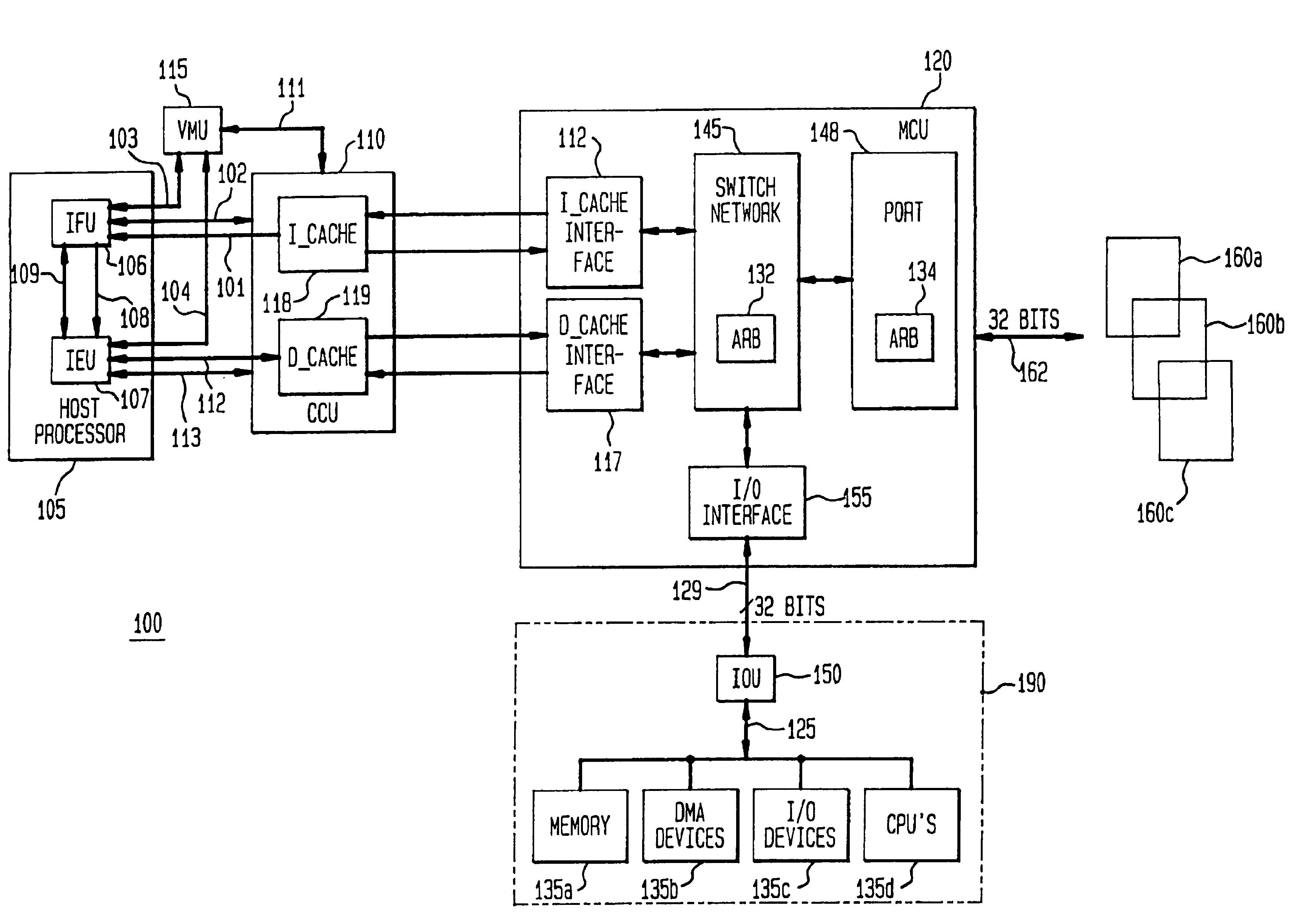
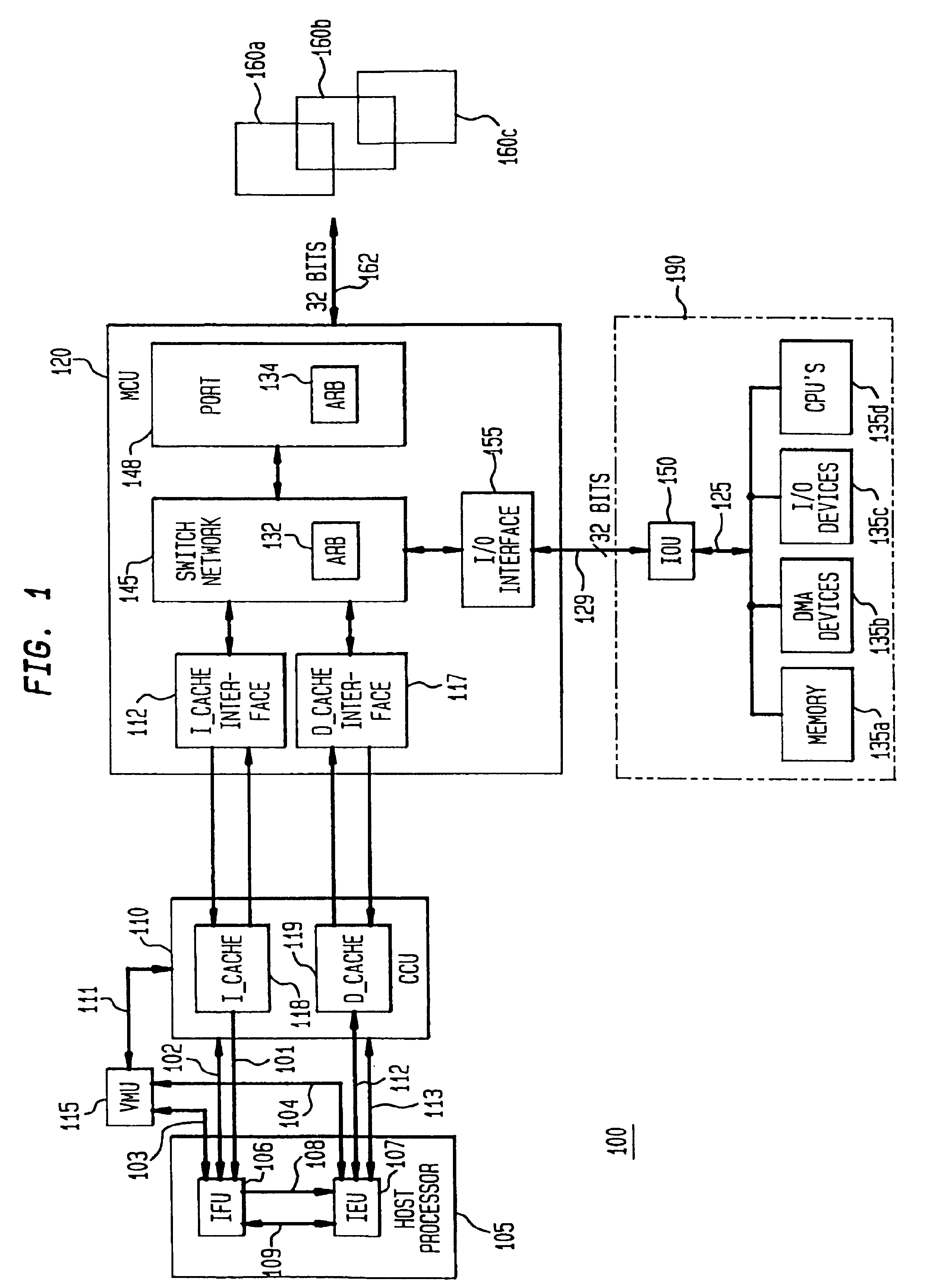
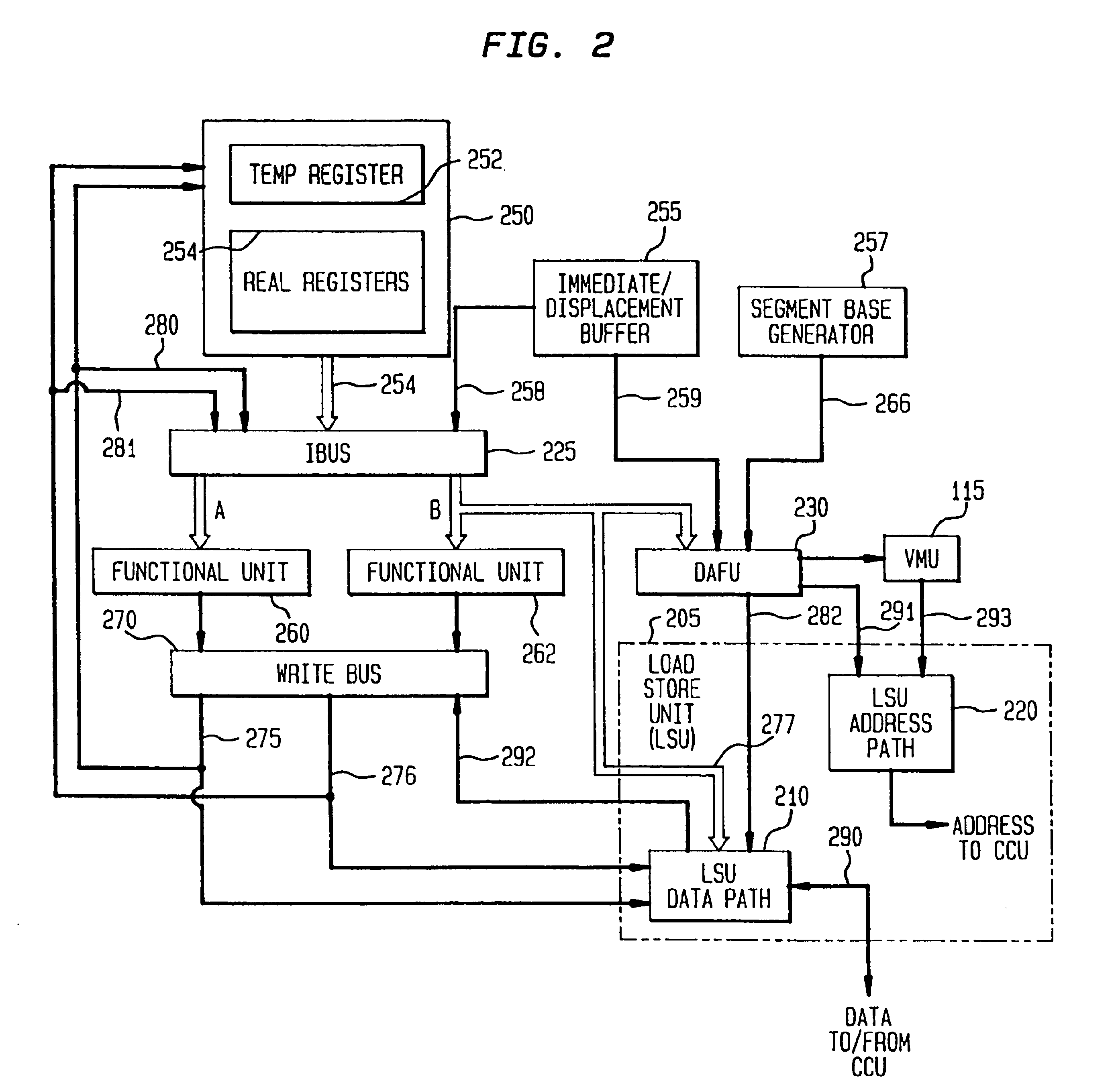
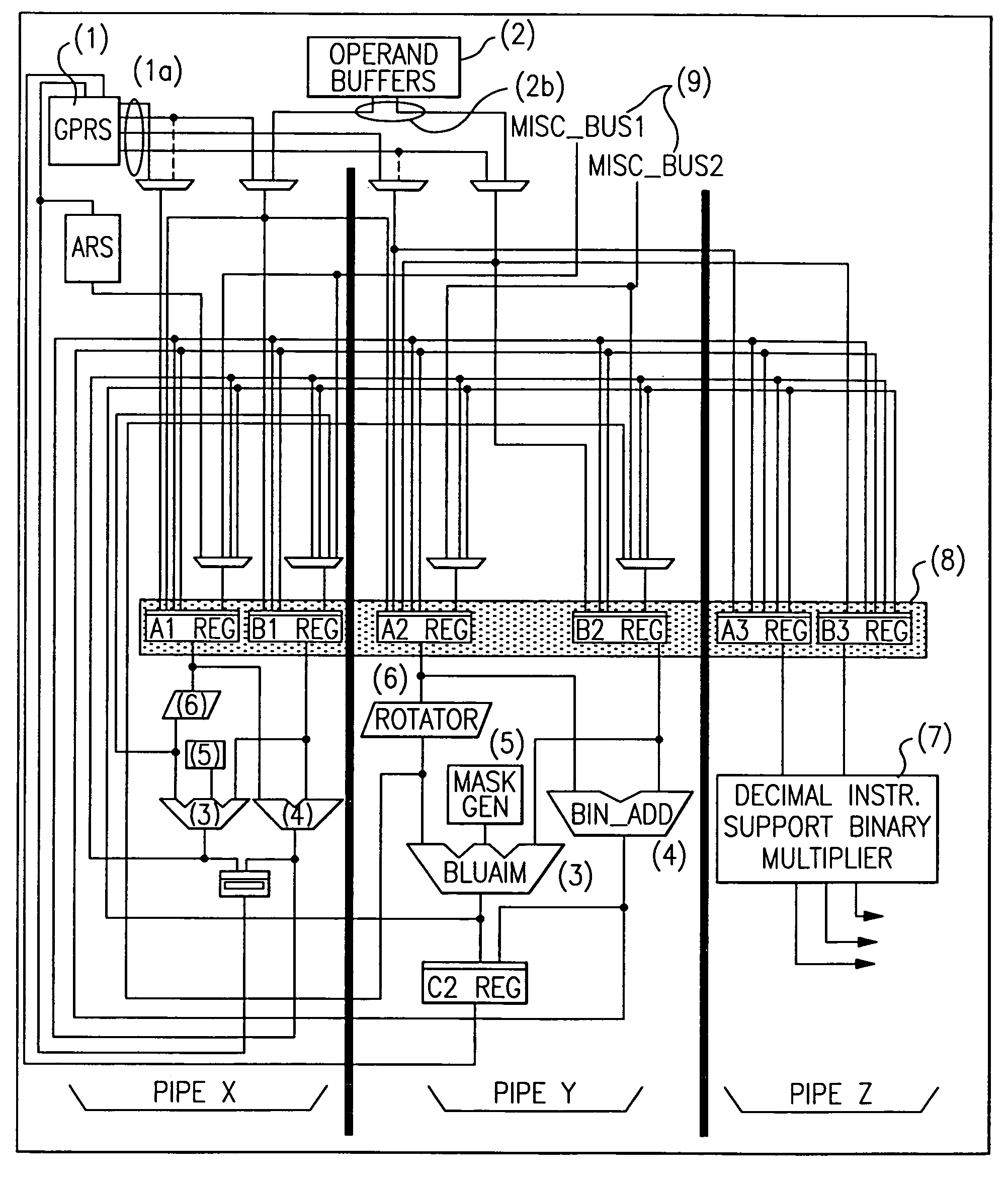
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Superscalar microprocessor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
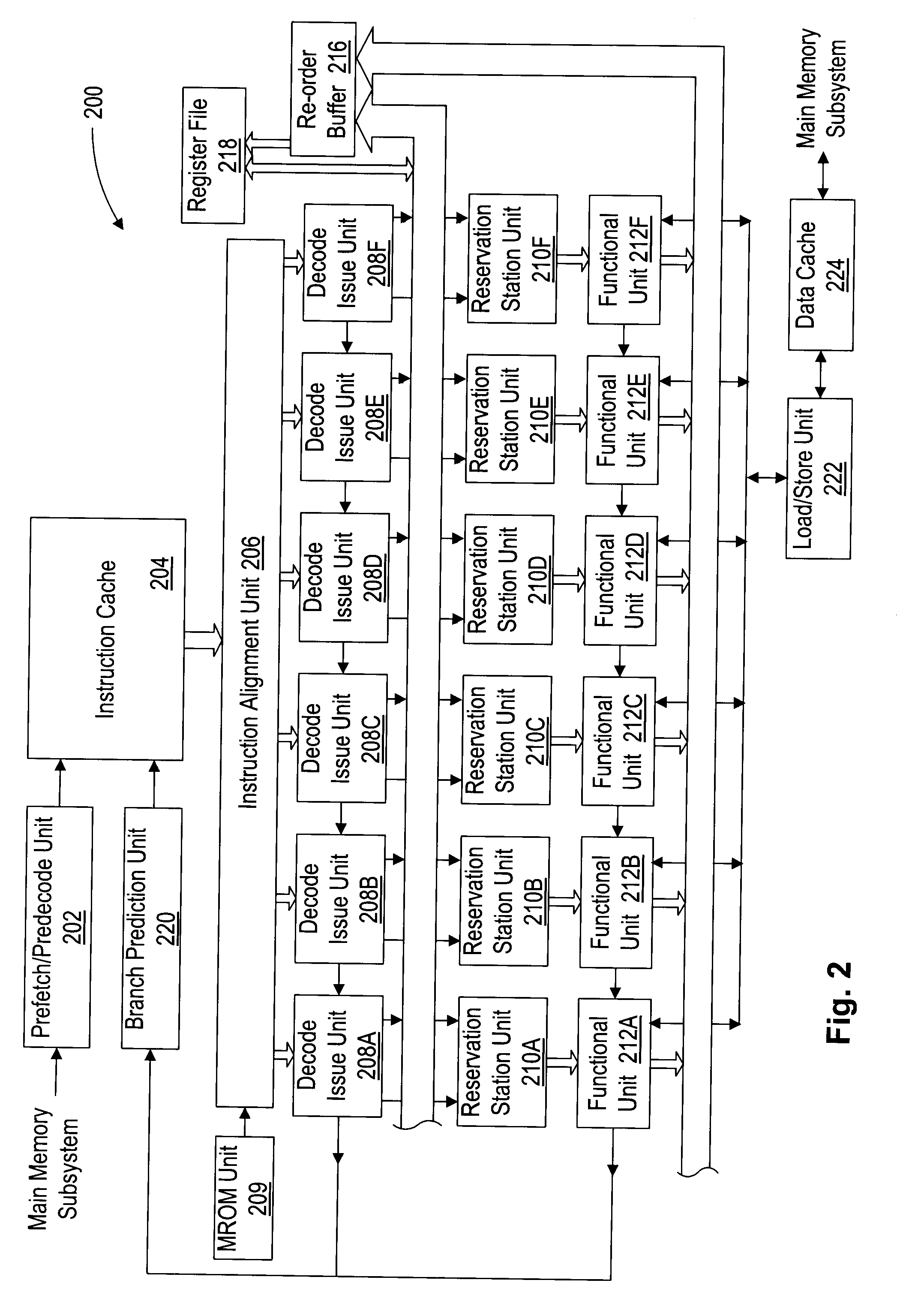
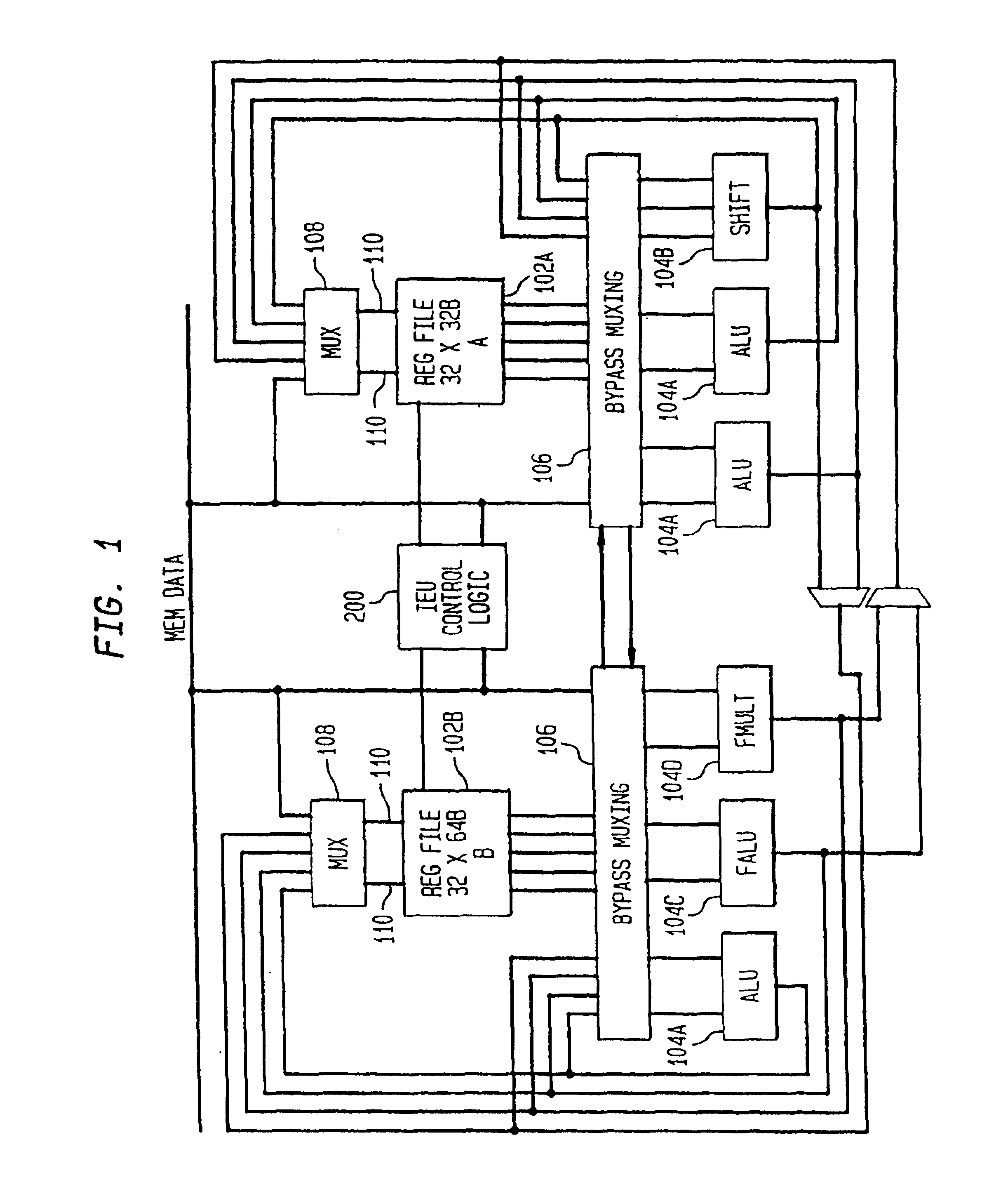
A superscalar processor is a specific type of microprocessor that uses instruction-level parallelism to help to facilitate more than one instruction executed during a clock cycle.
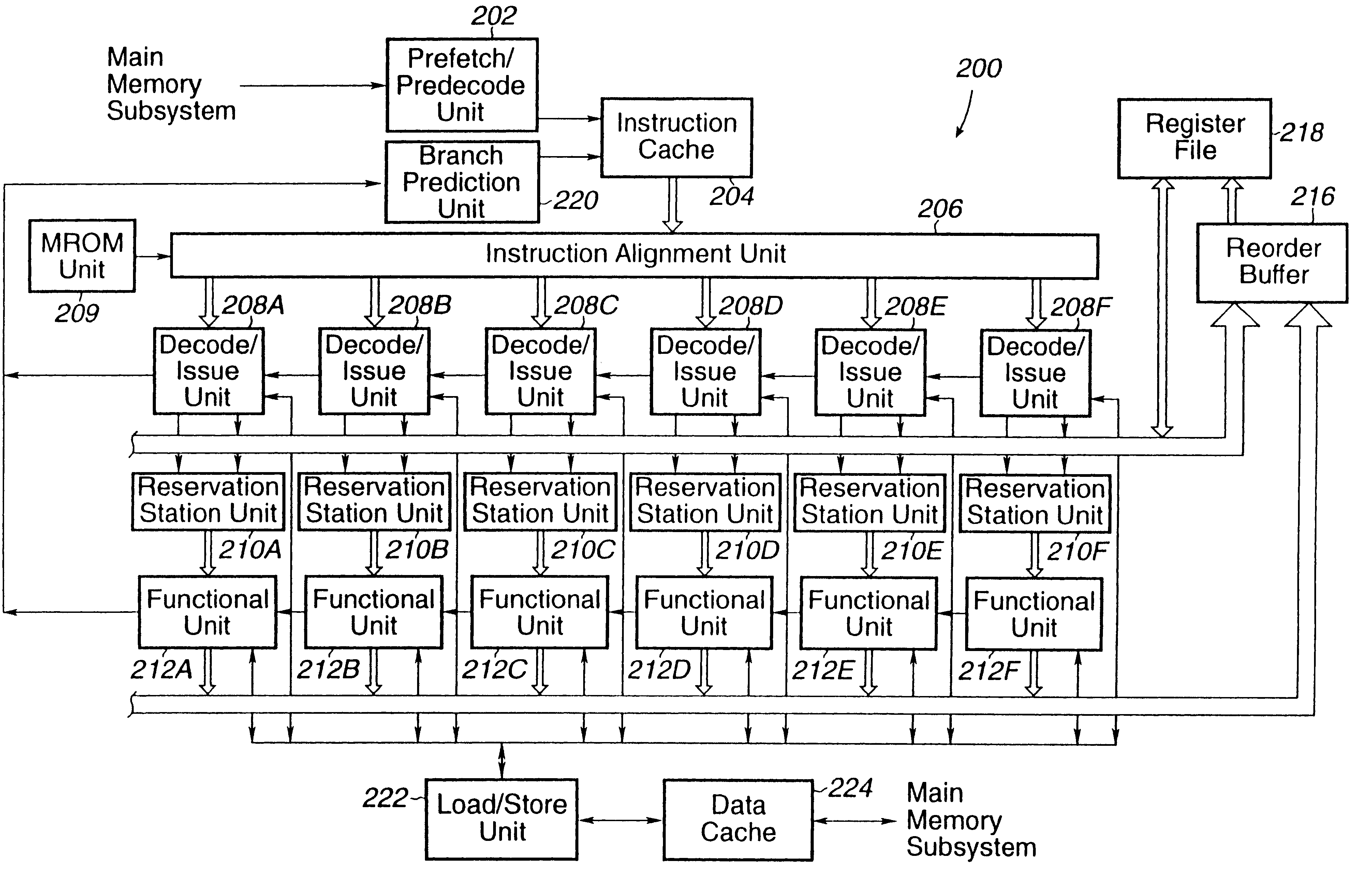
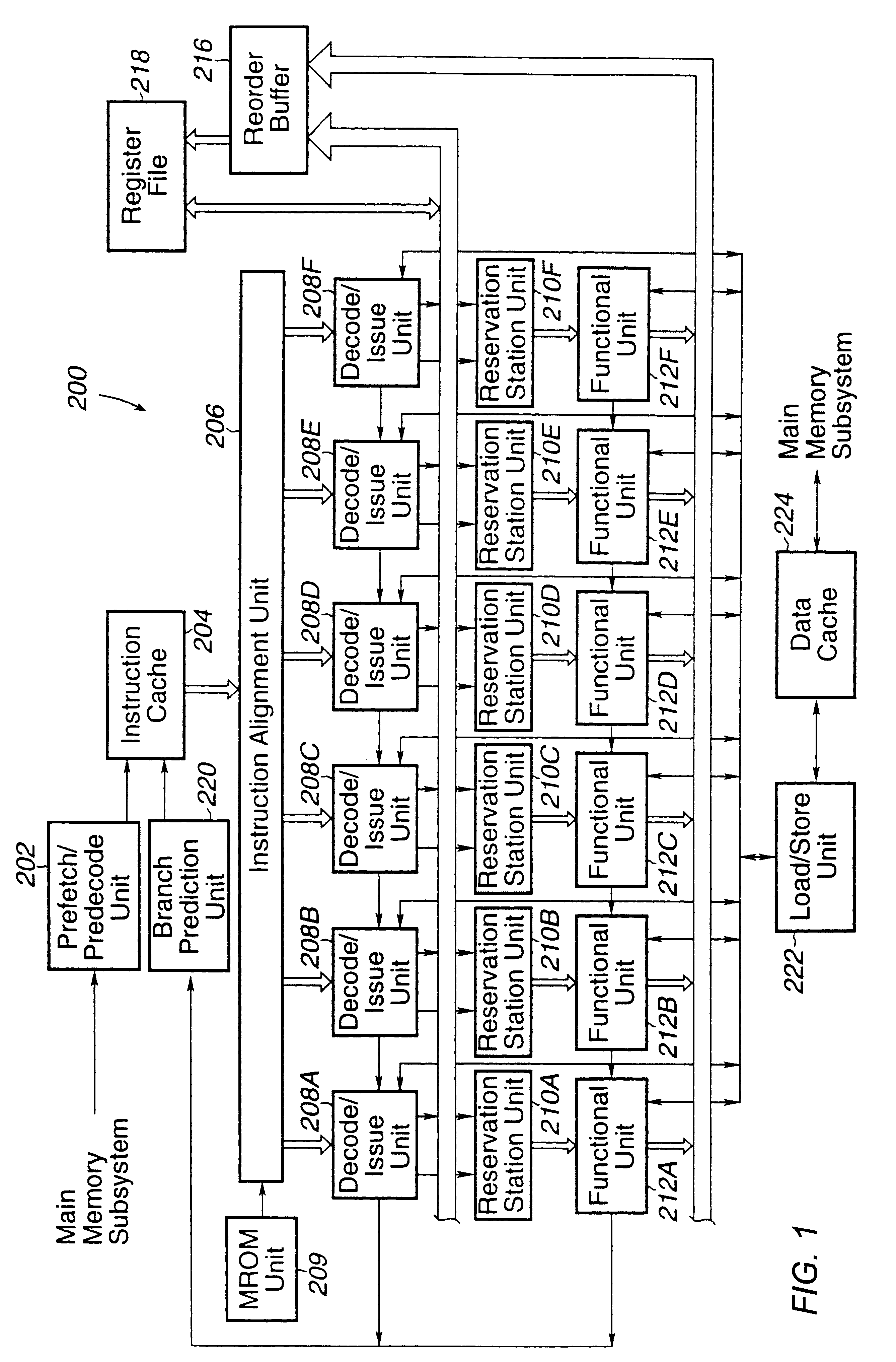
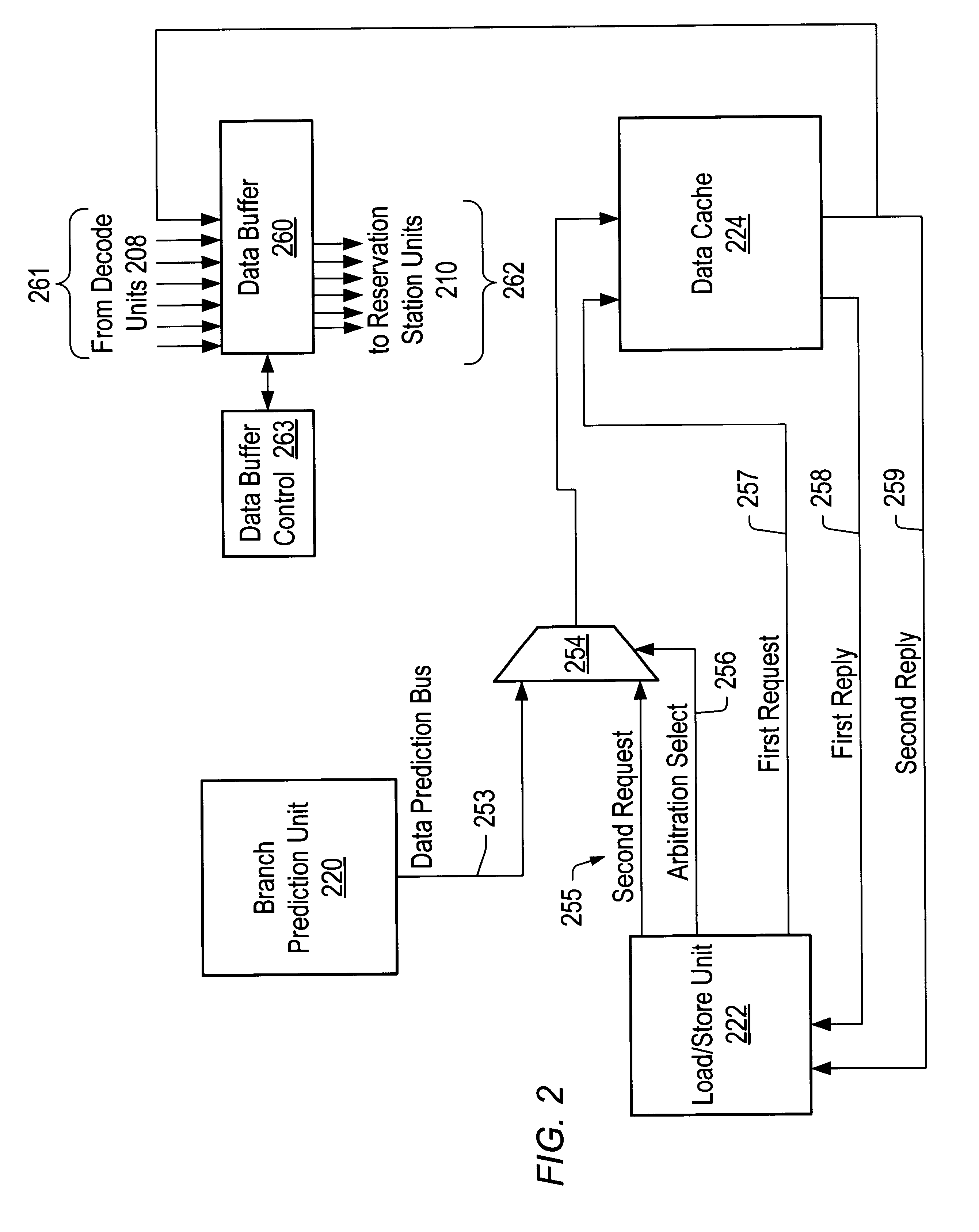
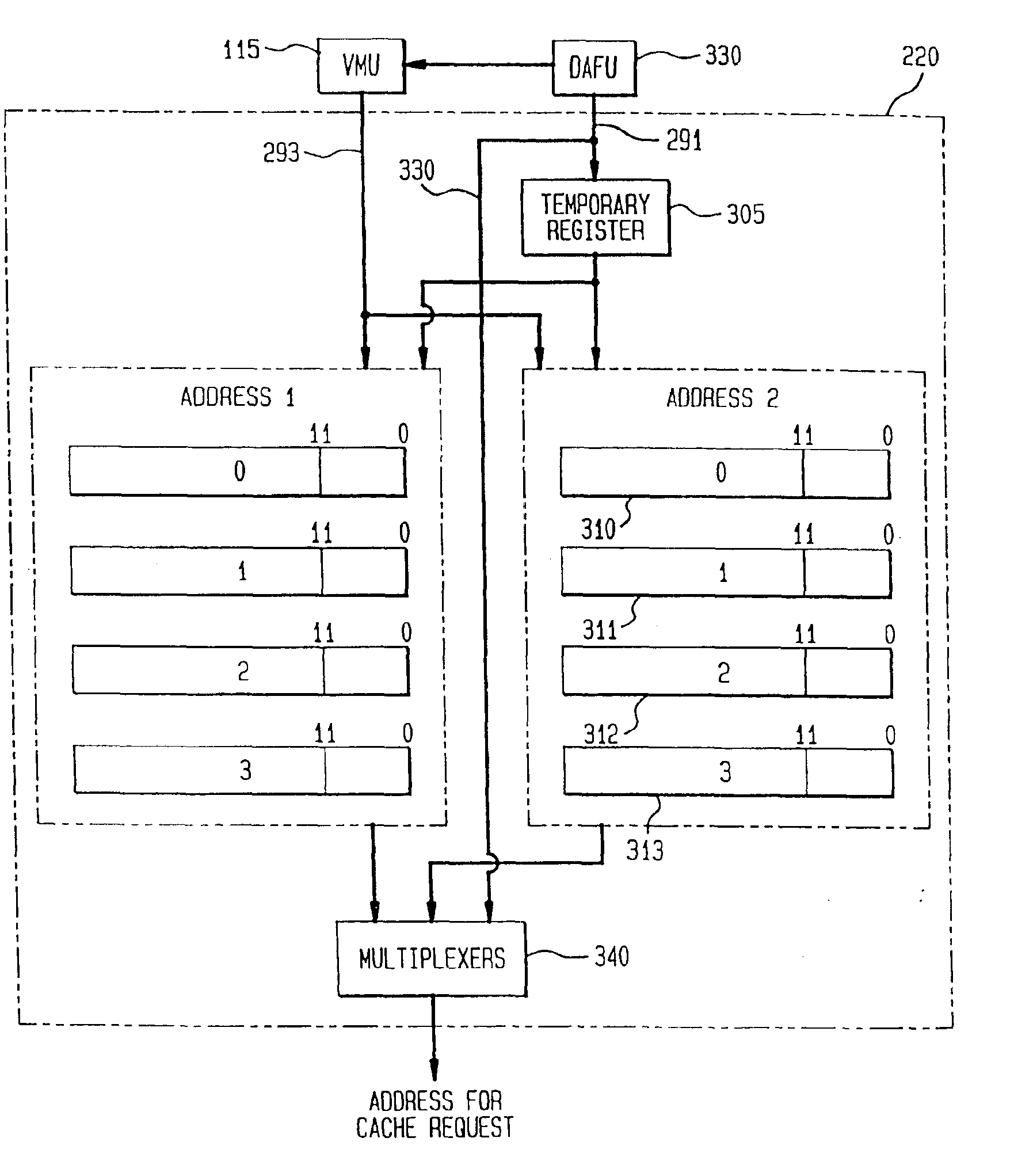
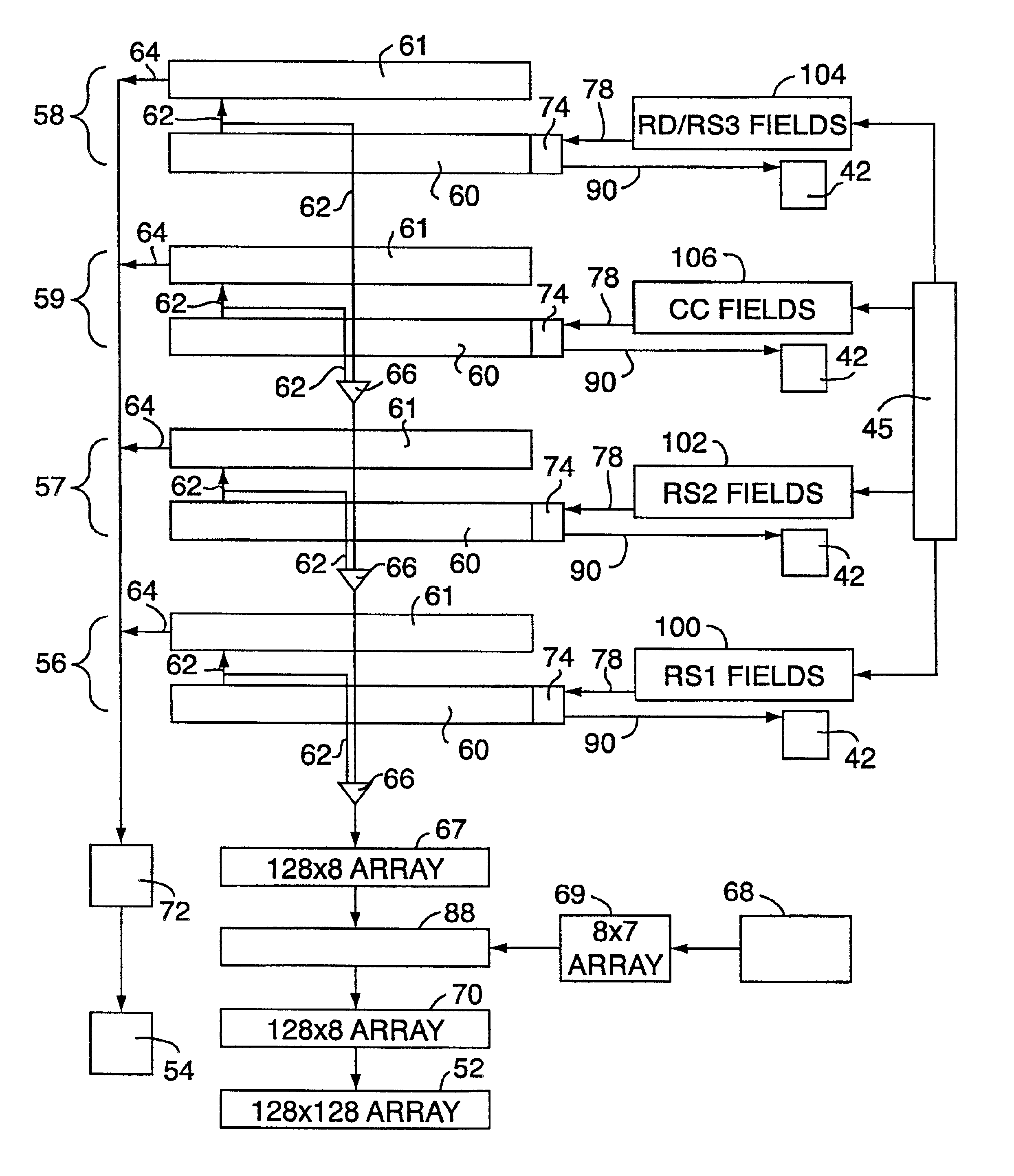
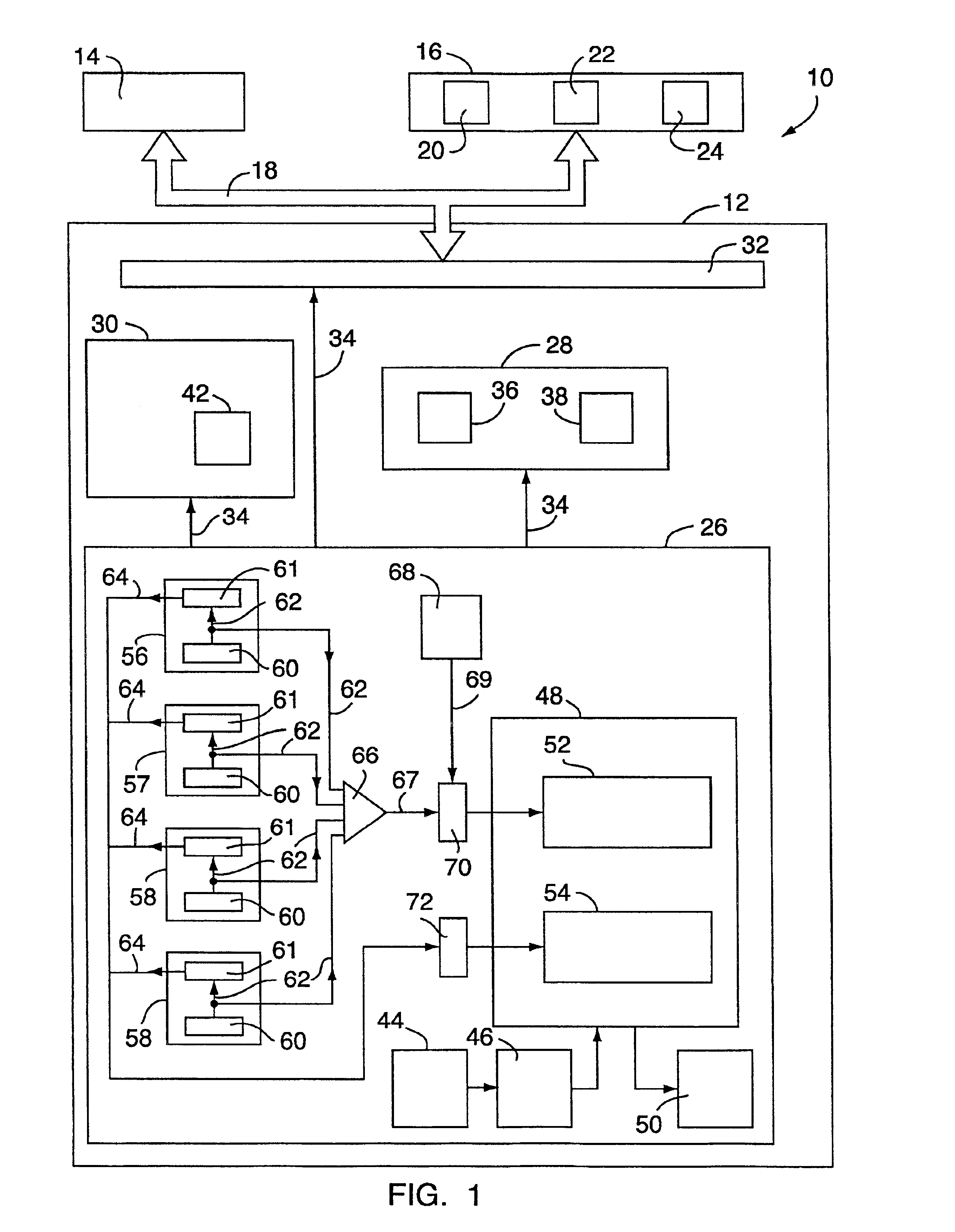
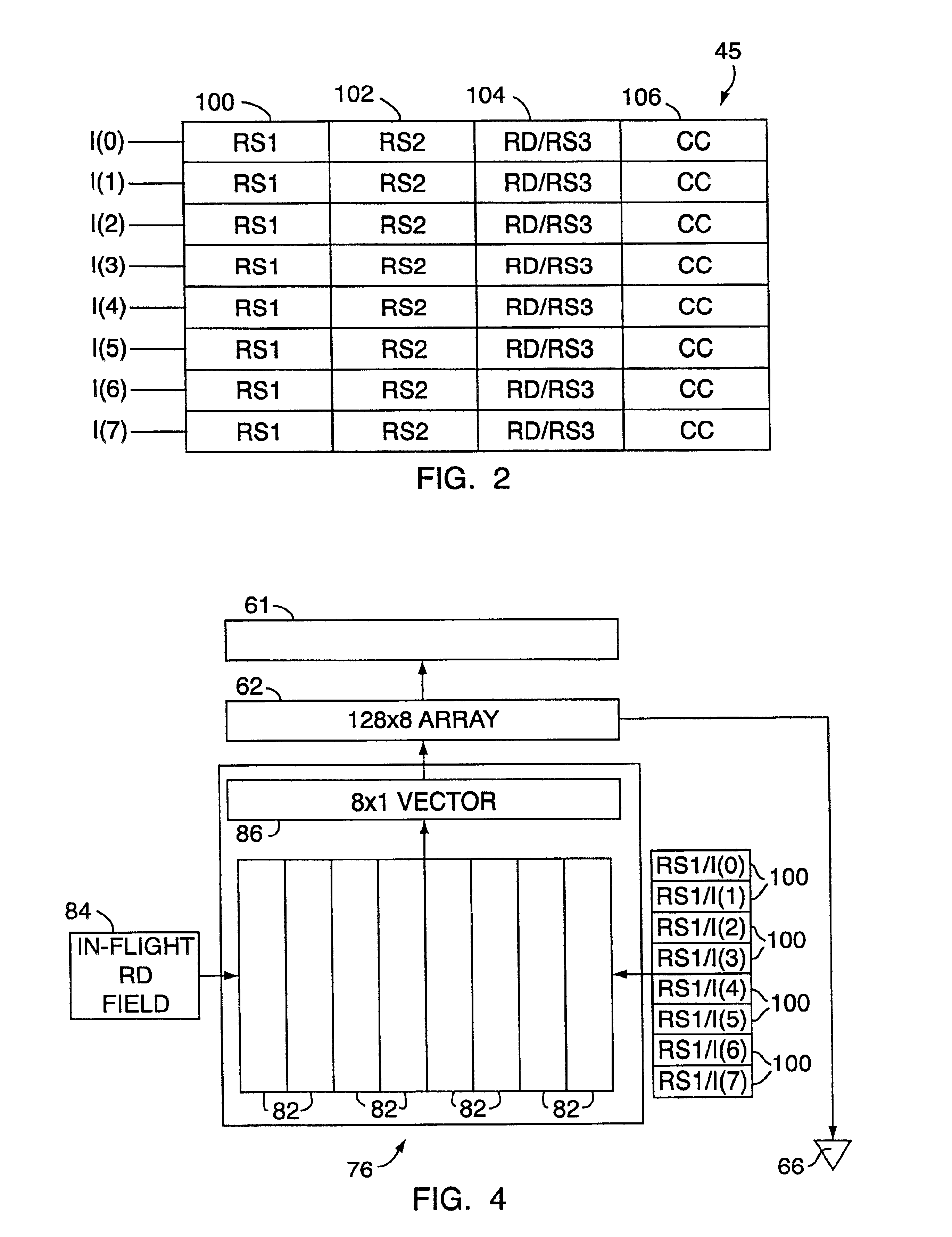
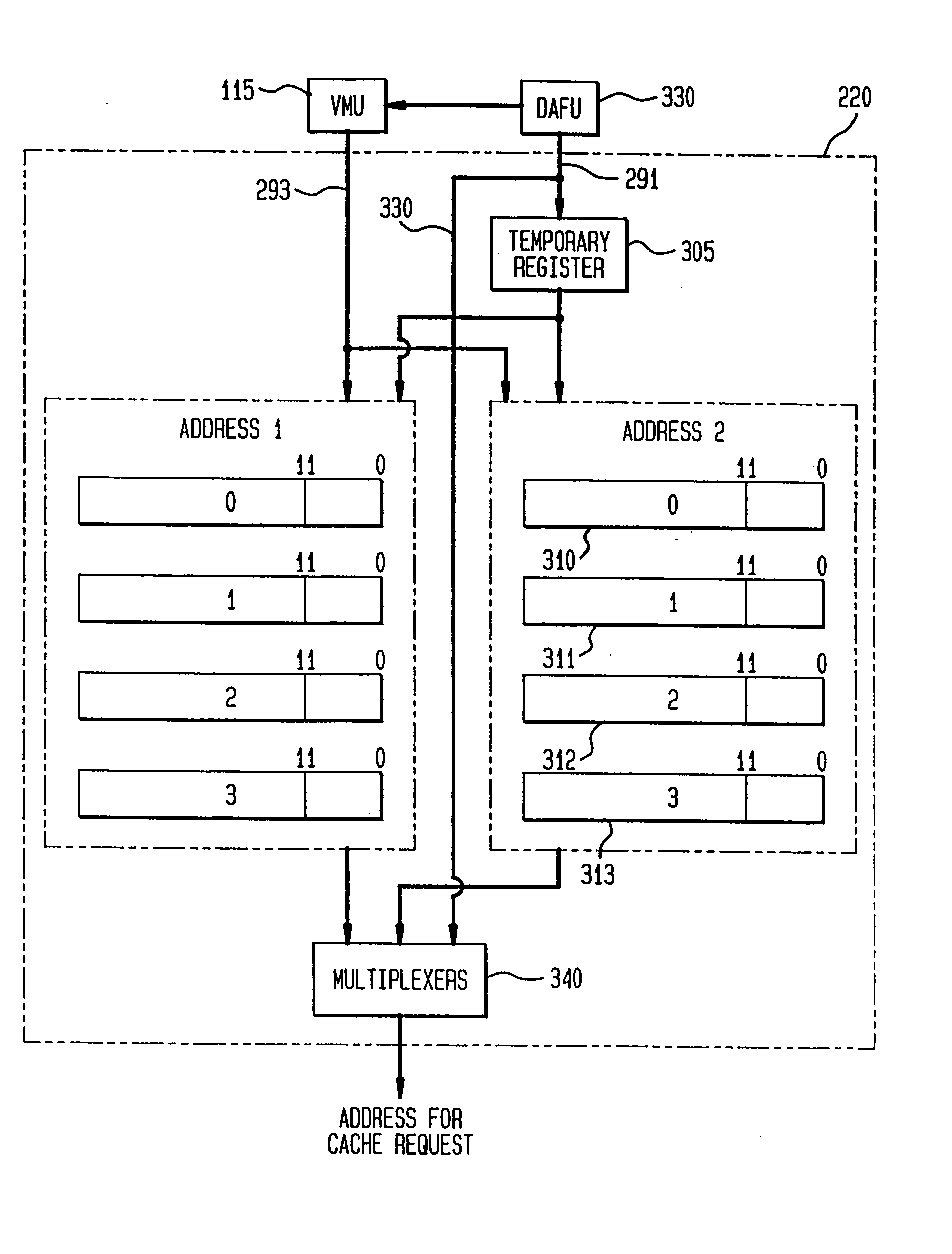
Data address prediction structure and a method for operating the same
