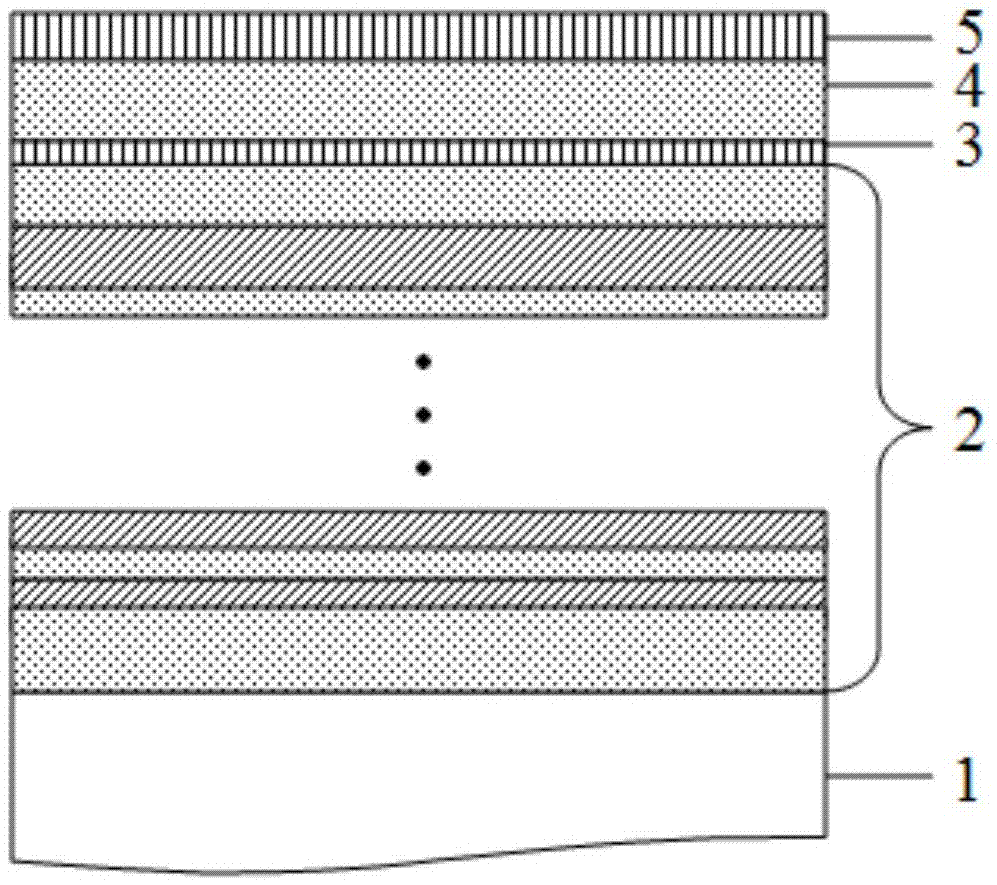
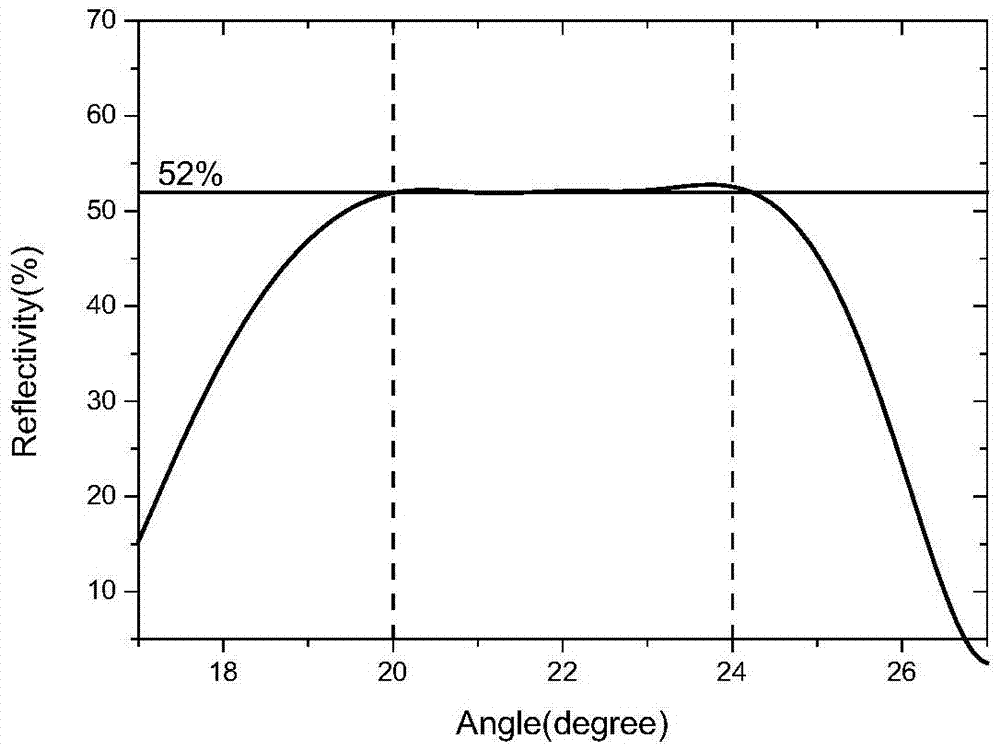
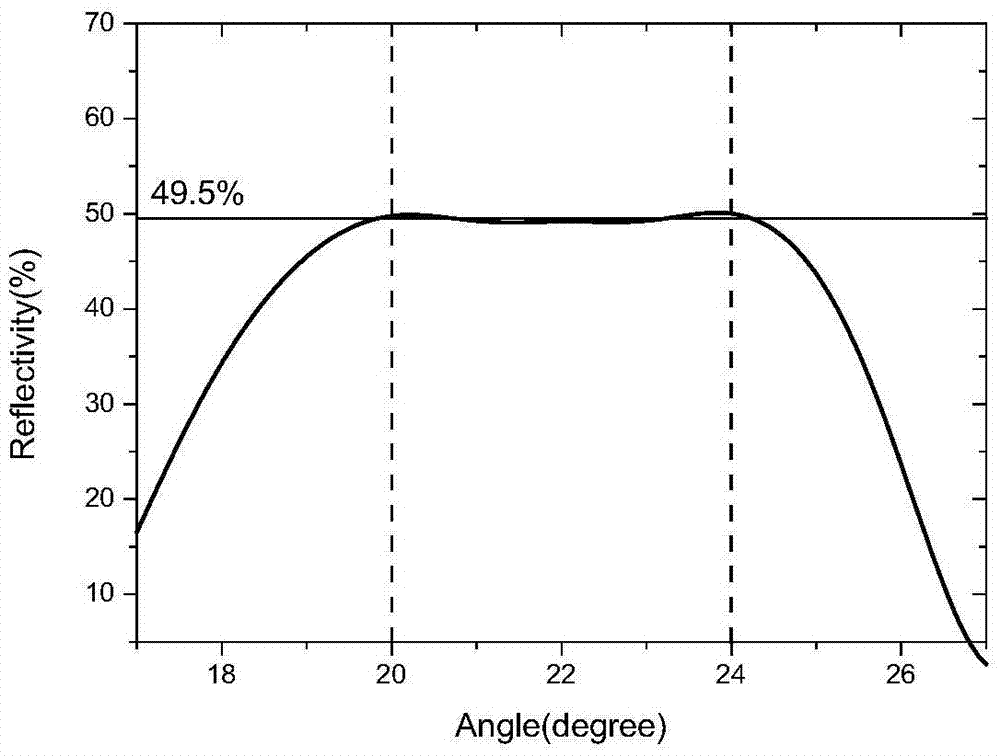
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Suppressed reflectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
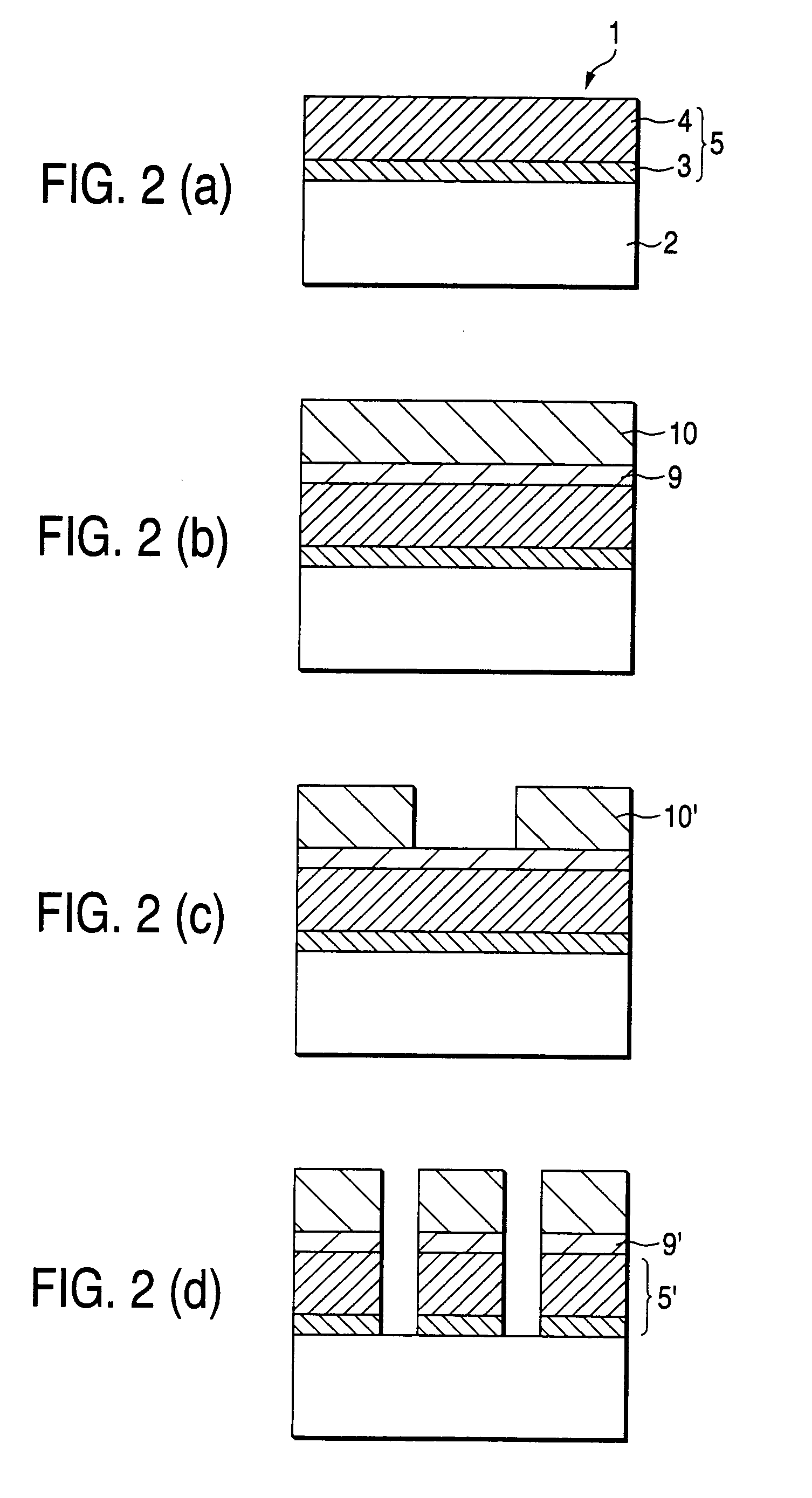
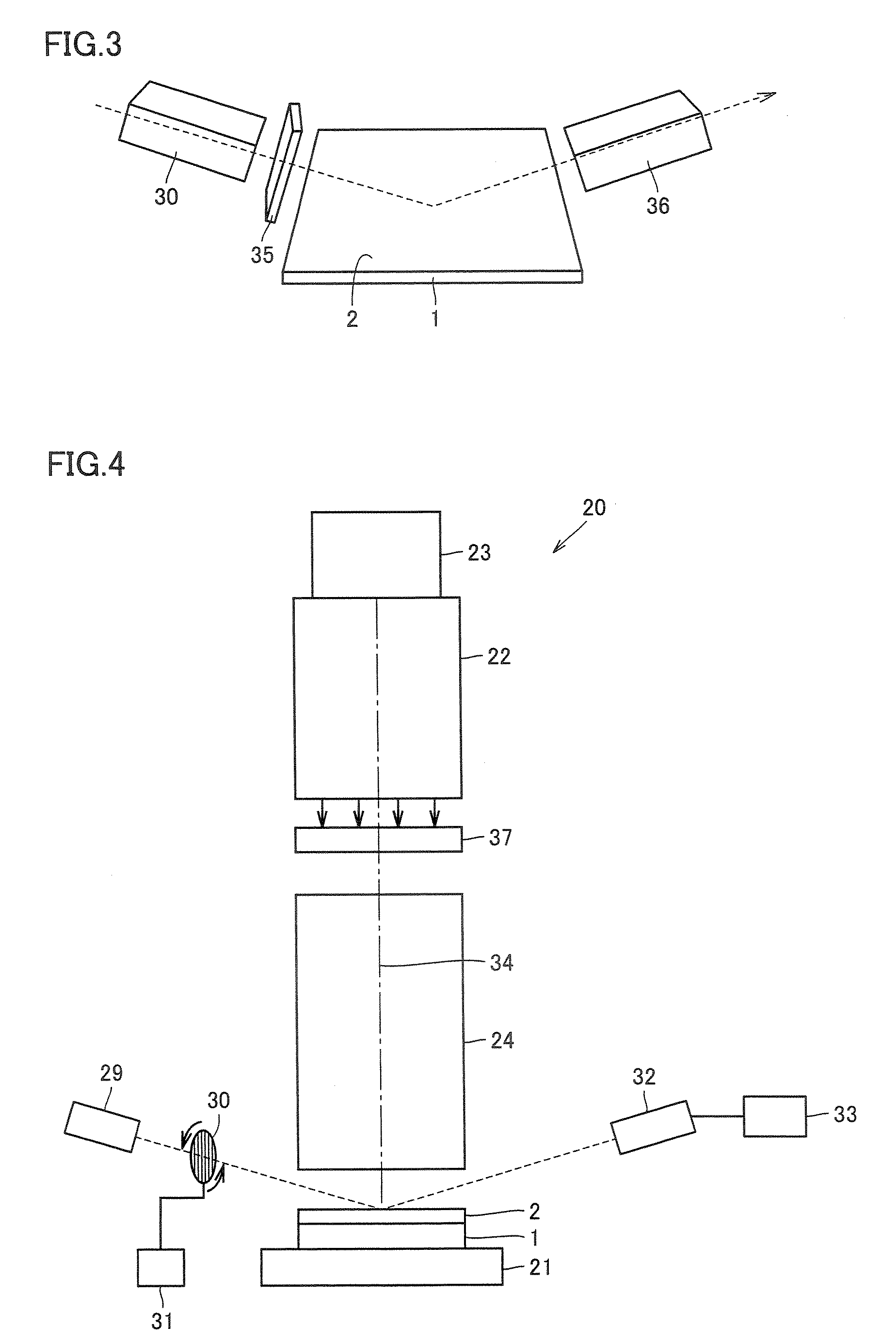
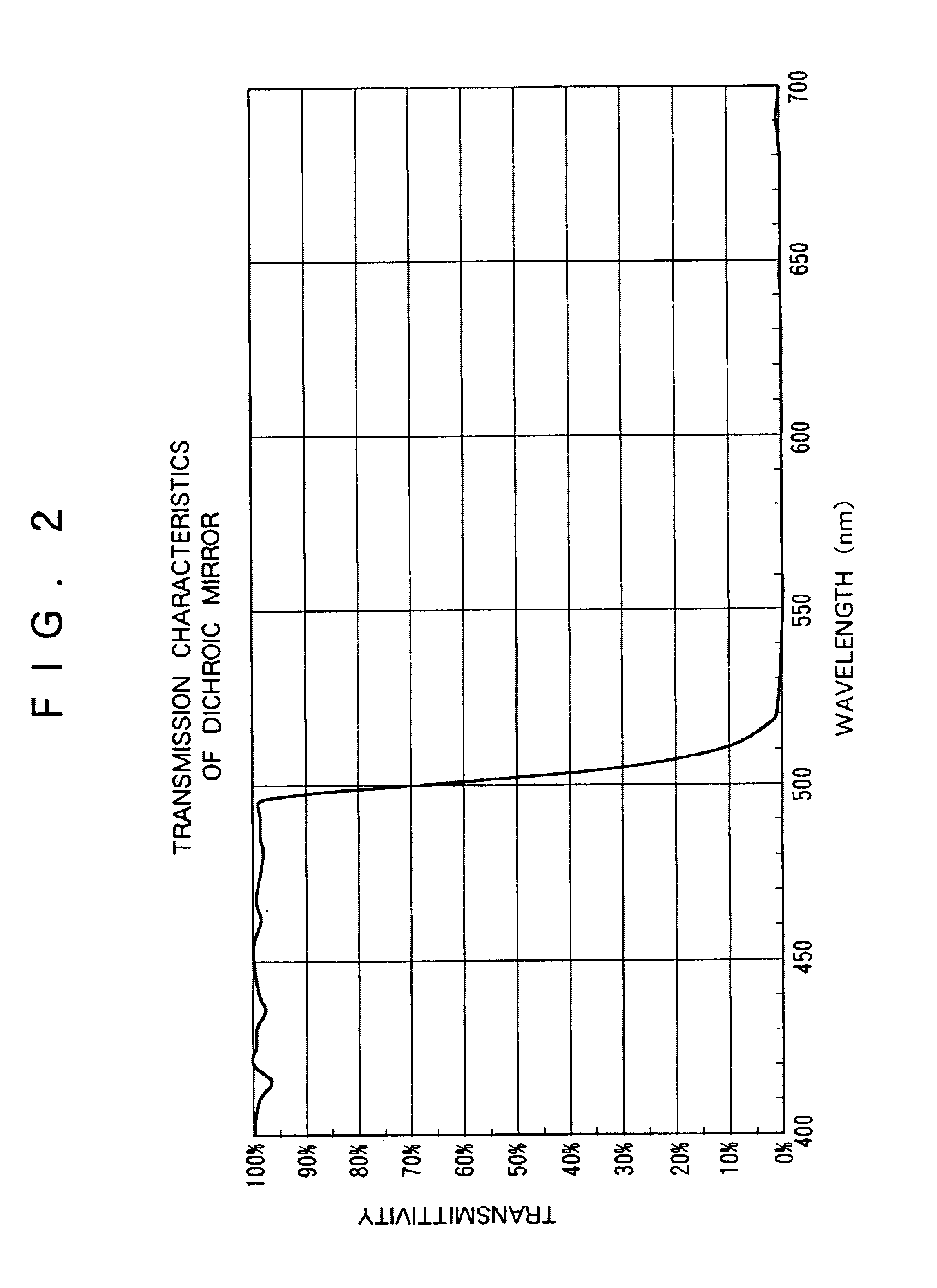
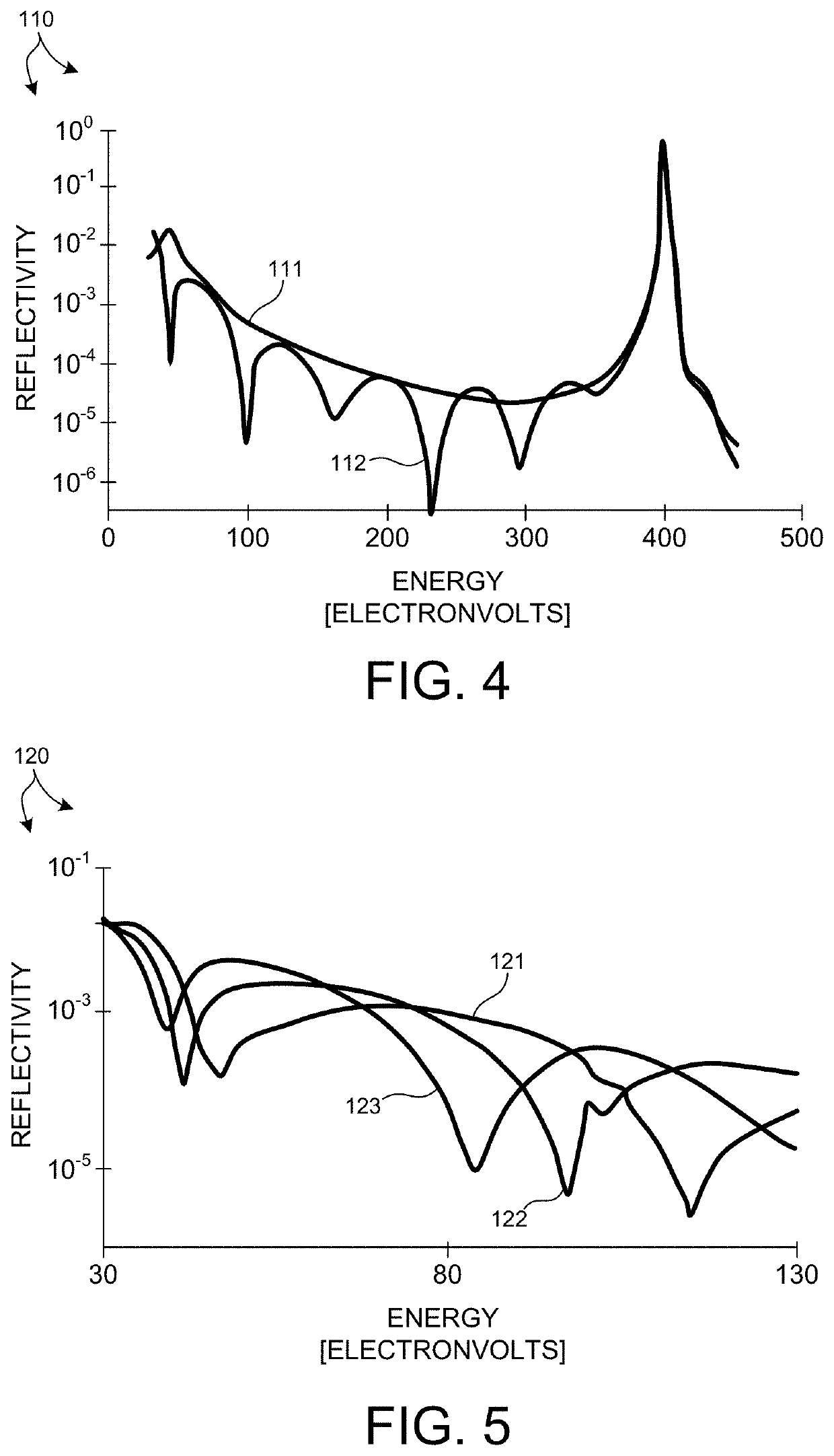
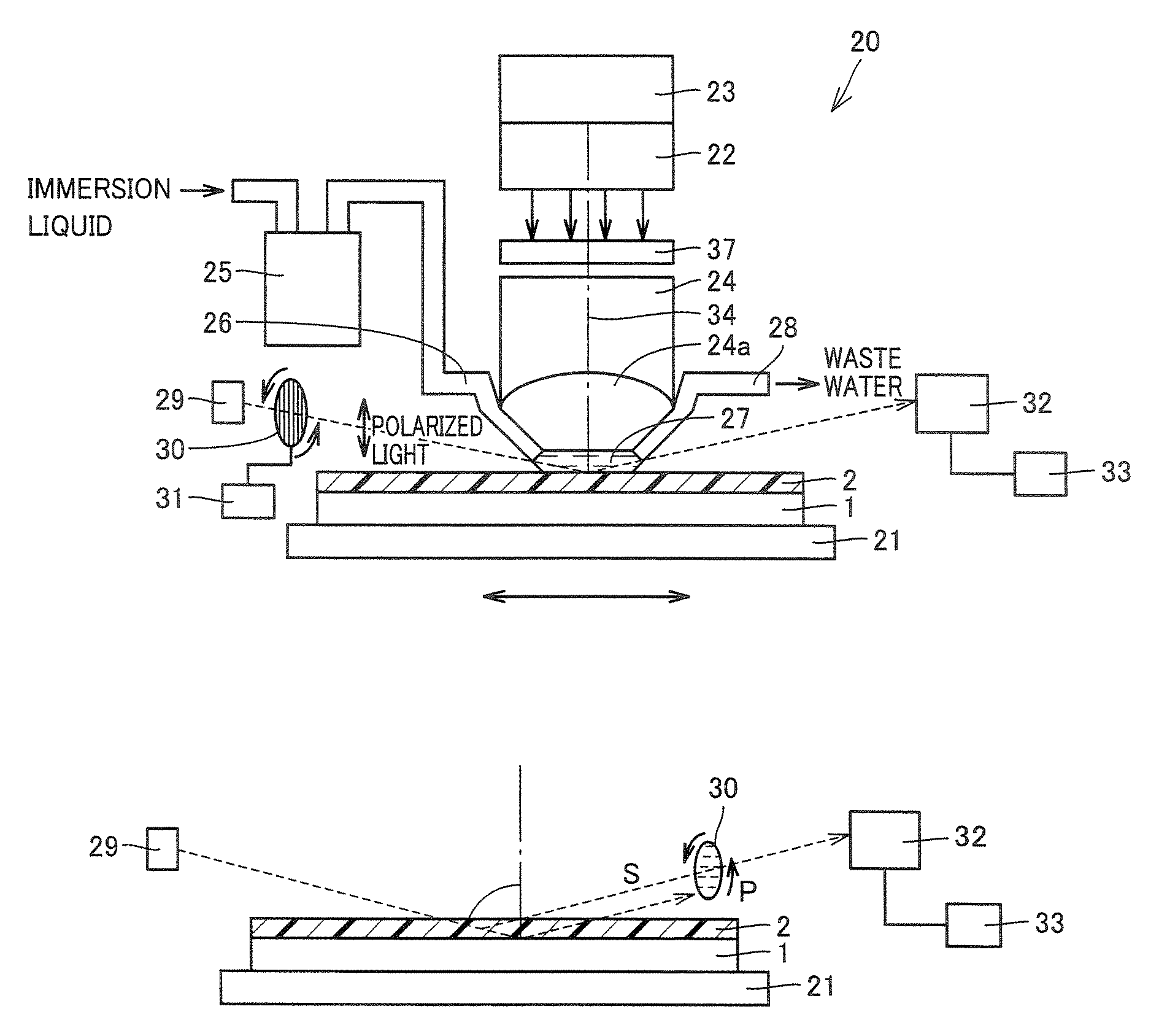
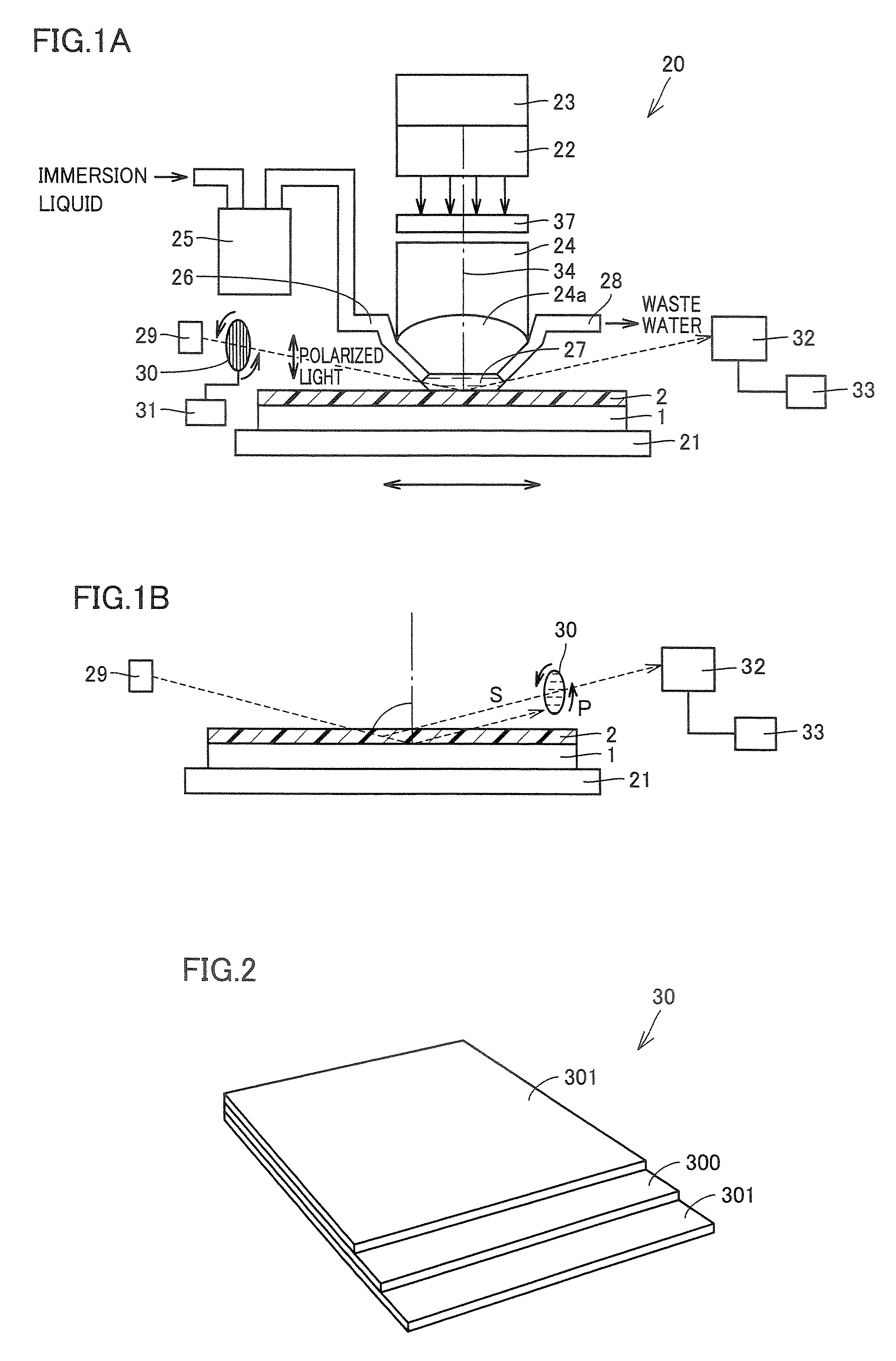
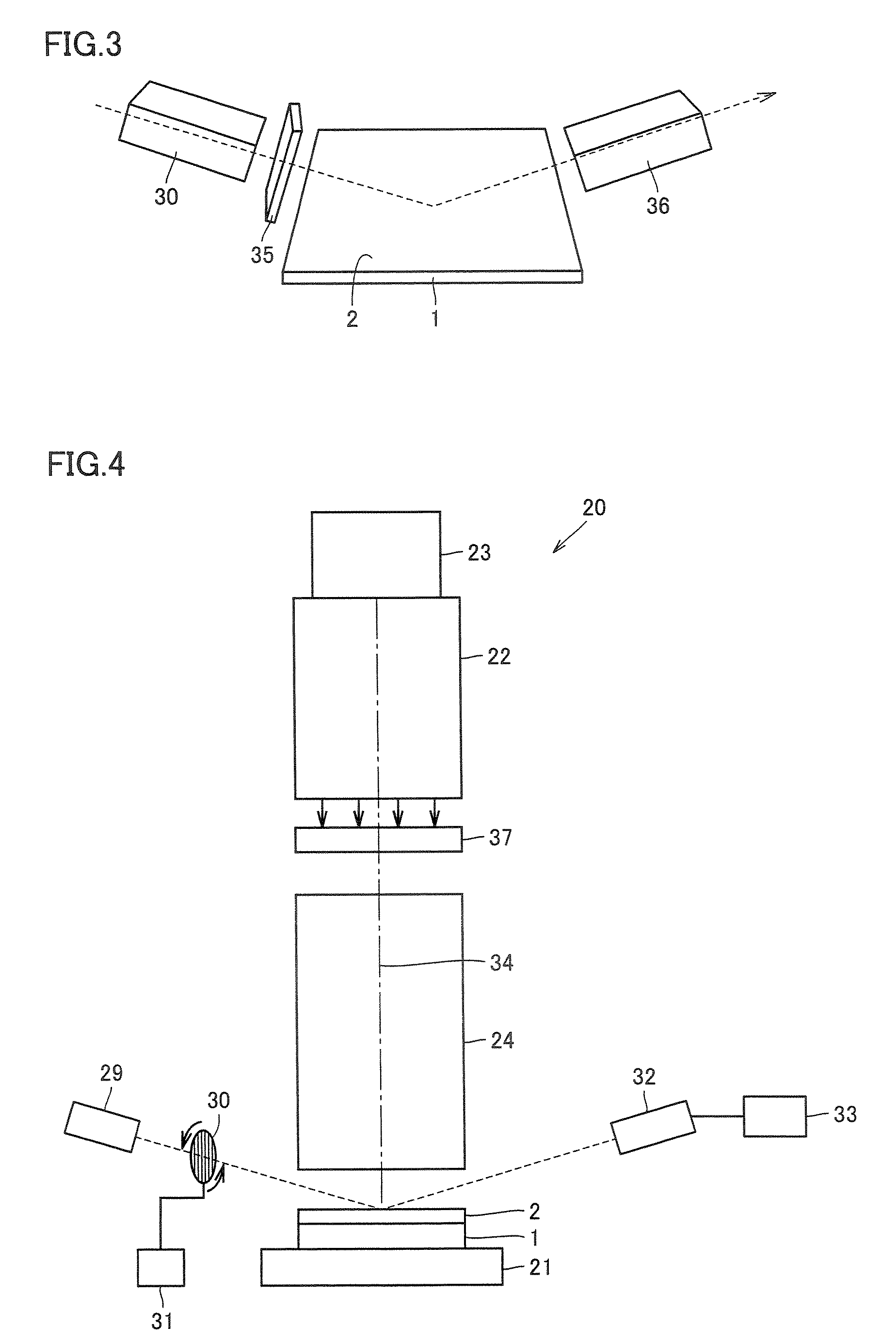
Reflective mask blank for EUV lithography
InactiveUS20080199787A1Low resistivityIncrease resistanceNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusLithographic artistHafnium
To provide a reflective mask blank for EUV lithography having an absorber layer which has a low reflectance in a wavelength region of EUV light or light for inspection of a pattern and which is easy to control to have a desired layer composition and thickness.A reflective mask blank for EUV lithography, which comprises a substrate, and a reflective layer to reflect EUV light and an absorber layer to absorb EUV light, formed in this order on the substrate, wherein the absorber layer contains tantalum (Ta) and hafnium (Hf), and in the absorber layer, the content of Hf is from 20 to 60 at. % and the content of Ta is from 40 to 80 at. %.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Halftone-type phase-shift mask blank, and halftone-type phase-shift mask
ActiveUS7011910B2Highly-accurate CD (critical-dimension) controlReduce surface reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarising elementsTransmittancePhase-shift mask
In a halftone-type phase-shift mask blank having a phase shifter film 5, the phase shifter film 5 has a phase adjustment layer 4 for primarily controlling the phase of exposure light, and a transmissivity adjustment layer 3 which is formed between a transparent substrate 2 and the phase adjustment layer 4 and primarily controls the transmissivity of exposure light. The transmissivity adjustment layer 3 has a thickness of 90 angstroms or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Light emitting element and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7683379B2Little changeSuppressed reflectivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesTransparent conducting filmLight emitting device
