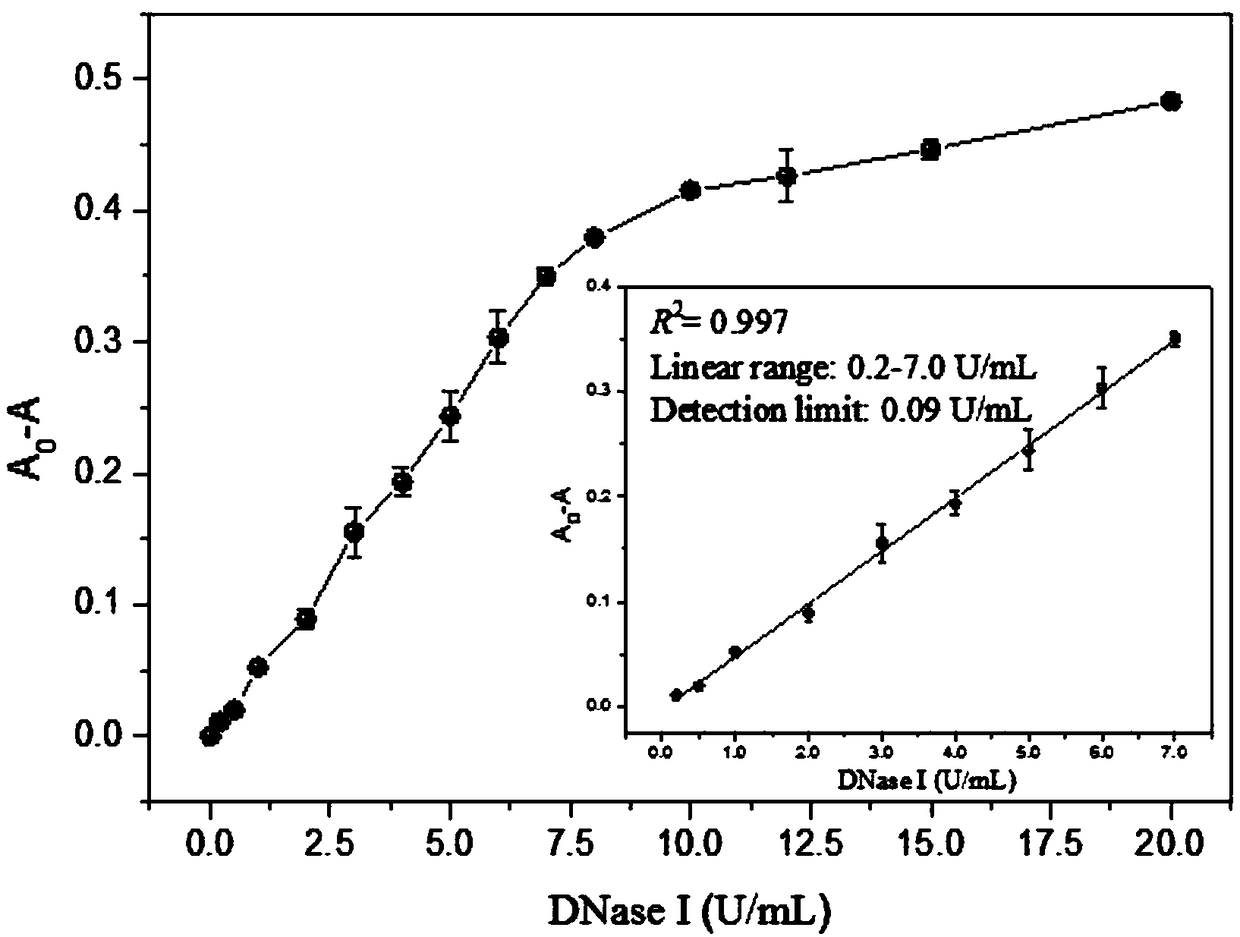
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Deoxyribonuclease I" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deoxyribonuclease I (usually called DNase I), is an endonuclease coded by the human gene DNASE1. DNase I is a nuclease that cleaves DNA preferentially at phosphodiester linkages adjacent to a pyrimidine nucleotide, yielding 5'-phosphate-terminated polynucleotides with a free hydroxyl group on position 3', on average producing tetranucleotides. It acts on single-stranded DNA, double-stranded DNA, and chromatin. In addition to its role as a waste-management endonuclease, it has been suggested to be one of the deoxyribonucleases responsible for DNA fragmentation during apoptosis.
Human amnion mesenchymal stem cell serum-free culture medium and culture method thereof
The invention relates to a human amnion mesenchymal stem cell serum-free culture medium and a culture method thereof. The culture medium is formed by adding human serum albumin, human transferrin, human insulin and sodium selenite into a DMEM / F12 basic culture medium. The culture method for the culture medium comprises the following steps of: digesting human amnion by using trypsin, then digesting the human amnion by using collagenase IV and deoxyribonuclease I, and filtering the mixture to obtain single cell suspension; and adding the human serum albumin, the transferrin, the insulin and the sodium selenite into the DMEM / F12 basic culture medium in a ratio of VDMEM to VF12 of 1:1, and putting human amnion mesenchymal stem cells in a 37 DEG C CO2 incubator with saturated humidity and volume fraction of 5 percent under the serum-free condition, wherein culture in vitro and amplification are realized by solution change and transfer of culture, potentiality of multi-direction differentiation is maintained, and the amplified cells can be induced in vitro to form cartilage cells, osteoblasts and adipocytes. The culture medium and the culture method have the characteristics of no other animal sources, wide source and no limitation of ethics.
