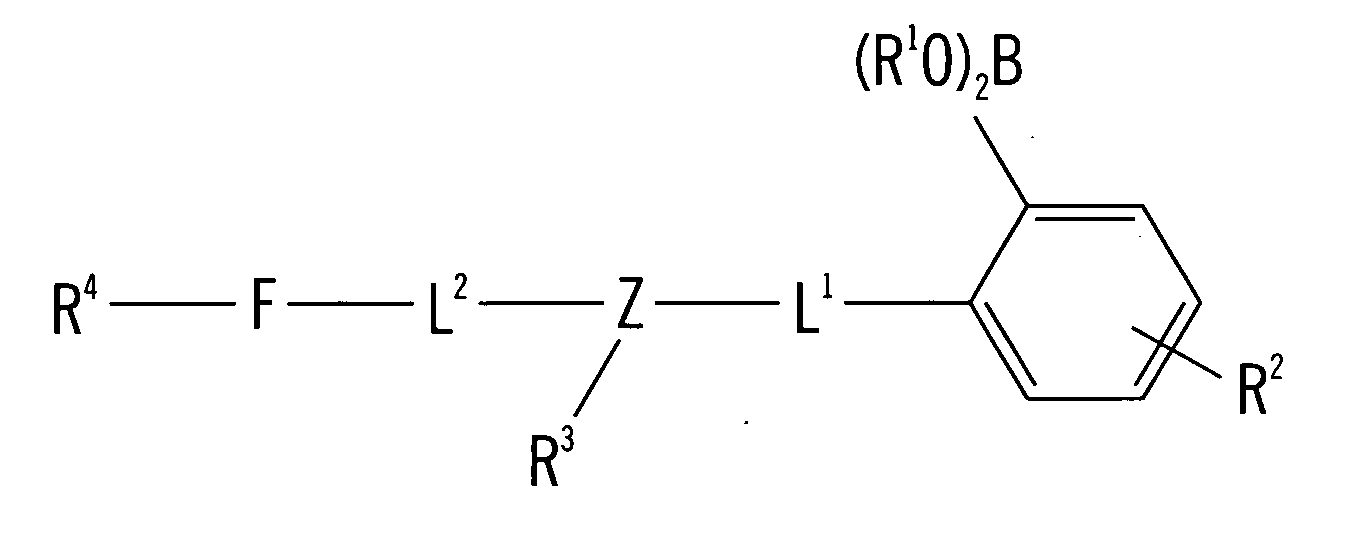
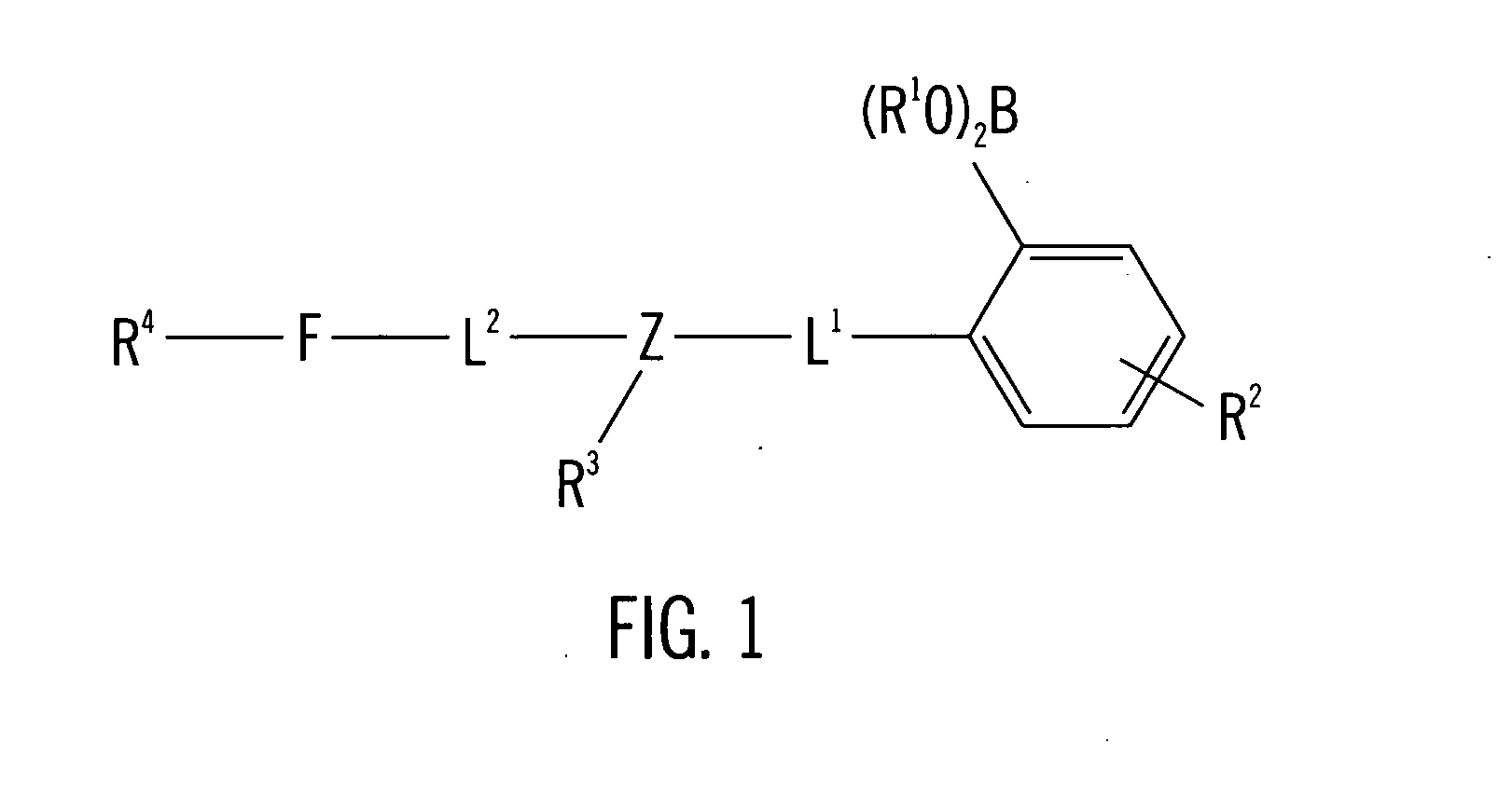
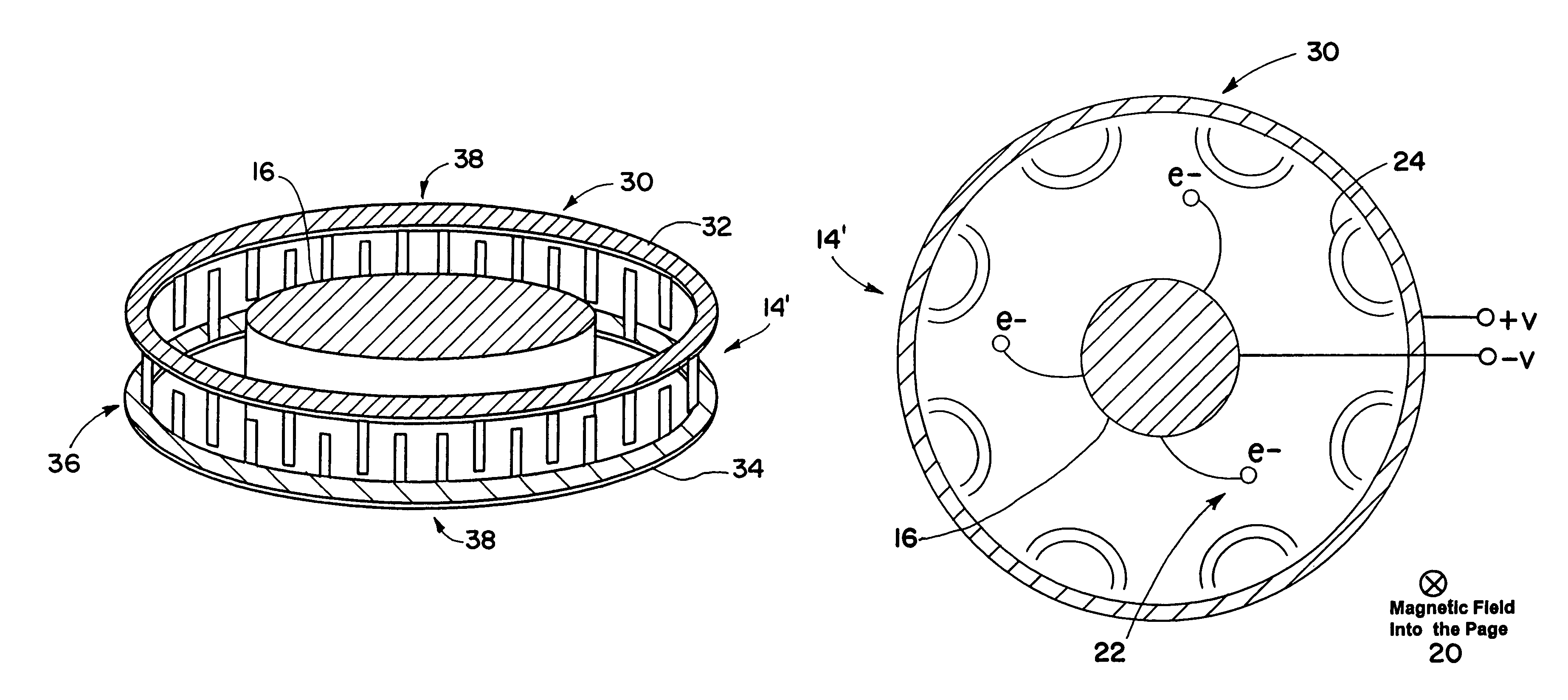
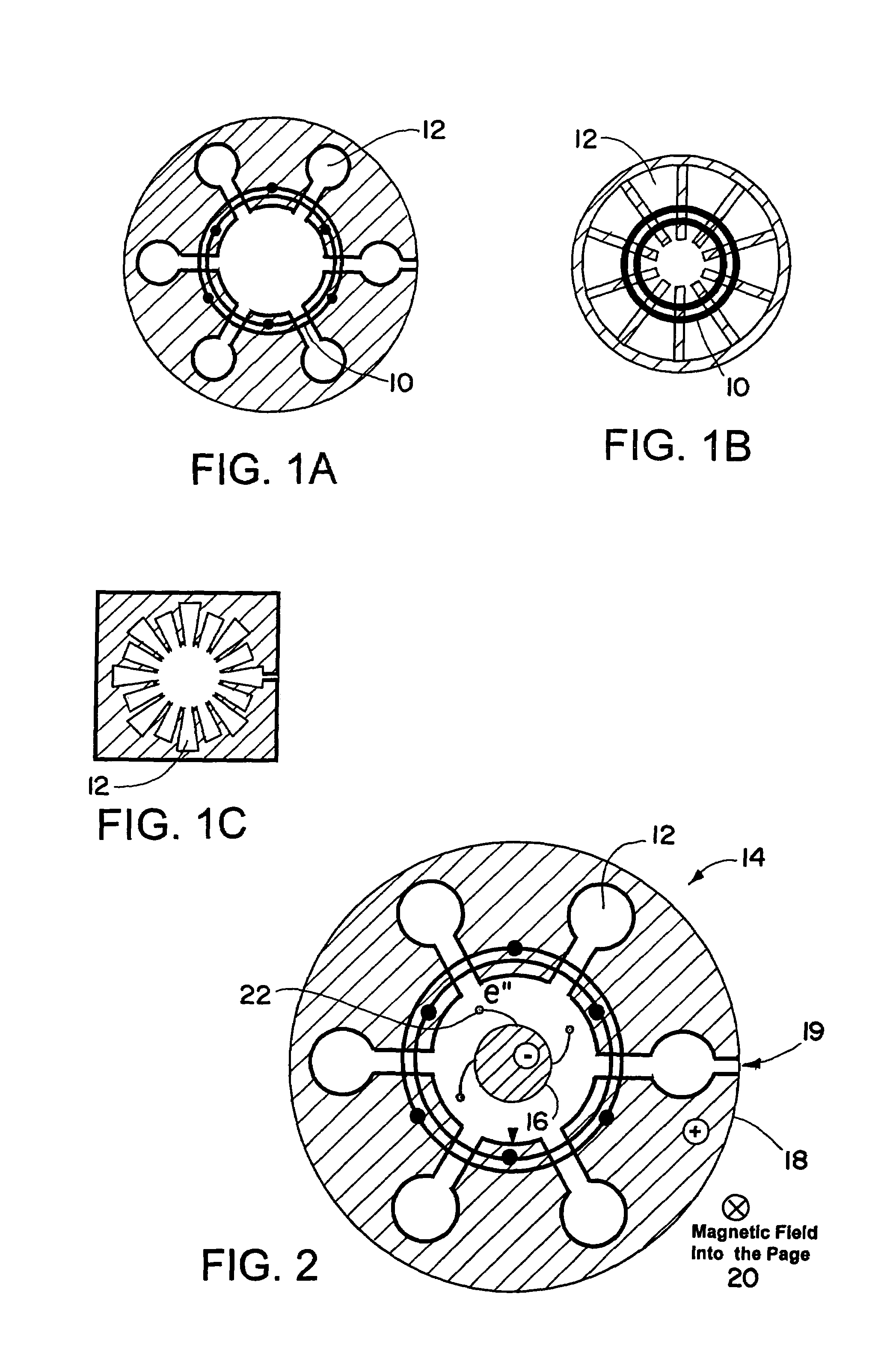
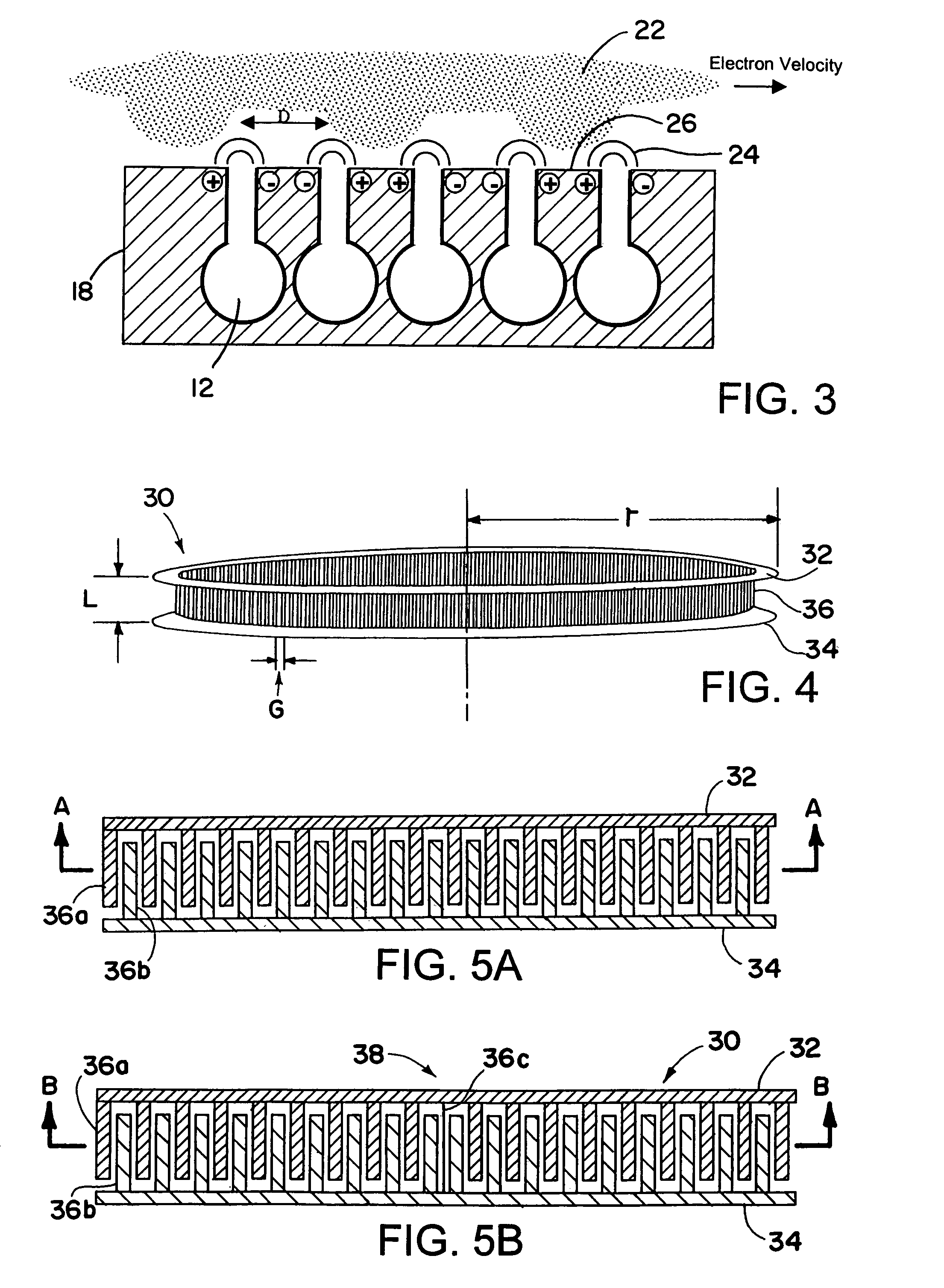
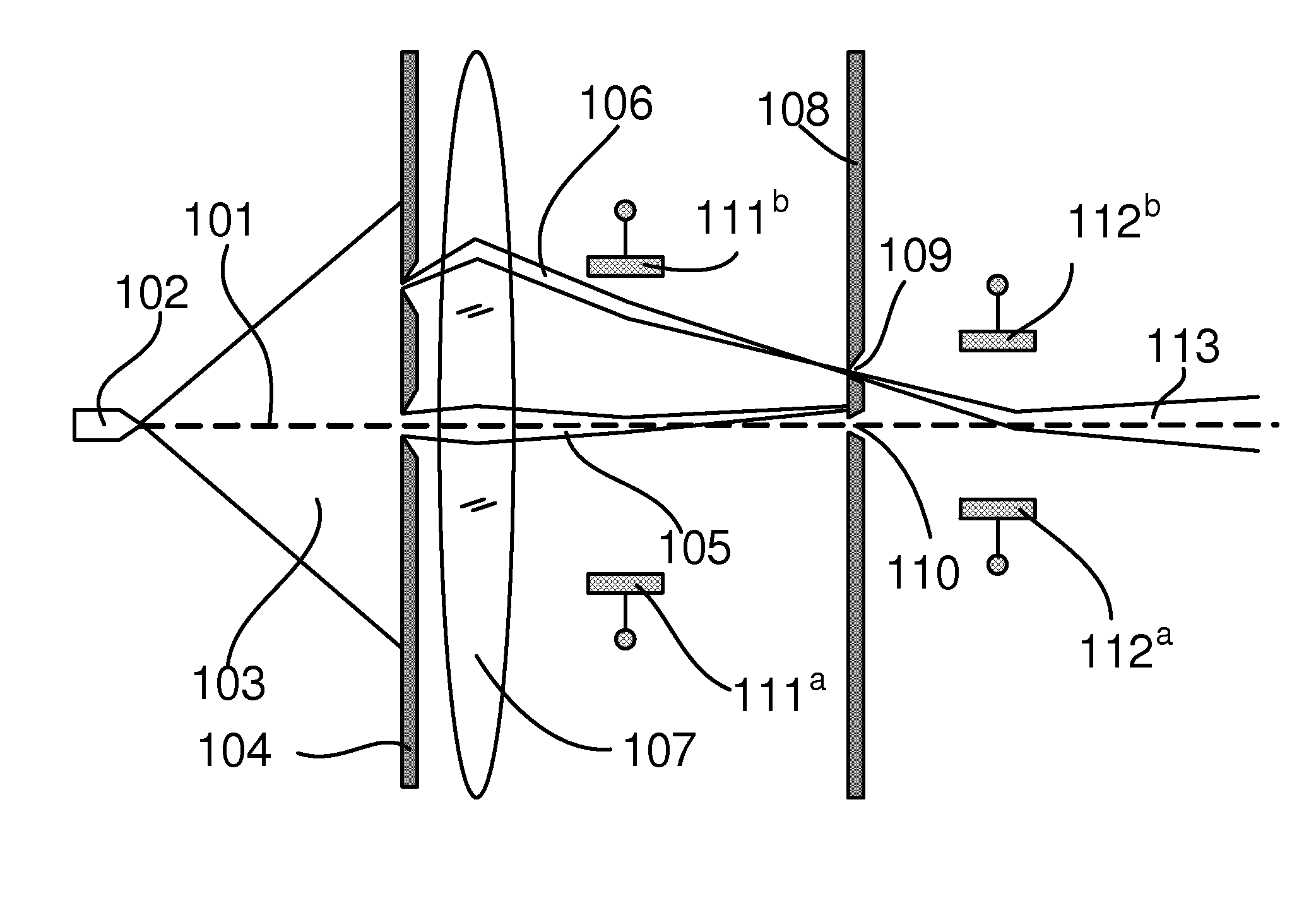
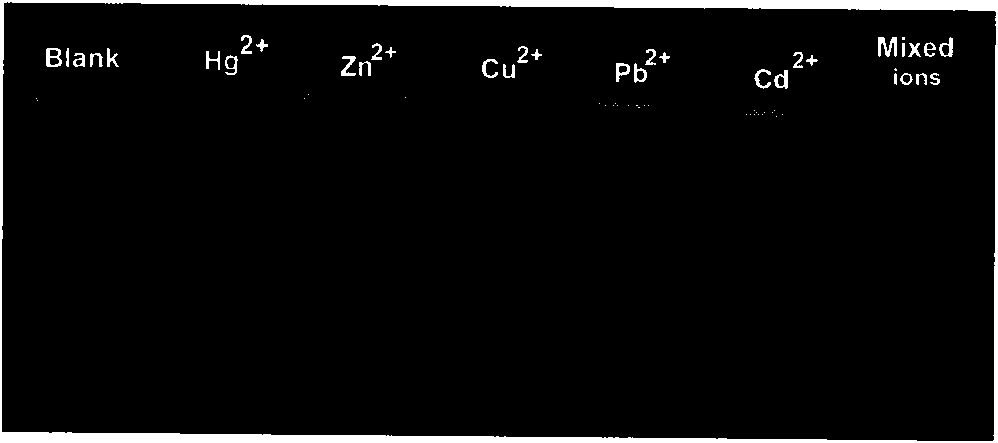Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
92 results about "Electron interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The interacting electron is known as the incident electron. Incident electrons may interact with: The nucleus of an atom. The orbital electrons of an atom.
