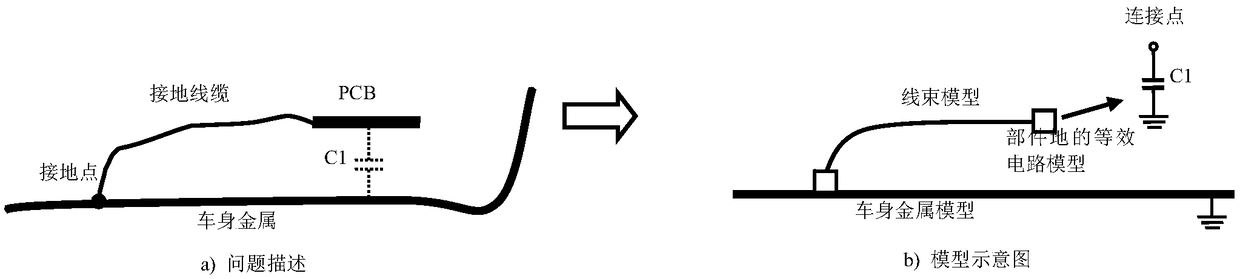Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1943results about "Measuring interference from external sources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
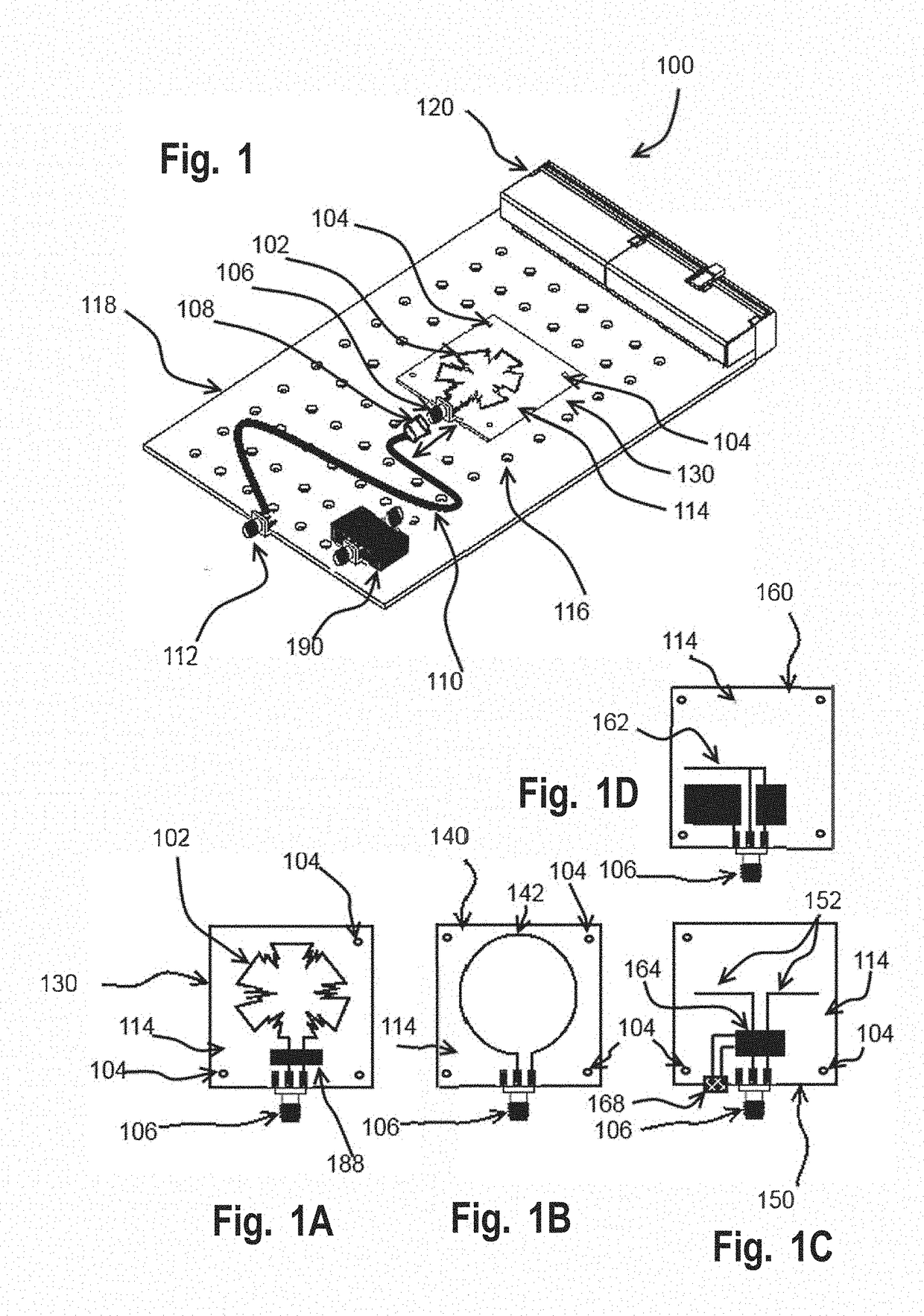
Detection of malicious software, firmware, IP cores and circuitry via unintended emissions
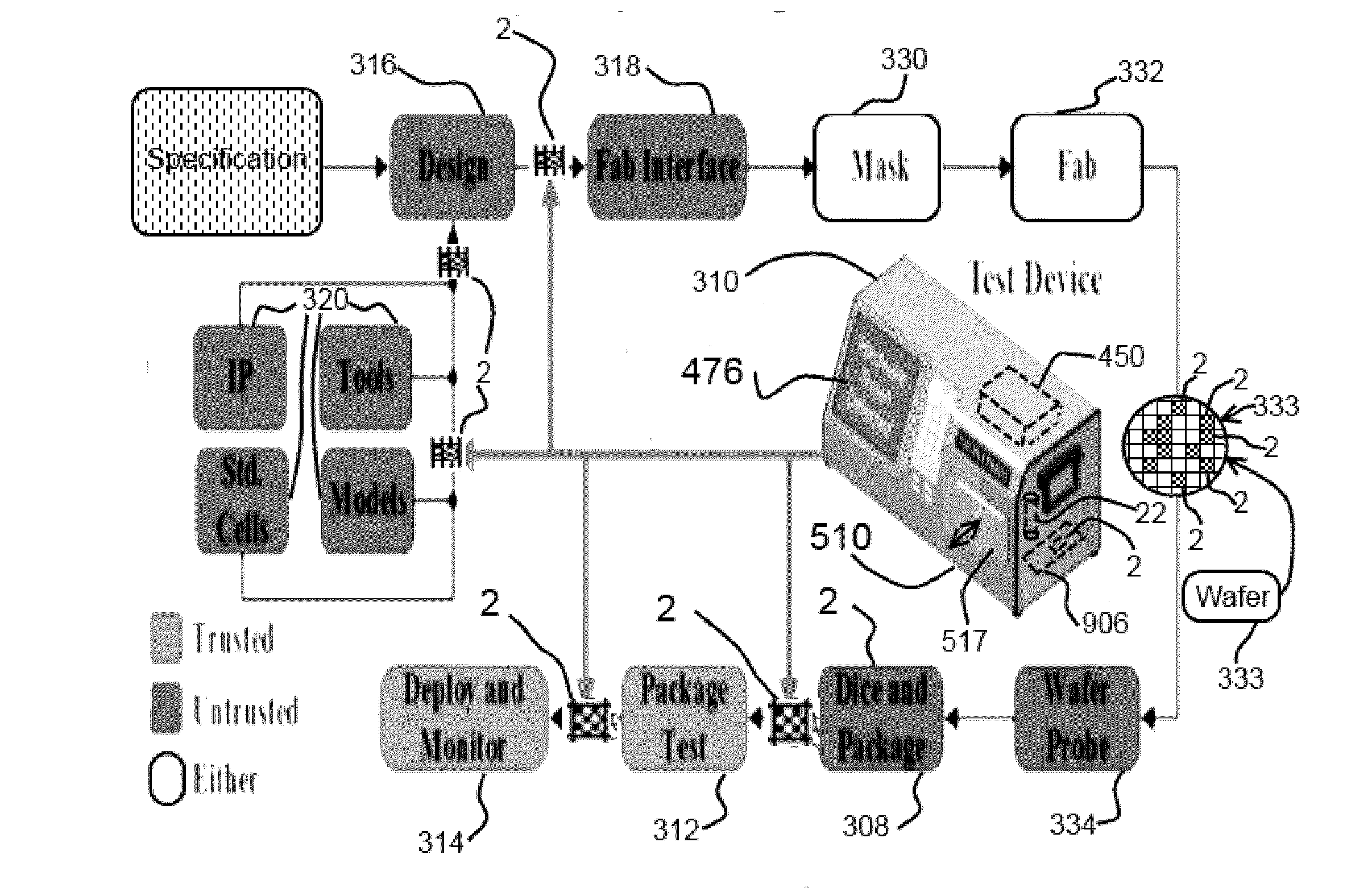
An apparatus for testing, inspecting or screening an electrically powered device for modified or unmodified hardware, firmware or software modifications including Malware, Trojans, adware, improper versioning, worms, or virus and the like, includes an antenna positioned at a distance from the electrically powered device and a signal receiver or sensor for examining a signal from the electrically powered device. The receiver or sensor collects unintended RF energy components emitted by the electrically powered device and includes one or more processors and executable instructions that perform analysis in a response to the acquired signal input while the electrically powered device is active or powered. The characteristics of the collected RF energy may be compared with RF energy characteristics of an unmodified device. The comparison determines one of a modified, unmodified or score of certainty of modified condition of the electrically powered device.
Owner:NOKOMIS
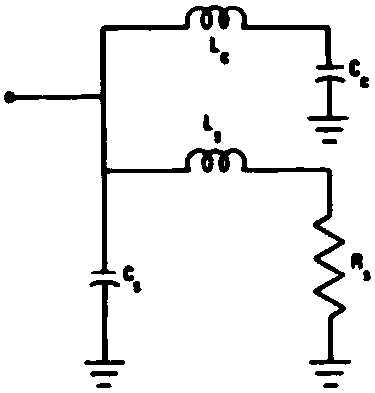
Electromagnetic interference analysis method and apparatus
InactiveUS20020045995A1Spectral/fourier analysisElectromagentic field characteristicsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
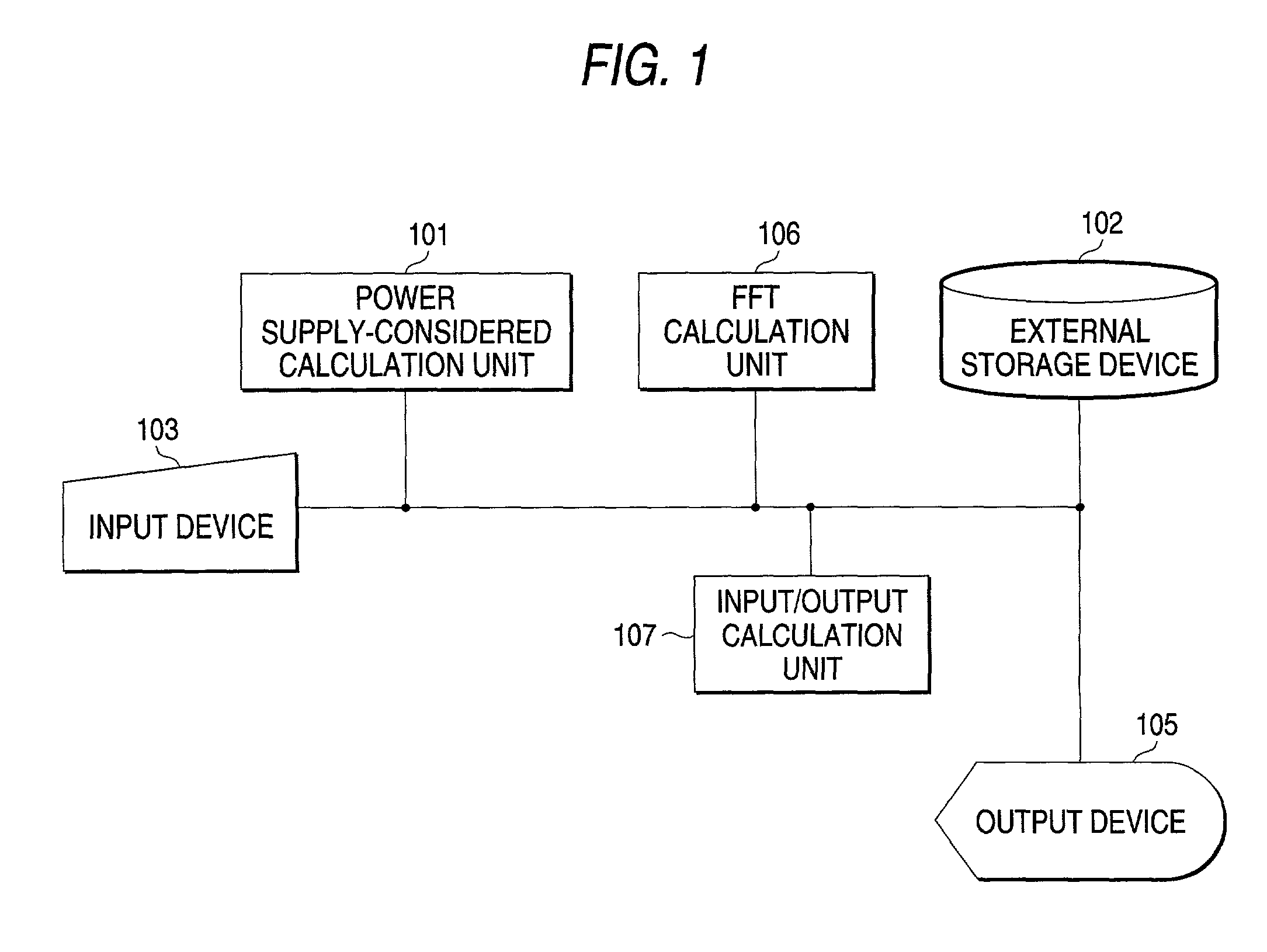
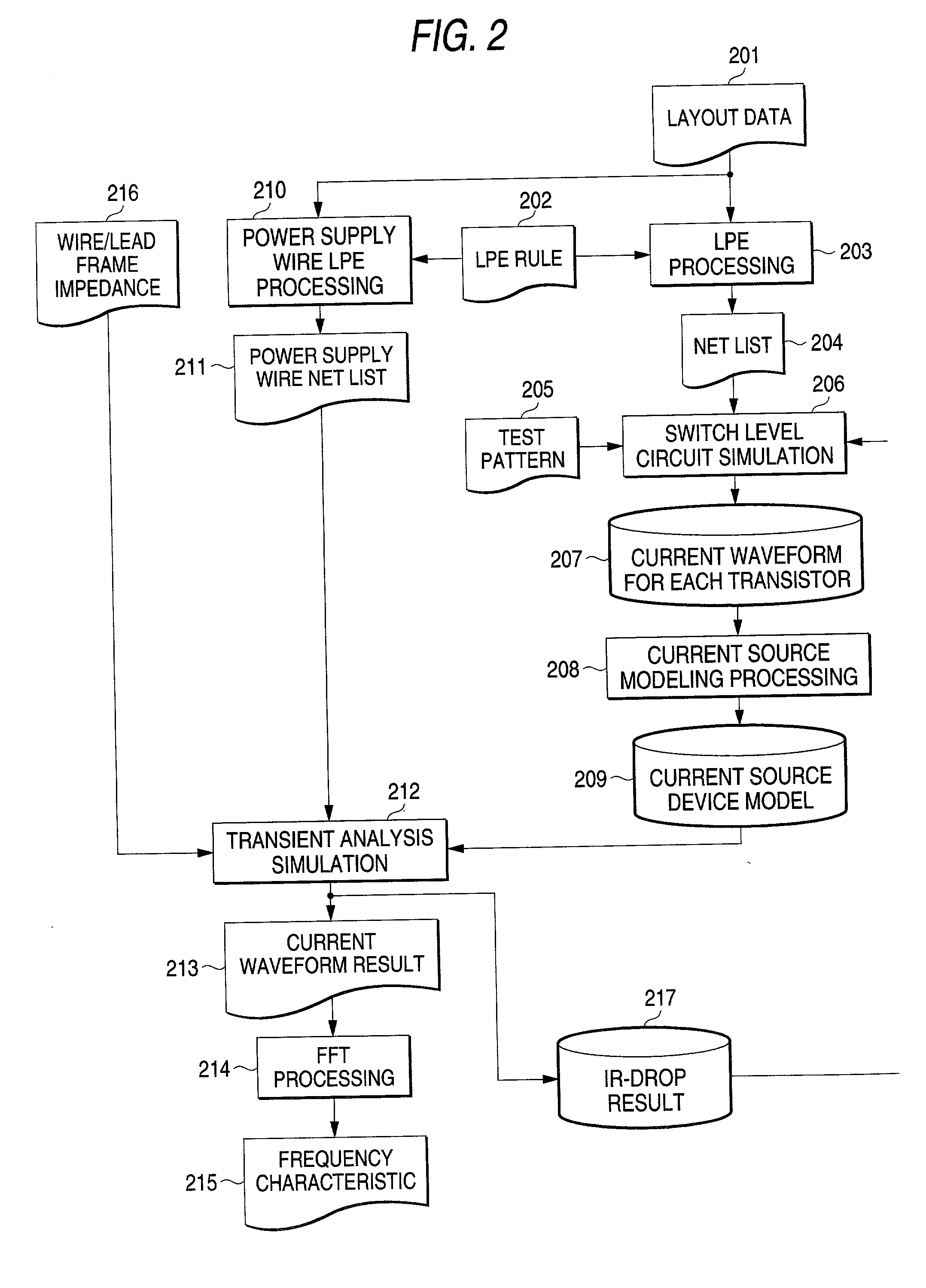
This invention is characterized to include a discrete analysis frequency width change specifying process for specifying in a particular frequency range a change in the discrete high-speed Fourier transform (FFT) analysis frequency width and a modeling process for allocating different discrete FFT analysis frequency widths to the specified frequency range and to a frequency range other than the specified frequency range and performing modeling. The EMI analysis method of this invention reflects on the gate level power supply current calculation the influence of decoupling by resistance, capacitance and inductance of the power supply and ground, thereby making it possible to evaluate the EMI of LSIs in simulation in a realistic time and to provide efficient EMI countermeasures through supporting the identifying of the EMI causing locations.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
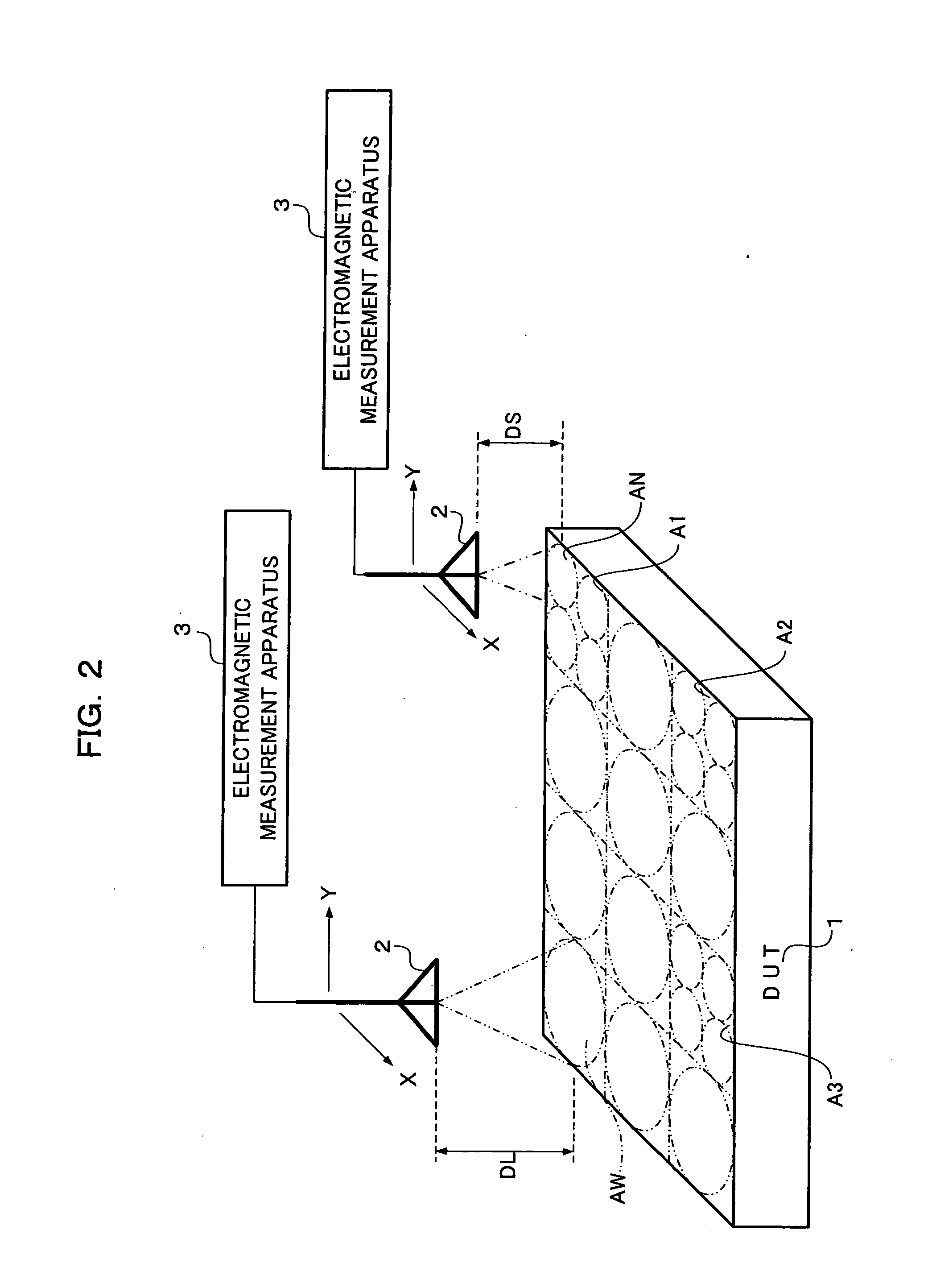
Method and apparatus of electromagnetic measurement
InactiveUS20070024293A1Smoothly measuredEasy to measureResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasuring interference from external sourcesElectromagnetic interferenceDirectivity
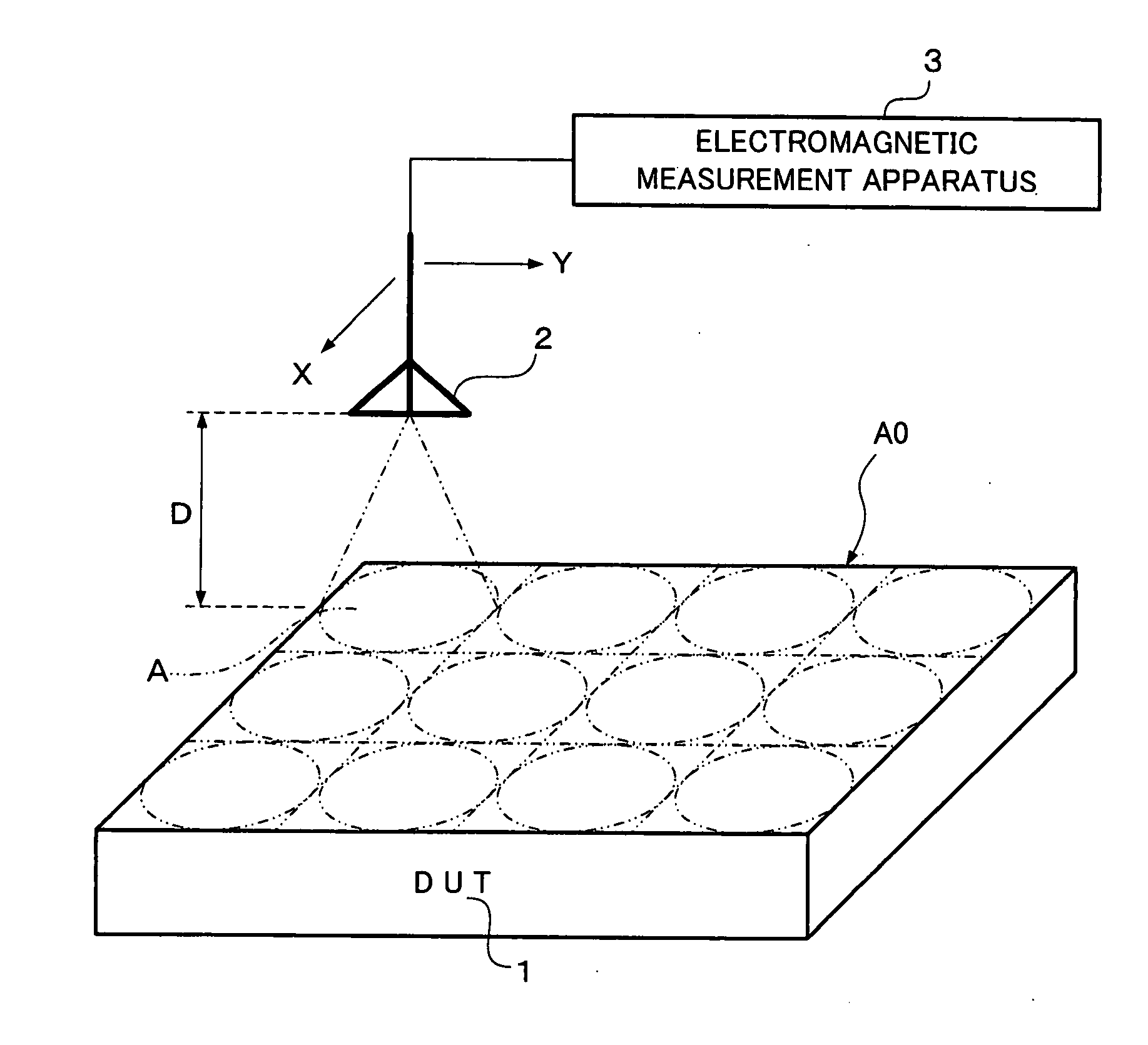
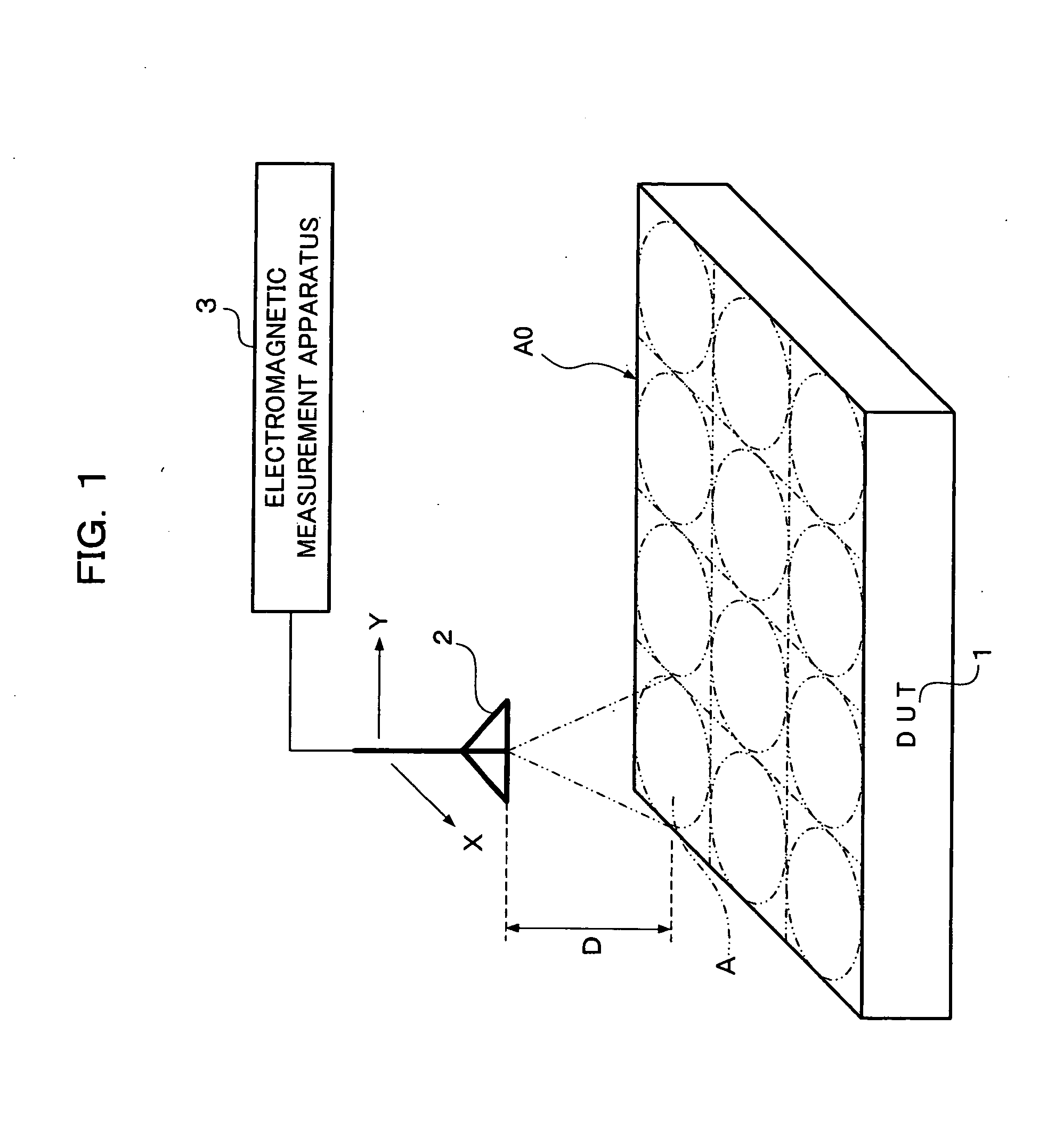
