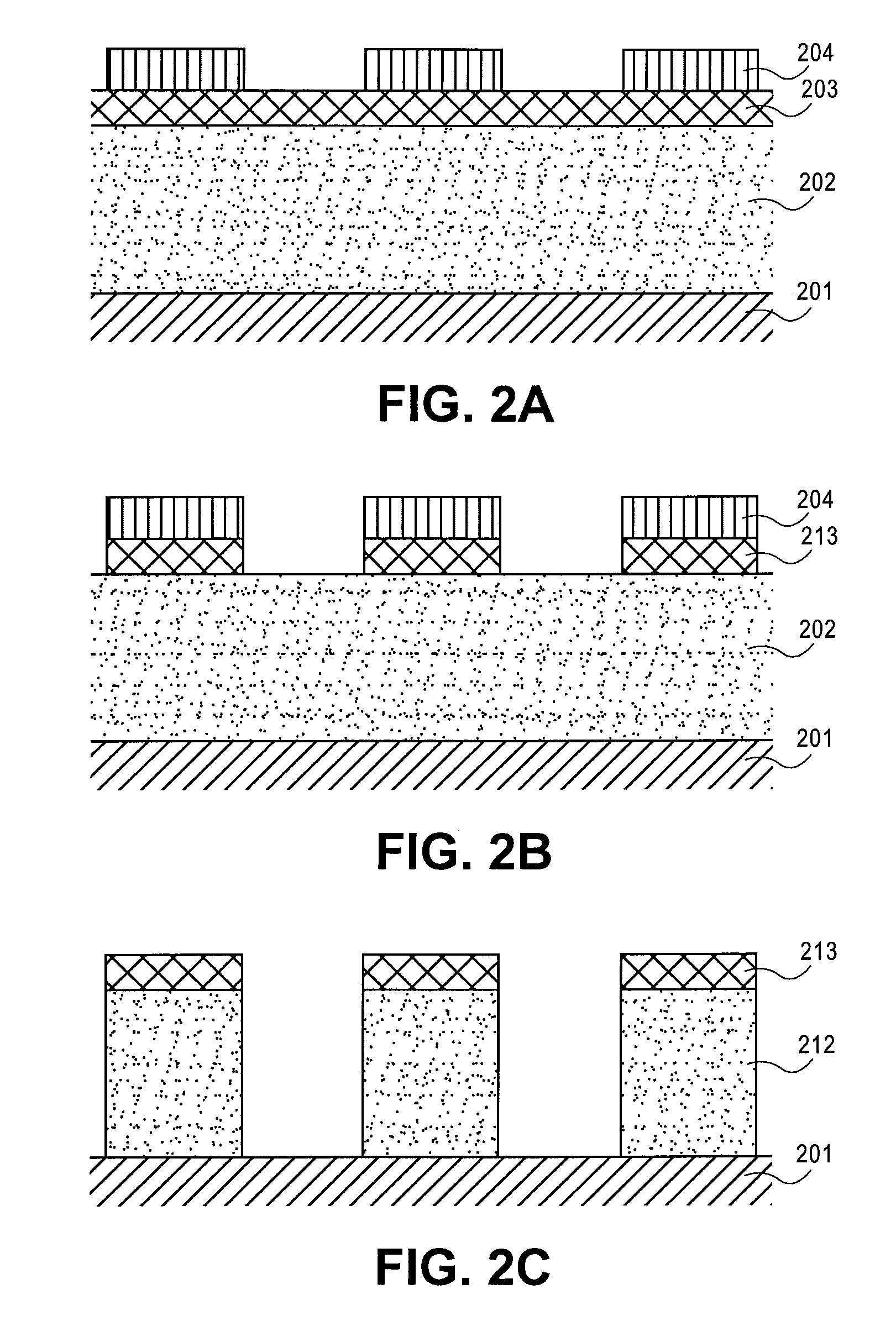
Air gap interconnects using carbon-based films
InactiveUS20100093168A1Improve electrical isolationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectPorous carbon
A method of forming an interconnect structure comprising: forming a sacrificial inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layer over a substrate, wherein the sacrificial IMD layer comprising a carbon-based film, such as amorphous carbon, advanced patterning films, porous carbon, or any combination thereof; forming a plurality of metal interconnect lines within the sacrificial IMD layer; removing the sacrificial IMD layer, with an oxygen based reactive process; and depositing a non-conformal dielectric layer to form air gaps between the plurality of metal interconnect lines. The metal interconnect lines may comprise copper, aluminum, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, tantalum nitride, titanium nitride, tungsten nitride, or any combination thereof. Carbon-based films and patterned photoresist layers may be simultaneously removed with the same reactive process. Highly reactive hydrogen radicals processes may be used to remove the carbon-based film and simultaneously pre-clean the metal interconnect lines prior to the deposition of a conformal metal barrier liner.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
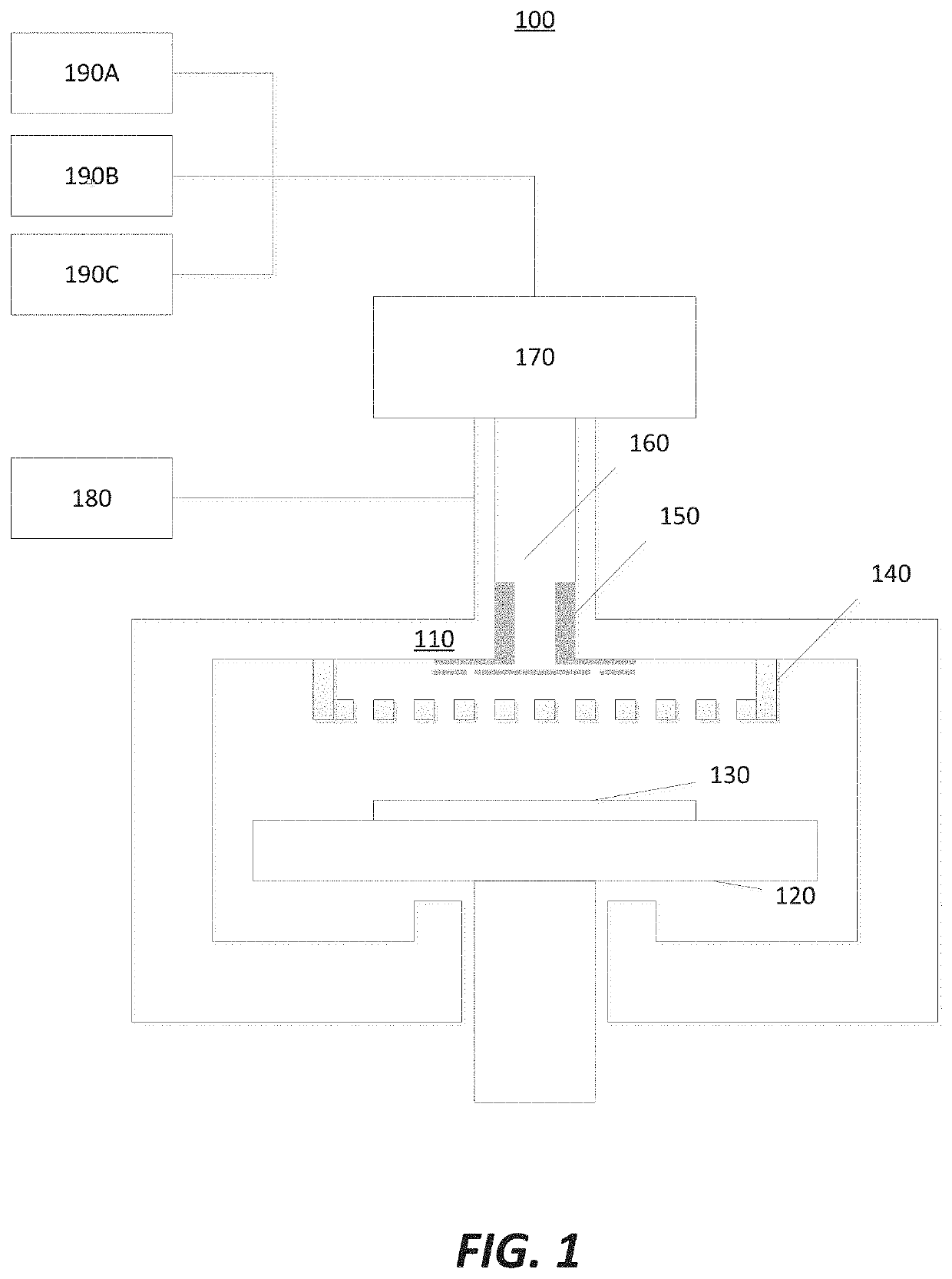
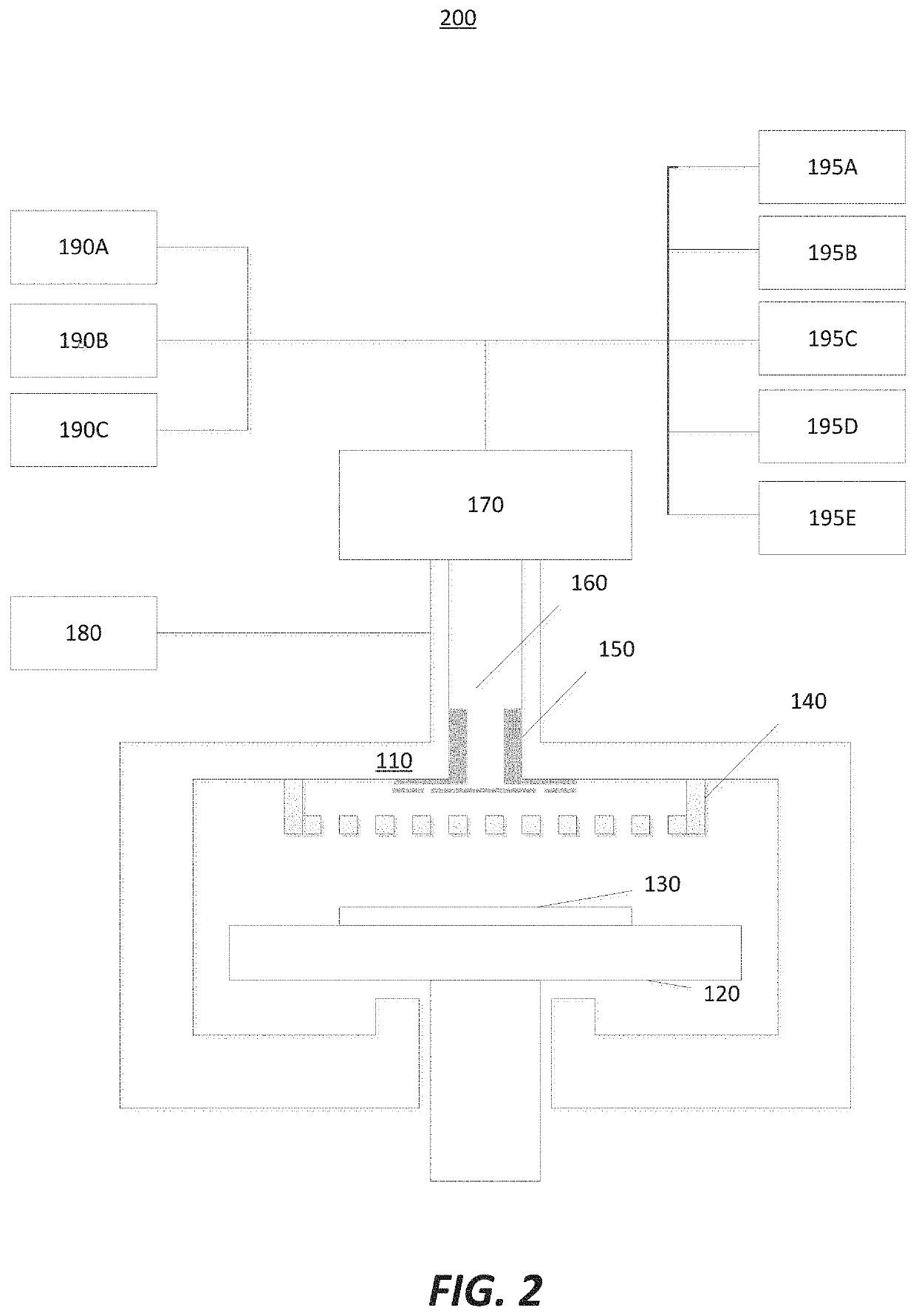
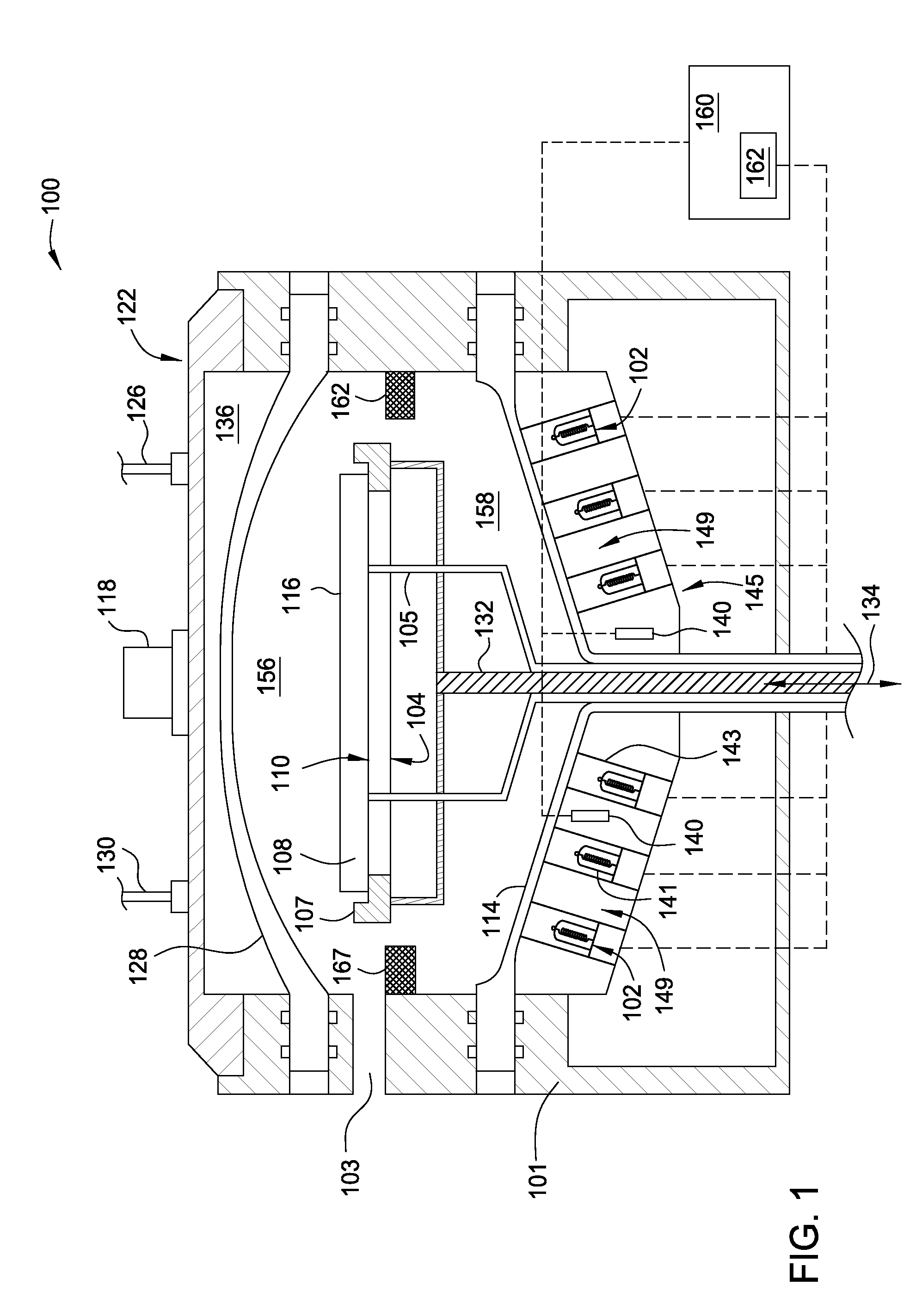
Apparatus for use with hydrogen radicals and method of using same
PendingUS20190348261A1To offer comfortExtend your lifeFouling preventionElectric discharge tubesEnvironmental engineeringChemical engineering
A system and method suitable for removing both carbon-based contaminants and oxygen-based contaminants from a substrate within a single process chamber are disclosed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of depositing barrier layer from metal gates
InactiveUS20050104112A1Improve performanceEasy to useTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricRemote plasma
A method of manufacturing a high performance MOS device and transistor gate stacks comprises forming a gate dielectric layer over a semiconductor substrate; forming a barrier layer over the gate dielectric layer by an ALD type process; and forming a gate electrode layer over the barrier layer. The method enables the use of hydrogen plasma, high energy hydrogen radicals and ions, other reactive radicals, reactive oxygen and oxygen containing precursors in the processing steps subsequent to the deposition of the gate dielectric layer of the device. The ALD process for forming the barrier layer is performed essentially in the absence of plasma and reactive hydrogen radials and ions. This invention makes it possible to use oxygen as a precursor in the deposition of the metal gates. The barrier film also allows the use of hydrogen plasma in the form of either direct or remote plasma in the deposition of the gate electrode. Furthermore, the barrier film prevents the electrode material from reacting with the gate dielectric material. The barrier layer is ultra thin and, at the same time, it forms a uniform cover over the entire surface of the gate dielectric.
Owner:HAUKKA SUVI +1
High temperature coatings for a preclean and etch apparatus and related methods
PendingUS20200131634A1Well formedElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingSemiconductor
A coating and a method to form the coating is proposed for a semiconductor film pre-clean and etch apparatus. The coating may be employed in environments where it is difficult to use a traditional coating or coating method. The coatings provide advantages including: an ability to effectively deliver hydrogen radicals and fluorine radicals to a wafer surface in one apparatus or individually in two apparatuses; a coverage of high aspect ratio features on critical components; an operability in high temperatures exceeding 150° C.; and a protection of a part with high aspect ratio features underneath the coating, thereby preventing metal and particles on a processed wafer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Plasma treatment for purifying copper or nickel
InactiveUS20060054184A1Reduce connection resistanceReduce impuritySoldering apparatusElectrostatic cleaningAlloyOxygen
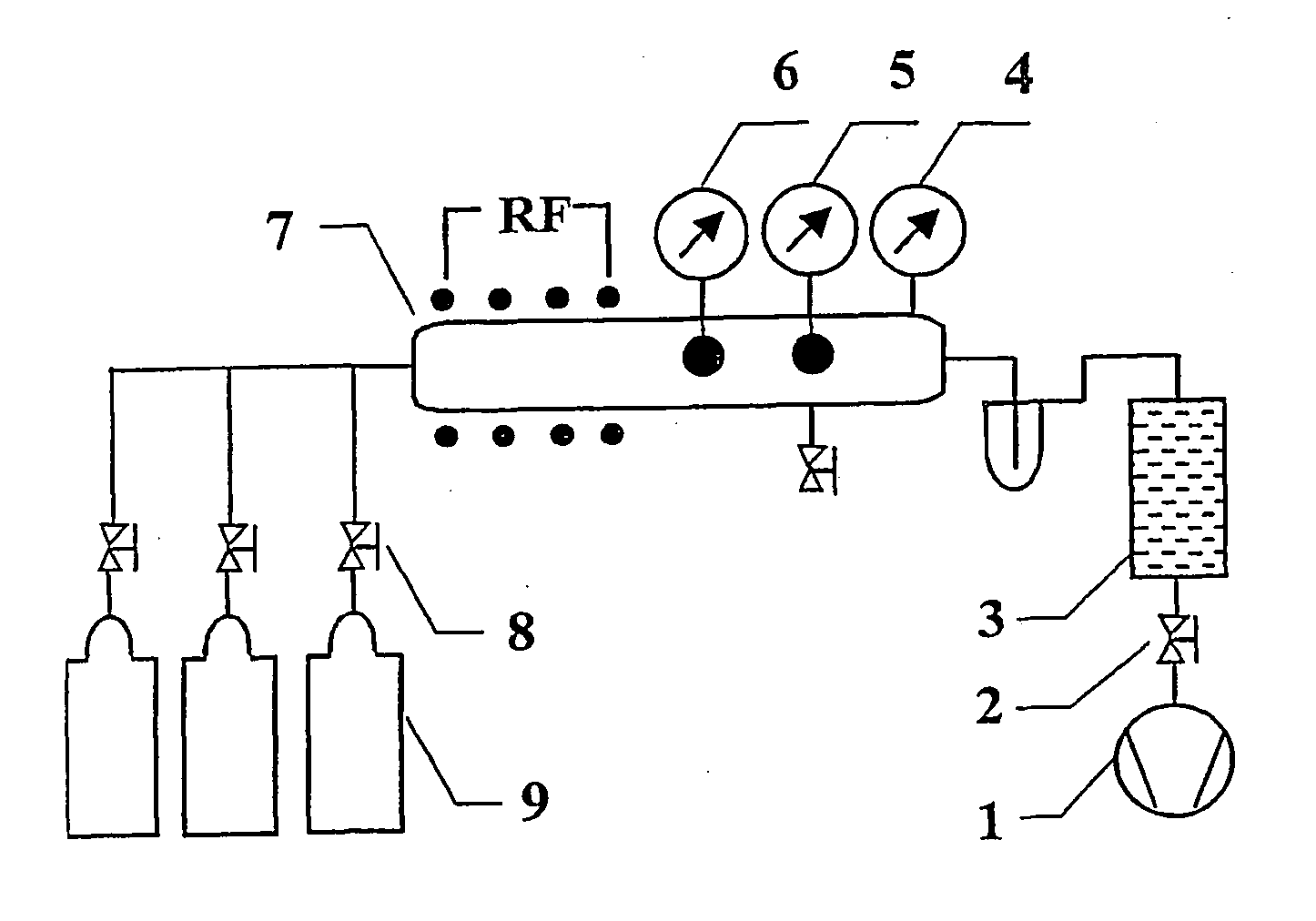
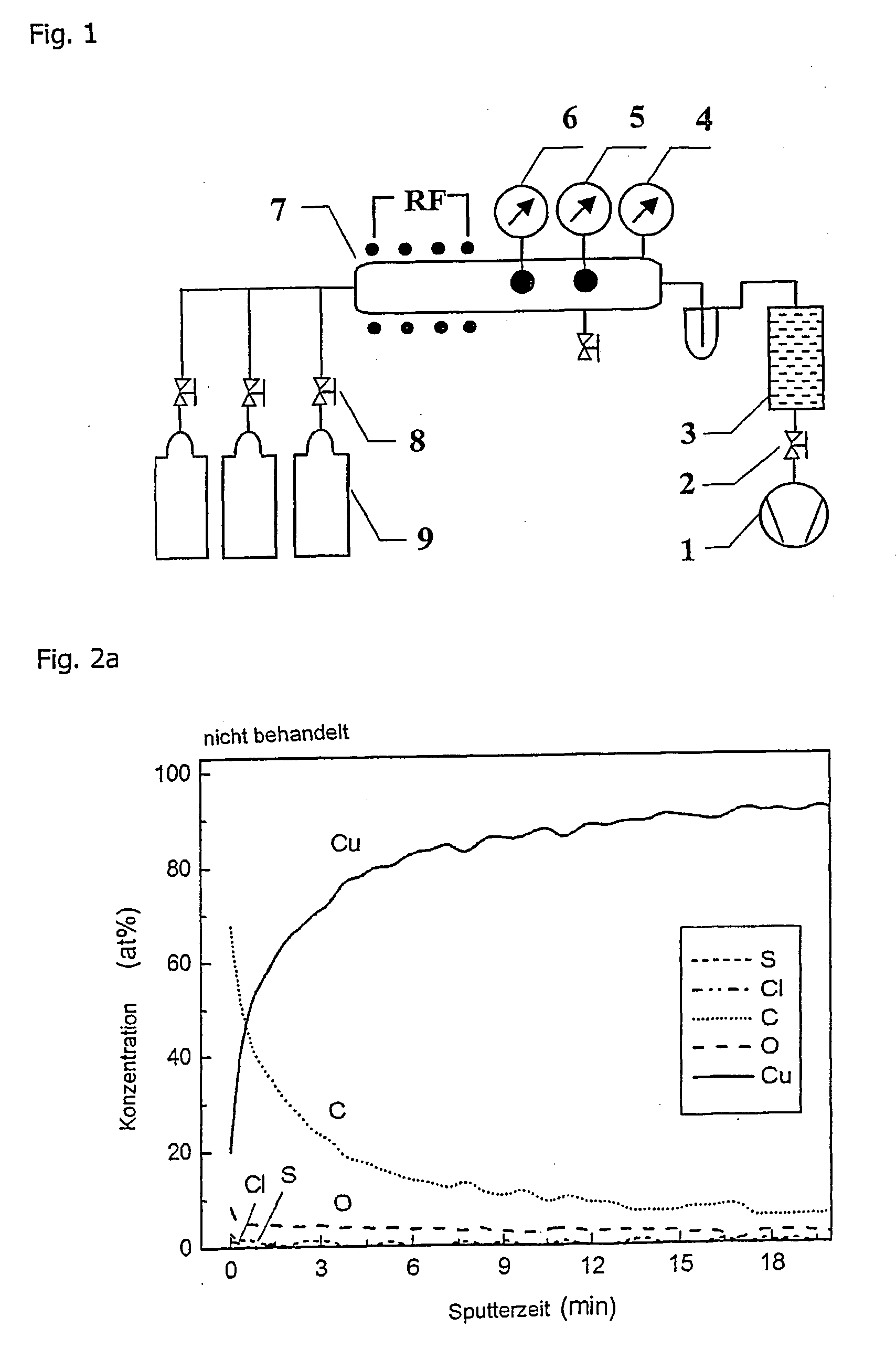
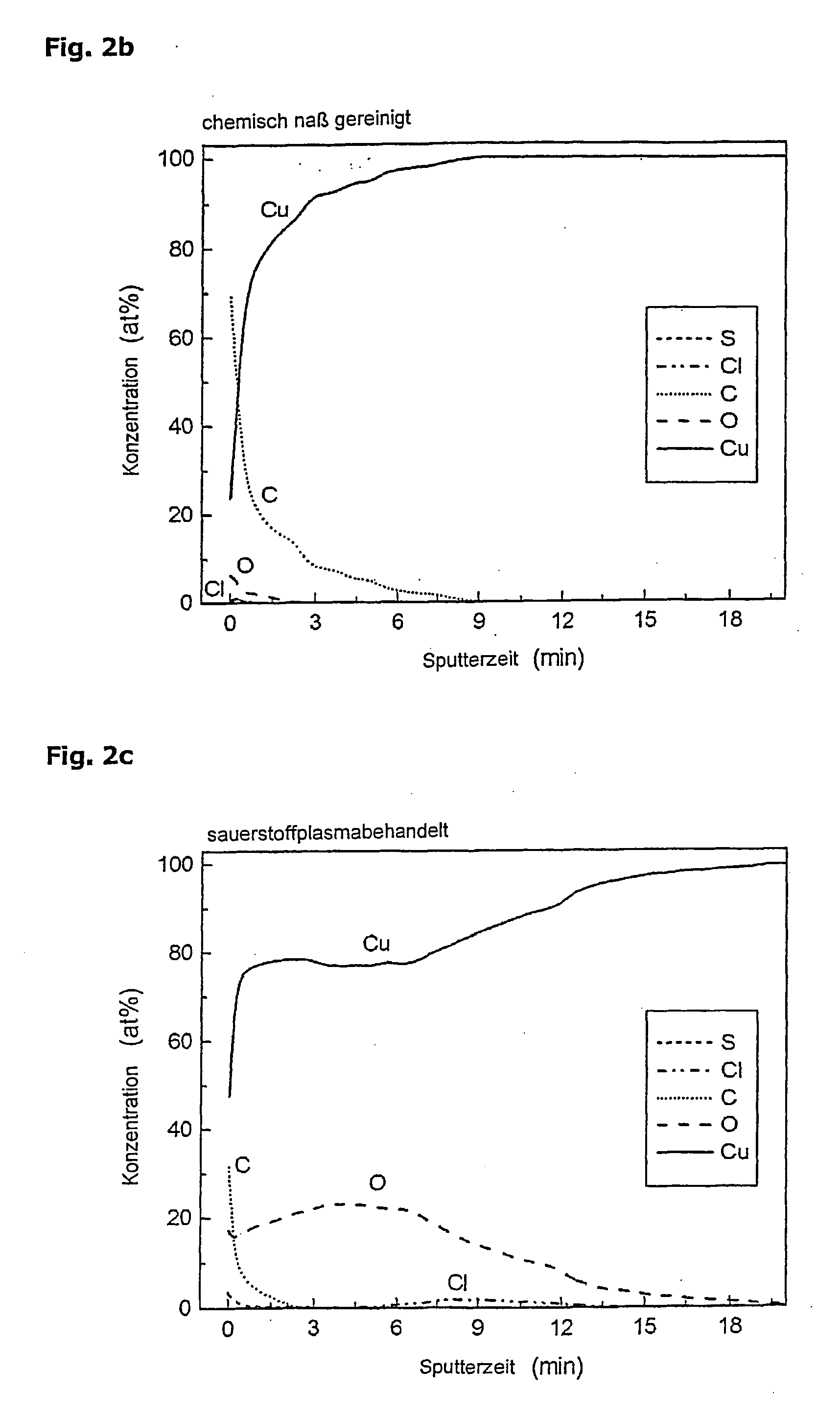
A method for treating electronic components made of copper, nickel or alloys thereof or with materials such as brass or plated therewith and includes the steps of arranging the components in a treatment chamber, generating a vacuum in the treatment chamber, introducing oxygen into the treatment chamber, providing a pressure ranging between 10−1 and 50 mbar in the treatment chamber and exciting a plasma in the chamber, allowing the oxygen radicals to act on the components, generating a vacuum in the treatment chamber, introducing hydrogen into the treatment chamber, providing a pressure ranging between 10−1 and 50 mbar in the treatment chamber and exciting a plasma in the chamber and allowing the hydrogen radicals to act on the components.
