Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
461results about "Pyroligneous acid production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
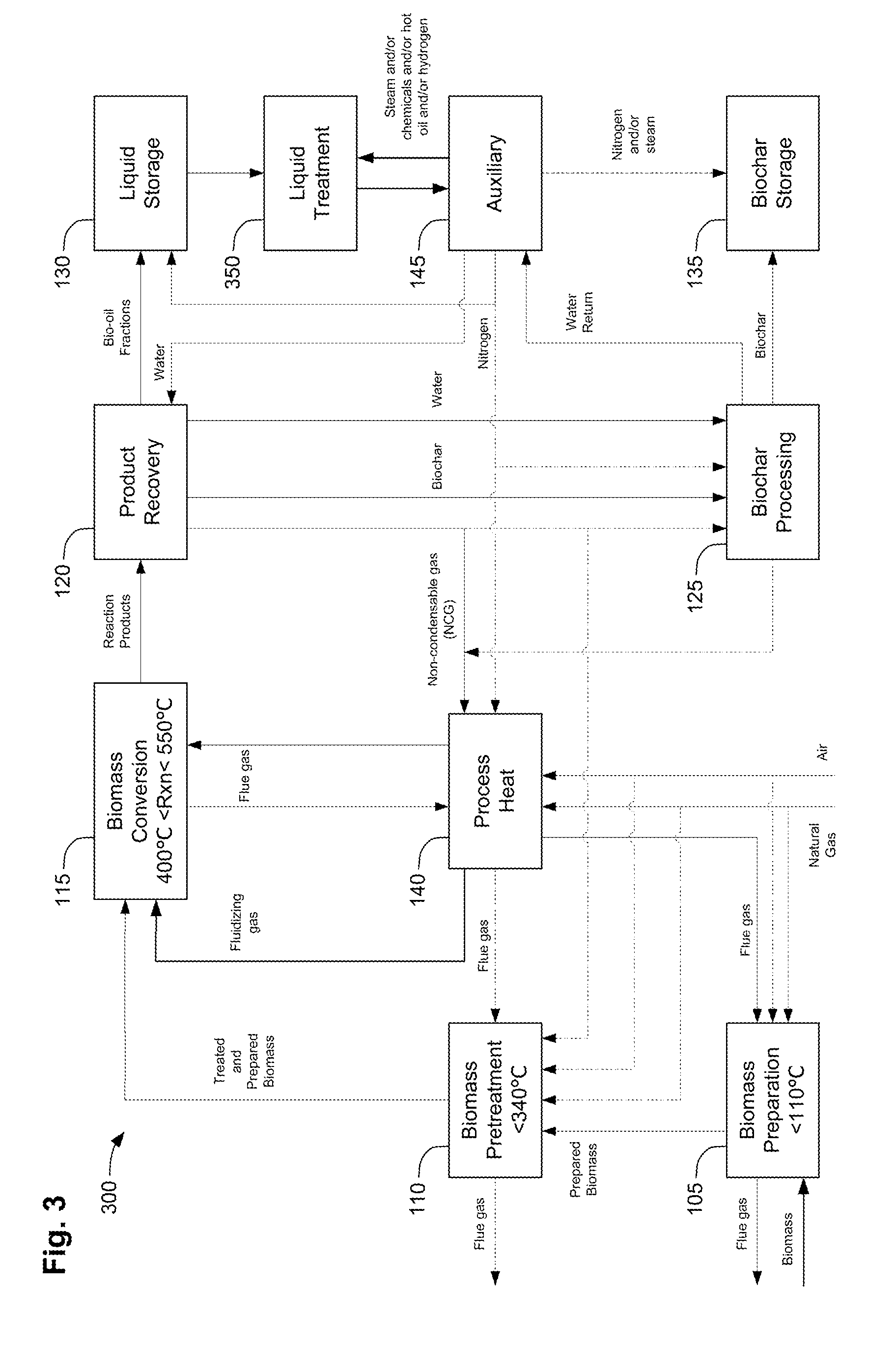
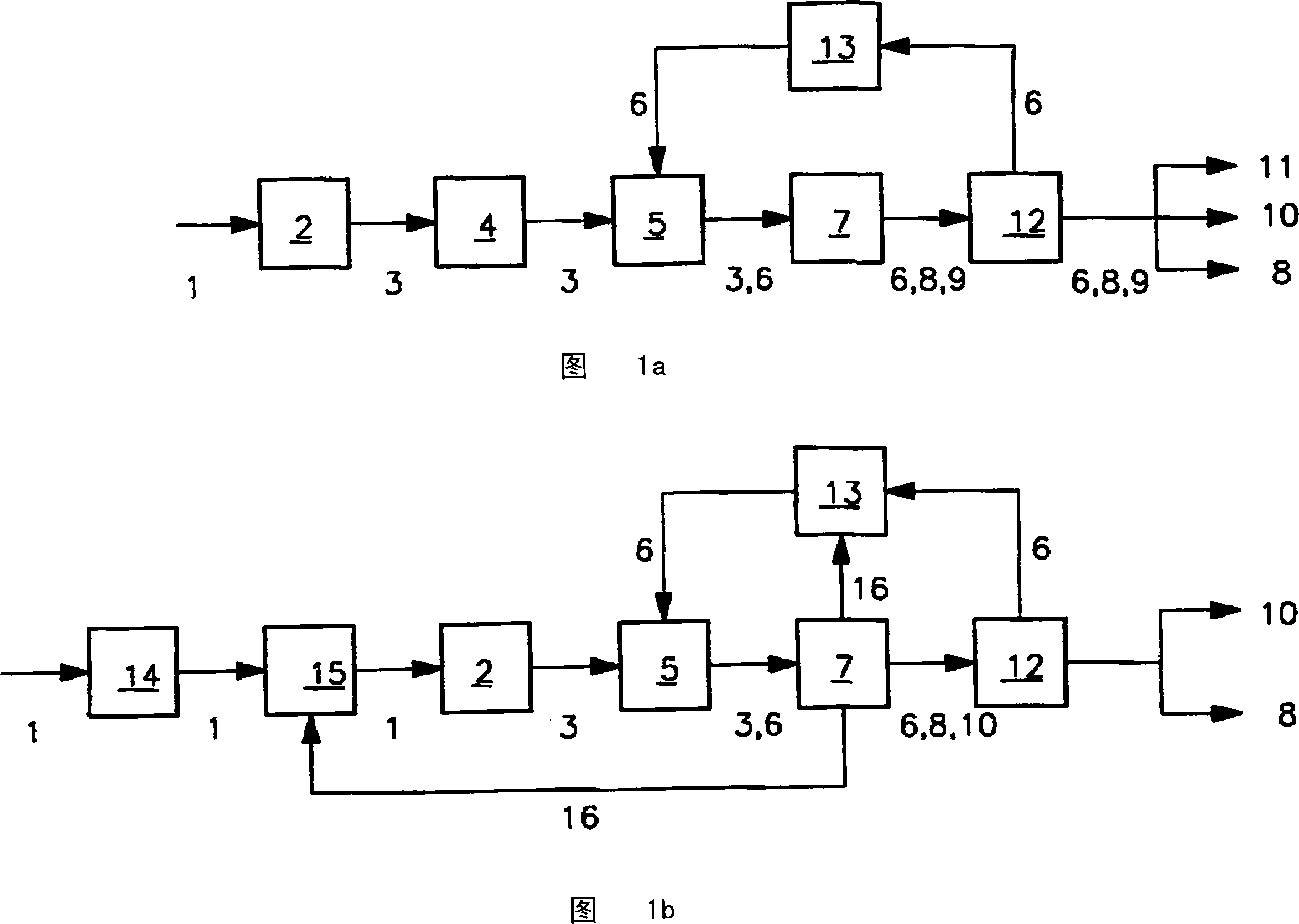
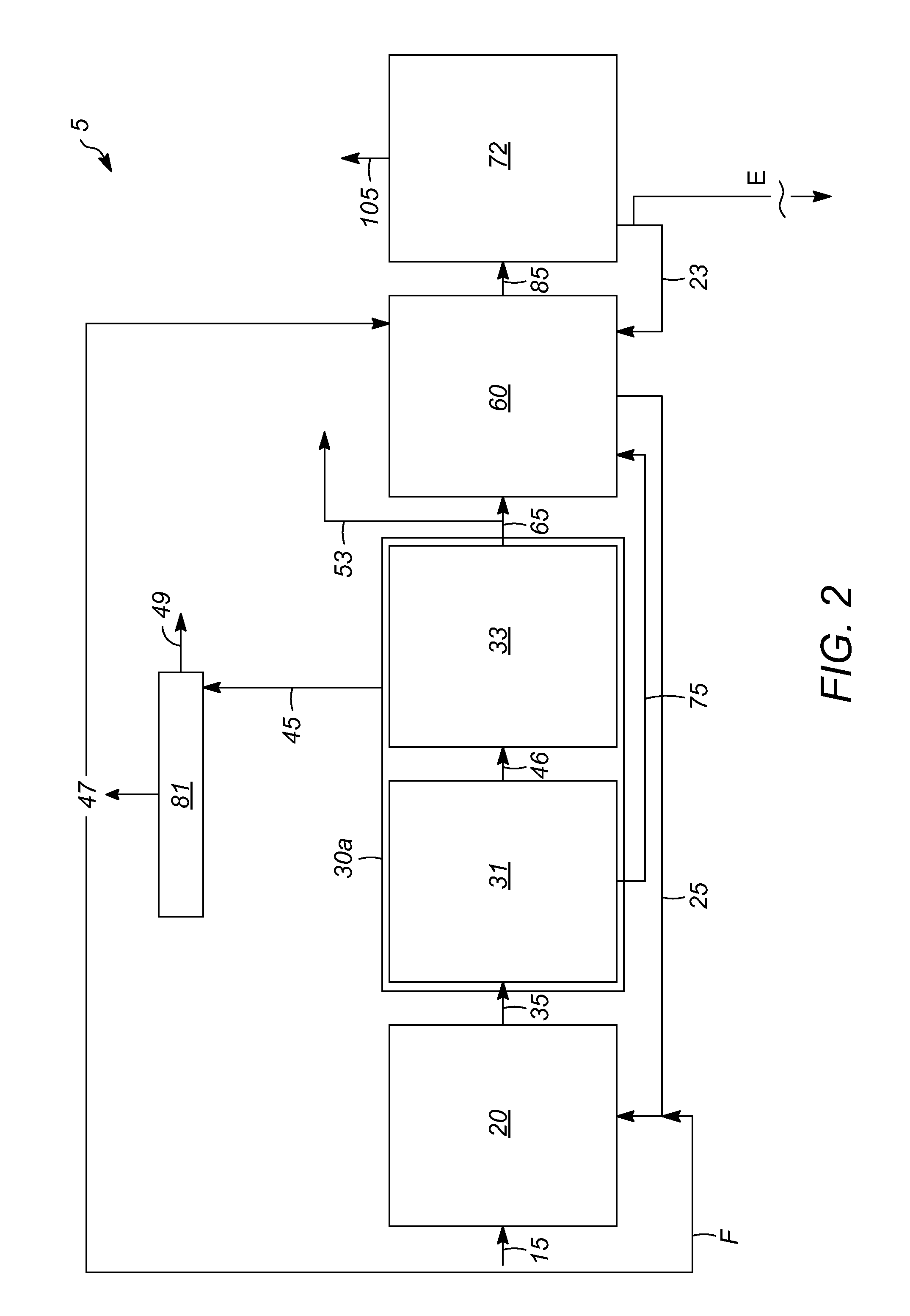
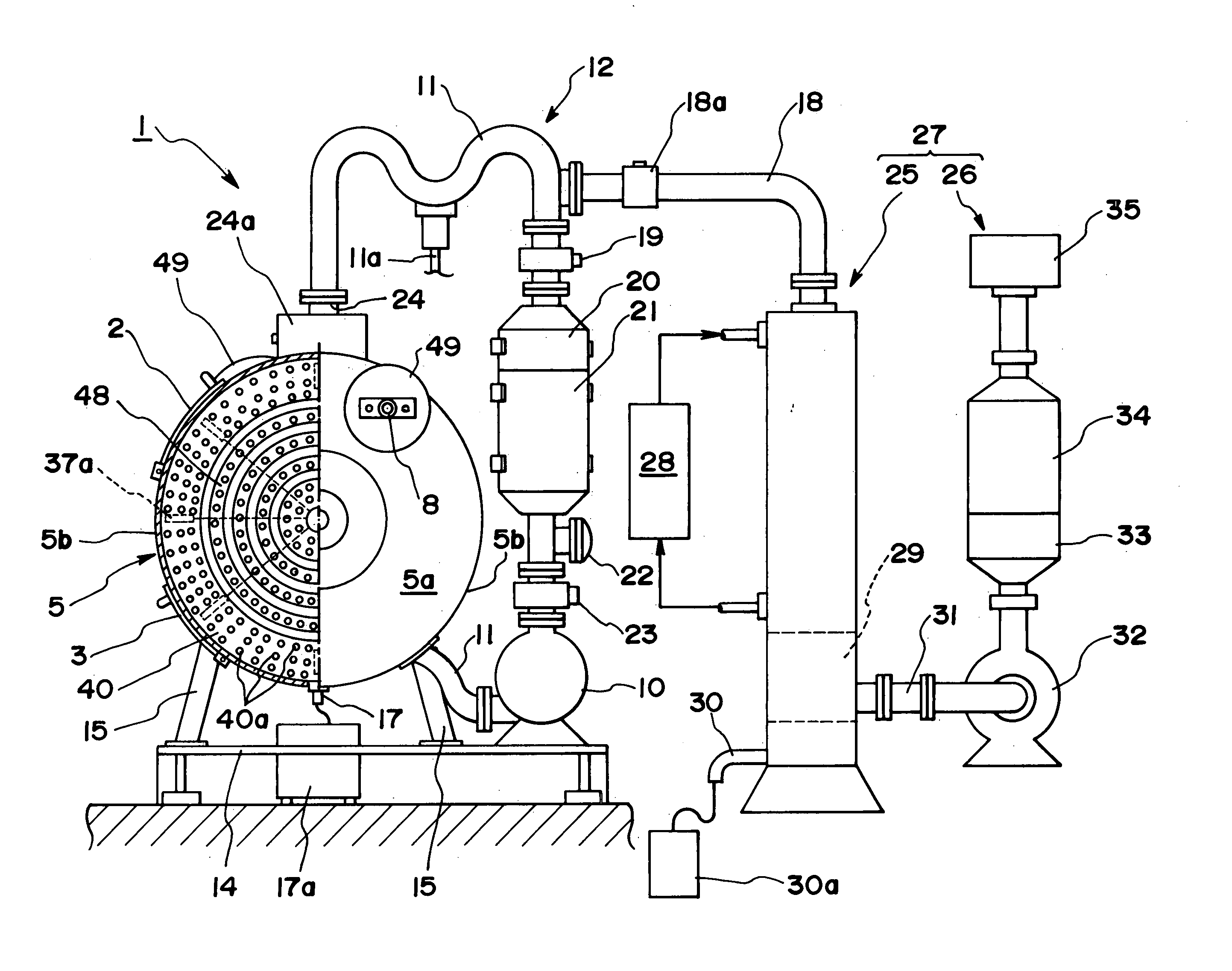
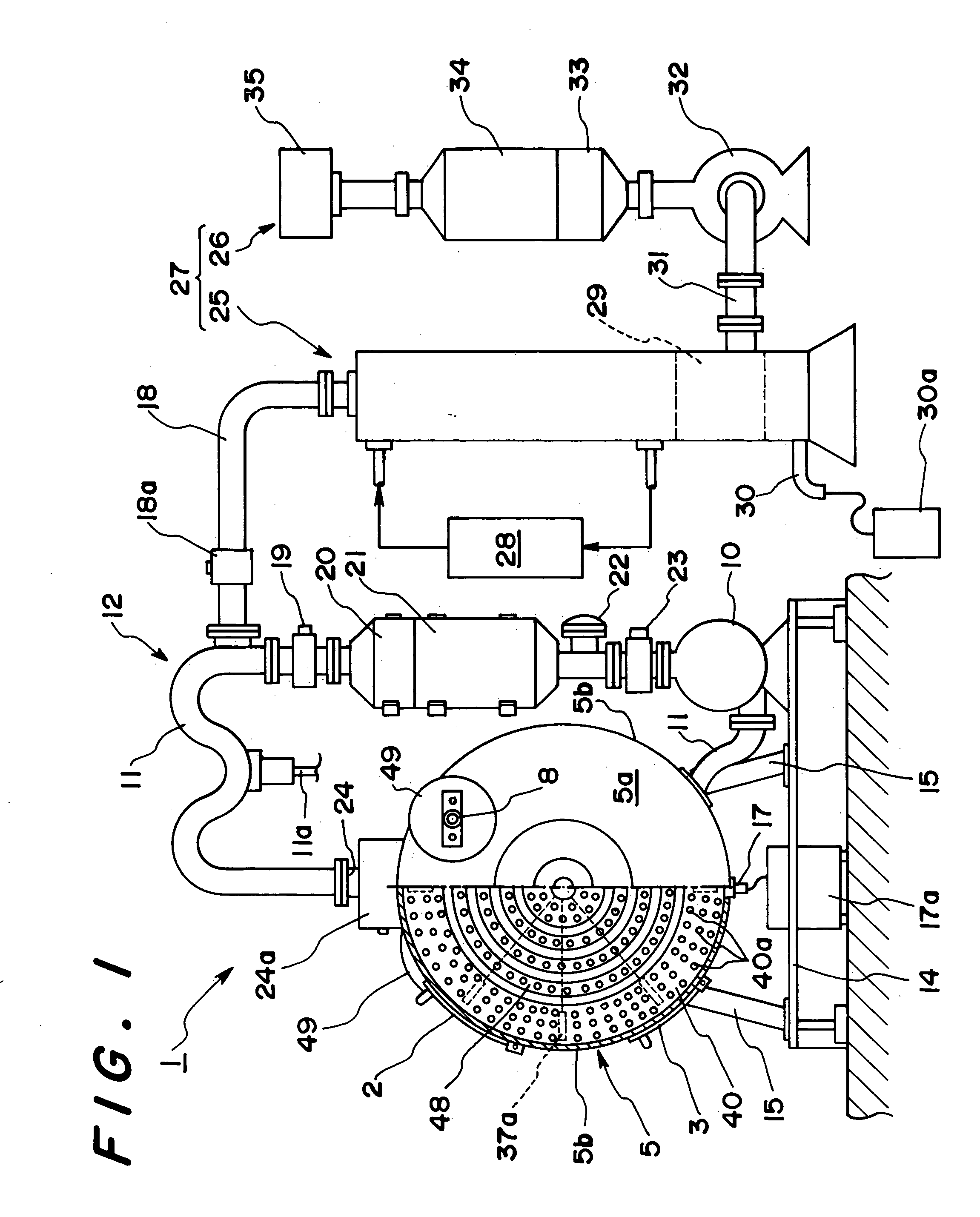
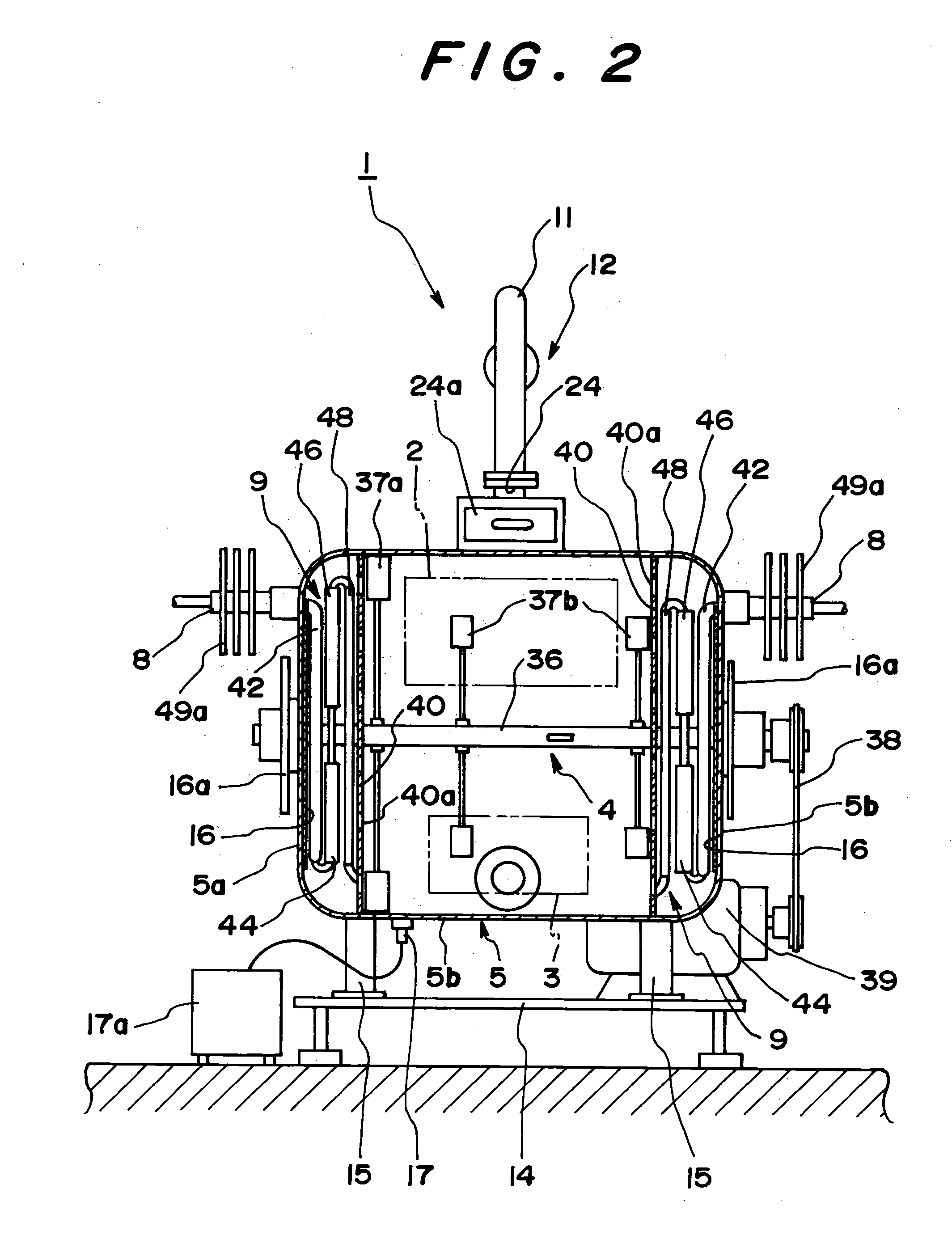
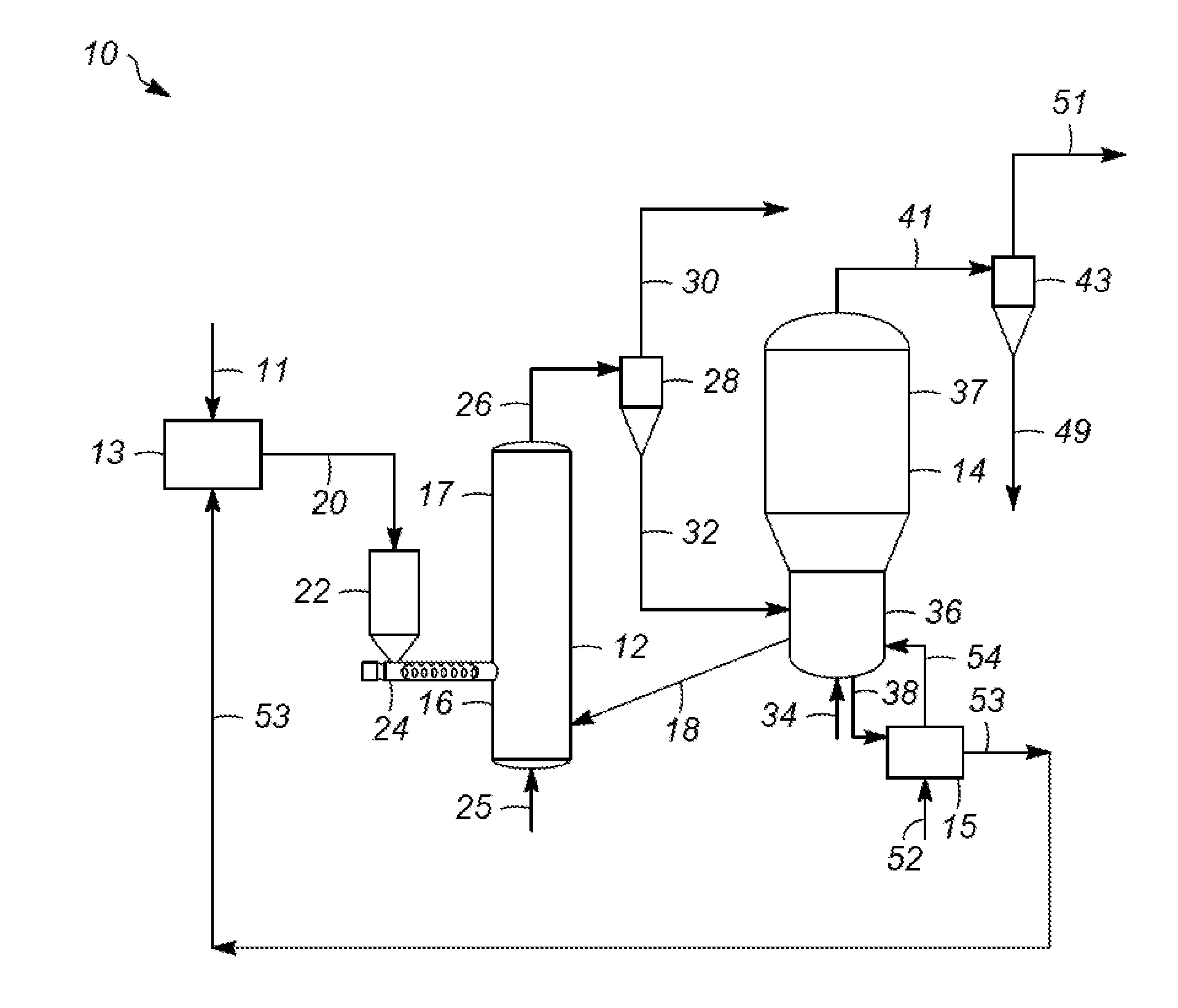
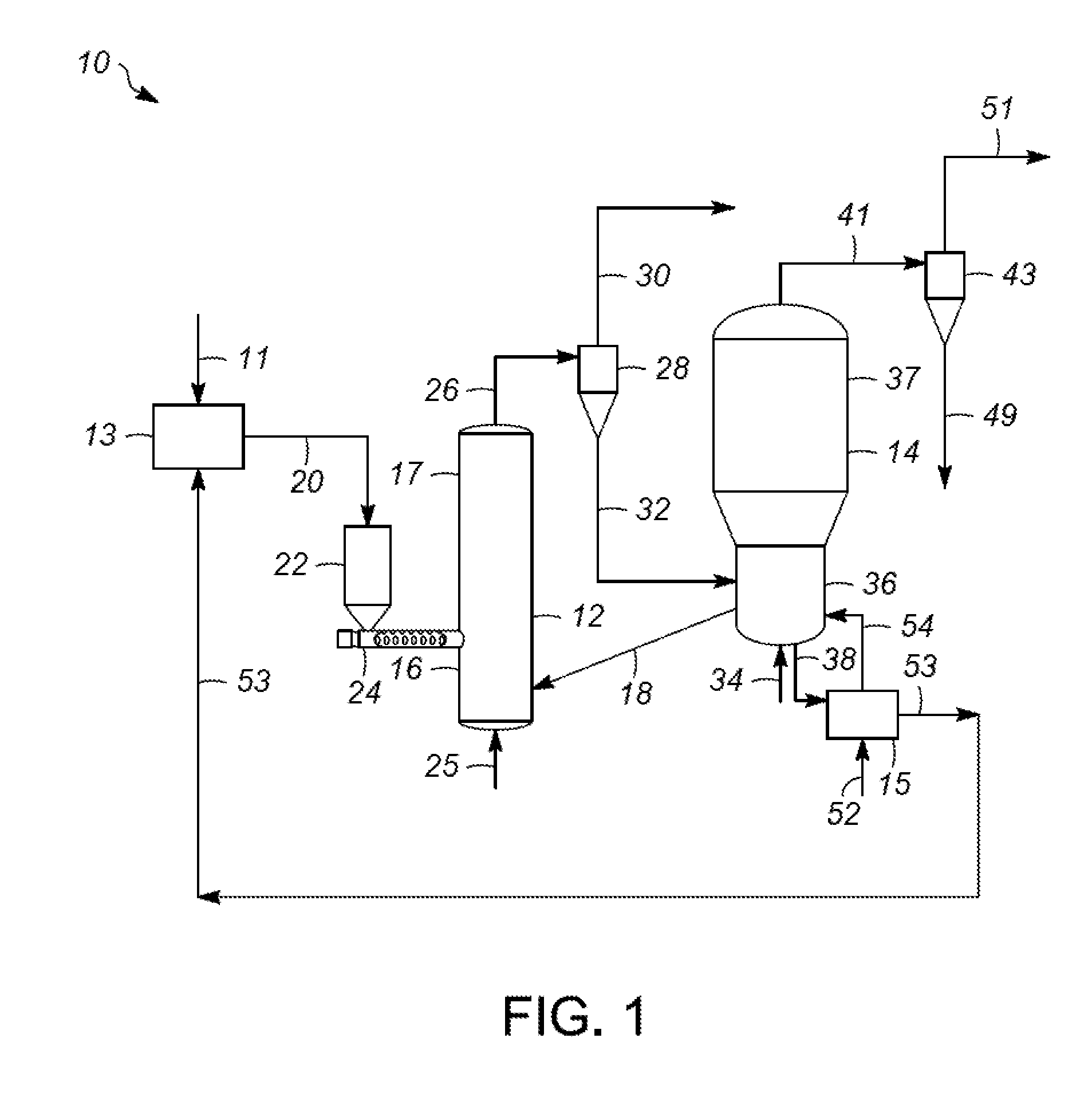
Biomass fast pyrolysis system utilizing non-circulating riser reactor
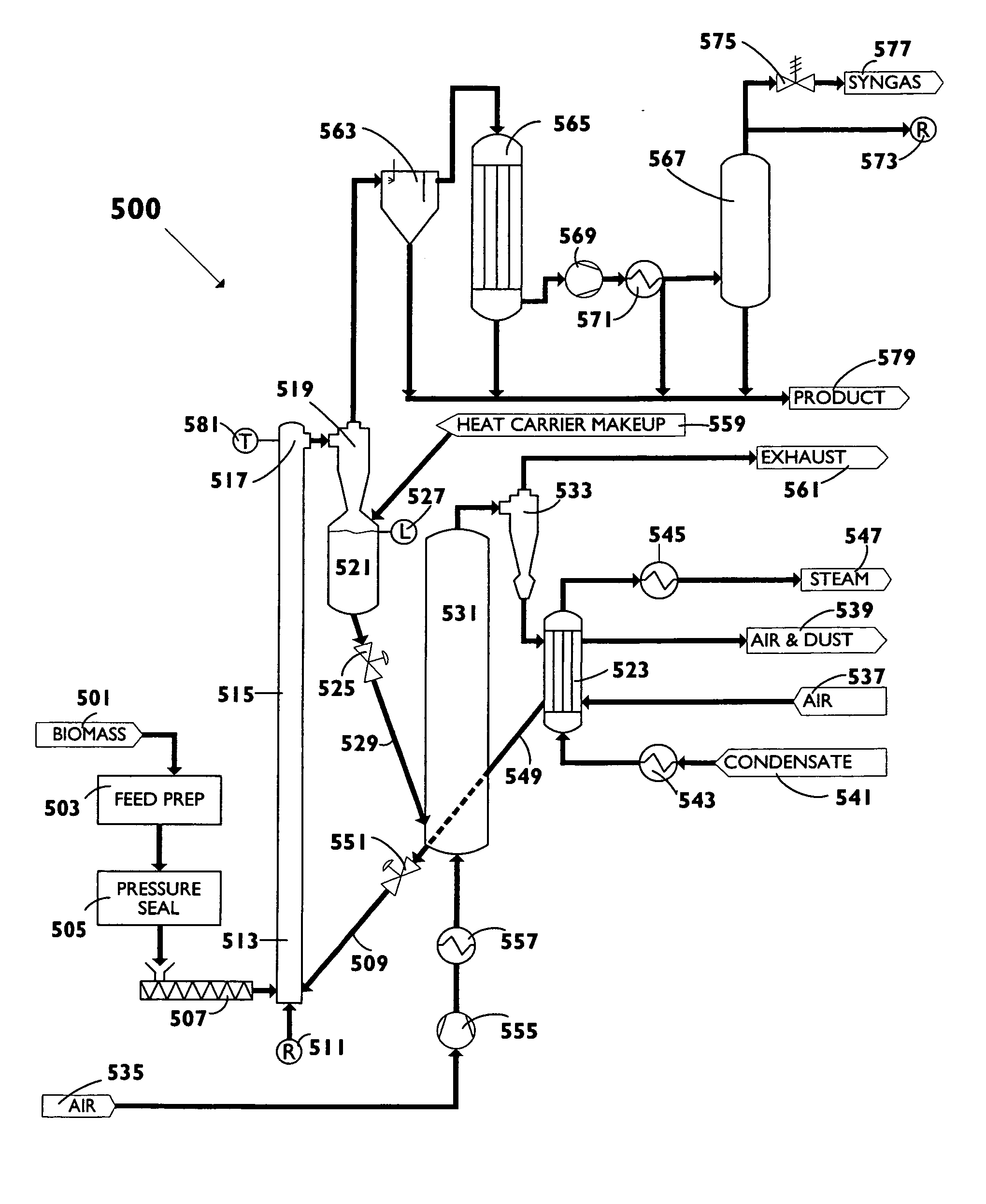
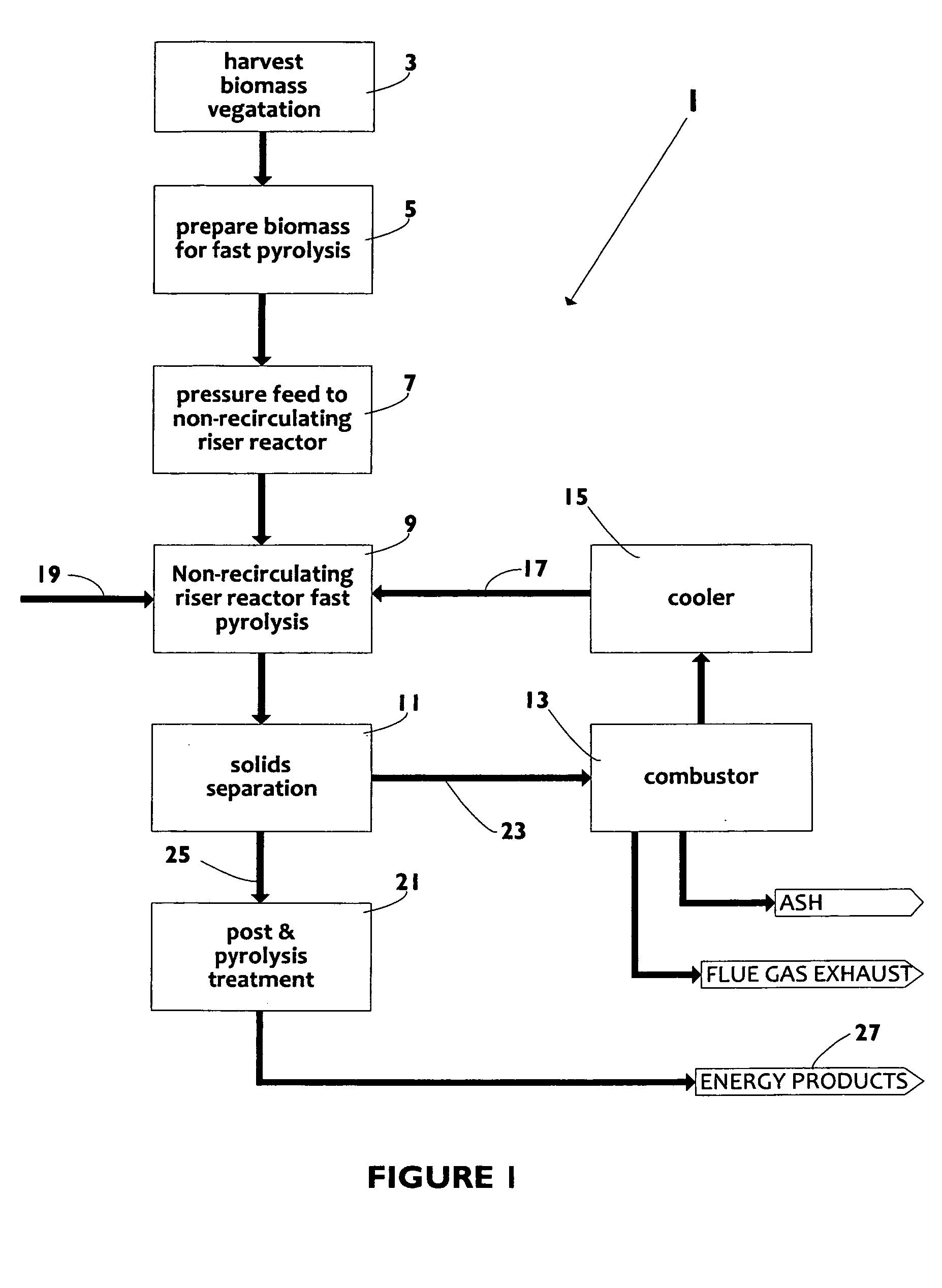
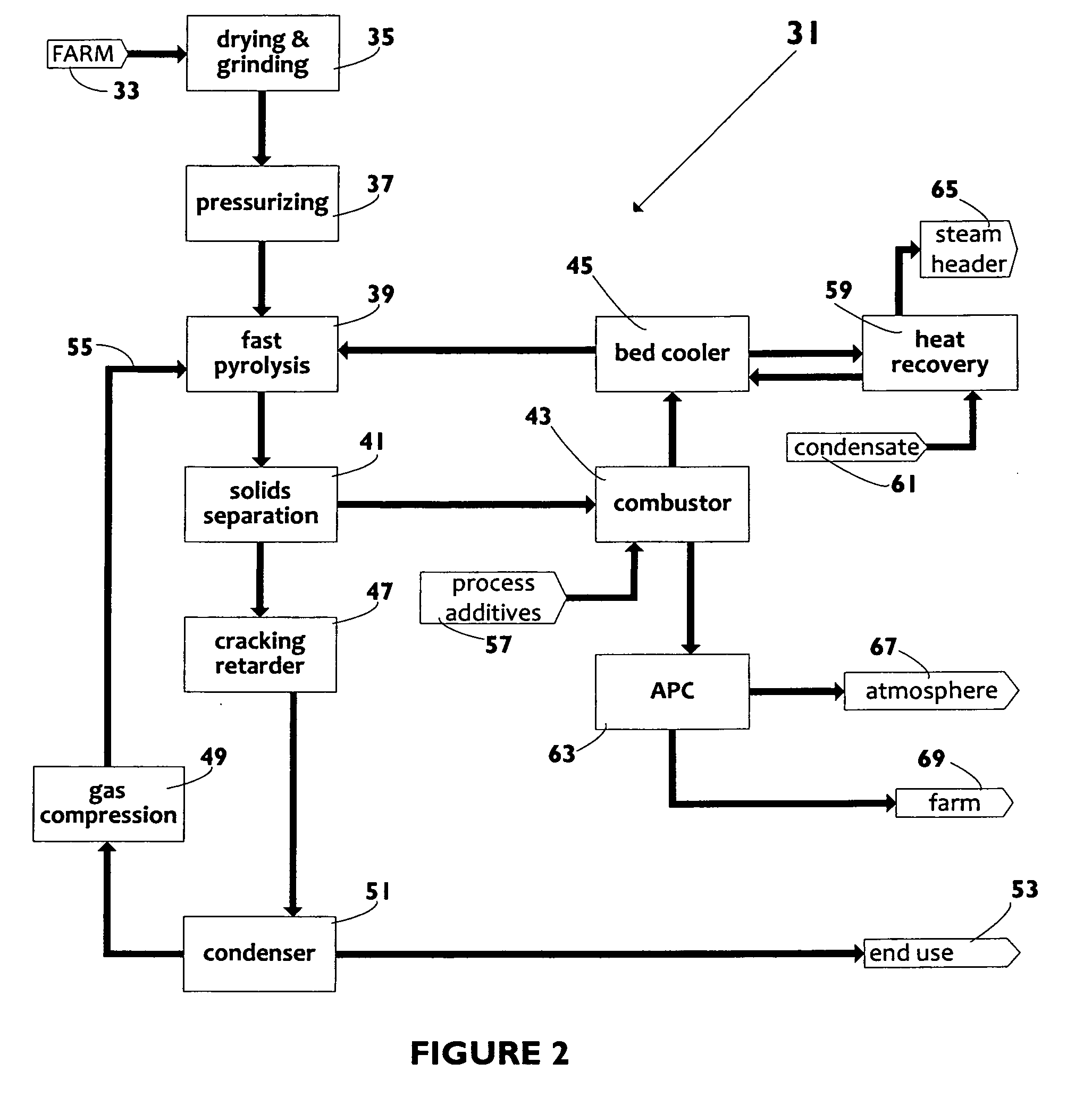
A biomass fast pyrolysis system for conversion of biomass vegetation to synthetic gas and liquid fuels includes: a) a non-circulating riser reactor for pyrolysis of biomass vegetation feedstock utilizing a heat carrier, the non-circulating riser reactor being physically structured and adapted to have a rate of reaction of at least 8,000 biomass vegetation feedstock lbs / hr / ft2, utilizing a ratio of heat carrier to biomass vegetation feedstock of about 7:1 to about 11.5:1, the riser reactor having a base input region at its bottom, a central reaction region and an output region at its top, the riser reactor including a cyclone disengager at its output region for separation of pyrolysis resulting char and heat carrier from the pyrolysis product gases, the cyclone disengager having an output downcomer and an output upcomer, the cyclone disengager output downcomer being connected to and feeding into a side combustor unit, the riser reactor being a non-circulating riser reactor in that the heat carrier is not returned directly to the riser reactor from the cyclone disengager and travels first down the cyclone disengager output downcomer to the side combustor unit; and, b) the side combustor unit for combusting pyrolysis resultant char and reheating the heat carrier the side combustor having a heat carrier downcomer connected to the base input region of the riser reactor.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENERGY GLOBAL
Fractional catalytic pyrolysis of biomass
ActiveUS20090165378A1Eliminate needBiofuelsIndirect heating destructive distillationCatalytic pyrolysisReactive gas
Methods for fractional catalytic pyrolysis which allow for conversion of biomass into a slate of desired products without the need for post-pyrolysis separation are described. The methods involve use of a fluid catalytic bed which is maintained at a suitable pyrolysis temperature. Biomass is added to the catalytic bed, preferably while entrained in a non-reactive gas such as nitrogen, causing the biomass to become pyrolyzed and forming the desired products in vapor and gas forms, allowing the desired products to be easily separated.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods for integrated fast pyrolysis processing of biomass