Owner:辽宁艾米奥干细胞与再生医学研究院有限公司
Separating and culturing process of human amnion mesenchyme stem cell and its medical composition
ActiveCN1810959AWide variety of sourcesUnrestricted by ethicsMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSingle cell suspensionCulture mediums
The present invention is separating and culturing process of human amnion mesenchyme stem cell and its medical composition. The separating and culturing process includes digesting human amnion successively with trypsin, collagenase and deoxyribonuclease, and filtering to prepare single cell suspension; culturing in DMEM / F12 culture medium with VDMEM and VF12 in the equal ratio and containing ox embryo blood serum in 10-20 vol% and basic fibroblast growth factor of ultimate concentration 10-20 ng / ml inside a culture box at 37 deg.c, saturated humidity and CO2 in 5 vol%; and replacing liquid and culture passage to proliferate and purify human amnion mesenchyme stem cell. The process has wide material source no ethnic limitation and wide application foreground. The medical composition may be used in various kinds of treatment.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH +4
Nuclease inhibitor cocktail
InactiveUS7163793B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismRibonuclease
Methods and compositions for inhibiting and / or inactivating nucleases by employing nuclease inhibitors are provided. The nuclease inhibitors comprise anti-nuclease antibodies and non-antibody nuclease inhibitors. The anti-nuclease antibodies of the present invention may be a polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies, and may be anti-ribonuclease antibodies, anti-deoxyribonuclease antibodies, or antibodies