In order to direct a probe having directivity that a received band is widened in accordance with a measurement distance, toward a DUT, shift the received band of the probe in sequence, receive electromagnetic, and measure electromagnetic interference, a plurality of long and short measurement distances between the probe and the DUT are set, and measurement at the long measurement distance and measurement at the short measurement distance are performed plural times. Herein, the measurement at the short measurement distance is performed on a received band where electromagnetic interference is measured by the measurement at the long measurement distance. Thus, measurement of electromagnetic interference can be performed with high accuracy in a short time.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
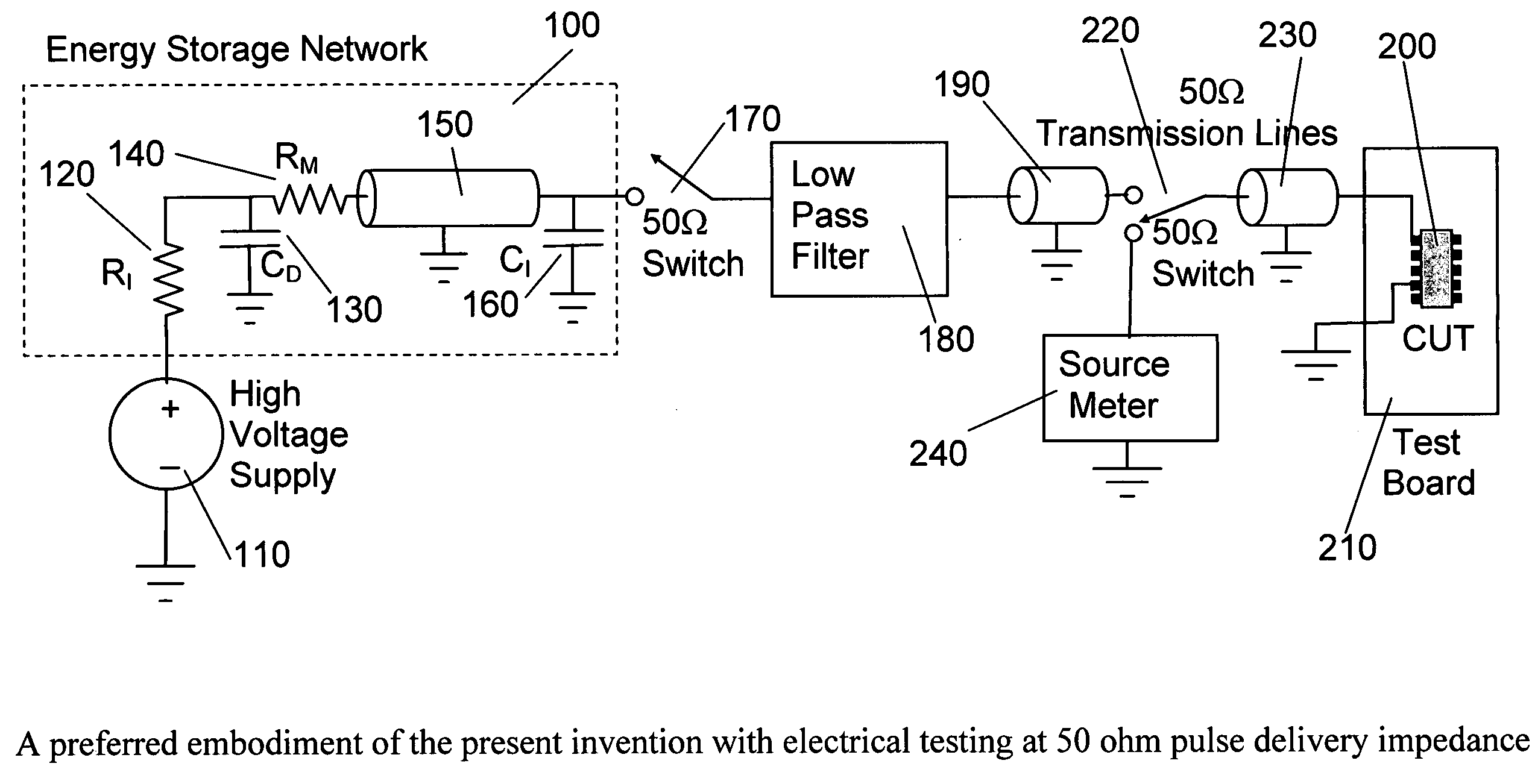
Test circuits and current pulse generator for simulating an electostatic discharge
InactiveUS20090134880A1Small distortionFast rise timeMeasuring interference from external sourcesIndividual semiconductor device testingElectrical conductorLow distortion
This invention is an electrostatic discharge testing circuit that can deliver current pulses to a component under test (CUT) with a custom amplitude versus time profile shape. Pulse generation with customized shapes is accomplished by discharging an energy storage network comprised of capacitor(s), transmission line(s) and other passive components. Current pulses compliant to the European International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 61000-4-2 standard can be so produced. These current pulses are delivered to the CUT with low distortion through a constant impedance electrical path, such as a combination of cables and controlled impedance conductors of printed wiring boards compatible with packaged IC devices, assemblies, and wafer probes. The current pulses can be delivered with various impedances, and measurements made that allow the CUT currents and voltages to be calculated.
Owner:GRUND EVAN
Coupled noise estimation method for on-chip interconnects
InactiveUS6029117AMeasuring interference from external sourcesComputer aided designCapacitanceEstimation methods
An efficient method for identifying potential noise failures in an integrated circuit design by predicting peak noise within a victim circuit of an integrated circuit. Initially, a victim circuit within an integrated circuit is located. An aggressor circuit within the integrated circuit is located which has a physical relationship with the victim circuit, normally proximity. The slope of a signal within the aggressor circuit is analyzed and the coupling currents induced in the victim circuit by the aggressor circuit are computed. The input slope of the aggressor circuit and the physical relationship between the victim circuit and the aggressor circuit are utilized to determine a peak current induced into the victim circuit utilizing modelled coupling capacitance. The peak current and the equivalent impedance of the victim circuit can be utilized to determine peak noise. Noise failures on integrated circuits can be avoided by detecting peak noise which is above acceptable levels.