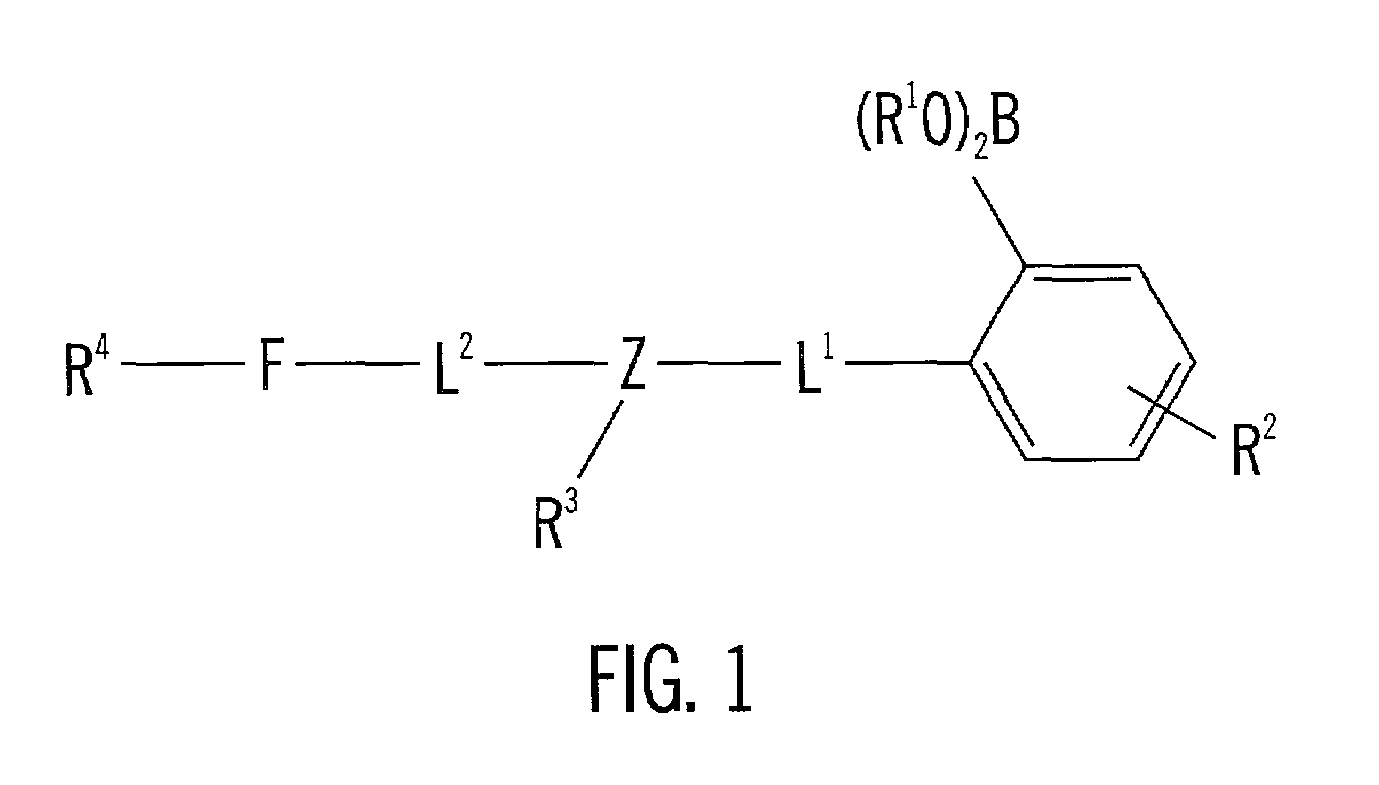
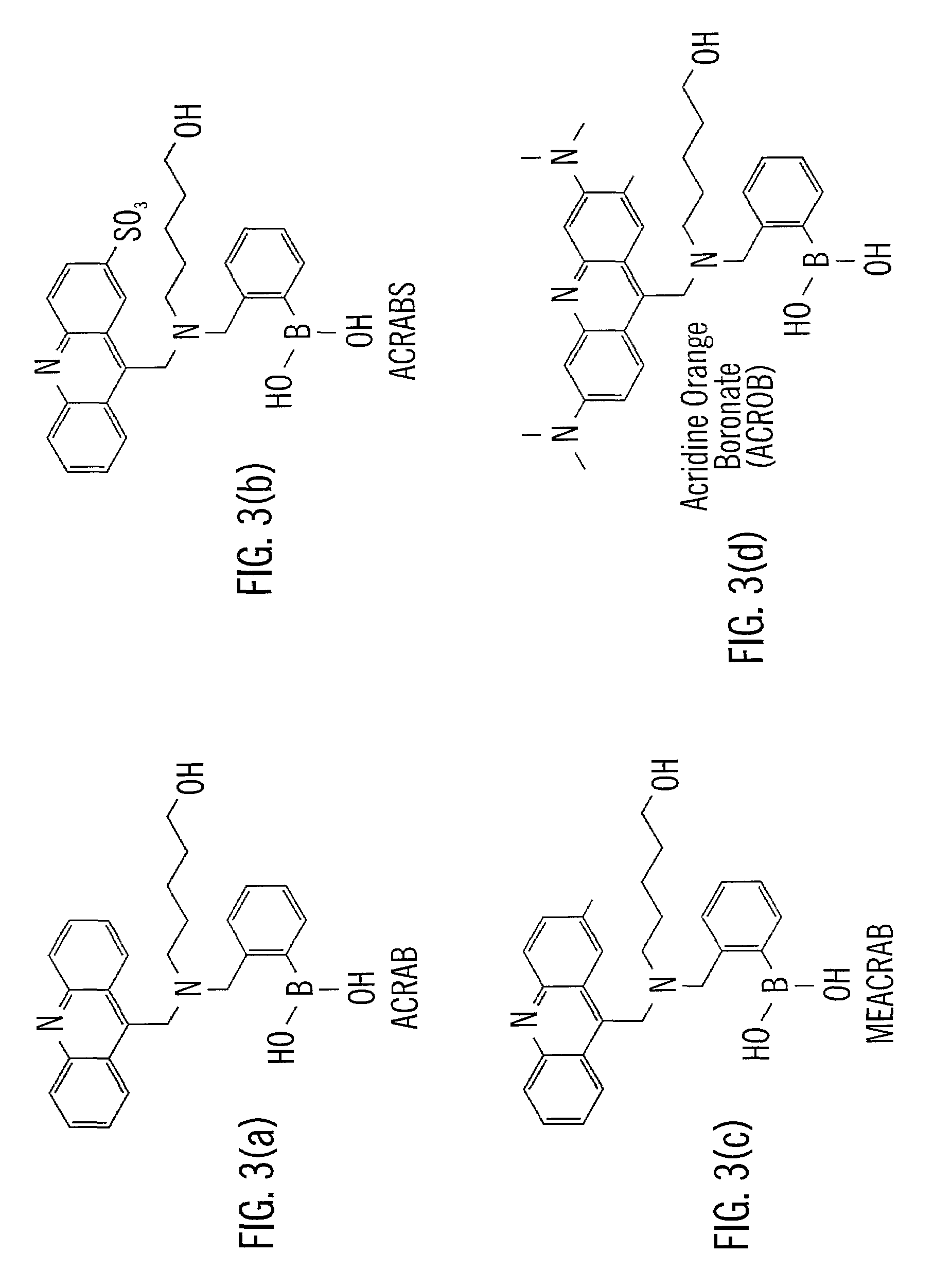
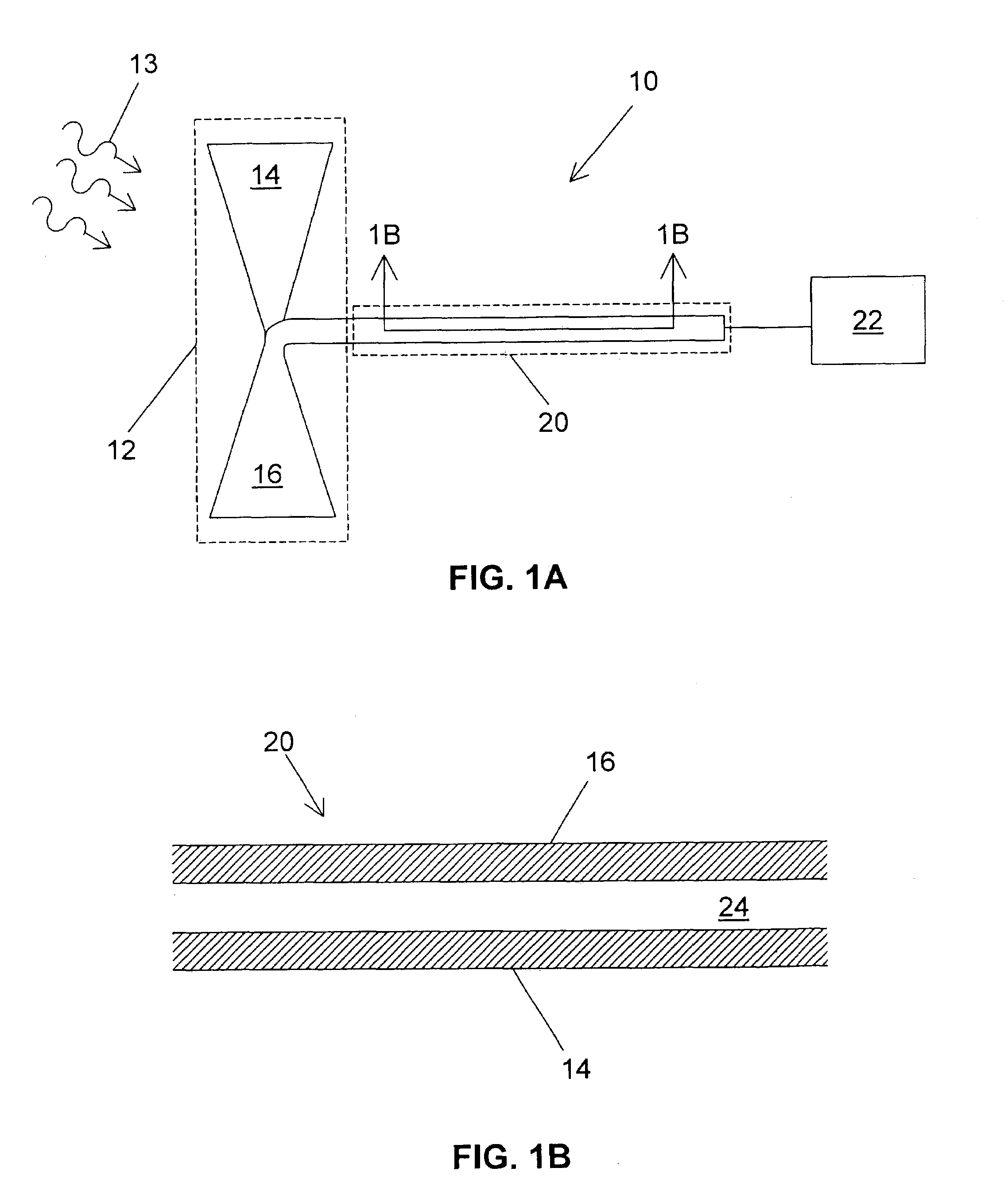
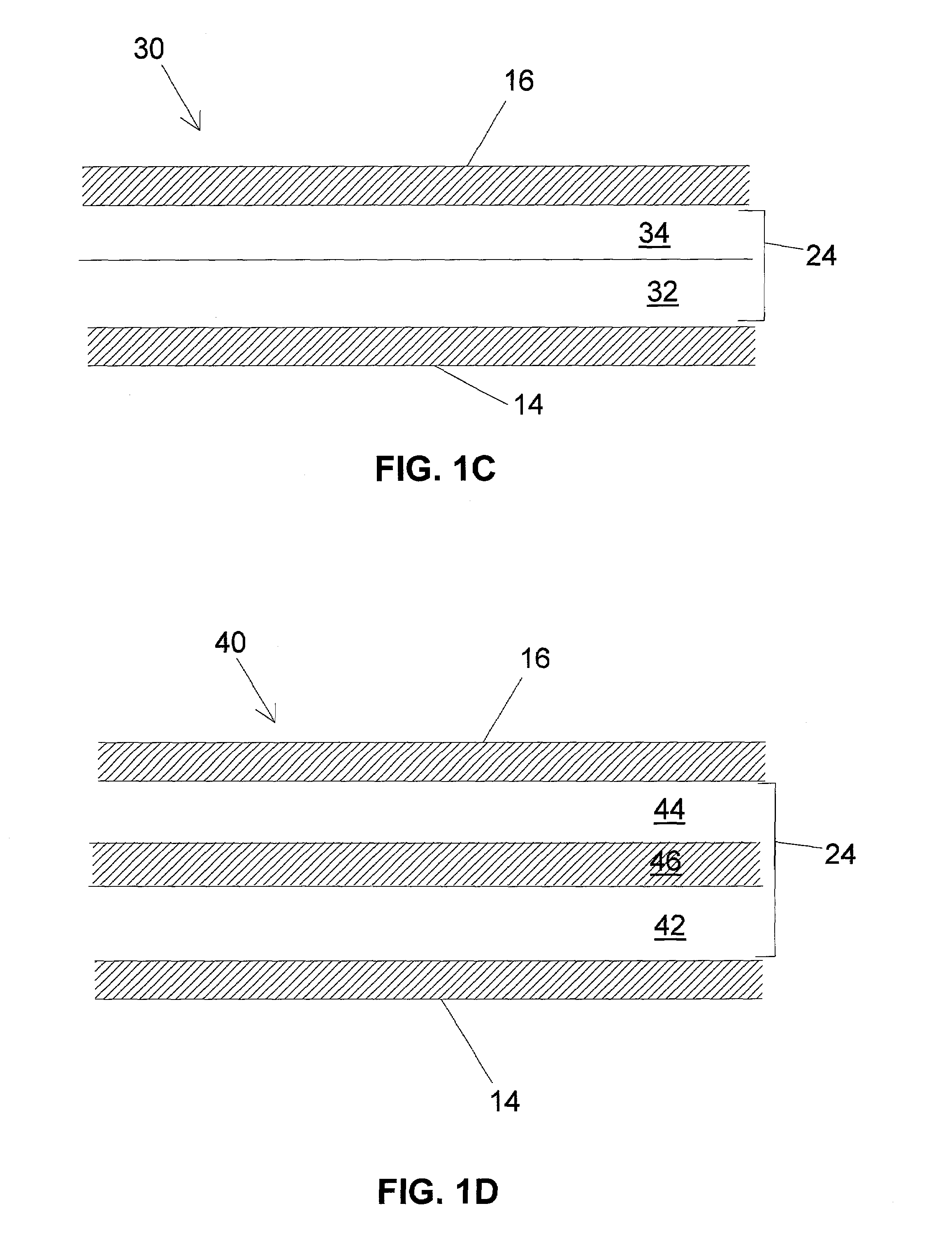
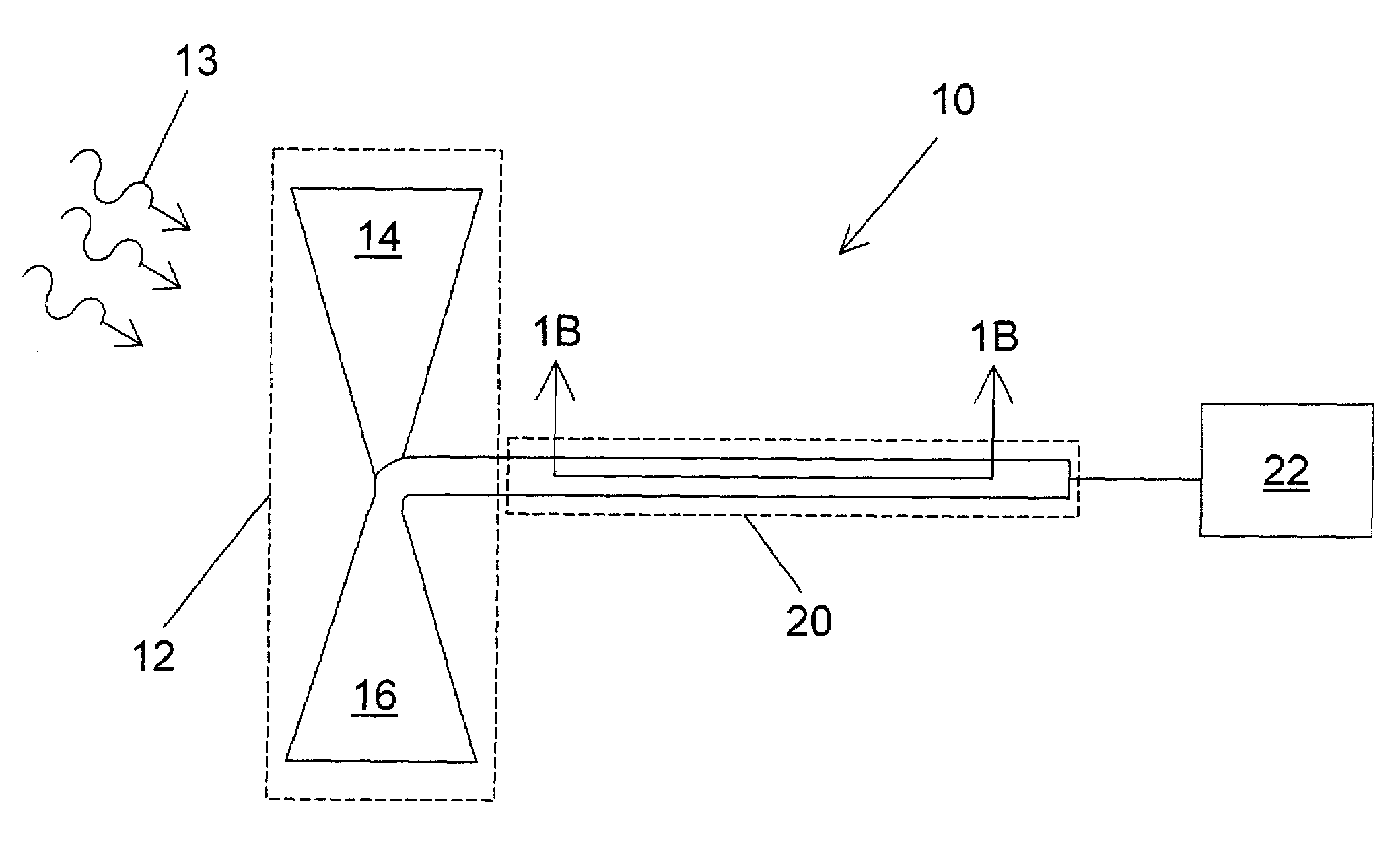
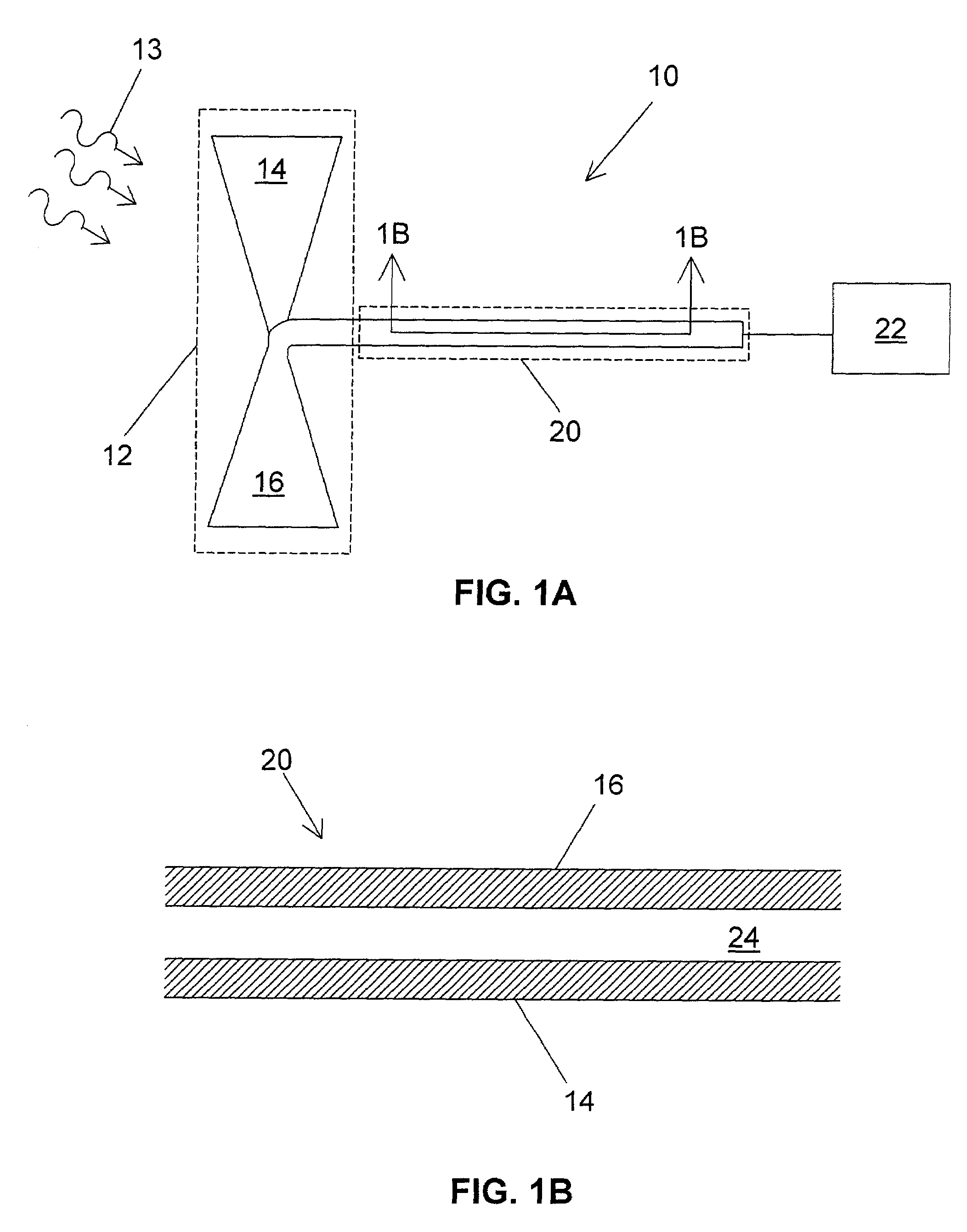
Analyte sensing via acridine-based boronate biosensors
InactiveUS7045361B2Improve sensor sensitivityIncrease overall biocompatibility and functioningMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
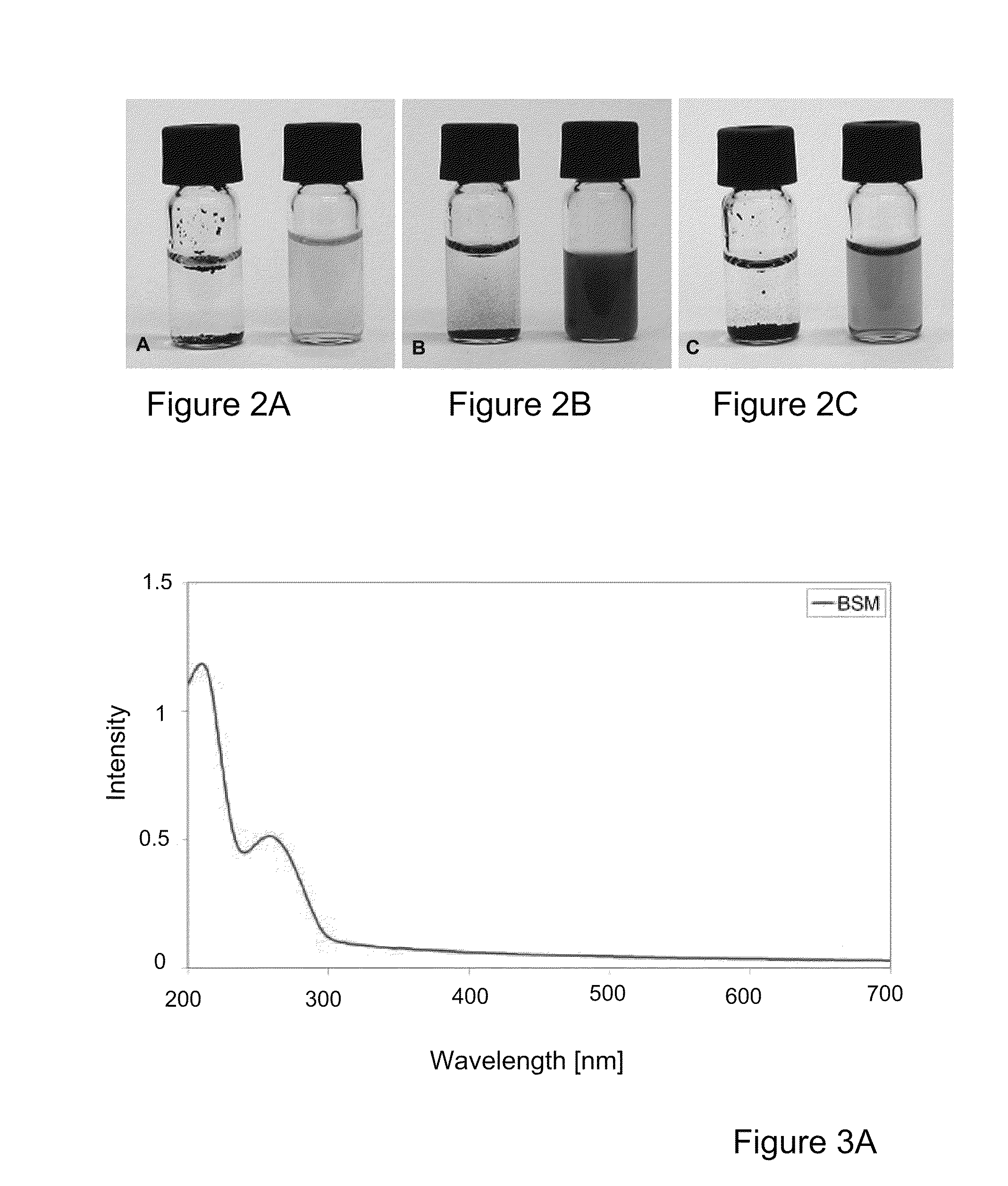
Fluorescent biosensor molecules, fluorescent biosensors and systems, as well as methods of making and using these biosensor molecules and systems are described. These biosensor molecules address the problem of obtaining fluorescence emission at wavelengths greater than about 500 nm. Biosensor molecules generally include an (1) an acridine-based fluorophore, (2) a linker moiety and (3) a boronate substrate recognition / binding moiety, which binds polyhydroxylate analytes, such as glucose. These biosensor molecules further include a “switch” element that is drawn from the electronic interactions among these submolecular components. This fluorescent switch is generally “off” in the absence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte and is generally “on” in the presence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte. Thus, the reversible binding of a polyhydroxylate analyte essentially turns the fluorescent switch “on” and “off”. This property of the biosensor molecules, as well as their ability to emit fluorescent light at greater than about 500 nm, renders these biosensor molecules particularly well-suited for detecting and measuring in-vivo glucose concentrations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Surface plasmon devices
InactiveUS7010183B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSoftware engineeringEngineering
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Surface plasmon devices
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Surface Plasmon Devices
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
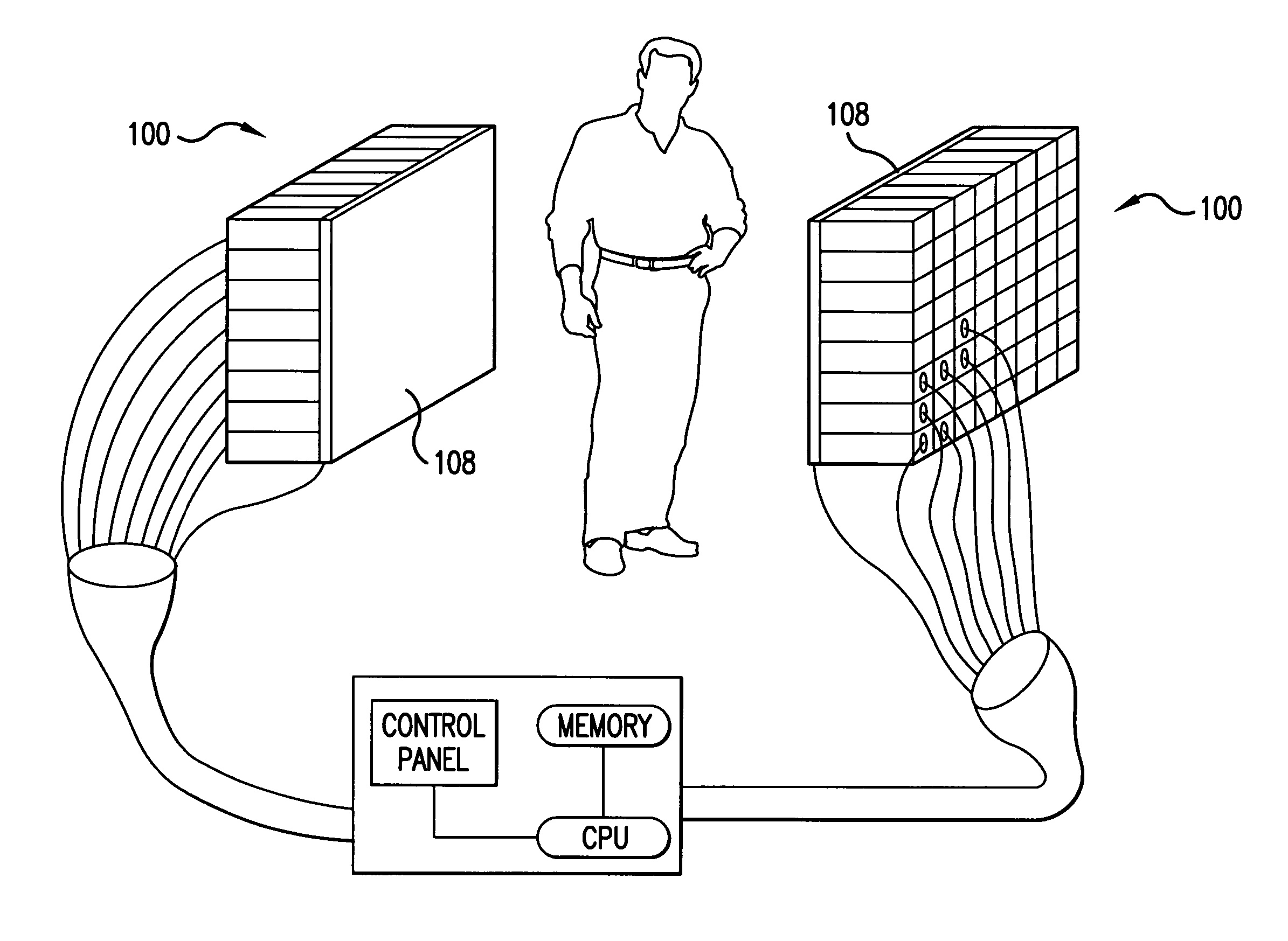
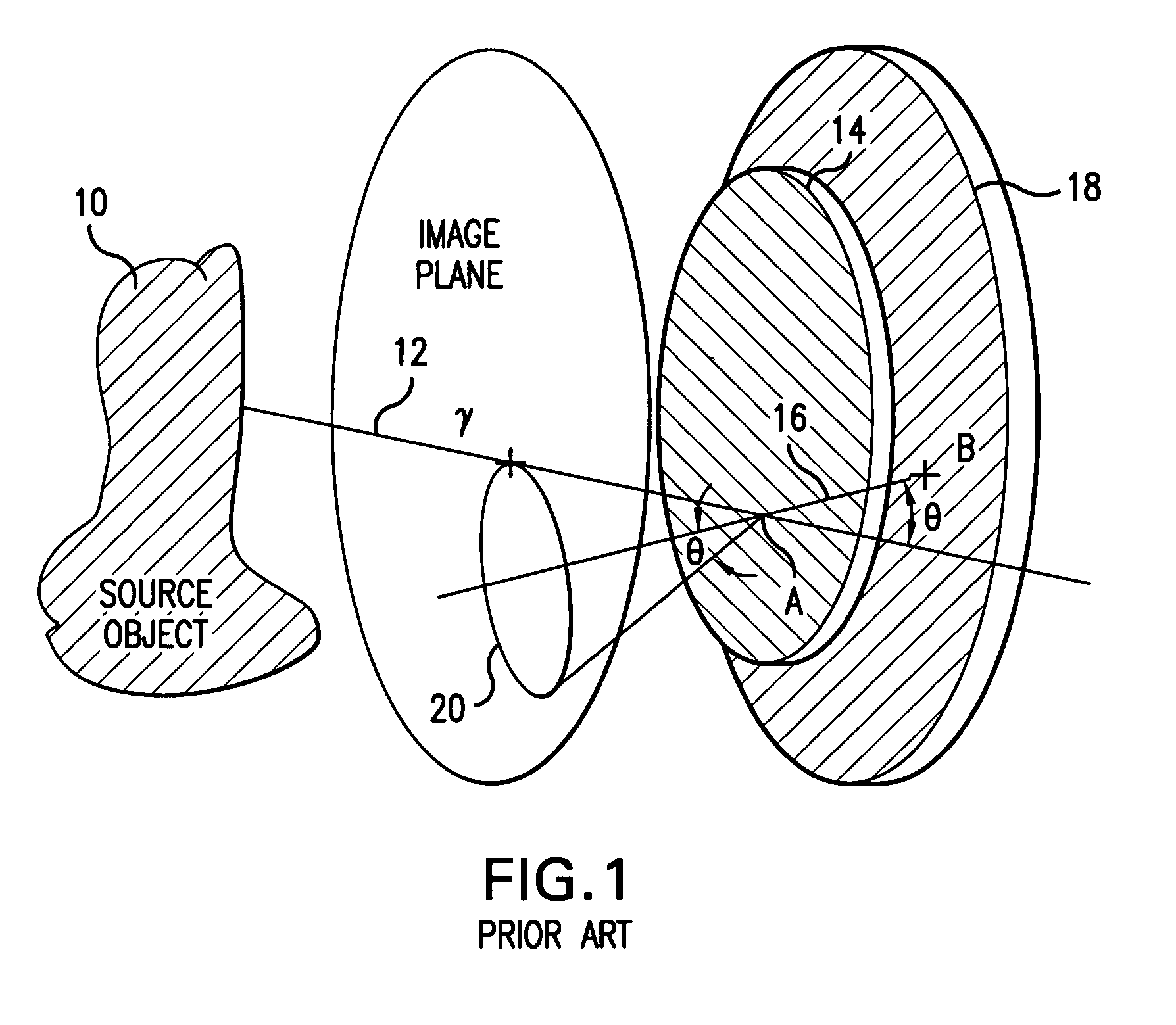
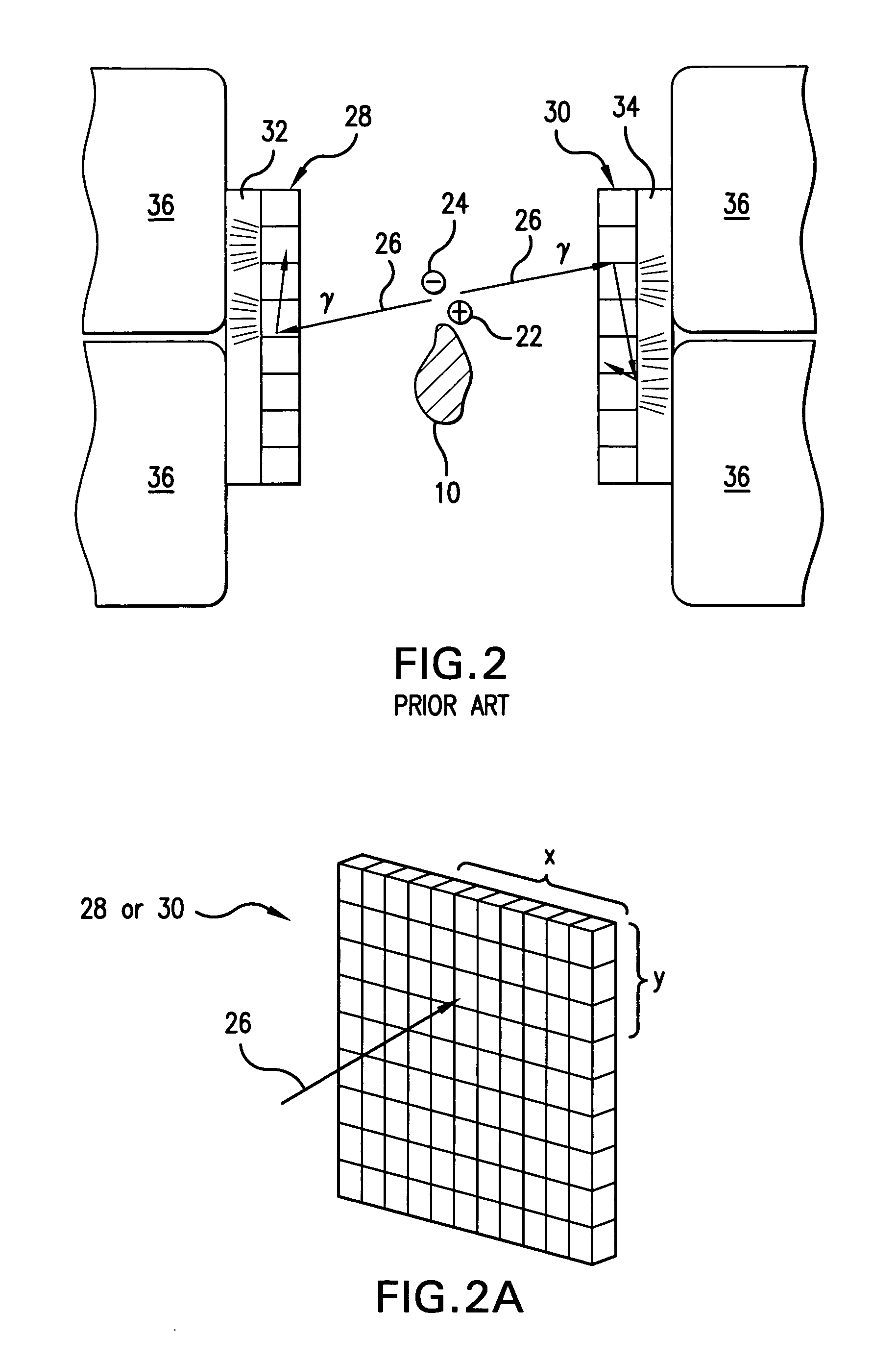
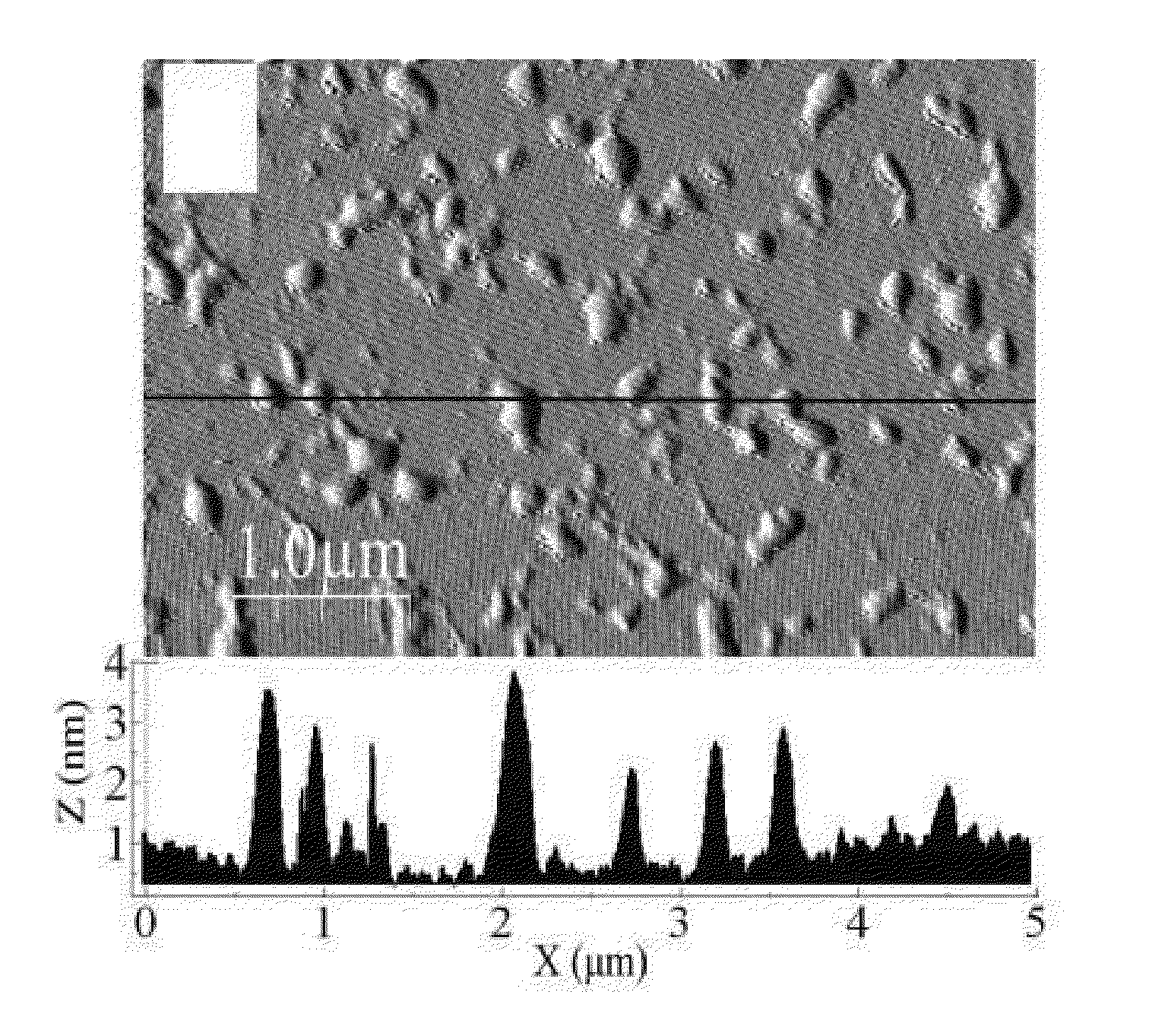
Nuclear imaging using three-dimensional gamma particle interaction detection
InactiveUS20050023474A1High resolutionReduce uncertaintySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayPerformed Imaging
