Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Low excitation energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20160126463A1Improve emission efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEmission efficiency
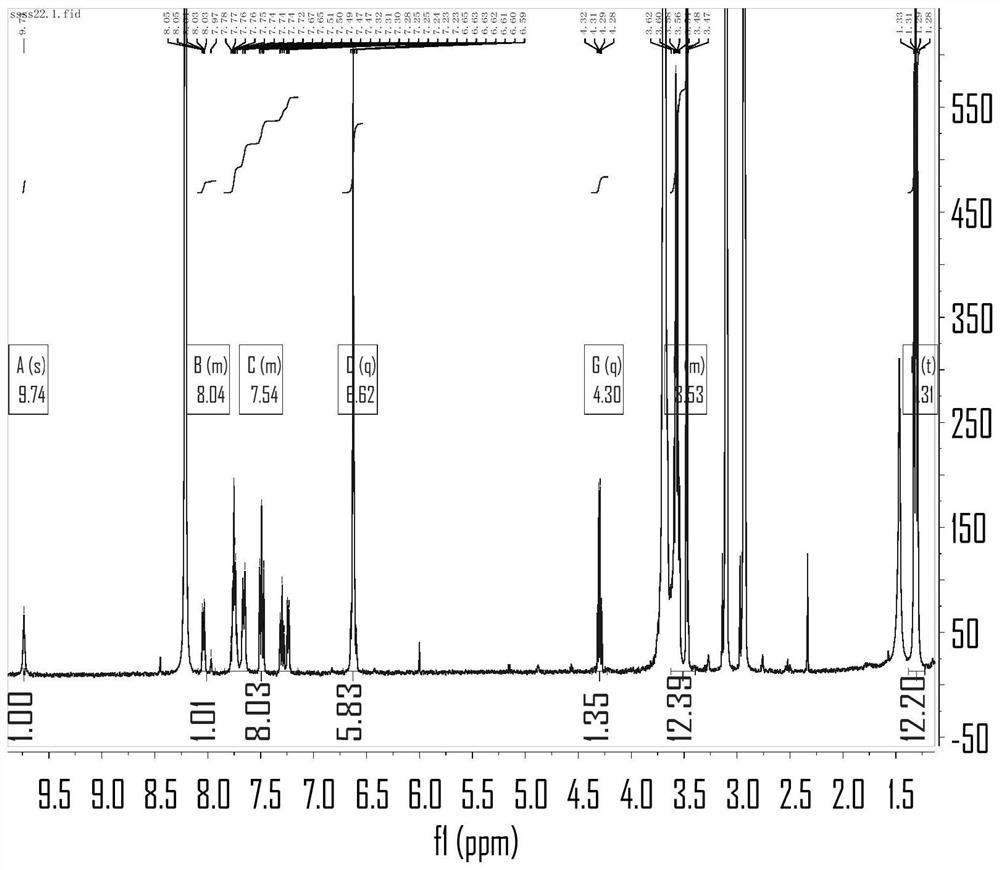
Provided is a light-emitting element with high emission efficiency including a fluorescent material as a light-emitting substance. In a light-emitting element including a pair of electrodes and an EL layer between the pair of electrodes, a delayed fluorescence component due to triplet-triplet annihilation accounts for 20% or more of light emitted from the EL layer, and the light has at least one emission spectrum peak in the blue wavelength range. The EL layer includes an organic compound in which an energy difference between the lowest singlet excited energy level and the lowest triplet excited energy level is 0.5 eV or more. The EL layer includes a benzo[a]anthracene compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Long decay luminescent powder and process for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20030183807A1Low excitation energyFree movementLuminescent compositionsAluminateSimple Organic Compounds
Phosphor powder with the basic composition comprising alkaline earth metal aluminate, an activator such as Eu and a co activator has been disclosed. The said phosphor has been synthesized by use of alkaline earth metal salt along with single phase alumina, an activator and a co-activator. The after glow decay was found to be more than 150 hours. The process uses a reducing agent in the form of carbon or an organic compound of carbon.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Single-photon and two-photon homocysteine fluorescent probes and use thereof
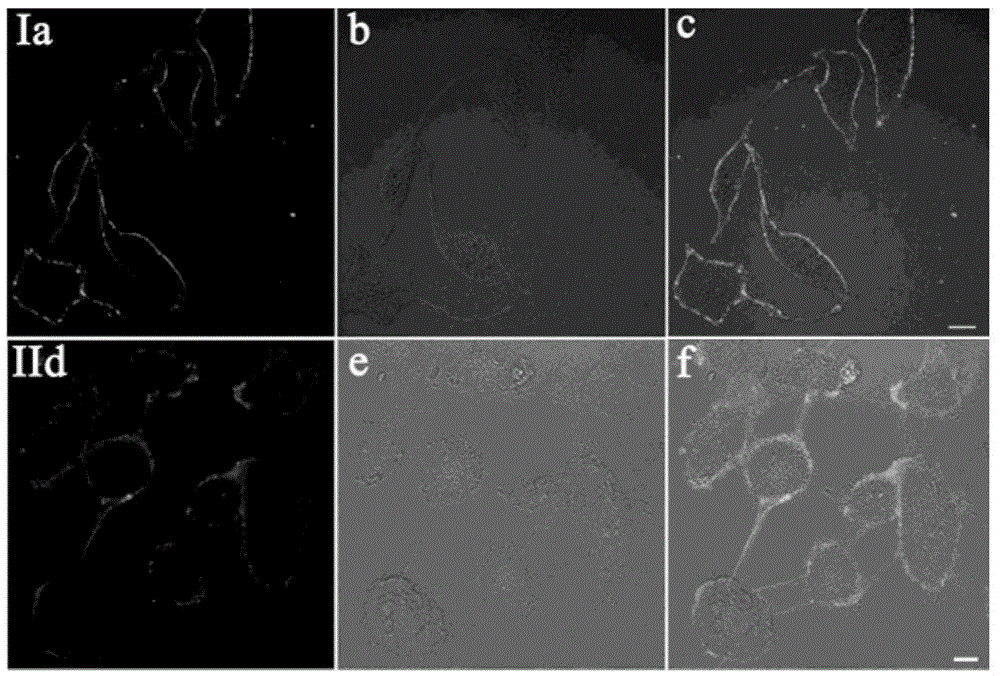
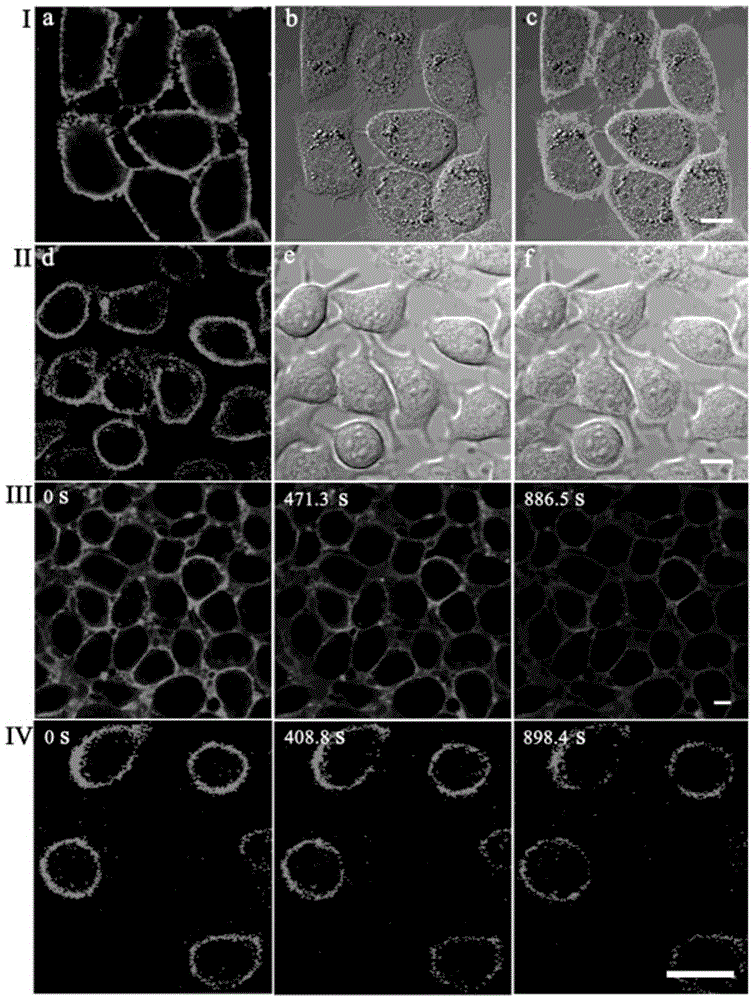
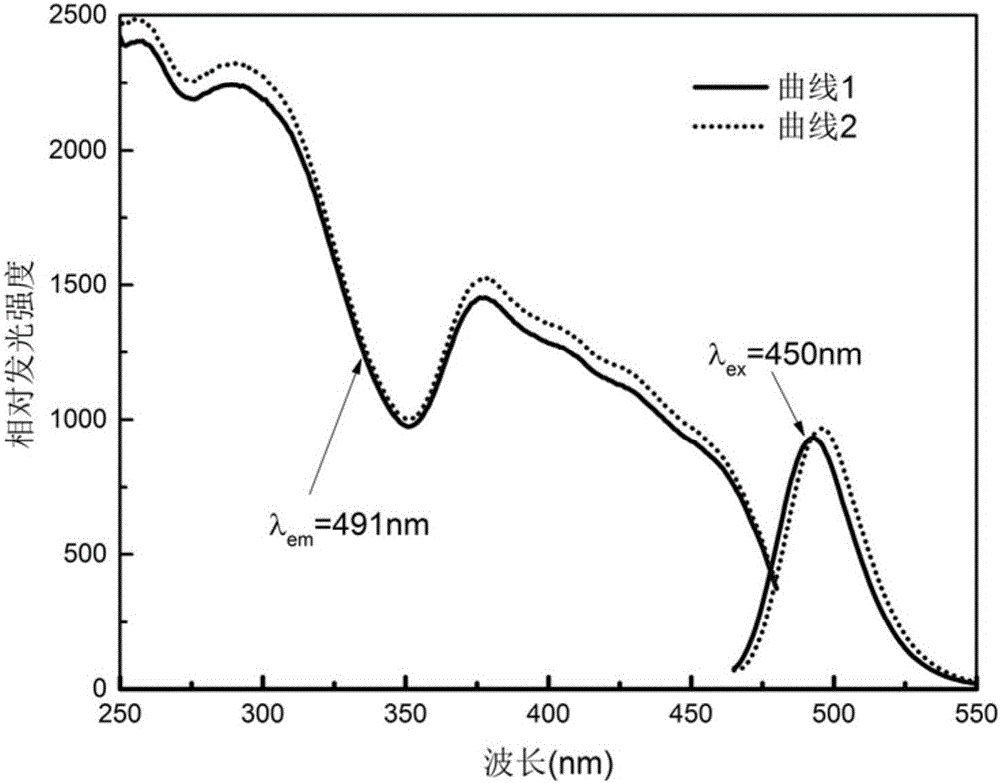
InactiveCN102127055ALow priceLow excitation energyOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCarbazoleFluorescent imaging
The invention discloses single-photon and two-photon homocysteine fluorescent probes, which are carbazole and pyridine aldehyde compounds. The general formula of the carbazole and pyridine aldehyde compounds is represented by (I), wherein R may be alkyl or hydroxyalkyl. The invention also discloses the use of the fluorescent probes in the observation of the expression and distribution of homocysteine in living cells. The probes have the characteristics of wide application range, low price and specific fluorescently imaging homocysteine in living cells.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
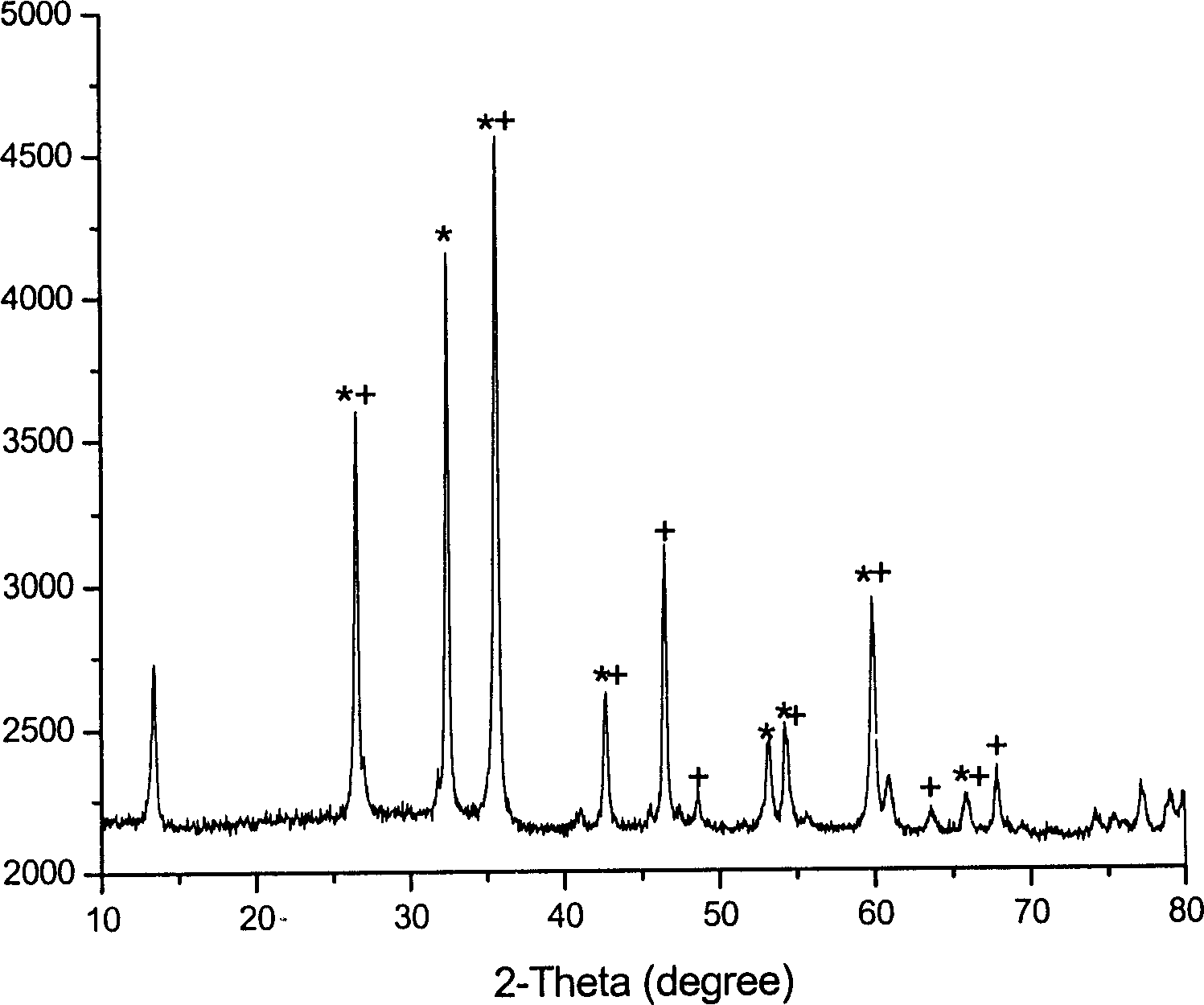
Rare earth nano silicate red phosphor and its preparation method
InactiveCN1702145AImprove light color purityFine particle sizeLuminescent compositionsLuminous intensityEngineering
The invention discloses a rare-earth nanometer metasilicate red fluorophor and the method for preparation. It contains the following setups: dissolving sensitizer activator substrate yttrium oxide in norbiline (or azotic acid), pressure-reduced distilling to eliminate water and excess acid, adding alcohol to prepare clear and transparent solution, and adding substrate silicon material to prepare transparent sol, pressure-reduced distilling to eliminate alcohol and acquiring powder solid, and adglutinating in 550-750 Deg. C by 2-4 hours to prepare the product. It prepares rare-earth nanometer red fluorescent powder in a low temperature (600 Deg. C) and a short time (3 hours), the average grain diameter being about 60-80 nm, the luminous intensity strong, chemical and optical property stable, the material easily obtained and cheap. Chemical expression formula of the rare-earth nanometer red fluorescent powder is as following: (YxSiy0z: Euj, Mn.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
