Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1056results about "Measurement leads/probes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
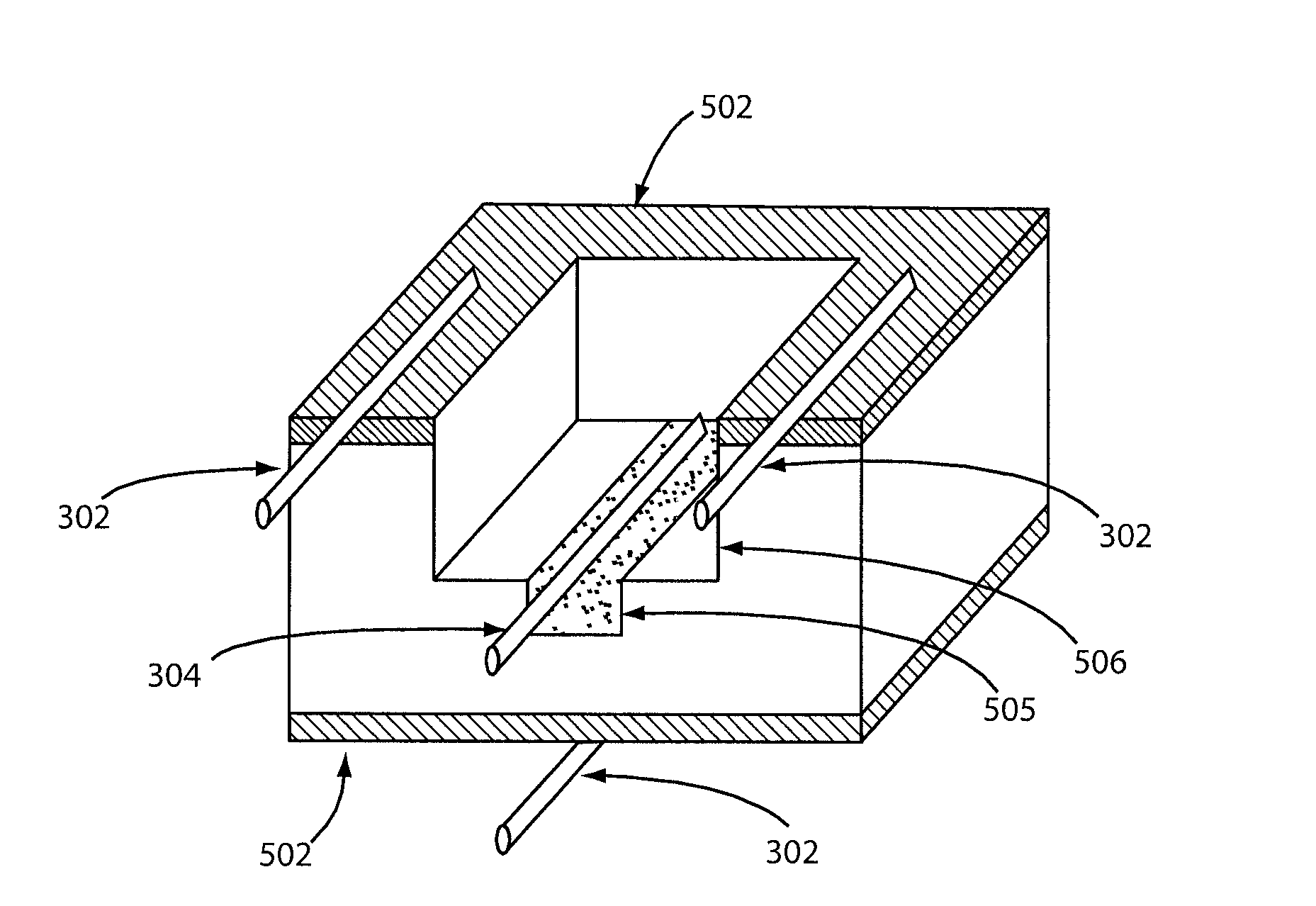
Near field antenna for object detecting device
ActiveUS20150333804A1Improve sensor sensitivityImprove sensing accuracyNear-field in RFIDMeasurement leads/probesWave structureCoaxial cable
A near field antenna adapted to an object detecting device, for sensing a plurality of units under test of at least an object under test. The near field antenna comprises a periodic guided-wave structure, a metallic reflection portion and at least two near field magnetic coupling antennas. The periodic guided-wave structure disposed below the object under test has a plurality of conductive units periodically arranged on a first plane. The metallic reflection portion is disposed under the periodic guided-wave structure to form an enclosed space. The near field magnetic coupling antennas are disposed on a second plane parallel to the periodic guided-wave structure, and are located in the enclosed space. The feed point and the ground point of each near field magnetic coupling antenna are fed by a coaxial cable with a feeding direction parallel to the periodically arranged conductive units.
Owner:AUDEN TECHNO
Apparatus and method for the testing of circuit boards, and test probe for this apparatus and this method
InactiveUS7015711B2Improve reliabilityLess calibration timeMeasurement leads/probesPrinted circuit testingTest probeTest point
An apparatus and a method for the testing of circuit boards, together with a test probe for this apparatus and this method, in which the contact tips of a test finger of a finger tester are monitored during the testing process by an optical detection device and their movement, at least when approaching a part of the circuit board test points of a circuit board to be tested, is corrected on the basis of the result determined by the optical detection device in such a way that the contact tip makes reliable contact with the circuit board test point concerned. The correction data hereby obtained may be used in the calculation of calibration data.
Owner:ATG TEST SYST
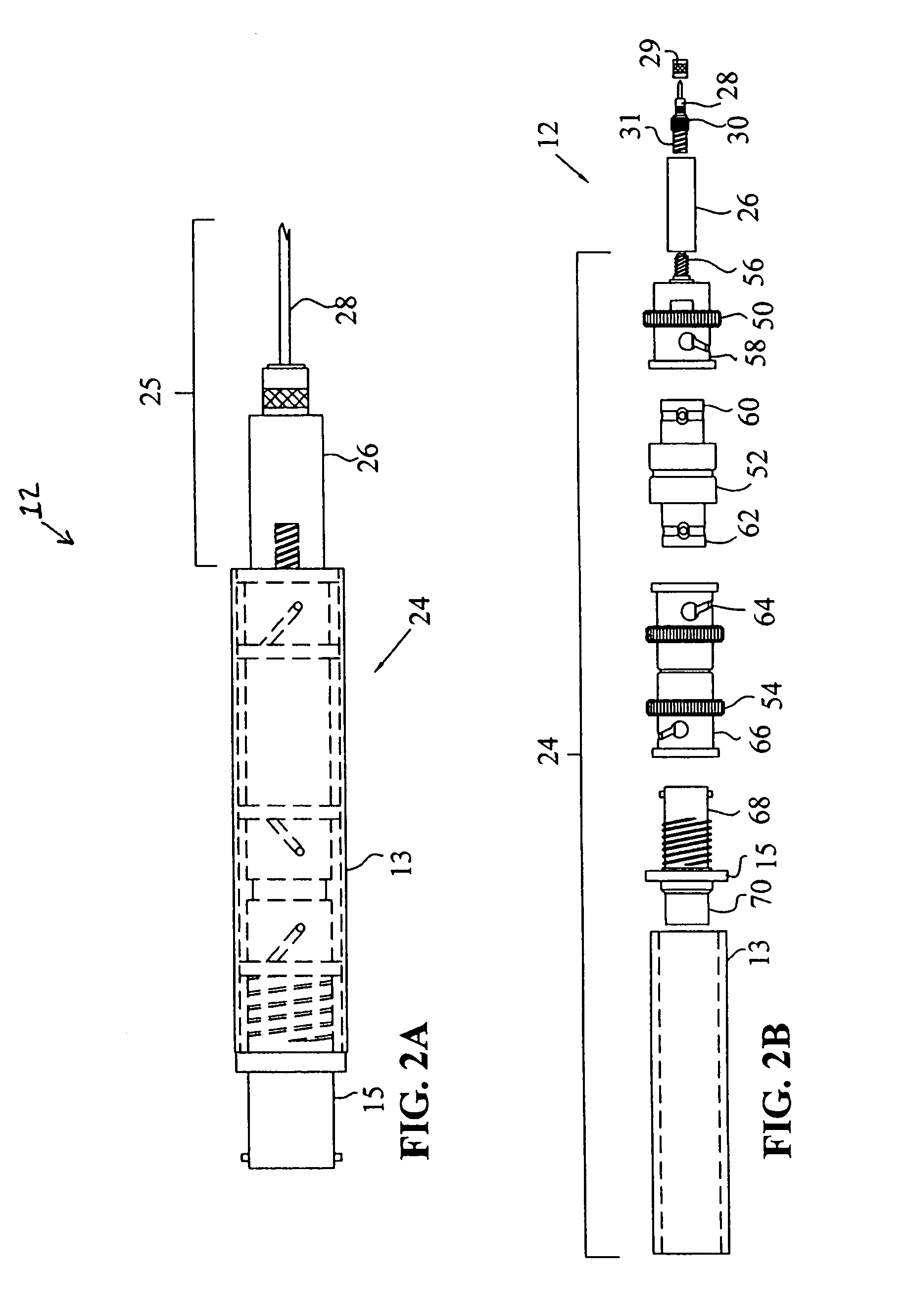
Probe device having a clip-on wireless system for extending probe tip functionality
InactiveUS20090212938A1Function increaseElectrical testingMeasurement leads/probesTelecommunications linkWireless transceiver
A probe device is provided that has a clip-on wireless device attached thereto for communicating over a wireless communication link with test equipment having a wireless transceiver attached thereto. The clip-on wireless device may have one or more components that provide additional functionality to the probe device over that which is currently available on most probe devices. Such components may include, for example, run / stop buttons, activity indicators, “headlight” LEDs, etc
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
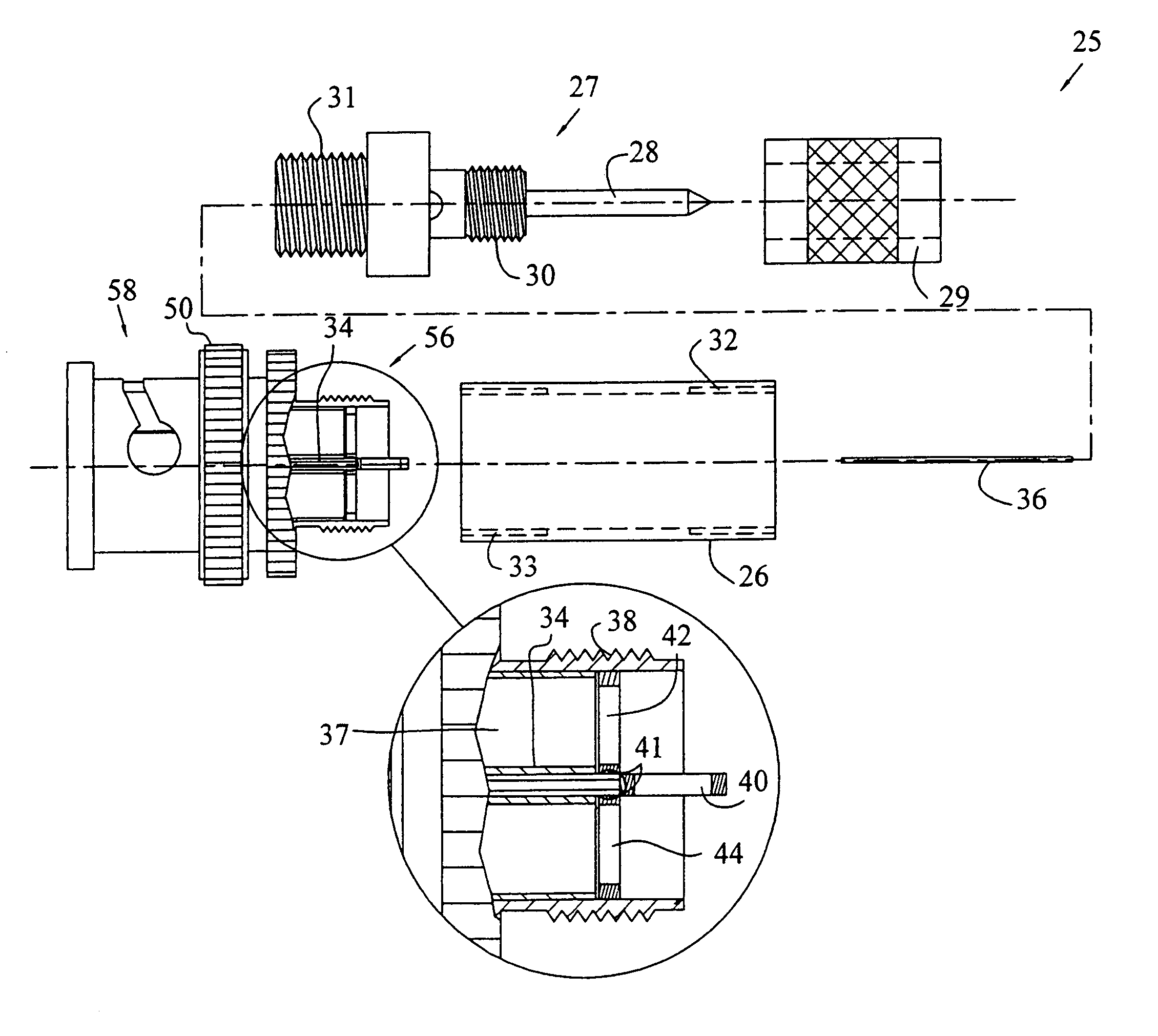
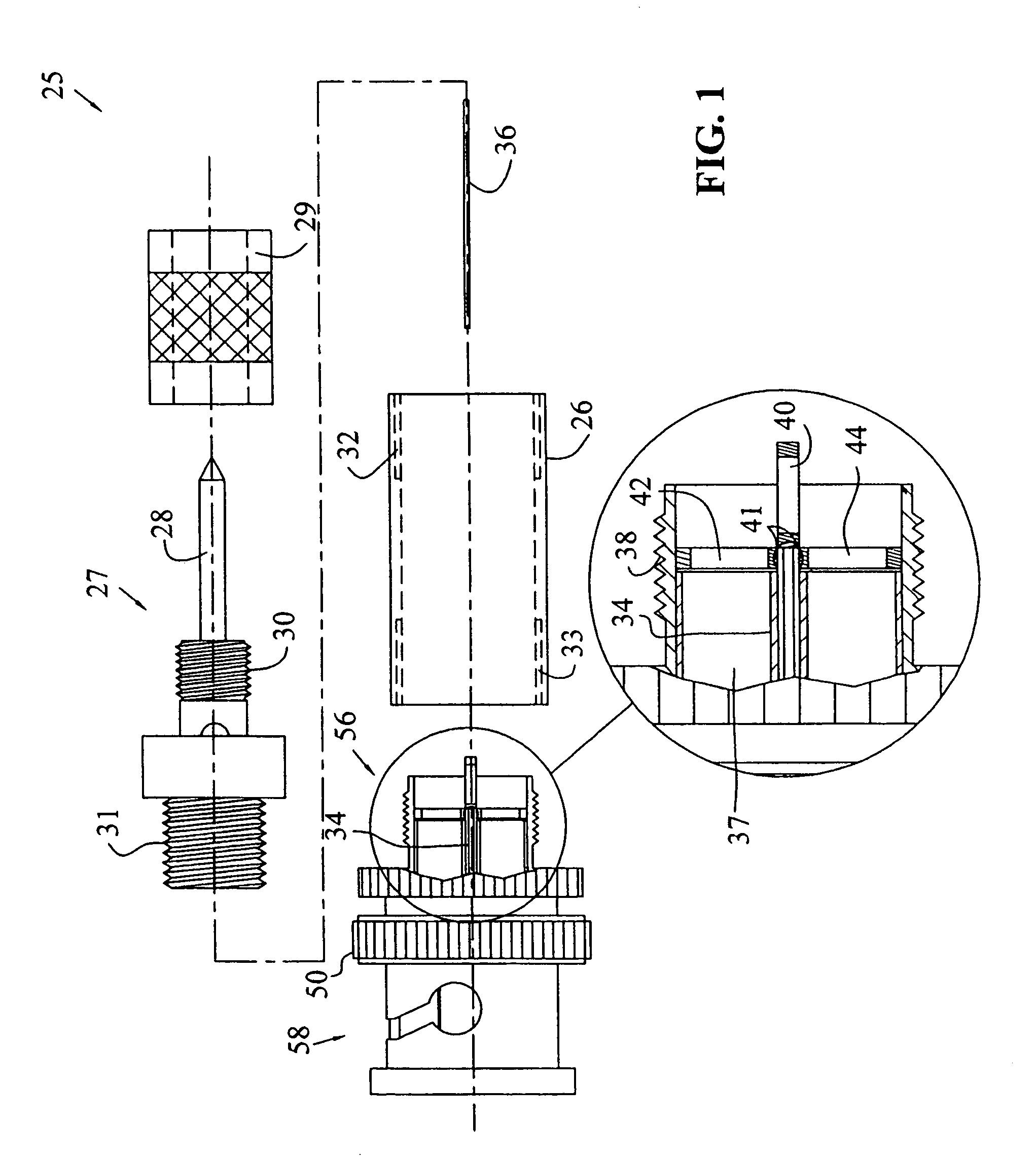
Ultra-broadband differential voltage probes
ActiveUS7015709B2Reduce parasitic inductanceError minimizationElectrical testingMeasurement leads/probesElectricityElectrical conductor
Passive balanced probes are disclosed for use with a signal analysis device. The probes are very low cost relative to typical commercially available probes and provide an extremely flat response over a frequency range of approximately 0 to at least 1.5 gigahertz. The probes include a probe body constructed primarily from conventional components, a first surface mount resistor electrically connected between a probe tip and a center conductor, and two surface mount resistors electrically connected and parallel between the center conductor and a conductive shield. The probes further include a coaxial cable for connection to an instrument combiner or other instrument connection device.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