Owner:IBM CORP
Using multiple antennas to characterize a computer system based on electromagnetic signals
ActiveUS20100033386A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringComputerized systemElectromagnetic shielding
Some embodiments of the present invention provide a system that characterizes a computer system parameter by analyzing a target electromagnetic signal radiating from the computer system. First, the target electromagnetic signal is monitored using a first antenna and a second antenna, wherein an axis of the second antenna is oriented non-parallel to an axis of the first antenna. Then, the target electromagnetic signal received from the first antenna and the target electromagnetic signal received from the second antenna are separately analyzed to characterize the computer system parameter.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
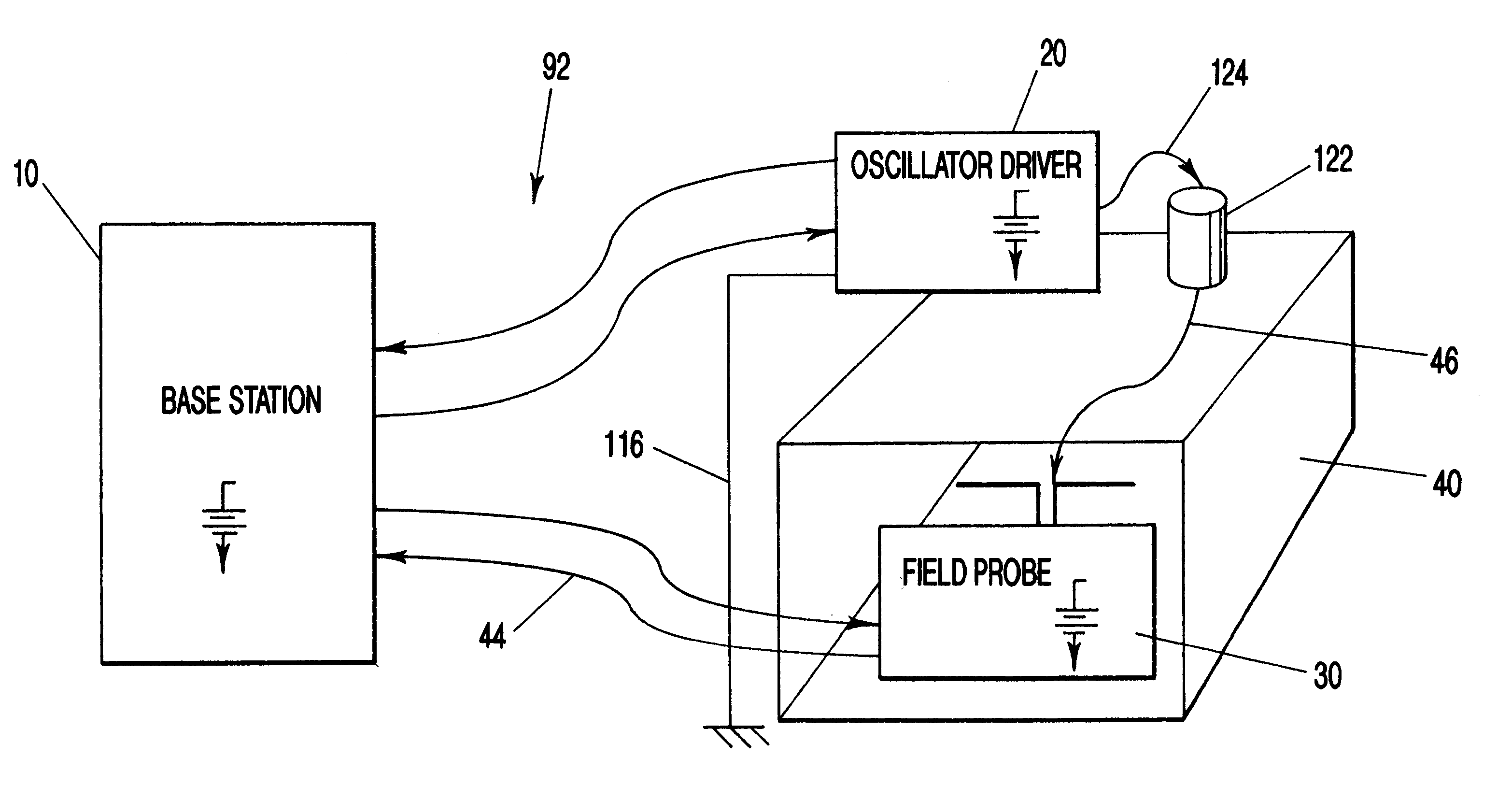
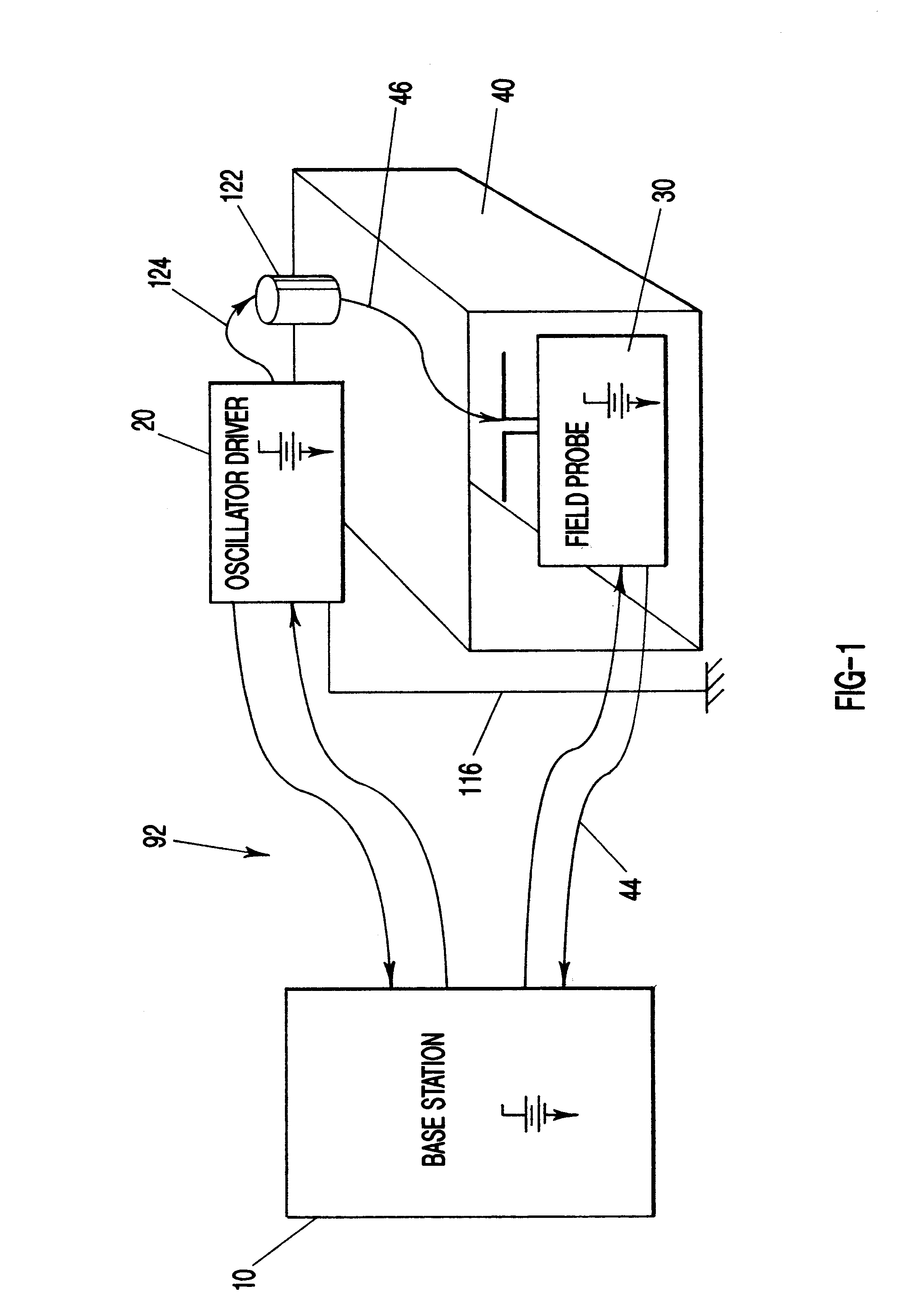
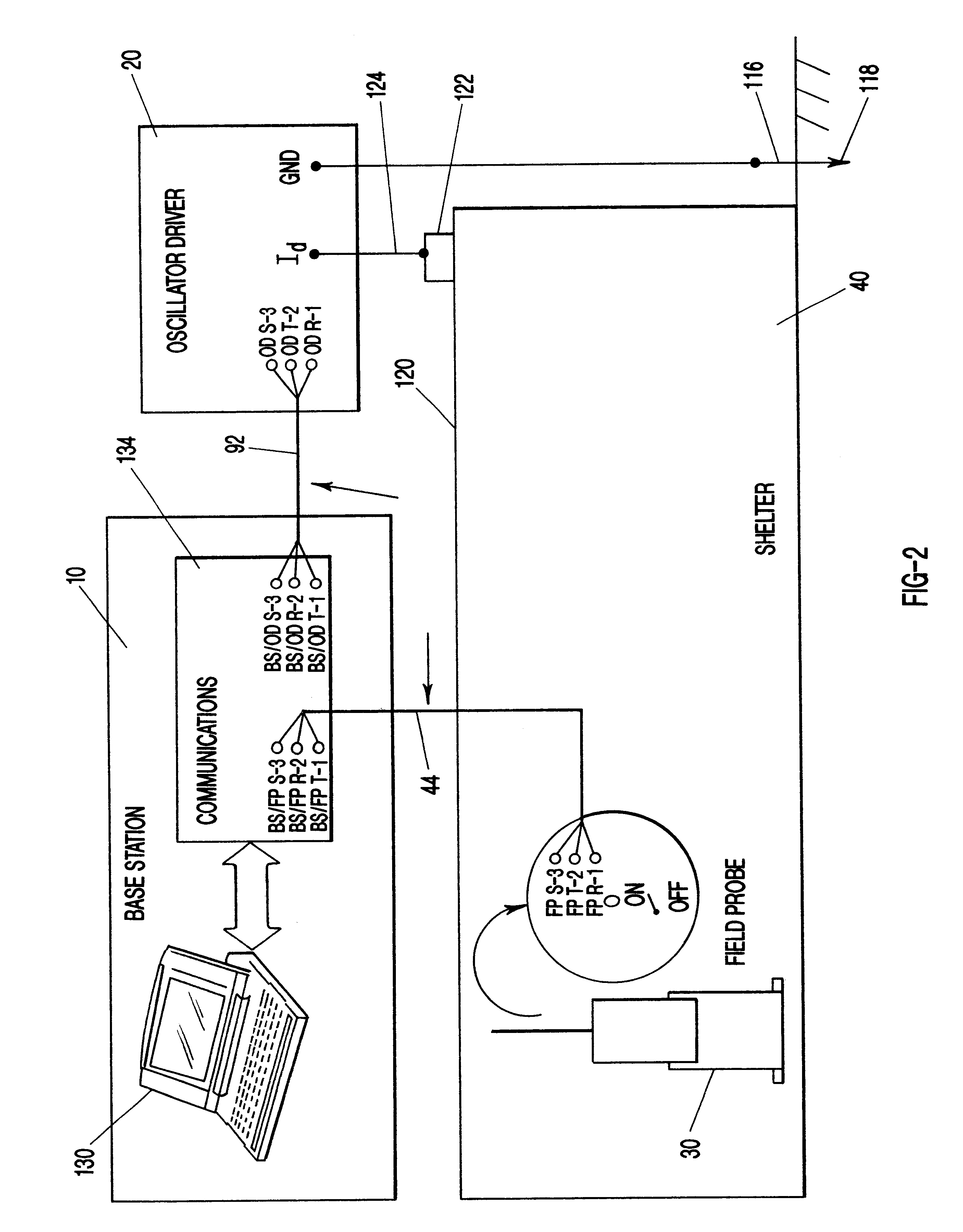
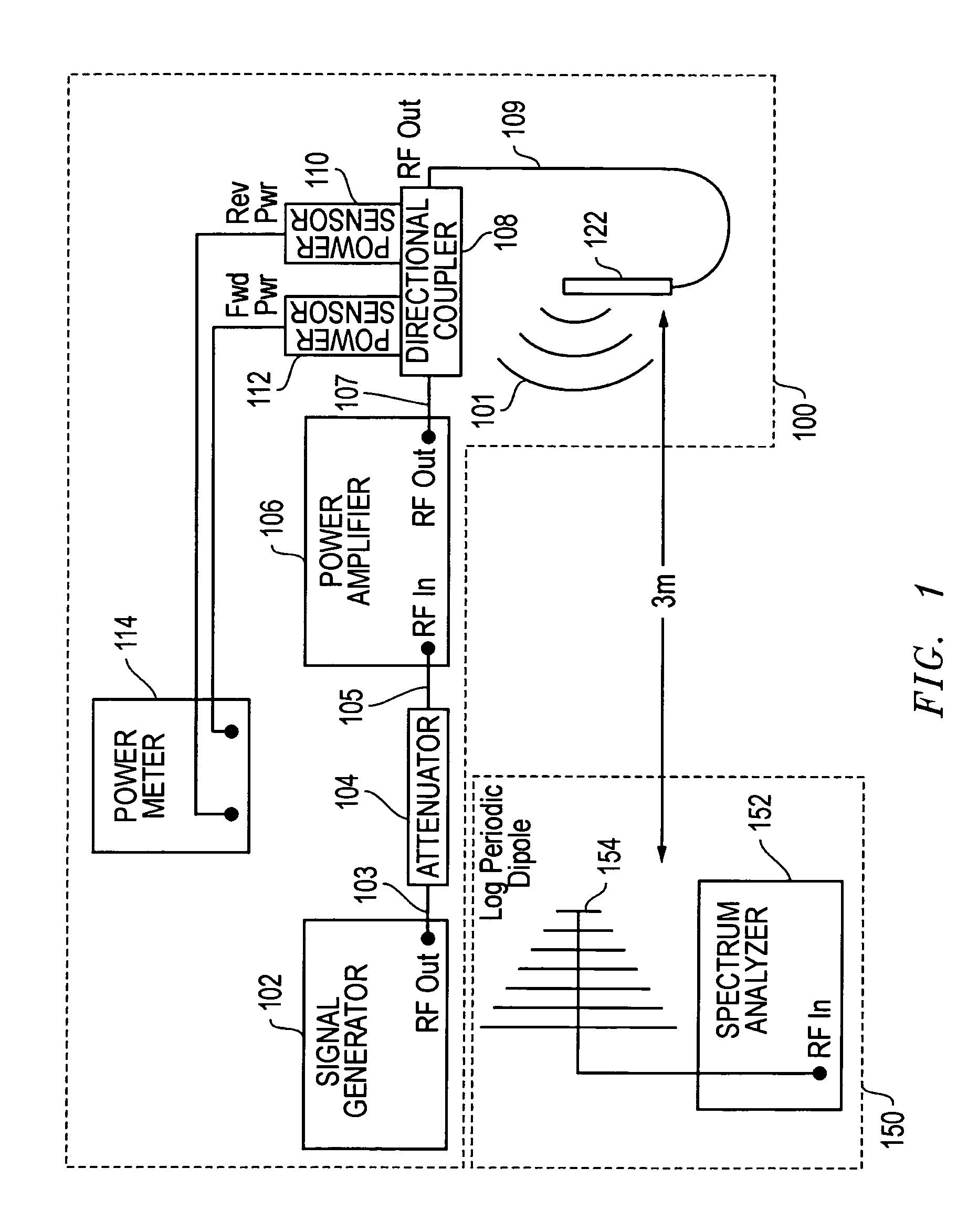
Transfer impedance measurement instrument system
InactiveUS6230105B1Electric cable installationsMeasuring interference from external sourcesMeasuring instrumentEngineering
An apparatus and method for measuring the transfer impedance of a structure. Oscillator driver 20 produces a small electrical drive signal into structure 40. Field probe 30 detects the electric field produced by the drive signal and is comprised of a skinny half-dipole and fat half-dipole antenna. Fat half-dipole 34 encloses synchronous detection circuitry. Power supplies are isolated for all components. Base station 10 communicates with oscillator driver 20 and field probe 30 via wireless links 92 and 44 to control the drive signal, the synchronous detection, and to determine the transfer impedance.