An improved method of, and apparatus for, nuclear imaging takes advantage of the ability to determine the depth of gamma ray / electron interaction within a semiconducting gamma ray detector to determine the (most highly probable) location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction within the detector. Lines of interaction constructed between opposing detector arrays, extending between the location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction in each detector associated with the coincident detection of gamma radiation, permits a positron-emitting object of interest to be imaged according to protocols known in the art, but with better spatial resolution than previously believed to have been known.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
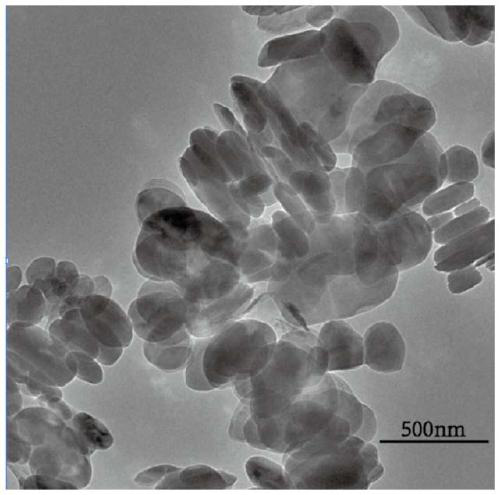
Magnetic carbon nanotube composite material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103041773AImprove bindingEasy to separateIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationSorbentHexamethylenediamine
The invention discloses a magnetic carbon nanotube composite material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding FeCl3.6H2O to an ethylene glycol solution; then adding anhydrous sodium acetate and polyethylene glycol; adding a carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotube; performing ultrasonic dispersion; adding hexamethylenediamine or ethanediamine; heating to 200-300 DEG C for reaction for 8-24h; and washing and performing vacuum drying to prepare the amino-modified magnetic Fe3O4-carbon nanotube composite material. The amino-modified magnetic Fe3O4-carbon nanotube composite material prepared by the invention is of nanoscale and superparamagnetism, can be stably dispersed in solutions, and can be quickly separated and enriched through a simple action of a magnetic field. As an adsorbent, the material is large in superficial area and has various active groups on the surface. The material can adsorb pigments from complex substrates through pi-pi electron interaction and hydrophobic effect of the carbon nanotube and can adsorb compounds such as organic acids and phenols through weak anion exchange effect of amino groups on the surfaces of magnetic nanoparticles.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of fabrication of high temperature superconductors based on new mechanism of electron-electron interaction
InactiveUS20070108437A1Dissimilar materials junction devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh-temperature superconductivitySingle crystal
The present invention is a superconducting tunnel junction comprising two thin films characterized in that the thin films have an indented surface facing each other and are separated by an insulator layer. Typically, the depth of the indents is in the range of 5 to 10 nm, the width of the indents is in the range of 50 to 200 nm, the thickness of the insulator layer is in the range of 1 to 3 nm, and the thickness of the films is less than electron mean free path of a material comprising said films, and is typically in the range of 50 to 100 nm. Preferably the films are single crystal films or amorphous films.