Owner:KOLEKTOR GRP D O O
Method of growing electrical conductors
ActiveUS7067407B2Quality improvementGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsElectrical conductorAtomic layer deposition
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for forming a high quality low temperature silicon nitride film
InactiveUS7172792B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureNitrogen
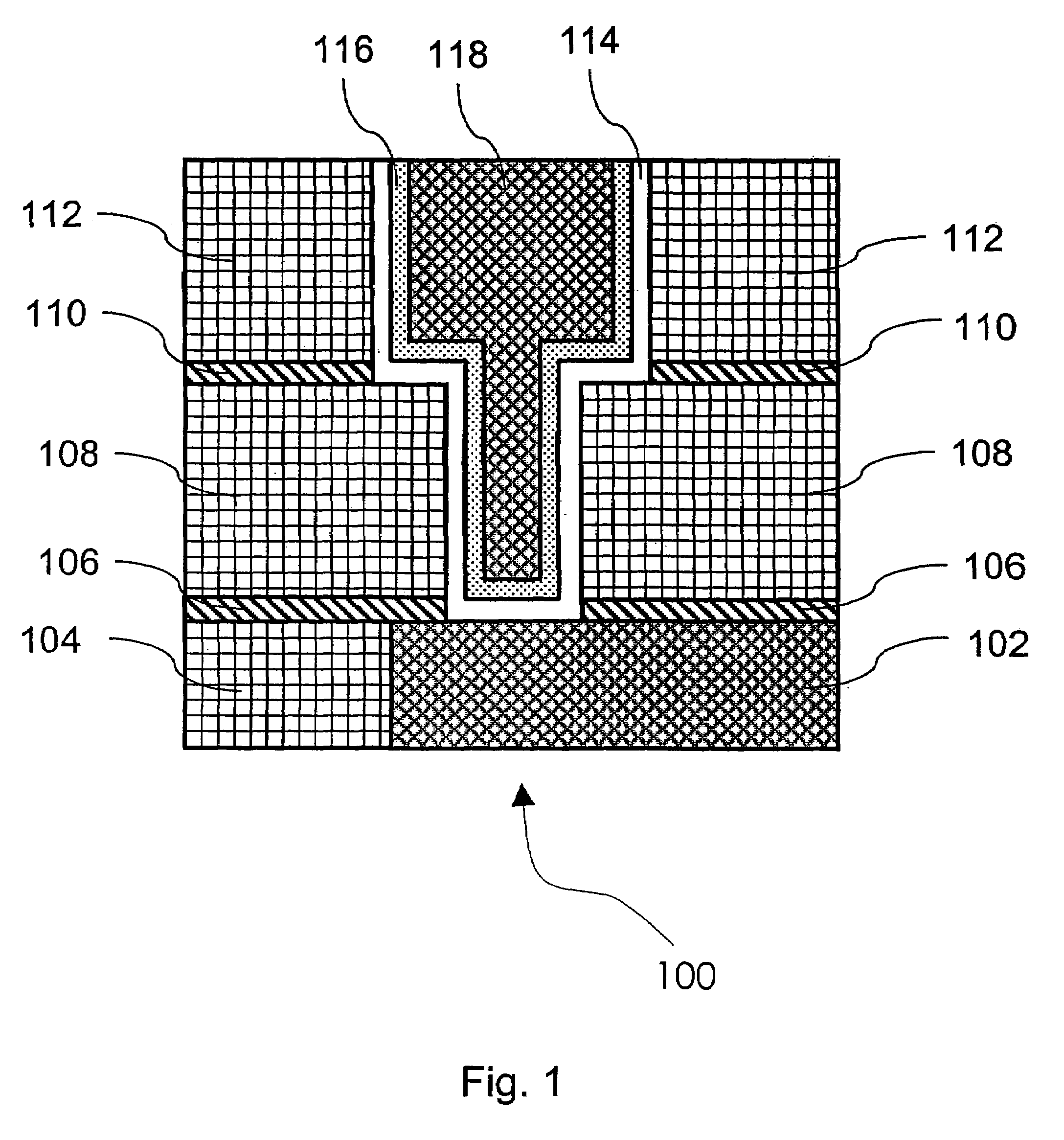
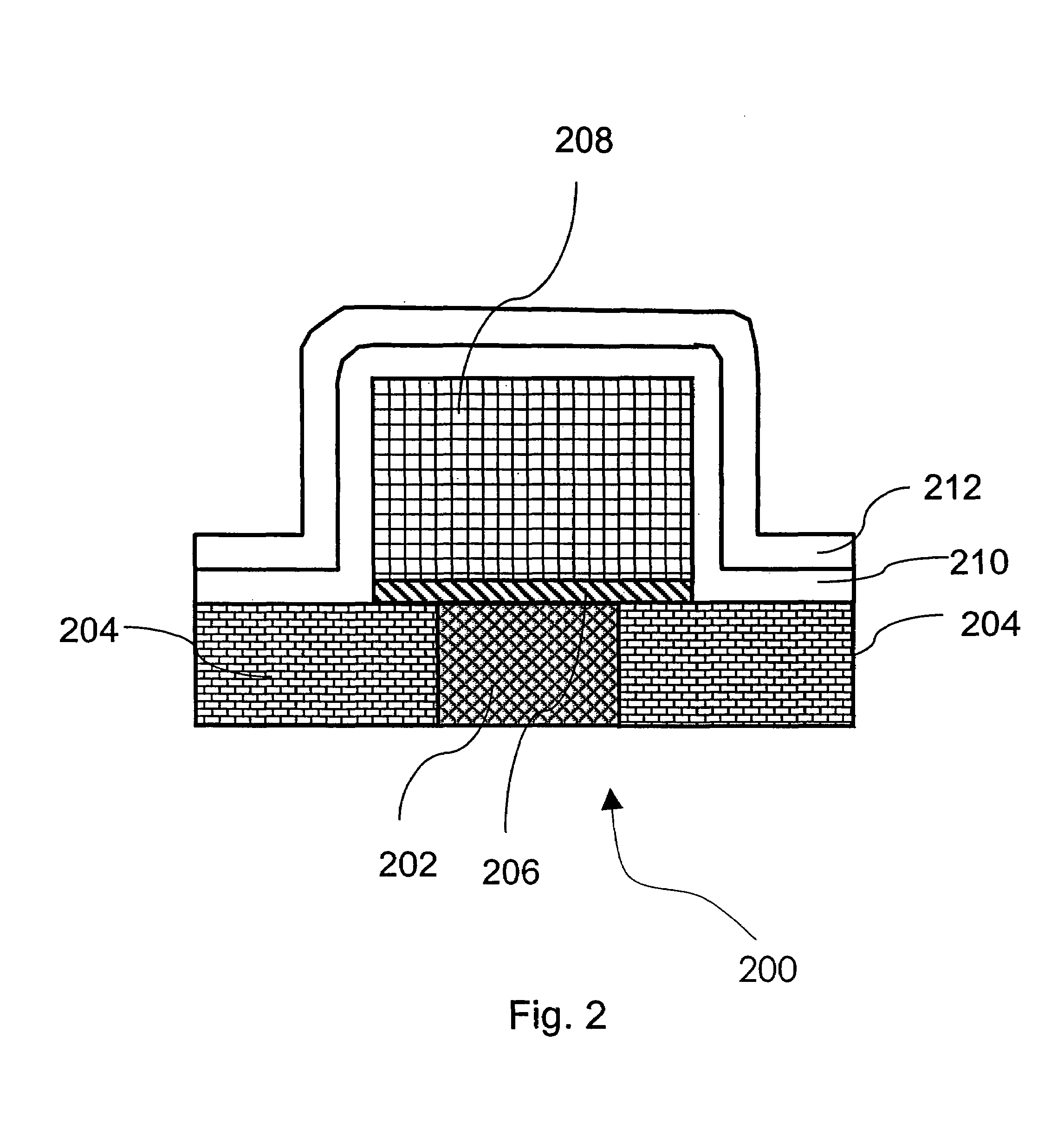
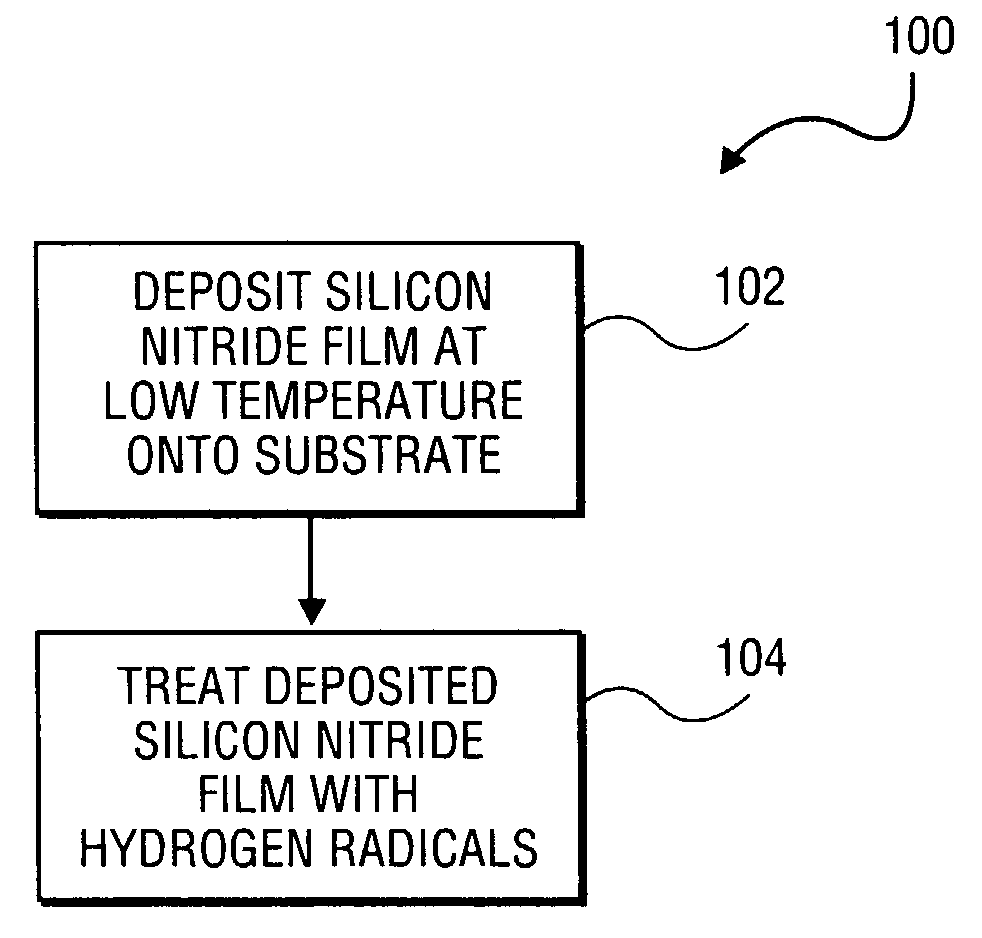
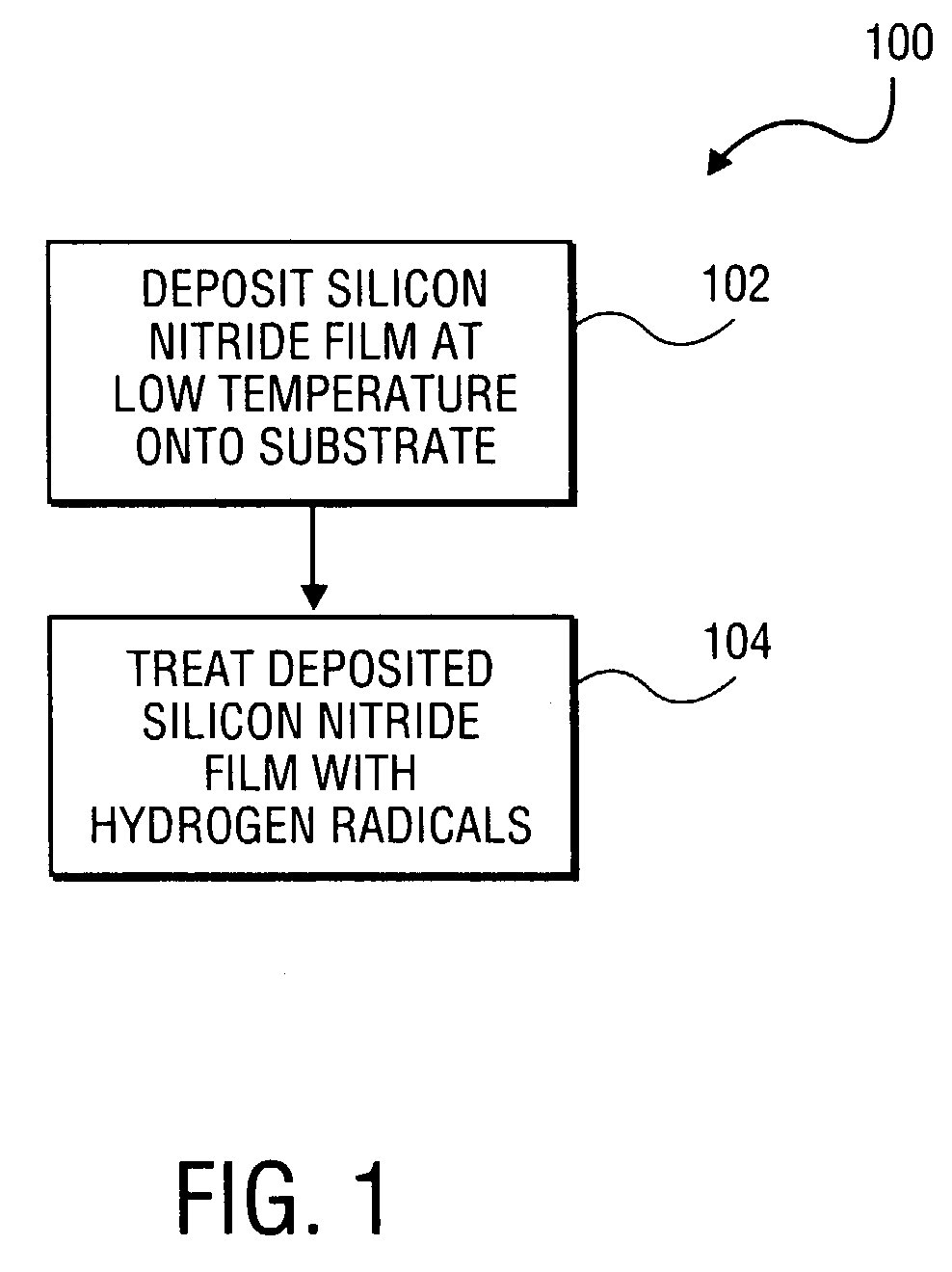
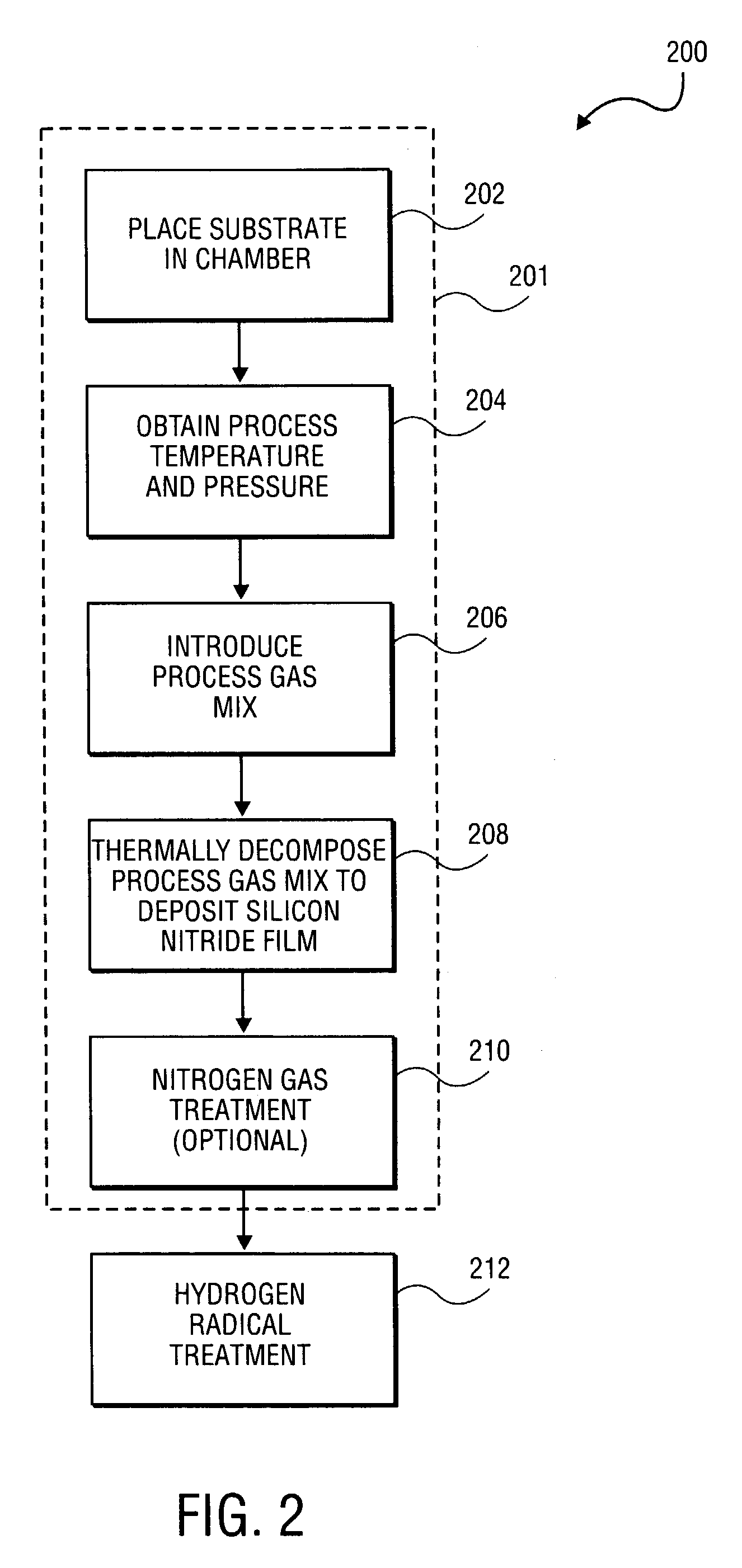
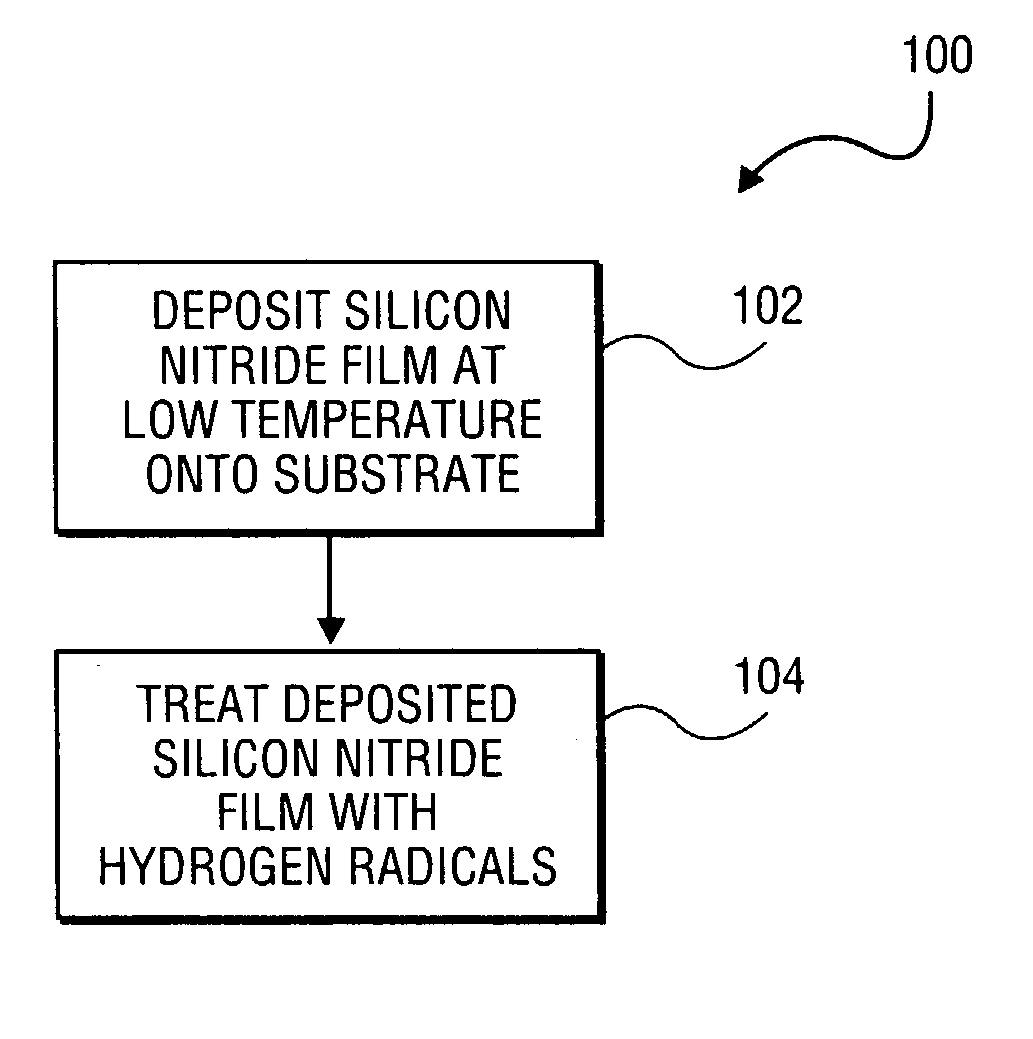
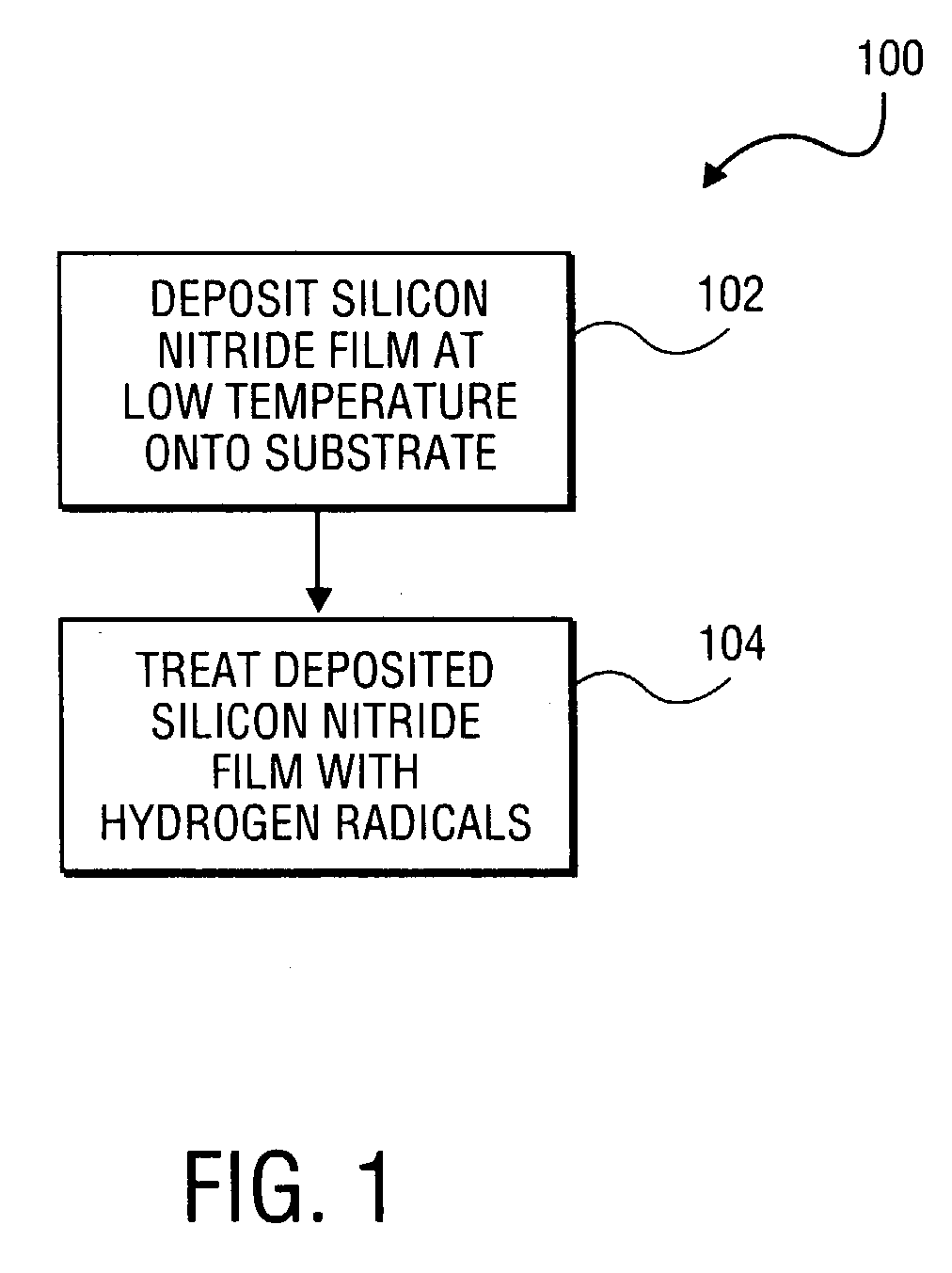
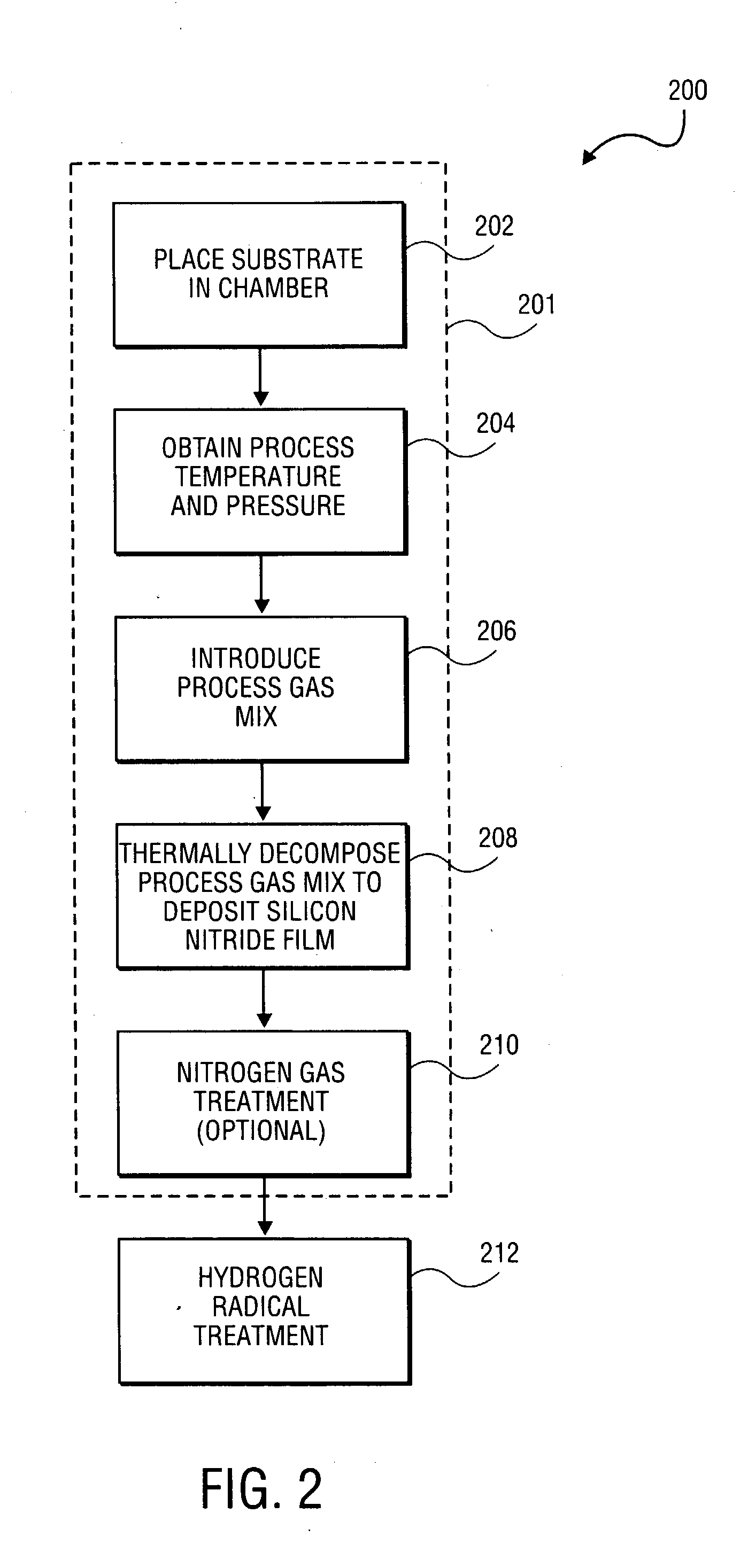
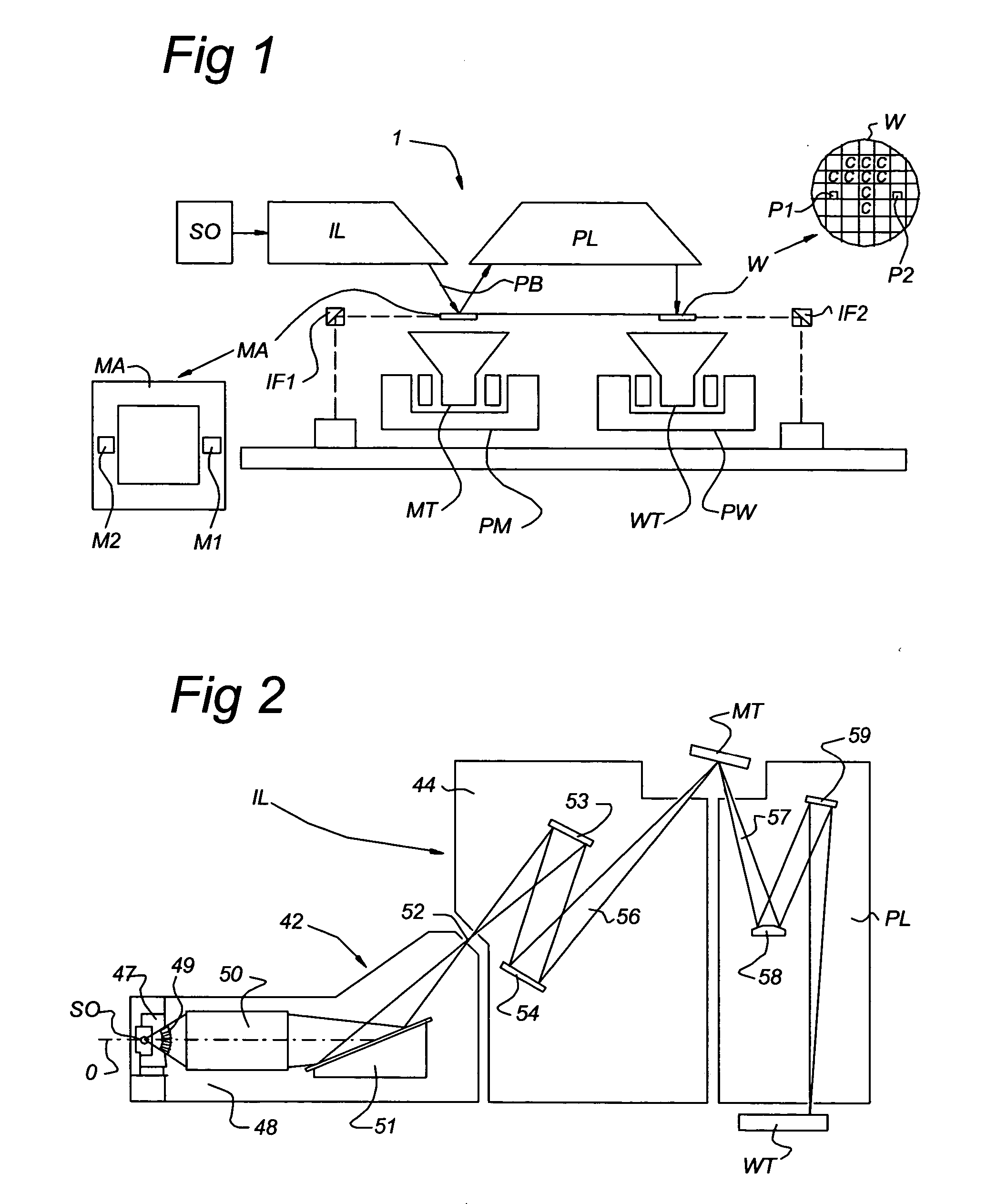
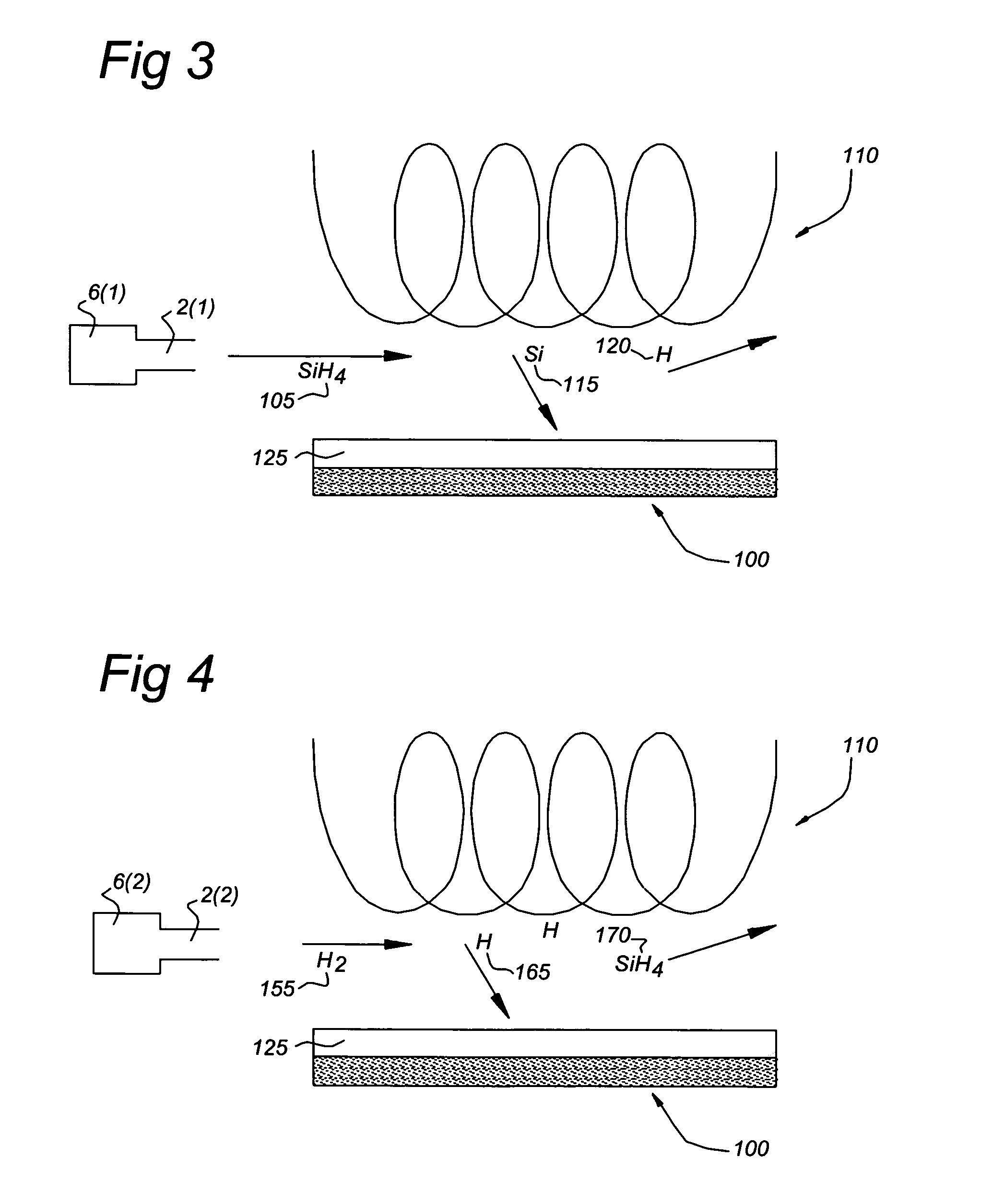
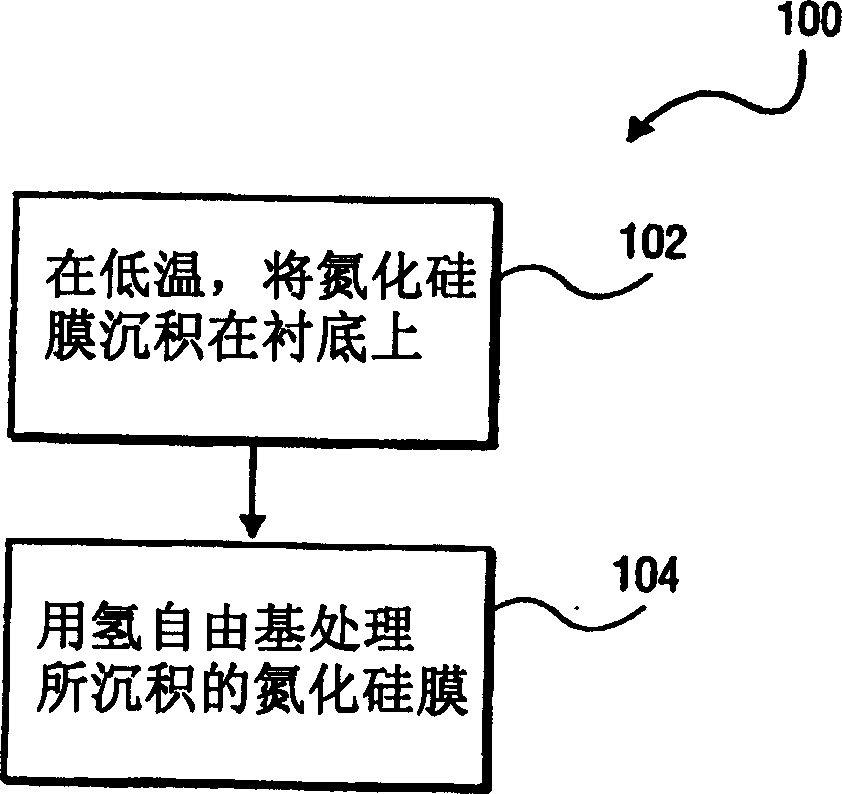
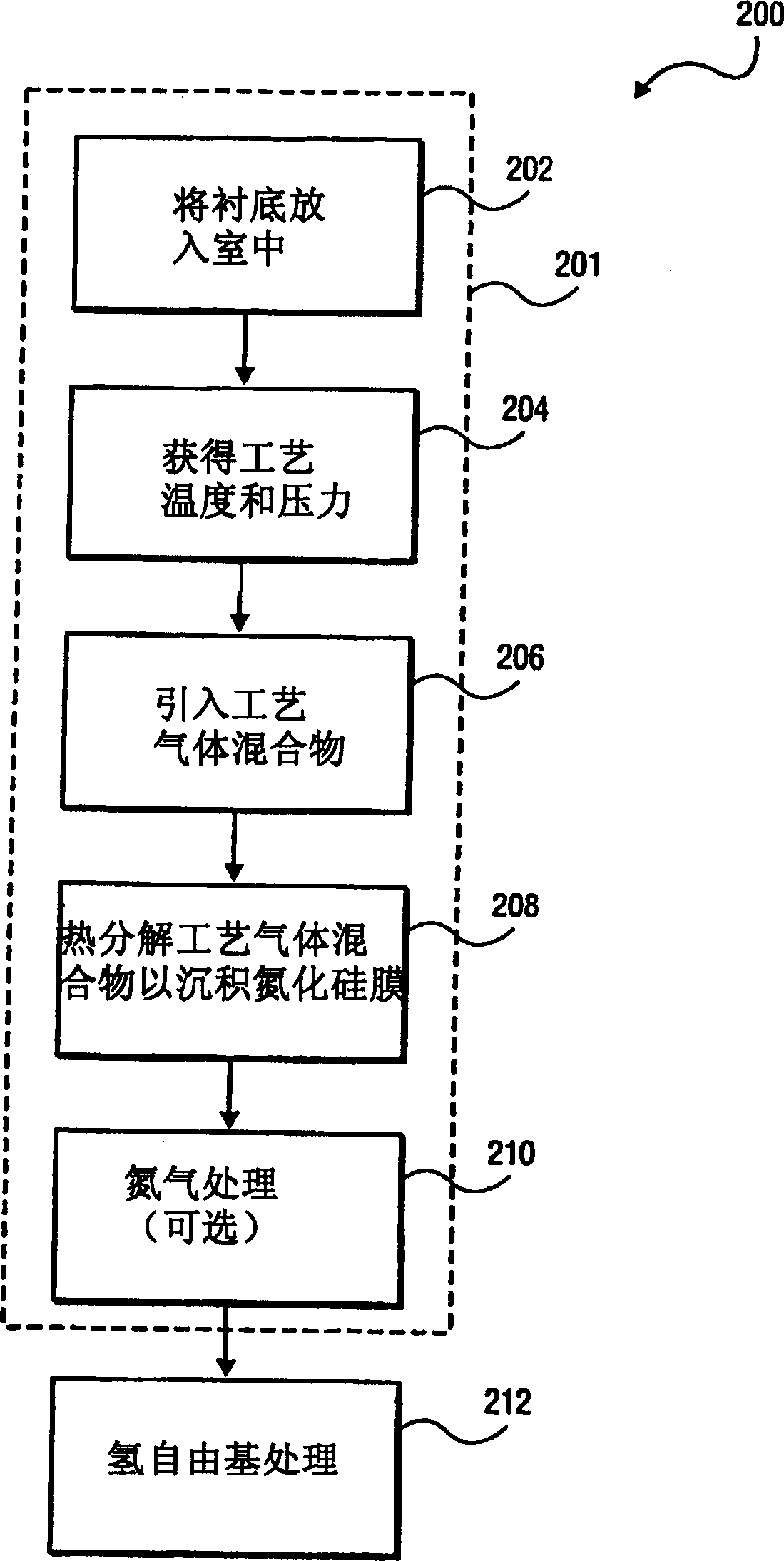
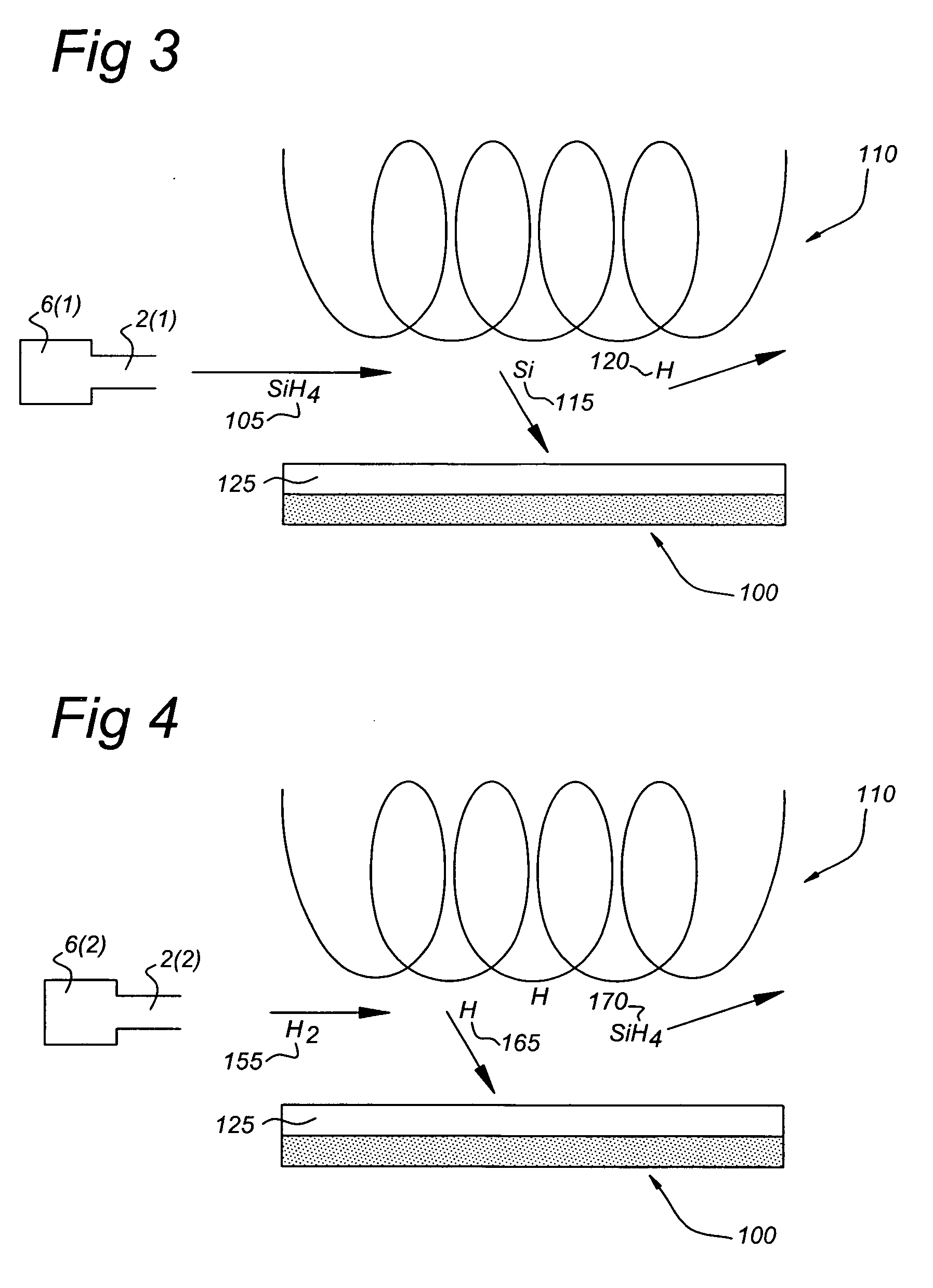
A method of forming a silicon nitride film is described. According to the present invention, a silicon nitride film is deposited by thermally decomposing a silicon / nitrogen containing source gas or a silicon containing source gas and a nitrogen containing source gas at low deposition temperatures (e.g., less than 550° C.) to form a silicon nitride film. The thermally deposited silicon nitride film is then treated with hydrogen radicals to form a treated silicon nitride film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for forming a high quality low temperature silicon nitride film
ActiveUS20040121085A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen radicalNitrogen
A method of forming a silicon nitride film is described. According to the present invention, a silicon nitride film is deposited by thermally decomposing a silicon / nitrogen containing source gas or a silicon containing source gas and a nitrogen containing source gas at low deposition temperatures (e.g., less than 550° C.) to form a silicon nitride film. The thermally deposited silicon nitride film is then treated with hydrogen radicals to form a treated silicon nitride film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for remote plasma source assisted silicon-containing film deposition
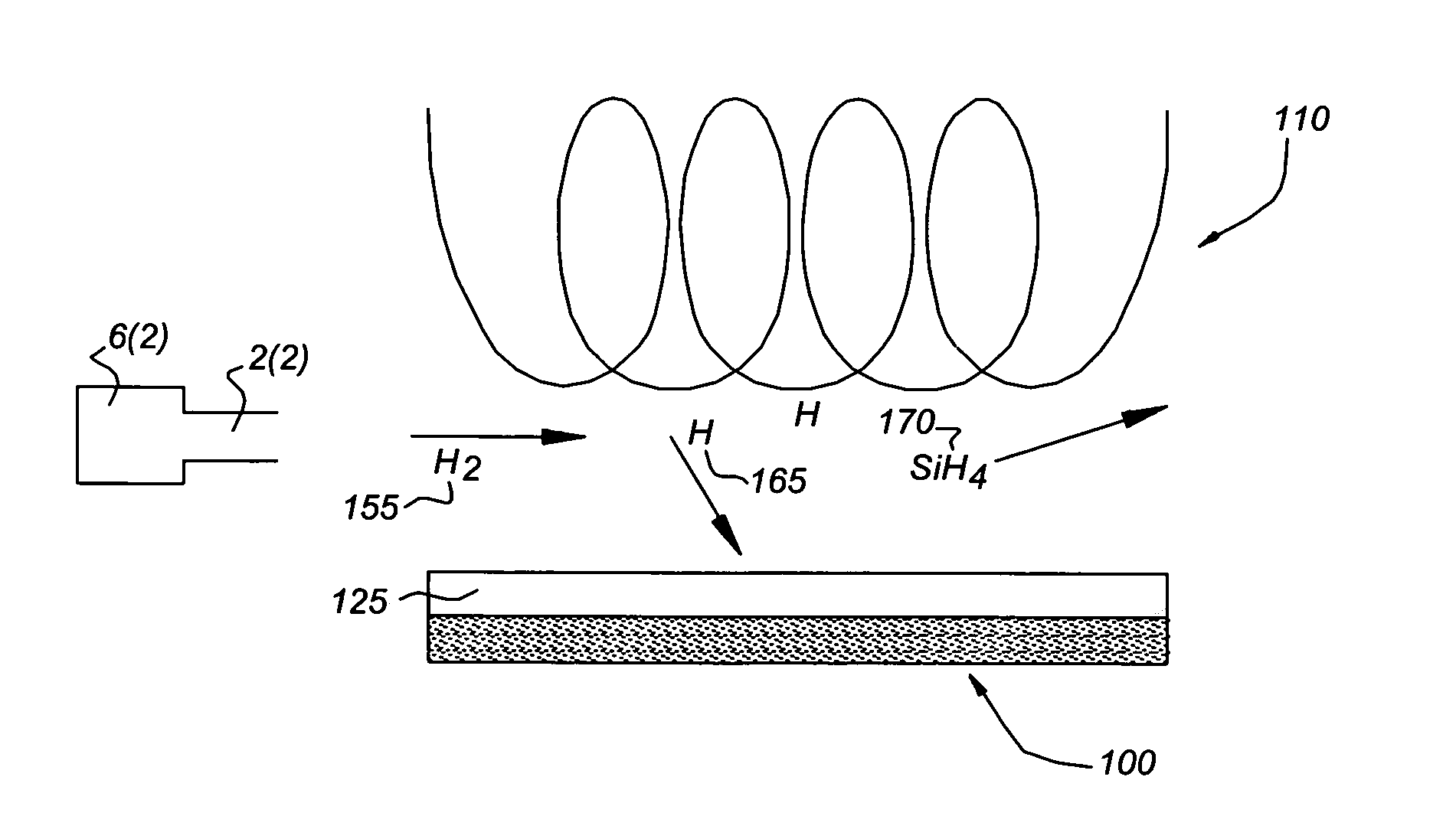
InactiveUS20130012030A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaMicrocrystalline silicon
An apparatus and methods for depositing amorphous and microcrystalline silicon films during the formation of solar cells are provided. In one embodiment, a method and apparatus is provided for generating and introducing hydrogen radicals directly into a processing region of a processing chamber for reaction with a silicon-containing precursor for film deposition on a substrate. In one embodiment, the hydrogen radicals are generated by a remote plasma source and directly introduced into the processing region via a line of sight path to minimize the loss of energy by the hydrogen radicals prior to reaching the processing region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Pre-clean of silicon germanium for pre-metal contact at source and drain and pre-high k at channel
