Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Reduce oxygen activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
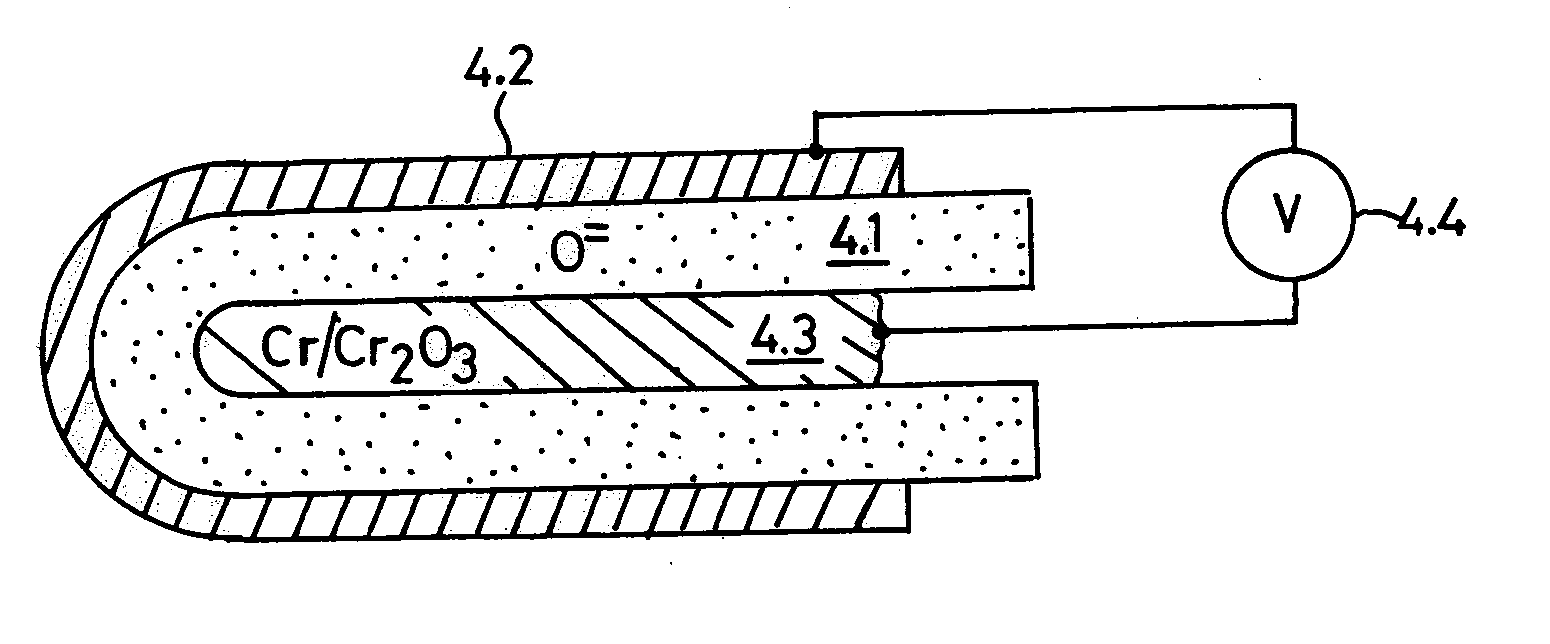
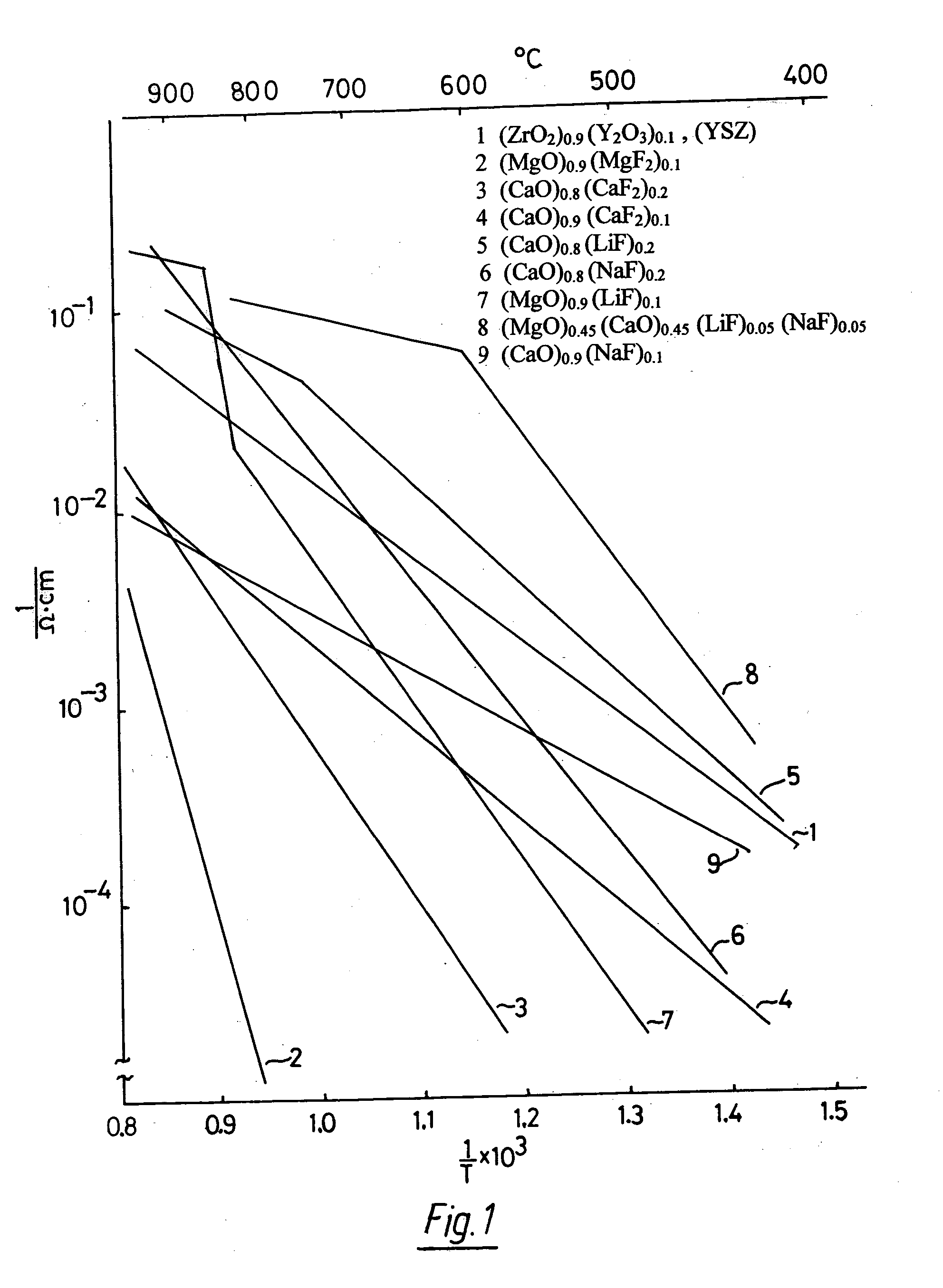
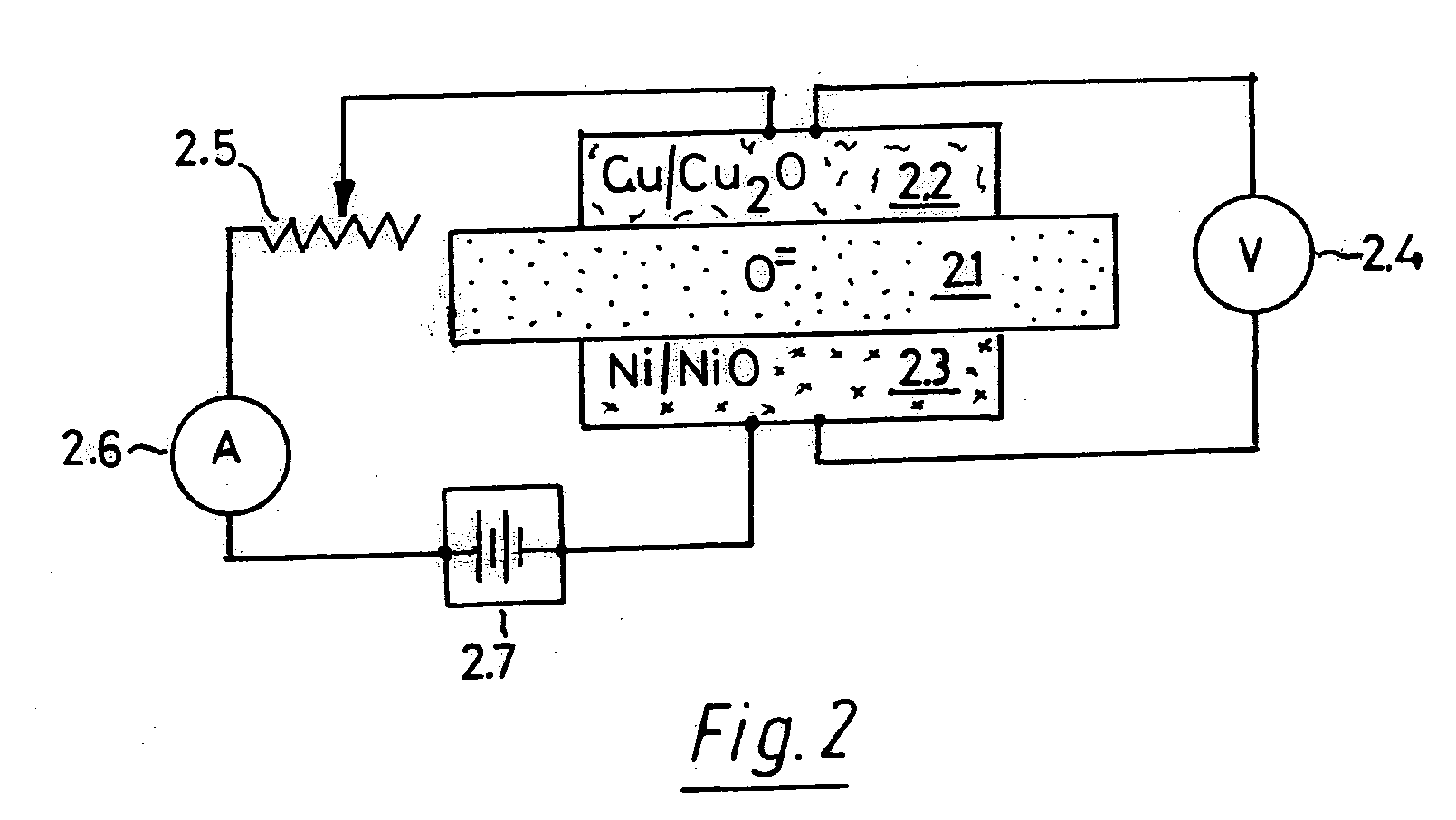
Oxygen ion conductors for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS20070054170A1Stable oxygen concentrationImprove electrode stabilityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrical conductorAlkaline earth metal
In solid oxygen ion conducting electrolytes for electrochemical cells based on magnesium oxide and calcium oxide, obtained by the addition of metal fluorides selected from elements in the groups of alkali metals and earth alkali metals to the host oxides of magnesium and calcium, conductivity values are obtained, which are comparable with those of stabilized zirconia, but the magnesium oxide and calcium oxide based oxygen ion conducting electrolytes have a superior thermodynamic stability and, therefore, can operate at much lower oxygen concentrations in comparison with other oxygen ion conducting electrolytes and without becoming noticeably electronically conductive.