to non-specific nucleases. A preferred embodiment comprises at least two nuclease inhibitors, and is referred to as a nuclease inhibitor cocktail. In some specific embodiments, the invention concerns methods of performing in vitro translation comprising obtaining a first nuclease inhibitor, which inhibitor is further defined as an anti-nuclease antibody, and placing the anti-nuclease antibody in an in vitro translation reaction. In many cases, the in vitro translation reaction comprises at least one nuclease, which may be a ribonuclease, a deoxyribonuclease, or a nonspecific nuclease. The invention also relates to kits for the performance of various microbiological procedures, which kits comprise the nuclease inhibitors described herein.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
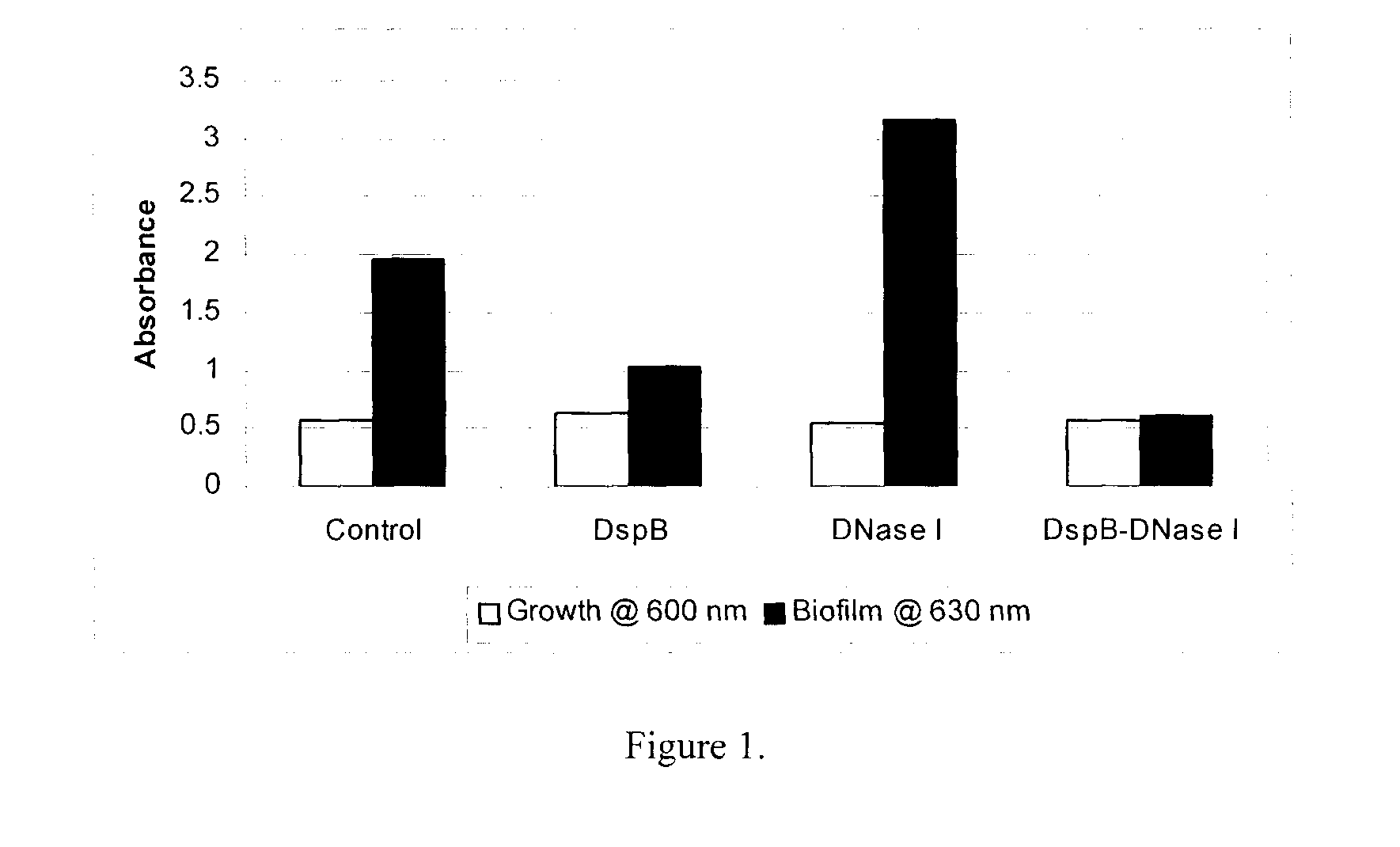
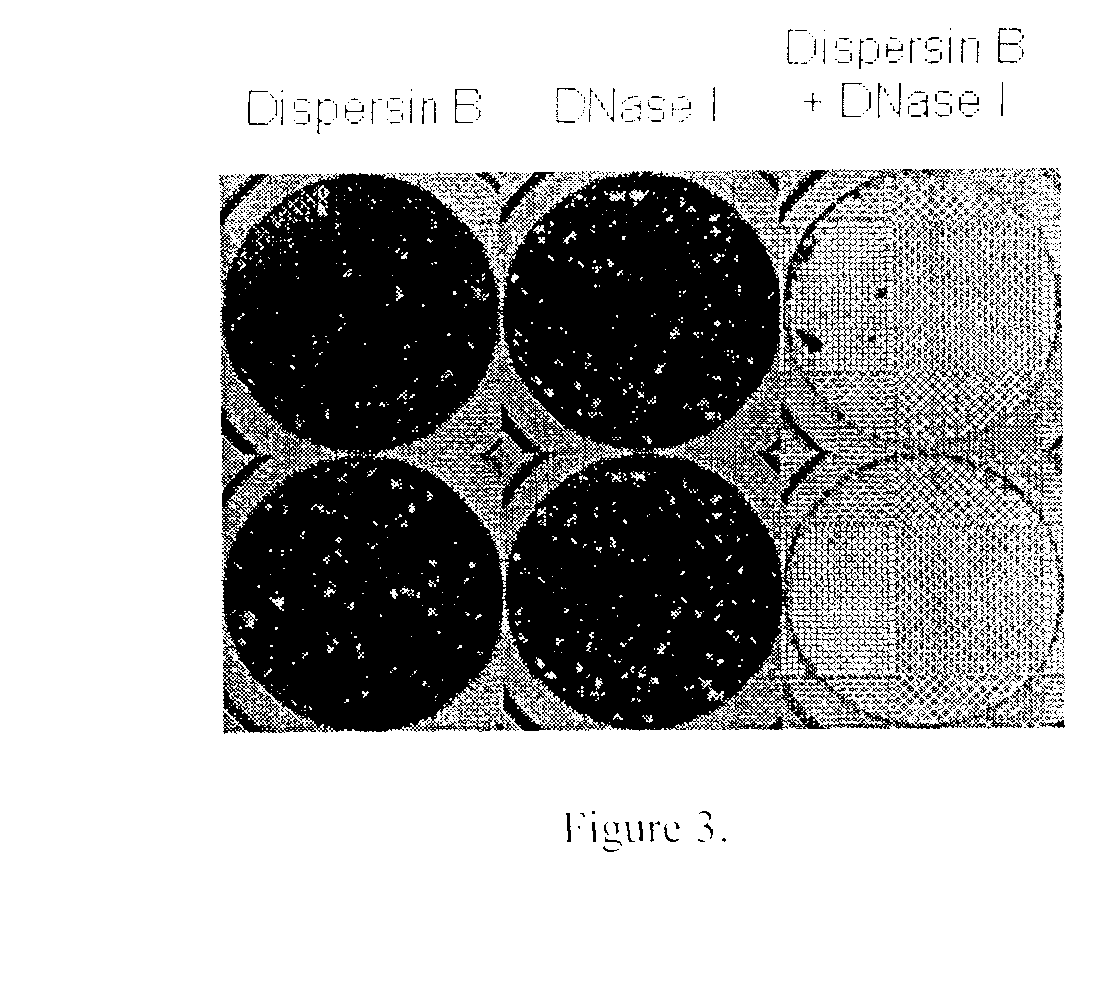
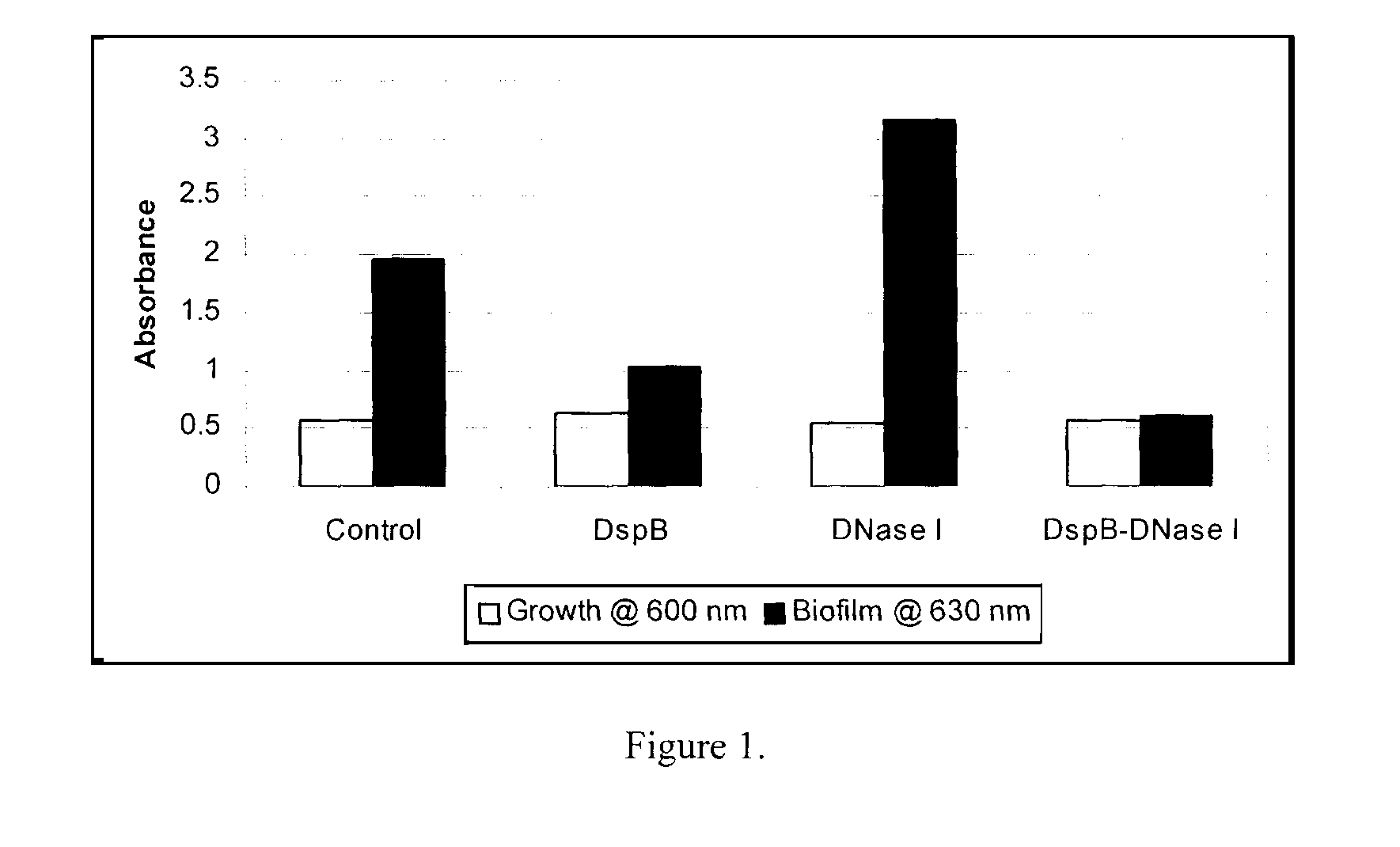
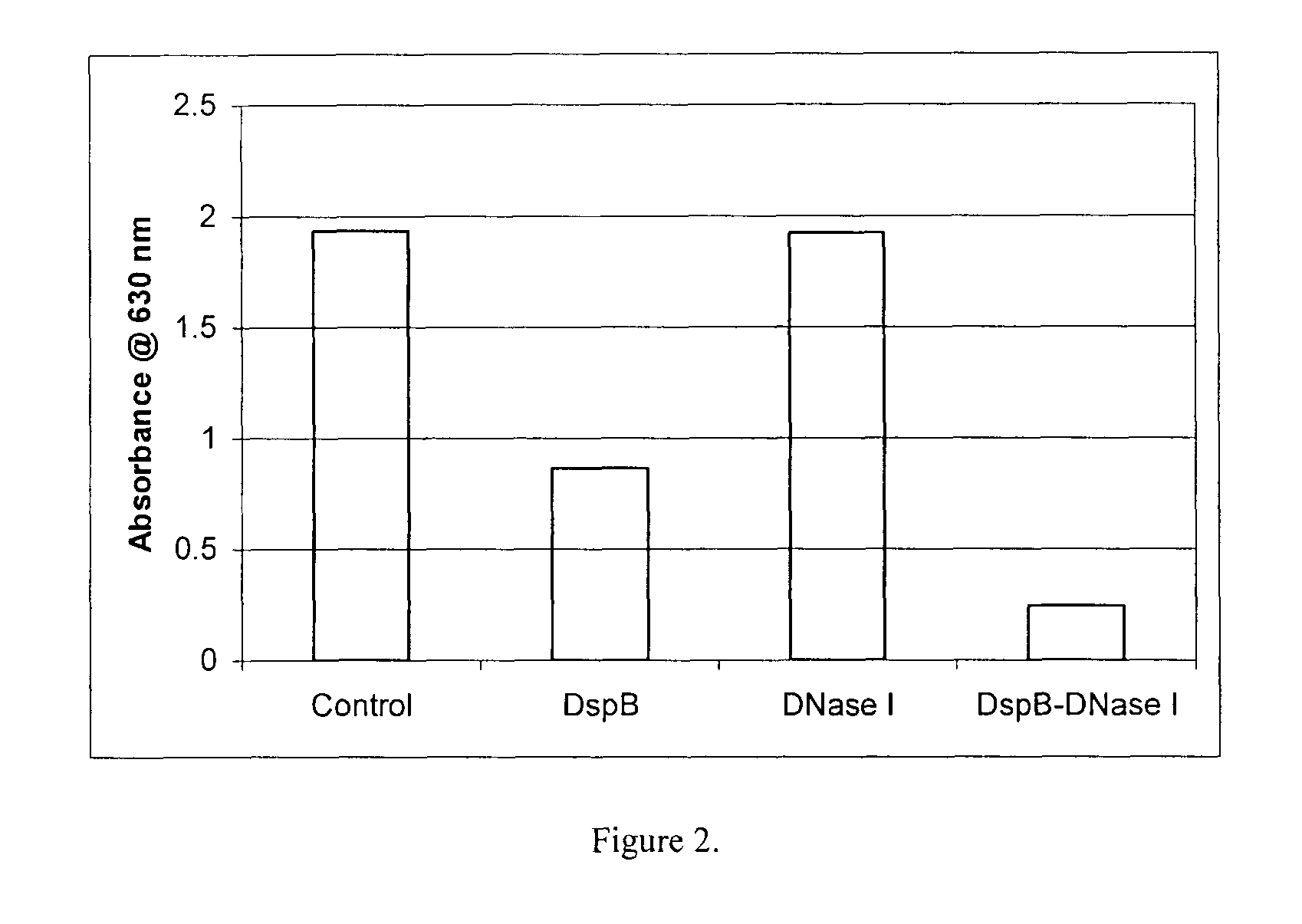
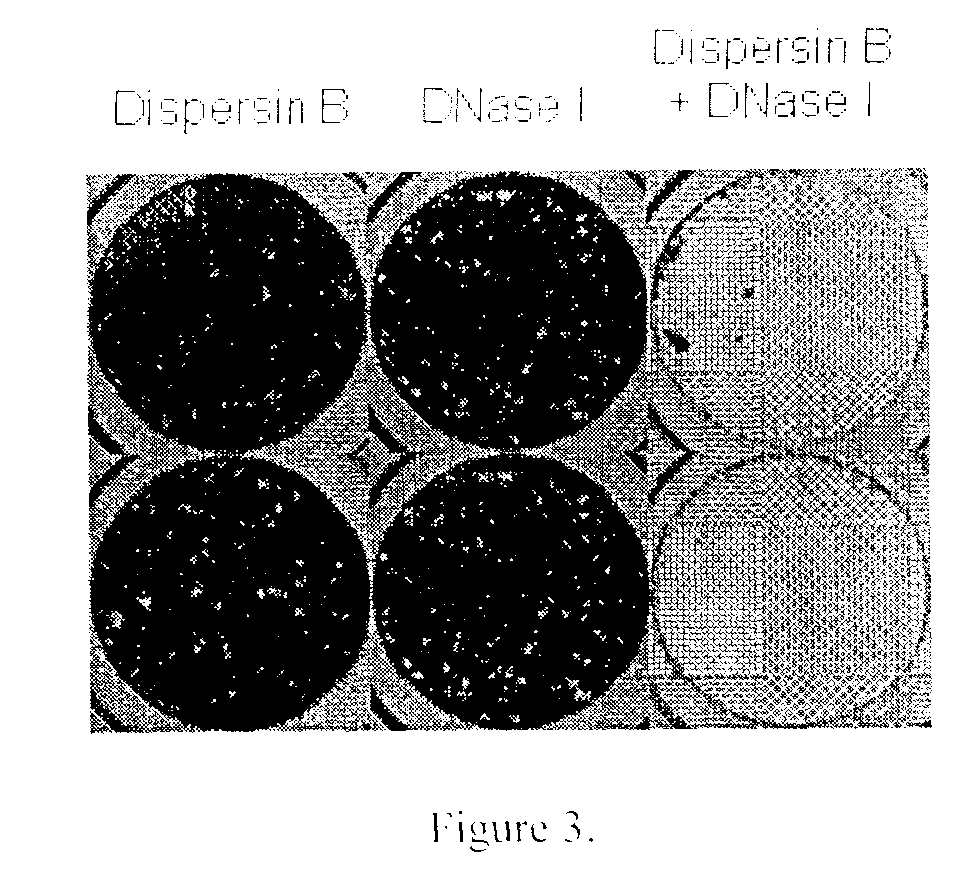
Dispersinb, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K-Based Antibiofilm Compositions and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110086101A1Avoid UTIsPrevents urinaryAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMicroorganismProteinase K
The present invention provides antibiofilm composition comprising two or more agents selected from the group consisting of DispersinB™, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K for preventing growth and proliferation of biofilm-embedded microorganisms in wound care, oral care, and disease-related infections and methods of treatment in mammals. The invention further provides methods for preparing medical devices, and wound care devices using an antibiofilm composition comprising two or more antimicrobial agents selected from the group consisting of DispersinB™, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K.
