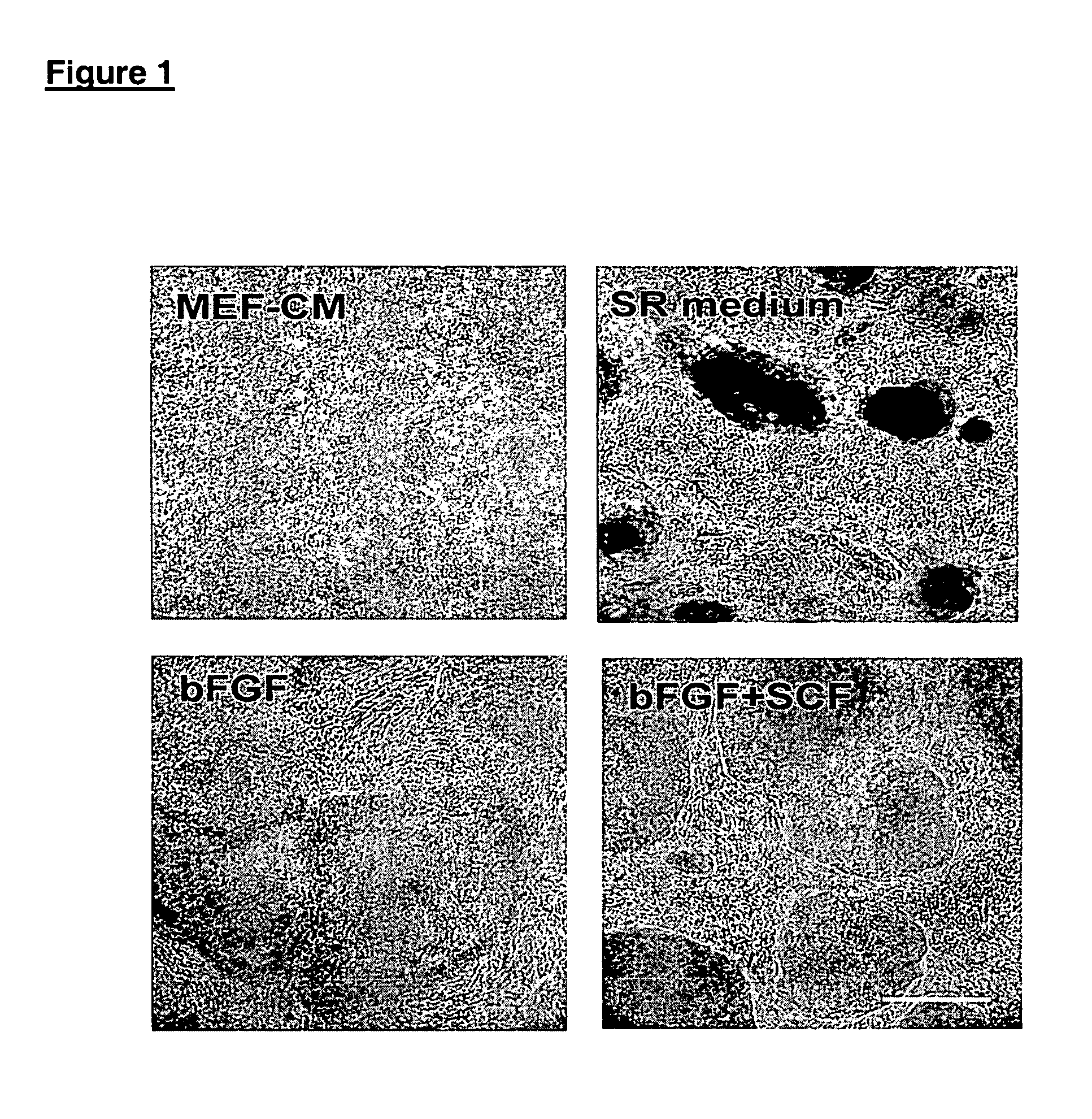
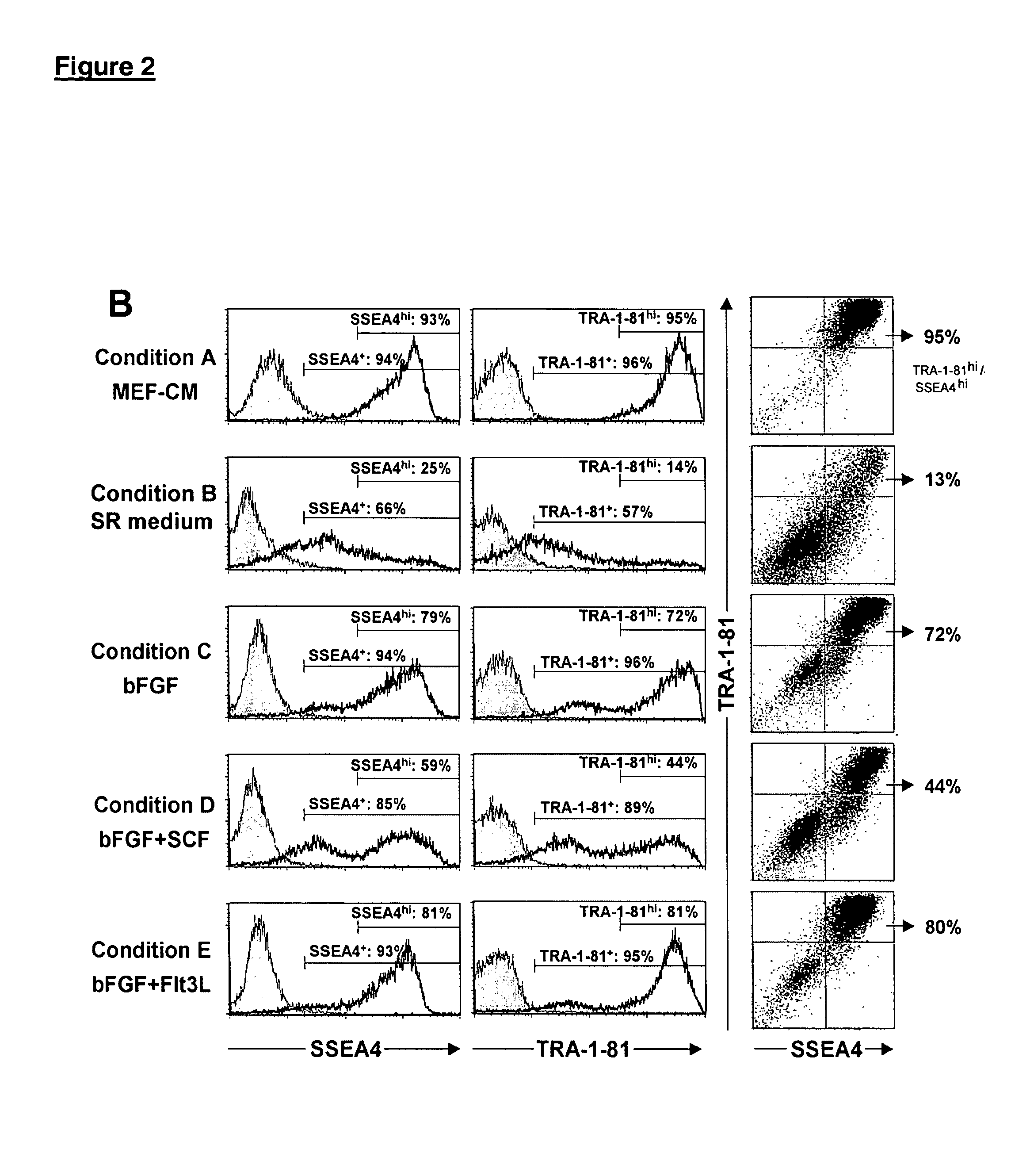
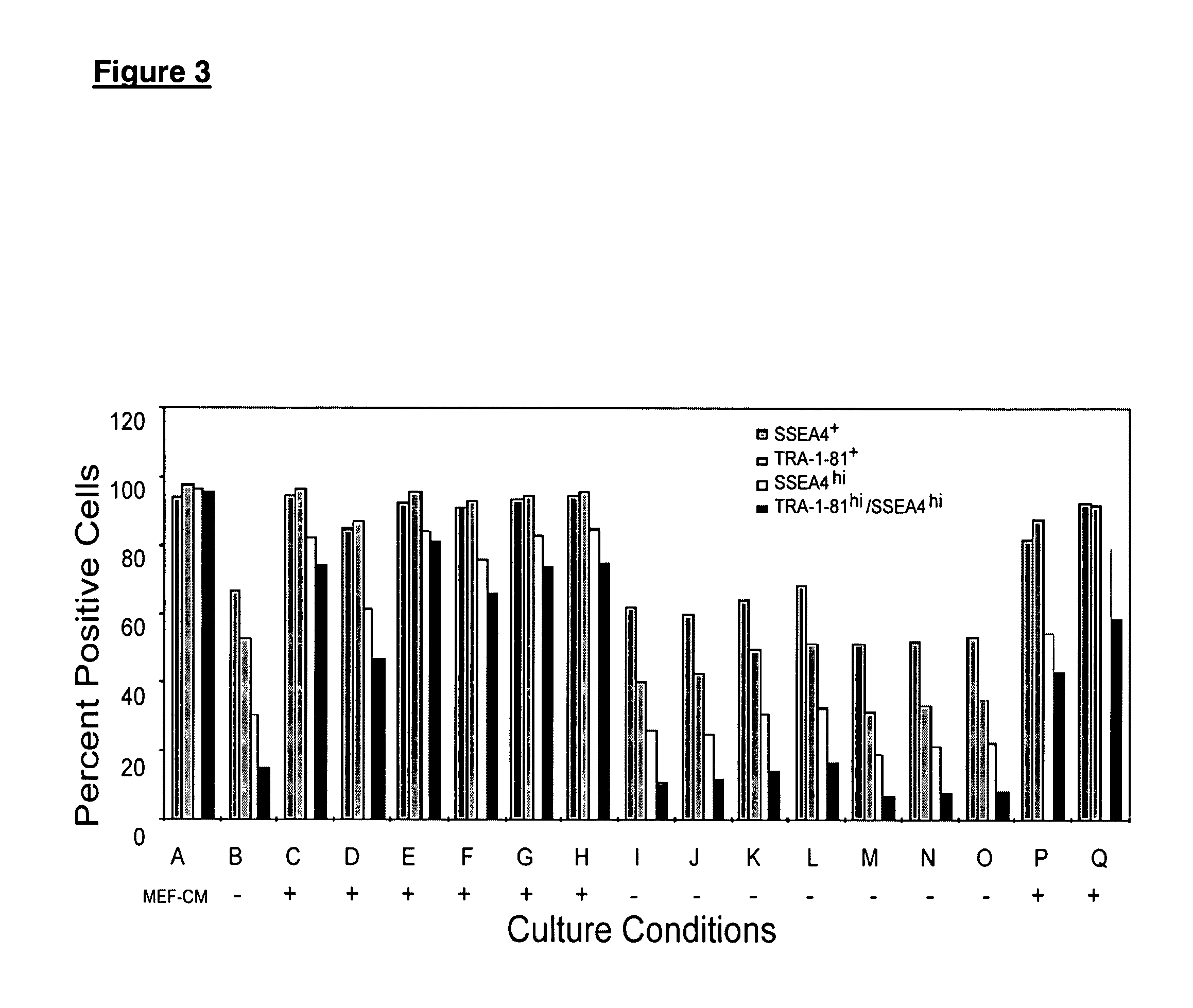
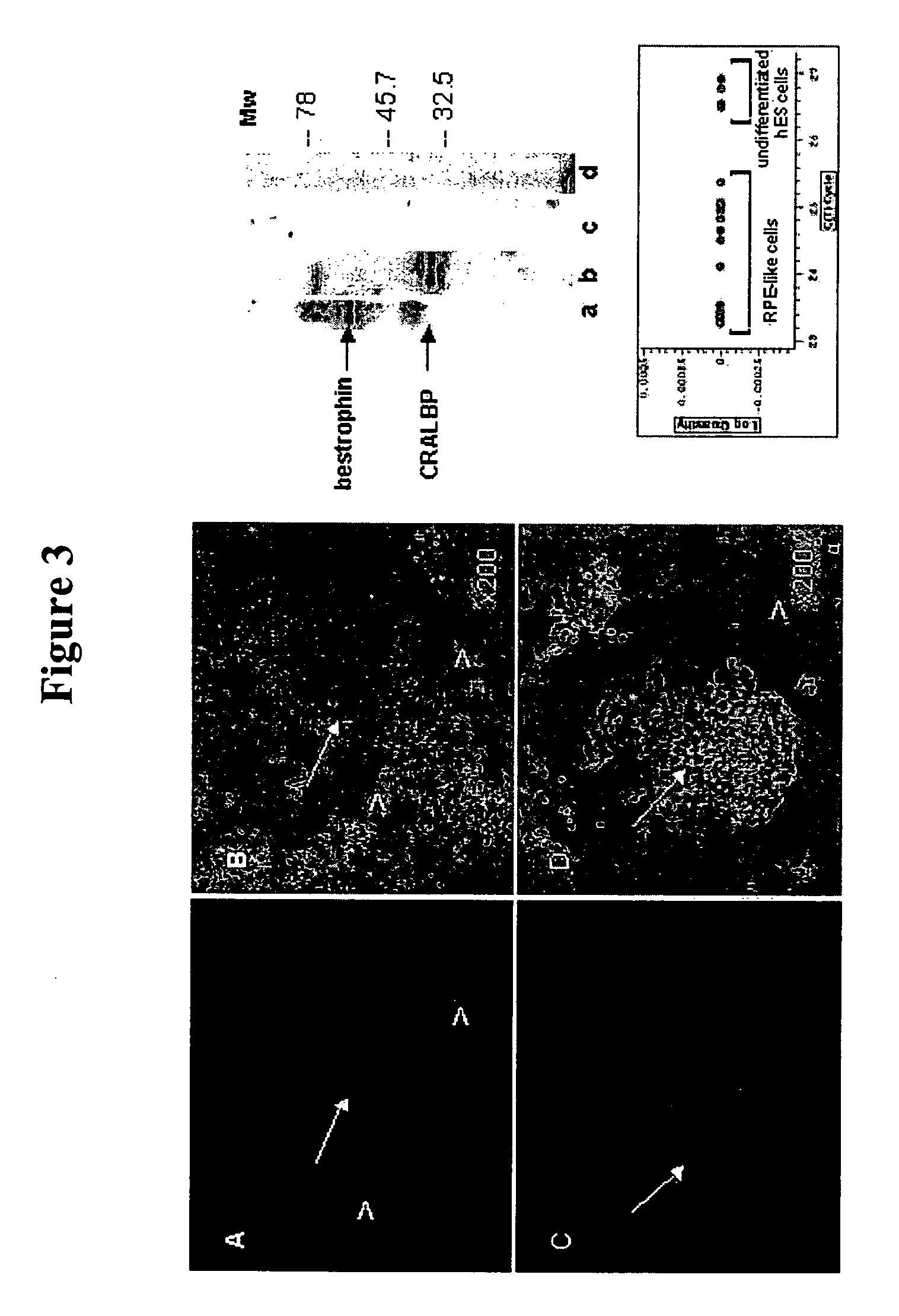
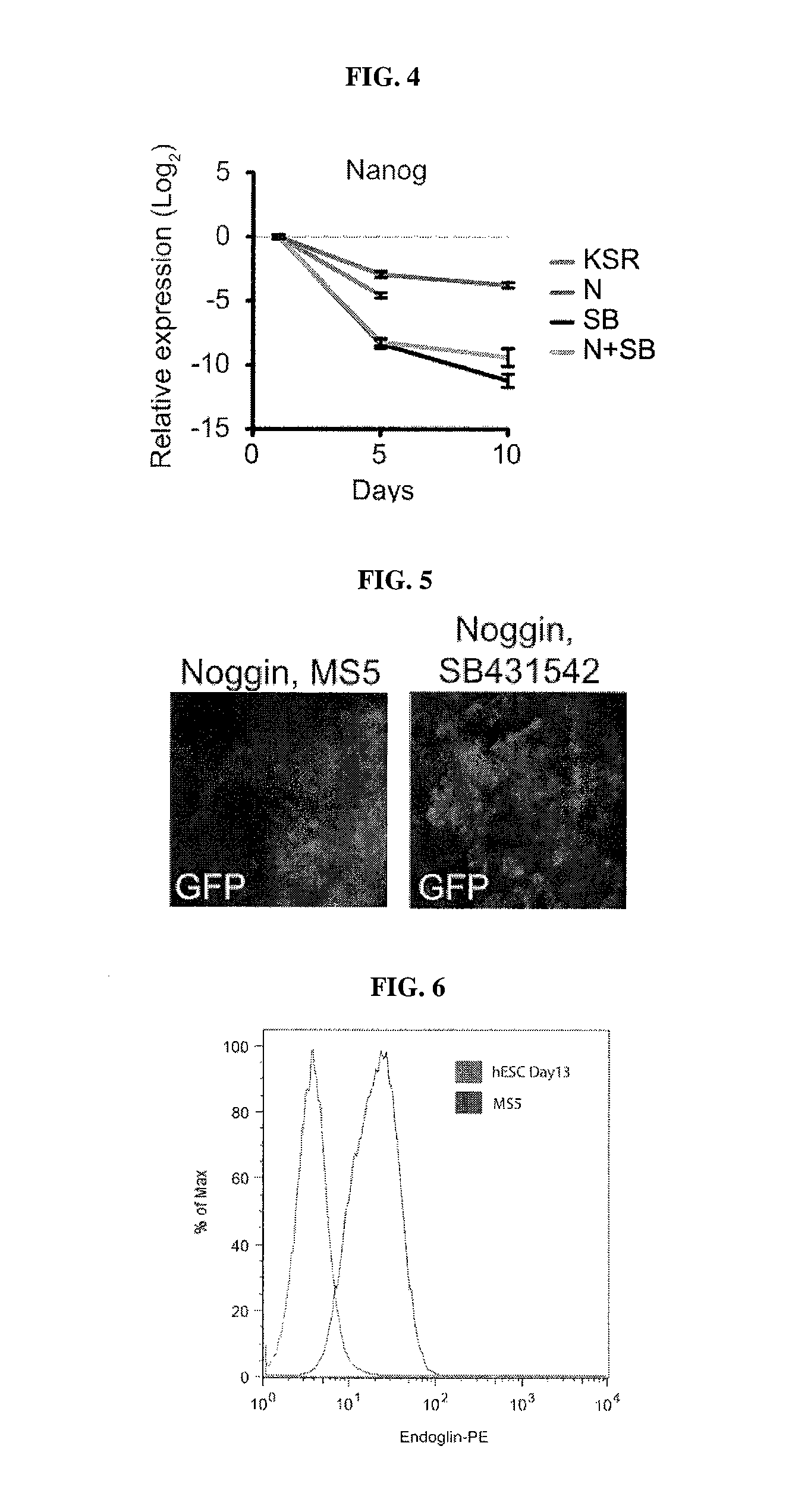
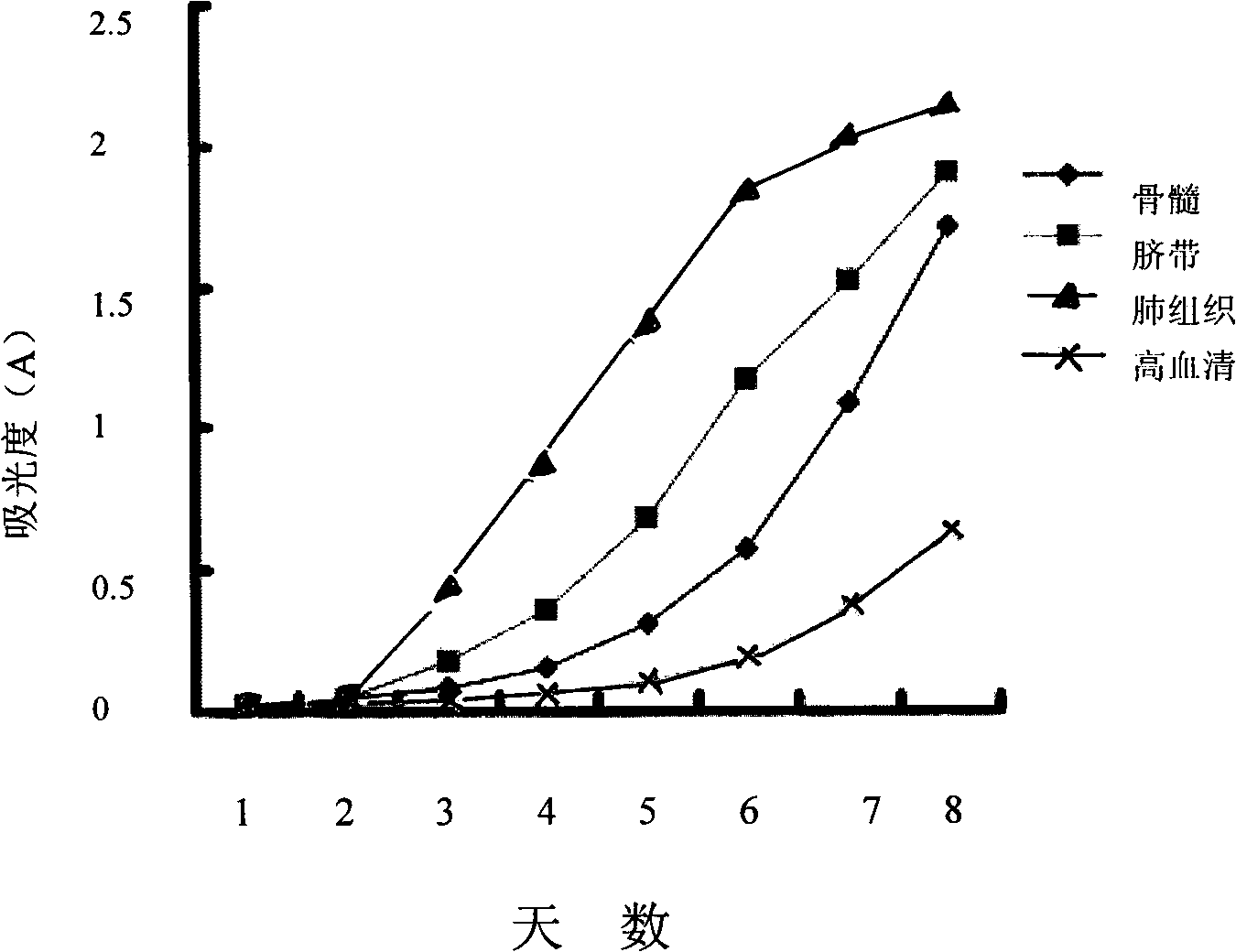
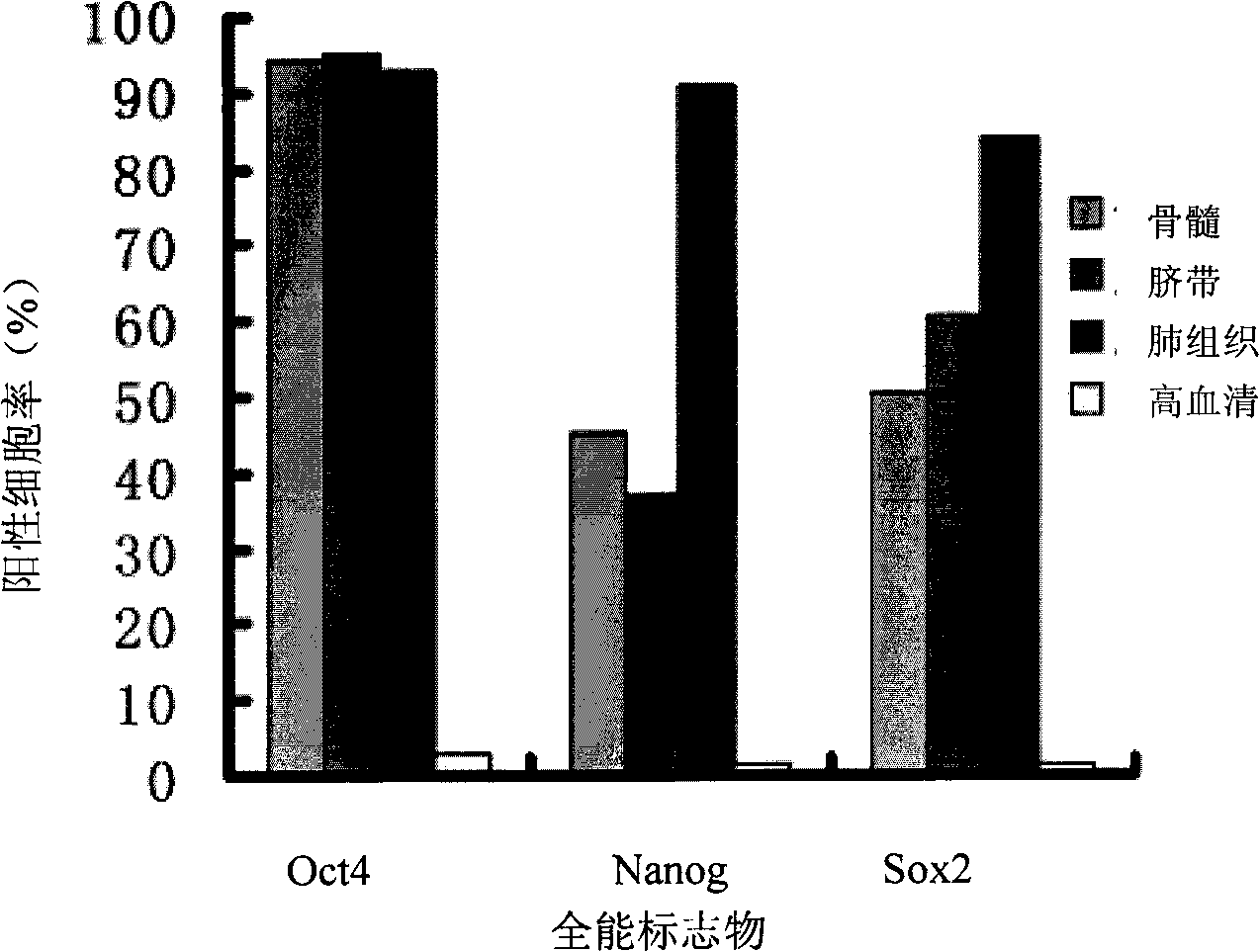
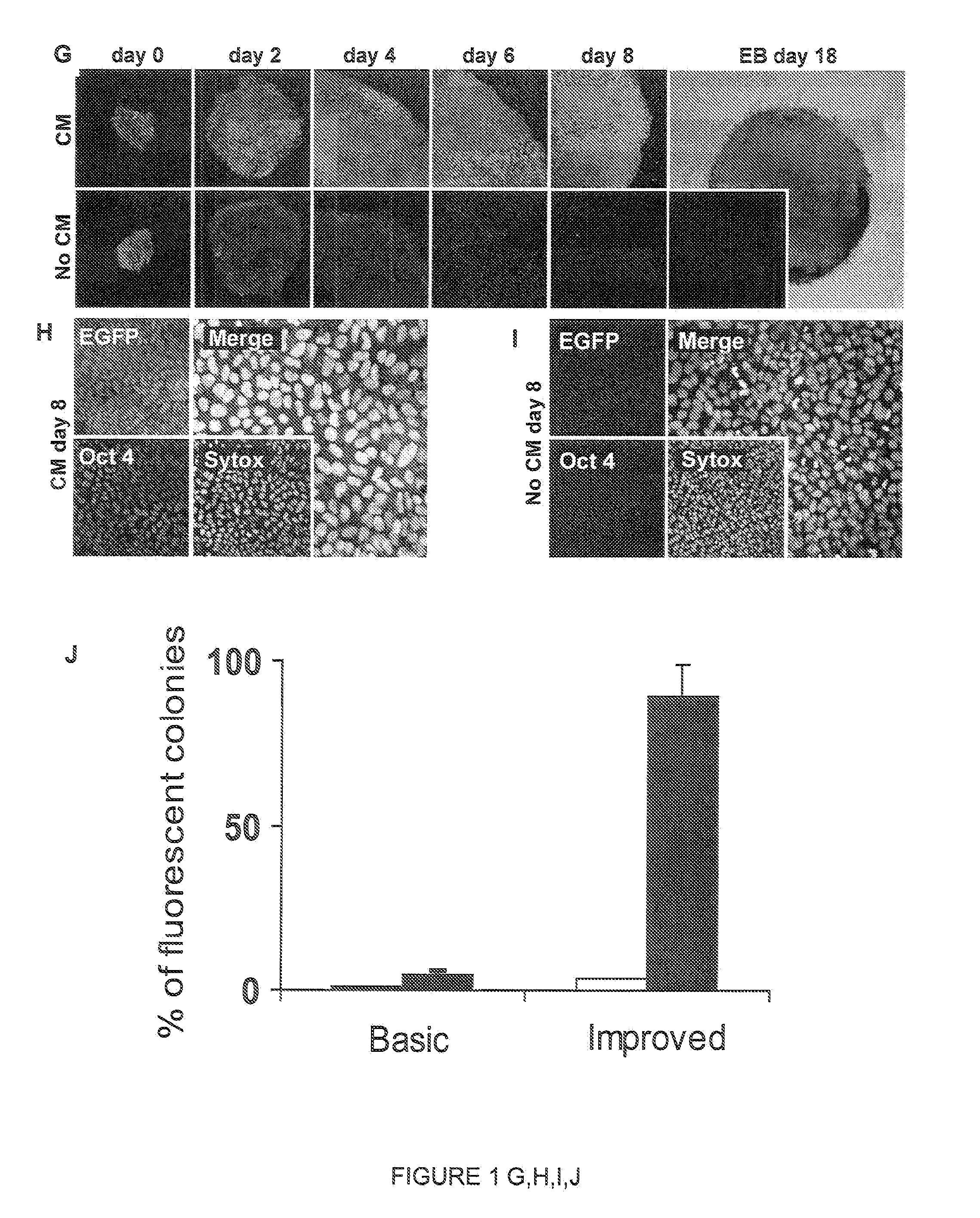
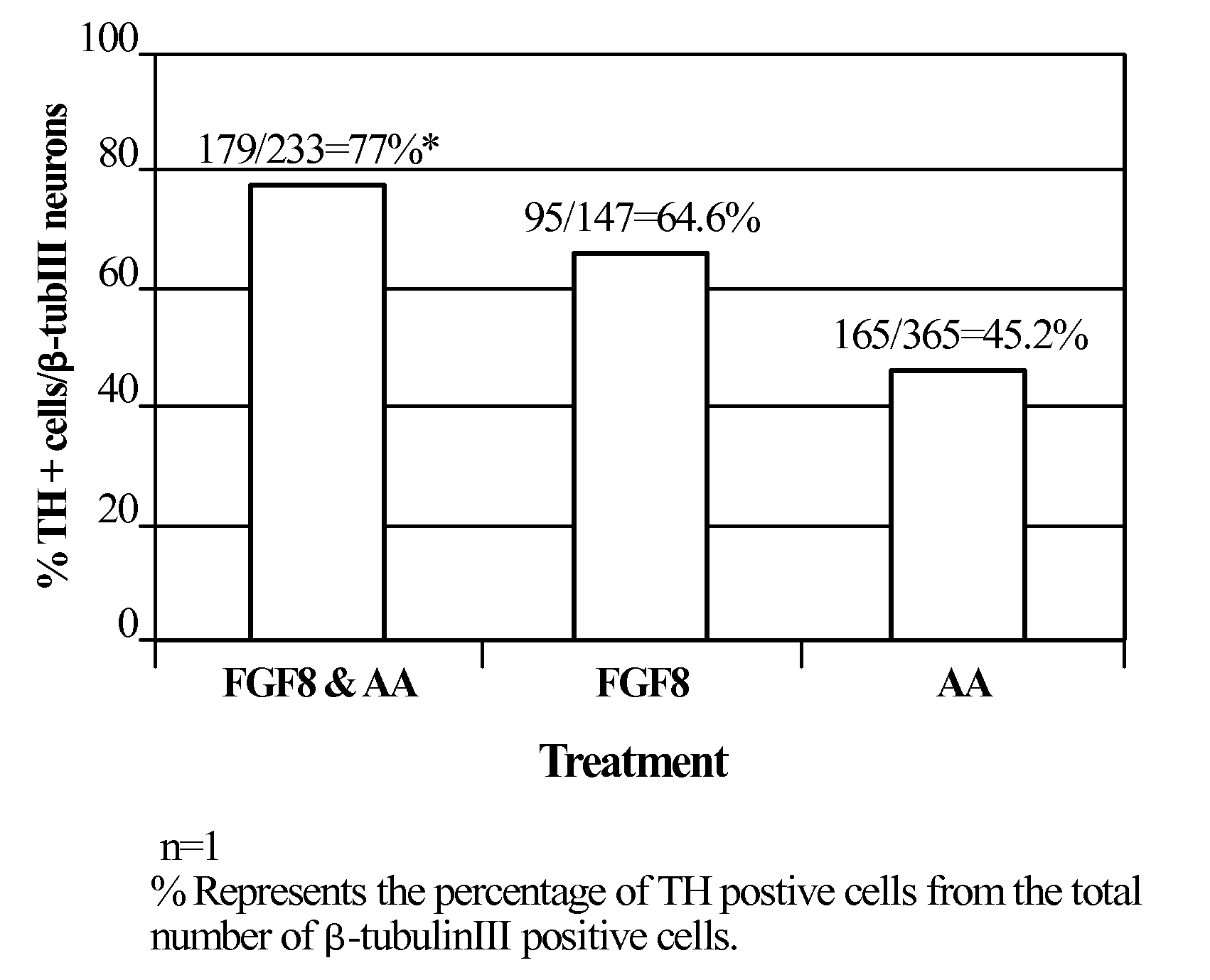
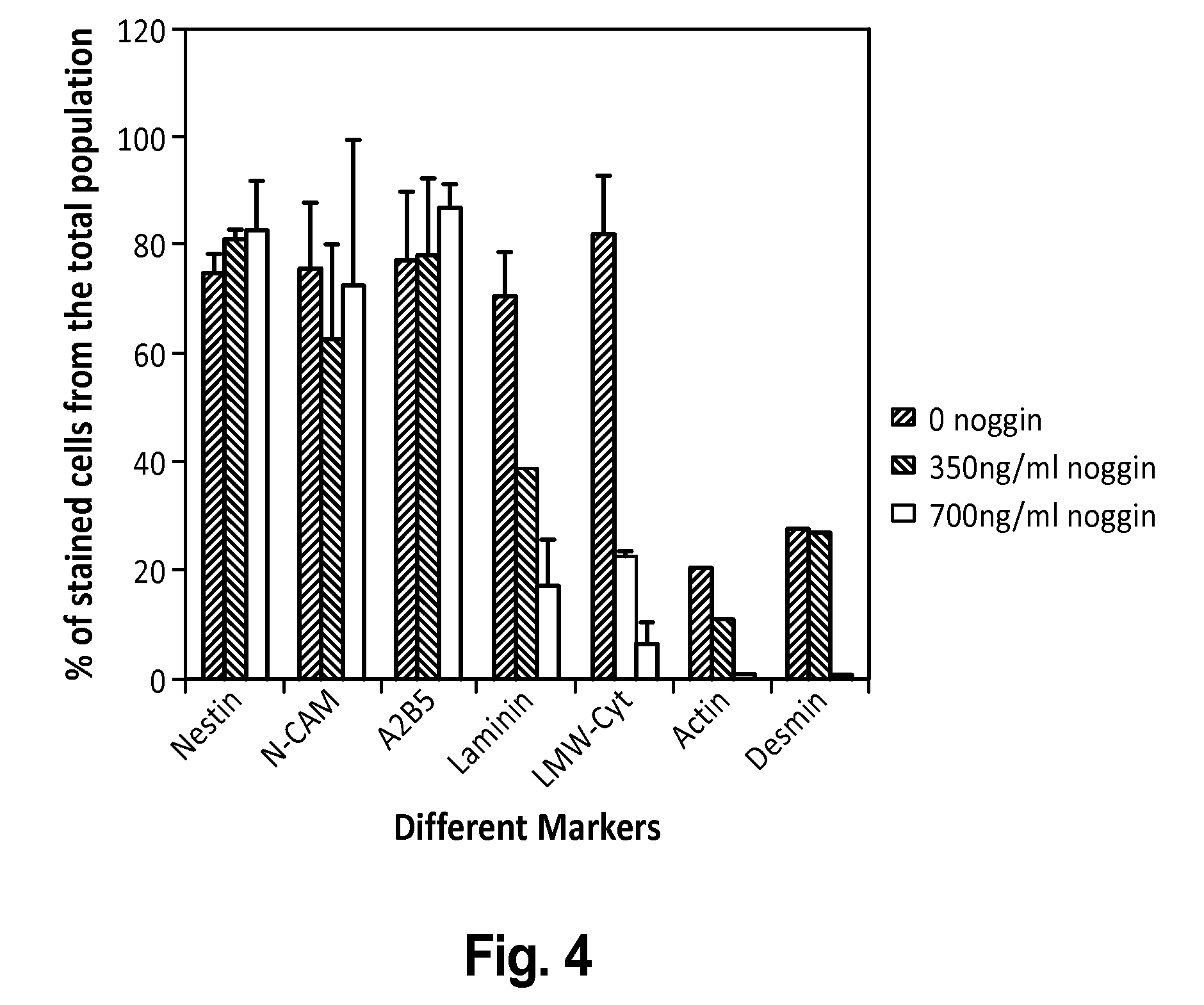
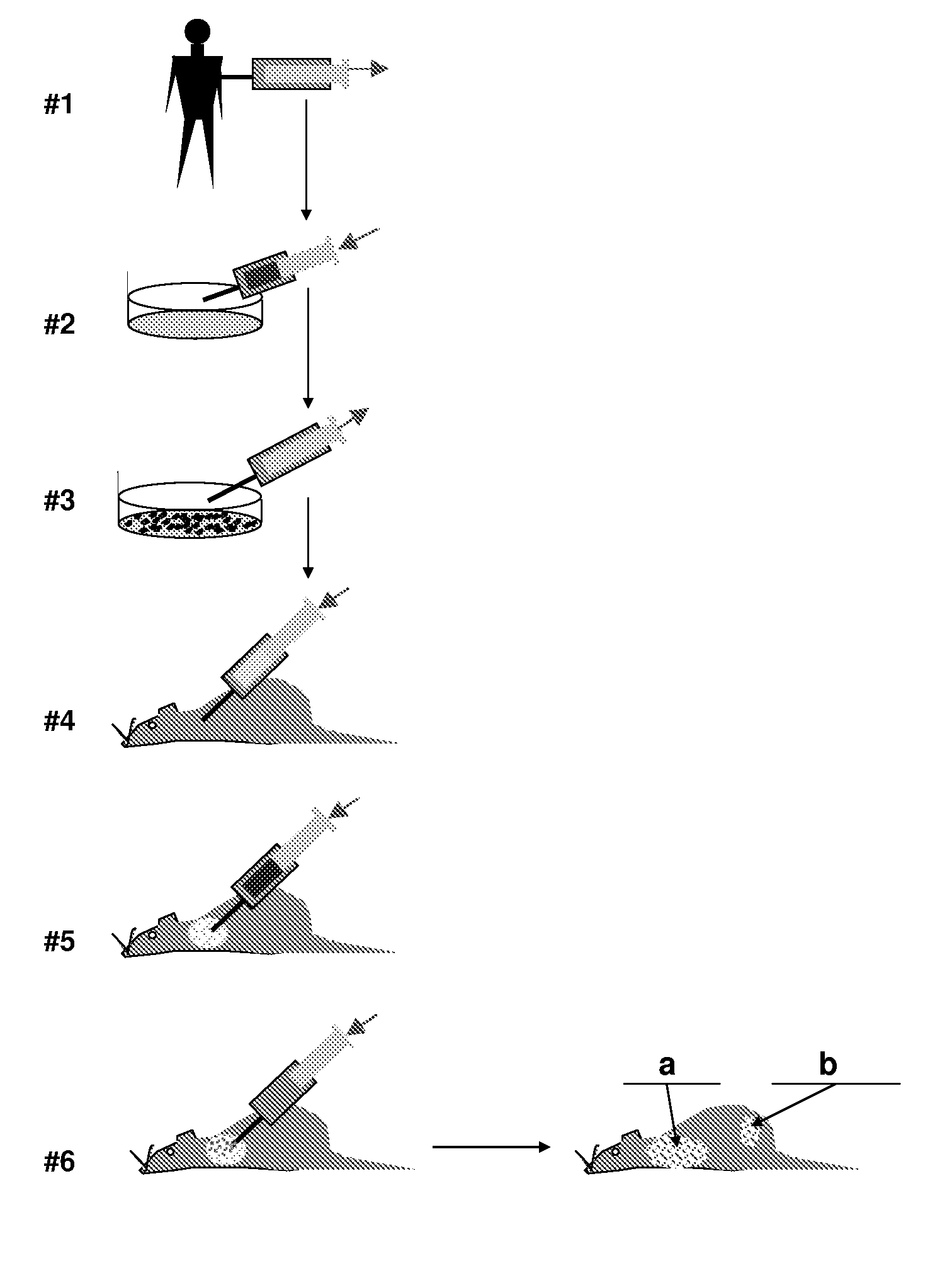
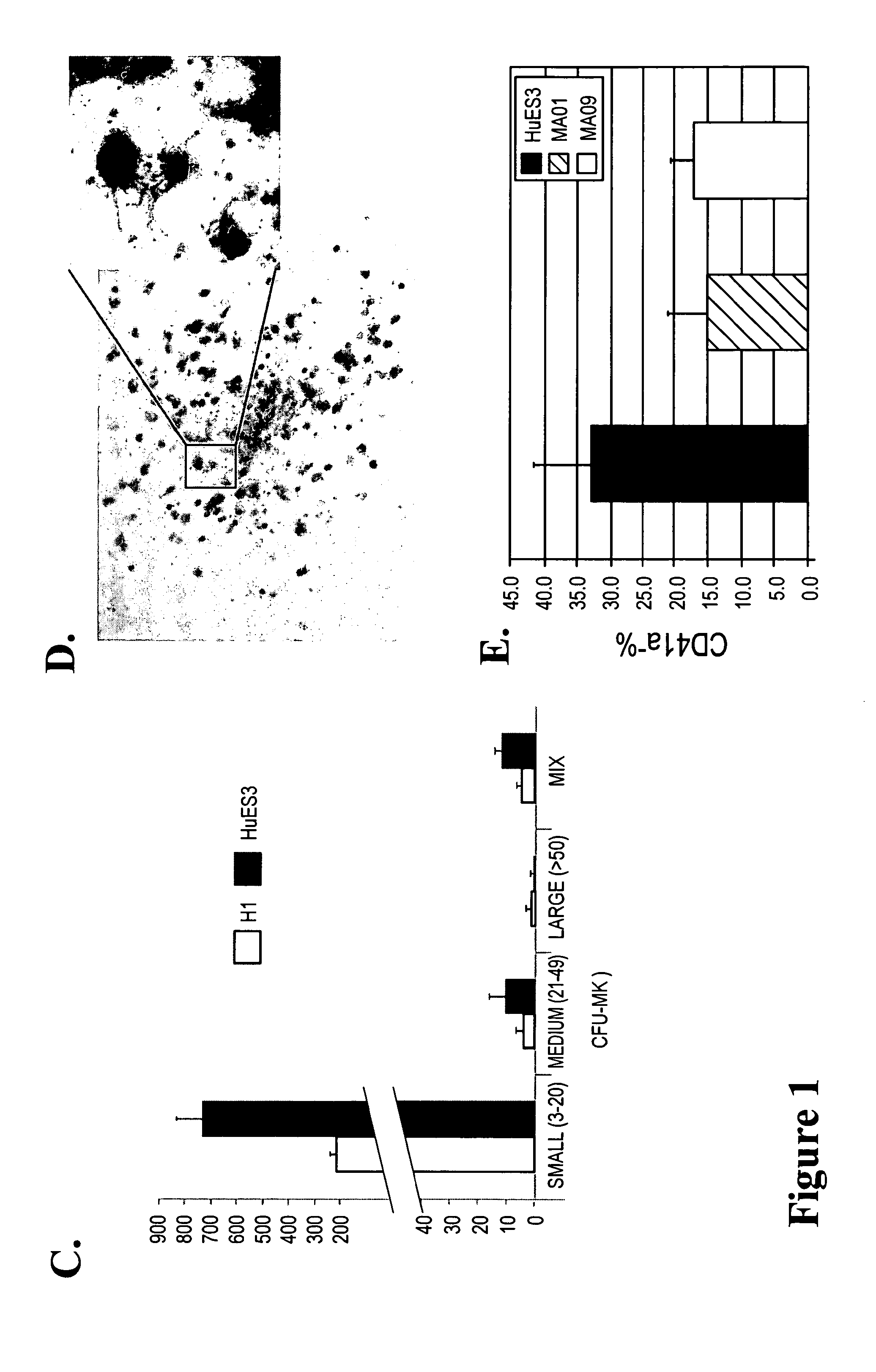
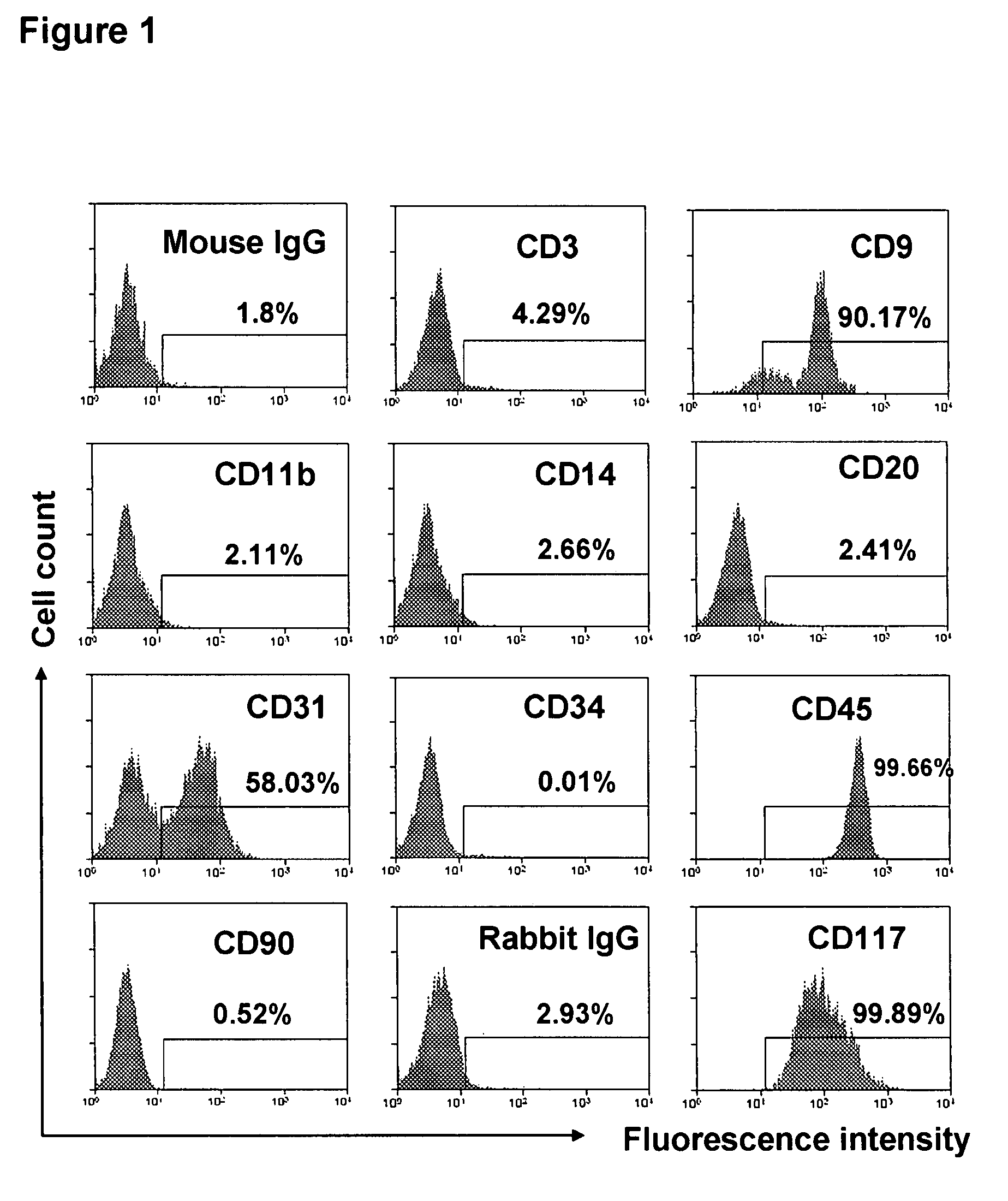
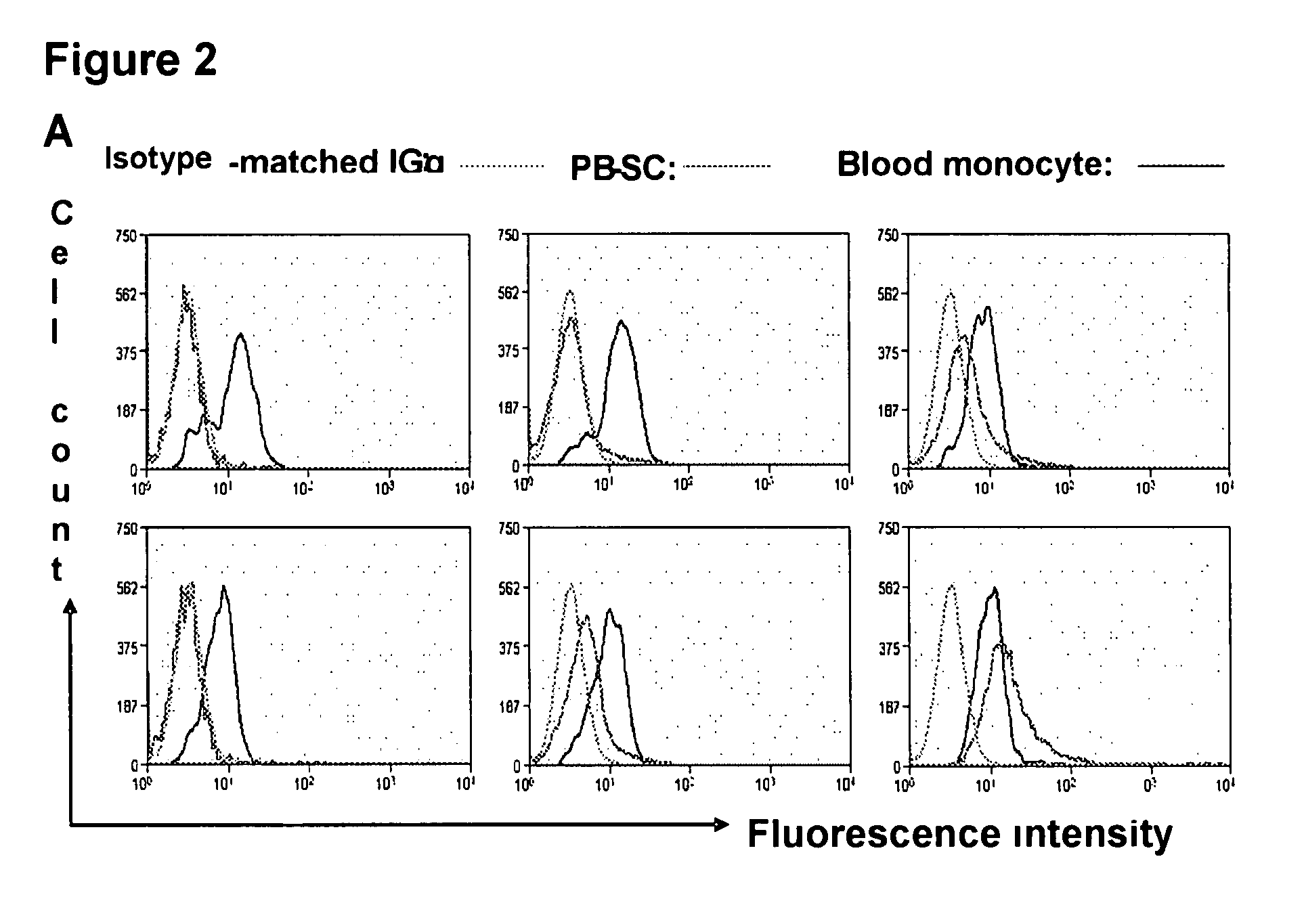
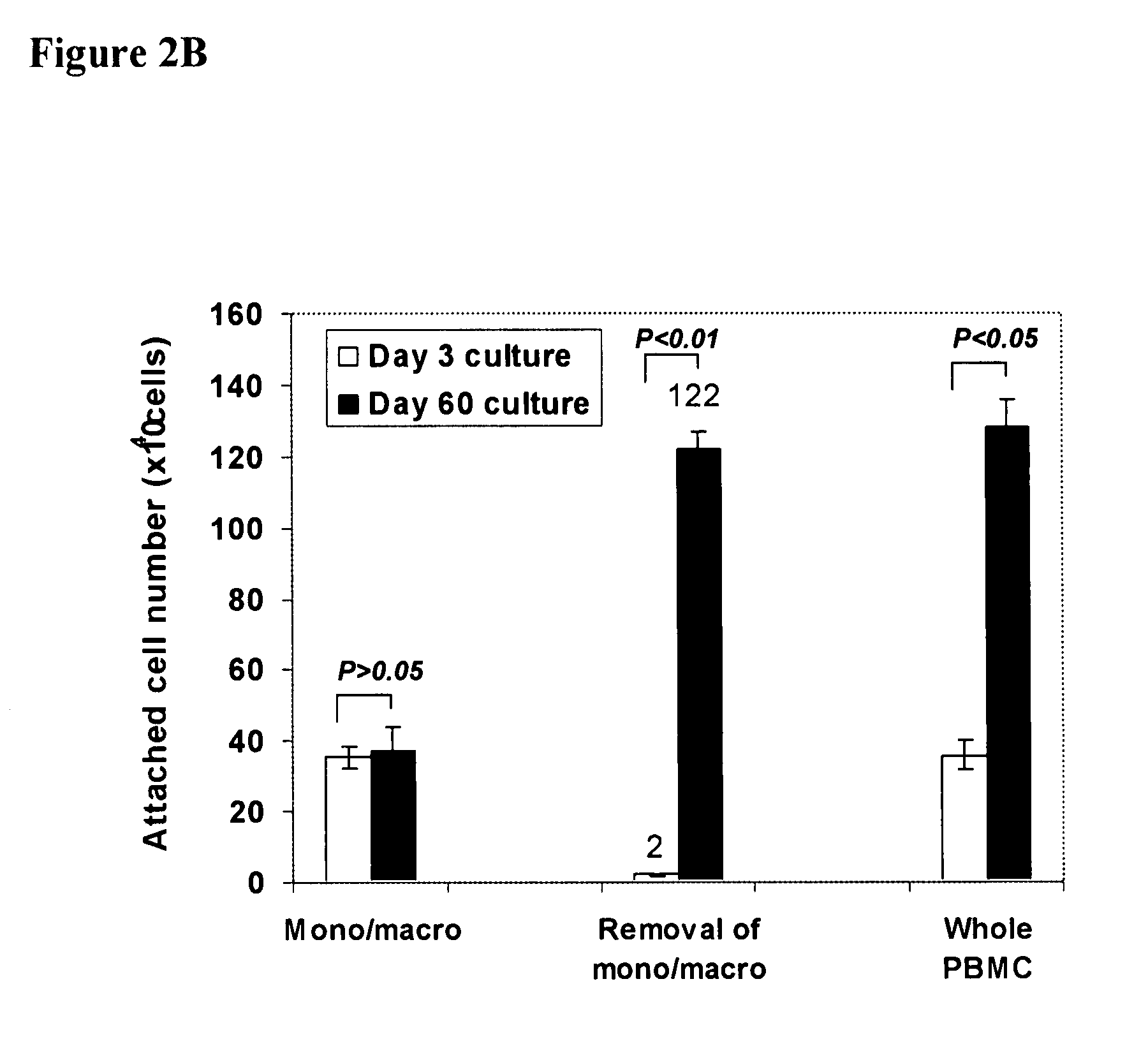
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
241 results about "Cells embryo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells or ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells.
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Chimeric bird from embryonic stem cells
Sustained cultures of avian embryonic stem cells are provided. Injection of avian embryonic stem cells into recipient embryos yields chimeras with a significant contribution from the embryonic stem cell phenotype. Transgene encoding exogenous proteins are stably integrated in the embryonic stem cells and are present in the somatic tissue of the resulting chimeras. The transgenes may encode exogenous proteins expressed in endodermal, ectodermal, mesodermal, or extra embryonic tissue. Breeding the resulting chimera yields transgenic birds whose genome is comprised of exogenous DNA.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
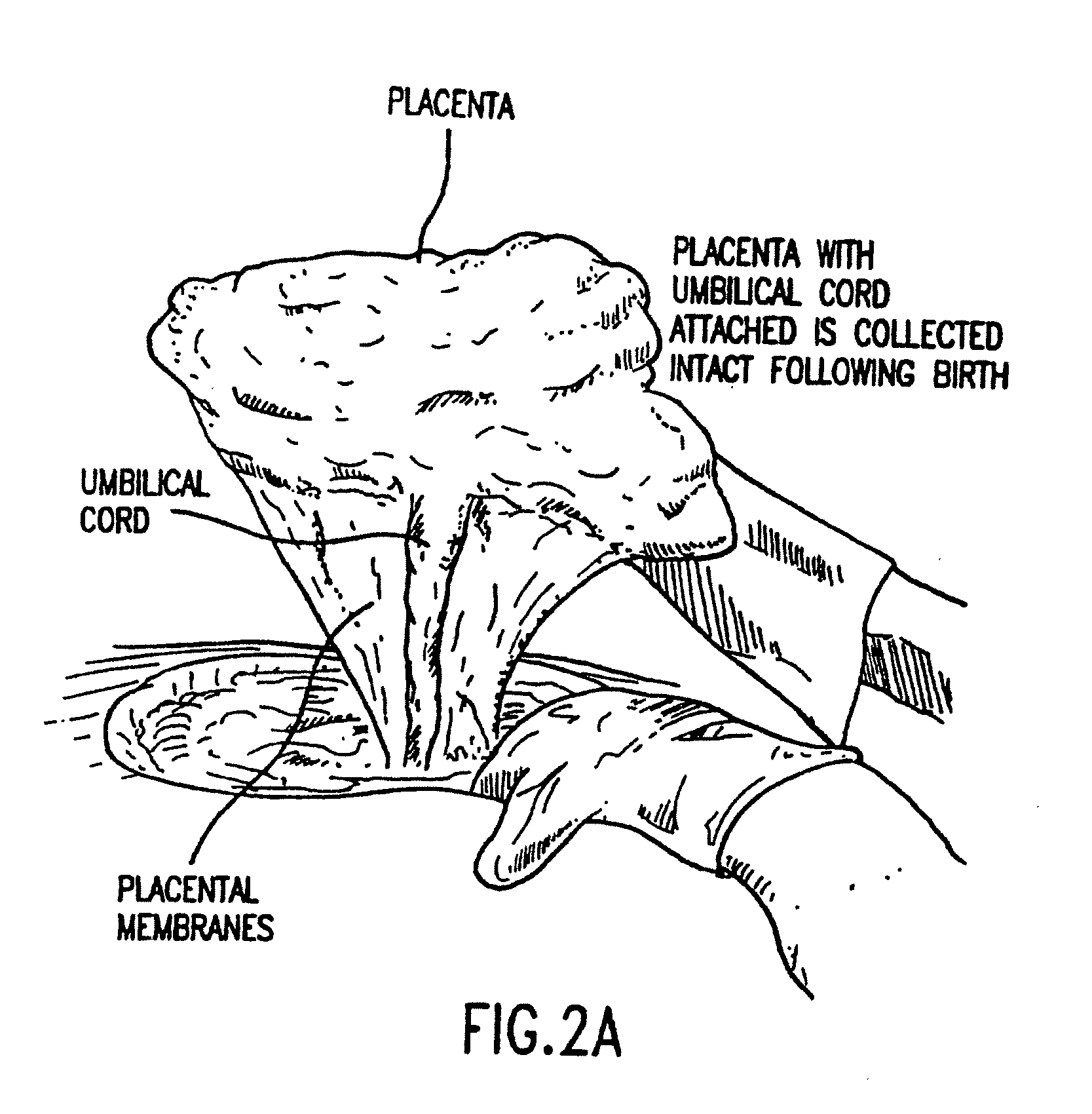
Tissue matrices comprising placental stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Pancreatic and liver endoderm cells and tissue by differentiation of definitive endoderm cells obtained from human embryonic stems
The invention relates to methods that allow for the efficient differentiation to form pancreatic endoderm cells from pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells and definitive endoderm cells. The invention is directly applicable to the ultimate generation of pancreatic beta cells that could be used as part of a therapy to treat or even cure diabetes. Additionally, the present invention may be used to generate liver endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cells and definite endoderm cells as well. This invention relates to a method for generating definitive endoderm and pancreatic endoderm cells from stem cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells using defined media in the absence of feeder cells. A simply two step procedure to provide pancreatic endoderm cells from embryonic stem cells represents further embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7455983B2Cost-effectiveRapid productionMicroorganismsDrug screeningGerm layerLipid formation