ActiveUS20160079062A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingFluorine containingSubstrate surface
The present disclosure generally relates to methods for removing contaminants and native oxides from substrate surfaces. The method includes exposing a surface of the substrate to first hydrogen radical species, wherein the substrate is silicon germanium having a concentration of germanium above about 30%, then exposing the surface of the substrate to a plasma formed from a fluorine-containing precursor and a hydrogen-containing precursor, and then exposing the surface of the substrate to second hydrogen radical species.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
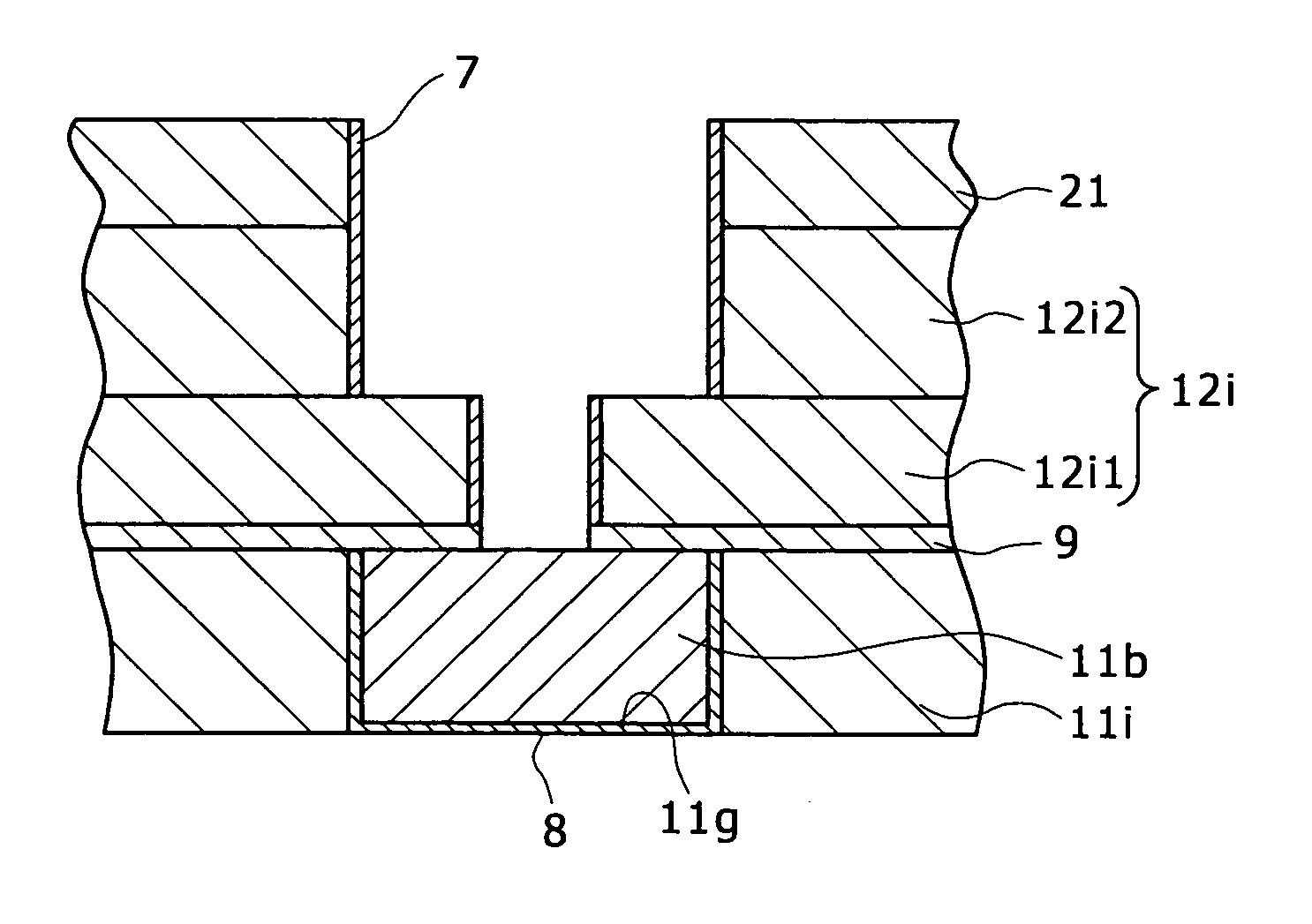
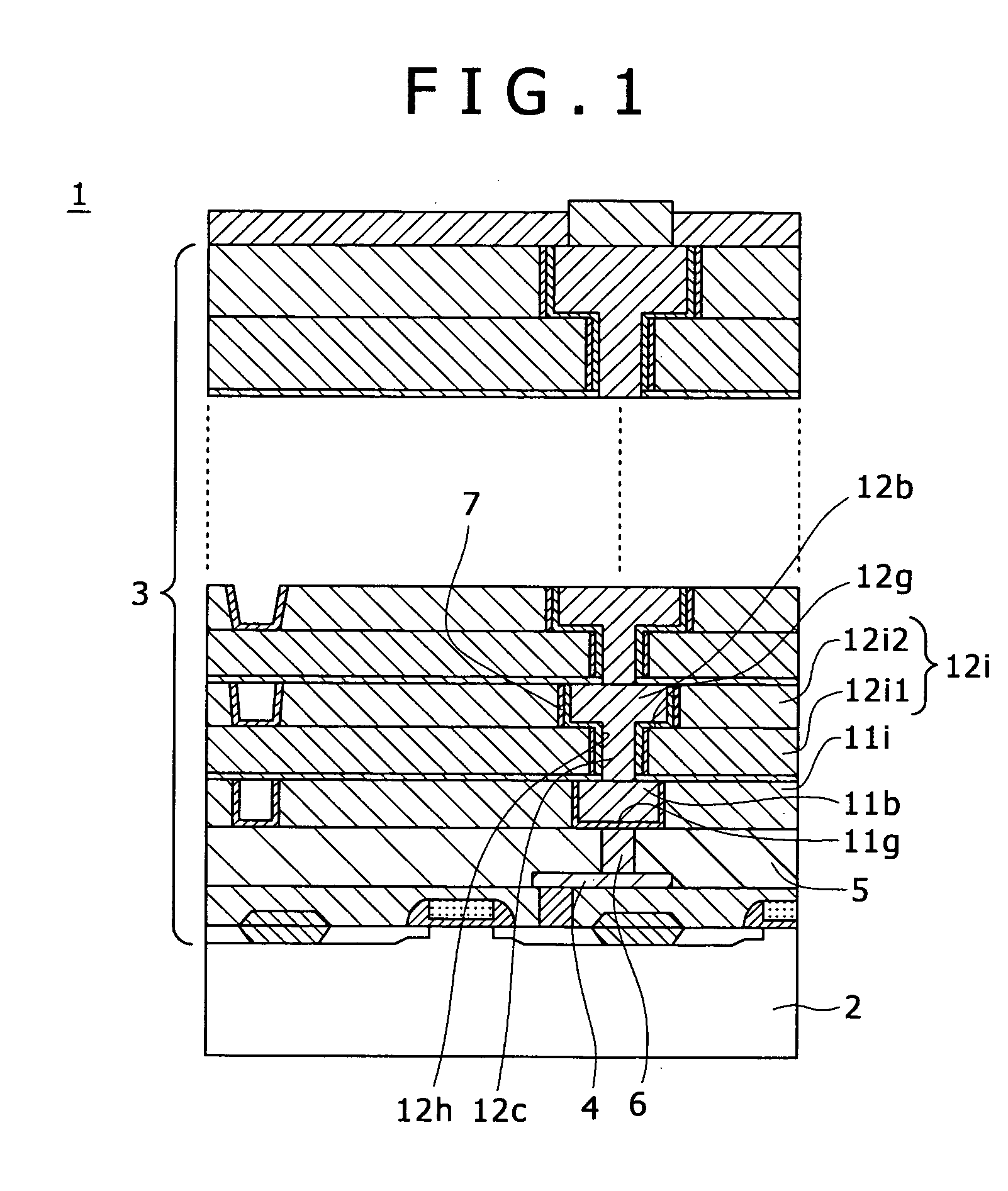
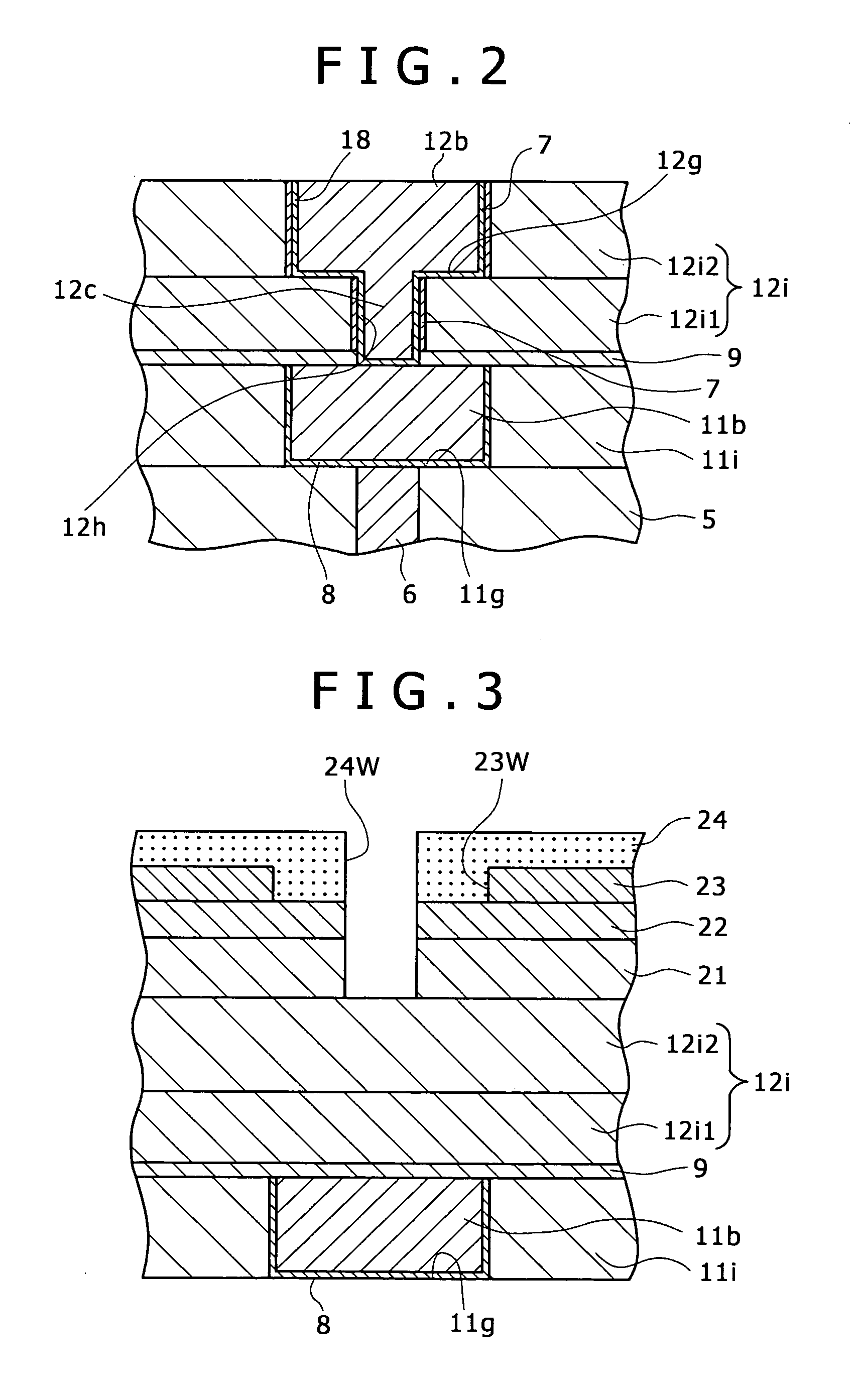
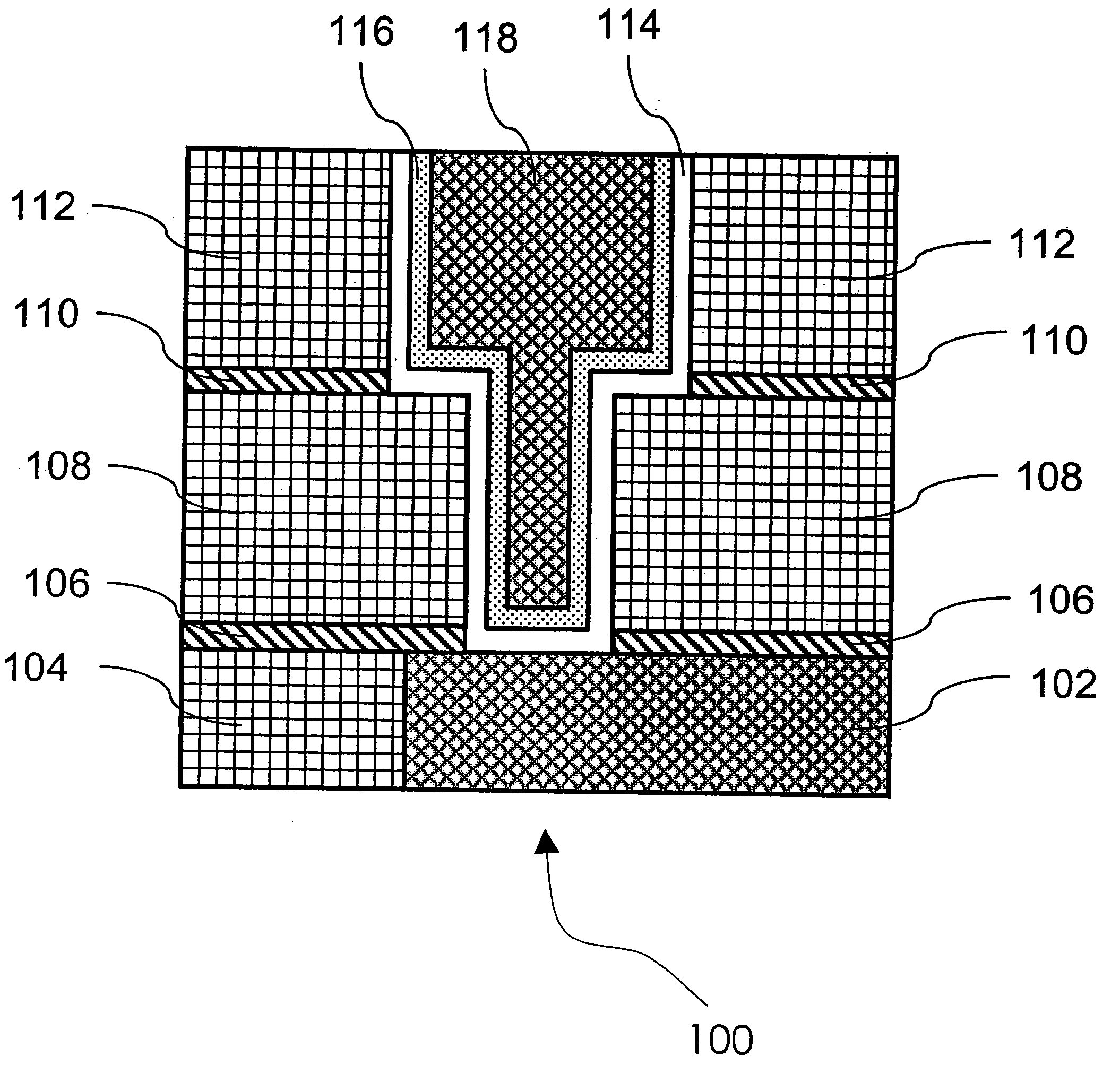
Multi-layer wiring structure, semiconductor apparatus having multi-layer wiring structure, and methods of manufacturing them
InactiveUS20060019485A1Low resistance contactStable, highly reliable high-density buried wiringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorInsulation layer
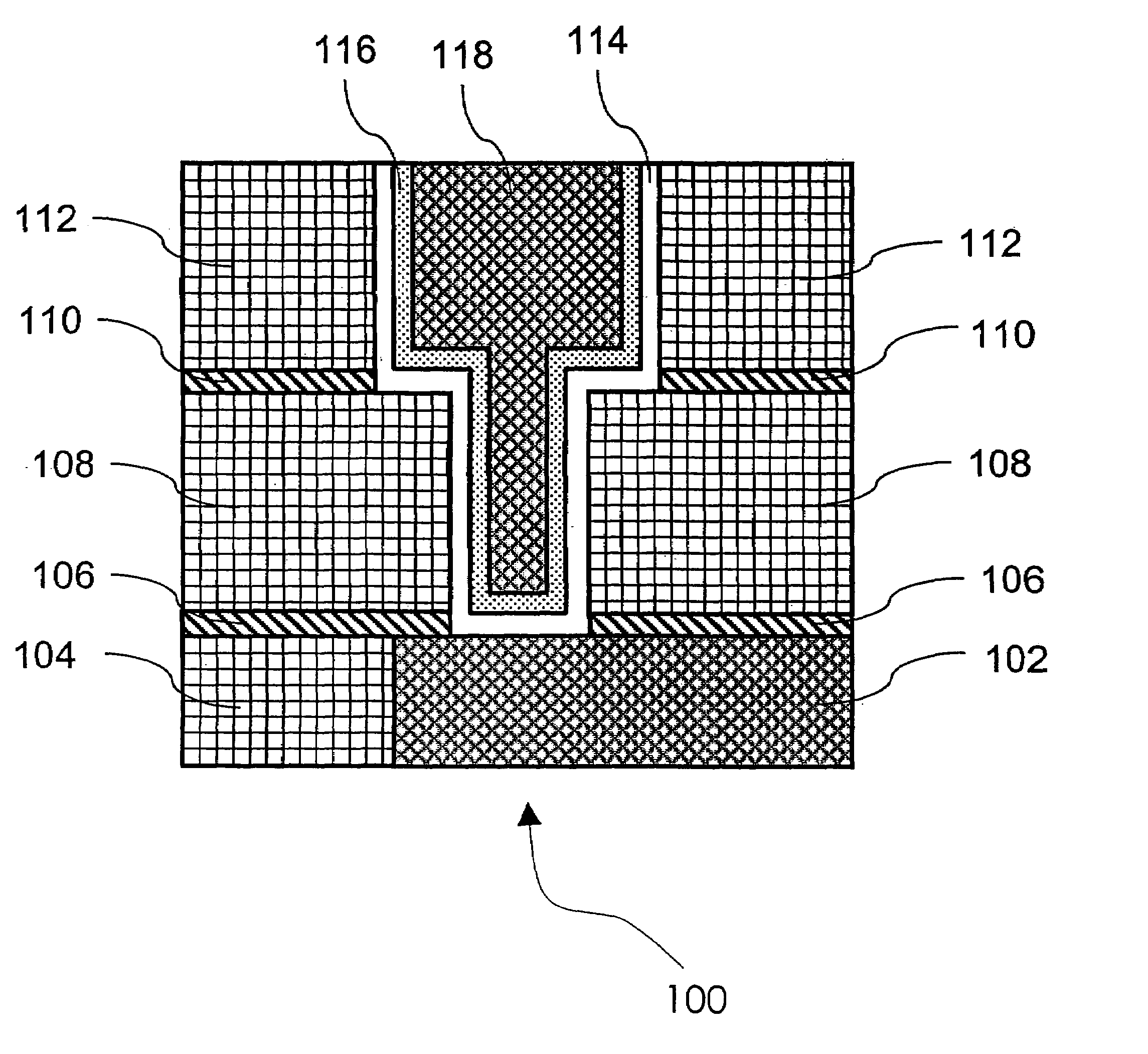
A multi-layer wiring structure including an upper layer wiring (second buried wiring) connected to a buried wiring (first buried wiring) in lower layer wiring grooves (first wiring grooves) through connection conductors, wherein a protective film capable of enduring a cleaning treatment with hydrogen radicals or hydrogen plasma applied to the surface of the first buried wiring at the time of forming the connection conductors is formed on the inside surfaces of the wiring grooves to be filled with he second buried wiring and the wiring connection holes to be filled with the connection conductors which surfaces are liable to be eroded upon exposure to the atmosphere used in the cleaning treatment, whereby erosion of the insulation layers at the time of the cleaning is obviated, sufficient cleaning can be performed, and deterioration of characteristics can be improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of growing electrical conductors
ActiveUS20050208754A1Good step coverageComplicated processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsElectrical conductorAtomic layer deposition
A method for forming a conductive thin film includes depositing a metal oxide thin film on a substrate by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The method further includes at least partially reducing the metal oxide thin film by exposing the metal oxide thin film to a gaseous inorganic reducing agent, thereby forming a metal layer. In preferred arrangements, the reducing agent comprises of thermal hydrogen (H2), hydrogen radicals (H*) and / or carbon monoxide (CO).