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Staphylococcus aureus multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101613745AStrong specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSmaIStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a staphylococcus aureus multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and a detection method thereof; the detection kit comprises PCR MIX; wherein, the PCR MIX contains 2*PCR buffer, 1.0-3.0mmol / L of MgCl2, 180-220mu mol / L of dNTP each, heat-resisting deoxyribonuclease nuc gene primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.1 and the concentration of SEQ NO.1 is 100-600nmol / L, plasma-coagulase clfA gene primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.3 and the concentration of SEQ NO.4 is 100-600nmol / L, SmaI restriction fragment specific sequence primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.5 and the concentration of SEQ NO.6 is 100-600nmol / L, 20-60U of Taq enzyme and bromophenyl blue dye. The multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and the detection method provided by the invention have simple configuration, the detection kit and the detection method can be used in industrialized production; the detection method is sensitive and has short detection cycle and strong maneuverability, so that the method can be widely applied in the fields of food hygiene, environmental monitoring, etc.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
Nuclease inhibitor cocktail
Methods and compositions for inhibiting and / or inactivating nucleases by employing nuclease inhibitors are provided. The nuclease inhibitors comprise anti-nuclease antibodies and non-antibody nuclease inhibitors. The anti-nuclease antibodies of the present invention may be a polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies, and may be anti-ribonuclease antibodies, anti-deoxyribonuclease antibodies, or antibodies to non-specific nucleases. A preferred embodiment comprises at least two nuclease inhibitors, and is referred to as a nuclease inhibitor cocktail. In some specific embodiments, the invention concerns methods of performing in vitro translation comprising obtaining a first nuclease inhibitor, which inhibitor is further defined as an anti-nuclease antibody, and placing the anti-nuclease antibody in an in vitro translation reaction. In many cases, the in vitro translation reaction comprises at least one nuclease, which may be a ribonuclease, a deoxyribonuclease, or a nonspecific nuclease. The invention also relates to kits for the performance of various microbiological procedures, which kits comprise the nuclease inhibitors described herein.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Construction method of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank
ActiveCN103422176AWide variety of sourcesUnrestricted by ethicsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLibrary creationSingle cell suspensionPancreatic hormone
The invention relates to a construction method of a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank. The construction method comprises the following steps: taking a human amnion for detection, flushing and washing the human amnion with a phosphate buffered solution, then smashing the human amnion, diluting with the phosphate buffered solution, digesting with trypsin, digesting with collagenase IV and deoxyribonuclease I, and filtering to obtain a single-cell suspension; by adding human serum albumin, transferring, insulin and sodium selenite into a DMEM / F12 basal culture medium with the ratio of VDMEM to VF12 being 1 to 1, placing human amnion mesenchymal stem cells in an incubator under the serum-free condition, and then performing liquid exchange and culture transfer; subjecting the mesenchymal stem cells obtained through in vitro culture and proliferation to liquid nitrogen refrigeration, and preserving the cells according to the gender of newborn infants, the ABO / Rh type and the HLA type; establishing cell information files, so that the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank is constructed. The method has the characteristics of no other animal derivation, wide source range and no ethic limitation. With adoption of the method, the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can be provided for cell therapy and other application.
Owner:沈阳艾米奥生物工程技术研发中心有限公司
DispersinB(TM), 5-fluorouracil, deoxyribonuclease I and proteinase K-based antibiofilm compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS8617542B2Prevents urinary and vascular infectionAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseWound care
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Multi-enzyme system for separating different tissues-derived primary culture cells of normal human and mammal, application and related kit thereof
InactiveCN101914504AEasy to freezePromote recoveryHydrolasesNervous system cellsBiotechnologyNeutral protease
The invention relates to a multi-enzyme system for separating different tissues-derived primary culture cells of a normal human and a mammal. The system comprises a plurality of 0.0125 to 0.125 weight percent of trypsin, 0.02 to 0.2 weight percent of collagenase I-IV, 0.0015 to 0.015 weight percent of hyaluronidase, 0.02 to 0.2 weight percent of neutral protease, 0.0015 to 0.015 weight percent of deoxyribonuclease I, 1 to 10 U / ml papain, 0.015 to 0.15 weight percent of pronase, 5 to 50 U / ml elastase and 0.01 to 0.1 weight percent of separase. The invention also relates to the application of the multi-enzyme system and a kit formed by the multi-enzyme system. The multi-enzyme system of the invention has the characteristics of reasonable design and capacity of separating the different tissues-derived primary culture cells of the normal human and the mammal highly specifically and highly sensitively; and the separated primary culture cells have the characteristics of high survival rate, high purity, easy cryopreservation and recovery, can be used for medicament experimental evaluation, medicament toxicity test and medicament therapeutic judgment, and are suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:刘东旭
Mixed enzyme for skin tissue dissociation, preparation method of mixed enzyme, dissociation kit and dissociation method
ActiveCN112708610AHigh activityImprove experimental efficiencyCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDNA - Deoxyribonucleic acidDeoxyribonuclease I
The invention discloses a mixed enzyme for skin tissue dissociation. The mixed enzyme is composed of collagenase II, trypsin and deoxyribonuclease I, wherein the concentration of the collagenase II is 2-4 mg / mL; the concentration of the trypsin is 1-3 mg / mL; and the concentration of the deoxyribonuclease I is 0.01-0.05 mg / mL. Besides, the invention further discloses a dissociation method for the skin tissue. The skin tissue is pretreated with a specific buffer solution, and tissue dissociation is conducted through the specific mixed enzyme, so that a skin tissue single-cell suspension with large number of single cells, good activity, few fragments and low clustering rate can be efficiently, rapidly and stably obtained. The screened and optimized mixed enzyme and concentration have higher pertinence and higher efficiency; more costs and time are saved compared with those in a method of combining a few collagenases in a broad spectrum; and a good tool is provided for single-cell related research of a skin tissue sample which is always difficult to dissociate.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
Methods and articles for detecting deoxyribonuclease activity
InactiveCN102333884AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismDNase activity
The disclosure provides articles and methods useful for detecting a discrete source of DNase activity. DNase-producing microorganisms can be detected. The device can further include selective agents and / or indicators to differentiate groups or species microorganisms. Methods of use include detecting or enumerating DNase- producing microorganisms.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
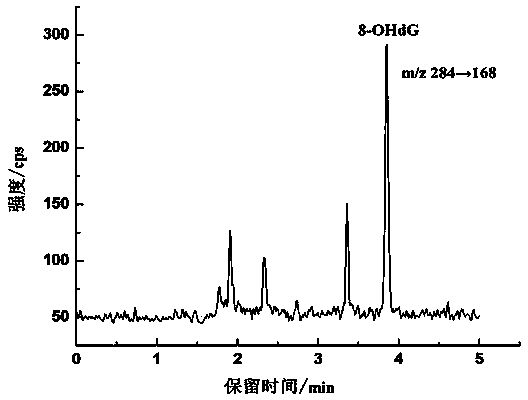
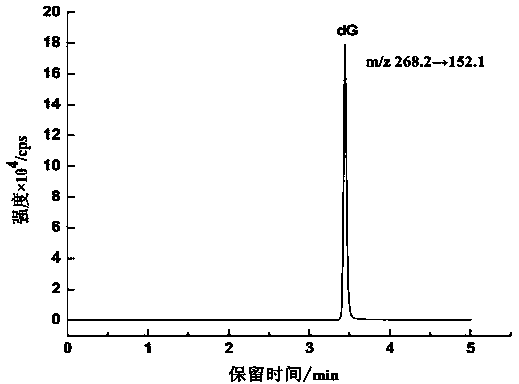
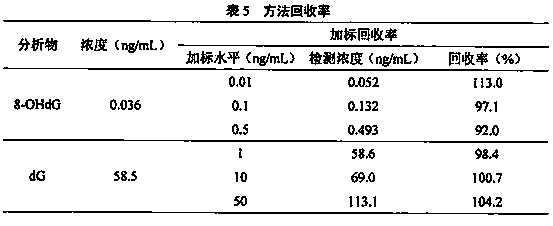
Method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 2'-deoxyguanosin (dG) in cell DNA
InactiveCN104181250AHigh sensitivityAvoid interferenceComponent separationDeferoxamine mesylateHydrolysate
The invention belongs to a cell DNA detection technology and in particular relates to a method for detecting 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 2'-deoxyguanosin (dG) in cell DNA. The method can be used for quantitatively detecting the change of the content of 8-OHdG and dG in cell DNA, caused by exposure of harmful ingredients in cigarette smoke, so that the purpose of evaluating DNA oxidation damage caused by induction of the harmful ingredients can be achieved. According to the method, deoxyribonuclease I and alkaline phosphatase are used for hydrolyzing DNA in a cell, and deferoxamine mesylate is added into enzymatic hydrolysate, so that the oxidation of dG in the enzymolysis process is avoided; enzymatic hydrolysate is detected by HPLC-MS / MS; the cell DNA oxidation damage degree is evaluated according to the value of 8-OHdG / 10<6>dG. By virtue of the method, the interference of high-concentration metal ions and artificial dG oxidation is removed, and thus the result is relatively accurate; the method is low in detection limit, high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and high in recovery rate.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Multi-enzyme system used for separating patient tumor tissue-originated primary cells, application method thereof, purpose thereof, and relative kit thereof
InactiveCN102373186AImprove the survival rate of cultureHigh culture purityHydrolasesTumor/cancer cellsPrimary cellCell separation
The invention relates to a multi-enzyme system used for separating patient tumor tissue-originated primary cells. The system comprises components of, by weight: 0.02 to 0.2% of collagenase I-IV, 0.001 to 0.01% of hyaluronidase, 0.01 to 0.1% of trypsin, 0.02 to 0.2% of proteinase neutral, 0.001 to 0.01% of deoxyribonuclease I, and 5 to 50U / ml of elastase. The invention also relates to an application method of the system, an application of the system, and a kit formed by the system. The multi-enzyme system is advantaged in reasonable design. With the system, patient tumor tissue-originated primary cells can be separated with high specificity and high sensitivity. The separated primary cells are characterized by high survival rate, high purity, easy cryopreservation and easy resuscitation. The system and the kit can be used in medicine experimental evaluation, medicine toxicity testing, and medicine therapeutic performance determination. The system, the method and the kit are suitable to be widely popularized.
