Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Constant impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acoustic impedance, a constant related to the propagation of sound waves in an acoustic medium. Electrical impedance, the ratio of the voltage phasor to the electric current phasor, a measure of the opposition to time-varying electric current in an electric circuit High impedance, when only a small amount of current is allowed through.
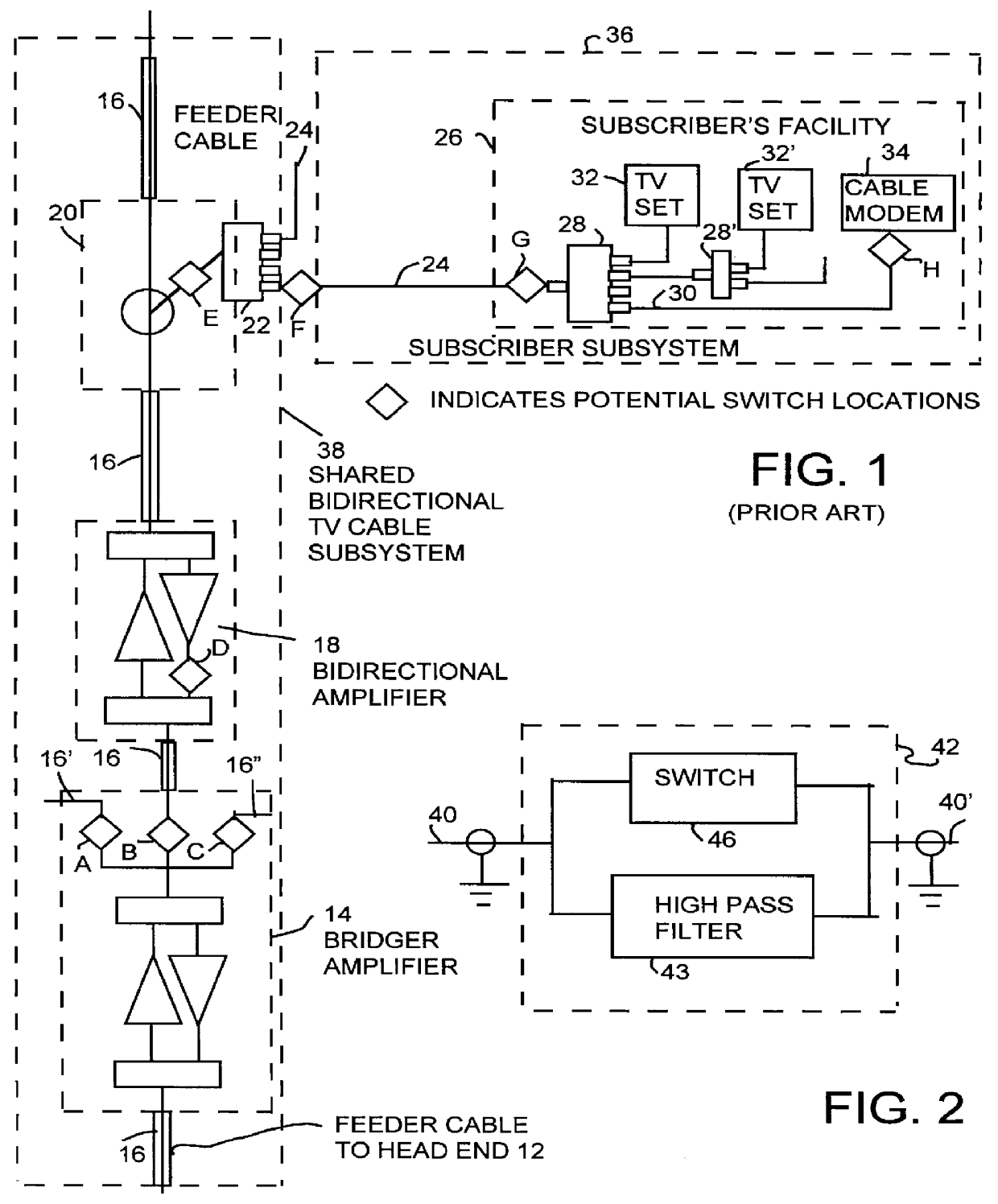
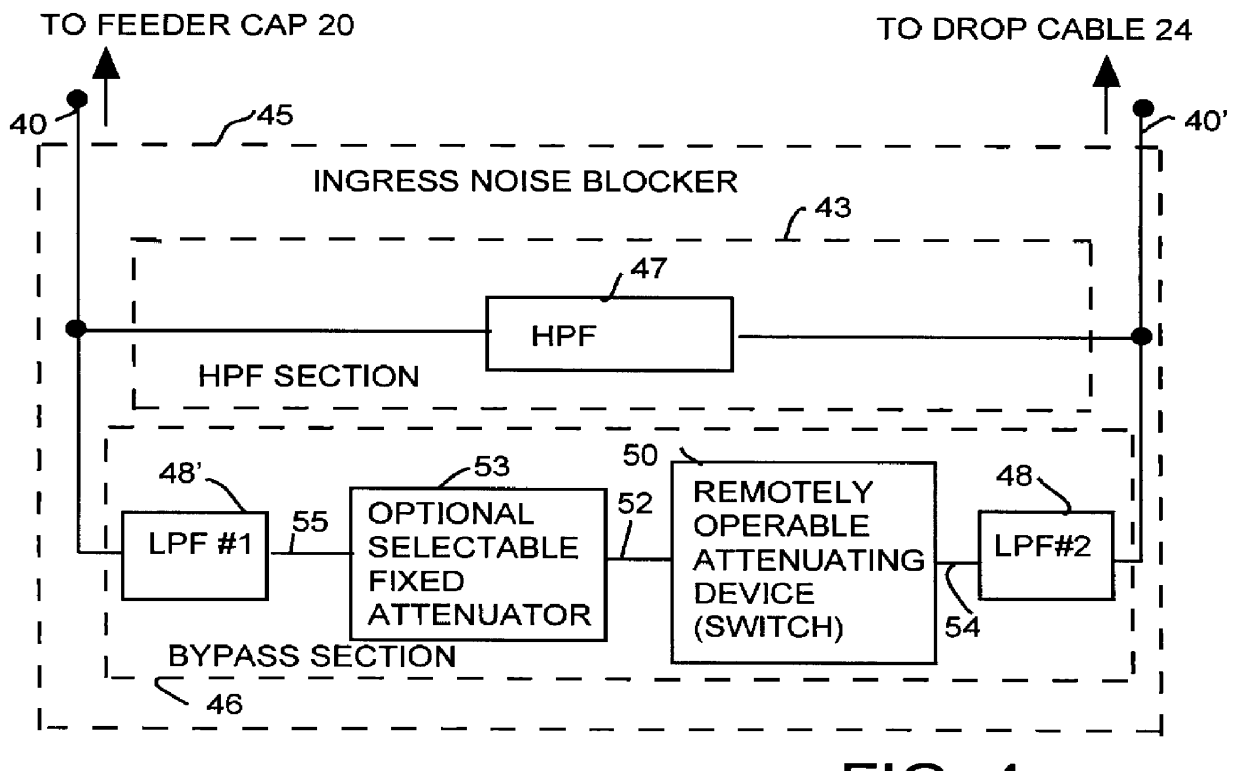
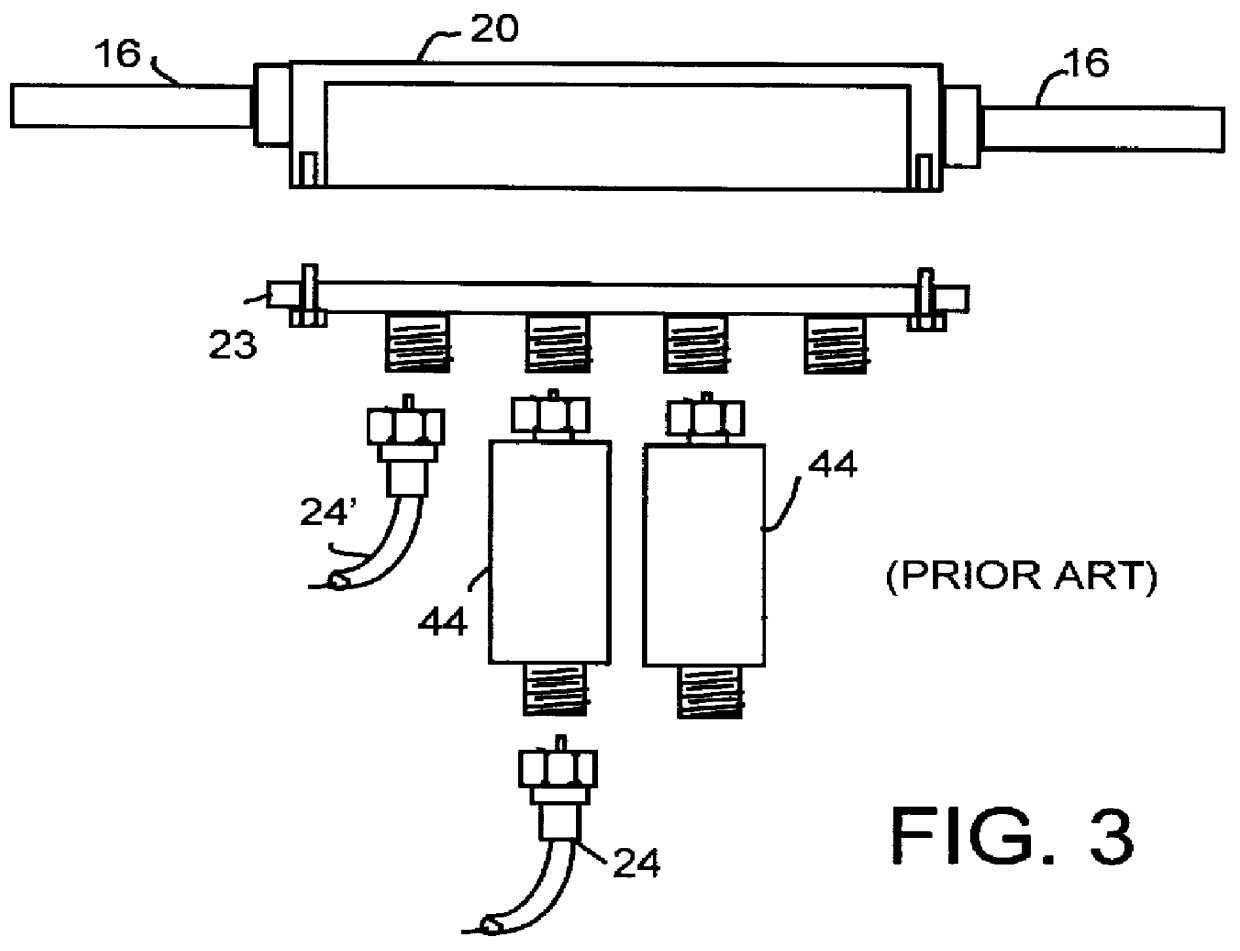
TV and data cable system ingress noise blocker
InactiveUS6094211APrevents loss of picture qualityLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal qualityModem device
This invention permits the upstream transmission of short packets of information in a cable TV system, and blocking upstream noise at all other times, and does so without interfering with image quality of normal TV viewing. A remotely operable ingress noise blocking filter is placed at the terminating junction between a subscriber's coaxial drop cable and a corresponding feeder tap in a cable TV system. The ingress noise blocking filter contains a high pass filter to pass the normal TV band. This high pass filter is bypassed by a section containing low pass filters and a switch operated when receiving a control signal from a cable modem during those short durations the cable modem is authorized to transmit an upstream signal. Low pass filters isolate the switching elements so that switching transients cannot occur in the downstream TV band. The level of the amplitude of the downstream signal is unaffected whether the switching elements are open or closed. Further, the switching arrangement provides a relatively constant impedance, both when the switching element is on and off to provide a high return loss and avoid signal reflections and maintain signal quality. In a diagnostic mode, the location of each noise source is determined by correlating the energy measured at each a set of frequencies across the band at the headend during those periods when the cable modem is allowed to transmit versus the energy received during those periods when the same cable modem is not authorized to transmit.
Owner:ARRIS INT
Dual spring probe coaxial contact system
ActiveUS7972173B1Reduce lossesFirmer engagementElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling contact membersContact padConstant impedance
A connector system includes first and second mateable connectors (12, 14) with coaxial contacts, wherein the first connector has movable center and outer contacts (20, 22) that are each biased forward by a separate spring (24, 26) to engage stationary contact pads (34, 36) of the mating second connector. A stationary tubular insulator (100) surrounds much of the movable center contact, and a stationary sheet metal shield (102) lies around the tubular insulator and within the outer contact. The front end of the movable outer contact forms an internal flange (80) with a hole (84) that allows the front end of the movable center contact to pass through. The shield front-end has an internal flange (112) that lies between the front end of the tubular insulator and the movable outer contact internal flange, to maintain a constant impedance through out the first connector.
