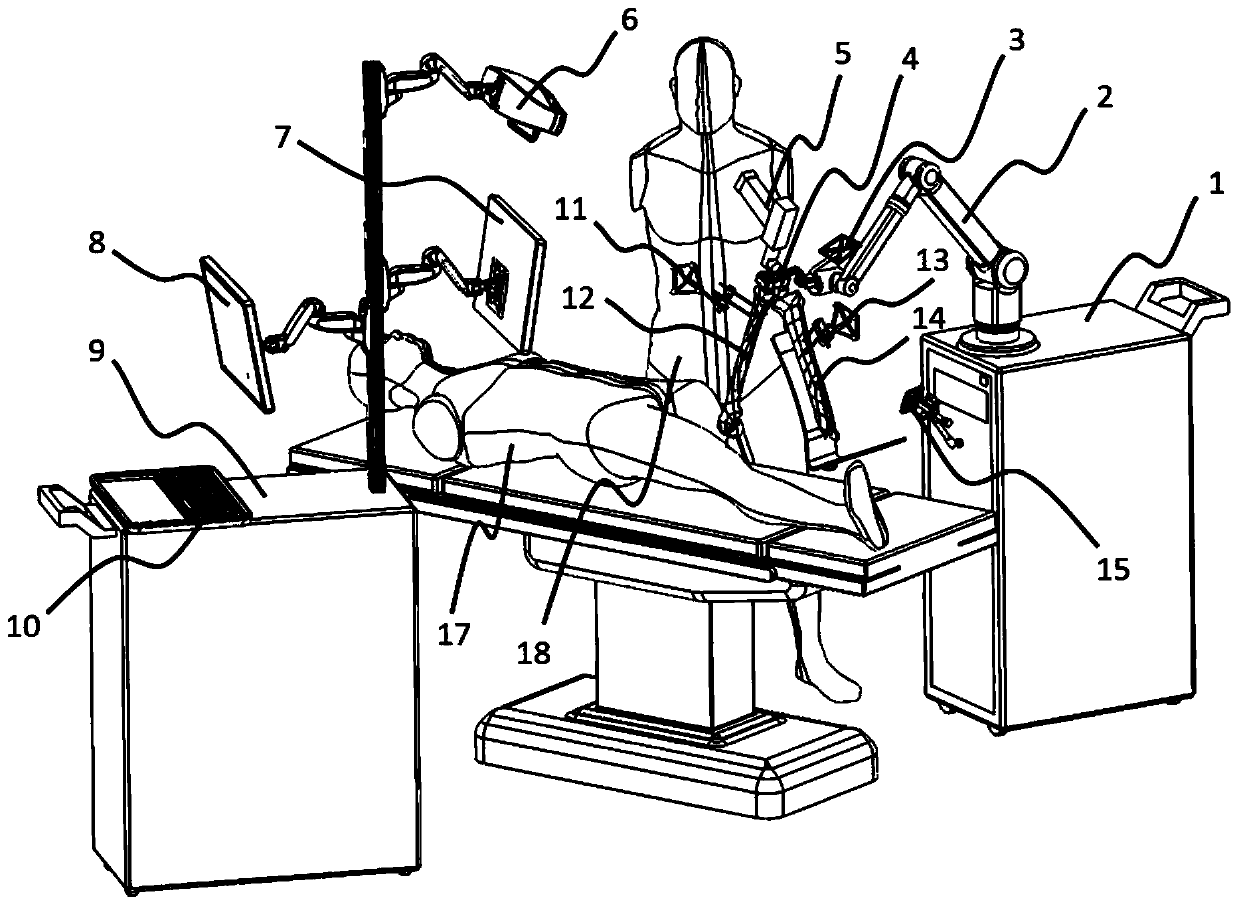
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
214 results about "Bone nailing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Prosthesis for cemented fixation and method for making the prosthesis
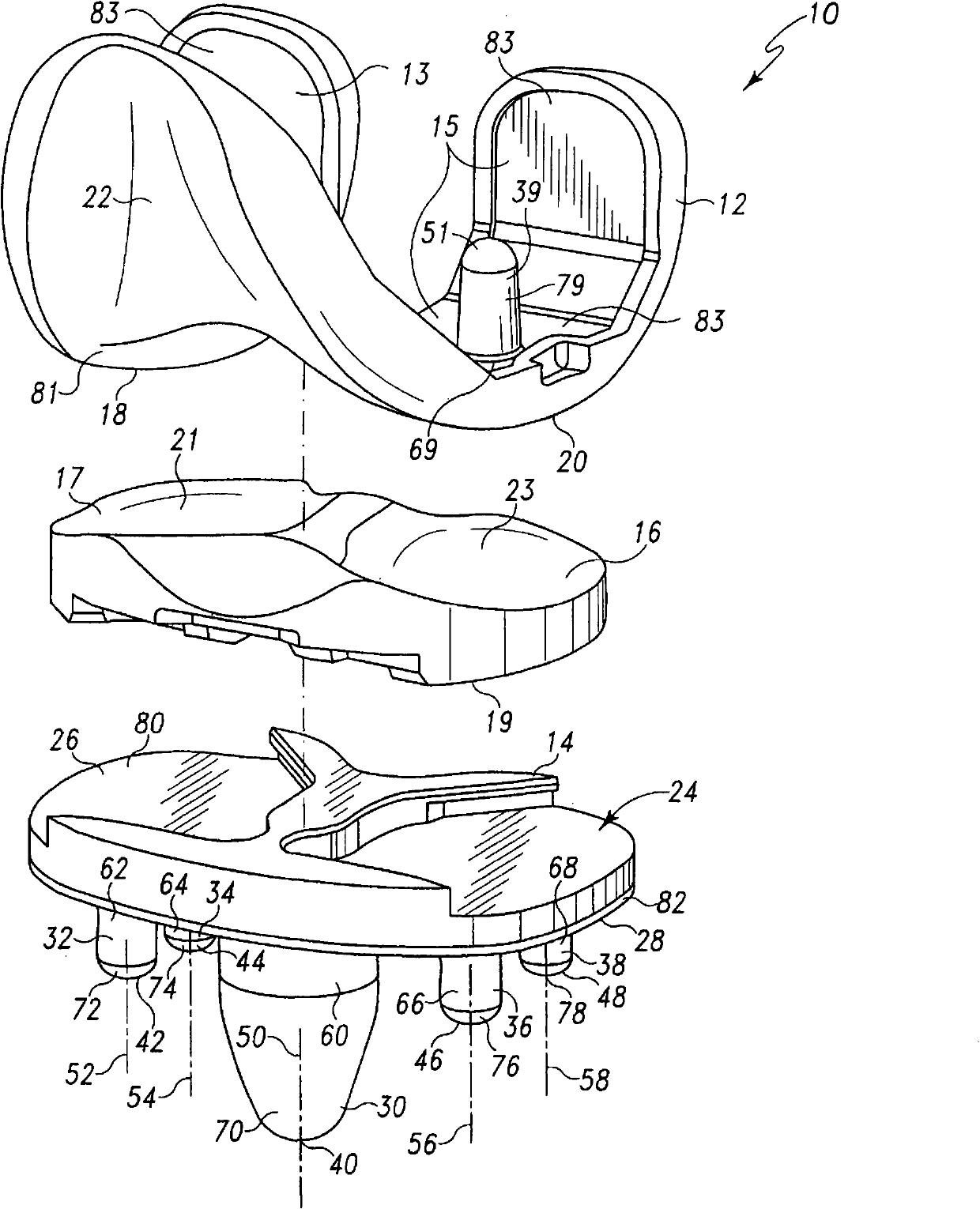
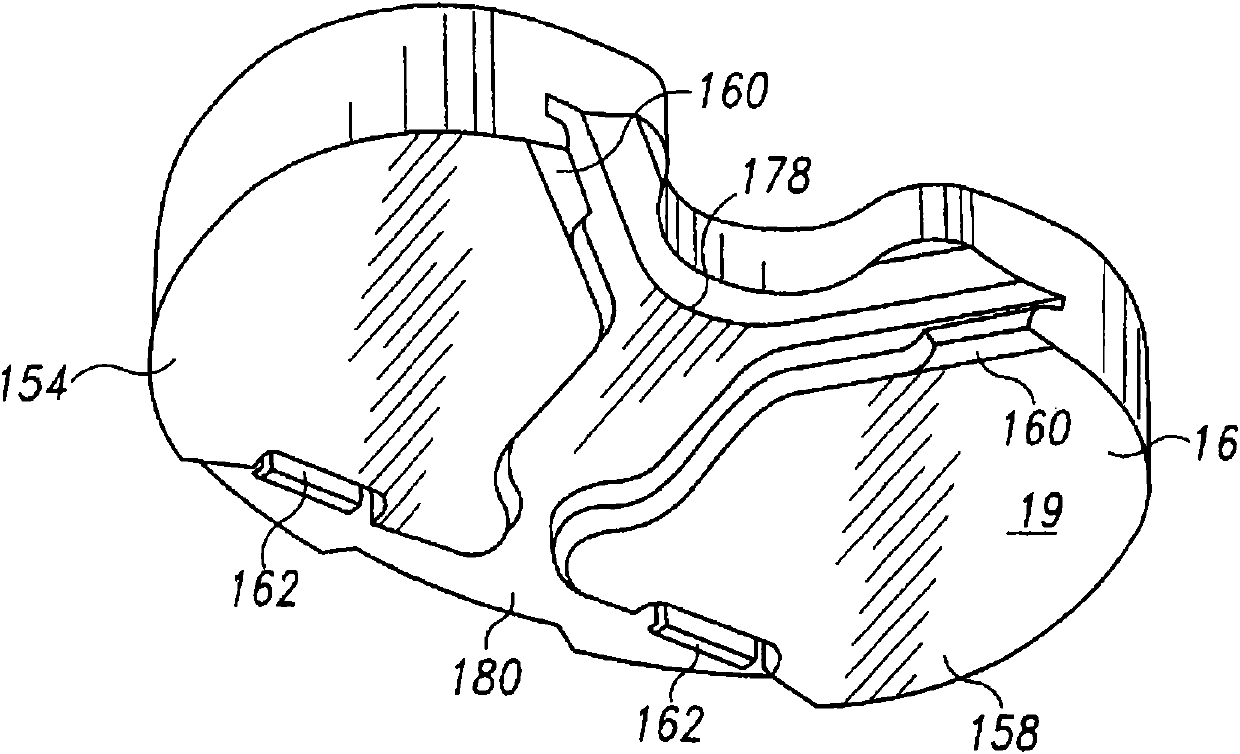
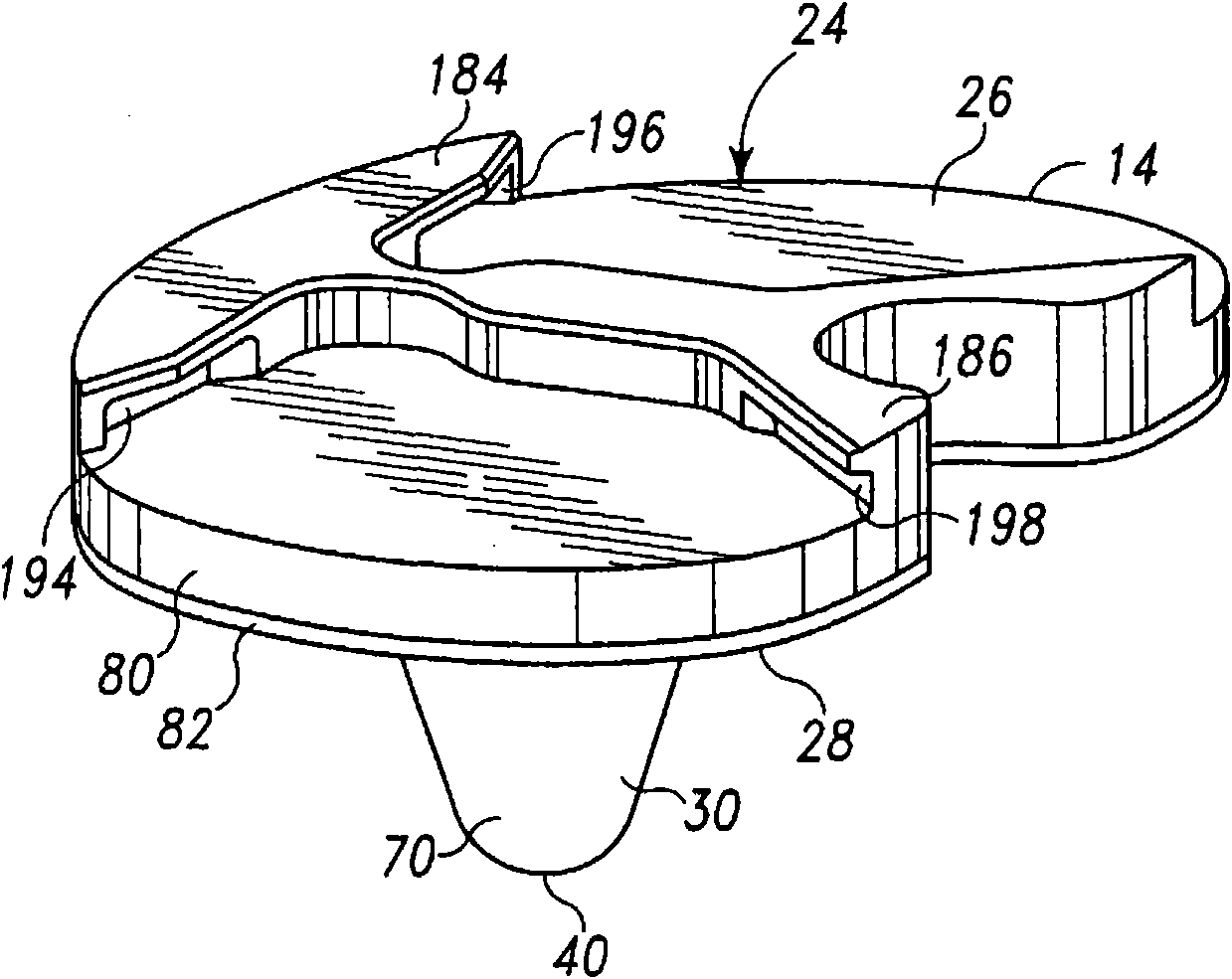
A joint prosthesis system (10) is suitable for cemented fixation. The system has two metal implant components (12,14) and a bearing (16). One of the metal implant components has an articulation surface (18,20,22) for articulation with the bearing. The other metal implant component has a mounting surface (26) for supporting the bearing. One of the metal implant components includes an extension (30,32,34,36,38,39), such as a stem or pegs, with an exposed outer surface (79). The metal implant component from which the extension extends comprises titanium and the exposed outer surface of the extension comprises a different form of titanium. A method of making the joint prosthesis is also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
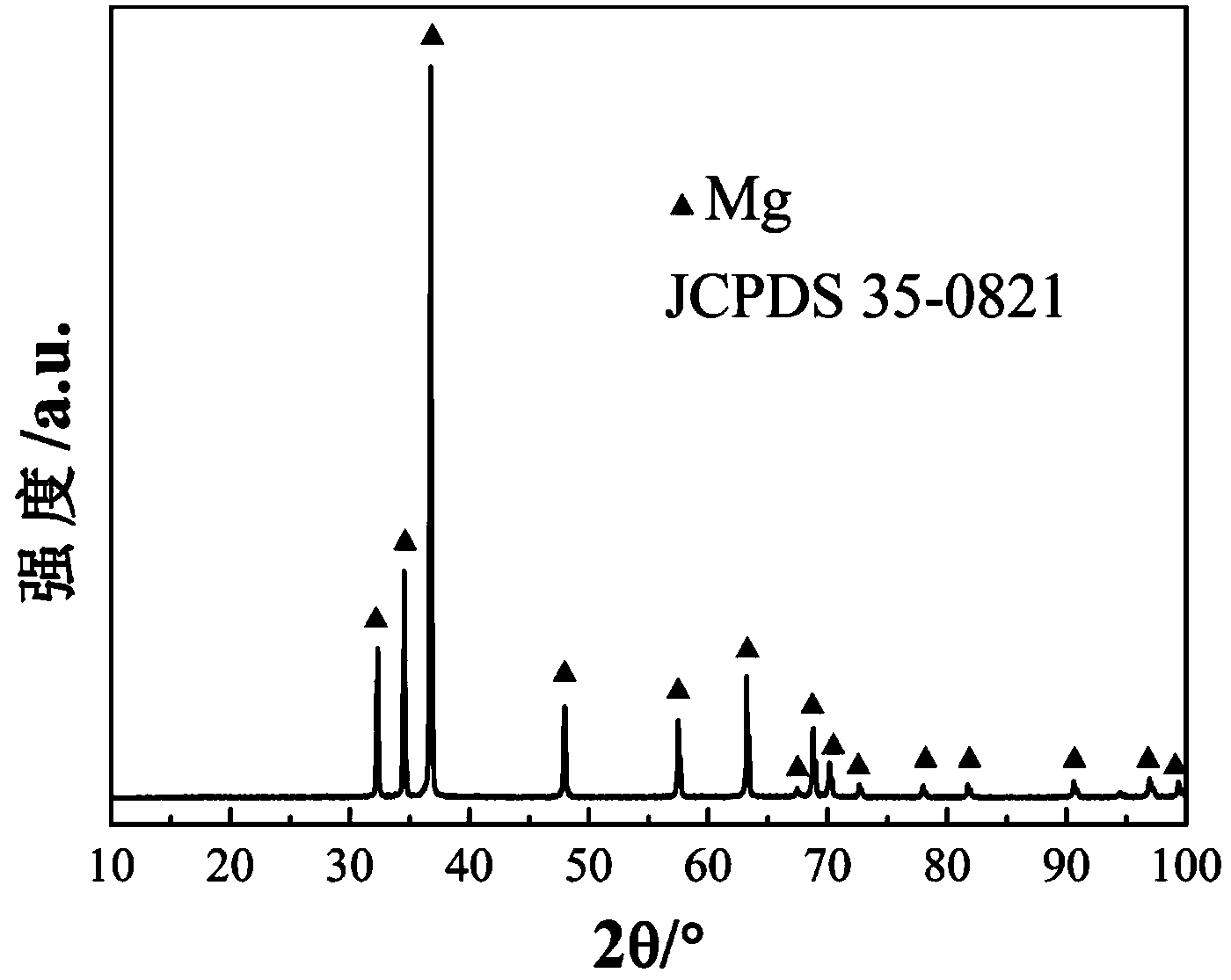
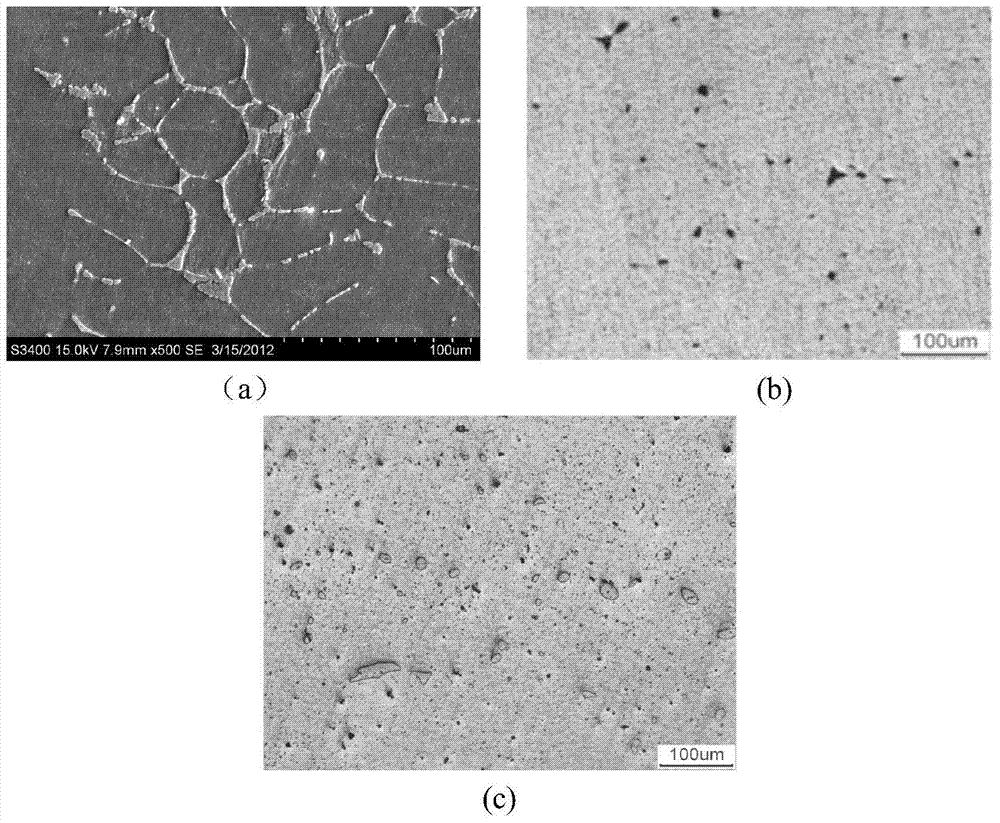
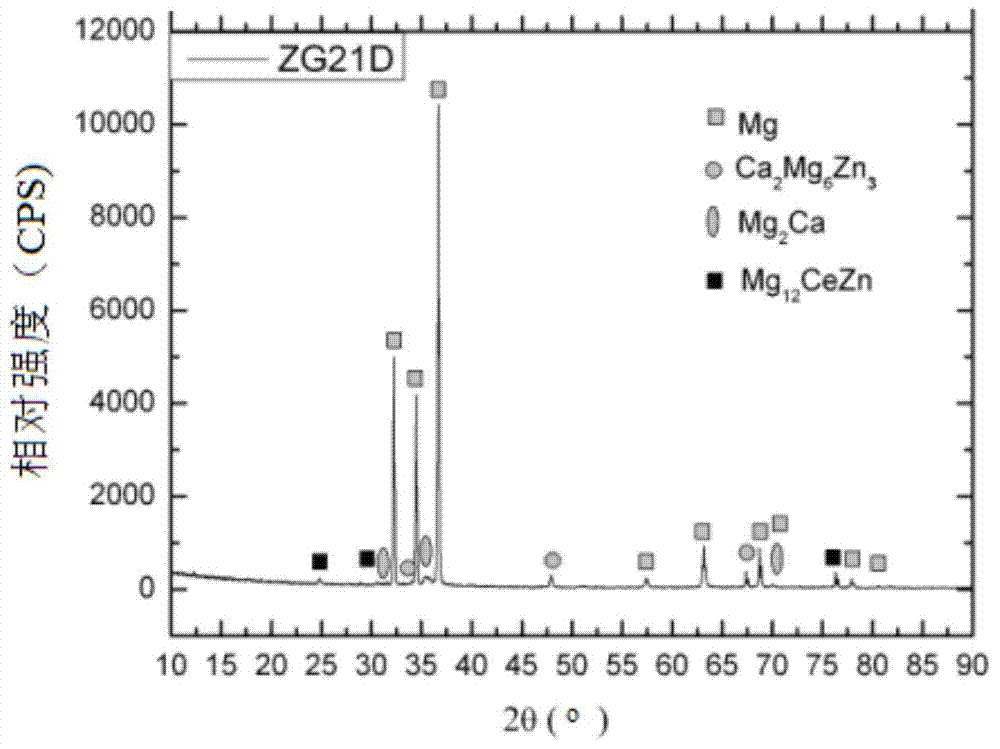
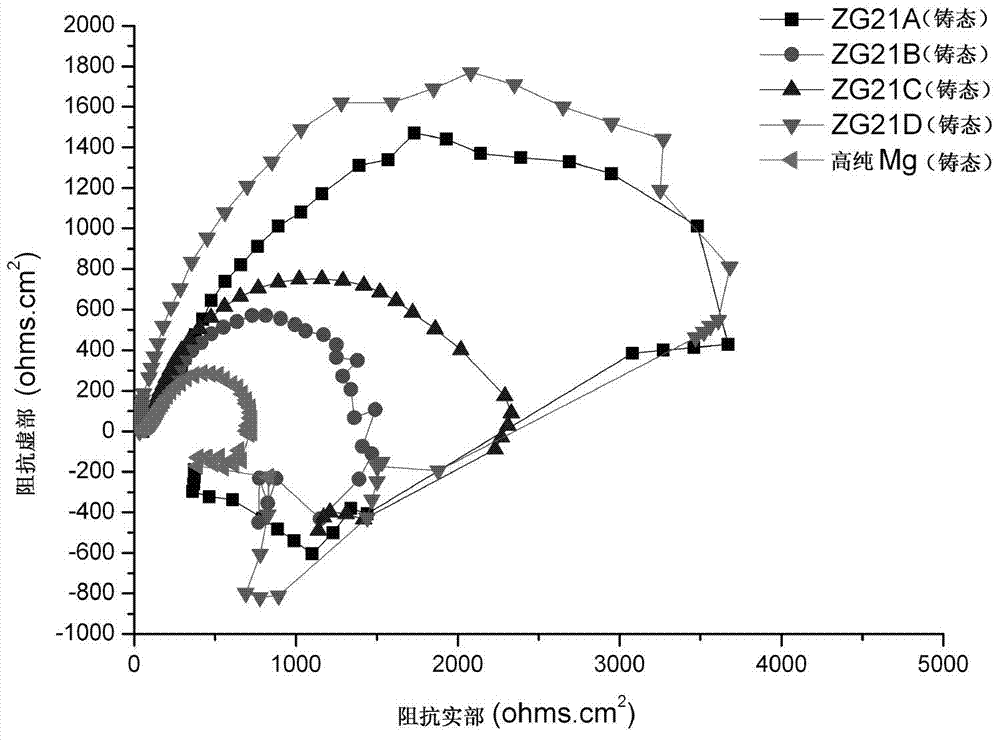
Degradable magnesium alloy implanting material for bone fixation and preparing method of degradable magnesium alloy implanting material
ActiveCN105349858AImprove and enhance mechanical propertiesImproved and enhanced biocompatibilityMg alloysBiomechanics
The invention relates to a degradable magnesium alloy implanting material for bone fixation and a preparing method of the degradable magnesium alloy implanting material. The implanting material is prepared from, by mass percent, 0.5-4% of Mg, 0.5-4% of Ag and the balance Y. The preparing method of the implanting material comprises the steps of ingot casting metallurgy, extruding, rolling and heat treatment. The prepared implanting material meets the requirement of plates, rods and profiles, wherein the plates, the rods and the profiles serve in biological fluid environments. By means of alloy materials, the good comprehensive mechanical performance needed by bone fixing materials is ensured, the beneficial effects of being capable of inhibiting bacteria, resistant to corrosion, free of cytotoxicity, good in biological mechanical property and the like are achieved, and the alloy materials can be degraded under the biological fluid environments. The implanting material can serve as bone nails or marrow nails or bone fraction plates or other various devices to be used under the medical conditions, and the comprehensive performance is good; and especially, the implanting material has both the biomechanical property and the biodegradable performance at the same time, and the typical defect of existing metal materials of a titanium alloy or stainless steel or high polymer materials in application of the department of orthopaedics is overcome.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biomedical degradable Mg-Zn-Zr-Sc alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103882274AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesAlloyBiological materials
The invention provides a biomedical degradable Mg-Zn-Zr-Sc alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: greater than or equal to 0.5% and less than or equal to 2% of Zn, greater than or equal to 0.3% and less than or equal to 0.8% of Zr, greater than 0% and less than or equal to 10% of Sc, and the balance of Mg. By utilizing the characteristics of favorable compatibility and high degradability of Mg in organisms, the Zn, Zr and Sc are reasonably added to further regulate and optimize the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg; and the alloy is prepared by a casting technique with lower cost. The Mg-Zn-Zr-Sc alloy does not have precipitated phase, and thus, is beneficial to inhibiting the couple corrosion, so the corrosion mode is uniform corrosion; the alloy has excellent corrosion resistance and favorable mechanical properties, and can be used in the fields of degradable bone plates, bone nails, vessel interventional therapy stents and other biological materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