Owner:刘东旭
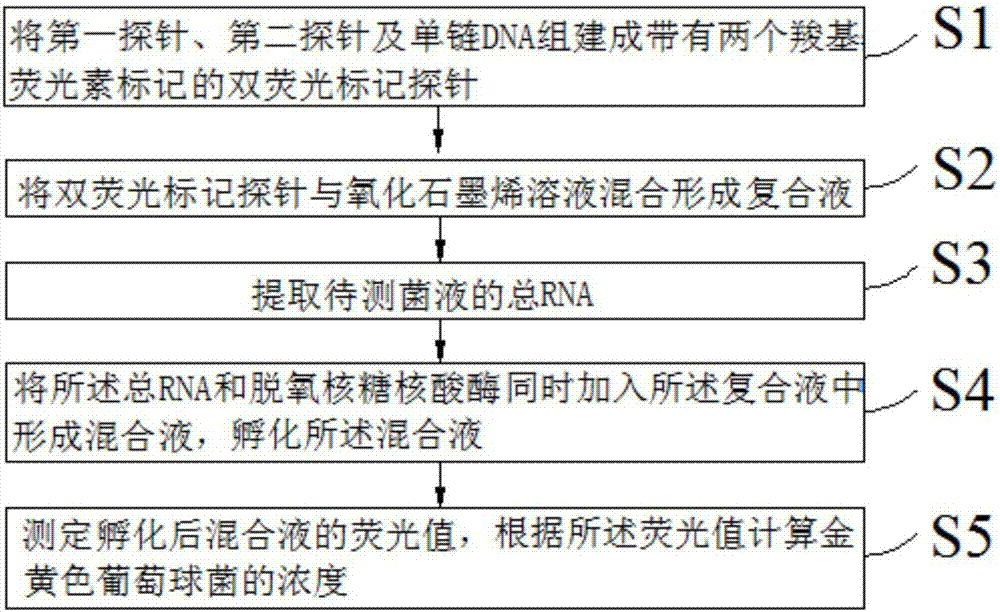
DNA probe, reagent kit and method for detecting deoxyribonuclease
PendingCN105648062ASuitable for routine quality control needsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNAQuenching
The invention provides a DNA probe, a reagent kit and a method for detecting deoxyribonuclease. The hairpin-shaped DNA probe serves as a substrate of deoxyribonuclease, and a fluorescence group and a corresponding fluorescence quenching group are marked at the two ends or the interior of the probe respectively. When the structure of the probe is complete, the fluorescence group and the fluorescence quenching group are located on the same DNA molecule, excited fluorescence of the fluorescence group is absorbed by the fluorescence quenching group, and the fluorescence group does not emit fluorescence; when the probe is degraded by deoxyribonuclease, the fluorescence group and the fluorescence quenching group are separated, and the fluorescence group can emit fluorescence normally. Whether deoxyribonuclease exists in a reaction system or not can be judged as long as the intensity of fluorescence emitted from the reaction system is detected with a real-time quantitative PCR instrument. The method can be widely applied to quality detection on residues of deoxyribonuclease in biological products or quantitative detection of deoxyribonuclease.
Owner:广州锐博生物技术有限公司
Method for preparing clinical-level adipose-derived stem cells
ActiveCN109652367AProliferate fastShort training periodCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHyaluronidaseDeoxyribonuclease I
The invention relates to a method for preparing clinical-level adipose-derived stem cells. Specifically, the method includes the steps of firstly, washing adipose tissue with double-resistance salinecontaining mycillin mixed liquid, and cutting off and removing adipose; secondly, conducting chylosis on the adipose tissue obtained in the first step; thirdly, adding the adipose tissue subjected tochylosis in the second step to an a-MEM containing an enzyme mixture to be digested, wherein the enzyme mixture contains I-type collagenase, hyaluronidase, deoxyribonuclease I and trypsin; fourthly, centrifuging digested liquid in the third step, and removing supernate to obtain the adipose-derived stem cells.