Owner:TAVKHELIDZE AVTO
Emissive, high charge transport polymers
The present invention generally relates to stable emissive aggregates of polymers. The aggregates are composed of various polymer molecules arranged in such a way as to allow extended electronic couplings between nearby polymer molecules, enhancing exciton transport, while minimizing the effects of quenching due to interchain interactions. For example, the polymer molecules may be arranged in a non-aligned, electronically-communicative manner (for example, at an oblique angle), stabilized by various methods such as chemical linkages or physical interactions. Within the aggregate, electronic interactions along the polymer molecule may extend to nearby polymer molecules, which may be observed as a shift in the absorption spectra relative to a random dispersion. Light emitted from the aggregate may be polarized in some cases, for example, linearly or circularly, which may be caused by chiral arrangements of polymers within the aggregate (the polymers themselves may or may not be chiral). These aggregates may find widespread use, for example, in enantiomeric detectors, electrochemical devices, photodetectors, organic diodes, sensors, light sources, or photovoltaic devices.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Electrodynamic profiling of genomic response in the cell
InactiveUS20060127879A1Highly preventive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCell EvaluationHydrogen
A method of cellular evaluation based on the electronic nature of cells is reveled though cellular reproductions use of a magnetic force. The dynamic process of nuclear response is shown to be electronic in nature relative to DNA mediating electrons hydrogen bonding in bases pairing of DNA though out the a cell cycle and finally during metaphase one see the magnetic component of interaction. The electrostatic understanding of magnetic force is not well defined in physics in the process of electrodynamic. Cells use electrodynamic interaction within the cell are being studied as the basis and using the cell to measure and define electrodynamic interaction with the system that is biological a call. Specifically DNA thought the electronic interaction interactions. It appears infrared spectrum holds promises to help in revel these mechanisms. The promise of understanding or merely evaluation of electrodynamic interaction holds great promise to science with the greatest medical implication to understand genomic responses in cells. Understanding how the DNA interacts within a cell dynamic transition are known to take place and these are regulated thought electrodynamic interaction.
Owner:FUCCIONE ANTHONY STEPHEN
Analyte sensing via acridine-based boronate biosensors
InactiveUS20050191761A1Good biocompatibilityFunction increaseMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
Fluorescent biosensor molecules, fluorescent biosensors and systems, as well as methods of making and using these biosensor molecules and systems are described. These biosensor molecules address the problem of obtaining fluorescence emission at wavelengths greater than about 500 nm. Biosensor molecules generally include an (1) an acridine-based fluorophore, (2) a linker moiety and (3) a boronate substrate recognition / binding moiety, which binds polyhydroxylate analytes, such as glucose. These biosensor molecules further include a “switch” element that is drawn from the electronic interactions among these submolecular components. This fluorescent switch is generally “off” in the absence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte and is generally “on” in the presence of bound polyhydroxylate analyte. Thus, the reversible binding of a polyhydroxylate analyte essentially turns the fluorescent switch “on” and “off”. This property of the biosensor molecules, as well as their ability to emit fluorescent light at greater than about 500 nm, renders these biosensor molecules particularly well-suited for detecting and measuring in-vivo glucose concentrations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
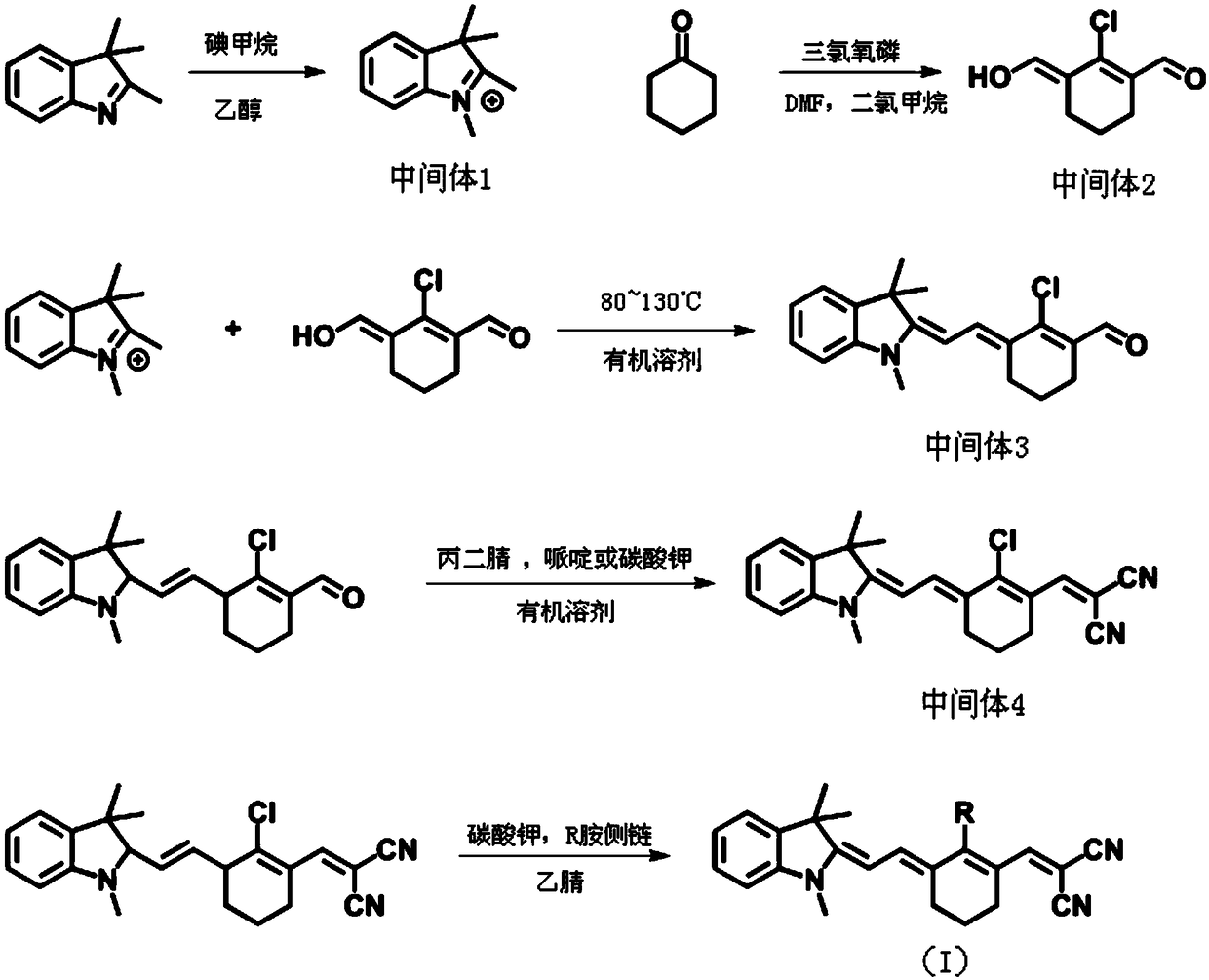