Owner:ISENBERG ARNOLD O
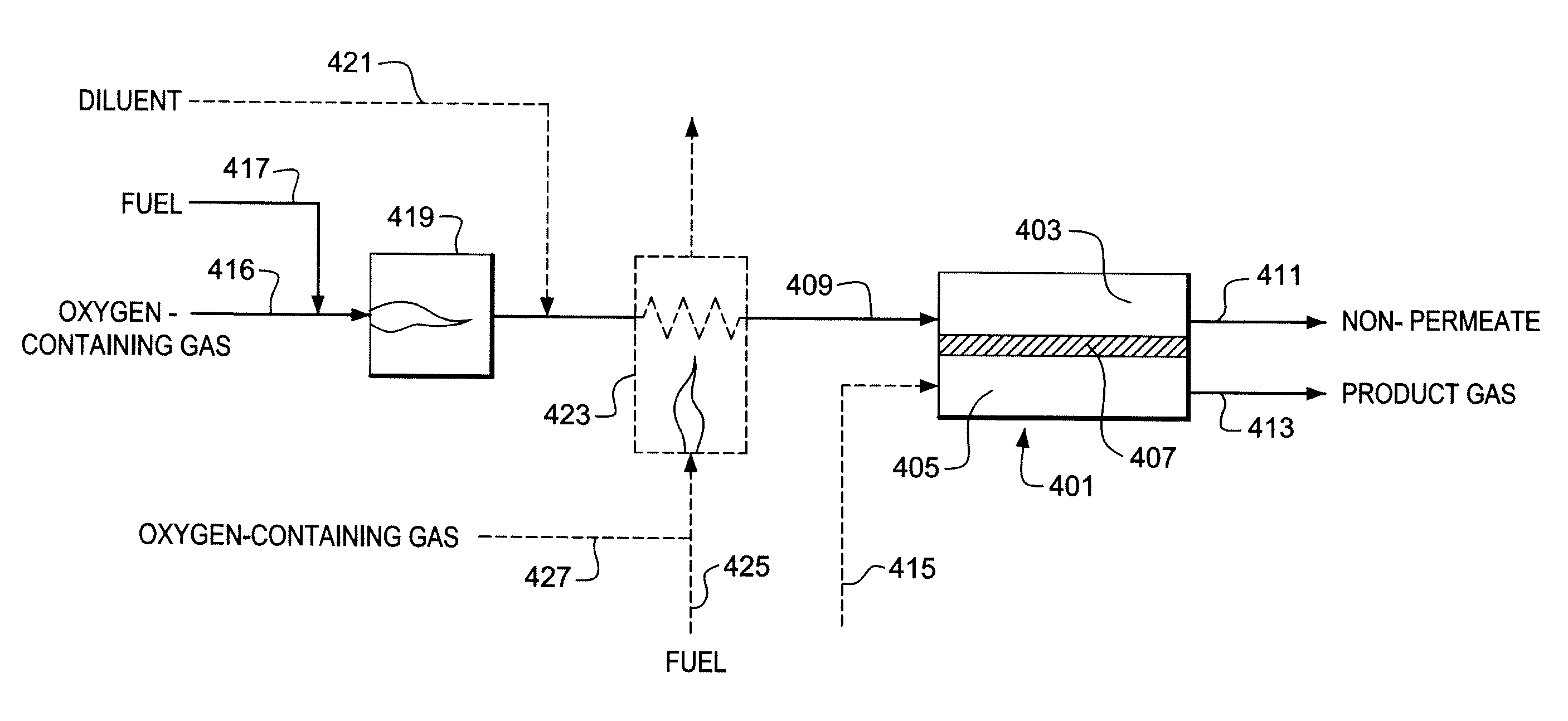
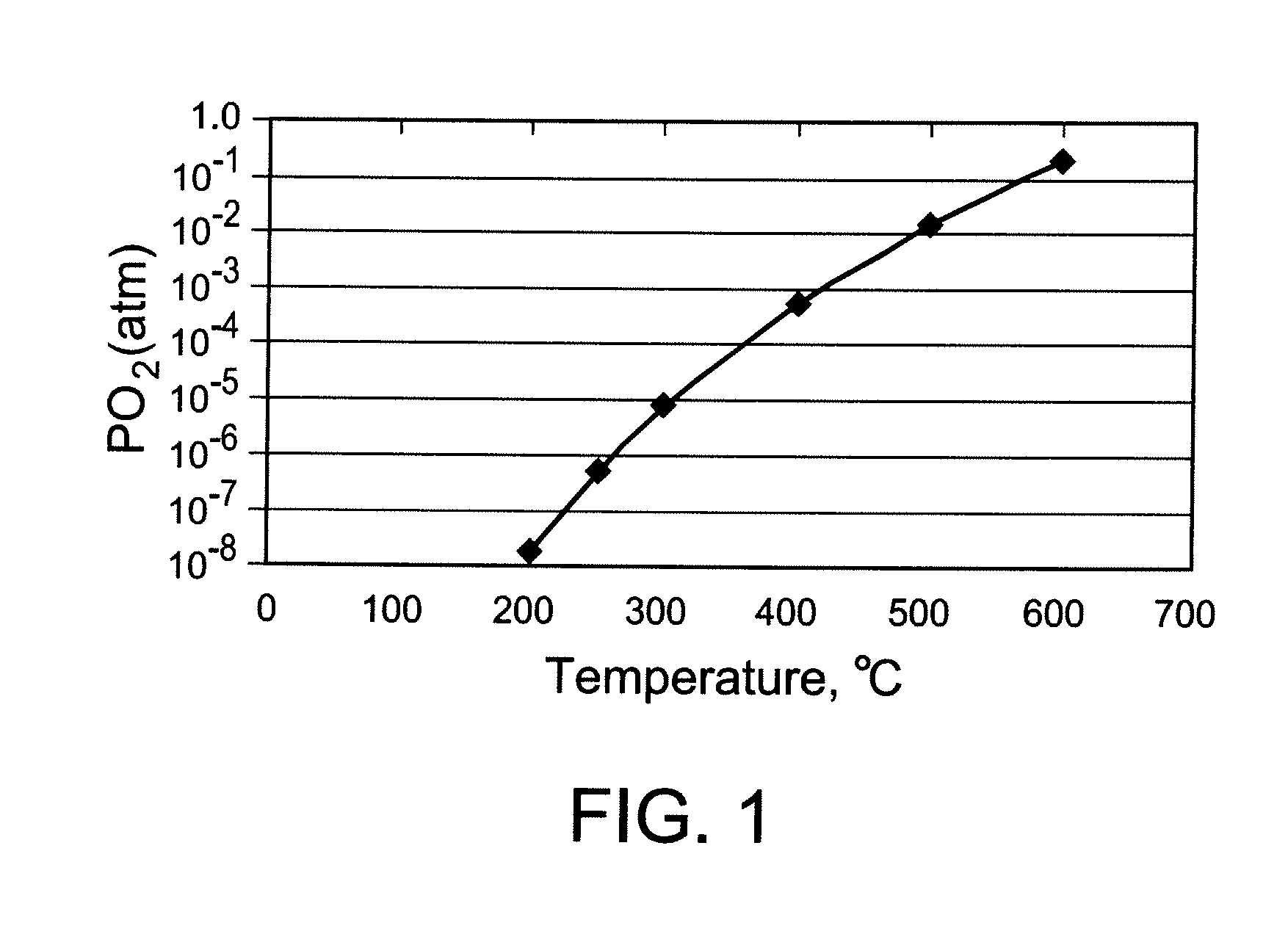
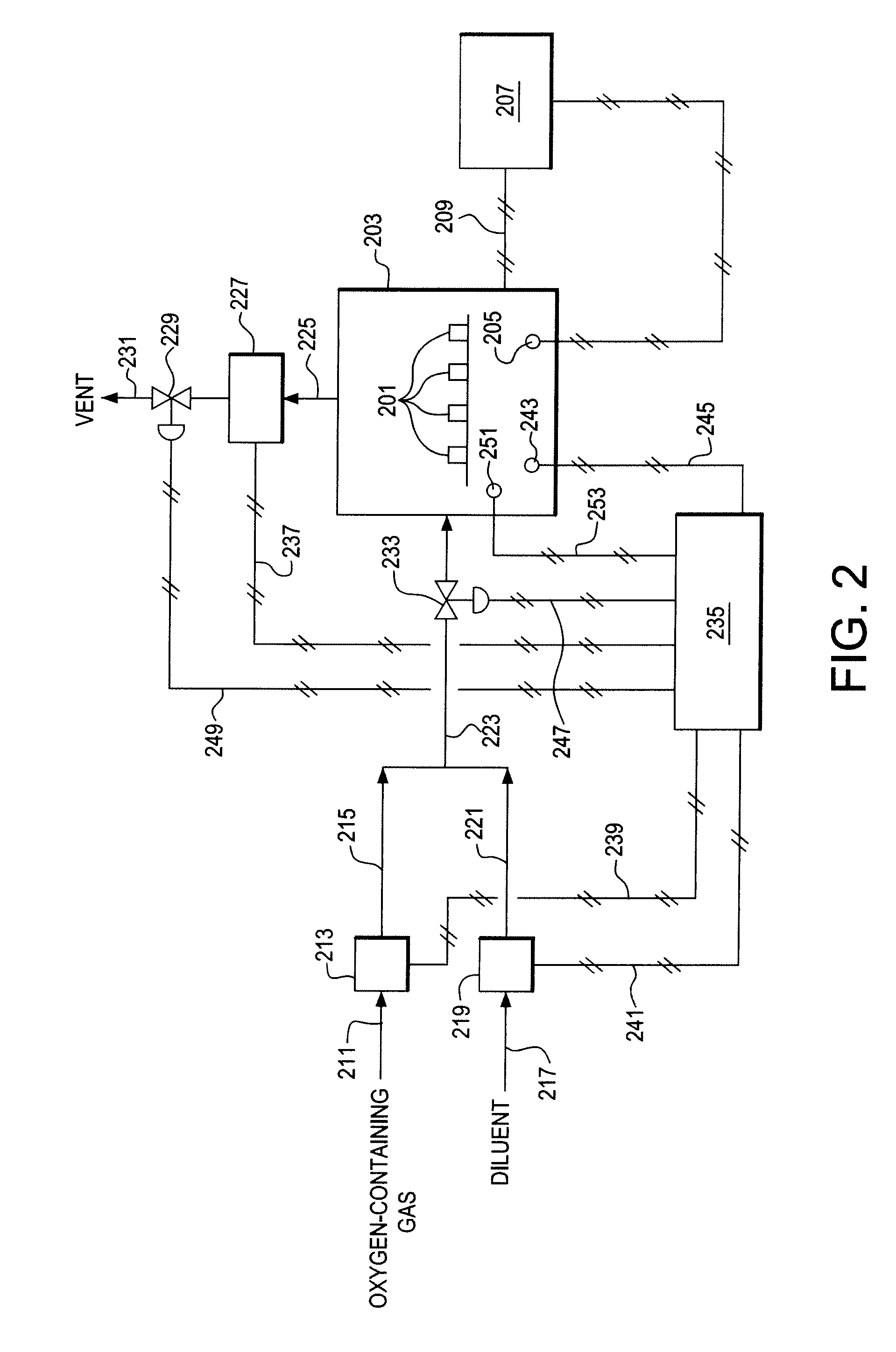
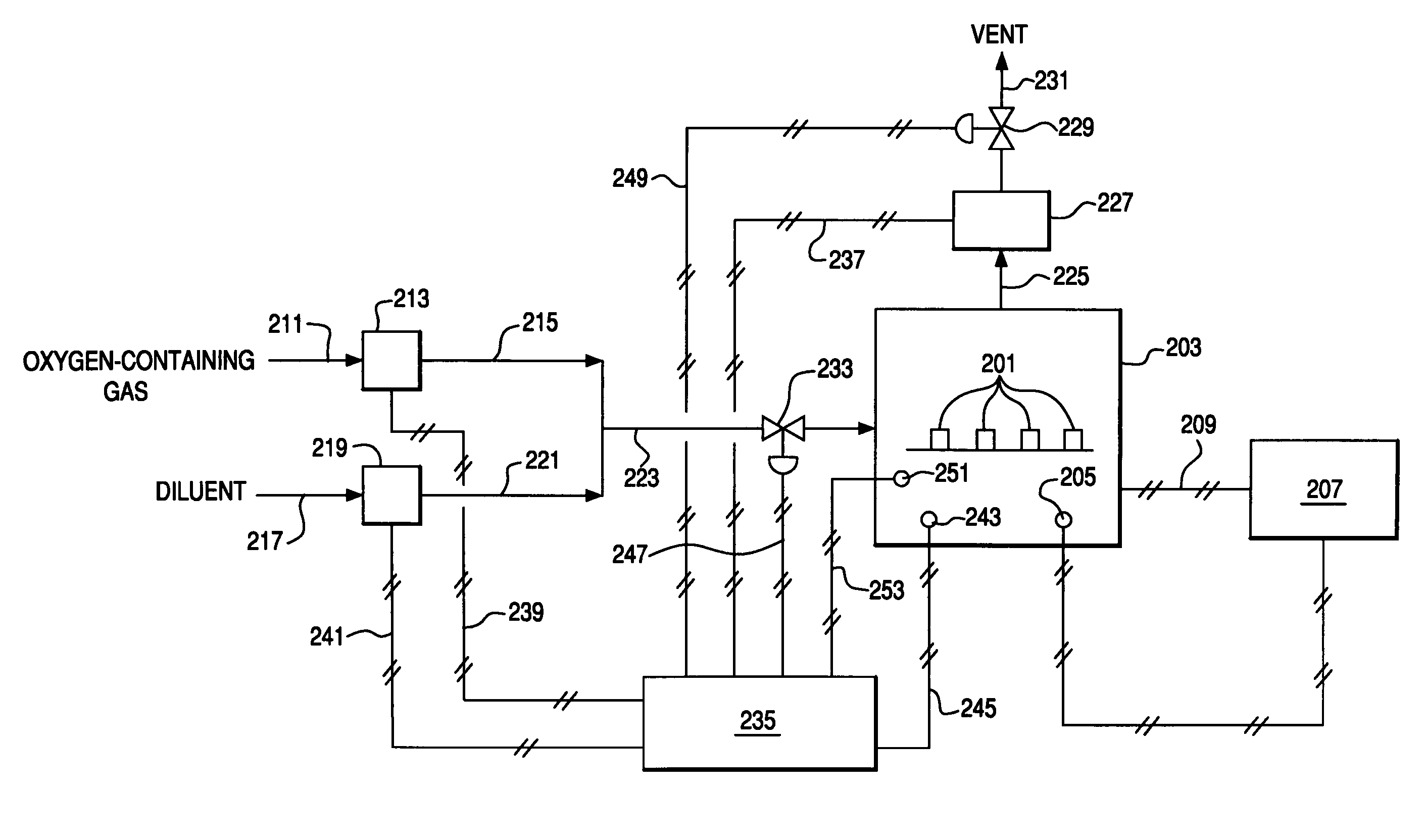
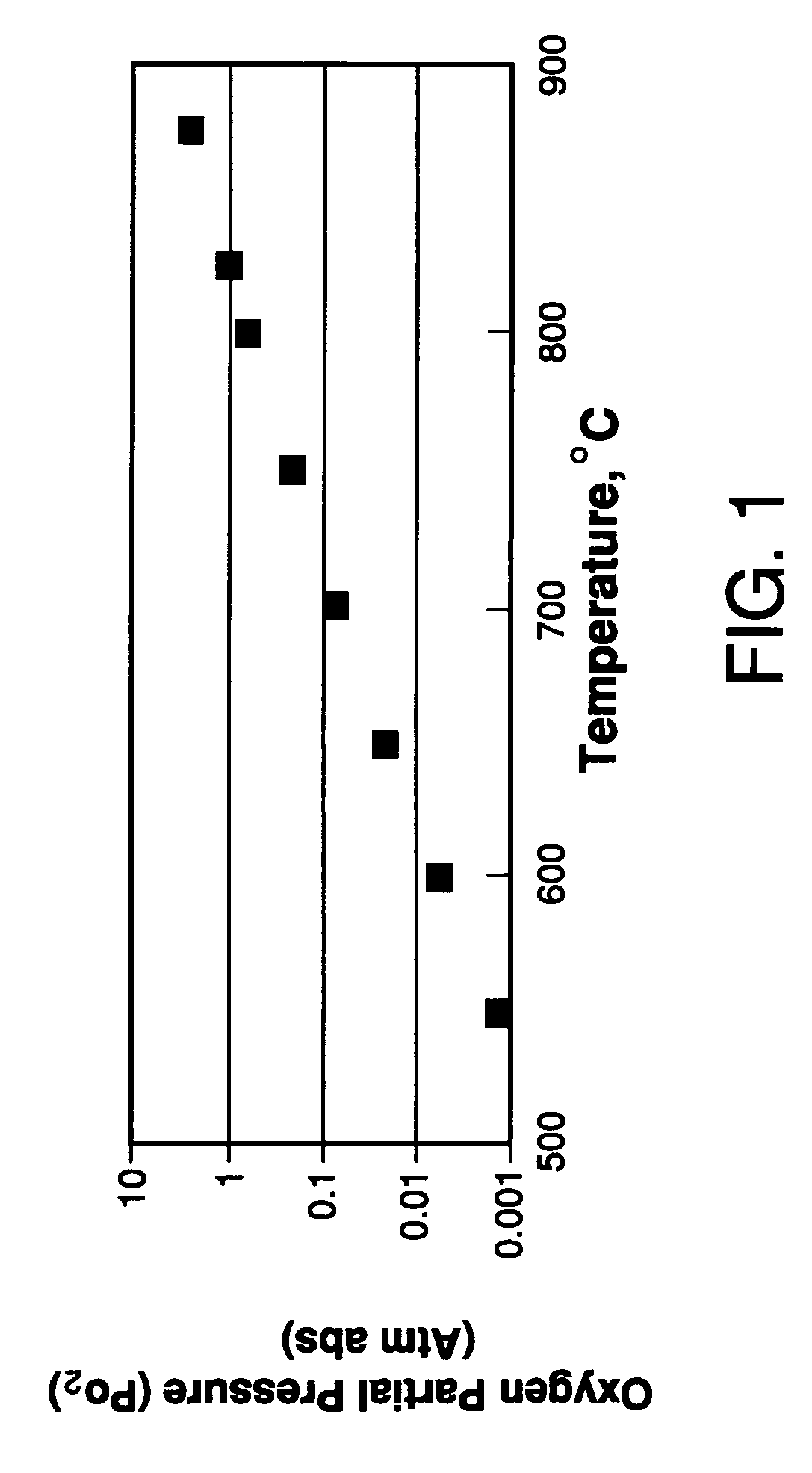
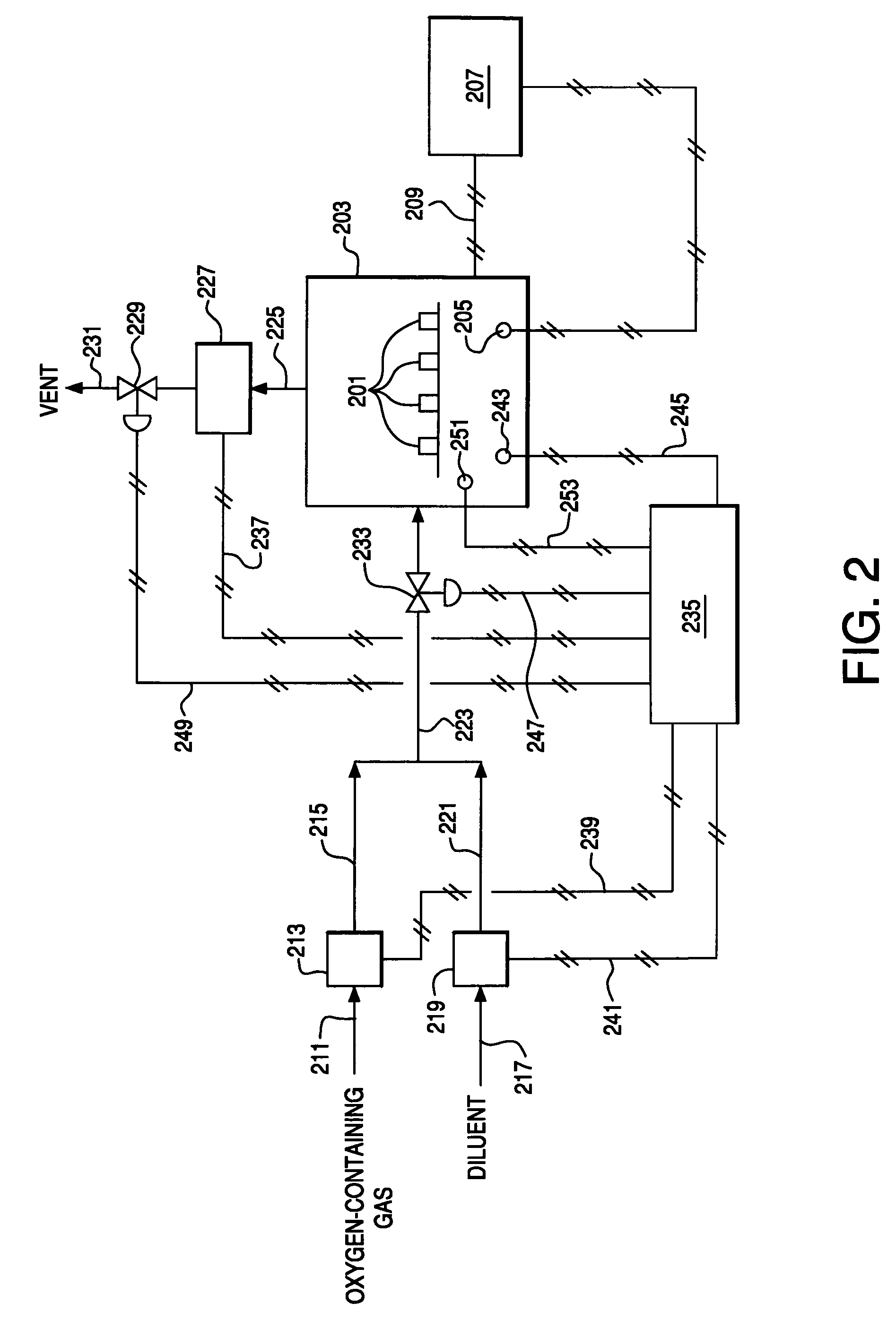
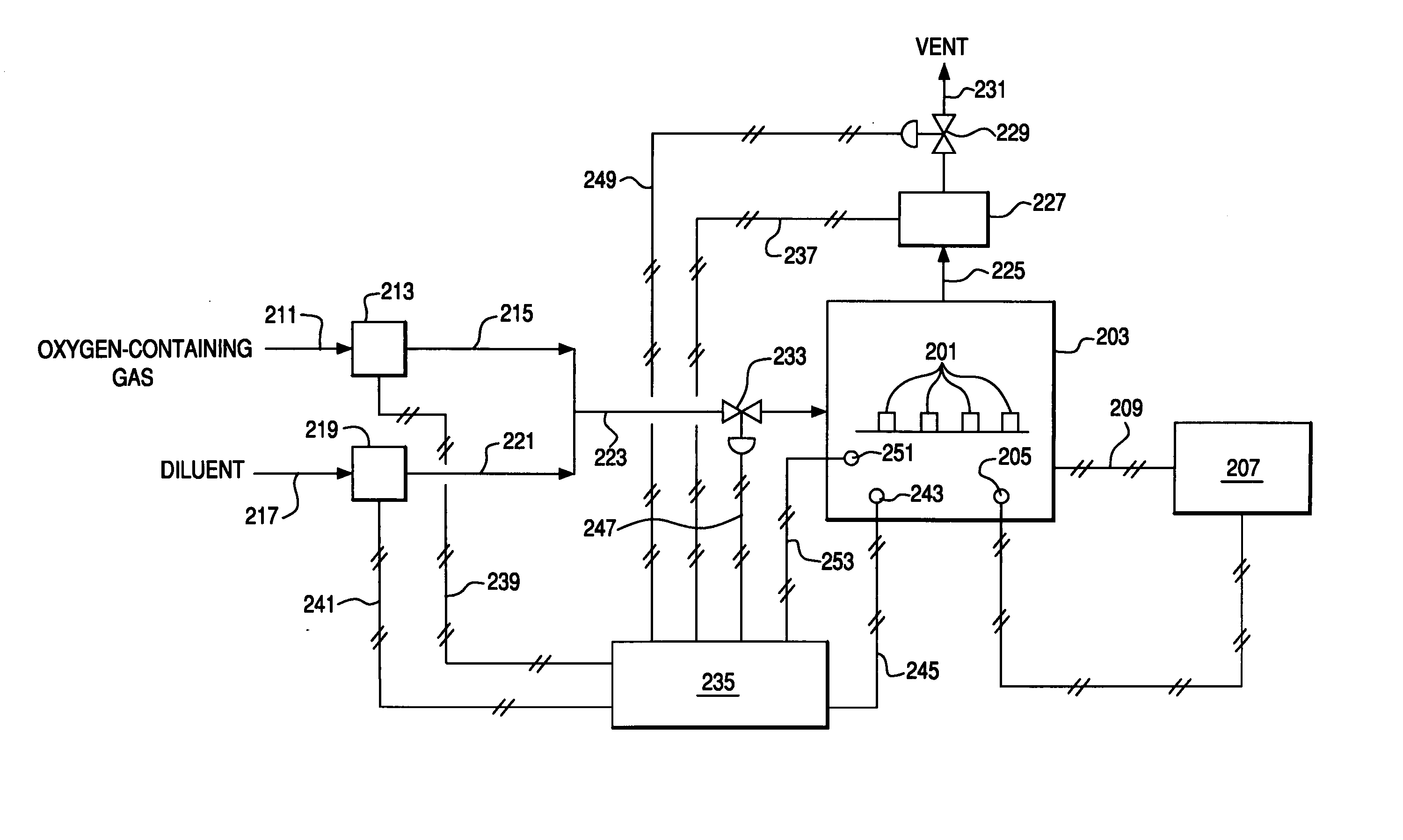
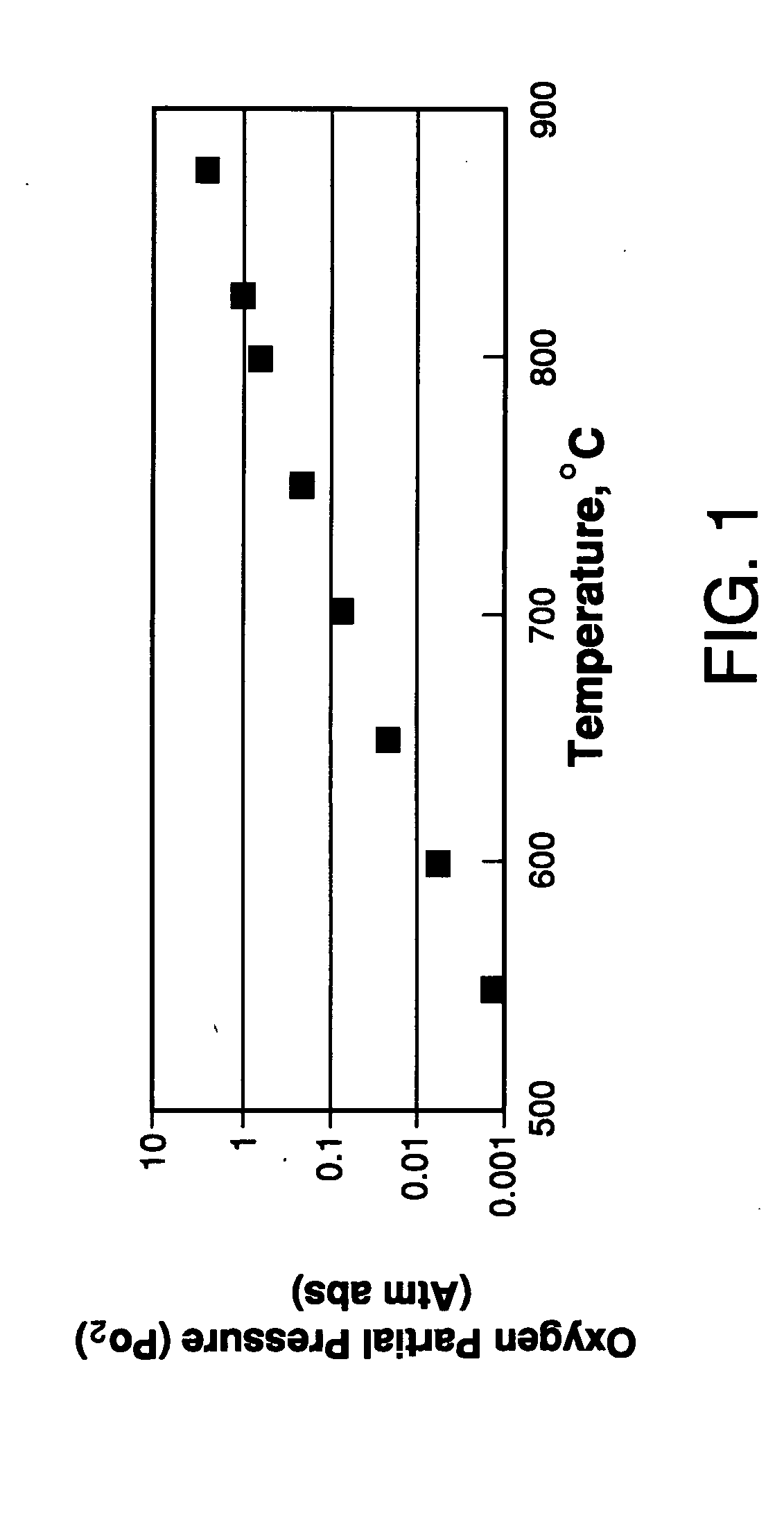
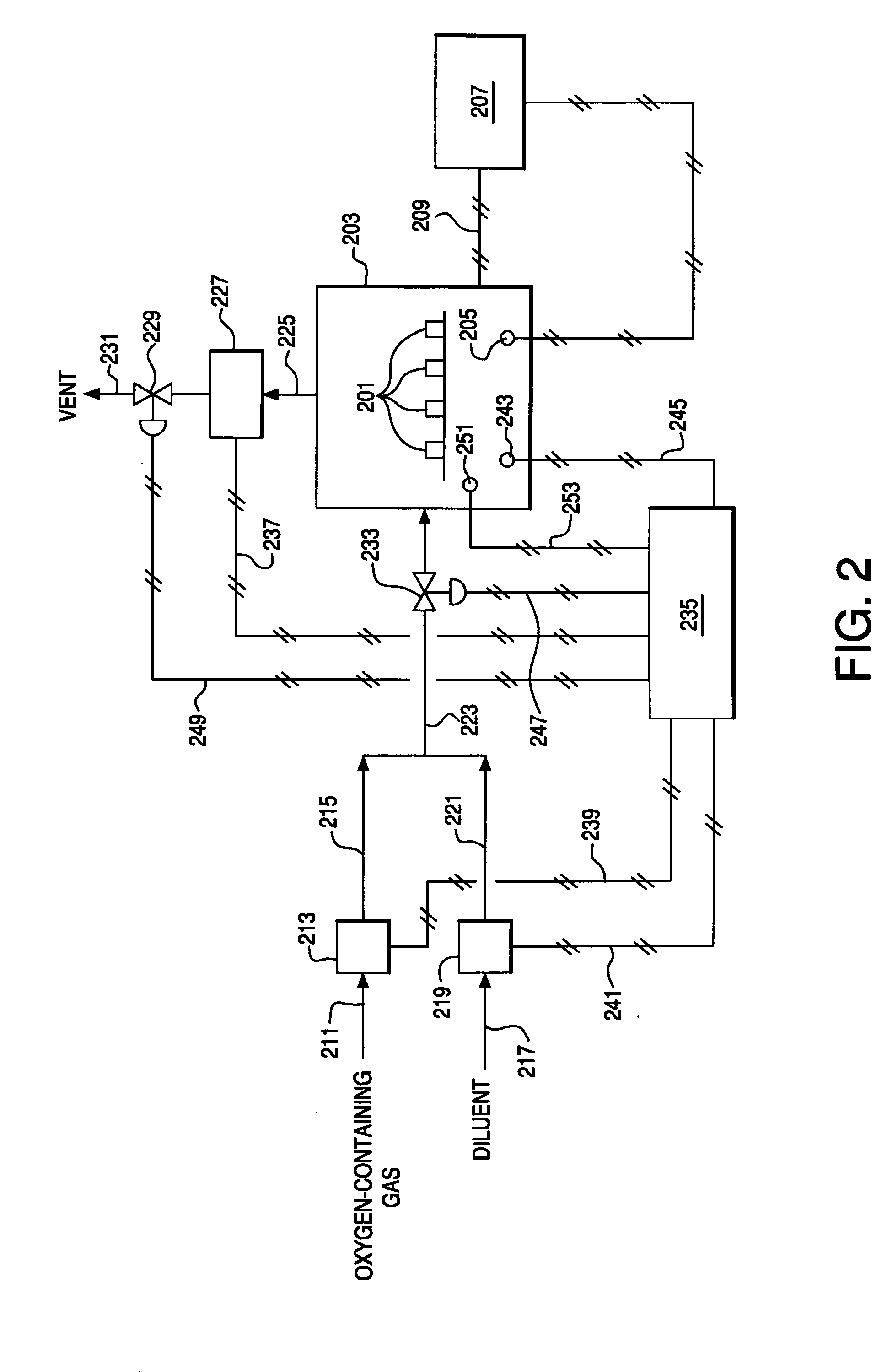
Use of Impure Inert Gases in the Controlled Heating and Cooling of Mixed Conducting Metal Oxide Materials
InactiveUS20110076213A1Accelerate the rate of decreaseIncreasing oxygen activityOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid degasificationOxygenMetal
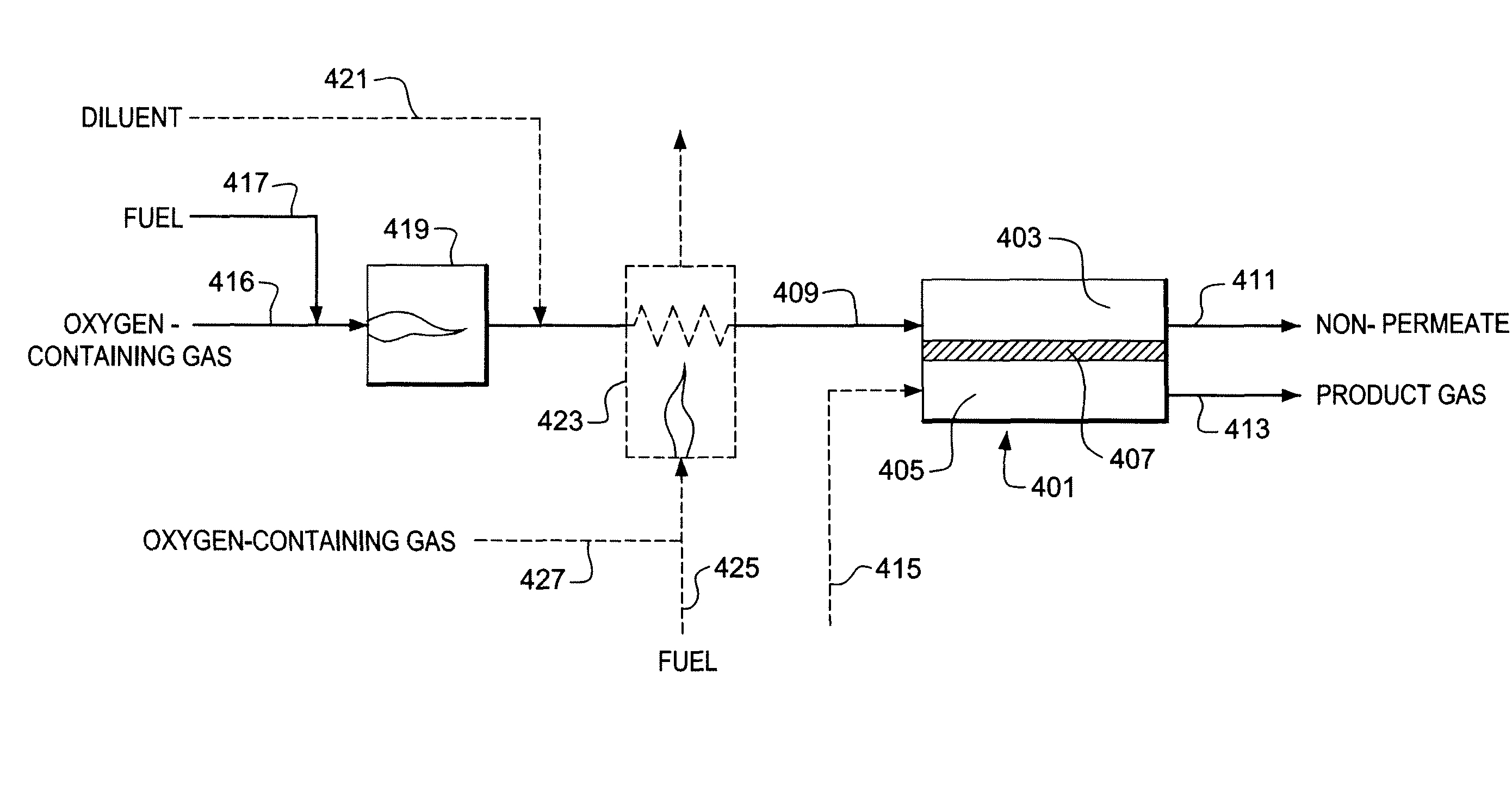
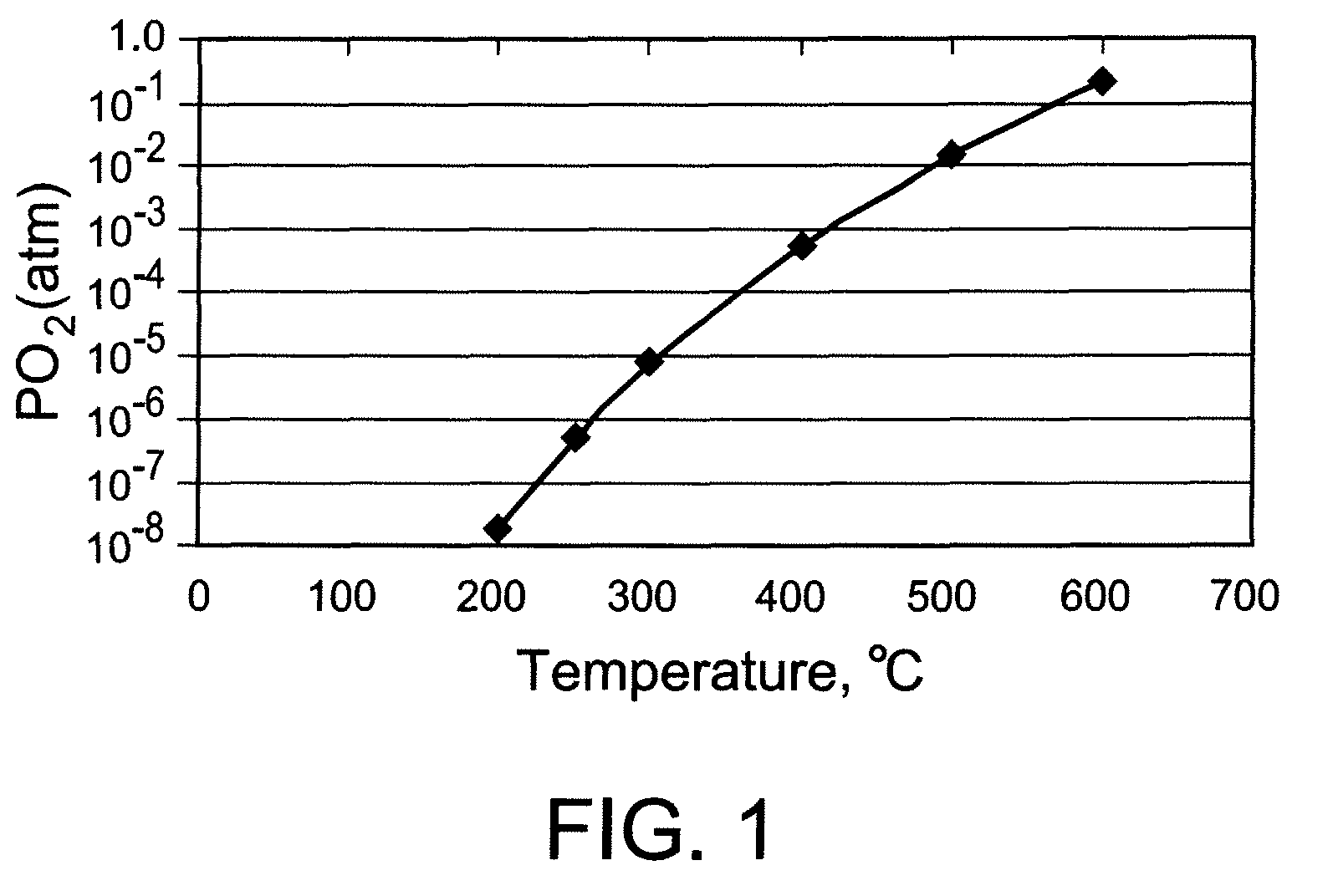
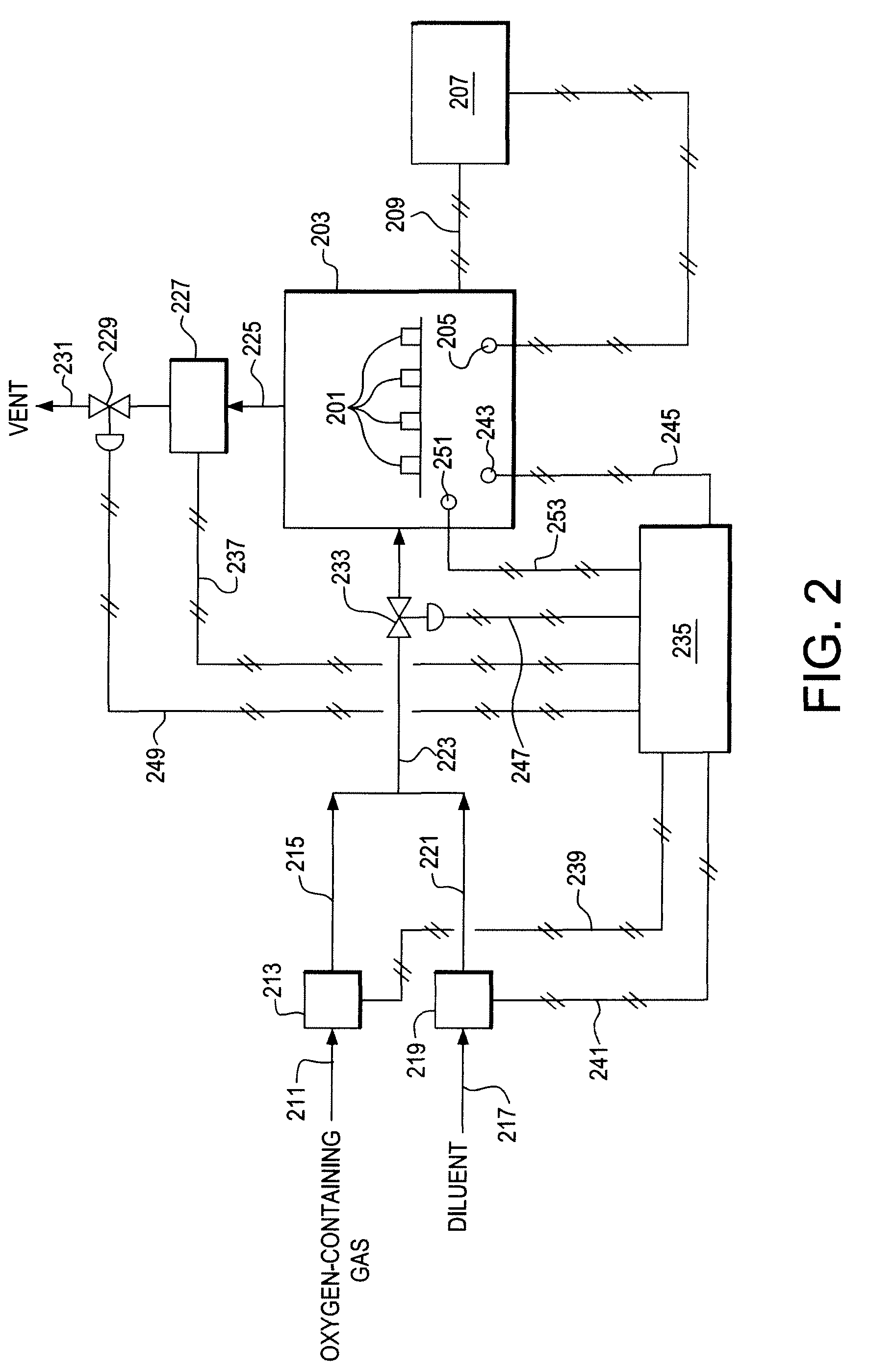
Method for processing an article comprising mixed conducting metal oxide material. The method comprises contacting the article with an oxygen-containing gas and either reducing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas during a cooling period or increasing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas during a heating