Owner:JILIN TUO HUA BIOTECH
Detection method for staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN107022612AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus cohniiTotal rna
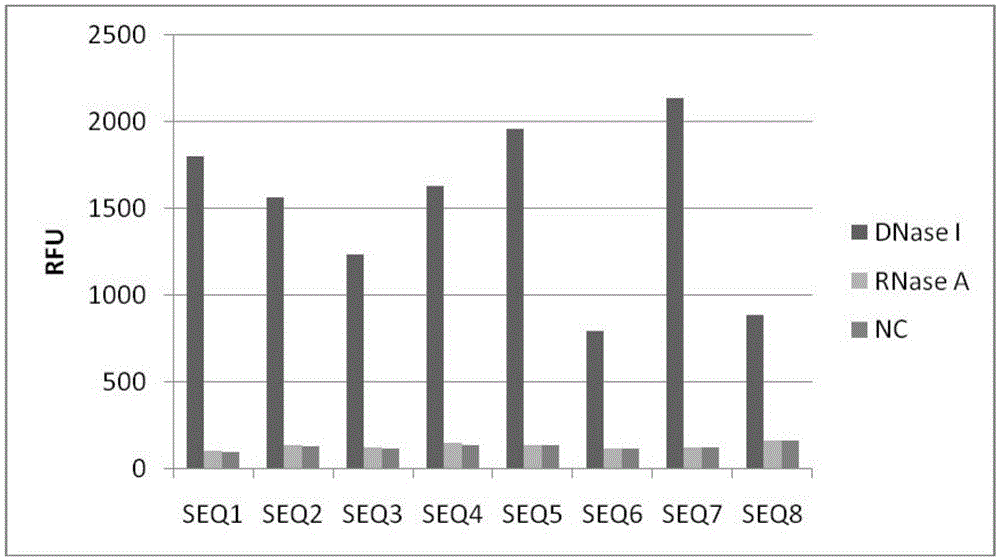
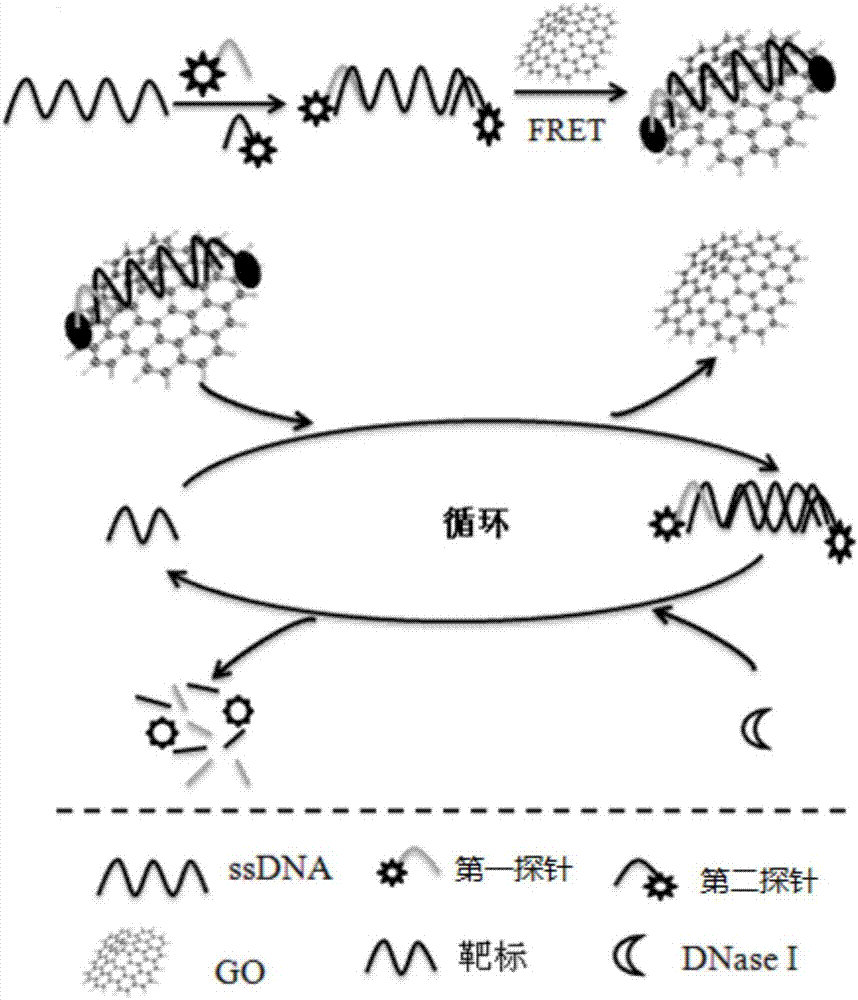
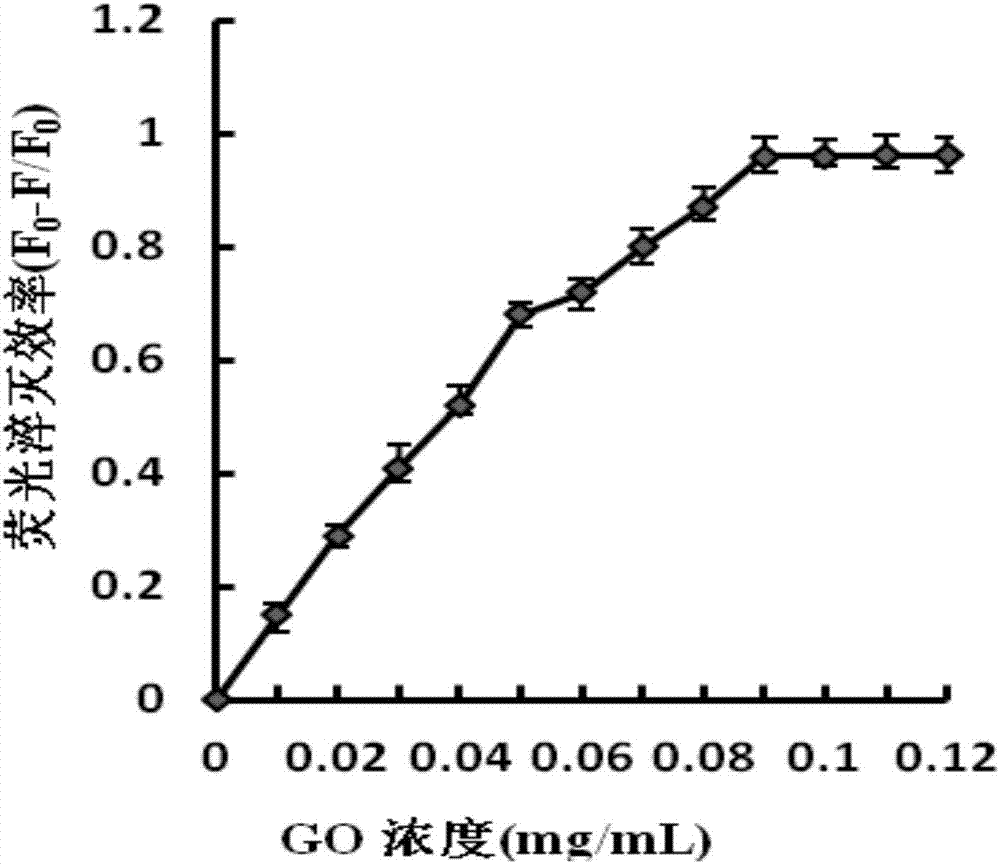
The invention discloses a detection method for staphylococcus aureus. The detection method comprises the following steps: preparing a double-fluorescence-label probe with two carboxy flouorescein labels from a first probe, a second probe and a single-chain DNA; mixing the double-fluorescence-label probe with a graphene oxide solution, thus forming a compound solution; extracting the total RNA of a bacteria solution to be detected; simultaneously adding the total RNA and deoxyribonuclease into the compound solution, thus forming a mixed solution, and incubating the mixed solution; measuring a fluorescence value of the incubated mixed solution, and calculating the concentration of the staphylococcus aureus according to the fluorescence value. According to the detection method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, a section of specifically recognized staphylococcus aureus 16S rRNA is used as a target to design the probe, and a double-fluorescent-label probe / graphene oxide system is built based on the fluorescence superposition principle; cyclic detection on the target is realized according to the characteristic of the deoxyribonuclease, so that a fluorescence signal is amplified, the sensitivity of the detection method for the staphylococcus aureus is improved, and the detection efficiency of the detection method is also improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA MEDICAL UNIV
Mesenchymal stem cell separated from placenta blood vessel with digestive enzyme composition
ActiveCN109628388AGood differentiation effectHigh purityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood Vessel TissueHyaluronidase
The invention relates to a mesenchymal stem cell separated from the placenta blood vessel with a digestive enzyme composition, in particular to the digestive enzyme composite used for a method for separating the placenta mesenchymal stem cell from the placenta blood vessel. A buffering solution containing tissue digestive enzymes is provided with added digestive enzymes which include pancreatic enzymes, deoxyribonuclease I, collagenase II, collagenase IV and hyaluronidase. In addition, the invention further relates to the method for separating the mesenchymal stem cell from the placenta bloodvessel, and the method includes the steps that the placenta is sterilized; the placenta vessel is separated from the placenta; cutting, cleaning and bloodiness filtering removal are conducted, so thatplacenta blood vessel tissue is obtained; mixed enzyme liquor is added for digestion; digestion is stopped, and interstitial fluid is filtered and collected; cell sediments obtained through centrifuging are original placenta mesenchymal stem cells, re-suspending is conducted, sampling is conducted, and the number nucleated cells and the survival rate of the nucleated cells are calculated; the obtained cells are subjected to refrigeration preservation or continuous passage and / or identified, detected and subjected to refrigeration preservation and database creation. Through the method, the efficiency of separating the mesenchymal stem cell from the placenta blood vessel can be improved effectively.