Cyanine fluorescent compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109180556ASolve the problem of not being able to pass the blood-brain barrierStrong penetrating powerOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsDouble bondStructural formula
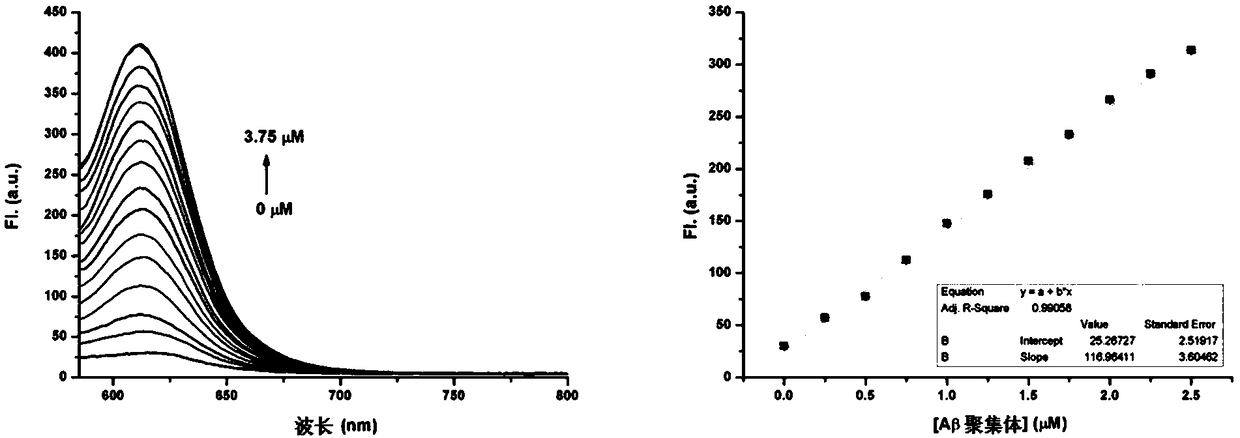
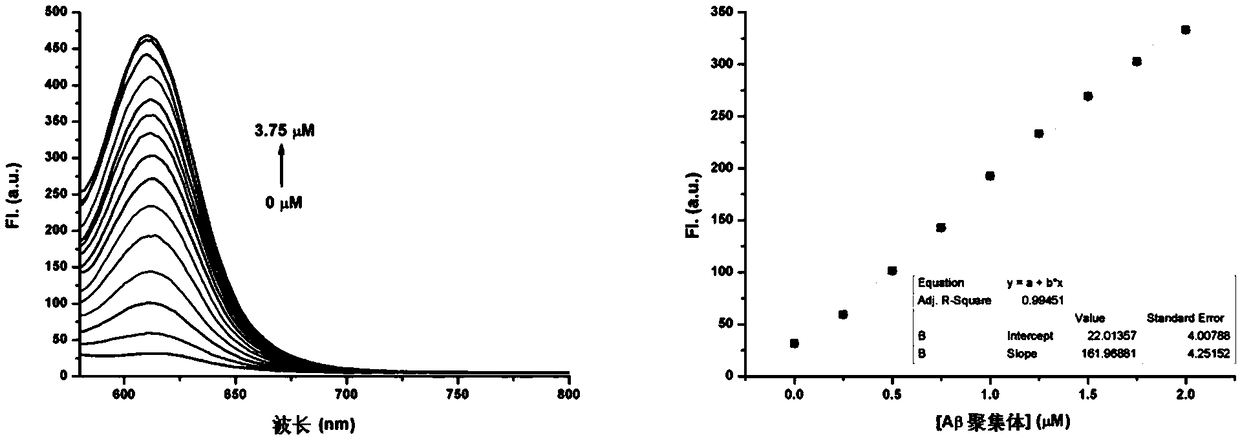
The invention belongs to the field of specific molecular recognition materials and discloses a cyanine fluorescent compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural general formula of the cyanine fluorescent compound is shown as a formula (I). The fluorescent compound disclosed by the invention adopts a classic cyanine dye structure, an electroneutral electron-drawing group is introduced into the R-group position, a conjugated structure of push-pull electron interaction is formed between the electron-donating group and the electron-drawing group in the structure,and the conjugated system for transition is increased by carbon-carbon double bonds, so that fluorescence produced by compound molecules moves to a near infrared region. Meanwhile, due to the introduced electroneutral group, the problem that most of the charged cyanine compounds cannot pass through the blood brain barrier is solved. The compound molecule has affinity to Abeta plaques, can be successfully applied to near infrared fluorescence imaging of the Abeta plaques, and has the advantages of being safe, non-radioactive, low in cost, low in background fluorescence interference, high in penetrating power in biological tissues and the like. The structural formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Imaging sensor
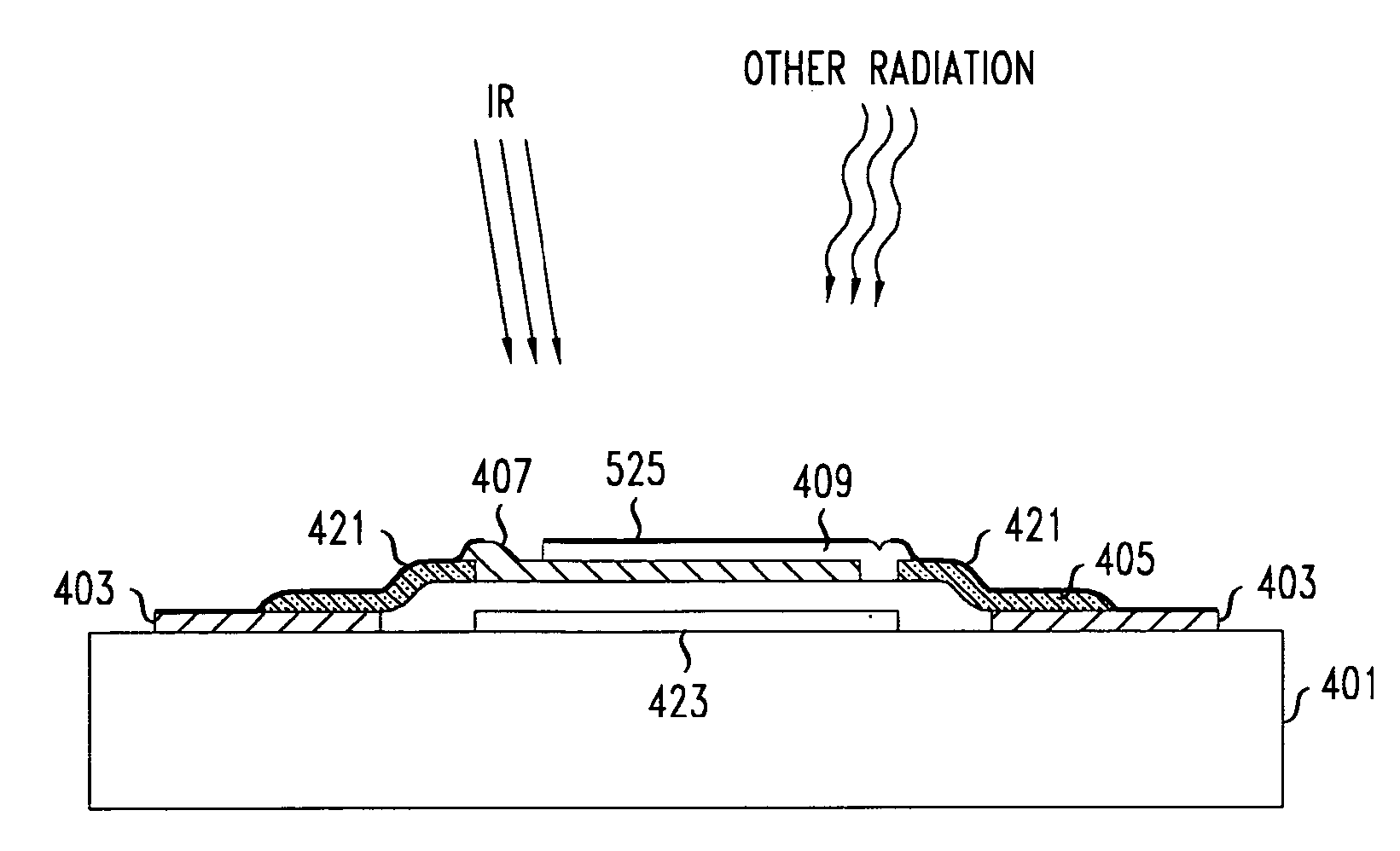
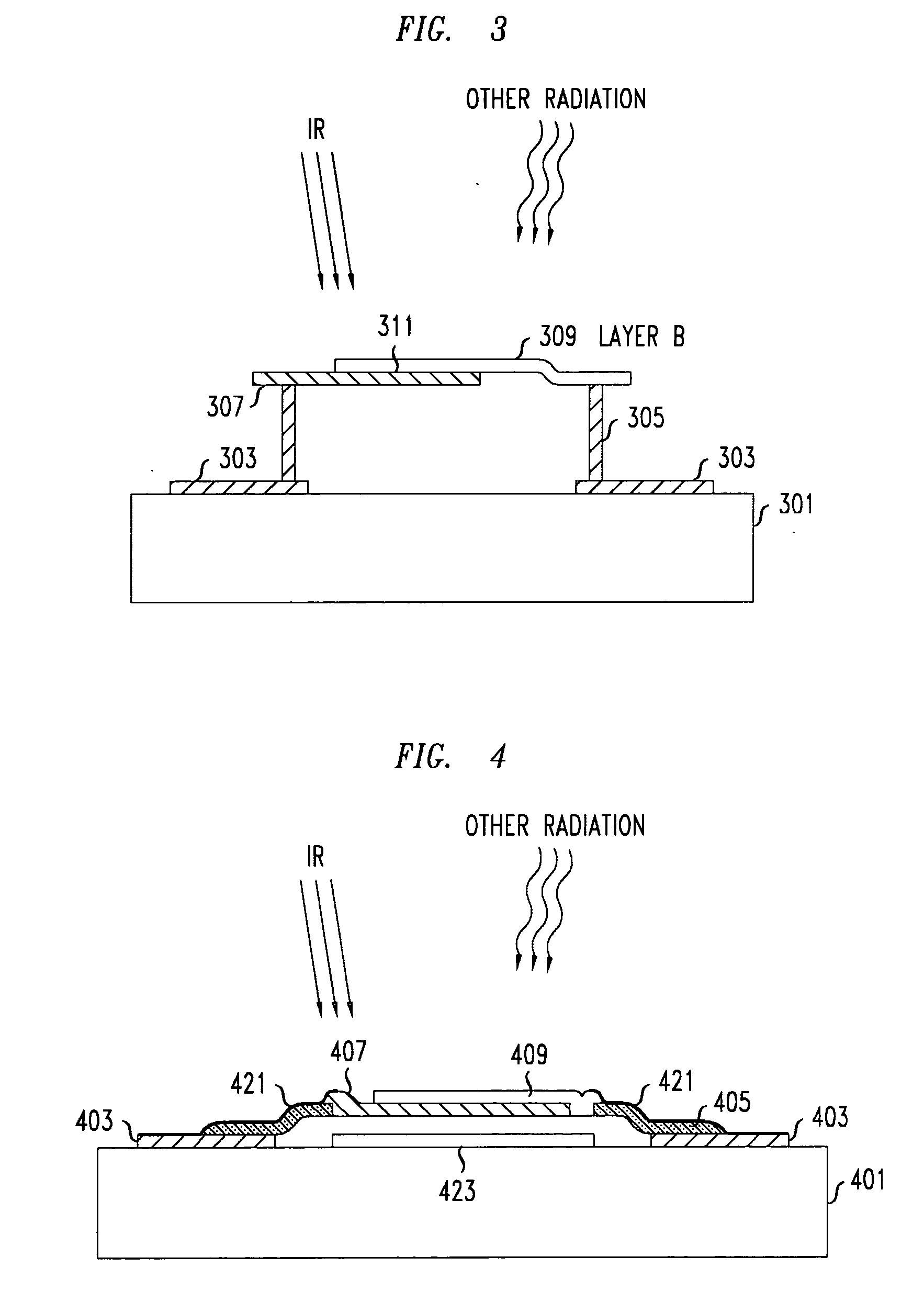
ActiveUS20070215805A1Avoid calibrationAvoid measuringMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSpectral bandsOperating point
A sensor that is responsive to at least two distinct spectral bands, e.g., infrared radiation and ultraviolet or infrared and visible light makes use of the junction of a diode-based bolometer as a photocell in addition to its temperature dependence for detecting infrared radiation. More specifically the diode bolometer is arranged to work in the conventional manner, in that an electrical characteristic of the diode, e.g., the temperature dependence of its current-voltage (I-V) curve, is used as the basis for measuring temperature, and hence, infrared radiation. Additionally, the same diode may be operated as a photocell to detect radiation that is capable of interacting with the electrons in the junction of the diode. This may be achieved by detecting a change in the operating point of the diode based given its present biasing in response to noninfrared radiation incident upon the diode.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Charged particle source with integrated energy filter
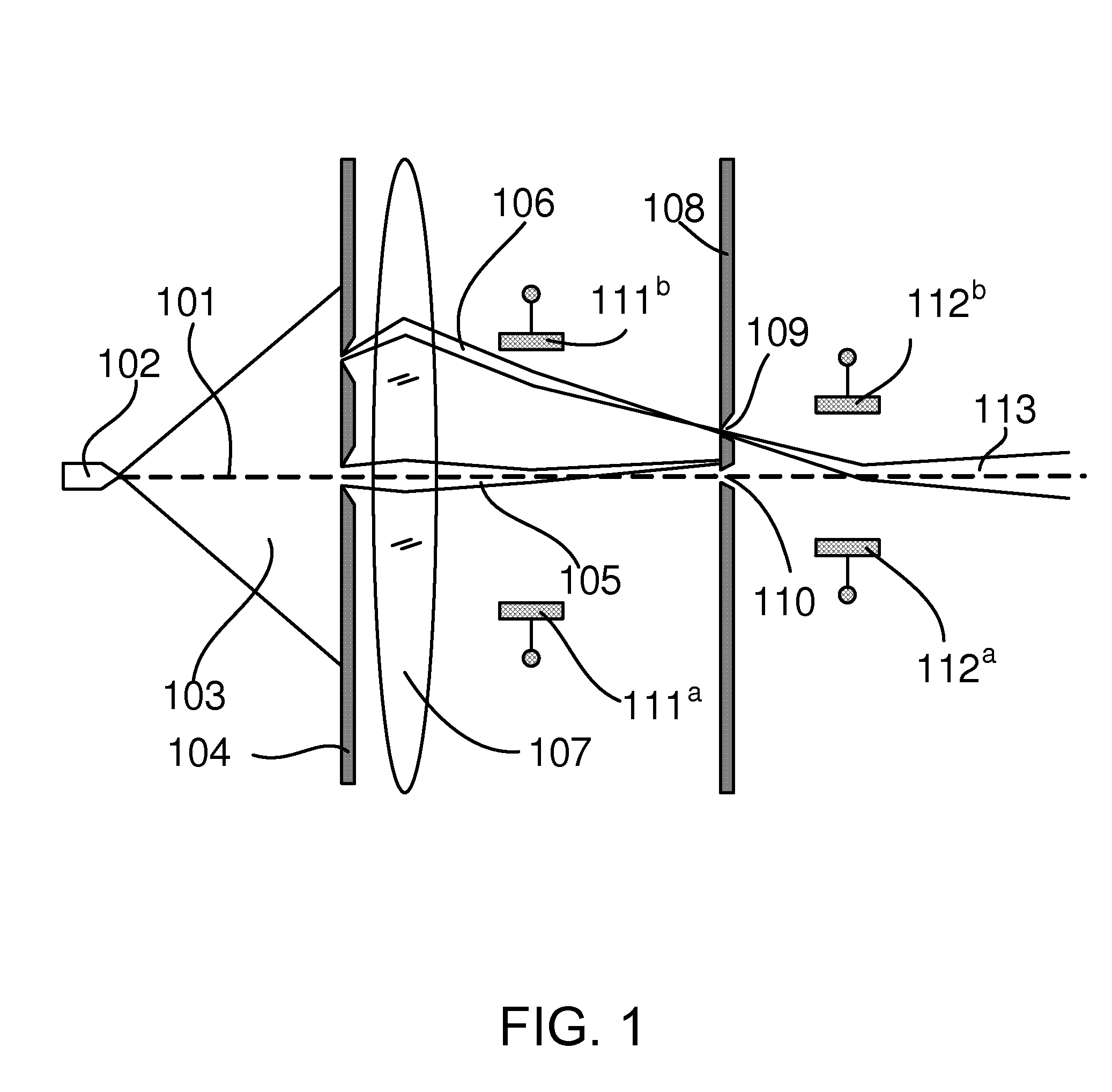
ActiveUS8461525B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamEnergy dispersion
Owner:FEI CO
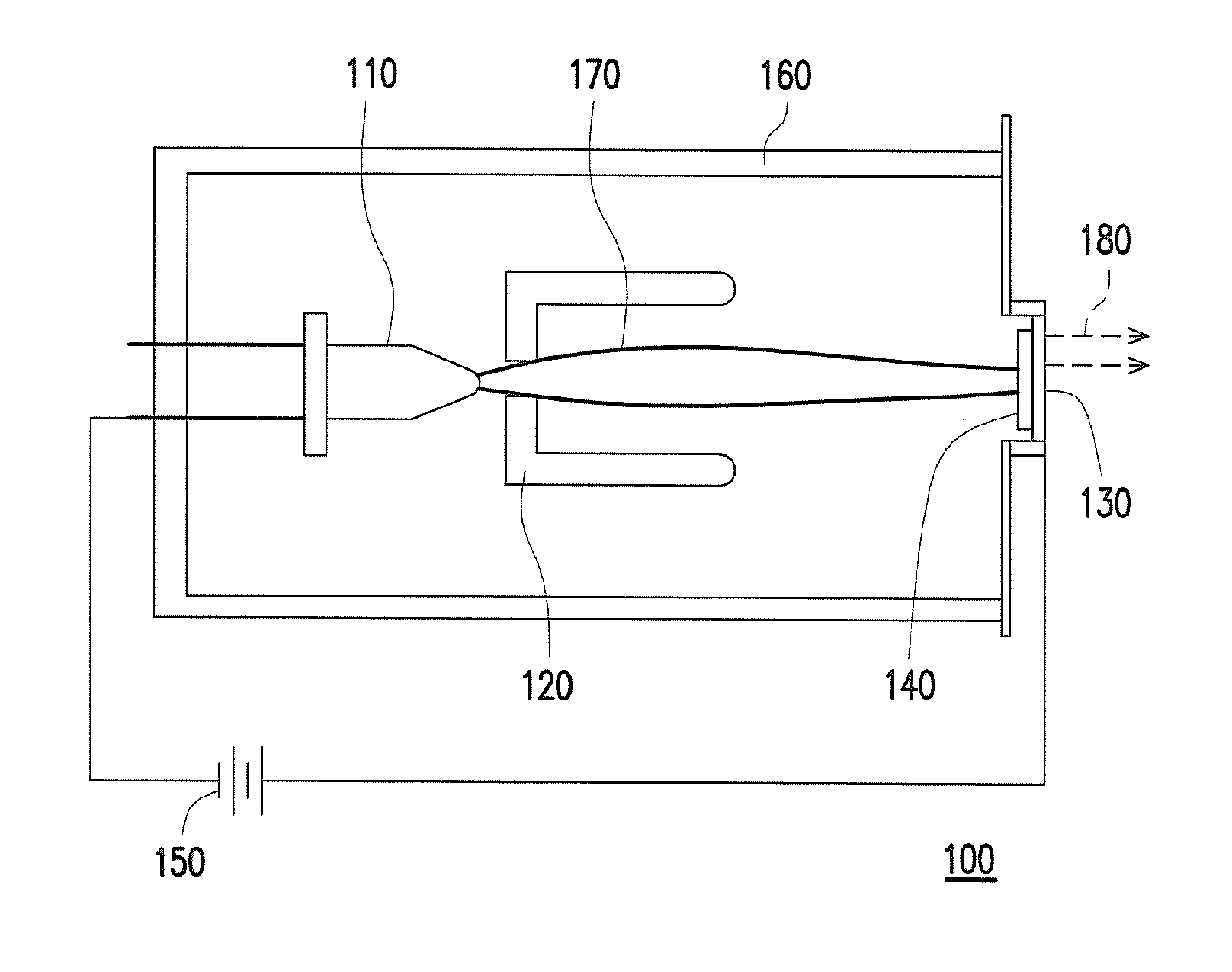
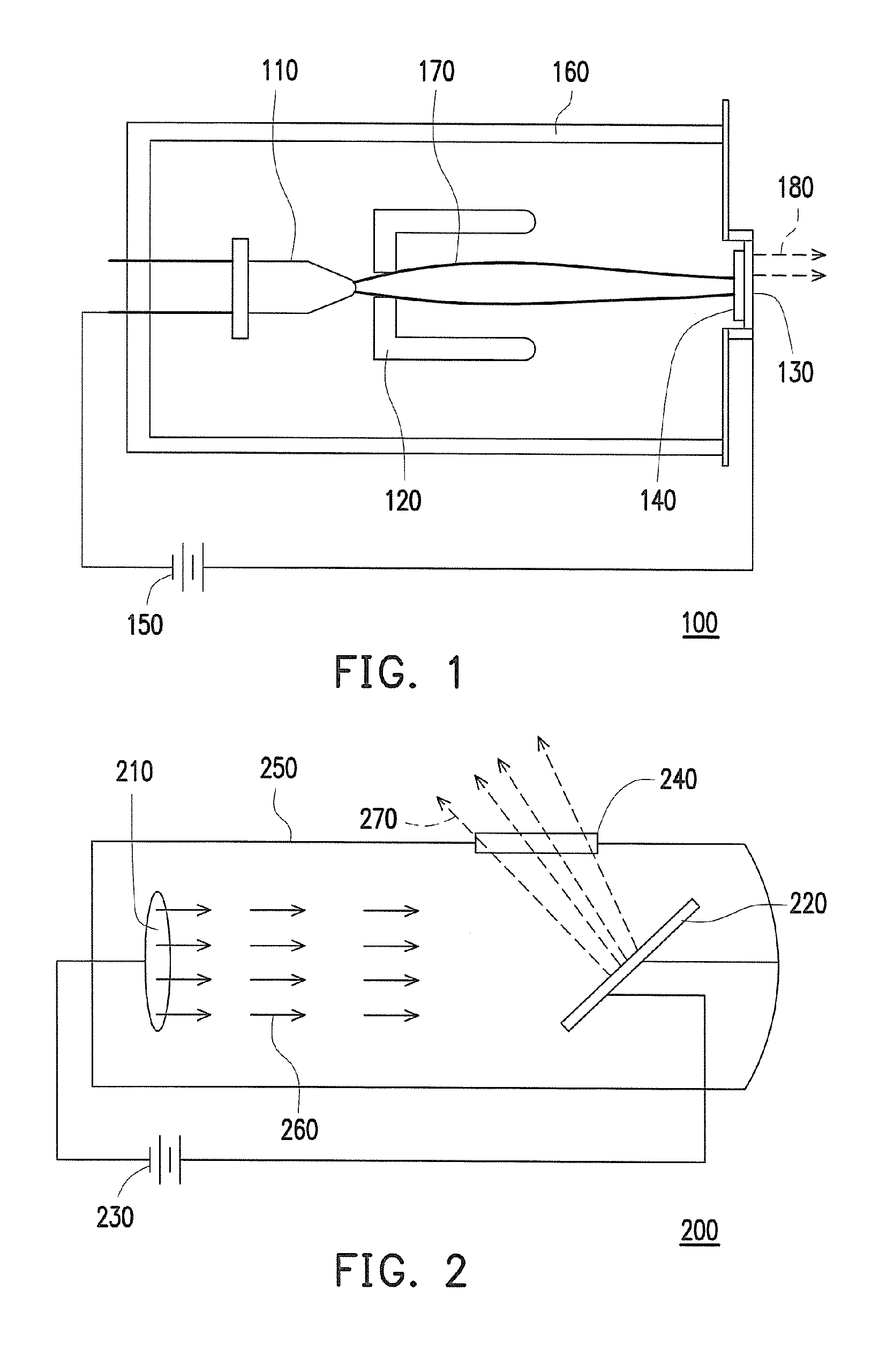
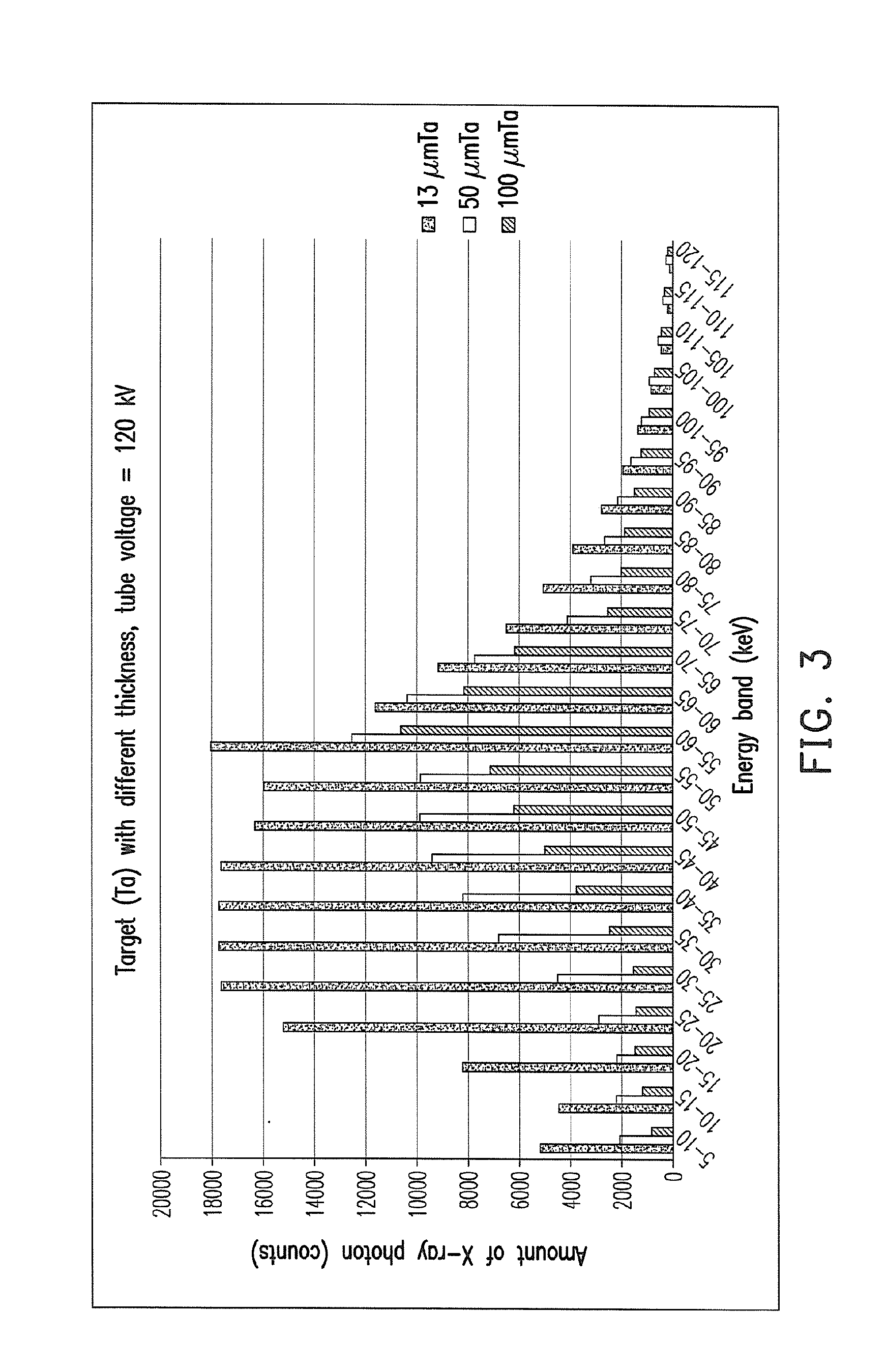
Composite target and x-ray tube with the composite target
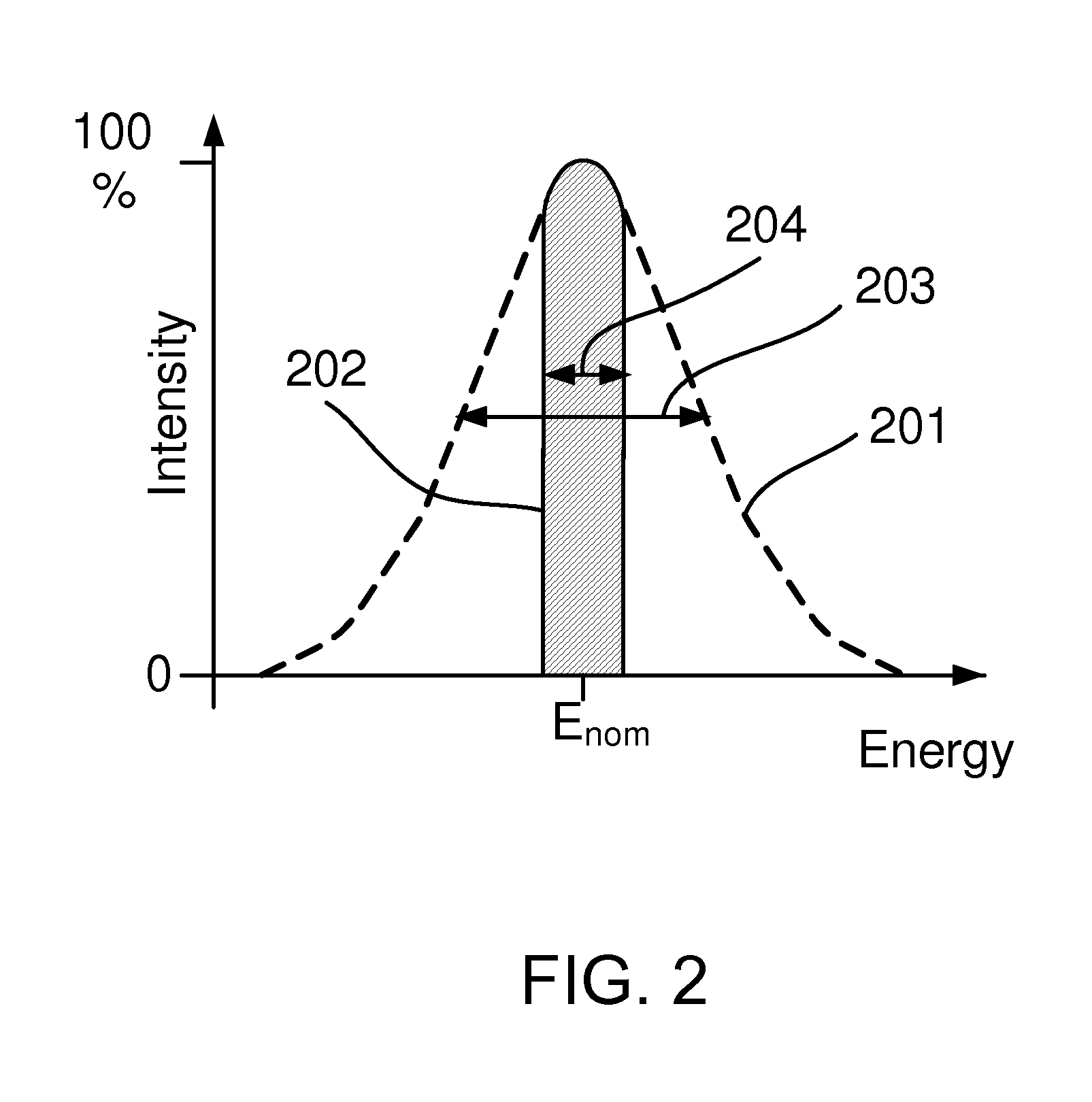
ActiveUS20170018392A1Sufficient long service lifeWeaken energyX-ray tube laminated targetsRadiation/particle handlingHigh energyX-ray
A composite target is provided and is interacted with an electron to generate an X-ray, and an energy of the electron can be changed by controlling a tube voltage at least. The composite target includes a target body and an interposing layer which is connected with the target body. The interposing layer moves a highest peak of an energy spectrum of the X-ray toward a high energy direction. The interposing layer may be a single metal or a metal mixture. Not only a low energy photon of the X-ray can be filtered by the interposing layer, but also a distribution of the low energy photon of the X-ray can be increased by increasing a thickness of the interposing layer. As the tube voltage is enhanced, an amount of a high energy photon of the X-ray generated is dramatically increased. An X-ray tube containing the above composite target is also provided.