period; during the cooling period, reducing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas during at least a portion of the cooling period and increasing the rate at which the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is reduced during at least a portion of the cooling period; and during the heating period, increasing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas during at least a portion of the heating period and decreasing the rate at which the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is increased during at least a portion of the heating period.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
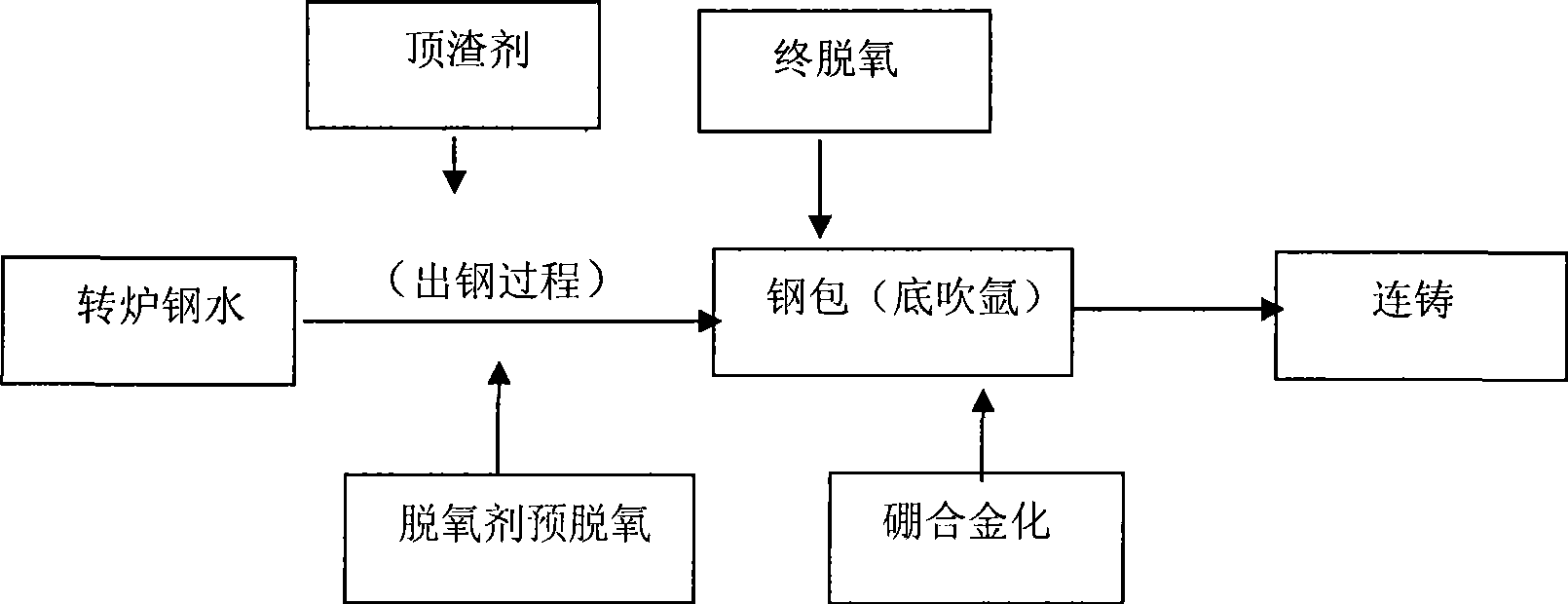
Method for producing boron steel by converter
InactiveCN101503746AAvoid stickinessAvoid water-prone mouthsManufacturing convertersAlloyMolten steel
The invention provides a method for producing boron steel in a converter, which is characterized in that argon subaeration is performed on a ladle in the whole process; a deoxidizer and alloys required by steel grades are begun to be added into the ladle for preliminary deoxidation and alloying under the condition of 1 / 4 tapping, and simultaneously a desulfurizer is added for desulfurization treatment; aluminum is added into the ladle in an argon blowing station for final deoxidation, and ferroboron is added into the ladle when the [O] is controlled to be between 0.0020 and 0.0040 percent; and the ferroboron is coated by an aluminum sheet and added into molten steel. The method has the advantages that: firstly, the method saves the refining procedure of an LF furnace and a vacuum furnace and has low production cost, short production procedure and high production efficiency; secondly, the pourability of the molten steel is good; thirdly, no requirement is put forward as for acid-soluble aluminum in the steel, so that the method solves the problems of pastiness of the molten steel, easy bonding of water gaps, reduction of the steel quality and the like caused by the increase of Al2O3 inclusion due to high acid-soluble aluminum; and fourthly, the recovery rate of boron can reach 60 to 75 percent and the wave range of the yield is small. Moreover, the method has good application prospect.