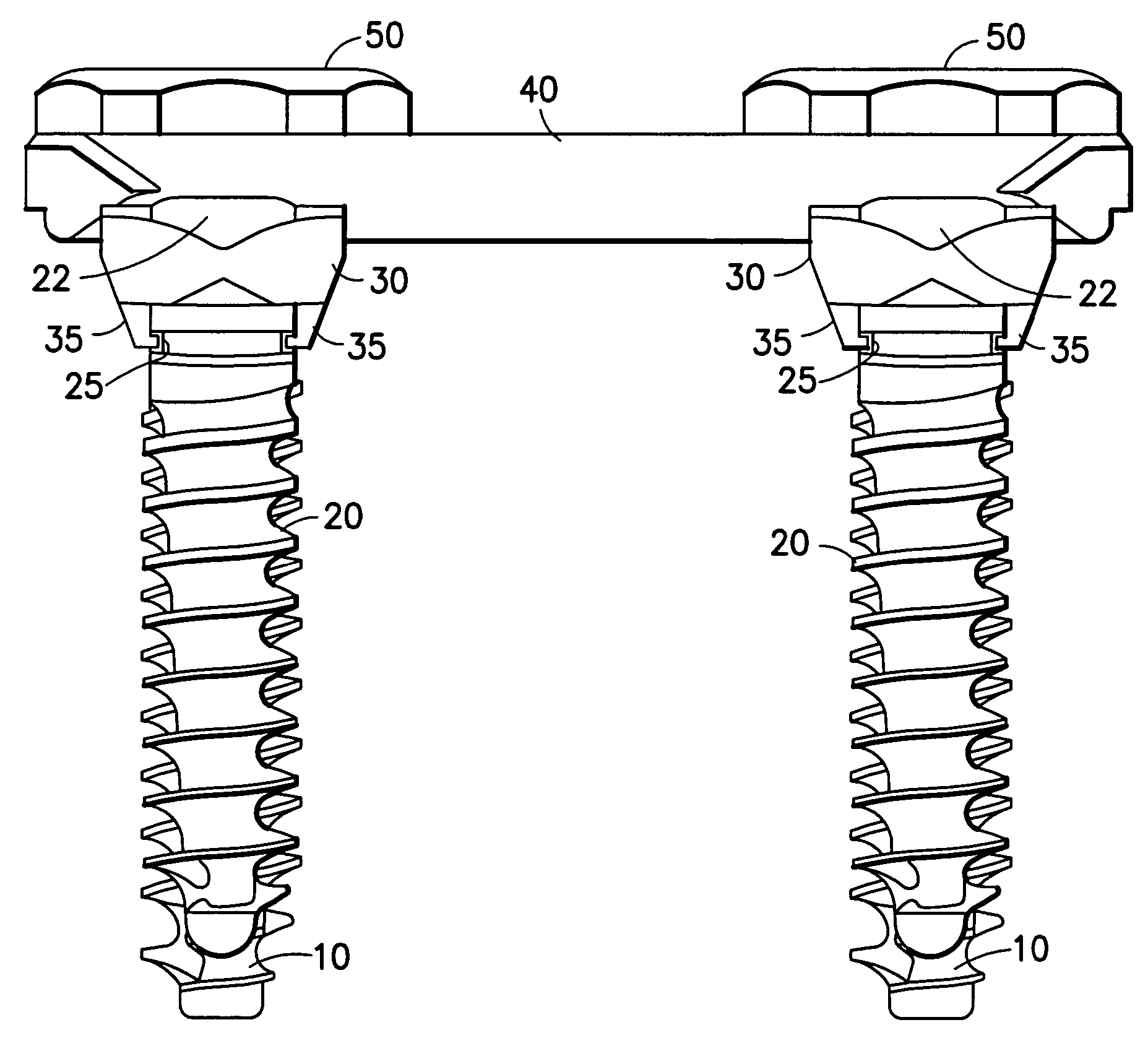
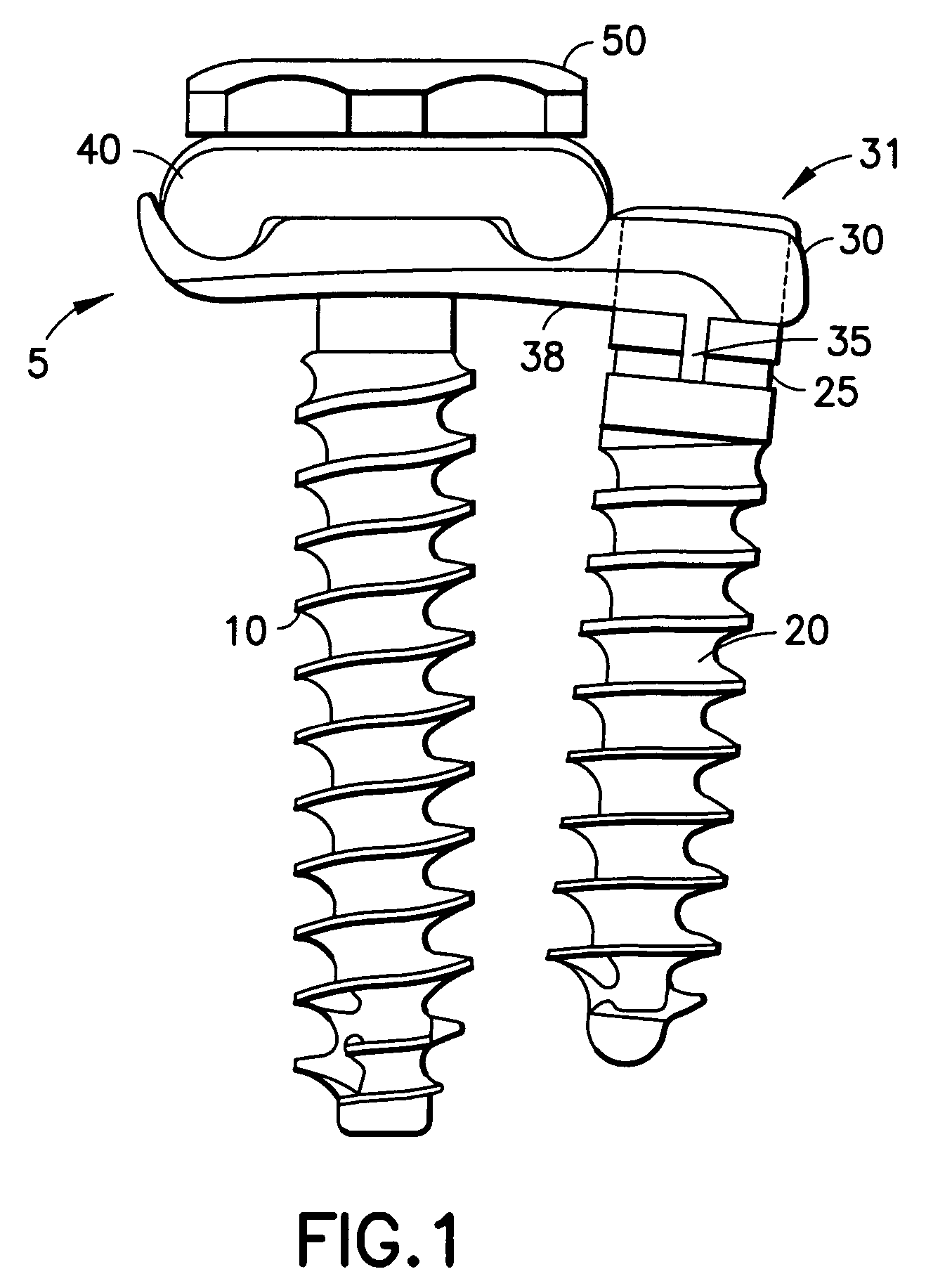
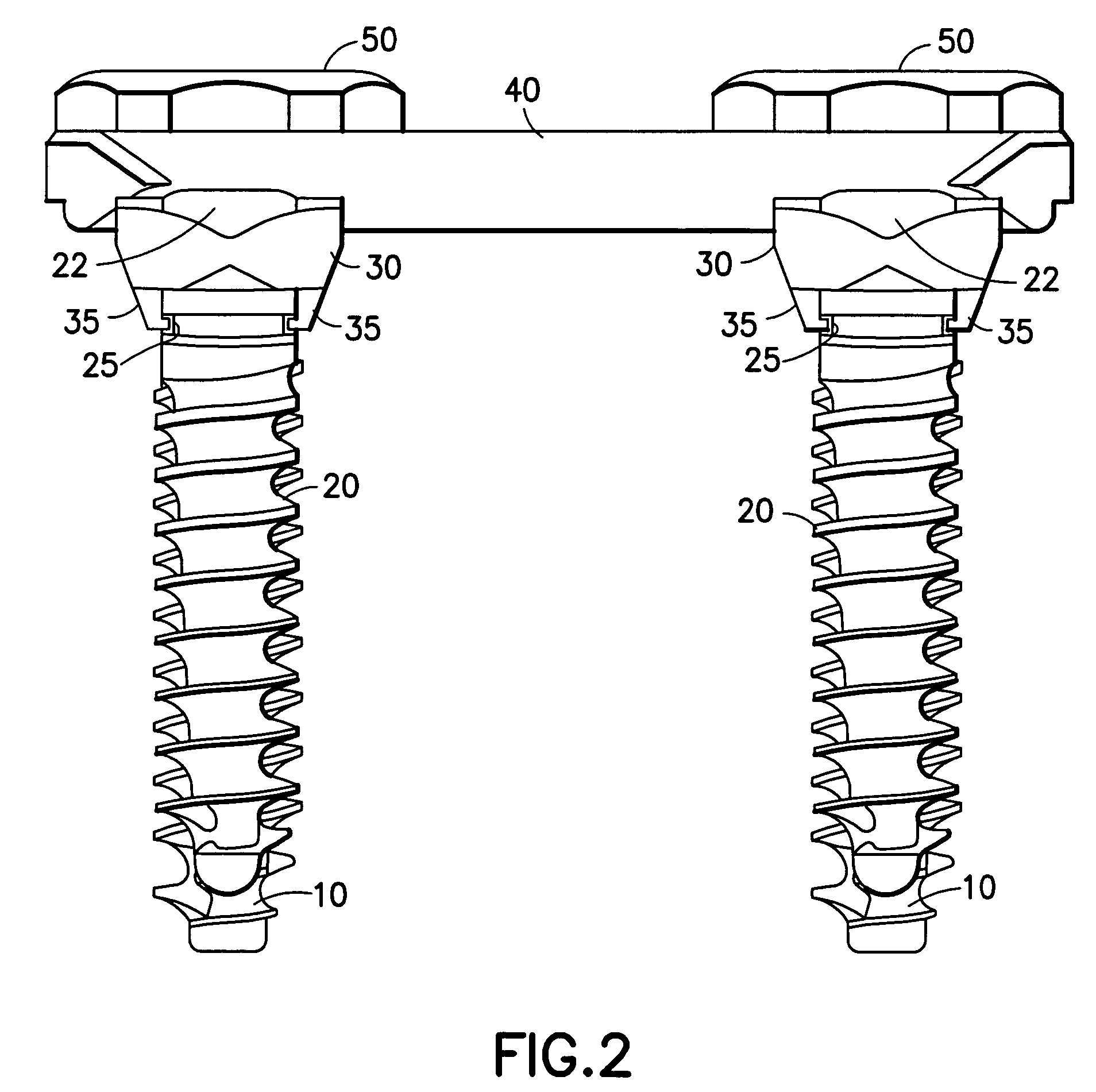
Locking mechanism for a bone screw
A locking mechanism for securing a bone screw 20 to a clamping element 30 of an osteosynthesis holding system 5 is provided. The bone screw 20 has a circumferential groove 25 located on a top portion of the screw 20 below a screw head 22. Snap catches 35 protrude from a bone-contacting surface 38 of the clamping element 30 and interlock with the groove 25 in the screw 20 when the screw 20 is inserted into the clamping element 30 (e.g., when the screw is screwed into a bone segment through a hole in the clamping element). A removal device 90 is provided for removing the screw 20, as a greater axial force is required to overcome the locking mechanism than is needed to engage the locking mechanism. A method for revision (removal) of the screw 20 from the locking mechanism is also provided.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104623739APromote growthSatisfy the requirement of strong fixed timeSurgeryMetallic material coating processesElemental compositionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws. The magnesium alloy consists of Mg of which the purity is more than 99.99wt%, Zn and adding elements, wherein the adding elements refer to one, two or three in Zr, Sr, Ca and Ag; and the magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 3 percent of Zn, 0.2-1.0 percent of Zr, 0-1.0 percent of Sr, 0-1.0 percent of Ca, 0.0-1.0 percent of Ag and the balance of Mg. The coated magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws have the advantages that after being subjected to comprehensive treatment, the magnesium alloy bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws have reasonable degradation rate, capacity of promoting new bone growth in the living body and high biocompatibility; particularly, after the bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws are treated by the mixed aqueous solution of hydrofluoric acid and calcium and phosphorus compounds, the corrosion rate can be regulated by virtue of the thickness of the surface fluorides and fluorapatite layer, and the requirement on rigid fixation time of the bone nails, bone plates and cancellous bone screws before internal fracture fixation within 3 months can be met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
All-biological controllable and degradable bone nail and using method thereof
InactiveCN103263697AGood biological propertiesGood biocompatibilityFastenersMg alloysMethyl carbonate
The invention relates to a novel all-biological controllable and degradable bone nail and a using method thereof. The bone nail is formed by combining an outer layer of threaded nail, an inner layer of magnesium alloy threaded nail and sealant, wherein the outer layer of threaded nail has the main component of carbon dioxide copolymer, and is prepared by a plastic processing method comprising the steps of: mixing material, pelleting, extruding, rolling, punching and the like; the center of the bone nail is provided with a threaded hole; a rabbet is formed in the front end of the bone nail; a standard 'cross-shaped' screw hole is formed in the position of a screw cap of the outer layer of threaded nail, and the outer layer of threaded nail can be implanted into a bone hole by the screw hole; and the inner layer of threaded nail made of magnesium alloy can be arranged in the threaded hole. The outer layer of threaded nail is combined with the inner layer of threaded nail, a specific amount of sealant made of ethyl methyl carbonate or ethyl acetate is coated at the exposed parts, the outer layer of threaded nail, the inner layer of threaded nail and the sealant can be used in a combined way or separately used, and the outer layer of threaded nail can be taken as a bone marrow fastening nail.
Owner:吉林金源北方科技发展有限公司
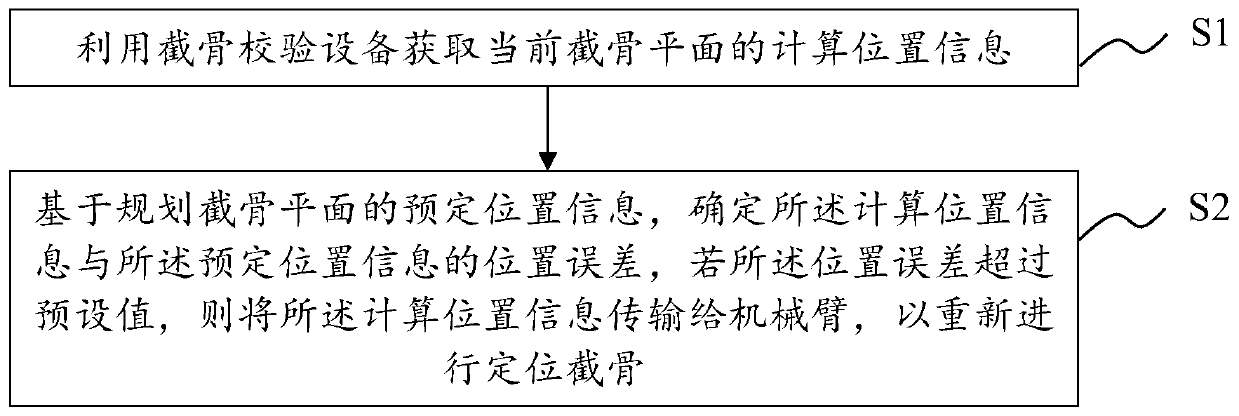
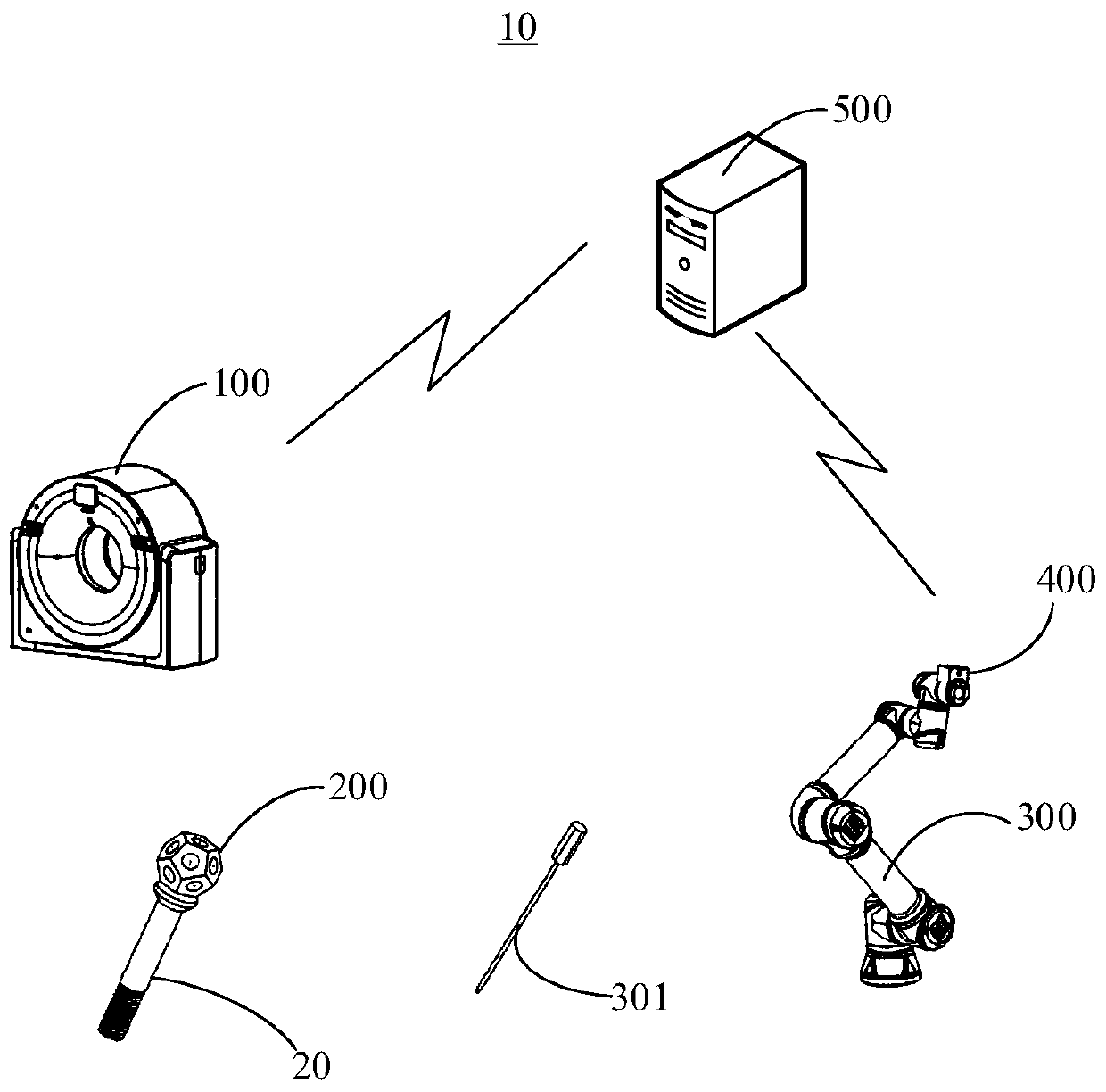