A light emitting device having little variation in the intensity of light emitted from the light emitting surface is provided. The light emitting device of exemplary embodiments of the present invention includes a laminated body with a first conductivity type layer and a second conductivity type layer, with a light emitting portion therebetween. The light emitting device also includes a metal thin film layer on the second conductivity type layer of the laminated body, and a transparent conductor on the metal thin film layer. The transparent conductor includes a single layer of transparent conductive film. The grain size in the light emitting surface of the transparent conductive film is not less than 30 nm and not greater than 300 nm.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
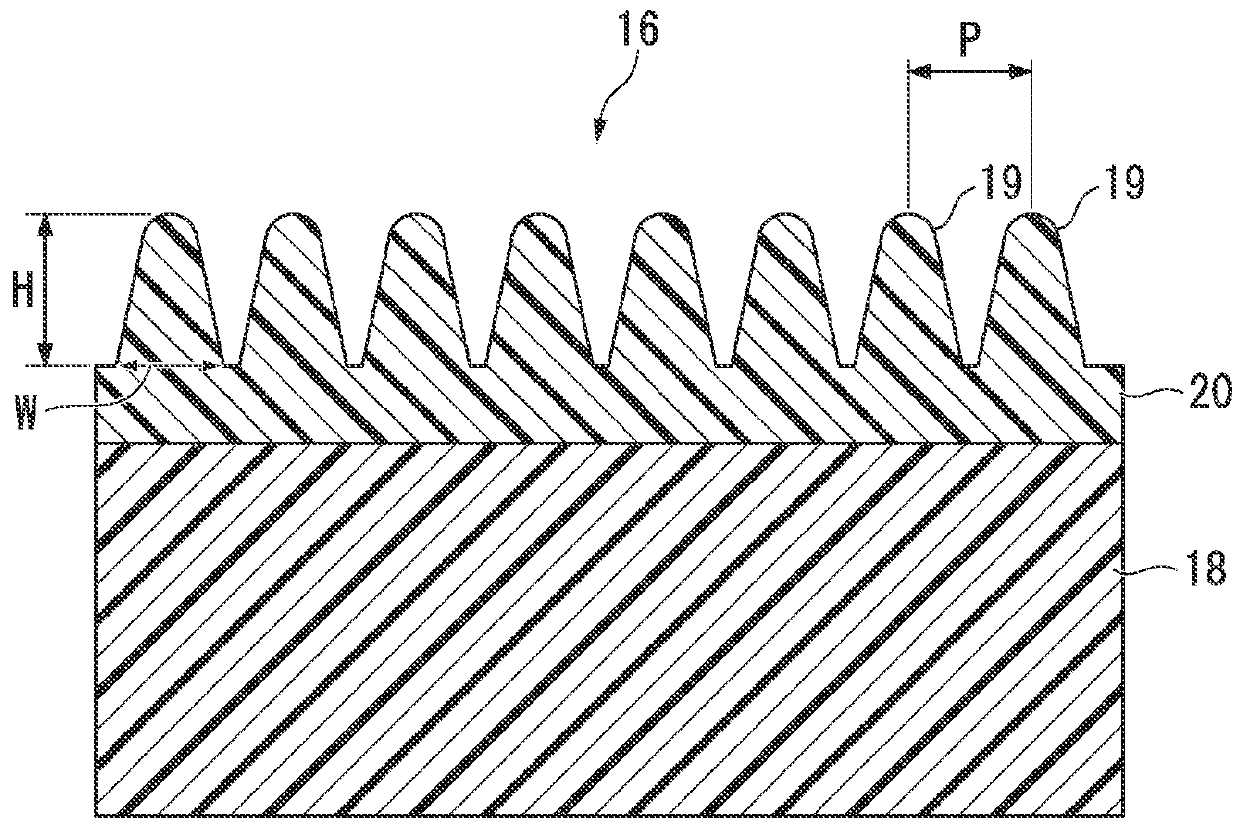
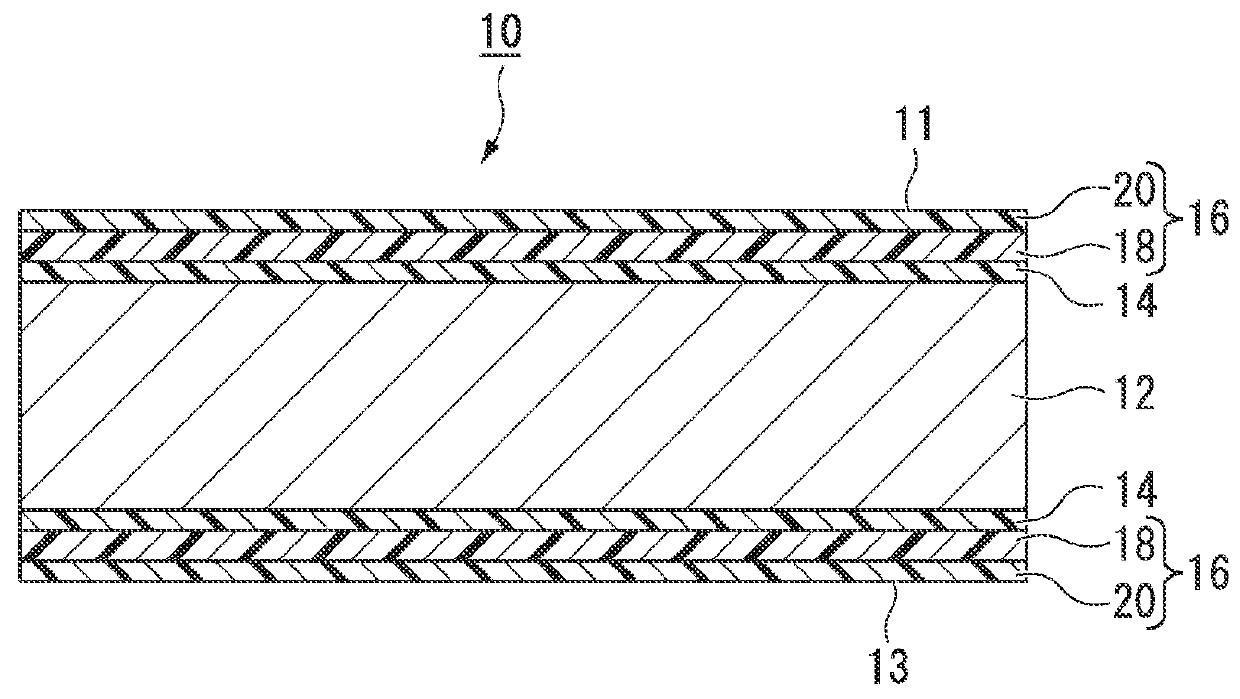
Antireflection article and display device
ActiveUS20120127580A1Abrasion resistance enoughSuppressed reflectivityCoatingsOptical elementsDisplay deviceTransmittance
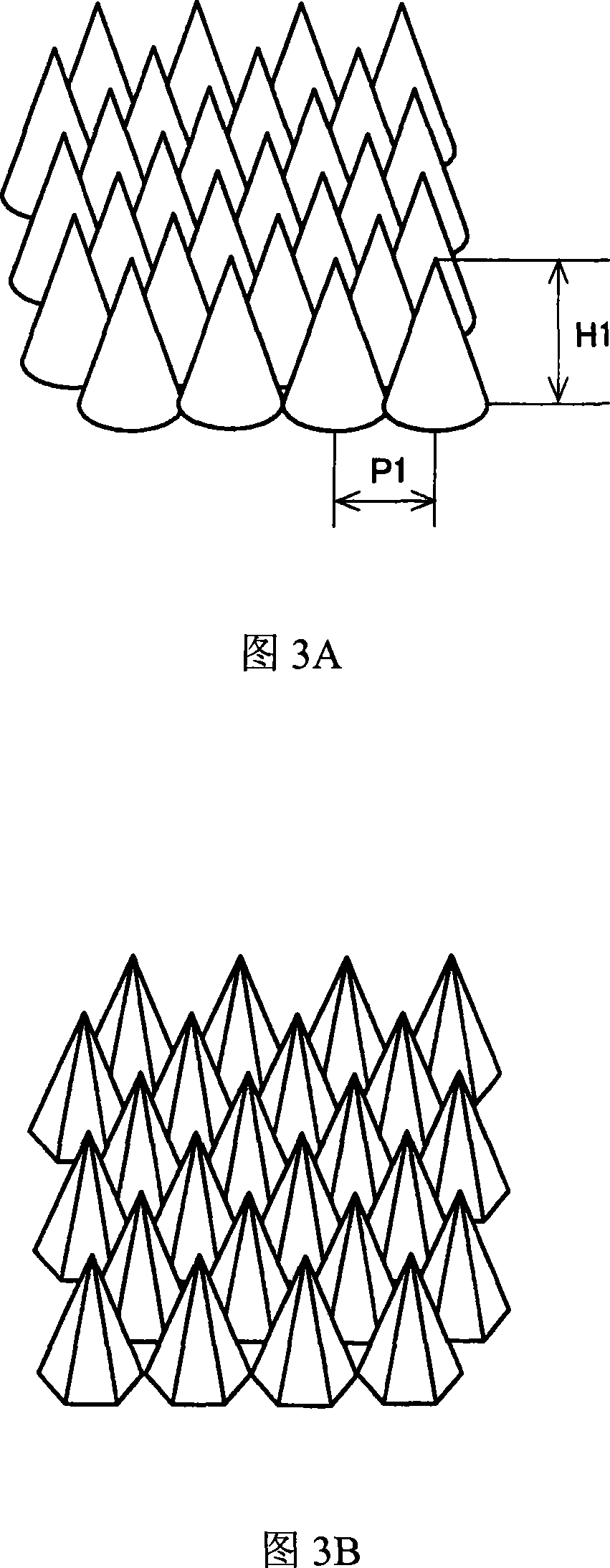
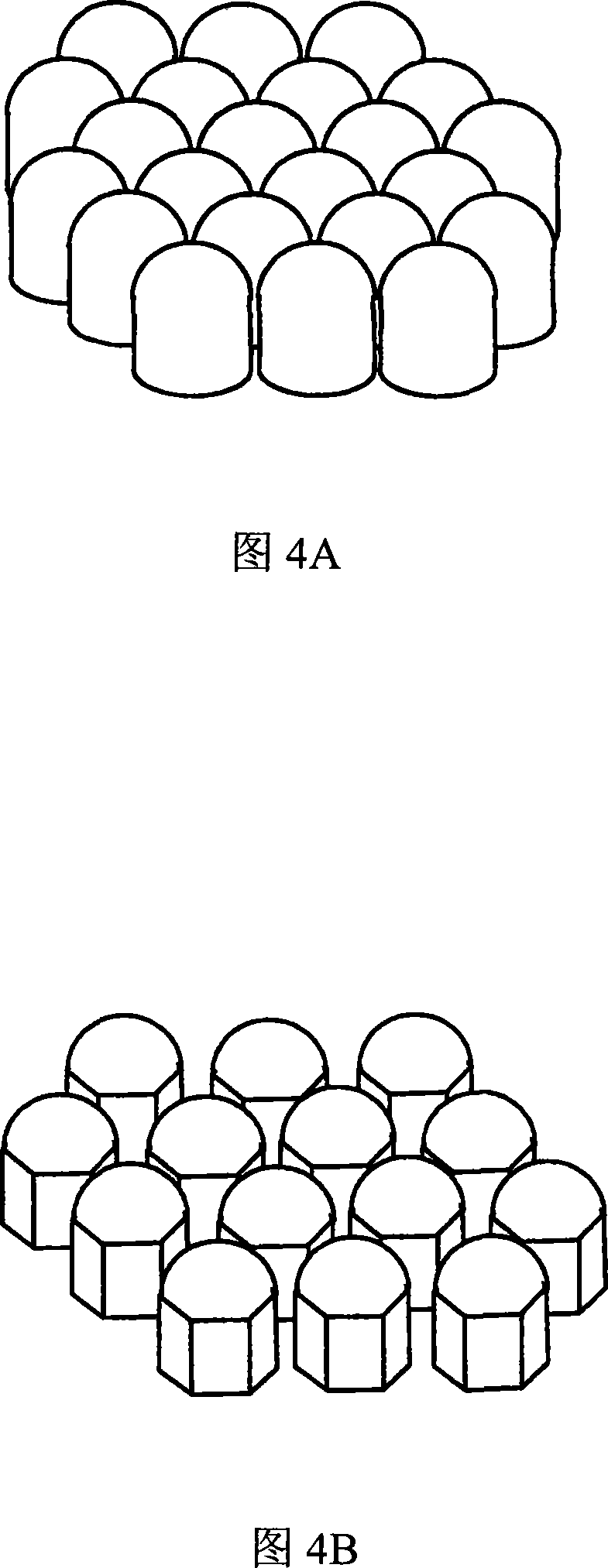
The present invention relates to an antireflection article of which the first surface has sufficient abrasion resistance and can suppress reflectance to a low level throughout the visible light region, and a display device. The present invention relates to an antireflection article that has light transmittance, in which a plurality of convex portions are disposed on a first surface positioned at a visible side and a second surface opposite to the first surface, the average gap of the convex portions is 400 nm or less, the ratio (H1 / W1) of the height H1 of the convex portions and the width W1 of the bottoms of the convex portions is 1.3 or more, in the first surface, and the ratio (H2 / W2) of the height H2 of the convex portions and the width W2 of the bottoms of the convex portions is larger than the ratio (H1 / W1), in the second surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Imaging optical system
InactiveCN101233429ASuppressed reflectivitySatisfactory mass production rateCoatingsLensProduction rateLength wave
An imaging optical system is provided with an optical plane, which at least includes one lens element and transmits an incoming light; and a reflection preventing structure, which is arranged at least at a section in a peripheral area around a center area which includes a center of the optical plane, on one or more optical planes. In the reflection preventing structure, structural units having a prescribed shape are periodically arranged in array at a pitch smaller than the shortest