Owner:新余钢铁股份有限公司
Controlled heating and cooling of mixed conducting metal oxide materials
InactiveUS7122072B2Reducing and increasing temperatureReduce oxygen activityCellsSemi-permeable membranesOxygenMetal
Method for processing an article comprising a mixed conducting metal oxide material, which method comprises (a) contacting the article with an oxygen-containing gas and reducing or increasing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas; (b) when the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is reduced, reducing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas; and (c) when the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is increased, increasing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Control method for plasticization of tire cord steel inclusion
The invention discloses a control method for plasticization of a tire cord steel inclusion, and belongs to the technical field of steel and iron smelting. The method comprises the following process steps of: performing a catch carbon process at an end point of a converter, wherein the mass fraction of end point carbon is 0.1-0.4 percent; performing deoxidization alloying on Si-Fe and Mn-Fe alloy during tapping of the converter, wherein 1.0-3.0 kg of Si-Fe alloy is added per ton of steel, and 3.0-6.0 kg of Mn-Fe alloy is added per ton of steel; adding ferrosilicon powder into the top of slag during LF ladle furnace refining, wherein the 0.5-1.5 kg of ferrosilicon powder is added per ton of steel; feeding 0.1-0.5 kg of magnesium wire per ton of steel into a ladle; and blowing argon to the ladle in two stages. The method has the advantages that: the special magnesium or zirconium ladle is not required any longer during production of tire cord steel; meanwhile, the inclusion control levelwhich meets the production requirement is achieved; and thus, the production cost per ton of steel is reduced, and the economic benefit is increased.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Low-alkalinity synthetic slag for external refining of boiler tube steel
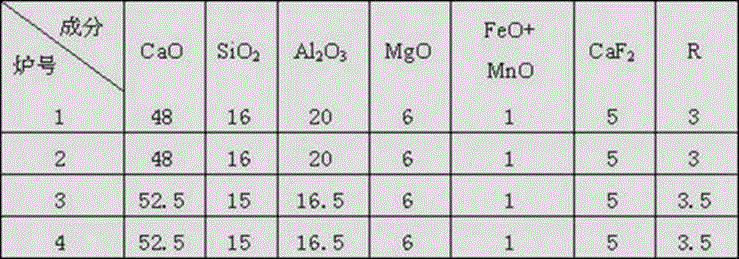
InactiveCN102912082AWater oxygen activity decreasedReduce oxygen activityProcess efficiency improvementChemical compositionSlag
The invention relates to a low-alkalinity synthetic slag for external refining of boiler tube steel, wherein CaO, Al2O3, MgO, SiO2 and CaF2 are used as basic components in the synthetic slag; the alkalinity range of the synthetic slag is controlled; and the synthetic slag comprises the following specific chemical compositions in percentage by weight: 48-55% of CaO, 18-25% of Al2O3, 6-8% of MgO, 14-18% of SiO2, 25% of CaF and smaller than 1% of MnO and FeO, wherein the alkalinity of the synthetic slag is 3-3.5. Compared with the traditional synthetic slag for external refining of boiler tube steel, the oxidbillity of refining slag is strictly controlled so that the content of MnO and FeO is smaller than 1%; the oxygen activity of liquid steel balanced with the synthetic slag is promoted to be decreased; and the total oxygen in the steel can be controlled between 12ppm and 15ppm. The alkalinity of the synthetic slag is kept between 3 and 3.5; and the refining slag keeps good melting, flowing, adsorption and desorption abilities of slag inclusion while having good deoxidating and desulphurizing abilities.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Improved blast furnace soft water closed circulation system and method
ActiveCN106498106AReduce the number of testsImprove leak detection efficiencyCooling devicesWater leakageWorking pressure
The invention discloses an improved blast furnace soft water closed circulation system and method. The system comprises a host controller, a cooling wall cooling unit, an expansion and degasification unit, a secondary circulation water unit and a primary circulation water supply unit. According to the improved blast furnace soft water closed circulation system and method, multiple water supply main pipes are adopted, the redundancy degree of the system is increased, and blast furnace production safety is guaranteed; a cooling wall is zoned, grading and leakage detecting are facilitated, the time needed for leakage detecting is reduced, and guarantees are provided for stable production and cost reduction; and secondary circulation water setting is reasonable, the work pressure of secondary circulation water cooling equipment is reduced, the risk of water leakage is reduced, and the gas contents in primary circulation water and secondary circulation water are reduced.
Owner:HUATIAN ENG & TECH CORP MCC
Controlled heating and cooling of mixed conducting metal oxide materials
InactiveUS20050106439A1Reduce oxygen activityReducing and increasing temperatureCellsMembranesOxideMetal
Method for processing an article comprising a mixed conducting metal oxide material, which method comprises (a) contacting the article with an oxygen-containing gas and reducing or increasing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas; (b) when the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is reduced, reducing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas; and (c) when the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is increased, increasing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