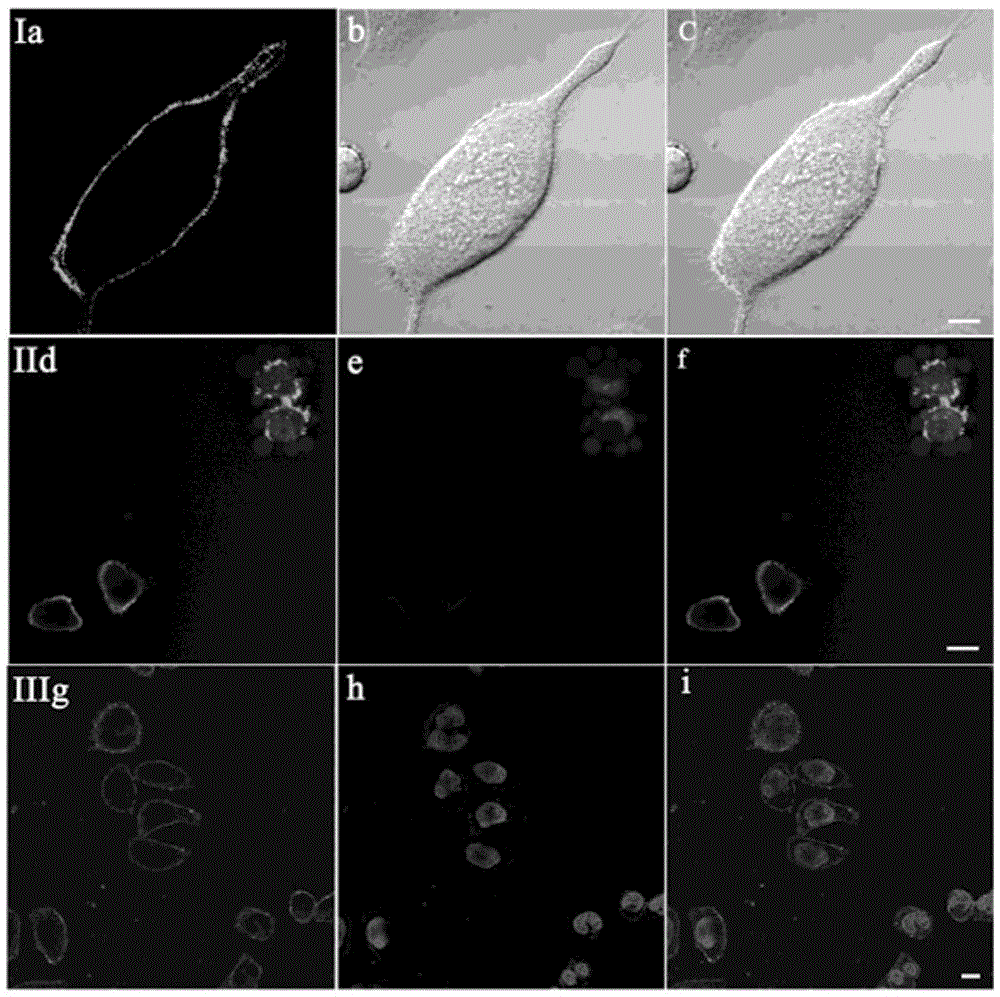
Two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe for imaging cell membranes in tissues based on molecular rotors
ActiveCN105566207ASmall molecular structureImprove photostabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceIodideCytotoxicity
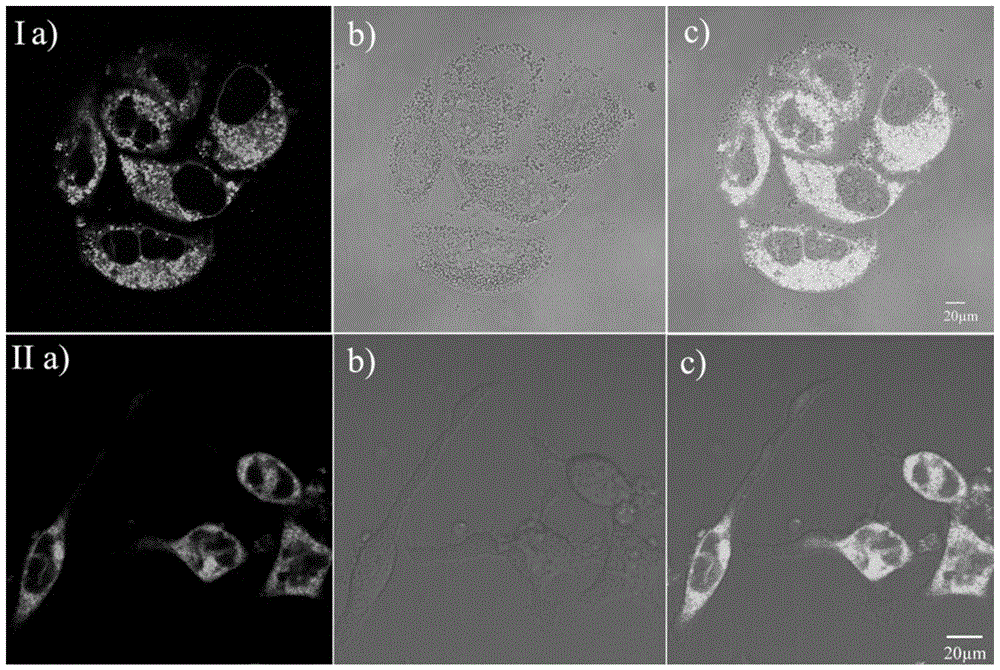
The invention discloses a two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe for imaging cell membranes in tissues based on molecular rotors. The chemical name of the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe is N,N-di((4-(2(minute)-(4(second)-dodecyl)pyridine-4(second)iodide)ethylene)phenyl)phenylamine, and a chemical structural general formula is as shown in a formula (I). The invention also discloses application of the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe in marking or displaying cell membrane forms in the tissues and in living cells. A test verifies that the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe can be used for uniformly and continuously dyeing the cell membranes, bright two-photon deep red light can be emitted after the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe is bound to high-viscosity cell membranes because the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe is a rotor type molecule, the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe is indicated to have a very good prospect by being used as a cell membrane fluorescent probe, and the blank of a cell membrane probe in tissue imaging is hopefully to be filled; meanwhile, the two-photon deep red emission fluorescent probe has the characteristics that the application range is wide, the light stability is good, the cytotoxicity is low, and the cell membranes can be specifically imaged in the living cells.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rare earth doped fluorescent powder and synthetic method thereof and application of fluorescent powder in LED devices
ActiveCN106047341AGood chemical stabilityImprove luminous efficiencyLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesSynthesis methodsElectronegativity
The invention discloses rare earth doped fluorescent powder and a synthetic method thereof and application of the fluorescent powder in LED devices, and belongs to the technical field of luminescent materials. The general chemical formula of the fluorescent powder is MS[2-y]AyO[2+y]N[2-y-4z / 3]Cz:Rx. According to the compound, C<4-> is substituted for N<3->, due to the fact that the electronegativity of C is smaller than that of N, the electron cloud expansion effect of the C<4-> is more obvious than that of the N<3->, after doping is conducted, rare earth ion 5d energy level splitting is increased, Stokes shift can change, and fluorescence parameters such as fluorescent peal and full half-peak width of the powder change. By adjusting generation of the above-mentioned doped ions, fluorescent powder with different fluorescent light colors and quantum efficiency can be obtained. The invention further discloses the application of the fluorescent powder in the field of LED devices. The fluorescent powder is applied to white LED light fixtures or light-emitting components which take blue LED or purple LED as a light source and can help to increase the color rendering indexes of the devices.