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by defined components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. The medium contains an isotonic buffer, a blend of essential nutrients such as protein and lipids, and an effective growth factor or combination of factors that promote proliferation while inhibiting differentiation. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium on an extracellular matrix according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Modalities for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the retina
ActiveUS20070031386A1Quality improvementReduce complexityBiocideSenses disorderCell basedRetinal progenitor
This invention relates to methods for improved cell-based therapies for retinal degeneration and for differentiating human embryonic stem cells and human embryo-derived into retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells and other retinal progenitor cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
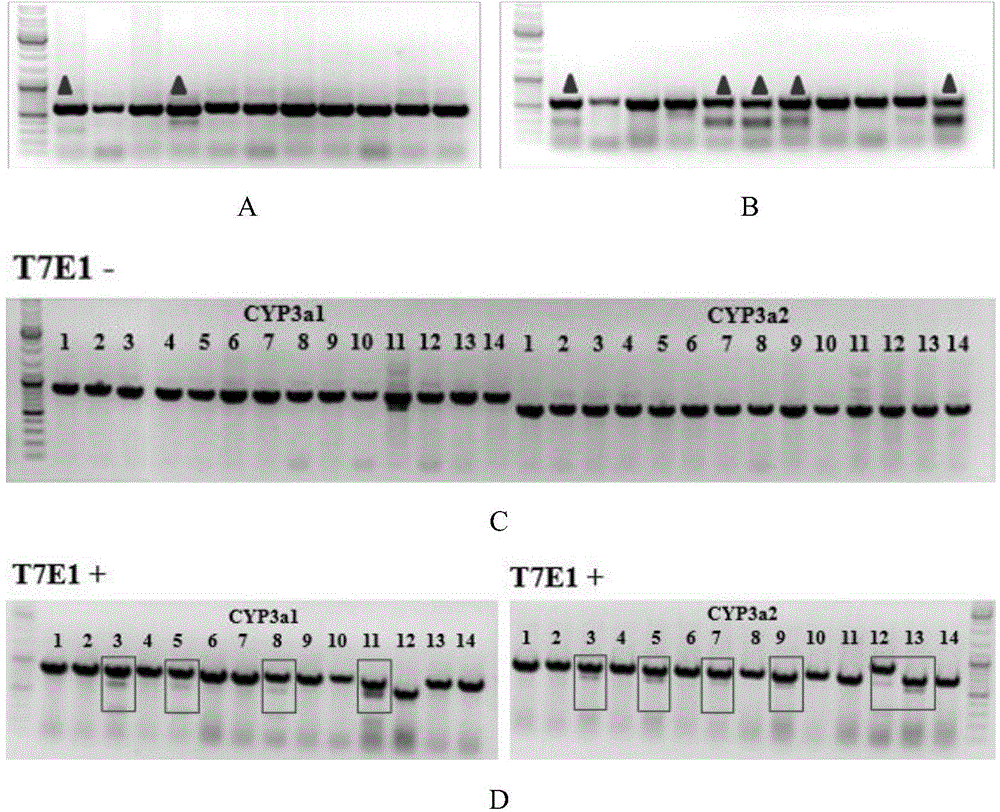
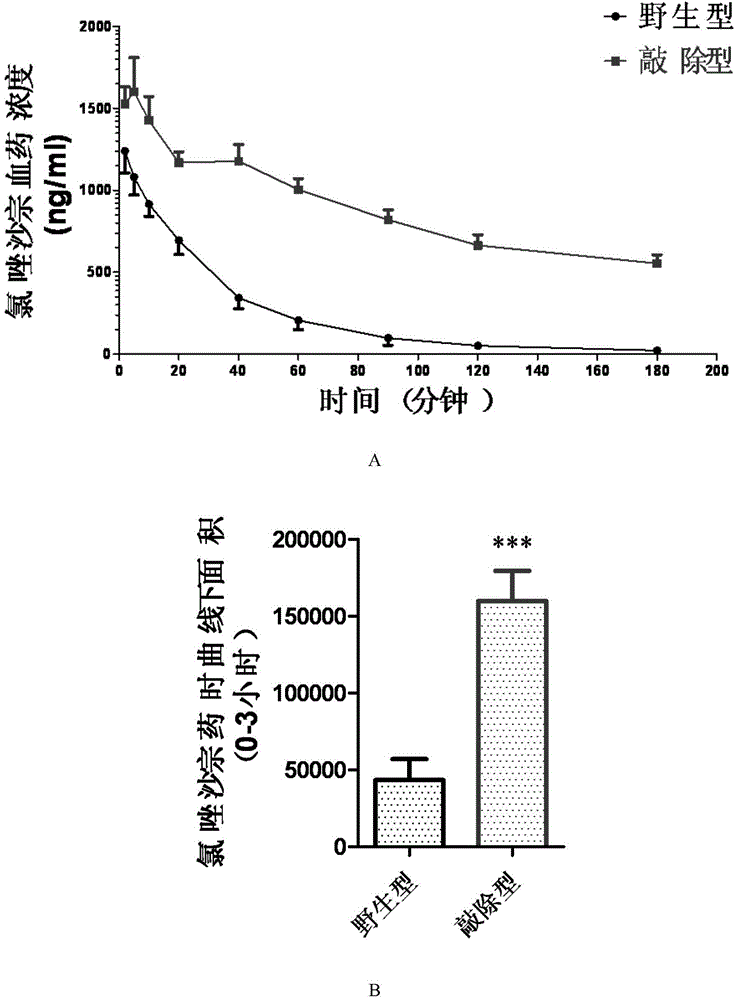
Cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and preparation method of liver microsome of the rats
ActiveCN106148416ADiverse in vitro modelsImprove transfer abilityMicroinjection basedFermentationHepaticaMicro injection
The invention provides a cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and a preparation method of liver microsome of the rats. The Cyp gene knock-out herein includes Cyp single gene knock-out and Cyp multiple gene knock-out. In the method, firstly a Cyp gene knocked-out rat is constructed by means of a CRISPR / Cas system, which includes selection of a knocked-out target site, in-vitro synthesis and transcription of sg RNA and Cas9m RNA, preparation of a pseudopregnant female rat, in-vitro micro-injection and transplanting of a single-cell embryo, and cultivation of the rat, and finally, a homozygote Cyp gene knocked-out rat can be cultured. Furthermore, the liver of the Cyp gene knocked-out rat is extracted and is subjected to homogenization and differential centrifugation to prepare the liver microsome of the rat in Cyp gene deletion. The invention also provides an application of the Cyp gene knocked-out rats and the liver microsome thereof in study on drug metabolism.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
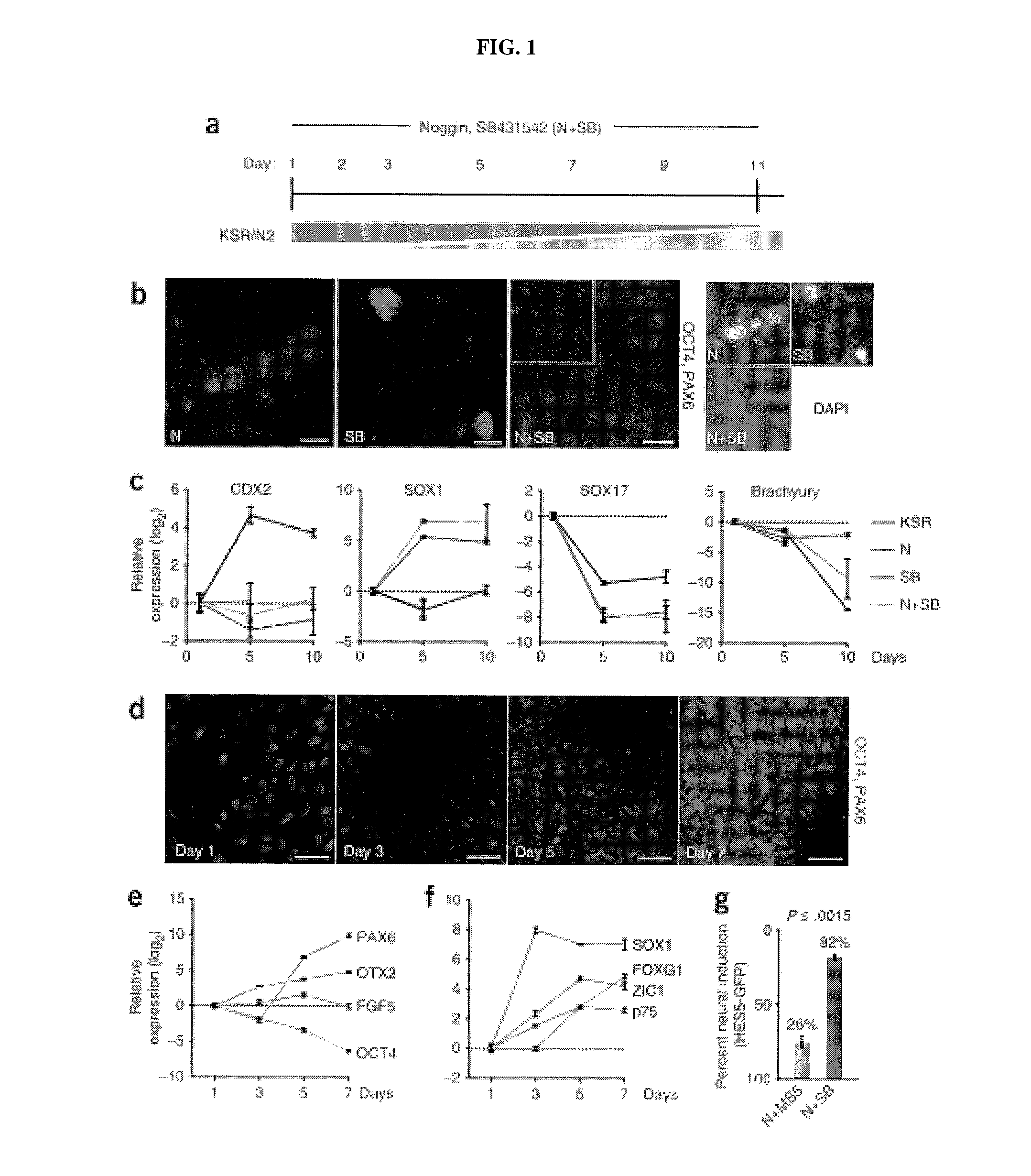
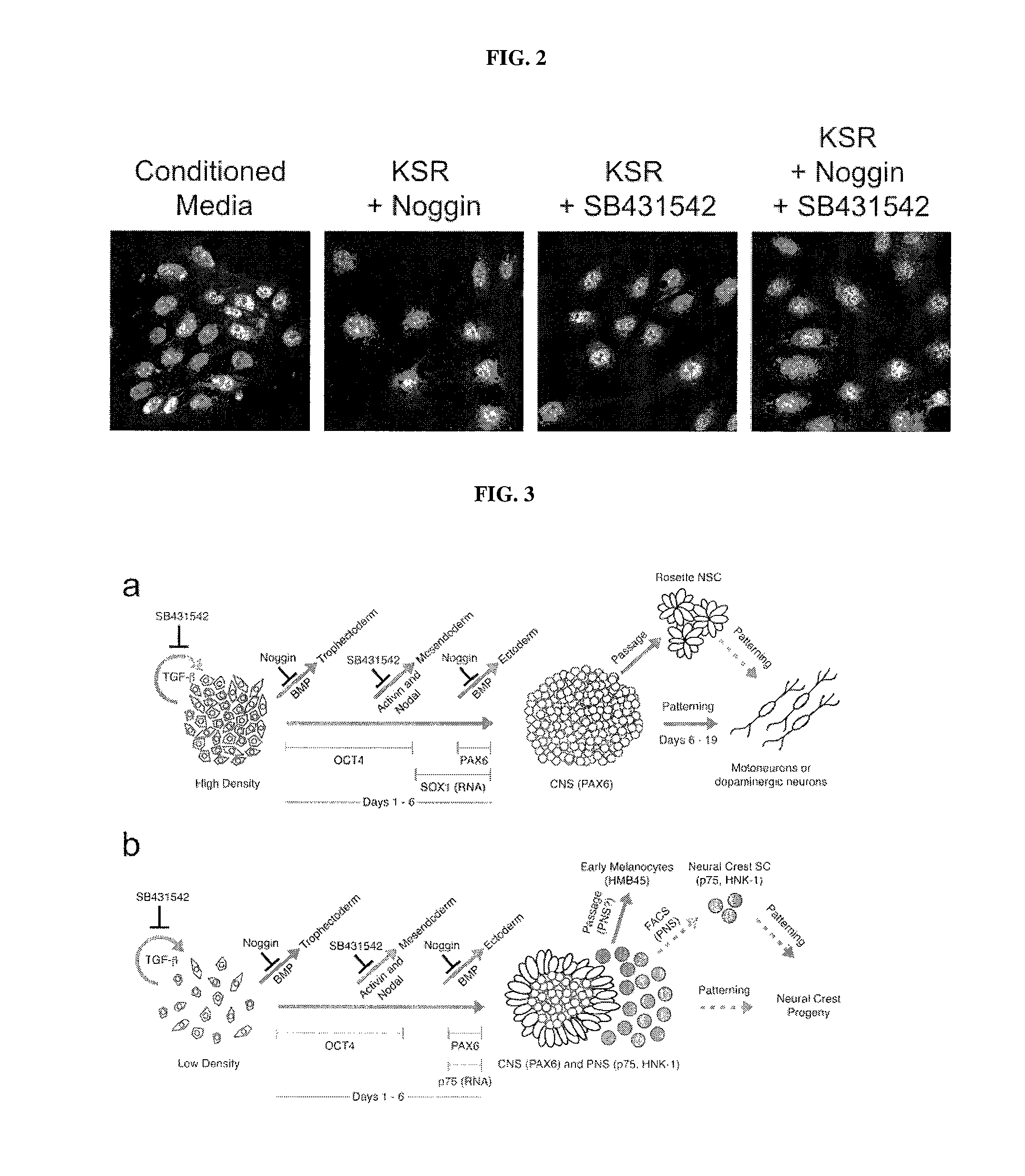
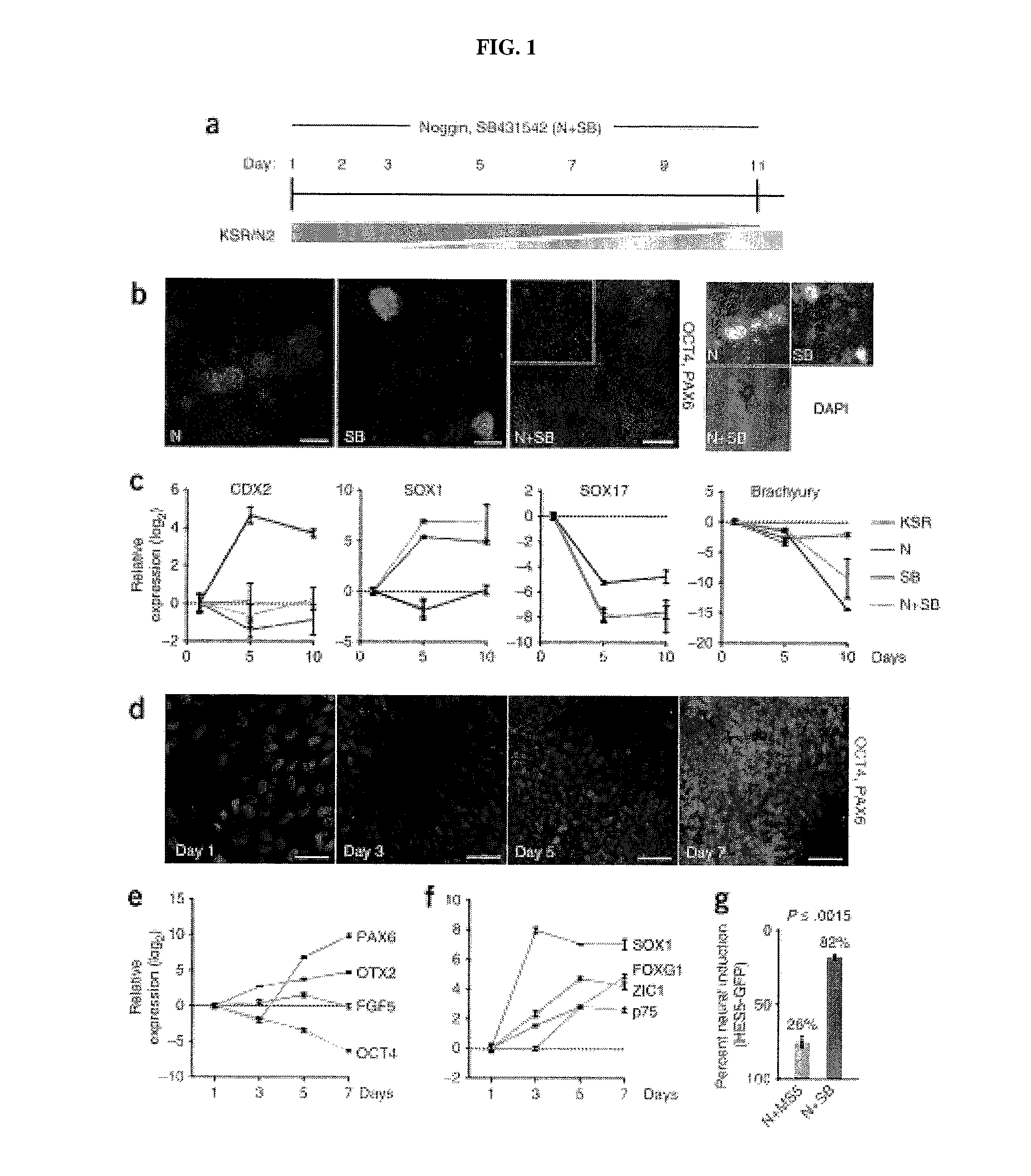
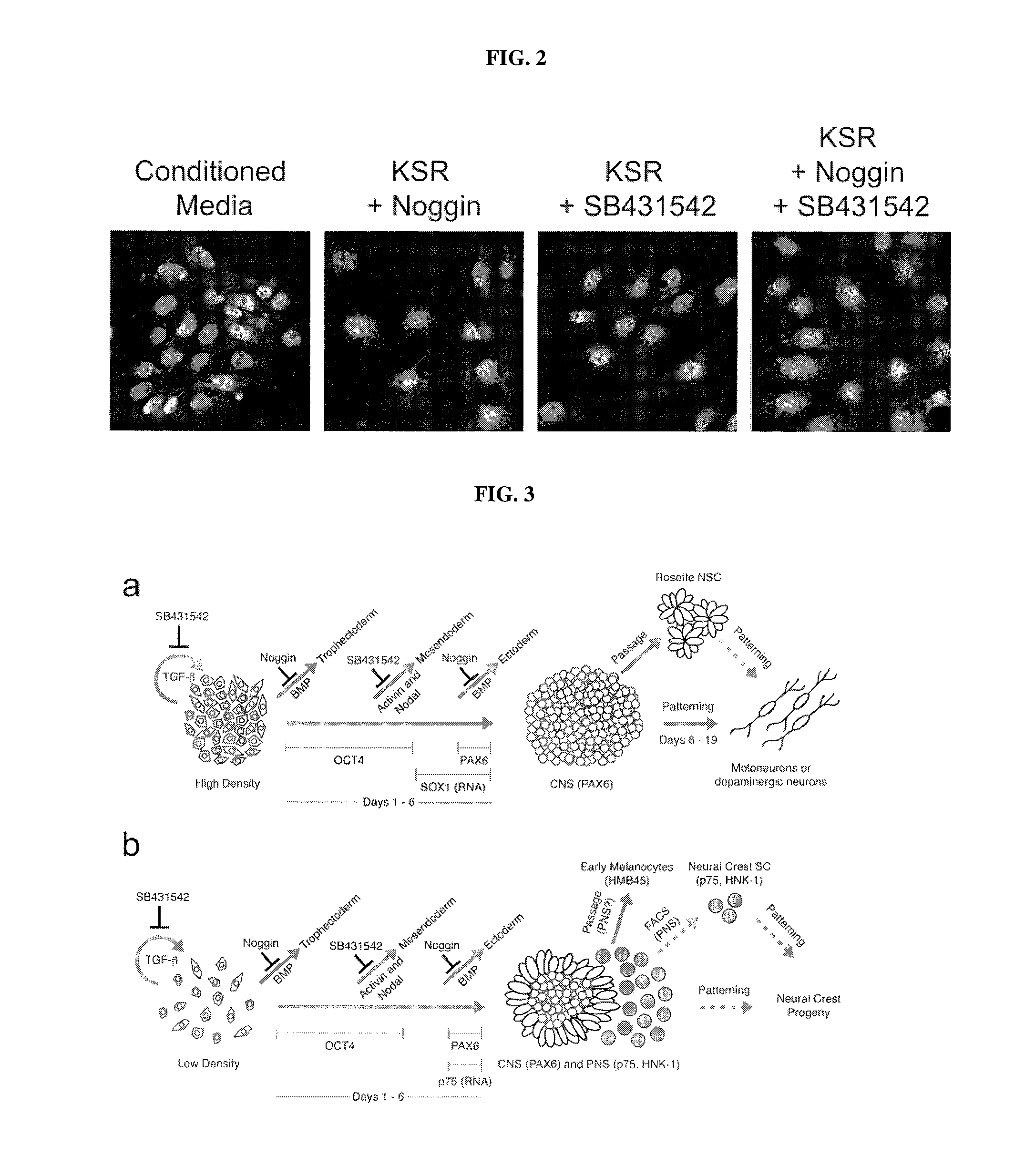
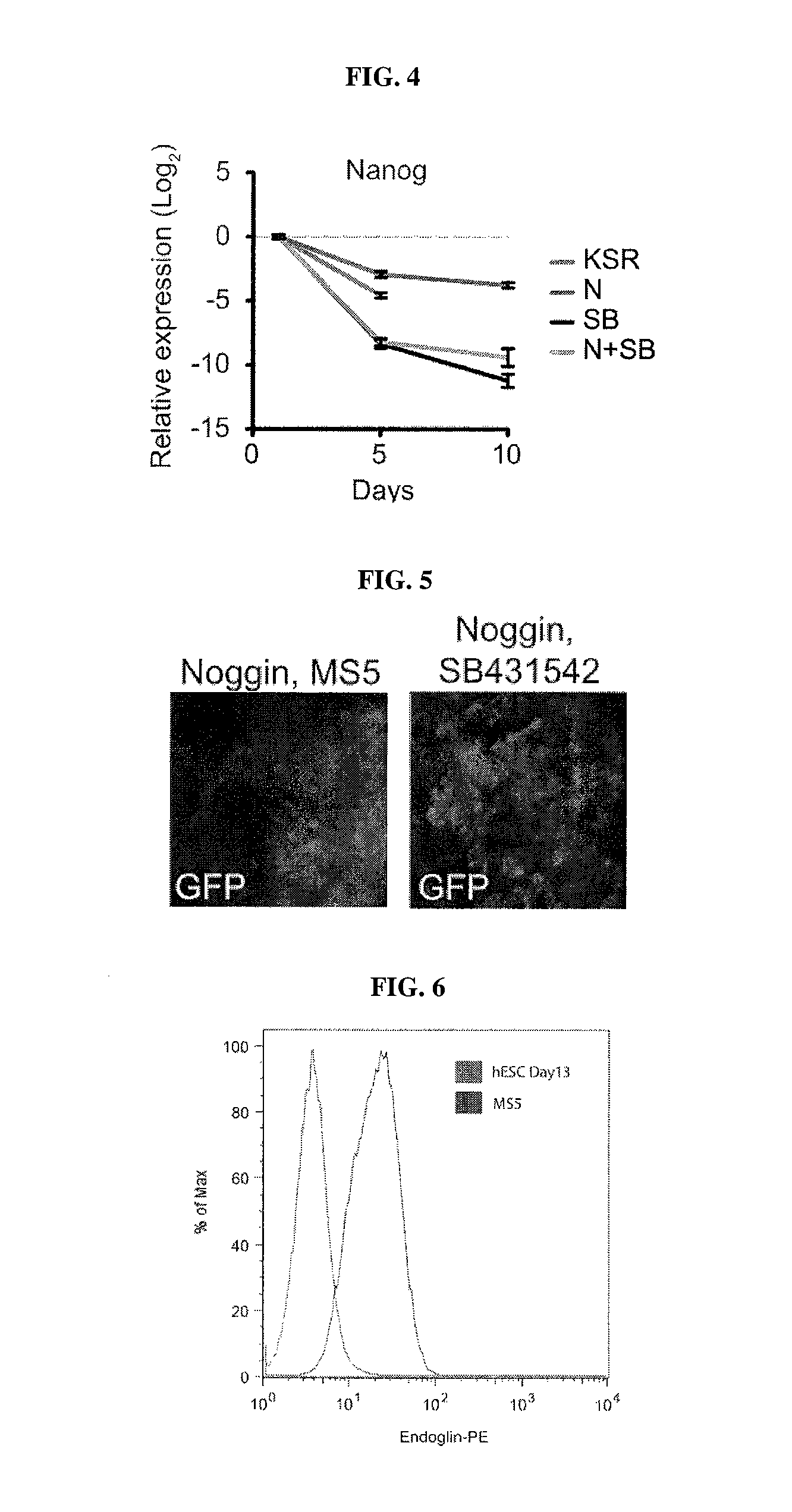
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20120094381A1Reducing DKK- protein functionImprove featuresCulture processNervous system cellsNeural plateDirected differentiation