Owner:ITT MFG ENTERPRISES LLC
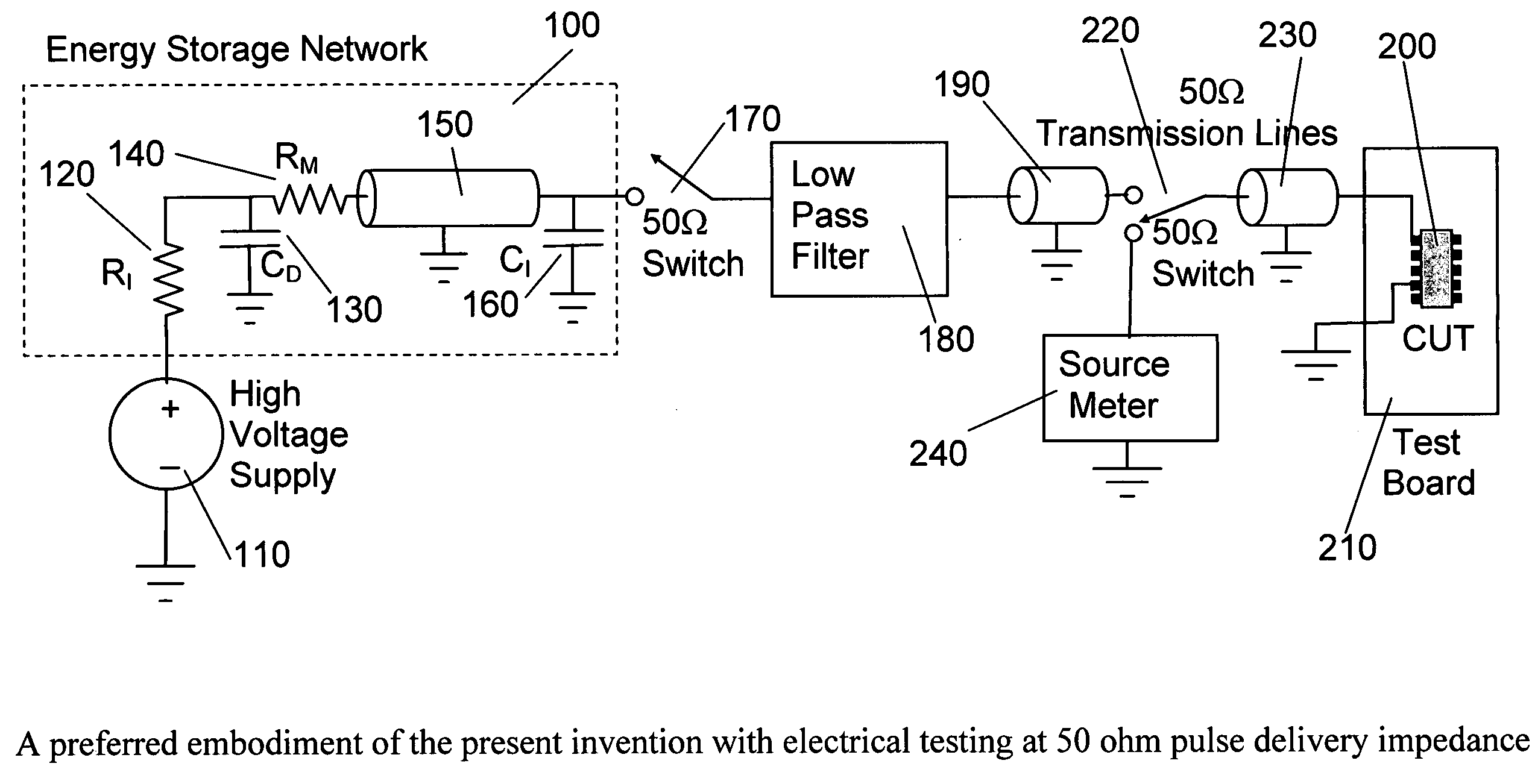
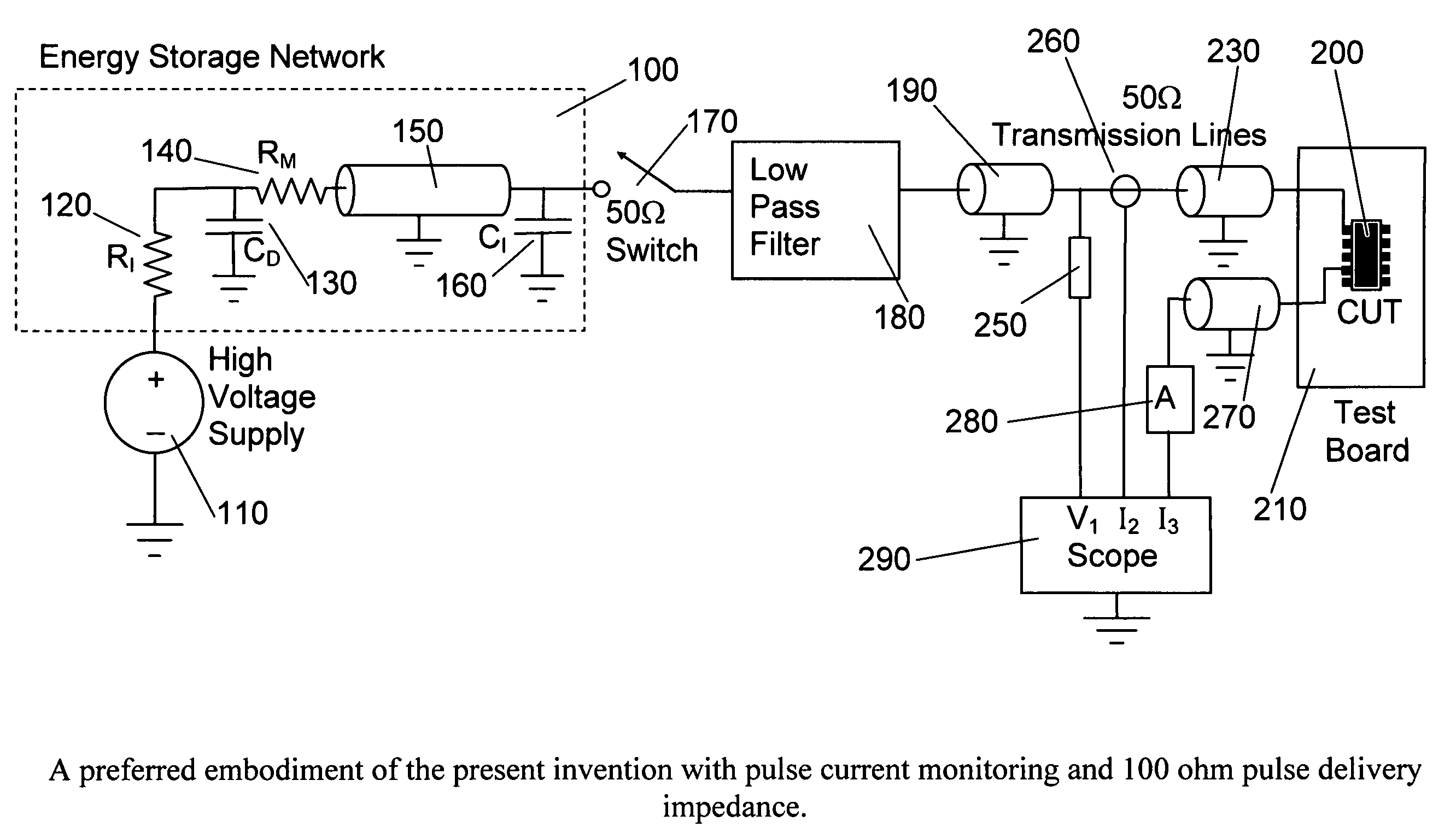
Test circuits and current pulse generator for simulating an electostatic discharge
InactiveUS20090134880A1Small distortionFast rise timeMeasuring interference from external sourcesIndividual semiconductor device testingElectrical conductorLow distortion
This invention is an electrostatic discharge testing circuit that can deliver current pulses to a component under test (CUT) with a custom amplitude versus time profile shape. Pulse generation with customized shapes is accomplished by discharging an energy storage network comprised of capacitor(s), transmission line(s) and other passive components. Current pulses compliant to the European International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 61000-4-2 standard can be so produced. These current pulses are delivered to the CUT with low distortion through a constant impedance electrical path, such as a combination of cables and controlled impedance conductors of printed wiring boards compatible with packaged IC devices, assemblies, and wafer probes. The current pulses can be delivered with various impedances, and measurements made that allow the CUT currents and voltages to be calculated.
Owner:GRUND EVAN
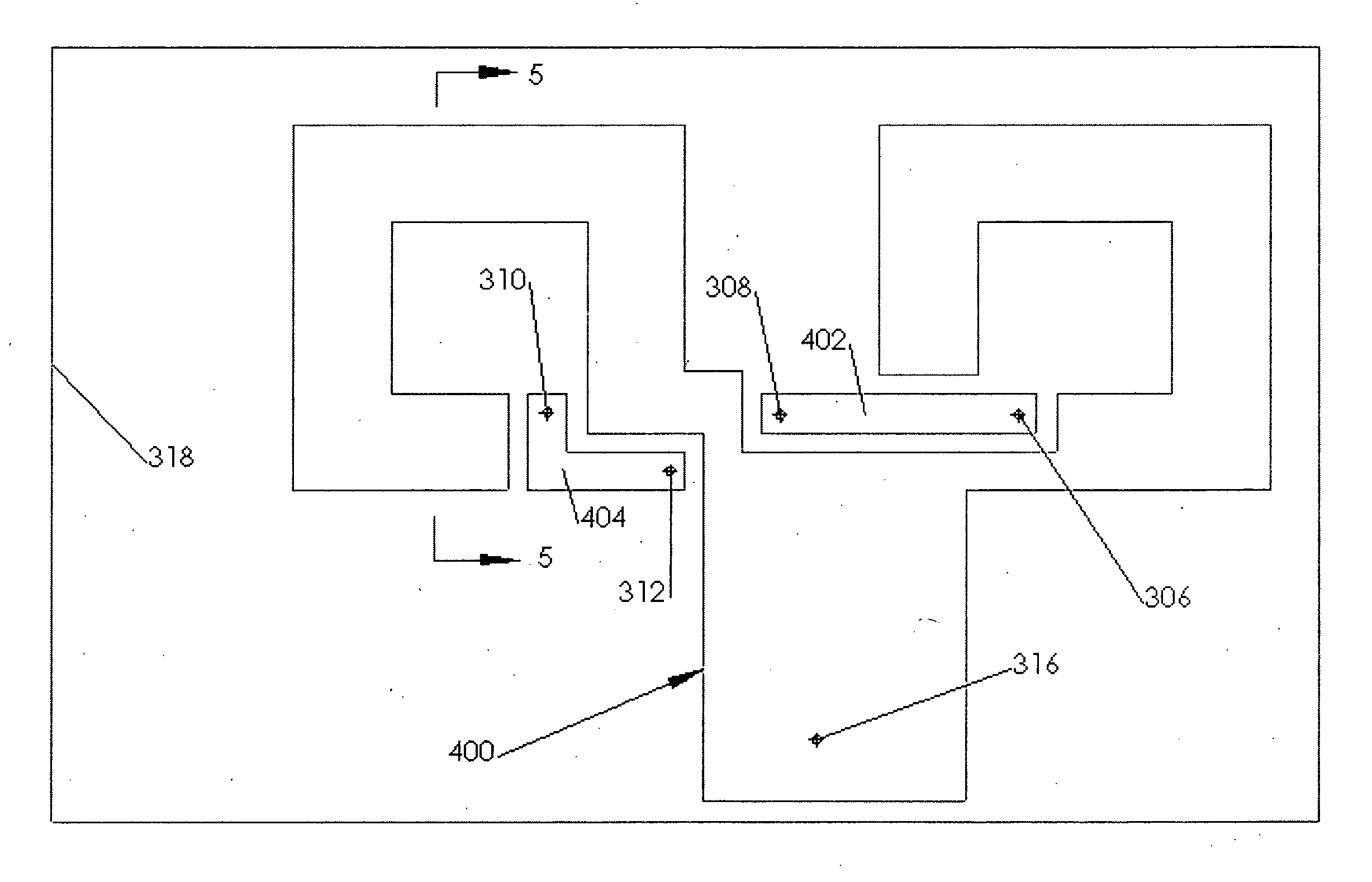
Constant impedance bullet connector for a semi-rigid coaxial cable
ActiveUS6863565B1Constant impedanceEasy to bendElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsConstant impedanceEngineering
A connector or first plug is provided for receiving a mating plug or second plug, forming a constant impedance connection. The center conductor of the first plug is supported for enhanced structural integrity with a cap attached over a portion of the center conductor that extends beyond the outer conductor portion of the same plug. The constant impedance connection consists of the two plugs partially or fully engaged. The mating plug has an outer conductor that projects beyond the inner conductor, and is made to receive the connector or first plug portions. Once engaged, the connector and mating plug have mating dimensions that satisfy an impedance equality expression for a relationship between the inner conductor cap's outer diameter, the outer conductor's inner diameter, and the dielectric constant.
Owner:PALCO CONNECTOR
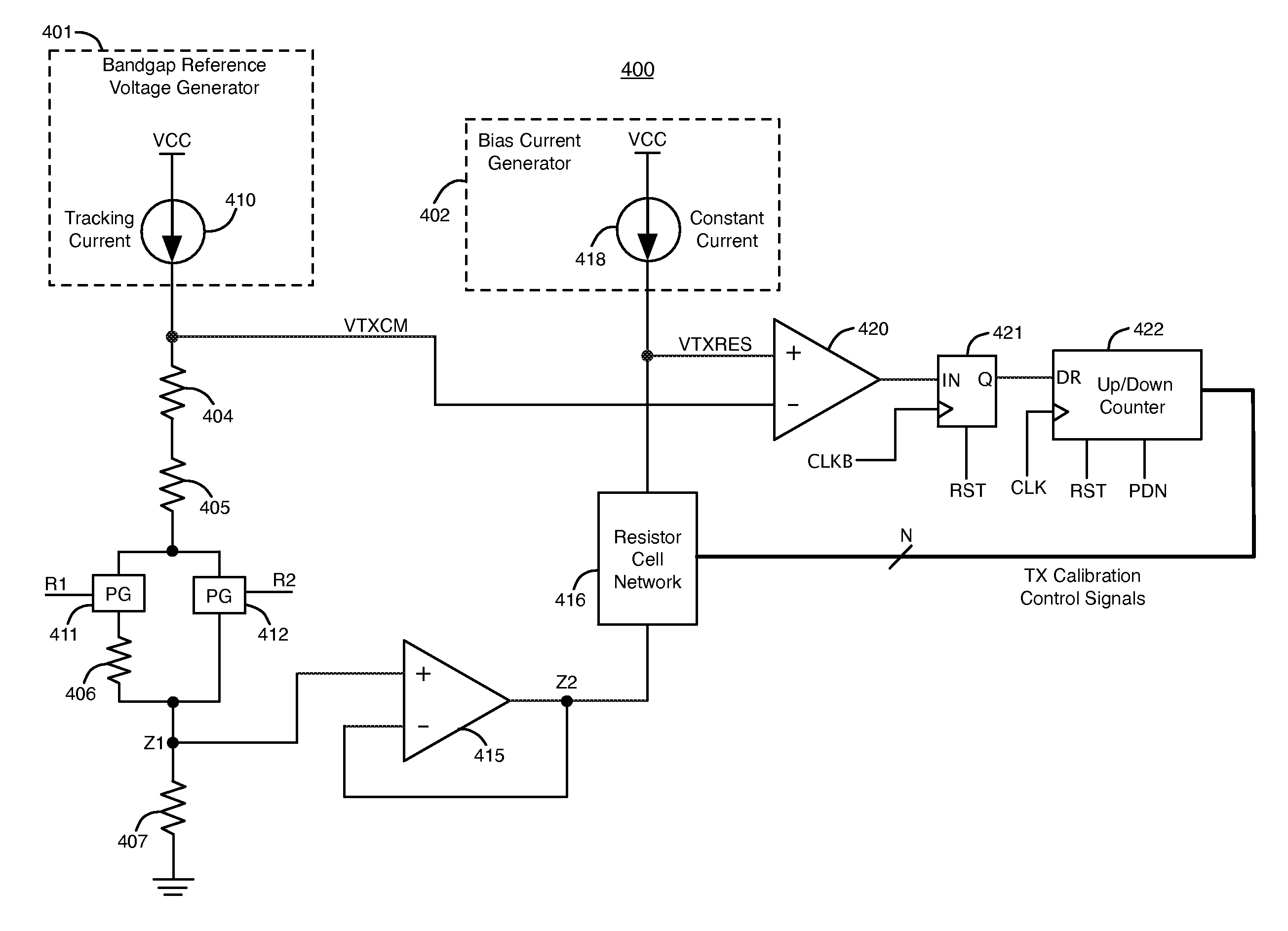
Techniques for calibrating on-chip termination impedances
InactiveUS7372295B1Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingConstant impedanceControl signal