ActiveUS20110258914A1Improve collection efficiencyMinimizes water contentDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsPre treatmentSafe handling
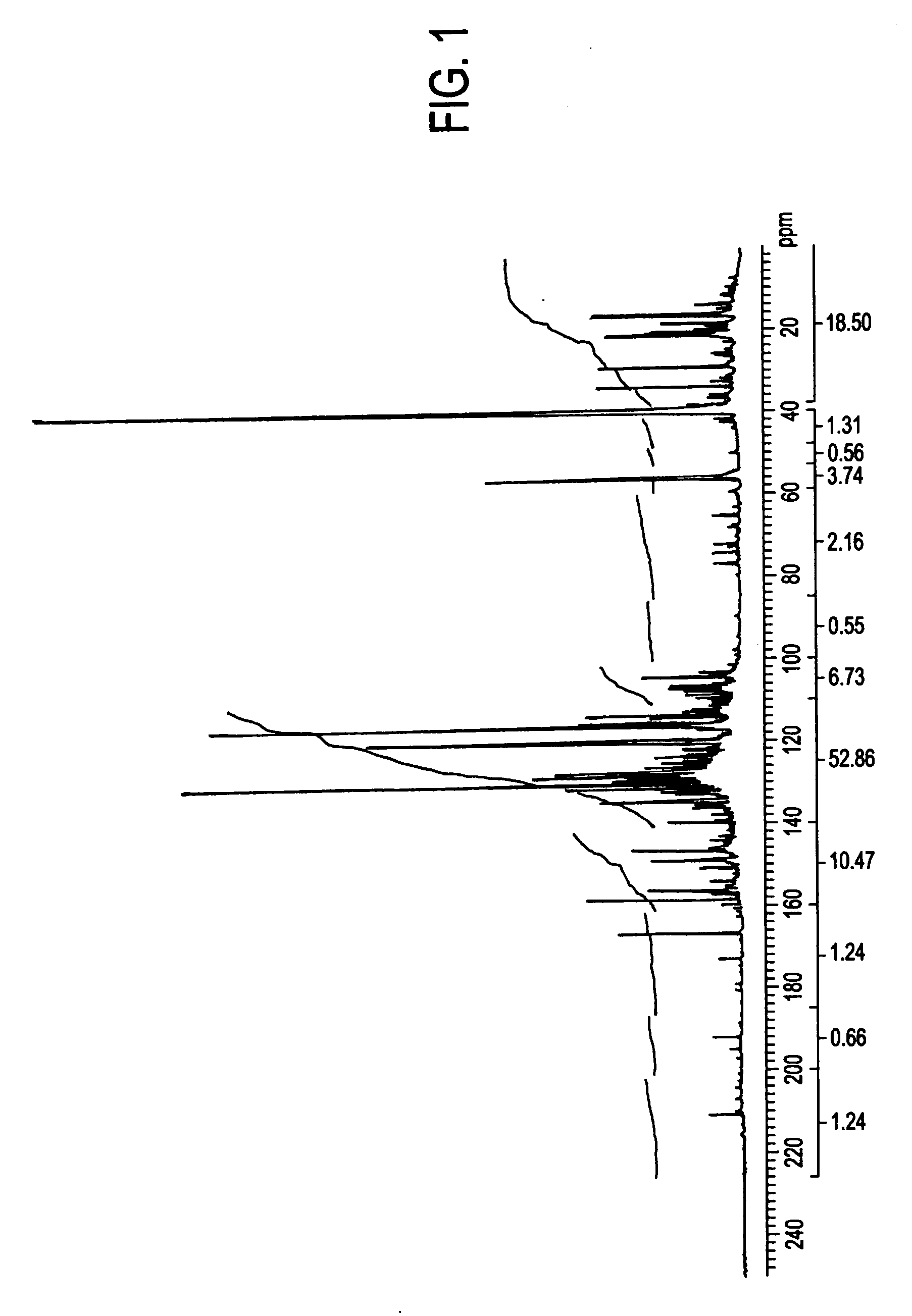
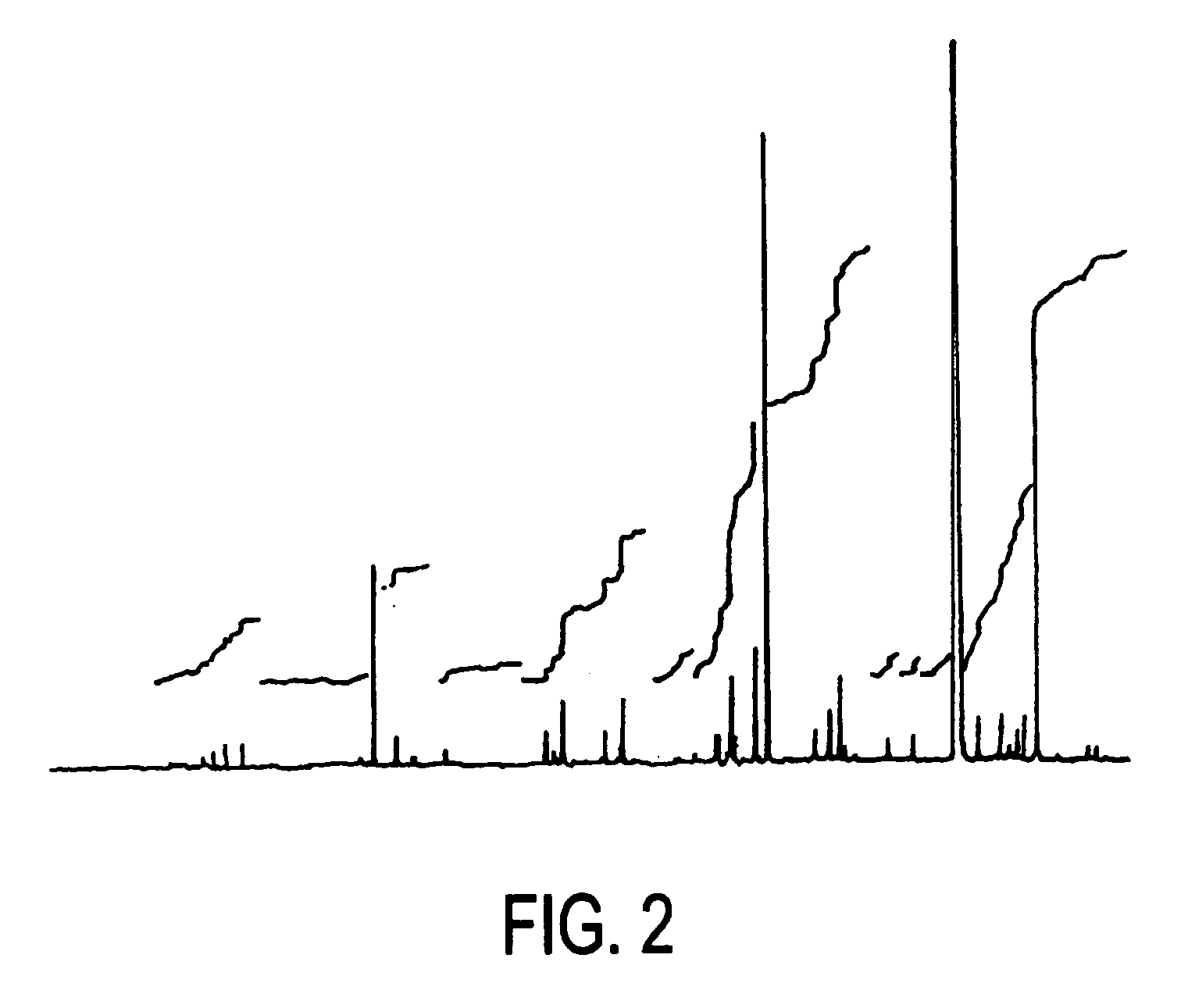
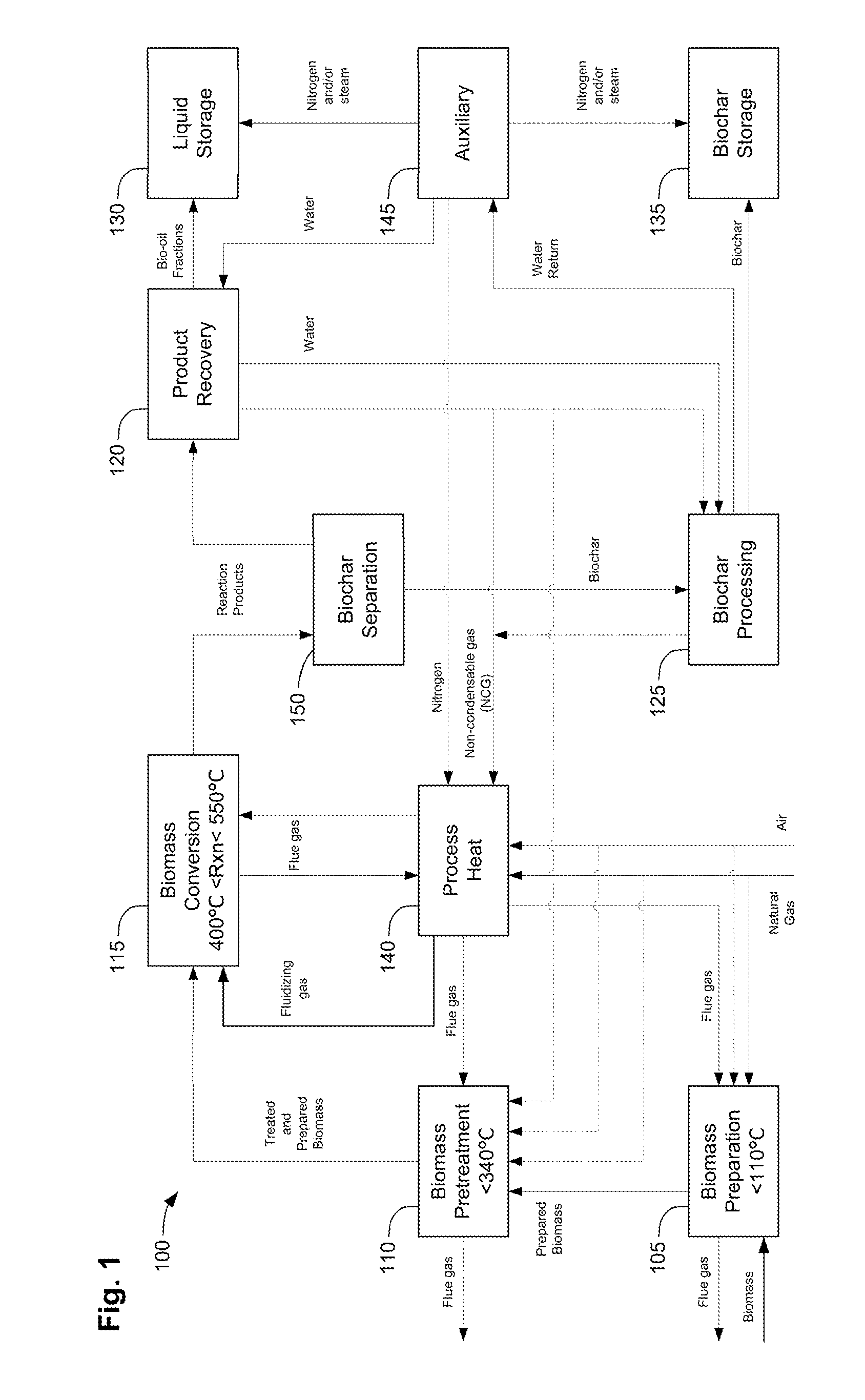
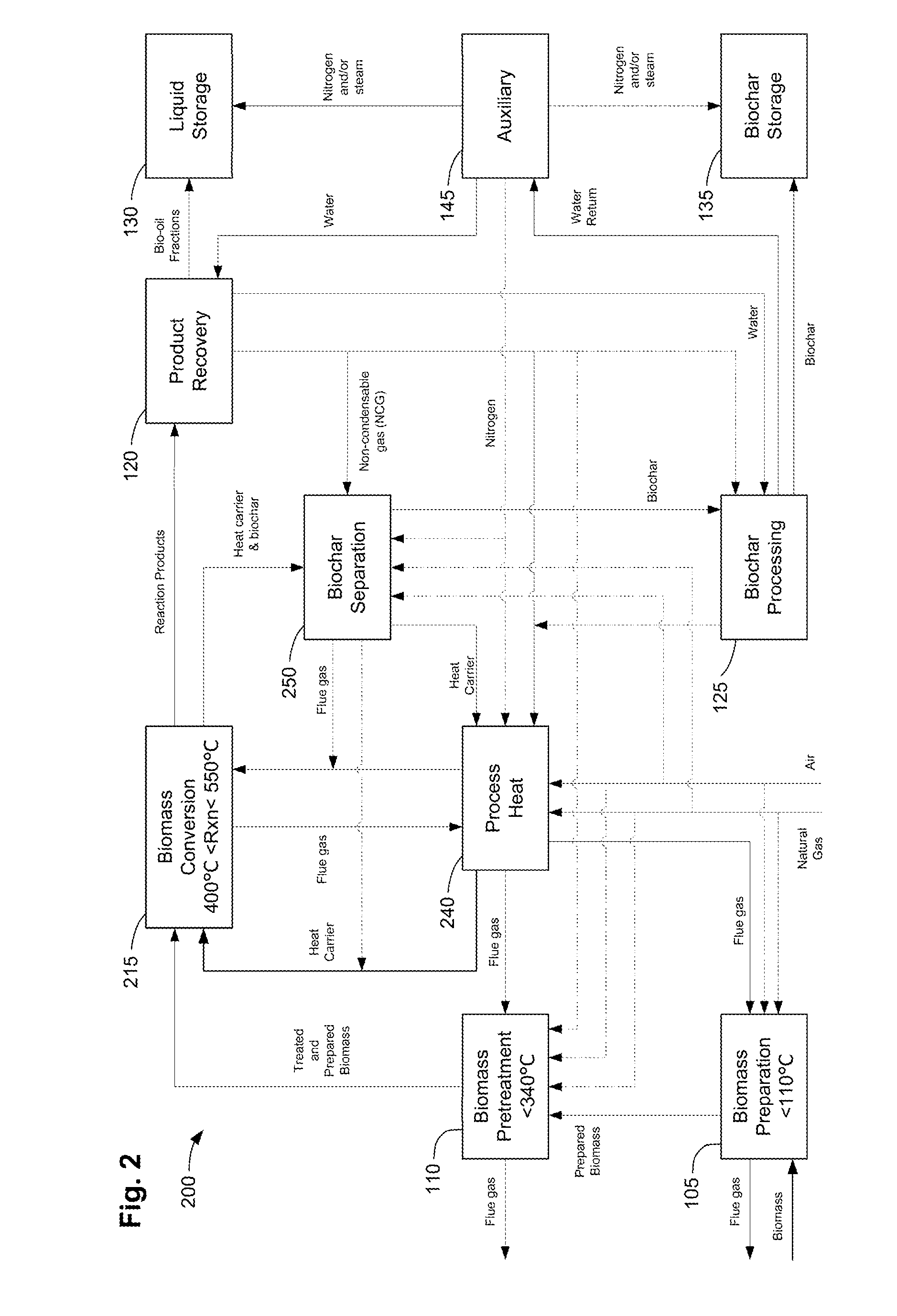
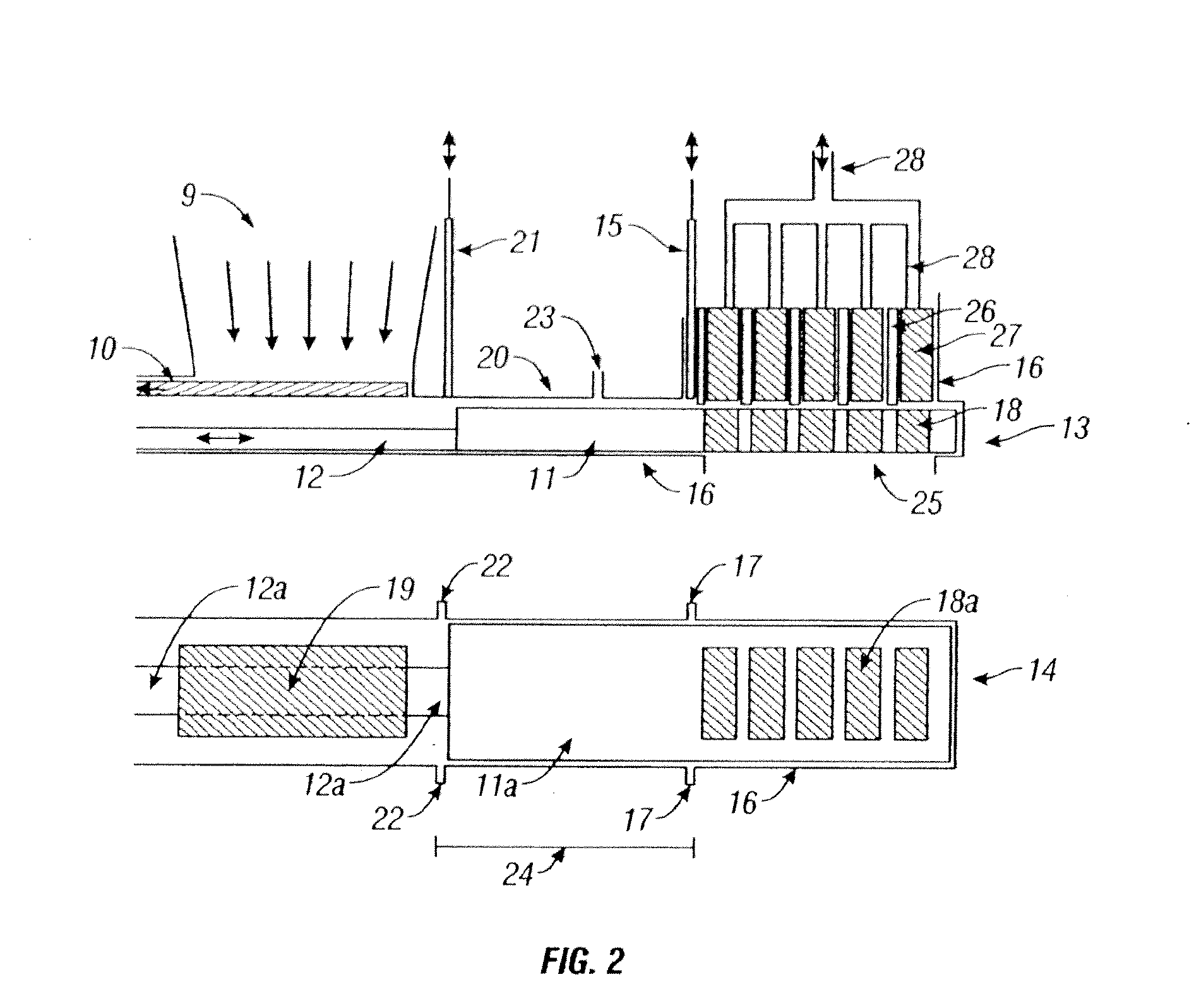
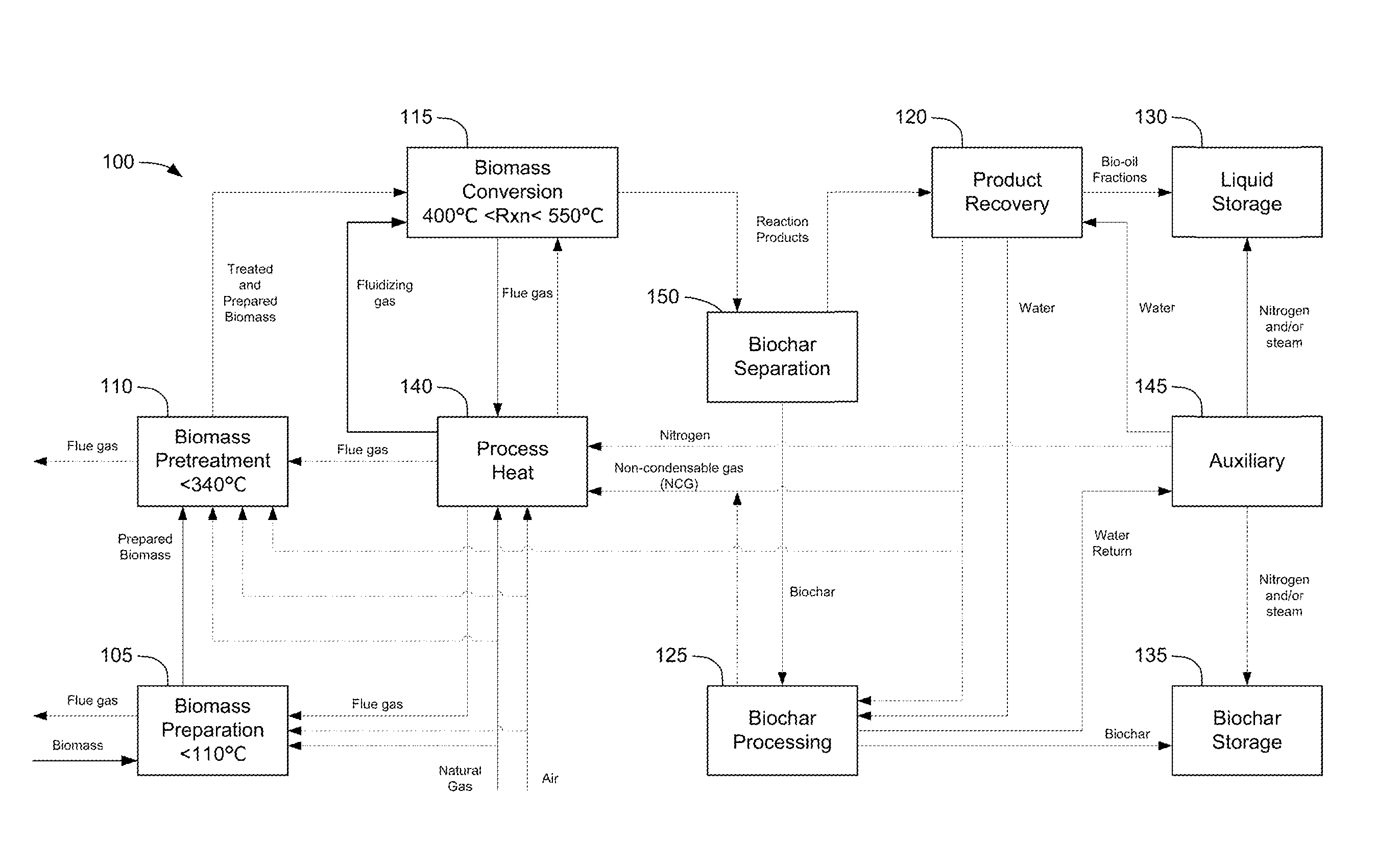
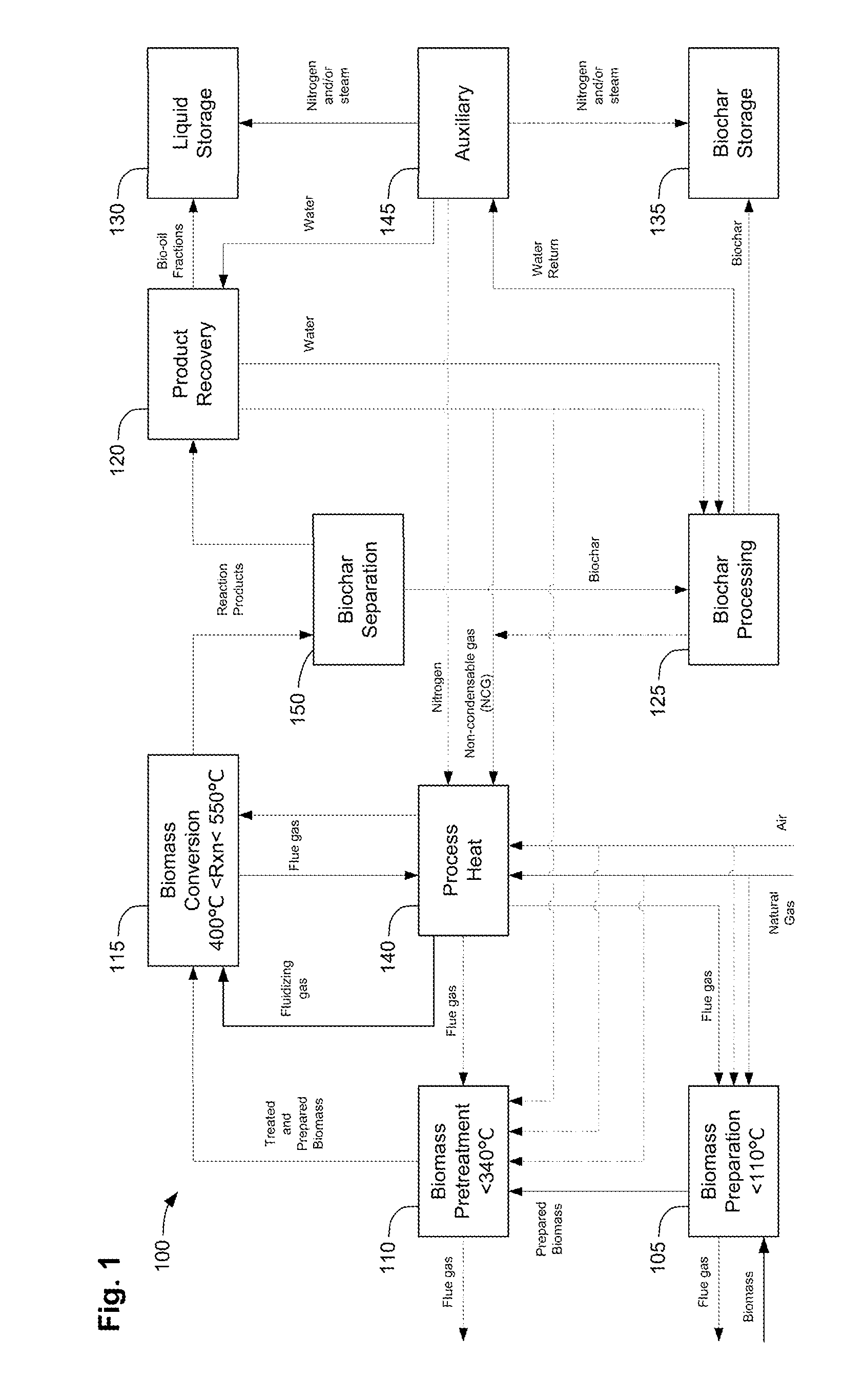
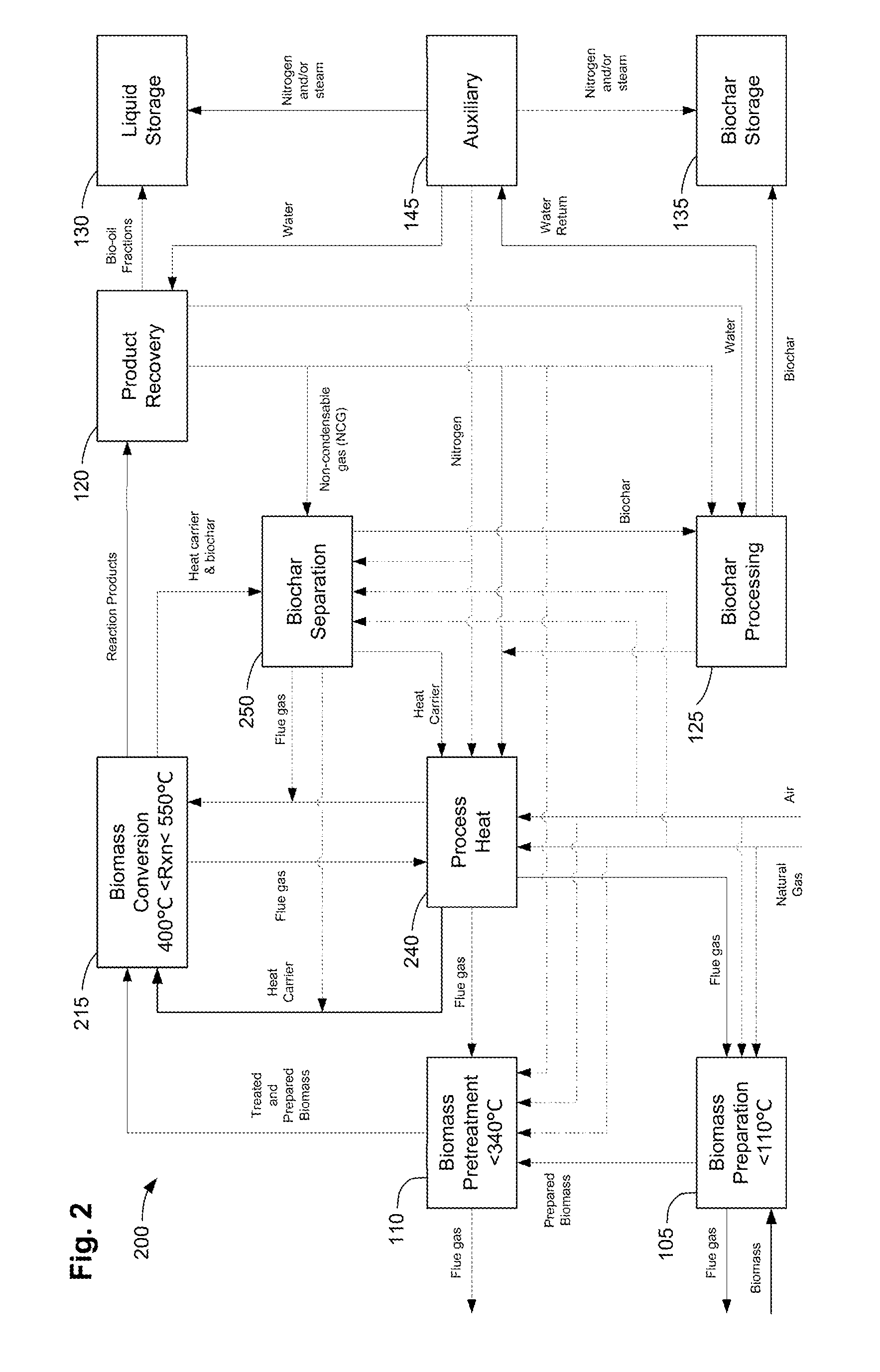
Methods, process, apparatus, equipment, and systems are disclosed for converting biomass into bio-oil fractions for chemicals, materials, feedstocks and fuels using a low-cost, integrated fast pyrolysis system. The system improves upon prior art by creating stable, bio-oil fractions which have unique properties that make them individually superior to conventional bio-oil. The invention enables water and low-molecular weight compounds to be separated into a final value-added fraction suitable for upgrading or extracting into value-added chemicals, fuels and water. Initial bio-oil fractions from the process are chemically distinct, have low-water content and acidity which reduces processing costs normally associated with conventional bio-oil post-production upgrading since fewer separation steps, milder processing conditions and lower auxiliary inputs are required. Biochar is stabilized so that it can be handled safely. The integrated fast pyrolysis process includes biomass storage, preparation, pretreatment, and conversion, product recovery and processing to create and store stable biochar and bio-oil fractions.
Owner:AVELLO BIOENERGY
System and method for biomass fractioning
ActiveUS20100180805A1Easy inputIncrease productionDrying solid materials with heatBiofuelsSyngasThin sheet
A biomass fractionator and method are described for inputting ground biomass and outputting several vapor streams of bio-intermediate compounds along with syngas and biochar. In one embodiment, a method for biomass fractioning, comprises dispensing biomass into thin sheets of ground biomass; subjecting the thin sheets to ramps of temperature; and selectively collecting various groups of compounds as they are released from the thin sheets.
Owner:COOL PLANET ENERGY SYST
Natural resin formulations
InactiveUS6844420B1Low viscosityImprove liquidityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiofuelsNatural resinDistillation
This invention is directed to a method of preparing a natural resin by liquefying wood, bark, forest residues, wood industry residues, or other biomass using rapid destructive distillation (fast pyrolysis). Fast pyrolysis produces both vapors and char from biomass, and following removal of the char from the product vapors, a liquid pitch product is recovered and processed by distillation, evaporation, or a combination thereof, in order to obtain a natural resin which may