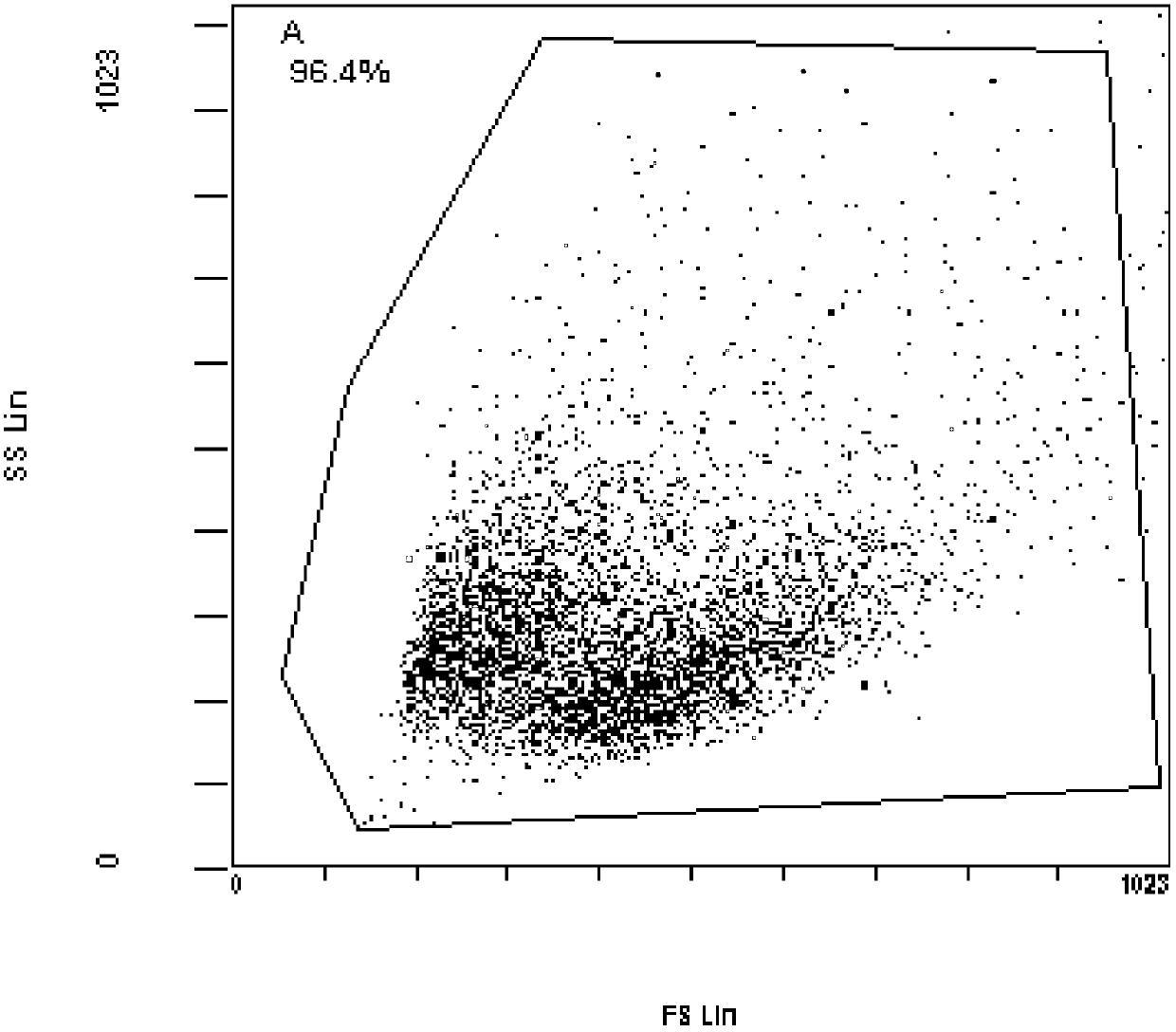
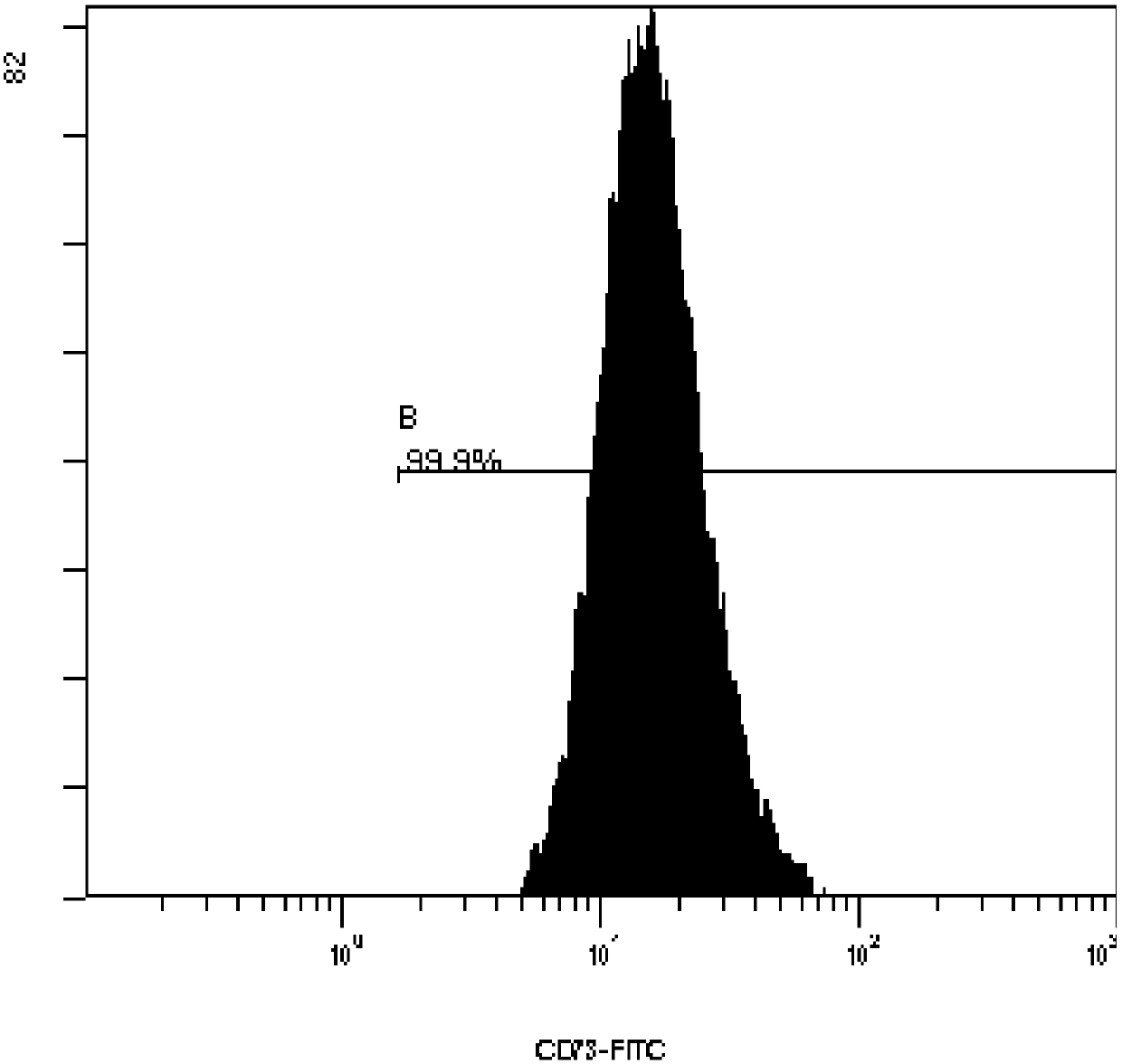
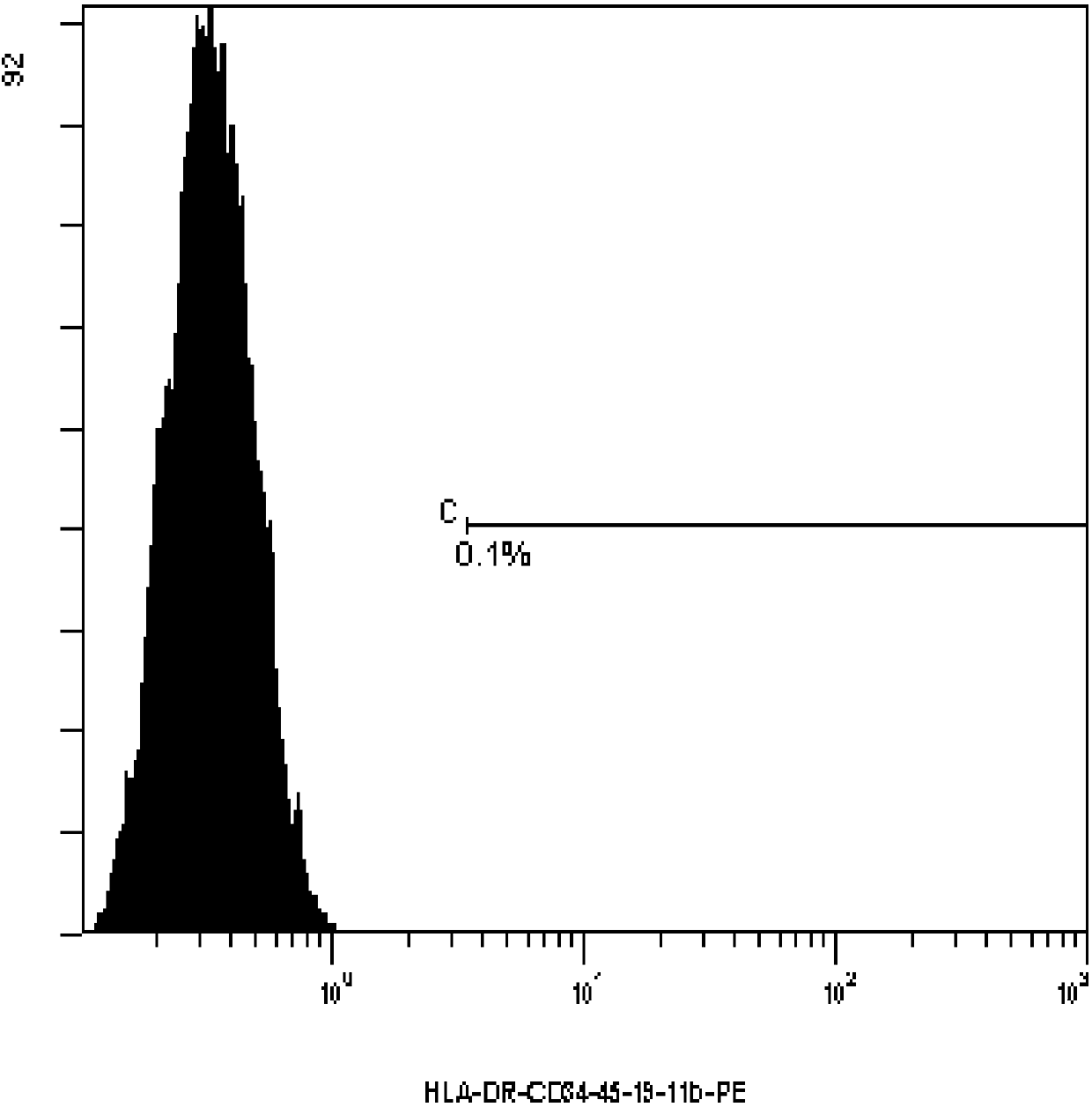
Mesenchymal stem cell separated from placenta blood vessel with digestive enzyme composition
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and digestive enzymes, applied in the field of isolating stem cells, can solve problems such as isolating mesenchymal stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Embodiment 1. Isolation, subculture, and cryopreservation of placental MSCs
[0087] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0088] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0089] (3) Cut the blood vessels into pieces of about 1.5 mm^3, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (5.8 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0090] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.2% collagenase II, 0.15% collagenase IV, 0.1% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) to digest for 1 hour;
[0091] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Embodiment 2, the isolation of placental MSC, subculture, cryopreservation
[0097] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0098] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0099] (3) Cut the blood vessels into 1mm^3 fragments, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (5.5 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0100] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.3% collagenase II, 0.1% collagenase IV, 0.15% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) to digest for 0.5h;
[0101] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the cleaning sol...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Embodiment 3, the isolation of placental MSC, subculture, cryopreservation
[0107] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0108] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0109] (3) Cut the blood vessels into 2 mm^3 pieces, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (4.7 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0110] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.1% collagenase II, 0.2% collagenase IV, 0.05% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) for digestion for 2 hours;
[0111] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the cleanin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com