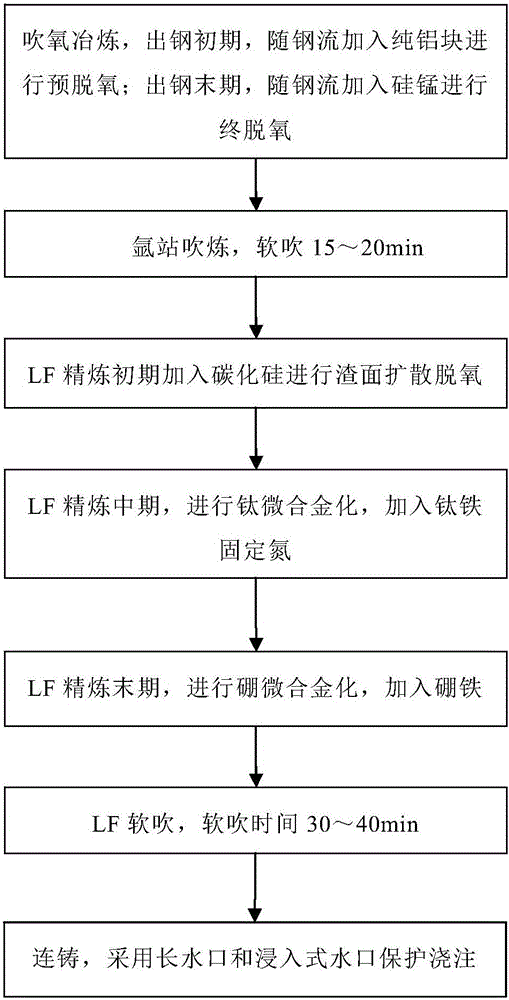
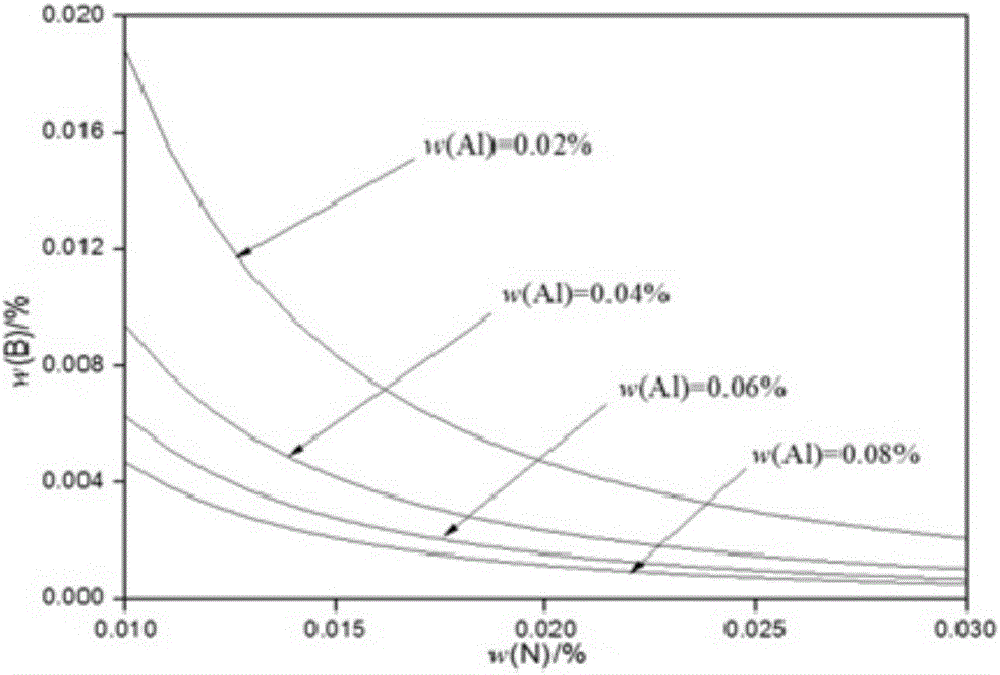
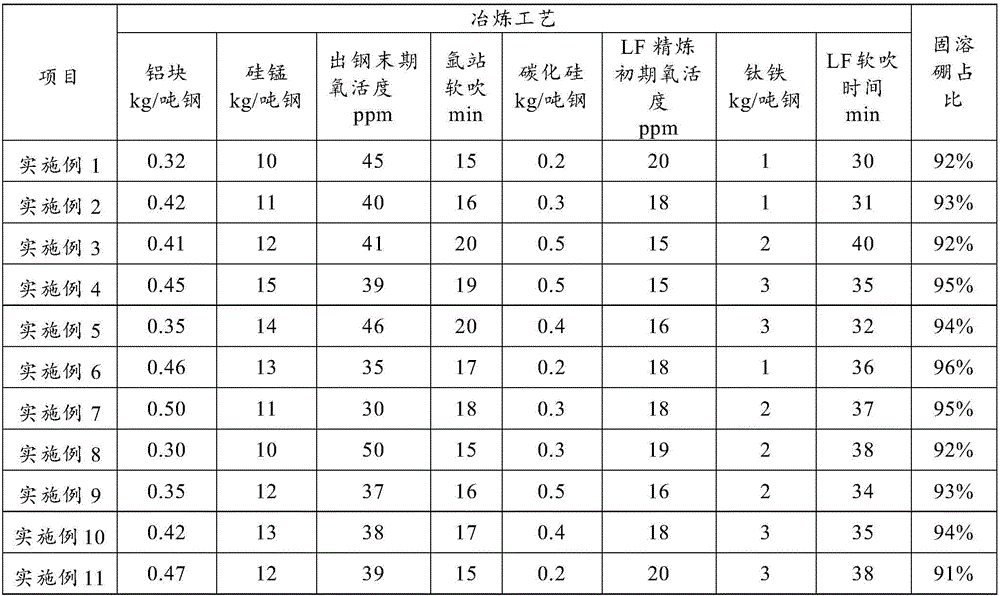
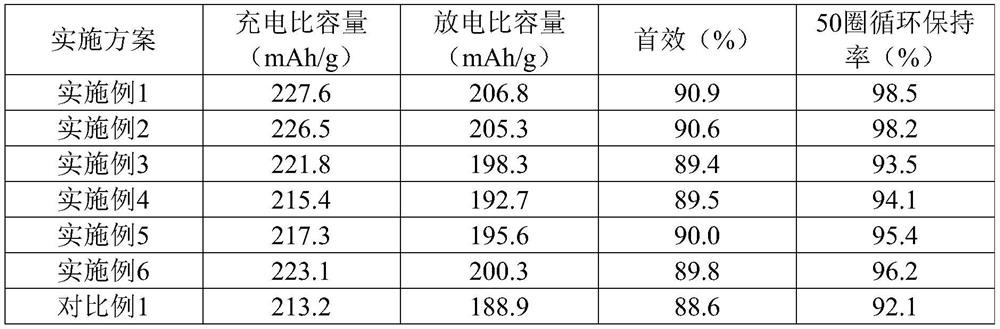
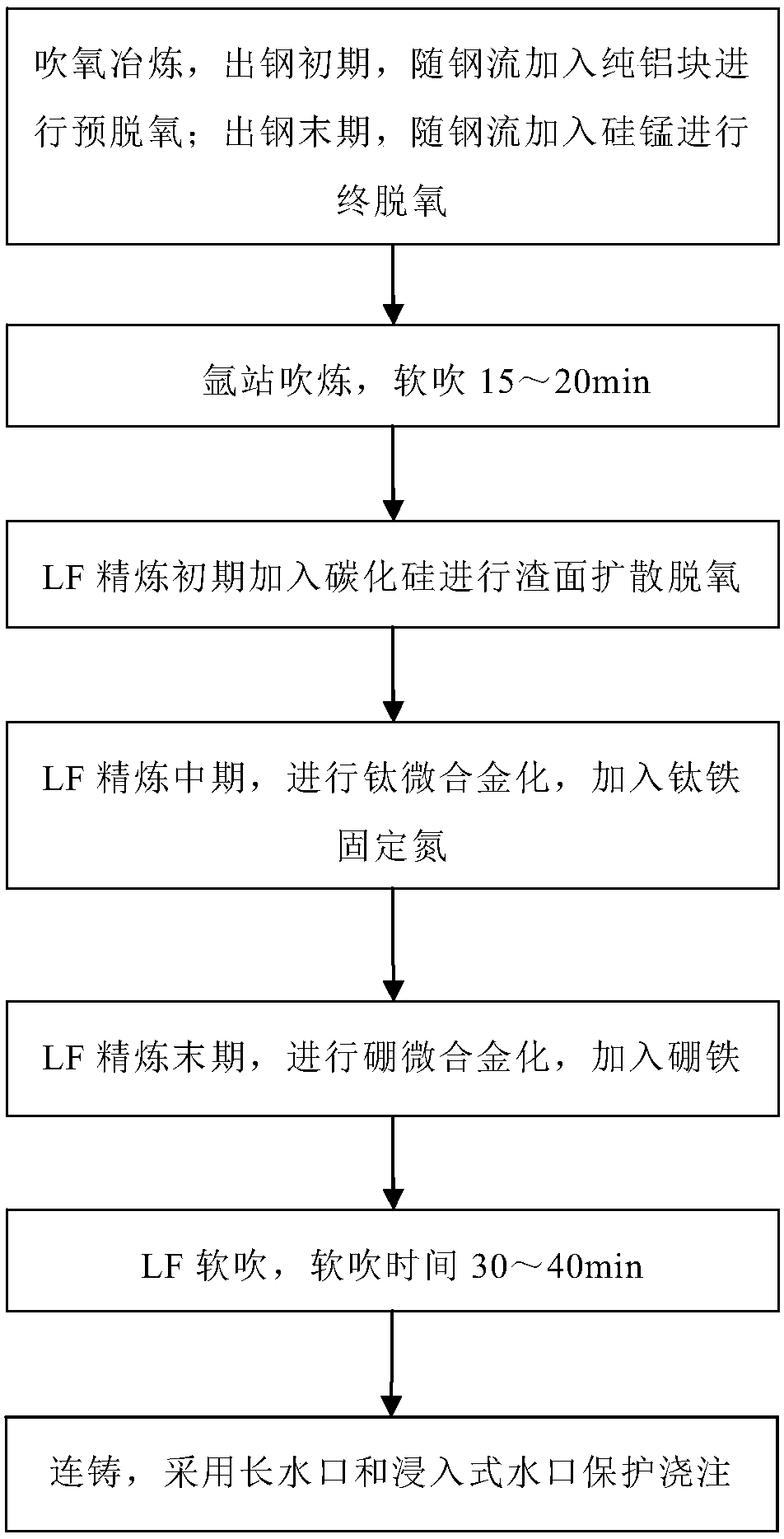
Smelting method for controlling existing form of boron in steel
The invention belongs to the technical field of steelmaking, and discloses a smelting method for controlling an existing form of boron in steel. The smelting method comprises the following steps of blowing oxygen and smelting: at the early stage of steel tapping, pure aluminum blocks are added along with the flow of steel for pre-deoxidation, and at the final stage of steel tapping, silicomanganese is added along with the flow of steel for final deoxidation; blowing at an argon station: soft blowing is performed for 15 to 20 min; adding silicon carbide for slag surface diffusion deoxidation at the early stage of LF refining; performing titanium micro alloying, and adding ferrotitanium for fixing nitrogen at the middle stage of LF refining; performing boron micro alloying, and adding ferroboron at the final stage of LF refining; performing LF soft blowing for 30 to 40 min; performing continuous casting: casting is protected by adopting a long nozzle and a submersed nozzle. The invention provides the smelting method for increasing the duty cycle of solid solution boron.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Use of impure inert gases in the controlled heating and cooling of mixed conducting metal oxide materials
InactiveUS8246719B2Reduce oxygen activityIncrease ratingsSemi-permeable membranesOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideOxygenMetal
Method for processing an article comprising mixed conducting metal oxide material. The method comprises contacting the article with an oxygen-containing gas and either reducing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas during a cooling period or increasing the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas during a heating period; during the cooling period, reducing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas during at least a portion of the cooling period and increasing the rate at which the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is reduced during at least a portion of the cooling period; and during the heating period, increasing the oxygen activity in the oxygen-containing gas during at least a portion of the heating period and decreasing the rate at which the temperature of the oxygen-containing gas is increased during at least a portion of the heating period.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Low-cost manufacturing method for non-quenched and tempered steel for car
ActiveCN105177399AGuaranteed purityShorten the smelting cycleProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceOxygen contentMolten steel
The invention discloses a low-cost manufacturing method for non-quenched and tempered steel for a car, and belongs to the technical field of alloy steel production. The low-cost manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out adaptive modification on an electric furnace, and shortening a smelting period within 45 minutes; carrying out full molten iron smelting, wherein charging amount of the molten iron is 90%-100%; controlling end point carbon content of molten steel to 0.10-0.30wt% and controlling oxygen activity in the molten steel to 0.010-0.020% by utilizing an eccentric bottom tapping mode of an electric furnace; reducing aluminum dosage to 0.35-0.70 kilogram / ton of molten steel; controlling oxygen activity in the molten steel to 0.0003-0.0005%; adding a calcium line into the molten steel, wherein the calcium dosage is 0.04-0.08 kilogram / ton of molten steel; and reducing oxygen content in non-quenched steel to be lower than 0.0020wt%. The low-cost manufacturing method has the advantages that the production cost is low, and using requirements of the non-quenched and tempered steel for the car are met.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
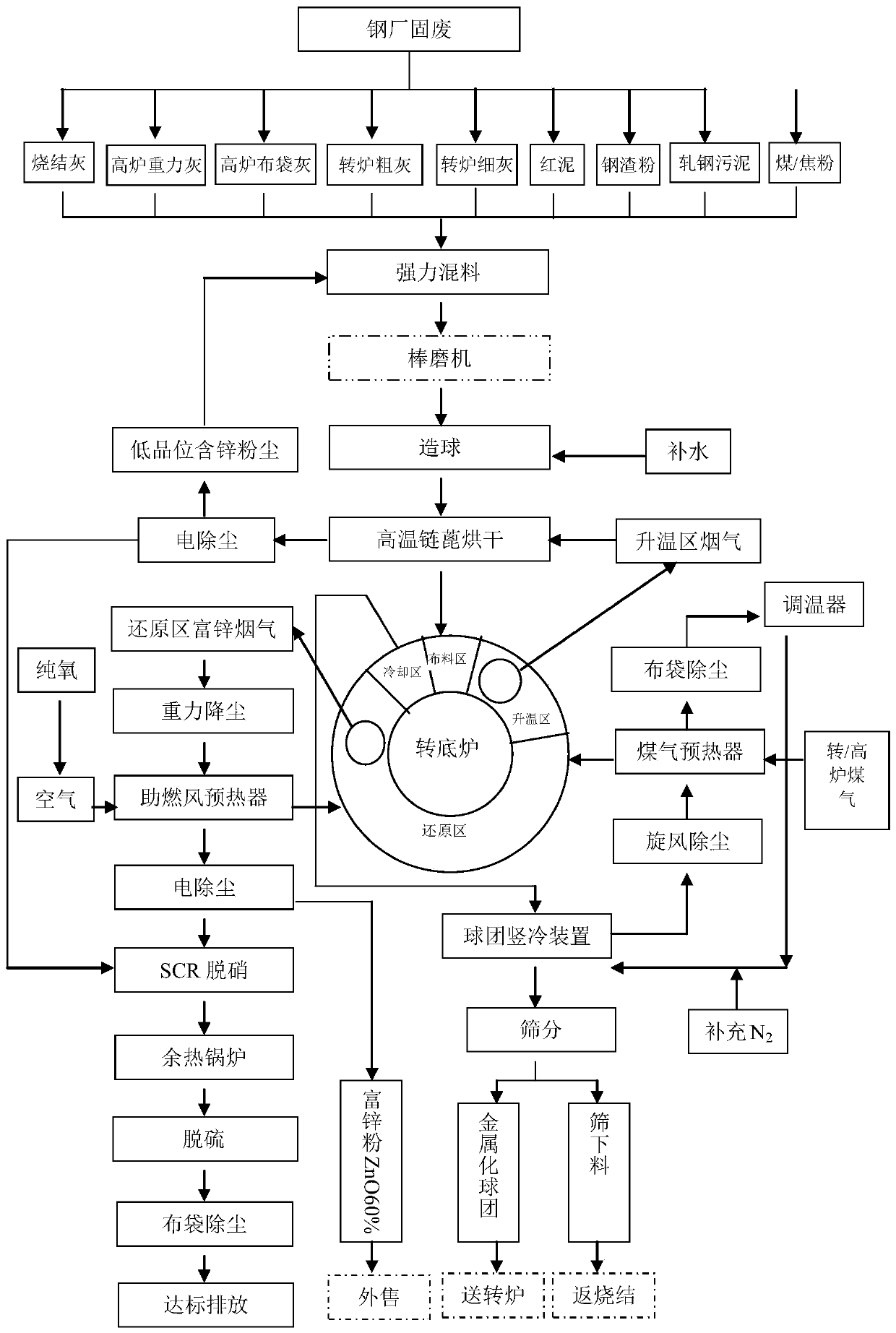
Method for treating solid waste through rotary hearth furnace
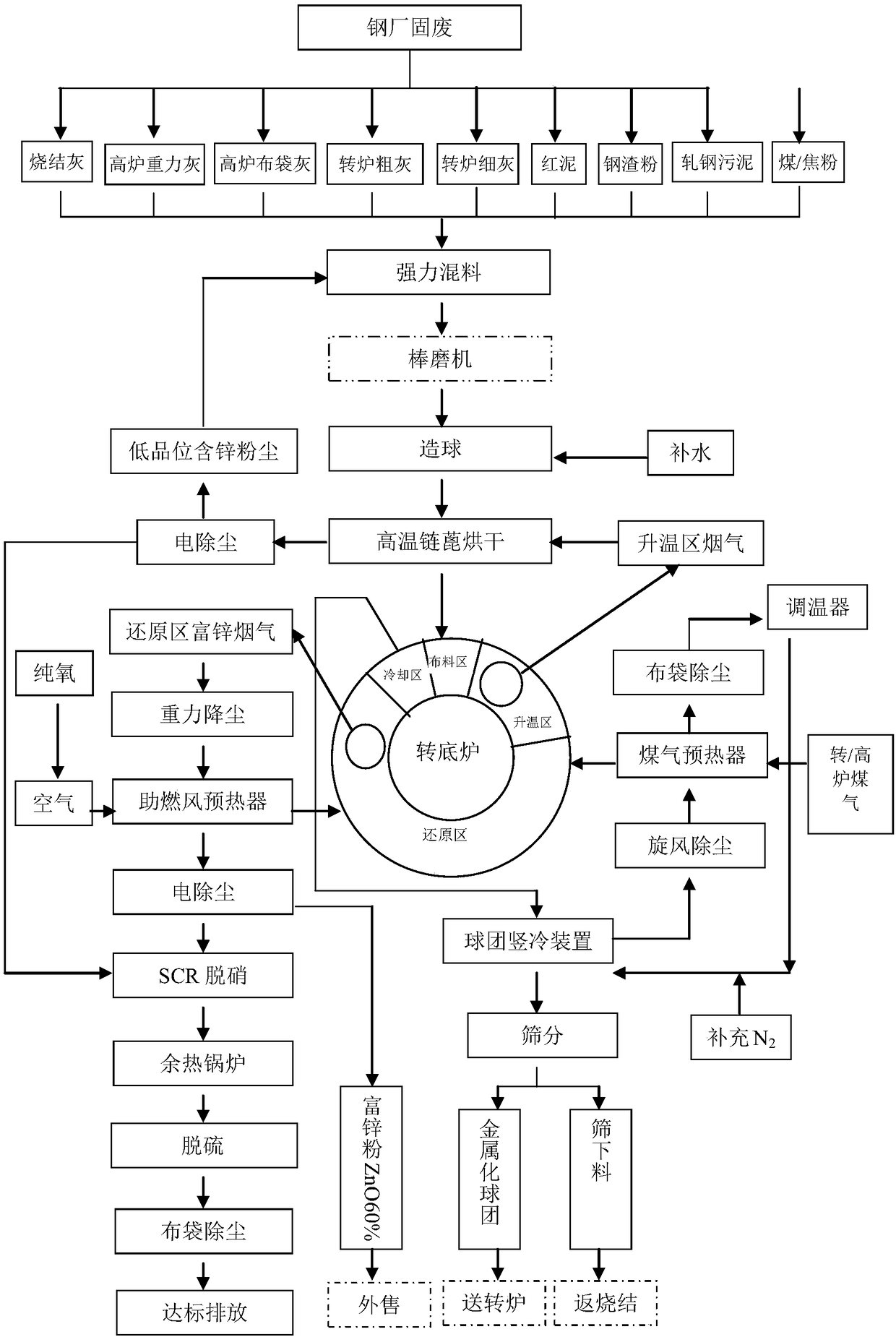
ActiveCN108611458AHigh strengthReduce pulverization rateRotary drum furnacesProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingHearth
The invention relates to a method for treating solid waste through a rotary hearth furnace and belongs to the technical field of steel mill solid waste treatment. The problems that in the prior art, recycled zinc oxide powder is low in grade, and finished metallized pellets are high in pulverization rate are solved. The method for treating the solid waste through the rotary hearth furnace comprises the following steps of pelletizing, reduction and zinc-contained powder recycling, and a drying stage is further performed between the pelletizing and the reduction. The method for treating the solid waste through the rotary hearth furnace provided by the invention can be used for treating solid materials generated in the production processes of sintering, ironmaking and steelmaking.