be in either liquid or solid form. The natural resin comprises a total phenolic content from about 30% to about 80% (w / w), and is a highly-reactive ligninic compound that has been found to be suitable for use within resin formulations without requiring any further extraction or fractionation procedures. Resins comprising up to 60% natural resin have been prepared and tested in board production and found to exhibit similar properties associated with commercially available resins. The natural resin may substitute for phenol, or for both phenol and formaldehyde within phenol-containing resins. Similarly, the natural resin can replace a substantial part of the components within urea-containing resins.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Microwave torrefaction of biomass
InactiveUS20110219679A1Increase flexibilityEasy to controlElectrical coke oven heatingBiofuelsMicrowaveTorrefaction
Owner:THE UNIV OF YORK
System and method for biomass fractioning
ActiveUS20110177466A1Easy inputIncrease productionDrying solid materials with heatOther heat production devicesSyngasThin sheet
A biomass fractionator and method are described for inputting ground biomass and outputting several vapor streams of bio-intermediate compounds along with syngas and biochar. In one embodiment, a method for biomass fractioning, comprises dispensing biomass into thin sheets of ground biomass; subjecting the thin sheets to ramps of temperature; and selectively collecting various groups of compounds as they are released from the thin sheets.
Owner:COOL PLANET ENERGY SYST
Methods for integrated fast pyrolysis processing of biomass
ActiveUS8100990B2Minimizes water contentImprove collection efficiencyDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsPre treatmentSafe handling
Methods, process, apparatus, equipment, and systems are disclosed for converting biomass into bio-oil fractions for chemicals, materials, feedstocks and fuels using a low-cost, integrated fast pyrolysis system. The system improves upon prior art by creating stable, bio-oil fractions which have unique properties that make them individually superior to conventional bio-oil. The invention enables water and low-molecular weight compounds to be separated into a final value-added fraction suitable for upgrading or extracting into value-added chemicals, fuels and water. Initial bio-oil fractions from the process are chemically distinct, have low-water content and acidity which reduces processing costs normally associated with conventional bio-oil post-production upgrading since fewer separation steps, milder processing conditions and lower auxiliary inputs are required. Biochar is stabilized so that it can be handled safely. The integrated fast pyrolysis process includes biomass storage, preparation, pretreatment, and conversion, product recovery and processing to create and store stable biochar and bio-oil fractions.