wavelength of light to be prevented from being reflected among the incoming light. The imaging optical system has a sufficiently suppressed reflectance on the optical plane, is easily handled and is excellent in mass productivity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070072351A1Highly accurate patternImprove detection accuracyTransistorPhotomechanical apparatusResistDevice material
An insulating film is formed on a main surface of a substrate. A conductive film is formed on the insulating film. A lower layer resist film, an intermediate layer, an anti-reflection film and an upper layer resist film are formed on the conductive film. A focal point at a time of exposure is detected by detecting a height of the upper layer resist film. In detecting the focal point at the time of exposure, a focal point detection light is radiated on the upper layer resist film. After detecting the focal point, the upper layer resist film is exposed and developed thereby to form a resist pattern. With the resist pattern as a mask, the intermediate layer and the anti-reflection film are patterned, and the lower layer resist film is developed. With these patterns as a mask, the conductive film is etched thereby to form a gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
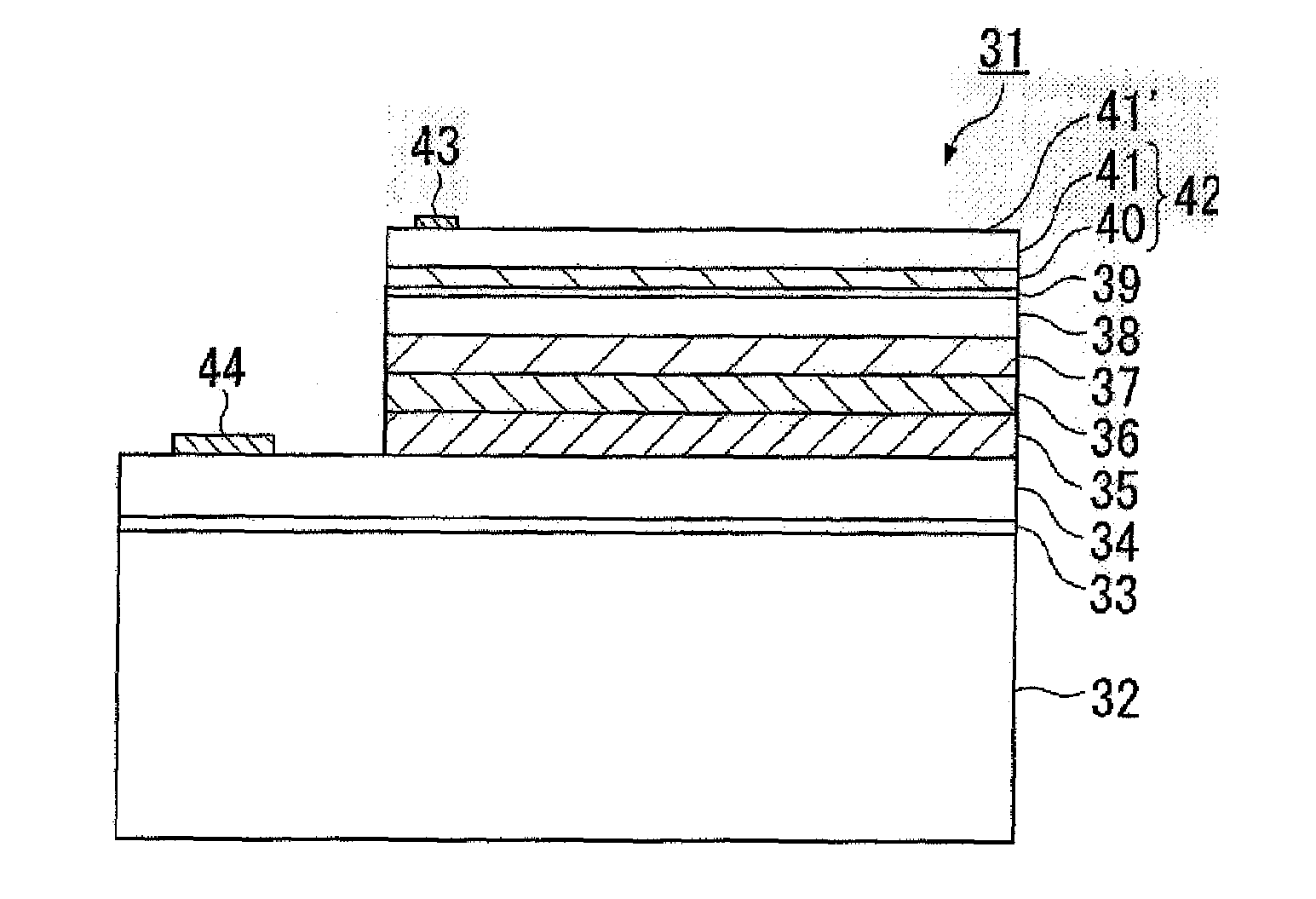
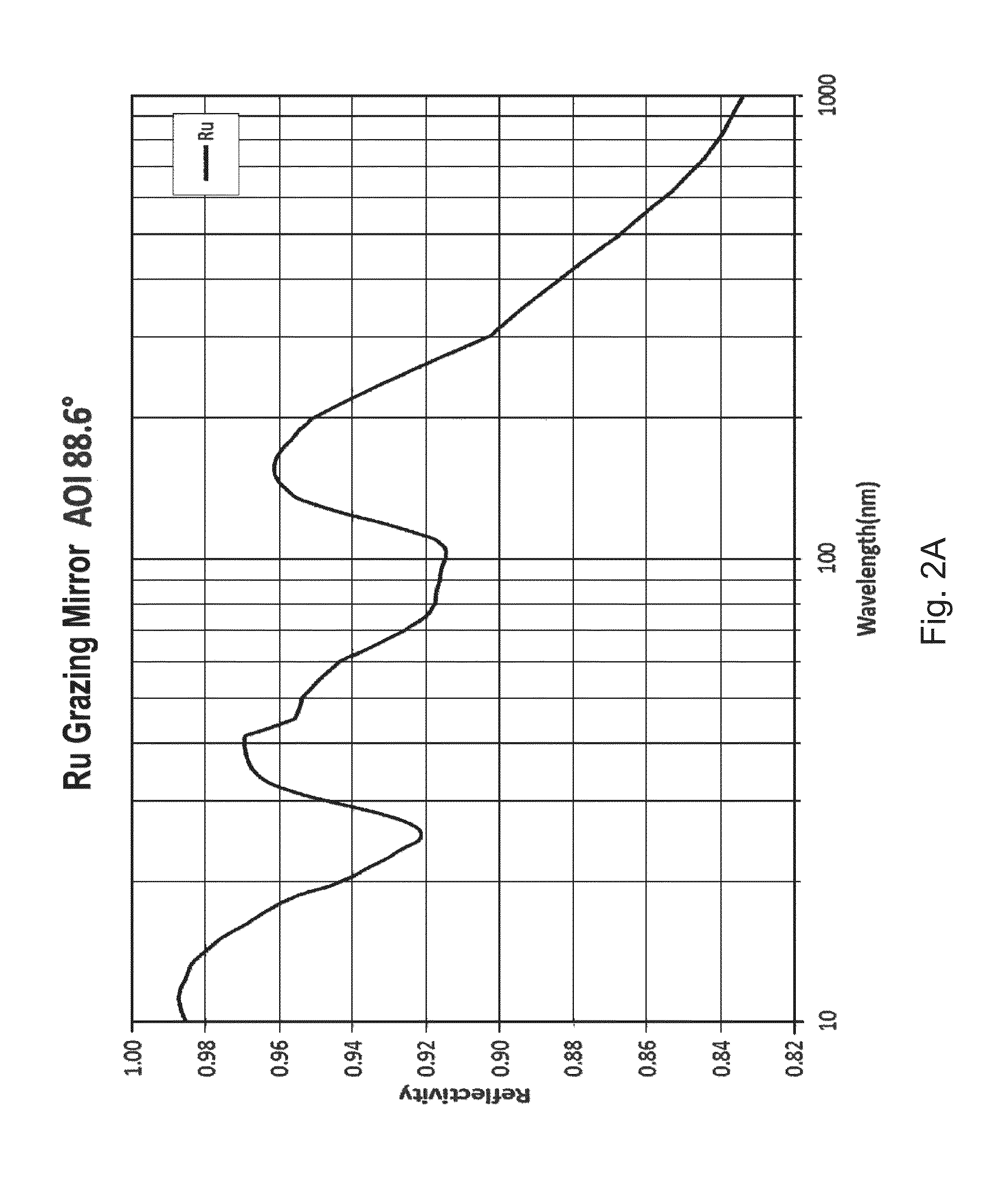
Carbon as grazing incidence EUV mirror and spectral purity filter
InactiveUS20140168758A1Overcomes and reduces disadvantageImprove reflectivityMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingCarbon layerOptical coating
A mirror for reflecting extreme ultraviolet light (EUV) comprising: a substrate layer; and an upper layer above the substrate layer, that reflects EUV wavelengths and refracts longer wavelengths, said upper layer being dense and hard carbon having an Sp2 to Sp3 carbon bond ratio of 0 to about 3 and a normal incidence EUV mirror comprising an optical coating on an uppermost surface which permits transmission of EUV and protects the surface from environmental degradation, said coating being dense and hard and having an Sp2 carbon bond ratio of 0 to about 3 and a thickness of 0.1 to about 5 nanometers. The invention also includes EUV mirror systems protected by a dense carbon layer and includes a multilayer EUV reflecting system having an out of band absorbing layer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
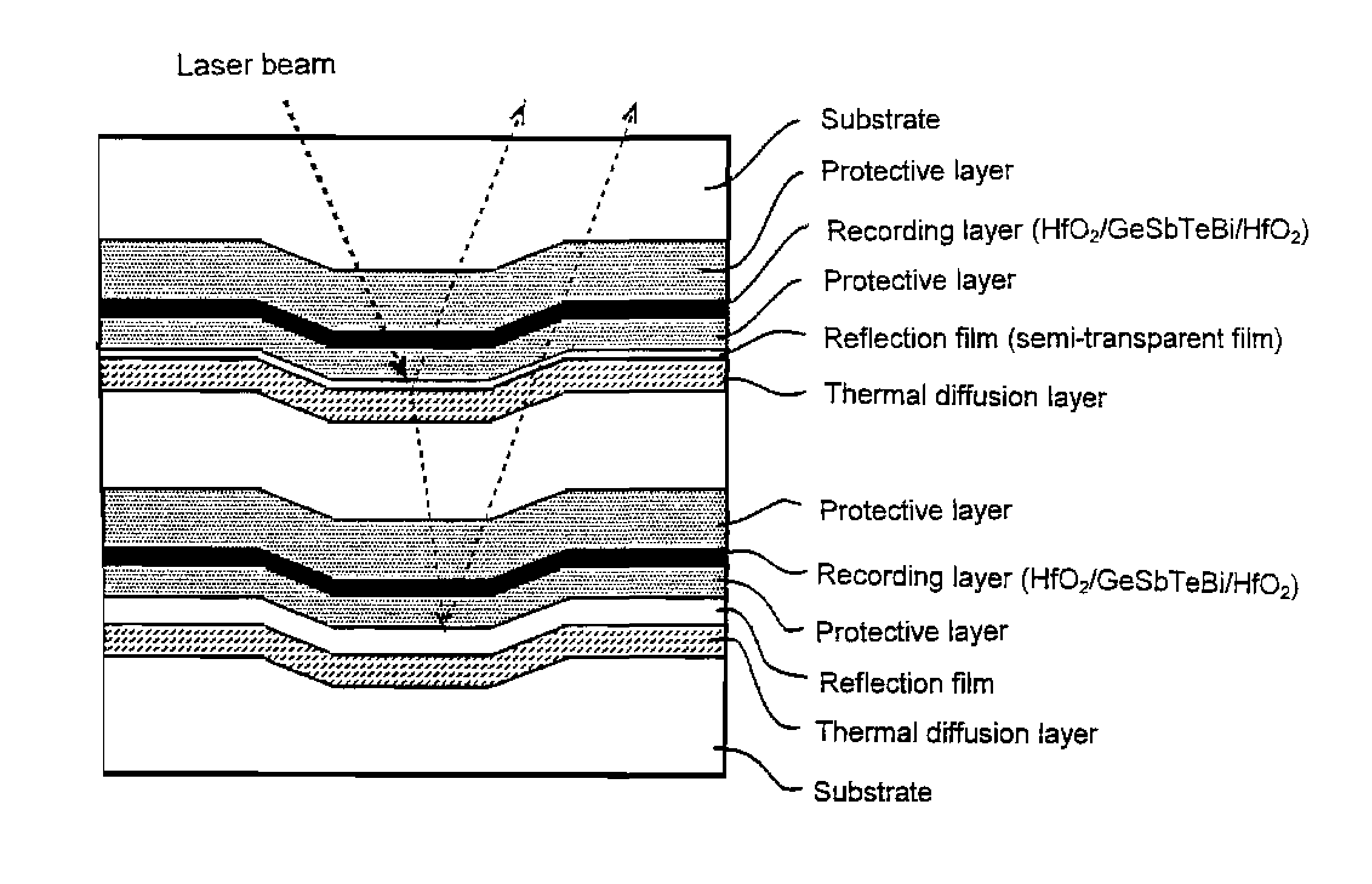
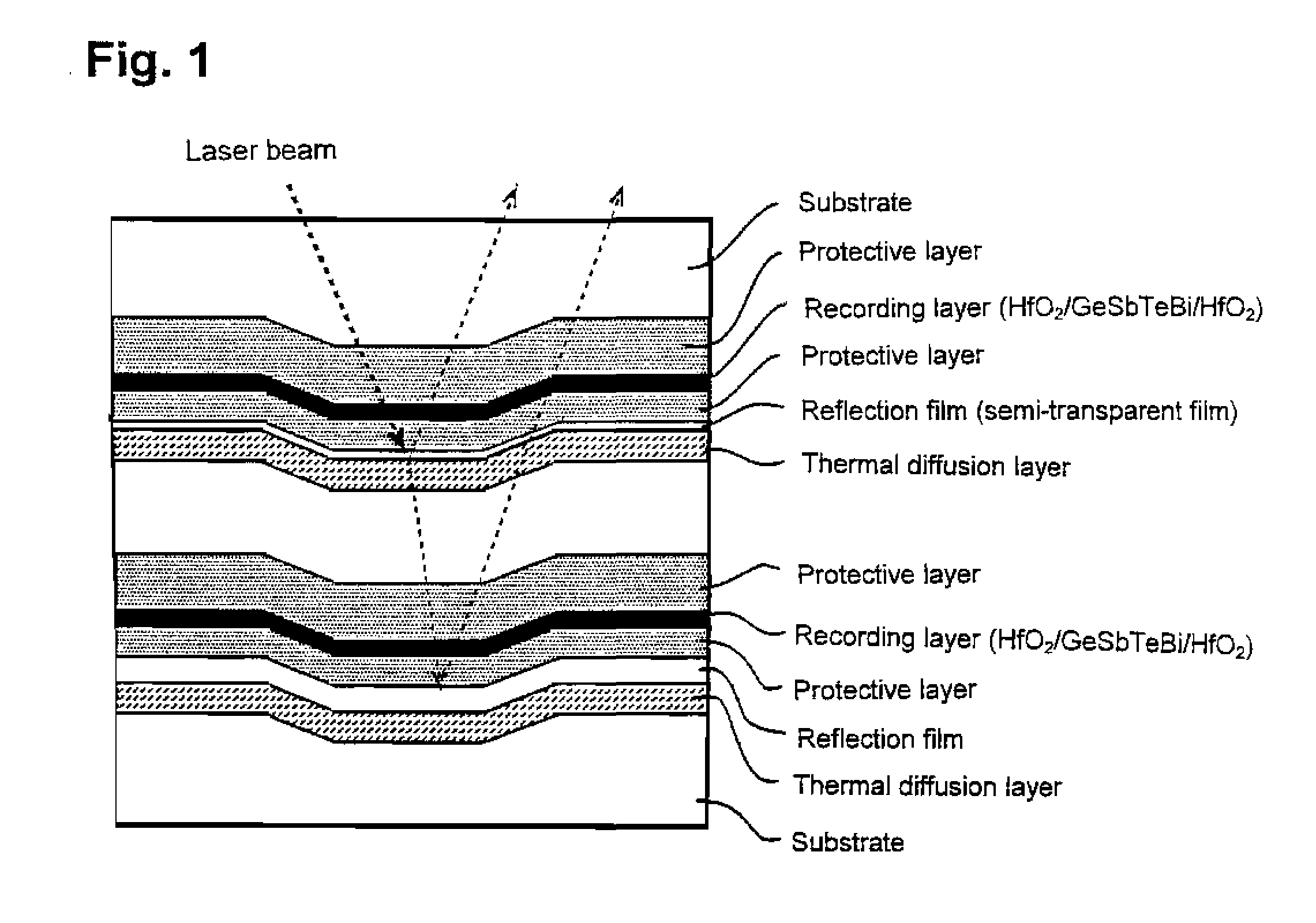