The present invention relates generally to the field of cell biology of stem cells, more specifically the directed differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, including human embryonic stem cells (hESC), somatic stem cells, and induced human pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) using novel culture conditions. Specifically, methods are provided for obtaining neural tissue, floor plate cells, and placode including induction of neural plate development in hESCs for obtaining midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons, motorneurons, and sensory neurons. Further, neural plate tissue obtained using methods of the present inventions are contemplated for use in co-cultures with other tissues as inducers for shifting differentiation pathways, i.e. patterning.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Complete medium with low serum concentration for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells and method for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells using same
The invention discloses a complete medium with low serum concentration for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells and a method for cultivating the mesenchymal stem cells using same. The complete medium comprises a cell basic medium, fetal calf serum with final concentration of 1-100 mul / ml, an epidermal growth factor with final concentration of 1-100 ng / ml, and a basic fibroblast growth factor with final concentration of 1-100 ng / ml. The complete medium with low serum concentration successfully reaches equal or even better function of promoting cell proliferation than a culture reagent with high serum concentration. The cultured cells have the typical biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells, and can also express an omnipotent mark of the embryonic stem cell and high express the idiosyncratic mark of the neuron under the condition of in vitro inducement. And the difference between the cell batches is little, the cost is low and the security is good. Compared with the prior cultivating method, the method has advantages of simple operation, low probability of pollution and high success ratio of cultivating cells.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Method of making embryoid bodies from primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7220584B2Efficiently formedDead animal preservationArtificial cell constructsCells embryoIndividual animal
Primate embryoid bodies are formed from primate ES cells. The ES cells form clumps. One then removes the clumps, as clumps, and permits incubation under non-adherent conditions. The development of embryoid bodies from primate ES cells is dependent on maintaining the aggregation of cells, as individualized cells will rapidly die.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of Inducing Differentiation of Embryo-Stem Cell Into Hepatocyte and Hepatocyte Induced by the Method
InactiveUS20080206733A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHepatocyte growth factorCultured cell