Owner:AVELLO BIOENERGY
Fractional catalytic pyrolysis of biomass
ActiveUS8202332B2Eliminate needBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic pyrolysisReactive gas
Methods for fractional catalytic pyrolysis which allow for conversion of biomass into a slate of desired products without the need for post-pyrolysis separation are described. The methods involve use of a fluid catalytic bed which is maintained at a suitable pyrolysis temperature. Biomass is added to the catalytic bed, preferably while entrained in a non-reactive gas such as nitrogen, causing the biomass to become pyrolyzed and forming the desired products in vapor and gas forms, allowing the desired products to be easily separated.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
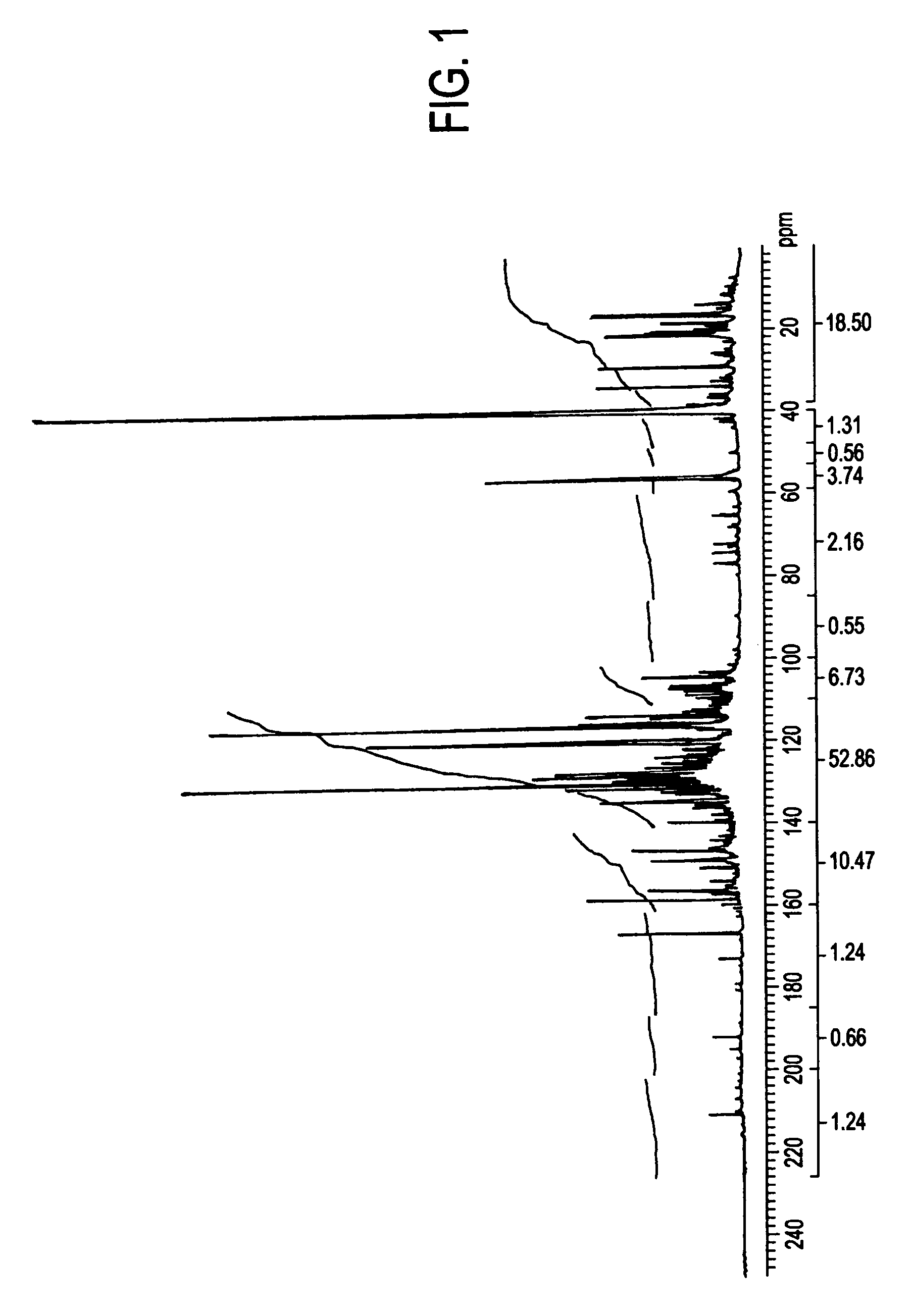
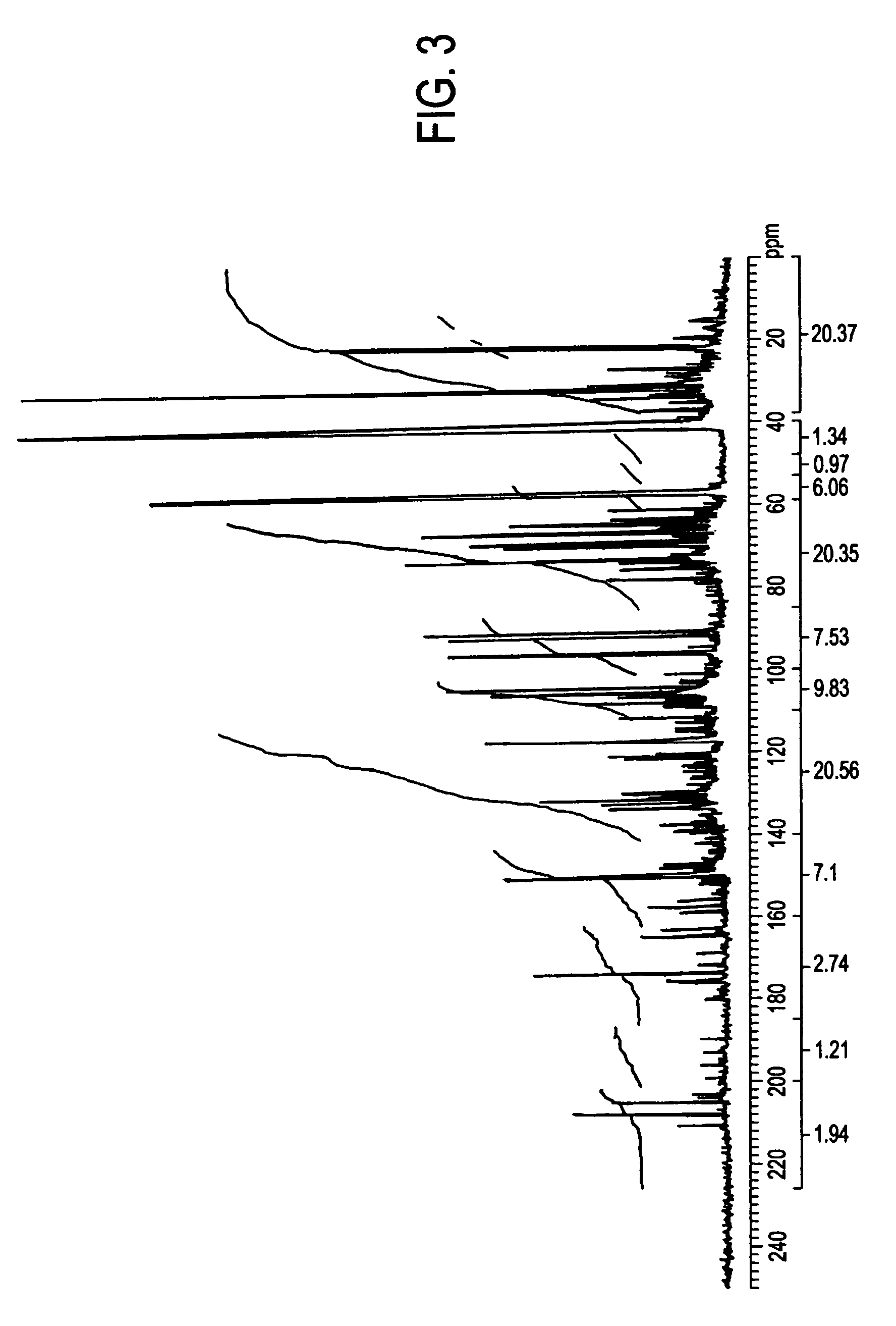
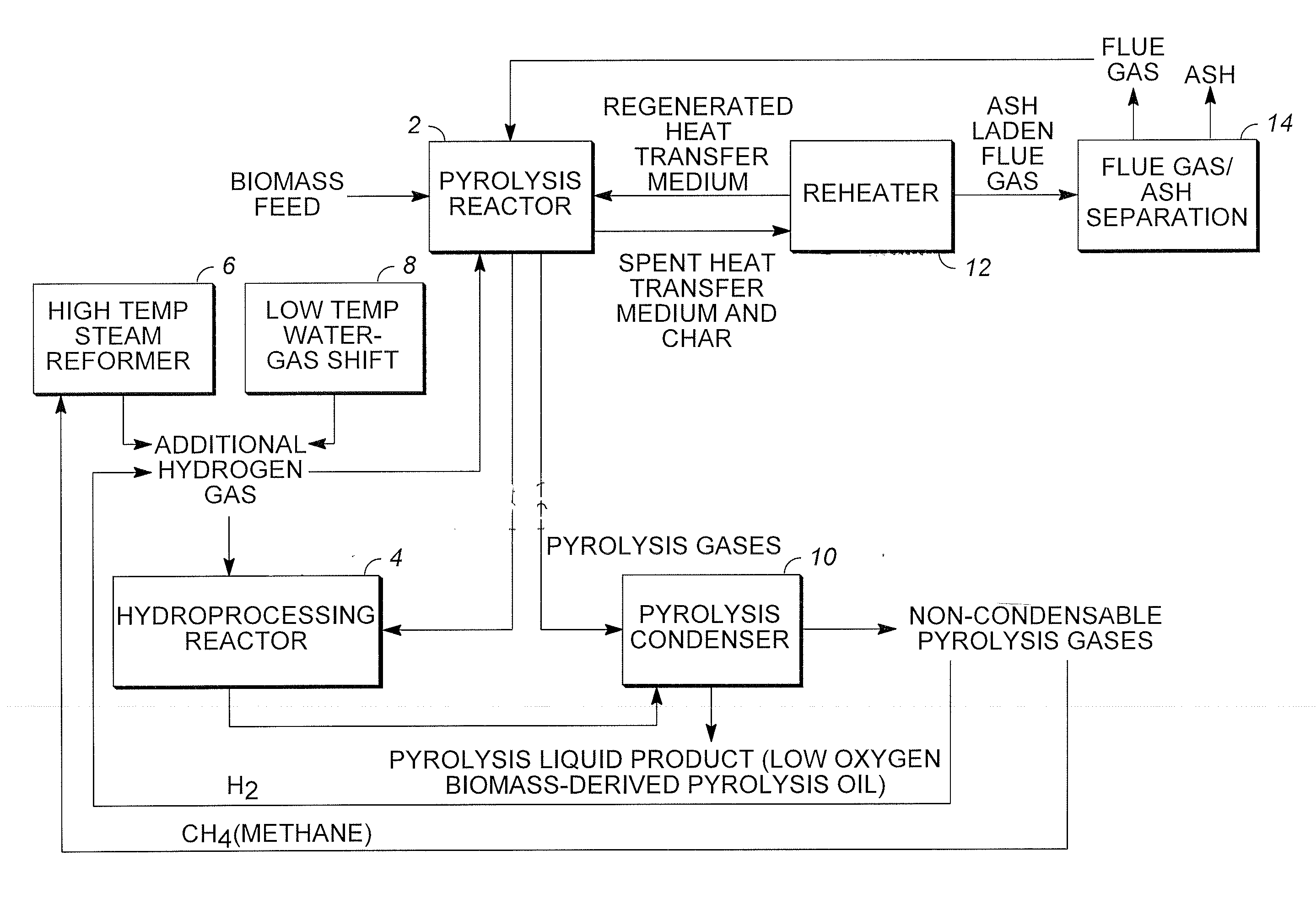
Low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same
InactiveUS20110201854A1Direct heating destructive distillationBiofuelsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
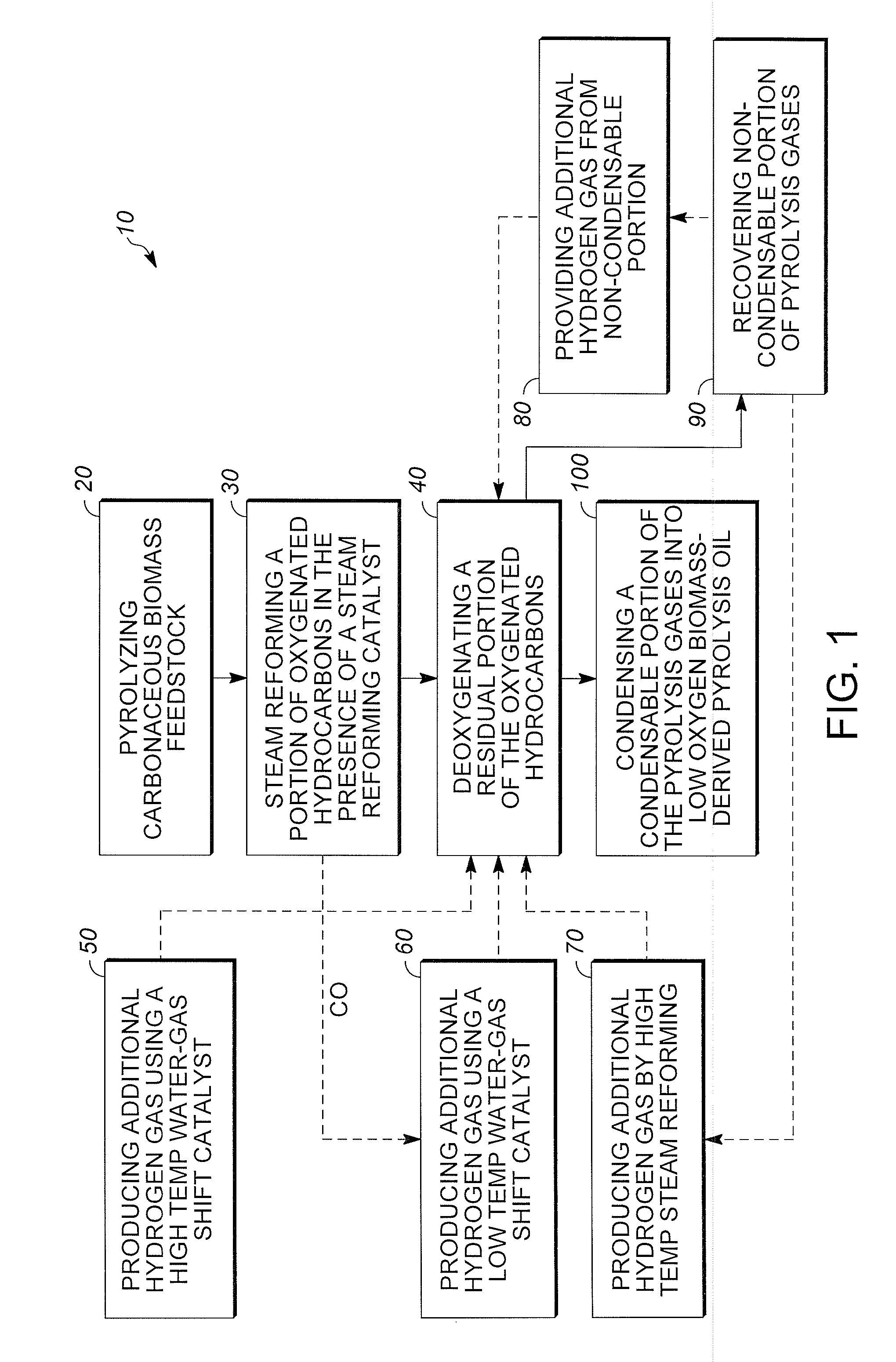
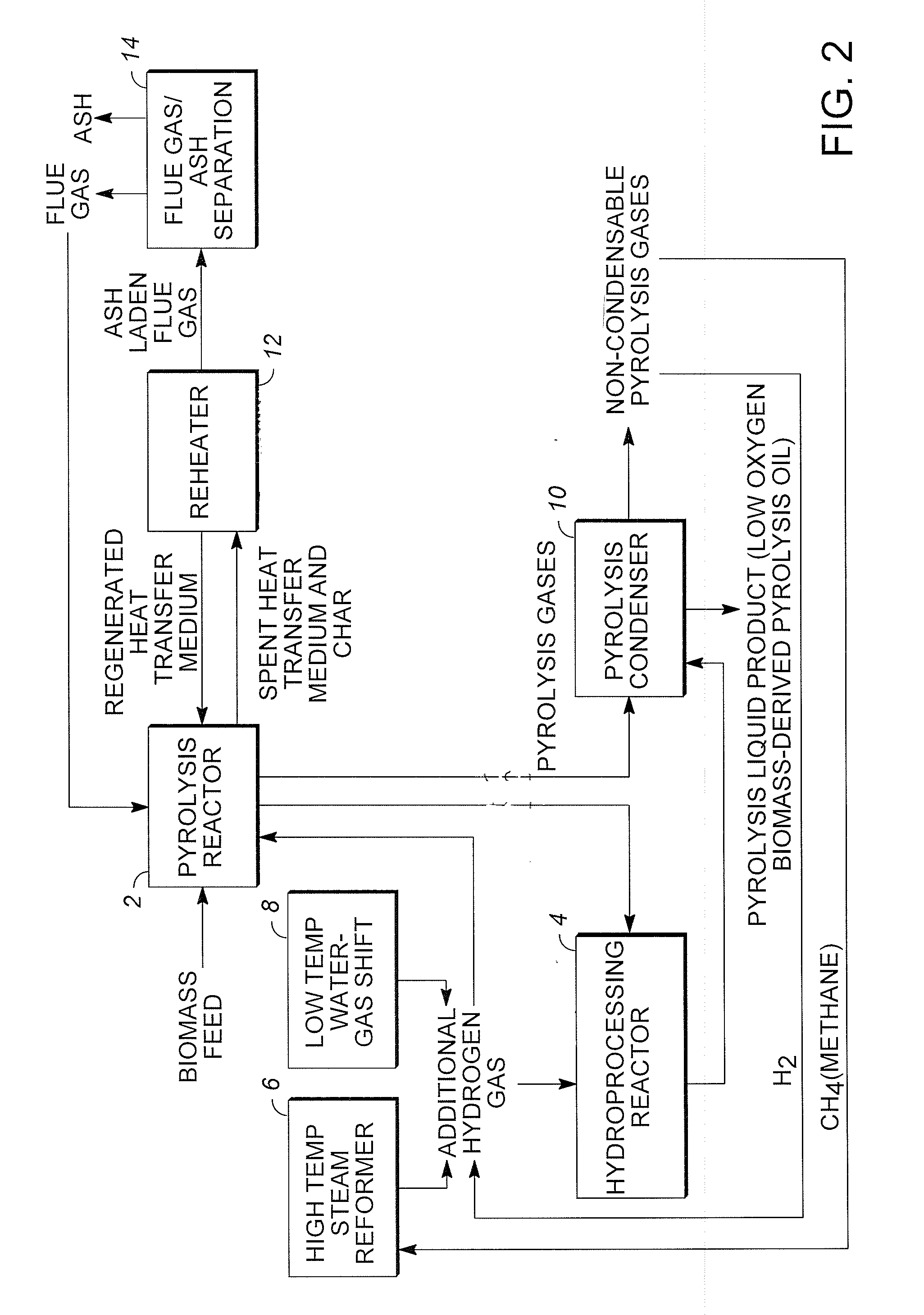
Methods are provided for producing low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil from carbonaceous biomass feedstock. The carbonaceous biomass feedstock is pyrolyzed in the presence of a steam reforming catalyst to produce char and pyrolysis gases. During pyrolysis, a portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons in the pyrolysis gases is converted into hydrocarbons by steam reforming also yielding carbon oxides and hydrogen gas. The hydrogen gas at least partially deoxygenates a residual portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons. Additional hydrogen gas may also be produced by water-gas shift reactions to deoxygenate the residual portion of the oxygenated hydrocarbons in the pyrolysis gases. Deoxygenation may occur in the presence of a hydroprocessing catalyst. A condensable portion of the pyrolysis gases is condensed to form low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UOP LLC
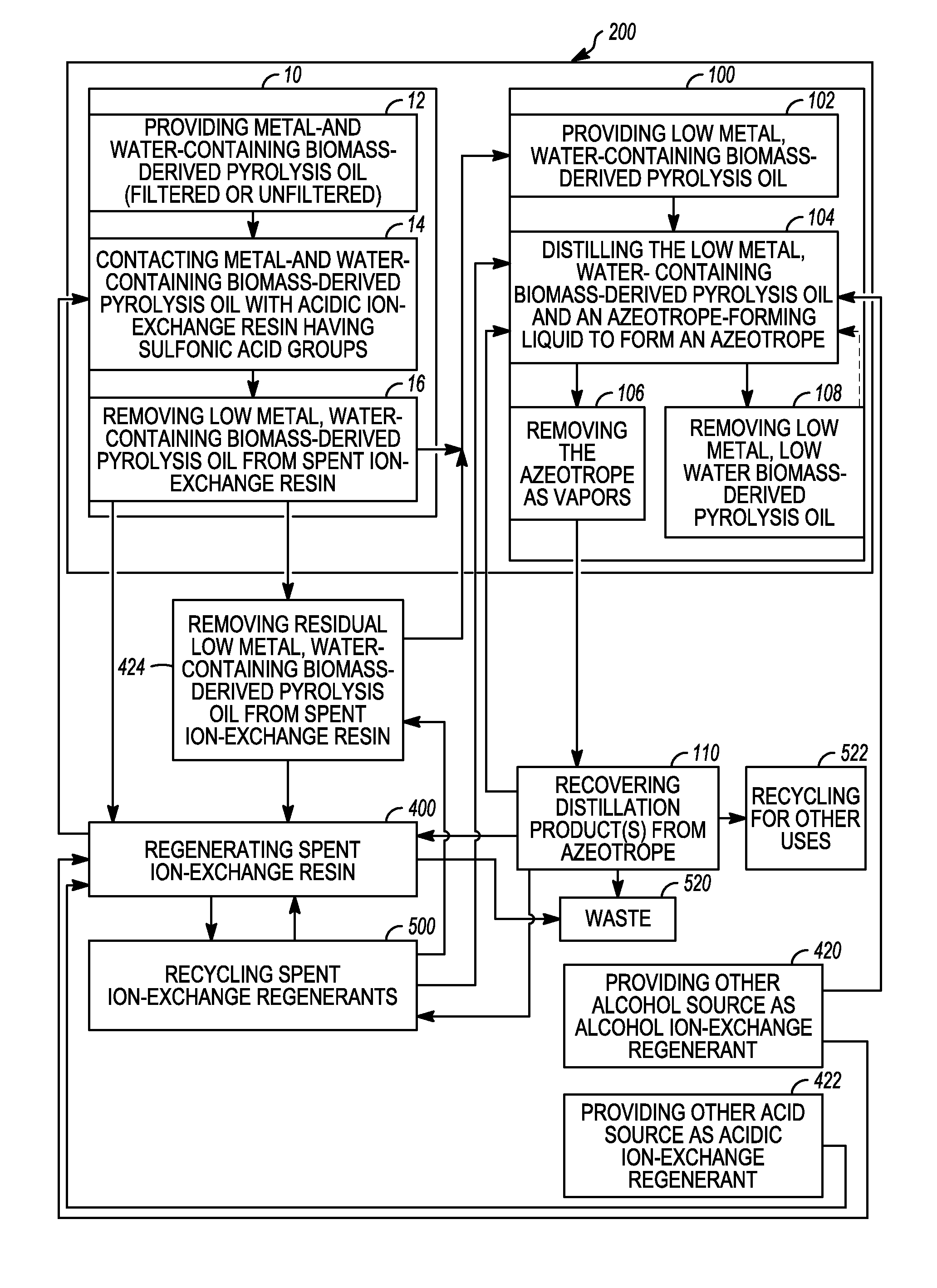
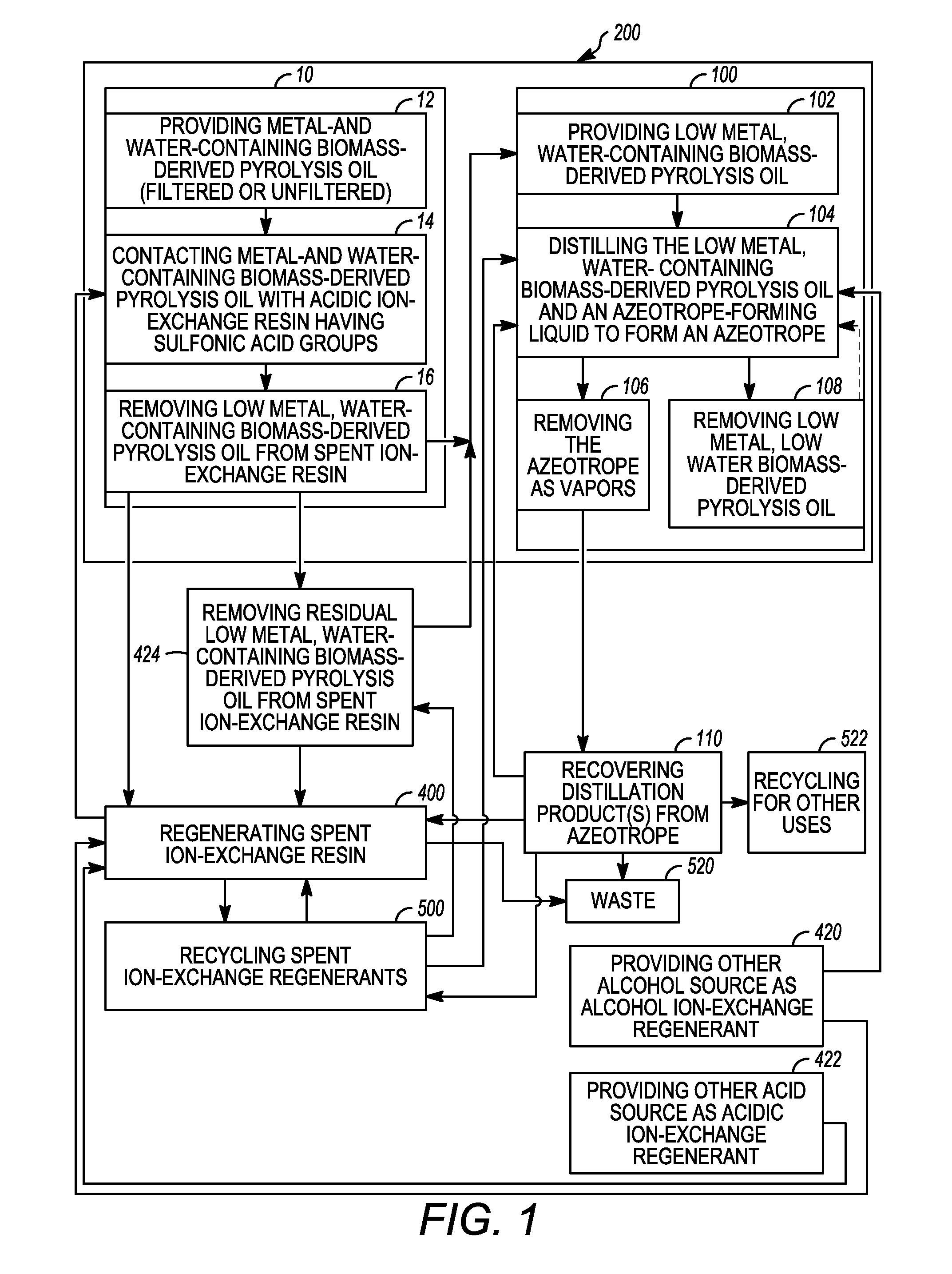
Low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same
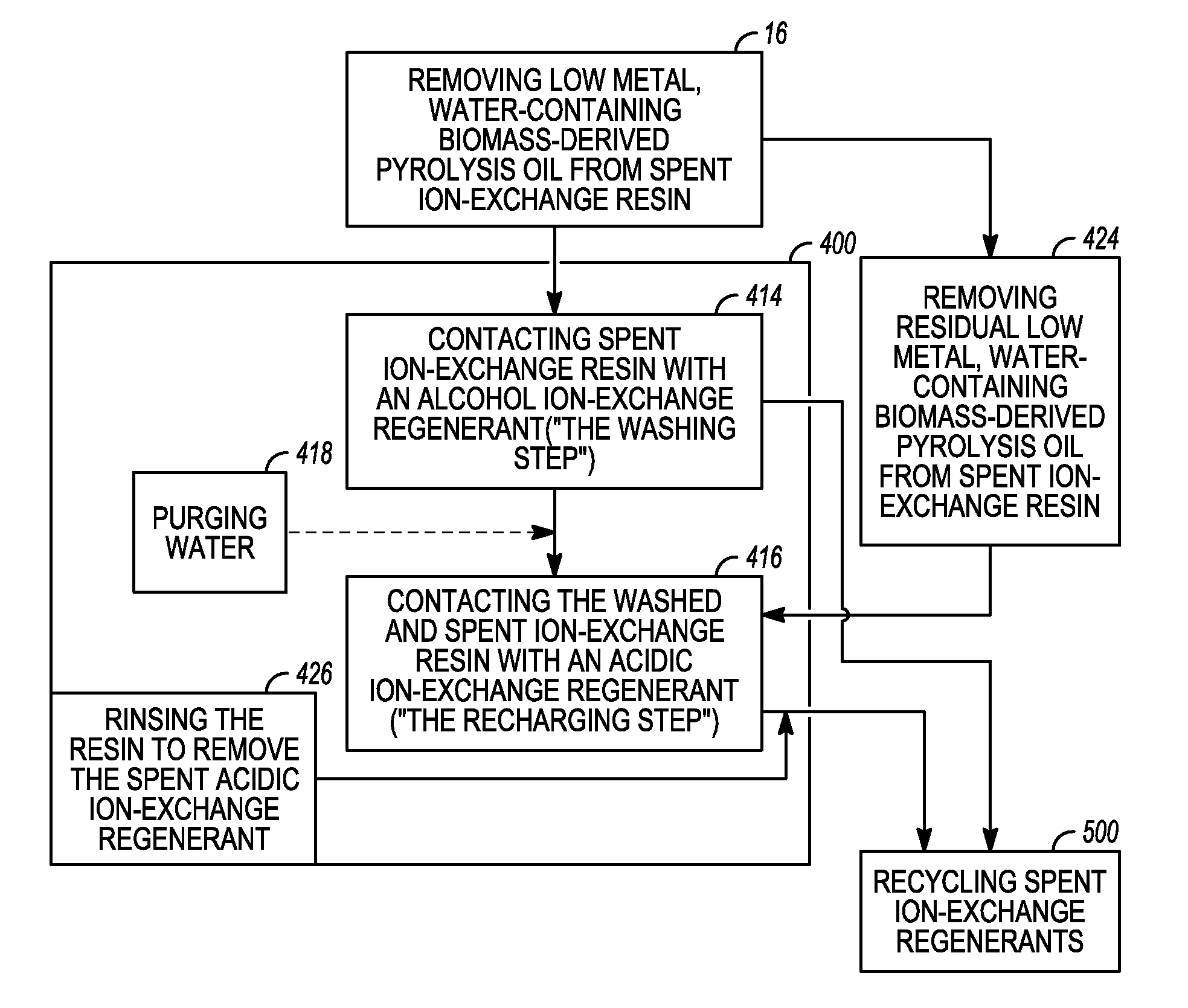
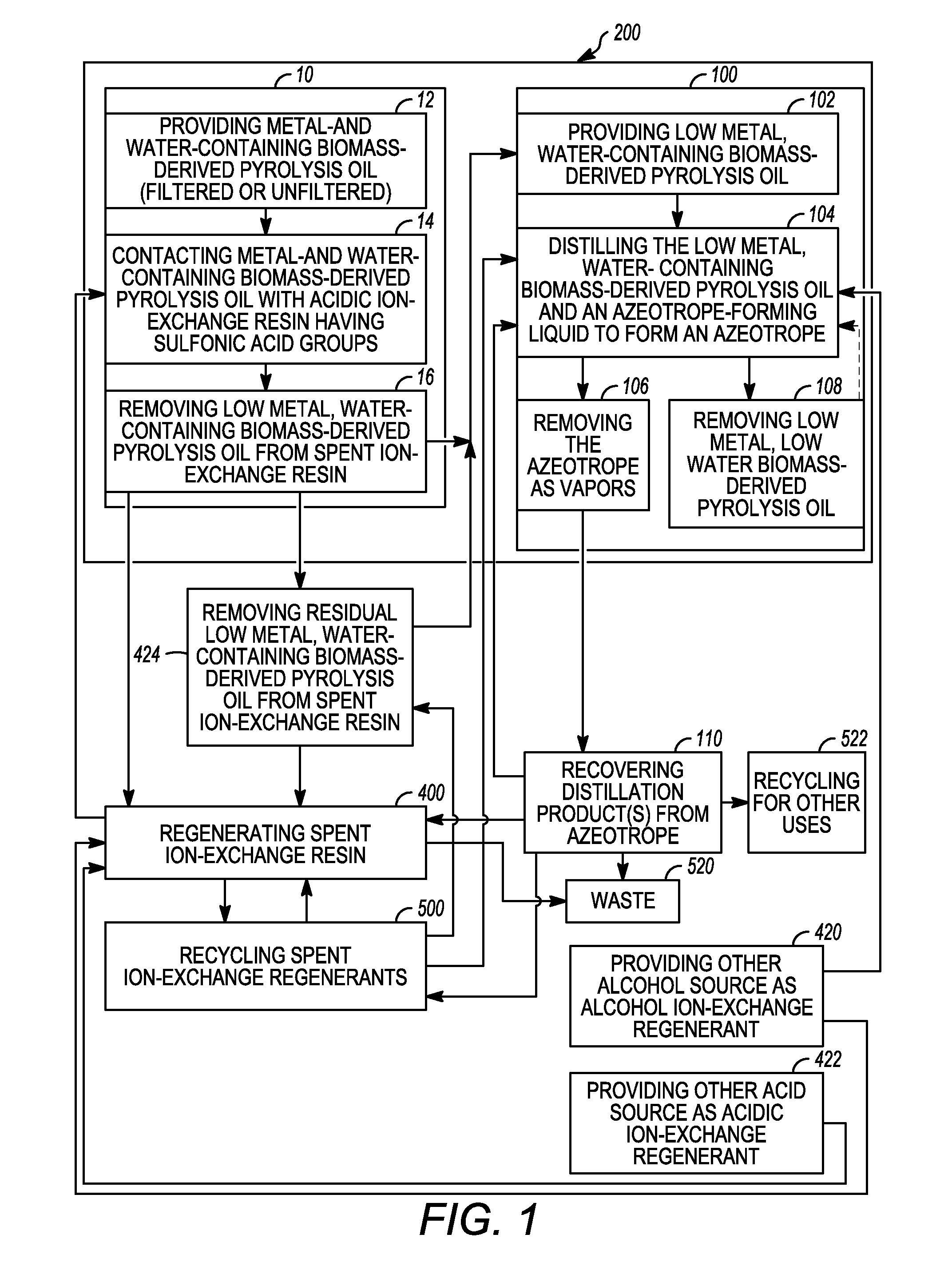
Low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same are provided. Metal- and water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is contacted with an acidic ion-exchange resin having sulfonic acid groups to produce a low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil. The low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is removed from the spent ion-exchange resin after ion-exchange. The low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is distilled to produce a low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oil and a distillation product. The distillation product comprises one or both of an alcohol ion-exchange regenerant and an acidic ion-exchange regenerant which may be used to regenerate the spent ion-exchange resin. The regenerated acidic ion-exchange resin may be recycled. The spent alcohol and acid ion-exchange regenerants may be recovered and recycled.