Osteotomy checking and testing method, checking and testing equipment, readable storage medium and orthopedic surgery system
ActiveCN110811832AHigh precisionAvoid re-pinningSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingOrthopedic ProceduresOrthopedic department
Owner:SUZHOU MICROPORT ORTHOBOT CO LTD
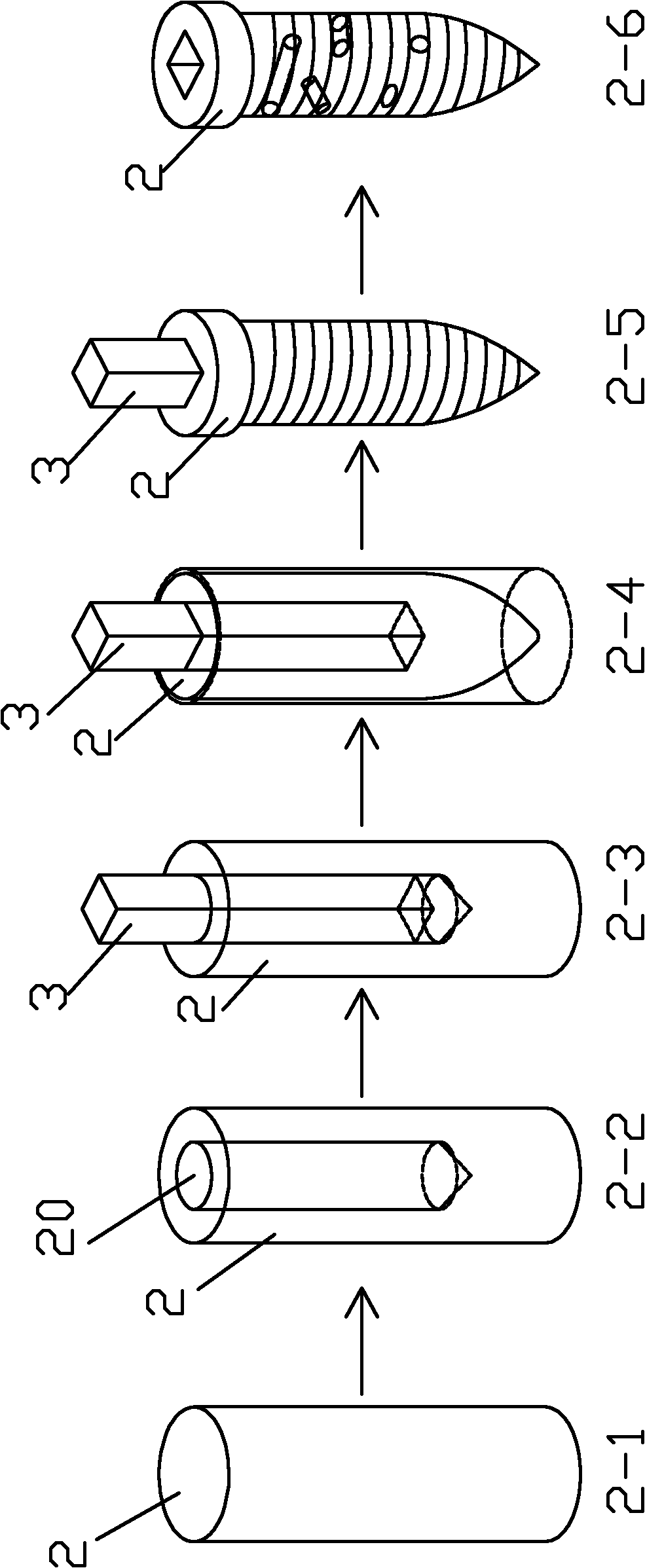
Alloy bone nail and manufacturing process thereof
The invention relates to an alloy bone nail and a manufacturing process thereof. The alloy bone nail is provided with a bone nail body, wherein the bone nail body is provided with an axial plug hole with a noncircular cross section and a plurality of non-axial through holes. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of: a, preparing a cylindrical alloy blank; b, drilling an axle hole along the axial direction of the cylindrical alloy blank; c, inserting a strip-shaped hard core body with a noncircular cross section into the axle hole to guarantee that the outer end face of the hard core body is protruded out of the end face of the alloy blank; d, placing the alloy blank in which the hard core body is inserted into a bone nail mould for forging and stamping to obtain a bone nail semi-finished product; e, trimming the bone nail semi-finished product and turning threads on the surface of the bone nail semi-finished product to manufacture a bone nail finished product; and f, taking the hard core body in the bone nail finished product out and drilling the plurality of through holes on the bone nail finished product along the non-axial direction. The bone nail is uniformly and stably stressed when implanted, and has a good implantation effect and a simple manufacturing process.
Owner:DONGGUAN EONTEC CO LTD
Biomedical magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106498251AGood biocompatibilityControllable degradation rateRare-earth elementCardiovascular stent
The invention provides a biomedical magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of biomedical metal materials. The alloy is composed of, by mass percentage, 0.05%-0.2% of Mn, 1%-4% of Zn, 0.05%-1% of Ca and the balance Mg, wherein the molar ratio of Zn to Ca is larger than 1.5. The novel human body biodegradable medical alloy is prepared through certain key technical parameters, such as a melting process and the alloy component ratio. The alloy does not contain rare earth elements and mainly contains the Mg-Zn-Ca phase, the alloy is mainly distributed in the crystal boundary, and less of the alloy is distributed inside a matrix. The alloy has excellent biocompatibility, prominent mechanical properties and excellent plastic processing properties and is controllable in degradation rate. According to the application characteristic of the alloy, the alloy can be used for preparing biodegradable cardiovascular stent materials, orthopaedic implants, bone plates, bone nails and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Degradable, high-toughness and ultrafine-grained magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy used for bone fixation and method for preparing same
The invention discloses a degradable, high-toughness and ultrafine-grained magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy used for bone fixation and a method for preparing the same by using an equal channel angular pressing technology with large deflection. The method comprises casting an ingot by using a magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy comprising 3.7 to 4.5 % of Zn, 1.0 to 1.5 % of rare earth elements, less than 0.5 % of Zr, less than 0.10 % of Mn, less than 0.01 % of Ni and the balance being Mg; cutting the ingot into cylindrical test pieces in accordance with channel sizes of an extrusion die; removing surface oil and oxide-film by conventional pre-treatment; and putting test pieces into equal channel die to heat with the furnace to 330 DEG C and then insulating, and continuously performing the equal channel angular pressing for more than and equal to 8 passes, with the test pieces rotating 180 DEG between adjacent passes. In the abovementioned way, the prepared magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy has an average microscopic grain size of less than 1.5 [mu]m, has advantages of good biocompatibility, high toughness, corrosion resistance and completely degradation in vivo, and can be used as degradable bone-fixation materials implanted in short-term, such as bone plate, bone nail and the like. The method provided by the invention is high in yield and simple in technology operation and equipment requirement, and had good prospects for industrial application.