InactiveUS6604190B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionReservation stationImplicit memory
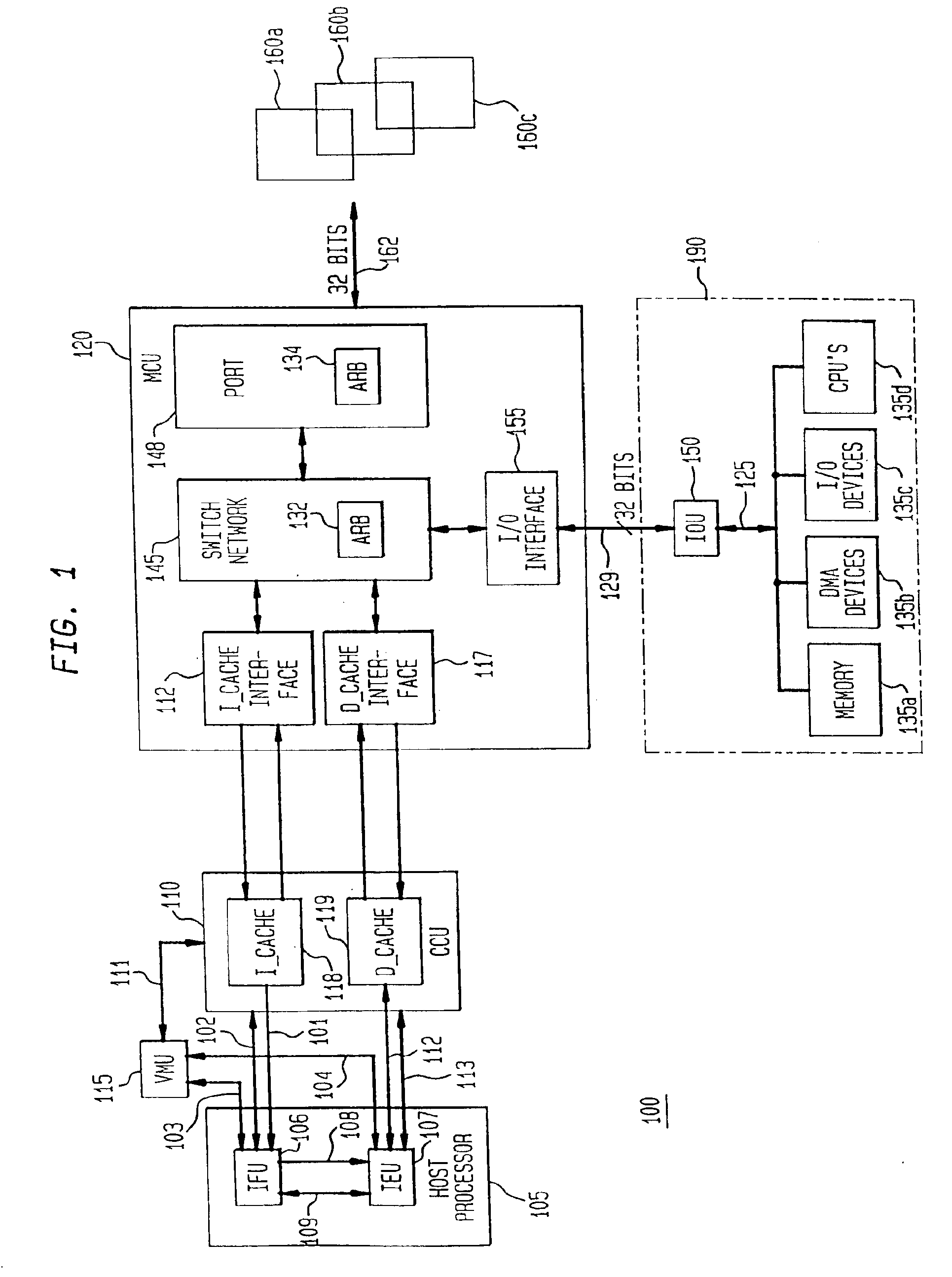
A data address prediction structure for a superscalar microprocessor is provided. The data address prediction structure predicts a data address that a group of instructions is going to access while that group of instructions is being fetched from the instruction cache. The data bytes associated with the predicted address are placed in a relatively small, fast buffer. The decode stages of instruction processing pipelines in the microprocessor access the buffer with addresses generated from the instructions, and if the associated data bytes are found in the buffer they are conveyed to the reservation station associated with the requesting decode stage. Therefore, the implicit memory read associated with an instruction is performed prior to the instruction arriving in a functional unit. The functional unit is occupied by the instruction for a fewer