Owner:BOLT
Radiation diagram measuring system for a transmitting antenna
InactiveUS20090231217A1Simpler and preciseOvercomes drawbackCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagentic field characteristicsEngineeringTransmitter antenna
Owner:THE SWATCH GRP RES & DEVELONMENT LTD
Transmission line pulse measurement system for measuring the response of a device under test
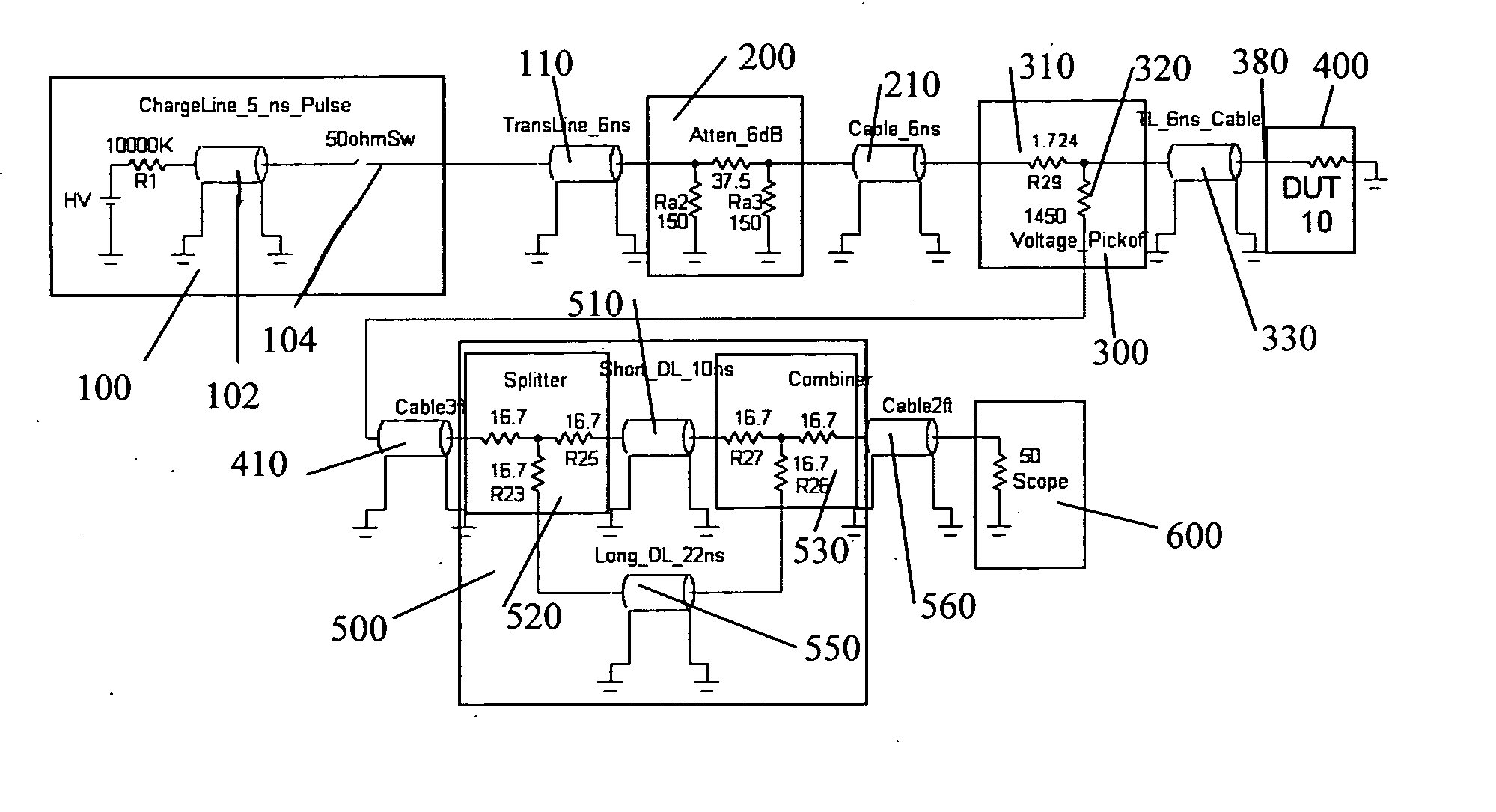
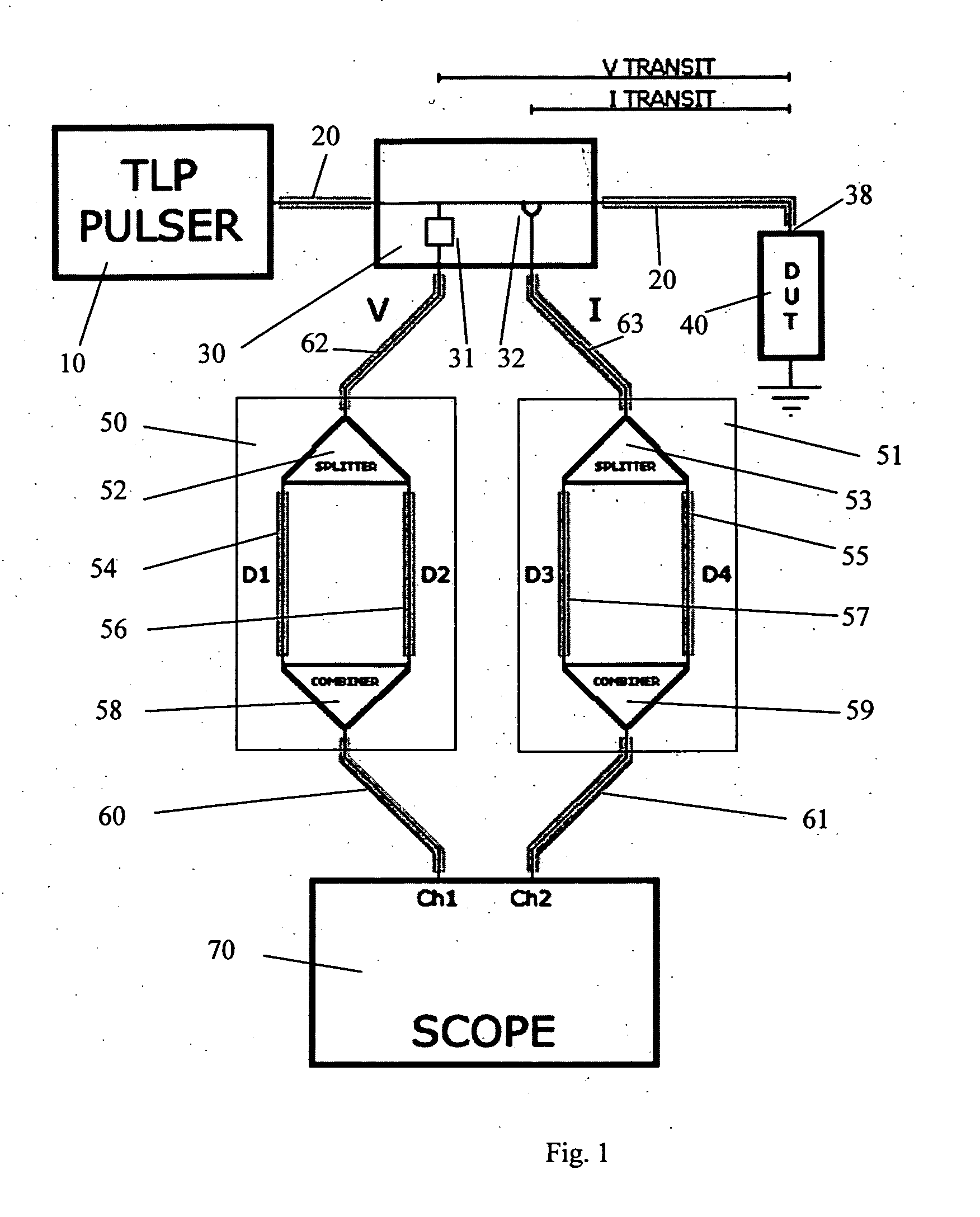
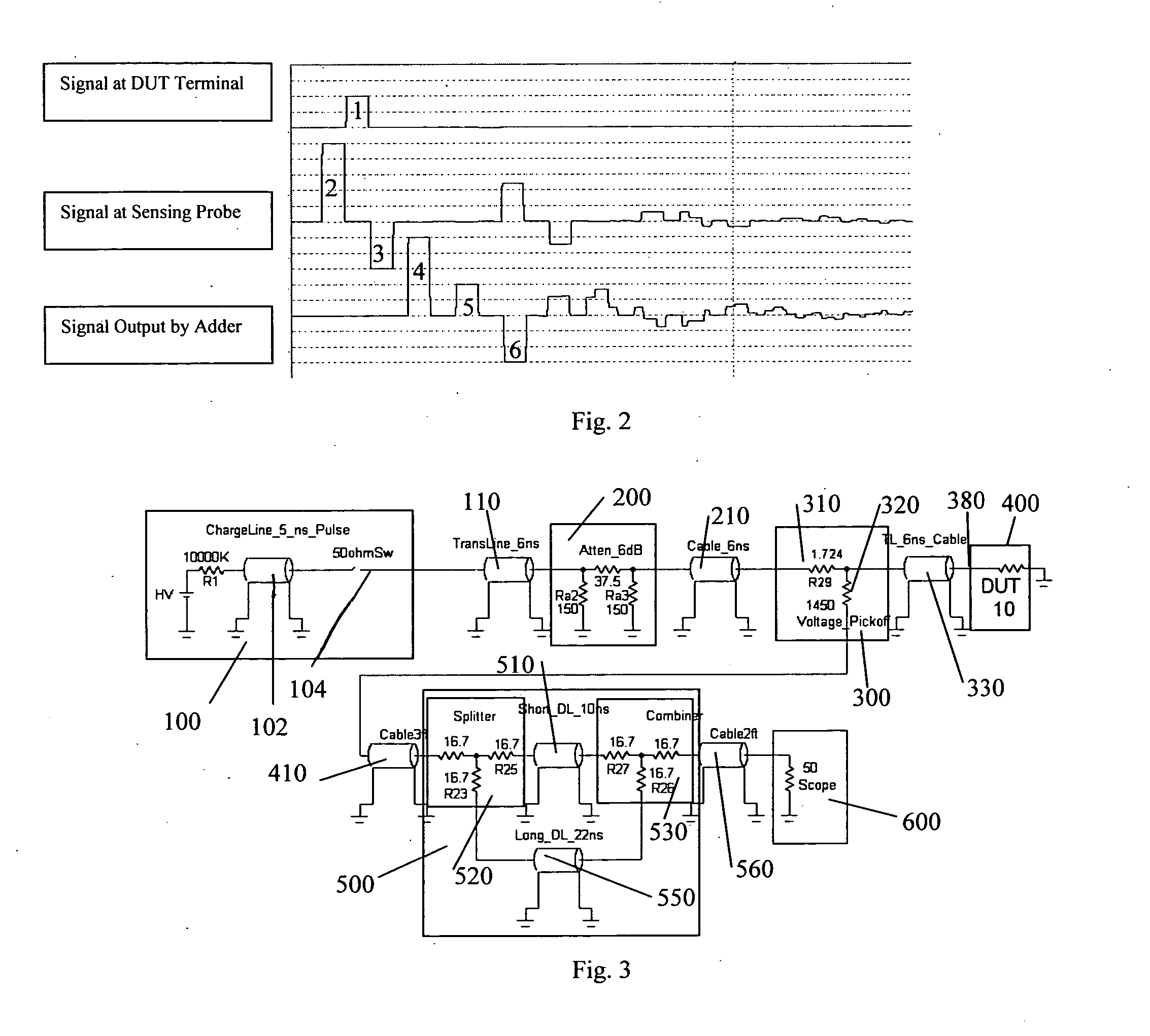
InactiveUS20070159186A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceConstant impedanceTransmission-line pulse
A Transmission Line Pulse (“TLP”) measurement system for testing devices such as integrated circuits (“ICs”), and especially for testing the electrostatic discharge (“ESD”) protection structures connected to terminals on such ICs. The TLP measurement system measures the pulsed voltage and / or current of a device under test (“DUT”) by recording voltage and / or current pulse waveforms traveling in a constant impedance cable to and from the DUT. The pulses going to and returning from the DUT are processed to create signal replicas of the voltage and current pulses that actually occurred at the DUT. Oscilloscope operating settings optimize the recording of these signal replicas by improving the measurement signal-to-noise ratio. This improved TLP system is especially useful when very short width pulses on the order of less than 10 nanoseconds are used to test the DUT's response.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
Radiation measurement system and method with synchronous high speed tracking laser based position measurement
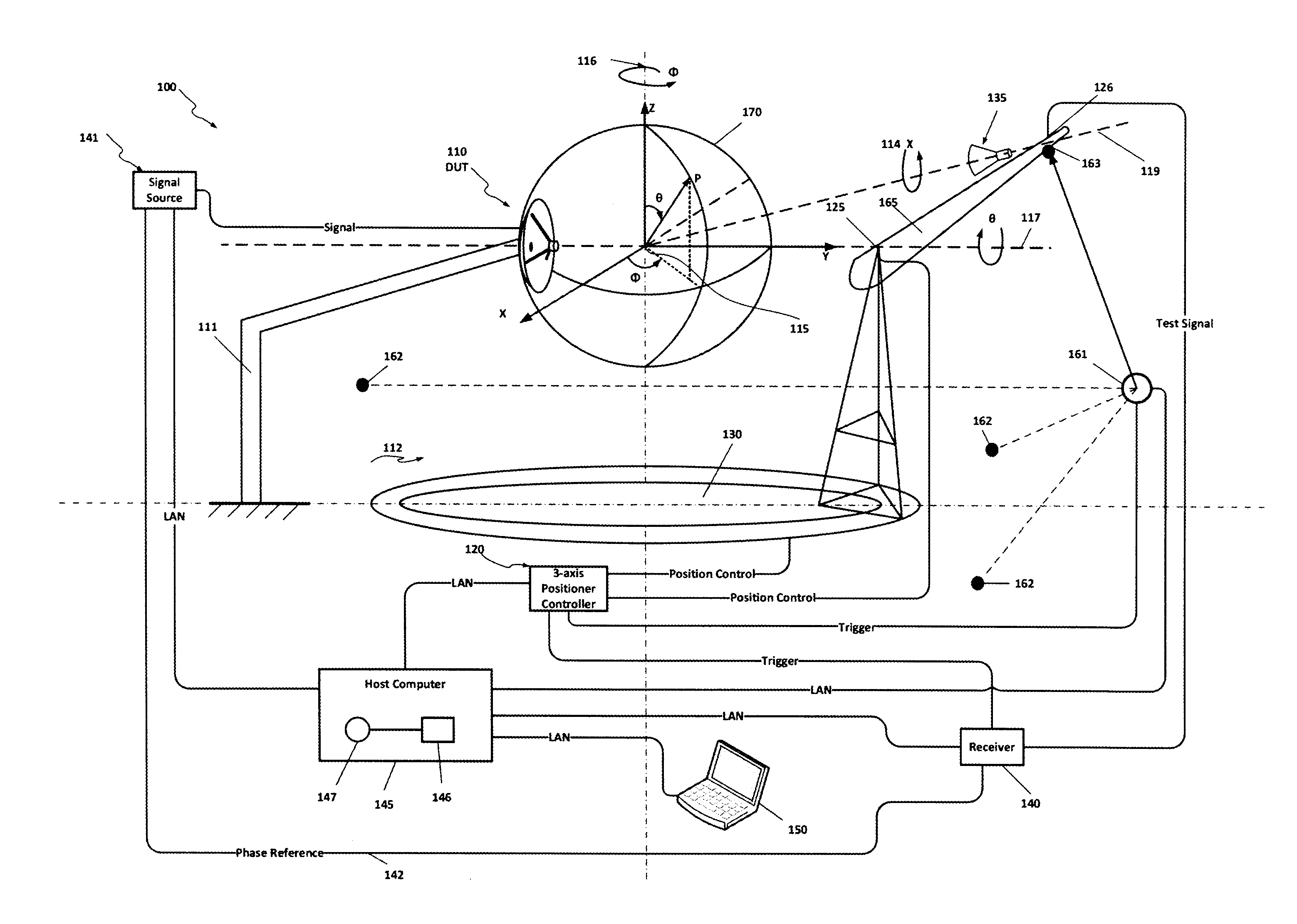
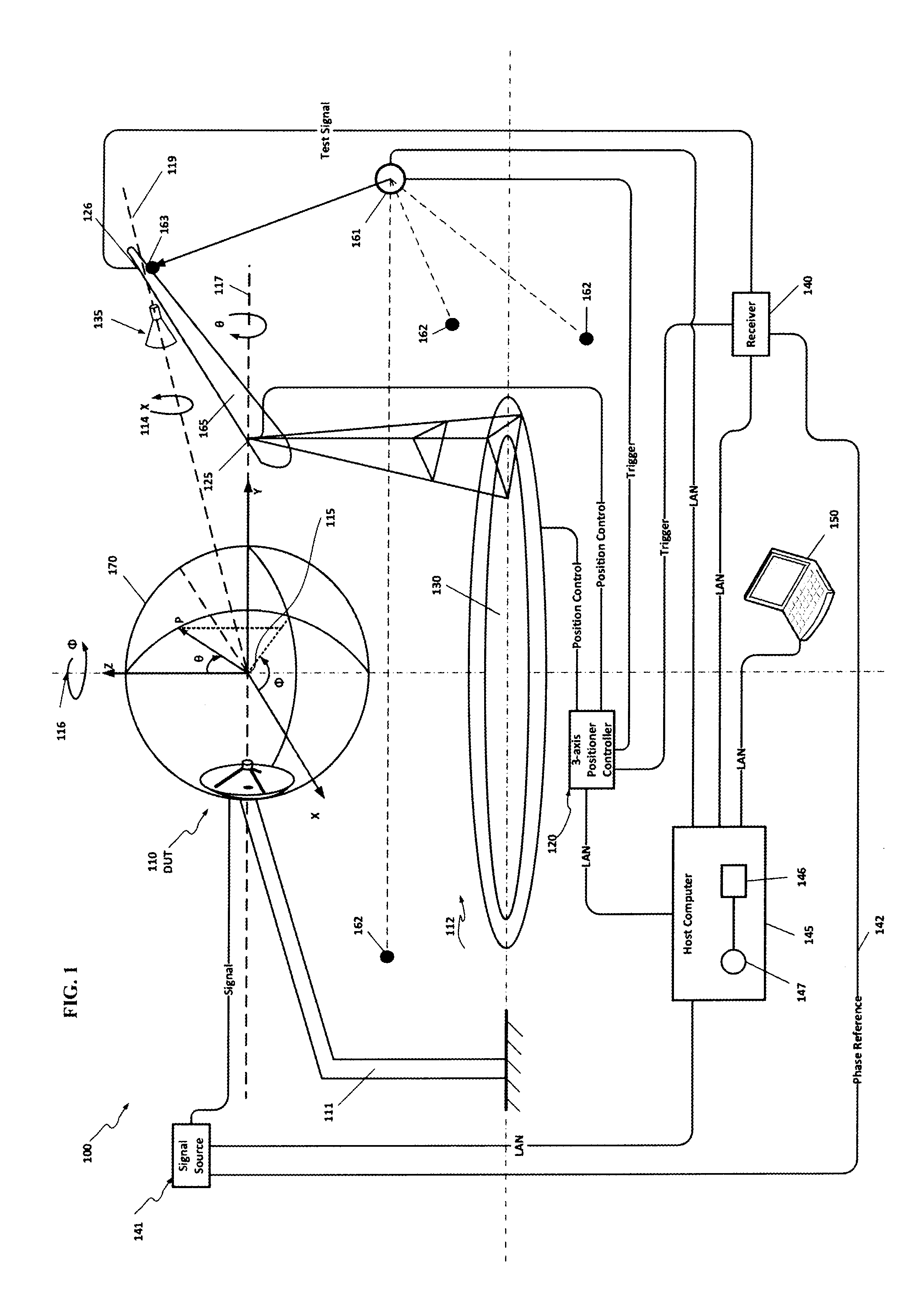
ActiveUS20150116164A1Improve performanceMeasurement leads/probesMeasuring interference from external sourcesRF probeMeasurement point
An Antenna measurement system incorporating high speed tracking laser-based global positioning capture synchronized with radio frequency (RF) measurements. A high speed tracking laser is used for collecting RF probe position data synchronously with corresponding near-field RF measurements. The probe may be moved across an arbitrary surface surrounding or adjacent to a device under test (DUT); however, it is not necessary for the probe position to be perfectly coincident with the surface, or any of the discrete points which make up the surface. Here, the probe position is determined relative to a global positioning coordinate system which is defined by a set of monuments which are in known positions relative to the global positioning coordinate system, and not the DUT. Any difference between the actual position of the probe, in the global position coordinate system, and a given one of the discrete measuring points, in the global position coordinate system, on the surface surrounding or adjacent to the DUT can be accounted for during post processing, thus eliminating the need for advanced or intermittent calibration to achieve precise near-field measurements.