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Magnesium alloy bone nail and preparation method and application thereof
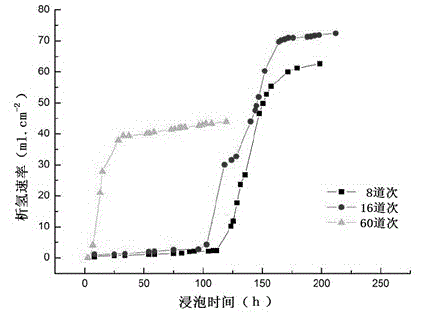
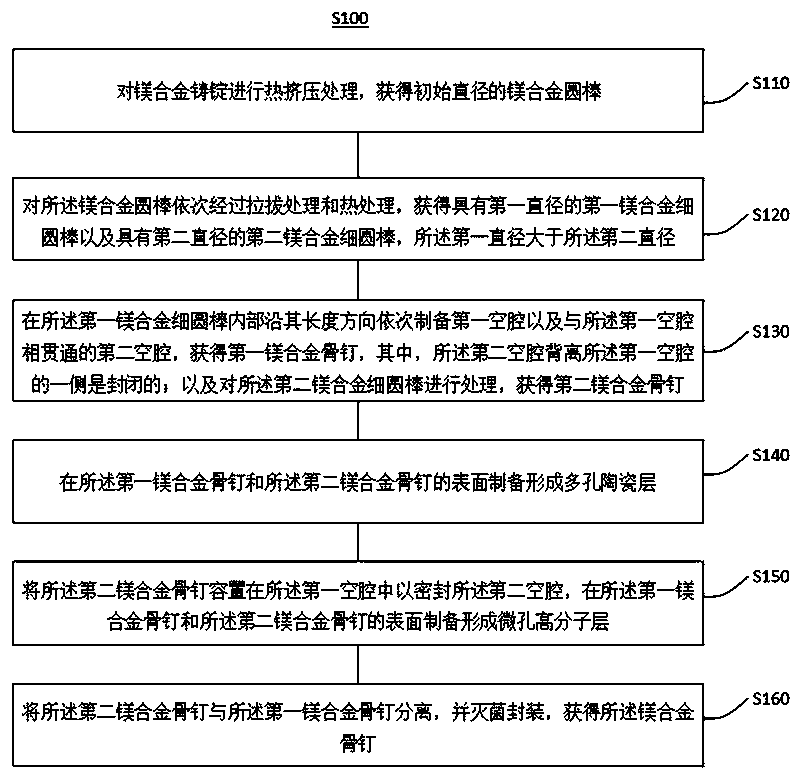
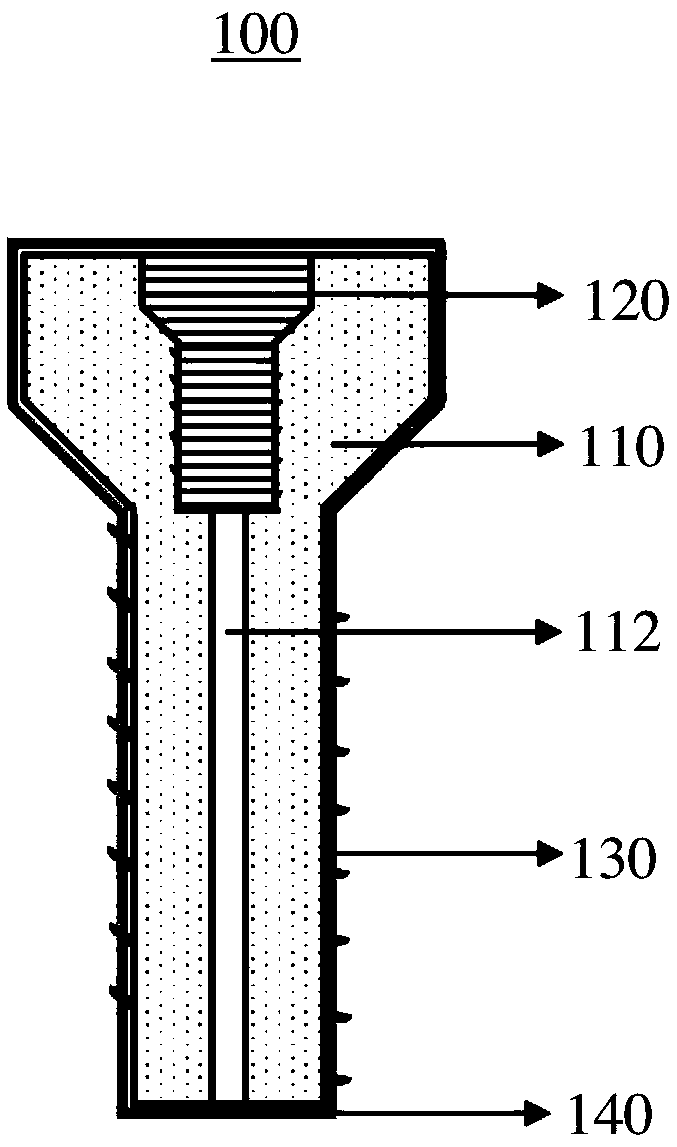
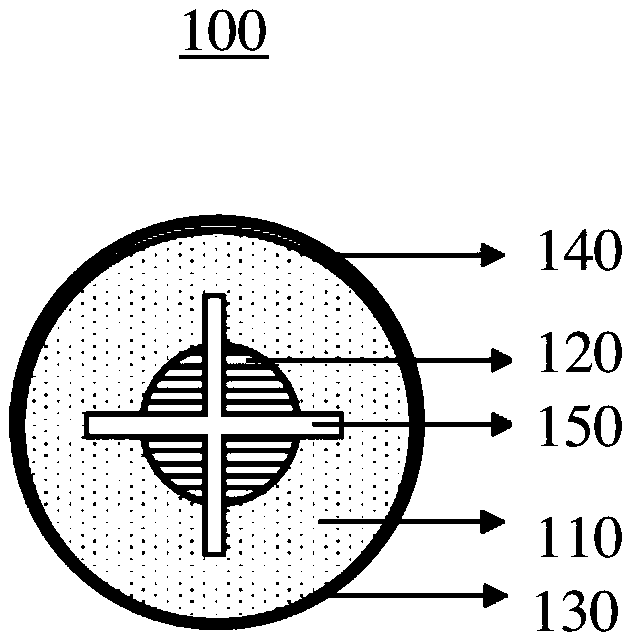
The invention provides a magnesium alloy bone nail and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out hot extrusion treatment on a magnesium alloy cast ingot to obtain a magnesium alloy round bar, and carrying out drawing treatment and heat treatment to obtain a first magnesium alloy thin round bar and a second magnesium alloy thinround bar; forming first cavity and a second cavity communicated with the first cavity sequentially in the first magnesium alloy thin round bar in the length direction of the first magnesium alloy thin round bar, and obtaining a first magnesium alloy bone nail, wherein one side, deviating from the first cavity, of the second cavity is closed; and processing the second magnesium alloy thin round bar to obtain a second magnesium alloy bone nail, forming porous ceramic layers on the surfaces of the first magnesium alloy bone nail and the second magnesium alloy bone nail, and forming a microporouspolymer layer on the overall surface of the two magnesium alloy bone nails to obtain the magnesium alloy bone nail. The degradation rate of the bone nail is slowed down and controllable through the porous ceramic layer, and medicine can be injected into the second cavity and slowly released through the microporous polymer layer.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL DEVICES (SUZHOU) SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dispersion strengthened medical Mg-Zn-Ce-Ca-Mn alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103757511AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceProsthesisMg alloysBiocompatibility
The invention relates to an in-vivo degradable dispersion strengthened biomedical polynary magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The in-vivo degradable dispersion strengthened biomedical polynary magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1.9-2.1% of Zn, 0.5-1.4% of Ce, 0.9-1.0% of Ca, 0.4-0.5% of Mn and the balance of Mg, and small and dispersed second phases are distributed in a magnesium matrix. An alloy cast ingot is firstly prepared by smelting according to design components, wherein the Ce can promote the second phases to realize intergranular discontinuous distribution, solution treatment is further performed to enable the second phases to be fully re-dissolved into a matrix phase, and then aging is performed to disperse and precipitate the small second phases in the magnesium matrix phase. Therefore, the obtained magnesium alloy has the advantages of high toughness, corrosion resistance, good biocompatibility and complete in-vivo degradation, and can be used for bone plates, bone nails, intravascular stents and other biological implants. The in-vivo degradable dispersion strengthened biomedical polynary magnesium alloy provided by the invention can significantly improve the defects of a microstructure of the magnesium alloy produced by a traditional melting and casting method, the effects are strengthened by aging precipitation of the small second phases, the processing properties and the mechanical properties are greatly upgraded, and the problem that the biological corrosion rate is too high in clinical applications is simultaneously solved. The process operation and the equipment requirements are simple, and industrial application prospects are good.