Owner:BEIJING YUJI SCI & TECH +2
Single/double-photon acidic cell organelle fluorescent probe and application thereof
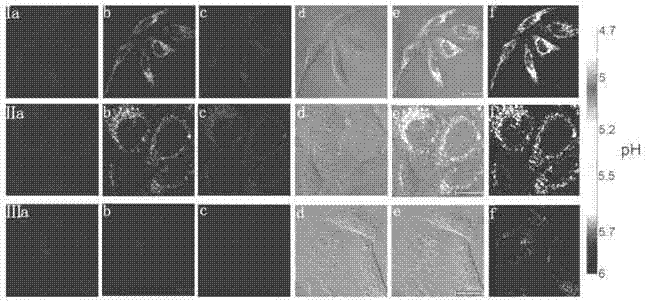
InactiveCN103087706AHigh light switch ratioLow priceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceActive cellFluorescent imaging
The invention discloses a single / double-photon acidic cell organelle fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is a carbazole pyridine compound, and the fluorescent probe is as shown in a general formula of (I). The invention also discloses an application of the fluorescent probe as the single / double-photon fluorescent probe for marking the acidic cell organelles in the display of the distribution of the acidic cell organelles inside a viable cell. The fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that application range is wide, price is low and the acidic cell organelles are specially and fluorescently imaged in an active cell; and the fluorescent probe has wide application prospect as a single-photon ratio type and double-photon optical switch type fluorescent probe for the acidic cell organelles.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
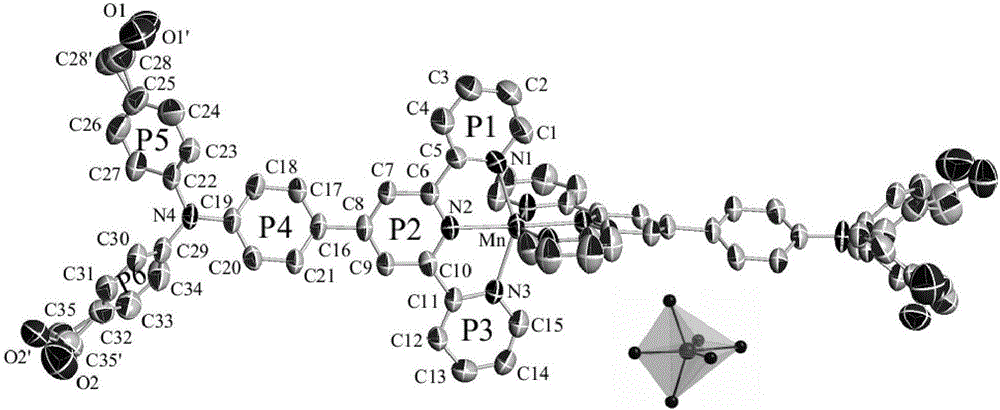
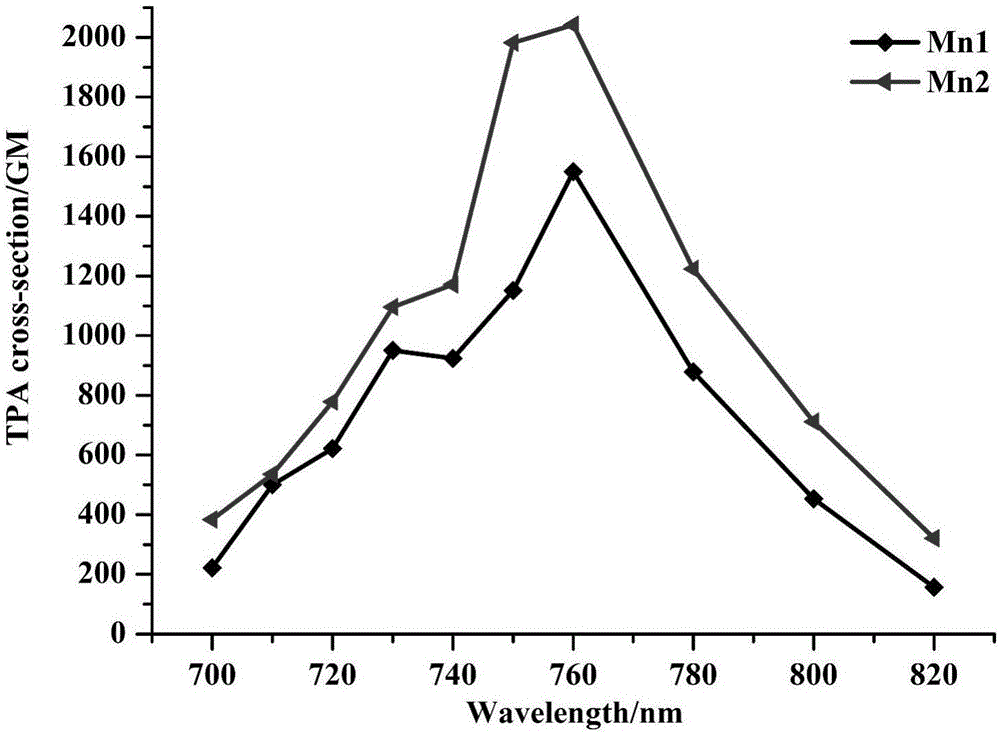
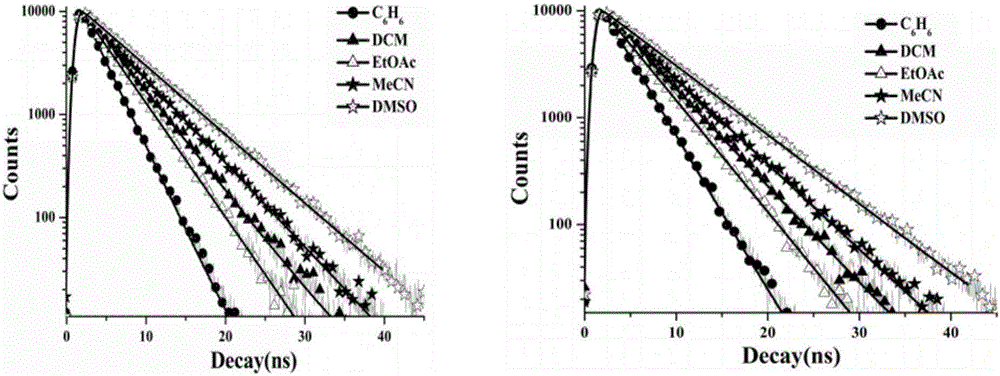
A triphenylamine terpyridine manganese complex having double functions including two-photon development and magnetic resonance development and a synthetic method thereof
ActiveCN106496103ALow excitation energyPenetratingOrganic chemistryIndividual particle analysisMagnetic contrastContrast medium
A triphenylamine terpyridine manganese complex having double functions including two-photon development and magnetic resonance development and a synthetic method thereof are disclosed. The structure formula of the complex is shown in the description. The complex has a two-photon development function and a magnetic resonance development function, and can be adopted as a contrast medium for double modes. Compared with a commercial nuclear magnetic contrast medium that is Gd-DTPA, the complex can be ingested by cells well so that magnetic resonance signals are enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
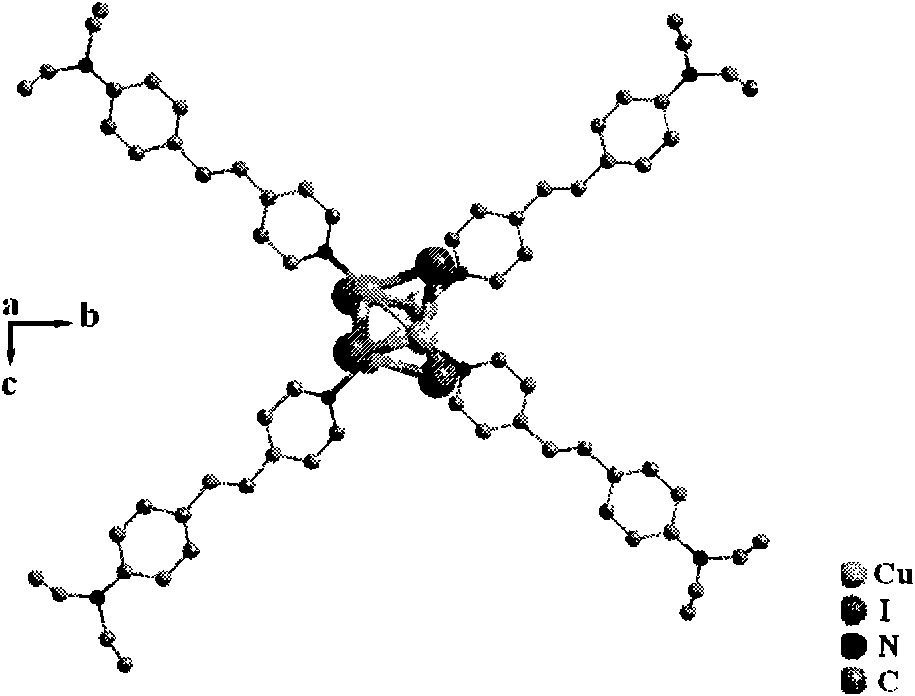
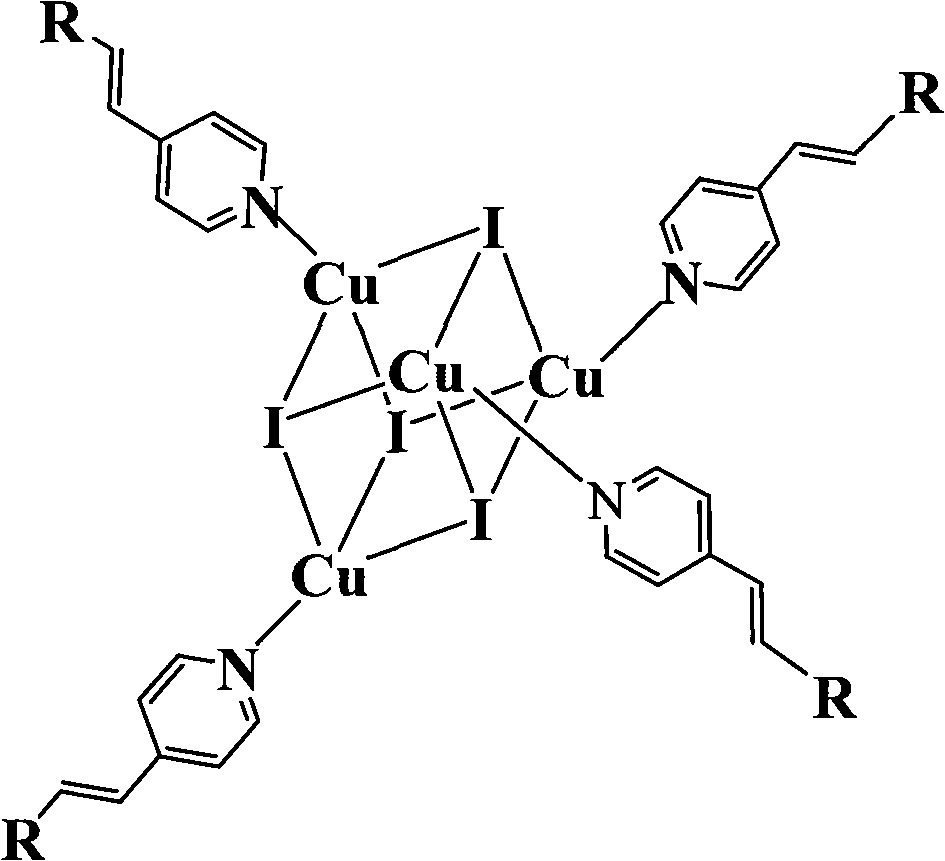
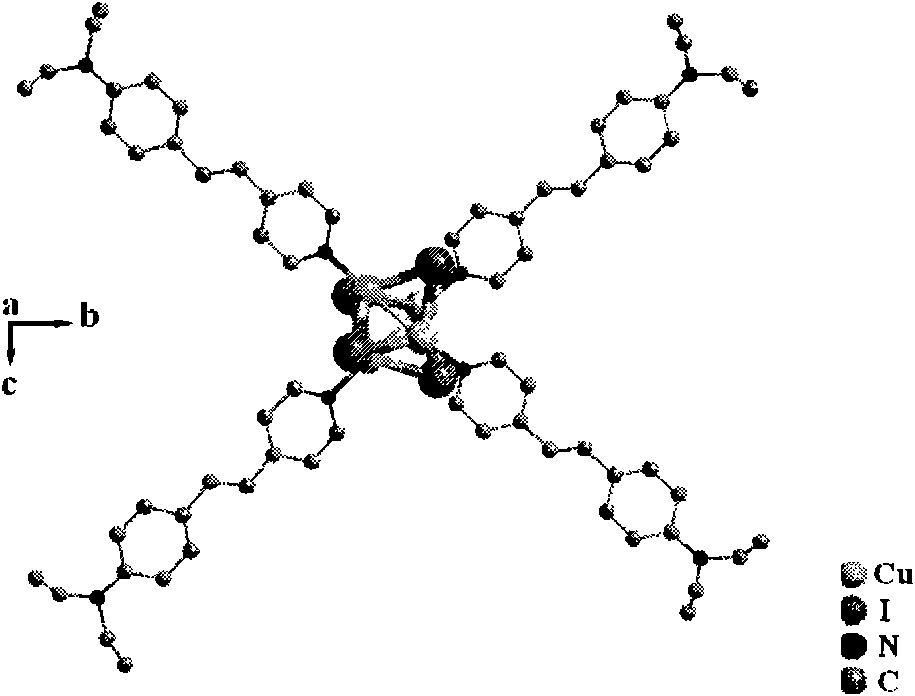
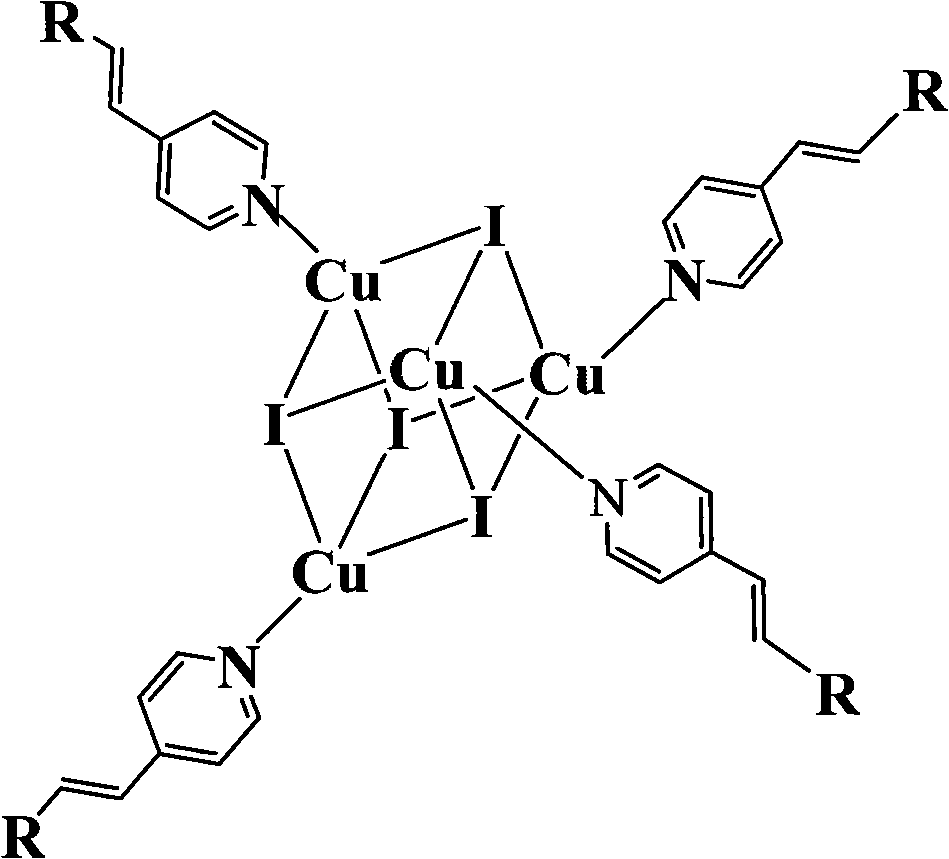
Copper cluster two-photon absorbing material with living cell developing function and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101787041AEasy to manufactureLow biological toxicityCopper organic compoundsLuminescent compositions4-MethylpyridineTwo-photon absorption
The invention provides a copper cluster two-photon absorbing material with a living cell developing function, which is a univalent copper cluster with a multi-branched general chemical formula. The copper cluster two-photon absorbing material is prepared by the steps of: firstly, preparing a pyridine ligand from 4-methylpyridine and 4-N,N-2R-aminobenzaldehyde; and secondly, synthesizing a target product by using the pyridine ligand and cuprous iodide.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN110229165AIncrease penetration depthEliminate background fluorescenceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceEthylenediamineOrganic solvent
The invention discloses an up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing a reaction on rhodamine B and ethylenediamine in a nitrogen gas atmosphere and an organic solvent to obtain rhodamine-ethylenediamine; and performing a reaction on the rhodamine-ethylenediamine and phenyl isothiocyanate to obtain the up-convertion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative. The up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative provided by the invention has the high-efficiency down-conversion fluorescence-enhanced response recognition characteristics for mercury ions and has the high-efficiency up-conversion fluorescence-enhanced response recognition characteristics for the mercury ions when used as a fluorescent probe.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