High frequency component, communication apparatus, and method for measuring characteristics of high frequency component
InactiveUS20010050550A1Easy to measureSuppresses radiation and incidenceMagnetic/electric field screeningMeasurement leads/probesCommunication deviceVIT signals
A high frequency component is constructed such that the characteristics of a high frequency circuit that cannot be measured only by an outwardly extending terminal electrode are easily measured at the final-product stage. In the high frequency component, a substrate has an electrode pattern provided including a signal measuring electrode pad. Additionally, chip components are mounted on the substrate. A metal cover has a hole provided near the signal measuring electrode pad. Through the hole, a probe of a measuring apparatus is inserted from the outside to abut with the electrode pad. With the arrangement, a voltage signal obtained at a predetermined point of the high frequency circuit is measured.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
AC coupled parameteric test probe
InactiveUS20070296435A1Increase signal couplingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement leads/probesElectricityCoupling parameter
A probe for contacting and testing ICs on a semiconductor device includes a dielectric insulating material tip. The dielectric tip does not contaminate the surface being probed unlike metal probe tips. A contact scrub is further not required with signals being capacitively or inductively coupled from the probe tip to the IC. Testing can be performed during early fabrication steps of the wafer without the need for applying a metalization layer to the wafer to form bond pads. Testing can be performed by inductively coupling an AC signal to the probe tip, with coupling enhanced by including a magnetic material in the dielectric probe tip. Using an AC test signal enables testing of ICs without requiring separate power and ground connections.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Method for testing semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6512392B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityMeasurement leads/probesIndividual semiconductor device testingLow voltageQuality assurance
Method for determining a more efficient quality assurance or reliability test screen without falsely rejecting, i.e., over stressing, short channel length devices during voltage stress test screening. Short channel lengths devices fabricated on a semiconductor wafer have a higher tendency to fail at voltage levels that would otherwise not harm long channel length devices. The failures, however, are not related to device defects. Protection to the more vulnerable devices is provided by determining the speed of the die prior to the voltage test screen, thus, segregating the devices based on operational speed performance. Next, a lower voltage is effetively applied during wafer probe test to the faster devices, which directly correspond to the population of short channel devices.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Probe pins zero-point detecting method, and prober
InactiveUS7023226B2Avoid damageImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementFault location by increasing destruction at faultProbe cardConductive materials
A zero-point detecting method of this invention is performed prior to testing the electrical characteristics of a wafer by bringing an object to be tested on a stage and probes of a probe card into contact with each other. The surface of a zero-point detection plate is made of a conductive material (e.g., copper). The zero-point detection plate is used to detect a zero point as a position where the surface of the object to be tested comes into contact with the probe pins.