With respect to a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cells into hepatocytes, in order to obtain safe hepatocytes that are adequately functionable and able to supply in large quantity, a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cell into hepatocyte, wherein the embryo-stem cells are cultured in the presence of deletion type hepatocyte growth factor is provided. Further, a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cells into hepatocytes comprising (a) a step of forming the embryoid body of the embryo-stem cells and (b) a step of culturing the embryoid body in the presence of deletion type hepatocyte growth factor is provided.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Methods for inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS7390659B2Effective treatmentImprove regenerative abilityBiocideNervous disorderProgenitorHuman animal
The present invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of an embryonic stem cell into a differentiated neural cell. The present invention further provides a method for producing differentiated neural cells, and a population of cells comprising the differentiated neural cells. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for repopulating a spinal cord in a subject, and a method for treating nervous tissue degeneration in a subject in need of treatment. The present invention further provides neural progenitor cells, differentiated neural cells, and uses of same. Also provided is a transgenic non-human animal containing the differentiated neural cells. The present invention is further directed to a method for isolating a population of differentiated neural cells. Finally, the present invention provides a method for identifying an agent for use in treating a condition associated with neuron degeneration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
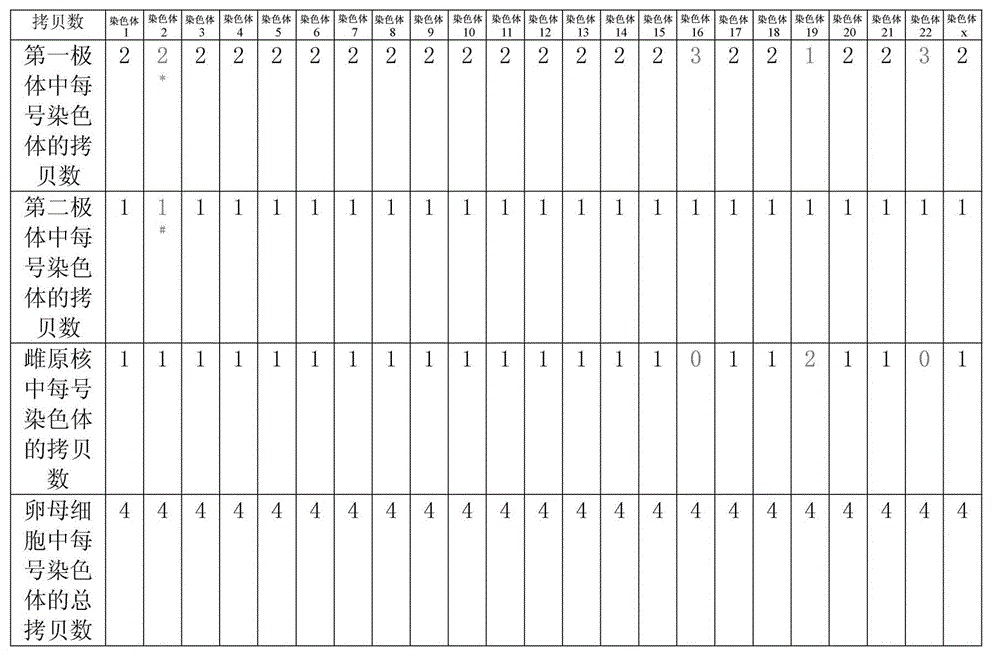
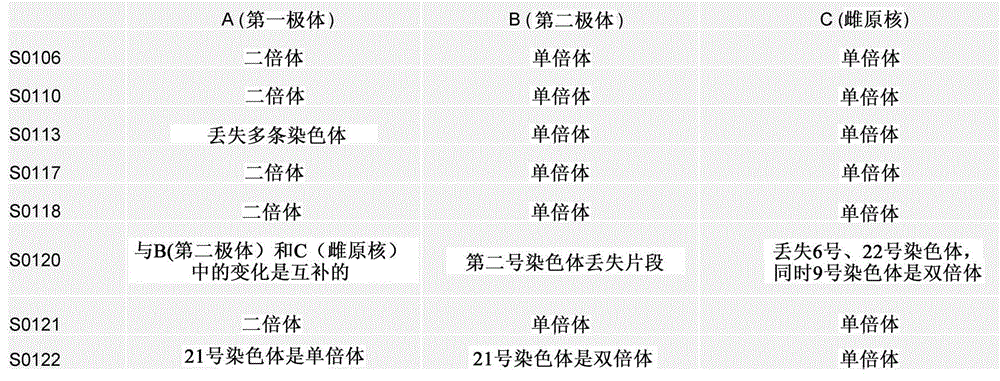
Selection of embryo of test tube baby through sequencing by single cell genome of polar body or embryo
Disclosed is a method for using a first polar body and a second polar body as well as a single-cell embryo to carry out whole-genome non-exponential amplification and high-throughput genome sequencing, so as to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis for genetic disease and testing for pathogenic genes causing repeated miscarriages. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining oocytes and embryos, and carrying out separation and genome amplification of first and second polar bodies and single-cell embryos; (2) establishing a genome sequencing library and sequencing, and carrying out bioinformatic analysis of the genome to obtain a gene spectrum and information concerning the number of copies of chromosomes and fragments thereof; (3) determining the chromosome ploidy of the polar bodies and embryos as well as information concerning defects, replication and point mutation in the chromosome fragments; (4) selecting normal or suitable embryos for implantation.