Owner:NANORAY BIOTECH CO LTD
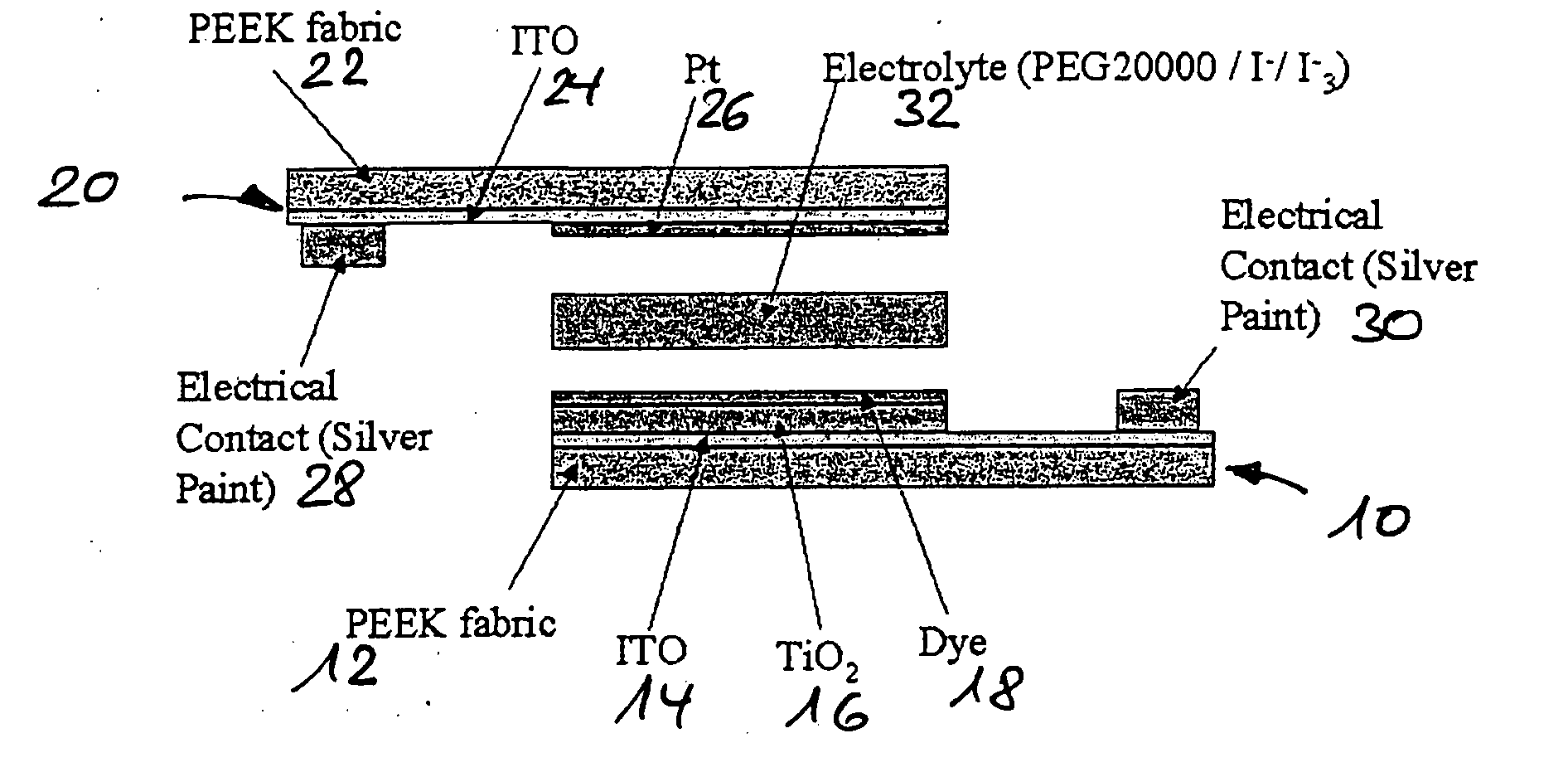
Photovoltaic Cell
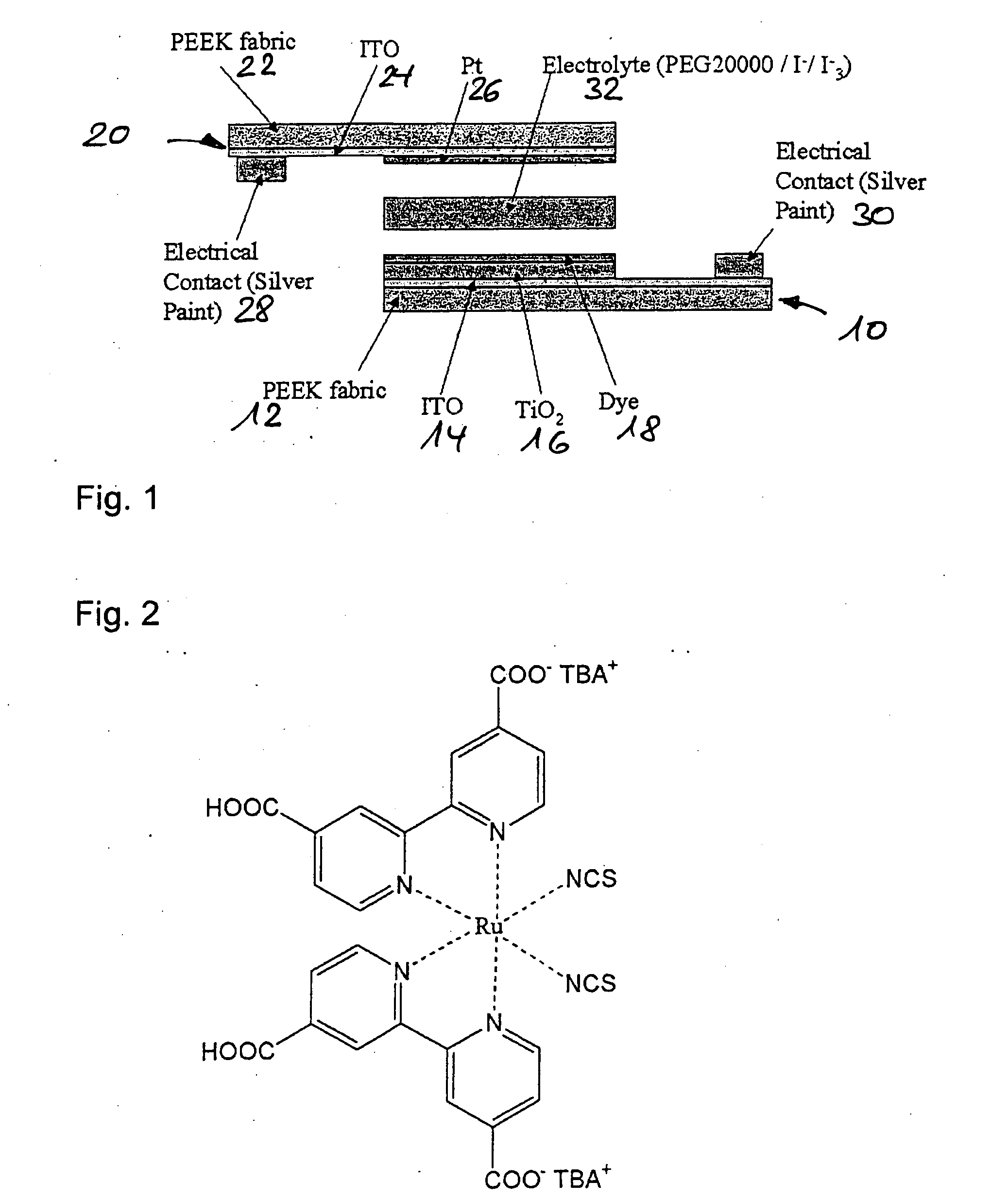
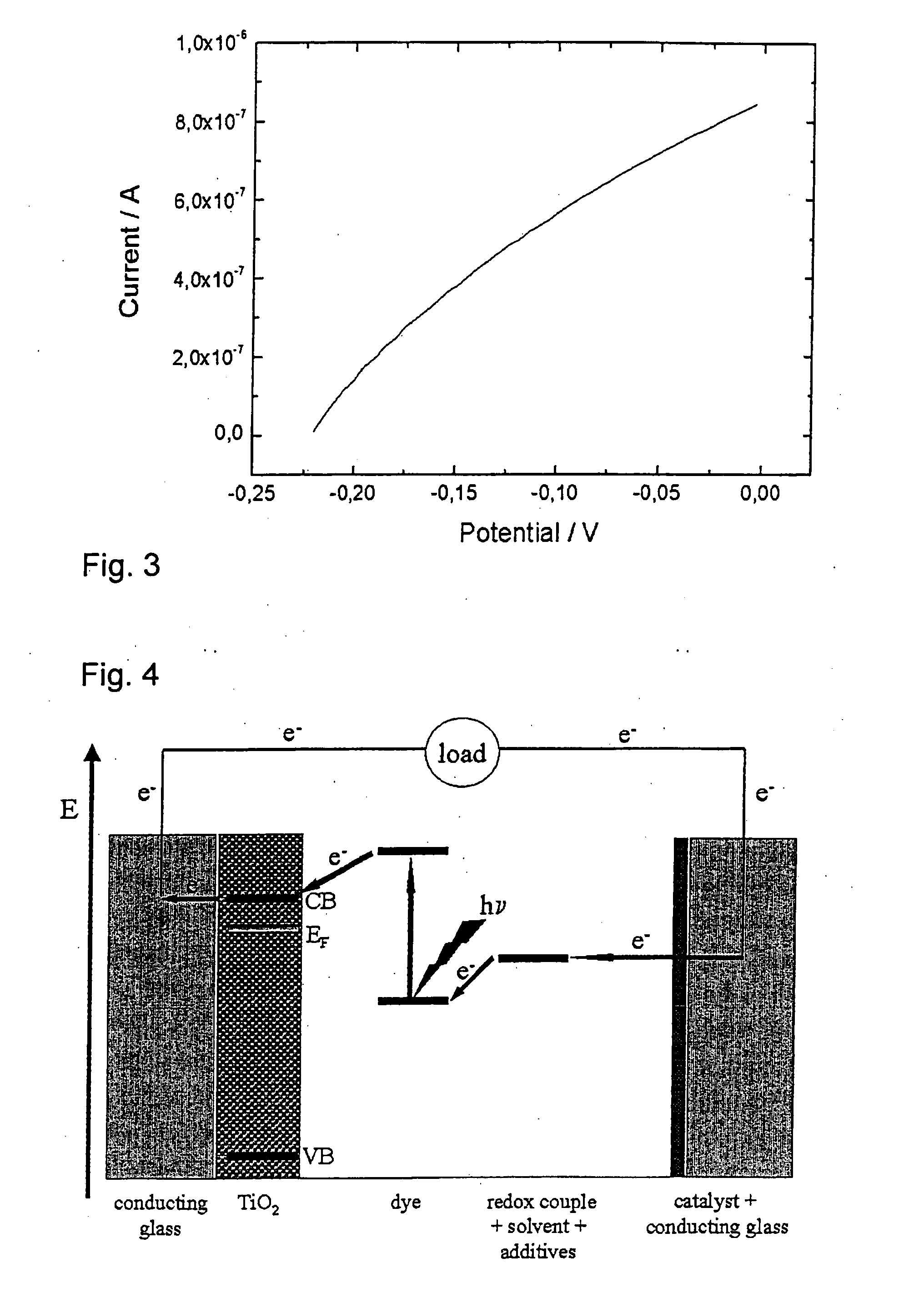
InactiveUS20090293950A1Good mechanical flexibilityMaintain good propertiesElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureFiberEngineering
A photovoltaic cell, particularly a color-sensitized solar cell, comprises a conductive support substrate, coated with a metal oxide semiconductor layer, a color layer embodied so as to electronically interact with the metal oxide semiconductor layer, an electrolyte later that is applied to the color layer, and a counter-electrode which is connected to the electrolyte layer. The support substrate and / or the counter-electrode is / are made from a flexible fabric composed of a plurality of interwoven fibers.
Owner:SEFAR +2
Multiplexing matrix-analyte stereo electronic interactions for high throughput shotgun metabolomics
InactiveUS20090065687A1High throughput metabolomicsMinimal background noiseParticle separator tubesIsotope separationChromatographic separationMetabolite
A shotgun metabolomics approach using MALDI-tandem mass spectrometry was developed for the rapid analysis of cellular metabolites. Through the use of neutral organic solvents to inactivate endogenous enzyme activities (i.e., methanol / chloroform / H2O extraction), multiplexed extraction conditions and combinatorial alterations in matrix stereoelectronic composition and analyte interactions, multiple suites of metabolites were directly ionized and quantitated directly from biologic extracts without the need for prior chromatographic separation. Through combinatorial alterations in 9-aminoacridine charge, aromaticity and stacking, a set of multiplexed conditions was developed that allowed identification of many hundreds of peaks corresponding to metabolites from mouse heart extracts. Identification of metabolite peaks was based on mass accuracy and isomeric species were assigned based on diagnostic fragment ions present during tandem mass spectrometry for many of the identified metabolite peaks.
Owner:PLATOMICS
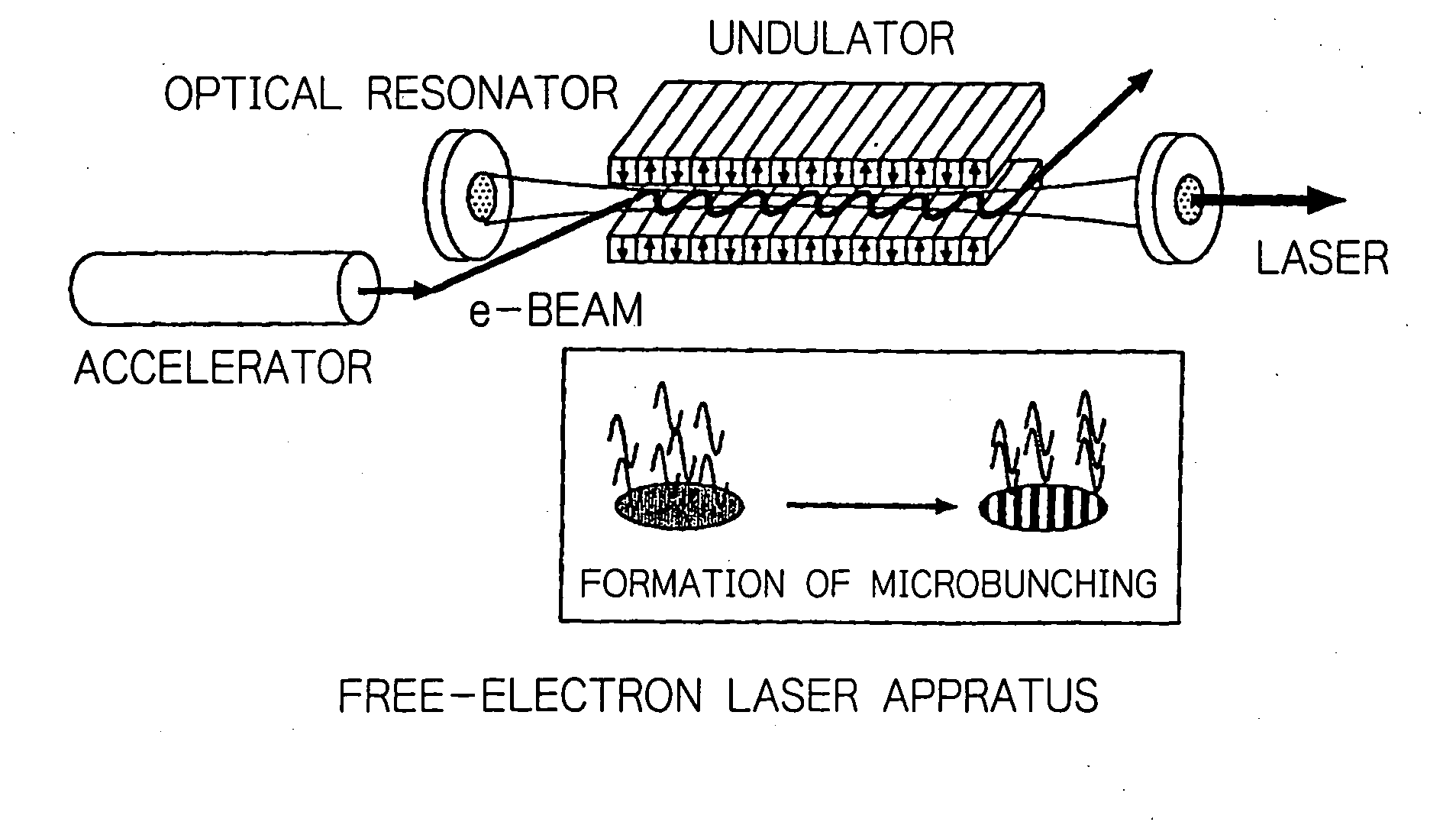
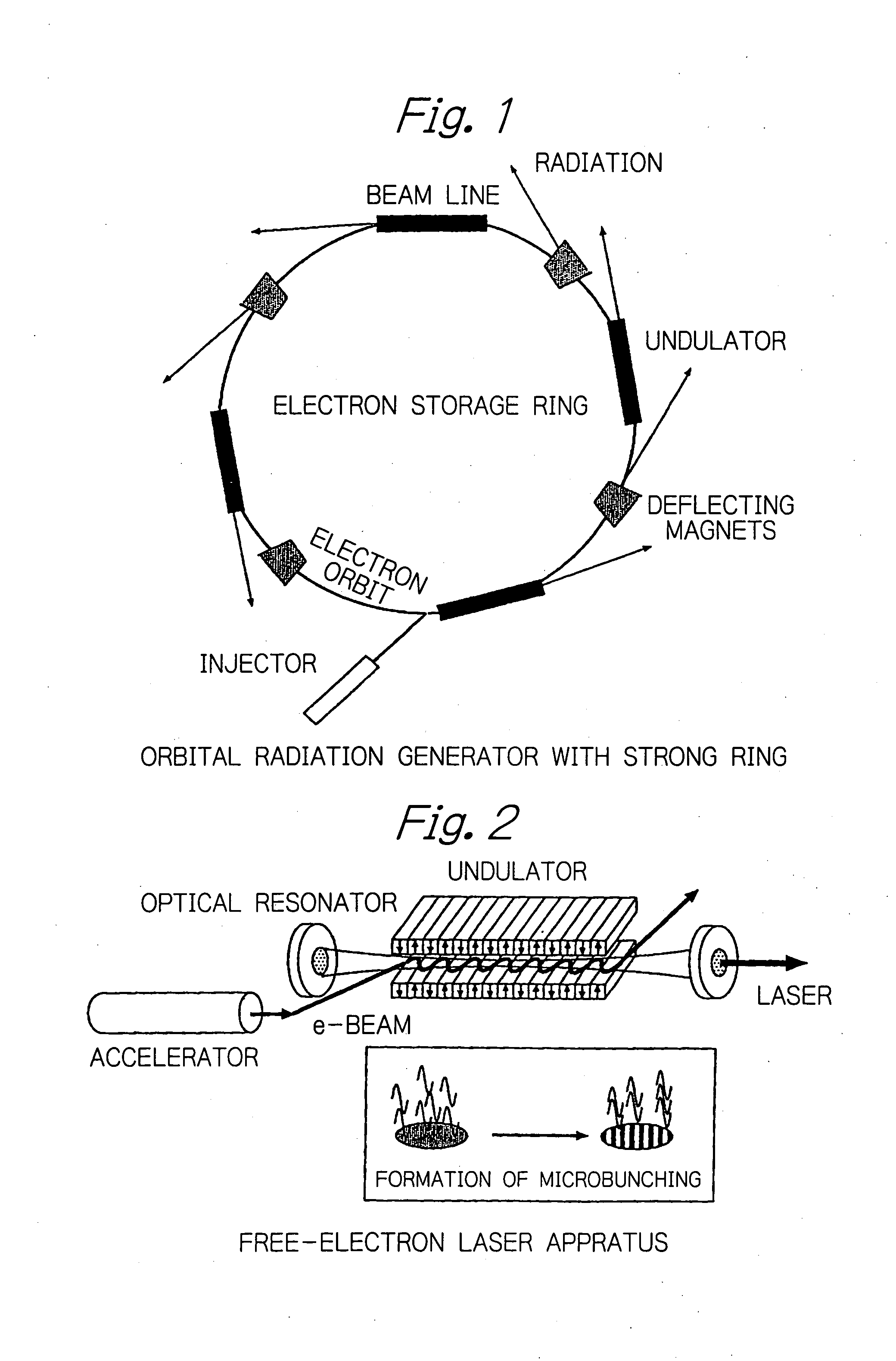
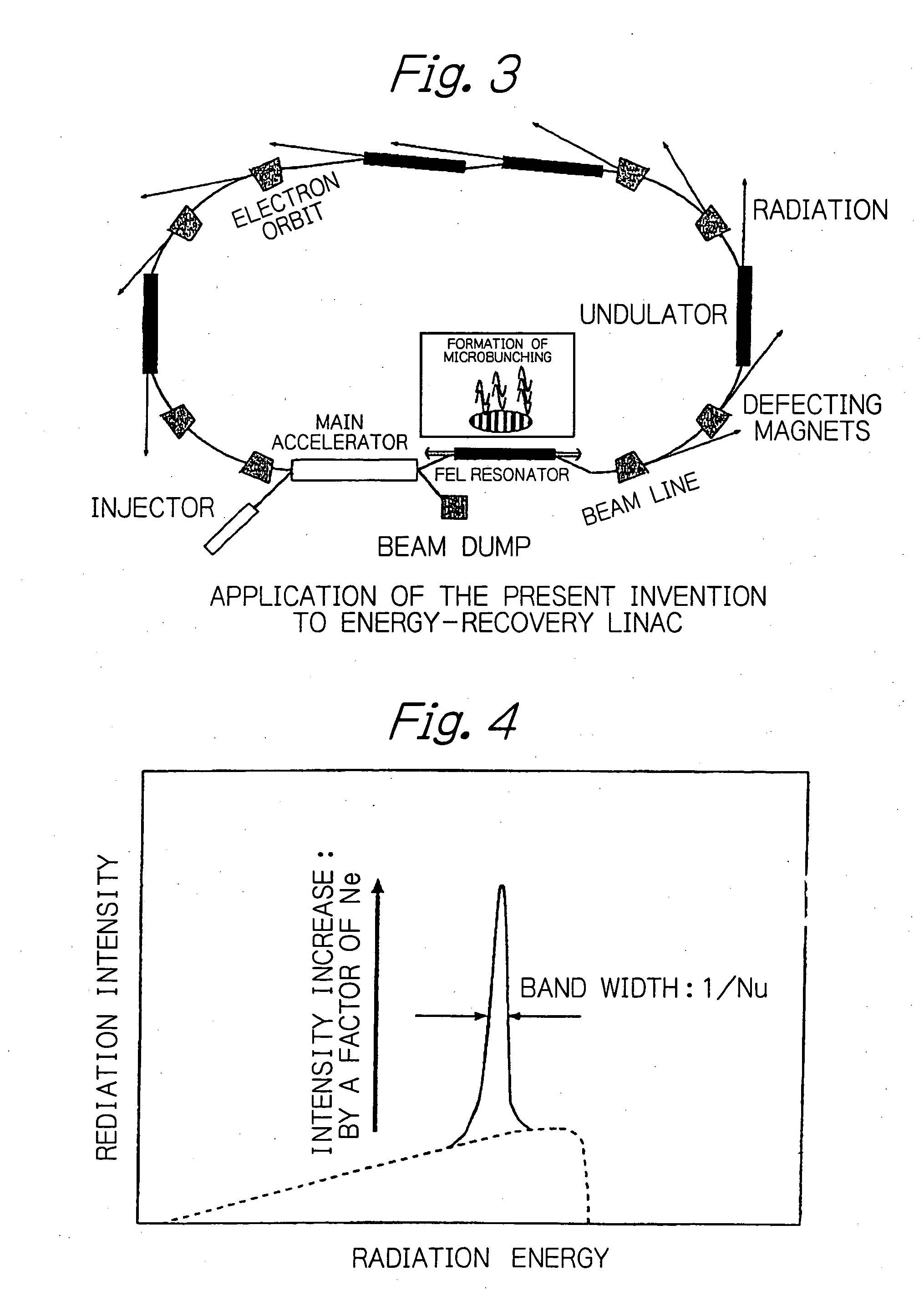
Method for enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines
InactiveUS20050175042A1Radiation/particle handlingExcitation process/apparatusEnergy recovery linacElectron bunches
In an electron accelerator such as an electron storage ring, a linac or an energy-recovery linac, accelerated electron bunches are subjected to light-electron interaction to have a varying profile of electron density and the thus modulated electron bunches are passed between deflecting magnets or injected into an undulator to generate high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation, thereby enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
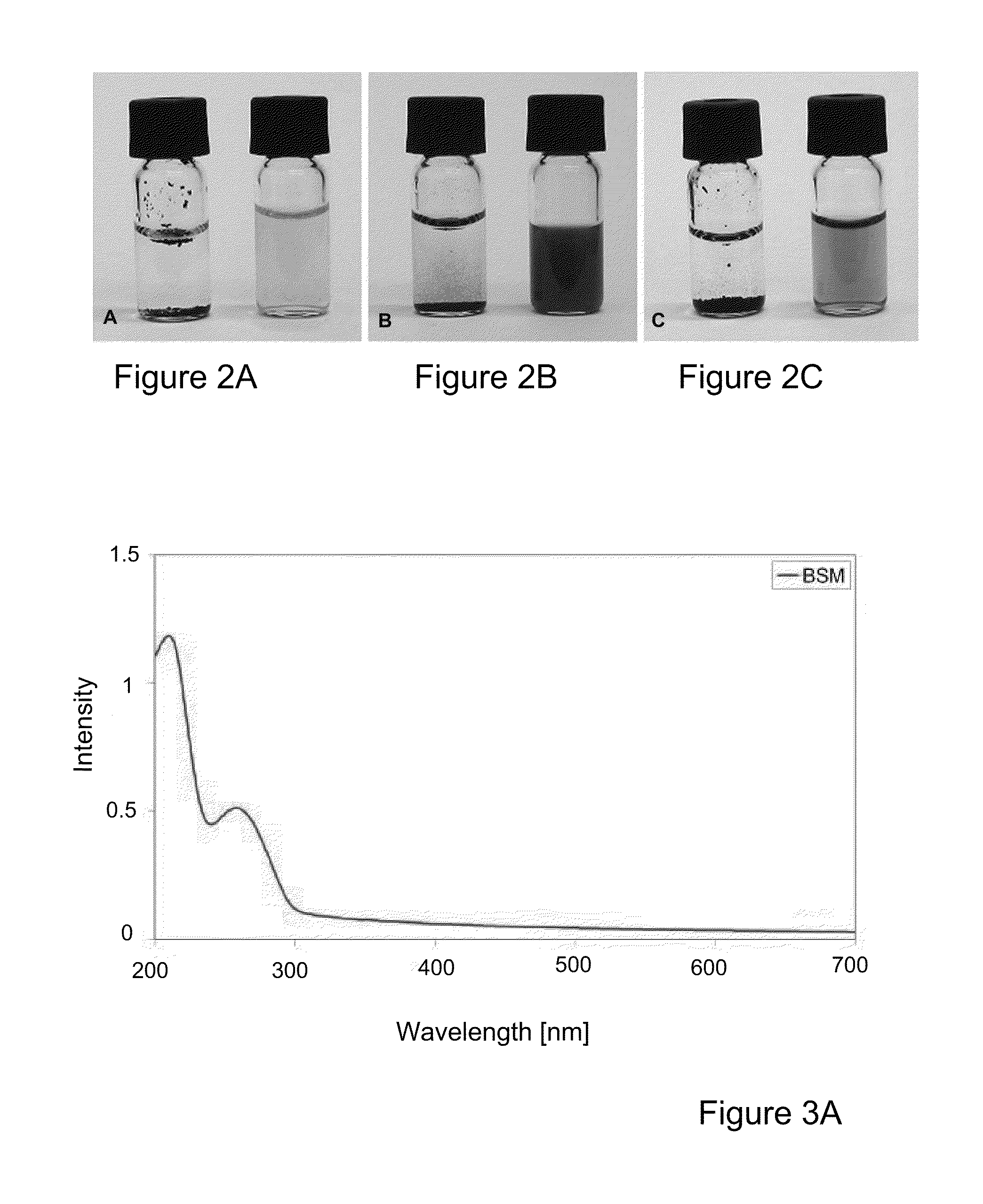
Analytical method for detecting trace mercury in aqueous medium based on the color change of fluorescence
InactiveCN101672780AApplicability restrictionsReduce manufacturing costFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceColor changes
The invention relates to a highly sensitive and selective identification method for detecting Hg<2+> in aqueous medium based on the color change of fluorescence in the sensor system. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) synthesizing water-soluble pyrene oligomer derivative through chemical and electrochemical technologies; and (2) performing molecular combination in aqueous phasebetween the derivative and short chain homopolynucleic acid with rich base T in the molar ratio of 1:1 and obtaining fluorescence probes used for the Hg<2+> detection. The invention adopts the colorchange of fluorescence in the sensor system caused by the pi electron interaction between molecular chains induced by Hg<2+> so as to realize the highly sensitive and selective detection of trace Hg<2+> in aqueous medium, provide an effective, simple and intuitive analysis method of the detection of trace ions in aqueous medium and have important meaning and actual application value for the detection of Hg<2+> in environmental water.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Nanomatrix separation of chromophores and uses thereof in luminescent devices
InactiveUS20110215716A1Minimizes interactabilityAvoid interactionMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLight emitting deviceChromophore
A system and process for controlling electronic interactions between two or more interactable materials.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Magnetron anode design for short wavelength operation
ActiveUS7265360B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectrical conductorPole piece
An electromagnetic radiation source is disclosed. The electromagnetic radiation source includes an anode having a first conductor, a second conductor positioned relative to the first conductor, a plurality of pole pieces coupled to at least one of the first conductor and the second, and at least one mechanical phase reversal positioned along the first conductor or second conductor. Adjacent pole pieces are separated by a gap. The electromagnetic radiation source also includes a cathode separated from the anode by an anode-cathode space, electrical contacts for applying a dc voltage between the anode and the cathode and establishing an electric field across the anode-cathode space, and at least one magnet arranged to provide a dc magnetic field within the anode-cathode space generally normal to the electric field. Electrons emitted from the cathode are influenced by the electric and magnetic fields to follow a path through the anode-cathode space and pass in close proximity to the plurality of pole pieces, and the gaps between adjacent pole pieces provide fringing fields which interact with the electrons to produce single mode operation at a desired operating frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Charged Particle Source with Integrated Energy Filter