A calibration circuit block includes a first resistor network, a second resistor network, and a feedback loop. The first resistor network includes a set of transistors and receives a constant current from a constant current source. The second resistor network receives a tracking current from a tracking current source. The impedance of the second resistor network changes with temperature and process variations on the integrated circuit. The tracking current source compensates for variations in the impedance of the second resistor network that are caused by process and temperature variations to maintain a constant reference voltage at the second resistor network. The feedback loop generates calibration control signals for controlling the conductive states of the transistors in the first resistor network. The feedback loop adjusts the calibration control signals to maintain a constant impedance in the first resistor network.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
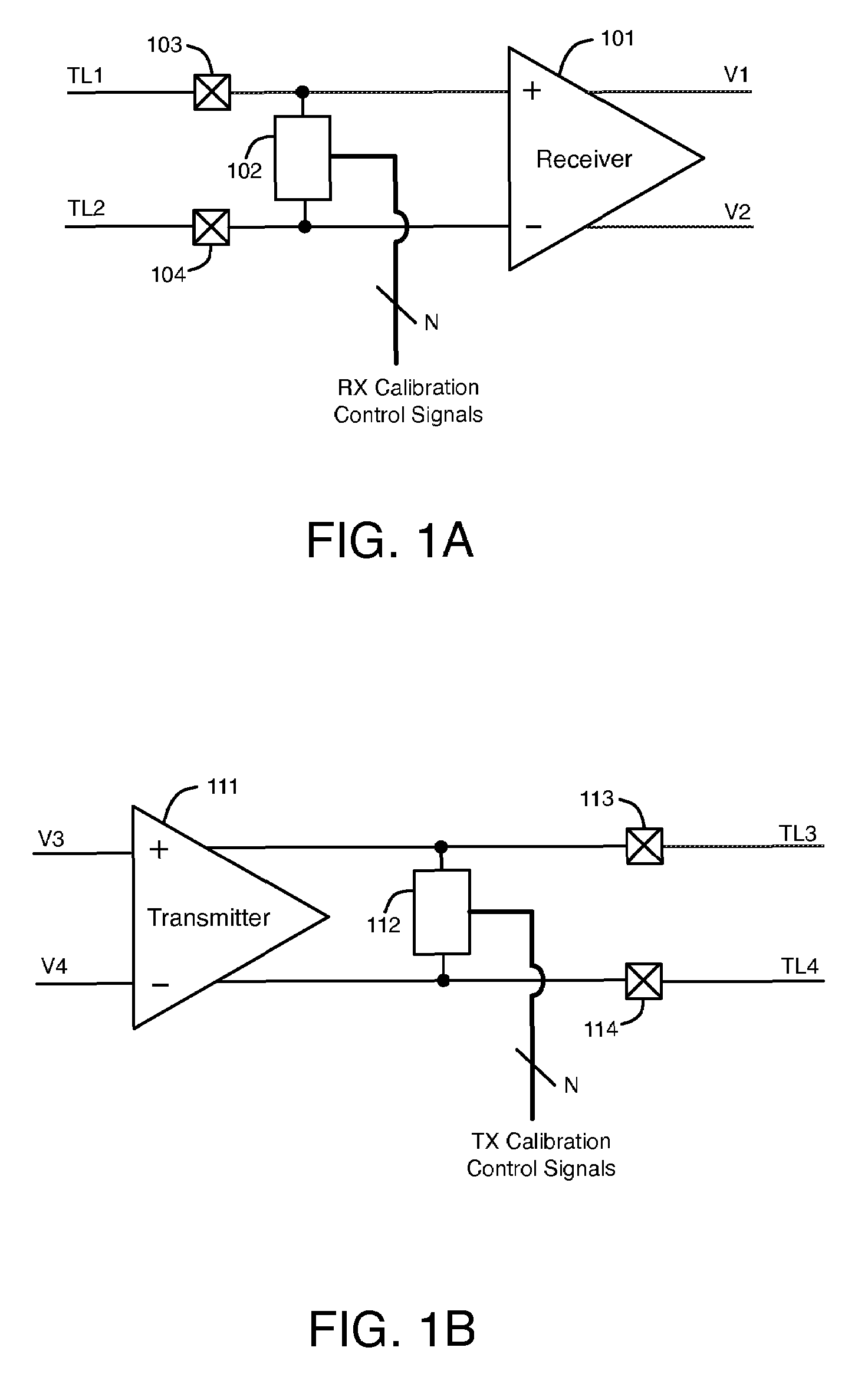
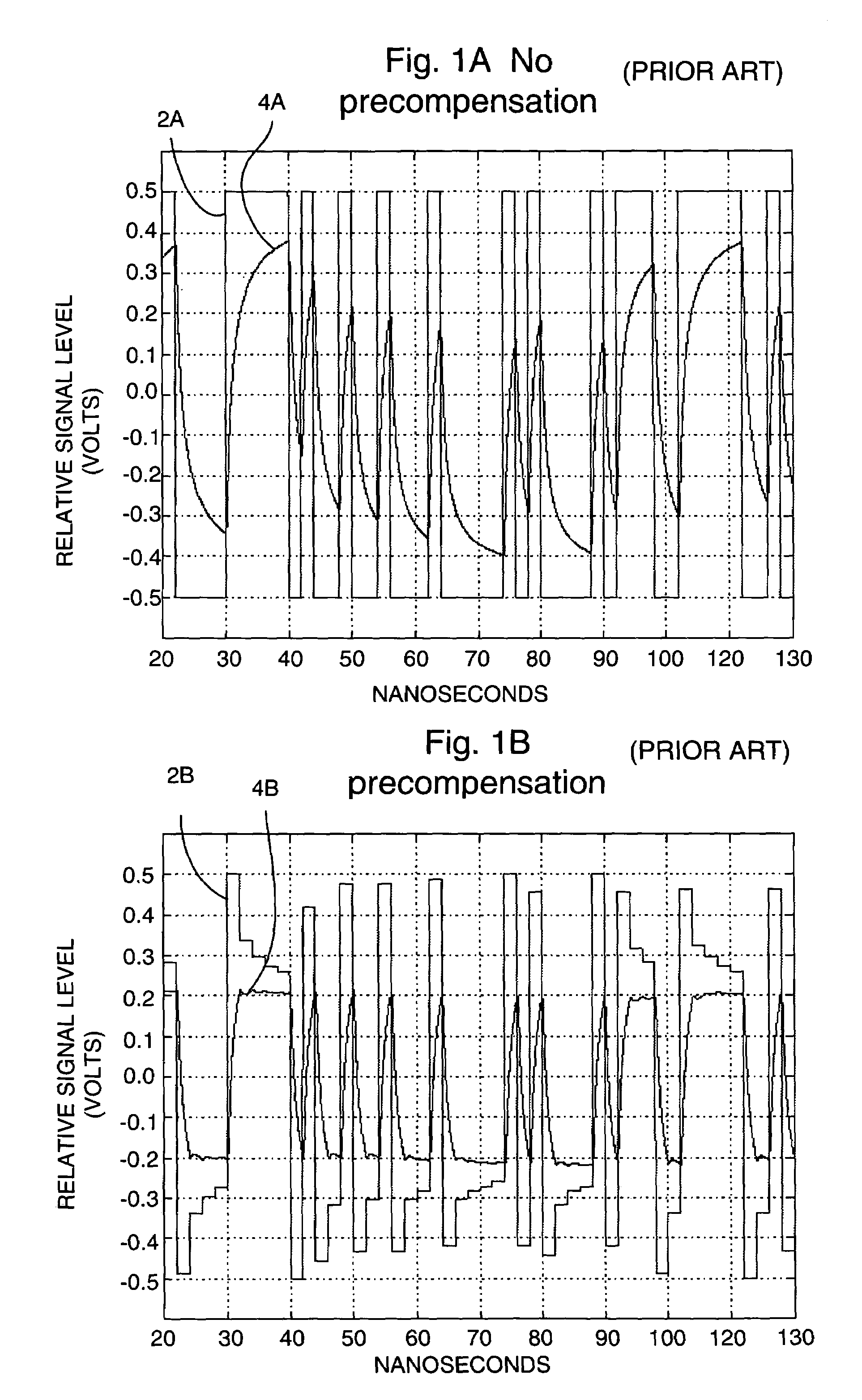
Pre-emphasis driver with constant impedance
InactiveUS7215144B2Reliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsElectrical conductorConstant impedance
An apparatus and method is disclosed for transmitting signals over a signal conductor using a precompensated driver that does not use a current source, and which drives the signal conductor with an impedance similar to the characteristic impedance of the signal conductor. Since no current source is used, the precompensated driver can operate at very low supply voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
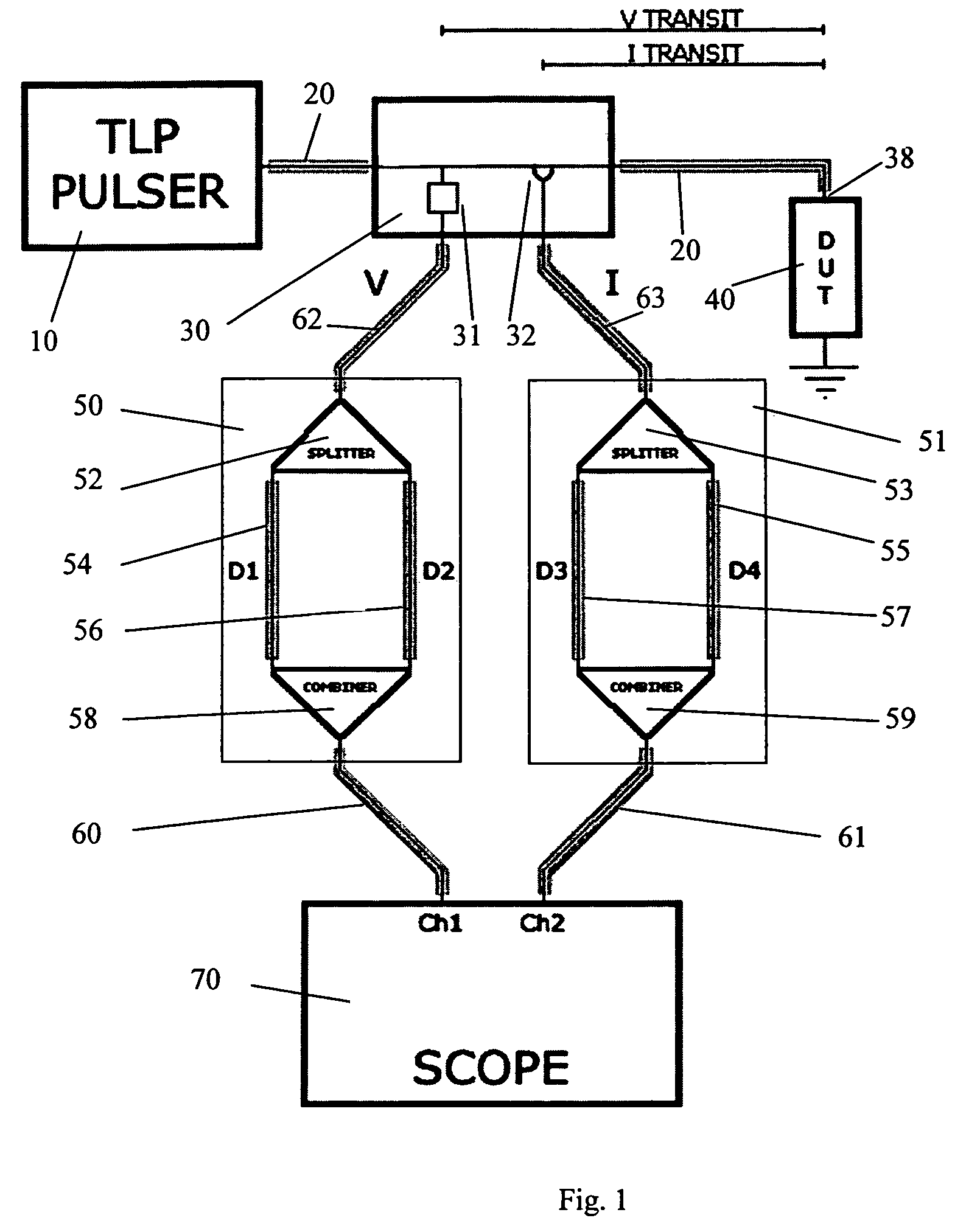
Transmission line pulse measurement system for measuring the response of a device under test
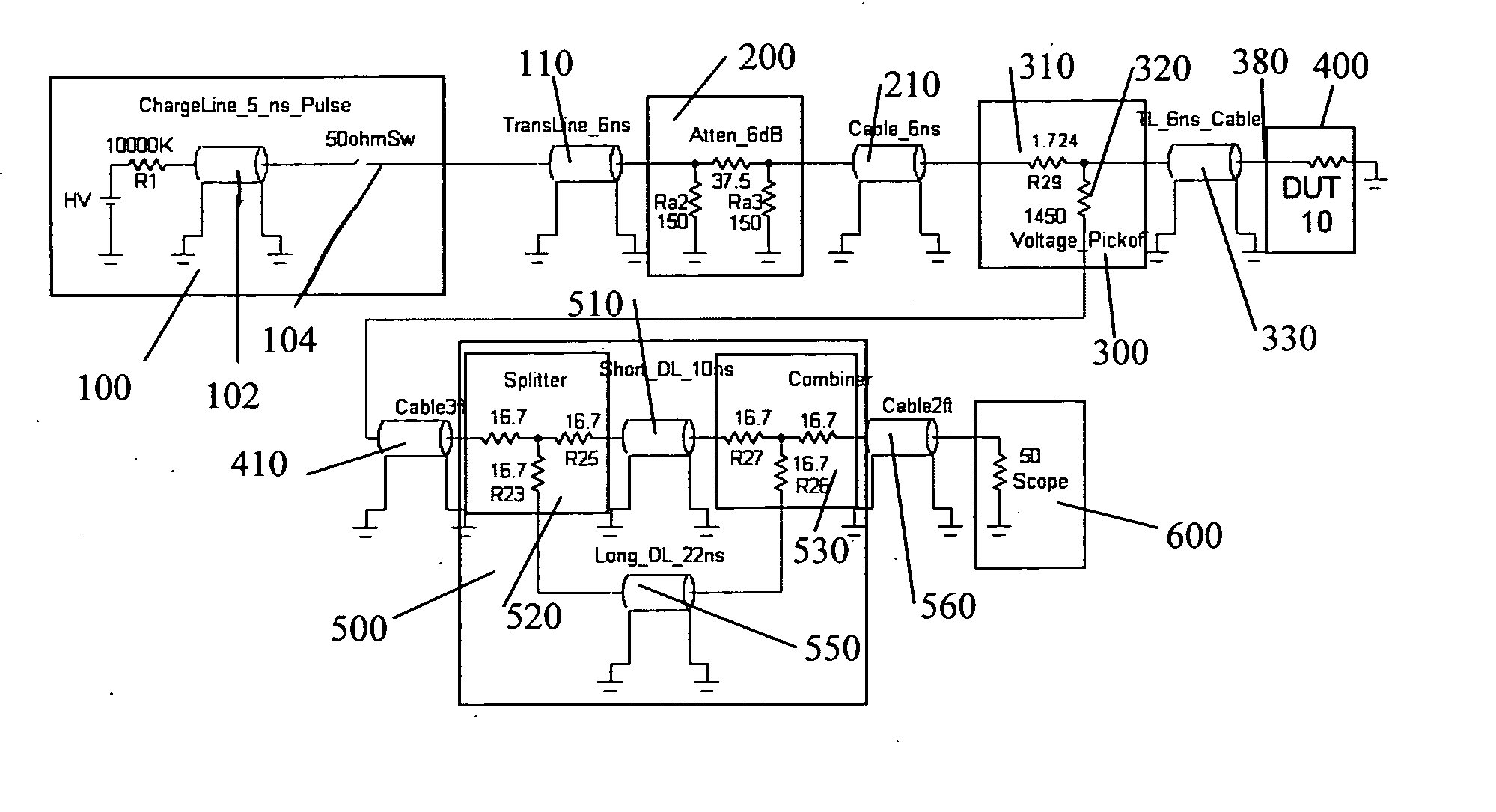
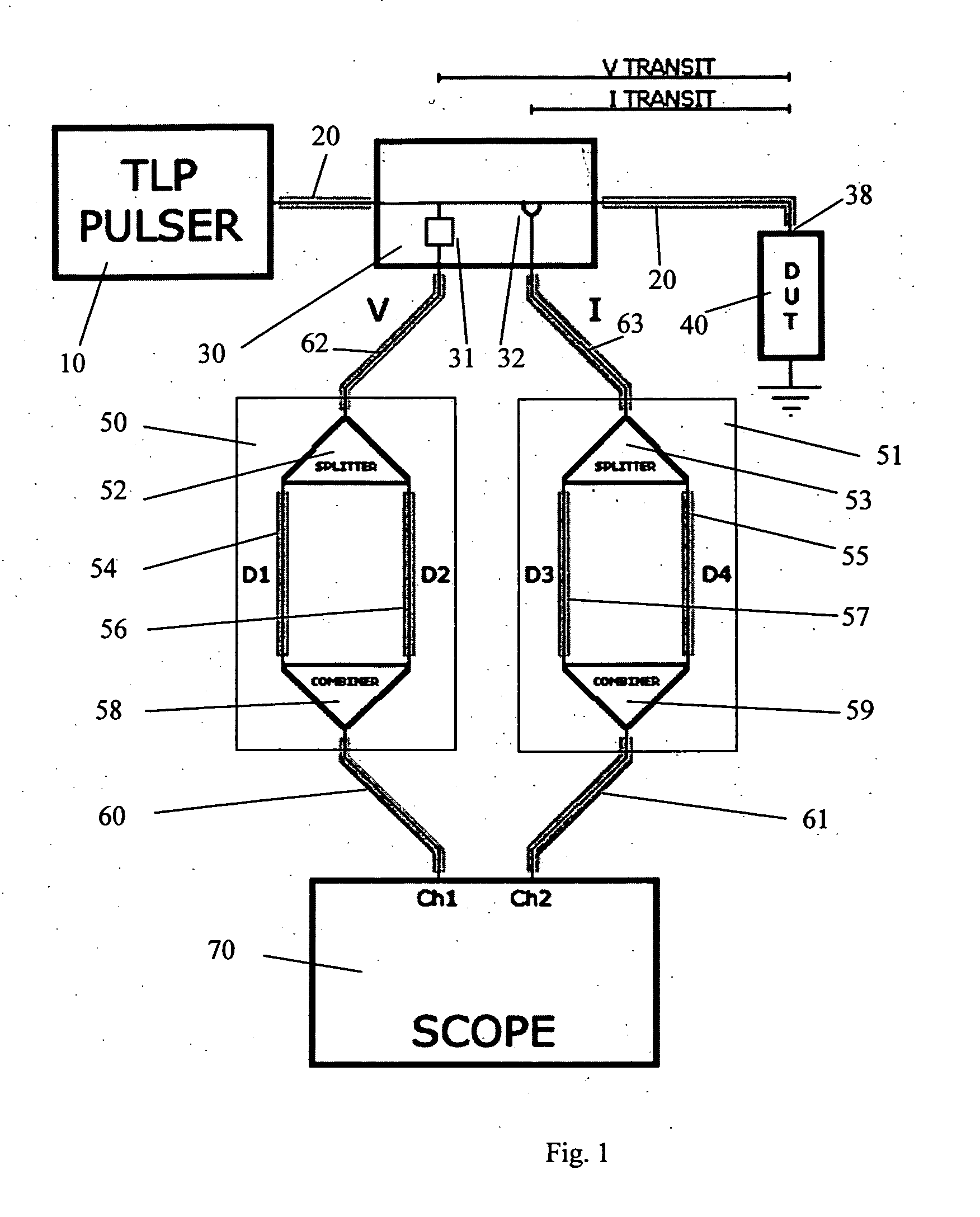
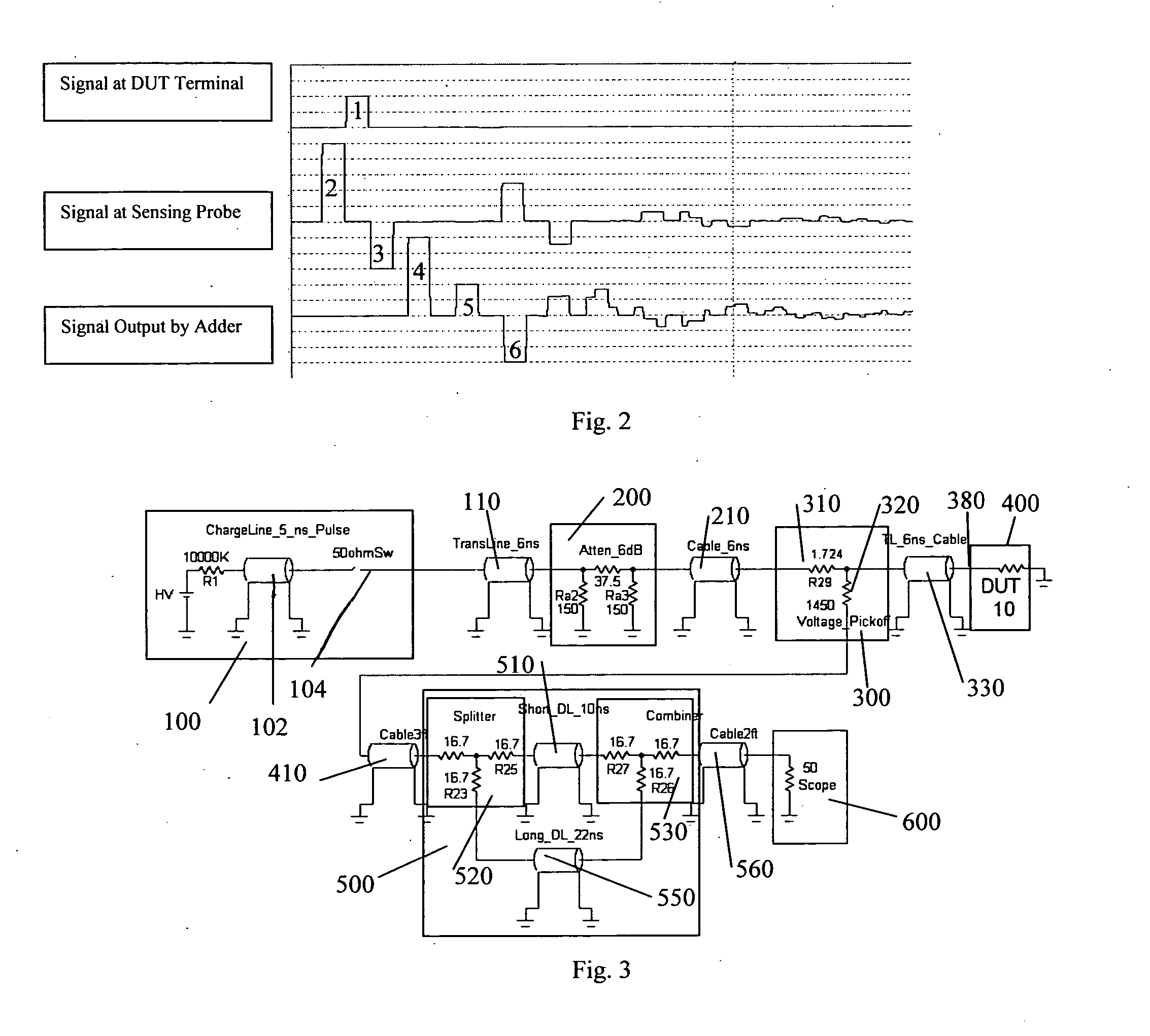
InactiveUS20070159186A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceConstant impedanceTransmission-line pulse
A Transmission Line Pulse (“TLP”) measurement system for testing devices such as integrated circuits (“ICs”), and especially for testing the electrostatic discharge (“ESD”) protection structures connected to terminals on such ICs. The TLP measurement system measures the pulsed voltage and / or current of a device under test (“DUT”) by recording voltage and / or current pulse waveforms traveling in a constant impedance cable to and from the DUT. The pulses going to and returning from the DUT are processed to create signal replicas of the voltage and current pulses that actually occurred at the DUT. Oscilloscope operating settings optimize the recording of these signal replicas by improving the measurement signal-to-noise ratio. This improved TLP system is especially useful when very short width pulses on the order of less than 10 nanoseconds are used to test the DUT's response.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