Owner:HARVARD UNIV +2
Apparatus and method for culturing stem cells
InactiveUS20120064627A1Simple and rapid and scalable cultureEasy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeat sensitivePolymer chemistry
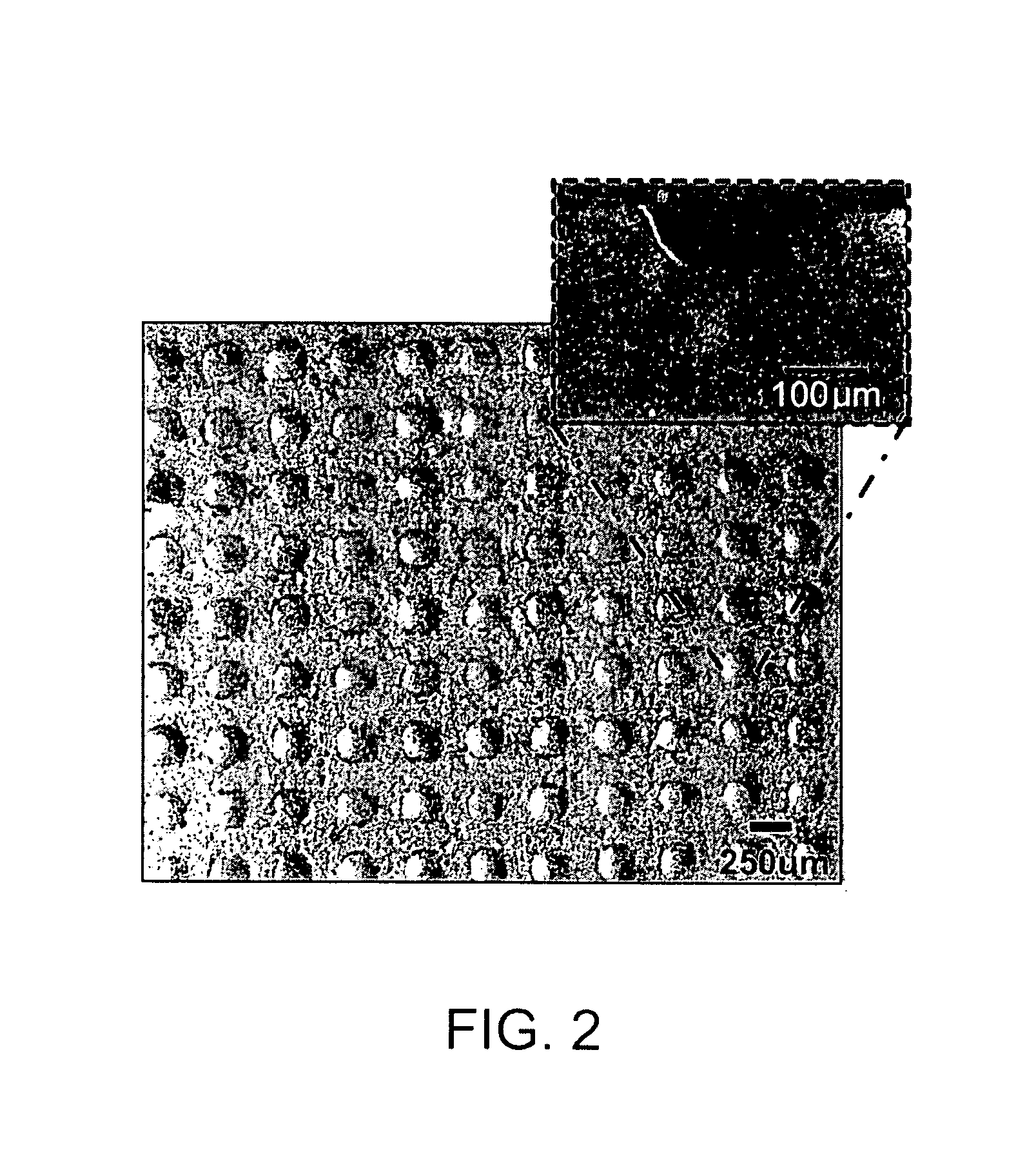
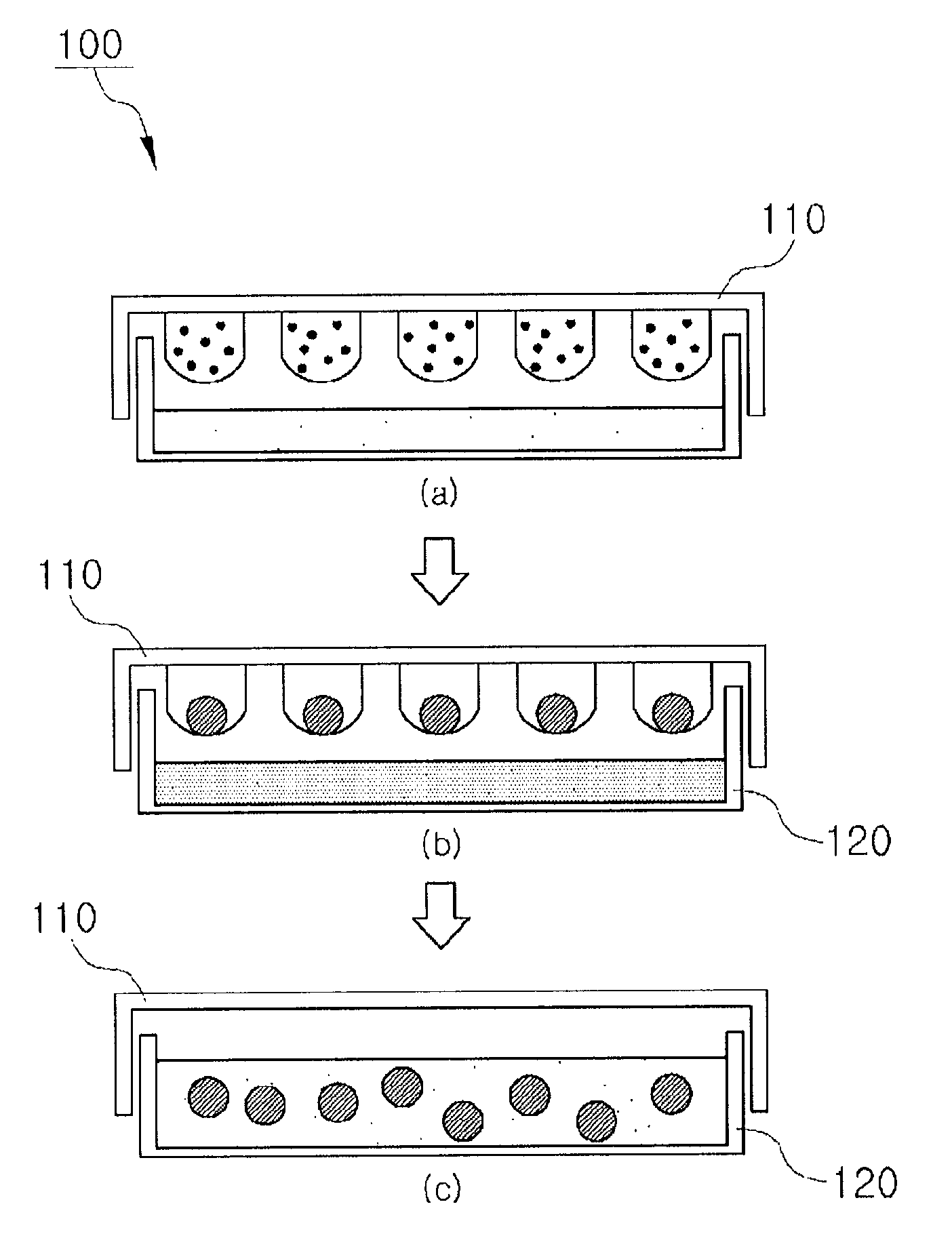
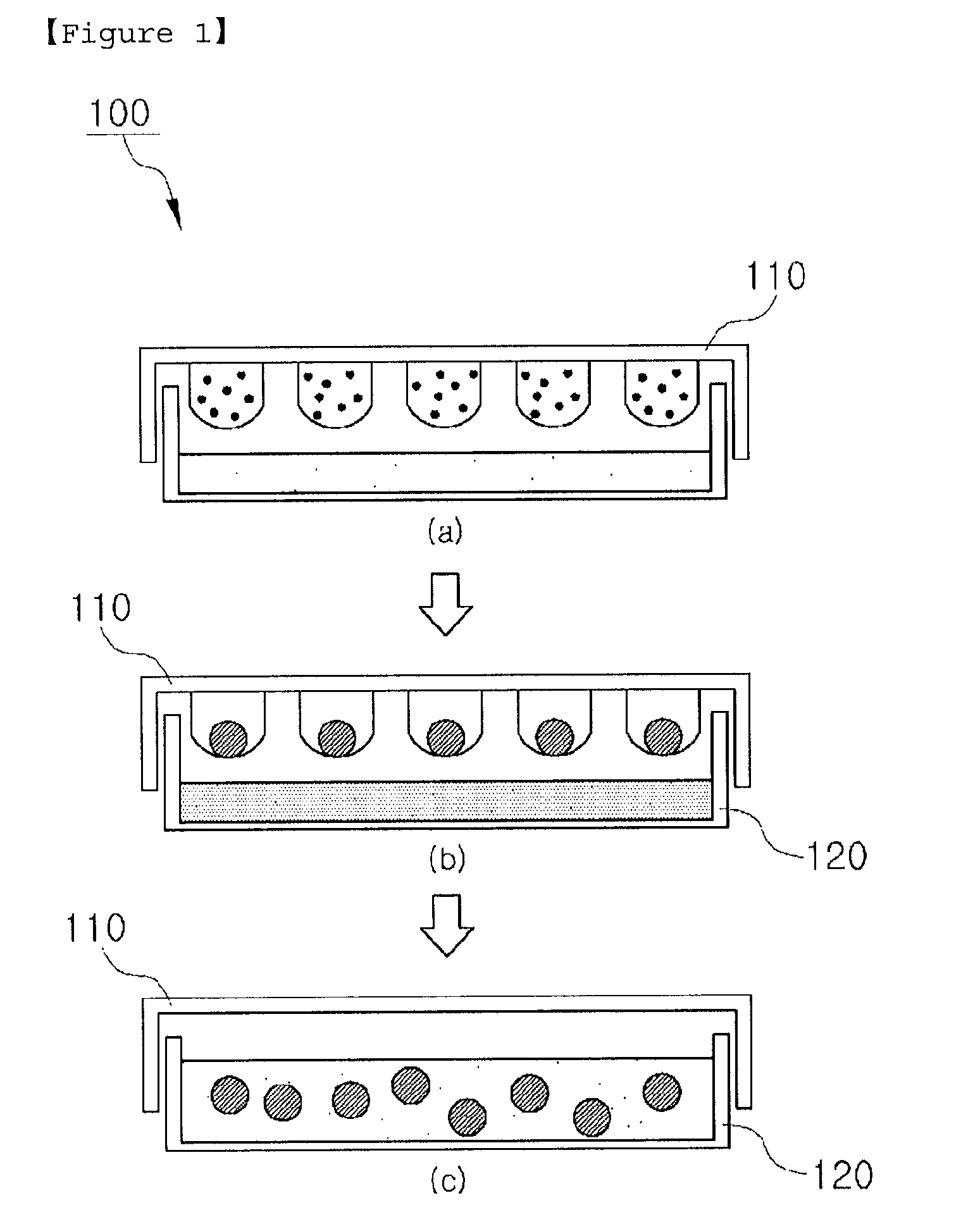
A method is provided to prepare a plurality of microwells suitable for the formation of embryoid bodies from embryonic stem cells. The method requires applying an image-forming material to a heat sensitive thermoplastic material in a designed pattern and heating the material under conditions that reduce the size of the receptive material by at least about 60% to create a mold. A polymer such as PDMS is then applied to the mold and removed to form the microwells. In an alternative aspect, the plurality of microwells on receptive material are prepared by etching a microwell designed pattern into a heat sensitive thermoplastic material support and then heating the material under conditions that reduce the size of the receptive material by at least about 60%.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
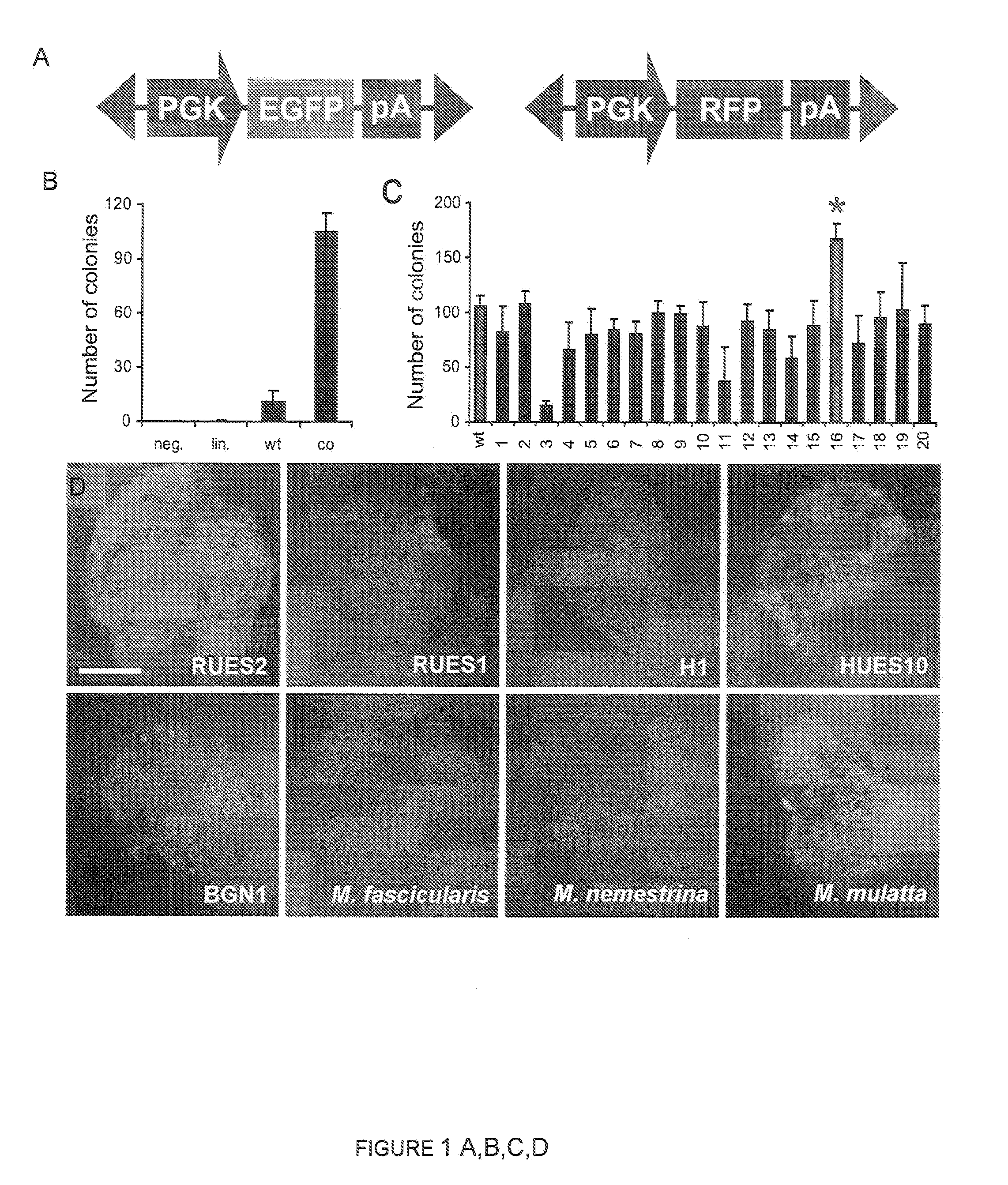
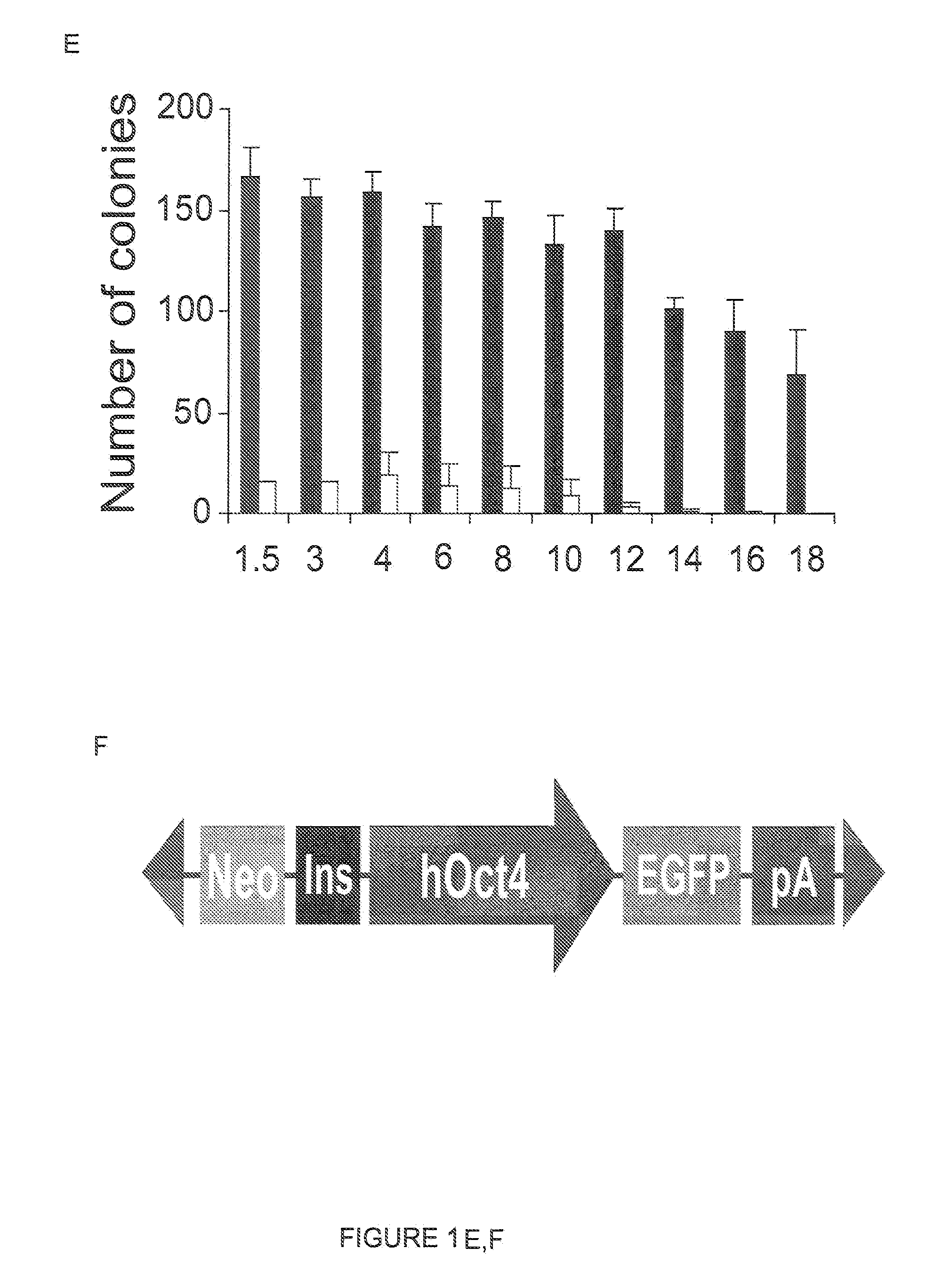
Compositions and Methods for Transposon Mutagenesis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100240133A1Increase heightIncreased frequency of transpositionSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNATransposon mutagenesisExogenous DNA
PiggyBac transposons and transposases with enhanced transposition activity in cells are provided. Also provided are associated methods and kits for both introducing exogenous DNA inserts into the genomes of host cells as well as for the removal of the inserts from the host cell genomes. Cells obtained by use of the compositions, methods and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells
The invention discloses an inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells. The method comprises the steps of: cultivating the human embryonic stem cells on a mouse embryonic fibroblast feed layer; sorting human embryonic stem cell clone groups in good state; grafting the groups on a human corneal stromal fibroblast layer processed by mitomycin C and cultivating for 7 days, wherein the human embryonic stem cells are differentiated to rosettes; separating and transferring the rosettes from the human corneal stromal fibroblast layer to a culture bottle; cultivating continuously for 7 days by using a neural crest stem cell culture medium; sorting the neural crest stem cells by a flow cytometry; adding the neural crest stem cells into the culture bottle; placing in a 5% CO2 incubator for incubating and cultivating at 37 DEG C by using a human corneal endothelial cell culture medium; changing the liquid every other day; and cultivating for about 10 days to obtain the corneal endothelial cells. The multiplication capacity of the corneal endothelial cells are similar to that of human corneal endothelial cells and the corneal endothelial cells can be transferred to 1-2 generations in vitro maximally. The corneal endothelial cells can be used as seed cells for cornea construction and transplant in tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