Owner:UOP LLC
Biomass pyrolysis
InactiveUS7998315B2Reduce probabilityReduce in quantityCombustible gas coke oven heatingDirect heating destructive distillationChemistryPyrolysis
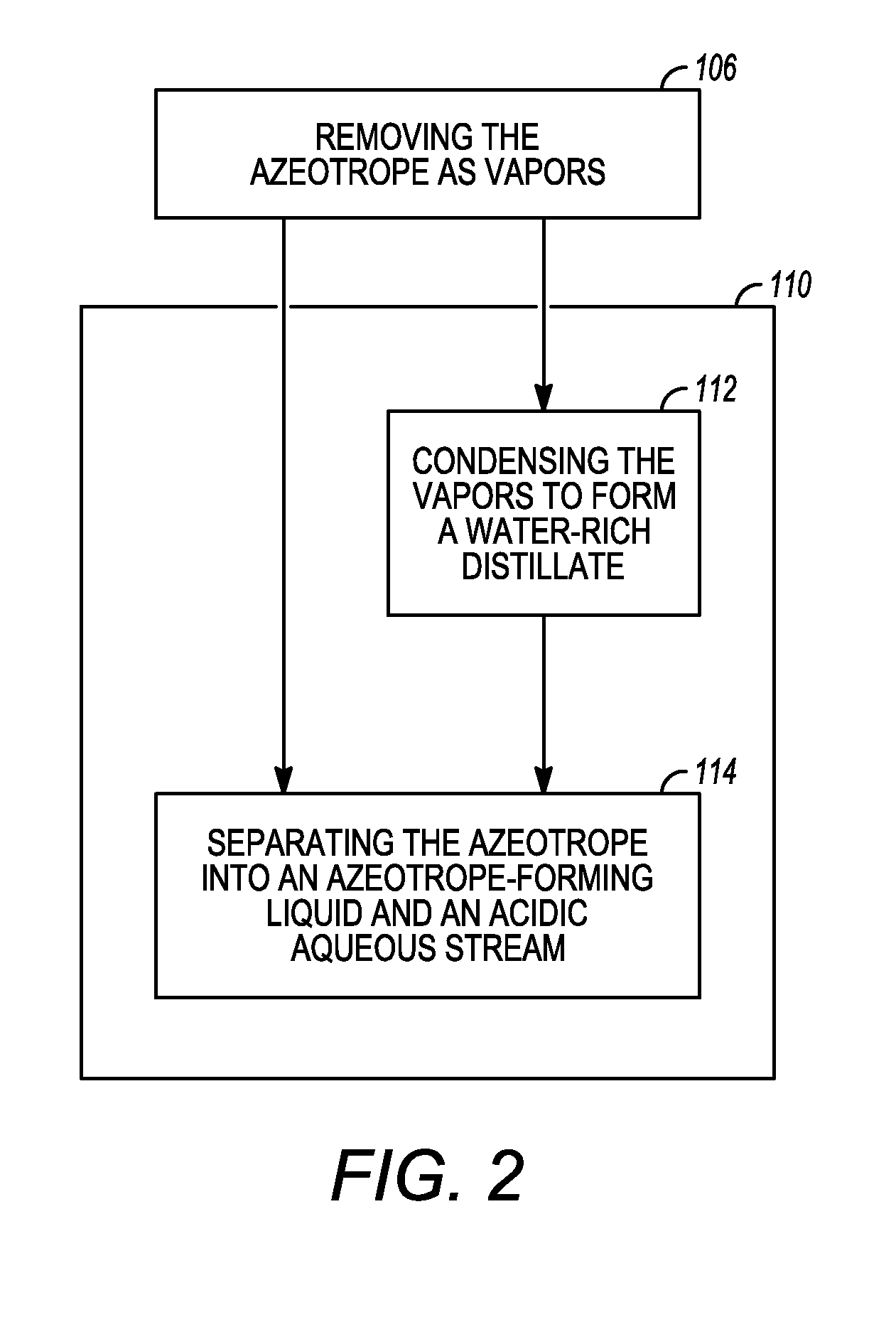
A process for pyrolyzing biomass is provided. The process comprises providing biomass to a pyrolysis reactor to produce a vapor product and condensing said vapor product to produce a condensed product, wherein a phase separation suppression agent is added during said process so as to promote the formation of a single phase condensed product.
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Production of stable biomass pyrolysis oils using fractional catalytic pyrolysis
ActiveUS20100212215A1Eliminate needImprove stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsMultiple metal hydridesCatalytic pyrolysisReactive gas
Methods for fractional catalytic pyrolysis which allow for conversion of biomass into a slate of desired products without the need for post-pyrolysis separation are described. The methods involve use of a fluid catalytic bed which is maintained at a suitable pyrolysis temperature. Biomass is added to the catalytic bed, preferably while entrained in a non-reactive gas such as nitrogen, causing the biomass to become pyrolyzed and forming the desired products in vapor and gas forms, allowing the desired products to be easily separated.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods and apparatuses for forming low-metal biomass-derived pyrolysis oil
Methods and apparatuses for forming a low-metal biomass-derived pyrolysis oil are provided. In an embodiment, a method for forming a low-metal biomass-derived pyrolysis oil includes washing biomass comprising a water-soluble metal component therein with wash water that is substantially free of water-soluble metals. The washed biomass and water containing water-soluble metal are separated after washing the biomass. The washed biomass is pyrolyzed in a pyrolysis process to form a pyrolysis vapor stream. A portion of the pyrolysis vapor stream is condensed to form a condensate. The wash water is derived from the washed biomass. In an embodiment of an apparatus, the apparatus comprises a washing stage, a biomass dryer, a pyrolysis reactor, a quenching system comprising a primary condenser and a secondary condenser, and a return line that connects the quenching system to the washing stage.
Owner:UOP LLC
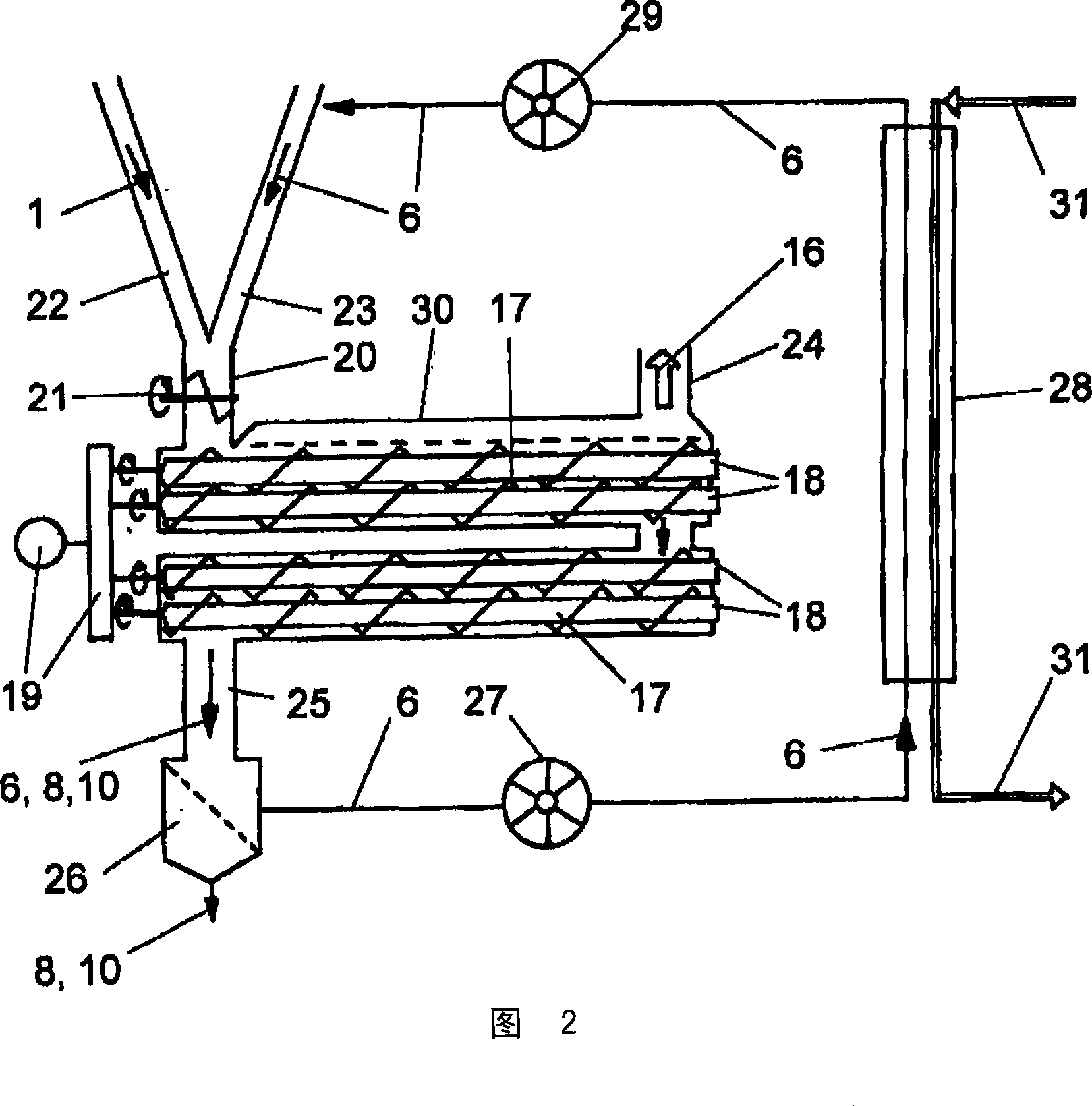
Method for the rapid pyrolysis of lignocellulose
InactiveCN101238197ASimple designReduce riskDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsCelluloseOxygen
Method for fast pyrolysis of lignocellulose including: mechanically comminuting the lignocellulose to lignocellulose particles; at least one of completely drying and preheating the lignocellulose particles; mixing the lignocellulose particles with heat transfer particles so as to provide a mixture; heating the heat transfer particles, prior to the mixing, to a temperature between 500° C. and 650° C.; and heating, in a pyrolysis reactor with oxygen excluded, the lignocellulose particles using the heat transfer particles so as to establish a temperature between 400° C. and 600° C. for 1 to 50 seconds and so as to react the lignocellulose particles so as to provide pyrolysis coke, pyrolysis condensate, and pyrolysis gas.
Owner:KARLSRUHE FORSCHZENT
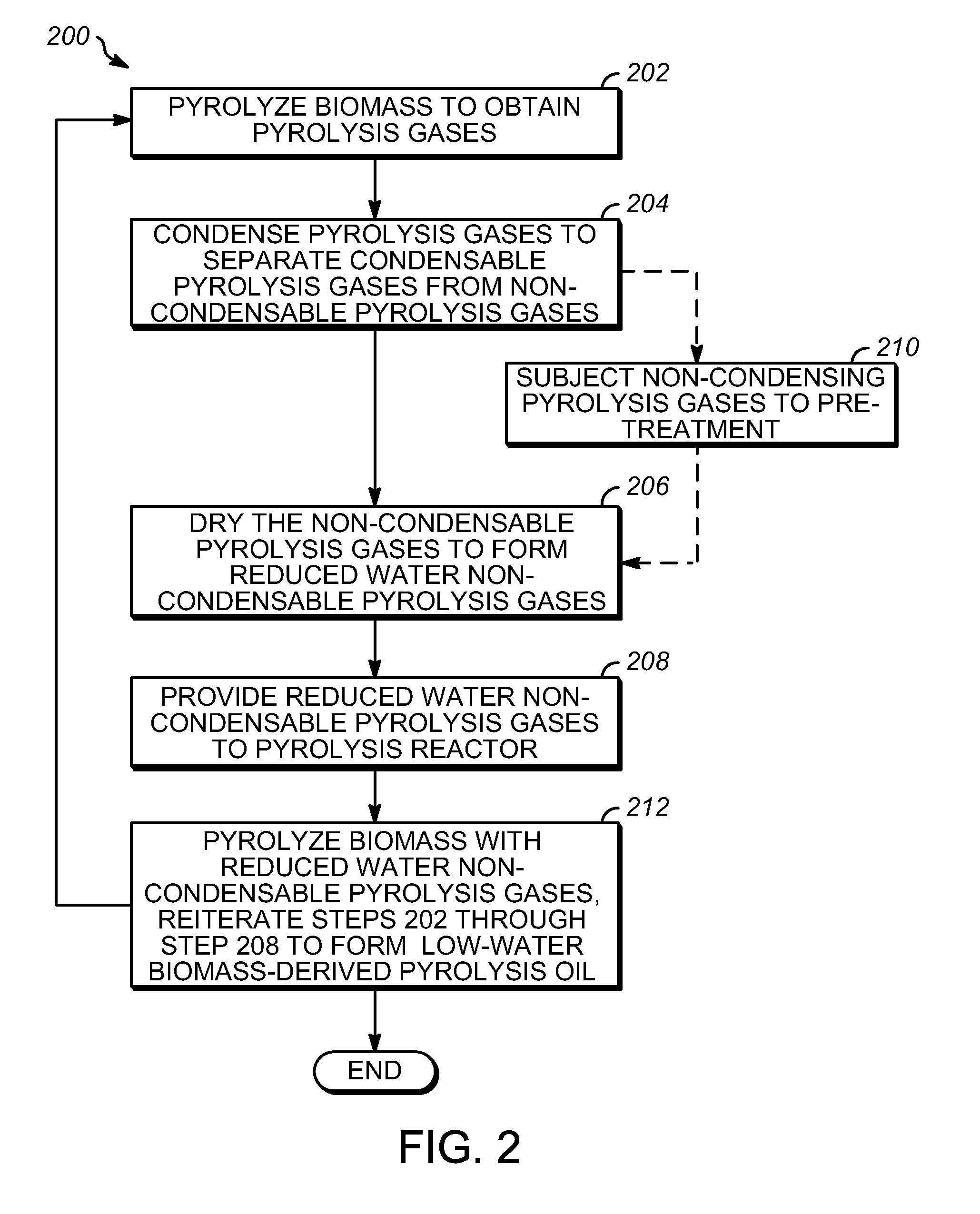
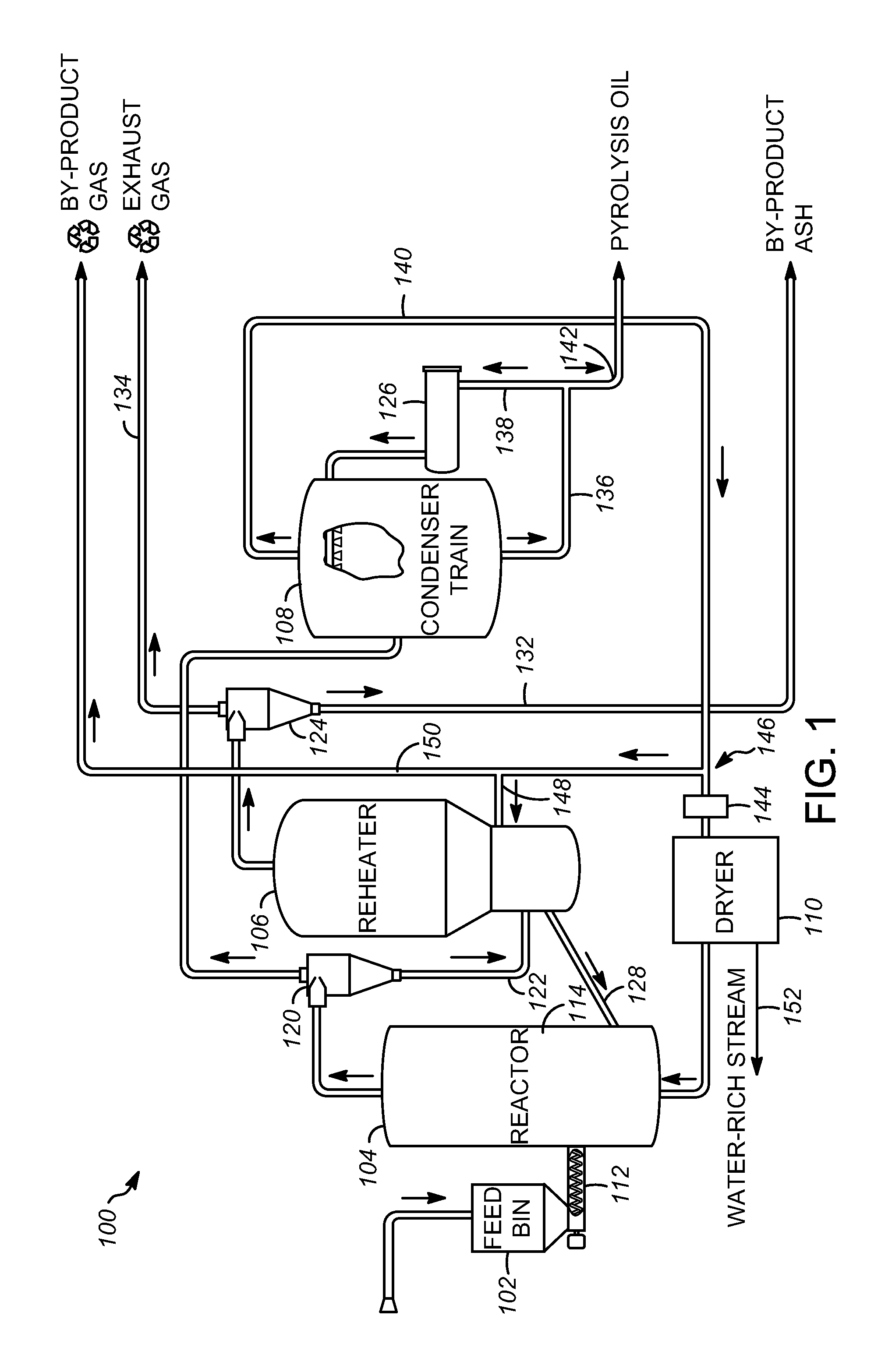
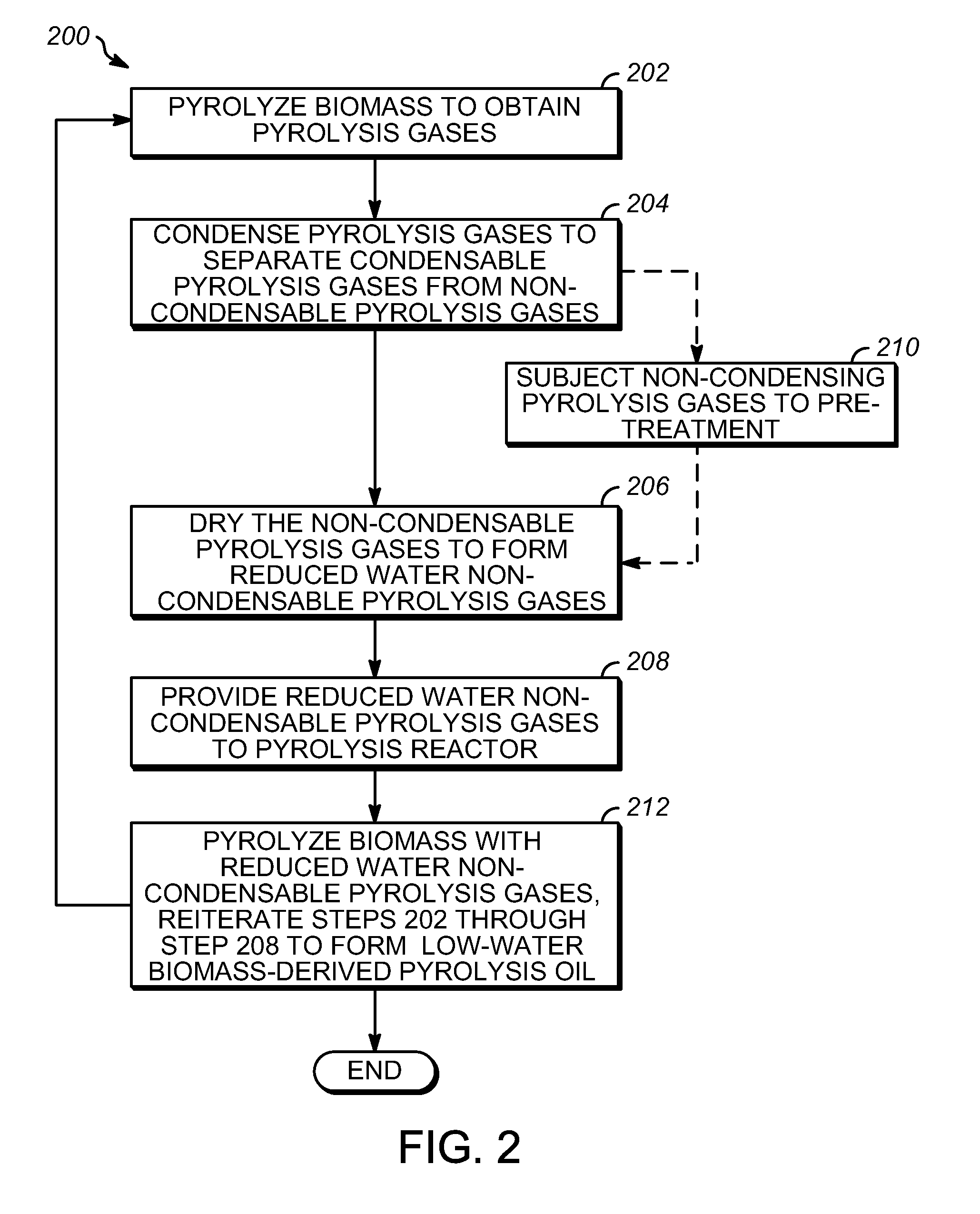
Low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and processes for producing the same