Owner:南通河海大学海洋与近海工程研究院 +1
Surgical navigation system, coordinate system registration system and method, equipment and medium
ActiveCN110711031AImprove accuracyMore room to moveSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersDistance detectionMedical imaging
Owner:WUHAN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE SURGICAL TECH CO LTD
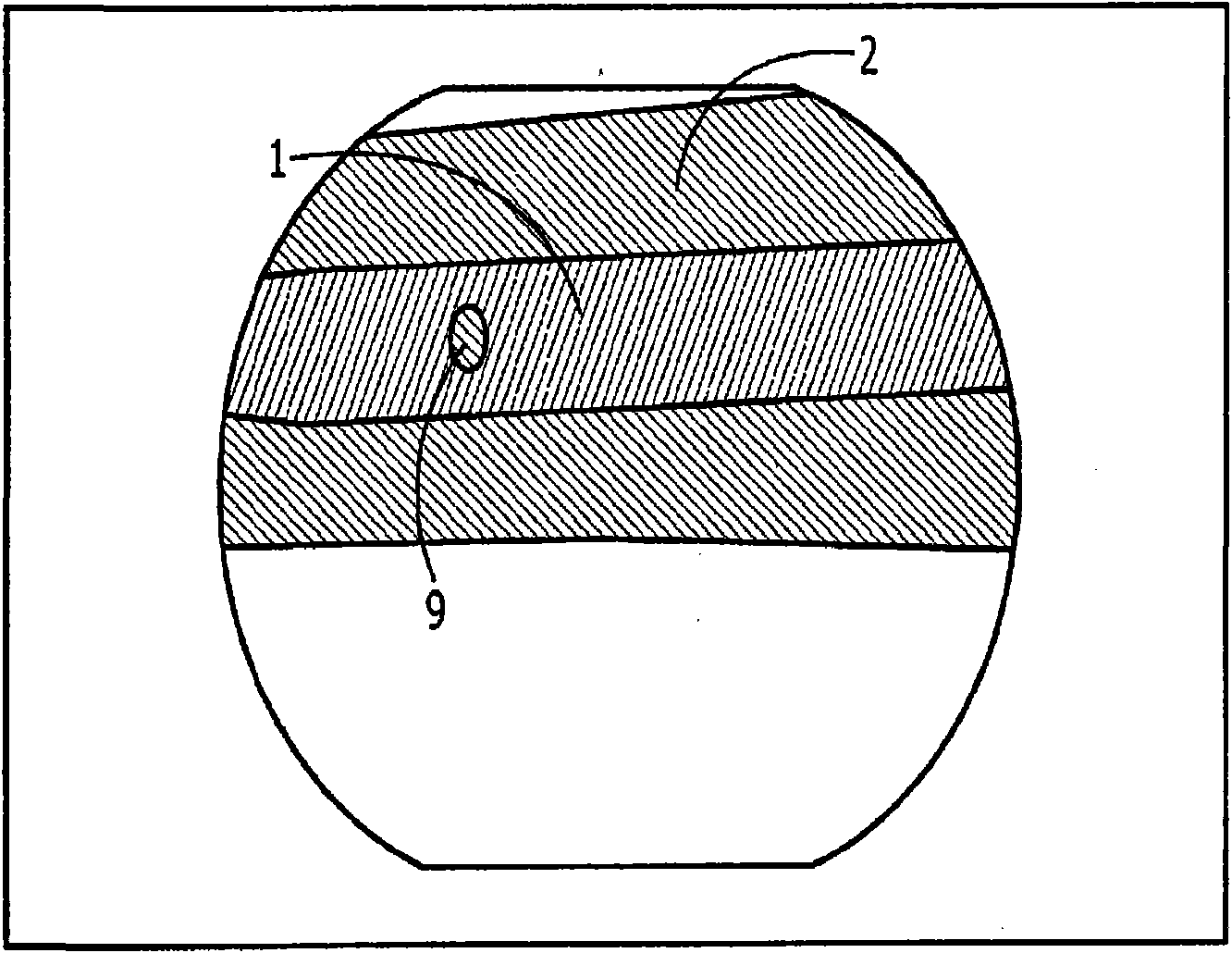
Coating for improving bioactivity of stainless-steel bone lamella and bone nail
InactiveCN102580169AImprove bindingImprove biological activityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMatrix nailBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a coating for improving bioactivity of a stainless-steel bone lamella and a bone nail. The Ti / TiB2 composite coating grows on the surface of a stainless-steel bone lamella and bone nail matrix (1), and the thickness of the Ti / TiB2 composite coating ranges from 500nm to 5mum; the inner layer of the composite coating, close to the bone lamella and bone nail matrix, is a pure-metal Ti layer (2) serving as a transition layer; and an external layer, namely a TiB2 layer (3), grows on the pure-metal Ti layer and serves as a function film layer. According to the invention, the pure-metal Ti layer grows on the surface of the bone lamella and bone nail matrix (1) by an ultrahigh vacuum magnetron sputtering method, and the TiB2 layer grows on the pure-metal Ti layer, so that the composite coating has better biocompatibility, frictional wear resistance and chemical stability, can effectively inhibit dissolution and seepage of toxic elements in stainless-steel matrix materials, and can reduce tissue reaction and aseptic loosening of the matrix, prolong the service life of the matrix and enhance the reliability of the matrix.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Directionally degradable and absorbable magnesium bone screw and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a directionally degradable and absorbable magnesium bone screw and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium bone screw comprises a bone screw, wherein the bone screw is made of pure magnesium or a magnesium alloy and has a thread, and the bone screw has different microstructure advantage orientations in the cross section and the longitudinal section respectively, so that the cross section is degraded faster than the longitudinal section during degradation and absorption of the bone screw. The microstructure advantage orientations of the bone screw made of the pure magnesium and the magnesium alloy are changed, so that certain crystal faces have advantage orientations in certain directions and have different microstructures in different directions, different degradation behaviors of different crystal faces of the magnesium and the magnesium alloy are fully utilized, and the degradation rate of the bone screw and growth of bone tissue are regulated to be well matched. The bone screw has different degradation rates in axial and radial directions, so that the bone screw has the characteristic of directional degradation, the intactness of the thread structure can be guaranteed at the early stage of implantation, and the early-stage pre-tightening force of the bone screw can be kept.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIGIN MEDICAL TECH
Carbon fiber pedicle screw and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN111419377ASolve the shielding effectSolve the problem of induced secondary fractureFastenersRadial planePolyether ether ketone
The invention provides a carbon fiber pedicle screw and a manufacturing method thereof. A screw body and a screw cap are prepared from carbon fiber composite polyetheretherketone, a screw positioningpin is arranged in the screw body, the screw positioning pin is arranged along the axial direction of the screw body, a screw cap positioning pin is arranged in the screw cap, the screw cap positioning pin is arranged in the radial plane of the screw cap, and the setting direction of the screw positioning pin and the setting direction of the screw cap positioning pin are perpendicular to each other. Through material modification, the modulus of a bone nail material is close to a bone modulus, so that the problems of stress shielding and induced secondary fracture are solved; for different types of patients, the material modulus is adjusted by adjusting a carbon fiber content, and different corresponding screw customization is further performed according to the patient conditions; tantalumpins convenient for X-ray imaging are implanted in the screw body and the screw cap as imaging positioning materials, so that monitoring of the state of the pedicle screw during and after operation isfacilitated, and mutually-perpendicular tantalum pins in the screw body and the screw cap can be more convenient and intuitive for three-dimensional positioning.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL
Aiming arm for locking of bone nails
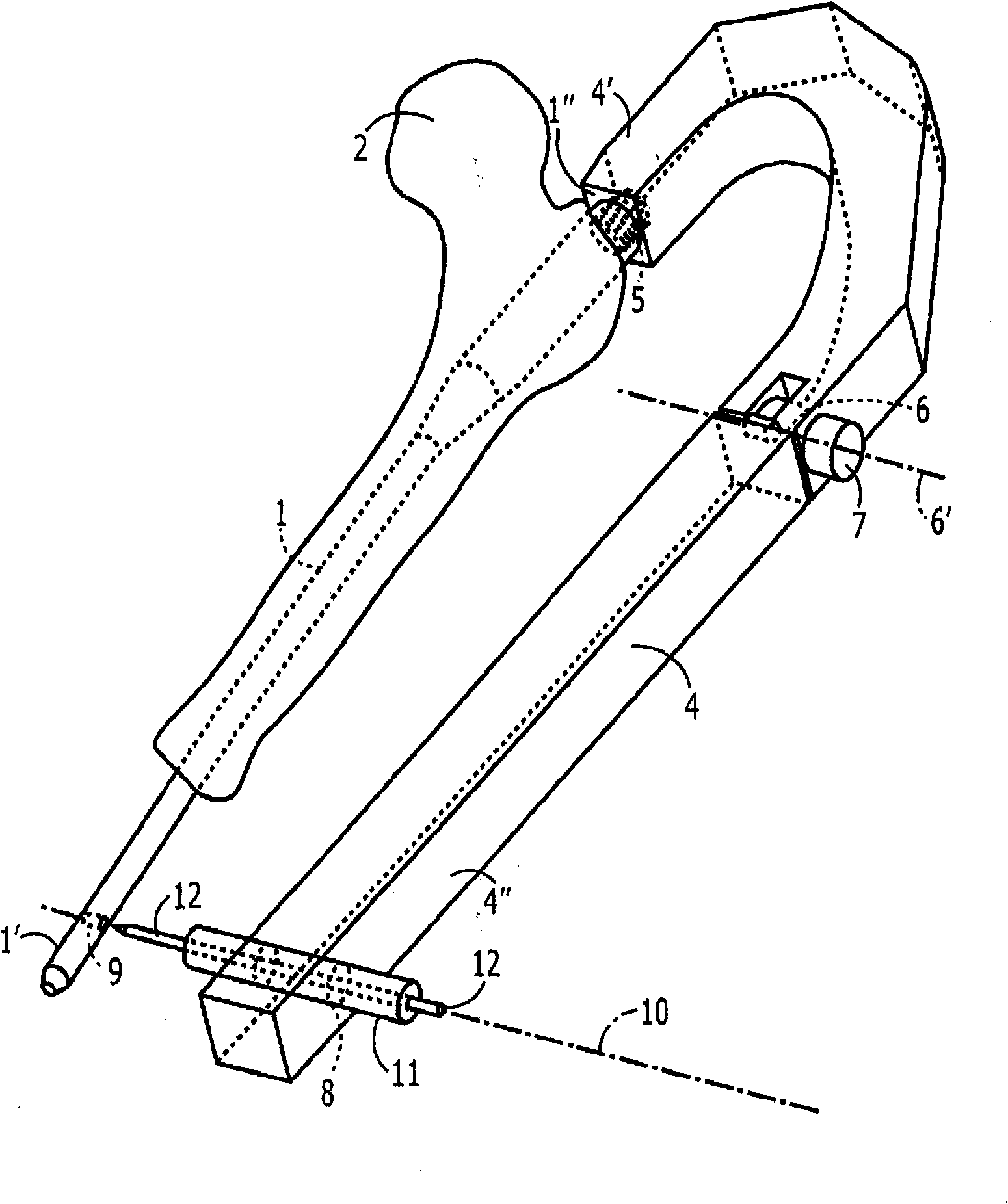
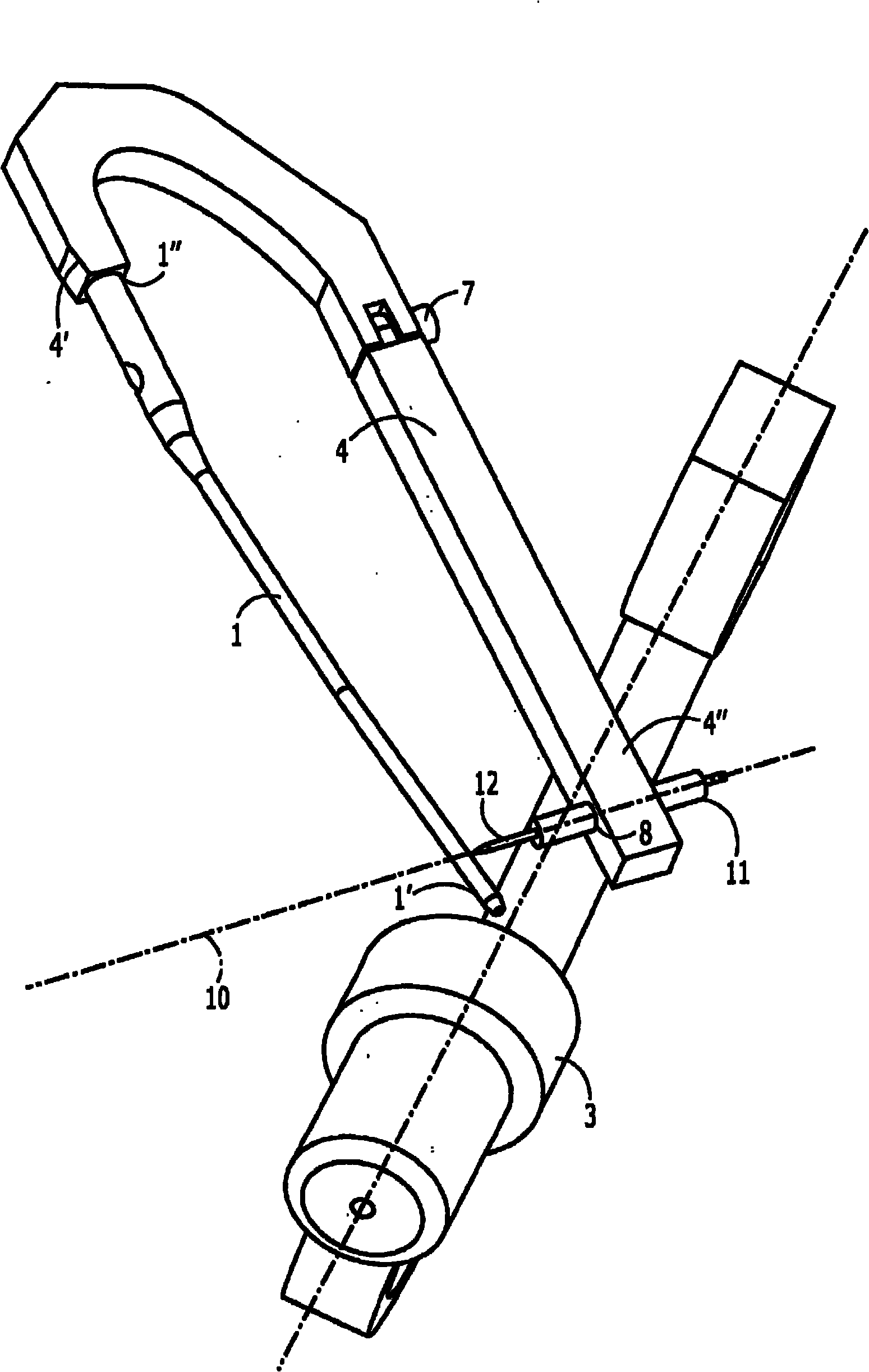
InactiveCN101801288AEasy to fixShorten the timeInternal osteosythesisBone drill guidesDistal portionPost implantation
An aiming arm (4) comprises a rigid distal member a distal portion (4') of which is configured to be releasably coupled to a proximal end (1' ') of an implant (1) to be implanted in a medullary canal of a bone (2), so that, when coupled to the proximal end of an implant, an orientation of the proximal end of the implant relative to the distal portion of the aiming arm remains constant in combination with a rigid proximal member (4'') a distal portion of which is rotatably coupled to a proximal end of the distal member. The proximal member includes an aligning feature (8) defining an axis. (10) aligned with an axis of a fixation element receiving hole (9) extending through a distal portion of the implant, the proximal member being rotatable after implantation of the implant, to an adjustedconfiguration in which the aligning feature is aligned with a post-implantation orientation of the fixation element.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
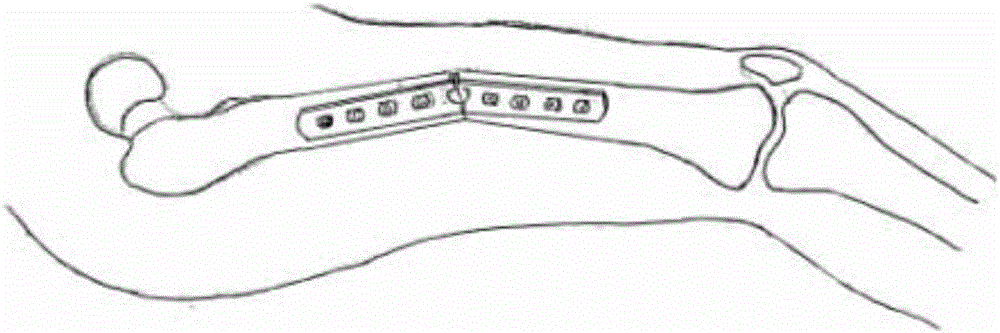
Anatomical individualized dynamic physiological bone pressurizing, locking and setting plate
The invention provides an anatomical individualized dynamic physiological bone pressurizing, locking and setting plate and belongs to the technical field of bone treatment instruments. The anatomical individualized dynamic physiological bone pressurizing, locking and setting plate aims at solving the problem that when an existing bone setting plate is used for fixing a fractured bone, stress shielding causes bone absorption at the broken ends of the fractured bone and nonunion of the fractured bone, and the bone setting plate is easily bent or easily breaks and the problem that the bone setting plate is large in external fixing volume and is inconvenient to carry after operation. The in-vivo external bone setting plate comprises an anatomical individualized locking plate, a right-angle fixing plate, a right-angle pressurizing plate and a physiological pressurizer, wherein the right-angle fixing plate and the right-angle pressurizing plate are installed in the middle of the anatomical individualized locking plate, the physiological pressurizer is installed between the vertical plate of the right-angle fixing plate and the vertical plate of the right-angle pressurizing plate, the anatomical individualized locking plate is provided with multiple screw holes, bone locking screws are installed in the screw holes, and the area, corresponding to the physiological pressurizer, of the anatomical individualized locking plate is an area free of holes and slots. The anatomical individualized dynamic physiological bone pressurizing, locking and setting plate is mainly used for internal and external fixation treatment of the fractured bone.