Owner:OCTEC INC +1
High density integrated circuit apparatus, test probe and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080100316A1High performance functional testingHigh temperature burn in applicationsManufacture of electrical instrumentsMeasurement leads/probesElastomerContact pad
The present invention is directed to a high density test probe which provides a means for testing a high density and high performance integrated circuits in wafer form or as discrete chips. The test probe is formed from a dense array of elongated electrical conductors which are embedded in an compliant or high modulus elastomeric material. A standard packaging substrate, such as a ceramic integrated circuit chip packaging substrate is used to provide a space transformer Wires are bonded to an array of contact pads on the surface of the space transformer. The space transformer formed from a multilayer integrated circuit chip packaging substrate. The wires are as dense as the contact location array. A mold is disposed surrounding the array of outwardly projecting wires. A liquid elastomer is disposed in the mold to fill the spaces between the wires. The elastomer is cured and the mold is removed, leaving an array of wires disposed in the elastomer and in electrical contact with the space transformer The space transformer can have an array of pins which are on the opposite surface of the space transformer opposite to that on which the elongated conductors are bonded. The pins are inserted into a socket on a second space transformer, such as a printed circuit board to form a probe assembly. Alternatively, an interposer electrical connector can be disposed between the first and second space transformer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
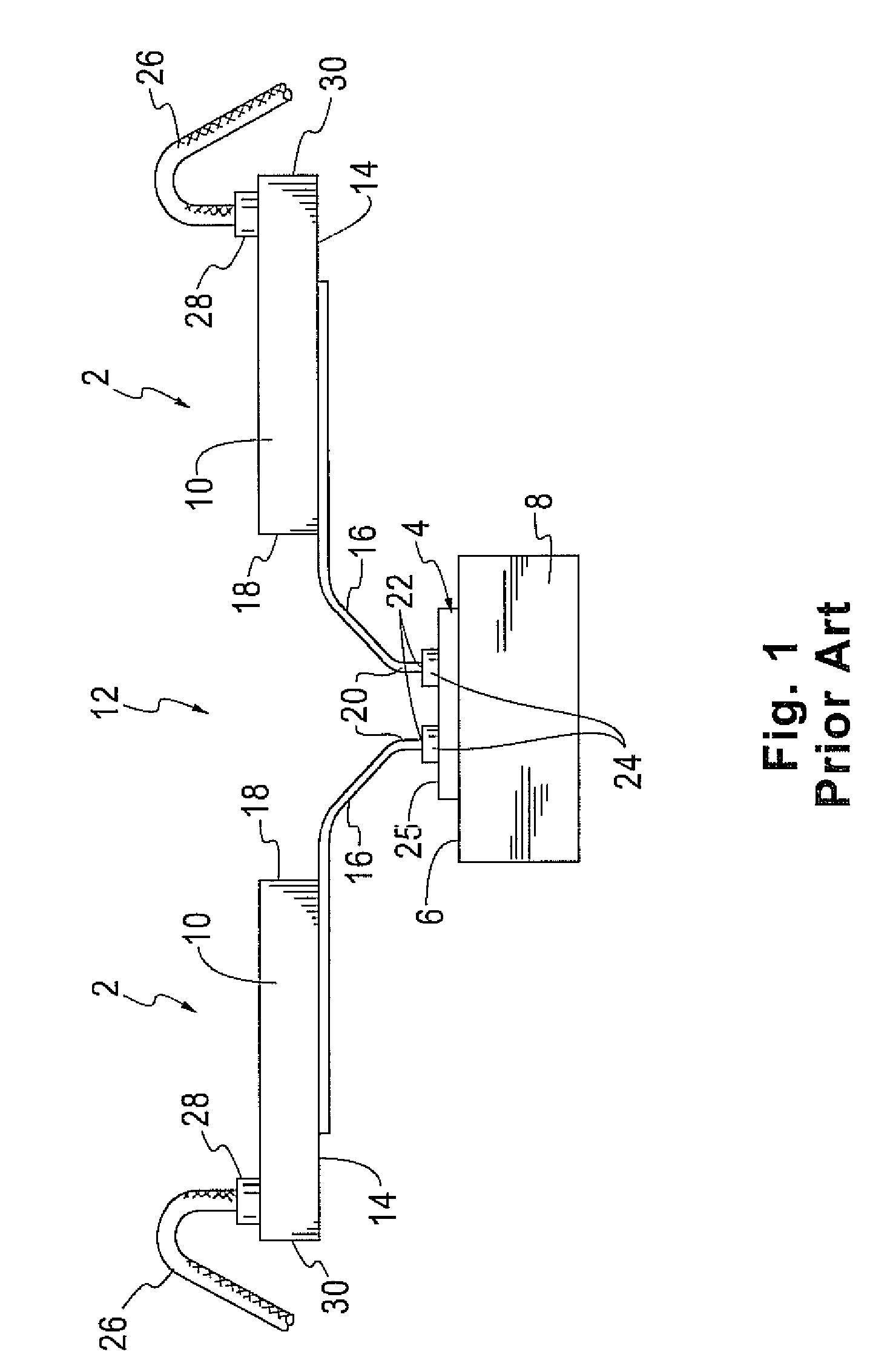
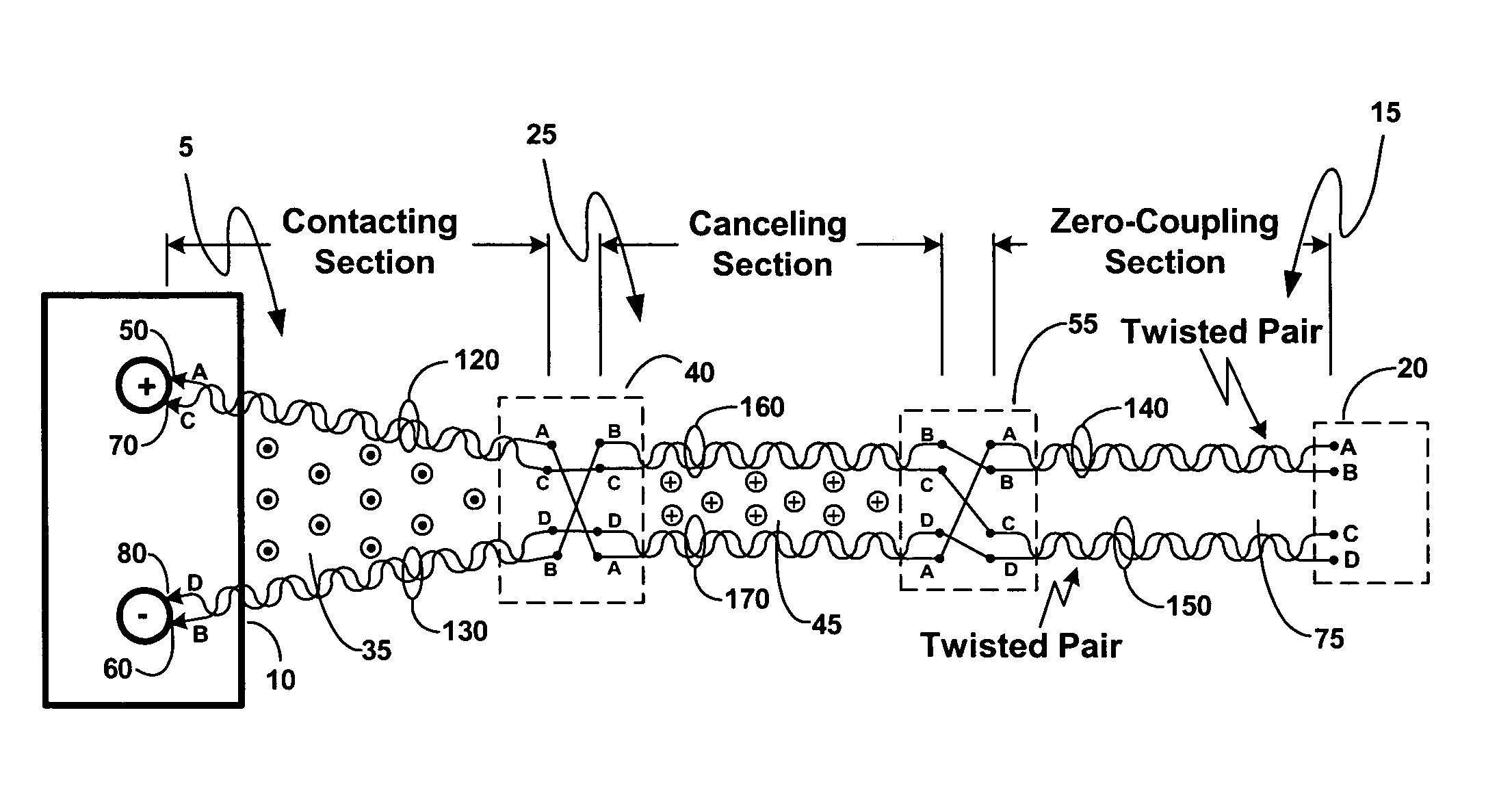
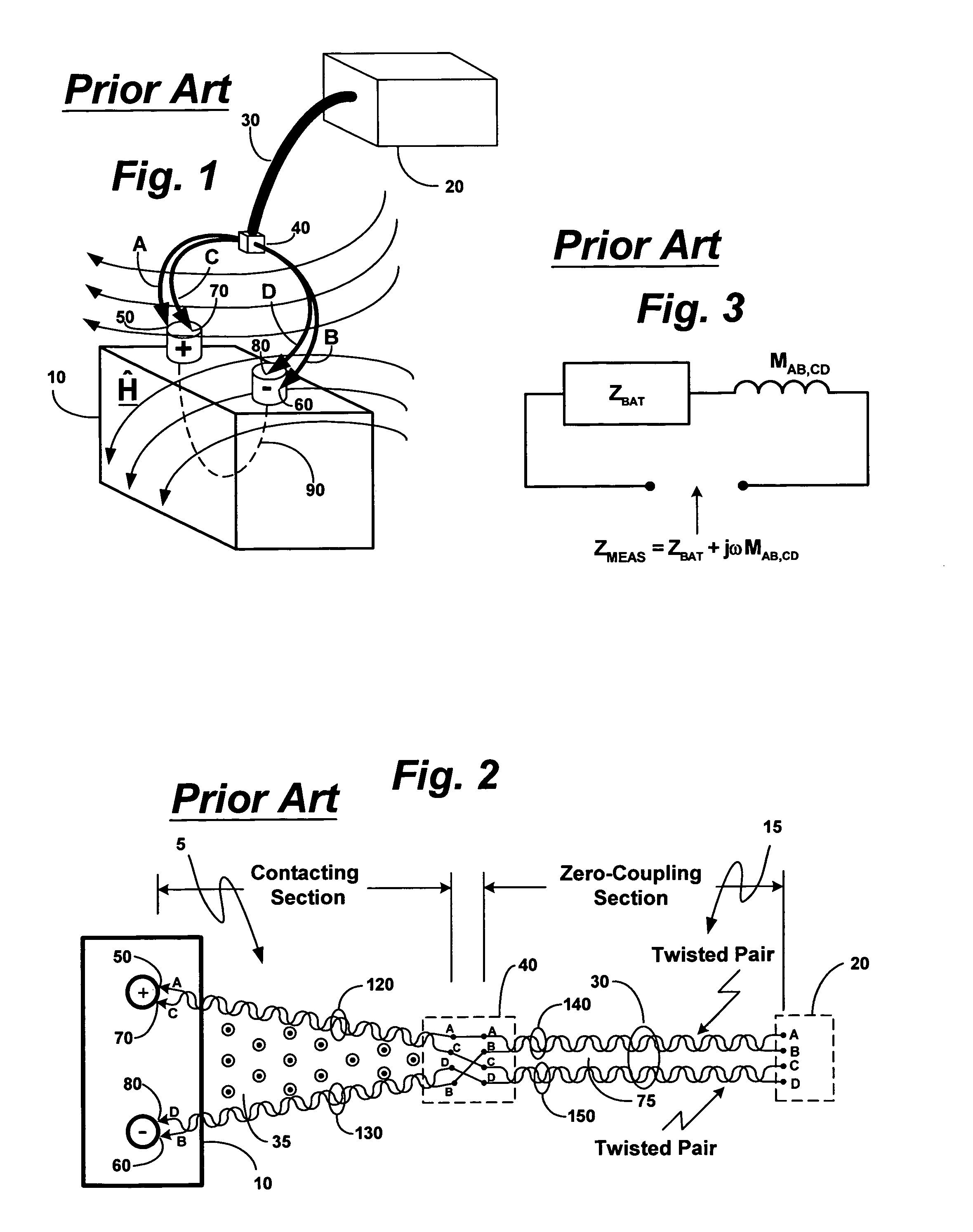
Broad-band low-inductance cables for making Kelvin connections to electrochemical cells and batteries
ActiveUS7106070B2Effectively cancellingResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A broad-band technique for reducing the distributed inductance of a four-conductor Kelvin cable is disclosed. A special inductance-canceling cable section is connected in tandem with the cable section contacting the cell / battery. Connections between the two cable sections are transposed such that conductors in each conductor pair of the canceling section connect to current-carrying and voltage-sensing conductors from different conductor pairs in the contacting section. The canceling section thereby exhibits a distributed negative mutual inductance between its current-carrying and voltage-sensing conductors that can effectively cancel the distributed positive mutual inductance introduced by the contacting section.In one embodiment, conductor pairs comprise pairs of insulated wires which may be twisted together. In other disclosed embodiments, conductor pairs comprise shielded coaxial cables.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
Touch sensor using graphene for simultaneously detecting a pressure and a position
ActiveUS20130285970A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh transparencyResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement leads/probesGrapheneAcoustics
A touch sensor capable of specifying a touch position and / or a degree of a touch pressure by using graphene as an electrode and / or a strain gauge, and more particular, a touch sensor capable of simultaneously detecting a pressure and a position by means of change in resistance by using graphene is provided.
Owner:GRAPHENE SQUARE
Signal Module With Reduced Reflections
InactiveUS20080273201A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityDielectric
Signal modules and methods for electrically interfacing with an electronic device are provided. The signal module includes a dielectric and a conductor extending through a surface of the dielectric. The surface of the dielectric is located away from perpendicular relative to an axis of the conductor and is located based on an electromagnetic field produced as a result of a signal flowing through the conductor.
Owner:INTEST CORP
Probe station thermal chuck with shielding for capacitive current
InactiveUS20070030021A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectCapacitanceElectricity
To reduce noise in measurements obtained by probing a device supported on surface of a thermal chuck in a probe station, a conductive member is arranged to intercept current coupling the thermal unit of the chuck to the surface supporting the device. The conductive member is capacitively coupled to the thermal unit but free of direct electrical connection thereto.