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
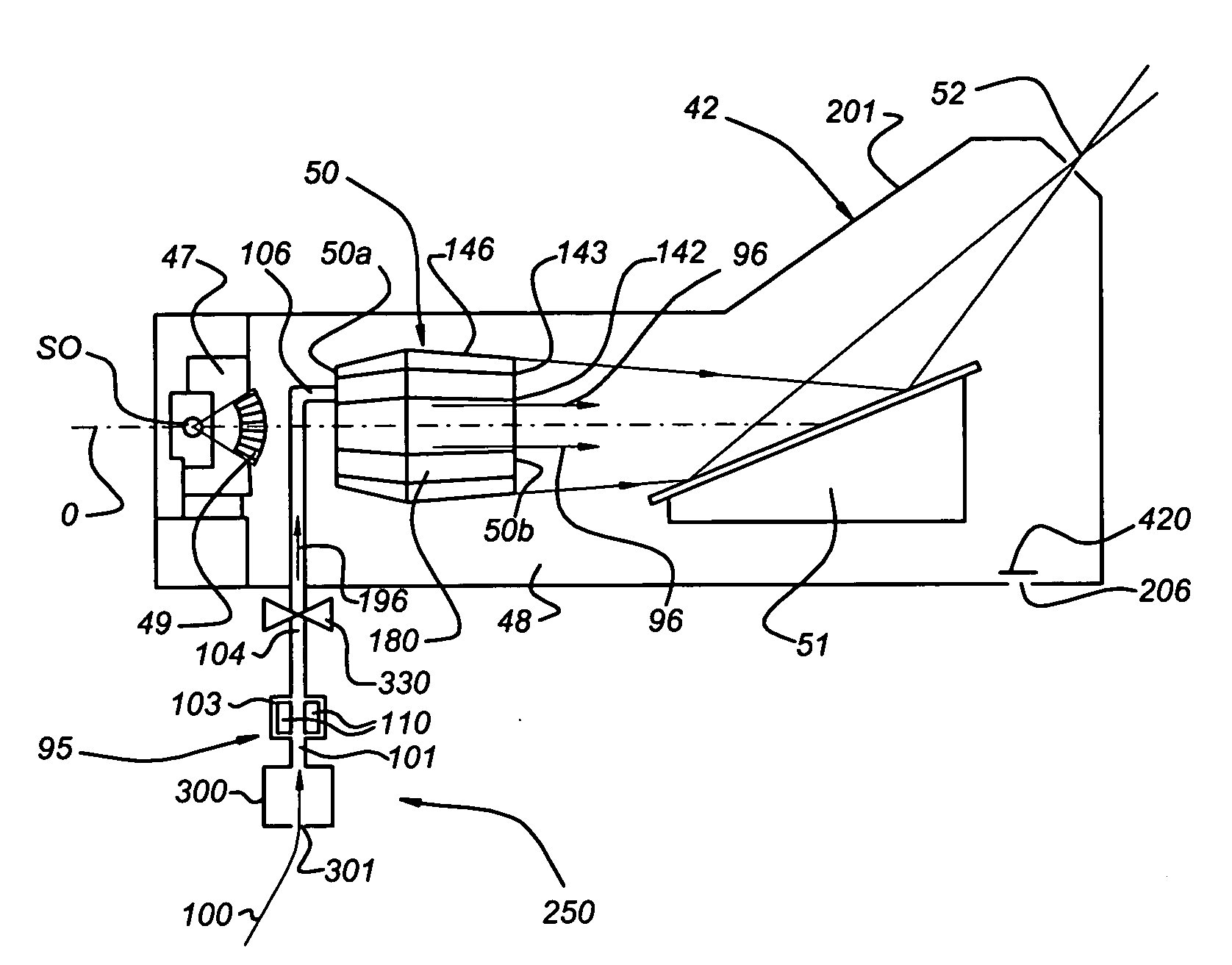
Extreme UV radiation source device and method for eliminating debris which forms within the device
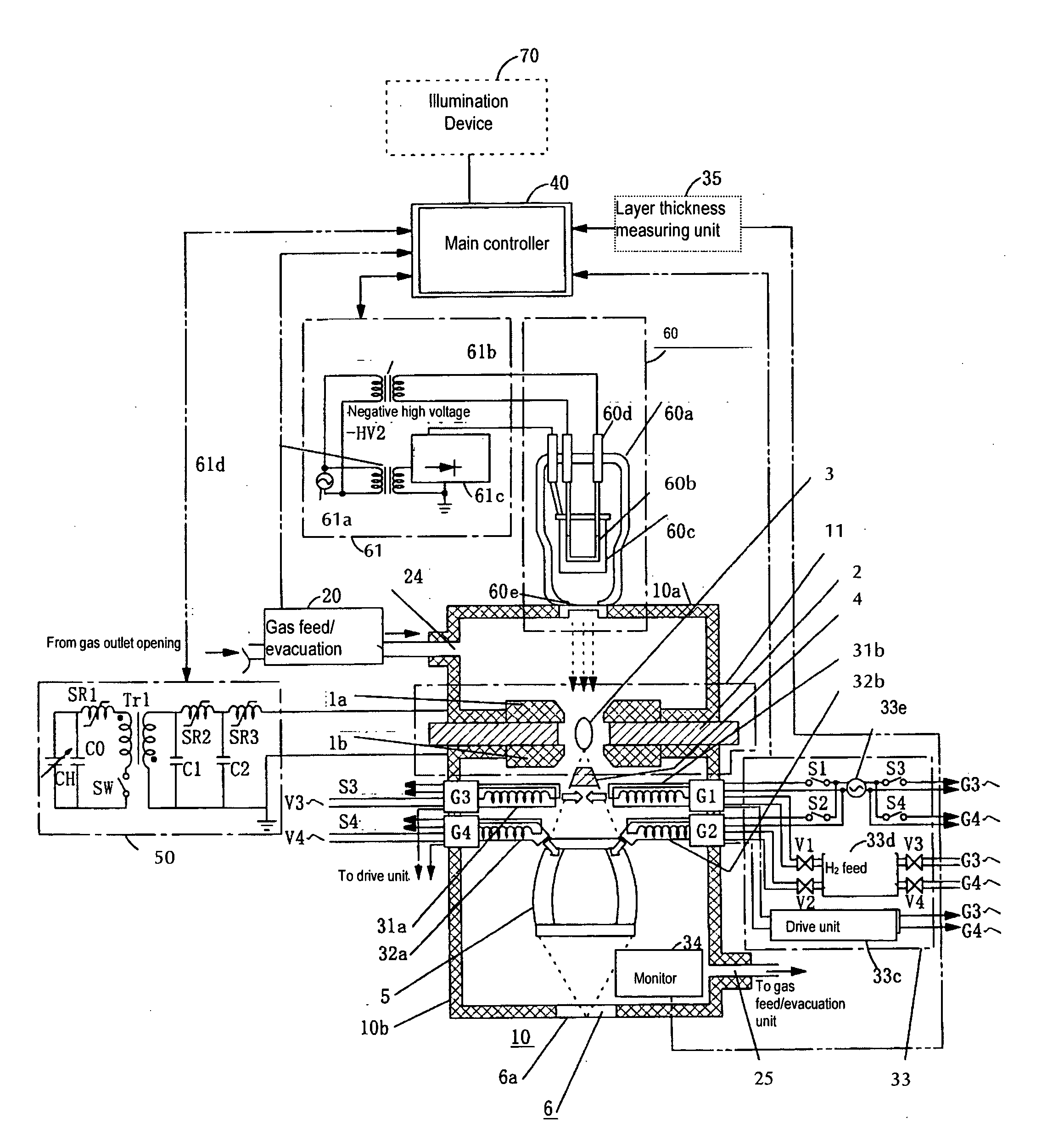
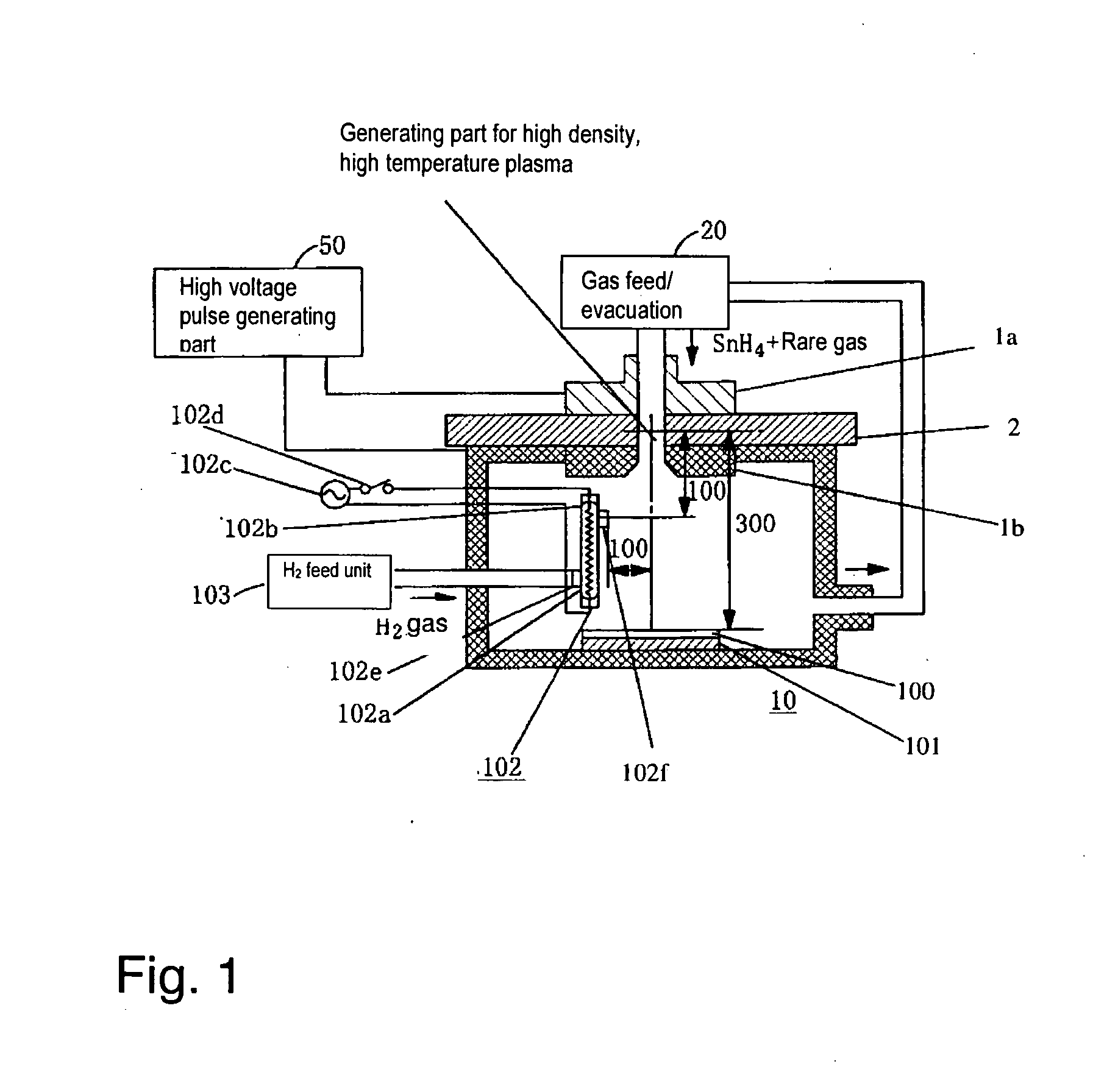
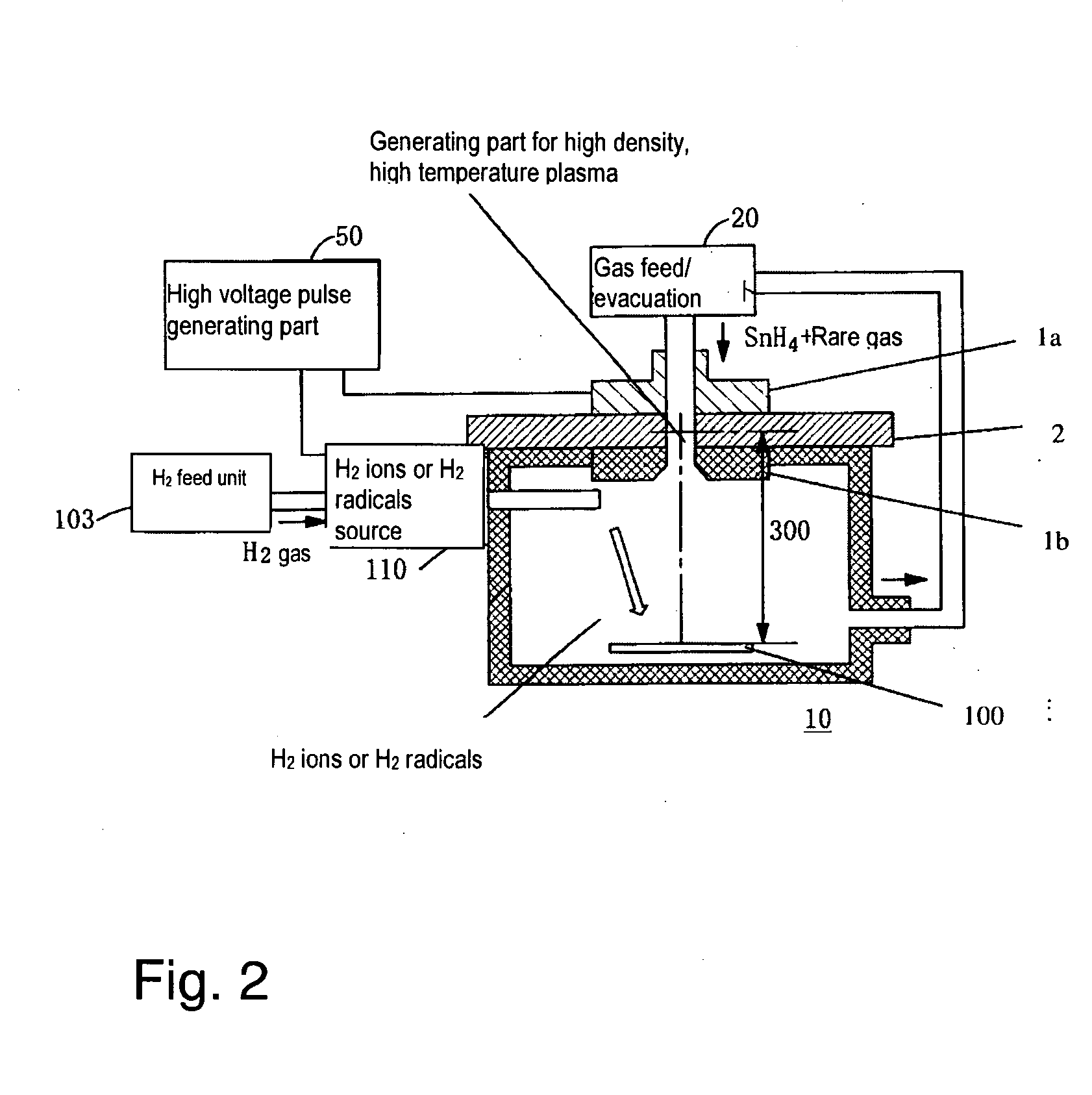
ActiveUS20060163500A1Reduction of performance of device is restrainedImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusHigh densityChemistry
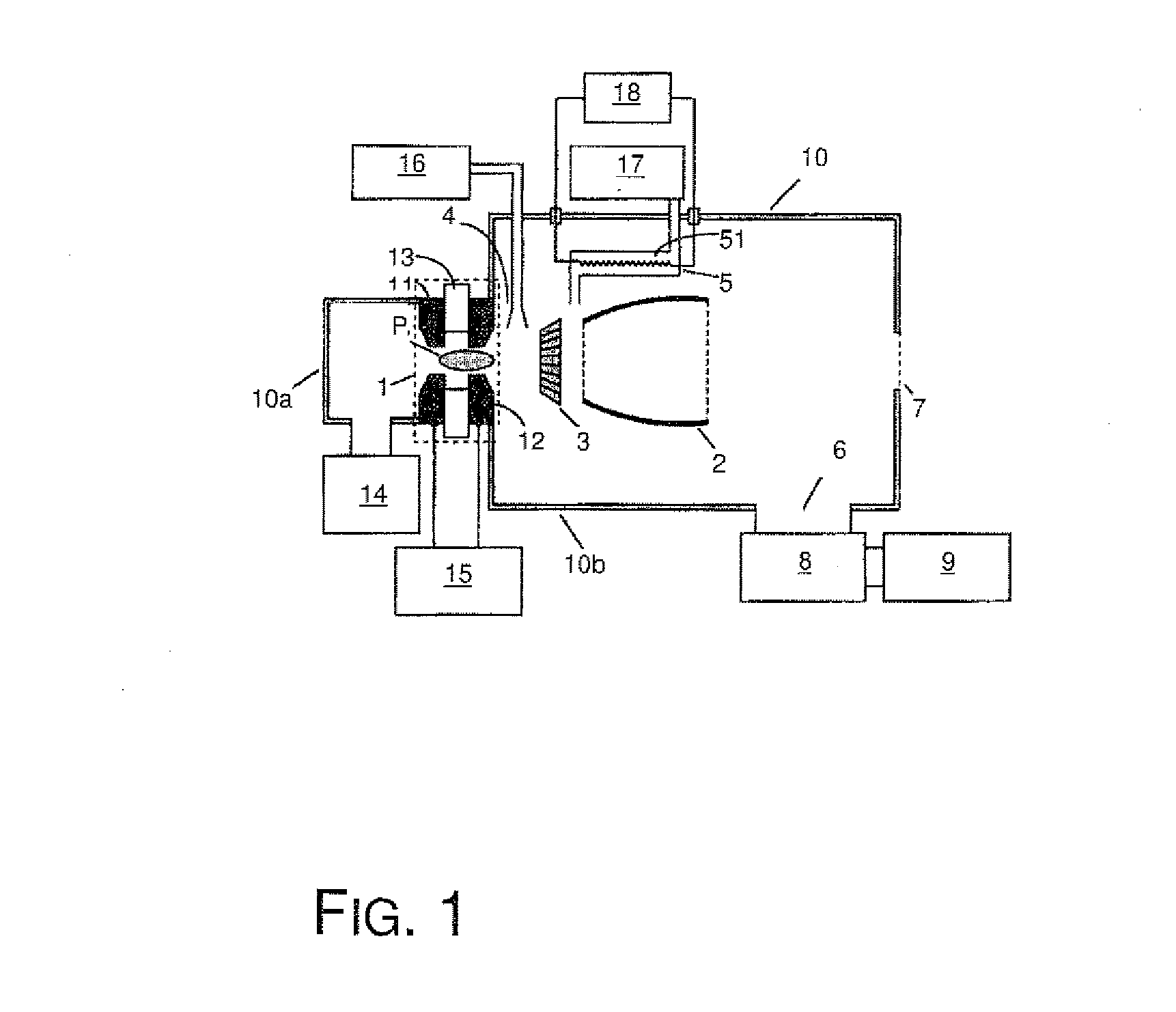
To suppress the adherence of debris as a result of a radiating fuel, such as tin or the like, within a vessel for forming high density and high temperature plasma of an extreme UV radiation source device, and to eliminate deposited tin and / or tin compounds with high efficiency, hydrogen radical producing parts are provided in the vessel; and hydrogen radicals are produced in the vessel so that deposition of tin and / or a tin compound is suppressed in the area with a low temperature of the device, such as a focusing mirror or the like, and the deposited tin and / or tin compound is eliminated.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
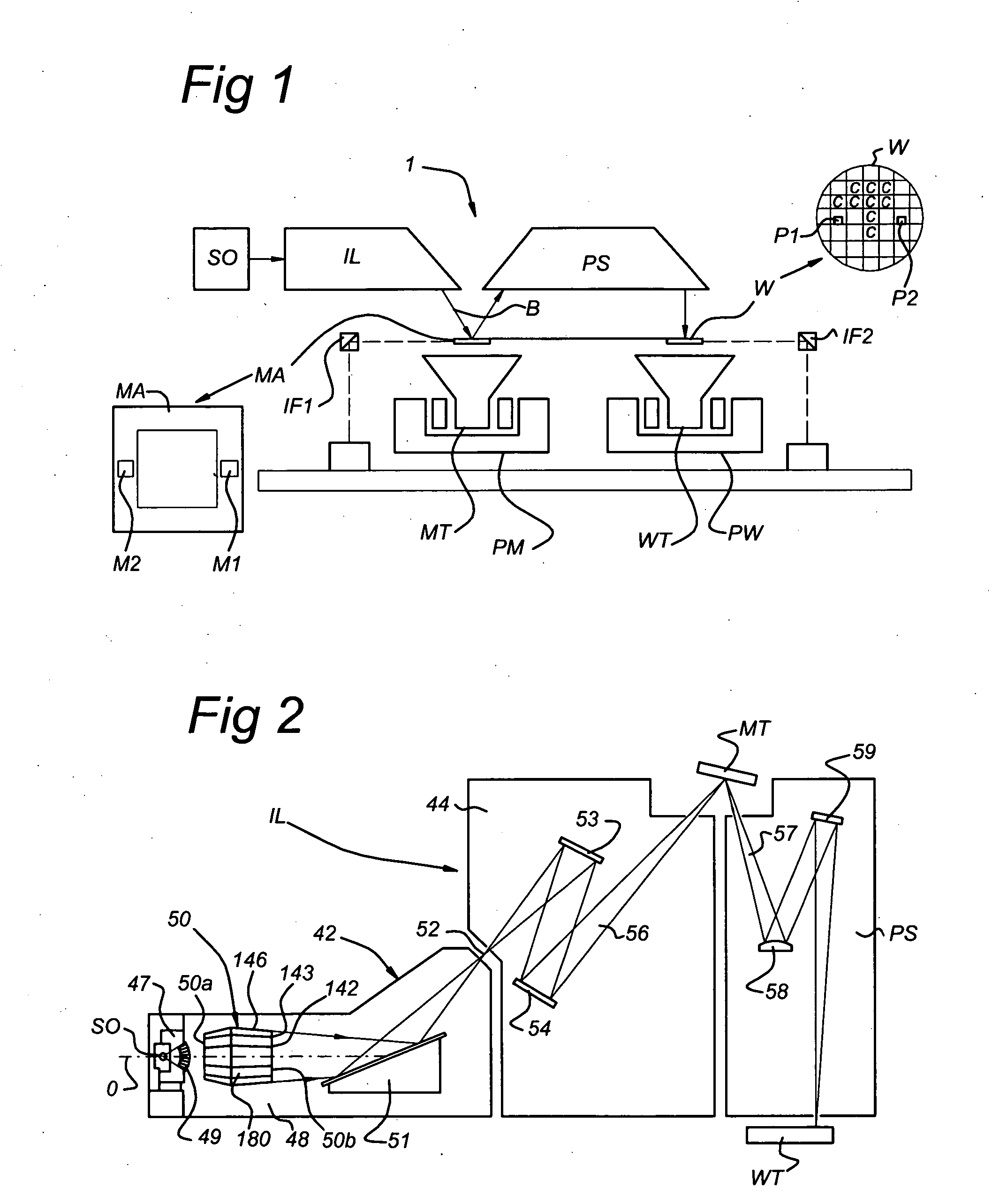
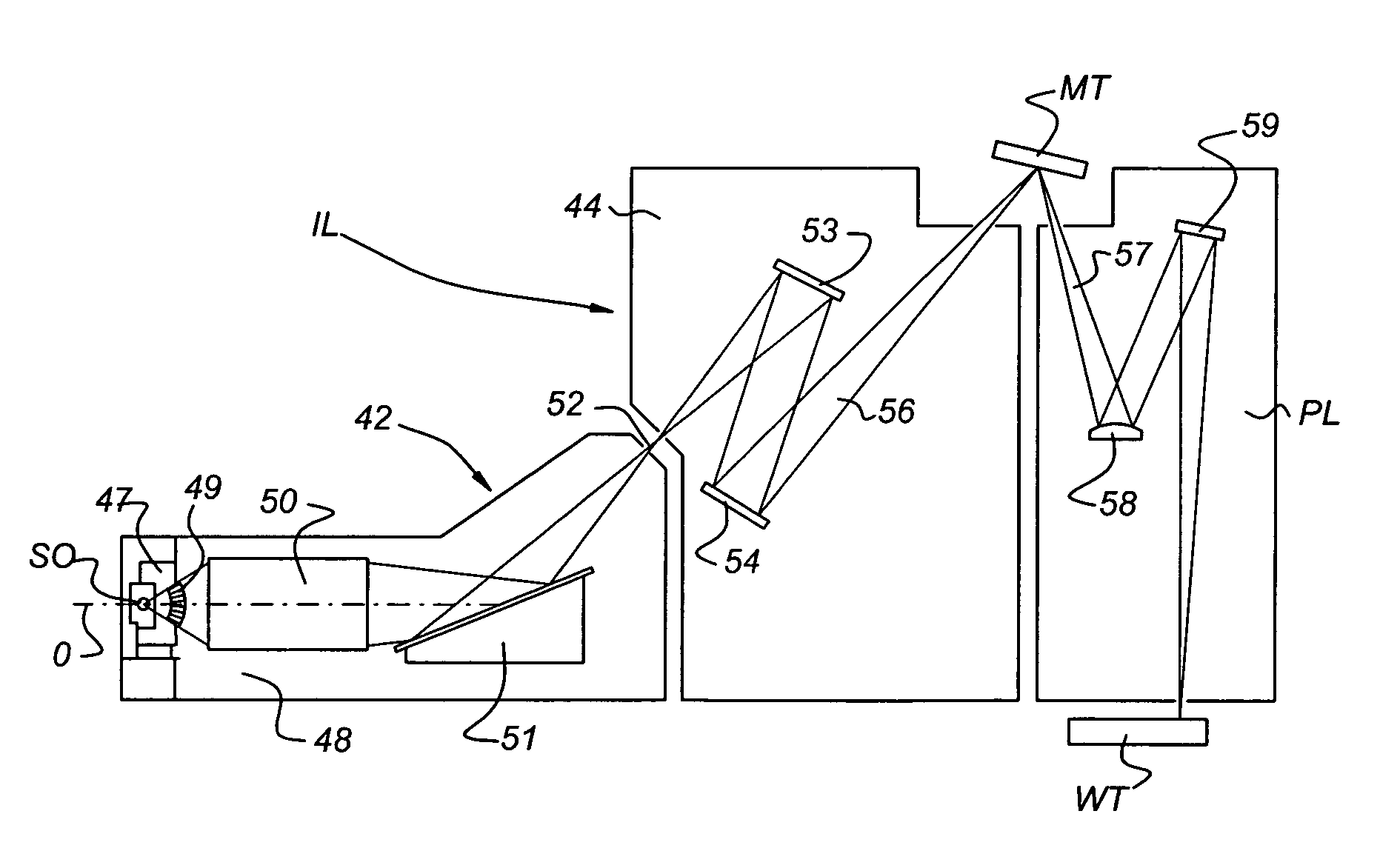
Method for the removal of deposition on an optical element, method for the protection of an optical element, device manufacturing method, apparatus including an optical element, and lithographic apparatus
ActiveUS20060072084A1Good removal effectFouling preventionRadiation/particle handlingEngineeringDeposition process
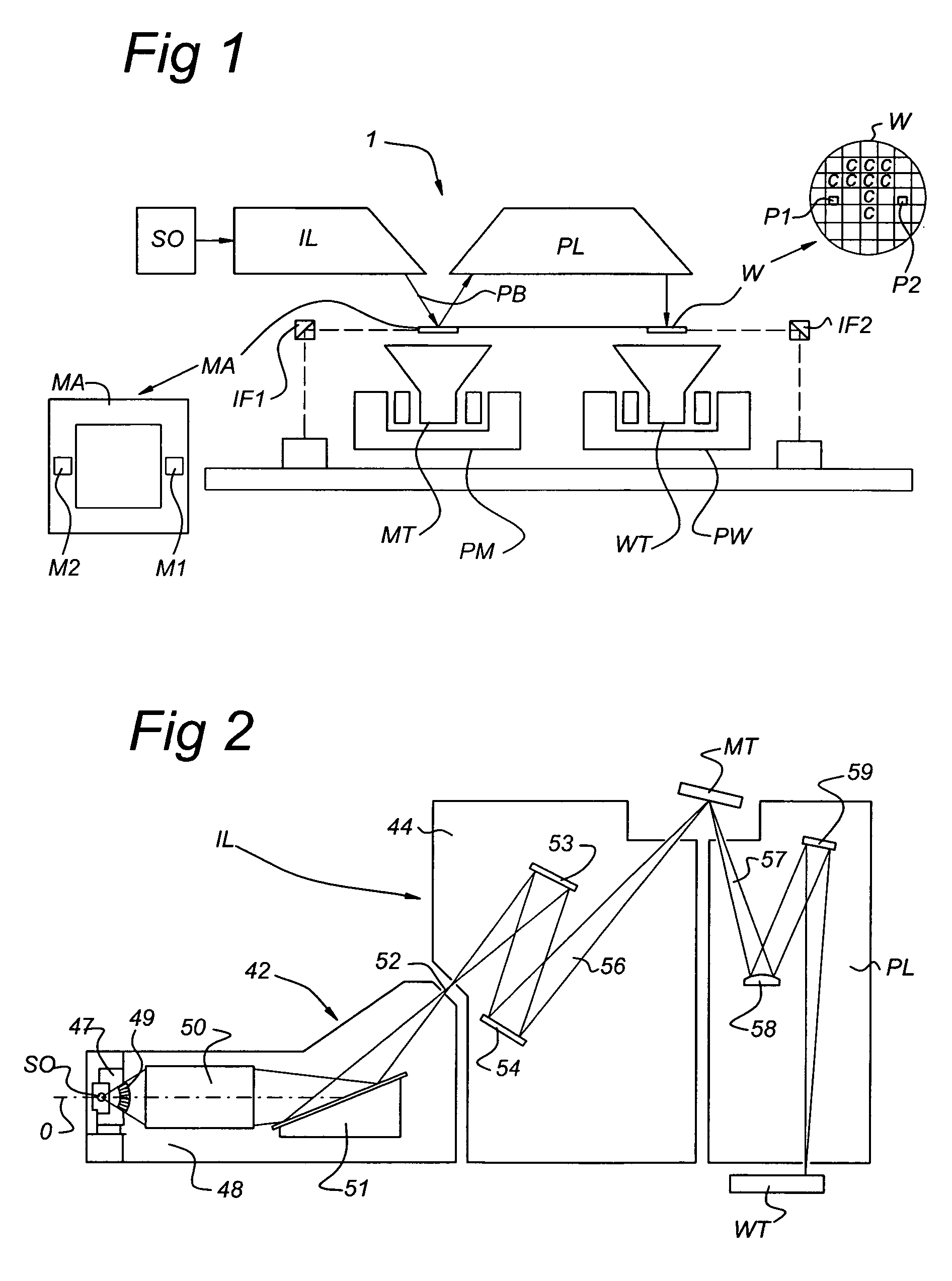
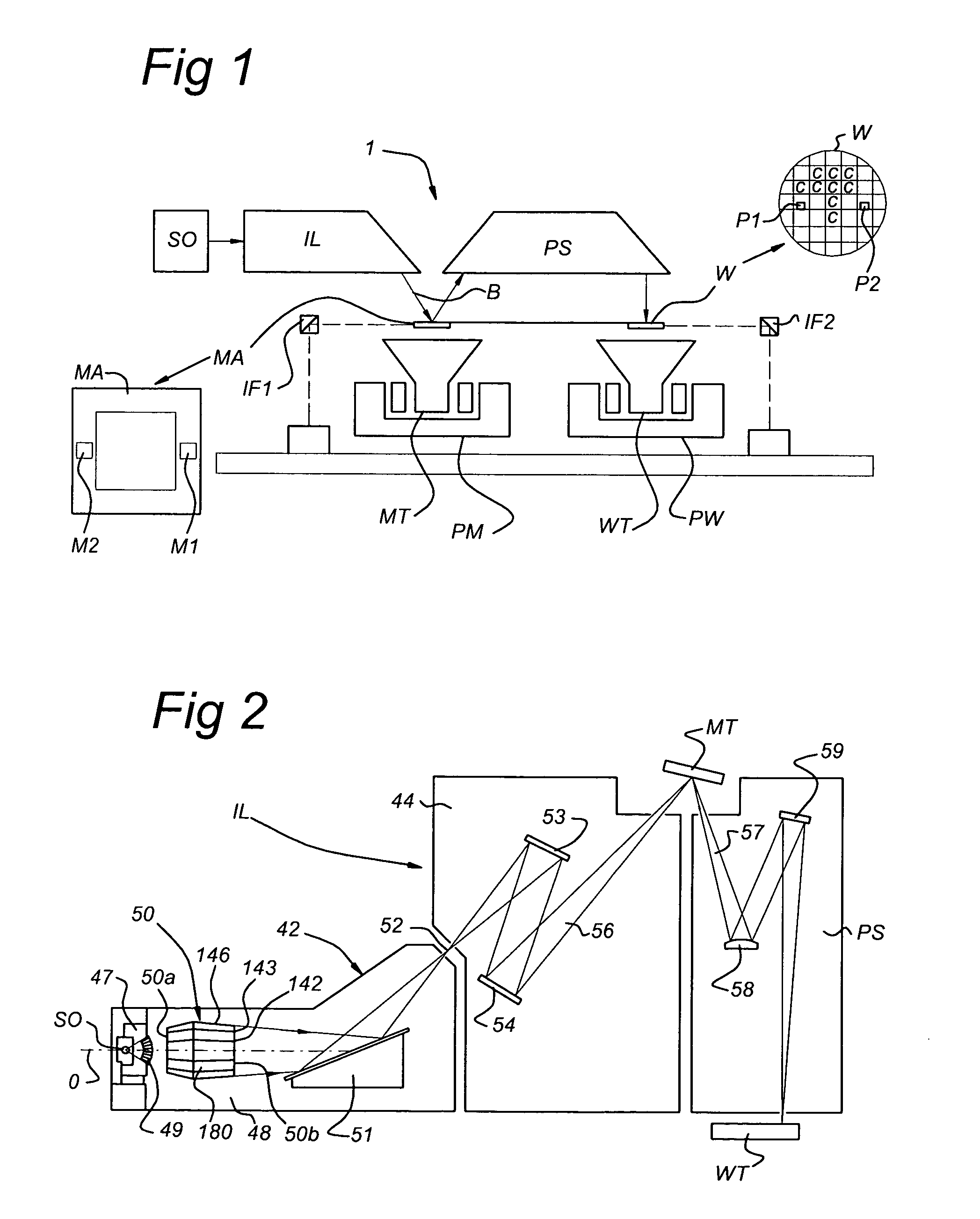
A method for the removal of a deposition on an optical element of an apparatus including the optical element includes providing an H2 containing gas in at least part of the apparatus includes producing hydrogen radicals from H2 from the H2 containing gas; and bringing the optical element with deposition into contact with at least part of the hydrogen radicals and removing at least part of the deposition. Further, a method for the protection of an optical element of an apparatus including the optical element includes providing a cap layer to the optical element by a deposition process; and during or after use of the apparatus, removing at least part of the cap layer from the optical element in a removal process as described above. The methods can be applied in a lithographic apparatus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
A method and apparatus for forming a high quality low temperature silicon nitride layer
InactiveCN1732288ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureNitrogen
A method of forming a silicon nitride layer is described. According to the present invention, a silicon nitride layer is deposited by thermally decomposing a silicon / nitrogen containing source gas or a silicon containing source gas and a nitrogen containing source gas at low deposition temperatures (e.g., less than 550 DEG C) to form a silicon nitride layer. The thermally deposited silicon nitride layer is then treated with hydrogen radicals to form a treated silicon nitride layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