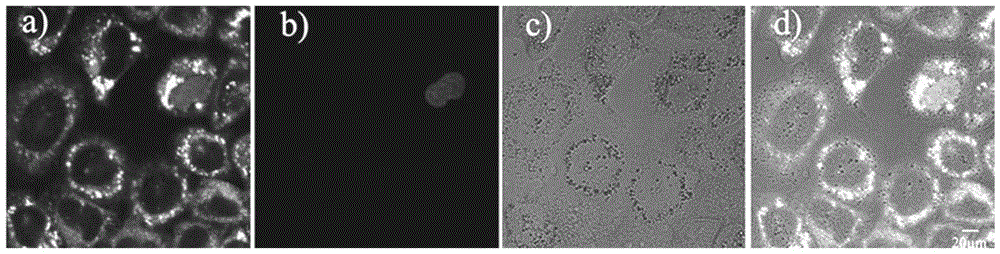
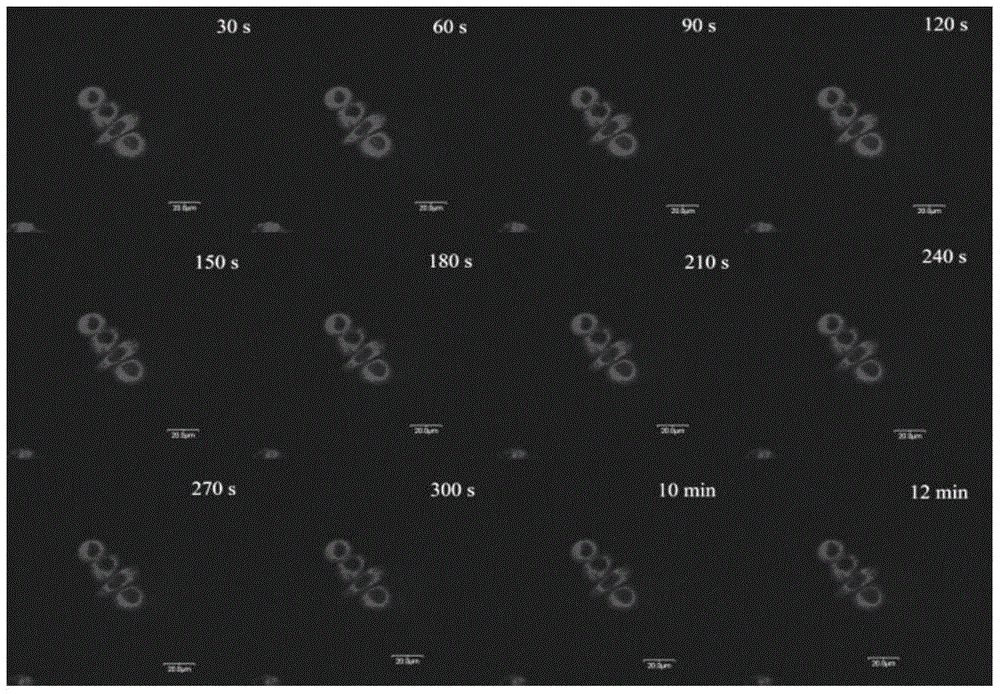
Membrane permeability dye with large two-photon fluorescence active cross section and application of membrane permeability dye
InactiveCN105153733AImprove developmentDevelopment is intuitiveStyryl dyesOrganic chemistryChemical structureConfocal
The invention discloses membrane permeability dye with a large two-photon fluorescence active cross section. The dye adopts triphenylamine heterocyclic chemical compounds, and the chemical structure of the dye is shown in the formula (I). The invention further discloses an application of the dye in displaying two-photon imaging of cytoplasm in a living cell. Experiments show that the dye has characteristics of larger two-photon fluorescence active absorption cross section, excellent cell membrane permeability, low toxicity and the like, also has the characteristics of wide application range, low price and good bio-compatibility with known probe DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) and has wide application prospect in the field of laser excitation fluorescence biomarkers.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
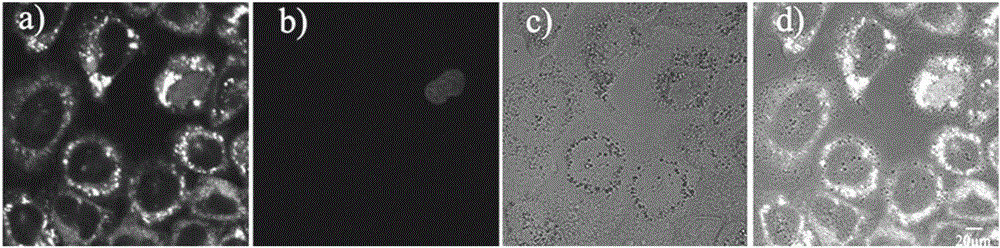
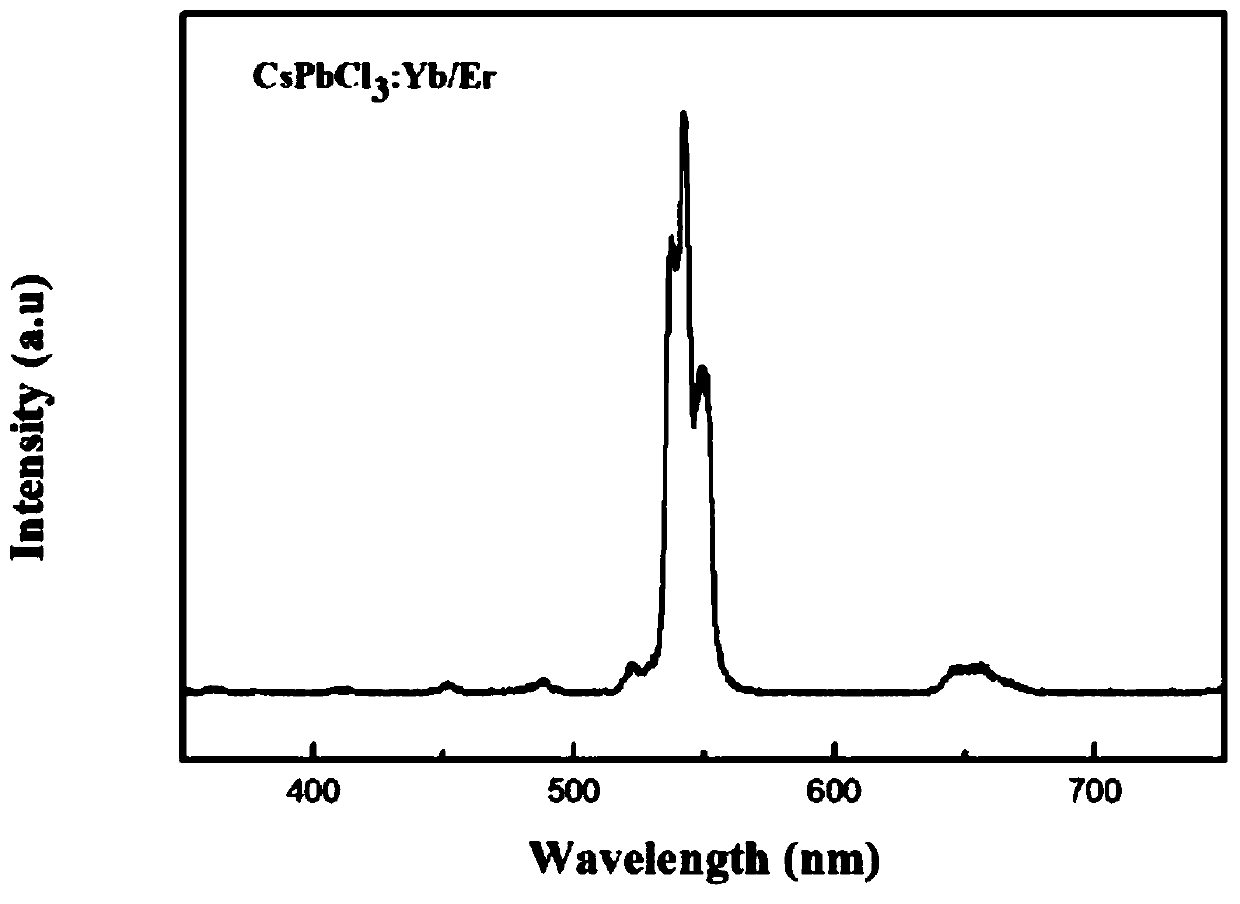
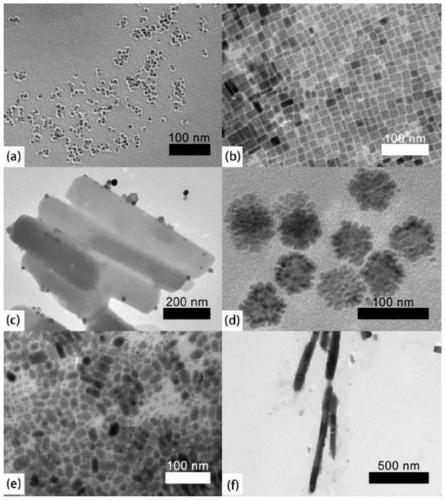
Up-conversion nano luminescent material with perovskite structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111253942AImprove performanceMorphological rulesNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsUpconversion luminescenceHalogen
The invention relates to the field of luminescent materials, in particular to an up-conversion nano luminescent material with a perovskite structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The up-conversion nano luminescent material is of a rare earth doped halogen perovskite (CsPbBr3) nano structure and has the following chemical general formula: AB<1-y-z>M<y>N<z>X3, wherein A =Cs, B = Pb, M = Yb, N = Er, X = Br, and y and z satisfy the following condition: 0.000188 <= y + z <= 0.000375. The material is stable in performance and regular in morphology, and the particle size is obviously smaller than that of an up-conversion luminescent material of a fluoride substrate synthesized under the same condition. Compared with the luminescence of a CsPbBr3 substrate, the up-conversion luminescence of the material has the advantages of low excitation energy, large penetration depth, small biological damage and the like, so that the application of the perovskite material in thebiological aspect can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Thiazole compound with strong two-photon effect and synthesis method thereof
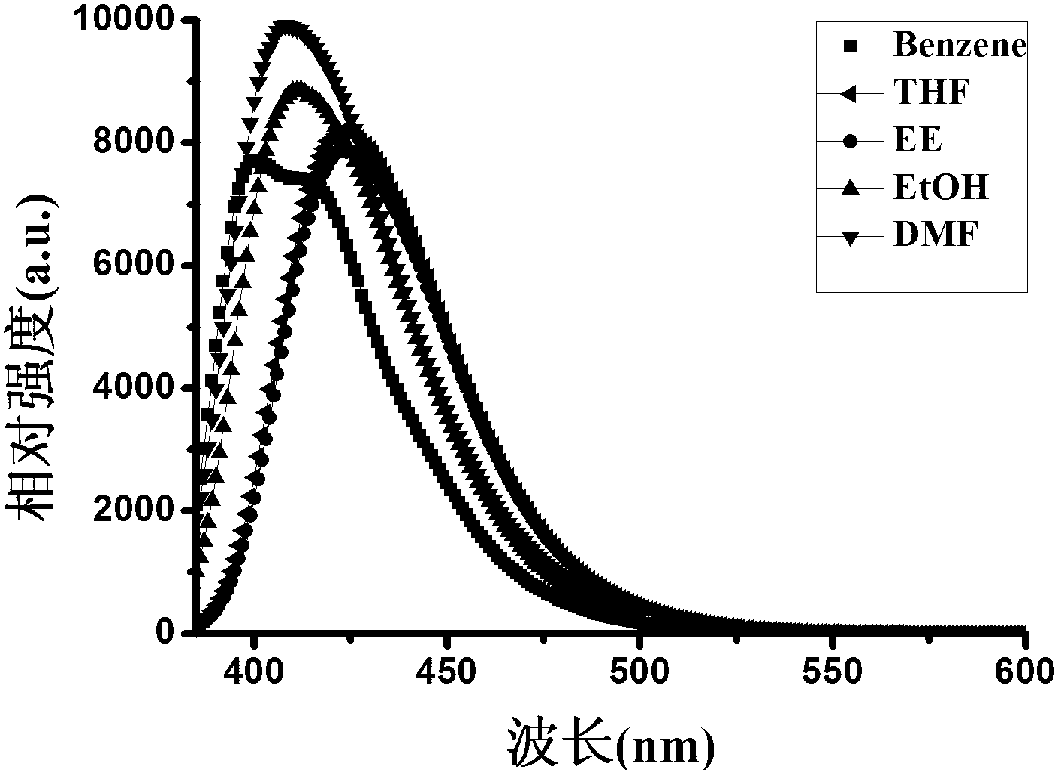
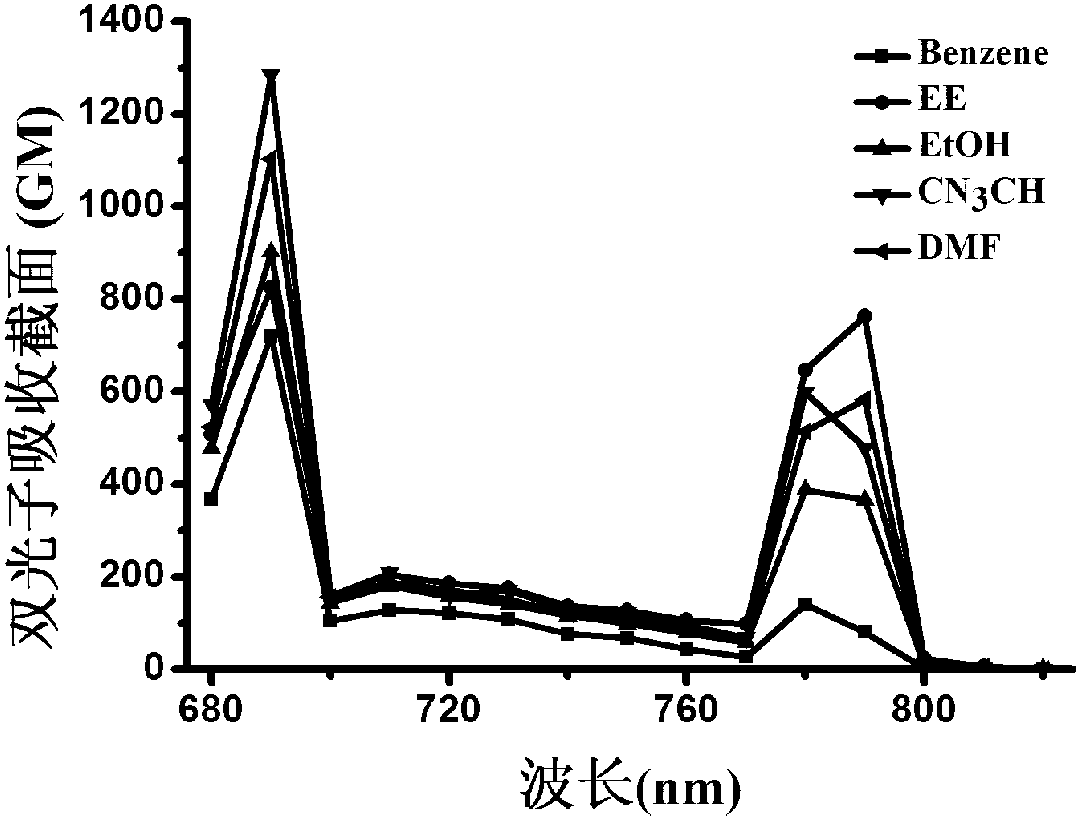
InactiveCN103058952AEnhanced two-photon absorption cross sectionLow excitation energyOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsSolubilityTwo-photon absorption
The invention discloses a thiazole compound with a strong two-photon effect and a synthesis method thereof. The structural formula of the thiazole compound with strong two-photon effect is as follows: the thiazole compound is small organic molecule two-photon fluorescence material with strong two-photon effect and has strong single photon fluorescence and two-photon fluorescence, a short wave of 690nm and a long wave of 790nm have larger two-photon absorption cross sections which respectively reach 1282GM and 763GM. The thiazole compound has the characteristics of low excitation energy and good solubleness and the like, has longer fluorescent lifetime in different solvent, and has an obvious application value, wherein the fluorescent lifetime in ethanol is the longest (1.73ns).