Owner:王兆年
Method for preparing nano structure with biological activity on surface of pure titanium
ActiveCN104027839AHigh biological activityHigh specific surface areaProsthesisAcid etchingTitanium surface
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Precipitation strengthening type implantable magnesium alloy and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN112813324AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceSolution treatmentIntravascular stent
The invention relates to a precipitation strengthening type biomedical magnesium alloy capable of being degraded in vivo and a preparation process of the precipitation strengthening type biomedical magnesium alloy. The magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 5.0-6.0% of Zn, 1.0-2.0% of Yb, 0.3-0.5% of Zr and the balance Mg. A submicron second phase is dispersed and distributed in a magnesium matrix. The process comprises the following steps: smelting an alloy ingot according to design components to ensure that initial grains are equiaxed, uniform and fine, carrying out solution treatment to ensure that the second phase is fully dissolved into the matrix, and carrying out aging treatment to fully disperse and separate out the submicron second phase. The magnesium alloy prepared by the process has the advantages of corrosion resistance, high strength, good biocompatibility and complete degradation in vivo, and is suitable for biological implants such as intravascular stents, bone nails, bone lamellas and the like which simultaneously require certain strength and corrosion service cycle. According to the precipitation strengthening type biomedical magnesium alloy and the preparation process, the heavy rare earth element ytterbium (Yb) is introduced into an alloy system so as to regulate and control the morphology and distribution of a precipitated phase, the corrosion resistance of a matrix alloy is effectively improved while the matrix is strengthened by means of dispersed precipitation of the fine second phase, and the problem of too fast corrosion in biomedicine is solved. The preparation process is universal and efficient, and has a good popularization prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
High-strength biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe alloy material with rapid biodegradability, and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe alloy material with rapid biodegradability, and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium alloy is prepared from the components in percentage by mass: 5.0 to 6.0 percent of Zn, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of Zr, 0.01 to 0.09 percent of Fe, and the balance Mg and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises the concrete steps of smelting, carrying out casting homogenization treatment, hot-extruding and carrying out artificial aging treatment, so that biomedical magnesium alloy sheets, rods and wires meeting the service requirement of the biological fluid environment are obtained. According to the high-strength biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe alloy material with rapid biodegradability provided by the invention, the alloy elements harmless to a human body are added into the magnesium alloy, so that the alloy has no any toxicity on the human body after being degraded in vivo, and has excellent mechanical property, favorable mechanical property and processability, and appropriate corrosion rate. The high-strength degradable biomedical Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe alloy material provided by the invention has the tensile strength being larger thanor equal to 360MPa and the yield strength being larger than or equal to 320MPa, and is suitable for preparing medical materials such as bone nails.