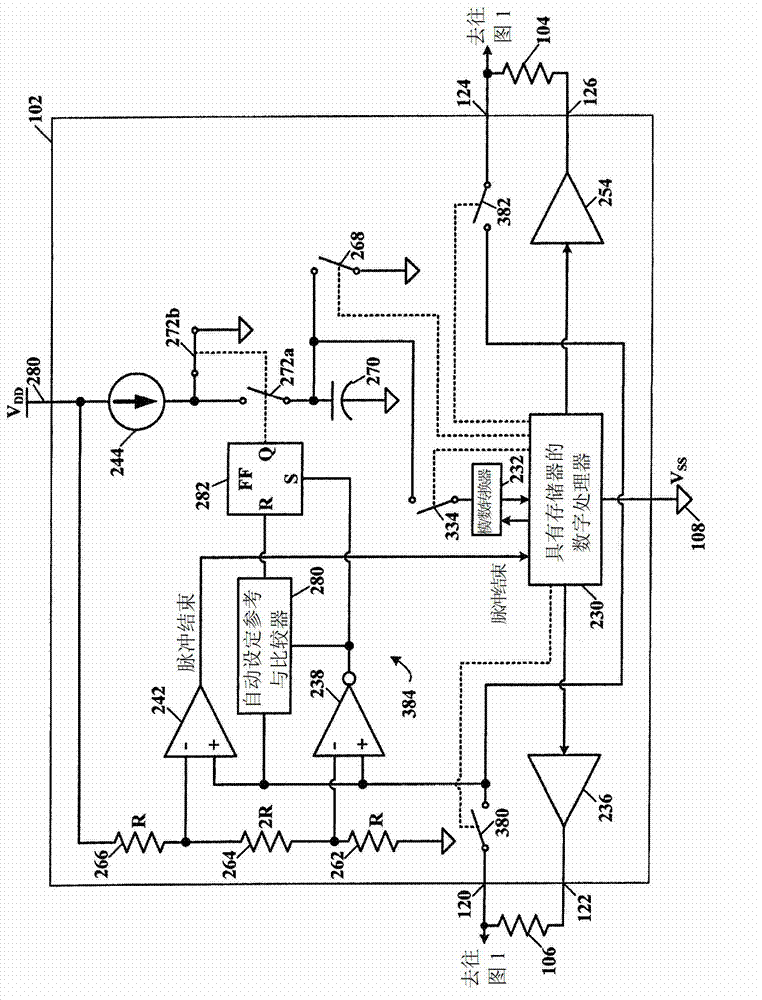
Bootstrapped low-voltage switch
A low-voltage constant-impedance analog switch based on a single MOSFET [328] as the main switching element. The constant-impedance on-state operation is obtained by connecting a charged capacitor [326] between the gate and source terminals of the MOSFET [328]. The switch can be compensated for the body effect, which may be necessary to obtain the required level of linearity. Low-voltage operation is made feasible by employing an internal feedback loop that locks in the switch's on-state. The switch can be implemented in a single-well CMOS bulk technology, and it can operate at supply-voltage differences that are only slightly higher than the technology's threshold voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Precompensated driver with constant impedance
InactiveUS20050258870A1Reliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsElectrical conductorConstant impedance
An apparatus and method is disclosed for transmitting signals over a signal conductor using a precompensated driver that does not use a current source, and which drives the signal conductor with an impedance similar to the characteristic impedance of the signal conductor. Since no current source is used, the precompensated driver can operate at very low supply voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
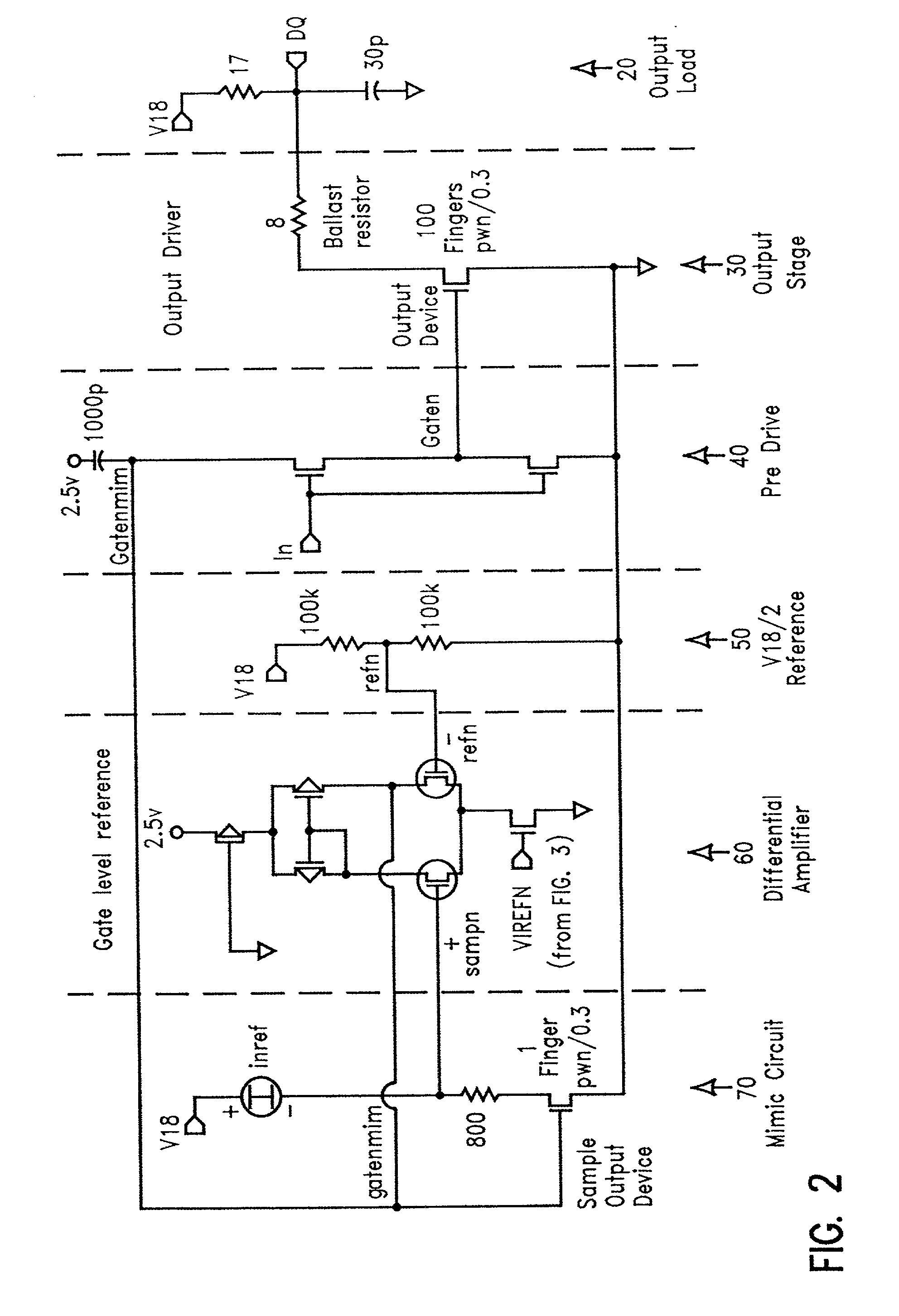
Constant impedance driver for high speed interface
InactiveUS6577154B2Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierConstant impedance
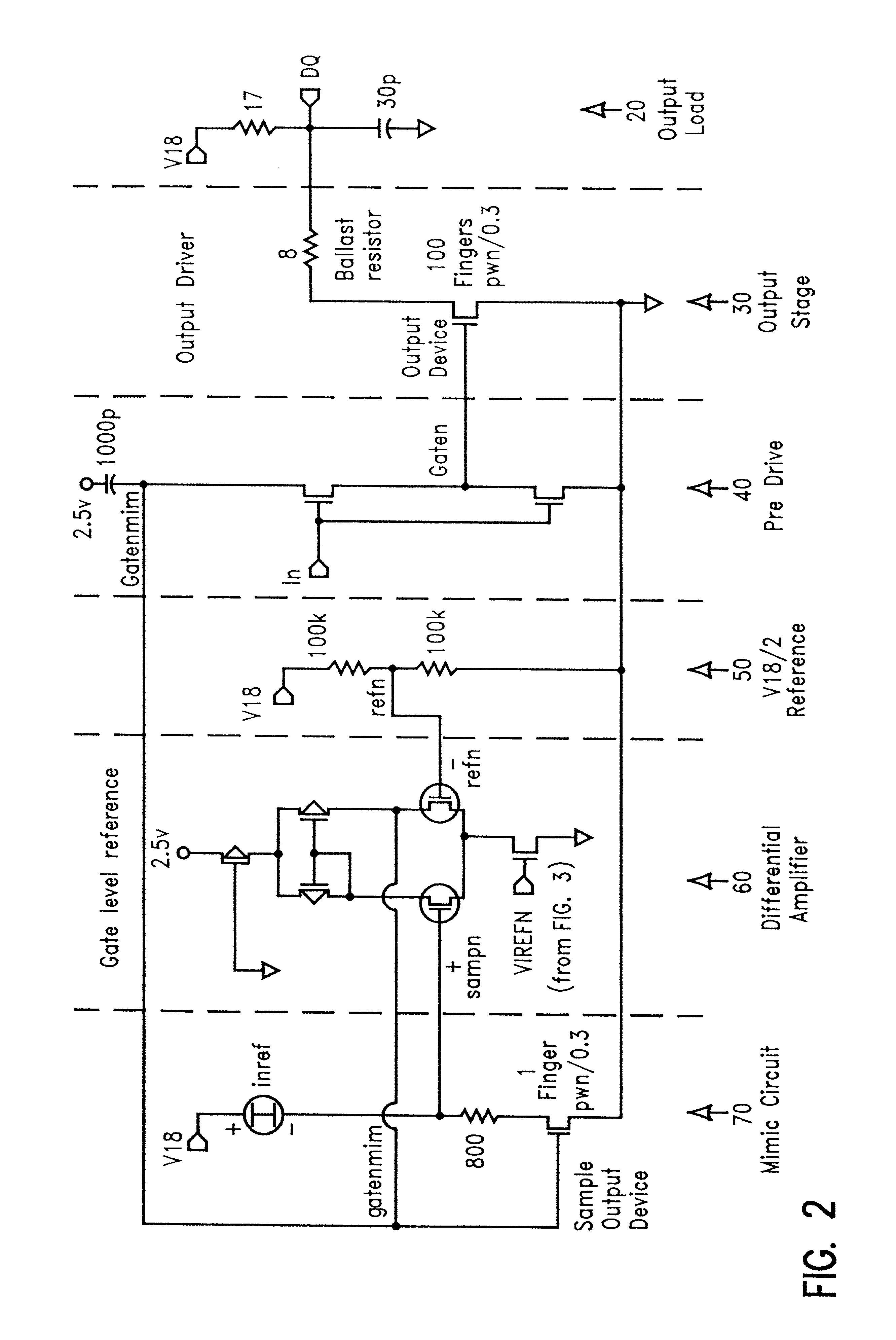
A compensated driver for maintaining constant impedance during data transfer from an integrated circuit comprises an output portion having an output device to transfer data from the integrated circuit and a mimic circuit portion having a sample output device scaled to a fraction of the output device adapted to accept a reference current and generate a sample voltage. A mimic circuit portion has a sample output device scaled to a fraction of the output device adapted to accept a reference current and generate a sample voltage. A differential amplifier portion is adapted to generate a control voltage in response to a reference voltage and the sample voltage. A predrive portion applies either a ground or the predetermined control voltage from the differential amplifier portion to the output stage portion in response to an input, the control voltage regulating the output device in the output stage portion to achieve a more constant impedance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
High level iboc combining method and apparatus for single input antenna systems