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS10236448B2Improve emission efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEmission efficiency
Provided is a light-emitting element with high emission efficiency including a fluorescent material as a light-emitting substance. In a light-emitting element including a pair of electrodes and an EL layer between the pair of electrodes, a delayed fluorescence component due to triplet-triplet annihilation accounts for 20% or more of light emitted from the EL layer, and the light has at least one emission spectrum peak in the blue wavelength range. The EL layer includes an organic compound in which an energy difference between the lowest singlet excited energy level and the lowest triplet excited energy level is 0.5 eV or more. The EL layer includes a benzo[a]anthracene compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20190214567A1Improve emission efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEmission efficiency
Provided is a light-emitting element with high emission efficiency including a fluorescent material as a light-emitting substance. In a light-emitting element including a pair of electrodes and an EL layer between the pair of electrodes, a delayed fluorescence component due to triplet-triplet annihilation accounts for 20% or more of light emitted from the EL layer, and the light has at least one emission spectrum peak in the blue wavelength range. The EL layer includes an organic compound in which an energy difference between the lowest singlet excited energy level and the lowest triplet excited energy level is 0.5 eV or more. The EL layer includes a benzo[a]anthracene compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
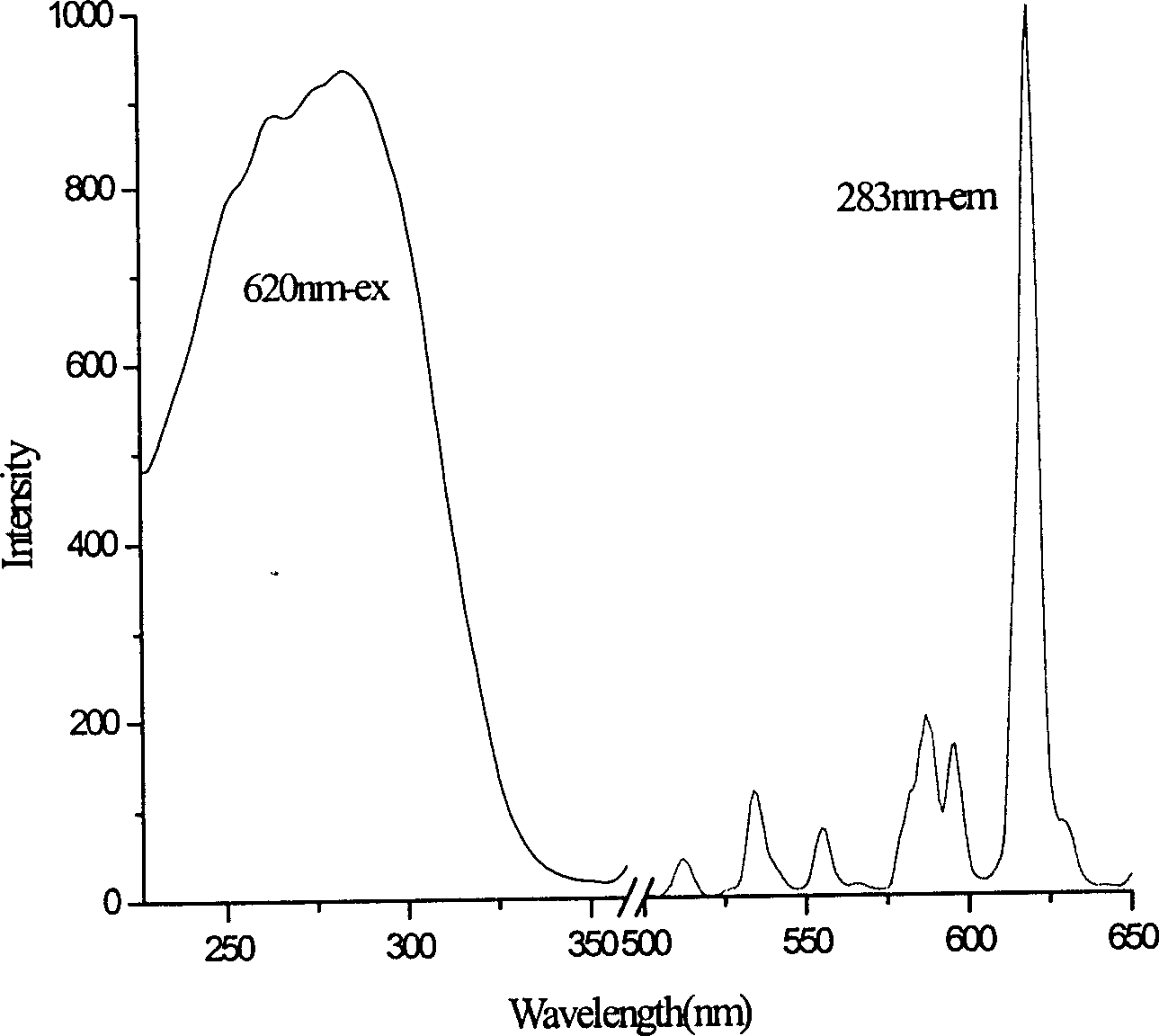
Manganese-doped metal sulfide red fluorescent powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105694864AMild reaction conditionsRaw material economyLuminescent compositionsReaction temperatureShielding gas
The invention discloses a manganese-doped metal sulfide red fluorescent powder and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of MnxM[7-x]In28S52(SH)4.[H<+>-DBN]8.[H<+>-PR]4, wherein M is Cd<2+> or Zn<2+>, DNB is 1,8-diazadicycloundecylenic-7-ene, and the molecular formula is C7H12N2; PR is piperidine of which the molecular formula is C5H11N; and x is the doping amount of manganese, and 0< x<=7. The manganese-doped metal sulfide red fluorescent powder is prepared by a solvothermal process. Under the excitation of 350-550nm light, the fluorescent powder can emit red fluorescence of which the central wavelength is 610-650nm, and the fluorescent powder has high luminescent intensity. Compared with the traditional red fluorescent powder synthesis process, the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple equipment, mild reaction conditions, high preparation speed and economical raw materials; the reaction temperature does not need to achieve 1000 DEG C; and the method does not use any rare earth ion, does not need any shielding gas during reaction, and thus, is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
LED lamp integrating single wire transmission drive control chip
InactiveCN101631407ALow costSimple control circuitPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsColloidLED lamp
The invention discloses an LED lamp integrating a single wire transmission drive control chip, which comprises an encapsulating colloid, a tube core and the single wire transmission drive control chip, wherein the tube core is connected with the output end of the single wire transmission drive control chip; and the tube core and the single wire transmission drive control chip are encapsulated into a whole to form the LED lamp which integrates the single wire transmission drive control chip and comprises an external power wire, an earth wire, an input signal wire and an output signal wire. The LED lamp has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, convenient use, improved hardware utilization ratio, easier circuit connection and high safety stability during PCB layout.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGQING MICRO ELECTRIC TECH
A low-inductance electromagnetic driver for non-exciting magnetic circuit
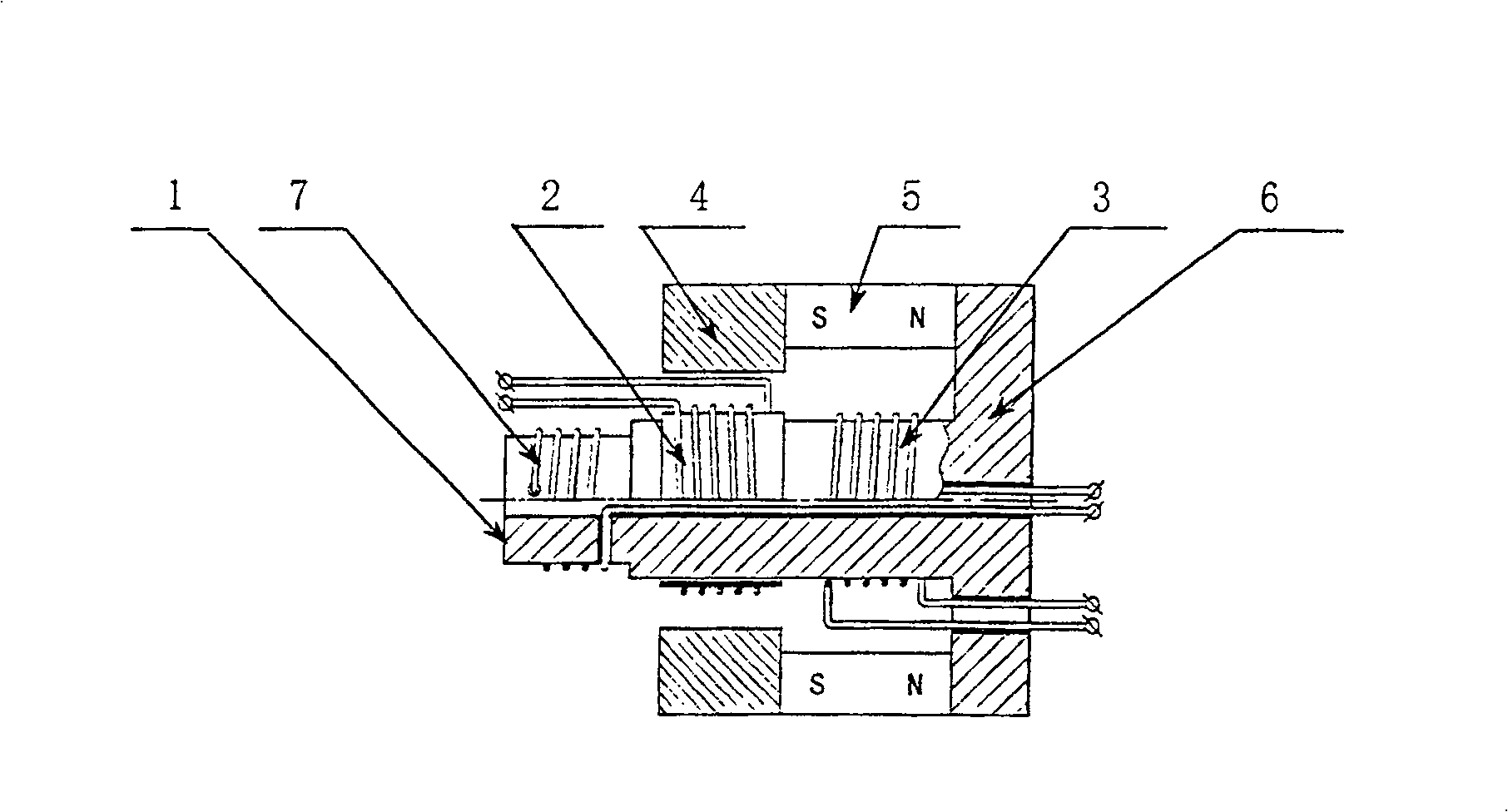
InactiveCN100479532CLow excitation energyReduce sound distortionTransducer detailsEngineeringLow inductance
The present invention relates to a low-inductance electromagnetic drive without driving magnetic flux circuit, which comprises a magnetic pole, a drive coil, an upper magnetic inductive board, a permanent magnet and a lower magnetic-inductive board. The magnetic pole is integrated with the lower magnetic-inductive board, and the permanent magnet is located between the upper magnetic-inductive board and lower magnetic-inductive board. The drive coil is wrapped around the magnetic pole and is movable in the axial direction. The electromagnetic drive further comprises the fastening coil, and the fastening coil is fastened to a certain proper place of the magnetic flux circuit of the drive coil. Furthermore, the fastening coil is connected with the drive coil in opposite phase. The present invention is characterized in that the drive source applies the excitation to the fastening coil in an equivalent quantity as the drive coil but in opposite phase, so that the excitation energy generated by the current flowing through the speaker for the magnetic flux circuit system is reduced to the minimum, the inductance quantity of the speaker is decreased to the minimum, and the sound distortion of the vibration system connected with the drive coil is decreased.