number of clock cycles, since it need not perform the implicit memory operation. Instead, the functional unit performs the explicit operation indicated by the instruction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
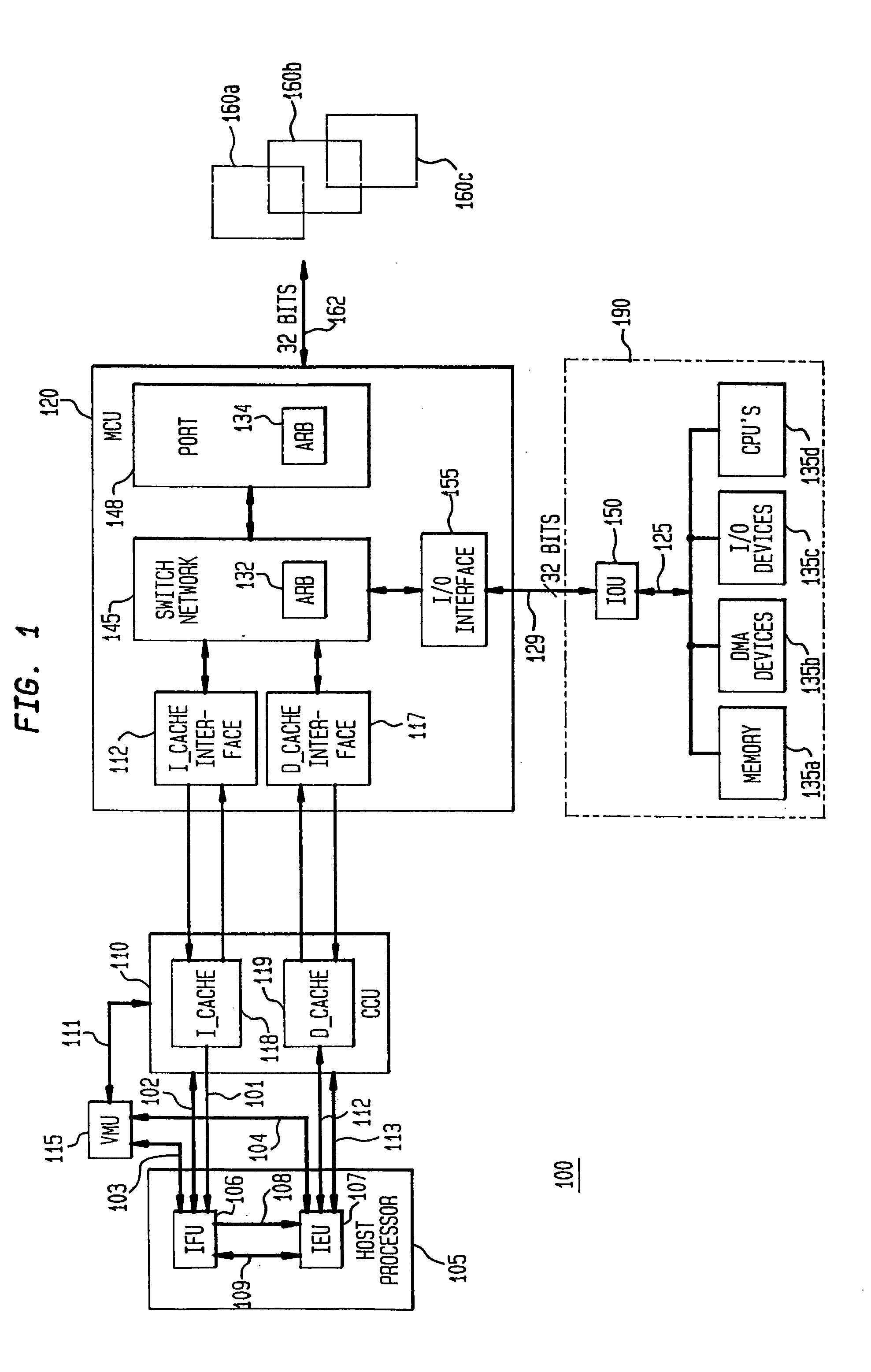
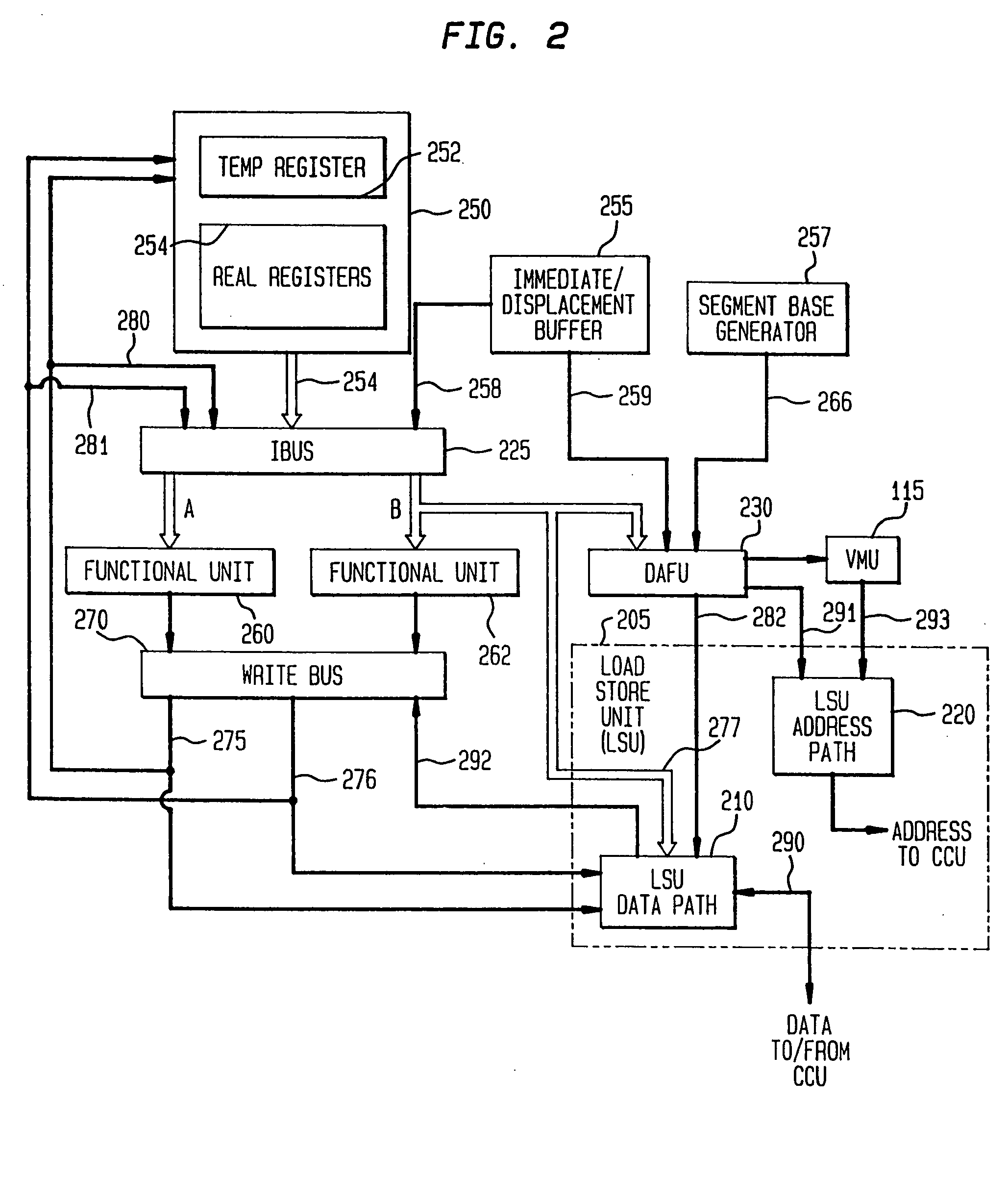
System and method for handling load and/or store operations in a superscalar microprocessor
InactiveUS7000097B2Runtime instruction translationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationExecution unitByte
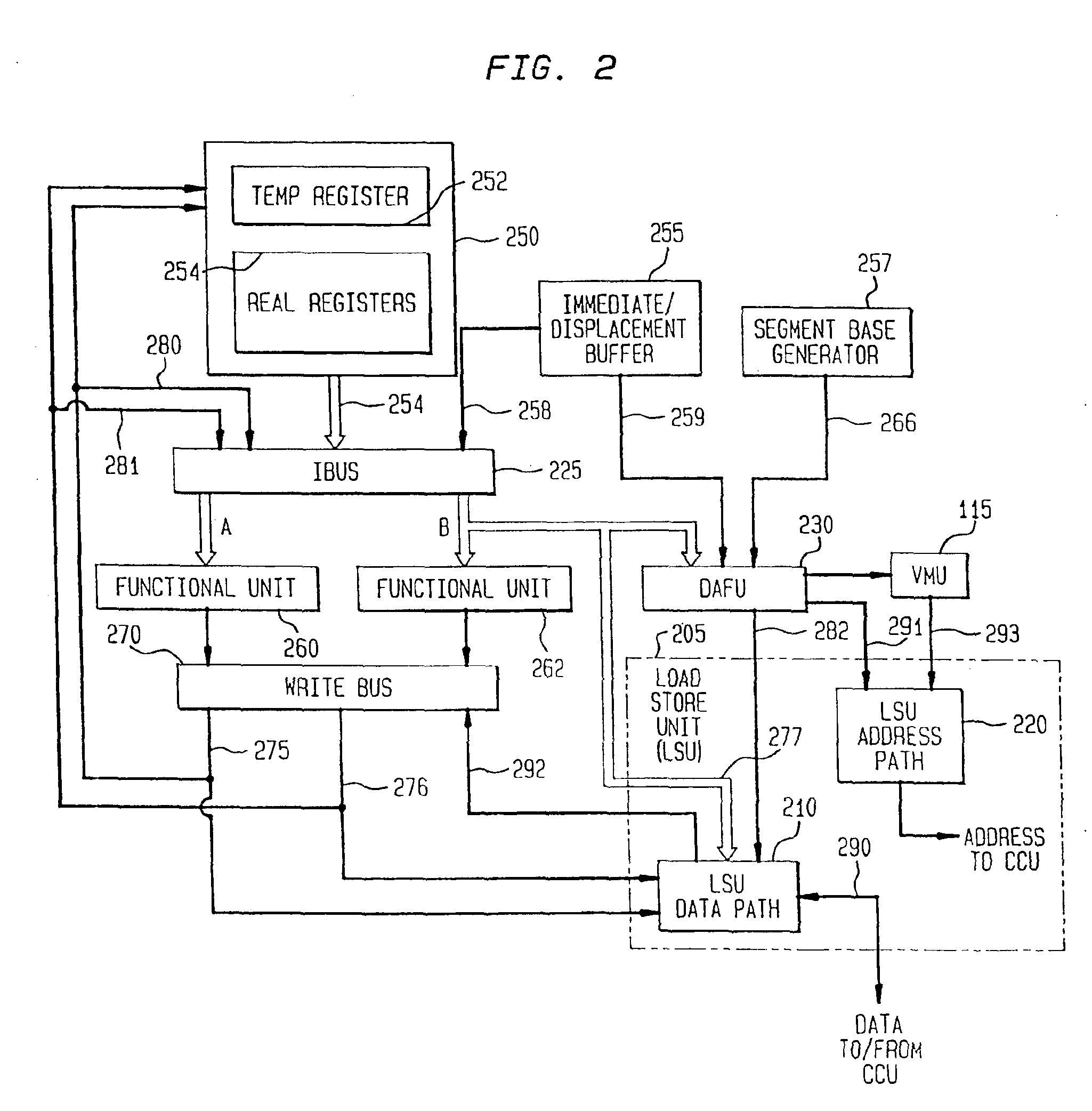
The present invention provides a system and method for managing load and store operations necessary for reading from and writing to memory or I / O in a superscalar RISC architecture environment. To perform this task, a load store unit is provided whose main purpose is to make load requests out of order whenever possible to get the load data back for use by an instruction execution unit as quickly as possible. A