Owner:M I TECH
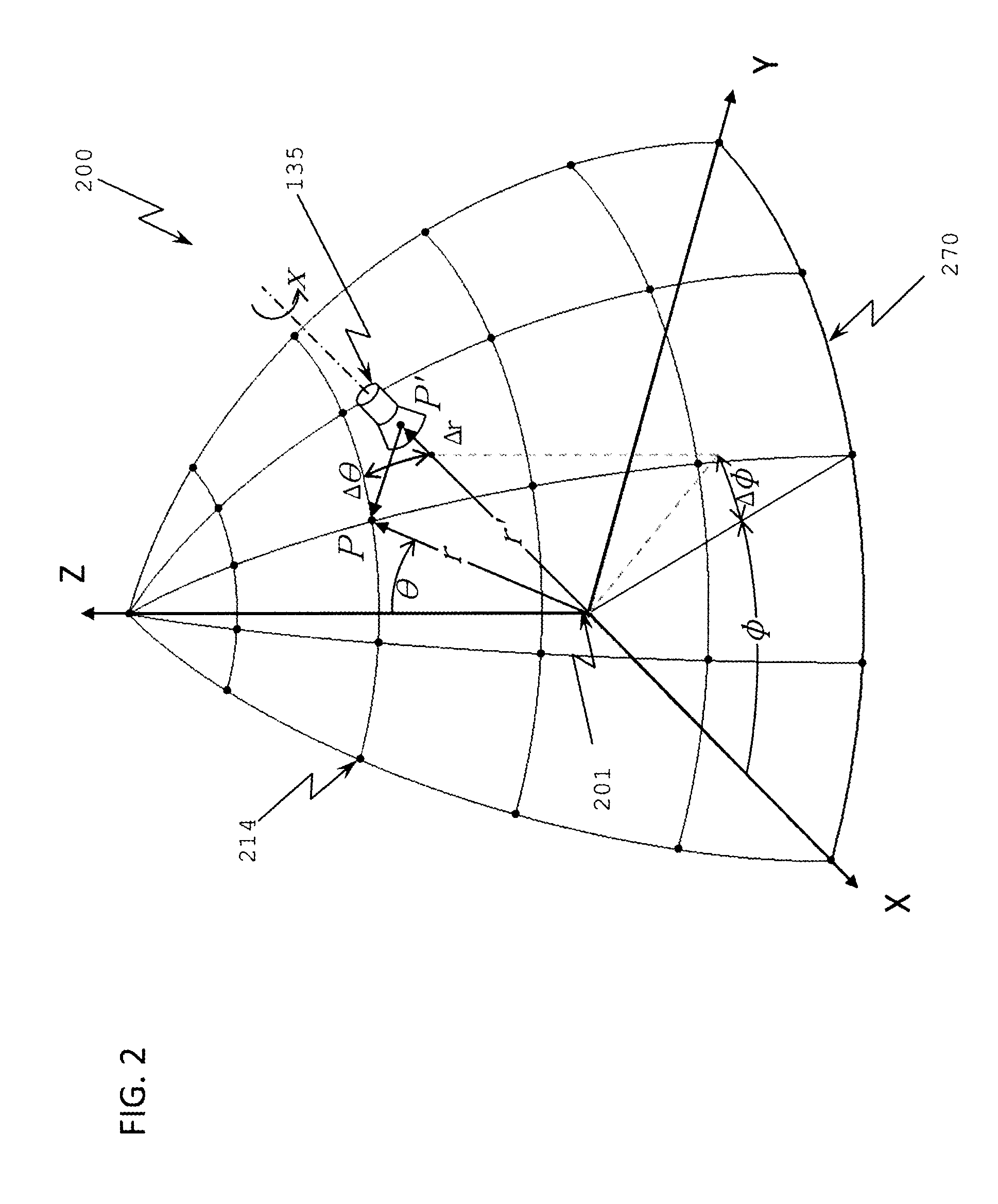
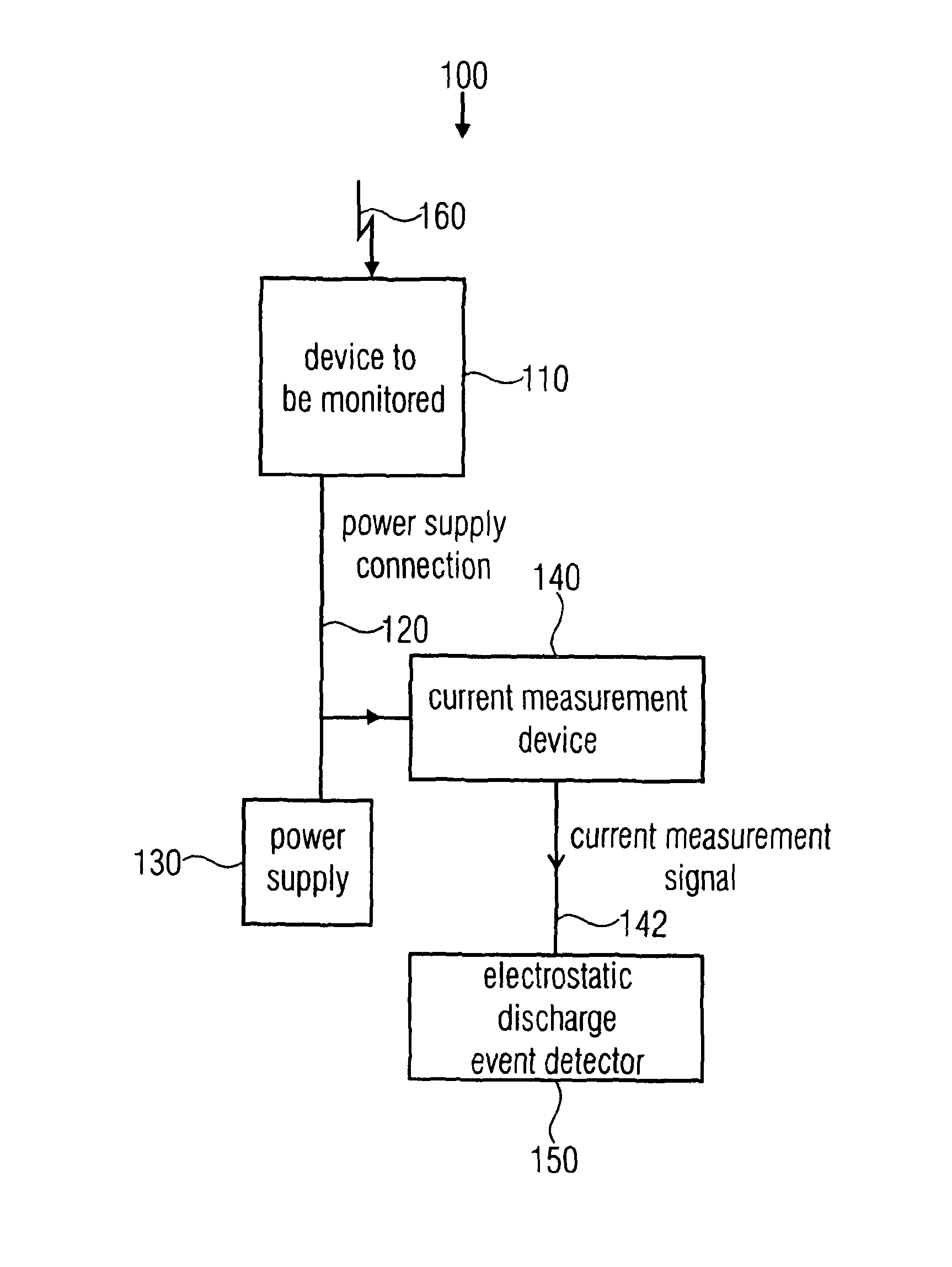
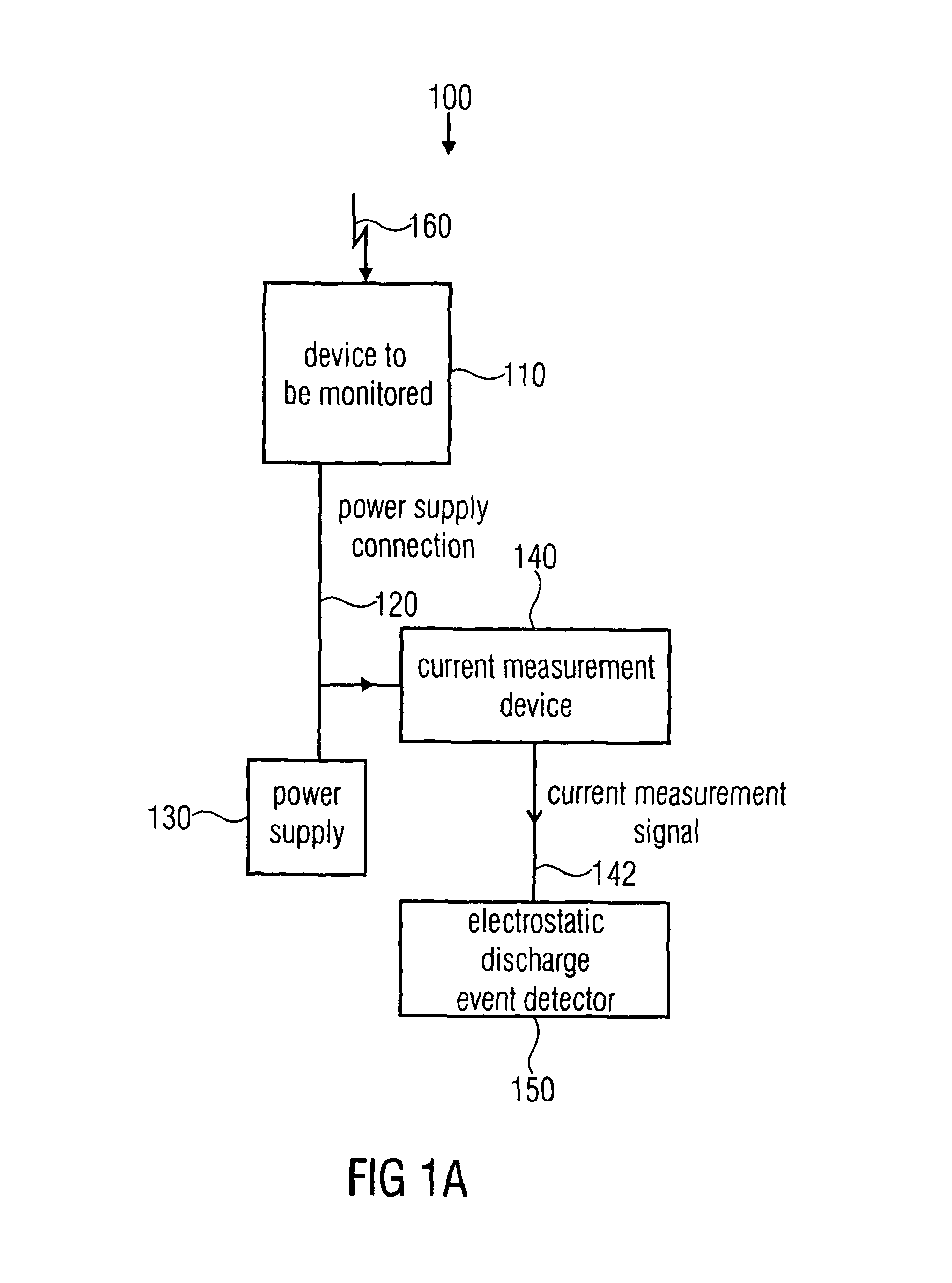
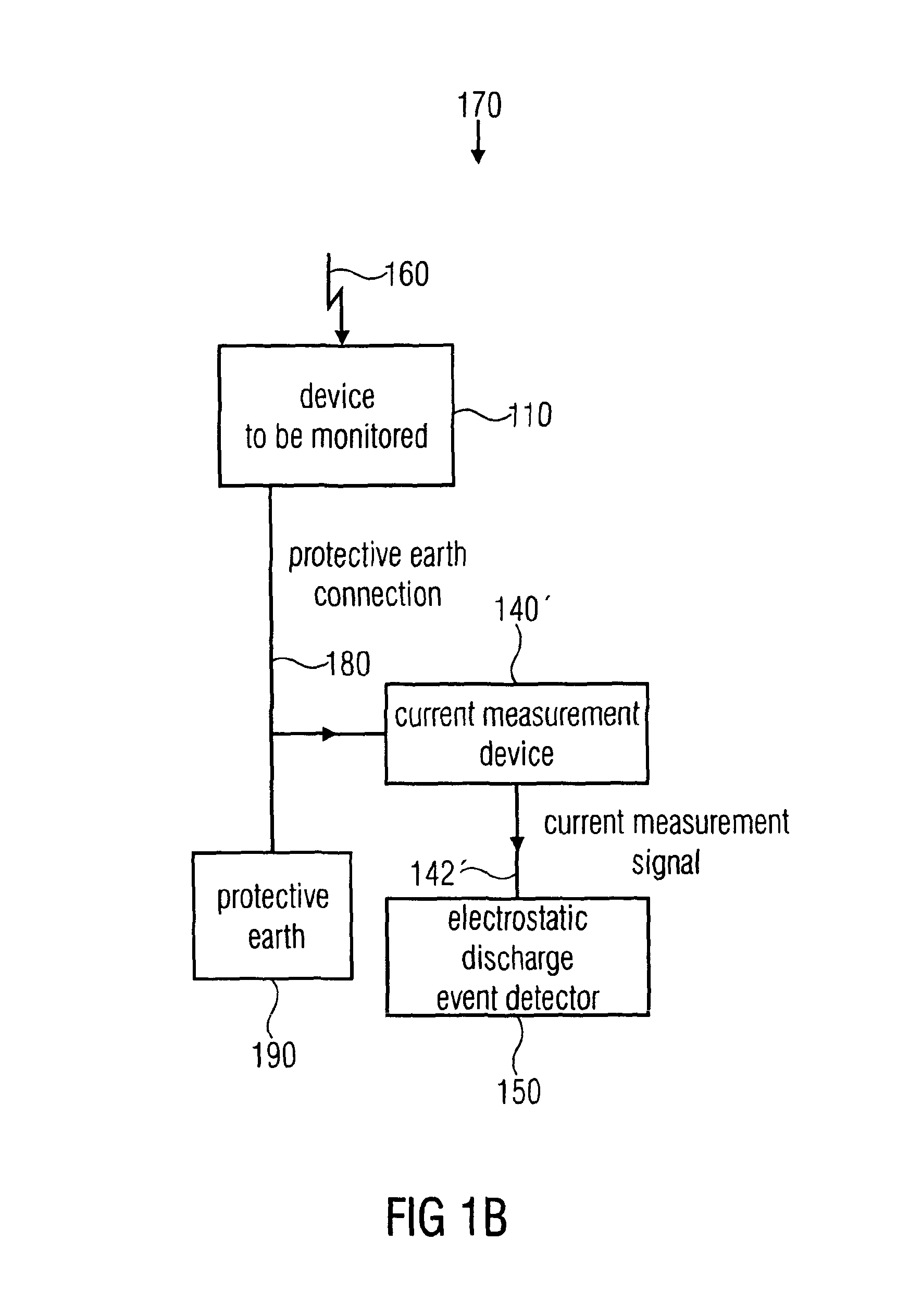
System, method and computer program for detecting an electrostatic discharge event
ActiveUS8594957B2Efficient detectionReliable indicationCurrent/voltage measurementElectromagentic field characteristicsMeasurement deviceElectrical current
A system for detecting an electrostatic discharge event with respect to a device to be monitored includes a current measurement device configured to measure a current flowing via a power supply connection connecting the device to be monitored with the power supply to obtain a current measurement signal representing the current or a current component. Alternatively, a current flowing through a protective earth connection connecting the device to be monitored with the protective earth is measured to obtain the measurement signal. The system includes an electrostatic discharge event detector configured to detect an electrostatic discharge event in response to a pulse of the current measurement signal. The system may optionally include data processing of current measurement signals or values.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
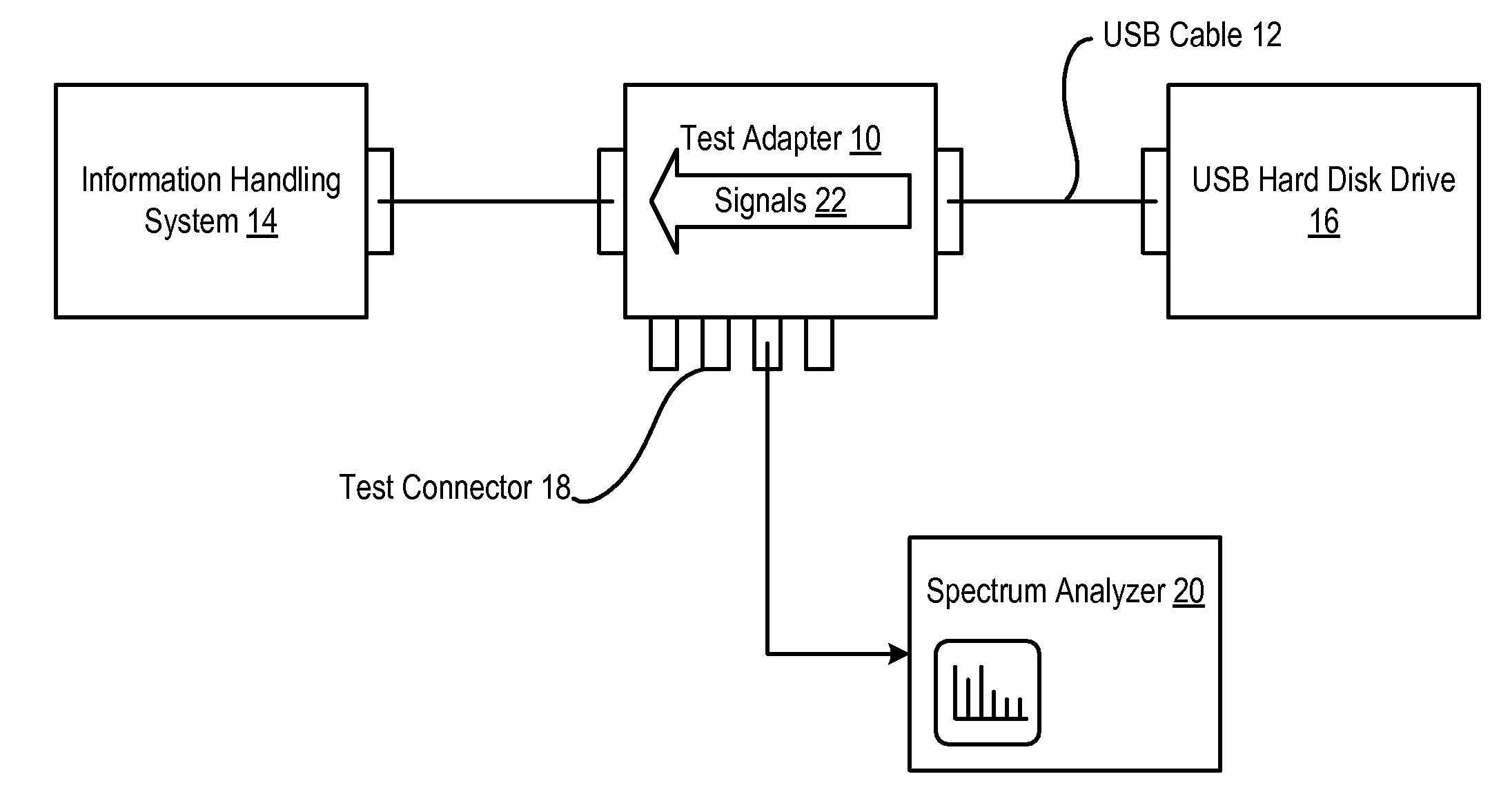
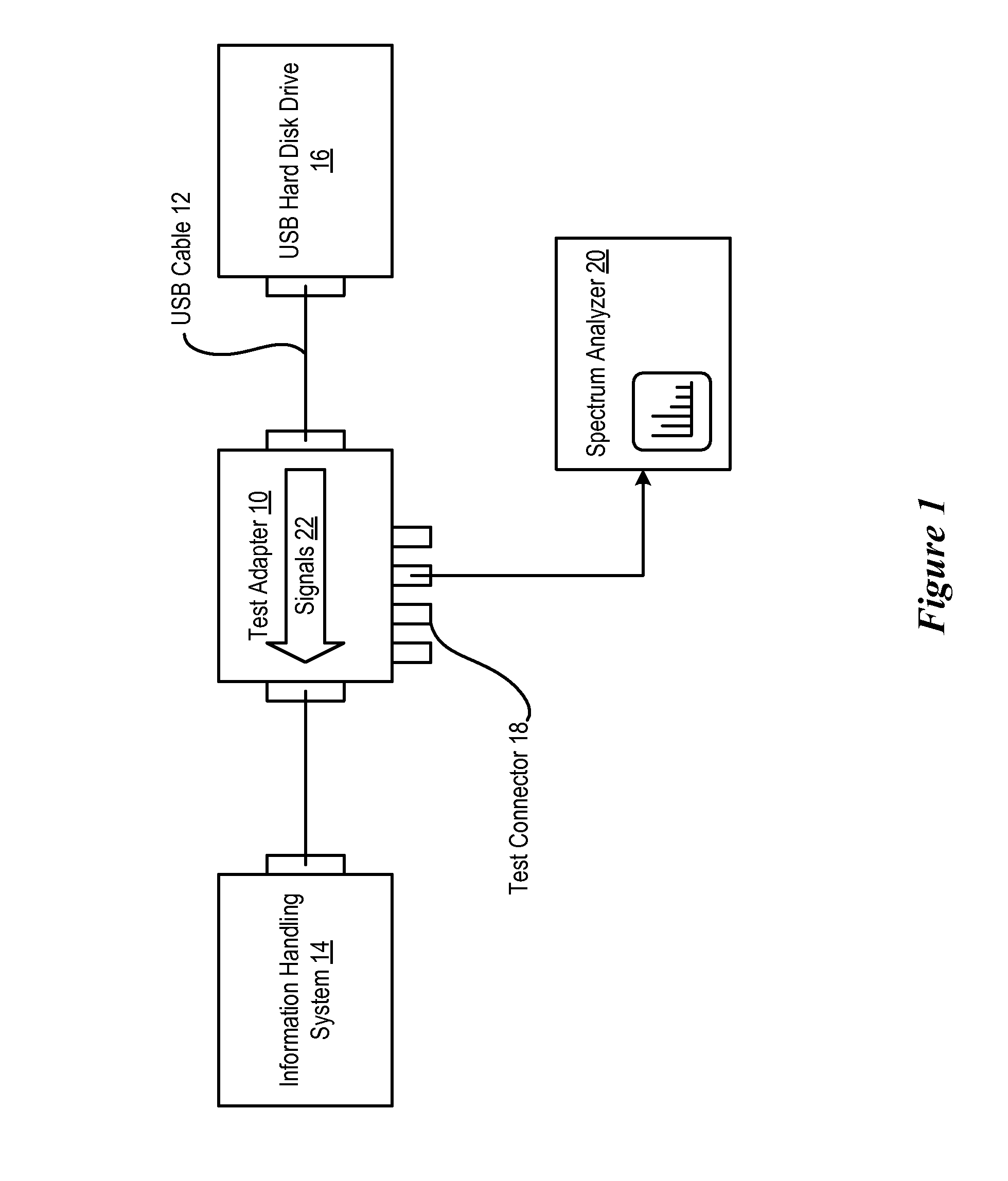
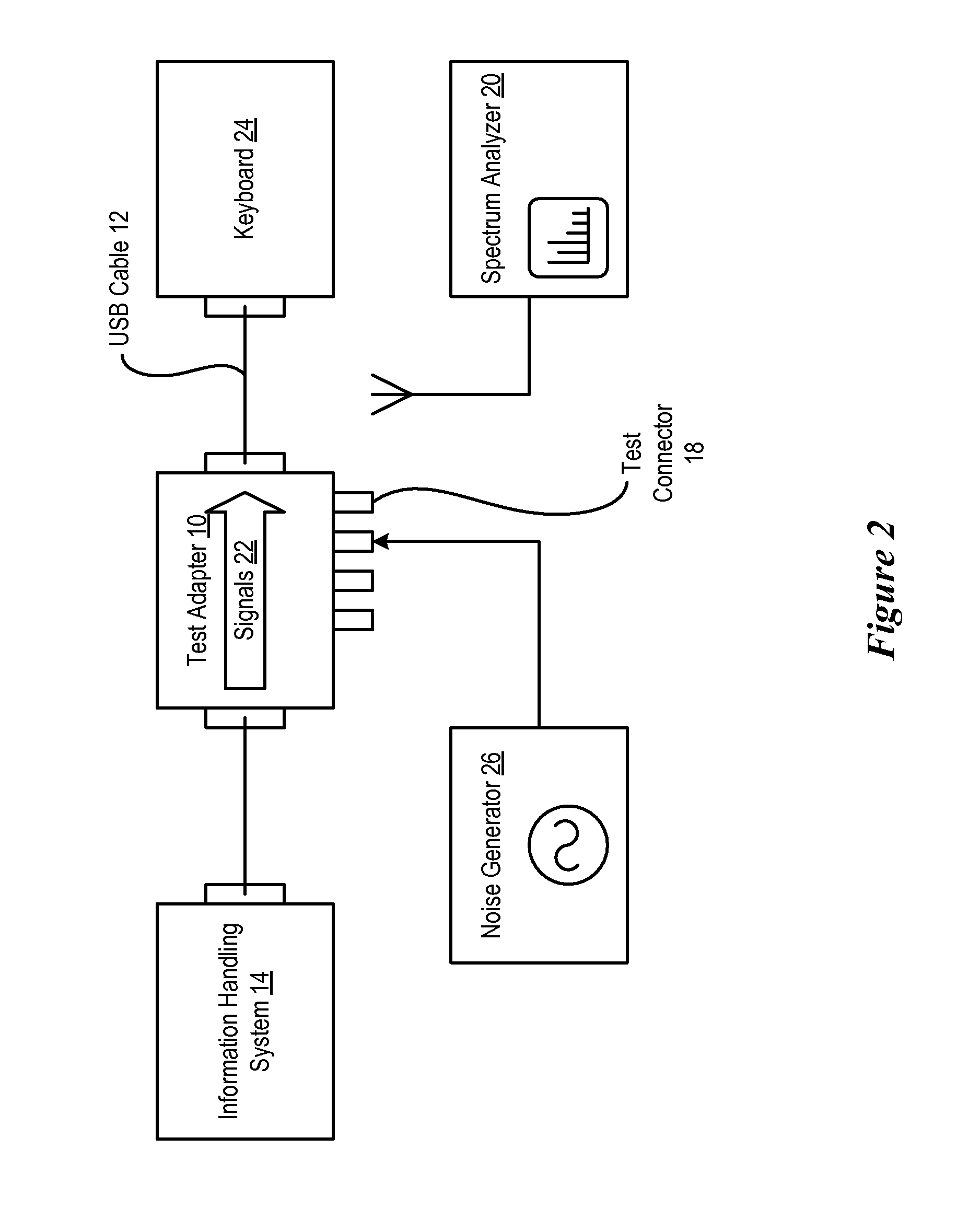
System and Method for Information Handling System Peripheral EMC Test
InactiveUS20080084218A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsResistance/reactance/impedenceGain controlElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
Electromagnetic compatibility of an information handling system and peripheral for achieving defined electromagnetic interference constraints is tested through a test adapter that interfaces with an external cable connecting the information handling system and peripheral. Signals from the external cable are passed through an isolation resistor and parallel capacitance to compensate for input capacitance of a signal tester. A common mode choke isolates a common mode component of the signal at the external cable. A noise generator applies a signal through the test adapter to the external cable to allow measurement of signals emitted from the peripheral due to injected noise.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Radome testing system