ActiveUS20130287144A1Improve complianceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsHybrid couplerConstant impedance
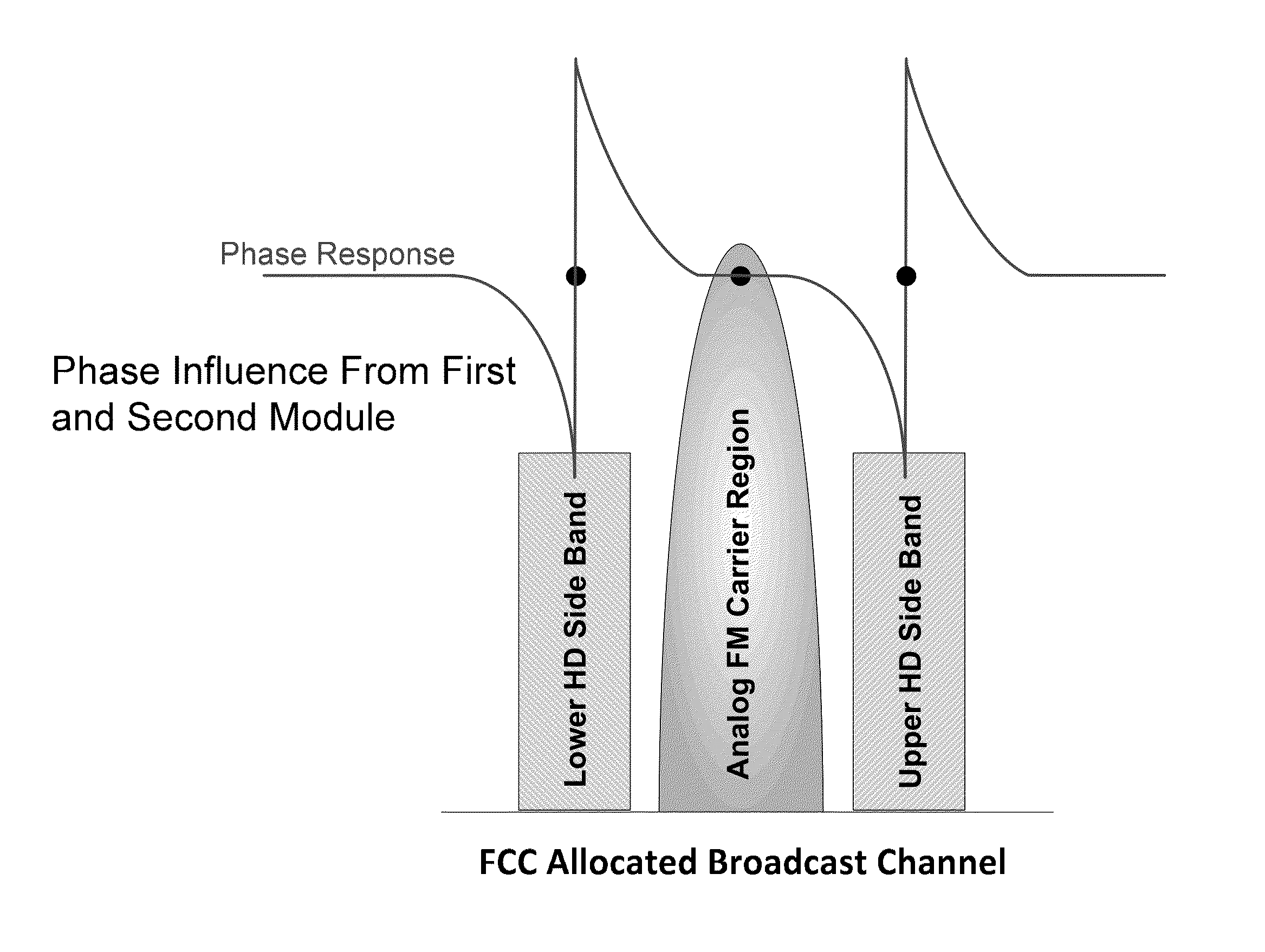
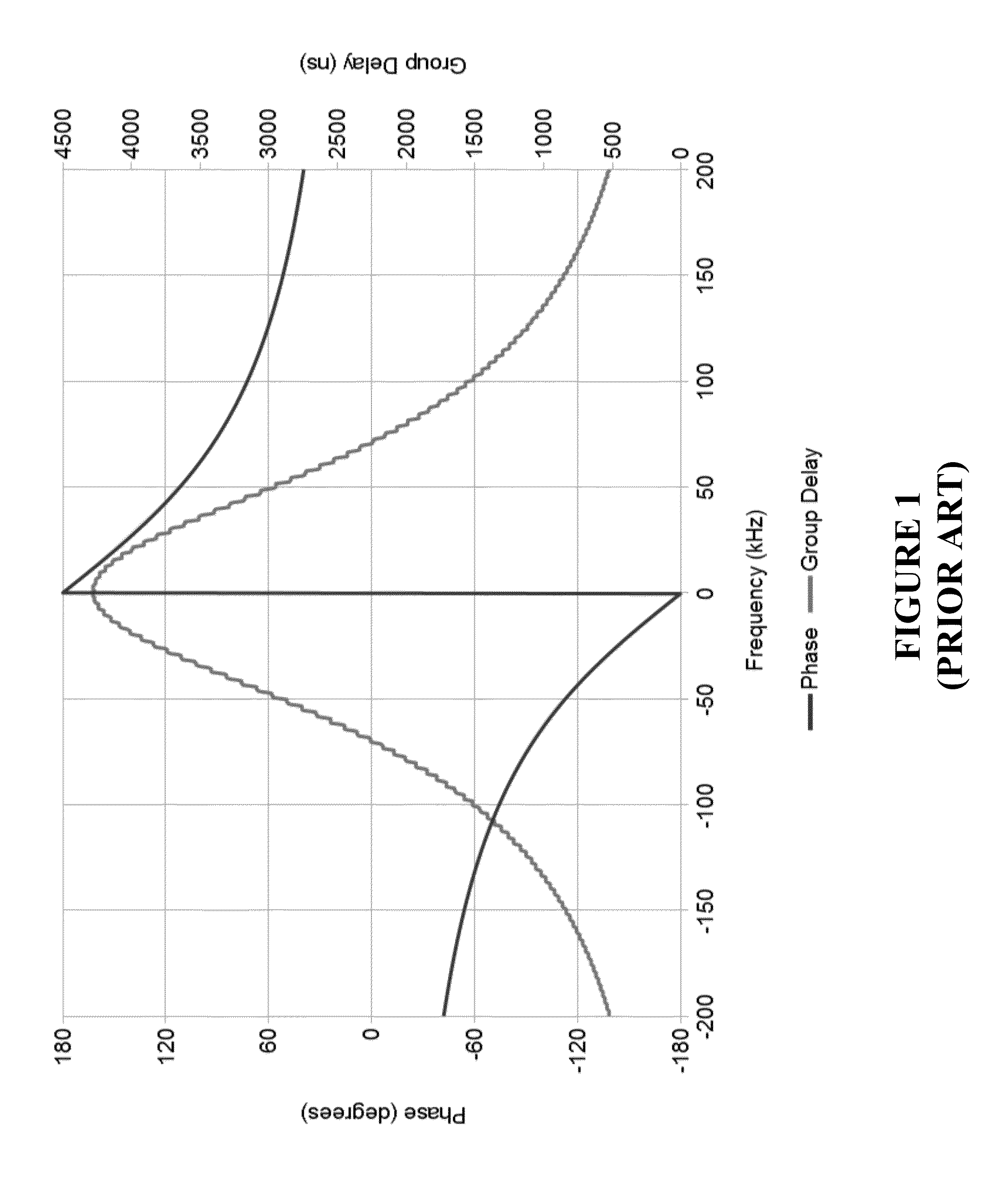
A phase shift is defined as a point in frequency at which the phase is changed from 0 degrees to 180 degrees. A device is provided for combining analog and digital in-band-on-channel (IBOC) signals to feed a common antenna utilizing phase shifting allpass filter modules to provide a 180 degree phase shift to specific IBOC channels within a constant impedance dual-hybrid circuit. The IBOC Allpass combiner includes one input 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler, one output 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler, a load resistor, and two phase shifting allpass filter modules. Each phase shifting allpass filter module is comprised of a two coaxial cavity resonators coupled to a 90 degree 3 dB quadrature hybrid coupler. Components and modules are coupled using mating transmission lines. The four coaxial cavity resonators are used as devices to produce two distinct phase shifts at isolated upper and lower IBOC side band frequencies. The circuit is designed for one center analog frequency and two sideband IBOC OFDM carrier frequencies, such that all frequencies will combine in phase at the common antenna input with minimal loss and minimal group delay. Out of phase and spurious emissions are ported to the load resistor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS RES
Coaxial tilt pin fixture for testing high frequency circuit boards
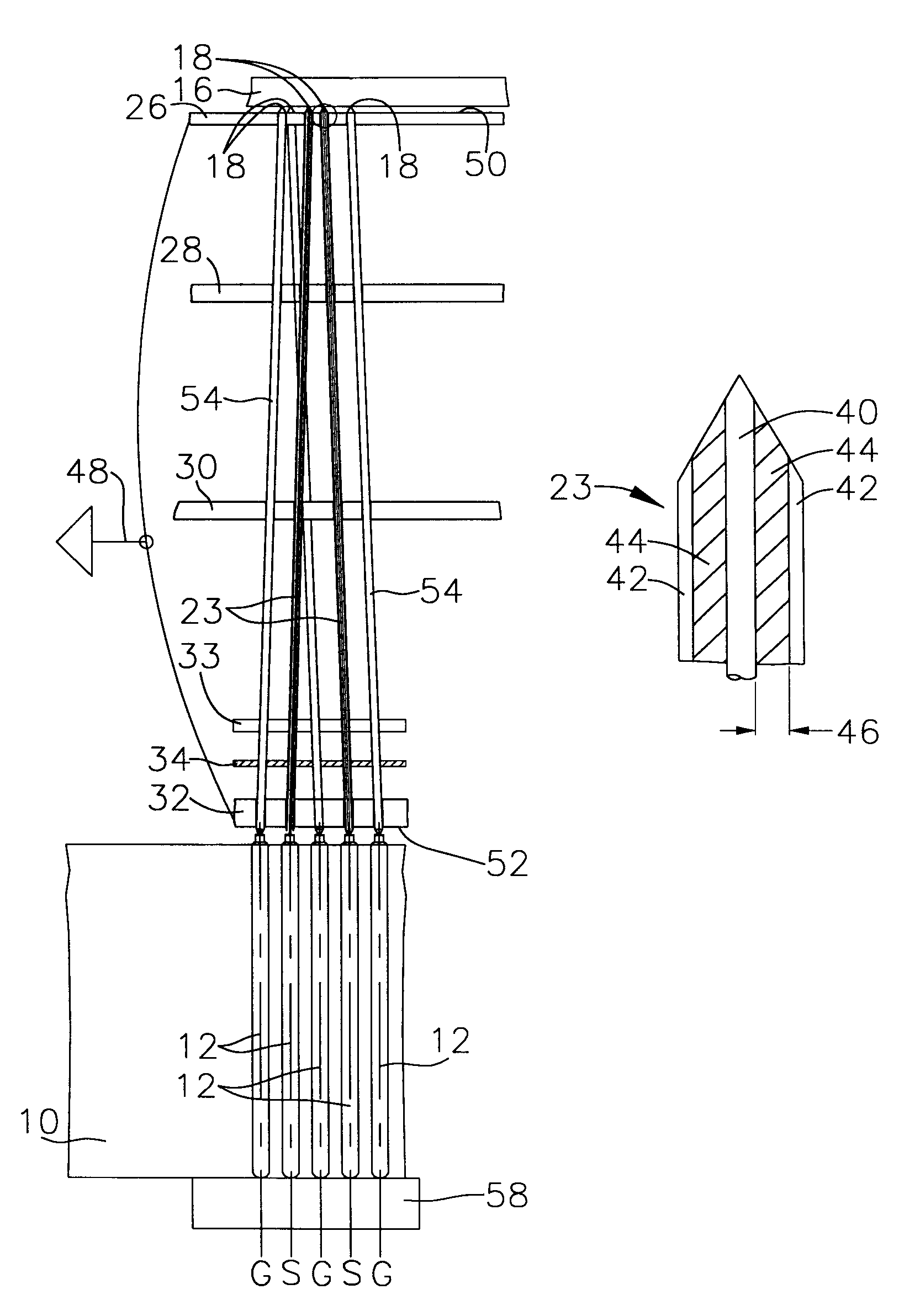
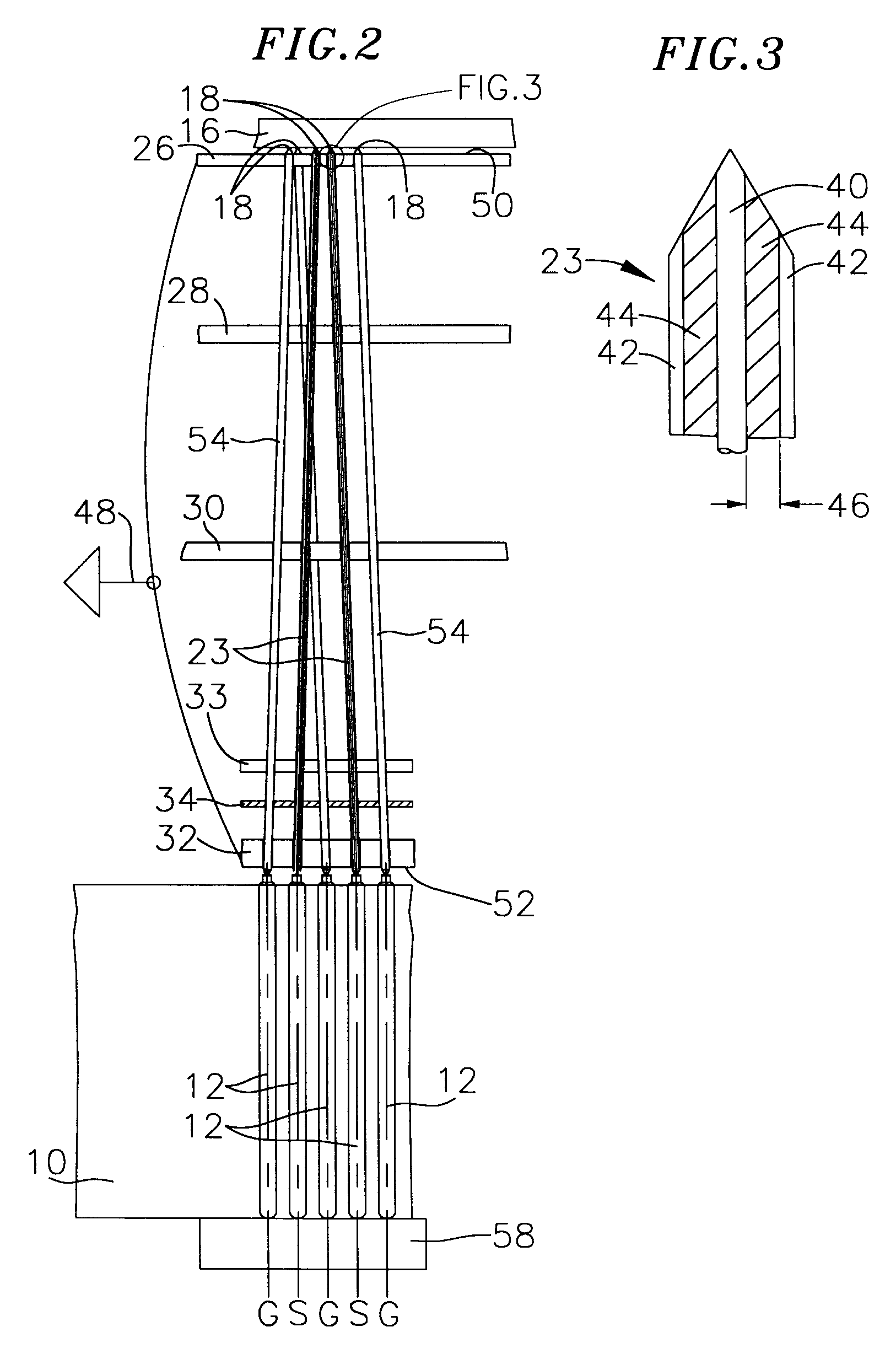
InactiveUS6414504B2Impedance of the coaxial pins remains constantEliminate gapsElectrical measurement instrument detailsContactless circuit testingConstant impedanceTest analysis
A translator fixture for use in testing high frequency or high speed digital circuit boards. The fixture has a pin supporting top plate and base plate and coaxial constant impedance test pins incorporated into the fixture to provide a signal path from a test analyzer to the circuit board under test. The board under test is coupled to an upper surface of the top plate. The impedance of the coaxial pins is matched to the impedance of the board under test as well as the impedance of the test analyzer. Force exerted on the coaxial pins ensures contact of the pins with test points on the circuit board under test. The force may be exerted by spring loaded probes mounted on a compliant test interface below the base plate. The force may also be exerted by Euler buckling the pins by relative movement between the circuit board under test and a second circuit board coupled to the base plate or to the test analyzer.