ActiveUS8519205B2Extensive contentReduce moistureDirect heating destructive distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryProduct gasWater content
Low water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and processes for producing them are provided. The process includes condensing pyrolysis gases including condensable pyrolysis gases and non-condensable gases to separate the condensable pyrolysis gases from the non-condensable gases, the non-condensable gases having a water content, drying the non-condensable pyrolysis gases to reduce the water content of the-non-condensable gases to form reduced-water non-condensable pyrolysis gases, and providing the reduced-water non-condensable pyrolysis gases to a pyrolysis reactor for forming the biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Petroleum pitch-based carbon foam
InactiveUS6833012B2Useful and reliableImprove efficiencyPigmenting treatmentHarvestersLow densityNet shape
Petroleum or coal tar pitch-based cellular or porous products having a density of preferably between about 0.1 g / cm<3 >and about 0.8 g / cm<3 >are produced by the controlled heating of mesophase carbon materials derived from coal tar or petroleum pitch having a softening point in excess of about 300° C. and preferably between about 300 and about 400° C. in a "mold" and under a non-oxidizing atmosphere. The porous product thereby produced, preferably as a net shape or near net shape, can be machined, adhered and otherwise fabricated to produce a wide variety of low cost, low density products.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE RES LAB
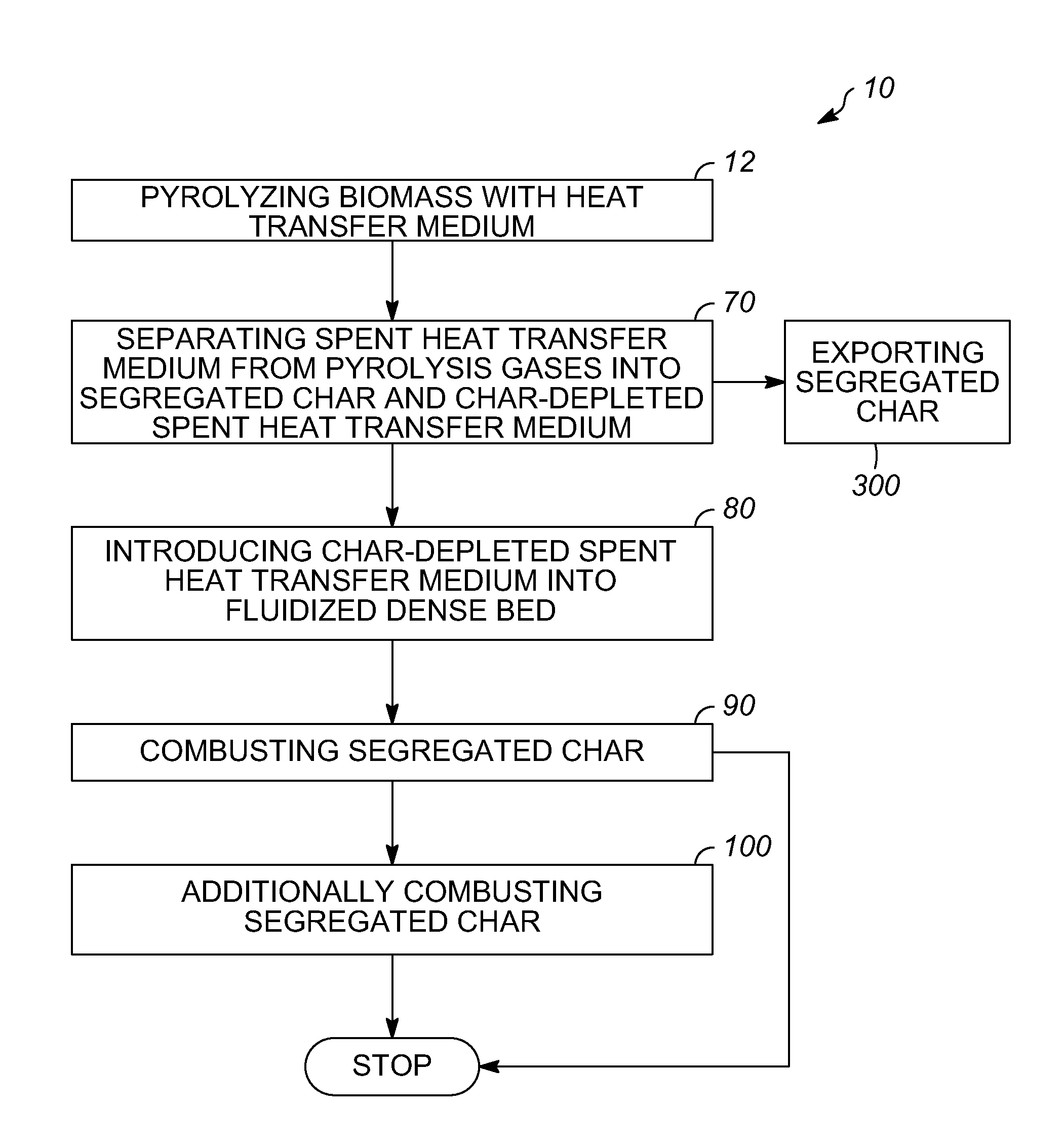
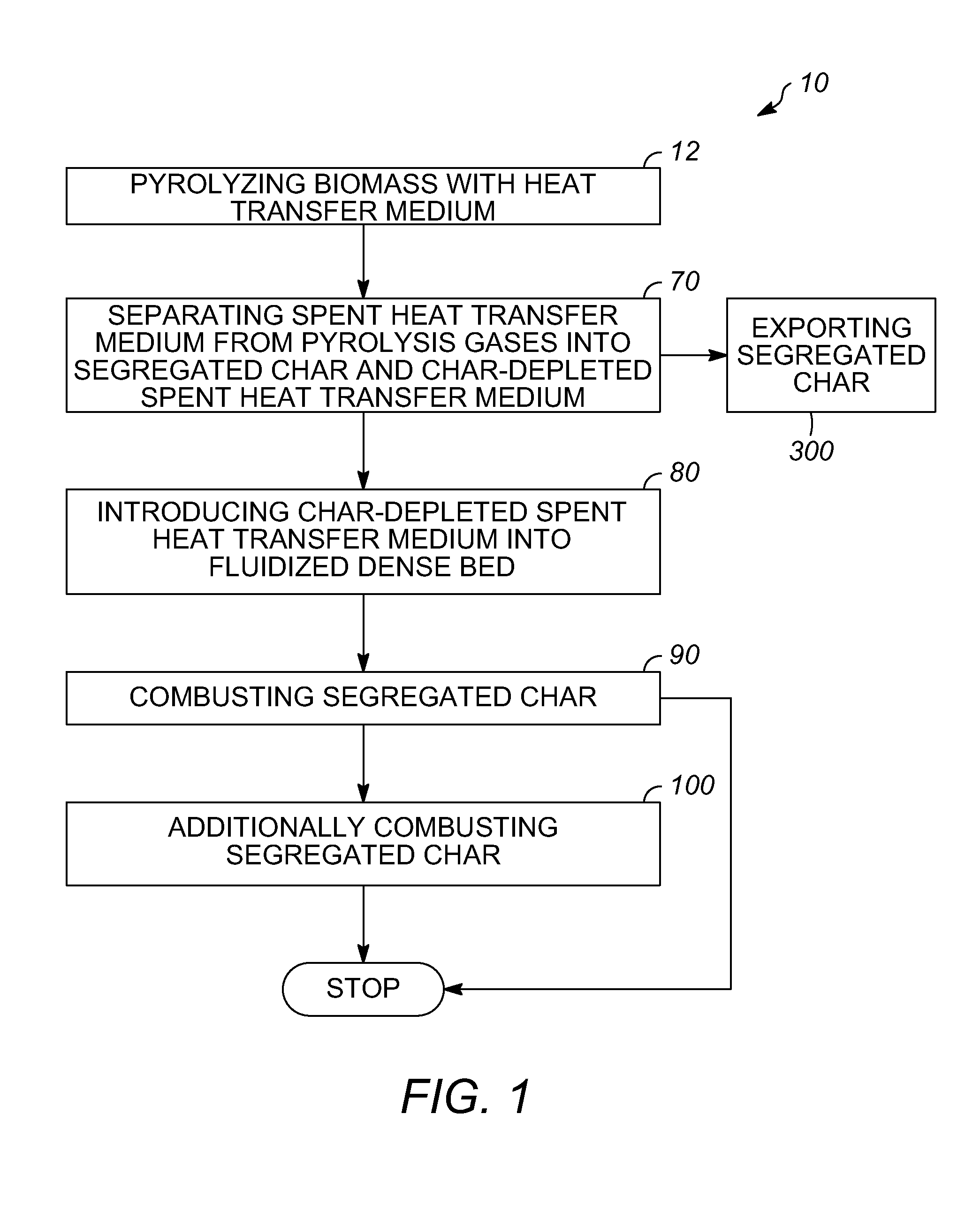
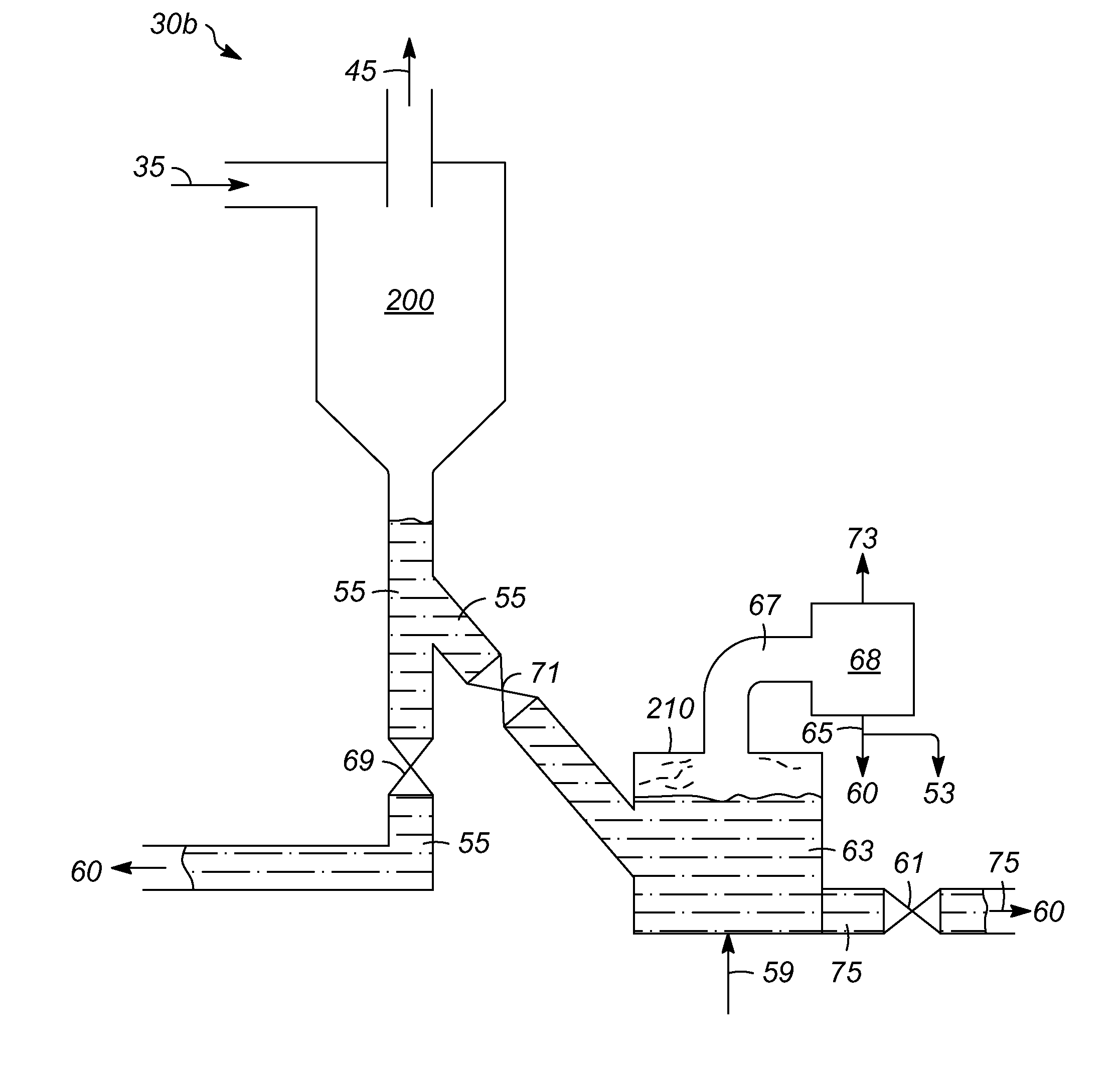
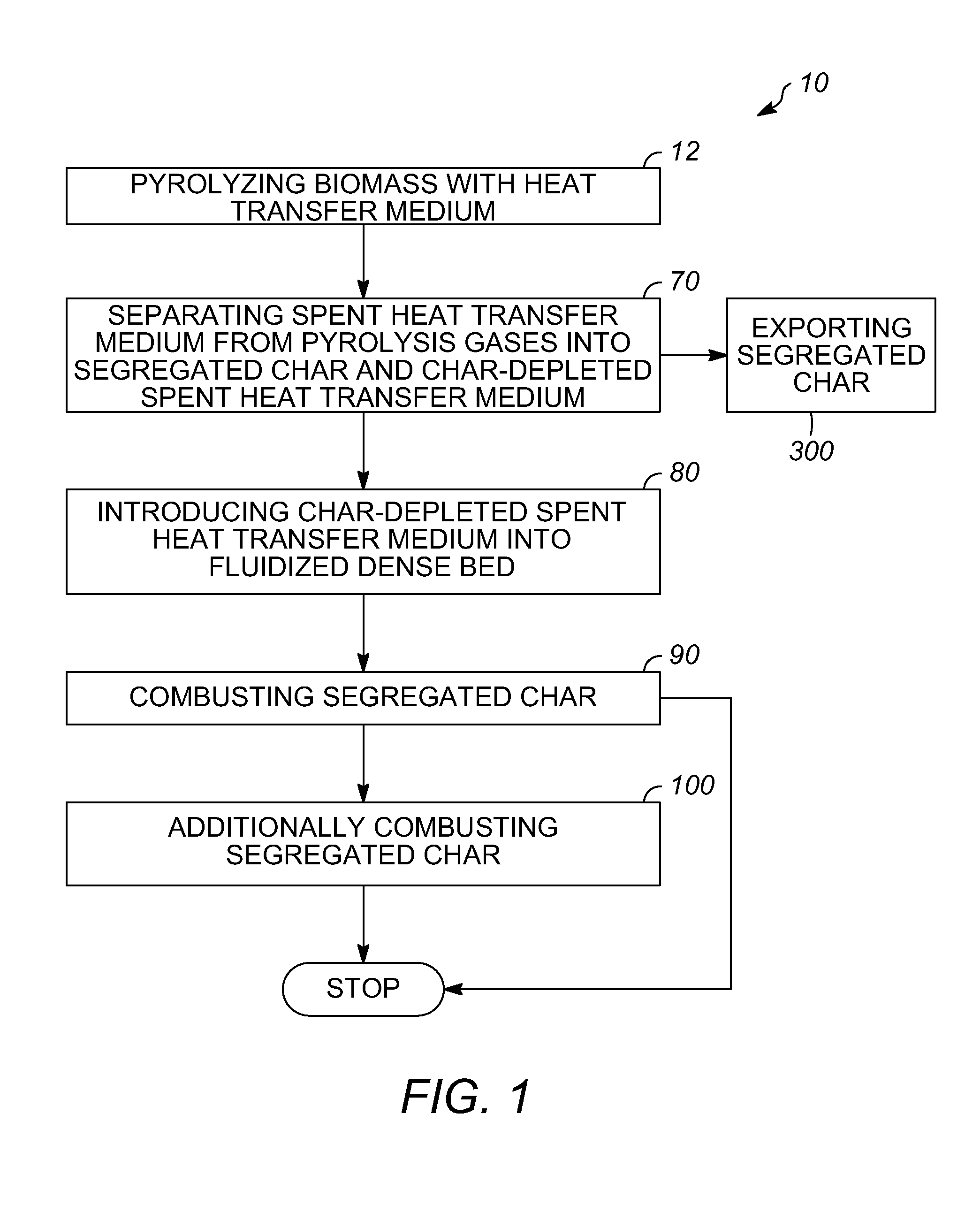
Char-handling processes in a pyrolysis system
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
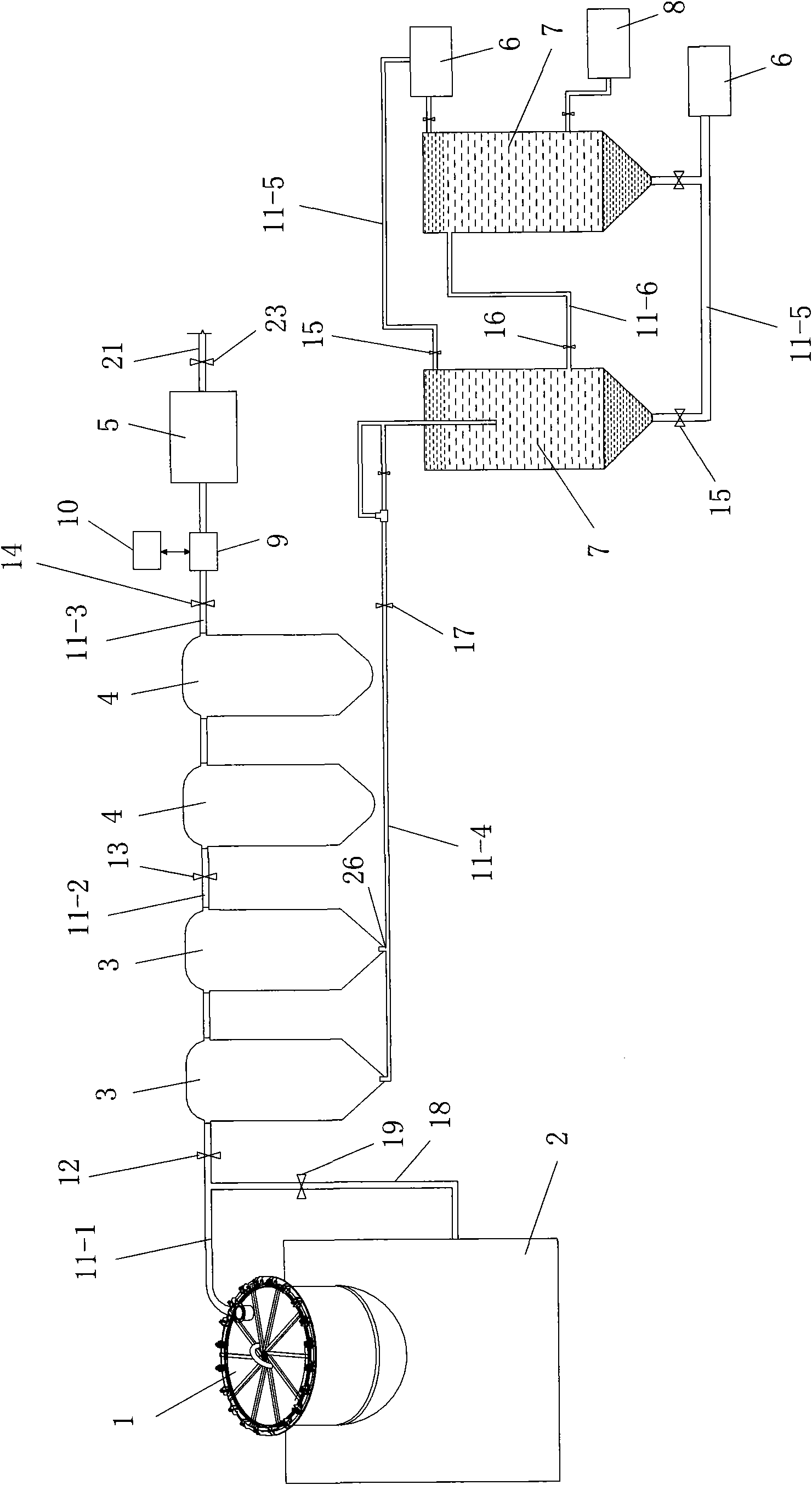
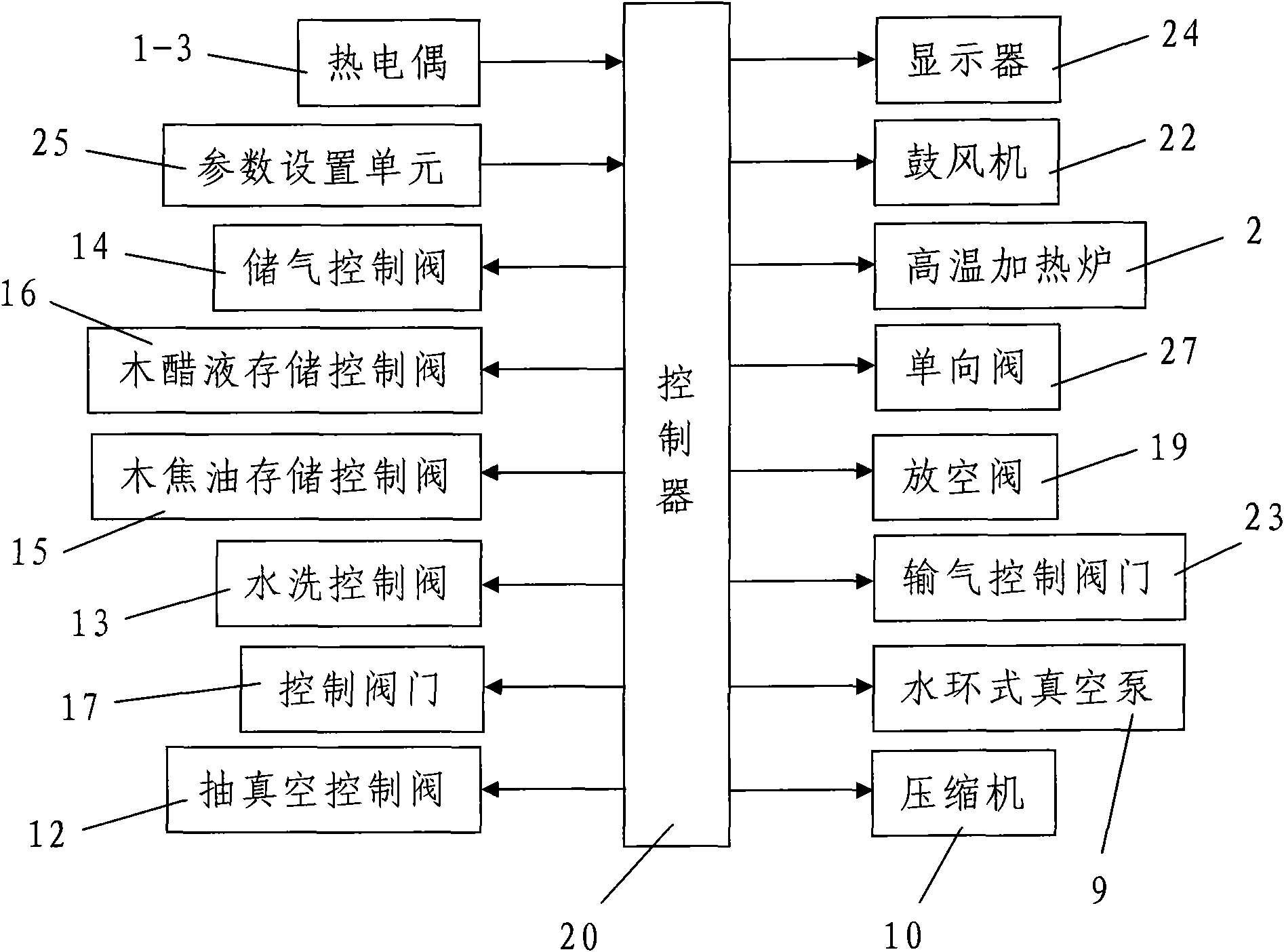
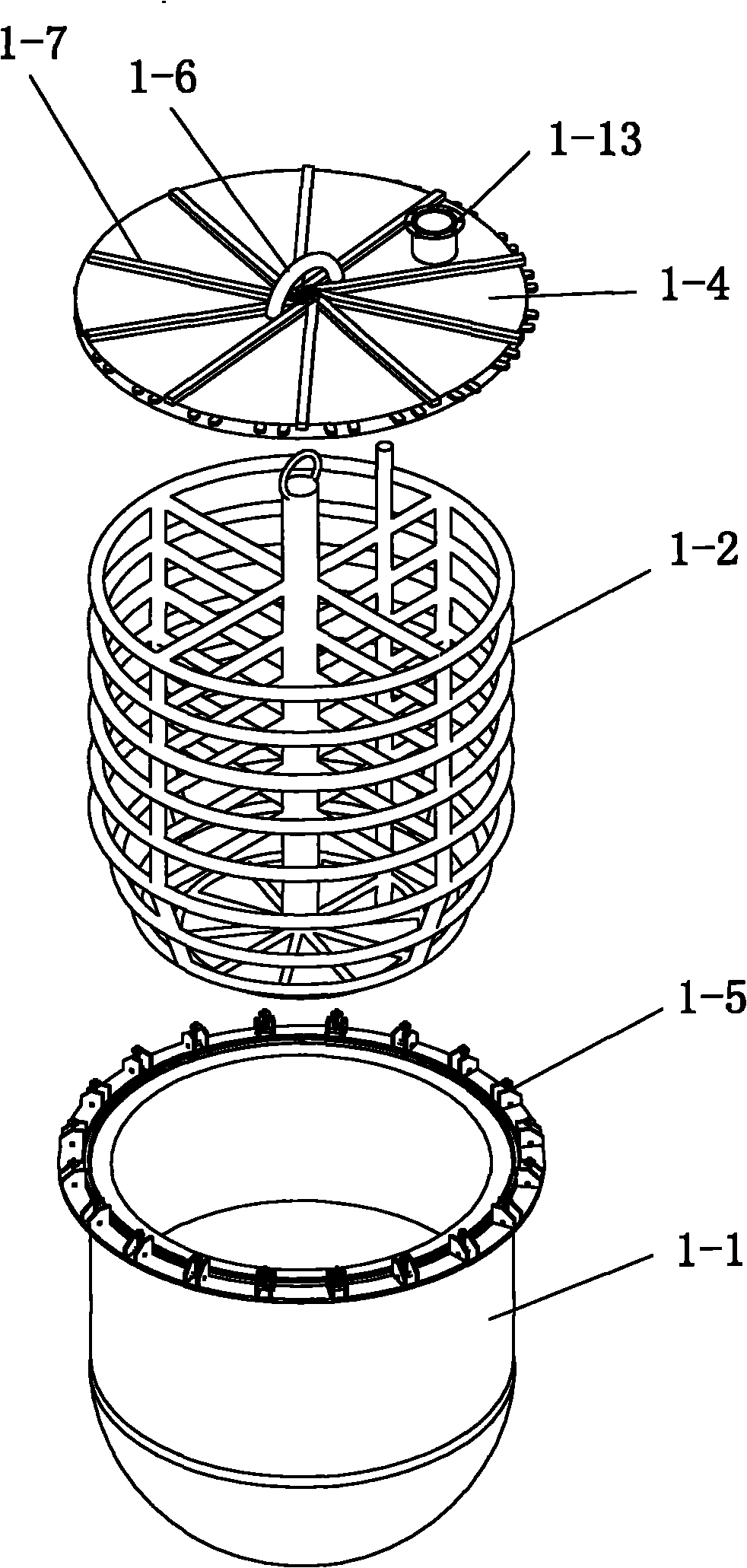
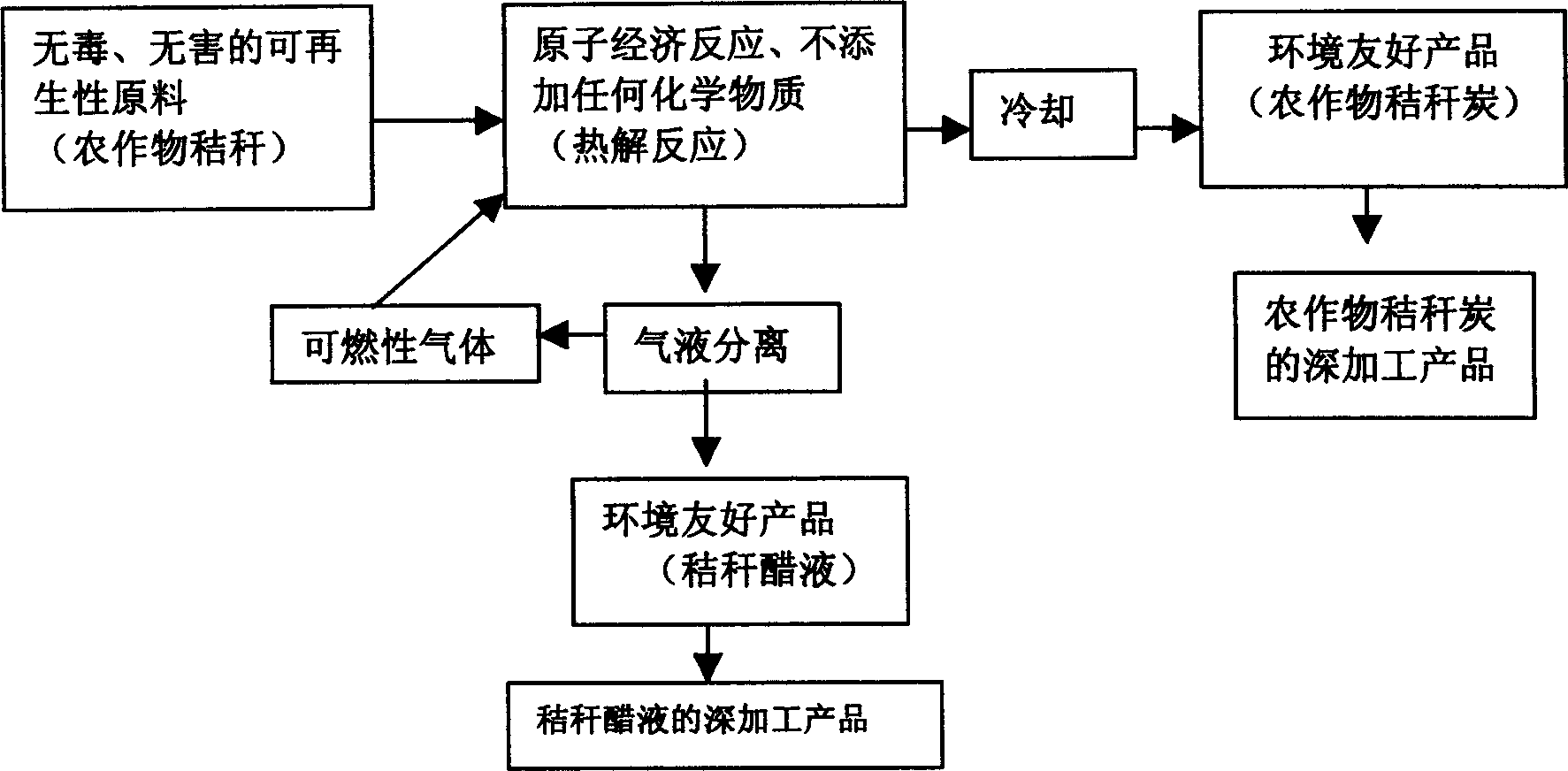
Co-production system and co-production method for biomass carbon, gas, wood tar and wood vinegar
InactiveCN101955780AFirmly connectedReasonable designBiofuelsPyroligneous acid productionSocial benefitsBiomass carbon
The invention discloses a co-production system and a co-production method for biomass carbon, gas, wood tar and wood vinegar. The co-production system comprises a biomass dry distillation kettle, a high-temperature heating furnace, a water cooling device, a washing device, a liquid separation device, a gas storage tank, a water-ring vacuum pump, a compressor, wood tar storage tank and a wood vinegar storage tank, wherein the liquid separation device separates wood vinegar and wood tar in the mixed liquid obtained by gas-liquid separation of the water cooling device; the co-production method comprises the following steps: 1, charging; 2, high-temperature carbonization: water cooling and gas-liquid separation, washing, gas storage and separation and storage of liquid matters; and 3, obtaining of the biomass carbon after the high-temperature carbonization. The co-production system for the biomass carbon, gas, wood tar and wood vinegar has the advantages of reasonable design, convenient processing, simple mounting arrangement, easy operation and good effect; and the co-production method has the advantages of convenient realization, high yield, low cost, fast co-production and relatively high production purity and has obvious economic and social benefits and wide popularization and application prospect.