PendingCN106405297ARealize azimuth adjustmentAvoid disturbing influenceWave based measurement systemsMeasuring interference from external sourcesRadarEngineering
The invention discloses a radome testing system, which comprises a scanning position turntable arranged on a horizontal working surface. A radar scanning mechanism is connected onto the scanning position turntable via a supporting arm; the supporting arm comprises a turntable supporting arm and a radar supporting arm; the turntable supporting arm is arranged at the upper part of the scanning position turntable; the upper surface of the turntable supporting arm is provided with a pitching arc rail; and the pitching arc rail is in sliding match with a pitching sliding table at the bottom part of the radar supporting arm to enable the radar supporting arm to move in relative to the arc curved surface of the turntable supporting arm. According to the radome testing system provided by the invention, interference effects on radome testing effects by the traditional radome supporting arm and the pitching shaft can be avoided.
Owner:DALIAN DONGSHIN MICROWAVE TECH
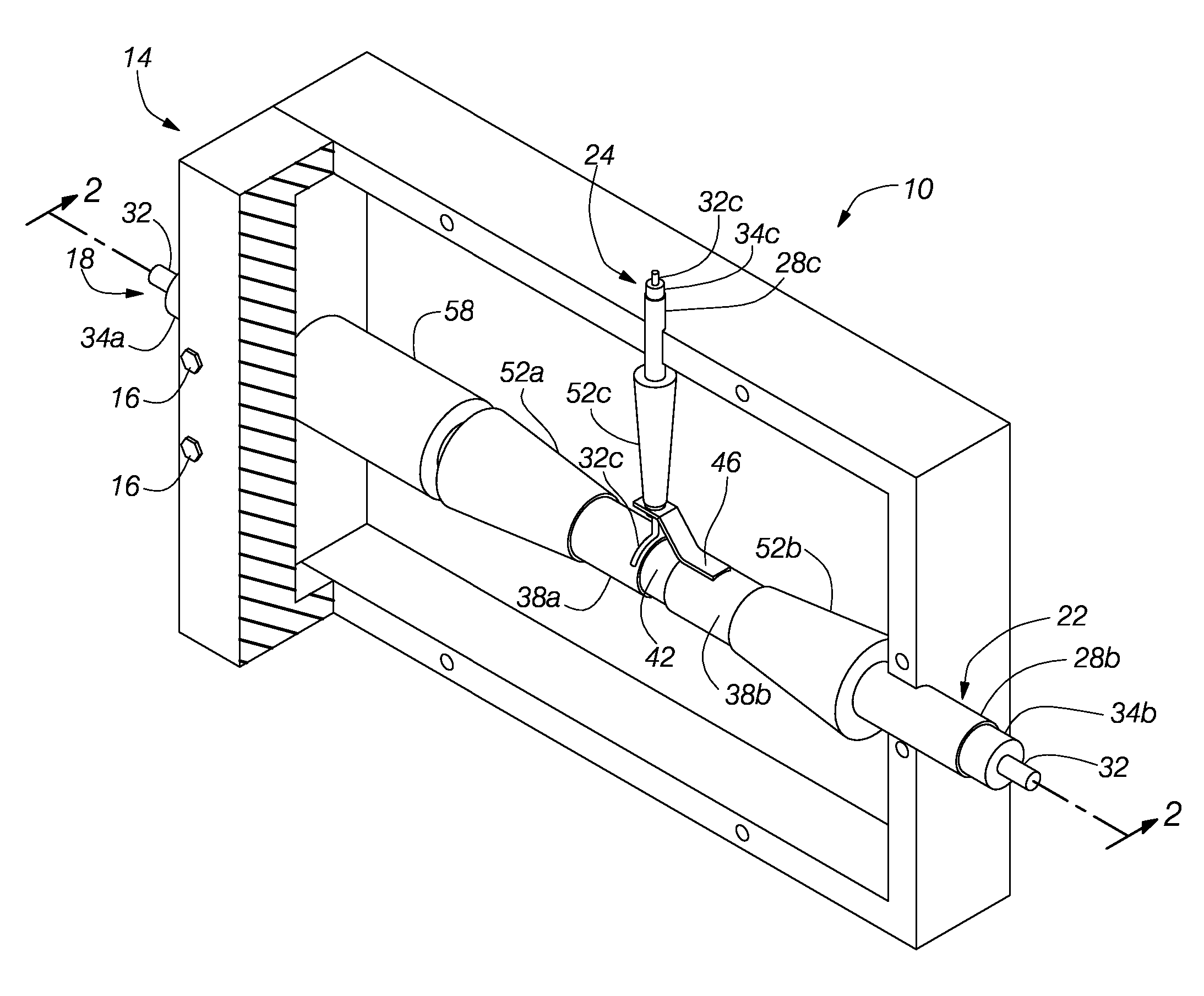
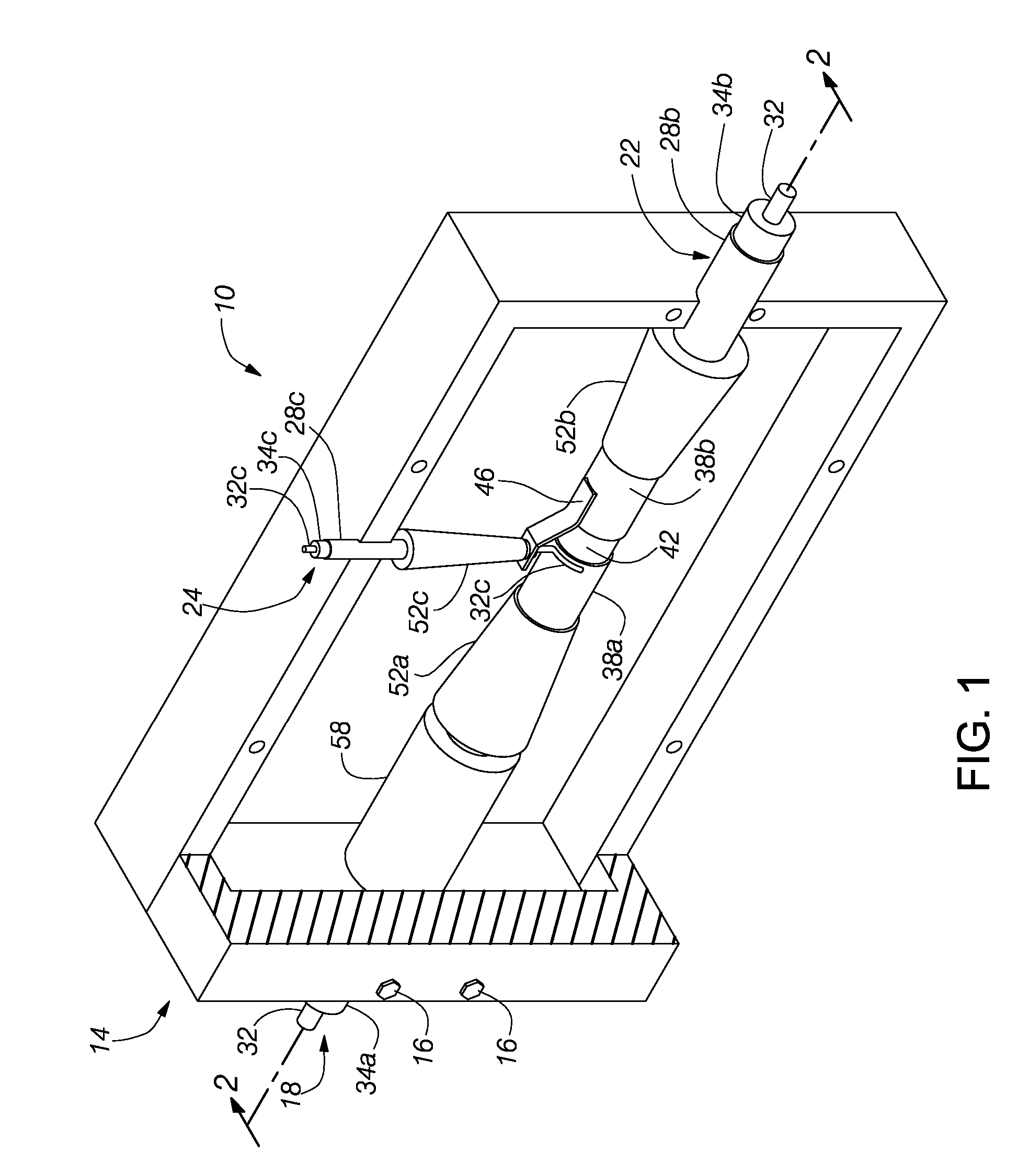
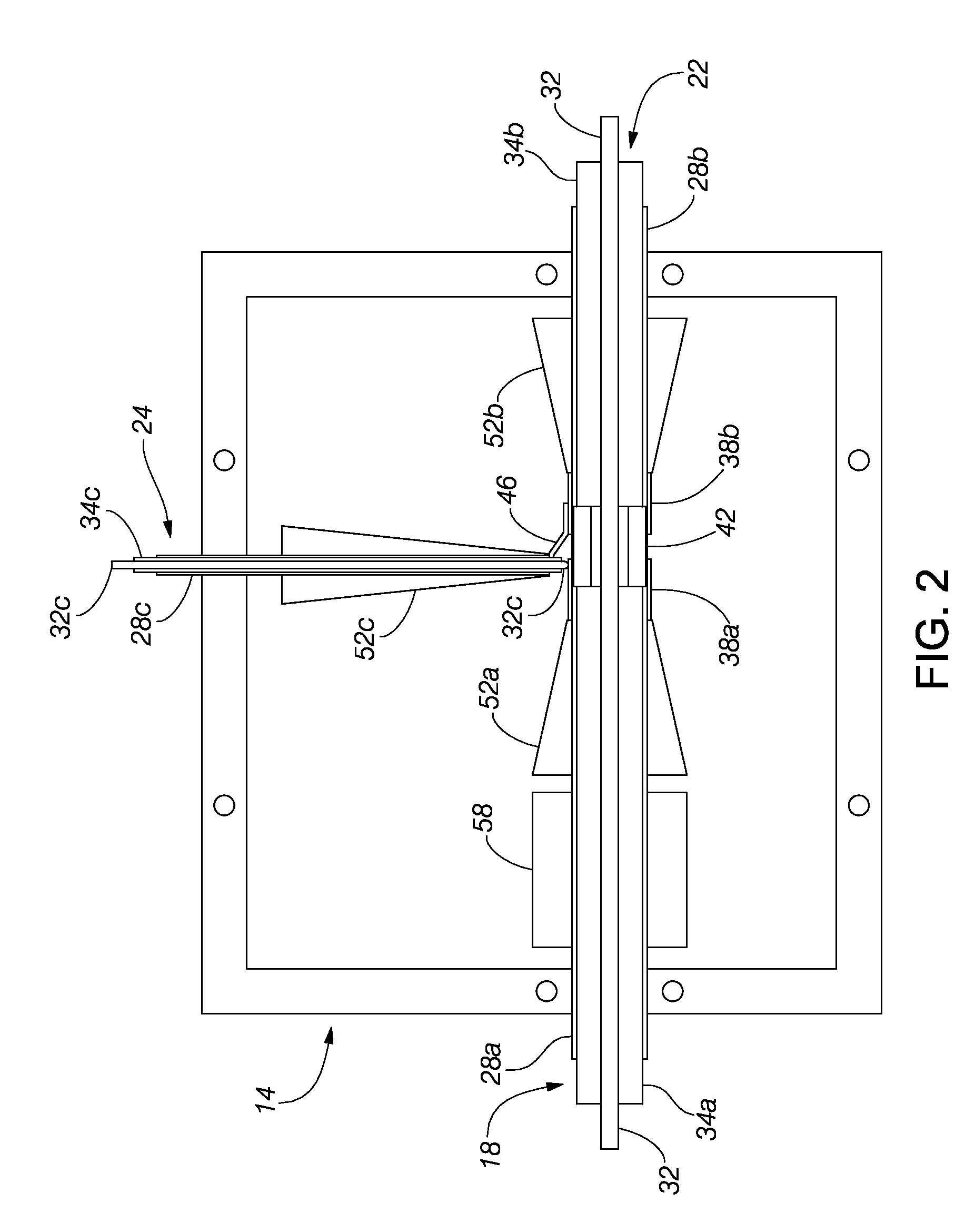
Method and Apparatus for Detection and Identification of Counterfeit and Substandard Electronics
ActiveUS20150137830A1Eliminate needResistance/reactance/impedenceSolid-state devicesElectronicsElectronic equipment
An apparatus for detecting a condition or authenticity of one or more electronic devices includes an enclosure having an antenna integrated therewithin, a fixture mounted within a hollow interior of the enclosure, the fixture being configured to receive the one or more electronic devices and connect one or more signals to each of the one or more electronic devices and a sensor and controller assembly connected to the antenna and configured to process a signature of an emission of a radiofrequency (RF) energy from of one or more electronic devices having the one or more signals connected thereto.