Owner:吴琪君
Copper cluster two-photon absorbing material with living cell developing function and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101787041BEasy to manufactureLow biological toxicityCopper organic compoundsLuminescent compositions4-MethylpyridineTwo-photon absorption
The invention provides a copper cluster two-photon absorbing material with a living cell developing function, which is a univalent copper cluster with a multi-branched general chemical formula. The copper cluster two-photon absorbing material is prepared by the steps of: firstly, preparing a pyridine ligand from 4-methylpyridine and 4-N,N-2R-aminobenzaldehyde; and secondly, synthesizing a target product by using the pyridine ligand and cuprous iodide.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Fluorescent probe for detecting pyroglutamamide aminopeptidase I as well as preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
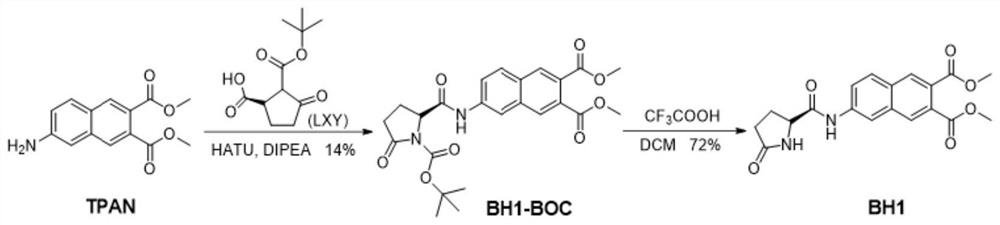
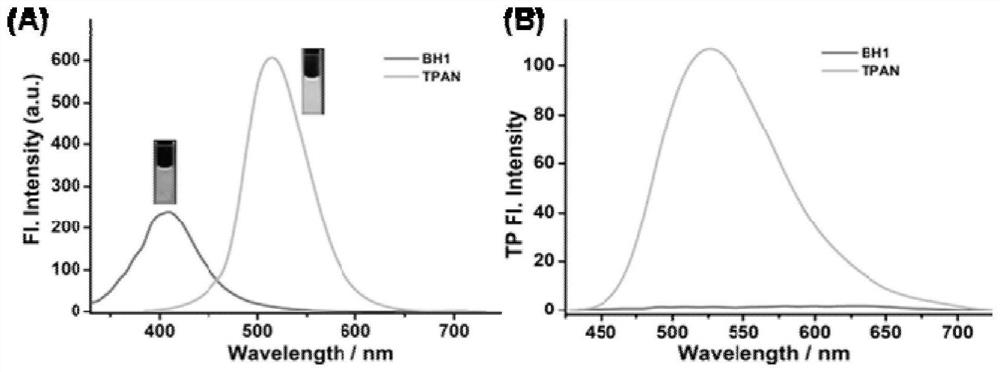
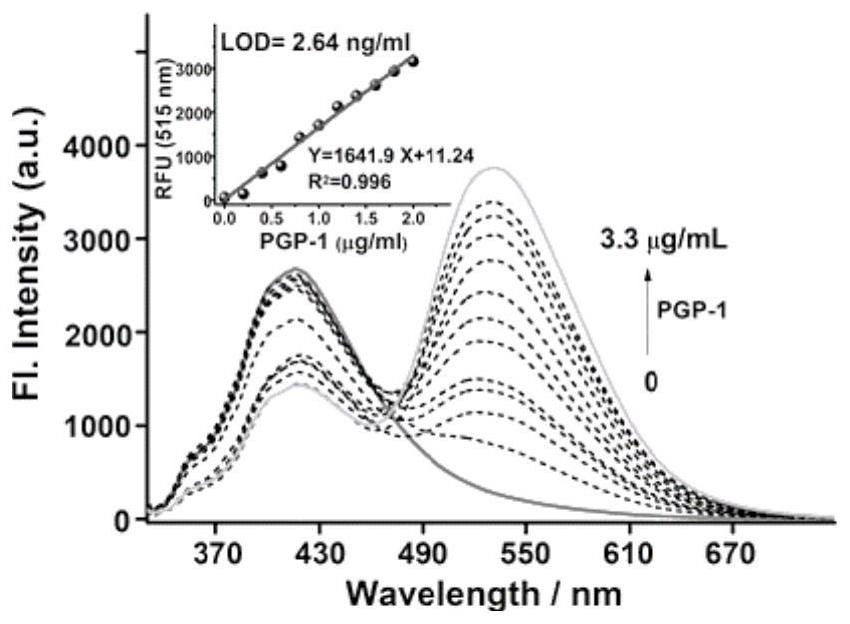
ActiveCN113845458AExcellent photophysical propertiesGood biocompatibilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesAminopeptidase I
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting pyroglutamamide aminopeptidase I as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing LXY, HATU and DIPEA, completely dissolving the mixture in a dry dichloromethane solution, and carrying out a stirring reaction at 0 DEG C; then adding a TPAN solution, further conducting stirring and reacting at room temperature, and carrying out purifying after the reaction is finished so as to obtain a dark red solid BH1-BOC; dissolving BH1-BOC in anhydrous dichloromethane, adding a prepared trifluoroacetic acid solution under an ice salt bath condition, and carrying out room-temperature stirring reaction after dropwise adding is completed; spin-drying a solvent, adding dichloromethane, and repeating the above operations multiple times until the trifluoroacetic acid is completely spin-dried; and purifying a crude product to obtain a red solid BH1.
Owner:西安天工生物医药研究所有限公司
A kind of efficient organic near-infrared fluorescent material and its preparation and application
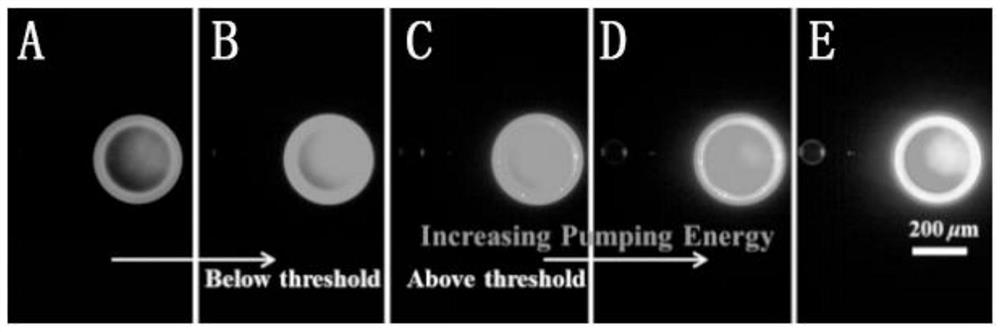
ActiveCN111253338BHigh fluorescence efficiencyEasy to synthesizePowder deliveryOrganic chemistryQuantum efficiencyNear infrared laser
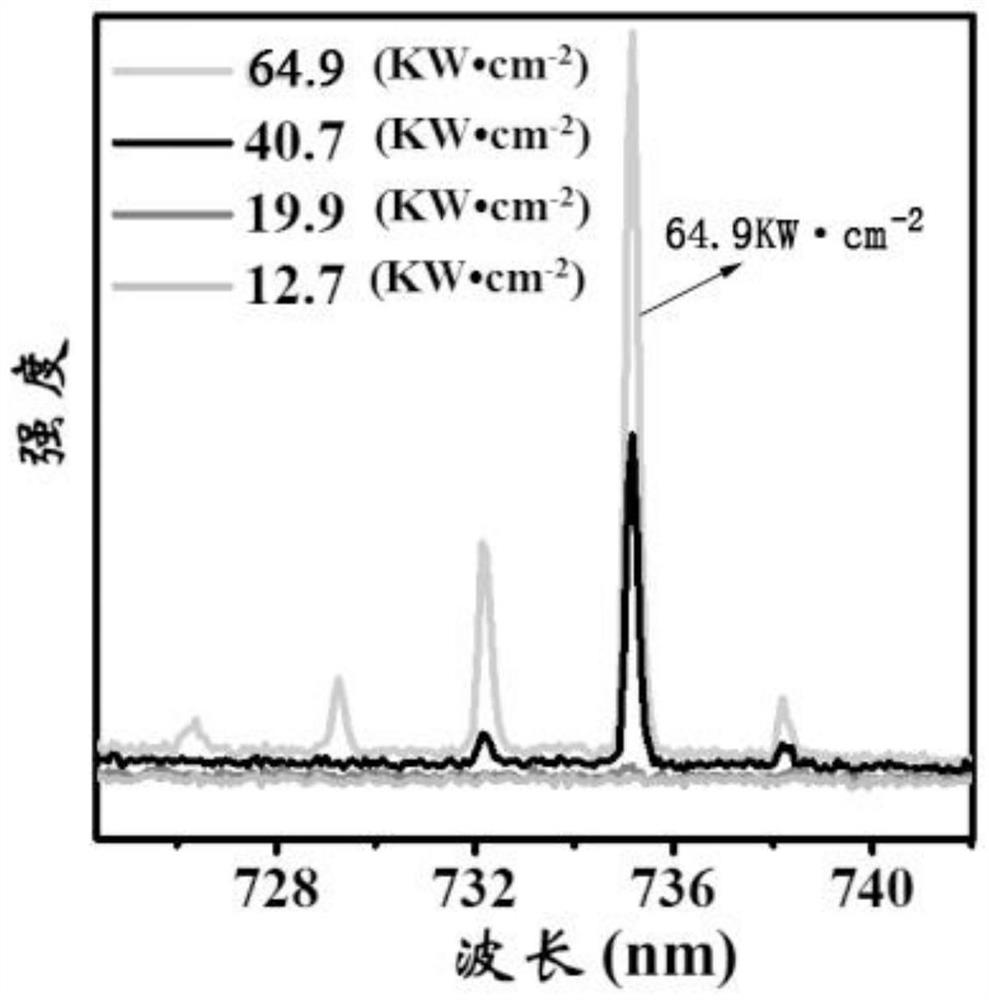
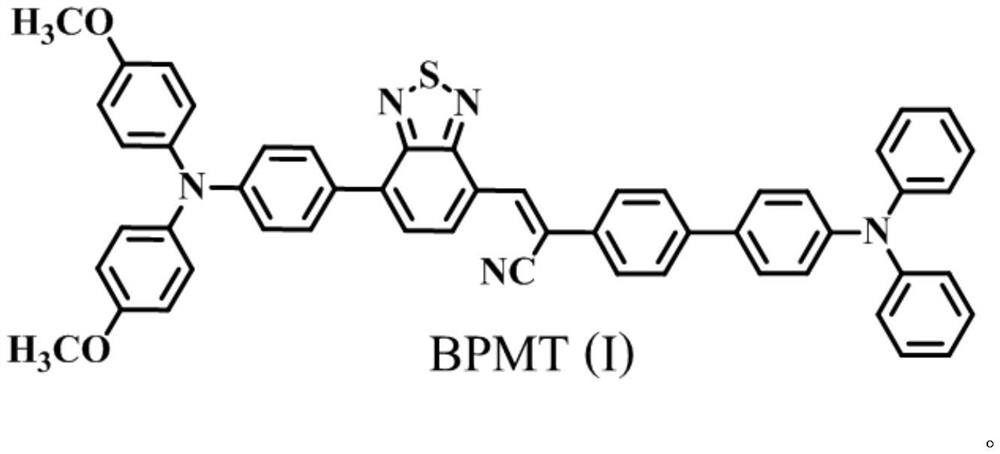
The invention discloses a high-efficiency organic near-infrared fluorescent material and its preparation and application. The material has a structure shown in formula (I), the maximum fluorescence emission peak is 701nm, and the absolute quantum efficiency is 48.7%. The material prepared by the material Near-infrared fluorescent polymer hemisphere, which can generate near-infrared laser at 735.2nm, and has a low threshold of 22.3kW·cm ‑2 And narrow half-width characteristics, can be used in flaw detection, medical imaging and other fields.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
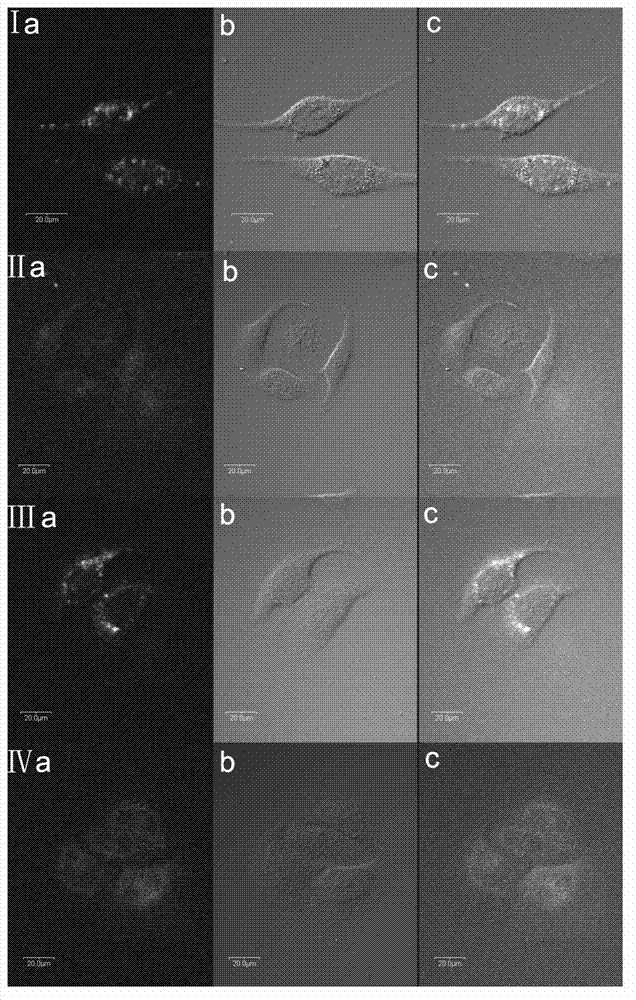
Mn (II) complex with AIE property and function of targeting living cell mitochondria as well as preparation method and application of Mn (II) complex
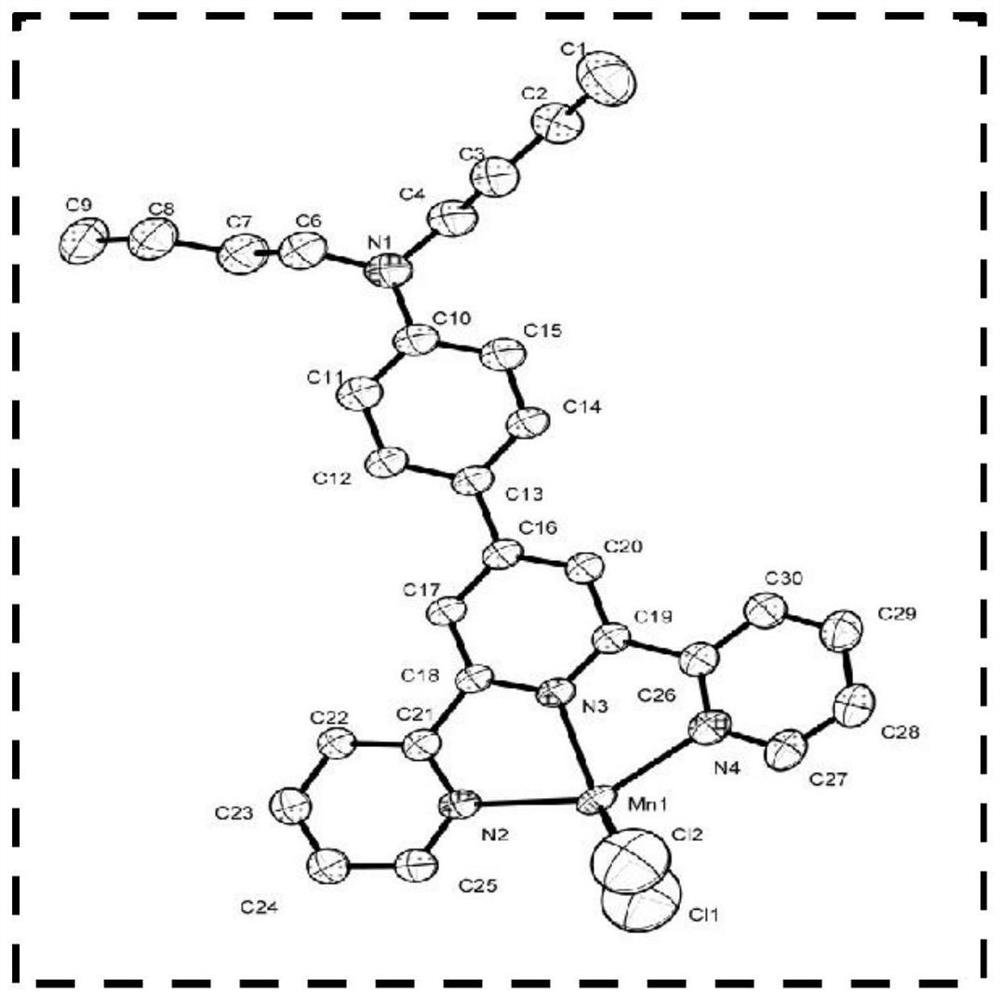
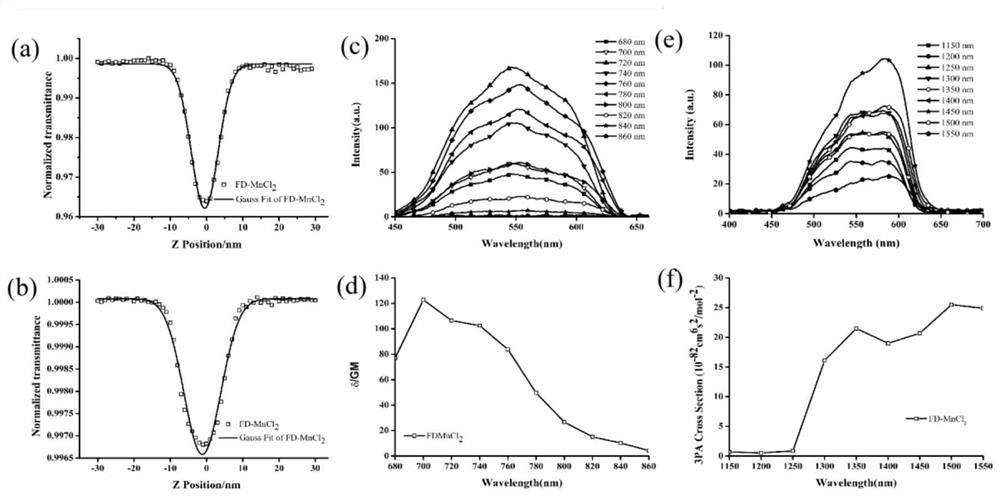
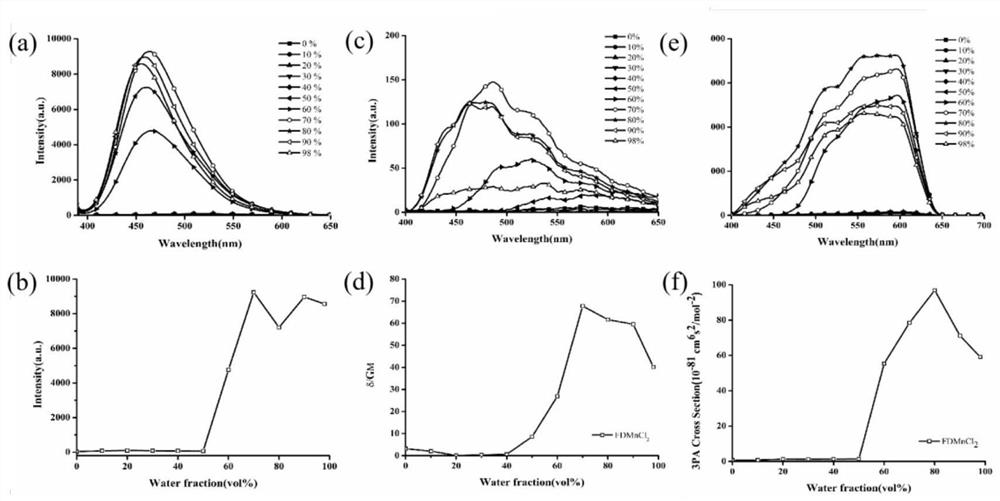
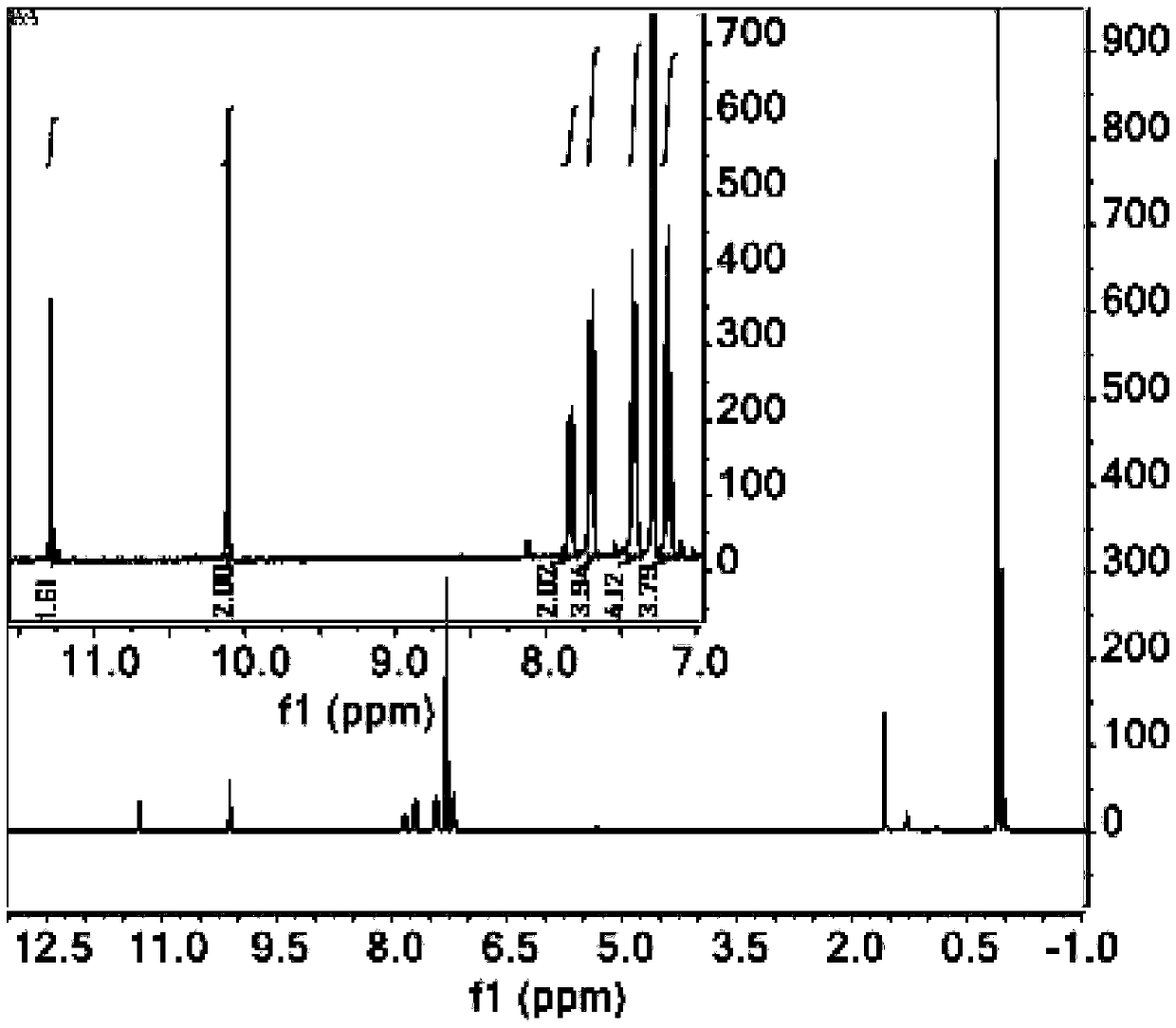
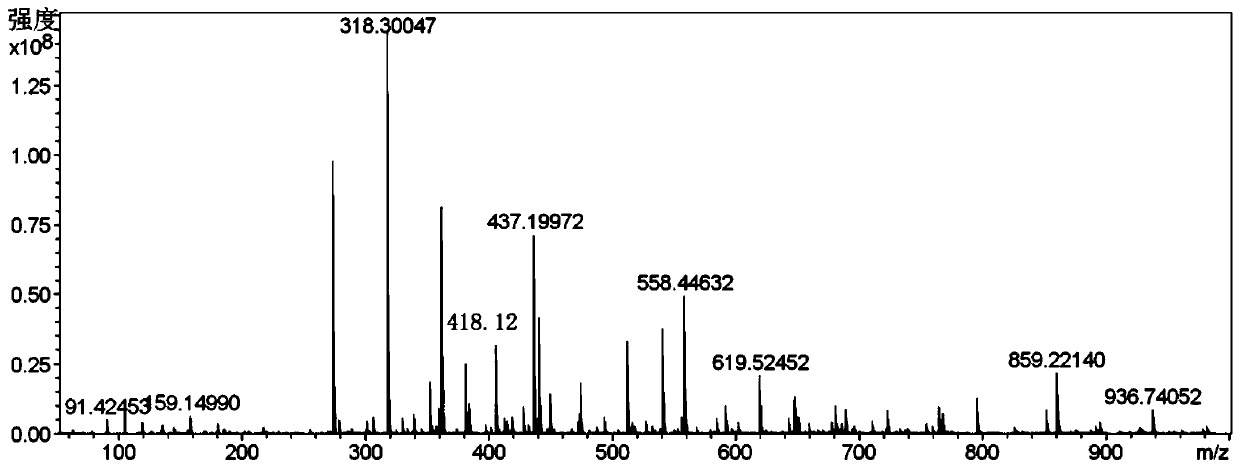
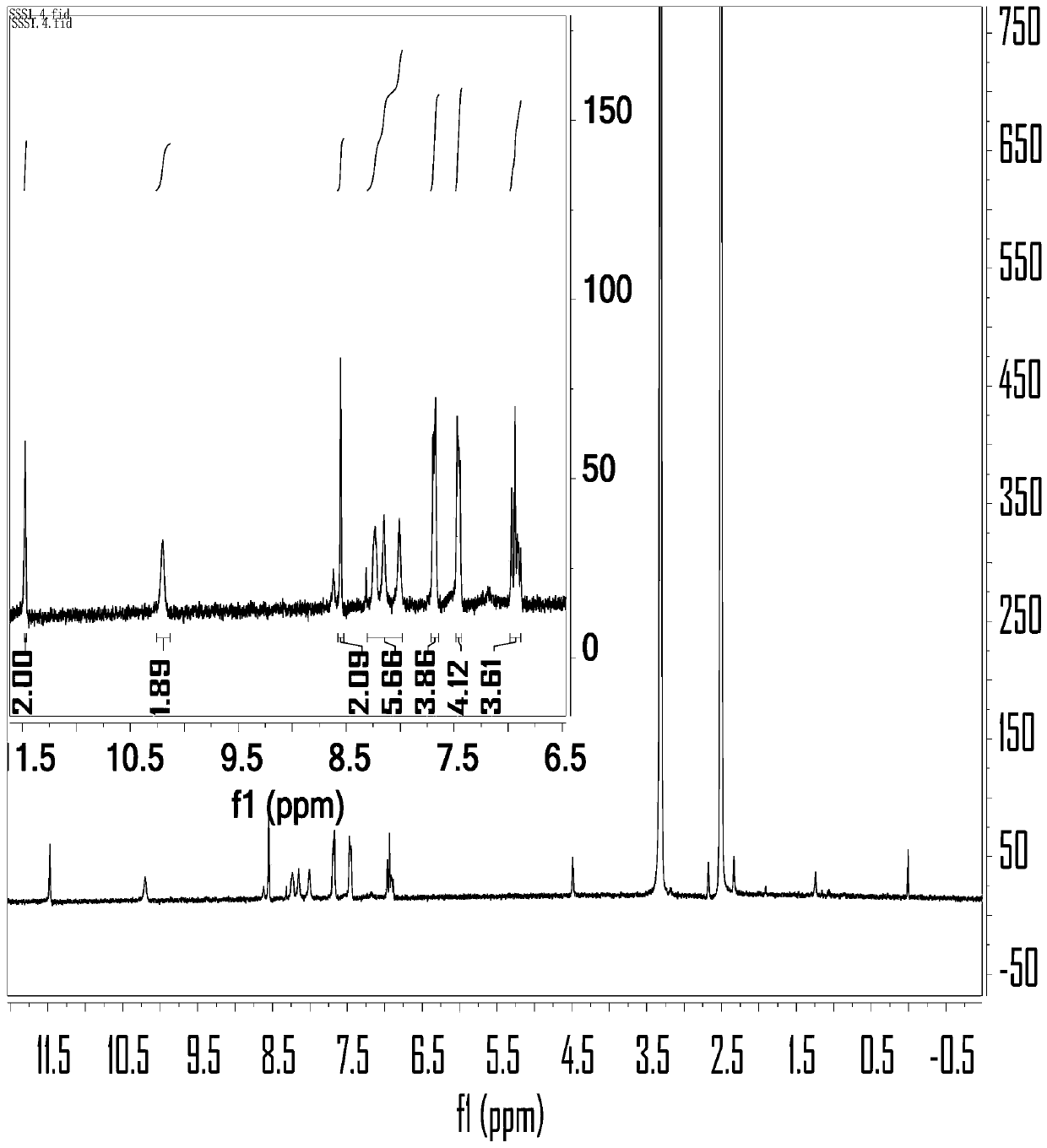
PendingCN113201018ABig Three Photon Absorption Cross SectionLow excitation energyFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsLong wavelengthBiophysics
The invention discloses a Mn (II) complex with AIE property and a function of targeting living cell mitochondria as well as a preparation method and application of the Mn (II) complex, and relates to the technical field of multiphoton absorption materials. The Mn (II) complex is called FD-MnCl2 for short, and the structural formula is shown in the specification. The novel terpyridyl Mn (II) complex synthesized by the invention is a multi-photon absorption material with a cell developing function. Compared with other materials, the complex has the characteristics of large three-photon absorption cross section, low excitation energy, long wavelength, strong penetrability, small light damage and the like. The complex can be used for multi-photon biological imaging, and has obvious application value.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Anthracene-thiosemicarbazide derivative, preparation method thereof and application of derivative as fluorescent probe