ActiveUS20110284763A1Avoid interactionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamEnergy dispersion
Owner:FEI CO
Bifunctional chemical, preparation and use for detecting nucleic acid
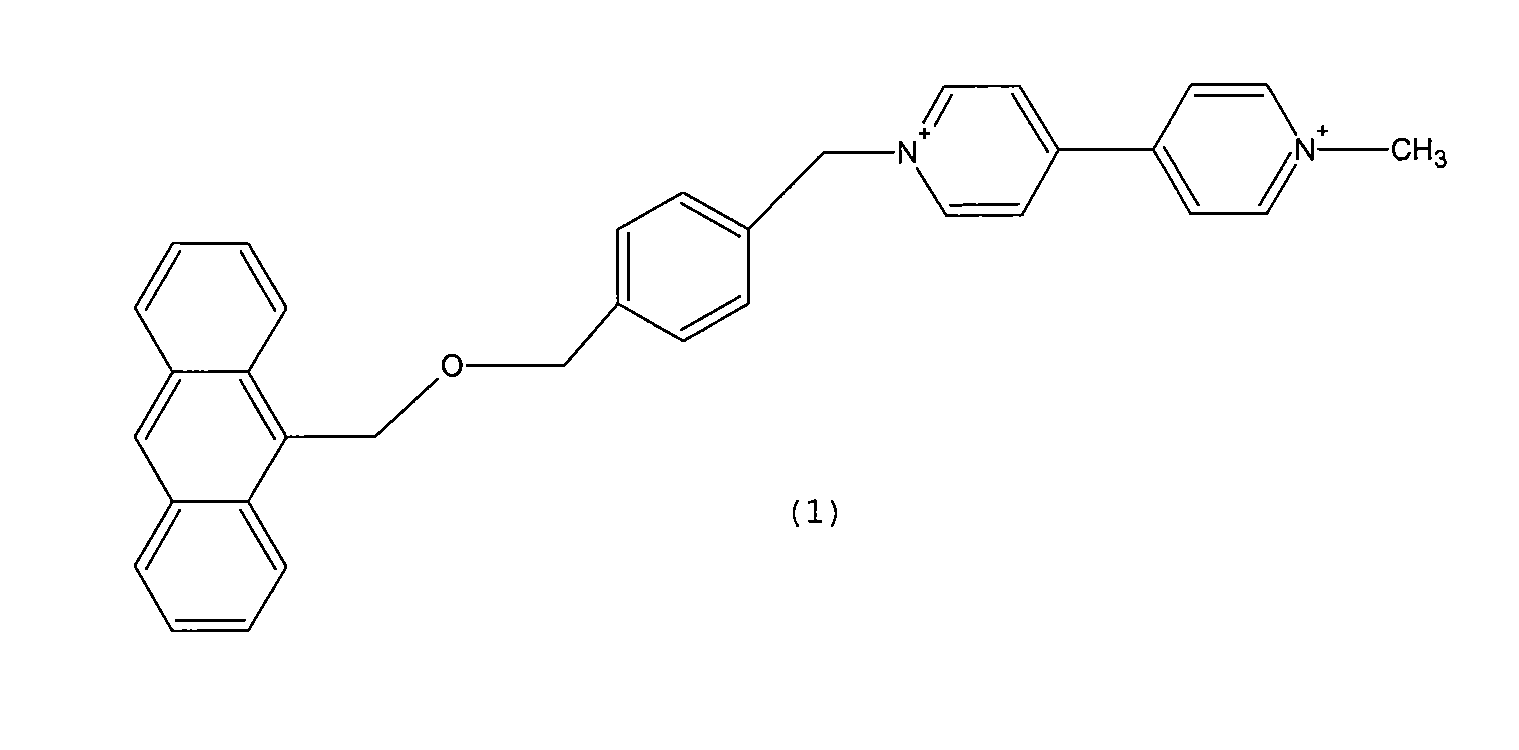
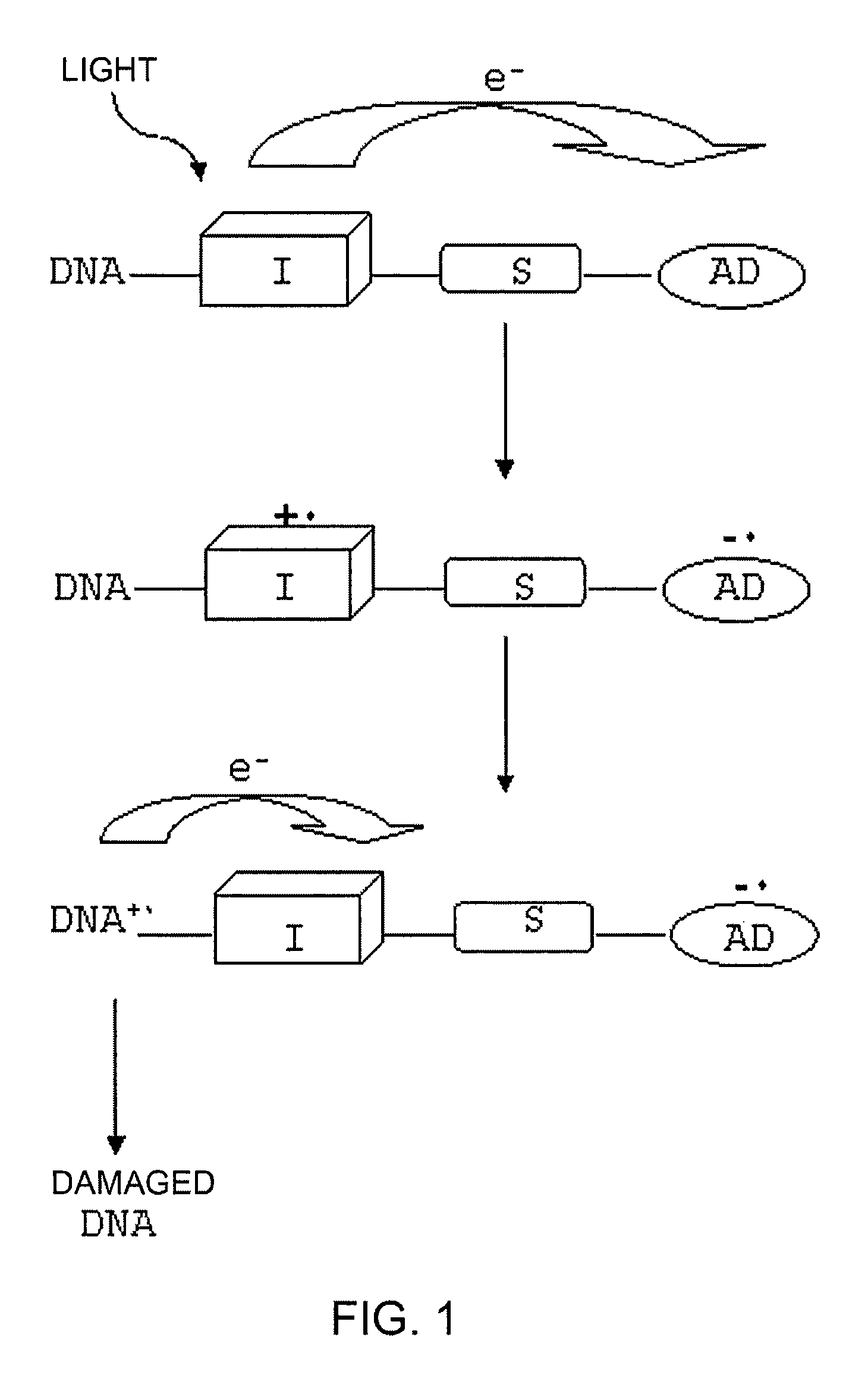
ActiveUS7799912B2Avoid changeAvoid splittingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCompound (substance)Nucleobase
A bifunctional compound comprising a molecular unit (I) intercalating between nucleobases (B) of nucleic acids, an active molecular unit (AD) capable of emitting a detectable signal, and optionally a spacer unit, in which the active molecular unit (AD) is selected from amongst chemical entities having a structure such as to interact electronically with the intercalating molecular unit (I) in such a way that, during the reaction of oxidation, the reduction-oxidation potential (EI+ / I) of the semicouple I+ / I defined by the intercalating molecular unit (I) is lower than the reduction-oxidation potential (EB+ / B) of the semicouple B+ / B defined by the nucleobases (B), and in such a way that, during the reaction of reduction, the reduction-oxidation potential (EI / I−) of the semicouple I / I− defined by the intercalating molecular unit (I) is higher than the reduction-oxidation potential (EB / B−) of the semicouple B / B− defined by the nucleobases (B). Moreover the use of the compound for detecting nucleic acids, a process for its synthesis, and a system comprising the same are described.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
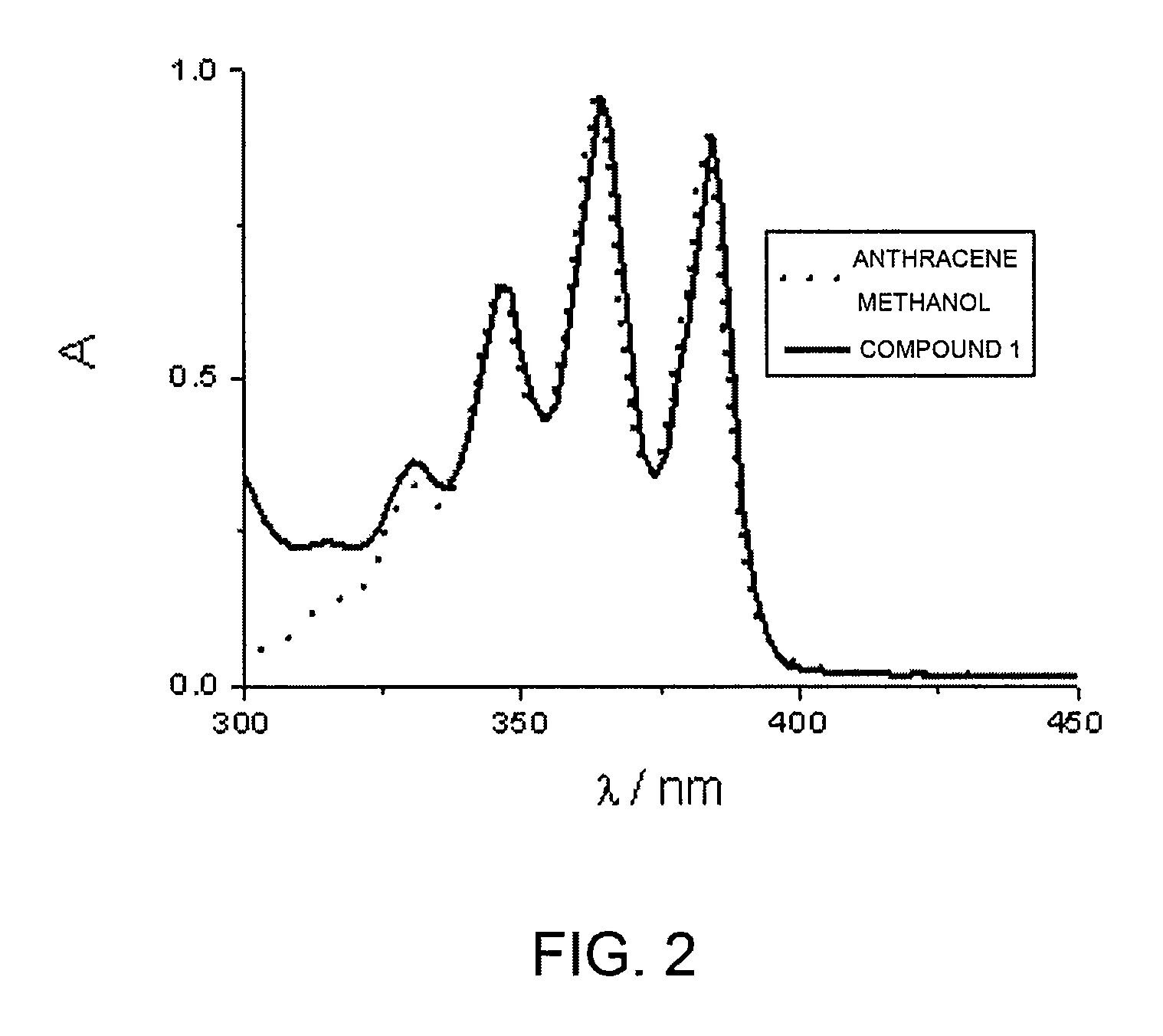
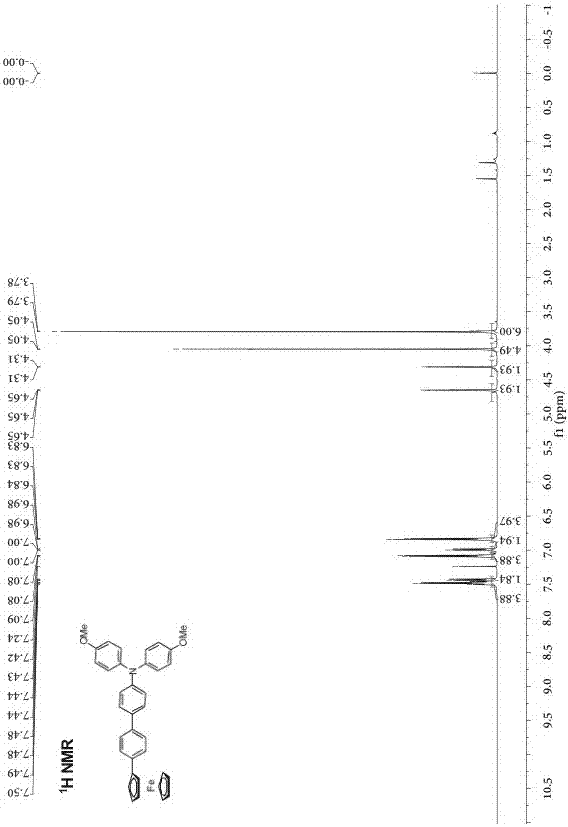
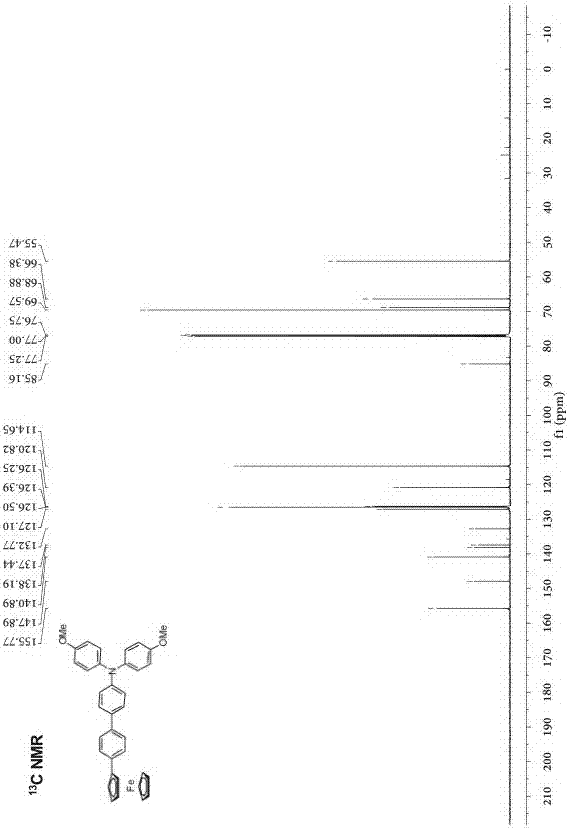
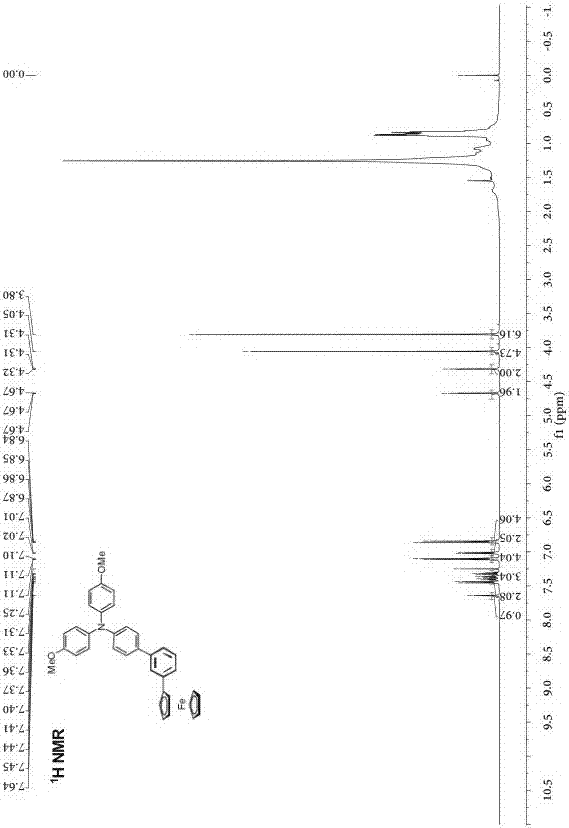
Phenyl-bridged compound with triarylamine and ferrocene end groups, method for preparing phenyl-bridged compound and application thereof
The invention discloses a phenyl-bridged compound with triarylamine and ferrocene end groups, a method for preparing the phenyl-bridged compound and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of photoelectric materials. A structural formula of the phenyl-bridged compound with the triarylamine and ferrocene end groups is shown. An R in the structural formula represents H or CH3 or OCH3; intermediate benzene ring joints are positioned at meta-positions or para-positions of respective benzene rings. The phenyl-bridged compound with the triarylamine and ferrocene end groups, the method and the application have the advantages that the phenyl-bridged compound is of a novel molecular structure, strong electron interaction between the end groups of the phenyl-bridged compound is discovered via tests by the aid of electrochemical processes, accordingly, novel molecular conducting wire materials can be developed on the basis of the phenyl-bridged compound, and a novel way for designing and synthesizing novel molecular conducting wires in follow-up procedures can be developed by the phenyl-bridged compound with the novel structure.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Pd/mesoporous Al2O3 catalyst capable of precisely regulating number of penta-coordinated Al<3+> in Al2O3 and preparation method and application of Pd/mesoporous Al2O3 catalyst
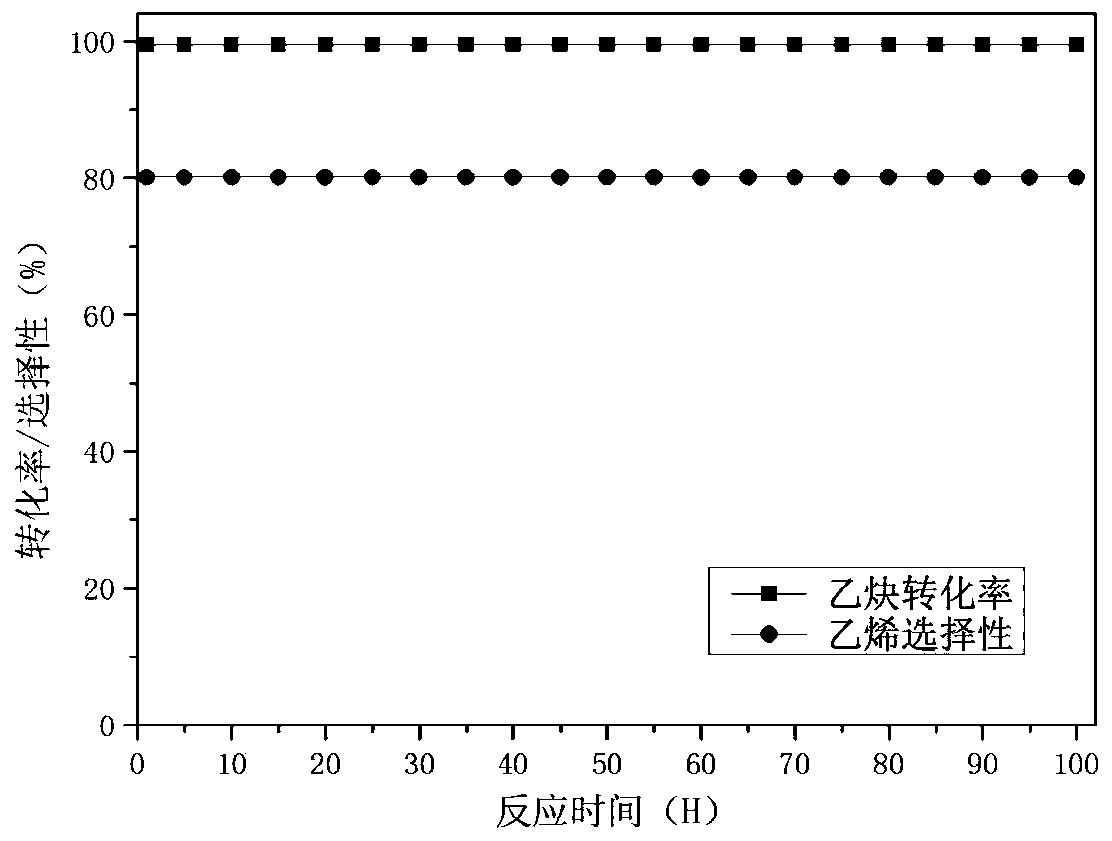
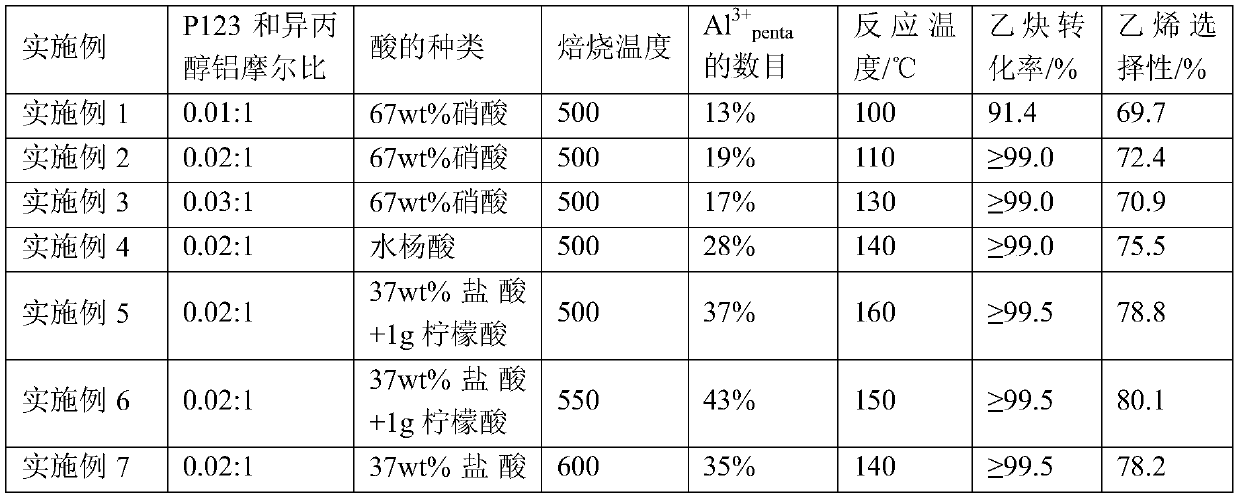
ActiveCN110586086ALow efficiencyFavor electron interactionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsEthyleneAcetylene
The invention provides a Pd / mesopore Al2O3 catalyst capable of precisely regulating the number of Al<3+><penta> in Al2O3 and a preparation method and application of the Pd / mesopore Al2O3 catalyst. Thepores of mesoporous Al2O3 in the catalyst are about 10 nm, the amount of Al<3+><penta> is raised to 43% when the catalyst is compared with commercial Al2O3, and Al<3+><penta> only appears on the surface of a carrier, and can be adopted as an important anchor site for a metal-carrier interface, so that the electronic interaction between the metal and Al2O3 defects is facilitated; the number of Al<3+><penta> in Al2O3 can be regulated precisely through change of an acid in the complex and change of the firing temperature, so that highly dispersed palladium nanoparticles are synthesized, the atomic efficiency is improved, precious metal is utilized to a maximum extent, and the cost of the catalyst is reduced; and a high conversion rate of acetylene is maintained, the selectivity to ethylene in the reaction is improved greatly, and meanwhile good stability is also achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Quantum limit catalysts and hydrogen storage materials
InactiveUS20050014640A1Promote formationMaintain good propertiesHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationChemical elementElectron density