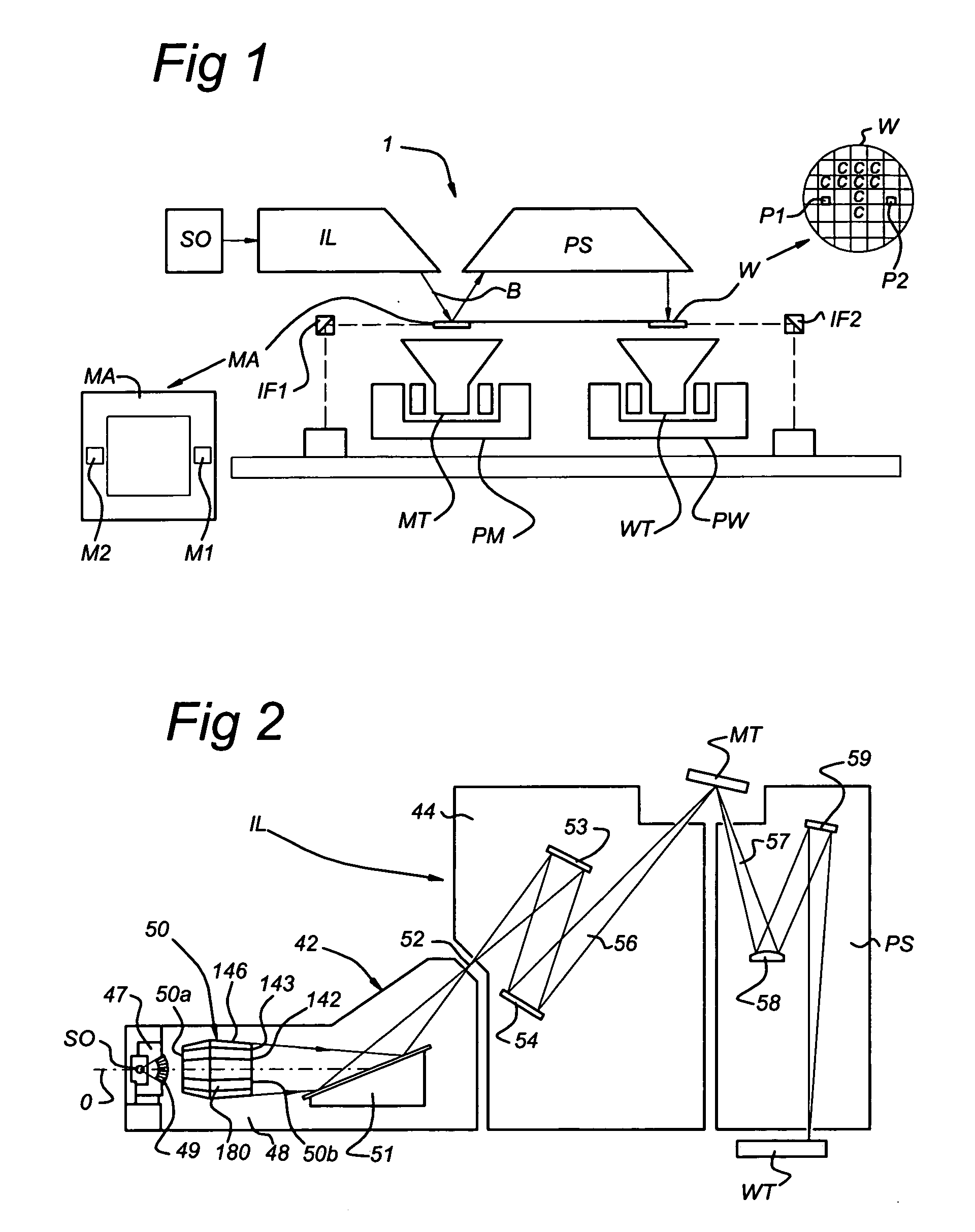
Lithographic apparatus including a cleaning device and method for cleaning an optical element
An EUV lithographic apparatus includes an EUV radiation source, an optical element and a cleaning device. The cleaning device includes a hydrogen radical source and a flow tube in communication with the hydrogen radical source. The cleaning device is configured to provide a flow of hydrogen radicals and the flow tube is arranged to provide a hydrogen radical flow at a predetermined position within the lithographic apparatus, for example for cleaning a collector mirror.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Implantable prostheses with improved mechanical and chemical properties
InactiveUS7083644B1Improved mechanical and chemical propertyImproved mechanical and thermal propertyBlood vesselsBiopolymerMechanical property
Prostheses with improved chemical and mechanical properties manufactured that includes a radiation resistant and hydrolytically stable biocompatible fabric having outer and first and second ends with a textile fabric that includes a naphthalene dicarboxylate derivative polymer having the general formula:wherein R1 and R3 are the same or different groups and are independently selected from the naphthalene dicarboxylate derivative repeating unit (I), a hydrogen radical and a methyl radical. R2 is an alkylene radical having 1 to 6 carbon atoms; n is from 10 to 200. Also contemplated are implantable prostheses that are flat constructions useful as patches and filters or tubular constructions useful as vascular grafts. A further aspect of this invention provides a method for making a radiation and thermal resistant and hydrolytically stable, steam sterilizable biocompatible prosthesis.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST +1
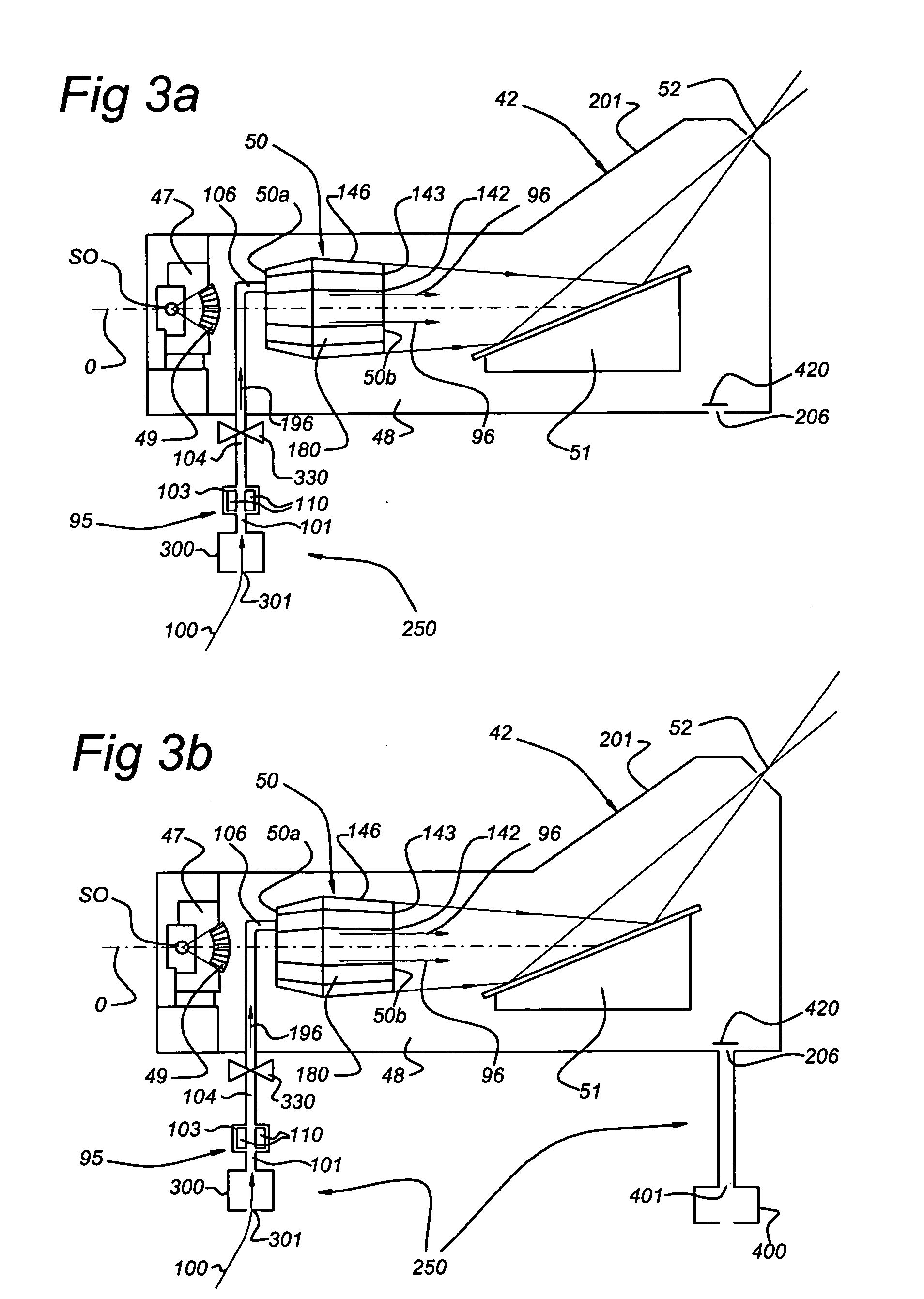
Method for cleaning a lithographic apparatus module, cleaning arrangement for a lithographic apparatus module and lithographic apparatus comprising the cleaning arrangement
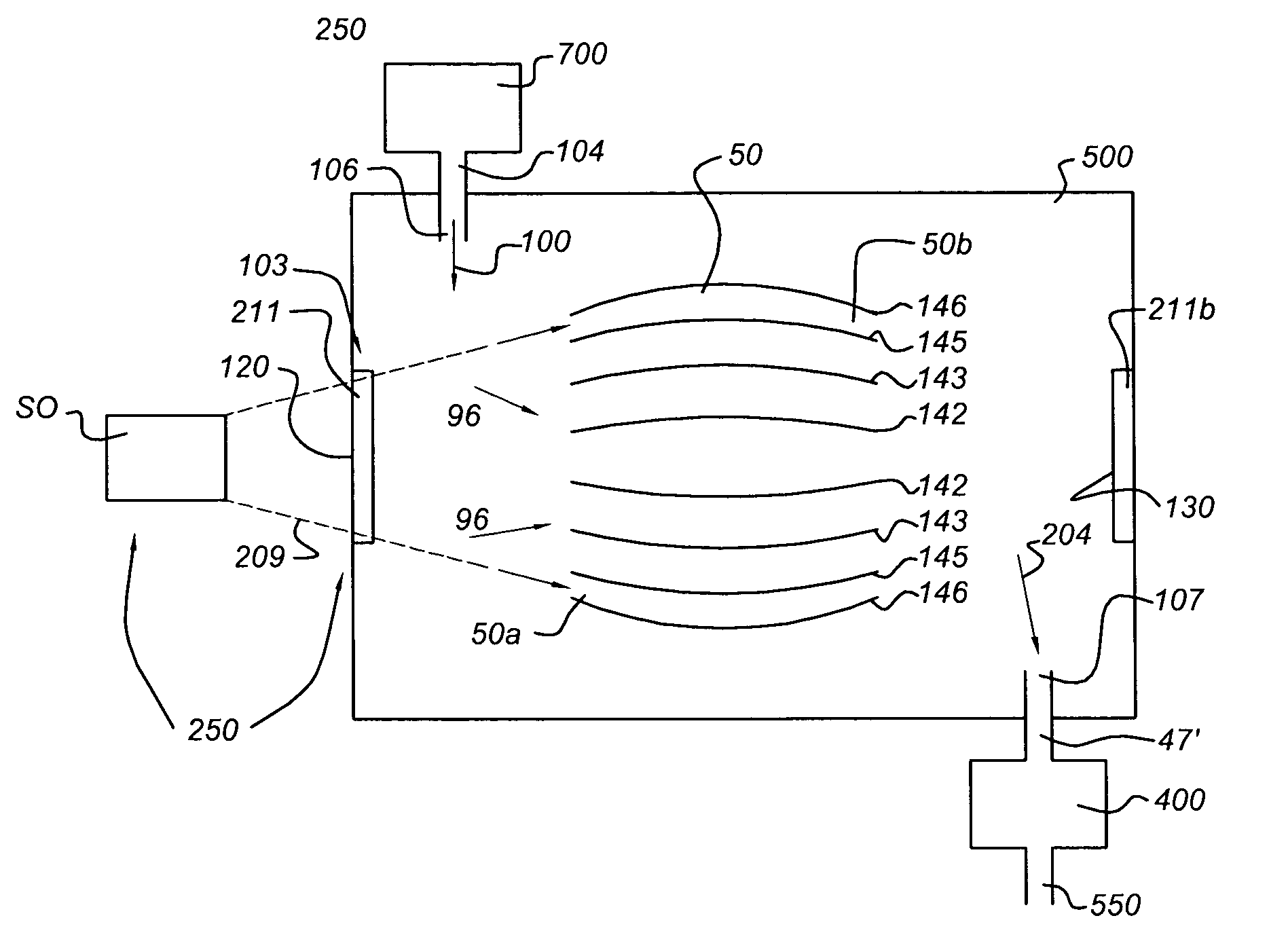
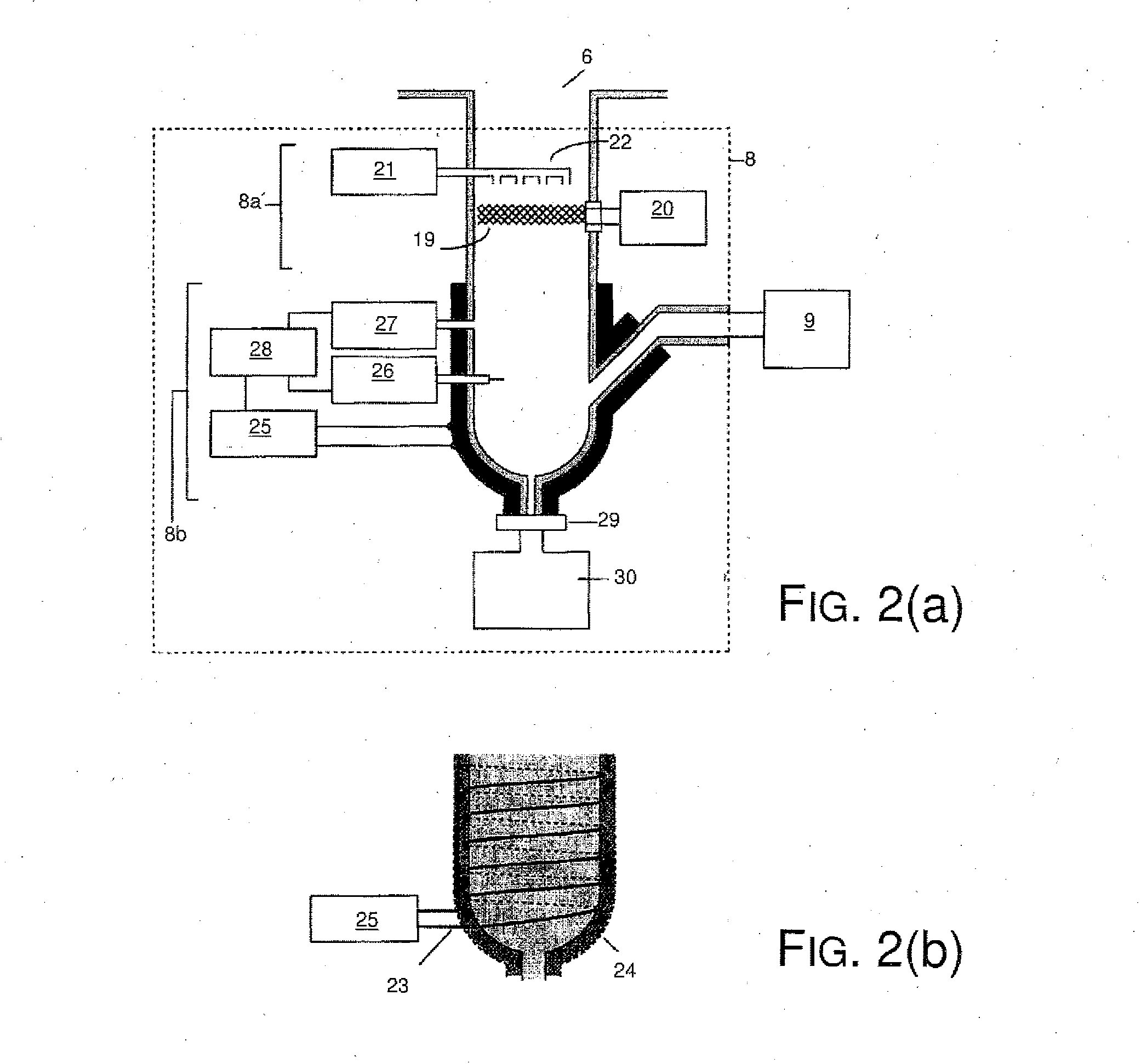
A cleaning arrangement for a lithographic apparatus module may be provided in a collector. The cleaning arrangement includes a hydrogen radical source configured to provide a hydrogen radical containing gas to at least part of the module and a pump configured to pump gas through the module such that a flow speed of the hydrogen radical containing gas provided through at least part of the module is at least 1 m / s. The cleaning arrangement may also include a gas shutter configured to modulate a flow of the hydrogen radical containing gas to at least part of the module, a buffer volume of at least 1 m3 in communication with the module, and a pump configured to provide a gas pressure in the buffer volume between 0.001 mbar (0.1 Pa) and 1 mbar (100 Pa). The cleaning arrangement may further include a gas return system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