load operation can only be performed out of order if there are no address collisions and no write pendings. An address collision occurs when a read is requested at a memory location where an older instruction will be writing. Write pending refers to the case where an older instruction requests a store operation, but the store address has not yet been calculated. The data cache unit returns 8 bytes of unaligned data. The load / store unit aligns this data properly before it is returned to the instruction execution unit. Thus, the three main tasks of the load store unit are: (1) handling out of order cache requests; (2) detecting address collisions; and (3) alignment of data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Instruction alignment unit for routing variable byte-length instructions
InactiveUS6393549B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionStart timeParallel computing
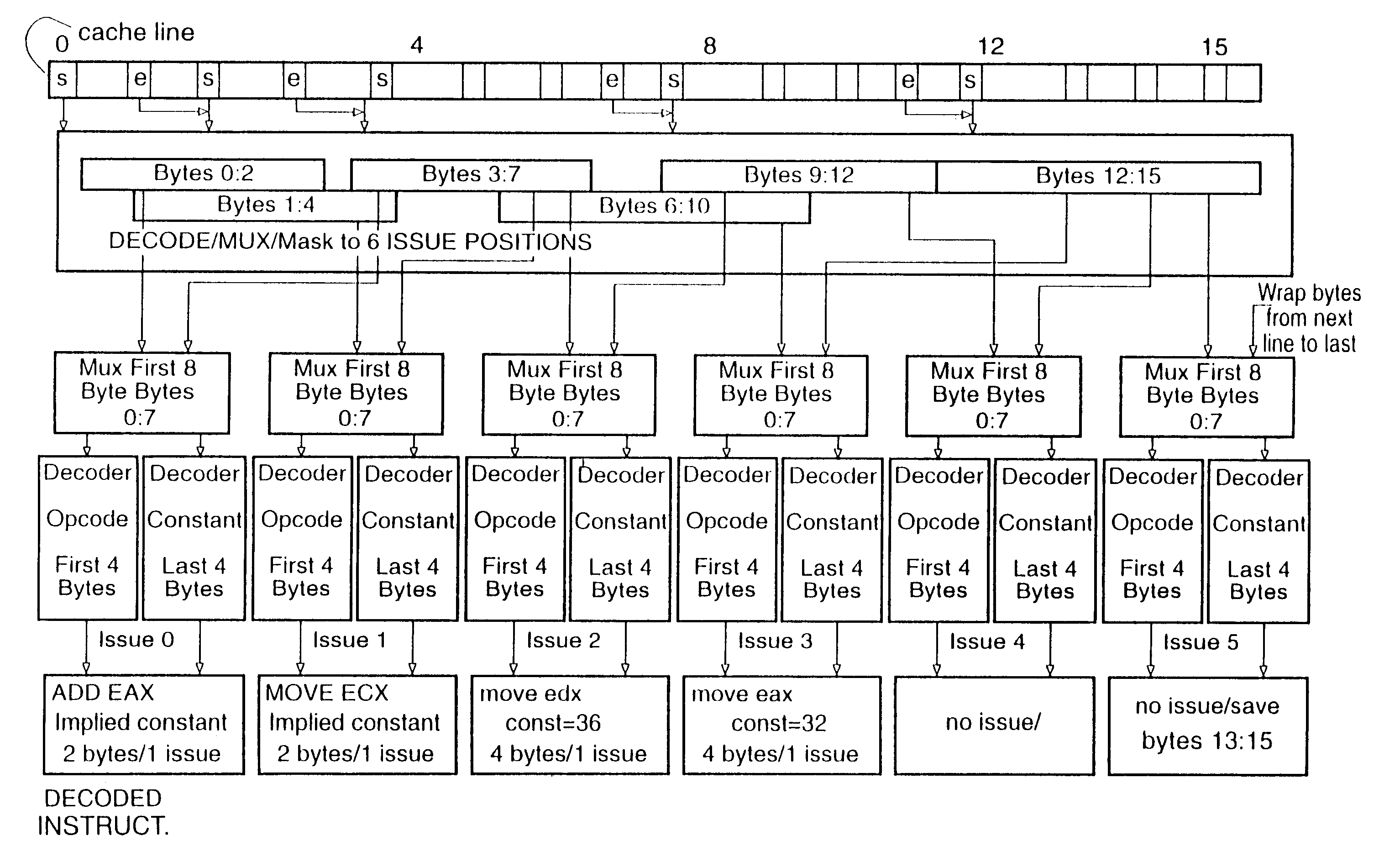
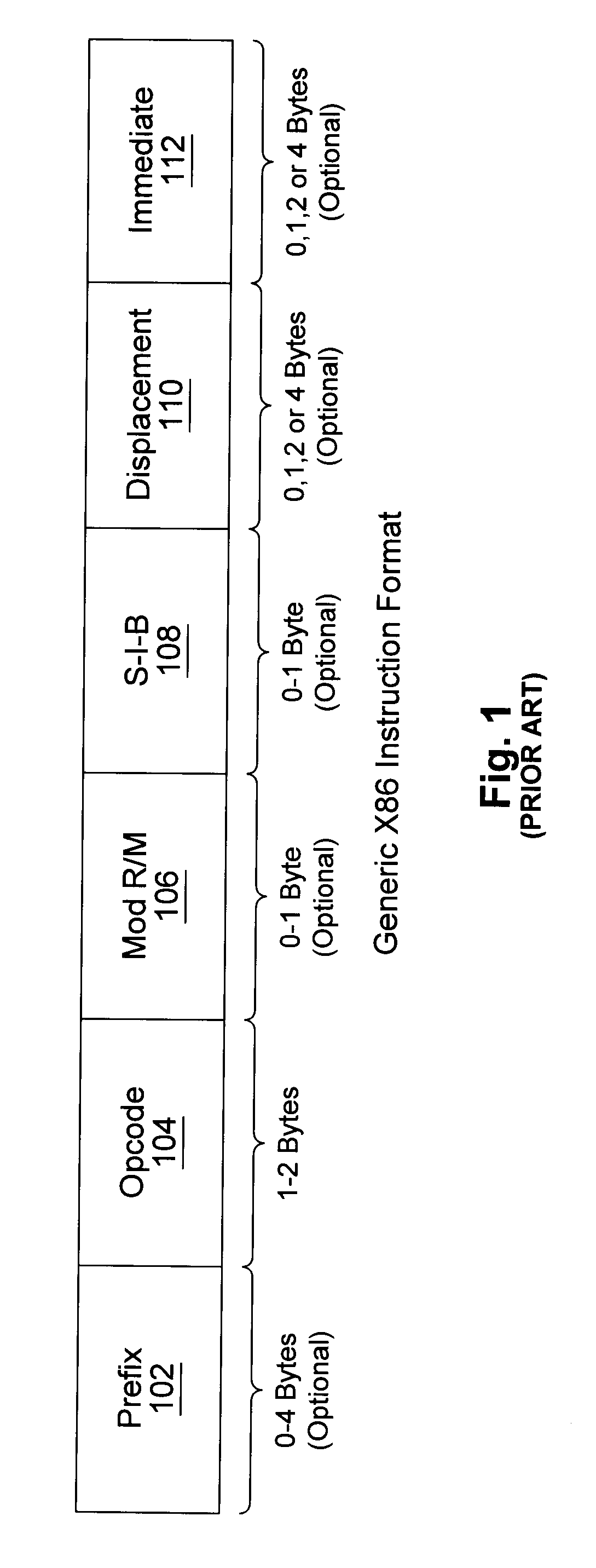