Owner:钢研晟华科技股份有限公司
Electrolytic method, apparatus and product
ActiveUS20150129432A1Shorten the timeEliminate currentPolycrystalline material growthElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisMolten salt
In a method for removing a substance from a feedstock comprising a solid metal or a solid metal compound, the feedstock is contacted with a fused-salt melt. The fused-salt melt contains a fused salt, a reactive-metal compound, and a reactive metal. The fused salt comprises an anion species which is different from the substance, the reactive-metal compound comprises the reactive metal and the substance, and the reactive metal is capable of reaction to remove at least some of the substance from the feedstock. A cathode and an anode contact the melt, and the feedstock contacts the cathode. An electrical current is applied between the cathode and the anode such that at least a portion of the substance is removed from the feedstock. During the application of the current, a quantity of the reactive metal in the melt is maintained sufficient to prevent oxidation of the anion species of the fused salt at the anode. The method may advantageously be usable for removing the substance from successive batches of the feedstock, where the applied current is controlled such that the fused-salt melt after processing a batch contains the quantity of the reactive metal sufficient to prevent oxidation of the anion species at the anode.
Owner:METALYSIS
Positive electrode material and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN109390565AStable structureAvoid or Mitigate Irreversible ChangesSecondary cellsPositive electrodesLithium-ion batteryExpansion ratio
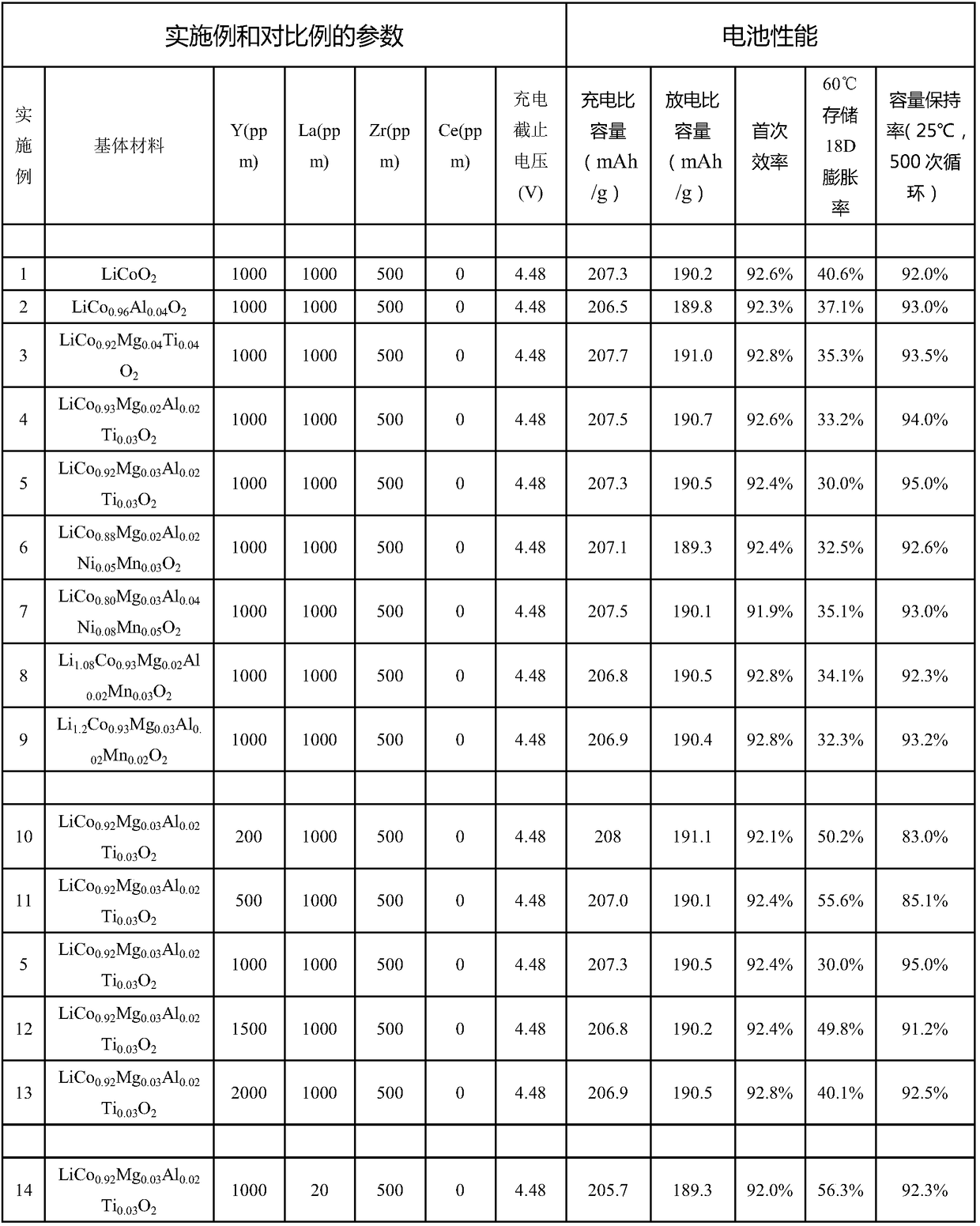
Embodiments of the invention provide a positive electrode material and a lithium ion battery. The positive electrode material comprises a base material and a coating material formed on at least a partof the surface of the base material. The general formula of the base material is Li<x>Co<y>M<1-y>O<2>, wherein x is no less than 1.0 and no more than 1.2; y is no less than 0.8 and no more than 1.0;M is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ti, Al, Zr, Ni and Mn; and the coating material comprises Y<2>O<3> and at least two selected from the group consisting of La<2>O<3>, ZrO<2>and CeO<2>. Compared with positive electrode materials that do not contain coating materials or coating materials therein contain only one or two of the above oxides, the positive electrode material provided in the embodiments of the invention allows a battery core prepared from the positive electrode material to have a low storage expansion ratio and a high capacity retention rate through the co-action of at least three oxides and improves cycle performance at a high charging cut-off voltage.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
Method for synergistically and deeply removing oxygen in metal hafnium by super-oxyphilic metal and calcium
ActiveCN112095022AReduce oxygen activityImprove removal effectTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusOptical coatingHafnium
The invention discloses a method for synergistically and deeply removing oxygen in metal hafnium by super-oxyphilic metal and calcium. The method comprises the following steps: filling specific positions of a reactor with materials such as super-oxyphilic metal, anhydrous calcium chloride, a hafnium raw material and a calcium reducing agent; and carrying out distillation-deoxidation and disassembly-cleaning so as to stably reduce the oxygen content of hafnium to be smaller than 100 ppm. The super-oxyphilic metal has extremely high oxygen affinity, and oxygen in calcium chloride fused salt canbe subjected to solid solution or forms oxide, so that extremely low oxygen potential is created, and the thermodynamic problem of deep deoxidation is solved; and the calcium chloride fused salt has high fluidity and high solubility to the calcium reducing agent and calcium oxide, so that the kinetics problem of deoxidation is solved. Through organic combination of purification and deoxidation ofCa, deep, efficient and stable removal of oxygen in the metal hafnium is realized. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement, good in oxygen removal effect and free of secondary pollution, and the product meets the use requirements in the fields of target material manufacturing, optical coating, electronic element manufacturing and the like.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Positive electrode material and lithium-ion battery
ActiveUS20190051893A1Lower performance requirementsImprove stabilitySecondary cellsPositive electrodesLithium-ion batteryRetention ratio
The examples of the present application provide a positive electrode material and a lithium-ion battery. The positive electrode material comprises: a substrate material; and a coating material formed on at least one part of a surface of the substrate material; the general formula of the substrate material being LixCoyM1-yO2, wherein 1.0≤x≤1.2, 0.8≤y≤1.0 and M is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ti, Al, Zr, Ni, Mn; the coating material includes Y2O3 and at least two selected from the group consisting of La2O3, ZrO2 and CeO2. The examples of the present application enable the battery prepared by the provided positive electrode material to have a lower storage expansion ratio, a higher capacity retention ratio, and improved cycle performance at a high charge cutoff voltage by the interaction of at least three kinds of oxides.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
Method for producing steel for high-efficiency alloy welding wires through continuous billet casting
ActiveCN102212749BReduce consumptionEliminate blanking processWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaProcess MeasuresSmelting process
The invention relates to a method for producing steel for high-efficiency alloy welding wires through continuous billet casting, belonging to the technical field of steel making. The method comprises the following processes: providing low-sulfur molten iron and scrap steel; smelting in a top / bottom blowing converter; pulling off slag and tapping; deoxidizing the ladle; alloying the molten steel; carrying out LF (Ladle Furnace) refining; carrying out RH (Ruhrstahl Heraeus) refining; carrying out fully-protected continuous casting by a continuous billet casting machine; and checking the cast billets, wherein the key processes comprise the end point control during converter smelting, the dose of deoxidizer, the control on the oxygen activity of the molten steel in the production process, thecontrol on the top slag during LF refining, the denitriding effect during RH refining, the regulation of sulfur and titanium contents in the refining process, the effect of protected casting and the like. The method is characterized by controlling oxygen and nitrogen contents in the molten steel through various process measures in the smelting process, thereby achieving the purpose of controllingthe reaction of titanium with oxygen and nitrogen, and reducing the possibilities that a submerged nozzle is blocked and crystallizer protecting slag is agglomerated. By using the method, the steel for high-efficiency alloy welding wires, of which the titanium content is 0.15-0.22%, can be stably produced.
Owner:BEIJING SHOUGANG CO LTD
Aluminum-containing steel slow-release deoxidation method and application
The invention discloses a slow-release deoxidation method for aluminum-containing steel and its application. The method includes converter smelting and refining processes; in the converter smelting process, calcium carbide is added to a ladle before and during tapping. The invention also discloses the application of the aluminum-containing steel slow-release deoxidation method in steelmaking. The present invention adopts the method of slow-release deoxidation of aluminum-containing steel, adding calcium carbide to the ladle before tapping, adding calcium carbide along with the steel flow during the tapping process, and utilizing the weak reducing property of the calcium carbide to slowly release and remove the steel during the entire tapping process. Oxygen in water can reduce the oxygen activity of molten steel to increase the yield of aluminum products, reduce the consumption of aluminum products, calcium alloy wire and other materials, and reduce the number of Al2O3 inclusions in molten steel. The deoxidation product of calcium carbide, CO, enhances the stirring ability of the molten steel during the discharge process, and plays a role in uniforming the composition of the molten steel. The invention has a stable production process, reduces production costs, and is suitable for smelting aluminum-containing steel with a silicon content of ≤0.1% and aluminum-containing steel with a carbon content of ≥0.1%.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for Producing Hydrogen and/or Other Gases from Steel Plant Wastes and Waste Heat
ActiveUS20160023896A1Speed up the processReduce chanceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesEnergy inputHydrogenProduct gas
A method for producing hydrogen and / or other gases from steel plant wastes and waste heat is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of providing molten waste from steel plant like molten slag in a reactor. The molten slag is contacted with water and / or steam in the presence of a reducing agent to form a stream of hydrogen and / or other gases. The hydrogen and / or other gases can then be extracted from the stream of gases from the reactor.
Owner:TATA STEEL
Positive electrode material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113328077AImprove conductivityImprove cycle stabilityPolycrystalline material growthSecondary cellsPhysical chemistrySingle crystal
The invention discloses a positive electrode material and a preparation method and application thereof. The positive electrode material comprises a single-crystal positive electrode material inner core and a CoxB layer located on the surface of the single-crystal positive electrode material inner core. According to the invention, the surface of the single-crystal positive electrode material is coated with the CoxB layer, so the oxygen activity of the surface / interface is reduced, side reactions are reduced, and the conductivity and the cycle performance of the material are improved. The introduction of the CoxB layer has a particularly remarkable improvement effect on the quaternary positive electrode material, and the conductivity and the cycling stability can be greatly improved under the original conditions of high capacity and low gas production, so the electrochemical performance of the positive electrode material is improved.
Owner:SVOLT ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Electrolytic method, apparatus and product
ActiveUS10066307B2Control rateInhibition of dissolutionProcess efficiency improvementPower flowElectrolysis
In a method for removing a substance from a feedstock comprising a solid metal or a solid metal compound, the feedstock is contacted with a fused-salt melt. The fused-salt melt contains a fused salt, a reactive-metal compound, and a reactive metal. The fused salt comprises an anion species which is different from the substance, the reactive-metal compound comprises the reactive metal and the substance, and the reactive metal is capable of reaction to remove at least some of the substance from the feedstock. A cathode and an anode contact the melt, and the feedstock contacts the cathode. An electrical current is applied between the cathode and the anode such that at least a portion of the substance is removed from the feedstock. During the application of the current, a quantity of the reactive metal in the melt is maintained sufficient to prevent oxidation of the anion species of the fused salt at the anode. The method may advantageously be usable for removing the substance from successive batches of the feedstock, where the applied current is controlled such that the fused-salt melt after processing a batch contains the quantity of the reactive metal sufficient to prevent oxidation of the anion species at the anode.