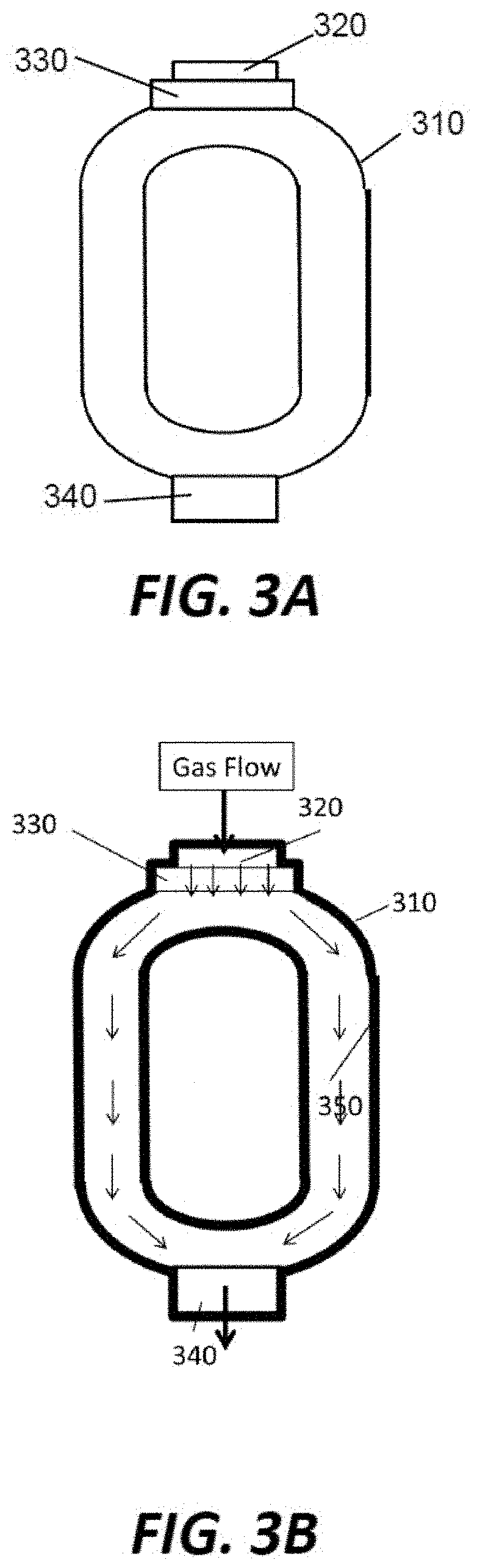
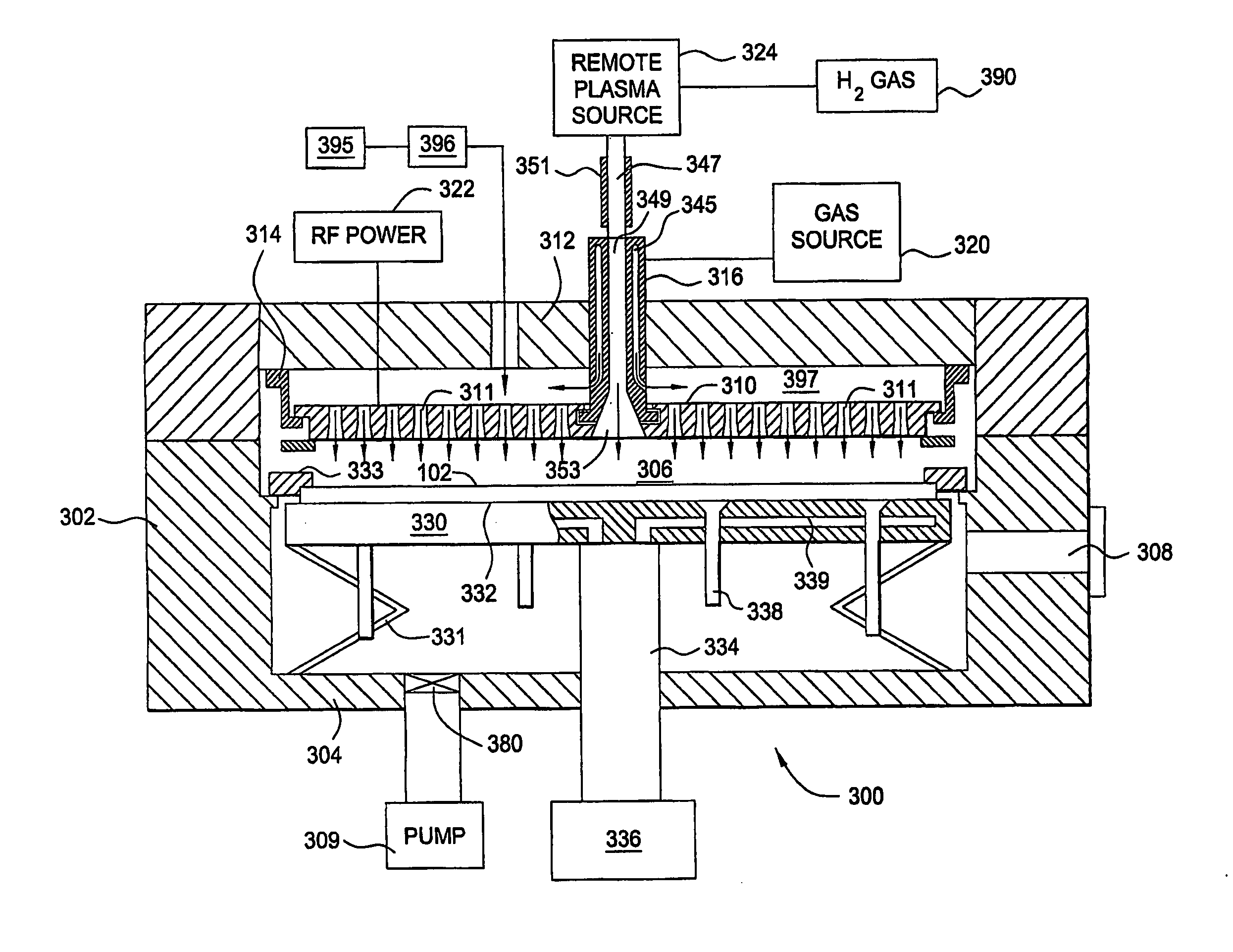
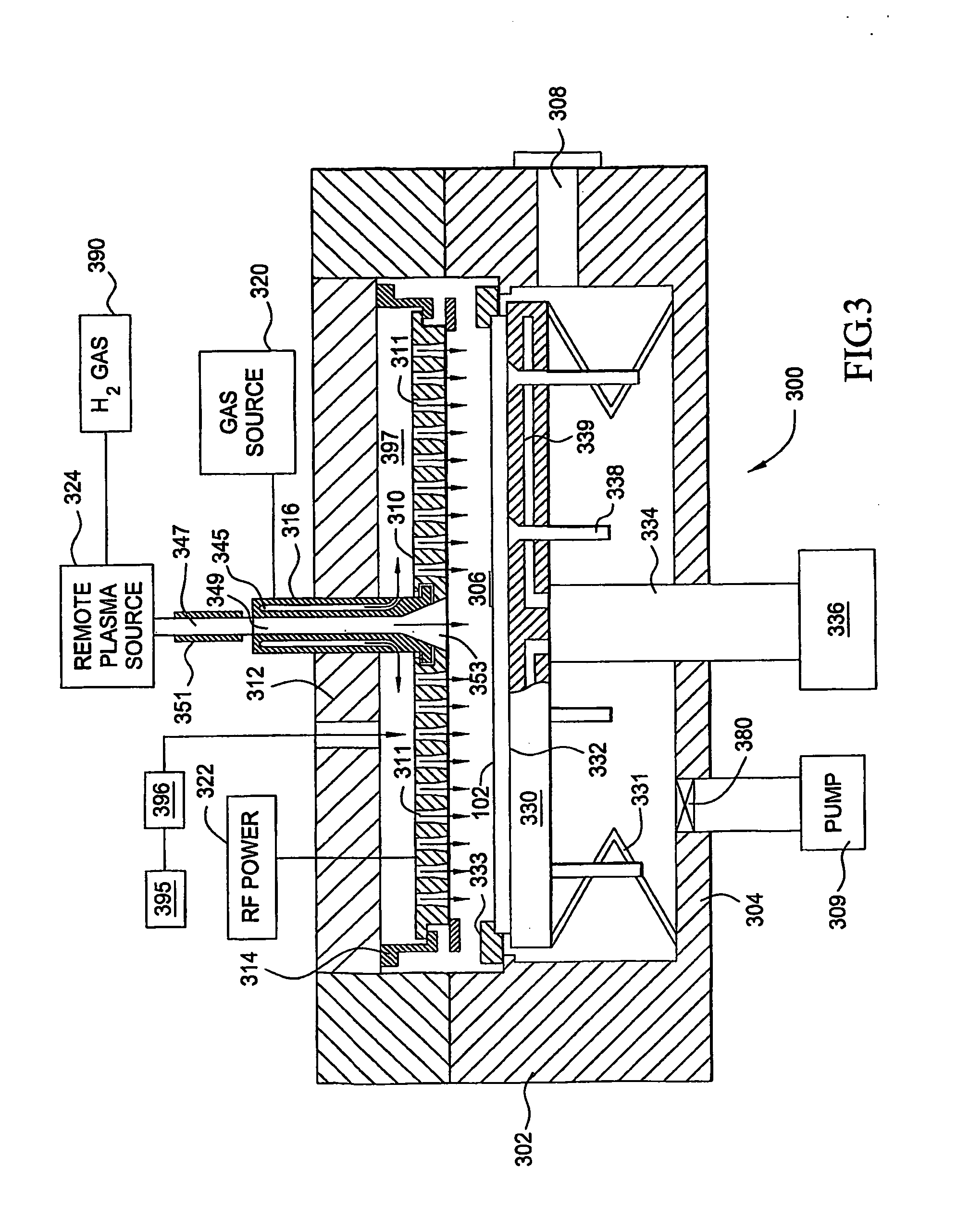
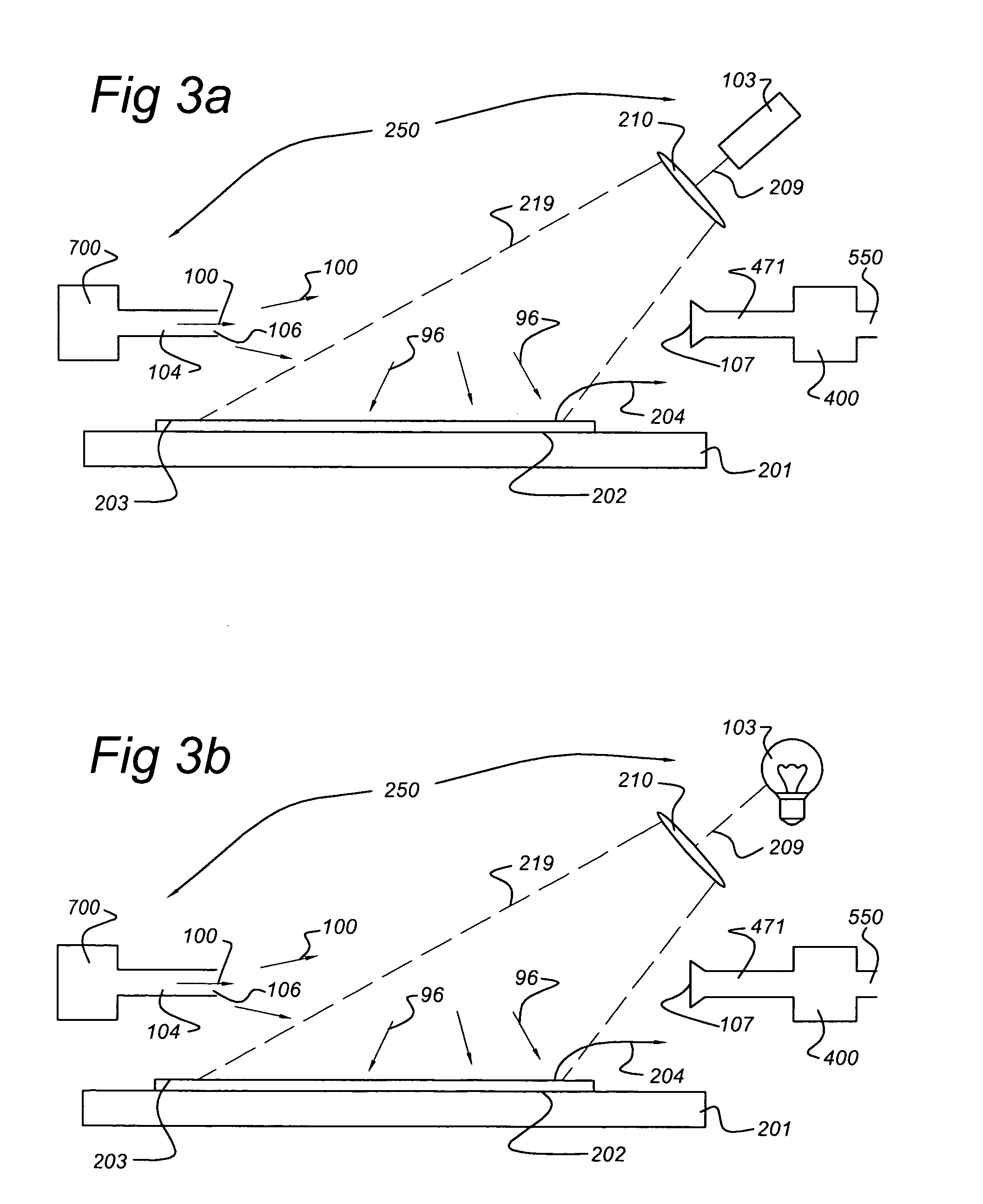
Water vapor passivation of a wall facing a plasma
InactiveUS7695567B2Easy to cleanHollow article cleaningVacuum evaporation coatingRemote plasmaWater vapor
A chamber passivation method particularly useful for hydrogen plasma cleaning of low-k dielectrics prior to coating a barrier layer into a via hole with hydrogen radicals are provided from a remote plasma source. For each wafer, the chamber is passivated with water vapor (or other gas even more chemabsorbed on plasma facing walls) passed through the remote plasma source prior to the ignition of the hydrogen plasma. The water vapor is absorbed on walls, such as alumina and quartz parts of the remote plasma source, and forms a protective mono-layer that endures sufficiently long to protect the walls during the generation of the hydrogen plasma. Thereby, the plasma facing walls, particularly of a dielectric such as alumina, are protected from etching.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for the removal of deposition on an optical element, method for the protection of an optical element, device manufacturing method, apparatus including an optical element, and lithographic apparatus
InactiveUS20070040999A1Good removal effectPhotomechanical apparatusElectrostatic cleaningSilane compoundsChemical compound
A method for the removal of a deposition on an optical element of an apparatus including the optical element includes providing an H2 containing gas and one or more additional compounds selected from the group of hydrocarbon compounds and silane compounds in at least part of the apparatus includes producing hydrogen radicals from H2 from the H2 containing gas; and bringing the optical element with deposition into contact with at least part of the hydrogen radicals and removing at least part of the deposition. Further, a method for the protection of an optical element of an apparatus including the optical element includes providing a cap layer to the optical element by a deposition process; and during or after use of the apparatus, removing at least part of the cap layer from the optical element in a removal process as described above. The methods can be applied in a lithographic apparatus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Lithographic apparatus comprising a cleaning arrangement, cleaning arrangement and method for cleaning a surface to be cleaned
InactiveUS20080001101A1Electrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotochemistryCarbon deposition