Owner:NEW MATERIAL INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF SCI
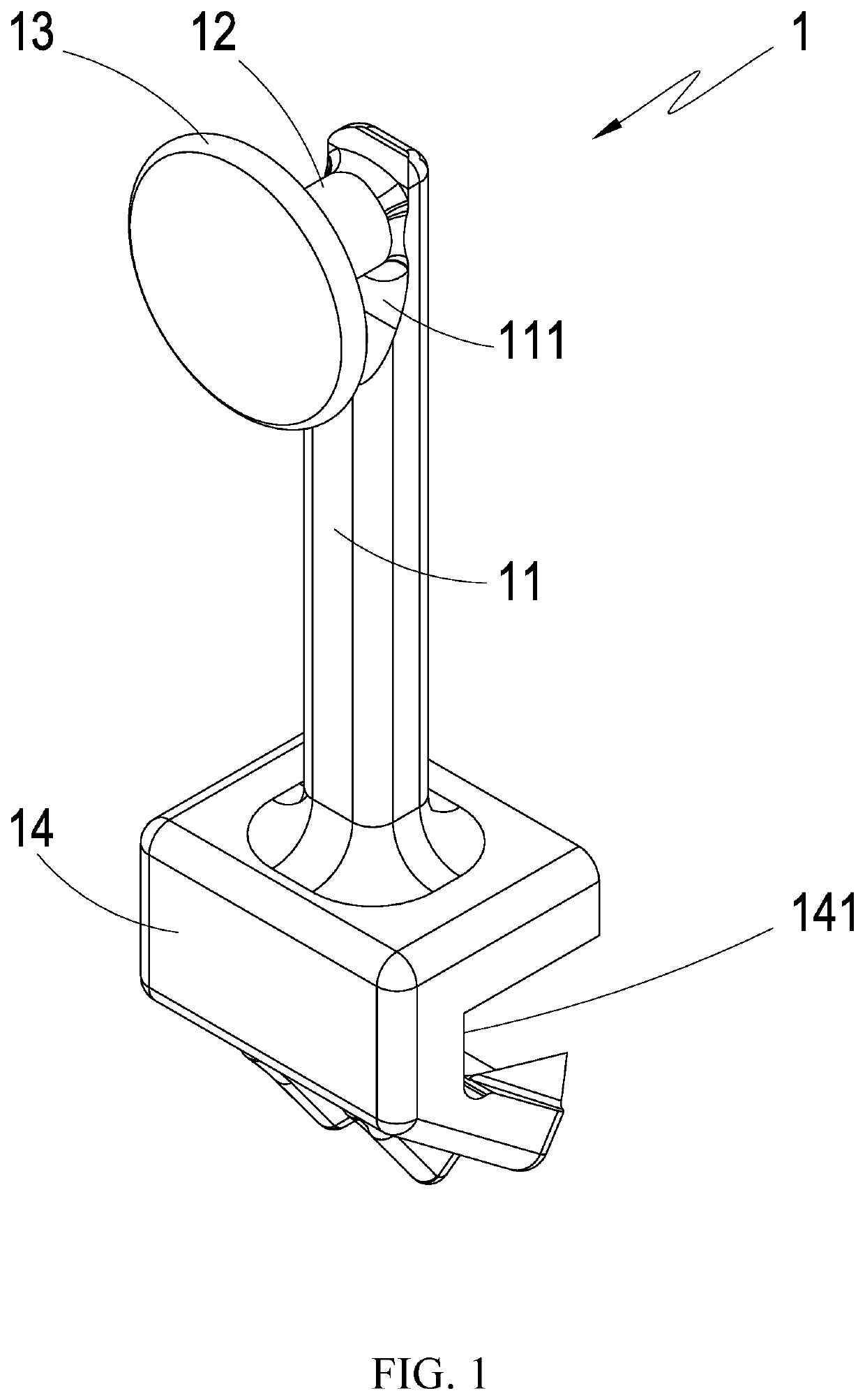
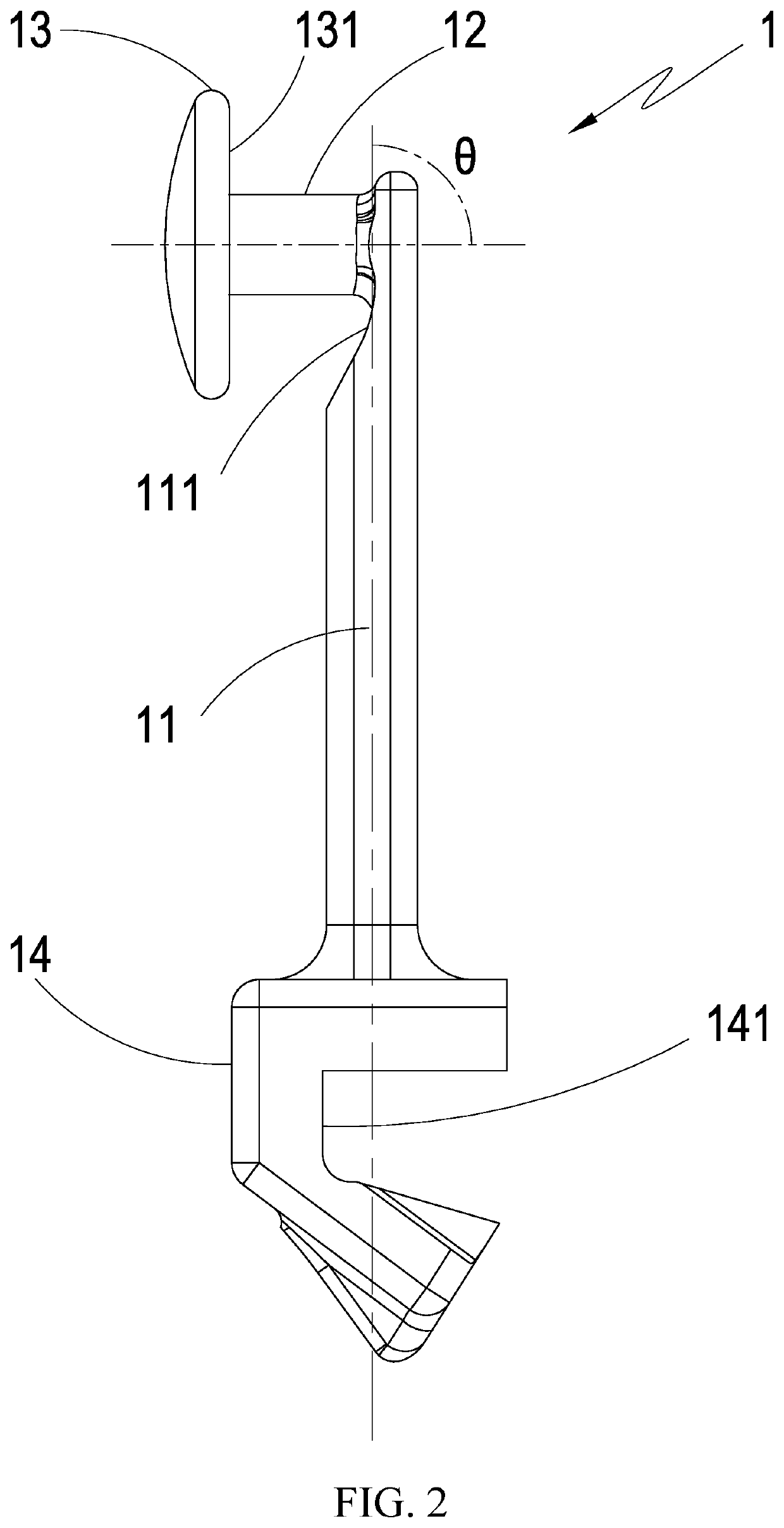
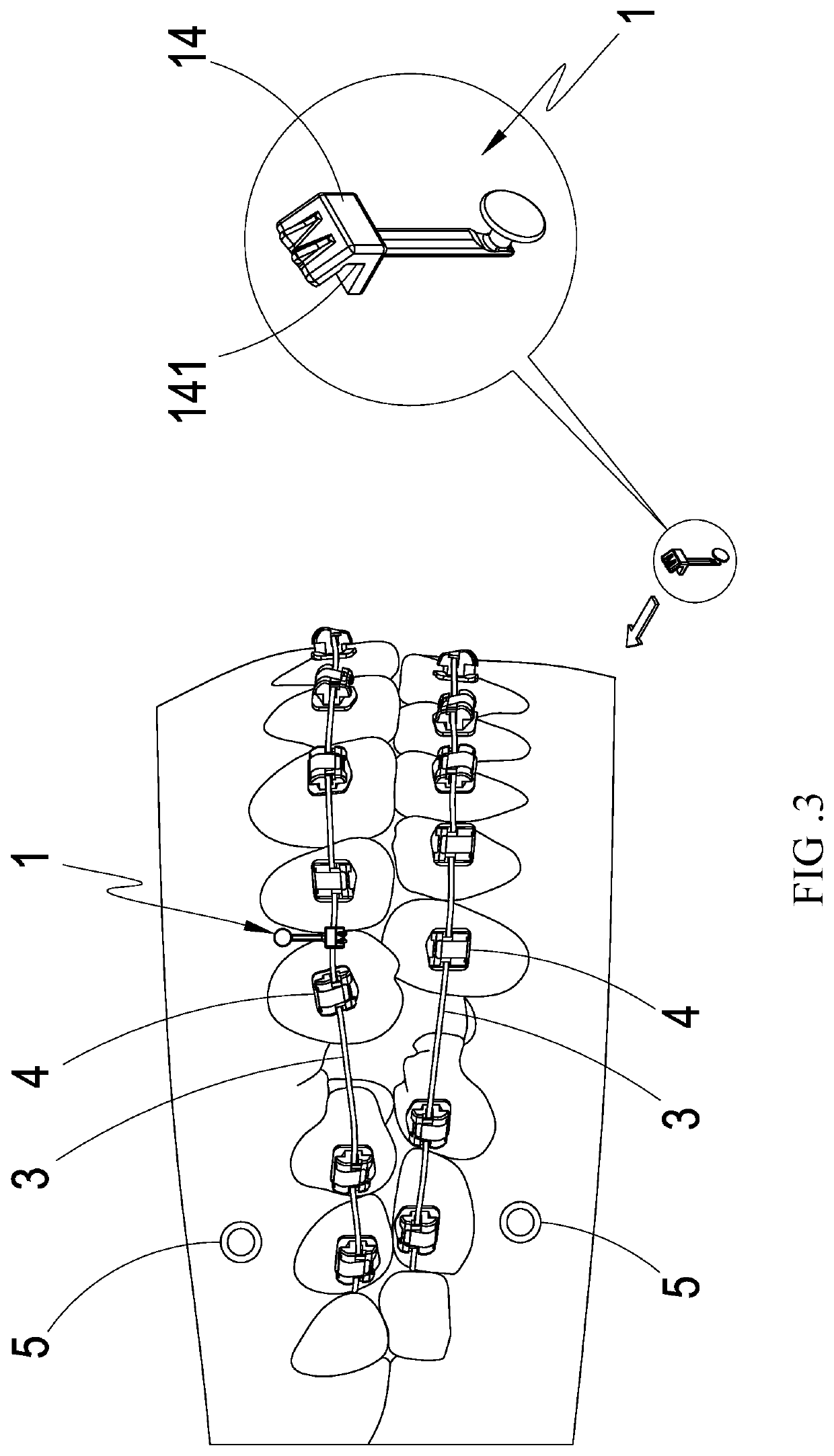
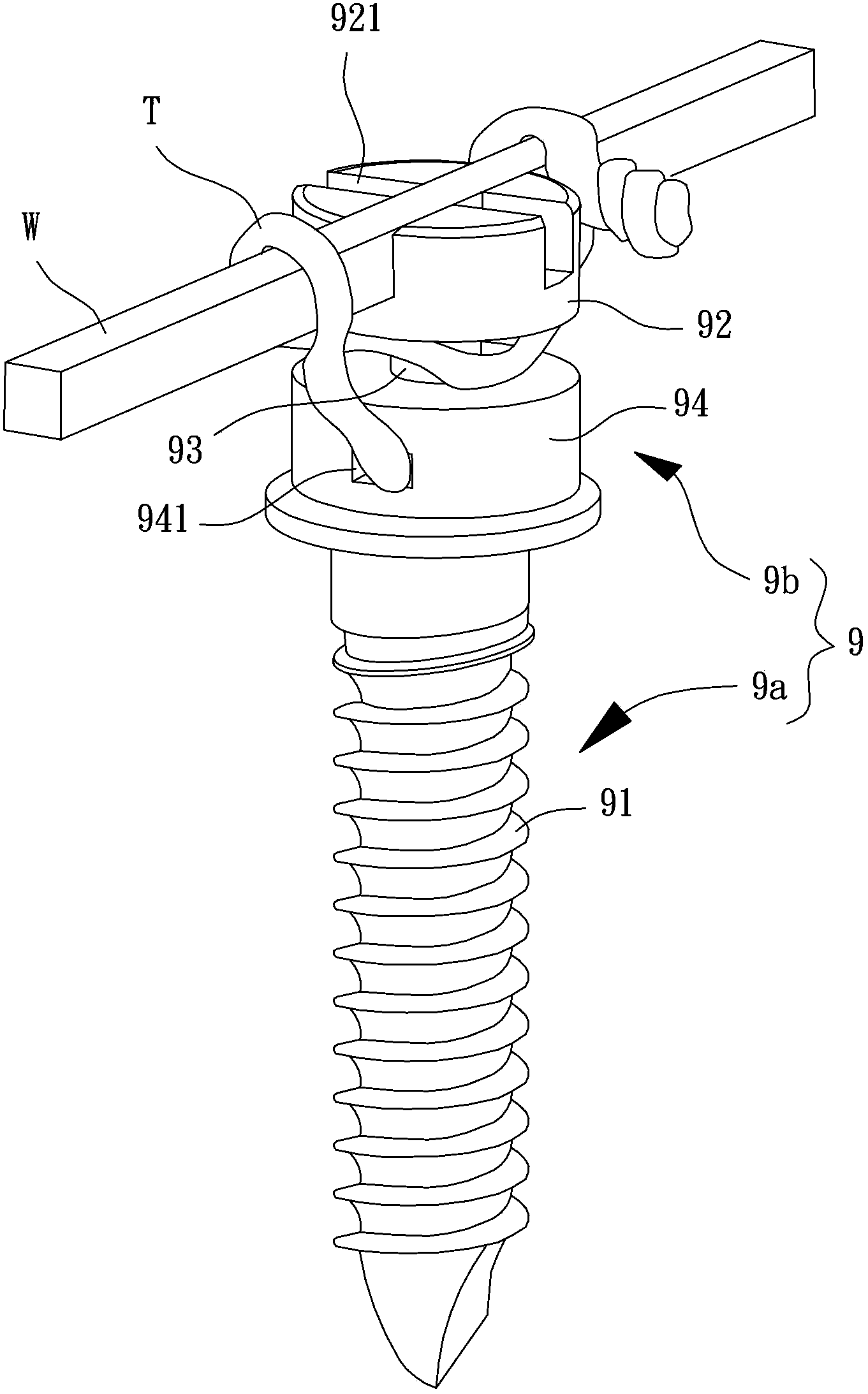
Dental traction device
InactiveUS20200163743A1Easily and rapidly and engagedEasy to useDental implantsArch wiresArch wiresDentistry
A dental traction device comprises an extension main-body, a tractive-body, a blocking-stopping-body, and a seat-body. When using, the dental orthotics are firstly set and the dental correction archwire connection is set, and the bone nail is set at the gum; then, the seat-body is fixed on the dental correction archwire; one end of the elastic element is bypass the blocking-stopping-body to stick and engage on the tractive-body and the other end is stuck and engaged on the bone nail; then the blocking-stopping-body is cooperated with the tractive-body to fix the elastic element to avoid falling-off; and the contraction elastic force of the elastic element generates the pulling force to the dental correction archwire and the teeth by using the extension main-body as the force moment to produce the traction correction effect; and so as to achieve the practicality and progressiveness which is convenient in use and avoids falling-off.
Owner:CHEN YI WEN +1
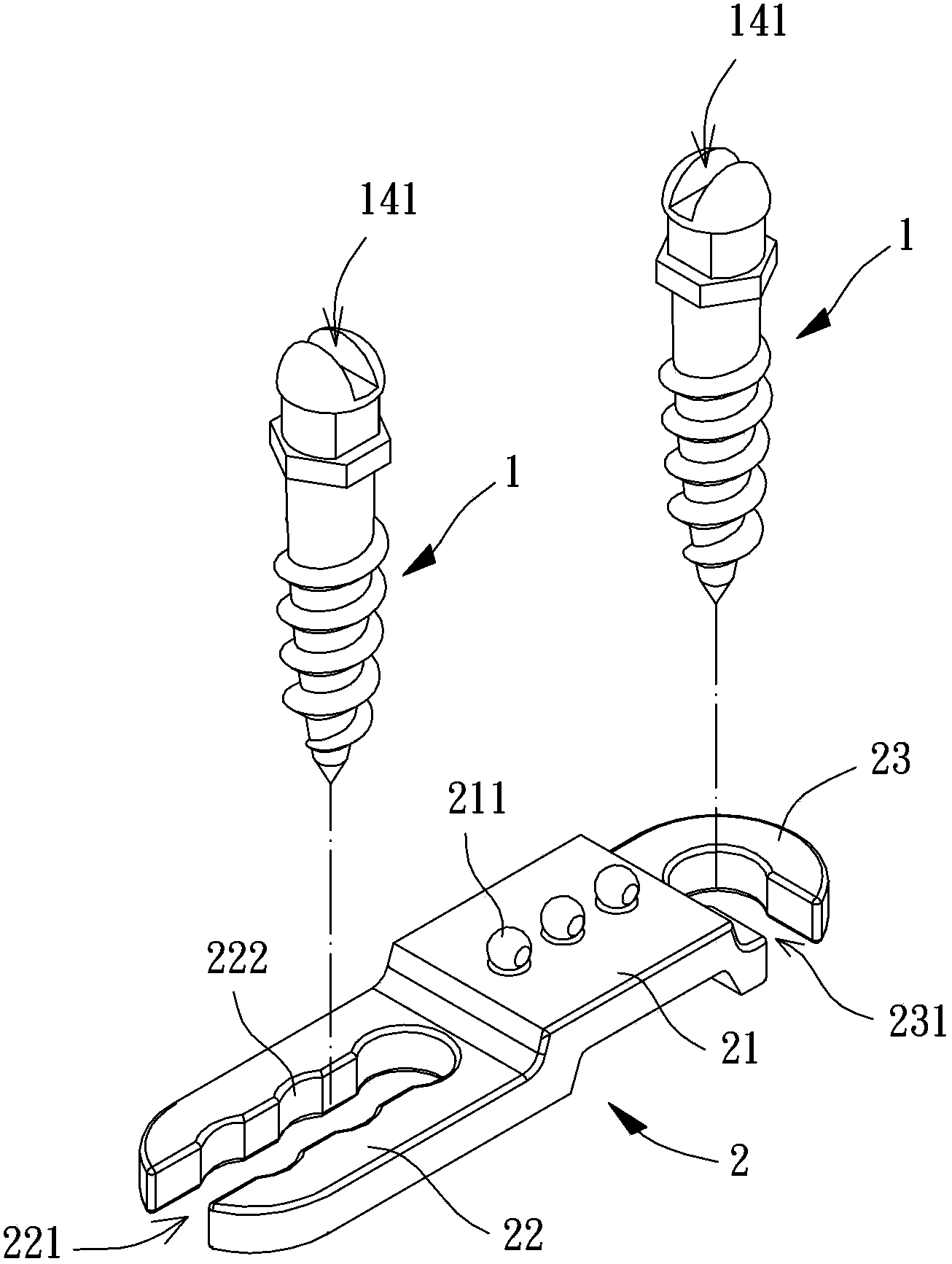
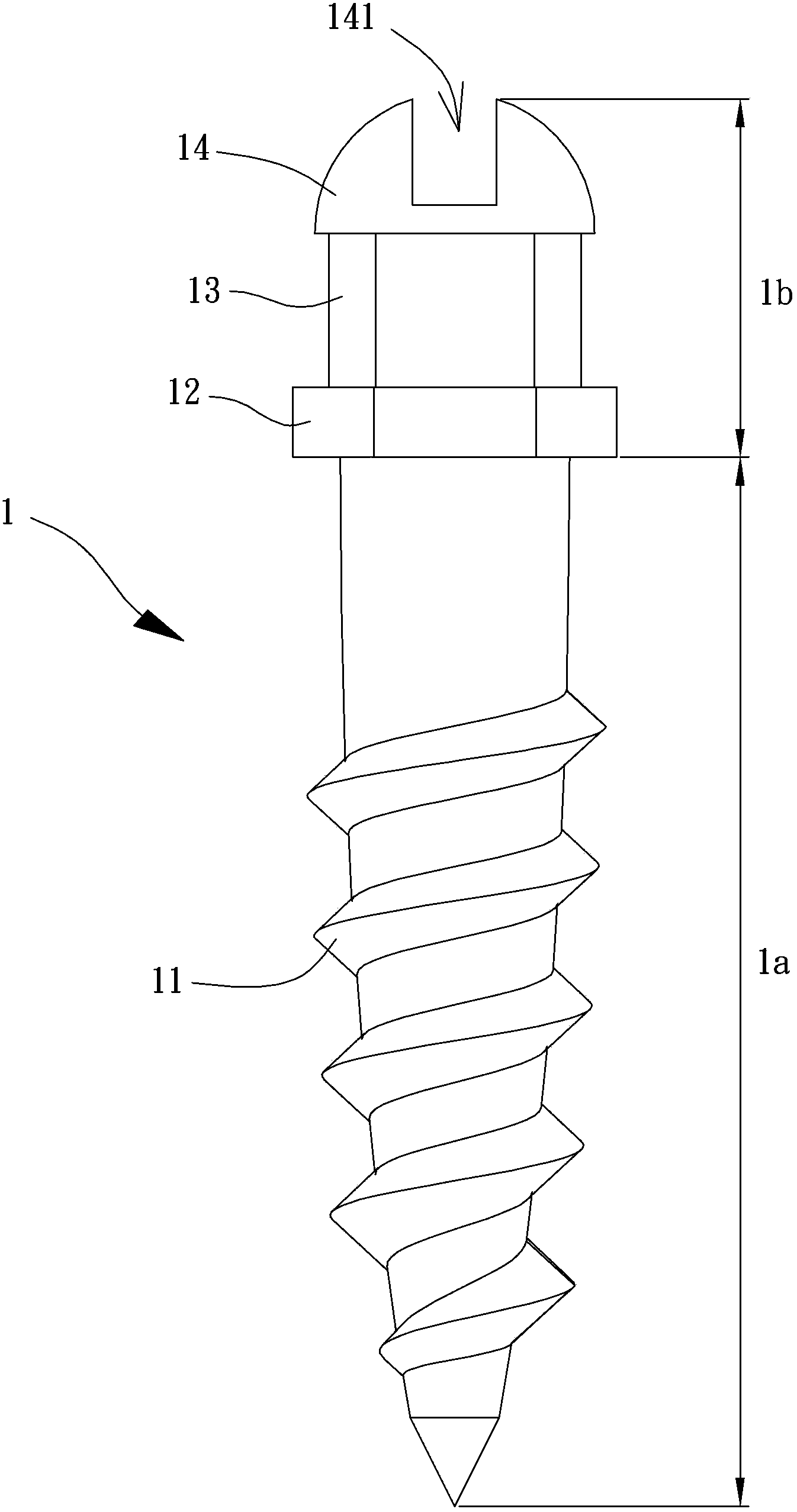
Orthodontics correction anchoring module , correction plate and surgery guidance device
InactiveCN103536370ADispersion Corrective Reaction ForceAvoid breakingBracketsBiomedical engineeringPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
This invention discloses an orthodontics correction anchoring module, comprising a bone nails and a correction plate. The bone nail comprises an exposed segment and an implanting segment which are connected. The exposed segment is provided with a first twistlock part, a buckling part and a second twistlock part. The first twistlock part is in proximity of the implanting part of the bone nail. The circumferential surface of the first twistlock part is not circular. The buckling part is positioned between the first twistlock part and the second twistlock part. The correction plate comprises a gapping segment, a positioning segment and a turn-lock part. The gapping segment is positioned between the positioning segment and the turn-lock part. The gapping segment comprises at least one hook sleeve part. The positioning segment and the twistlock parts are clasped at the buckling parts of the two bone nails. The orthodontics correction anchoring module can guide the two bone nail to appropriate positions on jawbone through a surgery guidance device in order to male the correction plate to connect to the two bone nails.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Antibacterial and tumor proliferation inhibiting degradable magnesium alloy bone nail and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113621858AMeet complex structural requirementsGuaranteed demandAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyBiocompatibilityAnti bacterial
The invention discloses an antibacterial and tumor proliferation inhibiting degradable magnesium alloy bone nail. The degradable magnesium alloy bone nail comprises the following components of, in percentage by weight, 0.01-0.05% of Ag, 1-2% of La, 0.2-0.4% of Ca and the balance of magnesium, and the sum of the weight percentages of the components is 100%. The alloy bone nail not only has excellent biocompatibility, but also has the functions of long-acting antibiosis and tumor proliferation inhibition. The invention further provides a preparation method of the degradable magnesium alloy bone nail.