Owner:陕西亿鑫生物能源科技开发有限公司
Low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and processes for producing the same
ActiveUS20120022171A1Large water contentReduce moistureDirect heating destructive distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryWater contentChemistry
Low water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and processes for producing them are provided. The process includes condensing pyrolysis gases including condensable pyrolysis gases and non-condensable gases to separate the condensable pyrolysis gases from the non-condensable gases, the non-condensable gases having a water content, drying the non-condensable pyrolysis gases to reduce the water content of the-non-condensable gases to form reduced-water non-condensable pyrolysis gases, and providing the reduced-water non-condensable pyrolysis gases to a pyrolysis reactor for forming the biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Process for extracting wood-vinegar fluid from almond
InactiveCN101074382AIncrease contentEasy extractionBiofuelsPyroligneous acid productionAdditive ingredientGas phase
Process for extracting wood vinegar liquid from apricot shell is carried out by removing sand and stone impurities from apricot shell, dry distilling, adding purified apricot shell into dry-distilling kettle, heating while decomposing at 450-550 degree under isolated air for 4-6 hrs, condensing for gas-phase product induced from dry-distilling kettle to obtain condensed crude wood vinegar liquid, laying aside above 30 days in container, separating out three layers, rectifying, removing impurities of upper and lower layer, rectifying for middle layer to obtain refined wood vinegar liquid. It's non-toxic, non-pollution, green, has high effective-ingredient content and better quality and smells good.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
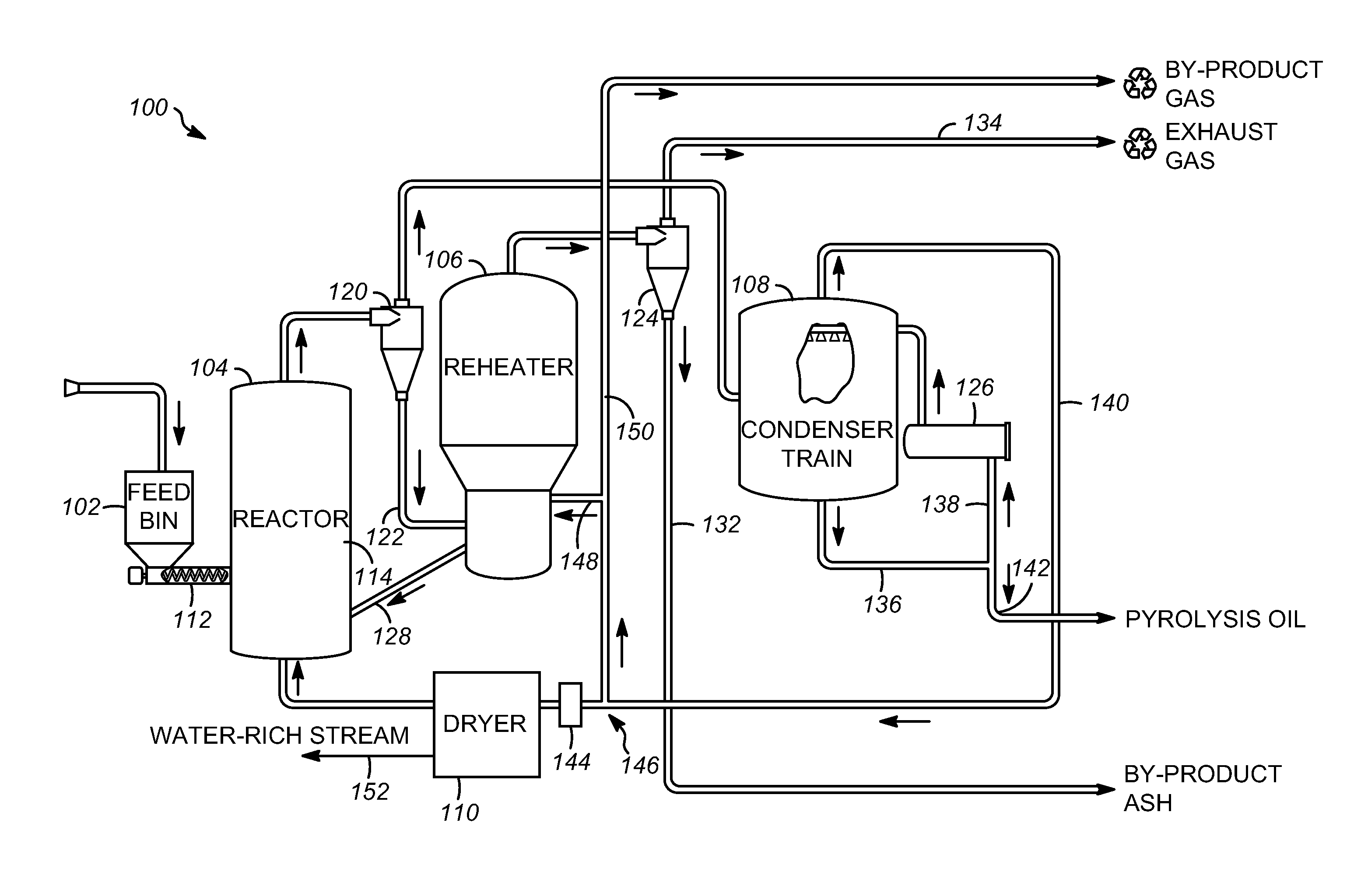
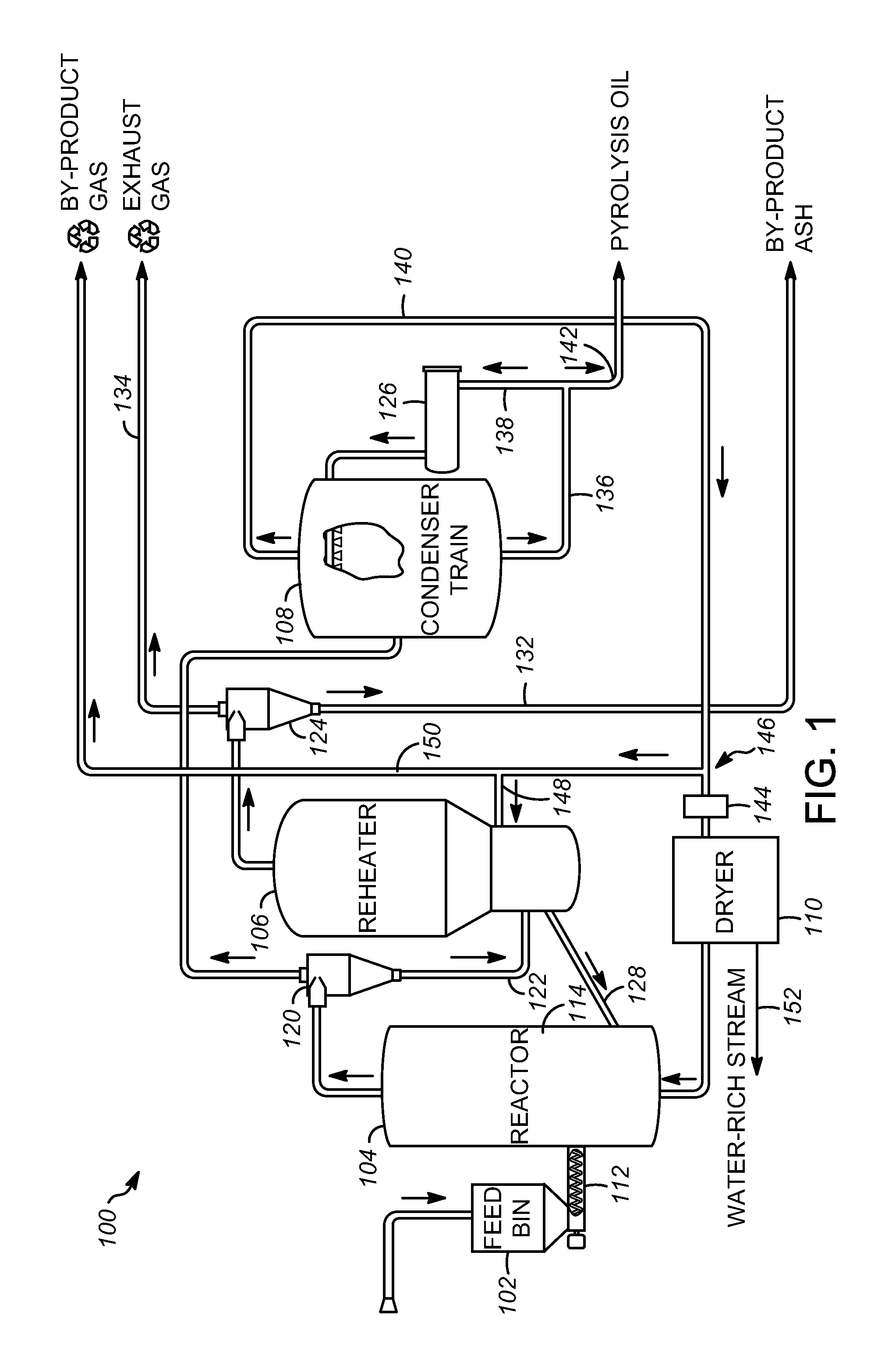
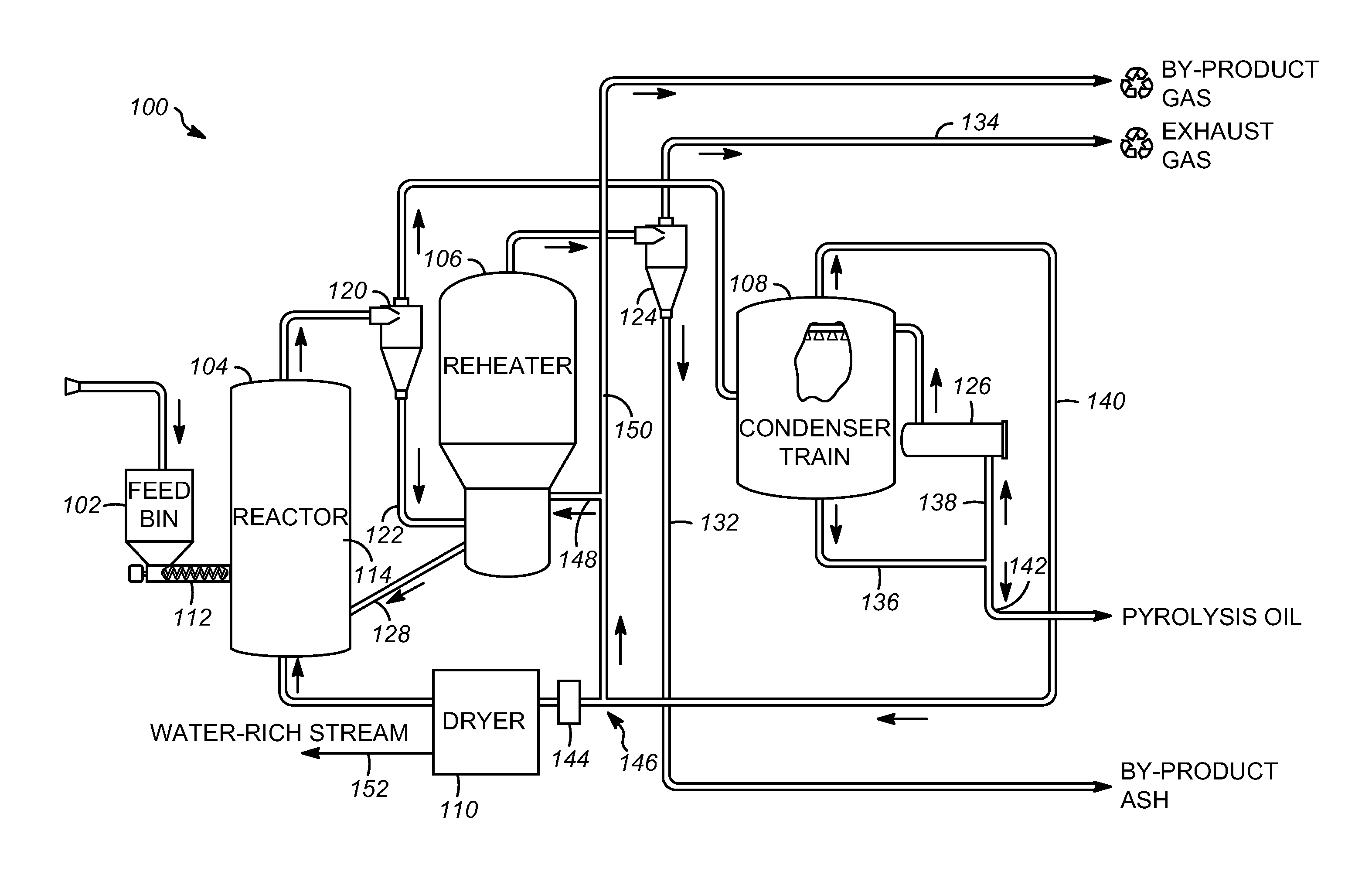
Char-handling processes in a pyrolysis system
Char-handling processes for controlling overall heat balance, ash accumulation, and afterburn in a reheater are provided. Carbonaceous biomass feedstock is pyrolyzed using a heat transfer medium forming pyrolysis products and a spent heat transfer medium. The spent heat transfer medium is separated into segregated char and char-depleted spent heat transfer medium. The char-depleted spent heat transfer medium is introduced into a dense bed of heat transfer medium fluidized by a stream of oxygen-containing regeneration gas. All or a portion of the segregated char is combusted in the dense bed using the stream of oxygen-containing regeneration gas. A portion of the segregated char may be exported out of the pyrolysis system to control the overall heat balance and ash accumulation.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Heat treatment system using superheated steam
The present invention provides a heat treatment system, which includes a treatment chamber having an input port and a discharge port for charging and discharging materials to be treated. A heating system including a plurality of pipe-like heaters positioned one after another in serial arrangement is provided so that the heating temperature is gradually increased for heating the steam or the atomized water introduced from the water feeding system into the heaters by applying voltage on the heaters to turn the steam and the atomized water to superheated steam, and for performing heat treatment on the materials to be treated by injecting the superheated steam into the treatment chamber. A circulating system is provided for sucking the superheated steam and the dry distillation gas in the treatment chamber and for supplying the steam and the gas again into the treatment chamber after deodorizing and filtering, and a control unit is provided for controlling operating conditions such as supply quantity of the steam, duration of treatment, etc.
Owner:AOKI IND +1
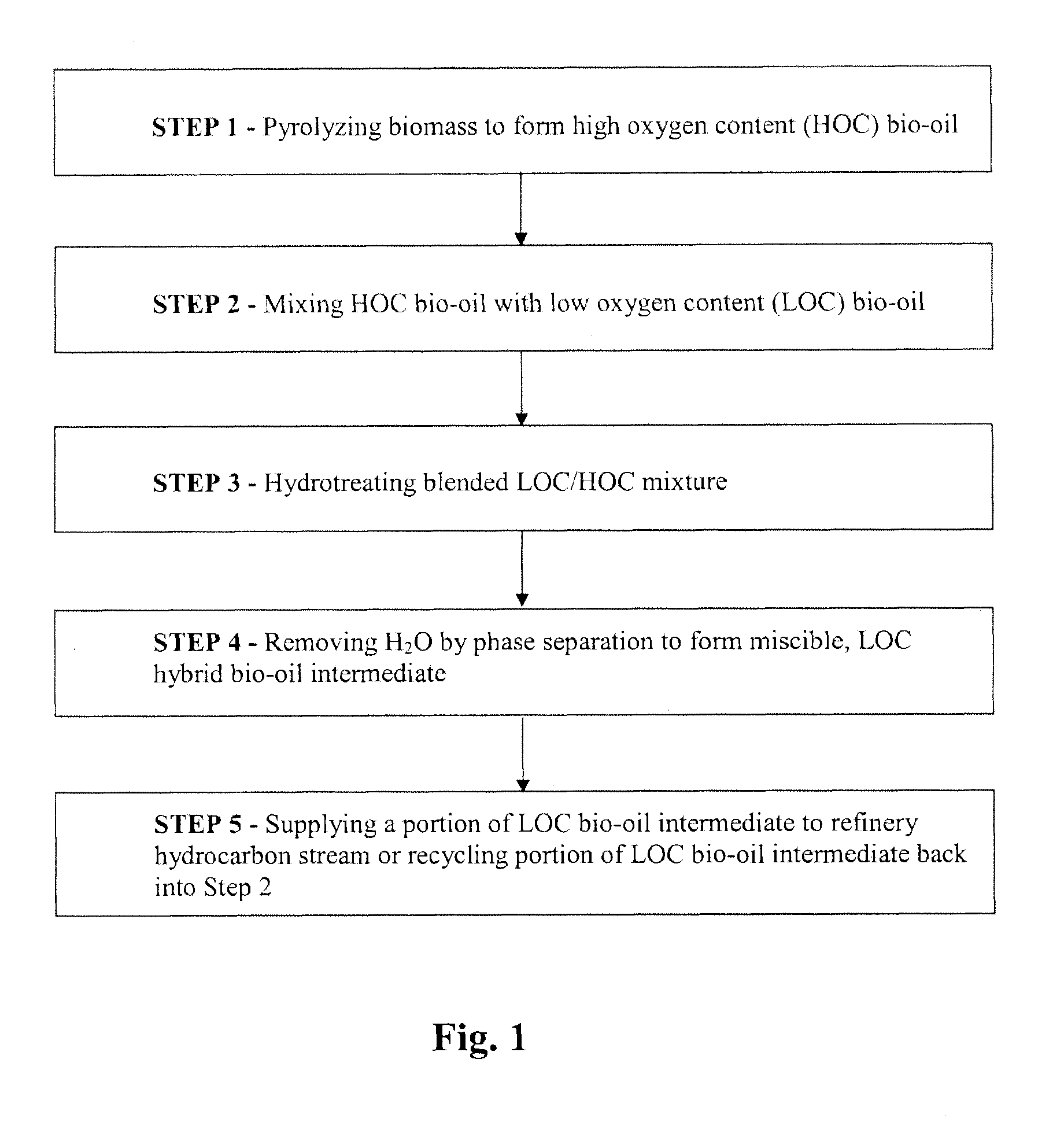
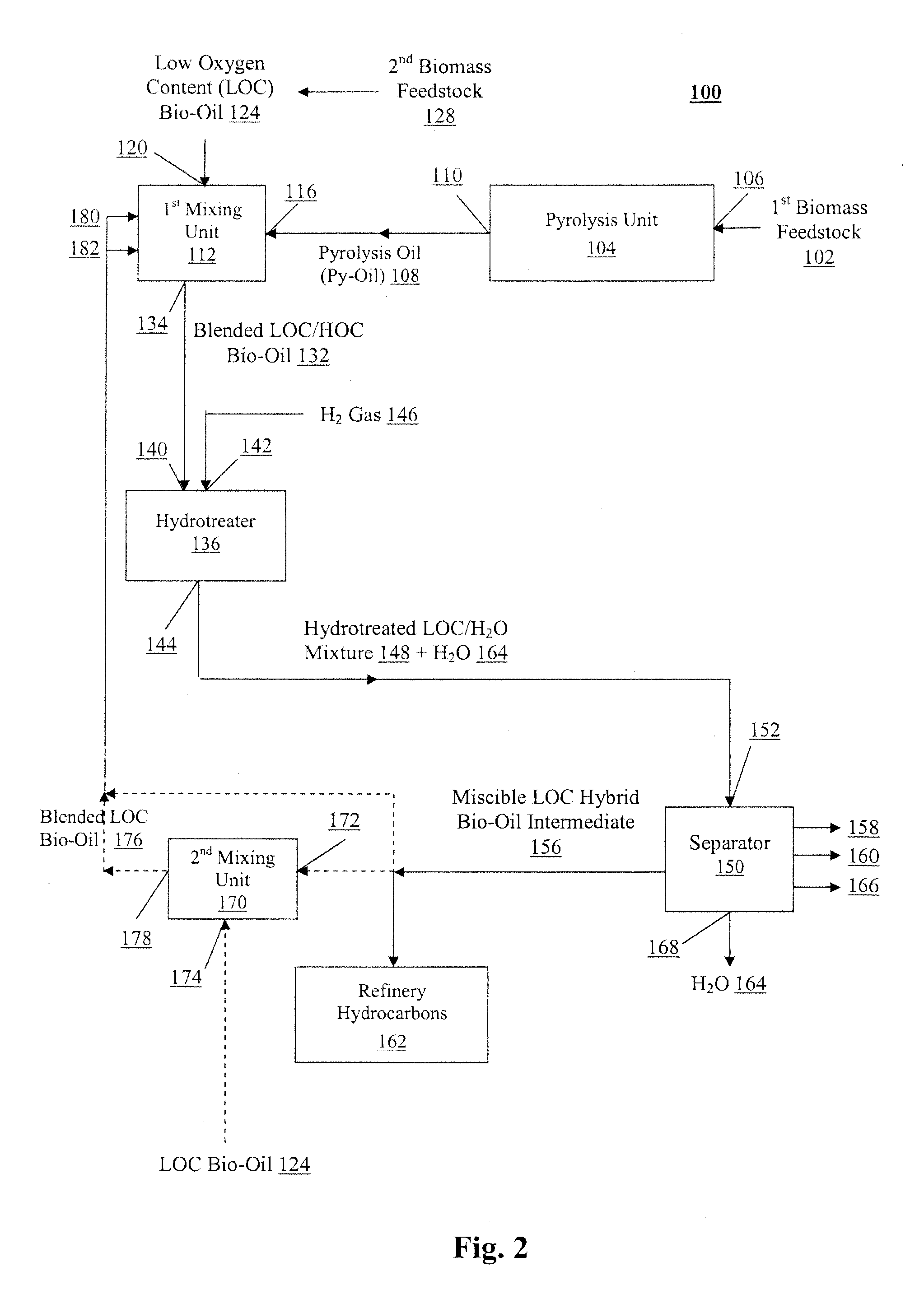
Process for producing a refinery stream-compatible bio-oil from a lignocellulosic feedstock
In one aspect, a method for rendering biomass-derived pyrolysis oil miscible with refinery hydrocarbons comprises mixing a high oxygen content bio-oil having an oxygen content of at least about 10 wt. % with a low oxygen content bio-oil having an oxygen content of less than about 8 wt. % to produce a blended oil. The blended oil may be hydrotreated to produce a deoxygenated hydrotreated mixture from which water is removed using a separator, resulting in a low oxygen content hybrid bio-oil intermediate miscible in refinery process streams. A portion of the low oxygen content hybrid bio-oil intermediate may be recycled with the high oxygen content bio-oil or removed for use in a refinery process stream for further hydroprocessing.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same
Low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oils and methods for producing the same are provided. Metal- and water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is contacted with an acidic ion-exchange resin having sulfonic acid groups to produce a low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil. The low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is removed from the spent ion-exchange resin after ion-exchange. The low metal, water-containing biomass-derived pyrolysis oil is distilled to produce a low metal, low water biomass-derived pyrolysis oil and a distillation product. The distillation product comprises one or both of an alcohol ion-exchange regenerant and an acidic ion-exchange regenerant which may be used to regenerate the spent ion-exchange resin. The regenerated acidic ion-exchange resin may be recycled. The spent alcohol and acid ion-exchange regenerants may be recovered and recycled.