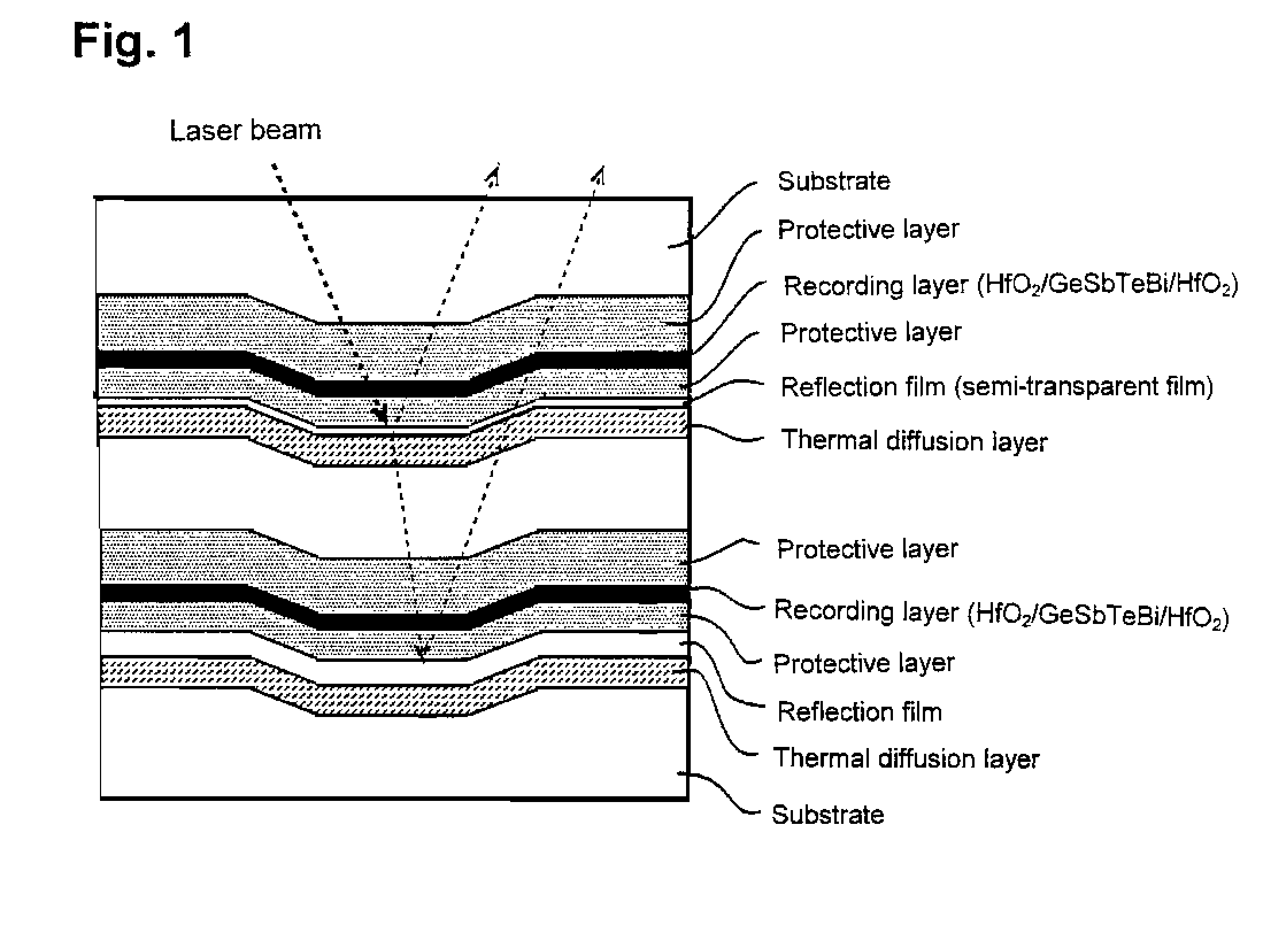
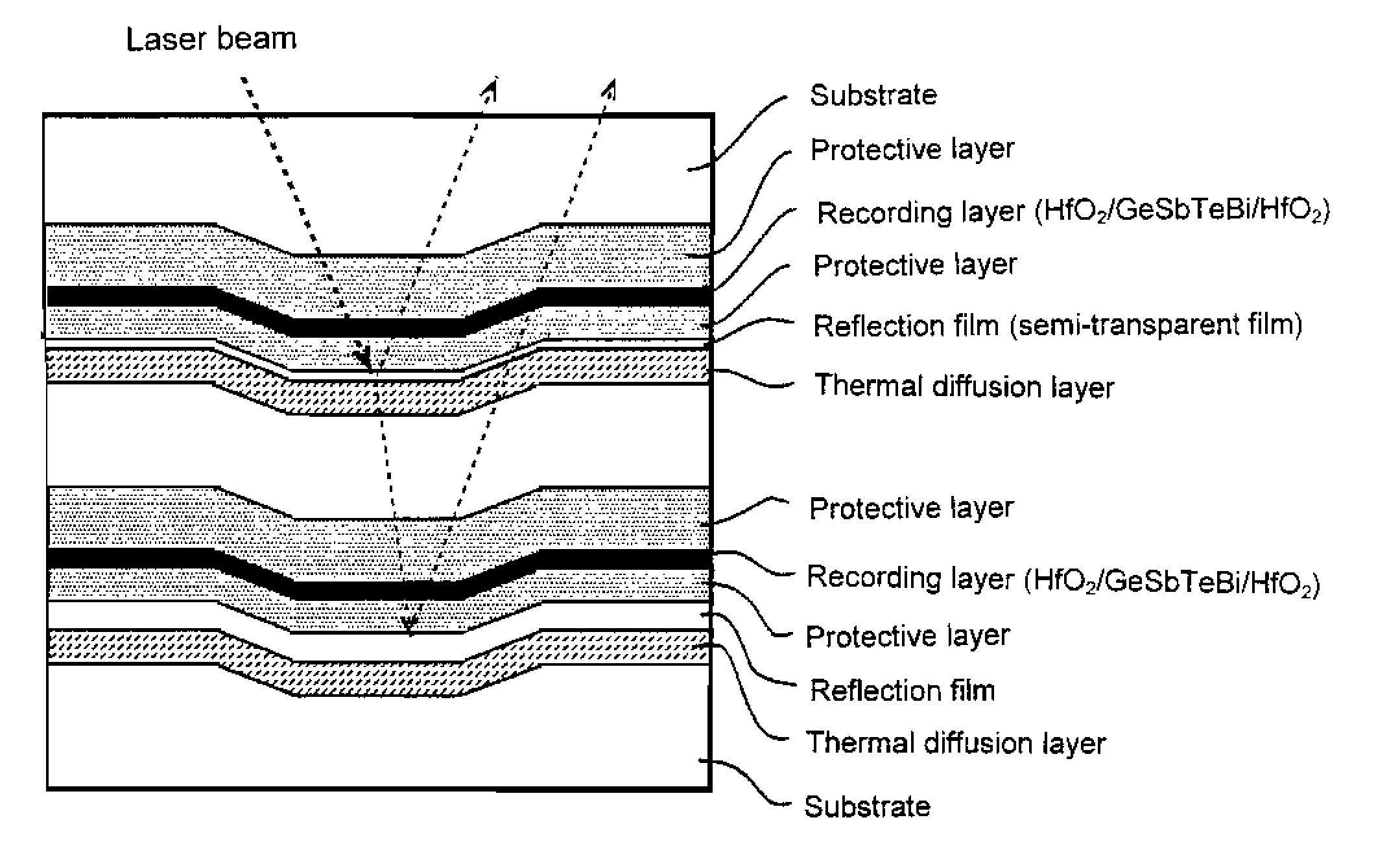
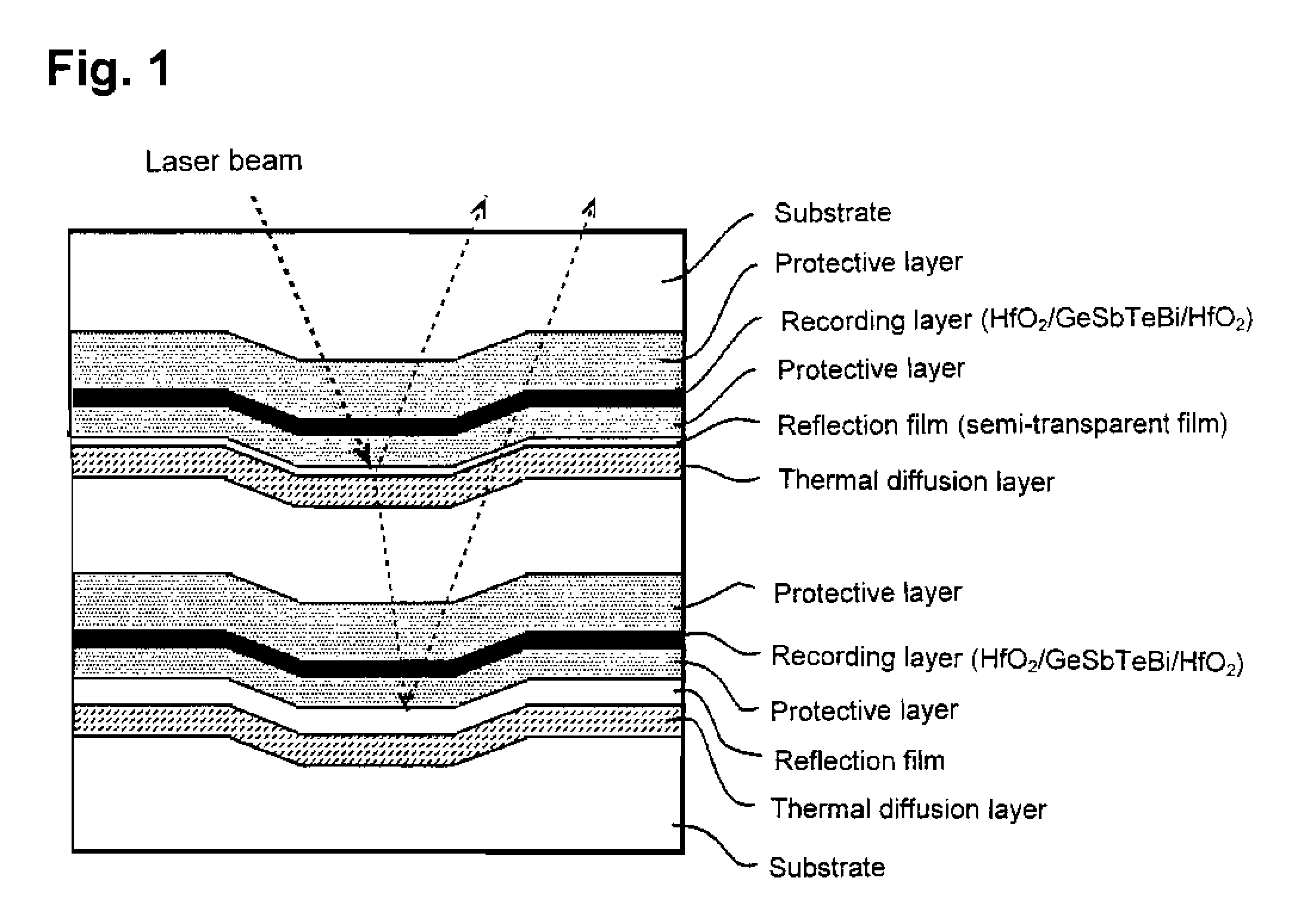
Thin film for reflection film or for semi-transparent reflection film, sputtering target and optical recording medium
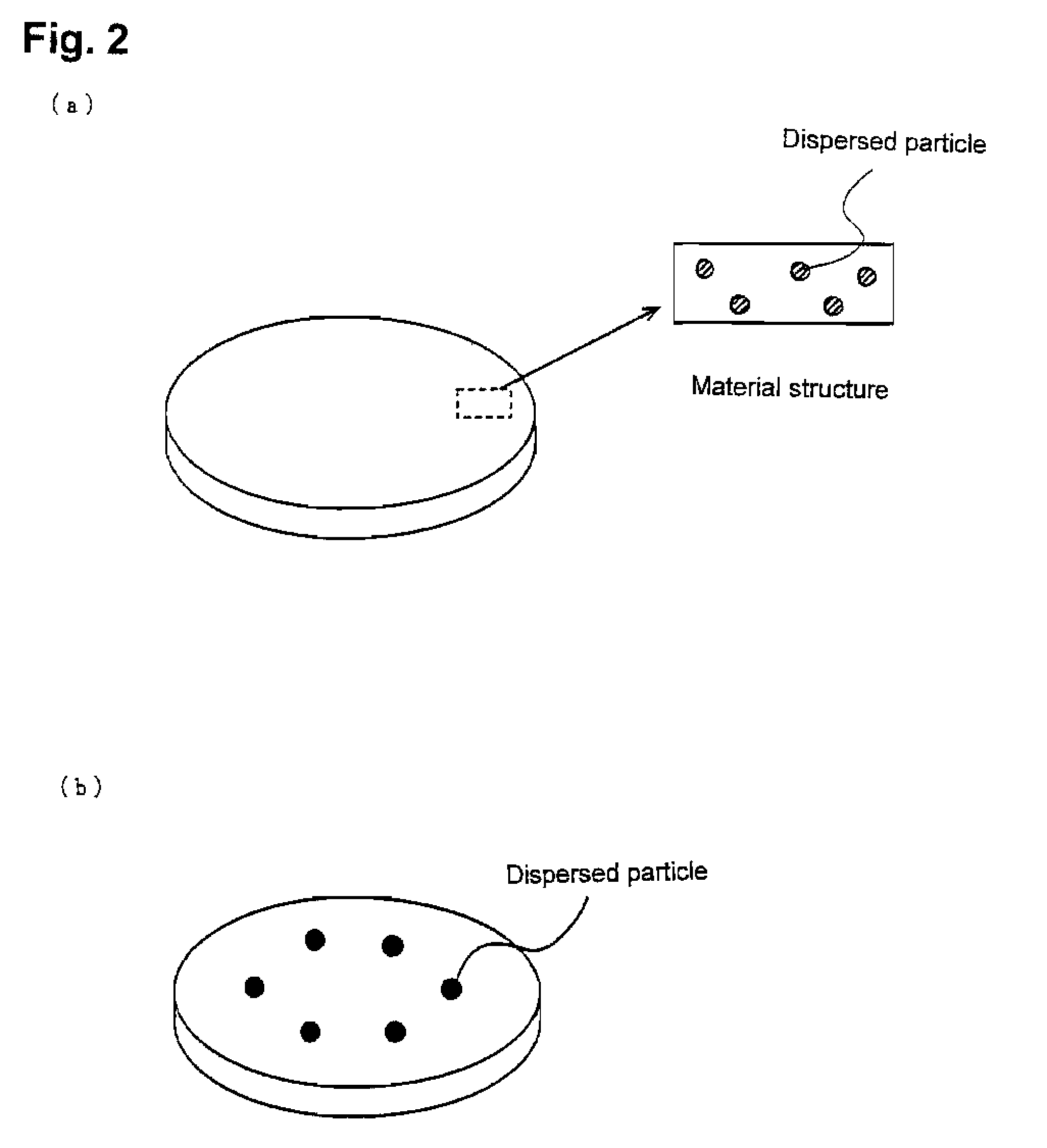
A thin film for reflective film or semi-reflective film comprising a matrix of silver or silver alloy and, dispersed therein, a compound phase of at least one member selected from among aluminum, magnesium, tin, zinc, indium, titanium, zirconium, manganese and silicon nitrides, oxides, composite oxides, nitroxides, carbides, sulfides, chlorides, silicides (excluding silicon), fluorides, borides, hydrides, phosphides, selenides and tellurides. In this thin film, in addition to the above aluminum, etc., there may be dispersed at least one member selected from among silver, gallium, palladium and copper nitrides, oxides, composite oxides, nitroxides, carbides, sulfides, chlorides, silicides, fluorides, borides, hydrides, phosphides, selenides and tellurides. This thin film as deterioration of its reflectance is low even in long-term use can prolong the service life of various equipment having the thin film applied thereto, such as optical recording medium or display, and is also applicable to semi-reflective / semi-transmissive films for use in optical recording medium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
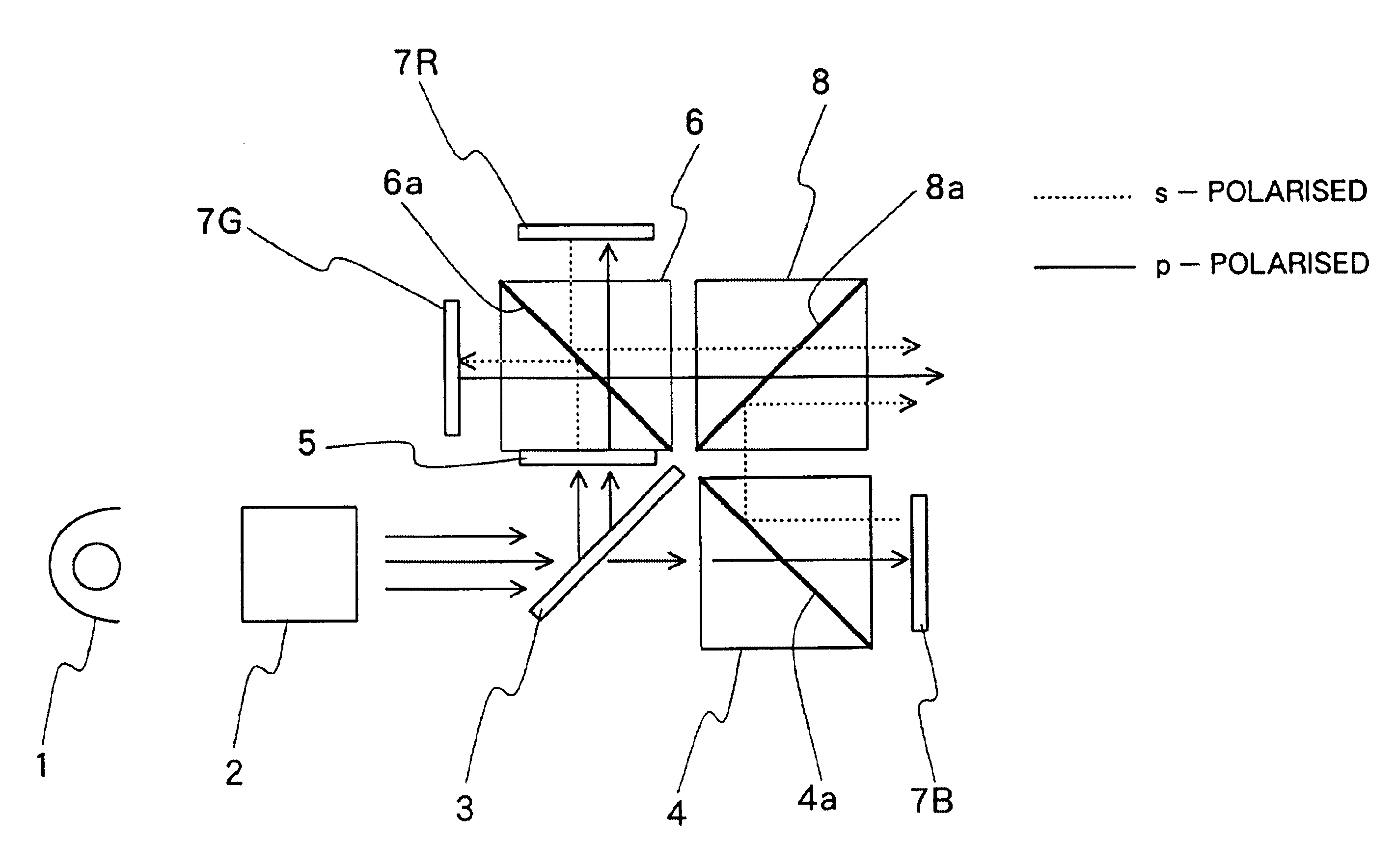
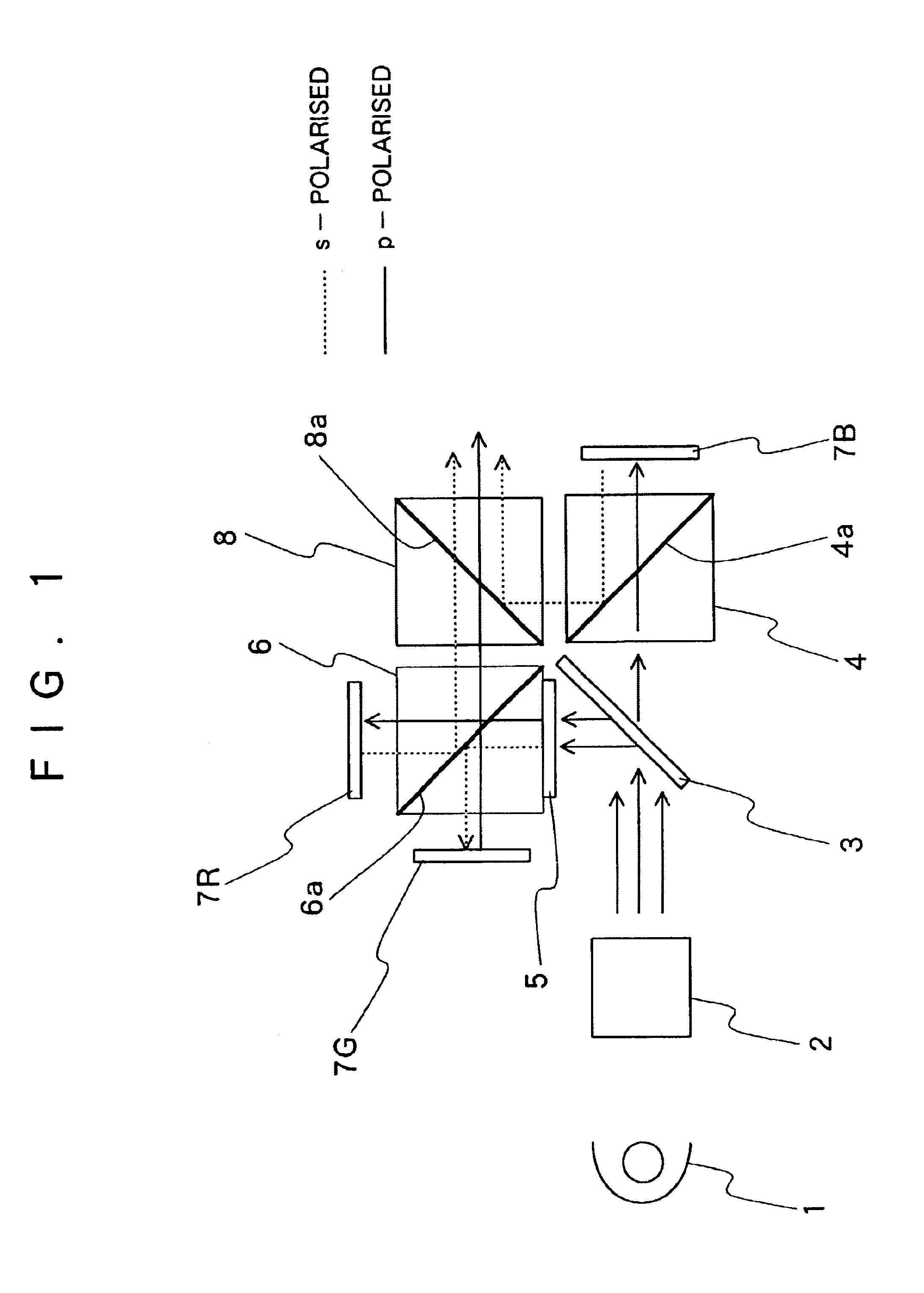
Reflection type liquid crystal projector
InactiveUS6980260B2Guaranteed high-quality imagingEasy constructionProjectorsColor photographyBeam splitterPhase difference
While illuminating light is separated into a first wavelength component illuminating light and second and third wavelength component illuminating lights by a dichroic mirror, the first illuminating light is reflected off a first liquid crystal display element to form a first wavelength component image light which is then reflected off or passed through the polarizing surface of a first polarizing beam splitter, whereas one of the second and third wavelength component illuminating lights has its polarizing surface 90°-converted by a ½ phase difference plate, the other one is passed through the plate without having its polarizing surface converted, the second and third wavelength components are separated from each other by a second polarizing beam splitter and respectively reflected off second and third liquid crystal display elements to obtain second.