Owner:METALYSIS
A low-cost manufacturing method of non-quenched and tempered steel for automobiles
ActiveCN105177399BGuaranteed purityShorten the smelting cycleProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceOxygen contentMolten steel
The invention discloses a low-cost manufacturing method for non-quenched and tempered steel for a car, and belongs to the technical field of alloy steel production. The low-cost manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out adaptive modification on an electric furnace, and shortening a smelting period within 45 minutes; carrying out full molten iron smelting, wherein charging amount of the molten iron is 90%-100%; controlling end point carbon content of molten steel to 0.10-0.30wt% and controlling oxygen activity in the molten steel to 0.010-0.020% by utilizing an eccentric bottom tapping mode of an electric furnace; reducing aluminum dosage to 0.35-0.70 kilogram / ton of molten steel; controlling oxygen activity in the molten steel to 0.0003-0.0005%; adding a calcium line into the molten steel, wherein the calcium dosage is 0.04-0.08 kilogram / ton of molten steel; and reducing oxygen content in non-quenched steel to be lower than 0.0020wt%. The low-cost manufacturing method has the advantages that the production cost is low, and using requirements of the non-quenched and tempered steel for the car are met.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
A smelting method for controlling the form of boron in steel
The invention belongs to the technical field of steelmaking, and discloses a smelting method for controlling an existing form of boron in steel. The smelting method comprises the following steps of blowing oxygen and smelting: at the early stage of steel tapping, pure aluminum blocks are added along with the flow of steel for pre-deoxidation, and at the final stage of steel tapping, silicomanganese is added along with the flow of steel for final deoxidation; blowing at an argon station: soft blowing is performed for 15 to 20 min; adding silicon carbide for slag surface diffusion deoxidation at the early stage of LF refining; performing titanium micro alloying, and adding ferrotitanium for fixing nitrogen at the middle stage of LF refining; performing boron micro alloying, and adding ferroboron at the final stage of LF refining; performing LF soft blowing for 30 to 40 min; performing continuous casting: casting is protected by adopting a long nozzle and a submersed nozzle. The invention provides the smelting method for increasing the duty cycle of solid solution boron.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
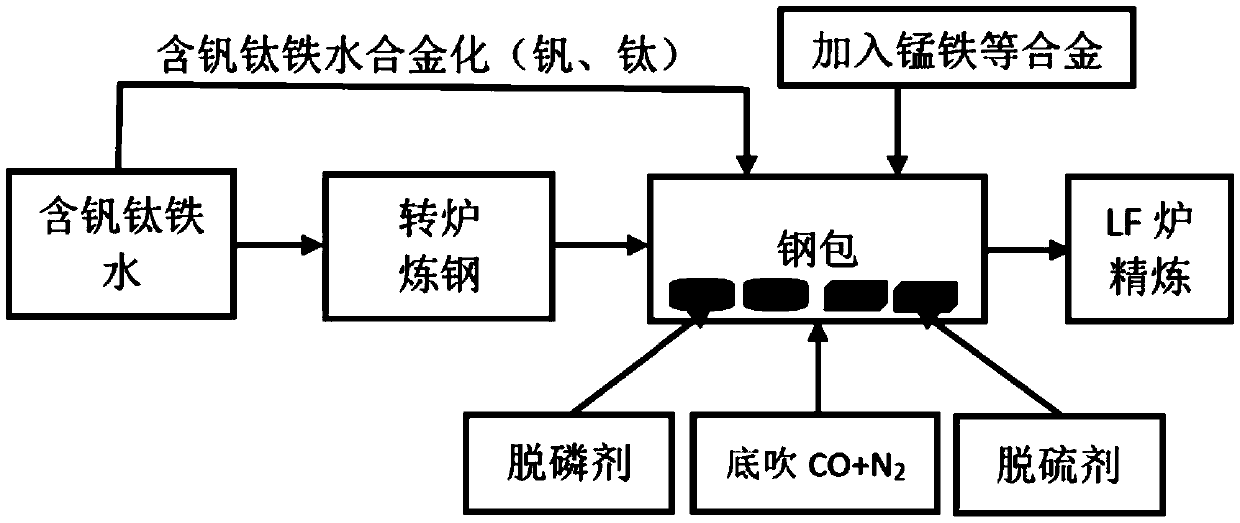
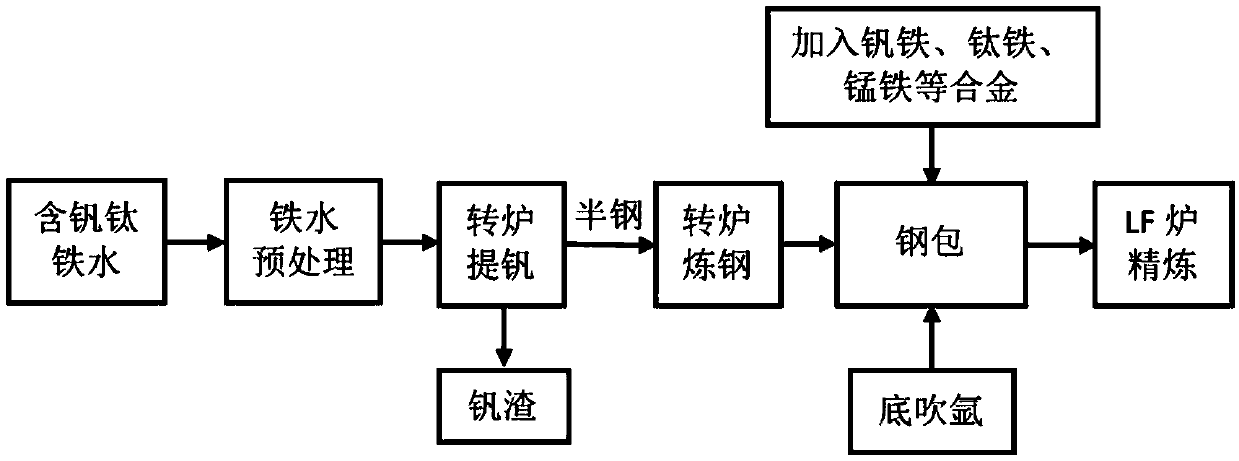
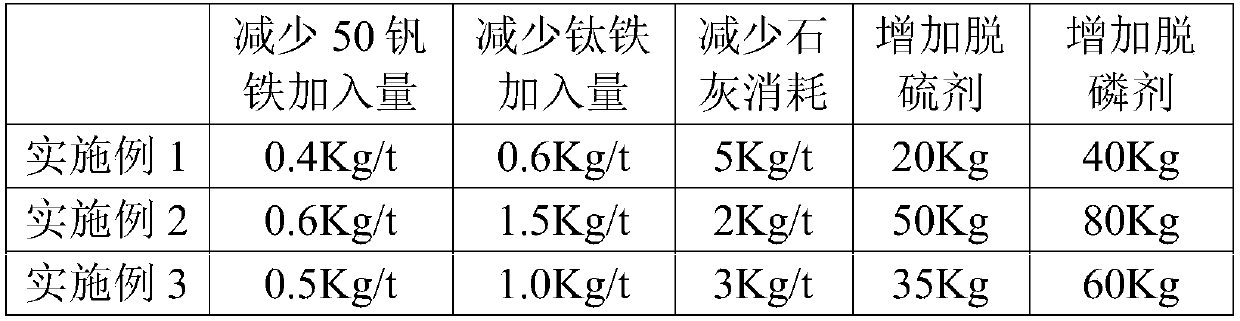
Automobile vanadium-titanium-containing steel alloying smelting method
The invention relates to the technical field of steel smelting, and particularly discloses an automobile vanadium-titanium-containing steel alloying smelting method. The method at least comprises thefollowing steps that part of vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is poured into a steel ladle filled with a desulfurizing agent and a dephosphorizing agent; the rest vanadium-titanium-containingmolten iron continues being smelted by a converter to obtain finishing molten steel, the molten steel is subjected to tapping and poured into the steel ladle to be mixed with the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron, mixed molten steel is obtained, and in addition, in the finishing molten steel tapping process, the steel ladle is subjected to bottom blowing CO and N2 mixed gas stirring; and the mixed molten steel is refined through an LF, and molten steel of vanadium-titanium-containing steel is obtained. According to the method, through the smelting method that the vanadium-titanium-containing steel for an automobile is directly alloyed, the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is maxed with the molten steel smelted by the converter, the effect that the automobile vanadium-titanium-containing steel is subjected to vanadium and titanium alloying through the element vanadium and the element titanium in the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is achieved, and the automobilevanadium-titanium-containing steel alloying cost can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
A method for treating solid waste in a rotary hearth furnace
ActiveCN108611458BHigh strengthReduce pulverization rateRotary drum furnacesProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingWaste treatment
The invention relates to a method for treating solid waste through a rotary hearth furnace and belongs to the technical field of steel mill solid waste treatment. The problems that in the prior art, recycled zinc oxide powder is low in grade, and finished metallized pellets are high in pulverization rate are solved. The method for treating the solid waste through the rotary hearth furnace comprises the following steps of pelletizing, reduction and zinc-contained powder recycling, and a drying stage is further performed between the pelletizing and the reduction. The method for treating the solid waste through the rotary hearth furnace provided by the invention can be used for treating solid materials generated in the production processes of sintering, ironmaking and steelmaking.
Owner:钢研晟华科技股份有限公司
Deformed steel bar converter slag washing desulfurization method
The invention belongs to the technical field of steel and iron smelting, and relates to a deformed steel bar converter slag washing desulfurization method. The deformed steel bar converter slag washing desulfurization method comprises the following steps: adding a top slag modifier into a steel ladle in a converter tapping process to control the components of steel ladle top slag, deoxidizing molten steel at first to reduce the oxygen activity in the molten steel, and then increasing the O<2-> ion concentration in the steel ladle top slag to desulfurize the molten steel; and stirring the steel ladle top slag and the molten steel by means of kinetic energy of the molten steel in the tapping process, and meanwhile, blowing argon or nitrogen into the steel ladle for stirring to accelerate a reaction between the steel and the slag. The deformed steel bar converter slag washing desulfurization method is optimized on the basis of an original technology, no equipment or facilities are added, original conditions are fully utilized, and implementation is easy; and meanwhile, a desulfurization material utilization rate is high, and the usage amount is reduced, so that the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Control method for plasticization of tire cord steel inclusion
The invention discloses a control method for plasticization of a tire cord steel inclusion, and belongs to the technical field of steel and iron smelting. The method comprises the following process steps of: performing a catch carbon process at an end point of a converter, wherein the mass fraction of end point carbon is 0.1-0.4 percent; performing deoxidization alloying on Si-Fe and Mn-Fe alloy during tapping of the converter, wherein 1.0-3.0 kg of Si-Fe alloy is added per ton of steel, and 3.0-6.0 kg of Mn-Fe alloy is added per ton of steel; adding ferrosilicon powder into the top of slag during LF ladle furnace refining, wherein the 0.5-1.5 kg of ferrosilicon powder is added per ton of steel; feeding 0.1-0.5 kg of magnesium wire per ton of steel into a ladle; and blowing argon to the ladle in two stages. The method has the advantages that: the special magnesium or zirconium ladle is not required any longer during production of tire cord steel; meanwhile, the inclusion control levelwhich meets the production requirement is achieved; and thus, the production cost per ton of steel is reduced, and the economic benefit is increased.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Alloying and smelting method of vanadium-containing titanium steel for automobile
The invention relates to the technical field of steel smelting, and particularly discloses an automobile vanadium-titanium-containing steel alloying smelting method. The method at least comprises thefollowing steps that part of vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is poured into a steel ladle filled with a desulfurizing agent and a dephosphorizing agent; the rest vanadium-titanium-containingmolten iron continues being smelted by a converter to obtain finishing molten steel, the molten steel is subjected to tapping and poured into the steel ladle to be mixed with the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron, mixed molten steel is obtained, and in addition, in the finishing molten steel tapping process, the steel ladle is subjected to bottom blowing CO and N2 mixed gas stirring; and the mixed molten steel is refined through an LF, and molten steel of vanadium-titanium-containing steel is obtained. According to the method, through the smelting method that the vanadium-titanium-containing steel for an automobile is directly alloyed, the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is maxed with the molten steel smelted by the converter, the effect that the automobile vanadium-titanium-containing steel is subjected to vanadium and titanium alloying through the element vanadium and the element titanium in the vanadium-titanium-containing molten iron is achieved, and the automobilevanadium-titanium-containing steel alloying cost can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Positive electrode material and lithium-ion battery
ActiveUS10741834B2Lower performance requirementsImprove stabilitySecondary cellsPositive electrodesElectrical batteryPhysical chemistry
The examples of the present application provide a positive electrode material and a lithium-ion battery. The positive electrode material comprises: a substrate material; and a coating material formed on at least one part of a surface of the substrate material; the general formula of the substrate material being LixCoyM1-yO2, wherein 1.0≤x≤1.2, 0.8≤y≤1.0 and M is at least one selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ti, Al, Zr, Ni, Mn; the coating material includes Y2O3 and at least two selected from the group consisting of La2O3, ZrO2 and CeO2. The examples of the present application enable the battery prepared by the provided positive electrode material to have a lower storage expansion ratio, a higher capacity retention ratio, and improved cycle performance at a high charge cutoff voltage by the interaction of at least three kinds of oxides.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
Improved Blast Furnace Soft Water Closed Circulation System and Method
ActiveCN106498106BReduce oxygen activitySmall volume expansionCooling devicesWater leakageEngineering
The invention discloses an improved blast furnace soft water closed circulation system and method. The system comprises a host controller, a cooling wall cooling unit, an expansion and degasification unit, a secondary circulation water unit and a primary circulation water supply unit. According to the improved blast furnace soft water closed circulation system and method, multiple water supply main pipes are adopted, the redundancy degree of the system is increased, and blast furnace production safety is guaranteed; a cooling wall is zoned, grading and leakage detecting are facilitated, the time needed for leakage detecting is reduced, and guarantees are provided for stable production and cost reduction; and secondary circulation water setting is reasonable, the work pressure of secondary circulation water cooling equipment is reduced, the risk of water leakage is reduced, and the gas contents in primary circulation water and secondary circulation water are reduced.
Owner:HUATIAN ENG & TECH CORP MCC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com