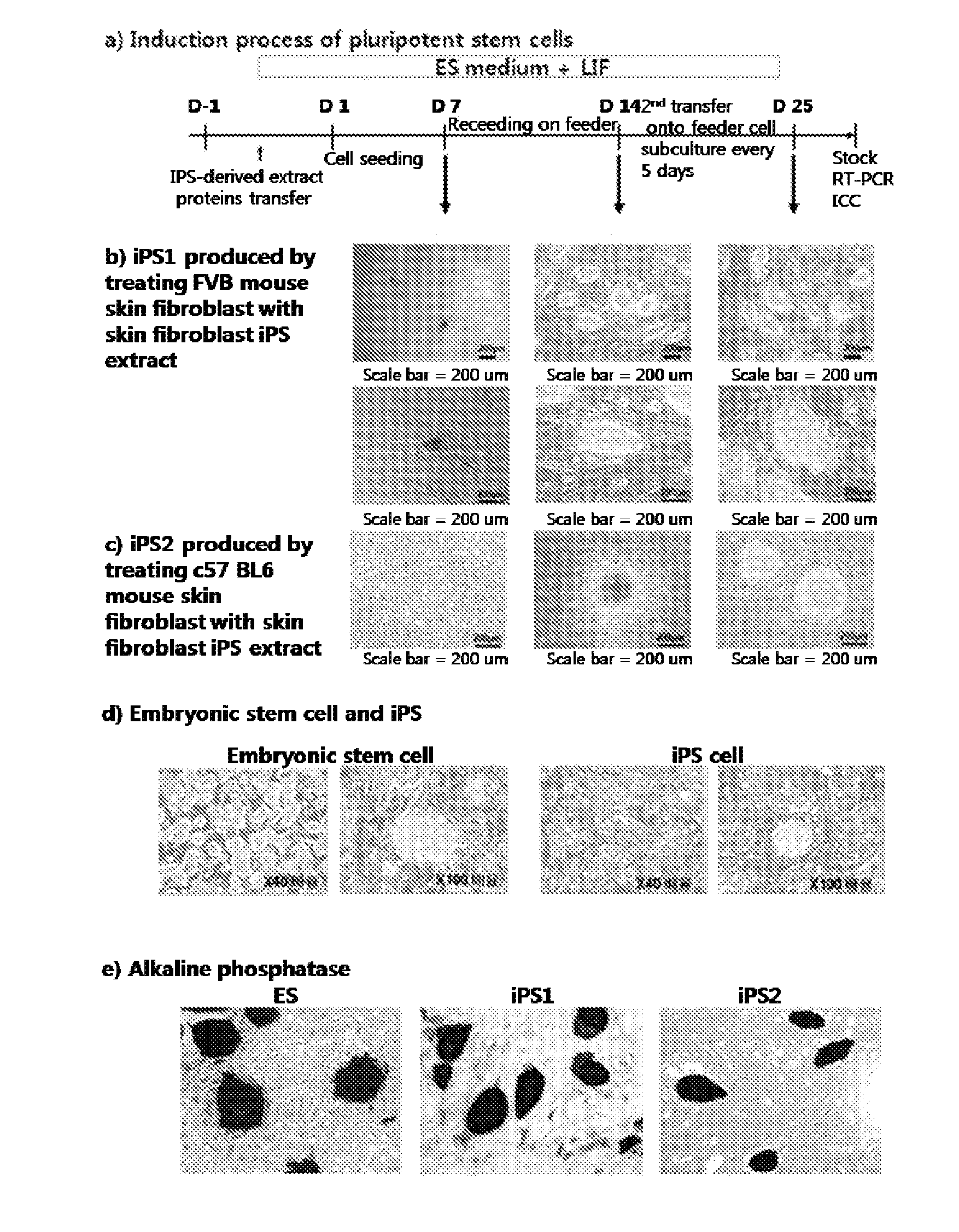
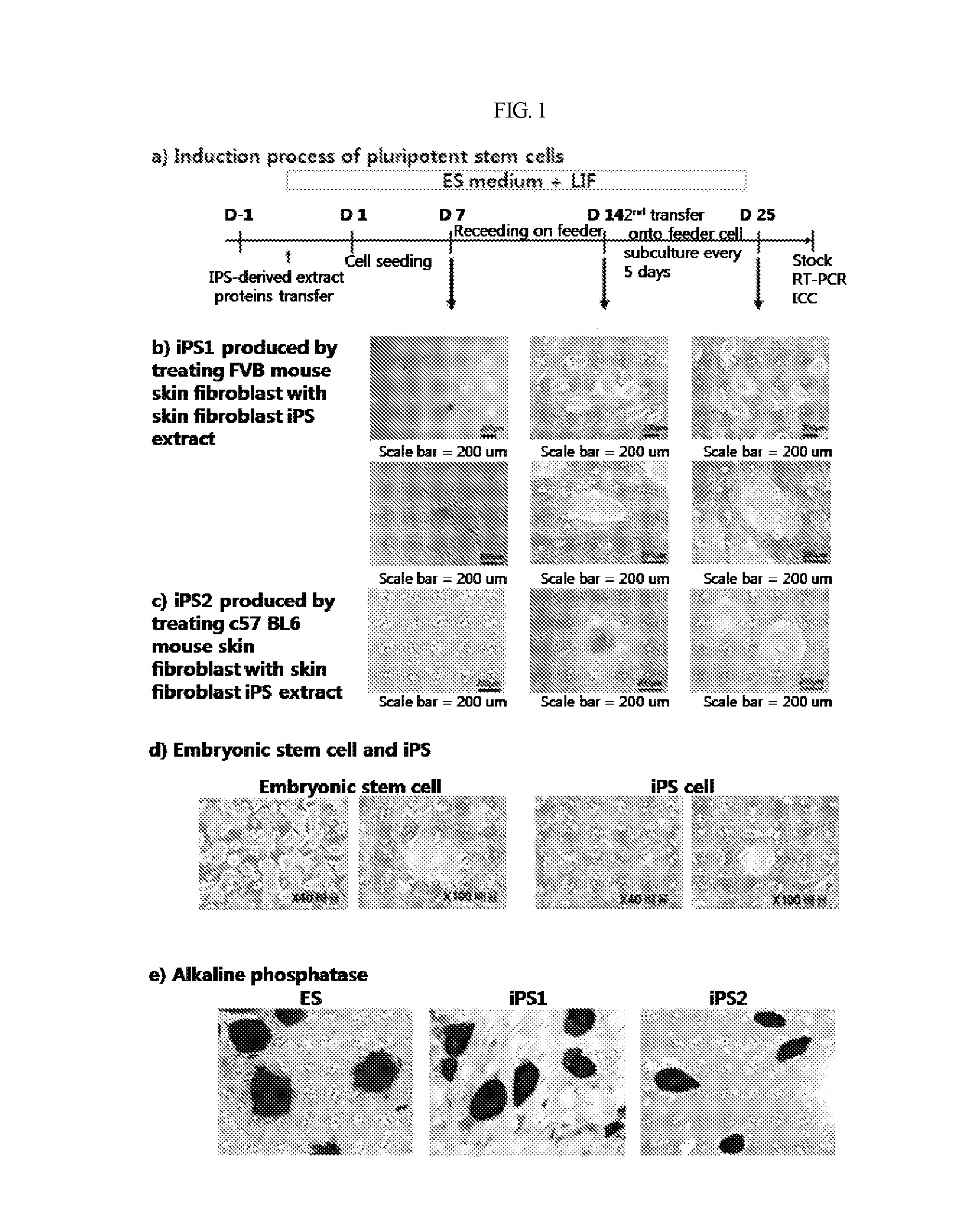
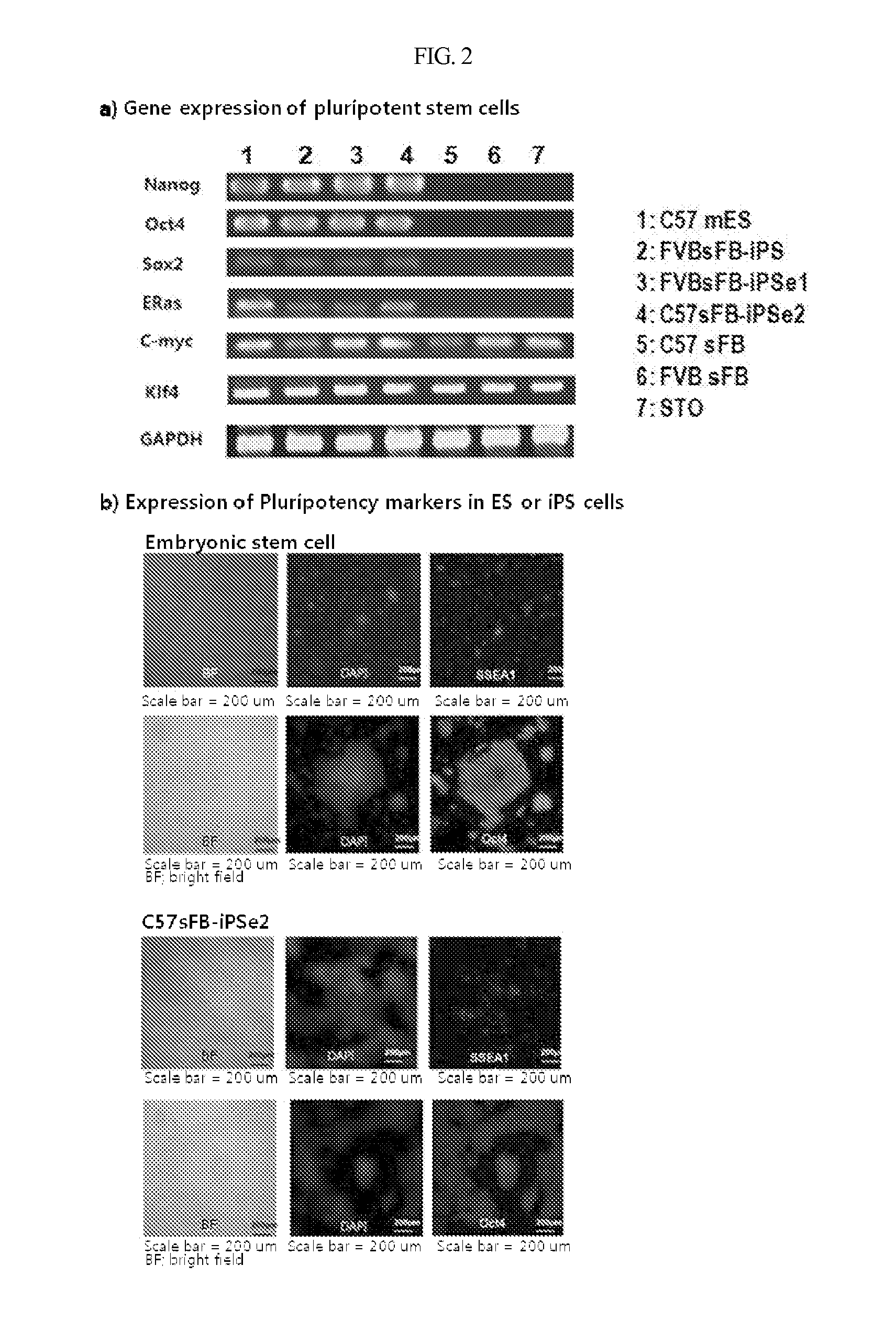
Method for producing induced pluripotent stem cells with high efficiency and induced poluripotent stem cells prouced thereby
ActiveUS20110256626A1Improve efficiencyPromote generationCell differentiationCulture processPresent methodSomatic cell
The present invention provides a method for producing customized pluripotent stem cells. Specifically, the present invention comprises following steps: extracting proteins from any of the dedifferentiated stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, the said dedifferentiated or pluripotent stem cells being prepared by any known method; introducing the protein extract into the adult somatic cells; and culturing the adult somatic cells to produce pluripotent stem cells having the same pluripotency as that of embryonic stem cells. In addition, pluripotent stem cells produced according to the present method and cell therapeutics comprising the same are provided. The method allows pluripotent stem cells to be produced very easily and at a significantly higher yield, compared to typical methods.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV HOSPITAL
Derivation of embryonic stem cells
This present invention provides novel methods for deriving embryonic stem cells, those cells and cell lines, and the use of the cells for therapeutic and research purposes without the destruction of the embryo. It also relates to novel methods of establishing and storing an autologous stem cell line prior to implantation of an embryo, e.g., in conjunction with reproductive therapies such as IVF.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Culture liquid for promoting ectogenesis of frozen embryo after thawing
InactiveCN102250832AImprove later developmental abilityQuality improvementEmbryonic cellsVitrificationCulture fluid
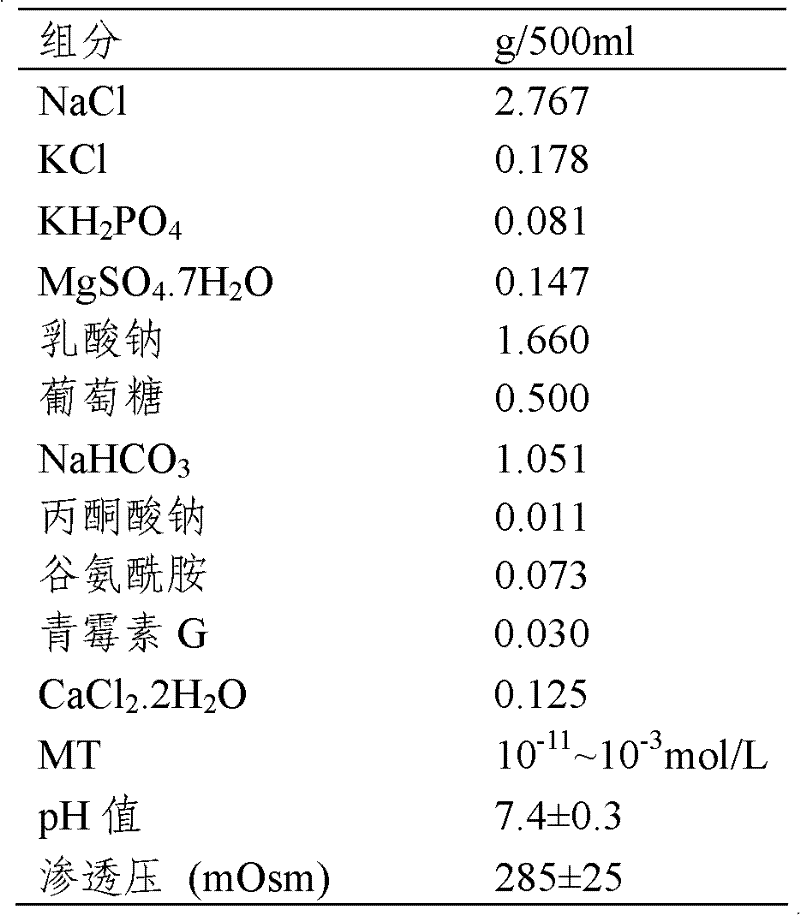
The invention provides a culture liquid for promoting ectogenesis of embryo vitrified by an open pulled straw (OPS) method after thawing. Frozen 2-cell embryo after thawing is cultured in the culture liquid containing 10<-9> mol / L of melatonin (MT), so that the blastula development rate of the embryo is improved and the number of the cells in the embryo is increased, thereby improving the embryo quality, and providing a beneficial reference for further developing the study of OPS cryopreservation of livestock embryos.