Owner:FORMFACTOR BEAVERTON INC
Apparatus and method for dynamic diagnostic testing of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6859031B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMagnetic property measurementsPhoton counting detectorElectricity
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Apparatus And Method For Limiting Over Travel In A Probe Card Assembly
InactiveUS20060261827A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingProbe cardDevice material
Methods and apparatuses for testing semiconductor devices are disclosed. Over travel stops limit over travel of a device to be tested with respect to probes of a probe card assembly. Feedback control techniques are employed to control relative movement of the device and the probe card assembly. A probe card assembly includes flexible base for absorbing excessive over travel of the device to be tested with respect to the probe card assembly.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Measuring method, inspection method, inspection device, semiconductor device, method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing an element substrate
InactiveUS6891391B2Easy to checkSimplify inspection stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSignal processing
An inspection method which simplifies an inspection step by eliminating the need to set probes on wiring or probe terminals, and an inspection device for performing the inspection step. A voltage is applied to each of inspected circuits or circuit elements to operate the same. Signal processing is performed on an output from each inspected circuit or circuit element during operation to form a signal (operation information signal) including information on the operating condition of the circuit or the circuit element. The operation information signal is amplified and the amplitude of an alternating current voltage separately input is modulated with the amplified operation information signal. The voltage of the modulated alternating current is read in a non-contact manner to determine whether the corresponding circuit or circuit element is non-defective or defective.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Probe pin assembly
InactiveUS6847221B2Avoid contactSolve the lack of spaceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement leads/probesVertical arrayElectrical and Electronics engineering
A prove pin assembly is provided in which the probe pins for a chip under test occupy the only space above the chip, not extending into the space above the adjacent chip. The probe pin assembly has a lateral array of parallel probe pins of a plurality of first perpendicular-type probe pins and a vertical array of parallel probe pins of a plurality of second perpendicular-type probe pins, wherein said lateral array of parallel probe pins and vertical array of parallel probe pins occupy different spaces for deformation above the region of the chip under test and fit in the limited planar range corresponding to the chip.
Owner:KIMOTO GUNSEI
Test method for yielding a known good die
InactiveUS20030237061A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor wafer is cut to singulate integrated circuit dice formed on the wafer. A die pick machine then positions and orients the singulated dice on a carrier base such that signal, power and ground pads formed on the surface of each die reside at predetermined positions relative to landmarks on the carrier base the die pick machine optically identifies. With the dice temporarily held in place on the carrier base, they are subjected to a series of testing and other processing steps. Since each die's signal pads reside in predetermined locations, they can be accessed by appropriately arranged probes providing test equipment with signal access to the pads during tests. After each test, a die pick machine may replace any die that fails the test with another die, thereby improving efficiency of subsequent testing and other processing resources.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Probe for testing a device under test
InactiveUS7161363B2Electrical testingManufacture of electrical instrumentsIntegrated circuitDevice under test
A probe measurement system for measuring the electrical characteristics of integrated circuits or other microelectronic devices at high frequencies.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Prober
InactiveUS6933736B2Reduce mechanical vibrationEasy to measureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingProbe cardSemiconductor
This invention is a probe apparatus including: a stage onto which a substrate to be processed is placed, a semiconductor device having a plurality of groups of electrode pads being formed on the substrate to be processed; a probe-card holding mechanism that holds a probe card provided with a group of probe needles corresponding to each group of electrode pads; and a driving mechanism that moves the stage and causes the group of probe needles to successively come in contact with the respective groups of electrode pads. A converting device that converts mechanical vibration energy generated in components of the probe apparatus into electrical energy, and an electrical circuit that discreates an electrical current based on the electric energy converted by the converting device are further provided.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
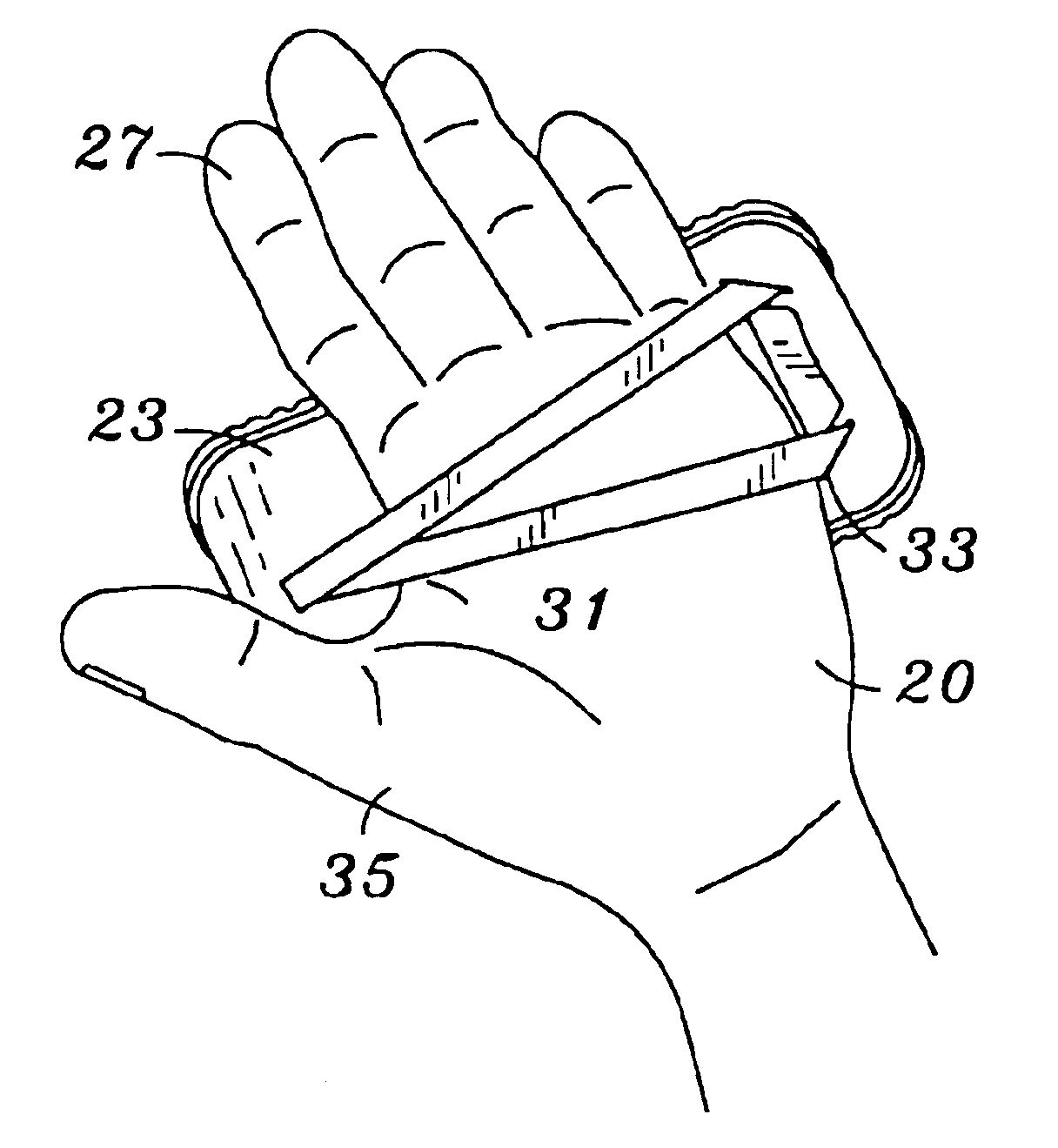
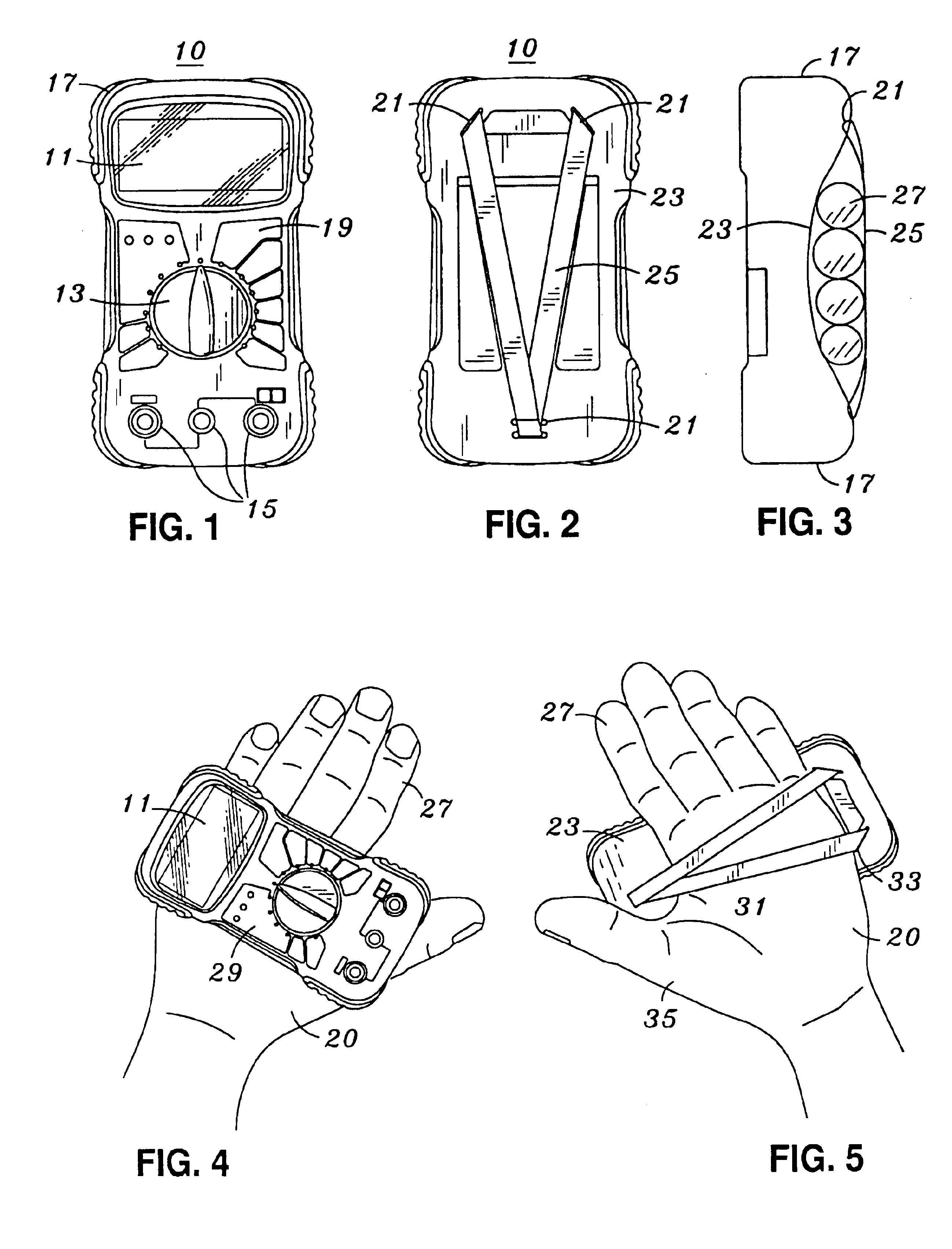
Hand mounted testing meter
ActiveUS6940270B2Secure supportDigital circuit testingMeasurement leads/probesTester deviceHand held
A hand held testing meter is provided which allows the meter to be viewed and securely supported on the user's hand, while the user's fingers are free to hold and manipulate test instruments. An elastomeric band is provided which is engageable to the meter extending substantially across the meter rear surface. The elastomeric band is resiliently extendable to securely receive a user's hand intermediate the meter rear surface and the elastomeric band.
Owner:INNOVA ELECTRONICS
Probe card
InactiveUS6933737B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement leads/probesProbe cardMeasurement device
In the probe card of the semiconductor device measurement device, measurement is to be done in the stability without damage beyond the needle diameter on the pad of the wafer by the probe needle. The straight probe needle 5 is inserted in the upper guide plate 2, the rotary guide plate 3 and the bottom guide plate 4. The rotary guide plate 3 is a little displaced, and the center of the probe needle 5 is bent. Under this condition, the stage with the wafer thereon is raised, and then the tip of the probe needle 5 reaches the pad on the surface of the wafer. The rotary guide plate 3 has a guide slot 7. The rotary guide plate 3 is moved in the horizontal plane. The fixed guide pin 8 moves along the guide slot 7. The probe needle 5 rotates like swinging. The probe needle 5 breaks through the natural oxide film stuck on the pad. In this way, the dispersion of the pressure of the probe needle 5 is prevented. Measurement can be done without damage beyond the needle diameter on the pad of the wafer. Moreover, the pitch of the probe needle 5 can be narrow, and assembling becomes easy.