A cleaning arrangement is provided for use in an EUV lithographic apparatus, for example an EUV lithographic apparatus with a Sn source. The cleaning arrangement includes a gas source for a hydrogen containing gas and a hydrogen radical source. The hydrogen radical source is a source of (UV) radiation which induces photo dissociation of the hydrogen. Radicals may reduce Sn oxides (if present) and my form volatile hydrides of Sn deposition and / or carbon deposition. In this way the cleaning arrangement can be used to clean optical elements from Sn and / or C deposition. The EUV source may be used as hydrogen radical source. An optical filter is used to remove undesired EUV radiation and transmit desired UV radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Polyurethane with shape memory property, composition containing it and shape memory fabric prepared therefrom
ActiveCN1648143AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh transparencyFibre treatmentNon-woven fabricsCross-linkPolymer science
The said polyurethane is prepared through preparing polymer with diisocyanate, hydroxyl-containing oligomer, chain expander with active hydrogen radical and chain expander with carboxylic radical, neutralizer with alkali radical, blocking agent, cross-linking agent and optional catalyst in certain proportion; and subsequent reaction in water to obtain polymer. The polyurethane features the blocking diisocyanate radical and hydroxyl radical and thus shape converting temperature of -30 deg.c to 100 deg.c. In temperature higher than the shape converting temperature, the polyurethane may have its shape converted; in temperature lower than the shape converting temperature, the polyurethane is unchanged in shape; and the polyurethane heated to the temperature higher than the shape converting temperature will restore original shape.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
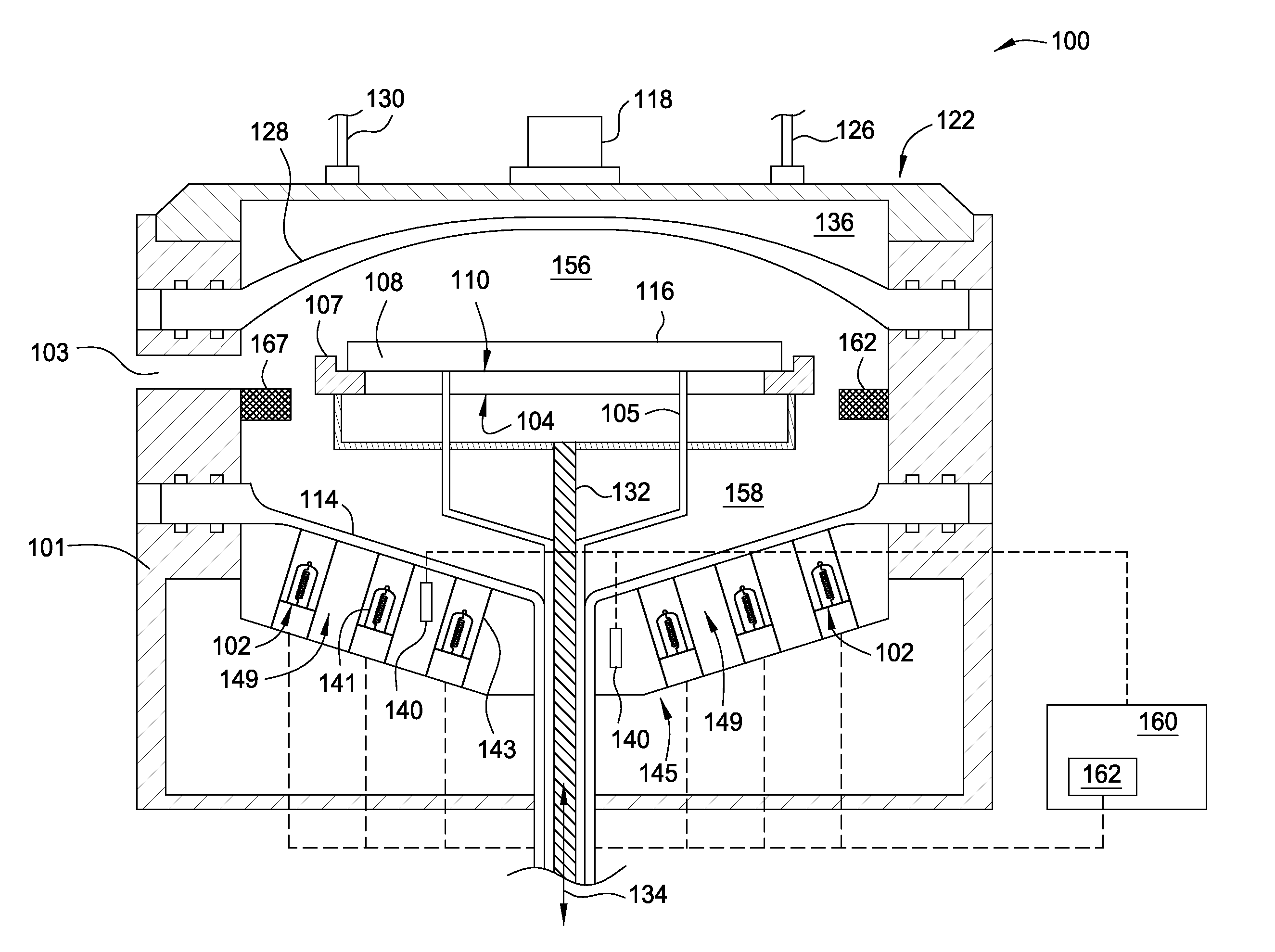
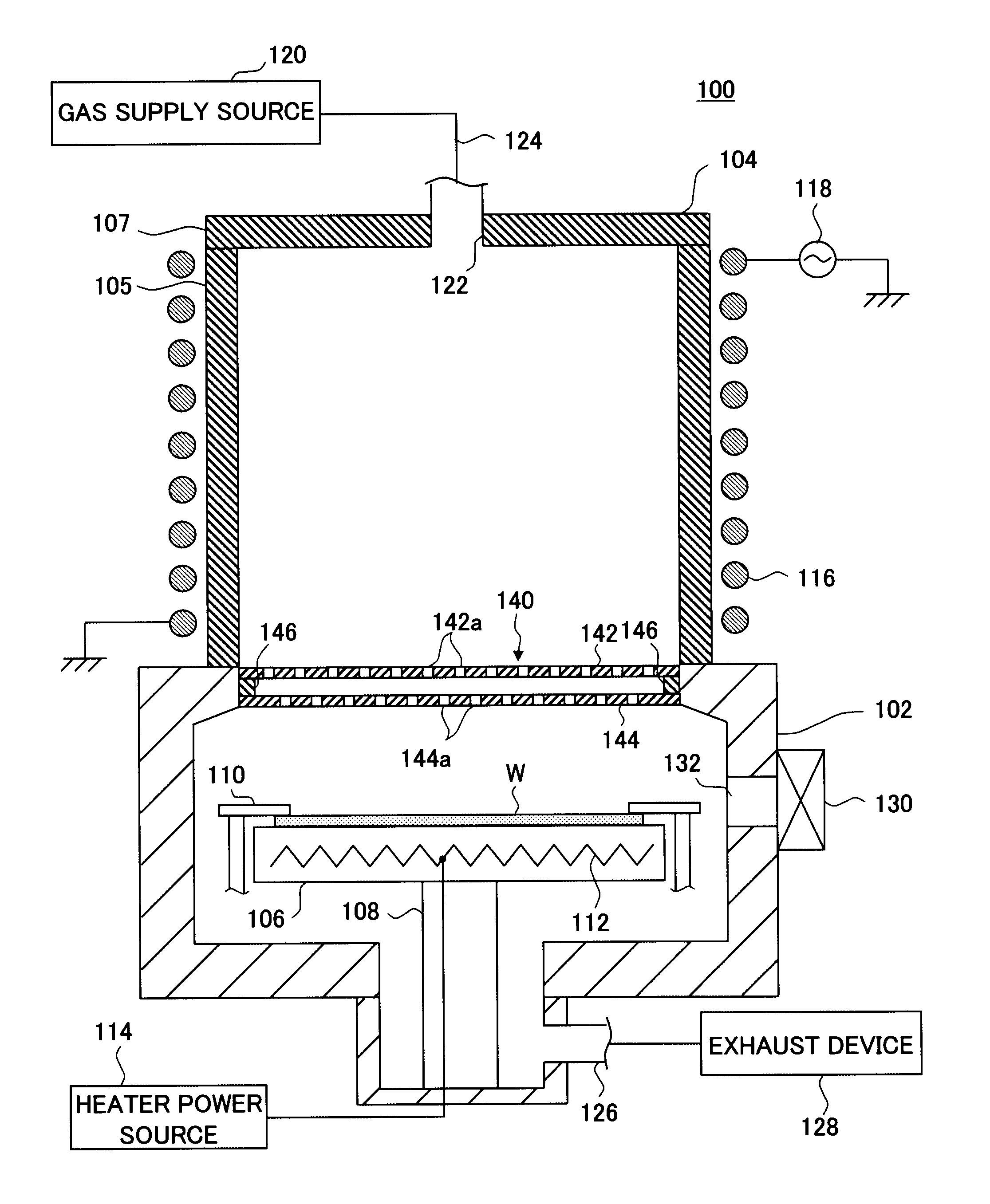
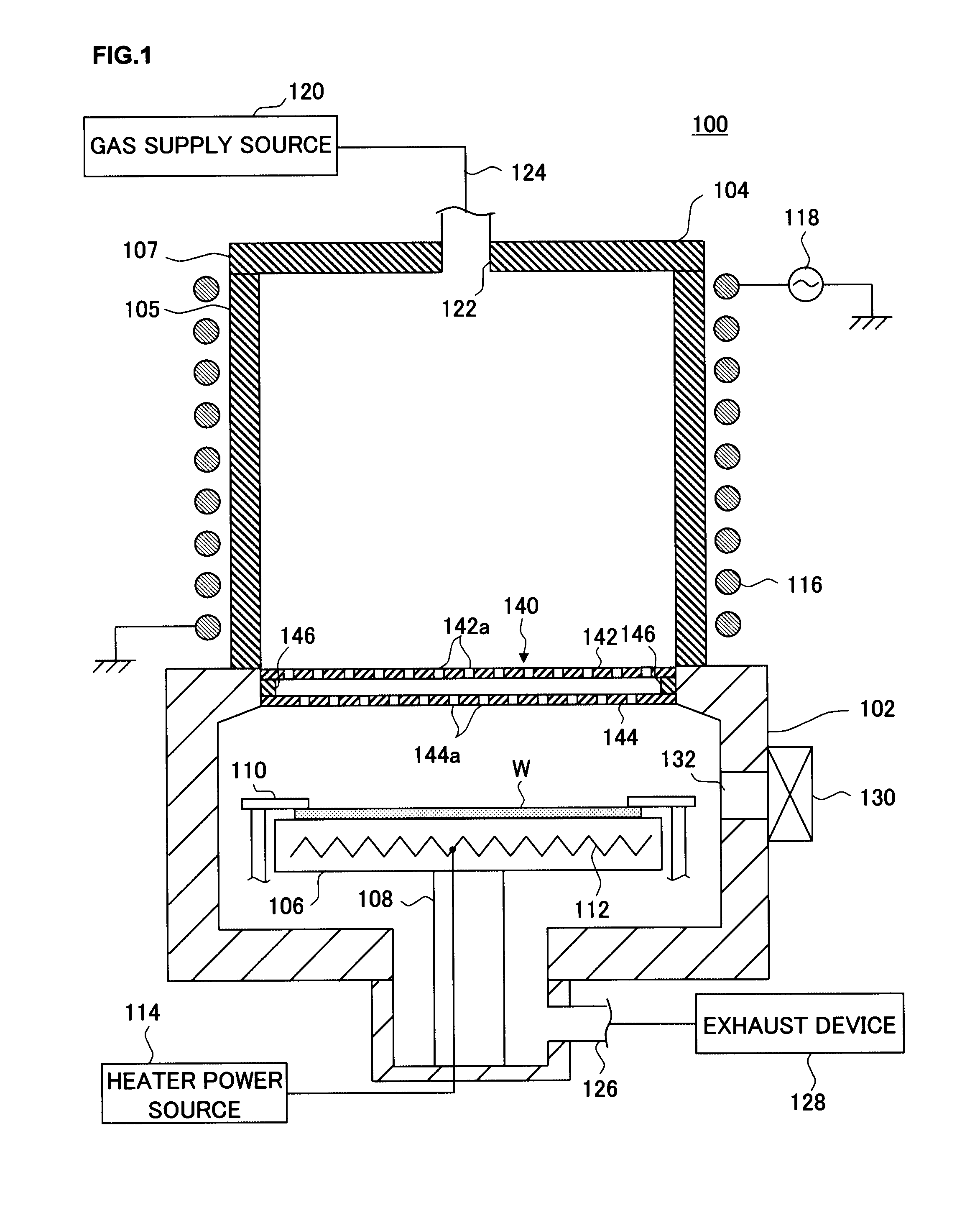
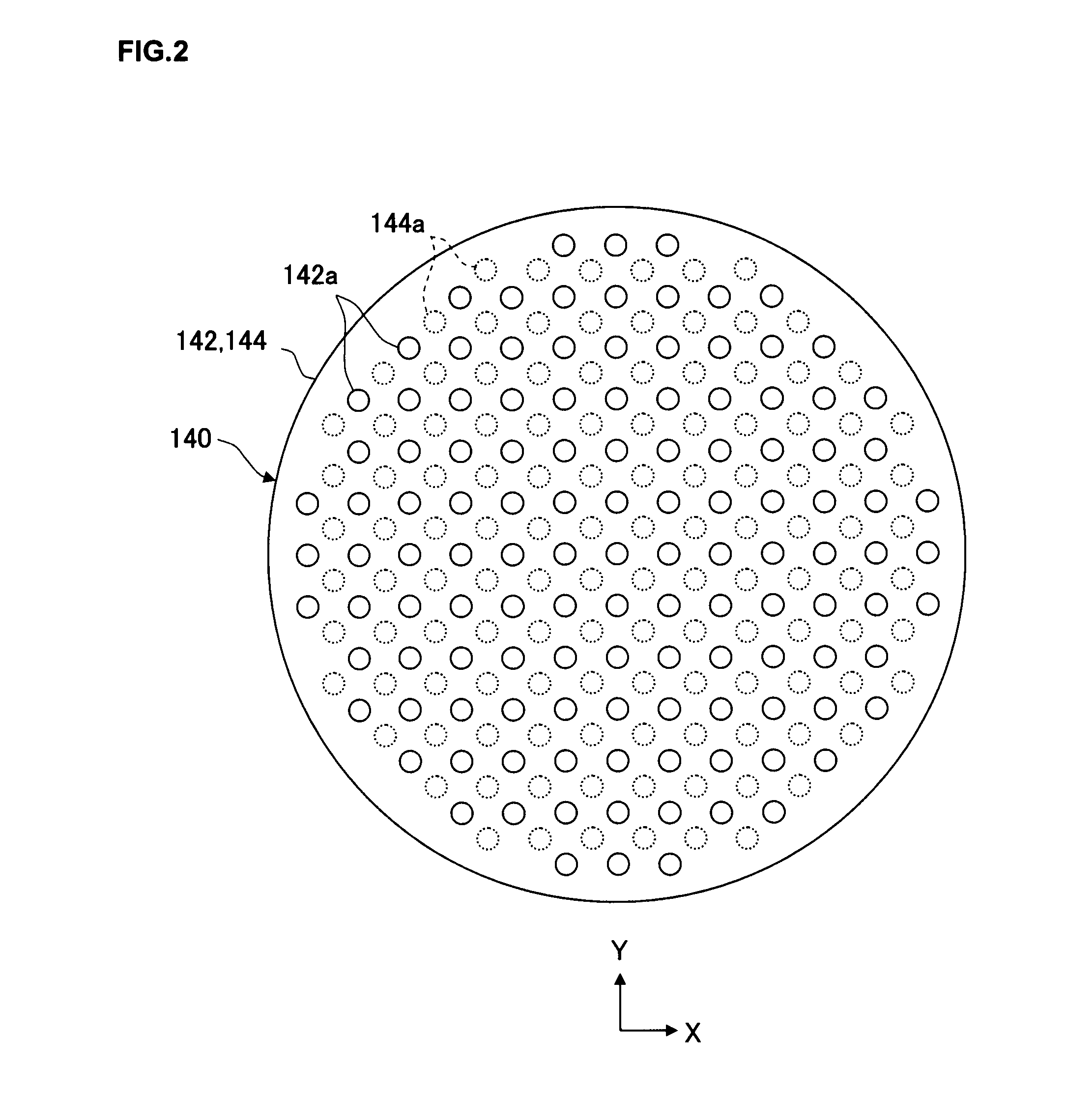
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20090008034A1Improve reliabilityEffectively preventing entry of scattered metal ionsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltraviolet lightsEngineering
A plasma generation chamber and a processing chamber are isolated from each other by a barrier wall member disposed between them. The barrier wall member includes two plate members and stacked one on top of the other over a gap, a plurality of through holes and, via which hydrogen radicals are allowed to pass, are respectively formed at the plate member and the plate member. The through holes at one plate member are formed with an offset relative to the through holes formed at the other plate member and the plate members are both constituted of an insulating material that does not transmit ultraviolet light.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Organopolysilozane compositions crosslinkable with elimination of alcohols to give elastomer