Owner:定州市中农大朝来农产品开发有限责任公司
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Generation of neural stem cells undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20090004736A1Improve portabilityPotent in vivoNervous disorderCulture processDiseaseNeurulation
The present invention relates to the generation of neural cells from undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. In particular it relates to directing the differentiation of human ES cells into neural progenitors and neural cells and the production of functioning neural cells and / or neural cells of a specific type. The invention also includes the use of these cells for the treatment of neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ES CELL INT
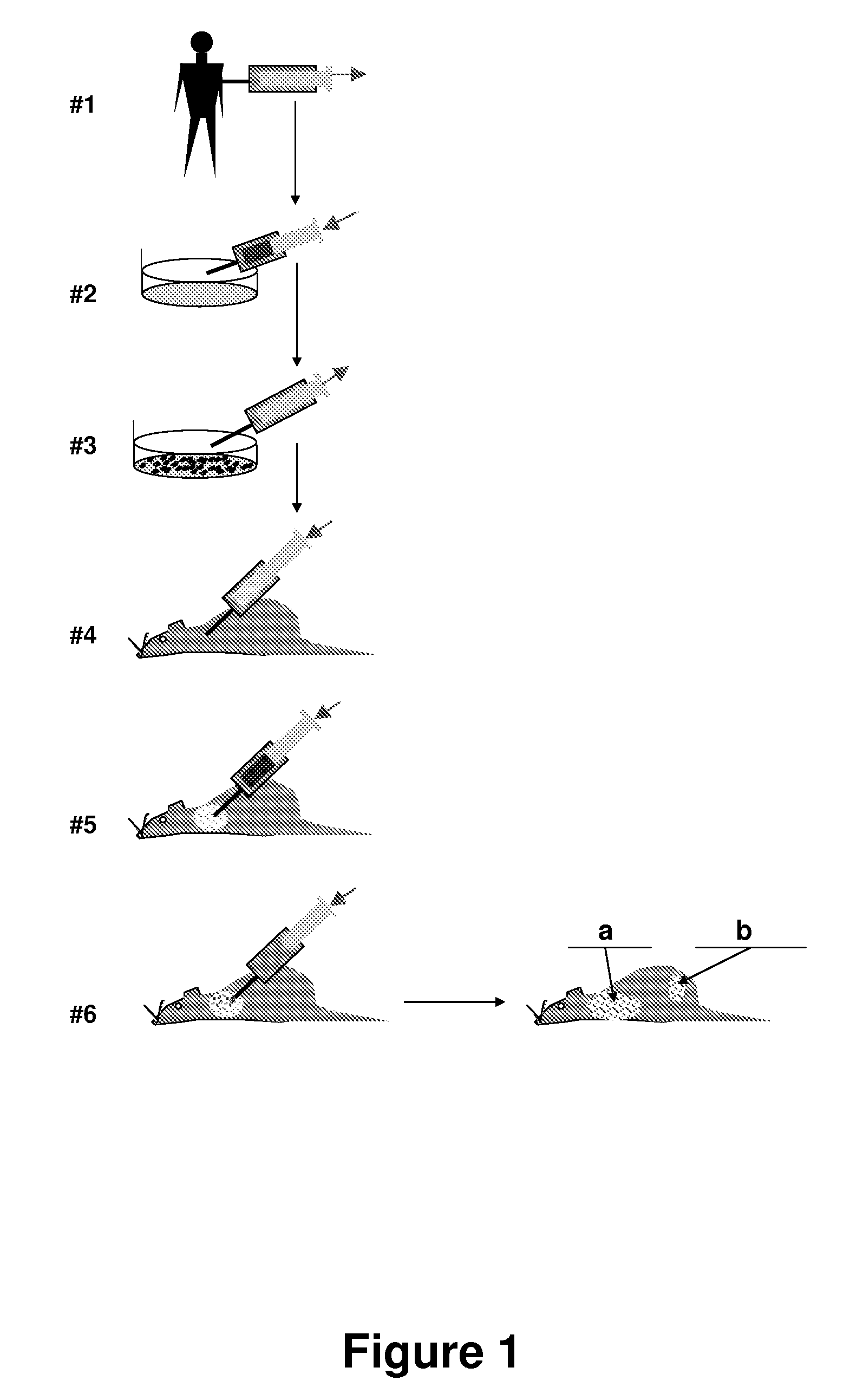
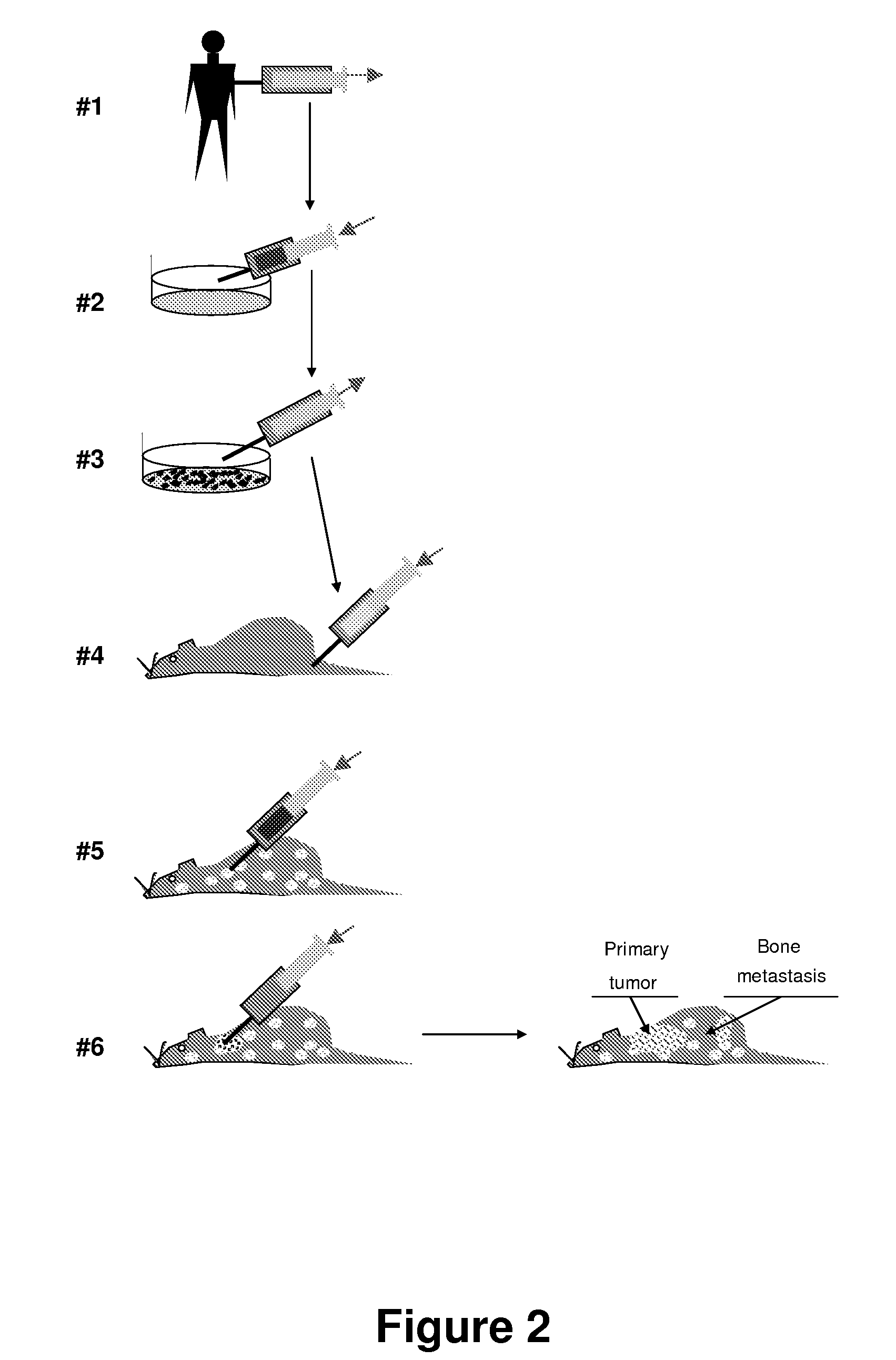
Animal models of tumor metastasis and toxicity
InactiveUS20070283453A1Promote repairPromote structural and functional repairDisease diagnosisAnimal husbandryHuman environmentHuman tumor
A method for conversion of an animal into an appropriate recipient of tumor cells derived from a different species. Animals for such purpose can be immuno-incompetent animals that are doubly grafted with orthotopic tissues, in which one grafted tissue (i.e., breast) is from an organ of the same class as the tumor of origin (graft A), and the second grafted tissue (i.e., bone) is from a organ of the same class as a target organ for metastasis (graft B). These dual grafted animals can be used to model human diseases. In one implementation, human tumor cells are orthotopically seeded in graft A in order to analyze the occurrence of metastasis in graft B. Methods and compositions are described for creating a multiorgan human environment in mice, by grafting human stem cells (mesenchymal, embryonic or others) into mice, e.g., injured to enhance specific tissue engraftment. Such chimeric mice can be used to grow human tumors and to study the occurrence of metastasis.
Owner:PROJECH SCI TO TECH
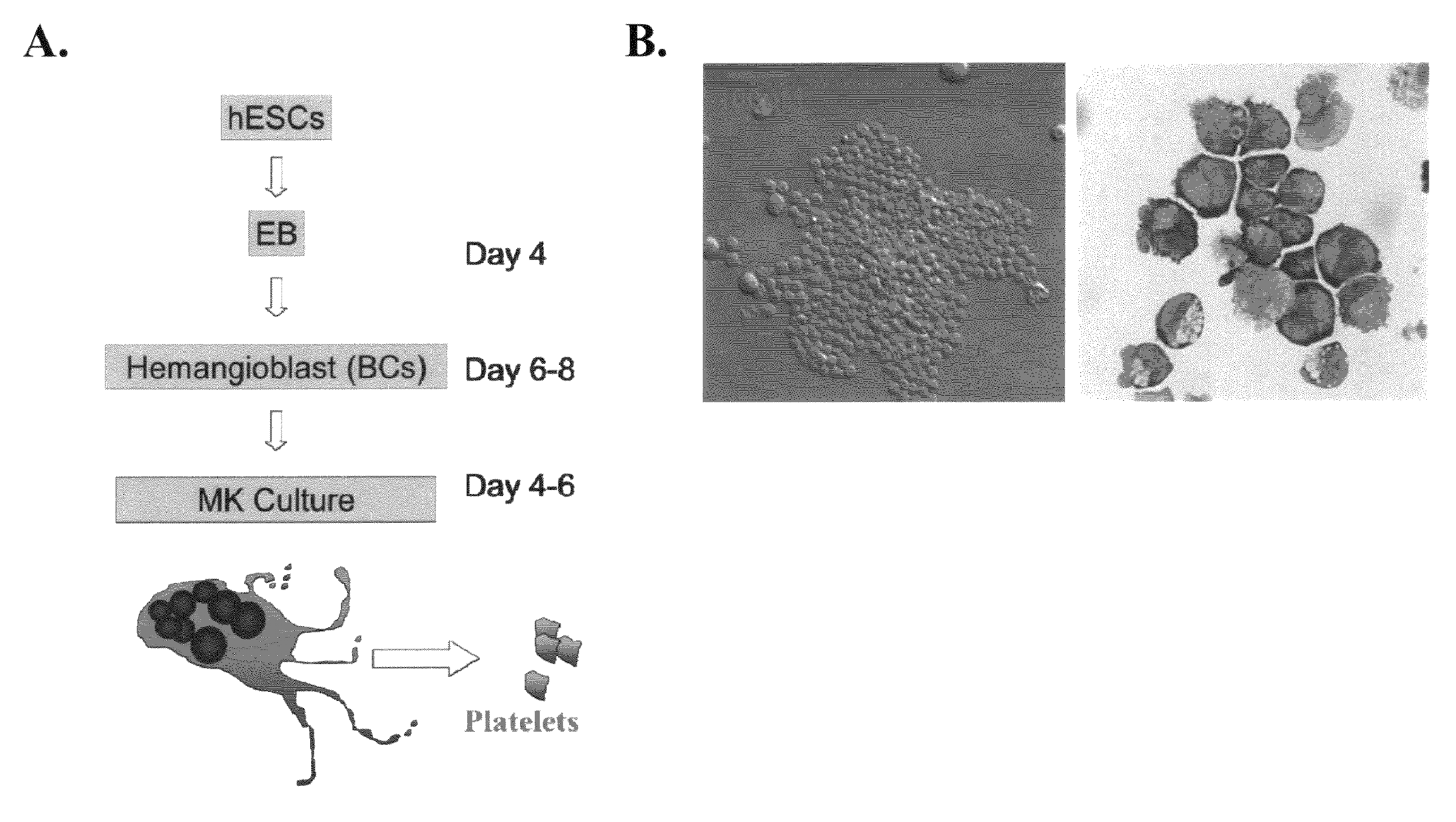
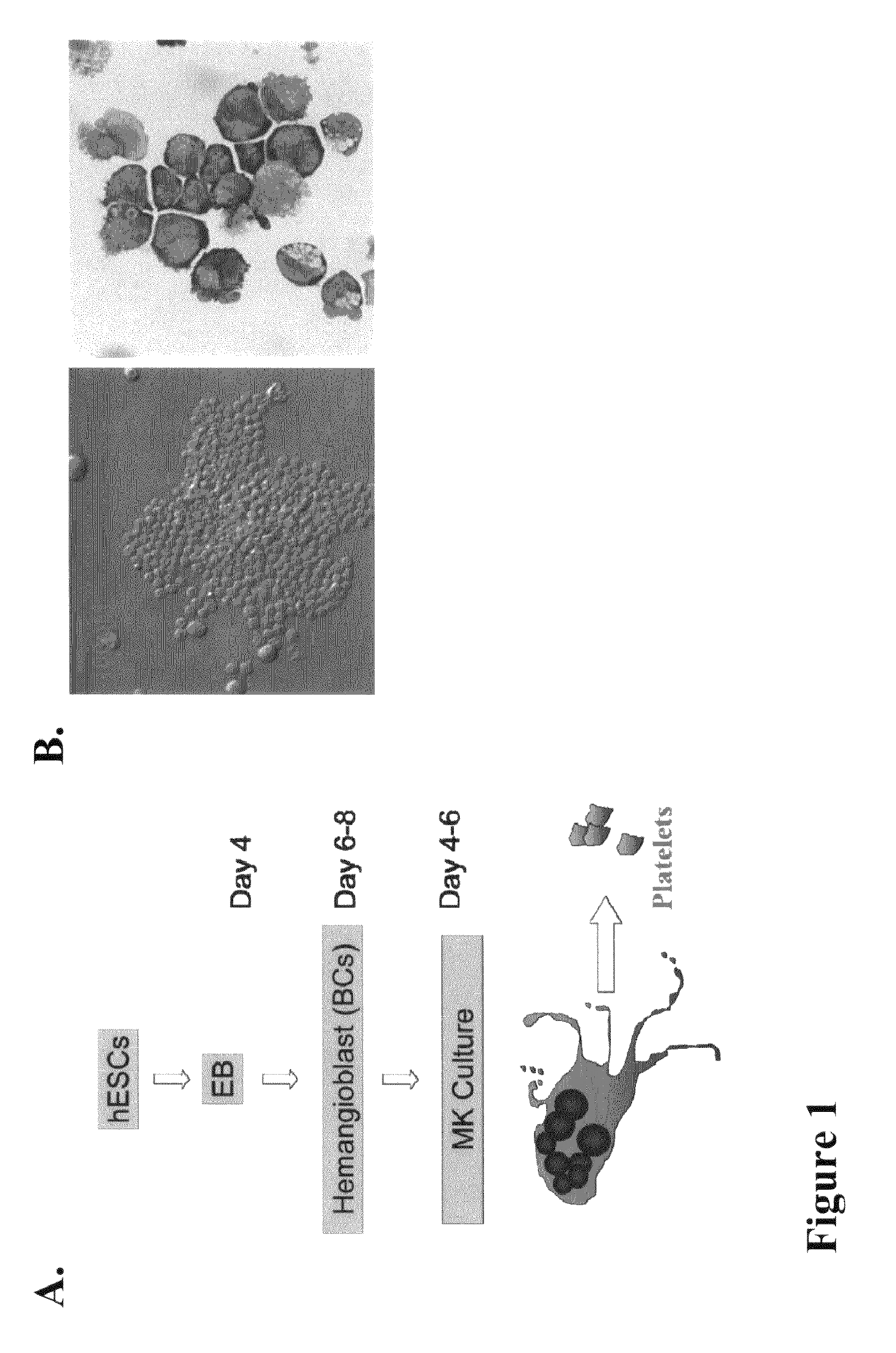
Large scale generation of functional megakaryocytes and platelets from human embryonic stem cells under stromal-free conditions
ActiveUS20120315338A1Transfusion is neededReduce or eliminate an immunity mediated host reactionCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsSerum igeBiology
The present invention provides a method of generating megakaryocytes and platelets. In various embodiments, method involves the use of human embryonic stem cell derived hemangioblasts for differentiation into megakaryocytes and platelets under serum and stromal-free condition. In this system, hESCs are directed towards megakaryocytes through embryoid body formation and hemangioblast differentiation. Further provided is a method of treating a subject in need of platelet transfusion.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Embryonic-like stem cells derived from adult human peripheral blood and methods of use
ActiveUS8835163B2High expressionPrevent proliferationBiocidePancreatic cellsHematopoietic cellAutoimmune disease
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla
InactiveCN102228001AImprove proliferation efficiencyRealize automated productionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFraxinusCotyledon plant
The invention discloses a micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla and relates to the micropropagation method. The problems of long reproductive cycle, low reproduction efficiency and poor offspring genetic stability in nursery stock propagation of fraxinus rhynchophylla are solved. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, sterilizing fraxinus rhynchophylla seeds, and culturing single cotyledons of zygotic embryos to obtain cotyledonal cell embryos; 2, performing maturation cultivation on the cotyledonal cell embryos; 3, performing sprouting cultivation on the cotyledonal cellembryos subjected to maturation cultivation to obtain regenerated plants; and 4, transplanting the regenerated plants into a culture medium to culture until new leaves are completely unfolded, and removing a covered plastic thin film. The micropropagation method has the advantages of short nursery stock reproductive cycle, high reproductive rate (culturing for 60 to 70 days) and high reproductionefficiency (each explant can generate 15 to 20 somatic embryos); the germination rate of the somatic embryos is up to 87 to 89.55 percent; the transplanting survival rate of the regenerated plants isup to 75 to 80 percent; and the regeneration plants with the same good characteristics as female parents can be generated in mass.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Cell culture dish for the embryoid body formation from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20100112684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCells embryoEmbryonic stem cell
The present invention relates to a cell culture dish for the erabryoid body formation from embryonic stem cells, which facilitates efficient and stable differentiation of embryonic stem cells by forming embryoid body in grooves on the bottom of a support adhered on the back of the lid for the culture dish by hanging drop culture.