Owner:IWASAKI CORRESPOND IND CO LTD
Probe cleaning sheet and cleaning method
InactiveUS20050255796A1Sufficient cushioning propertySoftly and efficiently cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingForeign matterRoom temperature
A probe cleaning sheet is provided, which can be used not only at a room temperature and high temperature but also in a low temperature environment with sufficient cushioning property and which can softly and efficiently clean a probe tip end. Specifically, the cleaning sheet has a layered structure including an elastic layer below a polishing layer, for removing, by contact with the polishing layer, foreign matter adhered on a tip end of a probe for semiconductor inspection, and the elastic layer is a polytetrafluoro-ethylene porous body layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Test fixture for testing backplanes or populated circuit boards
InactiveUS6194908B1Better and more stable electrical contactEliminate riskMeasurement leads/probesContactless circuit testingGrid basedEngineering
A test fixture for testing backplanes of a printed circuit board having at least one shrouded connector including a translator fixture having a plurality of spaced apart translator plates adapted for containing and supporting a plurality of translator pins and a probe plate rigidly connected to a top plate of the translator fixture having a plurality of spring probes extending through holes in the probe plate in electrical contact with the translator pins of the translator fixture to translate to signals from the connector to a grid base located below the translator fixture.
Owner:XCERRA
High performance time domain reflectometry
InactiveUS20120274338A1Easy alignmentProviding mechanical stabilityResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement leads/probesTime domainHigh bandwidth
Methods and systems for high-bandwidth time domain reflectometry include a printed circuit board (PCB) and a probe. The PCB includes at least one signal terminal connected to at least one signal via at least three guide terminals arranged around the at least one high-frequency signal terminal. At least one of the guide terminals is connected to at least one ground via. The probe includes at least one biased pin to contact the at least one signal terminal and at least three fixed guide pins arranged about the at least one biased pin to facilitate alignment of said at least one biased pin by first engaging at least one guide terminal area, such that the at least one mechanically biased pin is guided to the at least one contact point.
Owner:IBM CORP
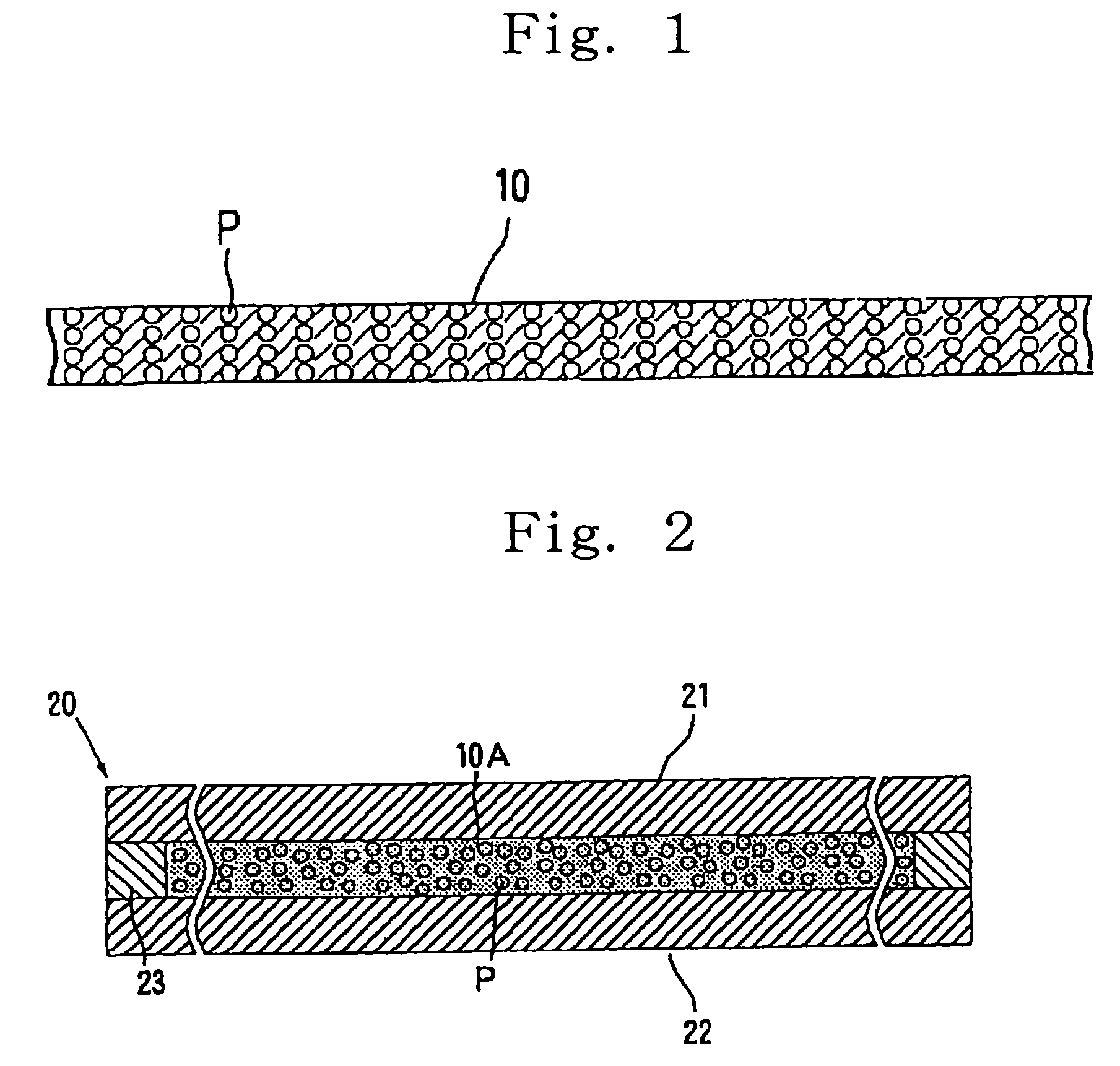
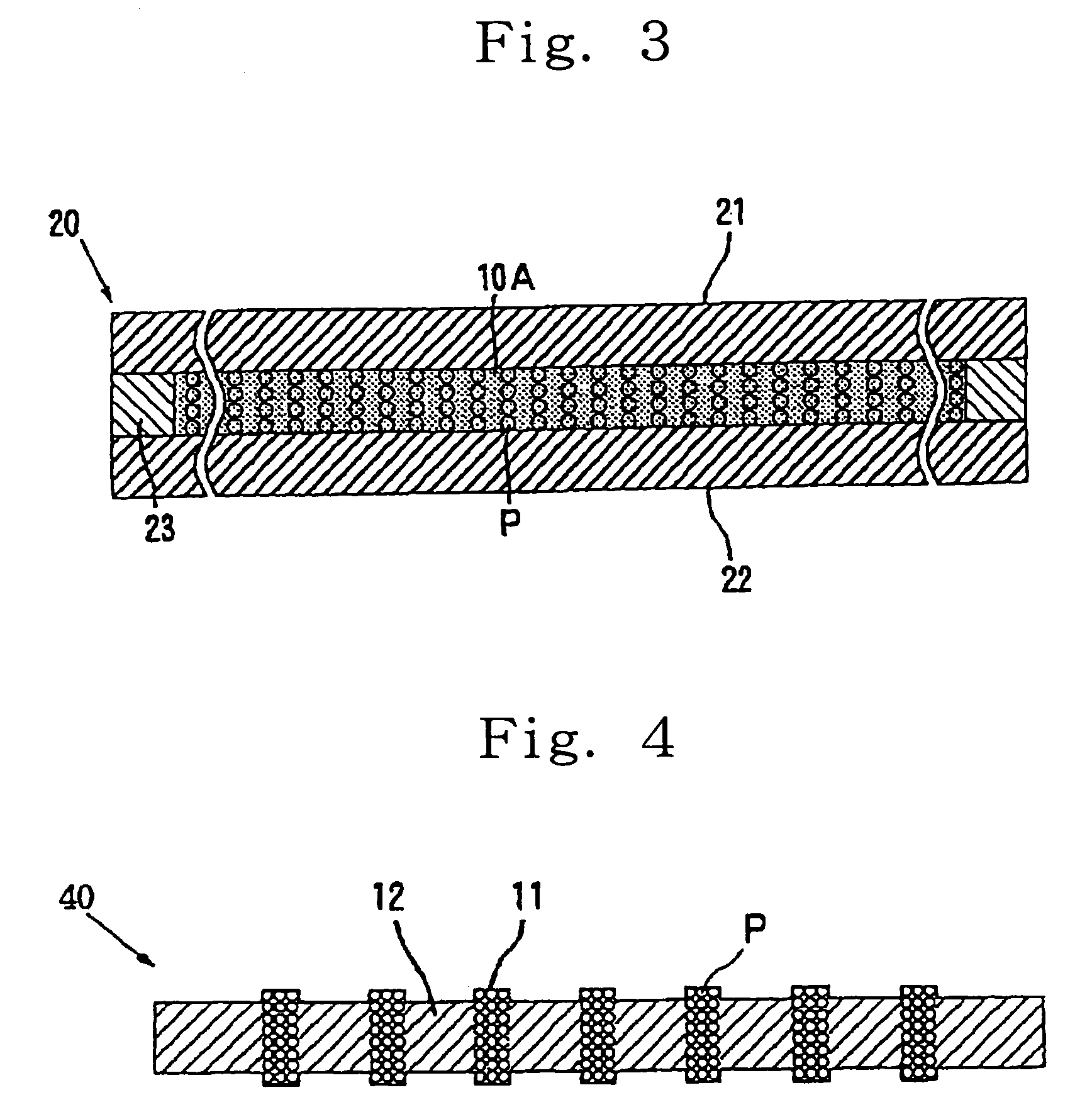
Anisotropic, conductive sheet and impedance measuring probe
InactiveUS7071722B2Improve reliabilityAvoid damageManufacture of electrical instrumentsCoupling contact membersPolymerMaterials science
An anisotropically conductive sheet of the invention formed by containing conductive particles exhibiting magnetism in a sheet base composed of an elastic polymeric substance in a state dispersed in a plane direction thereof and oriented so as to align in a thickness-wise direction thereof. A thickness of the sheet is 10 to 100 μm, a number average particle diameter of the conductive particles exhibiting magnetism is 5 to 50 μm, a ratio W1 / D of the thickness W1 to the number average particle diameter D of the conductive particles exhibiting magnetism is 1.1 to 10, a content of the conductive particles exhibiting magnetism is 10 to 40% in terms of a weight fraction.