Owner:DELAWARE CAPITAL FORMATION INC
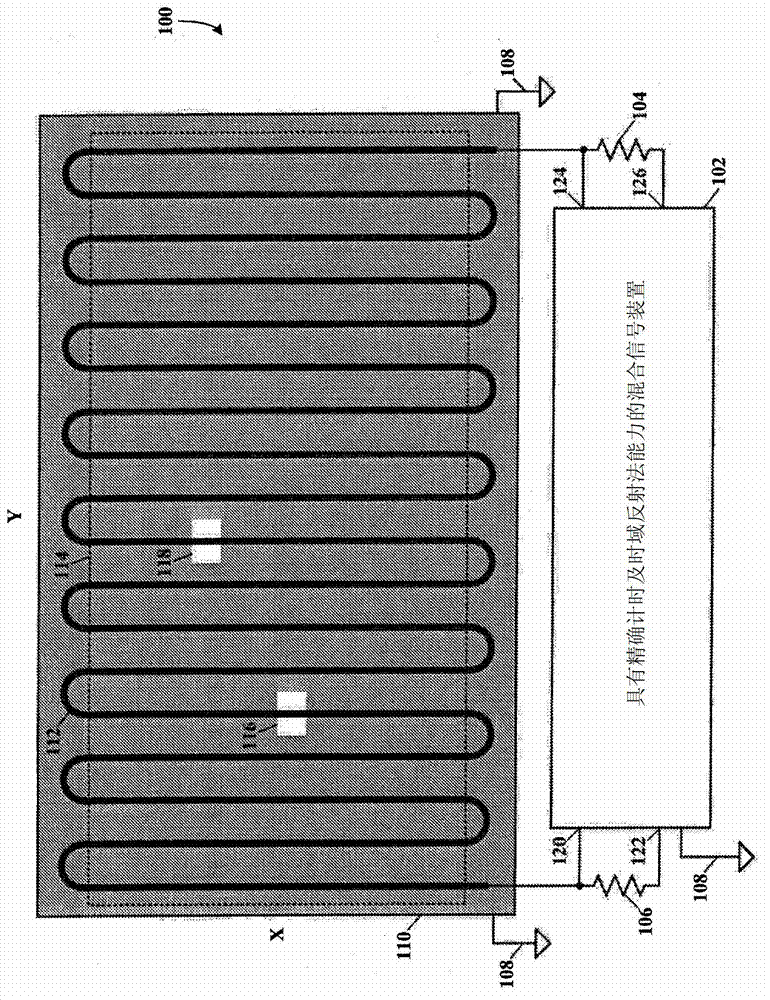
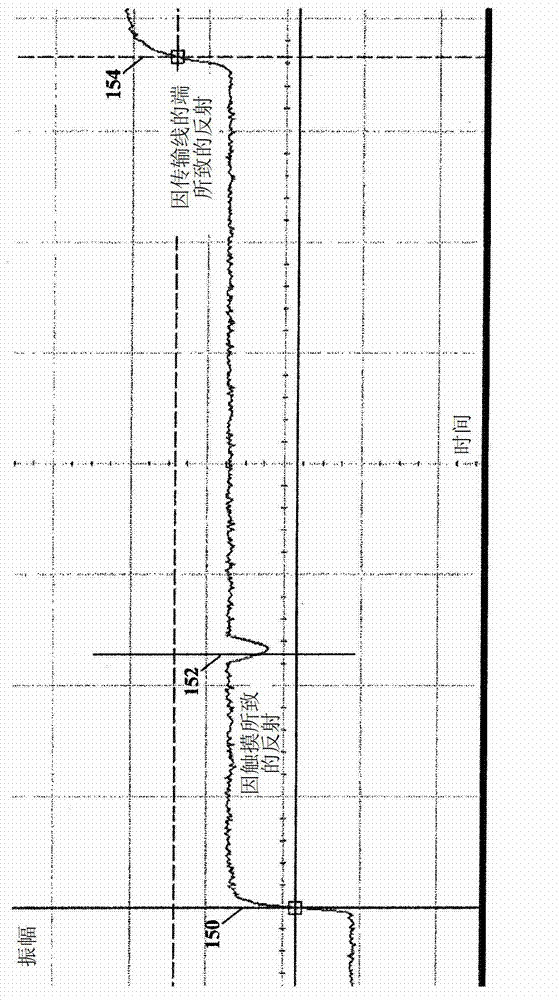
Touch sense using time domain reflectometry
A touch panel or screen has a serpentine transmission line fabricated on a substrate, e.g., printed circuit board, LCD, plasma or LED screen, etc., and has a constant impedance. A touch to the touch panel will cause a change of impedance of the transmission line at the location of the touch. Time domain reflectometry (TDR) is used for determining the location of the change of impedance of the transmission line by accurately measuring the return pulse time at the source of the initial pulse, and then converting the return pulse time to X-Y coordinates of the touch panel or screen.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
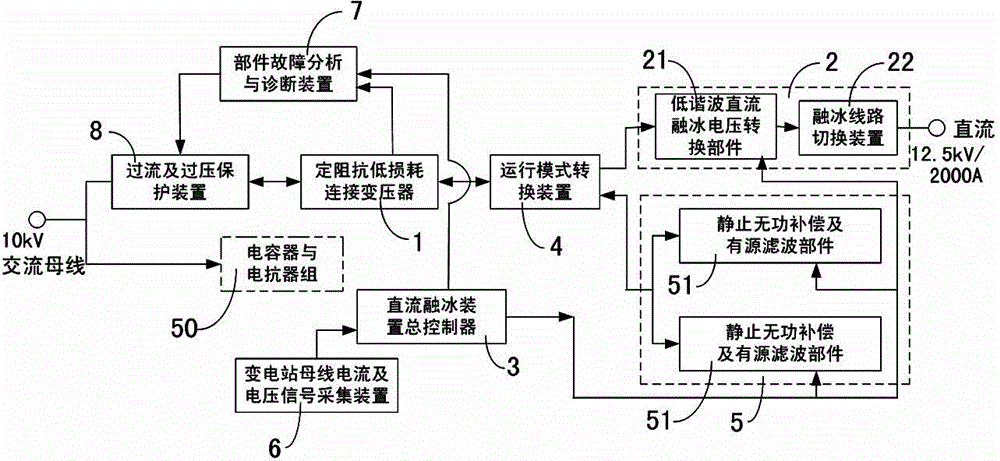
Intensive type DC de-icing device topology structure
ActiveCN104701796AIncrease usageRealize function expansionOverhead installationReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower flowTransformer
The invention discloses an intensive type DC de-icing device topology structure. The intensive type DC de-icing device topology structure comprises a constant impedance low-loss connection transformer, a de-icing branch, a DC de-icing device main controller, an operation mode transformation device, a reactive compensation and active filter branch and a transformer substation bus current and voltage signal acquiring device; the transformer substation bus current and voltage signal acquiring device is connected with a DC de-icing device main controller; the control end of a static reactive compensation and active filter part is connected with the DC de-icing device main controller; the input end of the operation mode transformation mode is connected with an C bus of a transformer substation through the constant impedance low-loss connection transformer, and while the output end of the operation mode transformation mode is respectively connected with the de-icing branch and the reactive compensation and active filter branch. The intensive type DC de-icing device topology structure can perform de-icing, reactive compensation and active filter, and is reliable to run; the de-icing and the reactive compensating capacity can be independently configured; therefore, the guidance is provided for the multifunctional topology structure of the de-icing device; the intensive type DC de-icing device topology structure can be widely applied to various transformer substations.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +3
Constant impedance in CMOS input and output gain stages for a wireless transceiver
InactiveUS6868262B2Easy constructionEasy to operateGain controlRadio transmissionCMOSWireless transceiver
An apparatus to provide a stage in a transmitter or receiver operating in wireless frequency ranges performing a gain control function between a final or an initial stage respectively and process circuitry for adjusting gain and providing a constant input impedance at its input and a constant output impedance at its output, providing a direct conversion transceiver in which constant impedance gain control circuits are provided in the receive and transmit paths, all of which are simple in construction and efficient in operation.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Transmission line pulse measurement system for measuring the response of a device under test
InactiveUS7545152B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nanosecond
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
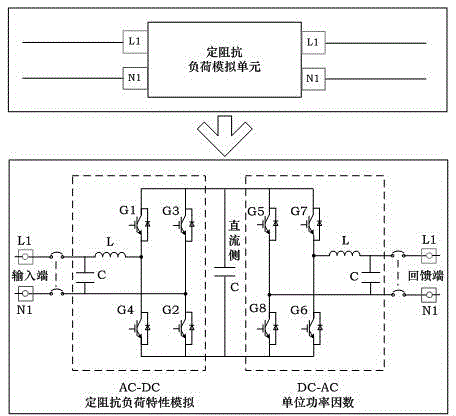
Anti-islanding protection testing circuit and method based on constant impedance load simulation
The invention aims to provide an anti-islanding protection testing circuit based on constant impedance load simulation; the circuit comprises a constant impedance load simulation unit, a monitoring unit and a measuring unit; the input end of the measuring unit is connected with the output end of a grid-connected photovoltaic inverter; the first output end of the measuring unit is connected with a 0.4kV power distribution network; a bypass switch is connected between the input end of the constant impedance load simulation unit and the first output end in parallel; the first input end of the monitoring unit is connected with the second output end of the measuring unit; the second input end of the monitoring unit is connected with the output end of the constant impedance load simulation unit; the third input end of the monitoring unit is connected with the second output end of the bypass switch. The constant impedance load simulation unit accurately simulates load characteristics of a parallel RLC (radio link control) load and feeds an active power output by the grid-connected photovoltaic inverter to the power distribution network in a unit power factor, so that the anti-islanding protection of the grid-connected photovoltaic inverter is enabled to be triggered in testing process; the circuit and the method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of no obvious heating, compact device and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
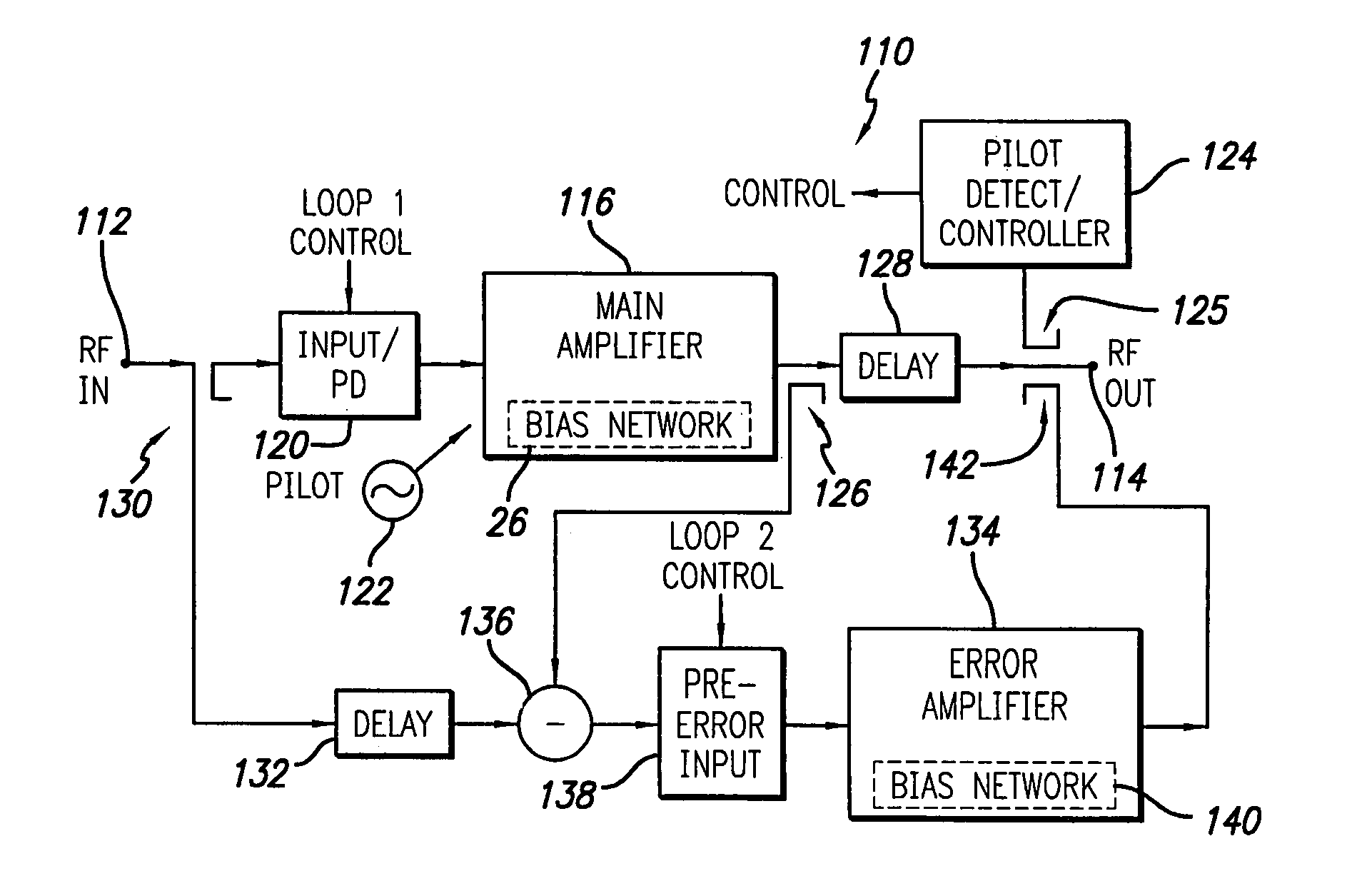
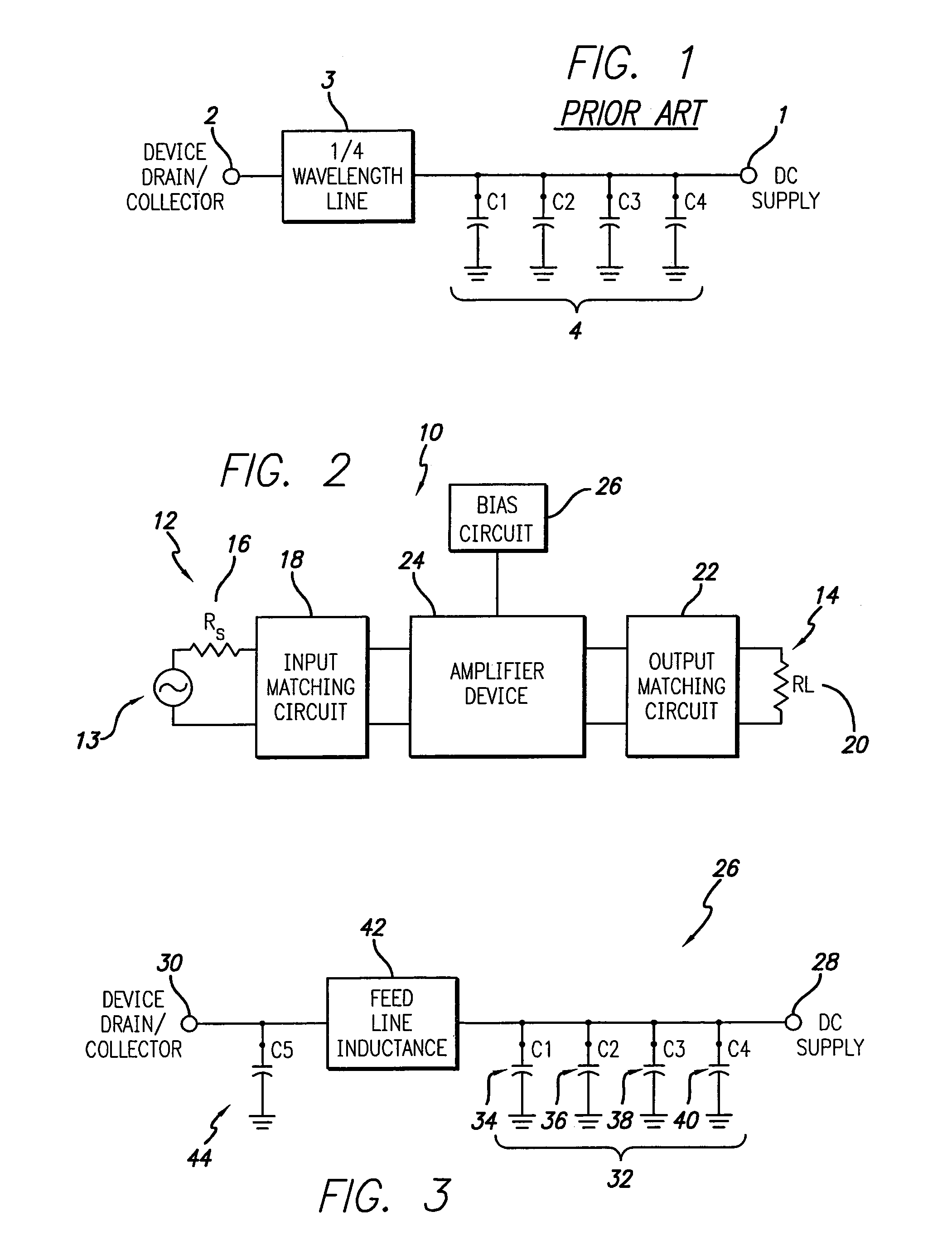
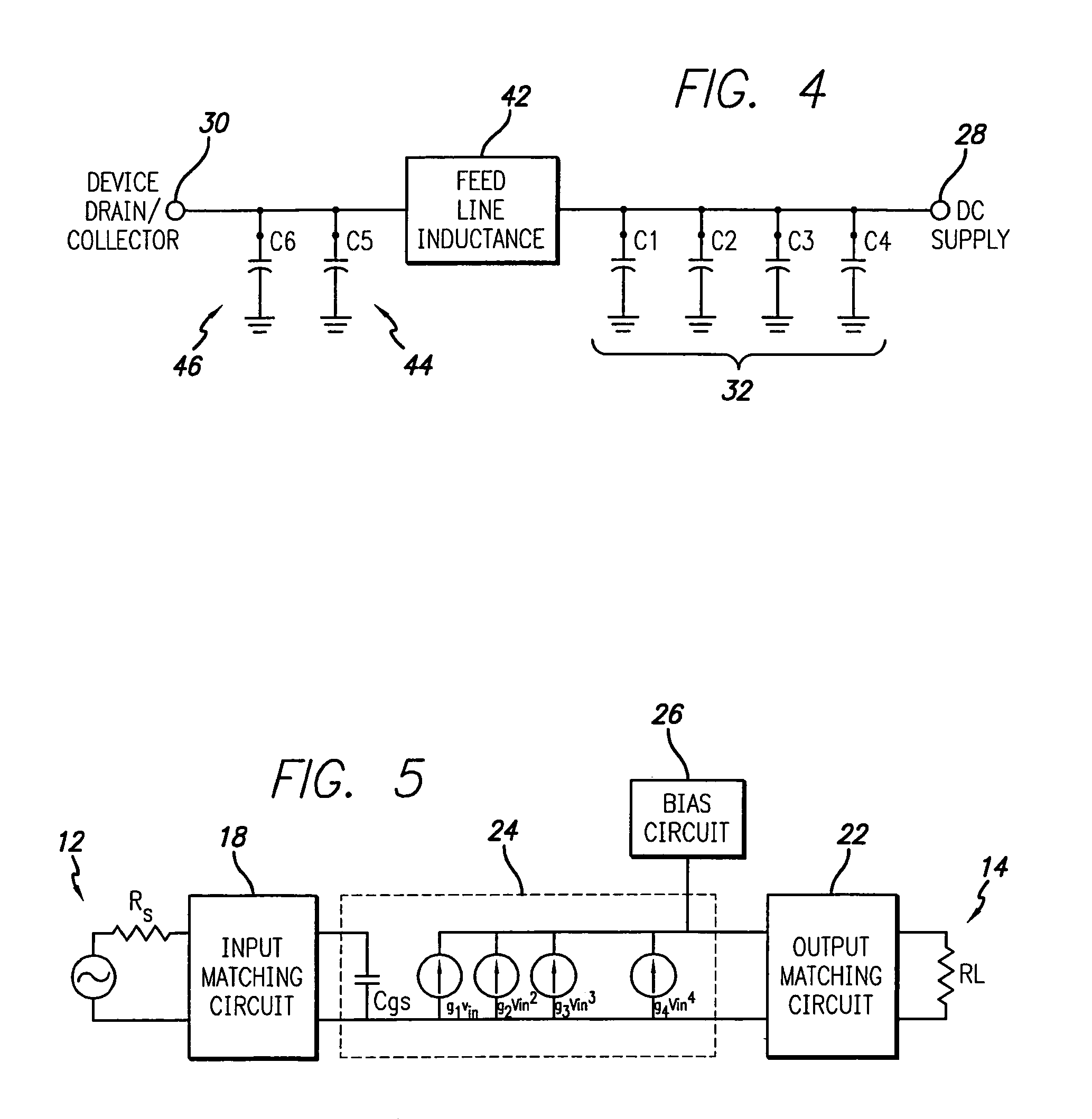
Feed forward amplifier employing bias circuit topologies for minimization of RF amplifier memory effects
InactiveUS7106134B2Minimize memory effectHigh impedanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationConstant impedanceLinearization