Owner:BOYALIFE
Method for preparing high-quality single-cell suspension by remarkably improving plaque digestion
InactiveCN111549019ADoes not affect activityDoes not affect concentrationHydrolasesArtificial cell constructsDigestion TreatmentSingle cell suspension
The invention discloses an artery plaque digestion method capable of remarkably improving the quality of a single-cell suspension. The kit comprises a collagen hydrolase I, a collagen hydrolase II, acollagen hydrolase IV, a collagen hydrolase XI, calcium chloride, deoxyribonuclease I, a phosphate buffer salt solution, a bovine serum albumin solution and an RPMI 1640 cell culture solution. The invention also discloses an application prospect of the polypeptide in digesting plaque tissues. The invention is invented mainly for digestion treatment of plaque tissues. Through combination of severalenzymes, plaque tissue can be digested into a single-cell suspension with a relatively high activity proportion, and the biological reaction of the plaque tissue is researched on the basis of singlecells, so that the situation that a large number of calcified cell debris, tissue impurities and the like influence a single-cell sequencing machine or a subsequent data analysis result is avoided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Rapid construction method of genome DNA sequencing library, and matched kit
PendingCN109853047AGet rid of the ultrasound stepLow costLibrary creationEnzyme digestionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a rapid construction method of a genome DNA sequencing library, and a matched kit. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting DNase I deoxyribonuclease I as a DNAfragmenting enzyme to fragment a sample DNA by enzyme digestion to obtain fragmented DNA; (2) directly adding a dA tail to the fragmented DNA to obtain DNA with the dA tail; (3) connecting the DNA with the dA tail with a joint to obtain a joint connected product; (4) carrying out magnetic-bead purification on the joint connected product; (5) carrying out polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on the joint connected product to obtain an amplification product; (6) carrying out magnetic-bead purification on the amplification product to obtain a genome DNA sequencing library product; and (7) carrying out fragment distribution inspection and library evaluation on the library product by adopting an agarose gel electrophoresis detection method. According to the invention, the DNase I is selected as the DNA fragmenting enzyme, so that the steps of tail end repair and phosphorylation are reduced, the library construction time is shorter, and cost is lower.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method of detecting methylated DNA in sample
InactiveUS20120219949A1Improve detection accuracyNovel methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strand dnaDeoxyribonuclease I
In order to simply obtain a methylated DNA sample, a method including bringing a sample which may include methylated DNA into contact with a protein capable of binding to methylated DNA to bind the methylated DNA in the sample to the protein, bringing the sample obtained into contact with at least one deoxyribonuclease to degrade DNA in the sample; and detecting methylated DNA which is not degraded by the deoxyribonuclease by the binding of the sample obtained to the protein is used. In the method, at least one type of deoxyribonucleases is a deoxyribonuclease different from a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme capable of degradating a single stranded DNA.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method for separating single cells from sample
PendingCN109666626AConvenient researchHigh yieldCell dissociation methodsPancreatic cellsNeutral proteaseTrypsin inhibitor
The invention relates to the field of single cell separation, and discloses a method for separating single cells from a sample. The method comprises the steps that the normal tissue sample is mixed with digestive juice for digestion, wherein the digestive juice contains VIII-type collagenase, neutral protease, a trypsin inhibitor and deoxyribonuclease; the ratio between enzyme activity units of the VIII-type collagenase, the neutral protease, the trypsin inhibitor and the deoxyribonuclease is (100-312.5):(1-5):(5000-25000):1. The method can achieve high-yield and high-activity extraction of the single cells under the condition that the total digestion time is short, especially pancreatic tissue, and the problem that existing pancreatic tissue single cells are relatively low in yield and activity is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
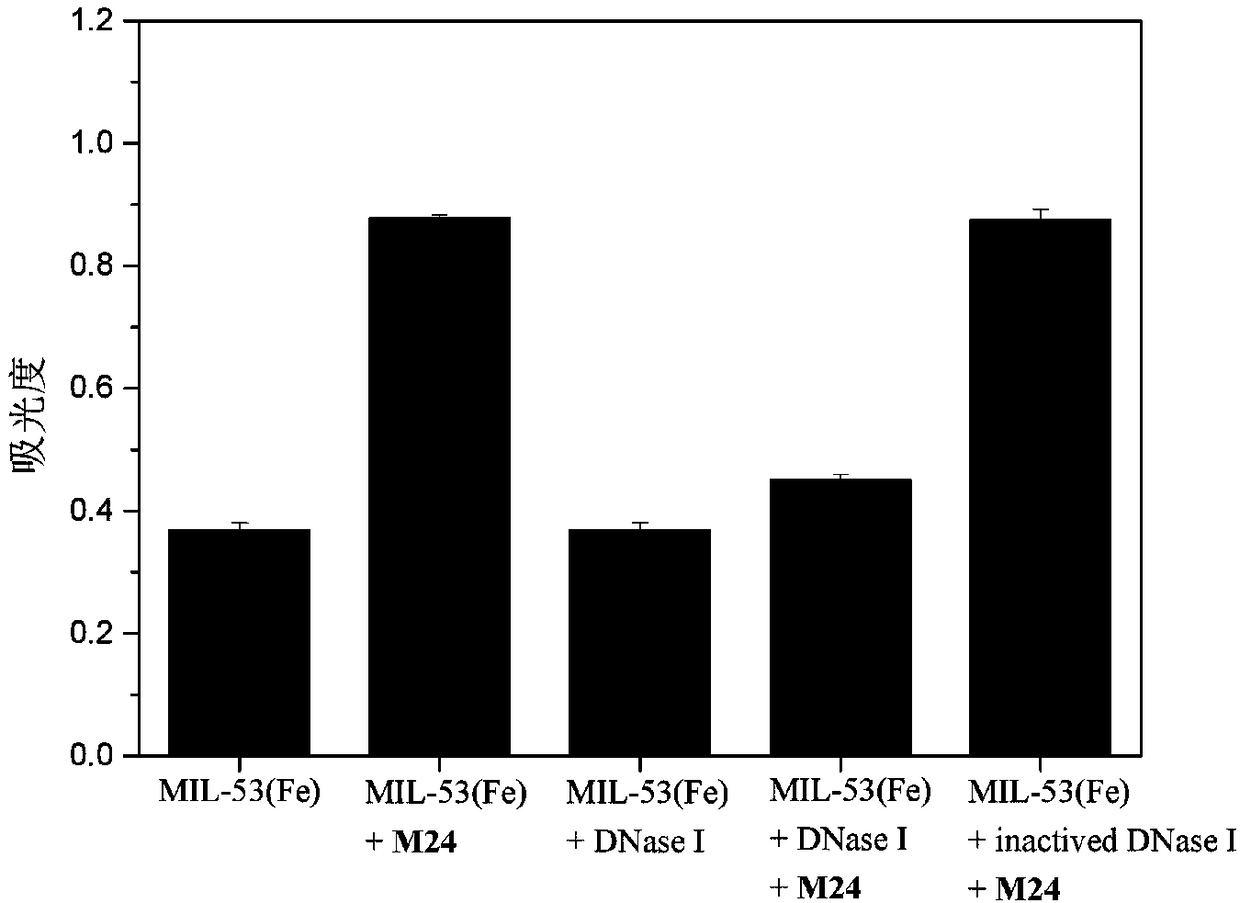
A DNase I activity colorimetric assay is provide
InactiveCN109207555AActive and reliableQuantitativeMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayPeroxidase
The invention discloses a colorimetric detection method for deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) activity based on DNA regulating MIL-53(Fe) peroxidase activity. The invention uses cheap 3, 3 ', 5, 5'-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) is a colorimetric substrate, which can regulate MIL-53 (Fe) peroxidase activity and the hydrolysis of ssDNA by DNase I, a biosensor is constructed to observe the activity of DNaseI with naked eyes. A colorimetric method with the advantages of low cost, simple operation and convenience has been developed. This method has high sensitivity and good stability, and is suitable forpopularization and application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Human amnion mesenchymal stem cell serum-free culture medium and culture method thereof
The invention relates to a human amnion mesenchymal stem cell serum-free culture medium and a culture method thereof. The culture medium is formed by adding human serum albumin, human transferrin, human insulin and sodium selenite into a DMEM / F12 basic culture medium. The culture method for the culture medium comprises the following steps of: digesting human amnion by using trypsin, then digesting the human amnion by using collagenase IV and deoxyribonuclease I, and filtering the mixture to obtain single cell suspension; and adding the human serum albumin, the transferrin, the insulin and thesodium selenite into the DMEM / F12 basic culture medium in a ratio of VDMEM to VF12 of 1:1, and putting human amnion mesenchymal stem cells in a 37 DEG C CO2 incubator with saturated humidity and volume fraction of 5 percent under the serum-free condition, wherein culture in vitro and amplification are realized by solution change and transfer of culture, potentiality of multi-direction differentiation is maintained, and the amplified cells can be induced in vitro to form cartilage cells, osteoblasts and adipocytes. The culture medium and the culture method have the characteristics of no other animal sources, wide source and no limitation of ethics.