ActiveCN110283110AIncrease penetration depthEliminate background fluorescenceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAnthraceneOrganic solvent
The invention discloses an anthracene-thiosemicarbazide derivative, a preparation method thereof and application of the derivative as a fluorescent probe. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde reacts with 9,10-diborate anthracene in a nitrogen atmosphere and in an organic solvent to obtain an intermediate product I; and then the intermediate product I reacts with thiosemicarbazide to obtain a copper ion fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe of the invention has efficient up-conversion and down-conversion fluorescence quenching response recognition characteristics of copper ions.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-photon and two-photon homocysteine fluorescent probes and use thereof
InactiveCN102127055BLow priceLow excitation energyOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCarbazoleFluorescent imaging
The invention discloses single-photon and two-photon homocysteine fluorescent probes, which are carbazole and pyridine aldehyde compounds. The general formula of the carbazole and pyridine aldehyde compounds is represented by (I), wherein R may be alkyl or hydroxyalkyl. The invention also discloses the use of the fluorescent probes in the observation of the expression and distribution of homocysteine in living cells. The probes have the characteristics of wide application range, low price and specific fluorescently imaging homocysteine in living cells.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
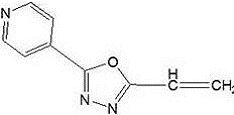
A kind of pyridyl-containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole water-soluble fluorescent polymer and its synthesis method
ActiveCN111072842BLow excitation energySimple processOrganic chemistryScale removal and water softeningDouble bondPhotochemistry
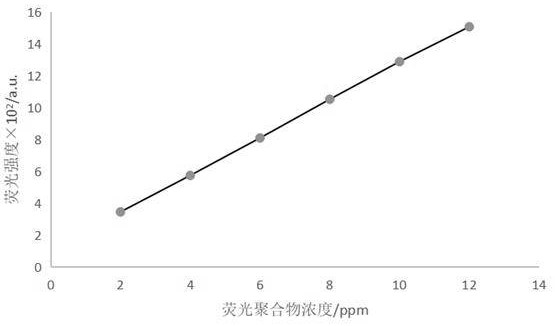
The invention discloses a water-soluble fluorescent polymer containing pyridyl 1,3,4-oxadiazole and a synthesis method thereof, which specifically includes: (1) acrylic acid and 4-formylhydrazide pyridine in a dry phosphorus oxychloride environment In the system, negative pressure heating and reflux reaction for 5-6 hours to obtain fluorescent monomers; (2) Initiate polymerization of the synthesized fluorescent monomers, acrylic acid and maleic anhydride aqueous solution to synthesize water-soluble fluorescent monomers with a viscosity average molecular weight of 5000-10000 Label the aqueous solution of acrylic-maleic acid copolymer. The present invention utilizes unsaturated carboxylic acid containing carbon-carbon double bond and formic hydrazide of 1,3,4-oxadiazole containing pyridyl group to synthesize fluorescent monomer containing unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond, and further polymerizes into water-soluble fluorescent monomer Labeled copolymer; the method is simple and easy to operate, has low excitation energy, good concentration fluorescence linearity, mild reaction conditions, safe and environmentally friendly synthesis process, and is easy to realize large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG TAIHE WATER TREATMENT TECH CO LTD
Terpyridyl complex two-photon material with cell development and preparation
InactiveCN101475581BLight damage is smallEnhanced two-photon absorption cross sectionIn-vivo testing preparationsZinc organic compoundsTwo-photon absorptionNon toxicity
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Rare earth compound two-photon absorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102093398BEasy to manufactureHigh fluorescence quantum yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsTwo-photon absorptionConfocal
The invention relates to a rare earth compound two-photon absorption material, which uses Eu(III) as a metal center and contains a complex of a structural formula below. The complex has a living cell two-photon absorption fluorographic characteristic and can be used for living cell fluorescence microscopy imaging.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivatives and their applications
ActiveCN110229165BEasy to prepareSimple purification methodOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesMercuric ion