Owner:SANO FUJI KOKI
Thin film for reflection film or for semi-transparent reflection film, sputtering target and optical recording medium
ActiveUS7951442B2Improve featuresInhibit migrationMirrorsPhotosensitive materialsIndiumDisplay device
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
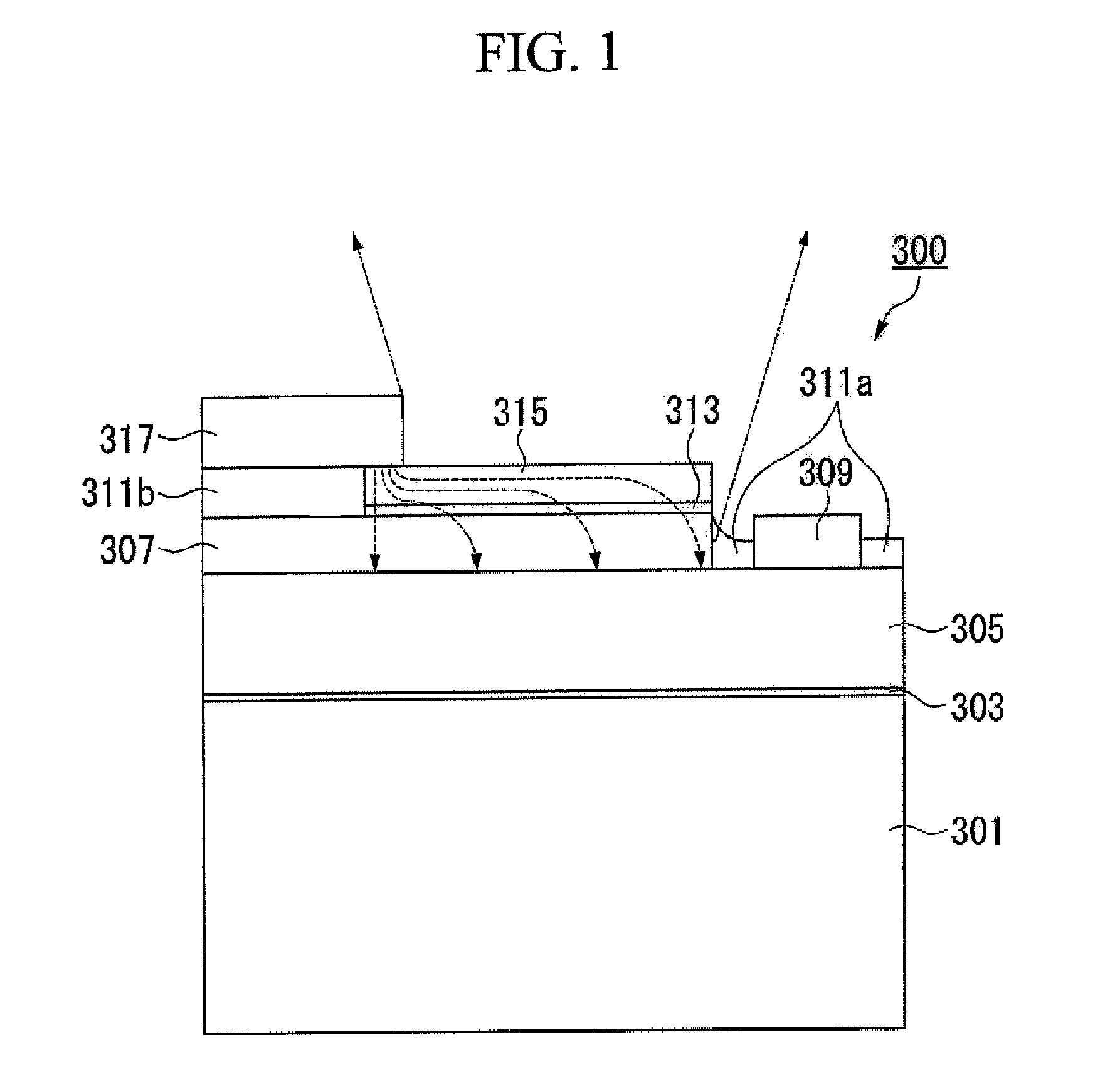
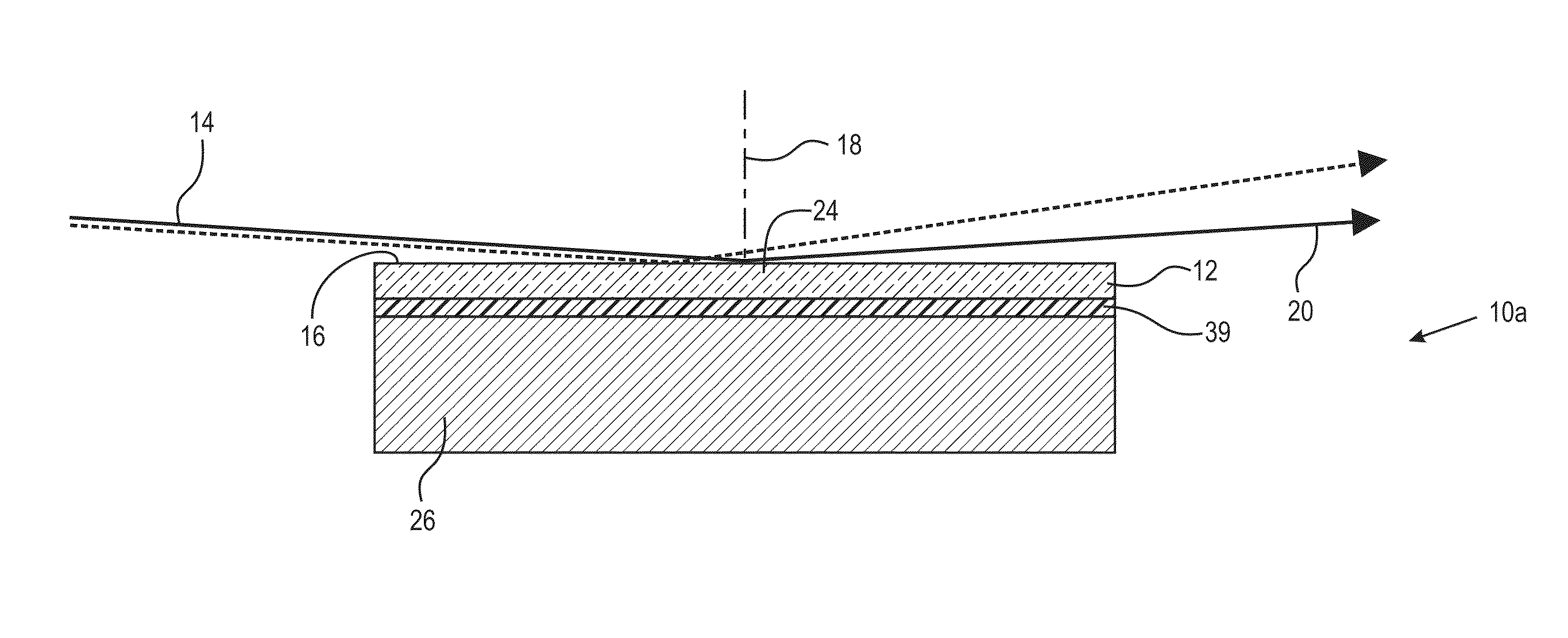
Soft x-ray optics with improved filtering
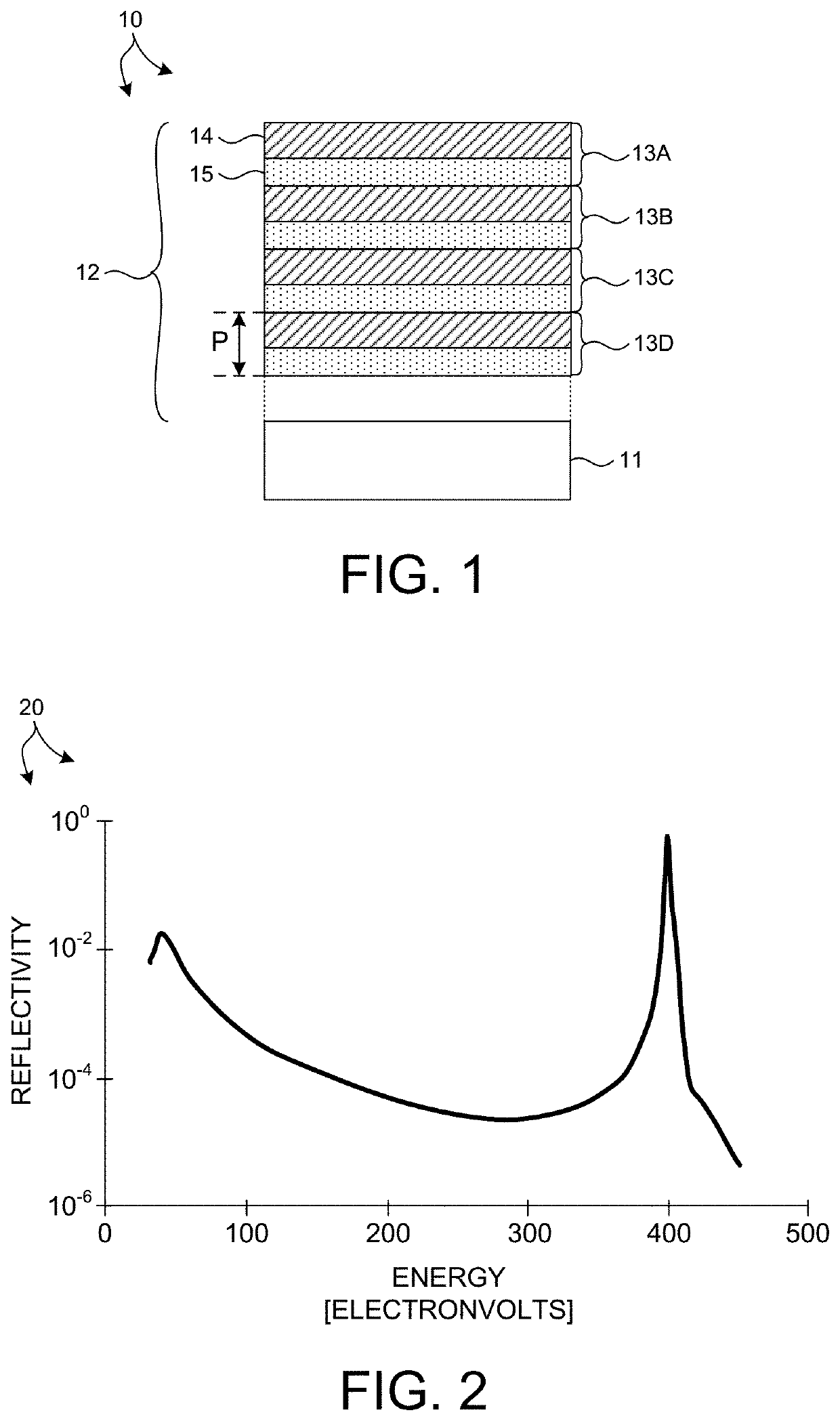
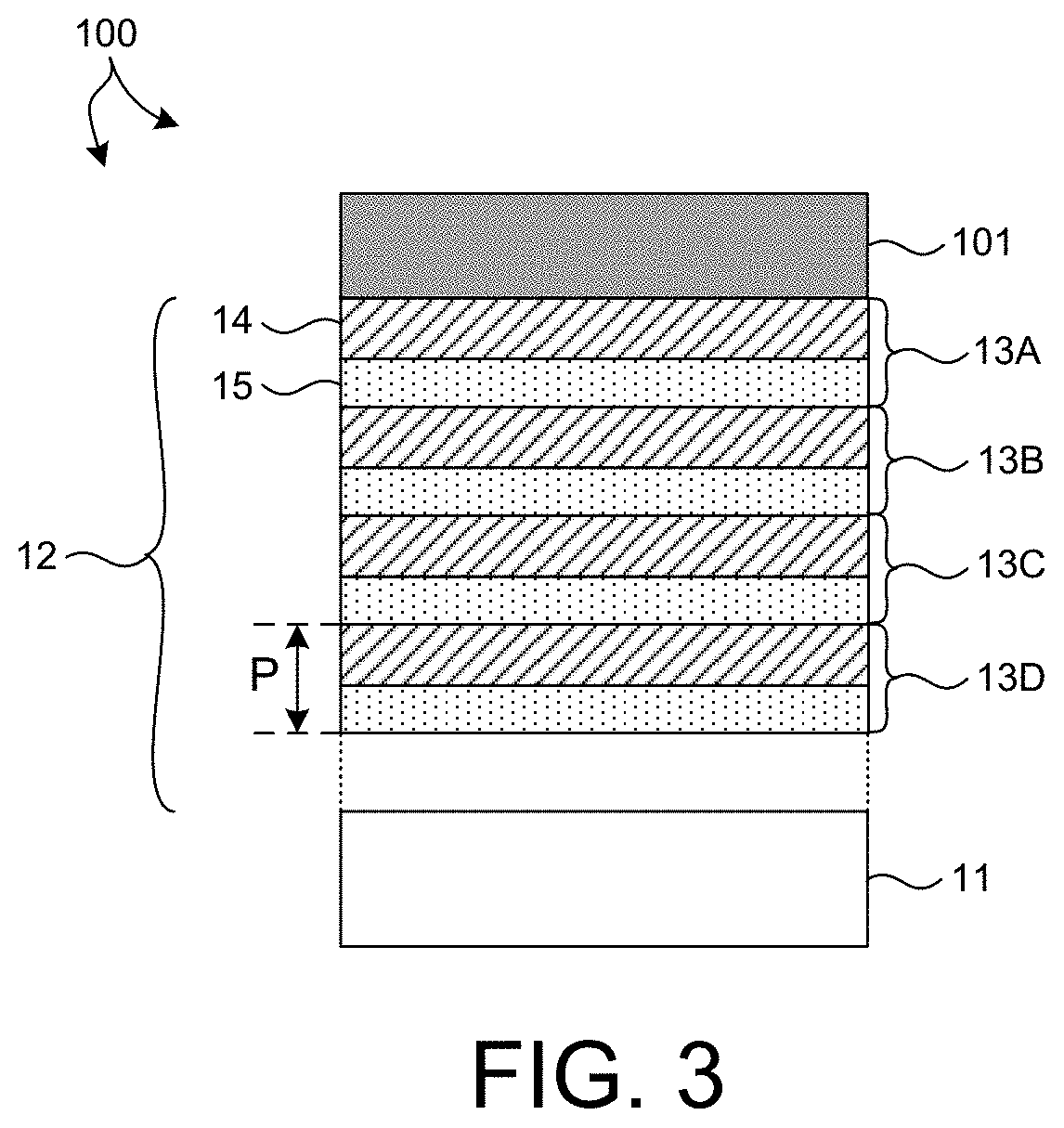
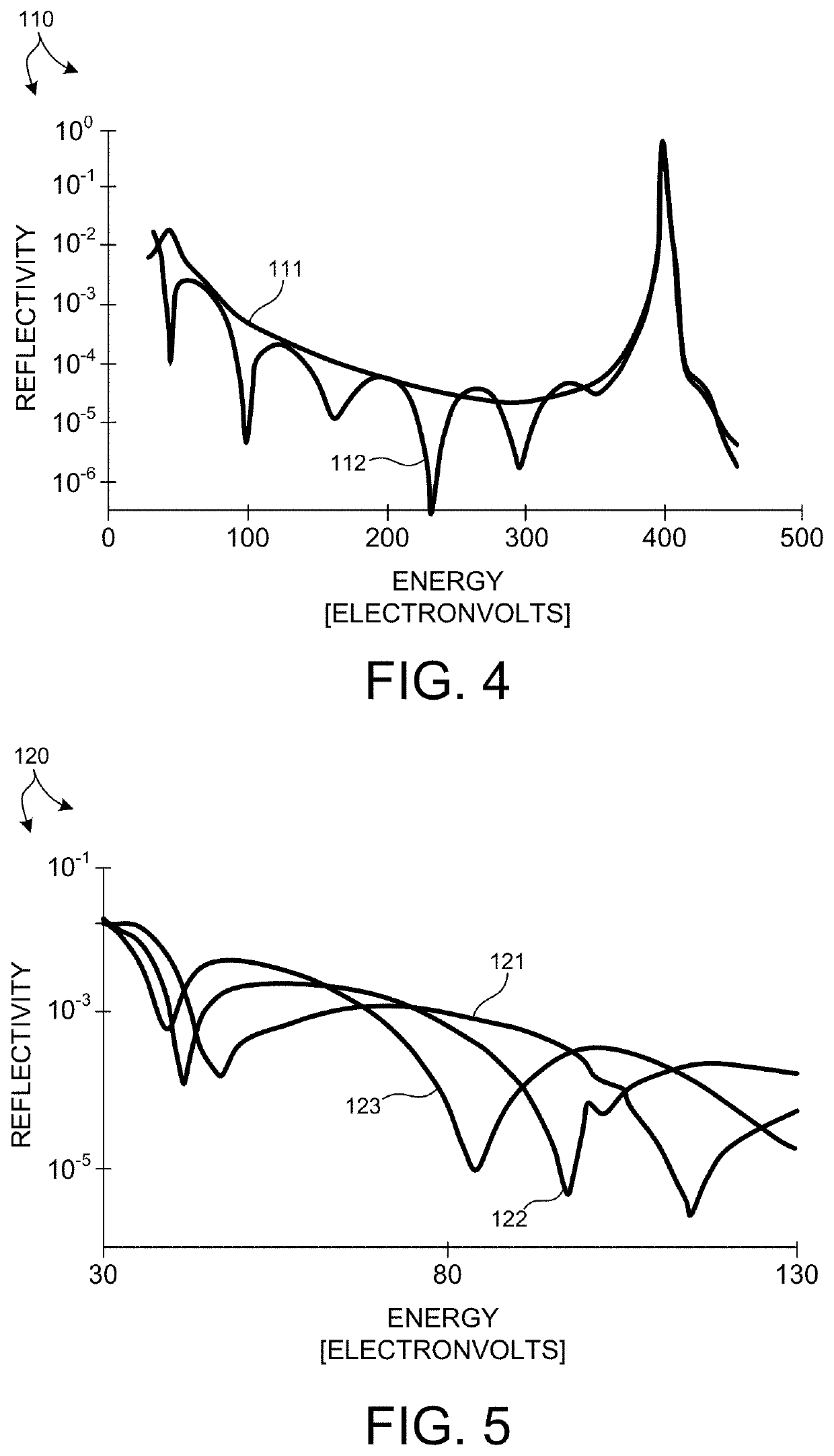
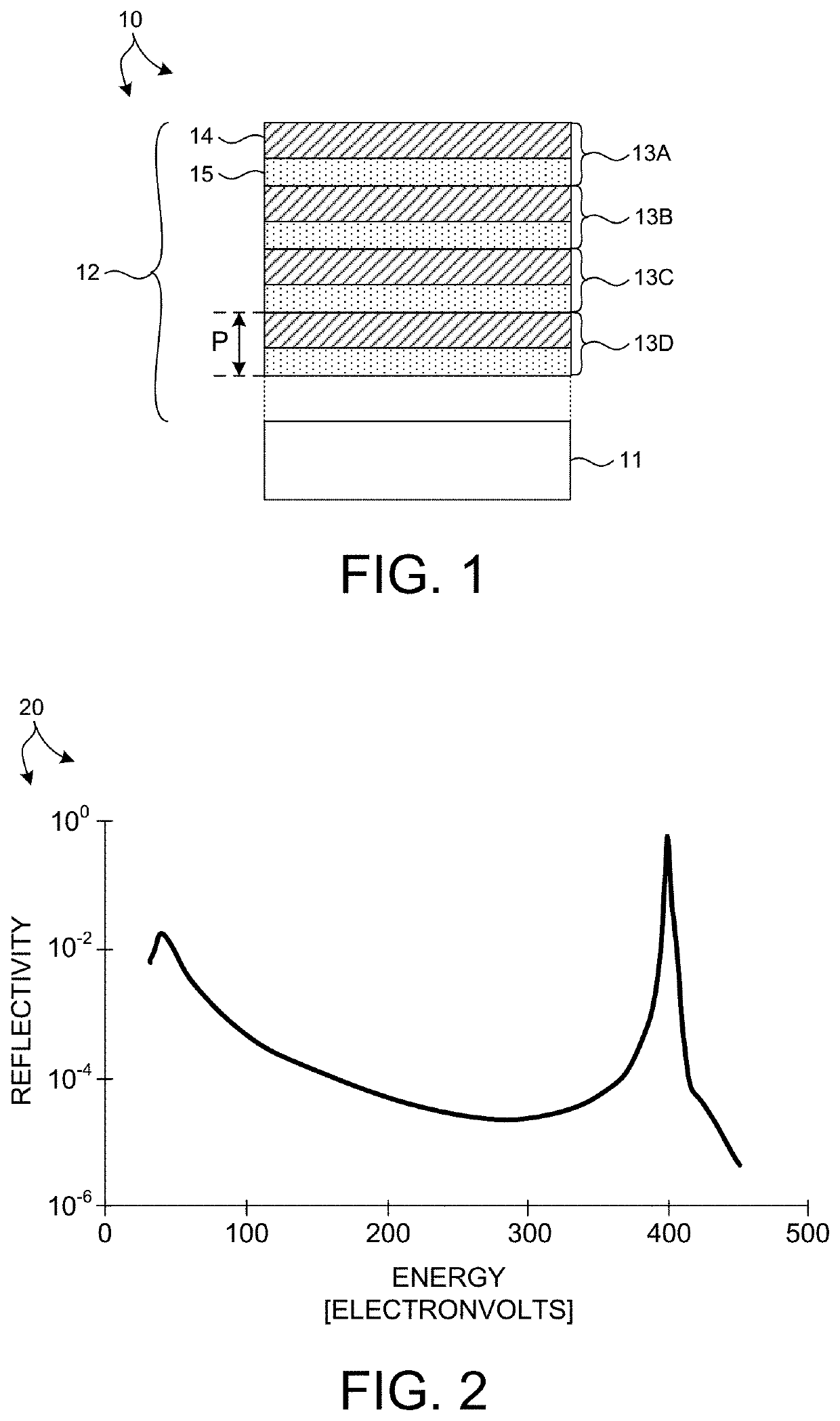
ActiveUS11143604B1Good optical performanceSuppressed reflectivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionInfraredDiffusion barrier
Optical elements that efficiently propagate x-ray radiation over a desired energy range and reject radiation outside the desired energy range are presented herein. In one aspect, one or more optical elements of an x-ray based system include an integrated optical filter including one or more material layers that absorb radiation having energy outside the desired energy band. In general, the integrated filter improves the optical performance of an x-ray based system by suppressing reflectivity within infrared (IR), visible (vis), ultraviolet (UV), extreme ultraviolet (EUV) portions of the spectrum, or any other undesired wavelength region. In a further aspect, one or more diffusion barrier layers prevent degradation of the integrated optical filter, prevent diffusion between the integrated optical filter and other material layers, or both. In some embodiments, the thickness of one or more material layers of an integrated optical filter vary over the spatial area of the filter.