Owner:NOKOMIS
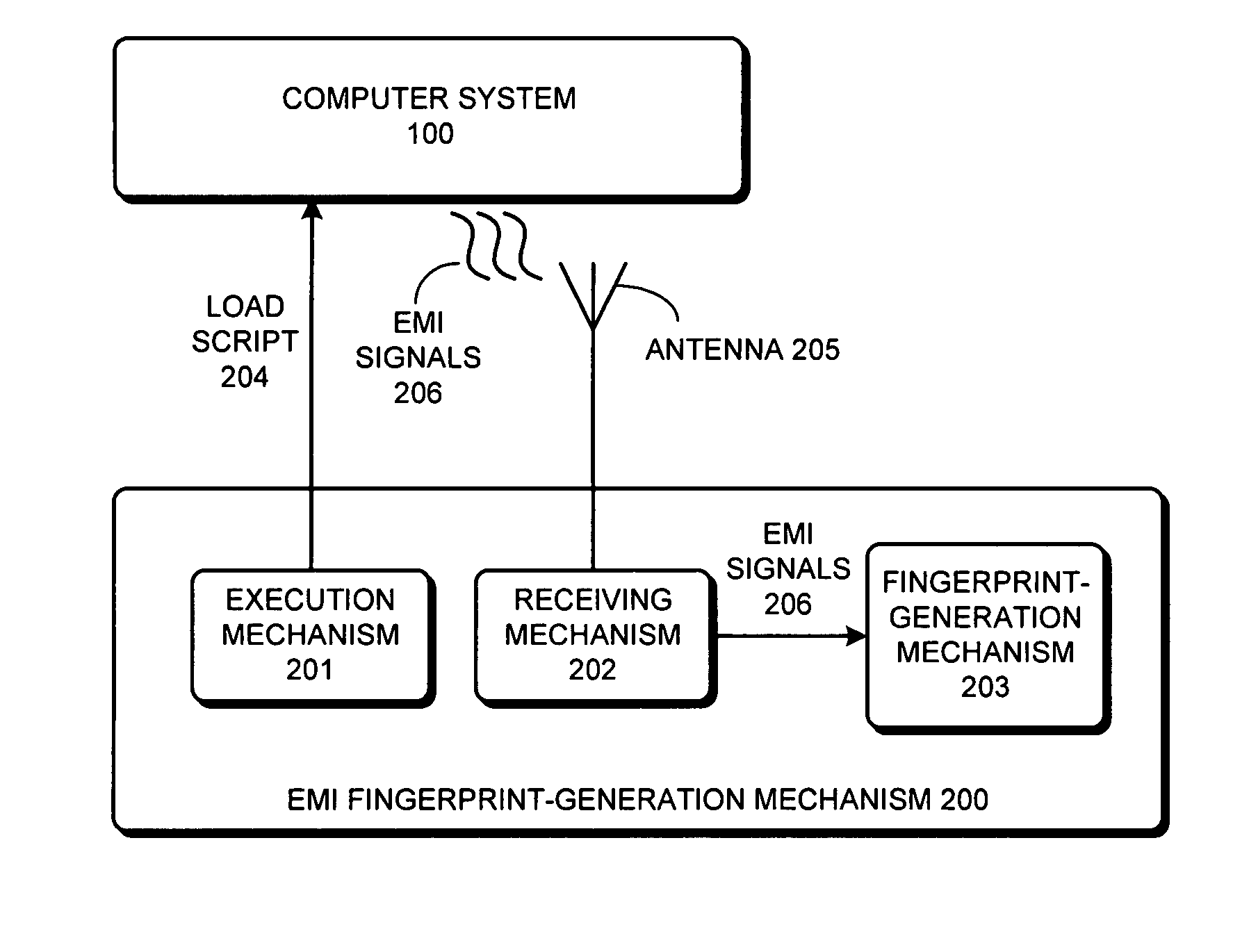
Method and apparatus for generating an EMI fingerprint for a computer system
ActiveUS7613580B2Spectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceParallel computingElectromagnetic interference
A system that generates an electromagnetic interference (EMI) fingerprint for a computer system is presented. During operation, the system executes a load script on the computer system, wherein the load script includes a specified sequence of operations. Next, the system receives EMI signals generated by the computer system while executing the load script. The system then generates the EMI fingerprint from the received EMI signals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
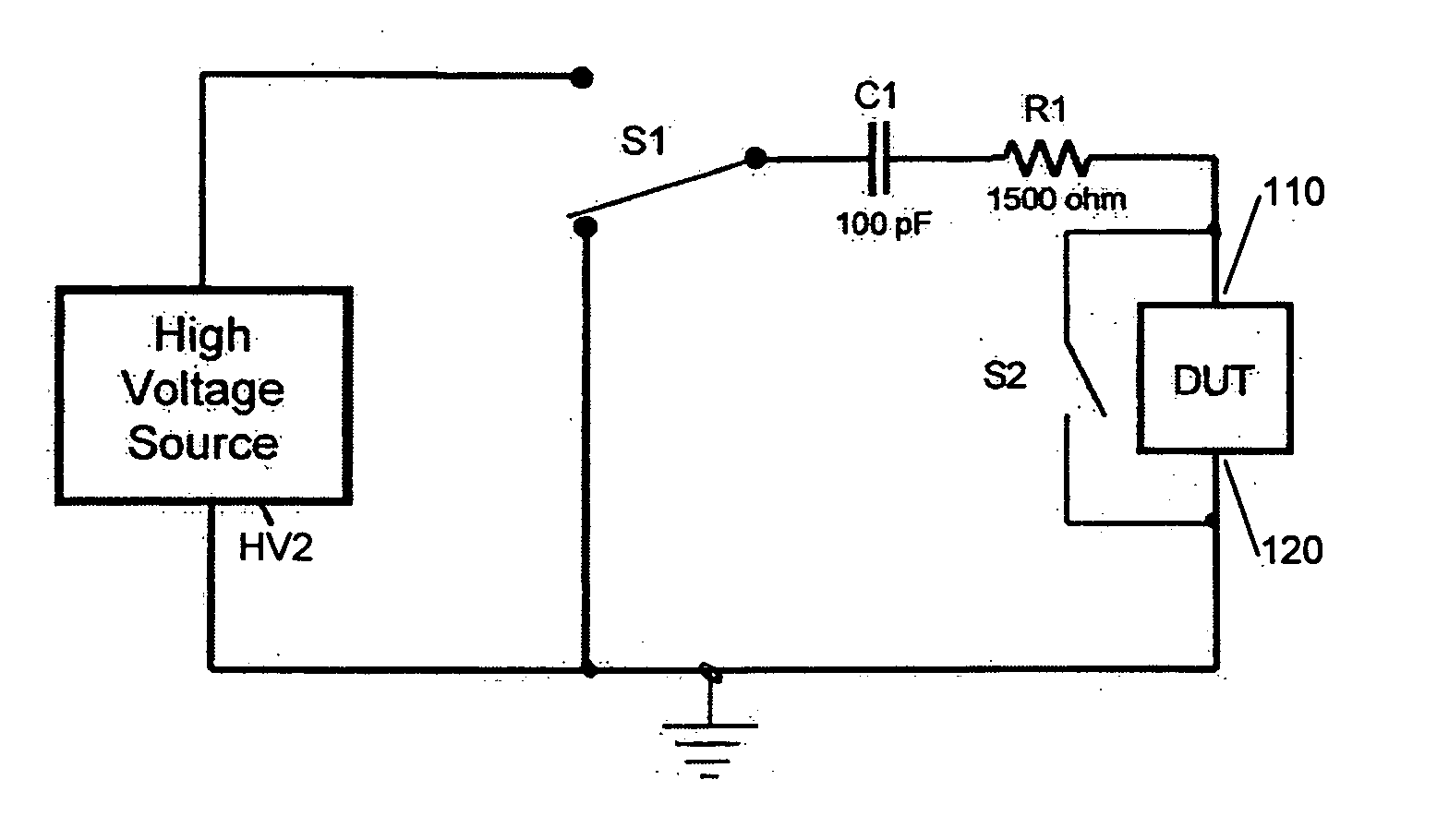
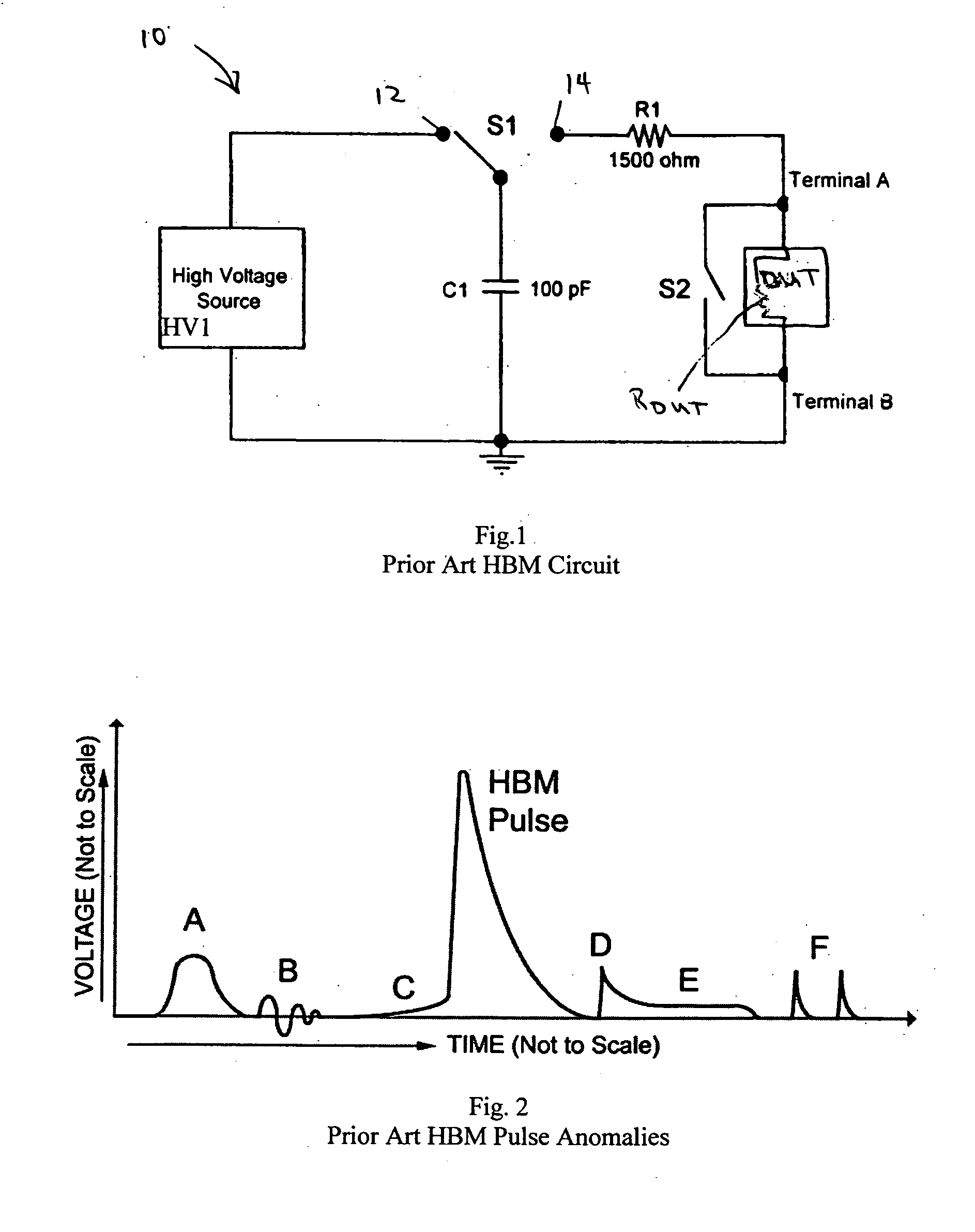
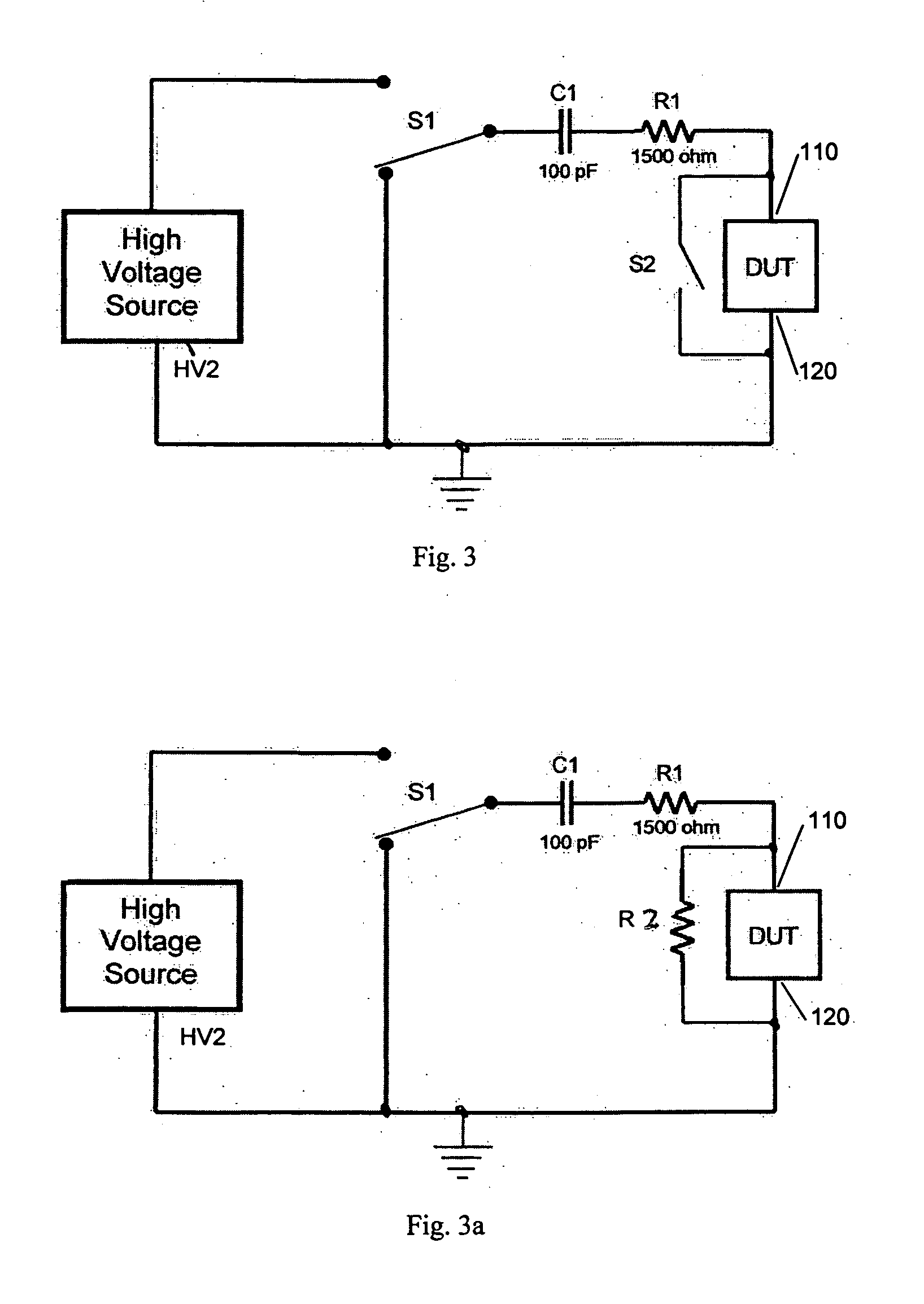
Circuit for minimizing or eliminating pulse anomalies in human body model electrostatic discharge tests
InactiveUS20070159205A1Without unwanted pulse distortionEliminates creationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMeasuring interference from external sourcesEngineeringElectrostatic discharge
A new circuit for producing simulated electrostatic discharges (ESD) based on the Human Body Model (HBM) is disclosed for testing integrated circuits. HBM ESD test systems provide stress pulses defined by industry standards. The pulses produced by prior art have small imperfections or anomalies. These anomalies can cause incorrect testing to certain devices. The improved ESD HBM test system herein disclosed provides pulses meeting the requirements of industry standards while reducing several anomalies to negligible levels.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
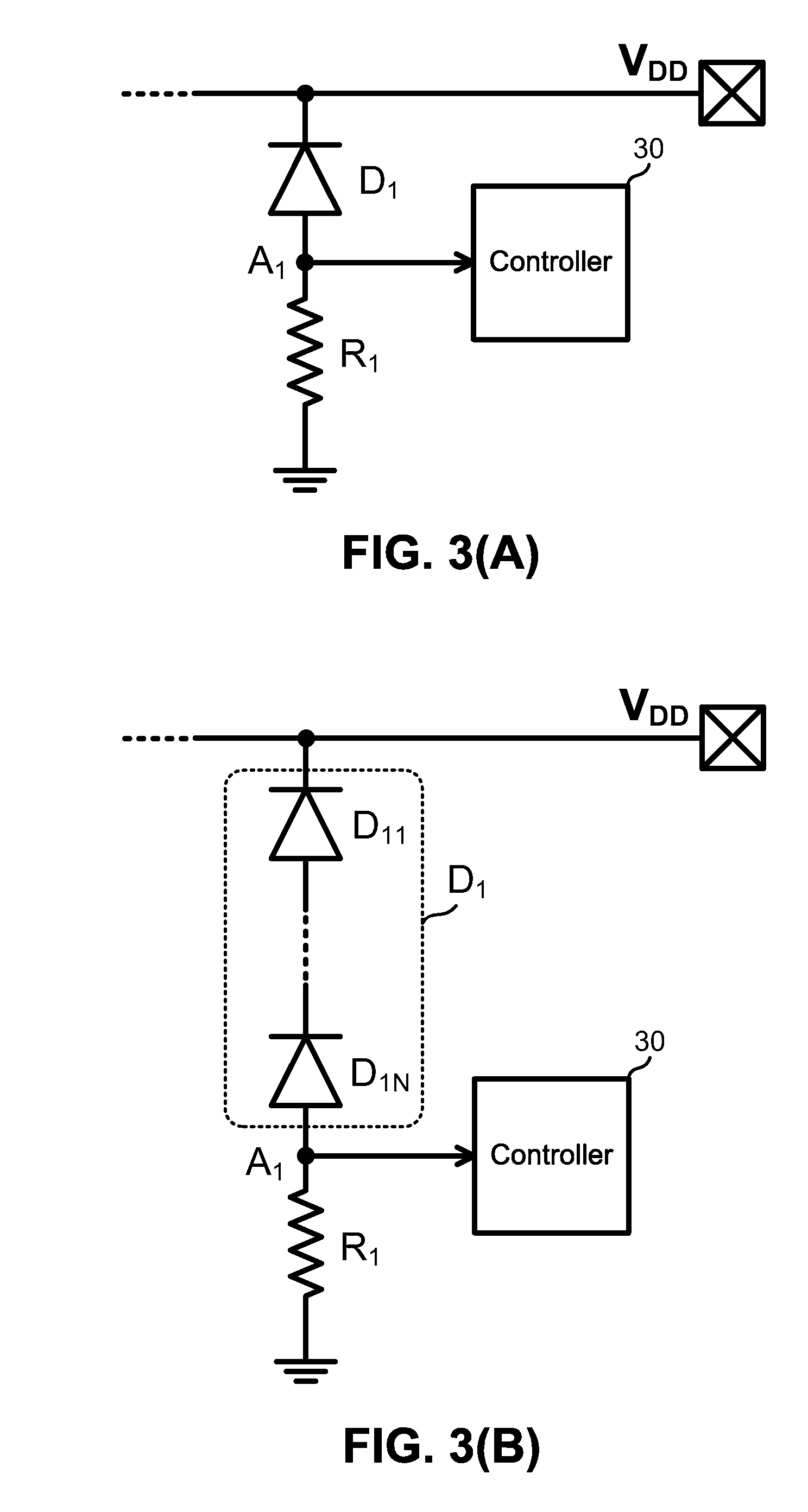
System-level ESD detection circuit
ActiveUS20090287435A1Easy to judgeCurrent/voltage measurementMeasuring interference from external sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An ESD detection circuit for detecting a level of an ESD voltage on a power rail is provided. The ESD detection circuit includes a resistive component, a diode unit, and a controller. The resistive component is coupled between a detection node and a ground node corresponding to the power rail. The diode unit is coupled between the power rail and the detection node in a forward direction toward the power rail. The controller, coupled to the detection node, is used for determining the level of the ESD voltage based on the voltage of the detection node and the breakdown voltage of the diode unit.