Owner:IND FOUND OF CHONNAM NAT UNIV
Feeder layer and serum independent embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7641897B2BiocideGenetic material ingredientsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
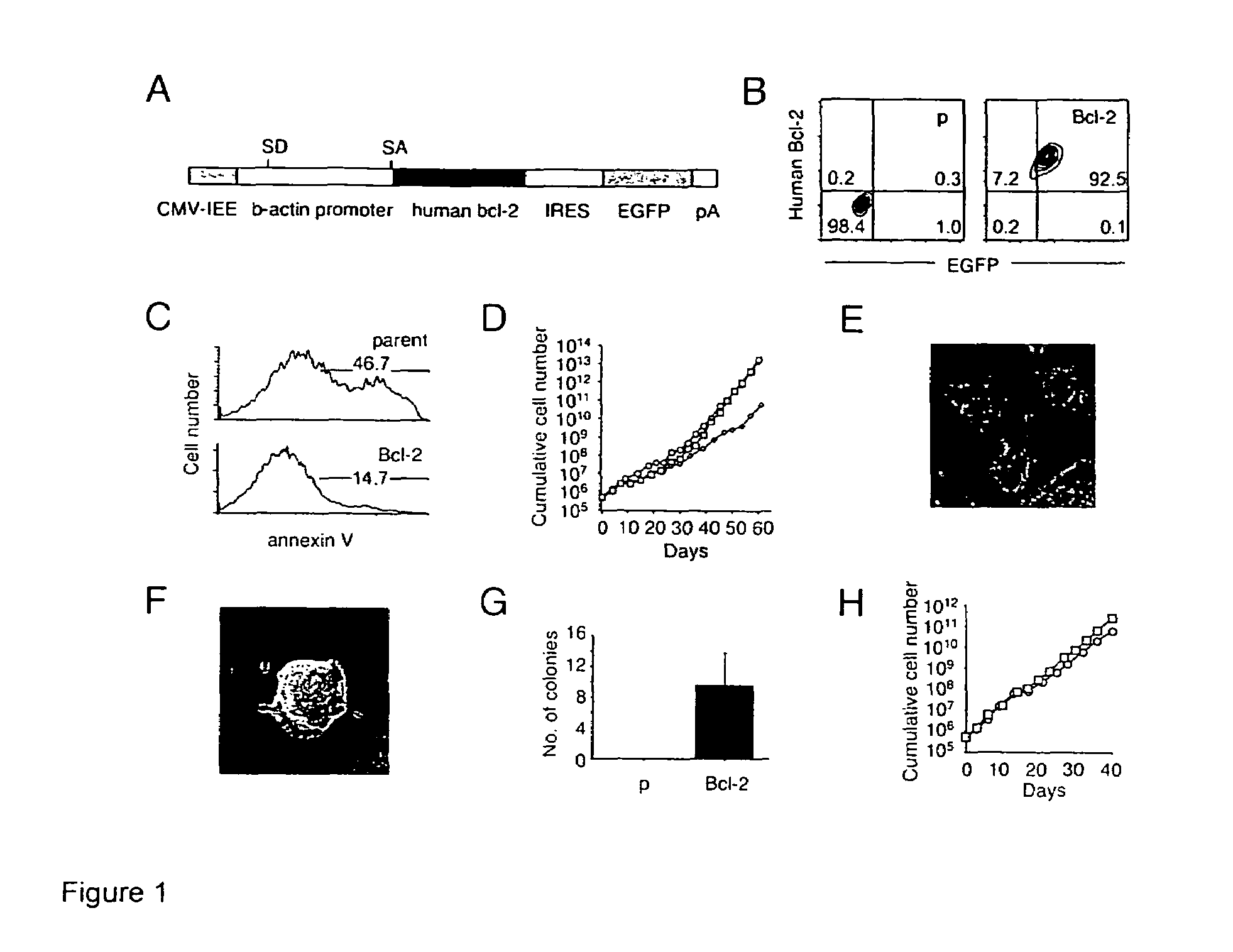
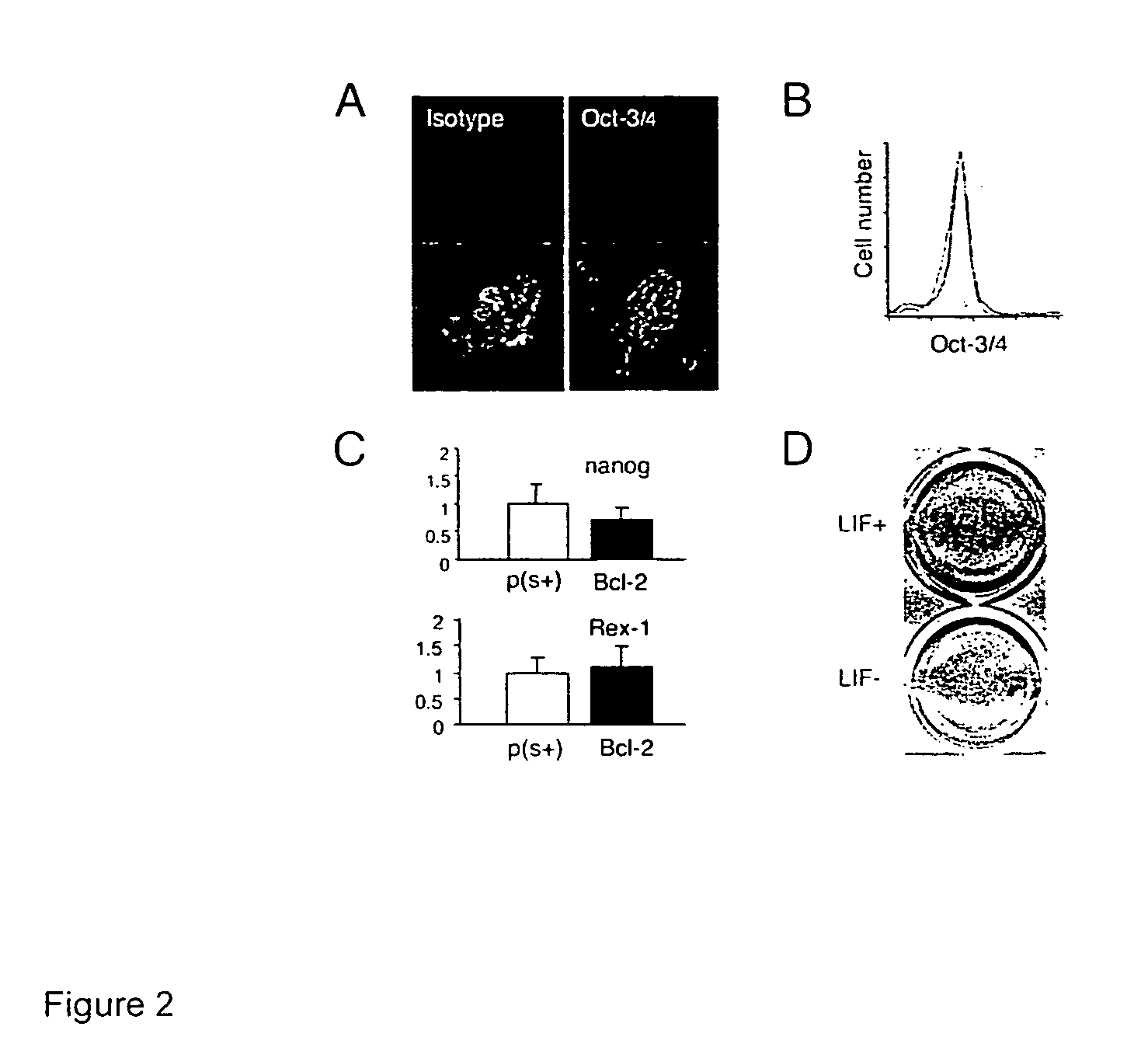
Undifferentiated primordial stem cells are manipulated to permit their long term growth in defined media lacking serum and feeder layer cells by shifting the apoptotic balance of the cells, through increasing the activity of Bcl-2 family anti-apoptotic proteins or decreasing the activity of Bcl-2 family pro-apoptotic proteins. In some embodiments of the invention, the Bcl family protein is Bcl-2. The ES cells sustain the characteristics of undifferentiated, pluripotent stem cells during long-term serum- and feeder layer cell-free conditions, including the ability to be expanded in vitro, but maintain their potential to differentiate into mature cell types.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods of mammalian retinal stem cell production and applications
The invention provides an in vitro method for producing isolated mammalian primitive retinal stem cells (pRSCs) comprising: (a) culturing isolated embryonic stem cells (ESCs) from a mammal in a cell culture medium that is free of feeder cells, feeder-conditioned medium or serum so as to produce and grow a culture of the isolated ESCs; and (b) contacting the culture of the isolated ESCs so grown with one or more of an inhibitor for Wnt or TGF-beta / BMP signaling so as to differentiate the isolated ESCs of (a) into primitive retinal stem cells thereby producing isolated mammalian pRSCs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
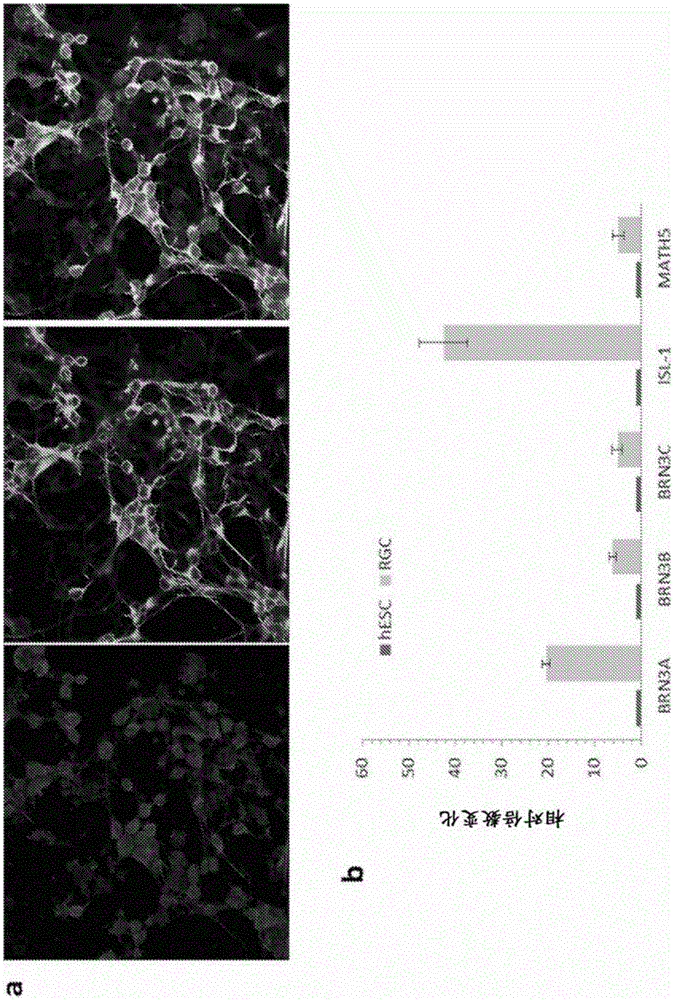
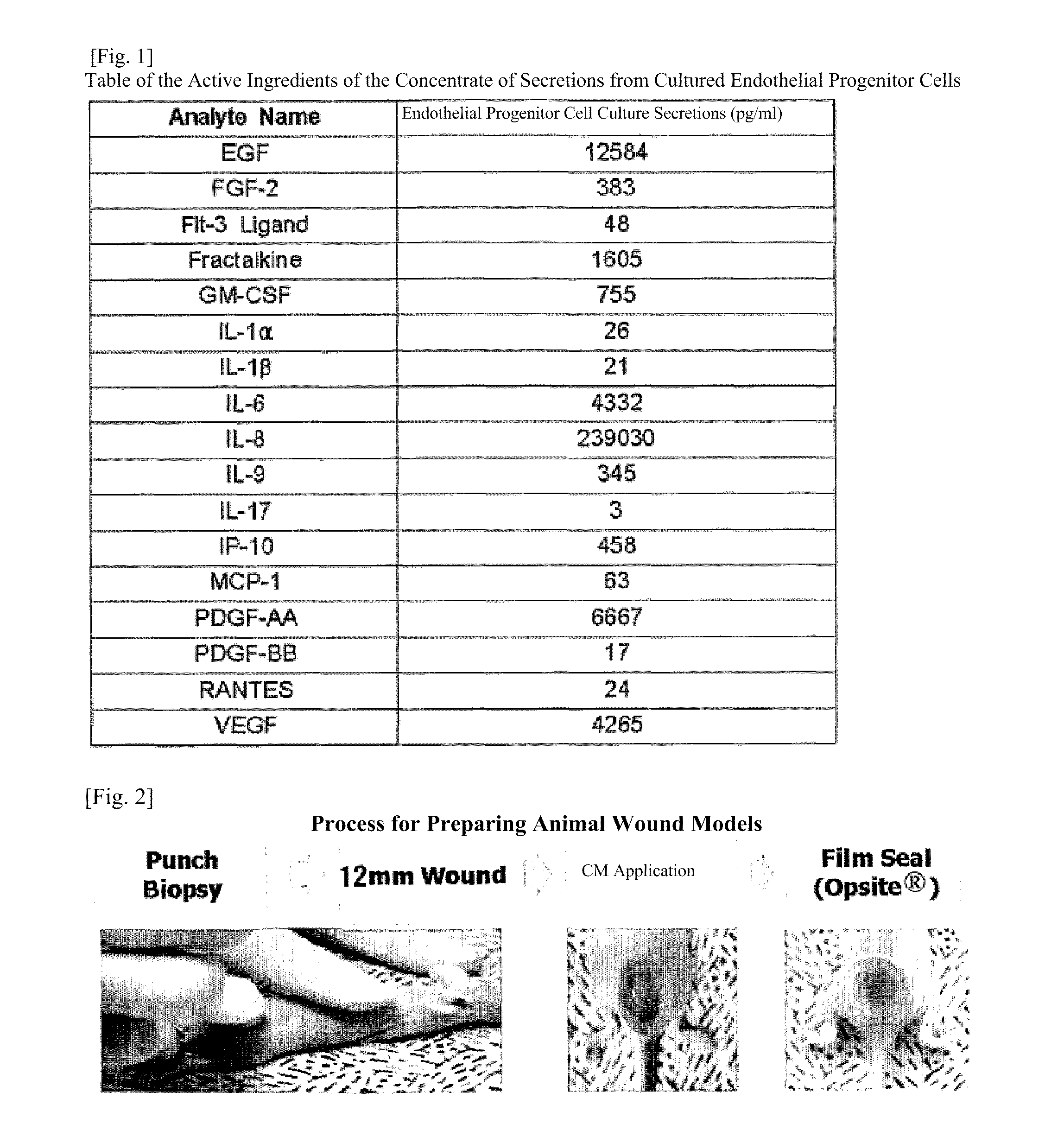
Composition for skin regeneration, containing a secretion in the culture of an embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial progenitor cell or fractions thereof, and use thereof
InactiveUS20110300102A1Improve wrinklesPrevent skin agingCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh concentrationCollagen VI
The present invention relates to a composition for skin regeneration, using a culture medium or a secretion in the culture of an embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial progenitor cell, and to the use thereof. As the present invention uses the secretion in the culture as a medicine and not the embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial progenitor cell itself, the risk of teratoma formation is prevented, and angiogenic activity is promoted to achieve improved effectiveness in healing wounds and burn wounds. The composition of the present invention, when used as a material in cosmetics, increases collagen synthesis and thus prevents skin aging. Particularly, the composition of the present invention in which the secretion in the culture is concentrated into a high concentration provides superior wound-healing effects as compared to a conventional human growth hormone (hGH).
Owner:CHABIO&DIOSTECH
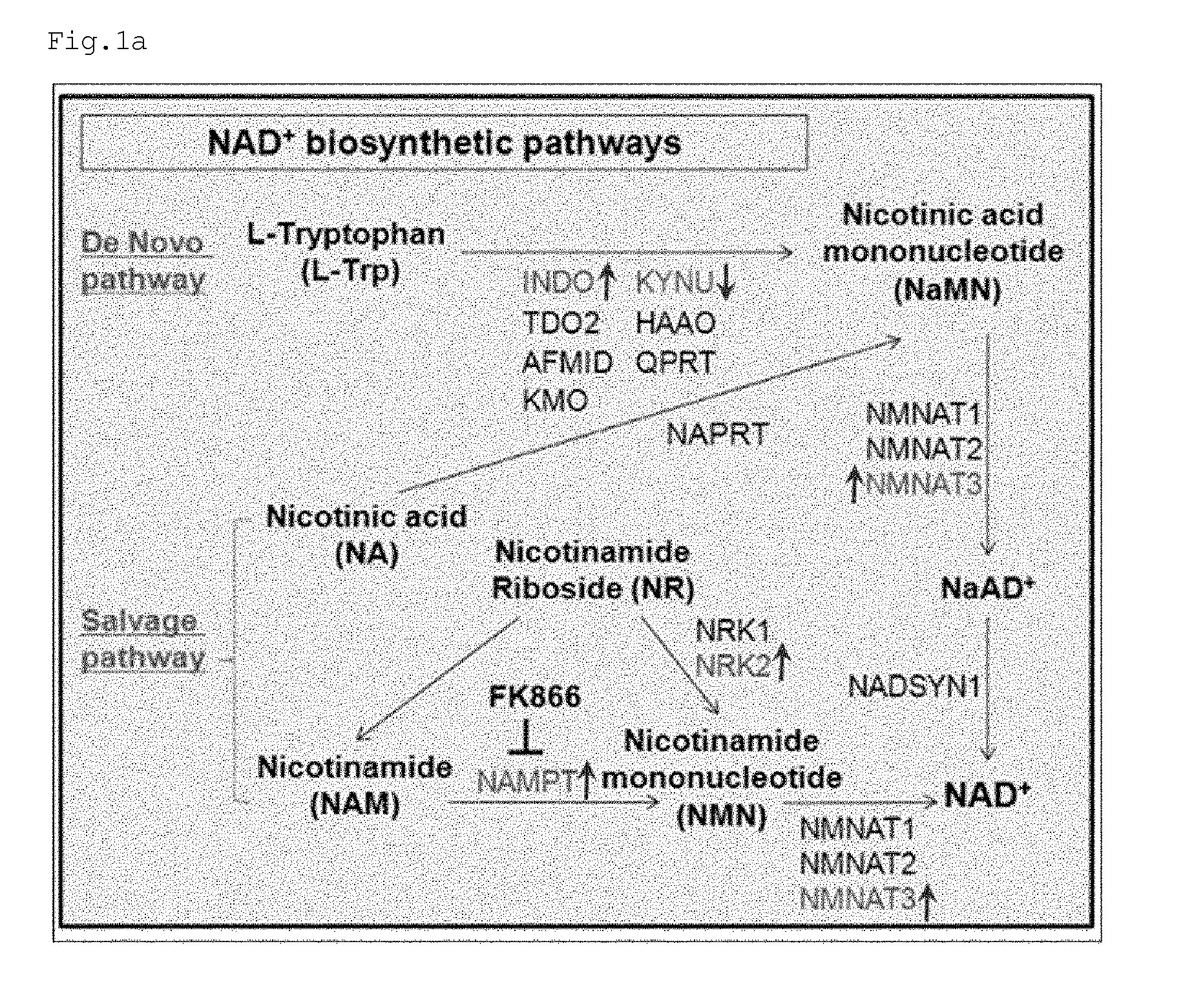
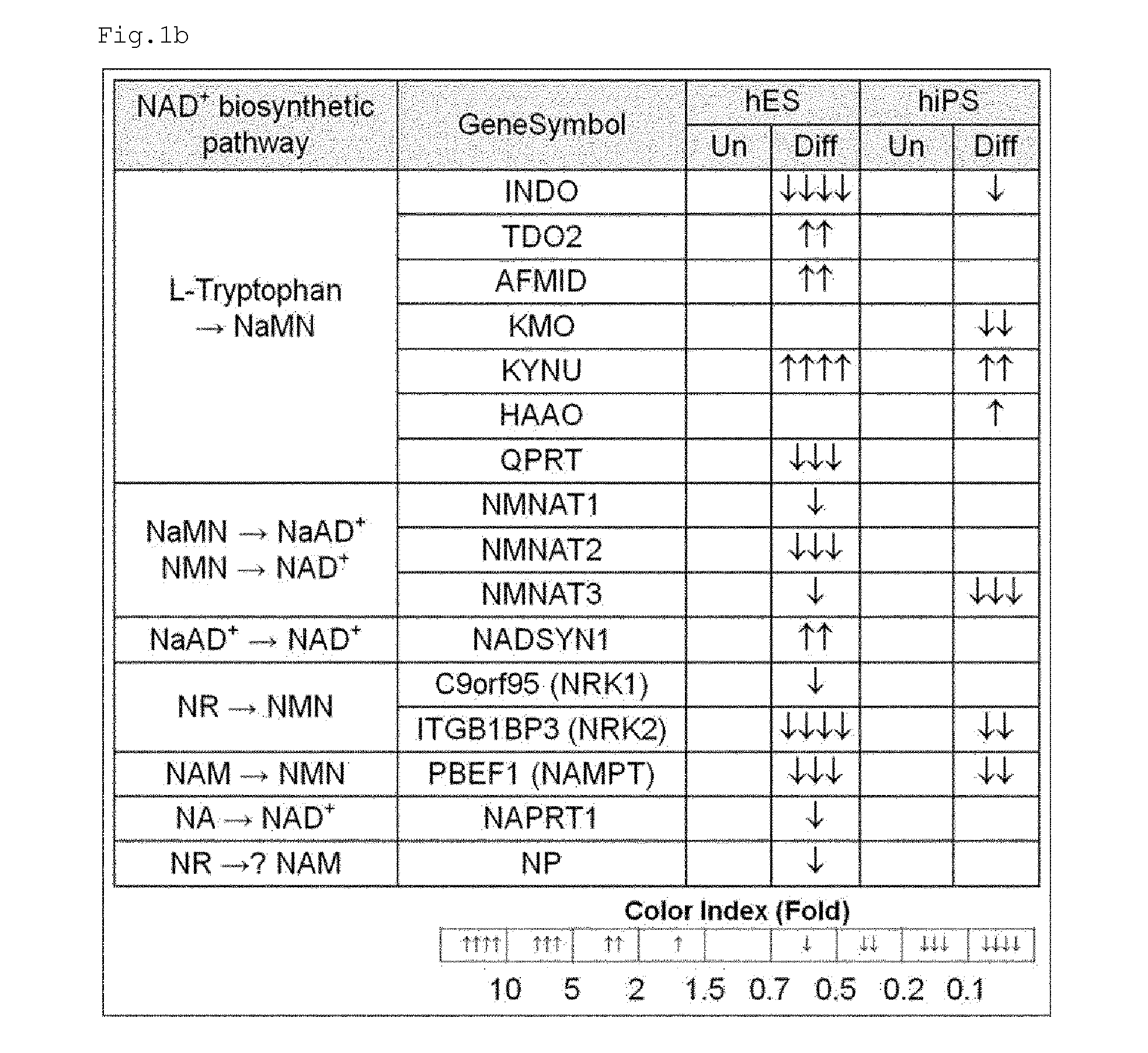
Metabolite for improving production, maintenance and proliferation of pluripotent stem cells, composition comprising the same, and method of culturing pluripotent stem cell using the same
InactiveUS20150072416A1Improve efficiencyInhibits induction of senescenceOrganic chemistryCulture processMetaboliteReprogramming
According to the present invention, when nicotinamide is added in a culture process for producing pluripotent stem cells from human differentiated cells, it can increase the efficiency of reprogramming and can significantly reduce the time required for induction of reprogramming. It was verified that nicotinamide inhibits the induction of senescence and oxidative stress in the reprogramming process and increases cell proliferation and mitochondrial activity to effectively improve culture conditions for induction of reprogramming. Particularly, the present invention will contribute to optimizing a process of producing induced pluripotent stem cells from a small amount of patient-specific somatic cells obtained from various sources, and thus it will significantly improve a process of developing clinically applicable personalized stem cell therapy agents and new drugs and will facilitate the practical application of these agents and drugs. In another aspect, according to the present invention, in defined culture conditions in which feeder cells and serum were not used, it was found that nicotinamide can provide a culture medium composition effective for maintaining the undifferentiated state of human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells, which are typical pluripotent stem cells. The invention can be effectively used for the development of a high-efficiency system for culturing large amounts of human pluripotent stem cells, which is required for the industrialization of human pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com