The invention discloses an up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing a reaction on rhodamine B and ethylenediamine in a nitrogen gas atmosphere and an organic solvent to obtain rhodamine-ethylenediamine; and performing a reaction on the rhodamine-ethylenediamine and phenyl isothiocyanate to obtain the up-convertion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative. The up-conversion fluorescent probe rhodamine derivative provided by the invention has the high-efficiency down-conversion fluorescence-enhanced response recognition characteristics for mercury ions and has the high-efficiency up-conversion fluorescence-enhanced response recognition characteristics for the mercury ions when used as a fluorescent probe.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A membrane-permeable dye with a large two-photon fluorescence active cross-section and its application
InactiveCN105153733BLarge two-photon fluorescence active cross sectionLow priceStyryl dyesOrganic chemistryChemical structureCell membrane
The invention discloses membrane permeability dye with a large two-photon fluorescence active cross section. The dye adopts triphenylamine heterocyclic chemical compounds, and the chemical structure of the dye is shown in the formula (I). The invention further discloses an application of the dye in displaying two-photon imaging of cytoplasm in a living cell. Experiments show that the dye has characteristics of larger two-photon fluorescence active absorption cross section, excellent cell membrane permeability, low toxicity and the like, also has the characteristics of wide application range, low price and good bio-compatibility with known probe DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) and has wide application prospect in the field of laser excitation fluorescence biomarkers.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
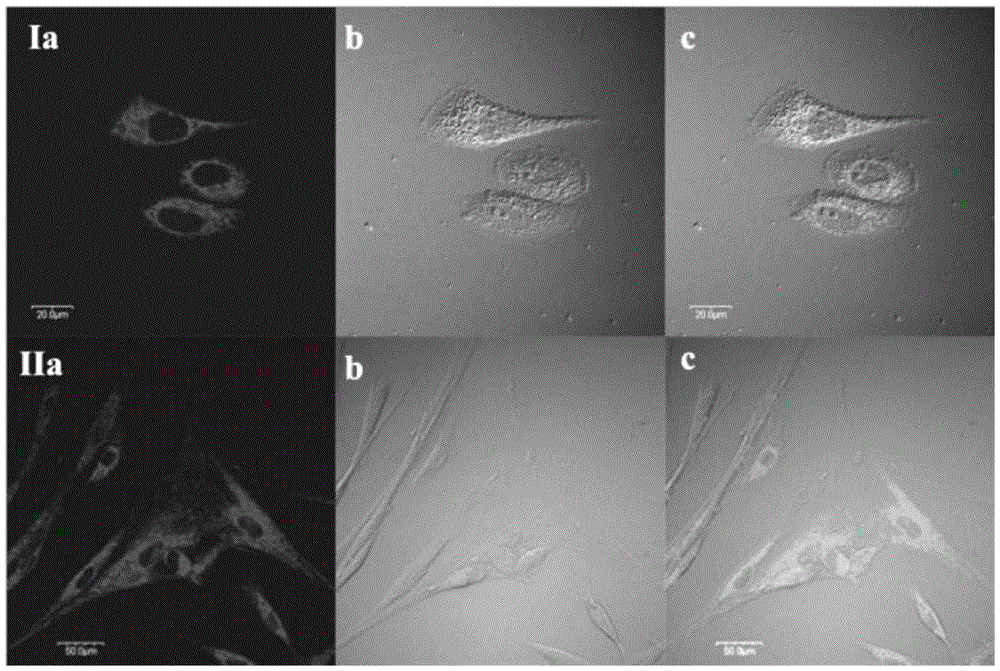
A rotor-type double-red mitochondrial fluorescent probe and its application
InactiveCN105062467BLarge absorption cross sectionLow priceOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementJulolidineBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a rotor-type two-photon mitochondrion fluorescence probe. The probe has a chemical name of 4-(2-(8-hydroxy-julolidine) vinyl)-1-picoline iodate, and a chemical structural formula as shown in a formula (I). Experiments prove that the probe is a novel fluorescence probe for selectively marking mitochondria of immortalized living cells (SiHa and HeLa cells) and normal living cells (HUVEC, BMSC and MC3T3-E1 cells). The probe is applicable to a TPM infrared excitation source and multiple laser wavelengths (458nm, 488nm, 514nm, 543nm and 561nm) of LSM. Compared with existing mitochondrion fluorescence probes with similar functions, the probe has the characteristics of low price, good two-photon performance, low excitation energy, good light stability and good biocompatibility, and has a great application value in the field of laser excited fluorescence biomarkers.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/92d21263-8c84-40ad-8565-dbd39a6fd1e3/US20160126463A1-20160505-D00000.PNG)
![Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/92d21263-8c84-40ad-8565-dbd39a6fd1e3/US20160126463A1-20160505-D00001.PNG)
![Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a] Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/92d21263-8c84-40ad-8565-dbd39a6fd1e3/US20160126463A1-20160505-D00002.PNG)








![Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bc02e739-7c5b-4d86-bb5d-3dd3328f6635/US10236448-D00001.png)
![Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bc02e739-7c5b-4d86-bb5d-3dd3328f6635/US10236448-D00002.png)
![Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device Benzo[a] anthracene compound, light-emitting element, display device, electronic device, and lighting device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bc02e739-7c5b-4d86-bb5d-3dd3328f6635/US10236448-D00003.png)
![Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/56db2831-33ab-4f60-b71c-31c522d9ede0/US20190214567A1-D00001.png)
![Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/56db2831-33ab-4f60-b71c-31c522d9ede0/US20190214567A1-D00002.png)
![Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device Benzo[a]Anthracene Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/56db2831-33ab-4f60-b71c-31c522d9ede0/US20190214567A1-D00003.png)