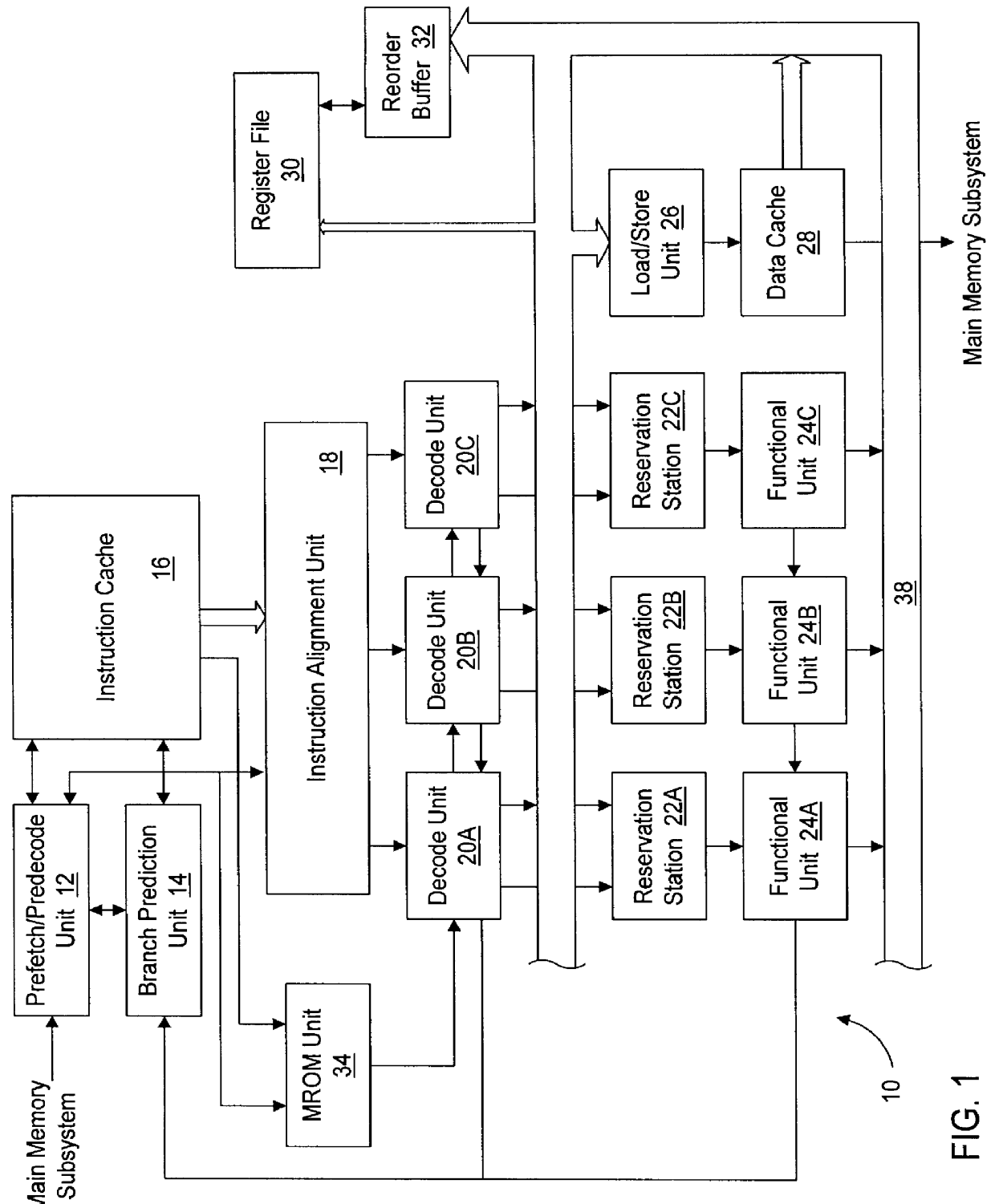
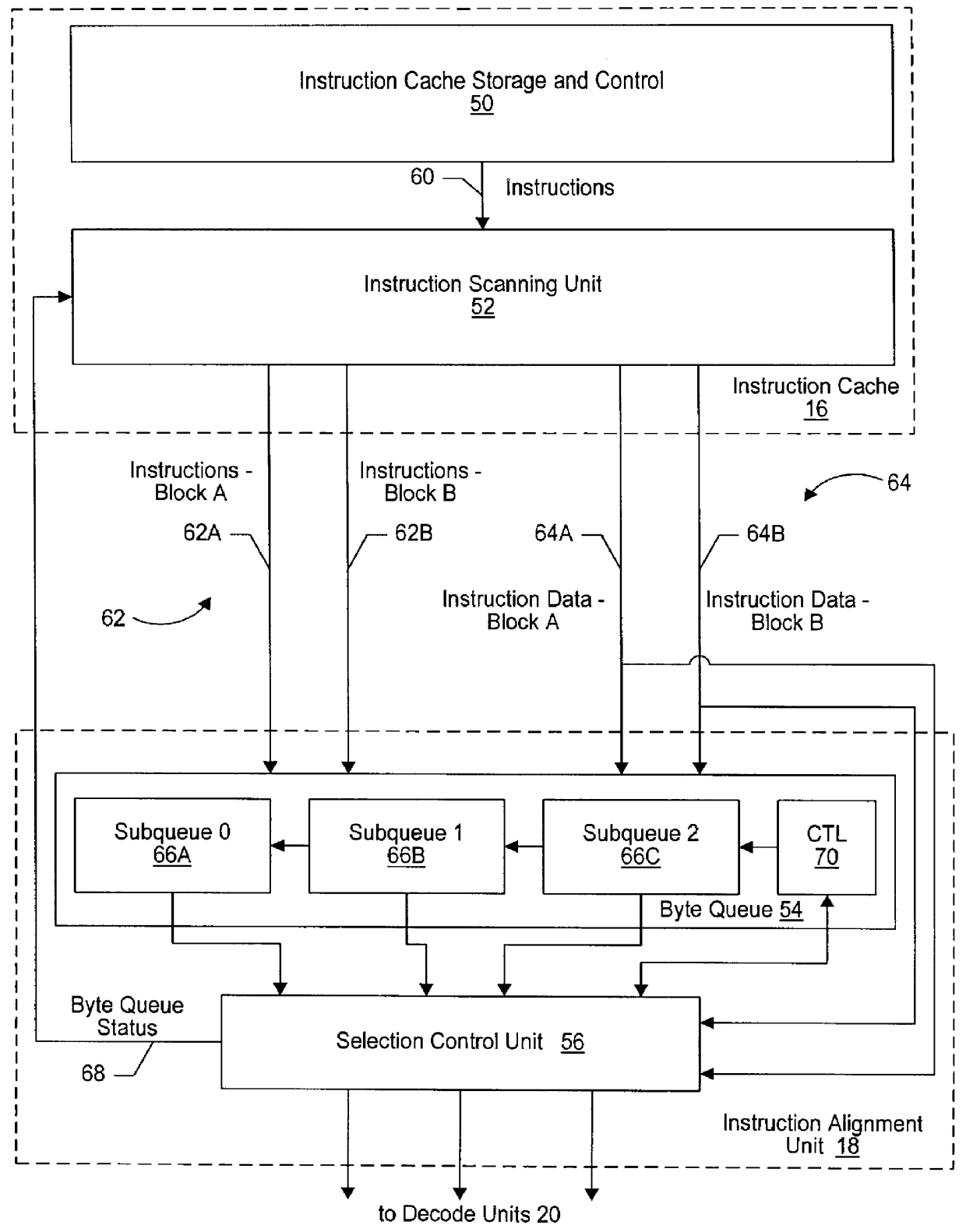
An instruction alignment unit is provided which is capable of routing variable byte length instructions simultaneously to a plurality of decode units which form fixed issue positions within a superscalar microprocessor. The instruction alignment unit may be implemented with a relatively small number of cascaded levels of logic gates, thus accomodating very high frequencies of operation. In one embodiment, the superscalar microprocessor includes an instruction cache for storing a plurality of variable byte-length instructions and a predecode unit for generating predecode tags which identify the location of the start byte of each variable byte-length instruction. An instruction alignment unit is configured to channel a plurality of the variable byte-length instructions simultaneously to predetermined issue positions depending upon the locations of their corresponding start bytes in