An RF power amplifier having reduced memory effects is disclosed. This is achieved by a novel design of the DC supply feed network to achieve low impedance across video frequencies, whilst maintaining the correct RF output matching. One or more transmission zeros are provided in the bias circuit transfer function, which are positioned in the video bandwidth so as to provide low and relatively constant impedance across the video bandwidth. Also, a parallel DC feed line may be employed to reduce impedance across the video bandwidth. The reduction in memory effects allows improved performance of predistortion linearization techniques and an implementation in a feed forward amplifier employing predistortion linearization is also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Differential/single-ended input stage
An input stage for an integrated circuit device provides constant gain in selectable modes of either differential or single-ended operation. In one embodiment, transconductance devices are arranged so that the input impedance of the input stage matches the signal source impedance, regardless whether the input stage is selected to operate in a differential mode or in a single-ended mode. In accordance with an alternative embodiment, constant-gain and constant-impedance conditions are maintained in a configuration that comprises and input signal attenuator. In one application, the input stage may serve as a low-noise amplifier (LNA) for an integrated transceiver.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
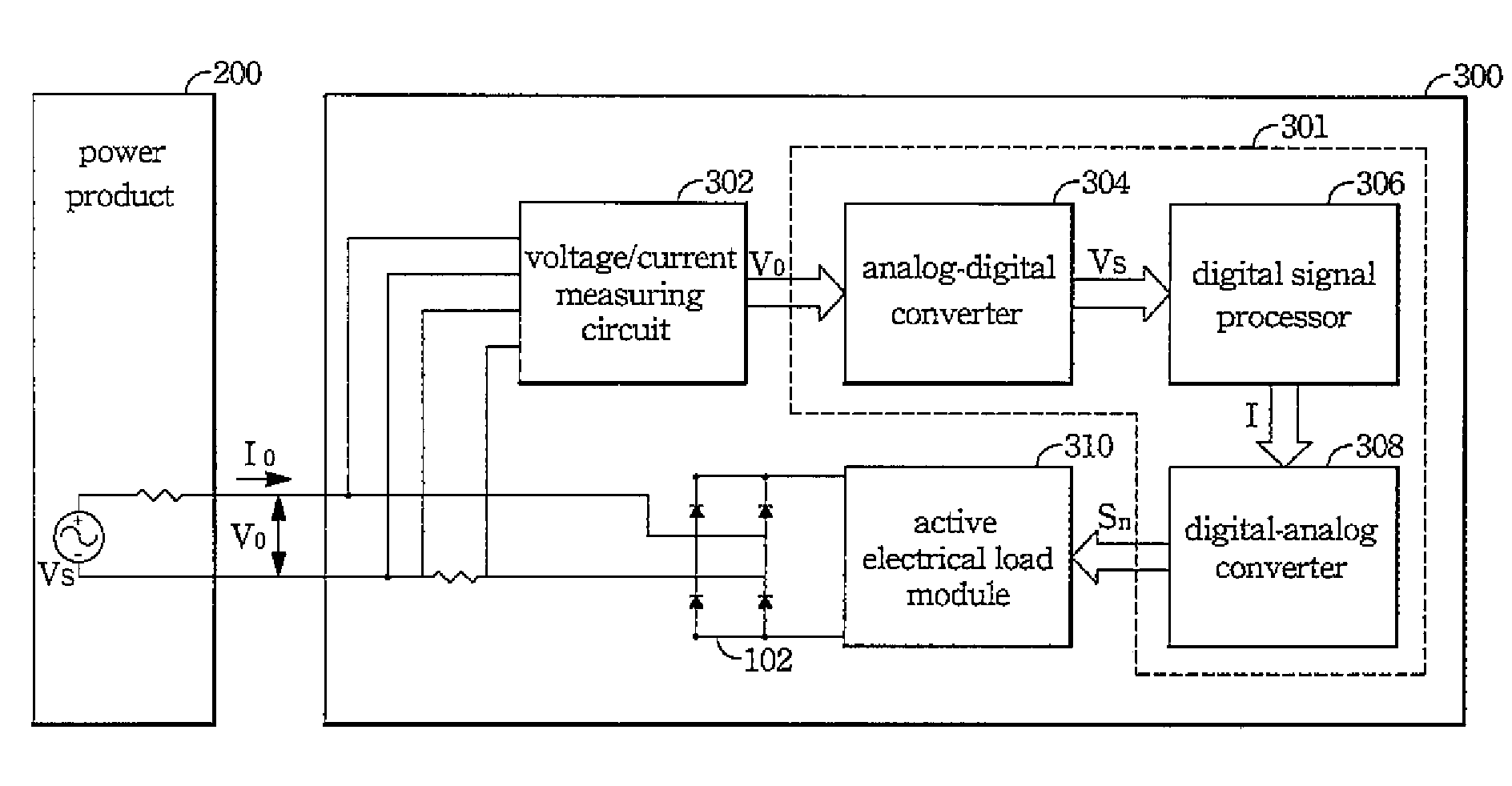
Device for simulating rectified constant impedance load and method thereof
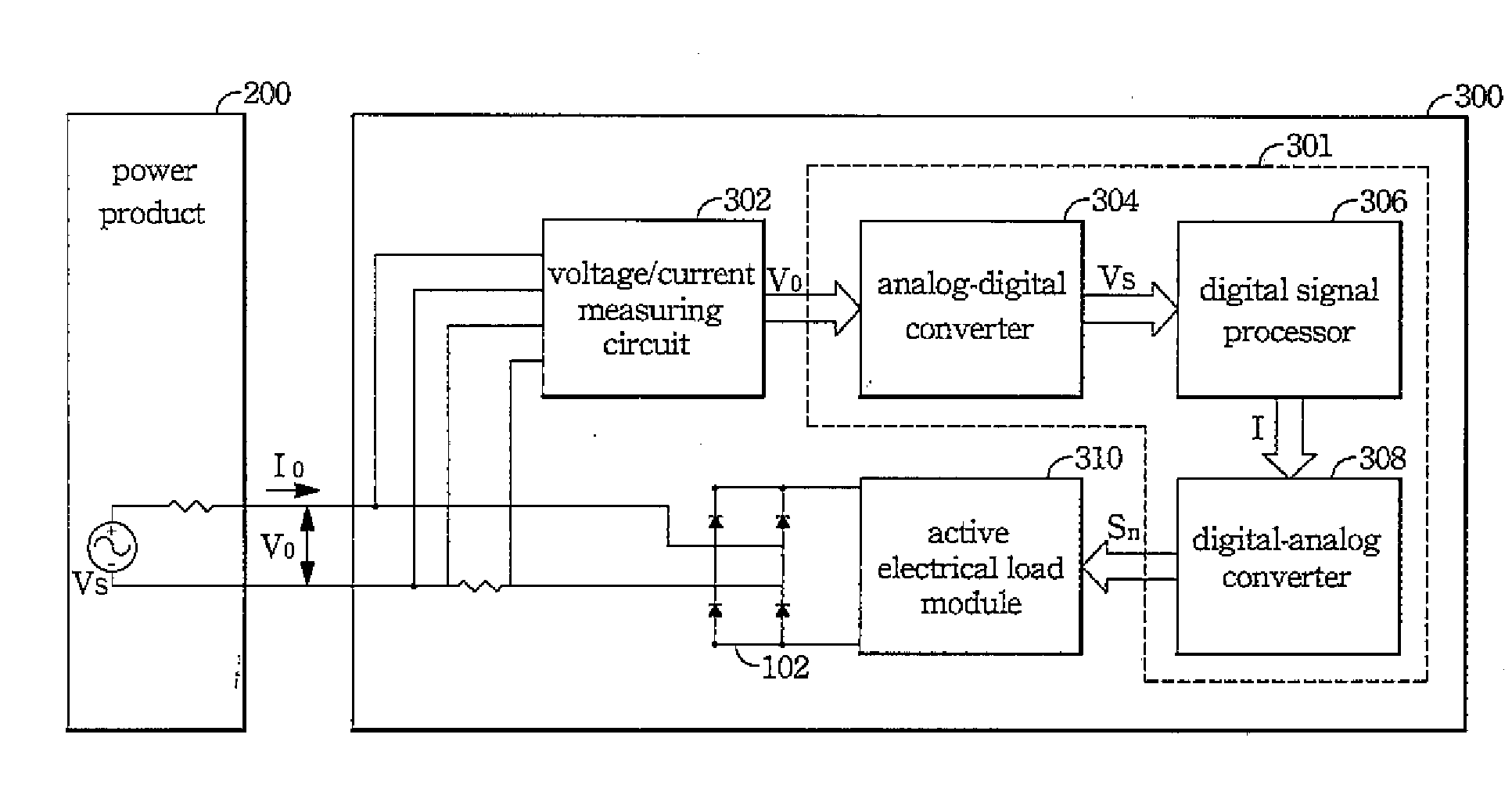
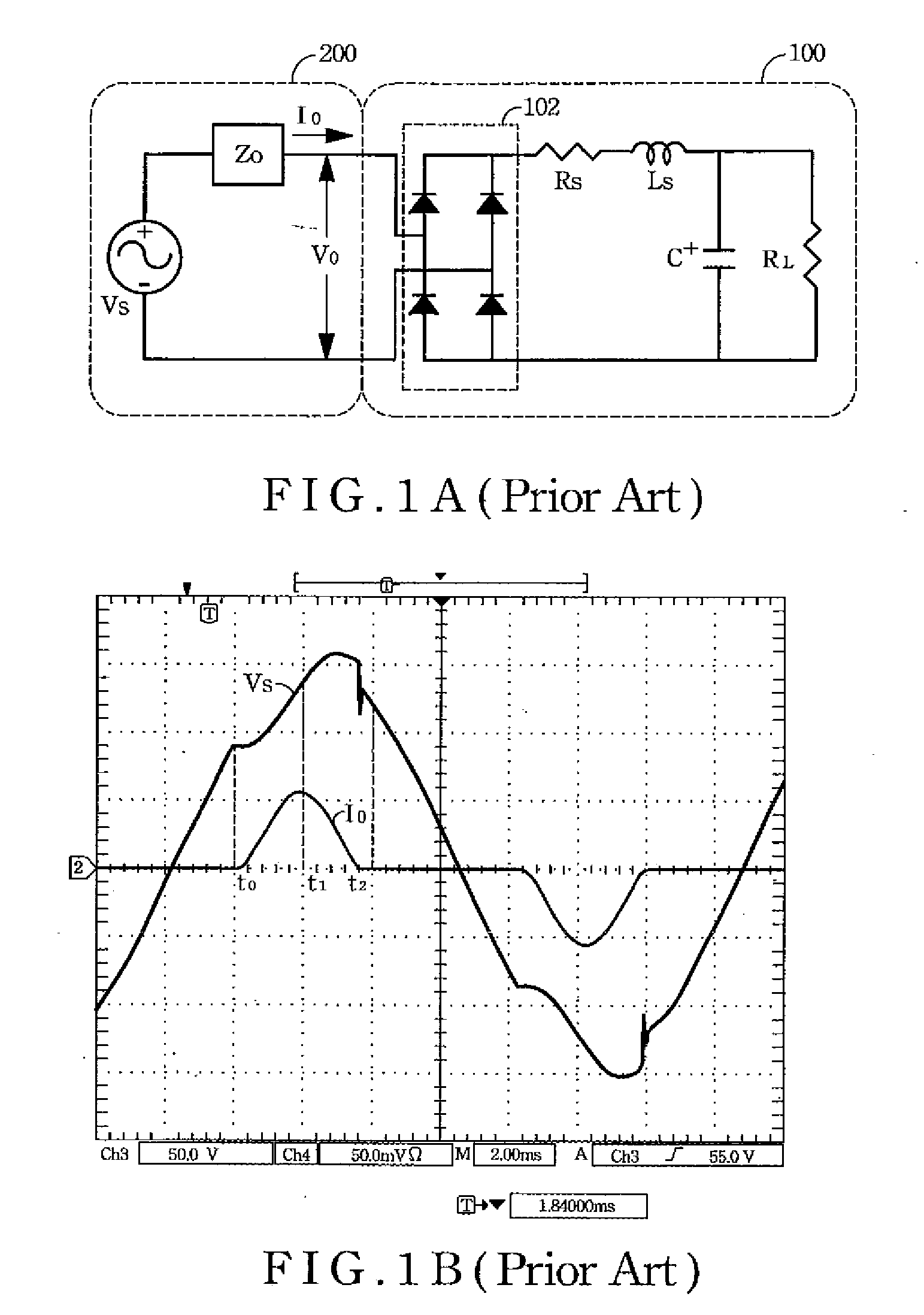
ActiveUS20090091958A1Broaden applicationSimulation is accurateAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDigital analog converterLoad model
The device for simulating a rectified constant impedance load provide by the present invention is to test a power product and comprises an analog-digital converter, a digital signal processor, a digital-analog converter, and an active electrical load module in order to replacing the passive components of a traditional rectified passive load. method for simulating a rectified constant impedance load being applied to test a power product and comprising the steps of: (S1) replacing the plurality of passive components of the rectified constant impedance load with a digital control module and an active electrical load module; (S2) establishing a passive load model function in order to represent the application relationships of the plurality of the passive components; (S3) executing the operation of the passive load model function by the digital control module in order to gain a load current value, and transferring the load current value to an analog control signal via the digital control module; and (S4) controlling the active electrical load module via the analog control signal so as to draw currents from the power product.
Owner:CHROMA ATE
Wiring board
InactiveCN1741706AMultilayer circuit manufacturePrinted circuit non-printed electric components associationElectrical conductorConstant impedance
A wiring board consists of flat board with the first surface and the second surface , conductor layer with wire , dielectric layer being overlapped alternatively with conductor layer on one of board surface , connecting through conductor , signal through hole and its conductor , protective hole and its conductor , the first and the second path terminal pads . It is featured as forming signal transmission path by setting conductor layer on one of board surface, forming coplanar wave guide with constant impedance 20 or strip line by surface conductor and wire, covering protective hole internal surface with its said conductor.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
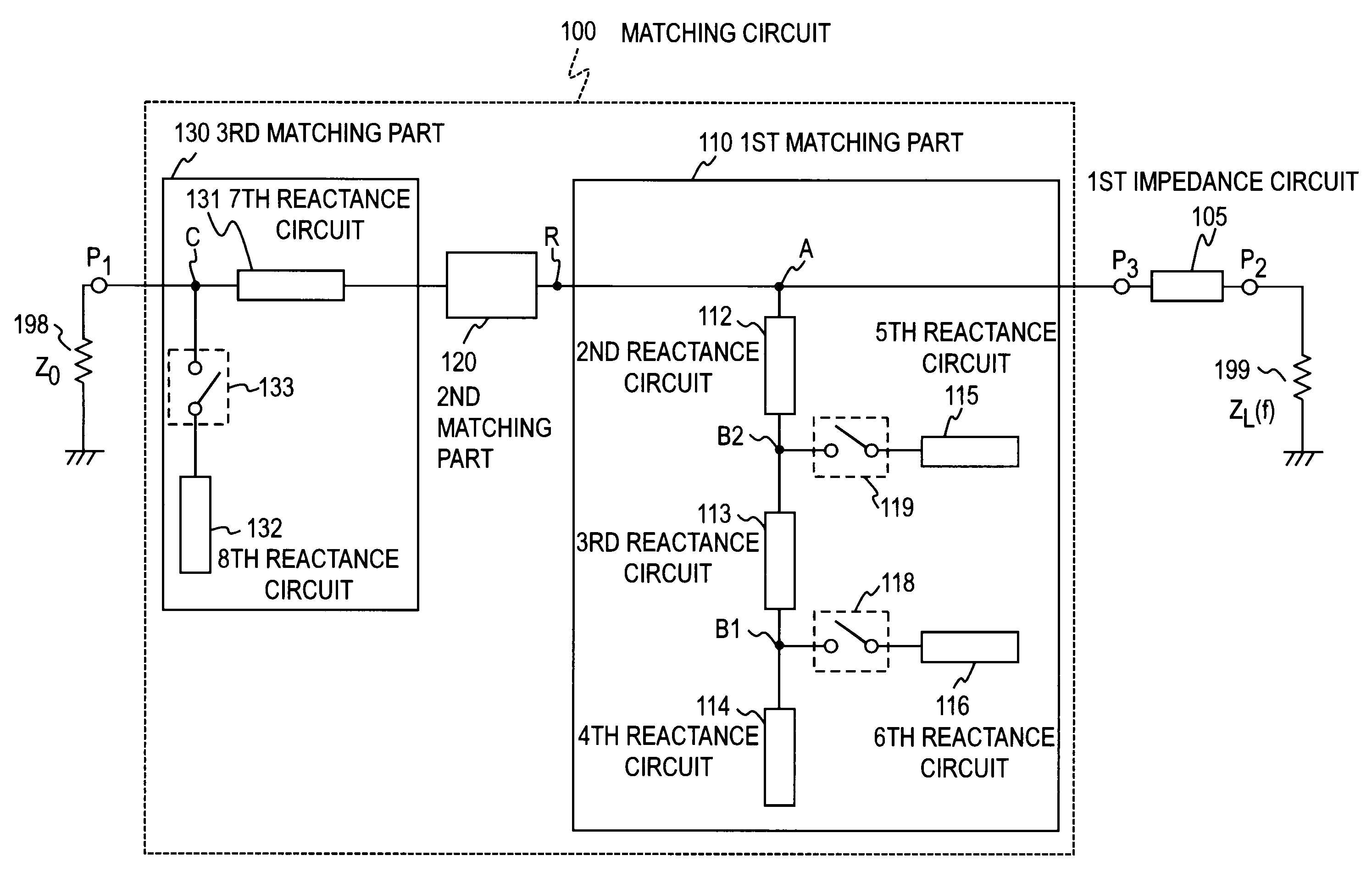
Matching circuit
InactiveUS20080278260A1Small designMultiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesConstant impedanceFrequency characteristic
First, second and third matching parts 110, 120, and 130 are connected in series between a circuit element 199 whose impedance has a frequency characteristic and a circuitry 198 having a constant impedance. The second matching part 120 has the capability of converting impedances. The first matching part 110 operates as an element having reactance values according to any of frequency bands selected by exclusive switching between on and off of switches 118, 119 and the third matching part 130 operates as an element having reactance values according to any of the frequency bands selected by switching between on and off of a switch 133, thereby providing matching in each frequency band. A seventh reactance circuit 131 is configured on the basis of an interdependence relation with the configuration of a fifth reactance circuit 115 and an eighth reactance circuit 132.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Homotopy-based distributed power supply and non-linear load containing short circuit current calculating method
ActiveCN106066918AFast convergenceSolution Accuracy ImprovementsSpecial data processing applicationsConstant powerConstant impedance
The invention discloses a homotopy-based distributed power supply and non-linear load containing short circuit current calculating method comprising the following steps: taking the distributed power supply as a node, and building a power distribution network system model according to connecting modes and parameters of each electrical part in the power distribution network; using an iteration type compensation current method to resolve the short circuit current of a power distribution network load model; determining whether the resolved short circuit current has converged or not, entering the next step if not, and storing the result and stop computing if the short circuit current has converged; converting all constant power loads into a constant impedance load model, using the iteration type compensation current method to compute the short circuit current, and computing short circuit voltage values of each node in the power distribution network system; building a homotopy equation, using calculated short circuit voltage values and current values to build an admittance matrix, and using a continuous method to resolve and update the admittance matrix, thus obtaining the convergence short circuit current solution. The homotopy-based distributed power supply and non-linear load containing short circuit current calculating method can simultaneously improve short circuit calculating performance in the aspects of convergence and resolving precision.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Differential/single-ended input stage