Owner:西安谢赫特曼诺奖新材料研究院有限公司
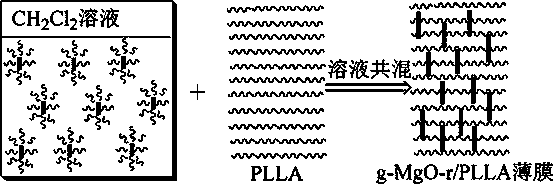
Preparation method of L-polylactide-modified MgO nano-rod composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of an L-polylactide-modified MgO nano-rod composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing an MgO nano-rod; 2) performing surface modification on the MgO nano-rod; 3) preparing the L-polylactide-modified MgO nano-rod composite material. The invention has the advantages that the preparation method is simple in technology and easy to implement; the prepared composite material can be used for preparing fracture inner fixing products including bone nails, bone lamellae, and cancellous bone screws; the osteogenic capability when the material is planted into an animal body is obviously better than that of PLLA; the preparation method adopts the MgO nano-rod as a reinforced bone frame, so that the improvement on composite material mechanic performance is more effective than that of MgO-NPs grains since crystal whisker distributed in the polymer matrix can improve the strength and plasticity of the composite material through four manners, namely load transmission, crack bridging, crack deflection, and extraction effect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
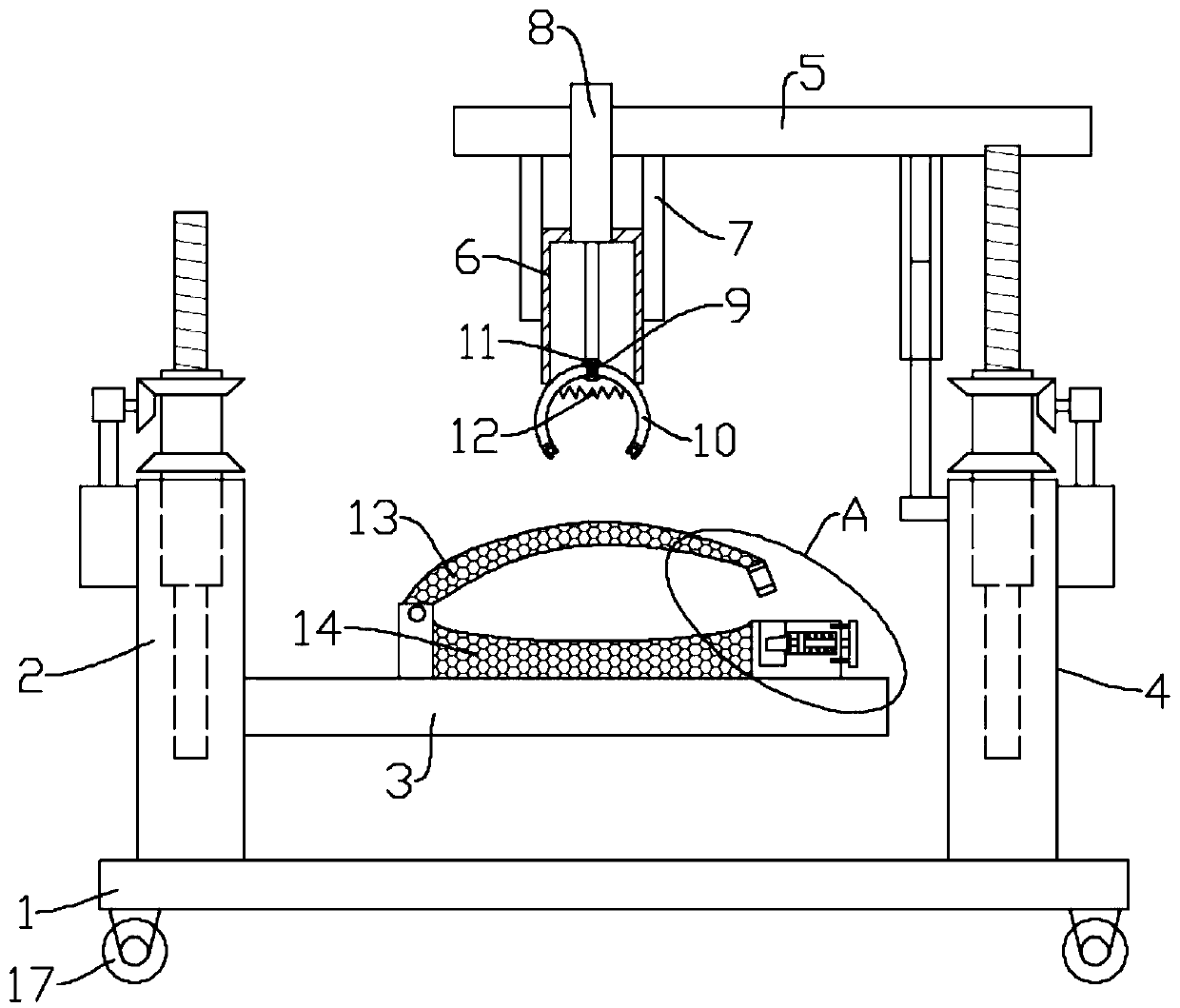
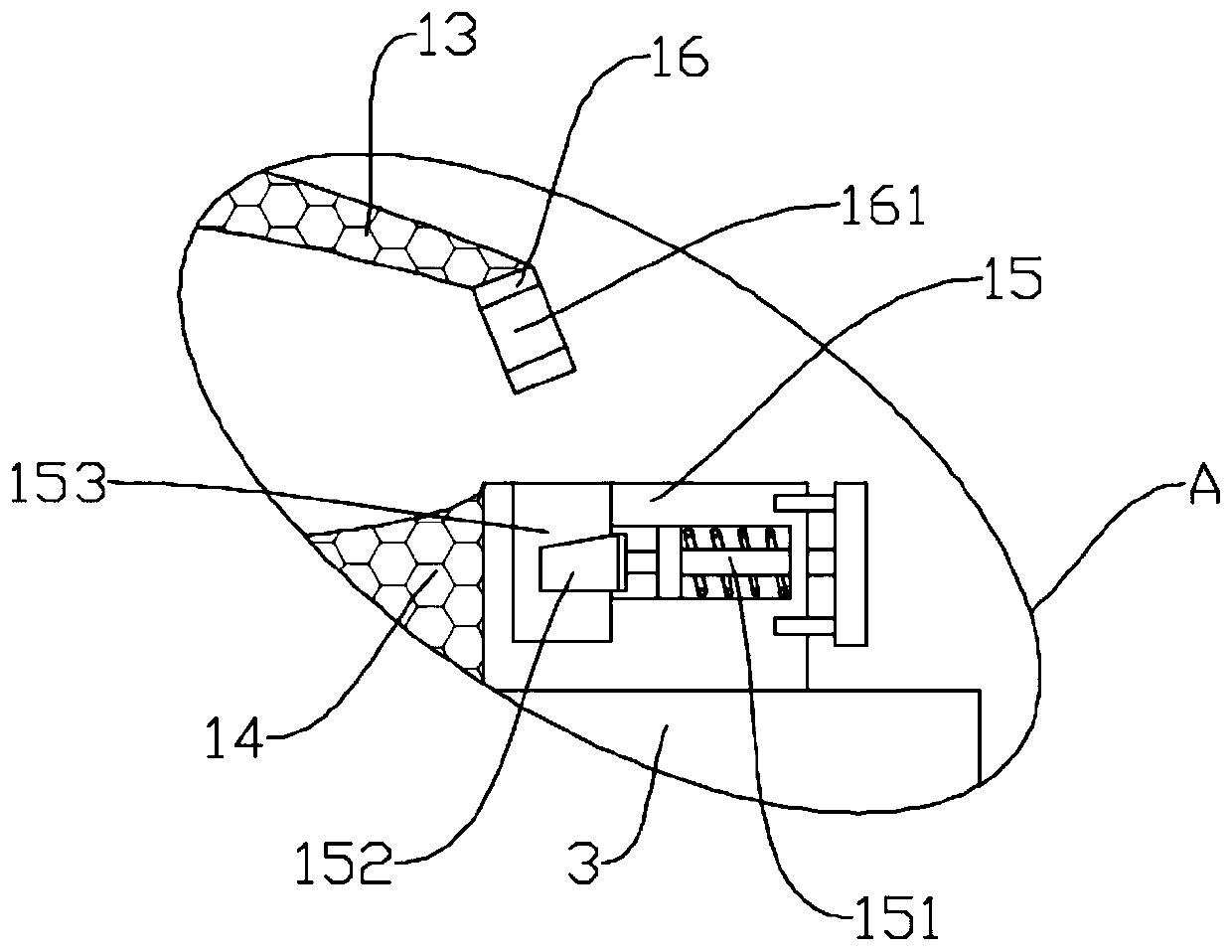
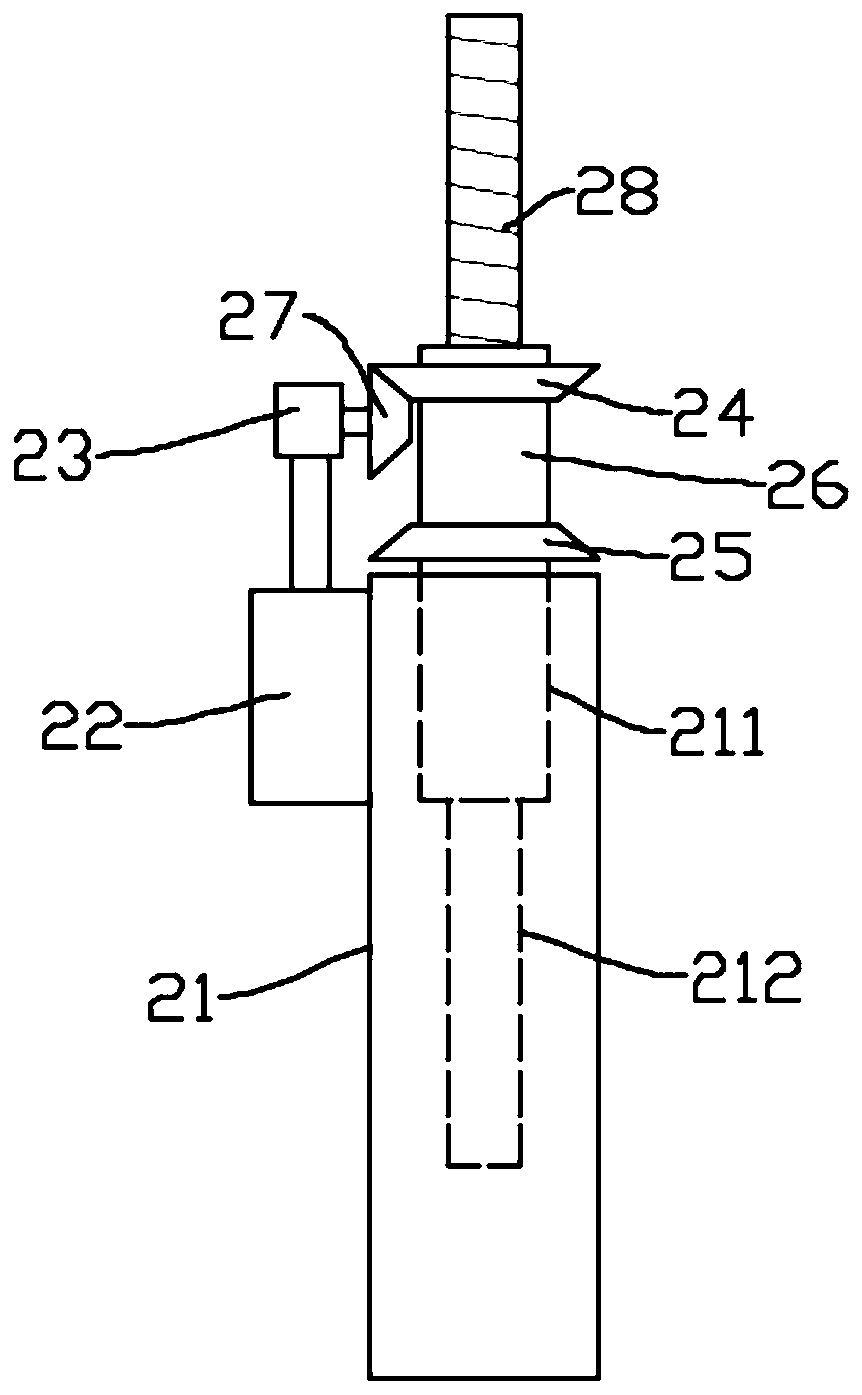
Operation nail taking device for orthopedics department
InactiveCN110897703AMeet the needs of useIncrease flexibilityInstruments for stereotaxic surgerySurgical forcepsOrthopedic departmentEngineering
The invention relates to the field of orthopedics, and particularly discloses an operation nail taking device for an orthopedics department. The device comprises a base, a first lifting supporting piece which is arranged on one side of the base and used for adjusting the height of a leg supporting assembly, and a second lifting supporting piece which is arranged on the other side of the base and used for adjusting the height of a nail taking part. The nail taking part comprises a supporting top plate and a supporting cylinder fixedly erected below the end of the supporting top plate through aninstallation supporting rod. An electric telescopic rod used for pushing a supporting base to move up and down in the supporting cylinder is installed on the top plate of the supporting cylinder. Thenail taking part further comprises two arc-shaped clamping pincers, and the top ends of the two arc-shaped clamping pincers are hinged to the supporting base through hinge shafts. According to the embodiment of the invention, the height of the leg supporting assembly can be adjusted; the electric telescopic rod can enable the free ends of the two arc-shaped clamping pincers to get close to each other so as to achieve the clamping effect on a bone nail; and then the nail taking effect can be achieved.
Owner:广东威尔科技推广有限公司
Shape memory composite bone nail and preparation, using method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of bone tissue repair, and particularly discloses a shape memory composite bone nail and preparation, a using method and application thereof. The shape memory composite bone nail comprises the following raw material components in percentages by mass: 1.8-2.2% of hydroxyapatite, 0.5-1.5% of RGD tripeptide and 96.5-97.5% of polyurethane. The polyurethaneis prepared from the following raw material components by reaction based on 100% of the polyurethane by mass: 55.0-57.0% of diphenylmethane diisocyanate, 14.0-16.0% of a chain extender and 28.0-30.0%of polycaprolactone glycol. The shape memory composite bone nail has a shape memory function, a self-regulated mechanical property and a tissue growth function; the hydroxyapatite does not affect theshape memory function, but also has good biological compatibility and histocompatibility, and is suitable for the field of repair of bone tissues.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
Biomedical degradable magnesium alloy bone nail and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111451944AReduce the rate of degradationDegradation rate can be effectively regulatedAbrasive machine appurtenancesMg alloysMetallurgy
Owner:东莞立德生物医疗有限公司
Antibacterial and degradable magnesium alloy nail and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN110302435AEnhance biological antibacterial effectImprove antibacterial propertiesSurgeryOsteoblastCalcification
The invention provides an antibacterial and degradable magnesium alloy nail and a manufacturing method thereof. The nail is prepared from the following components: 0.05~0.5% of Cu, 0.05~0.5% of Ag, 1.0~3.0% of Sr, 0.05~0.1% of Ta, and 0.4~0.8% of Ca, the content of each single impurity of inevitable Fe, Zn and Al is less than 0.05%, the total amount of the impurities is no more than 0.3%, and thebalance is Mg, the nail can generate microscale Ag+ and Cu2+ in an implanation cycle, under the environment of the Ag+ and Cu2+, probability of bacterial infection in an implanation part is significantly reduced, produced Sr2+ can participate calcification of bones, functions that formation of osteoblast is promoted and bone resorption of osteoclast is inhibited are provided, and development of skeletons and formation of osteoid are promoted, after Sr and Ta alloying, materials have chemical stability and physiological corrosion resistance, and degradation products have good biocompatibility,at the same time, according to the magnesium alloy nail, the structural design is novel, a process of the manufacturing method is simple, operation is convenient, and popularization is facilitated.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Broken nail removal device for orthopedics
ActiveCN110200692AGuaranteed expansion effectLabor-saving operationOsteosynthesis devicesBreaking nailsBone staple
The invention discloses a broken nail removal device for orthopedics. The device includes a holding member, a clamping part fixedly arranged at the lower part of the holding member and a nail removingpart fixedly arranged at the lower part of the holding member; the surface of the holding member is provided with multiple anti-skid lines; the clamping part is used for compressing the outer surfaceof a bone nail to fix the bone nail when the broken bone nail is removed and includes multiple clamping arms and a fastening ring which can move up and down relative to the clamping arms; the clamping arms are in outer expansion structure arrangement and have first ends connected to the holding member and second ends swinging relative to the first ends; and the fastening ring can drive the secondends to swing inwards so as to compress the bone nail during moving. The bone nail can be compressed through the cooperation of the clamping part and the outer wall of the bone nail, the cooperationof stopping and rotating can be performed through the nail removing part and the inner wall of the bone nail, and therefore, situations of slipping between the device and the bone nail can be guaranteed to not happen, and good nail removing effects can be achieved.
Owner:LISHUI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com