Owner:UOP LLC
Absorption and quench method for biomass pyrolysis product
ActiveUS20120167452A1High aromatic contentFaster quenching rateGas treatmentOrganic chemistryBoiling pointBiomass
A biomass pyrolysis product is quenched by direct cooling with a cold quench fluid and initial product separation is performed based on boiling point and solubility in the quench fluid. A properly chosen quench fluid may act as a selective solvent, thus providing dilution of unstable precursors of pyrolytic lignin or other heavy by-products, and / or separation of certain undesirable pyrolysis oil components such as water and light acids.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
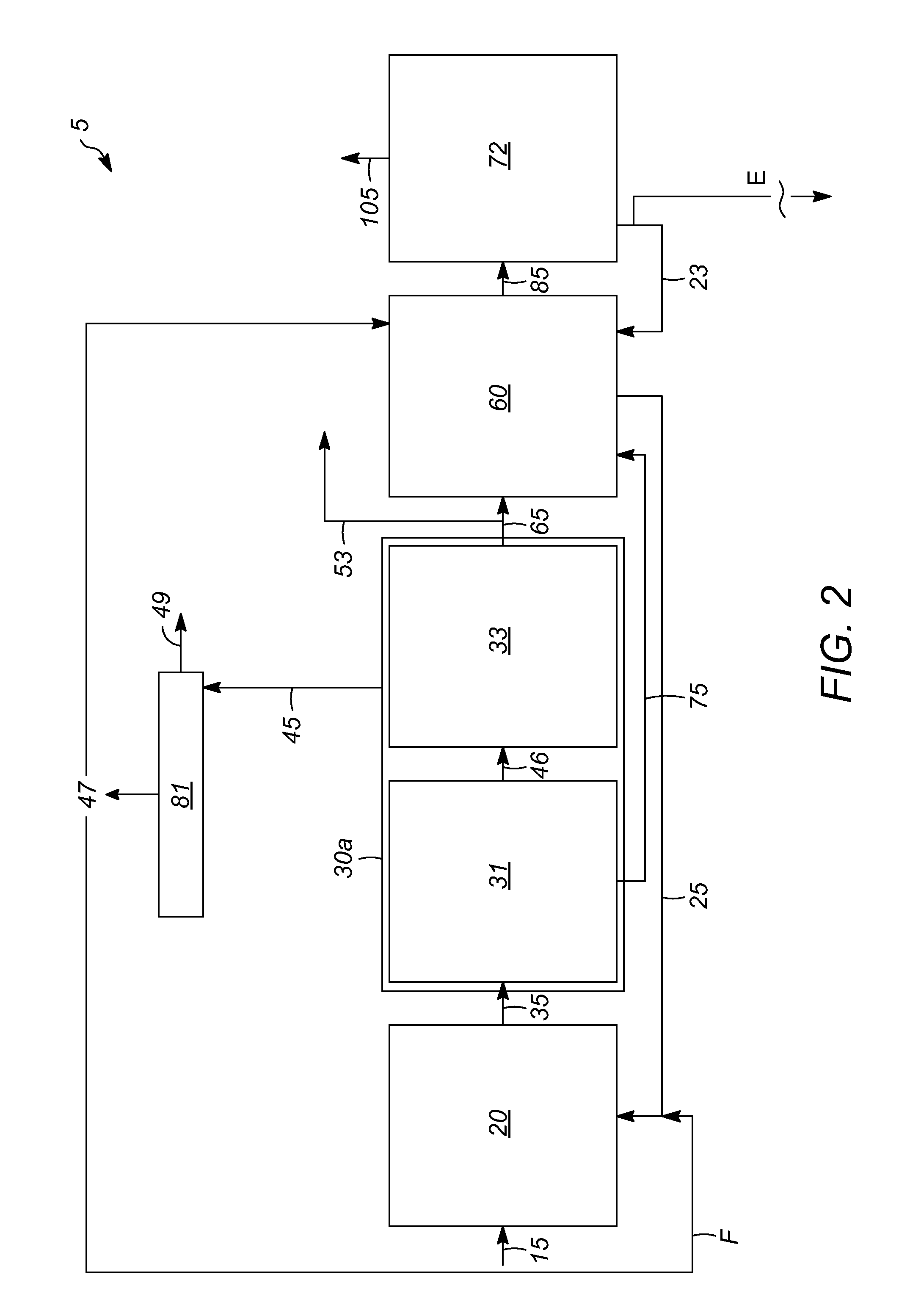
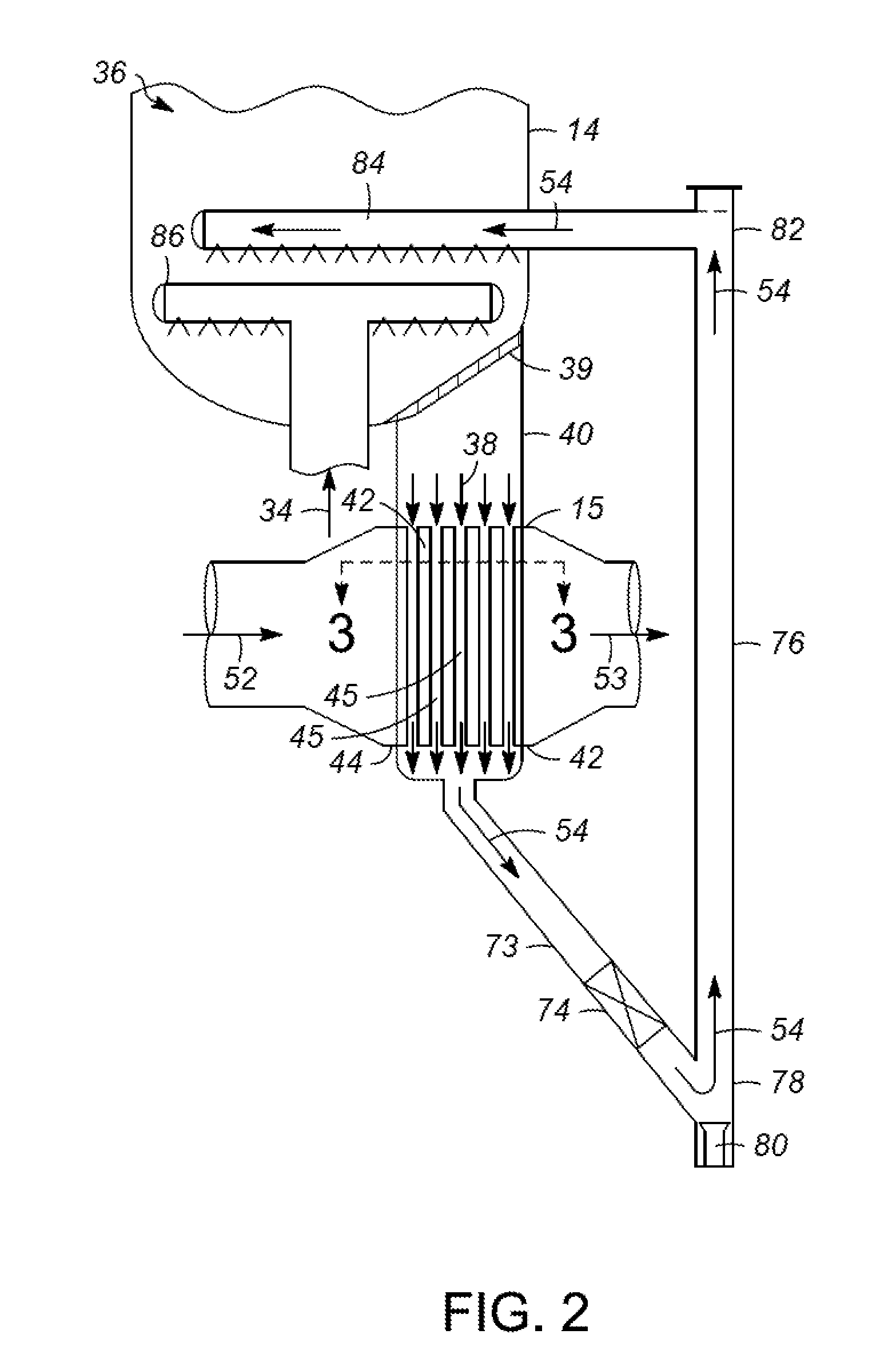
Apparatuses and methods for controlling heat for rapid thermal processing of carbonaceous material
ActiveUS20130075072A1Rapid heat treatmentThermal non-catalytic crackingDirect heating destructive distillationInorganic particleHeat carrier
Embodiments of apparatuses and methods for controlling heat for rapid thermal processing of carbonaceous material are provided herein. The apparatus comprises a reheater for containing a fluidized bubbling bed comprising an oxygen-containing gas, inorganic heat carrier particles, and char and for burning the char into ash to form heated inorganic particles. An inorganic particle cooler is in fluid communication with the reheater to receive a first portion of the heated inorganic particles. The inorganic particle cooler is configured to receive a cooling medium for indirect heat exchange with the first portion of the heated inorganic particles to form first partially-cooled heated inorganic particles that are fluidly communicated to the reheater and combined with a second portion of the heated inorganic particles to form second partially-cooled heated inorganic particles. A reactor is in fluid communication with the reheater to receive the second partially-cooled heated inorganic particles.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
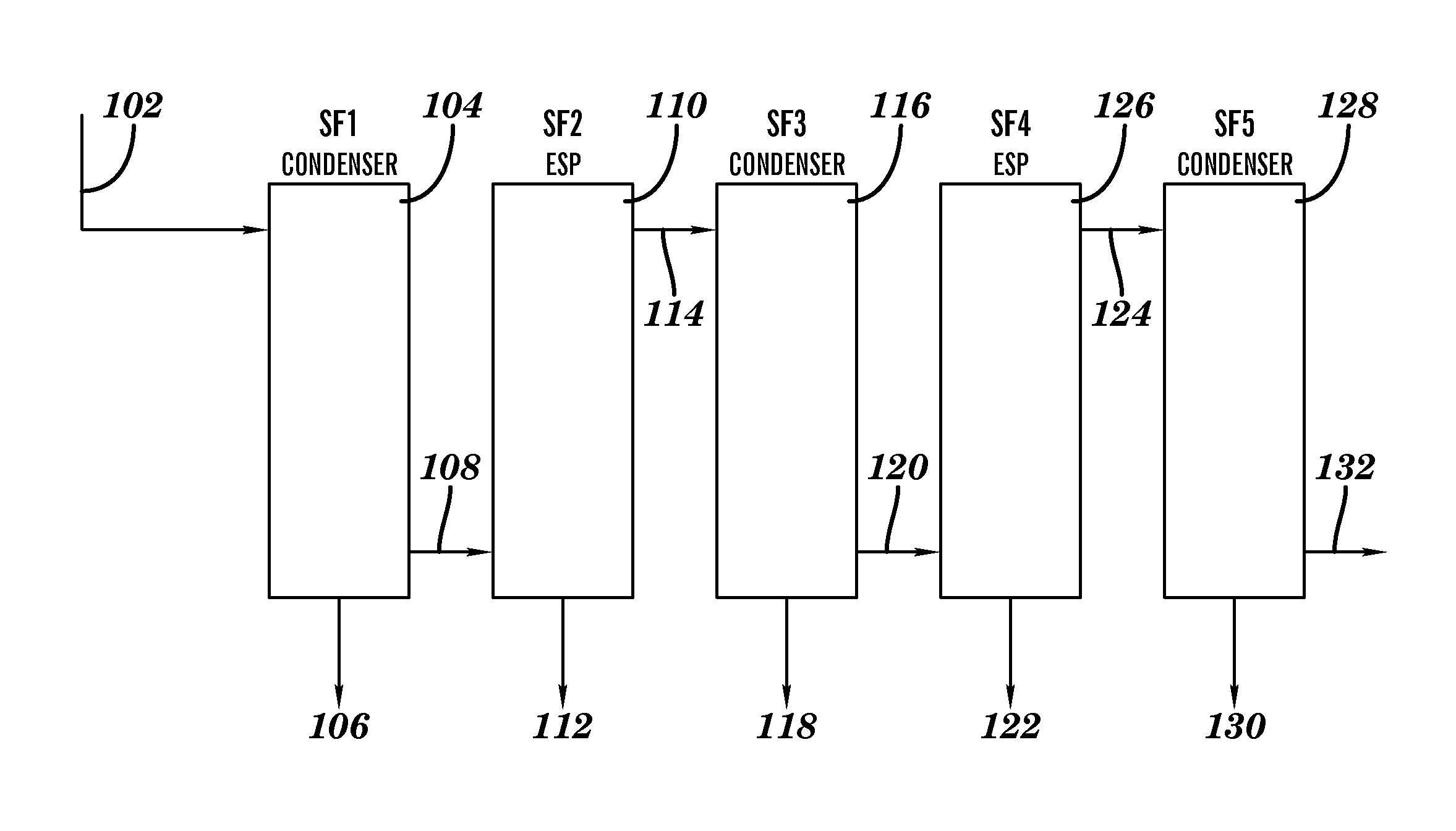
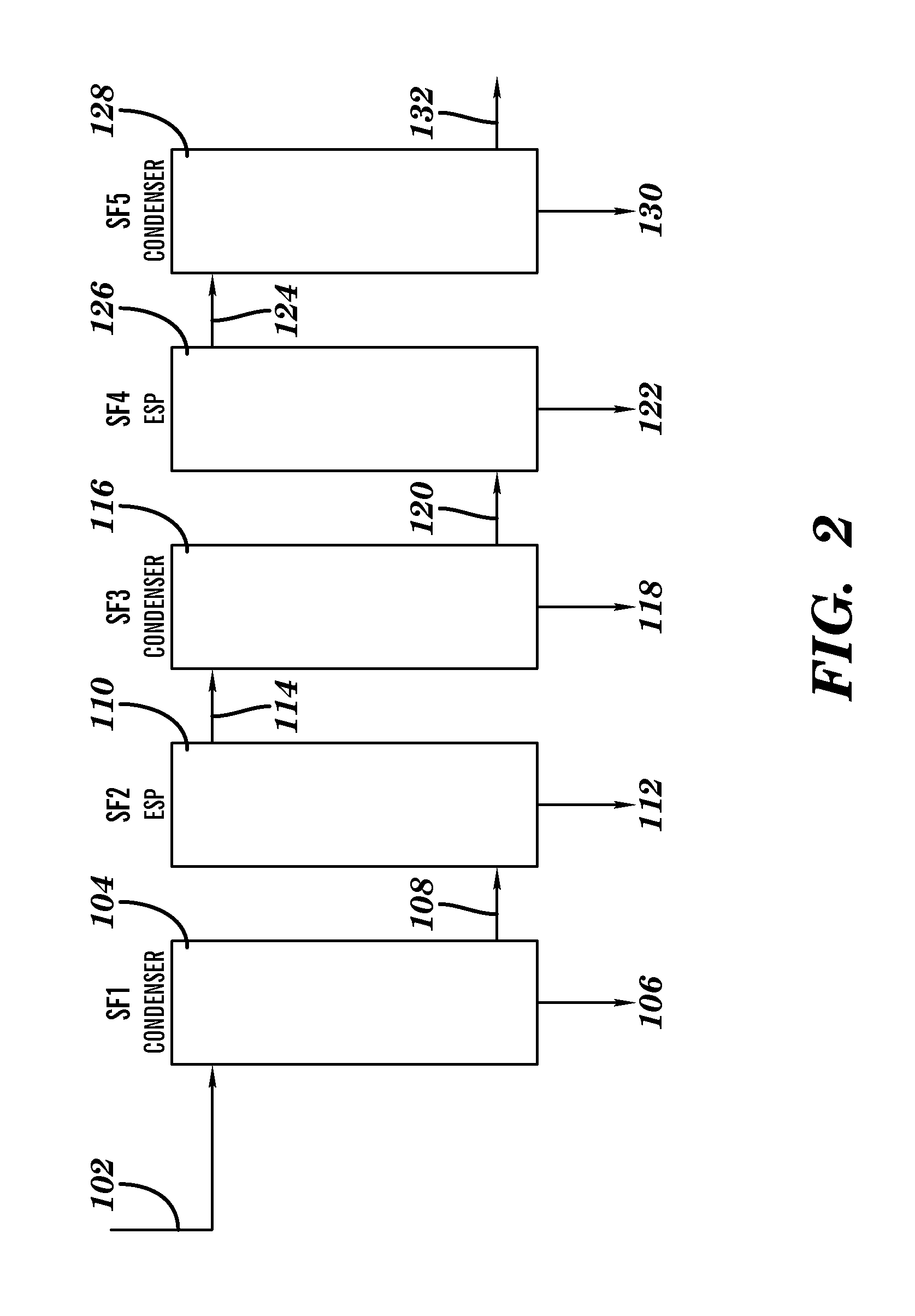
Bio-oil fractionation and condensation
ActiveUS8476480B1Reduced stabilityLower performance requirementsSolid waste disposalDirect heating destructive distillationHeat conductingFractionation
A method of fractionating bio-oil vapors which involves providing bio-oil vapors comprising bio-oil constituents is described. The bio-oil vapors are cooled in a first stage which comprises a condenser having passages for the bio-oil separated by a heat conducting wall from passages for a coolant. The coolant in the condenser of the first stage is maintained at a substantially constant temperature, set at a temperature in the range of 75 to 100° C., to condense a first liquid fraction of liquefied bio-oil constituents in the condenser of the first stage. The first liquid fraction of liquified bio-oil constituents from the condenser in the first stage is collected. Also described are steps for subsequently recovering further liquid fractions of liquefied bio-oil constituents. Particular compositions of bio-oil condensation products are also described.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for preparing stalk charcoal and stalk vinegar liquid form stalks of cropper
InactiveCN1563277AImprove fertilizer efficiencyImprove compactionBiofuelsPyroligneous acid productionCombustion chamberProduct gas
A method for preparing straw charcoal and straw vinegar liquid includes placing agricultural straw into retort for pyrolytic reaction of 4-12 h. at 300-600 deg.C under condition of oxygen being isolated or being provided with limitation; obtaining straw charcoal from solids through drying, precharring, charring and calcining; obtaining straw vinegar liquid and combustible gas by arrying out gas-liquid separation of pyrolysis gas and sending combustible gas back to combustion chamber as heating source.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
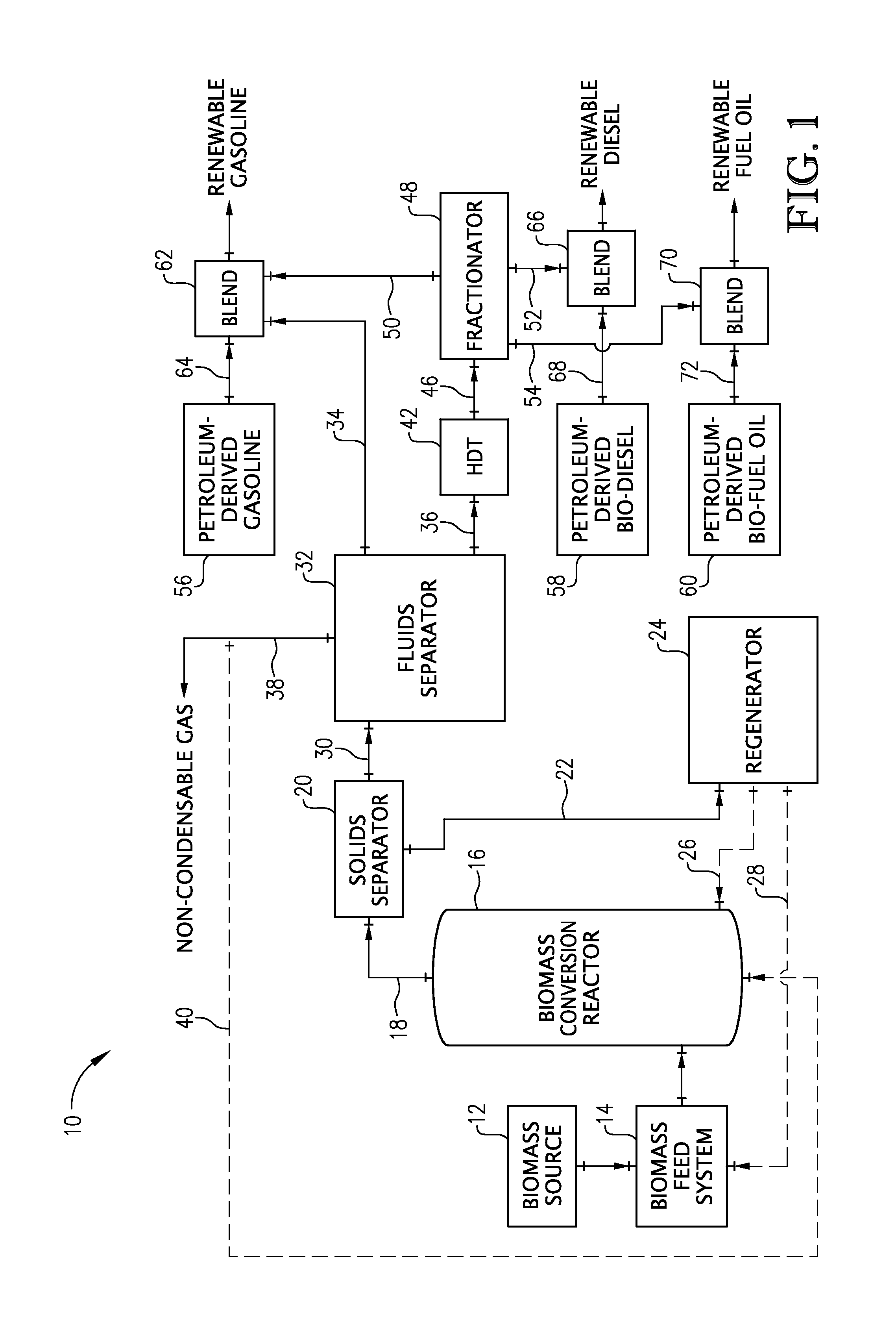
Production of renewable biofuels
A process and system for separating and upgrading bio-oil into renewable fuels is provided. The process comprises separating bio-oil into a light fraction and heavy fraction based on their boiling points. The heavy fraction is then subjected to hydrotreatment, while the light fraction is not subjected to hydrotreatment. At least a portion of the un-hydrotreated light fraction and at least a portion of the hydrotreated heavy fraction are blended with petroleum-derived gasoline to thereby provide a renewable gasoline, and at least a portion of the hydrotreated heavy fraction is blended with petroleum-derived diesel to thereby provide a renewable diesel.
Owner:MARD INC
Popular searches
Bio-feedstock Chemical/physical/physico-chemical processes Gas purification by non-gaseous materials condensation Hydrocarbon oils treatment Educts Carburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysis Gasification processes details Liquid carbonaceous fuels Special form destructive distillation Liquid-gas reaction processes
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com