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Constant impedance filter
A constant impedance filter maintains a constant input impedance for frequencies that are both inside the filter passband and outside the filter passband. The constant input impedance appears as a pure resistance. The constant impedance filter includes a plurality of filter poles that are connected in series. Each of the filter poles include an inductor, a capacitor, and a resistor. The value of the inductor, the capacitor, and the resistor are selected to provide a constant input impedance over frequency for each pole of the filter, which produces a constant input impedance for the entire filter over frequency. The constant impedance filter can be implemented as a low pass filter, a high pass filter, or a bandpass filter. Furthermore, the constant impedance filter can be implemented in a single-ended configuration or a differential configuration.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Device for simulating rectified constant impedance load and method thereof
ActiveUS8044678B2Constant loadSimulation is accurateAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcTest powerDigital analog converter
Owner:CHROMA ATE
Constant impedance driver for high speed interface
InactiveUS20020163360A1Constant impedanceMaintain impedanceReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierConstant impedance
A compensated driver for maintaining constant impedance during data transfer from an integrated circuit comprises an output portion having an output device to transfer data from the integrated circuit and a mimic circuit portion having a sample output device scaled to a fraction of the output device adapted to accept a reference current and generate a sample voltage. A mimic circuit portion has a sample output device scaled to a fraction of the output device adapted to accept a reference current and generate a sample voltage. A differential amplifier portion is adapted to generate a control voltage in response to a reference voltage and the sample voltage A predrive portion applies either a ground or the predetermined control voltage from the differential amplifier portion to the output stage portion in response to an input, the control voltage regulating the output device in the output stage portion to achieve a more constant impedance
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and apparatus for making an interconnection between power and signal cables
ActiveUS20160226203A1Reduced radiusCoupling device engaging/disengagingTwo-part coupling devicesPower cableConstant impedance
A method, system and apparatus for making an interconnection between power cables and signal cables. A single electrical interface in mid- or backplane applications is introduced to accommodate a wide range of board thickness variations while maintaining a desired interface relationship, using a connector plug bushing, a male connector having a sliding fit with the bushing, a first coaxial connector plug, a female connector plug with a housing width sized to provide a sliding fit within the connector plug bushing inner opening, and a second coaxial connector plug in the free end of the female connector plug for connection to the power and signal cables. A constant impedance connector is used with the interconnection of the RF signal and power cables.
Owner:THE PHOENIX OF CHICAGO
Test circuits and current pulse generator for simulating an electrostatic discharge
InactiveUS8278936B2Small distortionFast rise timeMeasuring interference from external sourcesIndividual semiconductor device testingLow distortionConstant impedance
This invention is an electrostatic discharge testing circuit that can deliver current pulses to a component under test (CUT) with a custom amplitude versus time profile shape. Pulse generation with customized shapes is accomplished by discharging an energy storage network comprised of capacitor(s), transmission line(s) and other passive components. Current pulses compliant to the European International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 61000-4-2 standard can be so produced. These current pulses are delivered to the CUT with low distortion through a constant impedance electrical path, such as a combination of cables and controlled impedance conductors of printed wiring boards compatible with packaged IC devices, assemblies, and wafer probes. The current pulses can be delivered with various impedances, and measurements made that allow the CUT currents and voltages to be calculated.
Owner:GRUND EVAN
Transmission line probe for nmr
InactiveUS20120081119A1Measurements using magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detection for transportSaddle coilCapacitance
A probe for an NMR device is disclosed in which a saddle coil is disposed on one side of a flexible insulating material, and an additional conductor is disposed on the opposite side. The additional conductor and the conductors of the saddle coil create a capacitance across the insulating material. This capacitance acts with the inductance of the saddle coil such that the probe itself forms a transmission line. The probe is thus inherently broadband and requires no tuning. It also presents a constant impedance, thus facilitating impedance matching to an NMR spectrometer. In a preferred embodiment, a chip resistor is disposed on the flexible insulating material, terminating the transmission line.
Owner:MURPHREE JR DENNIS HAAGA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com