a cache line. The issue position or positions to which an instruction may be dispatched is limited depending upon the position of the instruction's start byte within a line. By limiting the number of issue positions to which a given instruction within a line may be dispatched, the number of cascaded levels of logic required to implement the instruction alignment unit may be advantageously reduced.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
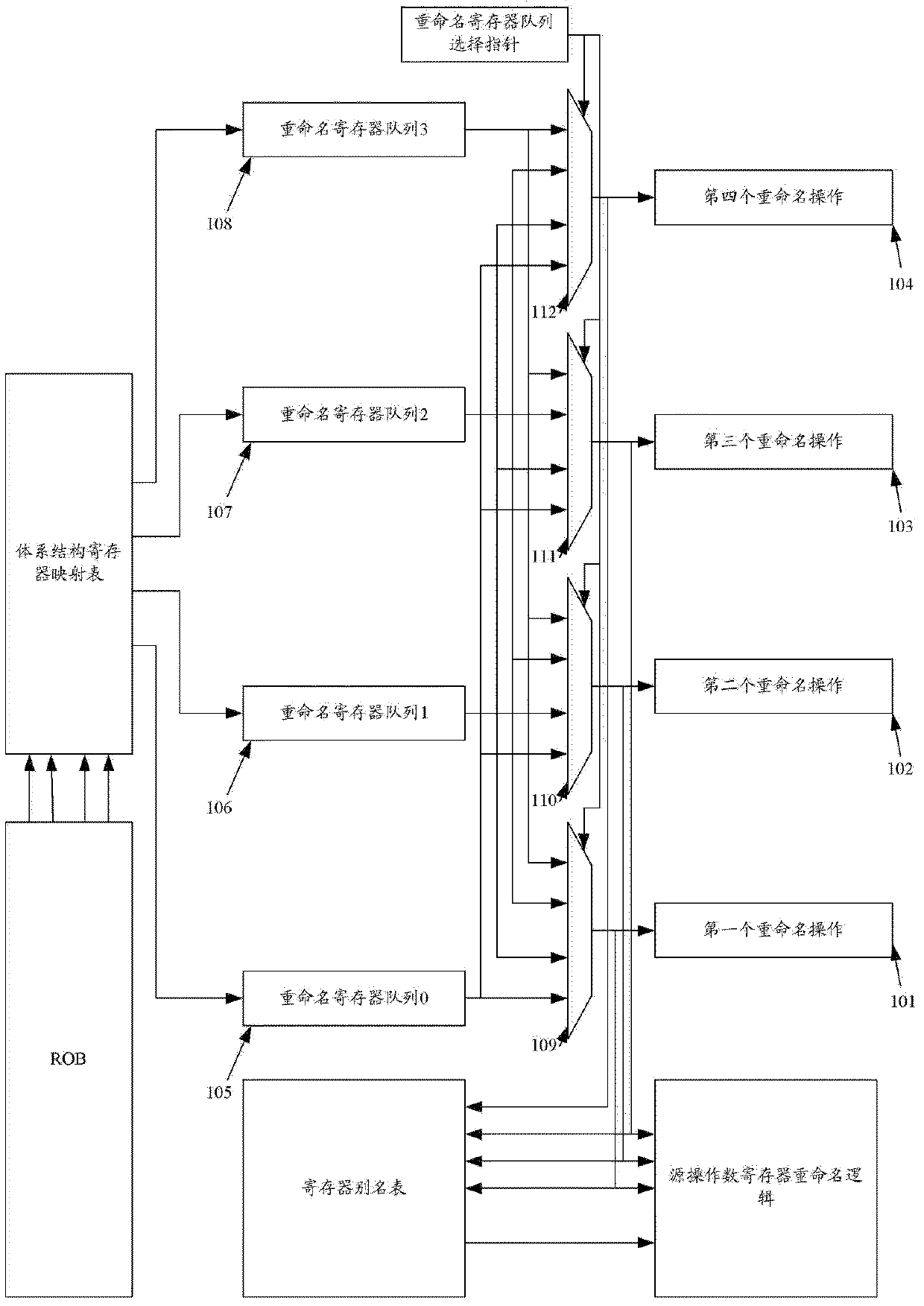
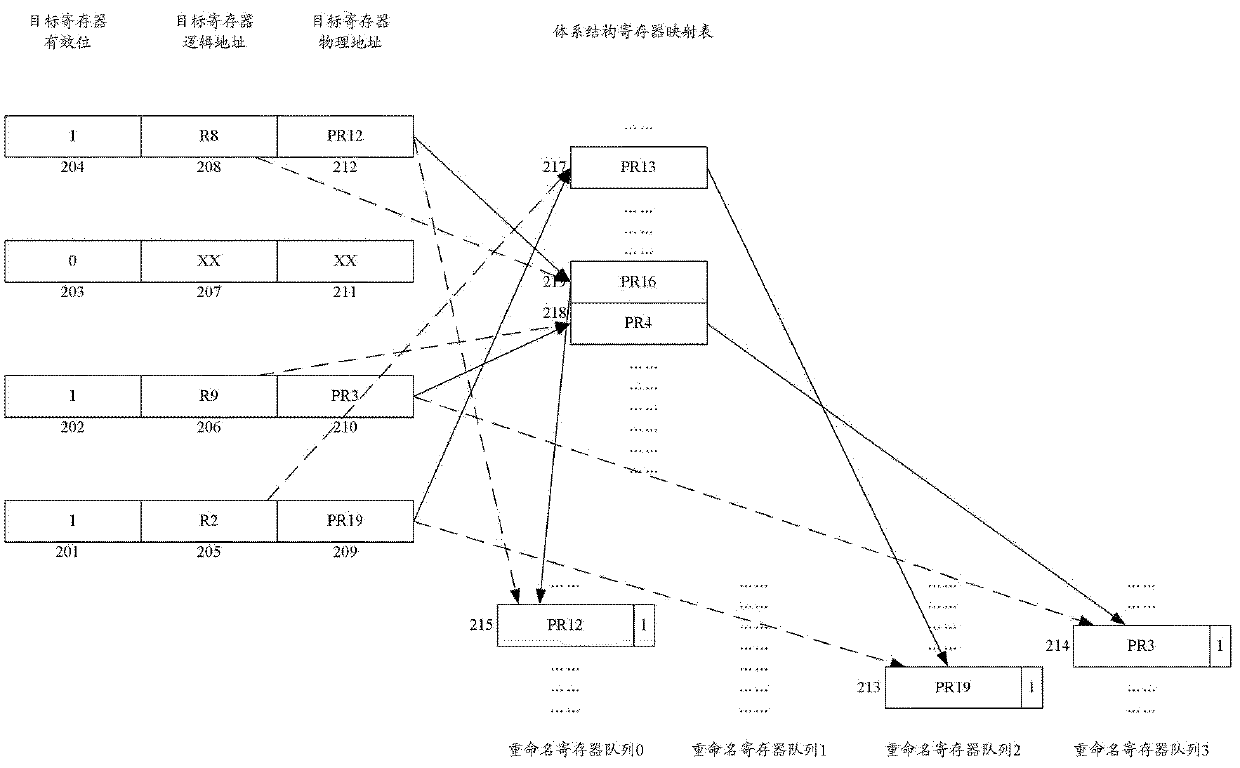
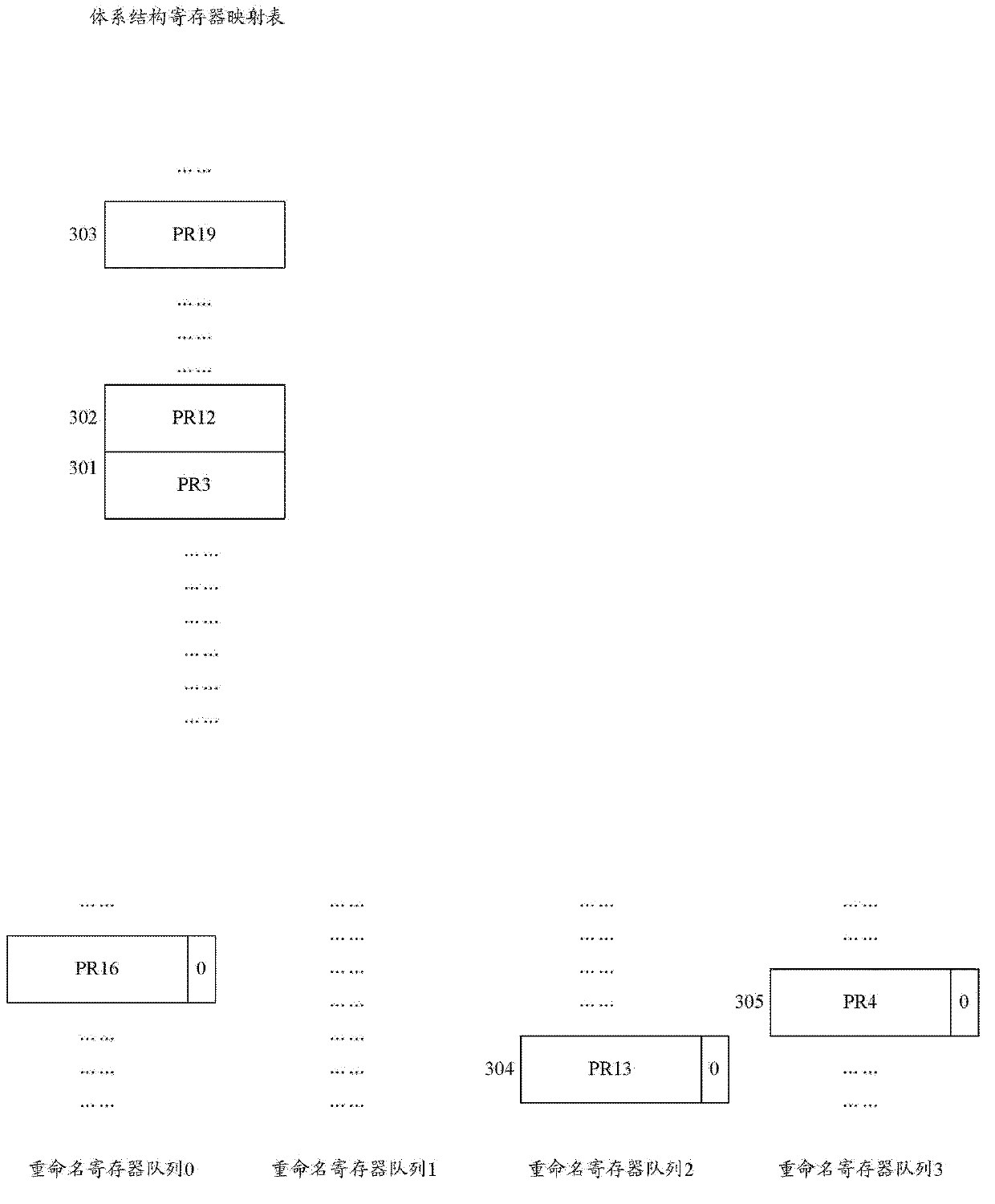
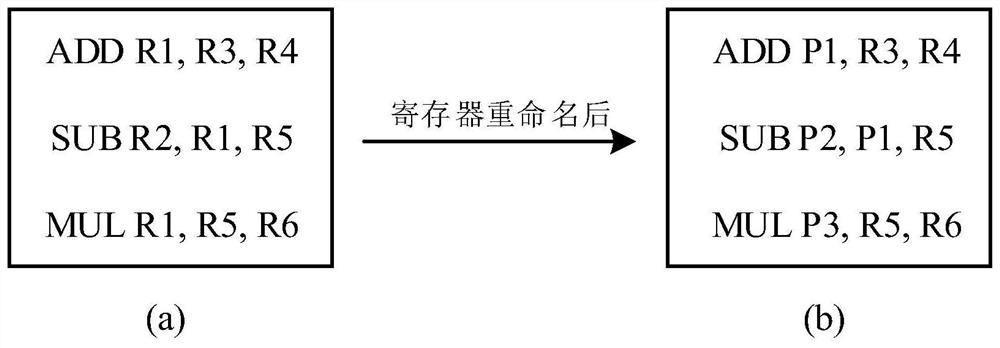
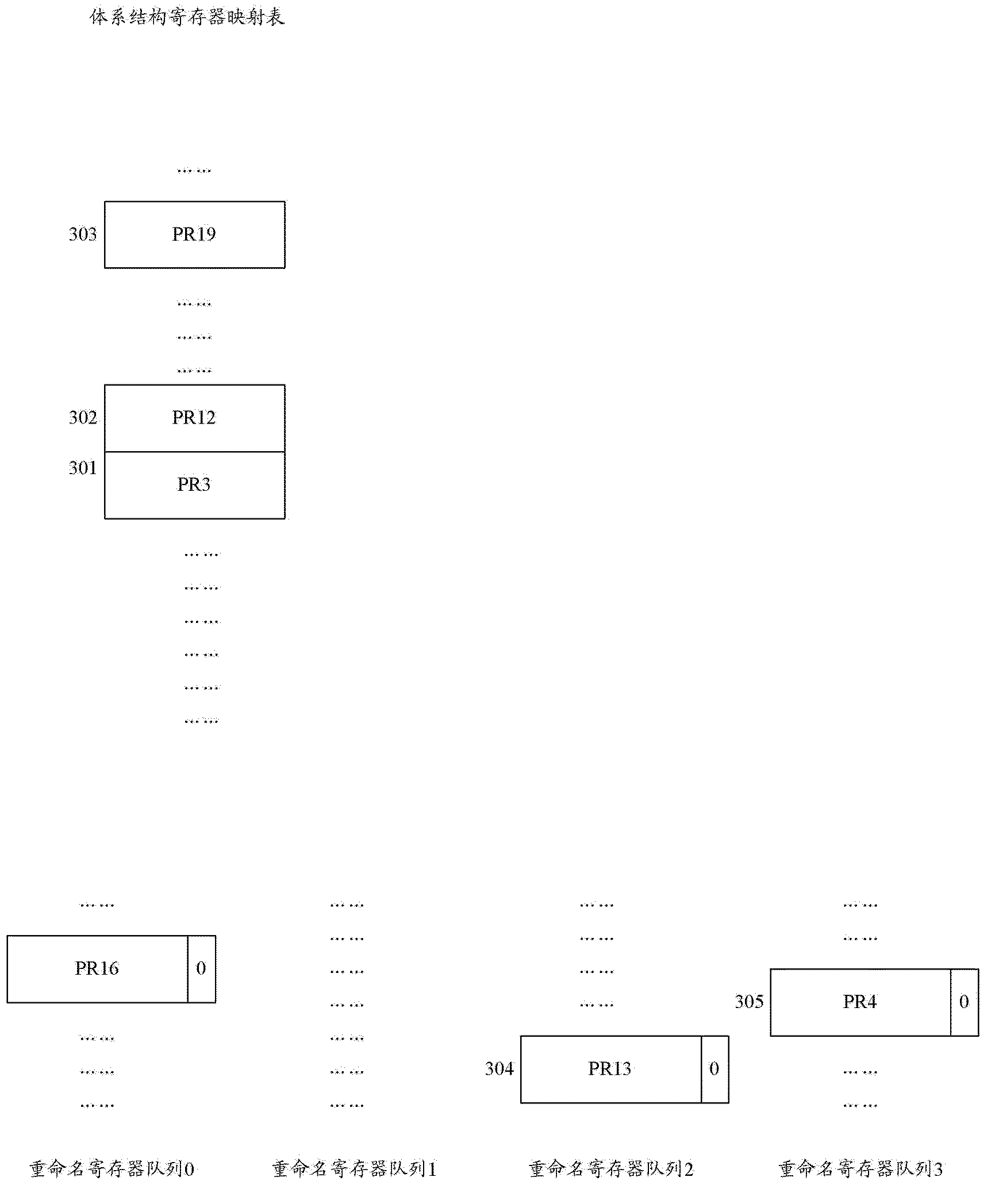
Register renaming system and method for managing and renaming registers
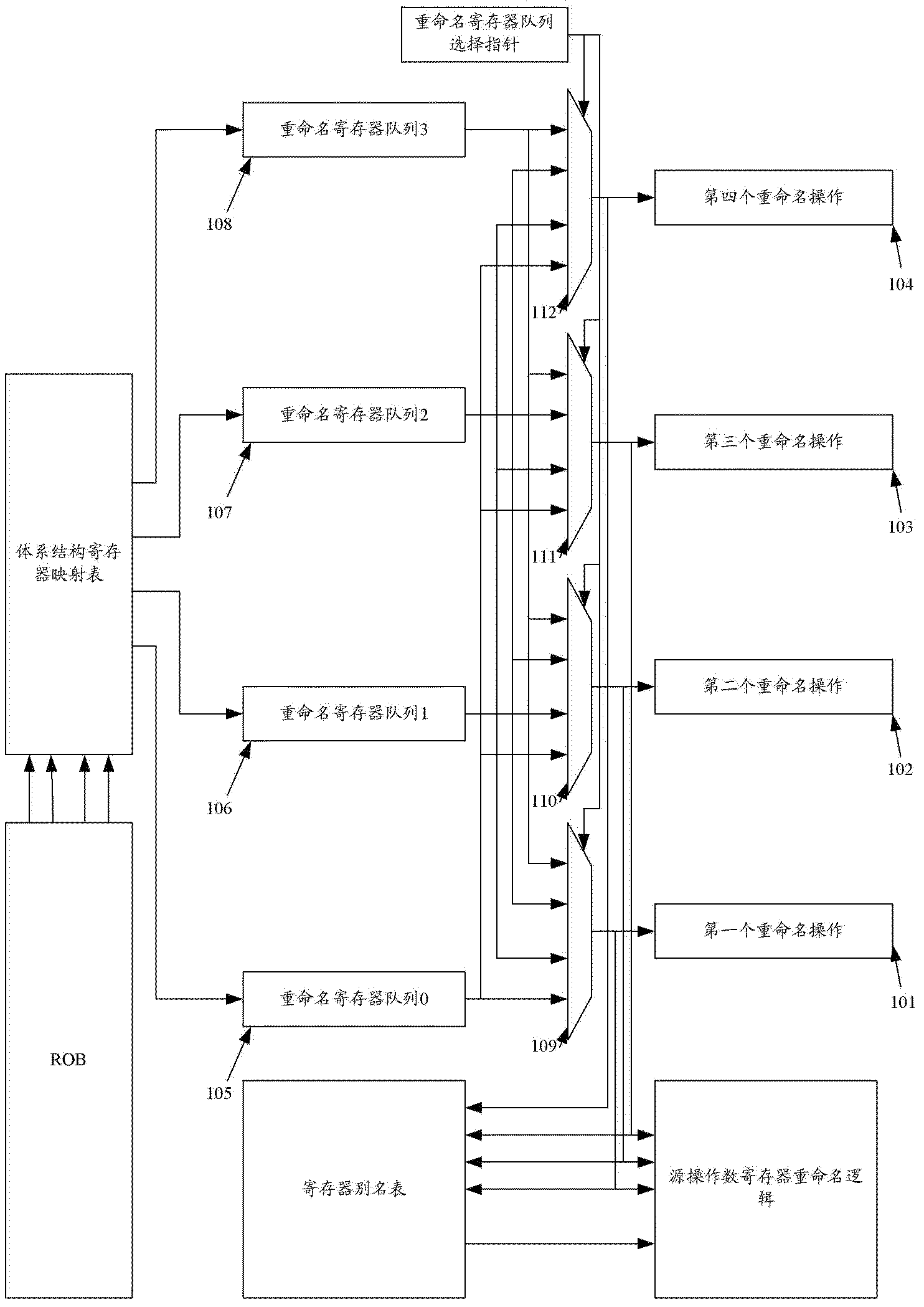
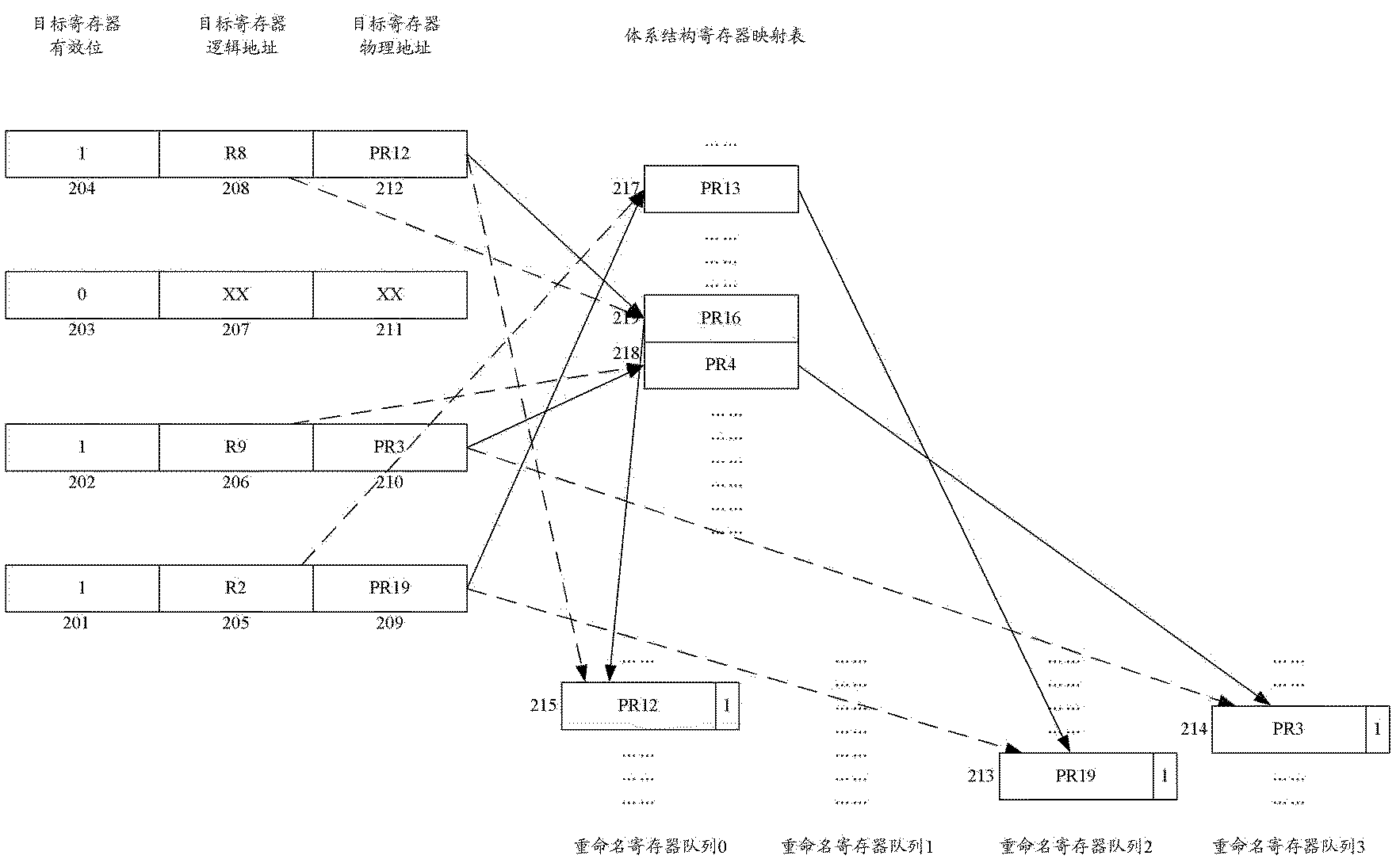
InactiveCN102566976AEasy to determineProcessing speedConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureTime cost
The invention relates to a register renaming system and method for managing and renaming registers. The invention specifically provides the register renaming system for managing and renaming the registers by adopting multiple renamed register queues, and the system comprises a physical register group, a register alias table (RAT), an architecture register mapping table (ARMT), a select finger of the renamed register queues, a decoder, a logic register renaming device, an RAT modifying device and an updating device of the renamed register queues. In addition, the invention further provides the method for managing and renaming the registers by adopting the multiple renamed register queues. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, renaming operation can be simultaneously performed on the multiple registers within a same period, the implementation method is simple, the time cost is small, and the register renaming system and method are suitable for superscalar microprocessors with higher transmission width.