Owner:AMAZING MICROELECTRONICS
Electronics card insitu testing apparatus and method utilizing unintended RF emission features
ActiveUS20180316082A1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsPower equipmentElectron
A diagnostic apparatus for analysis, testing, inspecting and / or screening an integrated and assembled electrically powered equipment rack and its populated cards and devices for measurement of degree of device aging, improper operation, degradation, condition, and / or Remaining Useful Life (RUL). The device includes an antenna card with a detachably attachable antenna module that can be positioned at a distance from the electrically devices under test and a signal receiver or sensor for examining a signal from the electrically powered device, but especially applied to rackmount supported electronics and / or chassis based electronics. The receiver or sensor collects unintended and / or intended RF energy components emitted by the electrically powered device and performs the above analysis in a response to the acquired signal input while the electrically powered device is active or powered.
Owner:NOKOMIS
Systems, methods, and apparatus for detecting lightning strikes
Certain embodiments of the invention may include systems, methods, and apparatus for providing detecting lightning strikes. According to an example embodiment of the invention, a method for determining a lightning strike event, classification, and location is provided. The method includes receiving lightning electrical current in least one down conductor, generating voltage and polarity signals based at least in part on the received lightning electrical current, storing the generated voltage and polarity signals, and determining the lightning strike event, classification, and location based at least in part on the stored voltage and polarity signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for evaluating electromagnetic interference
ActiveUS7242176B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceMeasuring interference from external sourcesElectronic systemsElectromagnetic interference
Systems and methods for evaluating electromagnetic interference that may be employed, for among other things, to evaluate electronic system immunity to radiated electromagnetic fields and / or to identify particular electronic system areas that are susceptible to electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Pulse modulated passive intermodulation (PIM) measuring instrument with reduced noise floor
ActiveUS9768892B1Transmitters monitoringTesting dielectric strengthAudio power amplifierMeasuring instrument
In an embodiment, a method for measuring passive intermodulation (PIM) associated with a device under test (DUT) includes generating a test signal using a measuring instrument and obtaining measurements of PIM for the DUT. The test signal comprises two or more tones each amplified to a target output power by a respective amplifier according to a duty cycle. Measurements are obtained by the measuring instrument during an active portion of each duty cycle over a sweep of frequencies. PIM is calculated for the DUT by averaging a plurality of measurements obtained for each frequency from the sweep of frequencies. The duty cycle is determined based on the target output power.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Package structure with conformal shielding and inspection method using the same
ActiveUS20130257462A1Accurate checkSimple resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsGround contactElectrical connection
A package structure with conformal shielding includes a substrate providing electrically connected inner grounding structures, a chip module mounted on the substrate, a molding compound covering the chip module and one surface of the substrate, and a conductive shielding layer covering the molding compound and the lateral sides of the substrate, and electrically connected with a part of the inner grounding structures. The substrate further provides one or multiple independent conductive structures electrically connected with the conductive shielding layer and exposed to the outside. By measuring the resistance value between one independent conductive structure and the conductive shielding layer or another independent conductive structure or one ground contact and then comparing the measured resistance value with a predetermined reference value, the EMI shielding performance of the package structure is determined.
Owner:UNIVERSAL SCI IND CO LTD +1
RF testing method and arrangement
InactiveUS20050046430A1Test accurateThe testing process is simpleMeasuring interference from external sourcesContactless circuit testingEngineeringComparator
An RF testing method and arrangement of an electronic device utilize sensors for measuring the electronic device under test in conjunction with production of the electronic devices. A comparator performs a comparison between measurement signals and corresponding reference signals from a reference supply and a decision unit determines defectiveness of the electronic device based on the comparison.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT TESTING OY
Prioritizing repair of signal leakage in an hfc network
ActiveUS20150181442A1Broadband local area networksTransmission monitoringEngineeringBase transceiver station
A method or apparatus of identifying for repair a signal leak in an HFC network, wherein a base transceiver station in the vicinity of the HFC network transmits a BTS signal over-the-air. The method comprises or apparatus performs the steps of: (a) identifying a location of the signal leak; (b) in the vicinity of the signal leak, detecting the BTS signal; (c) determining a level of the BTS signal; (d) defining a threshold level; (e) with the use of a processor, determining whether the level of the BTS signal meets or exceeds the threshold level; and (f) indicating for repair the signal leak if the level of the BTS signal meets or exceeds the threshold level.
Owner:ARCOM DIGITAL
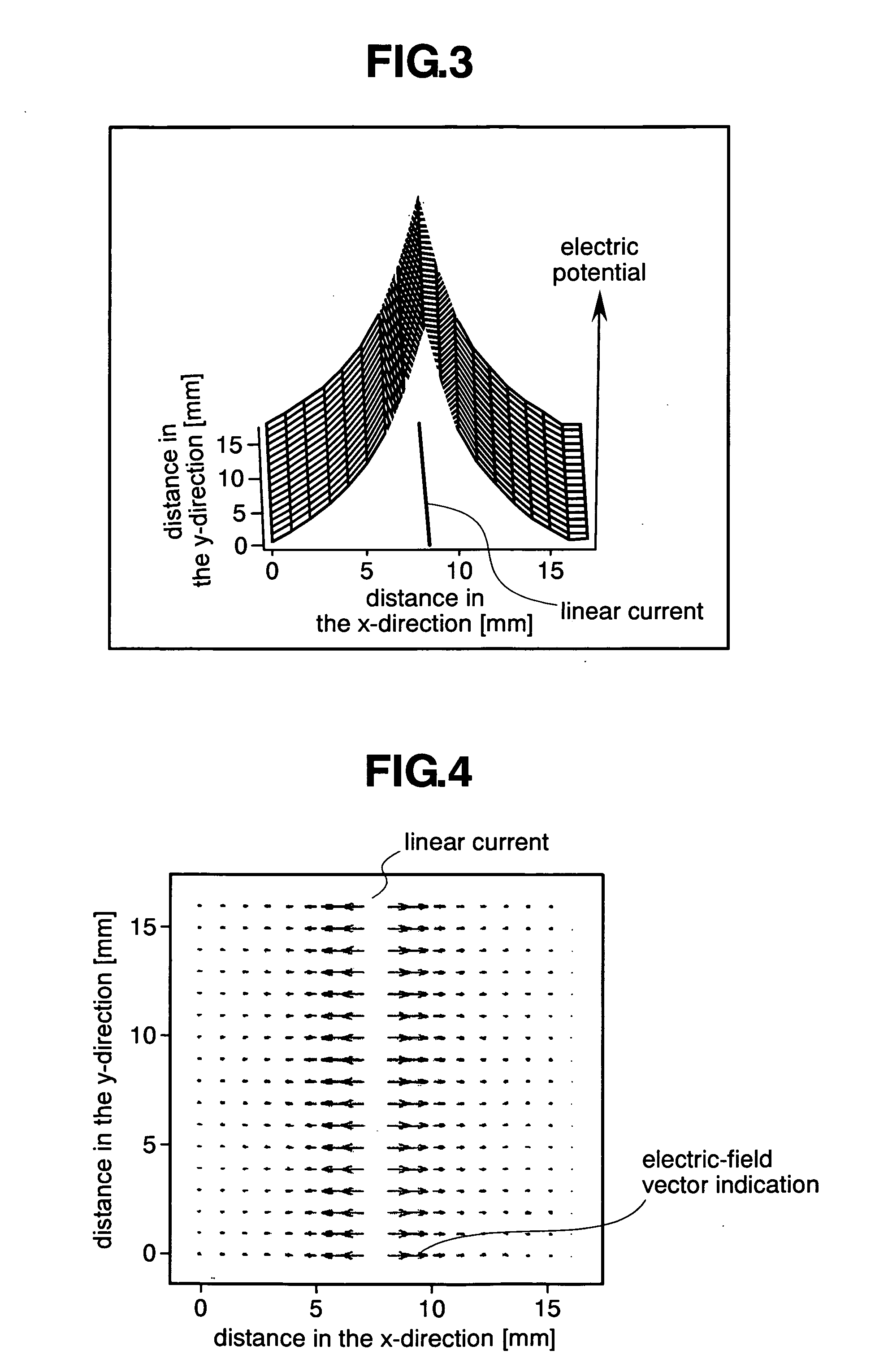
Method of measuring electric field distribution and electric field distribution measuring instrument
InactiveUS20060071669A1Convenient and accurateImprove accuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical field strengthMeasuring instrument
A method and apparatus for measuring an electric field distribution according to the present invention calculates a distribution of electric field intensity and its direction at arbitrary positions on the surface of the electronic apparatus or its circumference with use of data of measurement positions and measurement results of a potential distribution on a surface of an electronic apparatus. Further, it clearly indicates a flow of electromagnetic energy on the surface or in the circumference of the electronic apparatus by applying mathematical treatments to a magnetic field distribution at circumferential positions of the electronic apparatus. Thus, a distribution of high-frequency electric field generated from the electronic apparatus is measured with high accuracy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hand-held system and method for detecting impaired electric power equipment
ActiveUS20090210177A1Effective positioningEasy to useElectric devicesMeasuring interference from external sourcesHand heldElectric power equipment
A hand-held system and method for detecting impaired electric power equipment. An exemplary embodiment may receive electromagnetic radiation and process the resulting signal. For example, signal processing may be used to identify electromagnetic radiation having a particular pattern that is characteristic of electric power equipment. Furthermore, an embodiment may determine the time and / or location during testing. As a result, an exemplary embodiment may be useful for stationary and / or mobile testing of an electrical system.
Owner:EXACTOR INC
System and method for testing the electromagnetic susceptibility of an electronic display unit
InactiveUS20080088336A1Static indicating devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectromagnetic susceptibilityEngineering
A system and method for testing the electromagnetic (EM) susceptibility of an electronic display unit monitors the light emitted from the electronic display unit as EM noise is applied at a particular testing location of the electronic display unit. An error in the electronic display unit caused by the EM noise is detected using an electrical signal generated in response to the light from the electronic display unit.
Owner:AMBER PRECISION INSTUMENTS
Pulse current sensor
ActiveUS20070115008A1Accurate measurementImprove fidelityCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical conductorCoaxial transmission line
A sensor measures the current in high frequency pulses (e.g., pulses having fast rise times) that are transported on coaxial transmission lines. The sensor includes an entrance coaxial conductor and an exit coaxial conductor that are interconnected by a continuous inner conductor. The outer conductors of the two coaxial conductors are interrupted and are interconnected by a sensing resistor with a substantially constant resistance. An output sensor coaxial conductor has an inner conductor electrically connected to a first end of the sensing resistor and has an outer conductor connected to a second end of the sensing resistor. Tapered ferrite cores are placed around the three coaxial conductors proximate the connections to the sensing resistor. Preferably, the sensing resistor is a tubular resistor formed on a dielectric cylindrical tube. The sensor is enclosed within a continuous conductive housing.
Owner:BARTH JON E +1
Emi measuring method and its system
InactiveUS20060043979A1Shorten product development cycleSimple methodResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasuring interference from external sourcesTime domainPresent method
An electromagnetic interference (EMI) measuring method and its system for diagnosing EMI of various electronic devices and instructing user to improve design to satisfy Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) criterion. The measuring method according to the present invention includes acquiring a set of time domain signal waveforms from a group of uniformly distributed test points on equipment under test (EUT), and then processing, converting, comparing and analysing, and finally determining physical position of EMI on EUT. To implement the present method, the present invention provides an EMI measuring system. The system includes signal acquisition portion and signal analysis portion. The signal analysis portion takes computer as carrier, which establishes processing, converting, comparing and analysing modules on operating system platform of computer. The method steps and system structure according to the present invention are simple and convenient which are no restricted by ambience and the measuring result is reliable.
Owner:WU WEI
Method and device of electromagnetic compatibility assessment of whole vehicle grounding system
ActiveCN108387802ADetermining Electromagnetic CompatibilityTesting electric installations on transportMeasuring interference from external sourcesGround systemSimulation
The present invention discloses a method and a device of electromagnetic compatibility assessment of a whole vehicle grounding system. The method comprises the steps of: identifying parts, in a wholevehicle, influencing electromagnetic compatibility; employing a vehicle body structure digital model in a whole vehicle design file to establish a vehicle body model; employing wiring harness digitalmodel related to parts influencing the electromagnetic compatibility in the wiring harness digital model in the whole vehicle design file to establish a grounding network wiring harness model; employing an equivalent circuit mode to establish a grounding point and grounding connection model; employing the equivalent circuit mode to establish an equivalent circuit model of parts influencing the electromagnetic compatibility for the ground; performing simulation of a model of whole vehicle grounding system electromagnetic compatibility analysis to obtain a coupling relation between an interference source part and a sensitive body part through the ground; and performing analysis of the coupling relation to determine the electromagnetic compatibility performance of the whole vehicle groundingsystem. Compared to the prior art, the method and the device of electromagnetic compatibility assessment of the whole vehicle grounding system achieve analysis of electromagnetic compatibility performances of the whole vehicle grounding system in whole vehicle electrical design phase.
Owner:BEIJING JINGWEI HIRAIN TECH CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com