InactiveUS6254811B1Easy to useLow modulusSilicon organic compoundsBuilding repairsPhosphoric Acid EstersElastomer
Alkoxy RTV-1 compositions comprise the product of the reaction of(A) an HO-terminated organopolysiloxane,(B1) an alkoxysilane which has at least three alkoxy groups and / or its partial hydrolysates, and(B2) an alkoxysilane which has two alkoxy groups and / or its partial hydrolysates, in the presence of(C) an acid phosphoric ester of the general formula (I)wherea is 1 or 2,R1 and R2 are a hydrogen radical, methyl radical or hydroxyl radical,b and d are 2 or 3,c is an integer from 2 to 15,e is 0 or 1L comprises a radical -O-, -COO-, -OOC-, -CONR3-, -NR4CO- or -CO-,R3 and R4 are a hydrogen radical or C1-C10-alkyl radical, andM is a monovalent, unsubstituted or hydroxyl-, fluorine-, chlorine-, bromine-,C1-C10-alkoxyalkyl- or cyano-substituted C1-C20-hydrocarbon radical, with the proviso that on any given carbon atom not more than one radical R1 and R2 may be a hydroxyl radical.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Base method treating method and electron device-use material
InactiveUS20040235311A1Effectively terminateImprove film qualityTransistorSolid-state devicesNitrogenElectric properties
A method of processing a for an electronic device, comprising, at least: a nitridation step (a) of supplying nitrogen radicals on the surface of the electronic device substrate, to thereby form a nitride film on the surface thereof; and a hydrogenation step (b) of supplying hydrogen radicals to the surface of the electronic device substrate. By use of this method, it is possible to recover the degradation in the electric property of an insulating film due to a turnaround phenomenon which can occur at the time of nitriding an Si substrate, etc.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Device for producing extreme UV radiation
ActiveUS20070018119A1Avoid depositionEasy maintenanceRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsLiquid stateUltraviolet
An extreme UV radiation producing device in which adhesion of solid tin in the vacuum pump of an evacuation device is restricted, so that the maintenance period and the replacement period of the pump is prolonged is achieved by the provision of a treatment unit between a radiation source chamber and the evacuation device. The treatment device has a hydrogen radical producing part in which tin and / or a tin compound in the evacuated gas from the radiation source chamber is / are made into a tin hydride; and a heat treatment part in which the tin hydride is thermally decomposed and in which the tin produced liquefied and separated from the evacuated gas. The liquid tin is fed into a collecting / storage vessel and the evacuated gas from which the tin and / or a tin compound has been removed fed to the evacuation device.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com