Owner:KLA CORP
Thin film for reflection film or for semi-transparent reflection film, sputtering target and optical recording medium
InactiveUS20100047502A1Improve featuresInhibit migrationCellsOther chemical processesDisplay deviceComplex oxide
A thin film for a reflection film or a semi-transparent reflection film, having a compound phase formed of at least one chemical compound selected from the group consisting of a nitride, an oxide, a complex oxide, a nitroxide, a carbide, a sulfide, a chloride, a silicide, a fluoride, a boride, a hydride, a phosphide, a selenide and a telluride of dysprosium, gadolinium, erbium, praseodymium, samarium, lanthanum and yttrium, dispersed in a matrix formed of silver or a silver alloy. The thin film may disperse at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a nitride, an oxide, a complex oxide, a nitroxide, a carbide, a sulfide, a chloride, a silicide, a fluoride, a boride, a hydride, a phosphide, a selenide and a telluride of silver, and / or gallium, palladium or copper, in addition to dysprosium or the like, therein. The thin film keeps its reflectance without significant loss even after a long period of use, and prolongs the life of various devices which comprise the thin film as a reflection film, such as an optical recording medium and a display. The thin film is also applicable to a semi-reflective / semi-transparent film used in the optical recording medium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
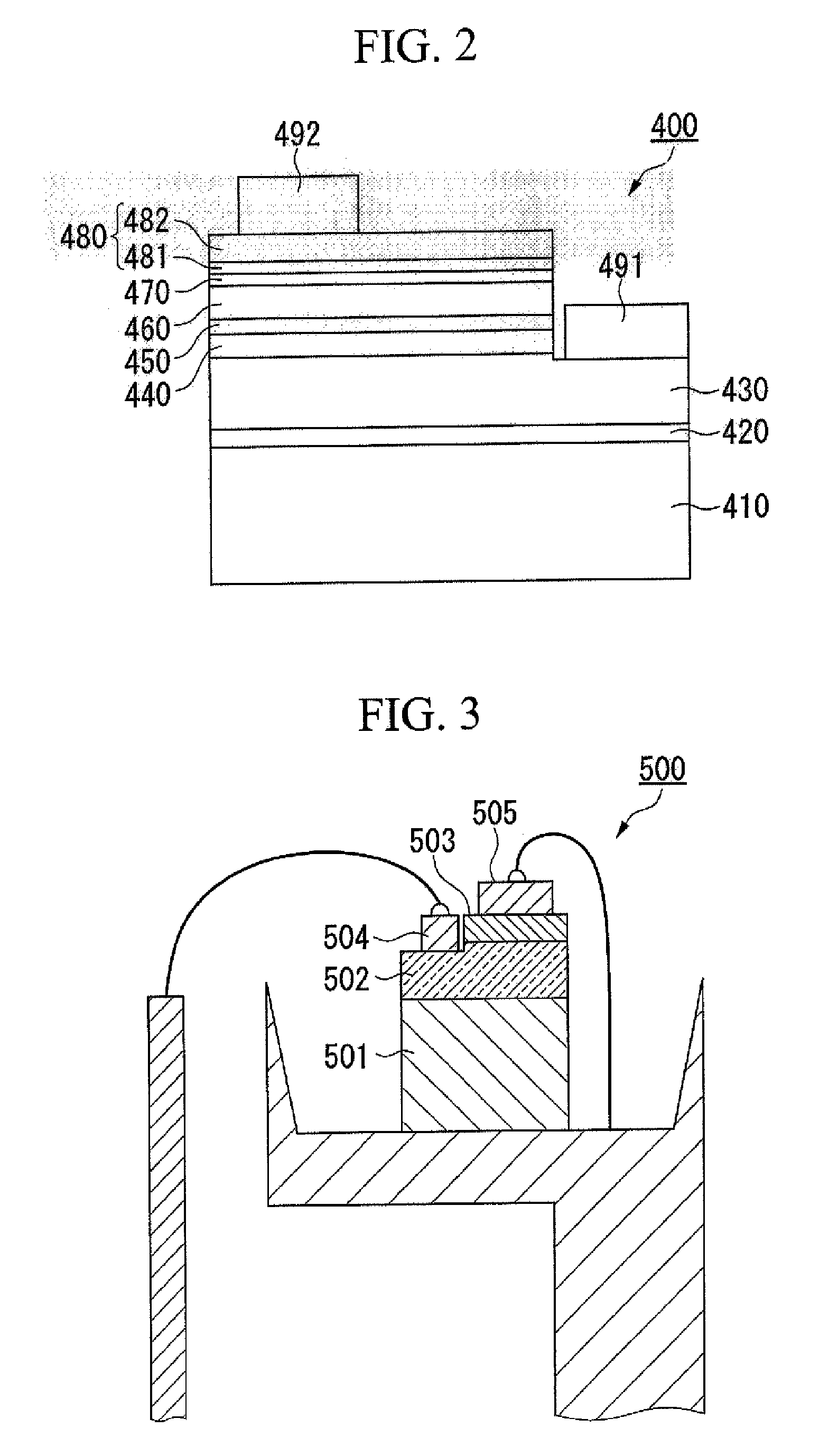
Soft X-Ray Optics With Improved Filtering
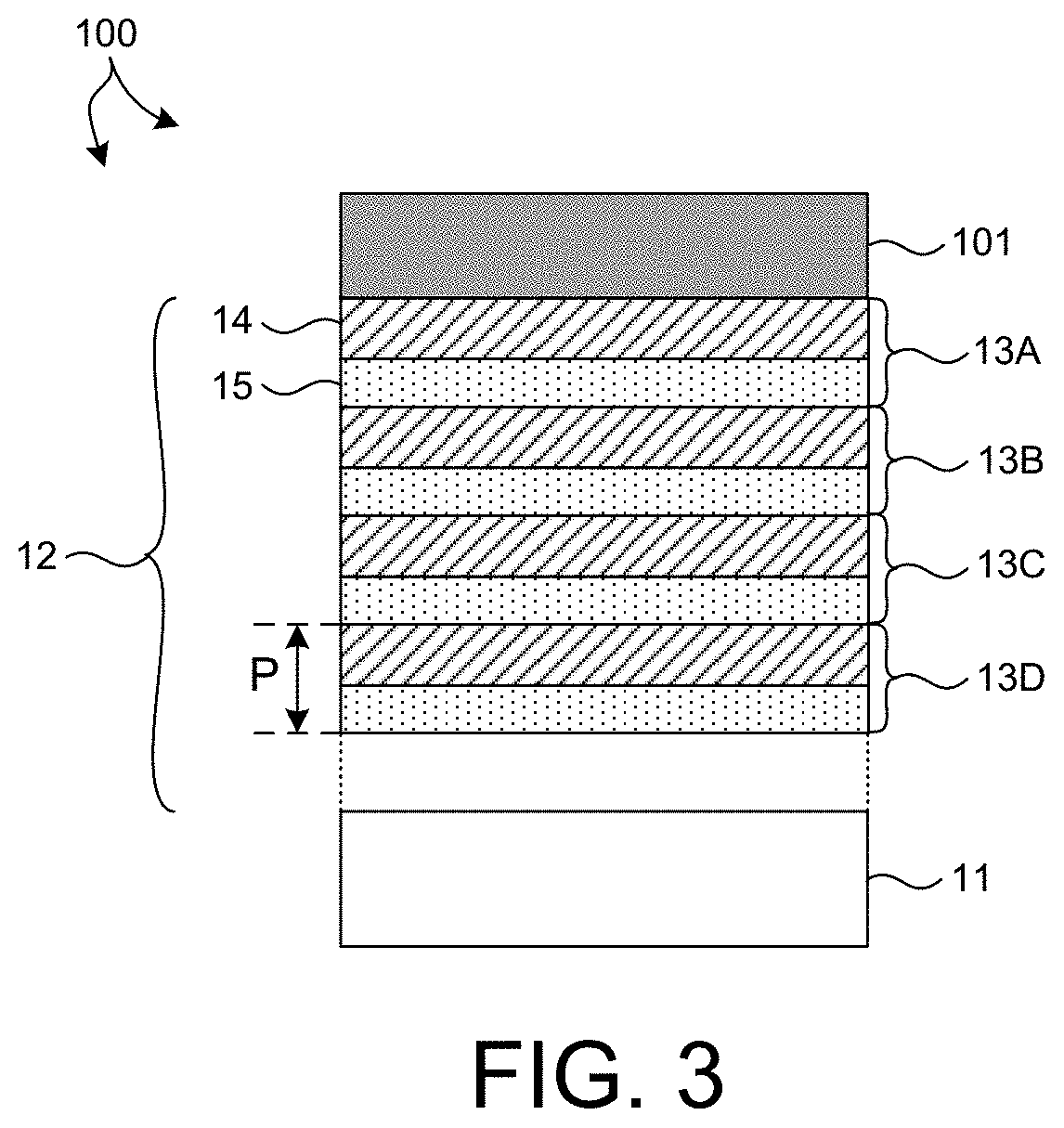
ActiveUS20210310968A1Inhibited DiffusionGood optical performanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionInfraredEngineering
Optical elements that efficiently propagate x-ray radiation over a desired energy range and reject radiation outside the desired energy range are presented herein. In one aspect, one or more optical elements of an x-ray based system include an integrated optical filter including one or more material layers that absorb radiation having energy outside the desired energy band. In general, the integrated filter improves the optical performance of an x-ray based system by suppressing reflectivity within infrared (IR), visible (vis), ultraviolet (UV), extreme ultraviolet (EUV) portions of the spectrum, or any other undesired wavelength region. In a further aspect, one or more diffusion barrier layers prevent degradation of the integrated optical filter, prevent diffusion between the integrated optical filter and other material layers, or both. In some embodiments, the thickness of one or more material layers of an integrated optical filter vary over the spatial area of the filter.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
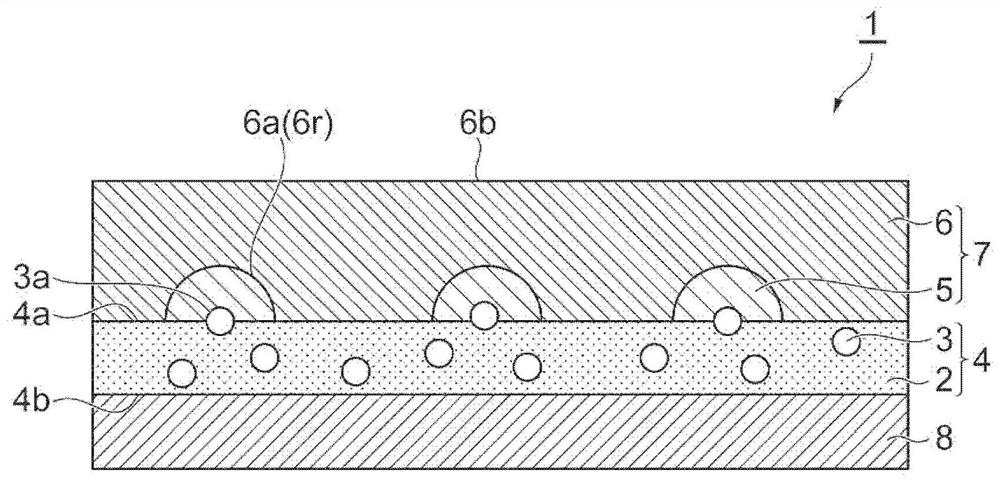
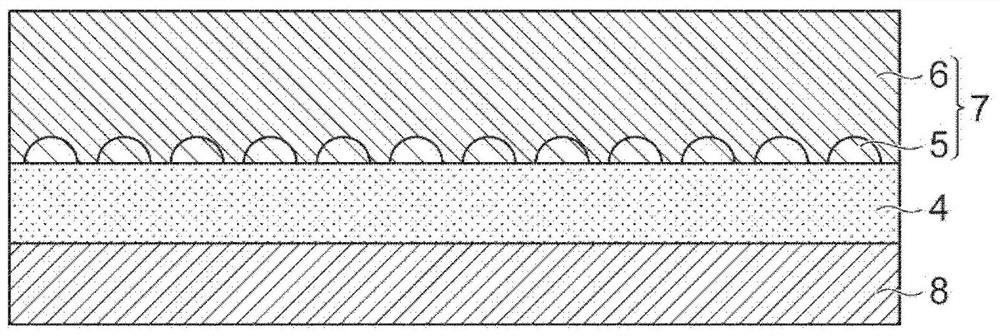
Sheet, metal mesh and method of manufacture
ActiveCN109306478BImprove tight adhesionSuppressed reflectivityPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPolymer sciencePolypyrrole
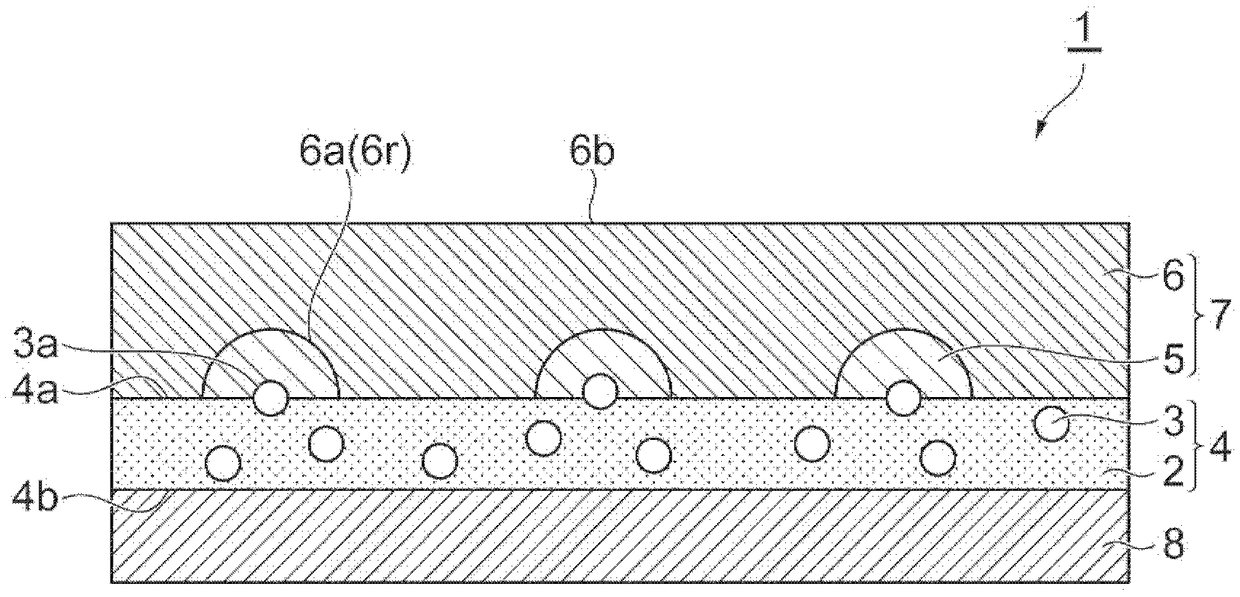
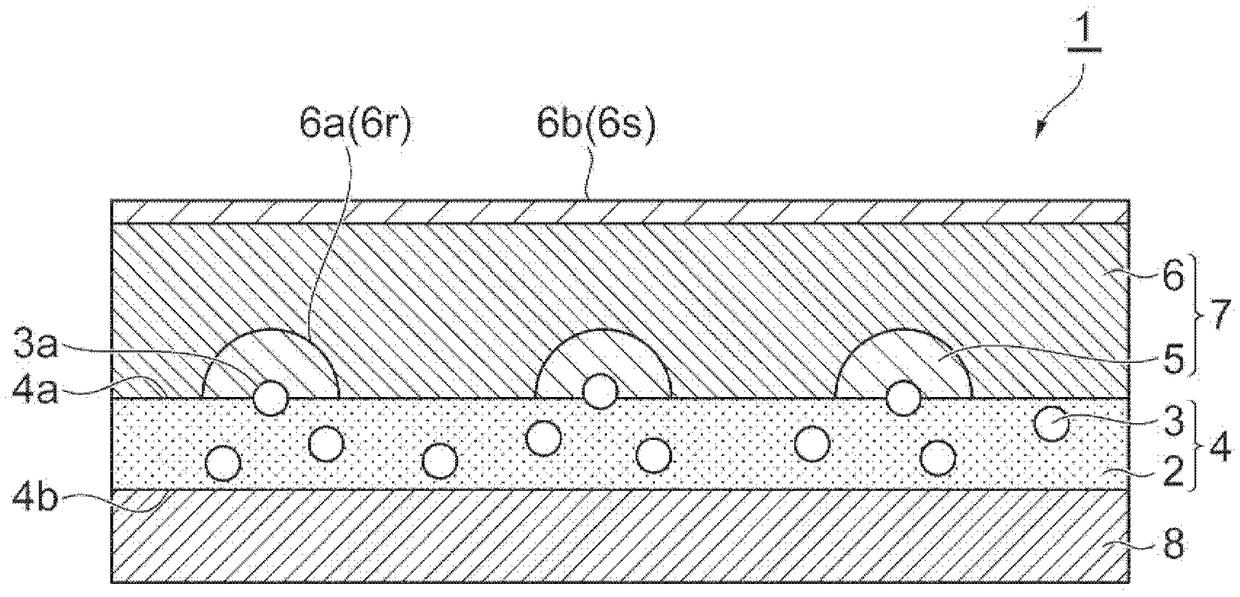
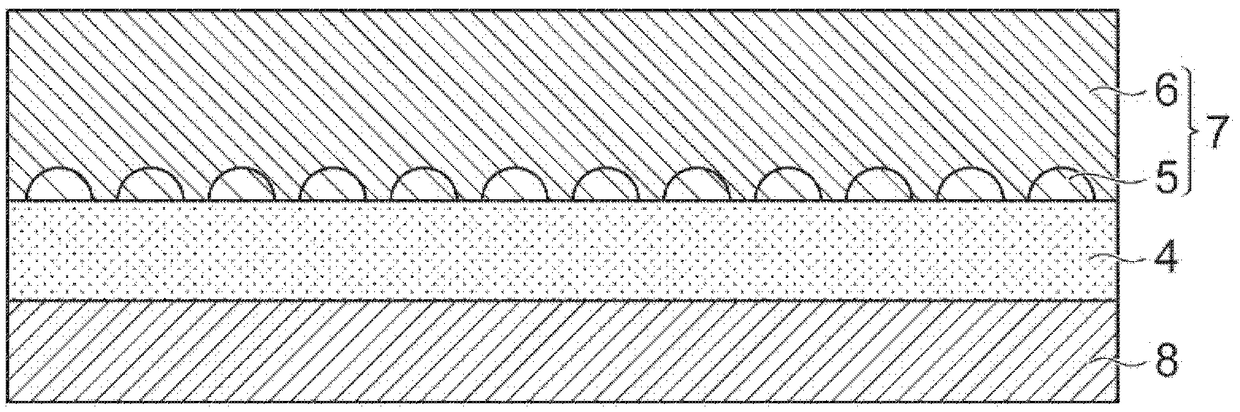
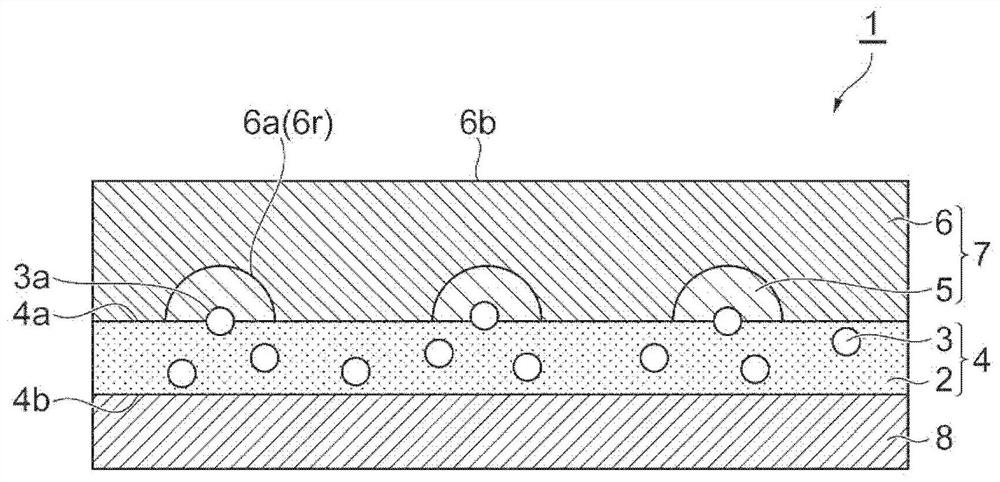
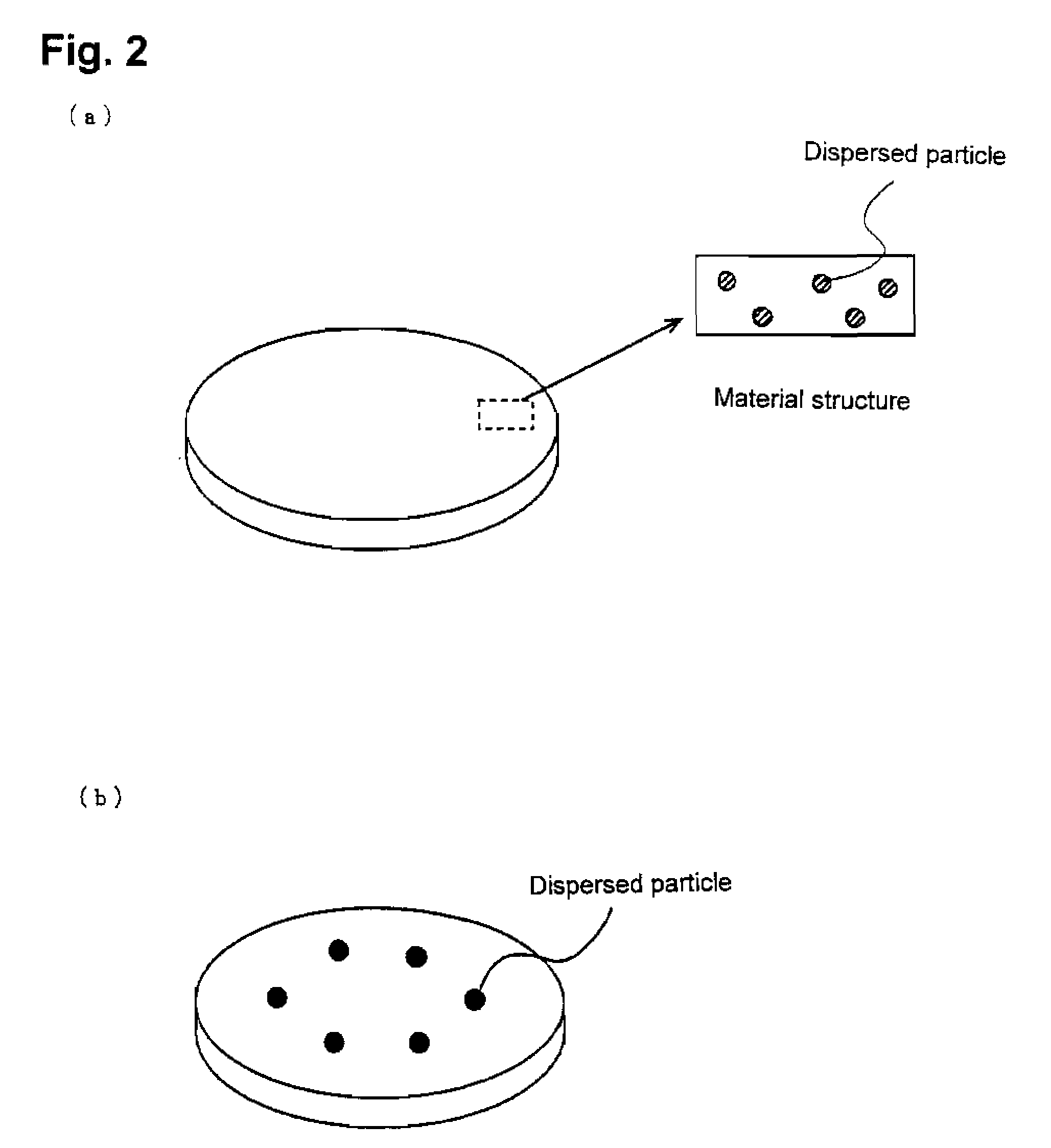
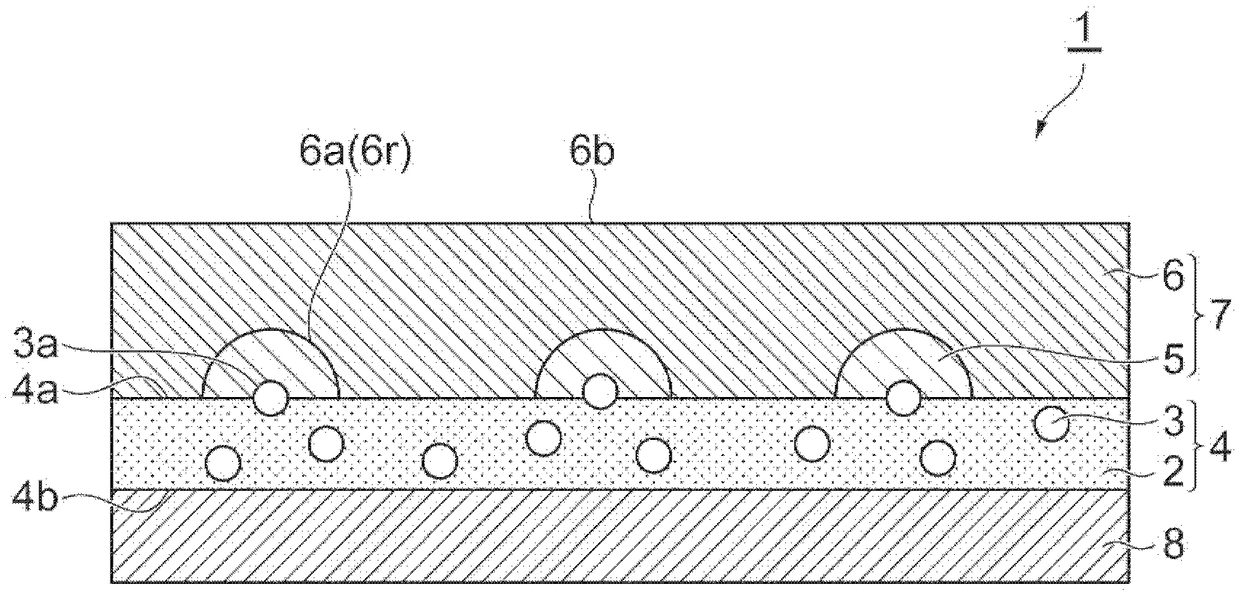
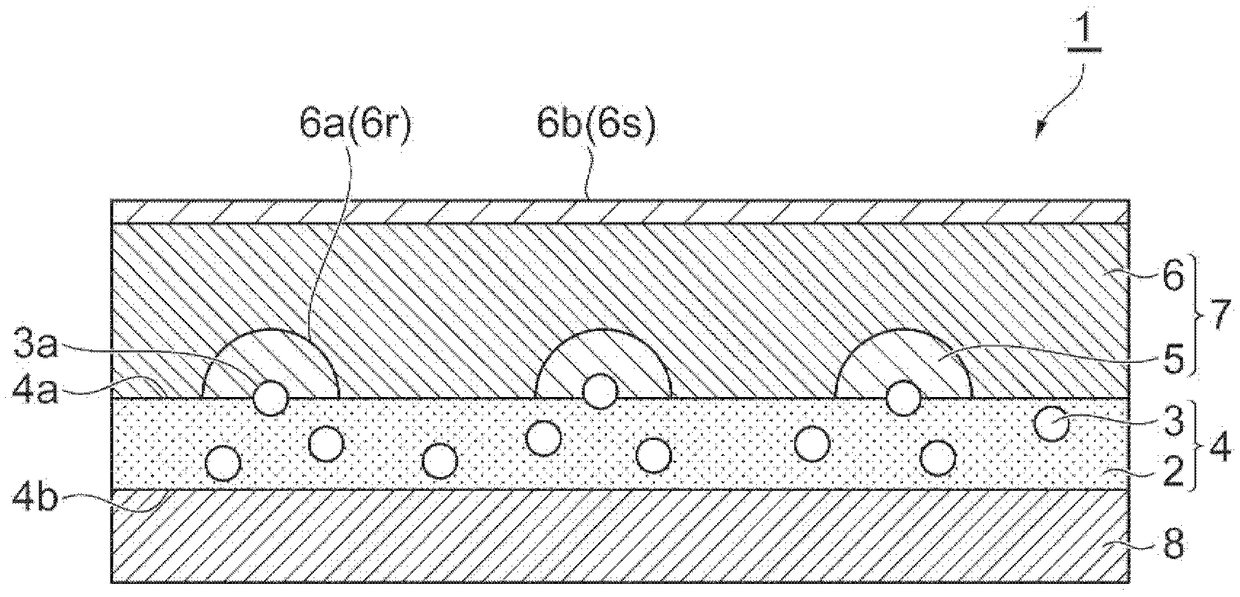
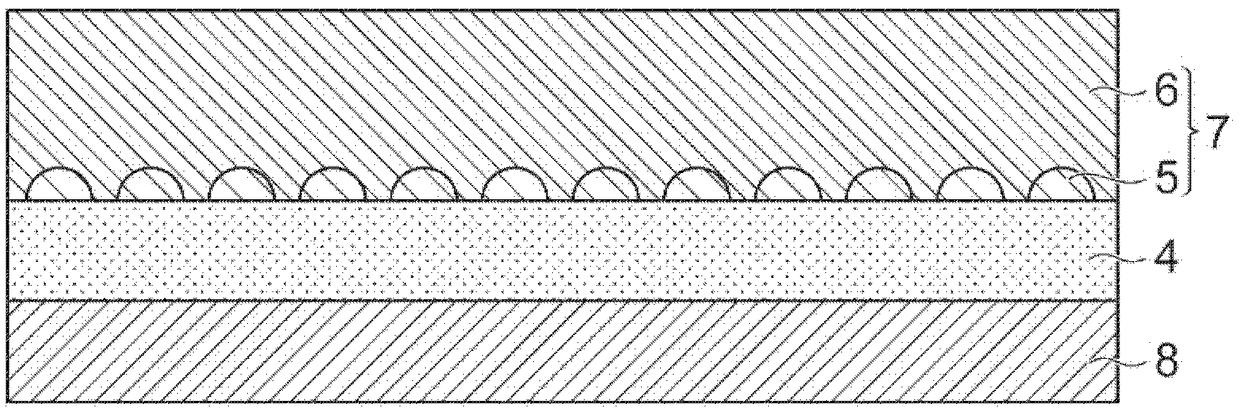
The sheet (1) involved in the present invention has: a resin layer (4) including a binder (2) and polypyrrole particles (3); an electroless coating (7) is provided on one of the resin layers (4) The side of the main surface (4a) has a first electroless plating film (5) and a second electroless plating film (6); and a transparent base material (8), which is arranged on the other main surface (4b) of the resin layer (4) side. At least a part of the polypyrrole particles (3) has an exposed surface (3a) exposed from one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4), and the exposed surface (3a) is dispersed on one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4). )superior. The first electroless plating film (5) is provided on one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4) so as to surround the respective exposed surfaces (3a) of the polypyrrole particles (3). The 2nd electroless plating film (6) is provided with the mode of covering the 1st electroless plating film (5), and one main surface (6a) of the 2nd electroless plating film (6) has the corresponding to the 1st electroless plating film (5) Recess (6r).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS7544619B2Highly accurate patternImprove detection accuracyTransistorPhotomechanical apparatusResistSemiconductor
An insulating film is formed on a main surface of a substrate. A conductive film is formed on the insulating film. A lower layer resist film, an intermediate layer, an anti-reflection film and an upper layer resist film are formed on the conductive film. A focal point at a time of exposure is detected by detecting a height of the upper layer resist film. In detecting the focal point at the time of exposure, a focal point detection light is radiated on the upper layer resist film. After detecting the focal point, the upper layer resist film is exposed and developed thereby to form a resist pattern. With the resist pattern as a mask, the intermediate layer and the anti-reflection film are patterned, and the lower layer resist film is developed. With these patterns as a mask, the conductive film is etched thereby to form a gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
optical stack
ActiveCN110720059BSuppressed reflectivityFull brightnessLayered productsOptical filtersPolarizerWavelength conversion
To provide an optical laminate capable of exhibiting sufficient luminance and good hue while suppressing reflectance when used in an image display device, thereby achieving cost reduction. The optical laminate of the present invention has a wavelength conversion layer that does not have a polarizing plate on the opposite side of the wavelength conversion layer when viewed from the absorption layer, and the wavelength conversion layer is a layer that converts part of the wavelength of incident light and emits light, The absorption layer is a layer containing a compound having an absorption peak between 480nm to 780nm wavelength, and the average reflectance R1 of the wavelength conversion layer at a wavelength of 380nm to 480nm is the same as the average reflectance R1 of the wavelength conversion layer at a wavelength of 490nm to 600nm The relationship of R2 is R2>R1, and the maximum peak value of the reflectance of the absorbing layer side of the optical laminate at a wavelength of 380 nm to 480 nm is P1, and the absorbing layer side of the optical laminate is at a wavelength of 490 nm to 600 nm. When the maximum peak value of the lower reflectance is P2, P2 / P1 is 0.7 to 1.5.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Thin Film For Reflection Film Or For Semi-Transparent Reflection Film, Sputtering Target and Optical Recording Medium
InactiveUS20100047507A1Excellent in reflectance-keeping characteristicImprove corrosion resistanceCellsRecording apparatusBorideDisplay device
The present invention provides a thin film for a reflection film or for a semi-transparent reflection film, which has at least one silver compound phase of nitride, oxide, complex oxide, nitroxide, carbide, sulfide, chloride, silicide, fluoride, boride, hydride, phosphide, selenide and telluride of silver, dispersed in a matrix formed of silver. The thin film according to the present invention keeps its reflectance without significant loss even after a long period of use, and can prolong the life of various devices which comprises the thin film as a reflection film, such as an optical recording medium and a display. The thin film can be also applied to a semi-reflective / semi-transparent film used in the optical recording medium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