Owner:ISC CO LTD
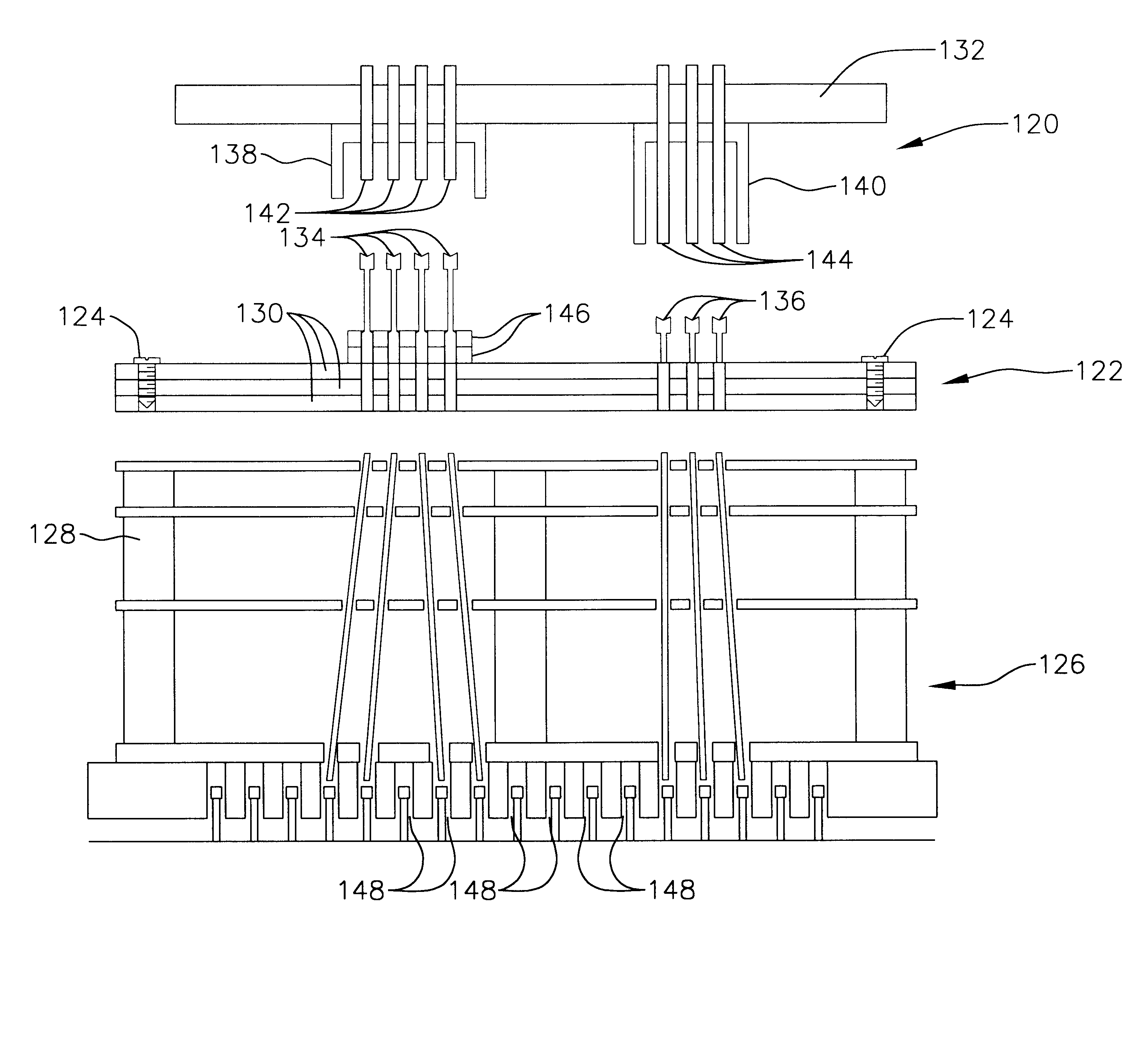
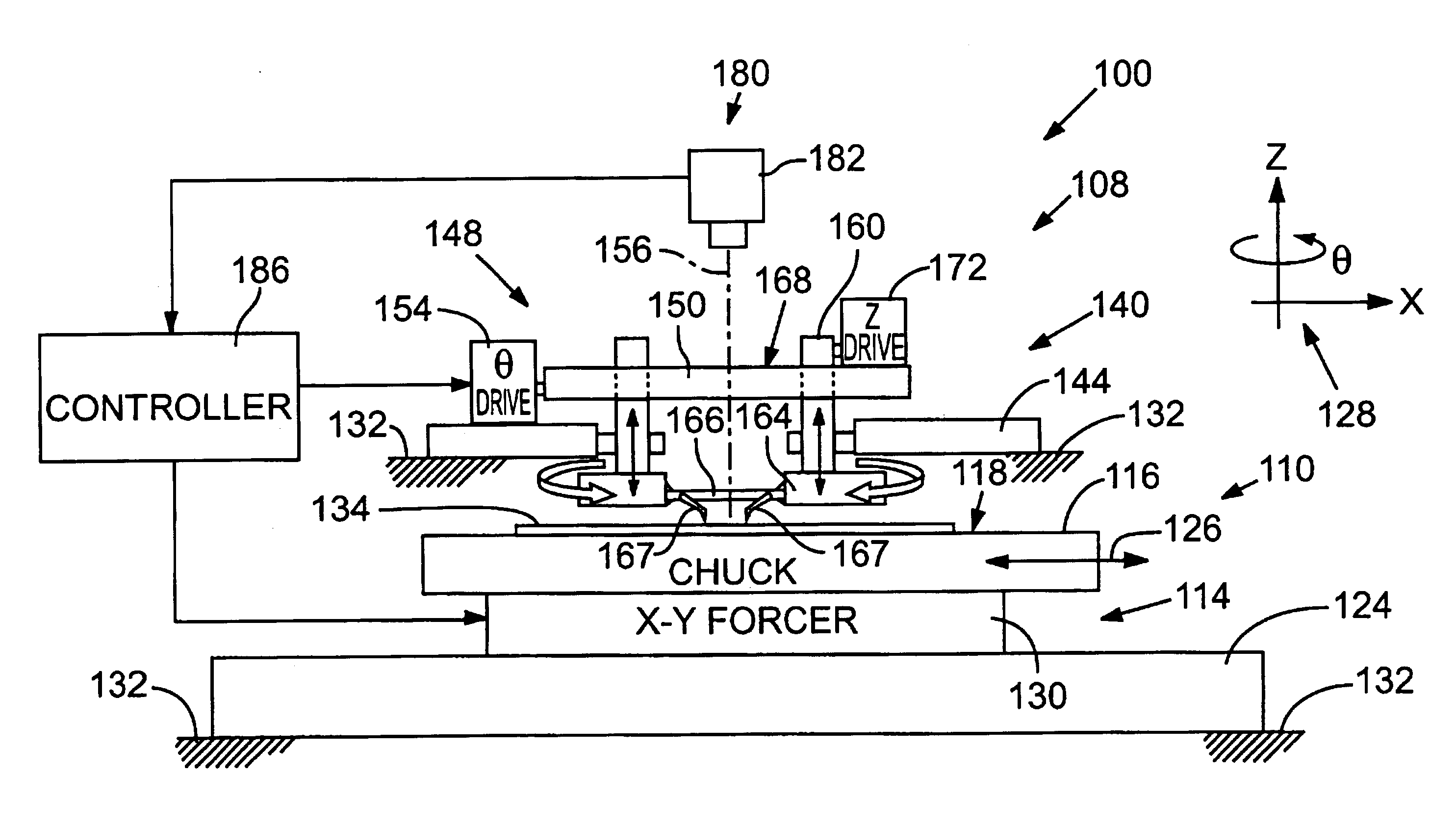
Test probe alignment apparatus
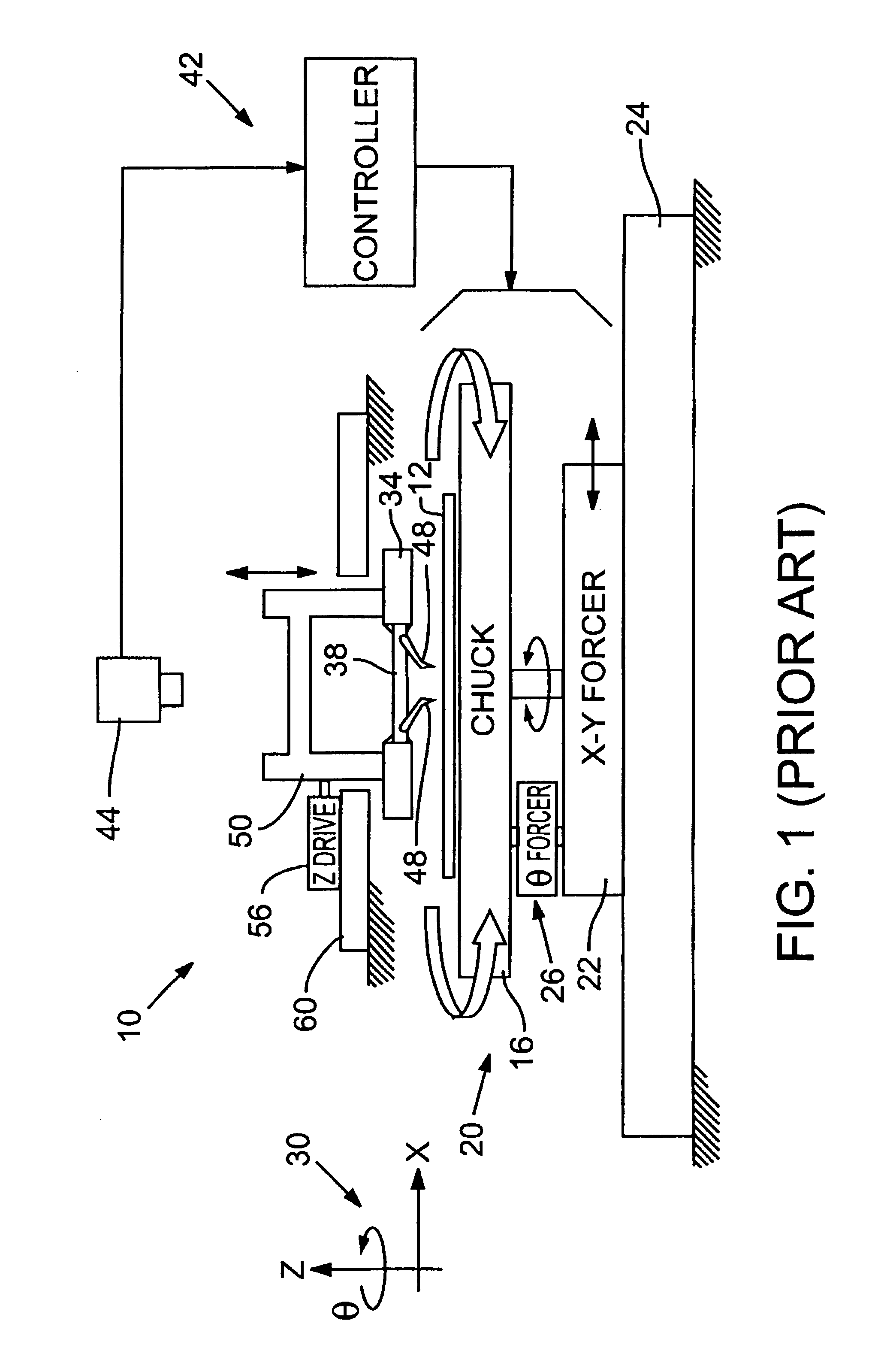
InactiveUS7119566B2Easy to participateAvoid vibrationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement leads/probesRotary stageProbe card
A test probe alignment apparatus includes a rotatable θ stage that is decoupled from a workpiece positioning stage so that the workpiece positioning stage can move a workpiece in an X-Y plane without moving the θ stage, thereby inhibiting vibration in and inertia of the workpiece positioning stage, and improving the speed and accuracy of workpiece movements. The θ stage is driven for rotation about an axis substantially perpendicular to the X-Y plane. The rotatable stage supports a carriage adapted for holding a probe card. The carriage rotates in concert with the θ stage to thereby align the probe card relative to the workpiece. A Z-stage is operatively engaged with the carriage for moving the carriage along the axis of rotation relative to the workpiece. A computer processor performs coordinate transformations on preprogrammed movement vectors, to adjust for angular misalignment of the workpiece as measured by a position sensor.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
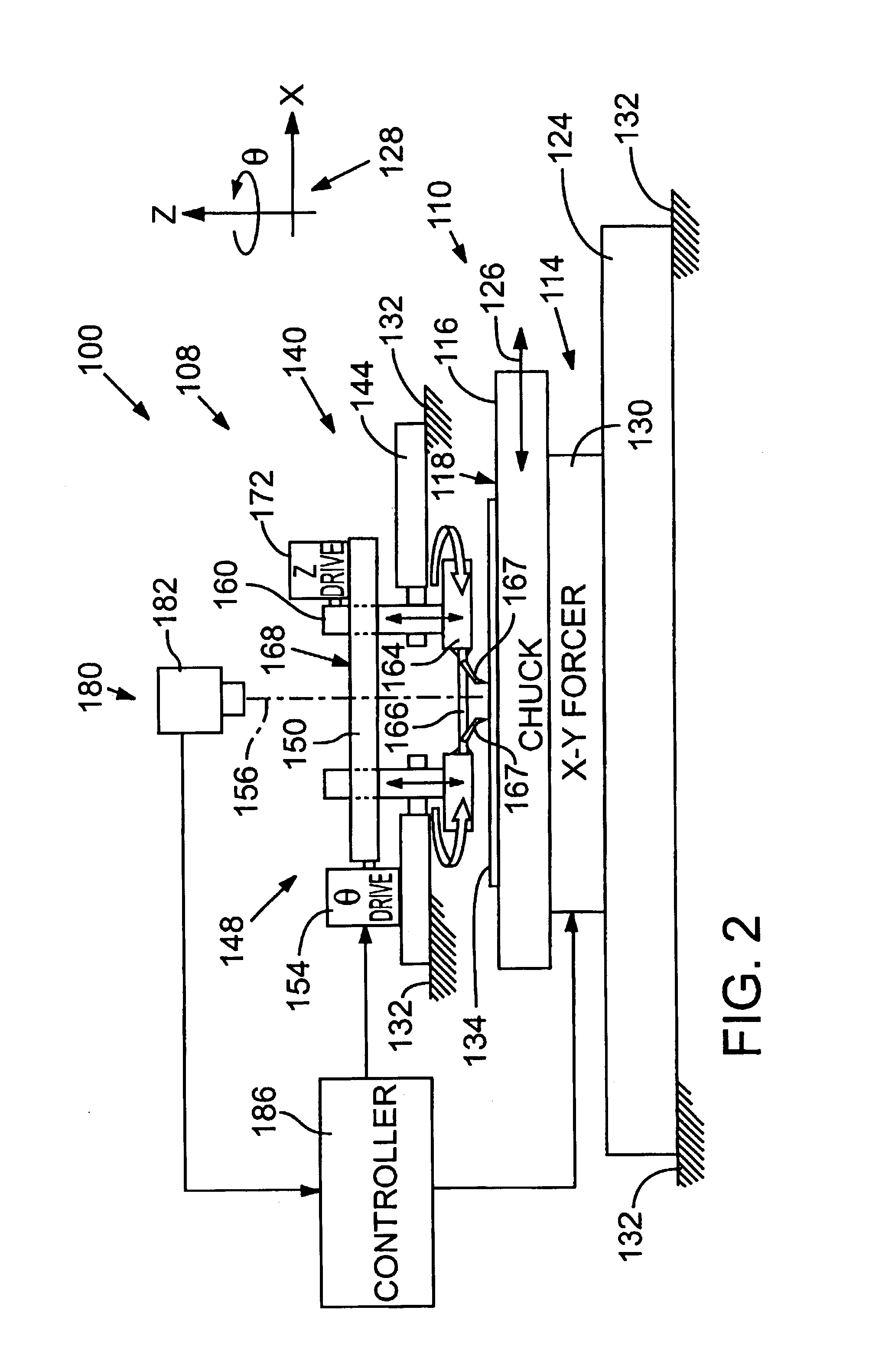
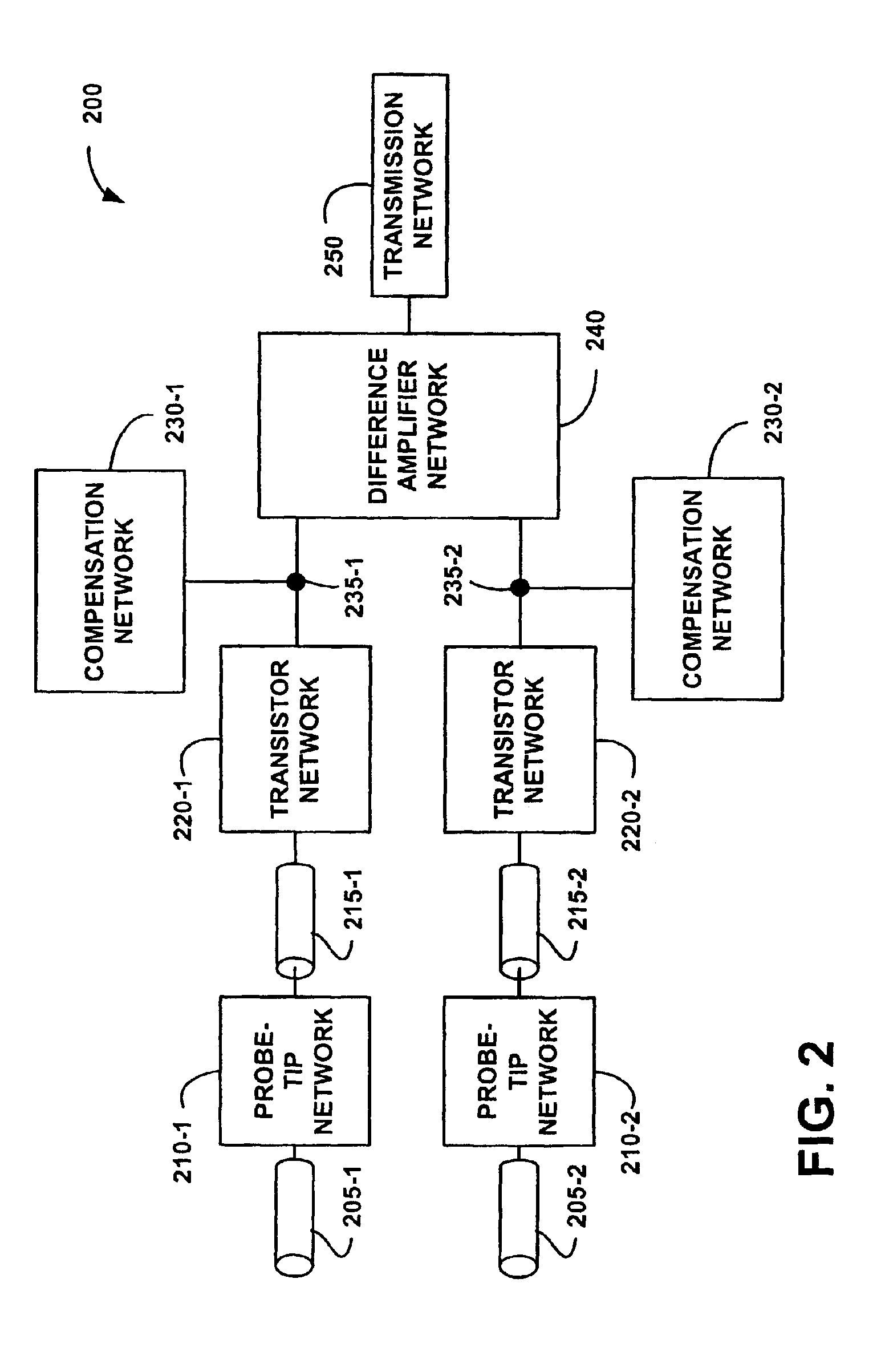
Differential voltage probe
A voltage probe includes a first signal lead configured to receive a first signal from a device under test, a first probe-tip network that is coupled to the first signal lead and that has a frequency response that includes a first transmission zero, a first