A quantum limit catalyst. The quantum limit corresponds to a size domain in which material properties are no longer constrained by the structure and bonding requirements imposed by the macroscopic length scale. The instant quantum limit catalyst is comprised of atomic aggregations whose dimensions correspond to the quantum limit. In the quantum limit, the atomic aggregations acquire structural configurations and electronic interactions not attainable in the macroscopic limit. The structural configurations possible in the quantum limit correspond to atomic aggregations having bond lengths, bond angles, topologies and coordination environments that differ from those found in the macroscopic limit. The electronic interactions possible in the quantum limit originate from wavefunction overlap and tunneling between atoms and lead to modifications in the magnitude and / or spatial distribution of electron density at catalytic sites to provide improved catalytic properties. The modifications in electron density and wavefunction characteristics (overlap and directionality) achieved in the quantum limit provide, in effect, “new” or “virtual” chemical elements whose structure and bonding deviate from those associated with the “standard” chemical elements of conventional materials. Combinations of virtual elements provide virtual alloys having structures and properties not available in conventional alloys. Representative quantum limit catalysts include materials comprised of quantum scale atomic aggregations of metal atoms. The aggregations include one or more metals and have sizes in the angstrom scale range. Examples including catalysts derived from Fe, Mg, V and Co are disclosed. Catalytic properties are exemplified in the context of hydrogen storage. Methods that may be used to prepare quantum limit catalysts include sonochemical synthesis, thermal decomposition, and reduction.
Owner:HARNYSS IP LLC +1
Surface plasmon coupling terahertz quantum well detector
InactiveCN103367518AImprove response rateIncrease working temperaturePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSemiconductor devicesWorking temperatureWavelength
The invention provides a surface plasmon coupling terahertz quantum well detector, which comprises a semiconductor substrate, a lower electrode, a multi-quantum well structure, an upper electrode and a metal grating, wherein the metal grating is used for realizing polarity deflection of incident photons. The incident photons can be enabled to be interacted with electrons in the upper electrode through adjusting the period of the metal grating, the width of a metal strip, and the electron doping density and the thickness of the upper electrode so as to from surface plasmons on the surface of the upper electrode. The device is located in a sub-wavelength range at a terahertz frequency band because the thickness is only 2-5mum. Therefore, evanescent waves corresponding to the surface plasmons can improve the sub-band absorption efficiency of the device at the resonant frequency, and improves the response rate and the working temperature of the device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amination hexagonal boron nitride as well as preparation method and application thereof
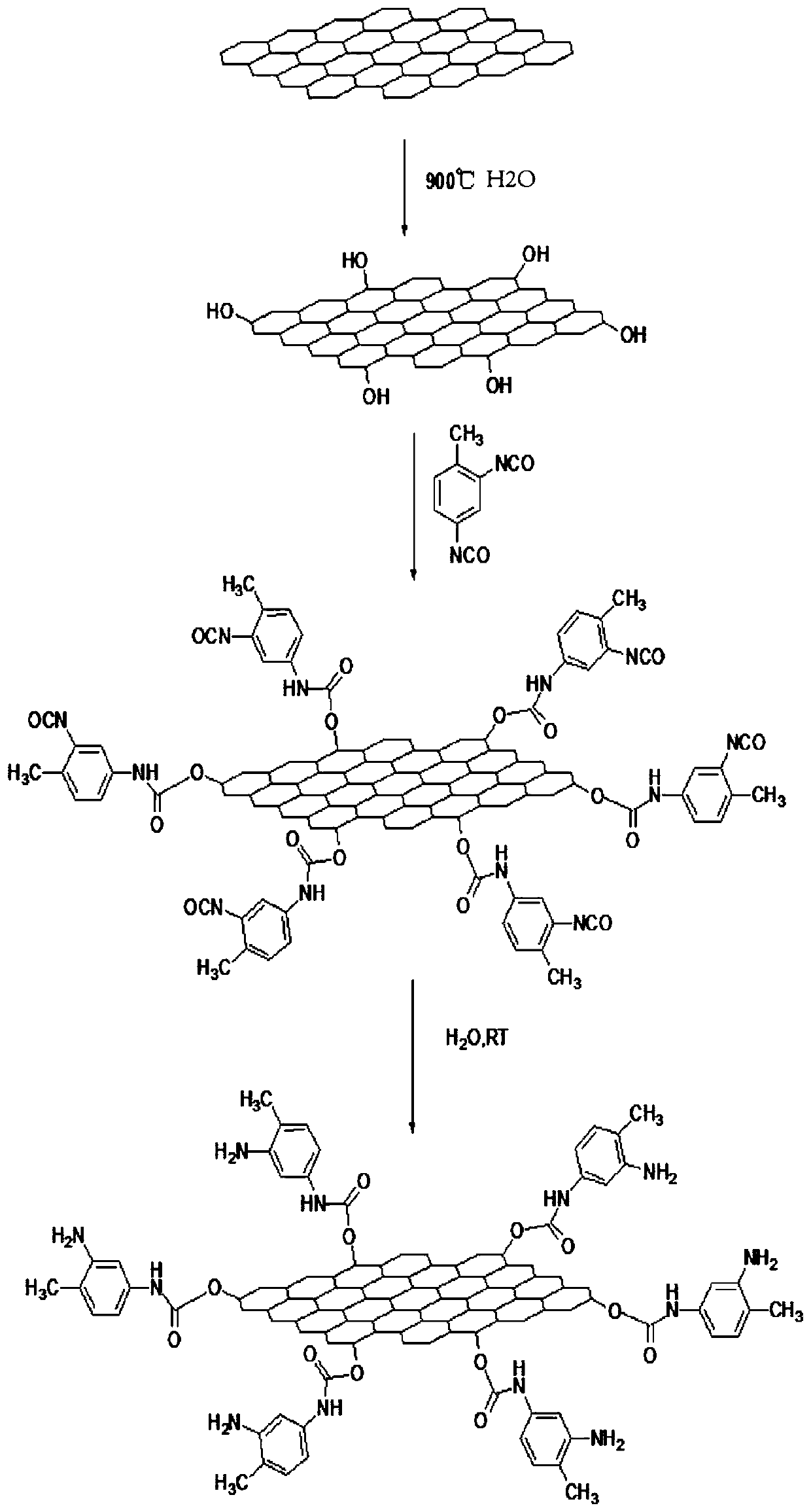
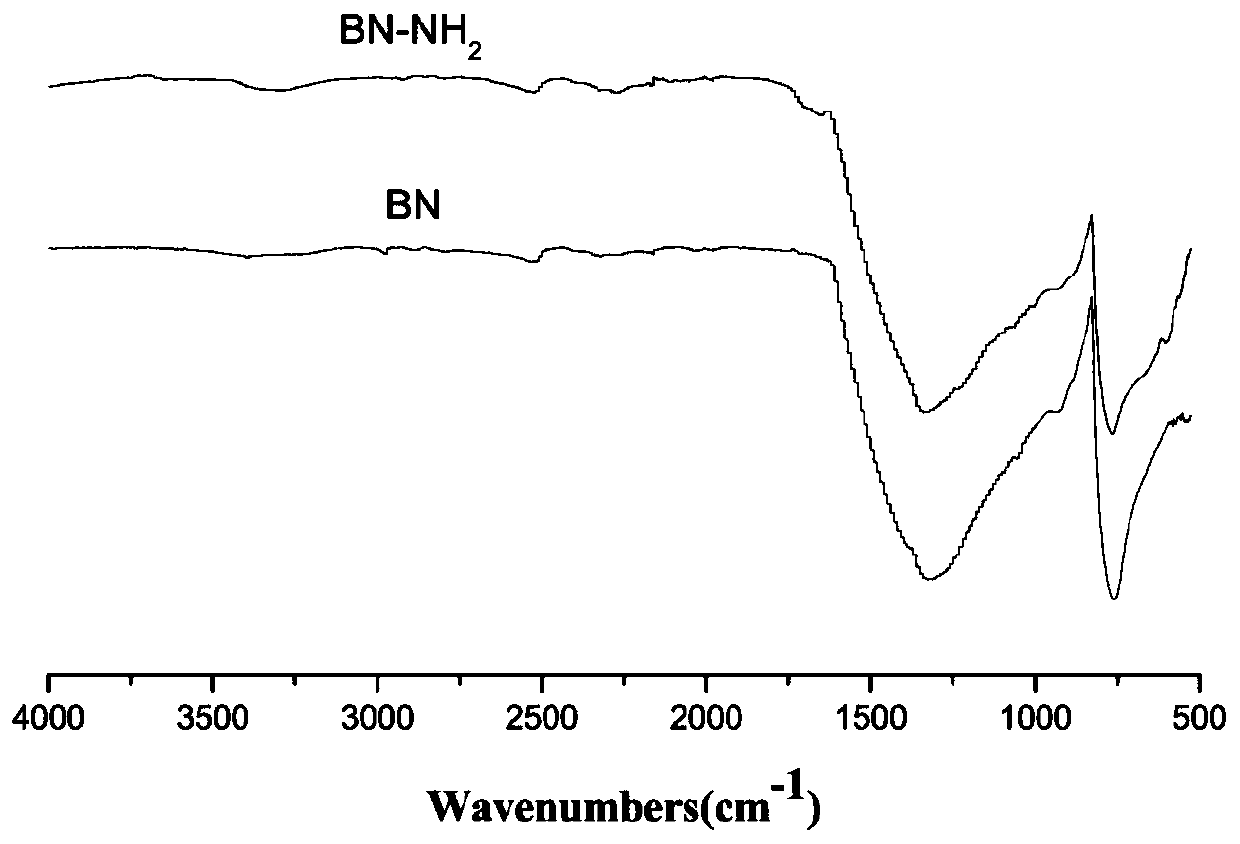
InactiveCN109810544AEvenly dispersedStable storagePigment physical treatmentPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsWater vaporHexagonal boron nitride
The invention provides amination hexagonal boron nitride as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Through amination modification and Pi-Pi electron interaction, hexagonal boron nitridedispersion liquid with dispersion uniformity and storage stability is obtained. The method comprises the following steps that commercial hexagonal boron nitride powder is calcined in a tubular furnace in vapor atmosphere to obtain hydroxylated modified boron nitride; the hydroxylated modified boron nitride power and excessive toluene diisocynate react to obtain an intermediate product; then, theintermediate product and excessive water react to obtain the amination hexagonal boron nitride. The operation of the method provided by the invention is simple; the reactant treatment is simple; the storage of the prepared amination hexagonal boron nitride is stable.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Layered inorganic nanocrystal photovoltaic devices
A non-sintered structure. The non-sintered structure includes a first non-sintered nanocrystal layer, and a second non-sintered nanocrystal layer wherein the first layer and the second layer are configured to interact electronically.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanomatrix separation of chromophores and uses thereof in luminescent devices
InactiveUS8917018B2Minimizes interactabilityAvoid interactionMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLight emitting deviceChromophore
A system and process for controlling electronic interactions between two or more interactable materials.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Nuclear imaging using three-dimensional gamma particle interaction detection
InactiveUS7397038B2High resolutionReduce uncertaintySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionDetector array
An improved method of, and apparatus for, nuclear imaging takes advantage of the ability to determine the depth of gamma ray / electron interaction within a semiconducting gamma ray detector to determine the (most highly probable) location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction within the detector. Lines of interaction constructed between opposing detector arrays, extending between the location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction in each detector associated with the coincident detection of gamma radiation, permits a positron-emitting object of interest to be imaged according to protocols known in the art, but with better spatial resolution than previously believed to have been known.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com