Owner:辽宁艾米奥干细胞与再生医学研究院有限公司
Method of detecting methylated DNA in sample
In order to simply obtain a methylated DNA sample, a method including bringing a sample which may include methylated DNA into contact with a protein capable of binding to methylated DNA to bind the methylated DNA in the sample to the protein, bringing the sample obtained into contact with at least one deoxyribonuclease to degrade DNA in the sample; and detecting methylated DNA which is not degraded by the deoxyribonuclease by the binding of the sample obtained to the protein is used. In the method, at least one type of deoxyribonucleases is a deoxyribonuclease different from a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme capable of degradating a single stranded DNA.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Scylla paramamosain double-stranded specific deoxyribonuclease as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a scylla paramamosain double-stranded specific deoxyribonuclease as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and relates to double-stranded specific deoxyribonucleases. The preparation method comprises the steps of extracting total RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) of hepatopancreas of scylla paramamosain, carrying out reverse transcription on the total RNA by using an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology to obtain cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), obtaining a new DSN (Duplex-Specific Nuclease) gene by utilizing a SMART II-RACE method, constructing a prokaryotic expression recombinant plasmid of the scylla paramamosain by utilizing a genetic recombination method and carrying out high-efficiency expression and purification in escherichia coli to obtain recombinant scylla paramamosain DSN with biological activity. The invention provides a recombinant vector, comprising the gene sequence of the scylla paramamosain double-stranded specific deoxyribonuclease. The invention provides a biological agent which contains the scylla paramamosain double-stranded specific deoxyribonuclease and is applied to degrading double-stranded DNA.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Preparation method of pathogenic bacterium DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) in clinical blood sample and kit
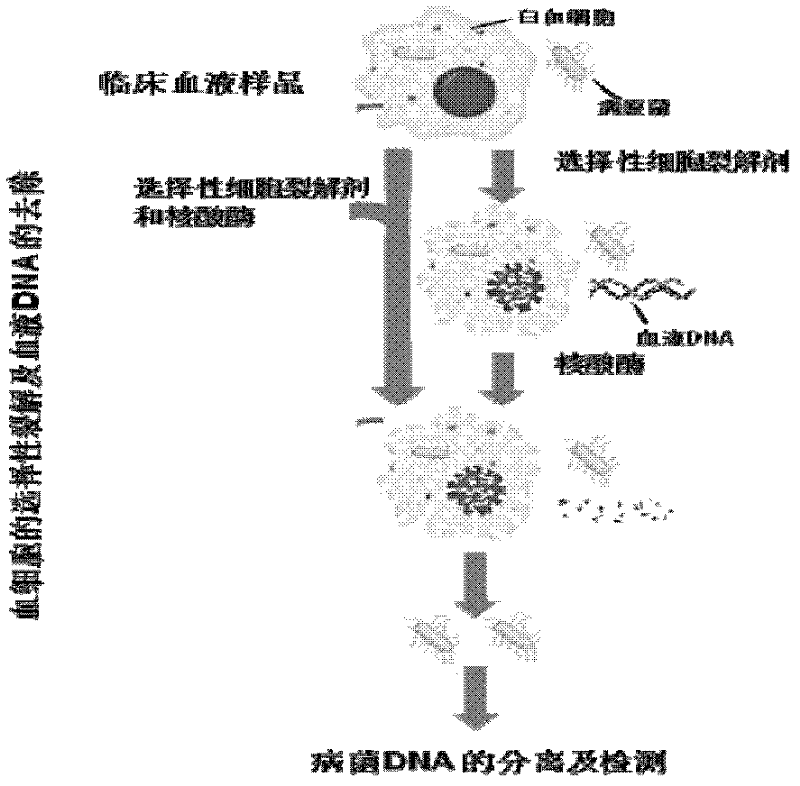
InactiveCN102250879AAvoid interferenceEfficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBacteroidesMicrobiology
The invention discloses a preparation method of pathogenic bacterium DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) in a clinical blood sample and a kit. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing the clinical blood sample with ox-bile or ox-bile powder and making the ox-bile or ox-bile powder crack non-pathogenic bacterium cells; during or after cracking of the non-pathogenic bacterium cells, adding desoxyribonuclease for degrading DNAs released after cracking of the non-pathogenic bacterium cells; centrifuging the mixture obtained in the previous step and collecting precipitates; and preparing pathogenic bacterium DNAs from the precipitates with the conventional method. In the invention, the ox-bile or ox-bile powder is used for cracking the non-pathogenic bacterium cells in the clinical blood sample to release the non-pathogenic bacterium cell DNAs according to the characteristic of the tolerance of malignant bacteria and fungi in the clinical sample to the ox-bile and the ox-bile powder, and desoxyribonuclease is used for degrading to selectively remove non-pathogenic bacterium DNAs, so that the pathogenic bacterium DNAs are enriched. By undergoing a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) on the DNAs, the interference of most of non-pathogenic bacterium DNAs on the PCR detection of pathogenic bacteria can be avoided, and the specificity and sensitivity of the PCR can be enhanced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INNOGENIX BIOMEDICINE TECH
Compound enzyme digestive juice as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112481190AShort digestion timeEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsVertebrate cellsSucroseRibonuclease
The invention provides a compound enzyme digestive juice as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The digestive juice comprises the following components with final concentrations: 100-200U / mL of type IV collagenase, 1-10U / ml of type II dispersive enzyme, 50-200U / ml of deoxyribonuclease I, 0.1-0.5 mM of PMSF, 10wt%-20wt% of ethylene glycol, 5wt%-10wt% of polysucrose, and sterilewater serving as a solvent, wherein the pH value of the digestive juice is 7.4-8.0. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing materials according to the final concentration of each component of the digestive juice; dissolving type IV collagenase, type II dispersive enzyme, deoxyribonuclease I, PMSF and polysucrose in sterile water, adding ethylene glycol, and uniformly mixing; and adjusting the pH value to 7.4-8.0, filtering and sterilizing to obtain the product. The compound enzyme digestive juice and the preparation method thereof are applied to the organoids technology. The digestive juice disclosed by the invention not only can be used for obtaining complete organoid, but also can be used for obtaining cell clusters with uniform dispersion sizes, and is short in digestion time, convenient to operate and stable in effect.
Owner:ACCURATE INT BIOTECHNOLOGY (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Small molecular double stranded RNA group prepared from yeast, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN102321625APrevent Lung CancerPrevention and treatment of viral diseasesOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAnti virusYeast
The present invention discloses a small molecular double stranded RNA group prepared from yeast, a preparation method and a use thereof. According to the present invention, the small molecular double stranded RNA group is prepared through adopting a mixture and the total RNA of the yeast as substrates, wherein the mixture comprises at least two selected from ribonuclease T1, deoxyribonuclease I and ribonuclease III, the yeast is the yeast which kills plasmids. The small molecular double stranded RNA group provided by the present invention can be provided for preparing cancer prevention care products, anti-cancer health care products and anti-virus health care products. The preparation method provided by the present invention is simple, and is easy to operate.
Owner:SHUIAI BIOTECH NANTONG
A kind of culture and cryopreservation method of amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN111139221BHigh yieldImprove survival rateCell dissociation methodsCulture processStem Cell IsolationNeutral protease
The invention relates to a method for culturing and freezing amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. The culturing method includes amniotic membrane tissue separation, amniotic mesenchymal stem cell separation, P0 generation amniotic mesenchymal stem cell culture and expansion culture. The culture method of amniotic mesenchymal stem cells of the present invention, in the separation stage of amniotic mesenchymal stem cells, adopts a special mixed enzyme digestive solution system (final concentration of each component in the digestive solution: 1.5-2U / mL neutral protease, 0.5mg / mL deoxyribonuclease I and 1mg / mL collagenase IV) for digestion, can more effectively separate amniotic mesenchymal stem cells from amniotic tissue, and then significantly improve the yield of P0 generation cells. The present invention adopts one-step digestion Compared with the traditional two-step digestion method, the operation is more convenient, and the cultured amniotic mesenchymal stem cells have good activity, high yield, high purity, and good repeatability.
Owner:赛瑞诺(北京)生物科技有限公司
Plaque tissue digestion kit and application thereof
ActiveCN108865975ACell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsSingle cell suspensionDigestion
The invention discloses a plaque tissue digestion kit. The plaque tissue digestion kit comprises L enzyme: Liberase Tm, E enzyme: elastinase, D enzyme: deoxyribonuclease I, and HBSS, wherein the HBSScontains BSA and EDTA. The invention further discloses application of the plaque tissue digestion kit in a plaque tissue. The kit is mainly invented for digesting the plaque tissue; the enzymes are combined, so that the plaque tissue can be quickly digested into single-cell suspension; biological reaction of the plaque tissue is researched on the basis of single cells, so that a condition that a flow cytometry upper machine or follow-up data analysis results are affected by a lot of calcified cell debris, large calcified tissues and the like is avoided.
Owner:浙江普罗亭健康科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com