compensation network that is coupled to the first probe-tip network and that has a frequency response that includes a first transmission pole, a second signal lead configured to receive a second signal from the device under test, a second probe-tip network that is coupled to the second signal lead and that has a frequency response that includes a second transmission zero, a second compensation network that is coupled to the second probe-tip network and that has a frequency response that includes a second transmission pole, and a differential amplifier circuit that is coupled to the first compensation network and to the second compensation network, and that is configured to provide a third signal that is responsive to the first signal and to the second signal. Methods and other systems for providing electrical connections to devices under test are disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Multiple-chip probe and universal tester contact assemblage
InactiveUS6970005B2Shorten the timeManufactured rapidly and economicallySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement leads/probesElectricityProbe card
A probe card assemblage for simultaneously testing one or more integrated circuit chips including an interposer having on one surface a plurality of protruding contact elements for electrically contacting one or more chips of a wafer positioned atop a layer of compliant material, and arrayed in a pattern corresponding to a chip pads, a series of conductive vias through the electrically insulating interposer which connect the chip contact elements with an arrangement of leads terminating in a universal arrangement of connectors on the second surface, and a probe card with connectors mating to those on the interposer. The connectors on the interposer is secured are secured to those on the probe card, thereby providing a vertical probe assemblage which makes use of ultrasonic energy to minimize scrub or over travel. The universal probe card is specific to a tester configuration and common to a family of circuits to be tested.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
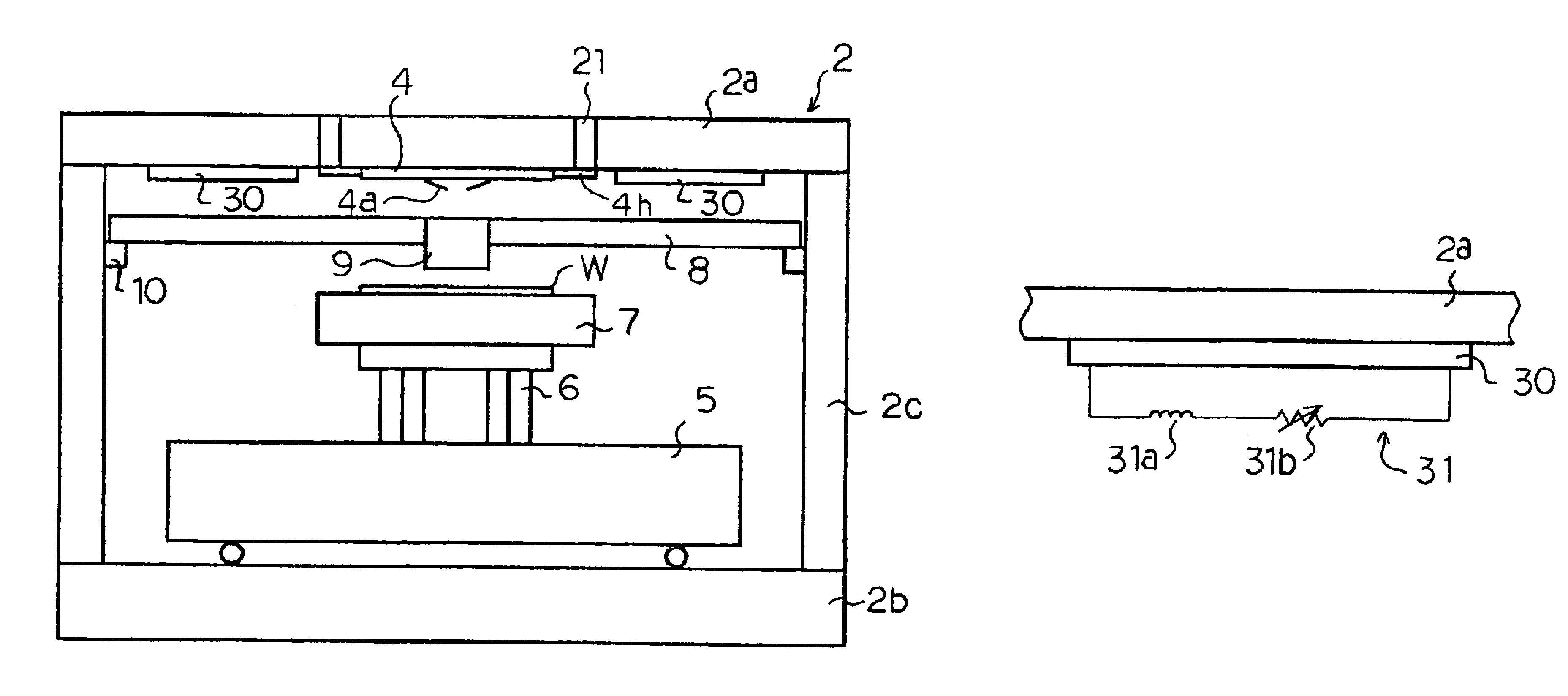
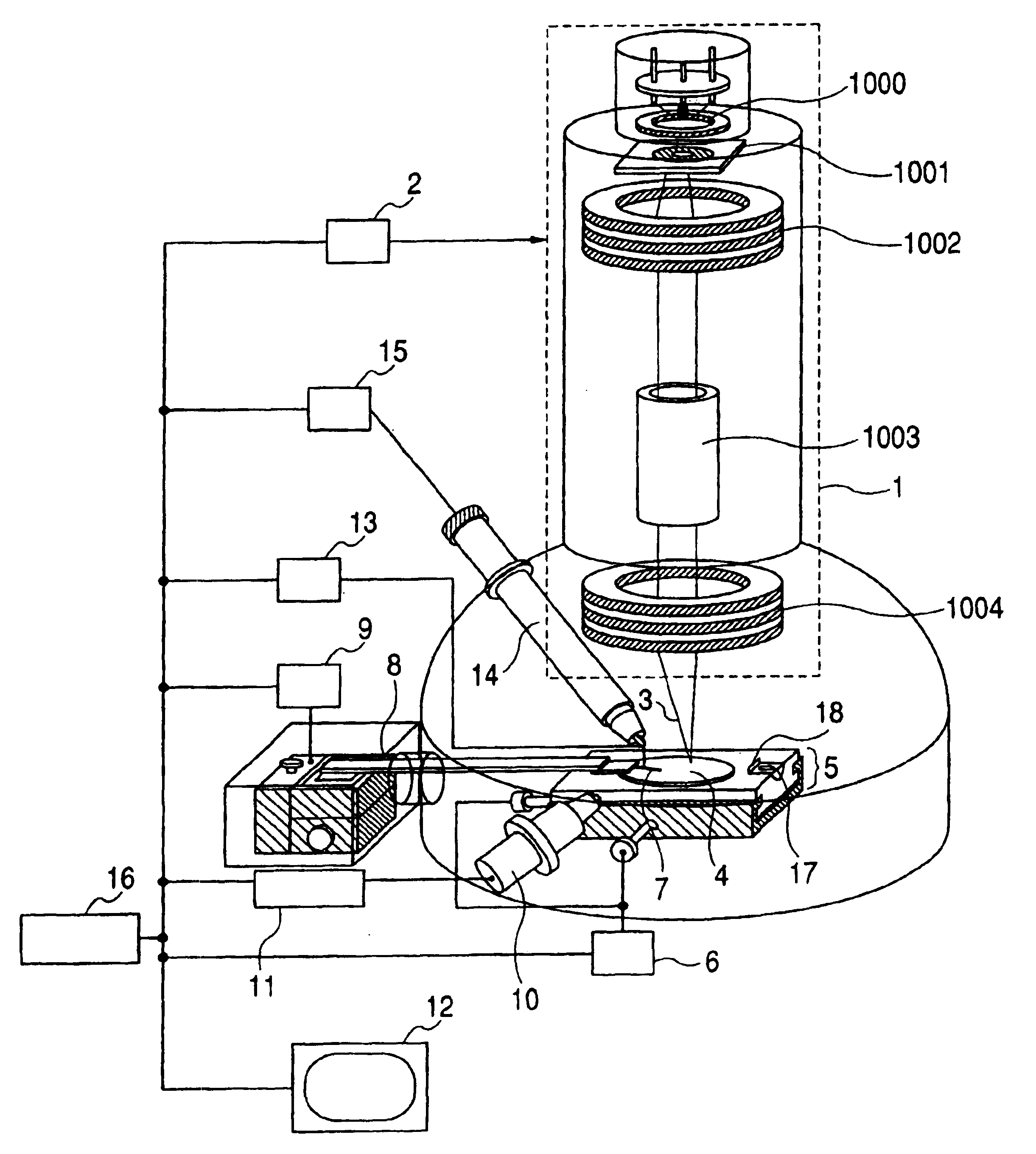
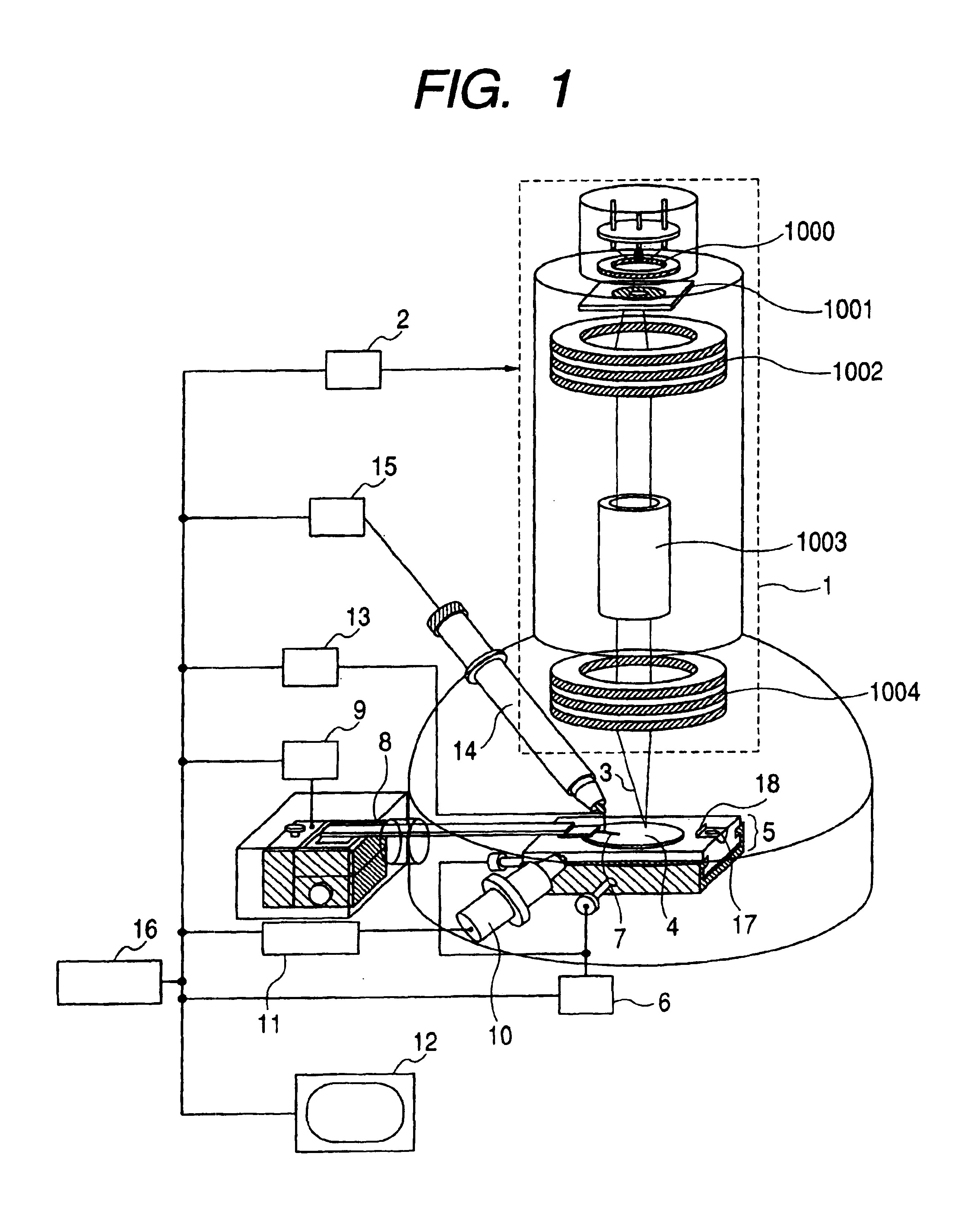
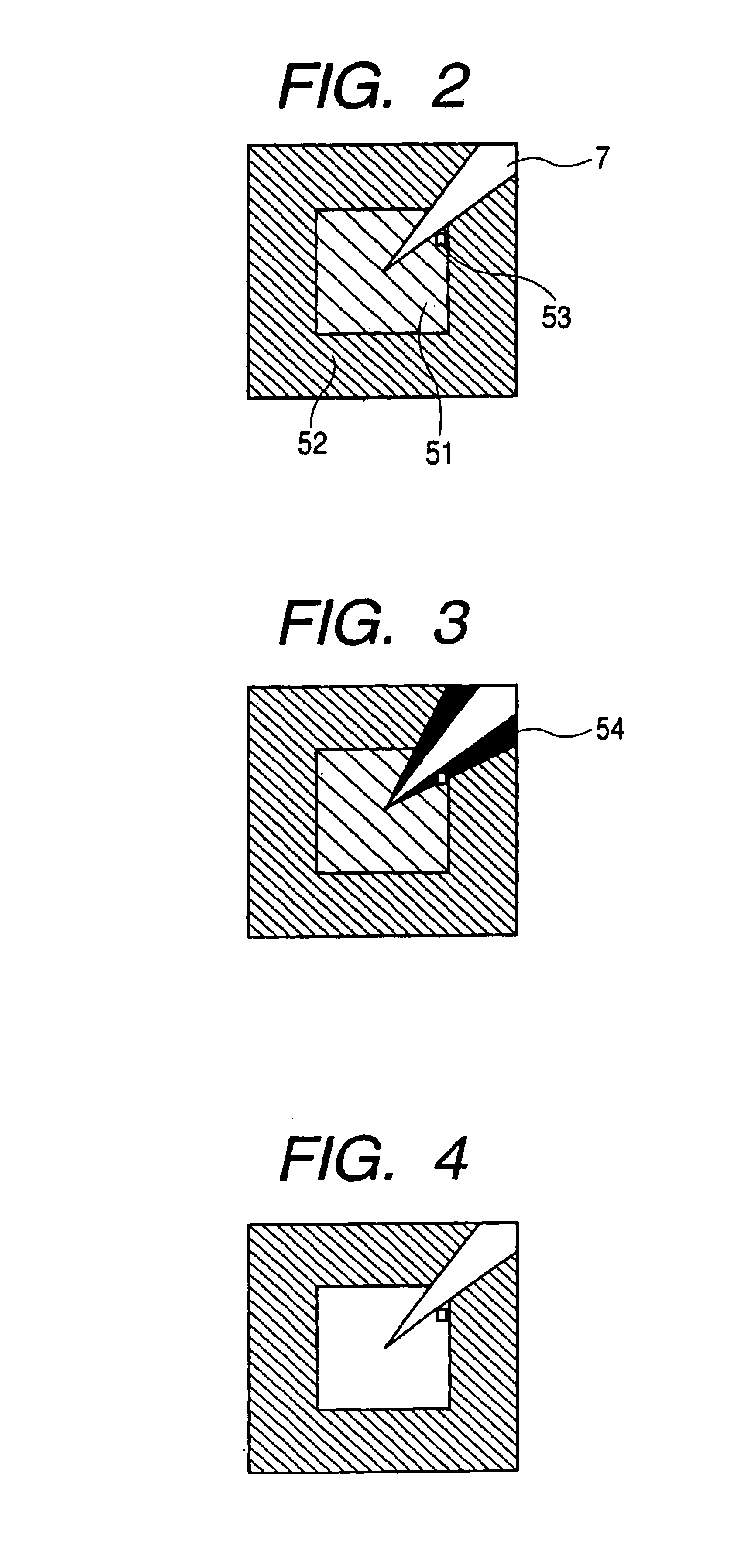
Probe driving method, and probe apparatus
InactiveUS6960765B2Easy to controlDecrease in luminanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInstrumental componentsIon beamSample image
A probe driving method and a probe apparatus for bringing a probe into contact with the surface of a sample in a safe and efficient manner by monitoring the probe height. Information about the height of the probe from the sample surface is obtained by detecting a probe shadow appearing immediately before the probe contacts the sample, or based on a change in relative positions of a probe image and a sample image that are formed as an ion beam is irradiated diagonally.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Popular searches
Near-field systems with capacitive coupling Antennas Sensing by electromagnetic radiation Near-field transmission Electromagnetic transmission Electric signalling details Radiofrequency circuit testing Oscillations generators Frequency to phase shift conversion Input/output processes for data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com