Angle broadband extreme ultraviolet multi-layer film having spectrum purification function
InactiveCN105445822ASimple structureEasy to preparePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusUltravioletBroadband
The invention relates to an angle broadband extreme ultraviolet multi-layer film having a spectrum purification function, and belongs to the extreme ultraviolet photoetching technology field. The angle broadband extreme ultraviolet multi-layer film having the spectrum purification function is, from bottom to top, constituted by a substrate, an aperiodic MoSi alternately-arranged multi-layer film, a first spectrum absorption layer, a spacing layer, and a second spectrum absorption layer. The first spectrum absorption layer, the spacing layer, and the second spectrum absorption layer are used to form a spectrum purification structure layer. The multi-layer film is provided with a spectrum purification function. The angle broadband extreme ultraviolet multi-layer film is advantageous in that the spectrum purification layer is disposed on the aperiodic angle broadband extreme ultraviolet multi-layer, and then the spectrum purification function of inhibiting the deep ultraviolet waveband can be realized, and the extreme ultraviolet waveband reflectivity is basically not affected, and then the extreme ultraviolet waveband reflectivity can be reduced; the structure of the multi-layer film is simple, and the production method is simple.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sheet material, metal mesh and method for manufacturing thereof
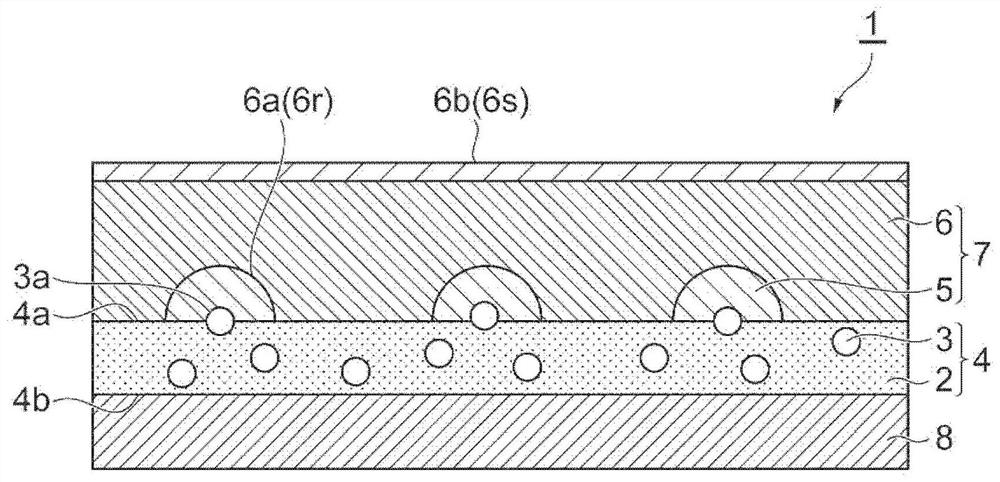
ActiveCN109306478AImprove tight adhesionSuppressed reflectivityPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPolymer sciencePolypyrrole
A sheet material includes a resin layer (4) containing a binder (2) and polypyrrole particles (3), an electroless plating film (7) provided on the side of one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4)and including first electroless plating films (5) and a second electroless plating film (6), and a transparent base material (8) provided on the side of the other main surface (4b) of the resin layer(4). At least part of the polypyrrole particles (3) has an exposure surface (3a) exposed from the main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4), and the exposure surface (3a) is dispersed at the main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4). The first electroless plating films (5) are arranged at the main surface surface (4a) of the resin layer (4) in a mode round the exposure surfaces (3a) of the polypyrrole particles (3). The second electroless plating film (6) is arranged in a mode of covering the first electroless plating films (5), and the main surface (6a) of the second electroless plating film (6) as a recess portion (6r) corresponding to the first electroless plating films (5).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
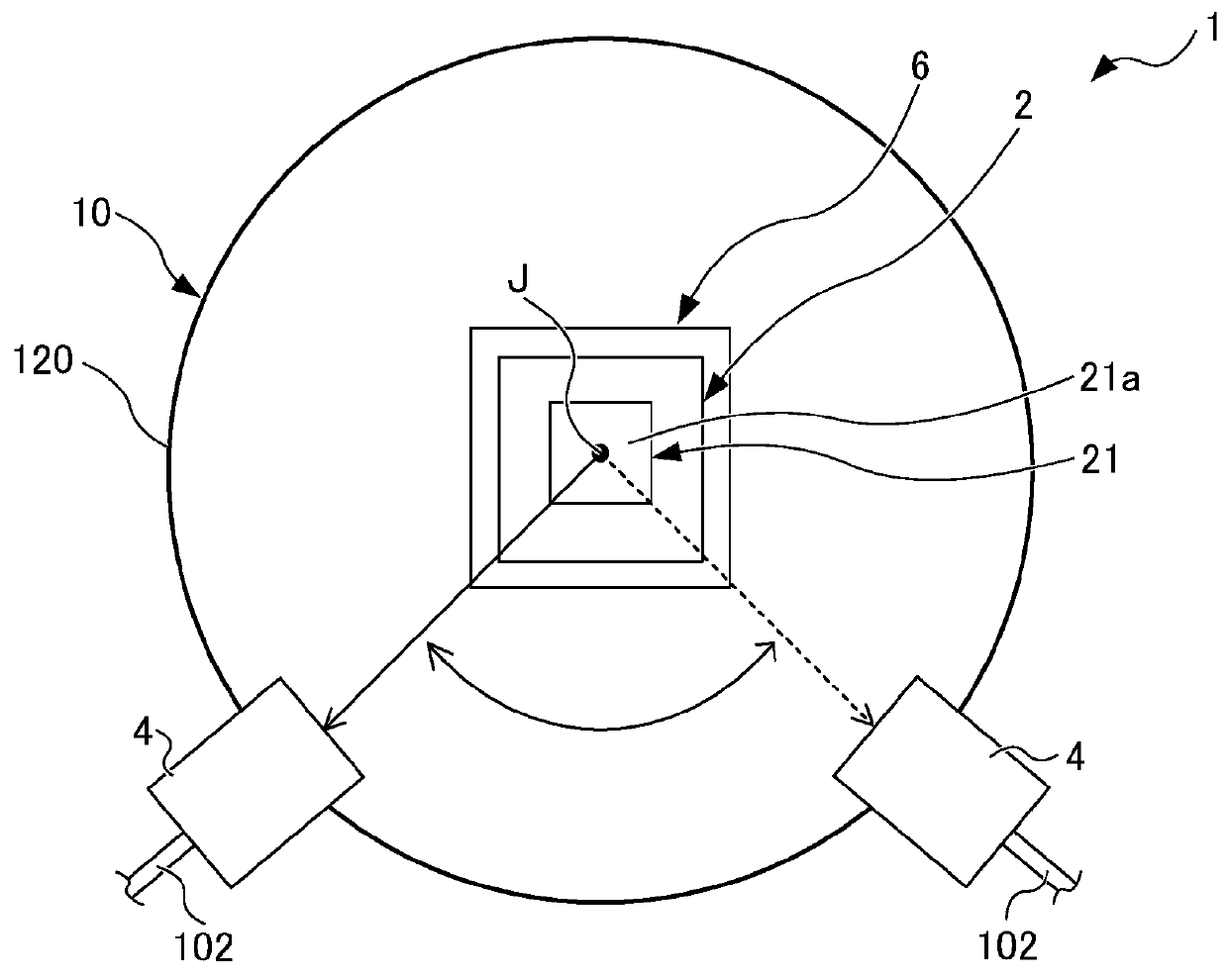
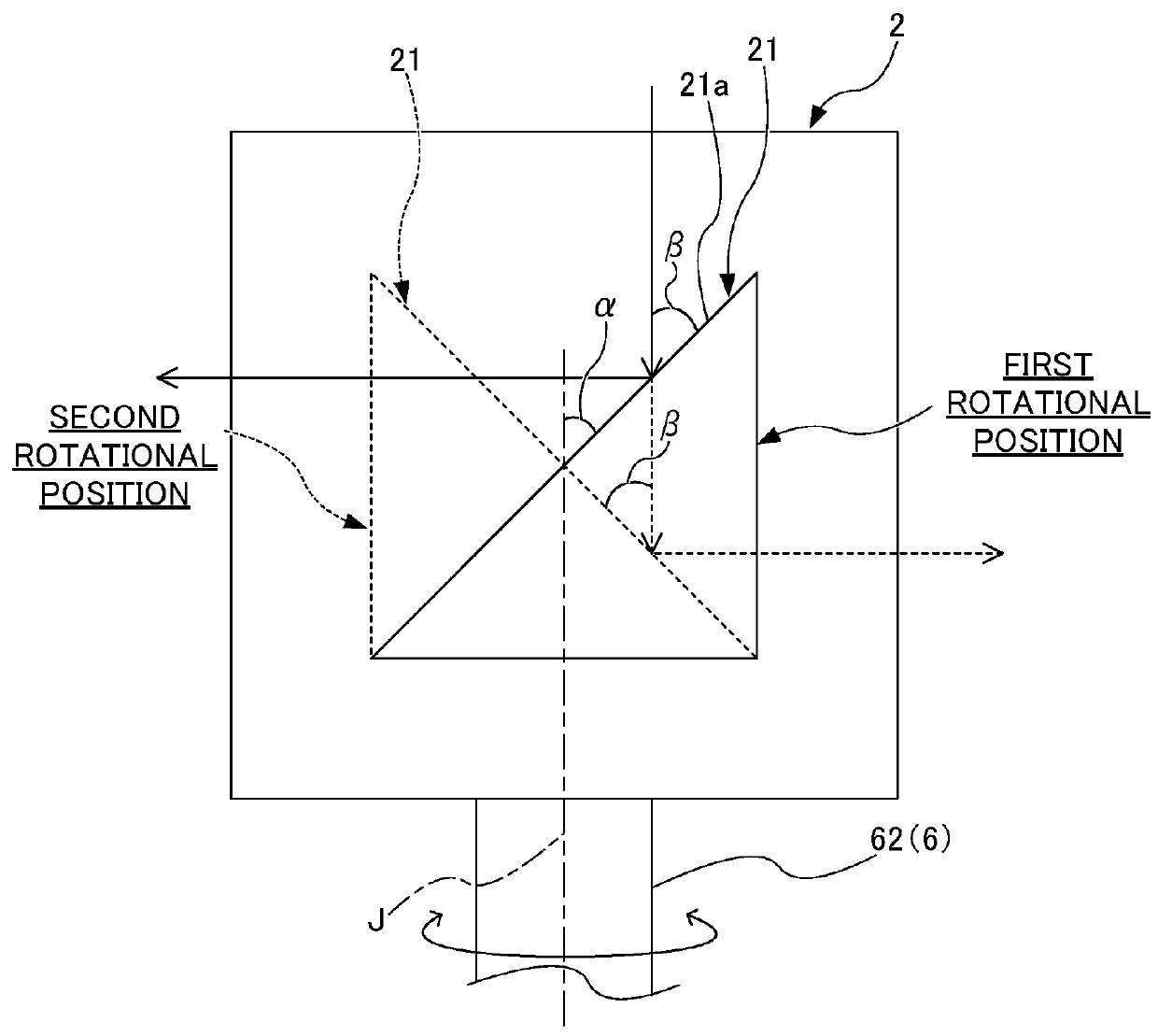
Beam distributor
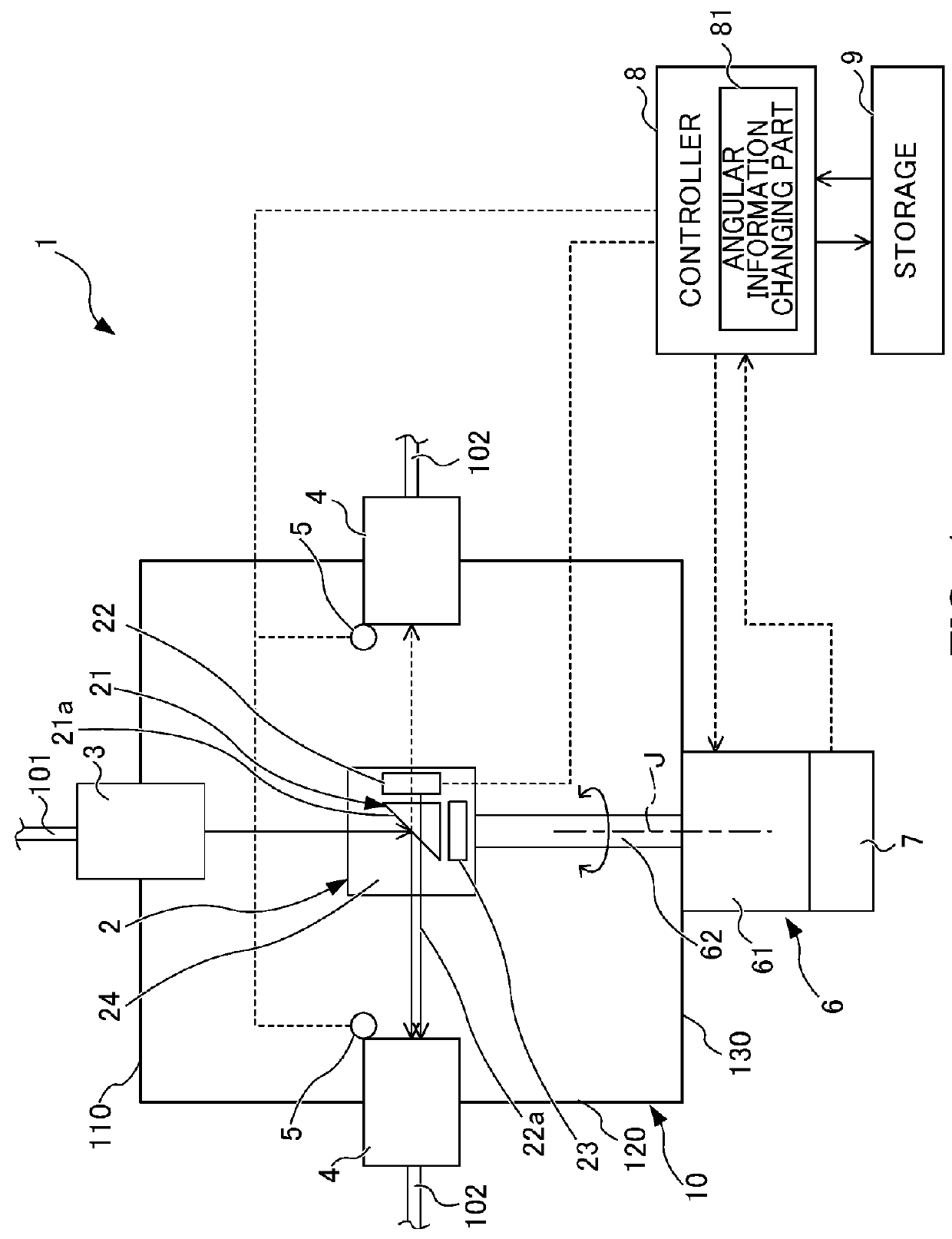
ActiveUS20180106971A1Suppressing reflectivity reductionReduce reflectivityCoupling light guidesOptical axisClassical mechanics
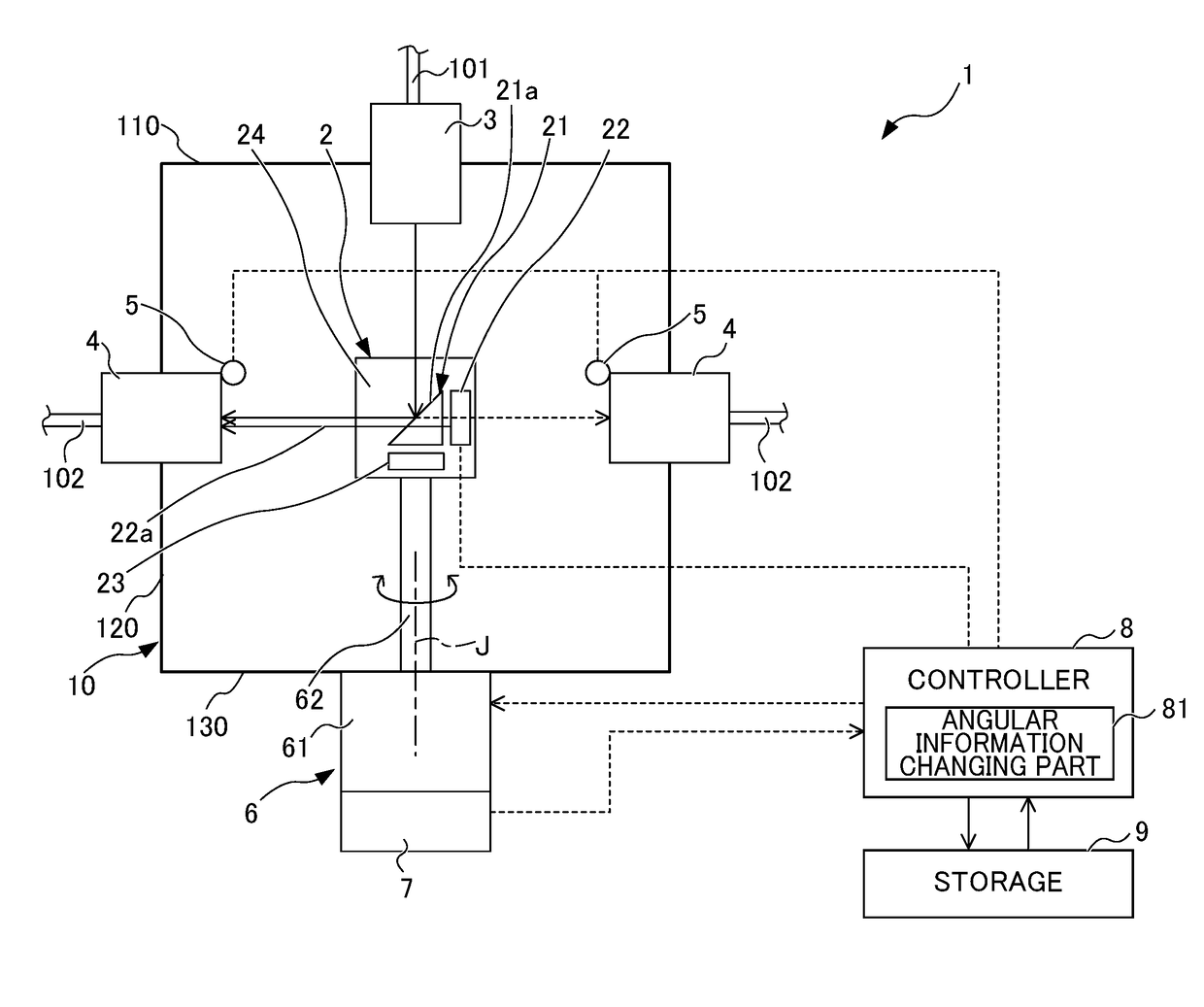
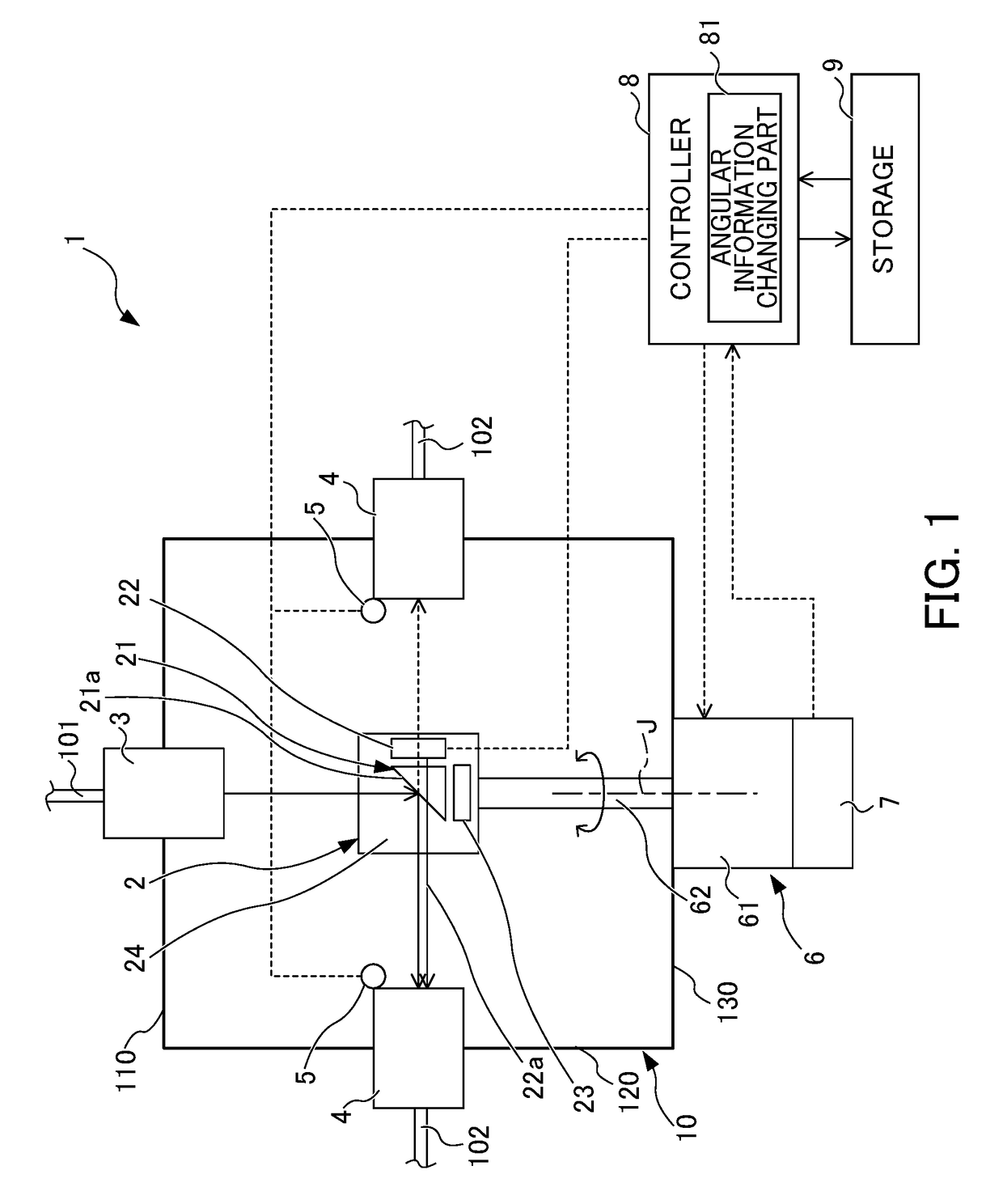
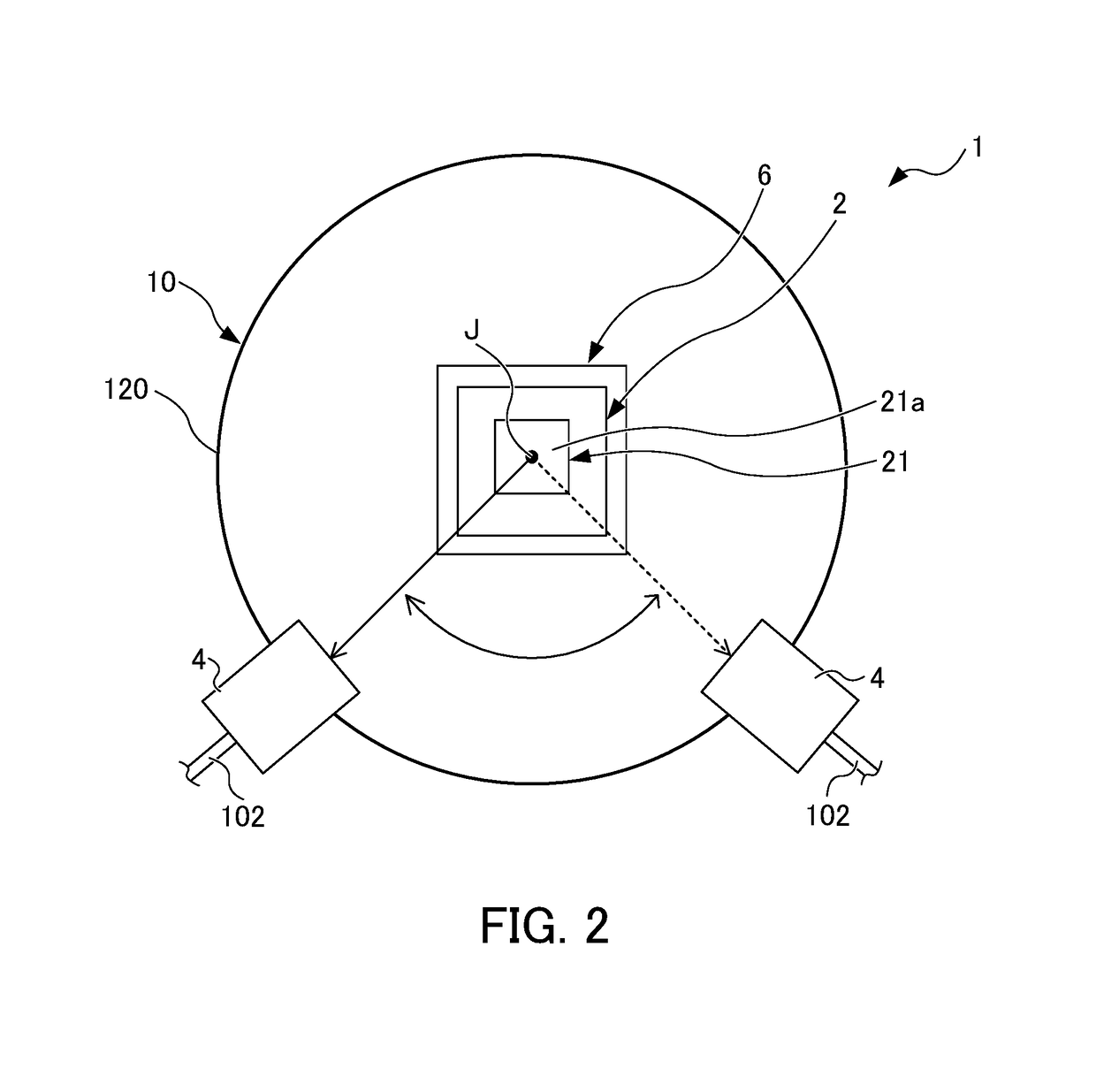
The beam distributor includes a housing, at least one beam entrance, two or more beam exits, a motor, and a beam turning part fixed to a rotary axis member of the motor and changing a direction of a beam input to the inside of the housing through the beam entrance so as to guide the input beam to the beam exit. A rotary axis of the motor is arranged parallel to an optical axis of the beam so as to input the beam to the beam turning part at a constant angle independently of a rotational angle about the rotary axis of the motor. The beam exit is arranged in a direction to which the direction of the beam is changed by the beam turning part in response to rotation of the rotary axis member. A storage stores an angular information recorded in advance about the rotary axis.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Antireflection article and display device
ActiveUS9335445B2Solve the lack of resistanceSuppressed reflectivityOptical elementsDisplay deviceTransmittance
The present invention relates to an antireflection article of which the first surface has sufficient abrasion resistance and can suppress reflectance to a low level throughout the visible light region, and a display device. The present invention relates to an antireflection article that has light transmittance, in which a plurality of convex portions are disposed on a first surface positioned at a visible side and a second surface opposite to the first surface, the average gap of the convex portions is 400 nm or less, the ratio (H1 / W1) of the height H1 of the convex portions and the width W1 of the bottoms of the convex portions is 1.3 or more, in the first surface, and the ratio (H2 / W2) of the height H2 of the convex portions and the width W2 of the bottoms of the convex portions is larger than the ratio (H1 / W1), in the second surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Optical laminate
ActiveCN110720059ASuppressed reflectivityFull brightnessLayered productsOptical filtersPhysical chemistryPolarizer
Provided is an optical laminate which is capable of exhibiting sufficient luminance and good hue, while suppressing the reflectance in cases where the optical laminate is used in an image display device, and which enables reduction in the cost. An optical laminate according to the present invention comprises a wavelength conversion layer and an absorption layer; this optical laminate does not havea polarizing plate on a surface of the wavelength conversion layer, said surface being on the reverse side of the absorption layer-side surface; the wavelength conversion layer emits light by converting some of the wavelengths of incident light; the absorption layer contains a compound that has an absorption peak within the wavelength range of from 480 nm to 780 nm; the relationship of the average reflectance R1 of the wavelength conversion layer for the wavelength range of from 380 nm to 480 nm and the average reflectance R2 of the wavelength conversion layer for the wavelength range of from490 nm to 600 nm satisfies R2 > R1; and if P1 is the maximum peak value of the reflectance of the absorption layer side of the optical laminate in the wavelength range of from 380 nm to 480 nm and P2is the maximum peak value of the reflectance of the absorption layer side of the optical laminate in the wavelength range of from 490 nm to 600 nm, P2 / P1 is from 0.7 to 1.5.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Beam distributor
ActiveUS10067294B2Reduce reflectivitySignificant energy lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical axisClassical mechanics
The beam distributor includes a housing, at least one beam entrance, two or more beam exits, a motor, and a beam turning part fixed to a rotary axis member of the motor and changing a direction of a beam input to the inside of the housing through the beam entrance so as to guide the input beam to the beam exit. A rotary axis of the motor is arranged parallel to an optical axis of the beam so as to input the beam to the beam turning part at a constant angle independently of a rotational angle about the rotary axis of the motor. The beam exit is arranged in a direction to which the direction of the beam is changed by the beam turning part in response to rotation of the rotary axis member. A storage stores an angular information recorded in advance about the rotary axis.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090227046A1Highly accurate patternImprove detection accuracyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistSemiconductor
An insulating film is formed on a main surface of a substrate. A conductive film is formed on the insulating film. A lower layer resist film, an intermediate layer, an anti-reflection film and an upper layer resist film are formed on the conductive film. A focal point at a time of exposure is detected by detecting a height of the upper layer resist film. In detecting the focal point at the time of exposure, a focal point detection light is radiated on the upper layer resist film. After detecting the focal point, the upper layer resist film is exposed and developed thereby to form a resist pattern. With the resist pattern as a mask, the intermediate layer and the anti-reflection film are patterned, and the lower layer resist film is developed. With these patterns as a mask, the conductive film is etched thereby to form a gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Display device
PendingUS20220181591A1Suppressed reflectivityWithout usingElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device includes a light-emitting element layer including a plurality of light-emitting elements in each of which a first electrode, a function layer including a light-emitting layer, and a second electrode are disposed in this order from a thin film transistor layer side, and the first electrode includes a first transparent electrode, a reflective metal layer, and a semi-transparent metal layer in this order from the side opposite to the light-emitting layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Thin film for reflection film or for semi-transparent reflection film, sputtering target and optical recording medium
ActiveUS7910190B2Excellent in reflectance-keeping characteristicImprove corrosion resistanceMirrorsLayered productsBorideDisplay device
A thin film for a reflection film or a semi-transparent reflection film, which has a compound phase comprising at least one selected from the group consisting of a nitride, an oxide, a complex oxide, a nitroxide, a carbide, a sulfide, a chloride, a silicide, a fluoride, a boride, a hydride, a phosphide, a selenide and a telluride of gallium, palladium or copper, dispersed in a matrix formed of silver or a silver alloy. The compound phase in the thin film may include at least one compound selected from the group consisting of nitride, oxide, complex oxide, nitroxide, carbide, sulfide, chloride, silicide, fluoride, boride, hydride, phosphide, selenide and telluride of silver. The thin film of the present invention minimizes the deterioration of the reflectance even after a long period of use, and can prolong the life of various devices which use the thin film as a reflection film, such as an optical recording medium and a display. The thin film can be also applied to a semi-reflective / semi-transparent film used in the optical recording medium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
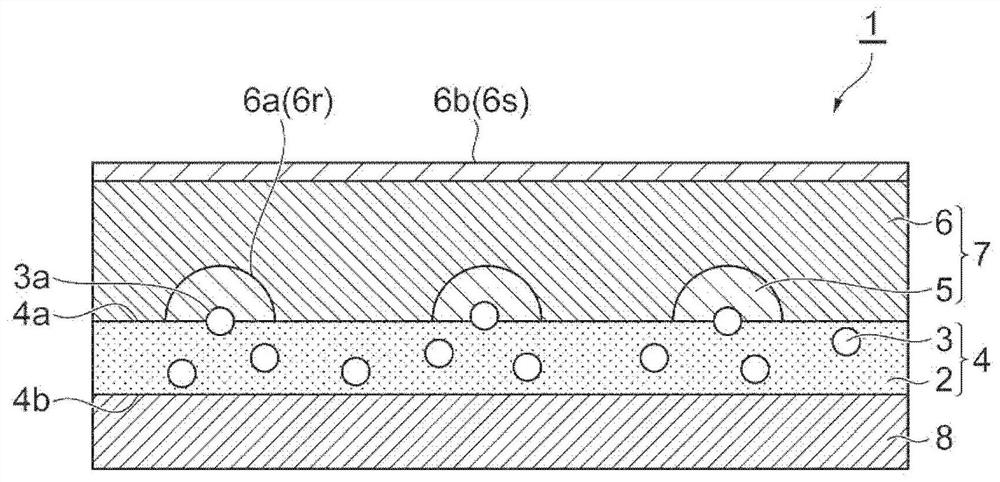
Sheet, metal mesh, wiring board, display device, and manufacturing method thereof
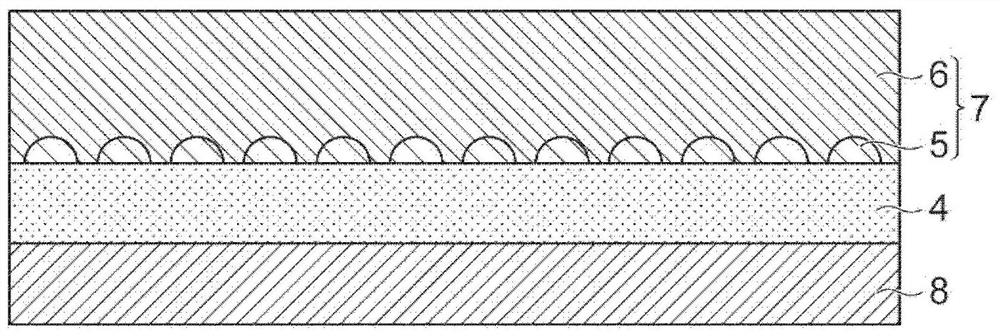
ActiveCN109306479BImprove tight adhesionSuppressed reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsPtru catalystElectrolysis
The sheet (1) related to the present invention has: a resin layer (4), which includes a binder (2) and catalyst particles (3); an electroless plating film (7), which is provided on the resin layer (4) One main surface (4a) side and has the 1st electroless plating film (5) and the 2nd electroless plating film (6); And base material (8), it is arranged on the other main surface (4b) of resin layer (4) )side. At least a part of the catalyst particle (3) has an exposed surface (3a) exposed from one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4), and the exposed surface (3a) is dispersed on the one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4) . The first electroless plating film (5) is provided on one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4) so as to surround the respective exposed surfaces (3a) of the catalyst particles (3). The 2nd electroless plating film (6) is provided with the mode of covering the 1st electroless plating film (5), and one main surface (6a) of the 2nd electroless plating film (6) has the corresponding to the 1st electroless plating film (5) Recess (6r).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
A Non-contact Dynamic Measurement System of Rotary Shaft Torque Based on High Precision Key Phase
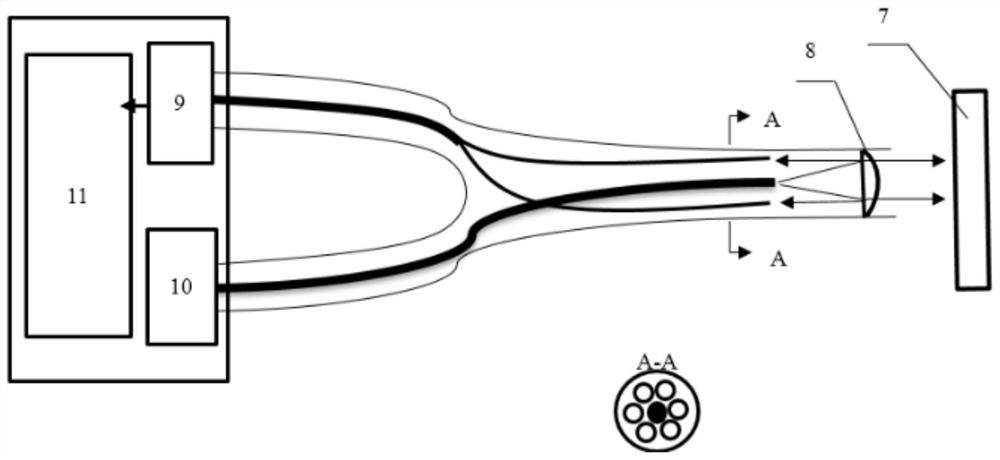
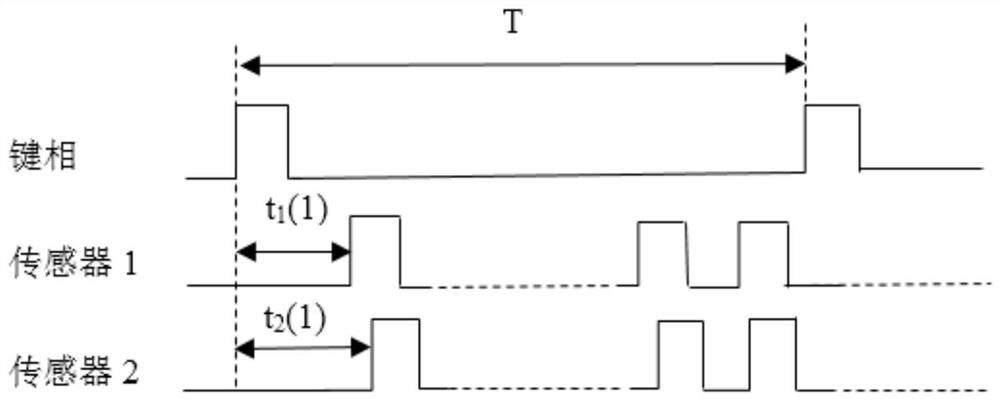
ActiveCN106525302BEnables direct measurementEliminate cumulative errorsWork measurementTorque measurementRotational axisSignal processing circuits
Owner:善测(天津)科技有限公司
Thin film for reflection film or for semi-transparent reflection film, sputtering target and optical recording medium
ActiveUS20100040898A1Increase contentExcellent in reflectance-keeping characteristicCellsMirrorsBorideDisplay device
A thin film for a reflection film or a semi-transparent reflection film, which has a compound phase comprising at least one selected from the group consisting of a nitride, an oxide, a complex oxide, a nitroxide, a carbide, a sulfide, a chloride, a silicide, a fluoride, a boride, a hydride, a phosphide, a selenide and a telluride of gallium, palladium or copper, dispersed in a matrix formed of silver or a silver alloy. The compound phase in the thin film may include at least one compound selected from the group consisting of nitride, oxide, complex oxide, nitroxide, carbide, sulfide, chloride, silicide, fluoride, boride, hydride, phosphide, selenide and telluride of silver. The thin film of the present invention minimizes the deterioration of the reflectance even after a long period of use, and can prolong the life of various devices which use the thin film as a reflection film, such as an optical recording medium and a display. The thin film can be also applied to a semi-reflective / semi-transparent film used in the optical recording medium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
Sheet material, metal mesh, wiring substrate, display device and manufacturing methods therefor
ActiveCN109306479AImprove tight adhesionSuppressed reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsMetal meshElectroless plating
The invention relates to a sheet material (1) provided with: a resin layer (4) including a binder (2) and a catalyst particle (3); a non-electrolytic plated film (7) provided on one main surface (4a)side of the resin layer (4) and having a first electroless plating film (5) and a second electroless plating film (6); and a base material (8) disposed on the other main surface (4b) side of the resinlayer (4). At least a part of the catalyst particles (3) has an exposed surface (3a) exposed from one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4), and the exposed surface (3a) is dispersed on one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4). The first electroless plating film (5) is provided on one main surface (4a) of the resin layer (4) so as to surround the exposed surface (3a) of each of the catalyst particles (3). The second electroless plating film (6) is provided so as to cover the first electroless plating film (5), and one main surface (6a) of the second electroless plating film (6) is provided corresponding to the concave (6r) of the first electroless plating film (5).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com