Owner:北京国睿中数科技股份有限公司
Superscalar processor having content addressable memory structures for determining dependencies
InactiveUS6862676B1Lower requirementRapid designMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerScalar processorOrder processing
A superscalar processor having a content addressable memory structure that transmits a first and second output signal is presented. The superscalar processor performs out of order processing on an instruction set. From the first output signal, the dependencies between currently fetched instructions of the instruction set and previous in-flight instructions can be determined and used to generate a dependency matrix for all in-flight instructions. From the second output signal, the physical register addresses of the data required to execute an instruction, once the dependencies have been removed, may be determined.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
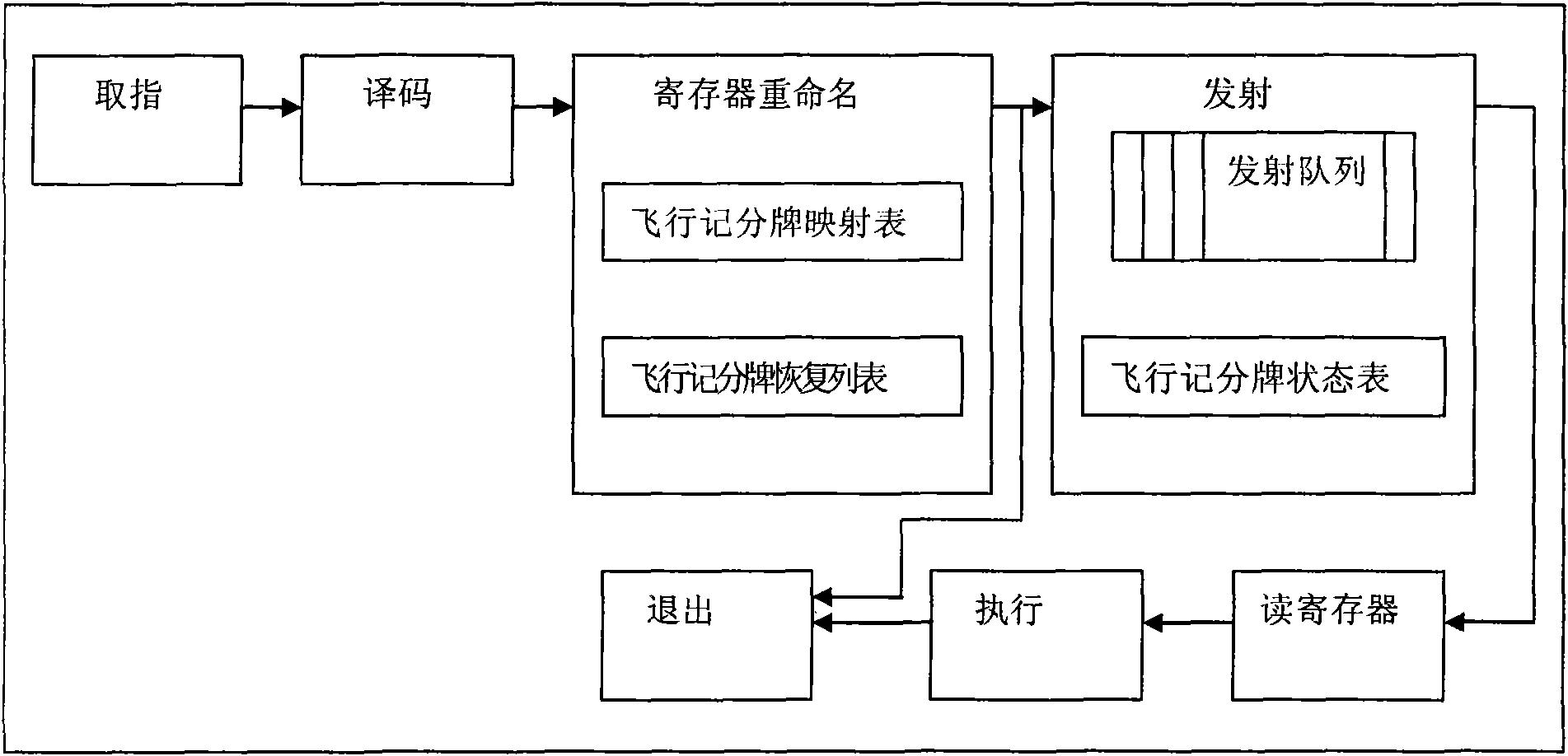
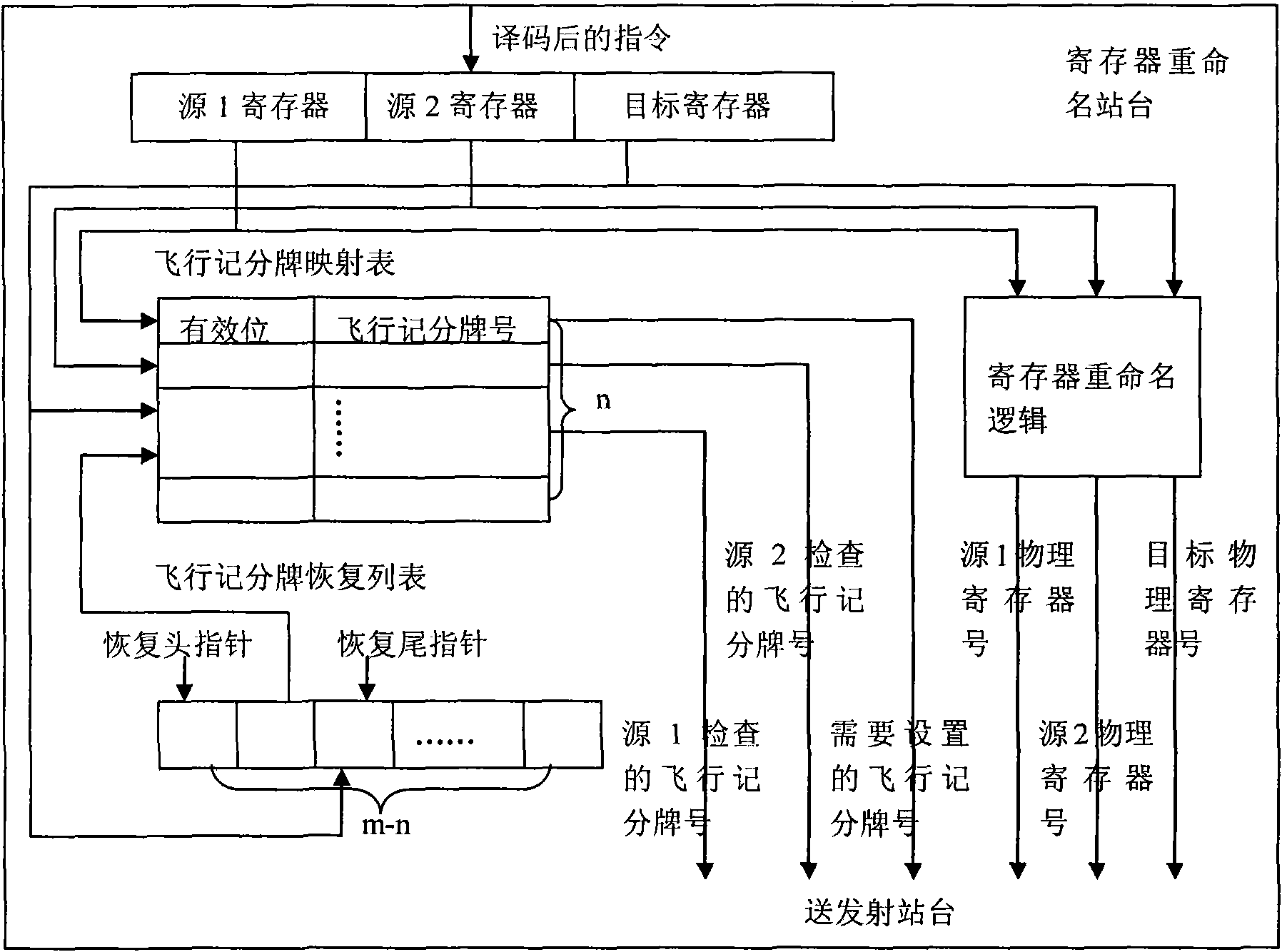
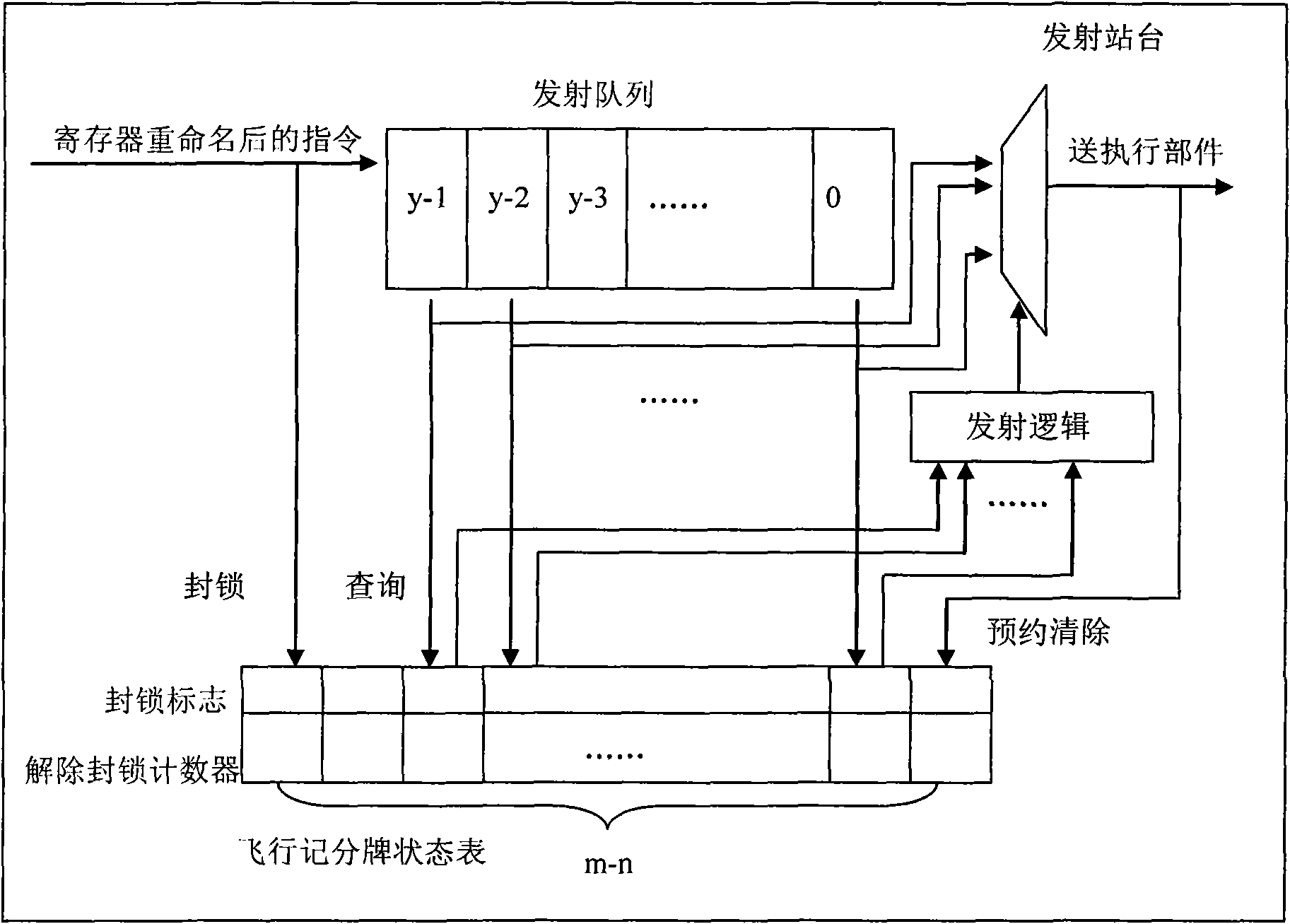
Flying scoreboard device for controlling out-order transmission in superscale microprocessor
ActiveCN101566942AShort delay shortPerformance is not affectedConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerSuperscalar microprocessor
The invention discloses a flying scoreboard device for controlling out-order transmission in a superscale microprocessor, comprising a flying scoreboard mapping table, a flying scoreboard recovering list and a flying scoreboard state table. For an effective command of a target register, the device tracks the state of the command target register dynamically; for an effective command of a source register, the device provides information whether the command source register is readable in real time to judge whether the command can be transmitted to an executive component. The device solves read-after-write relevance caused by use of a register between commands through less hardware resources, ensures accuracy of out-order transmission and execution of commands, and improves the energy consumption ratio of the microprocessor.
Owner:上海高性能集成电路设计中心
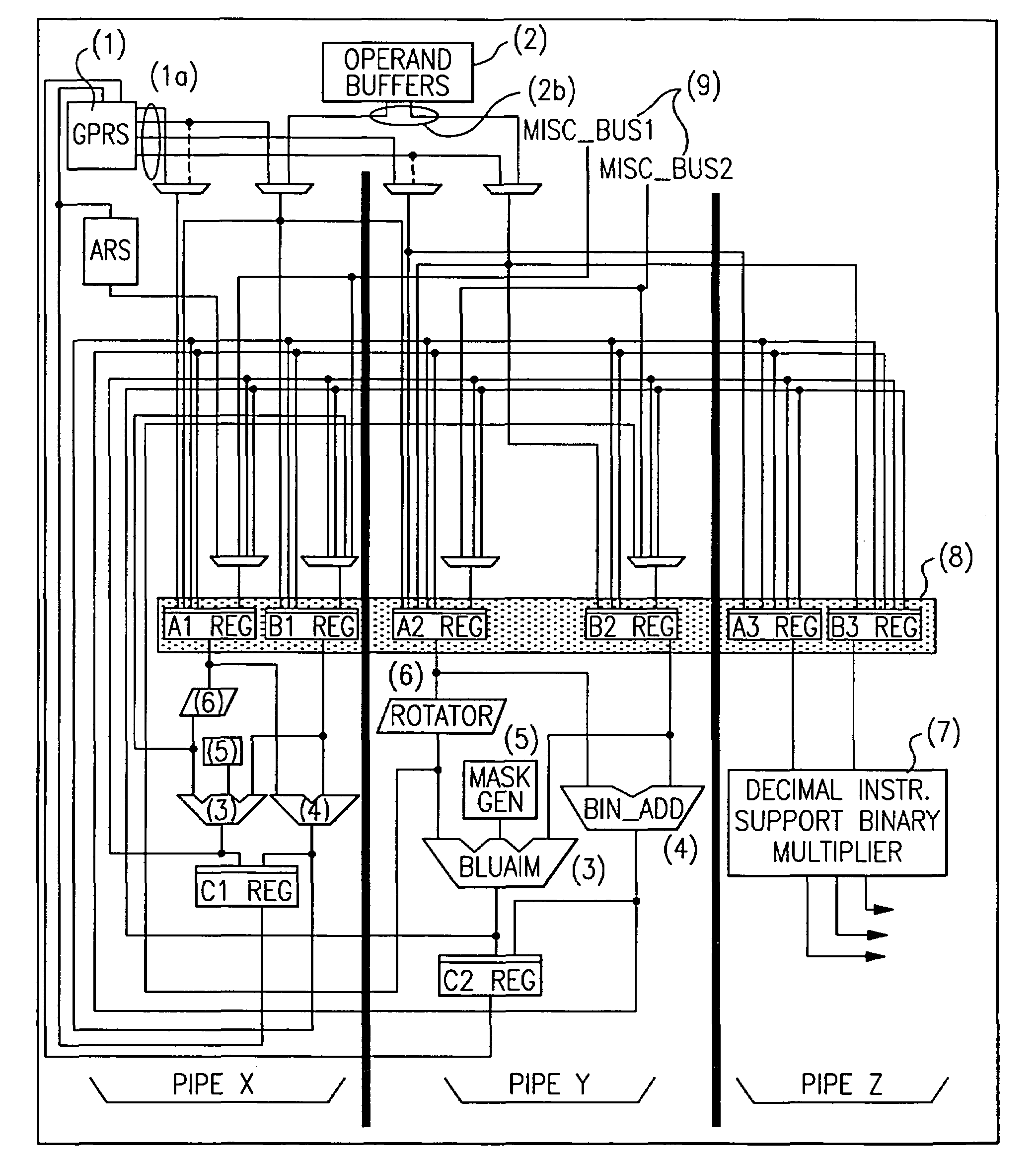
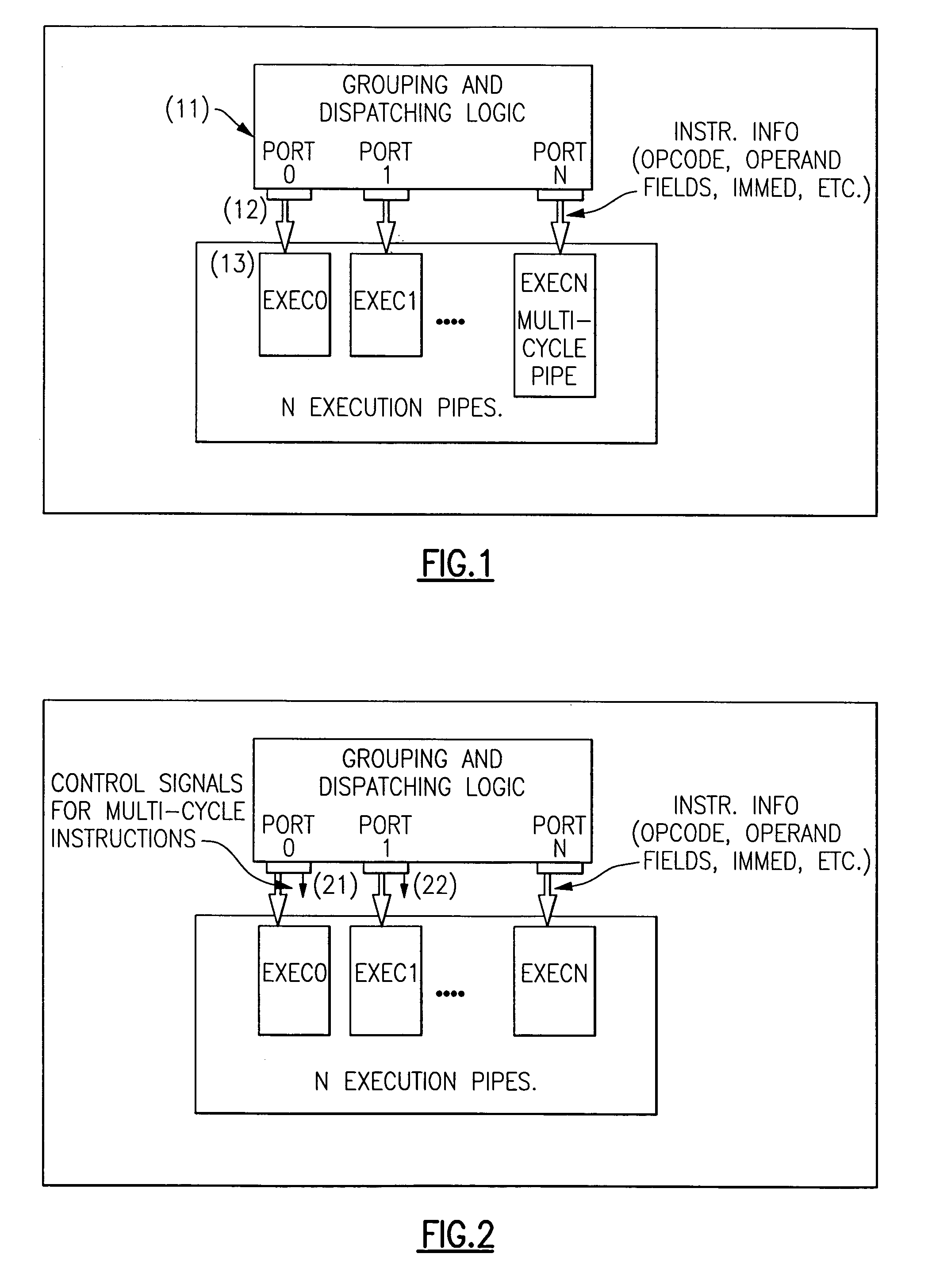
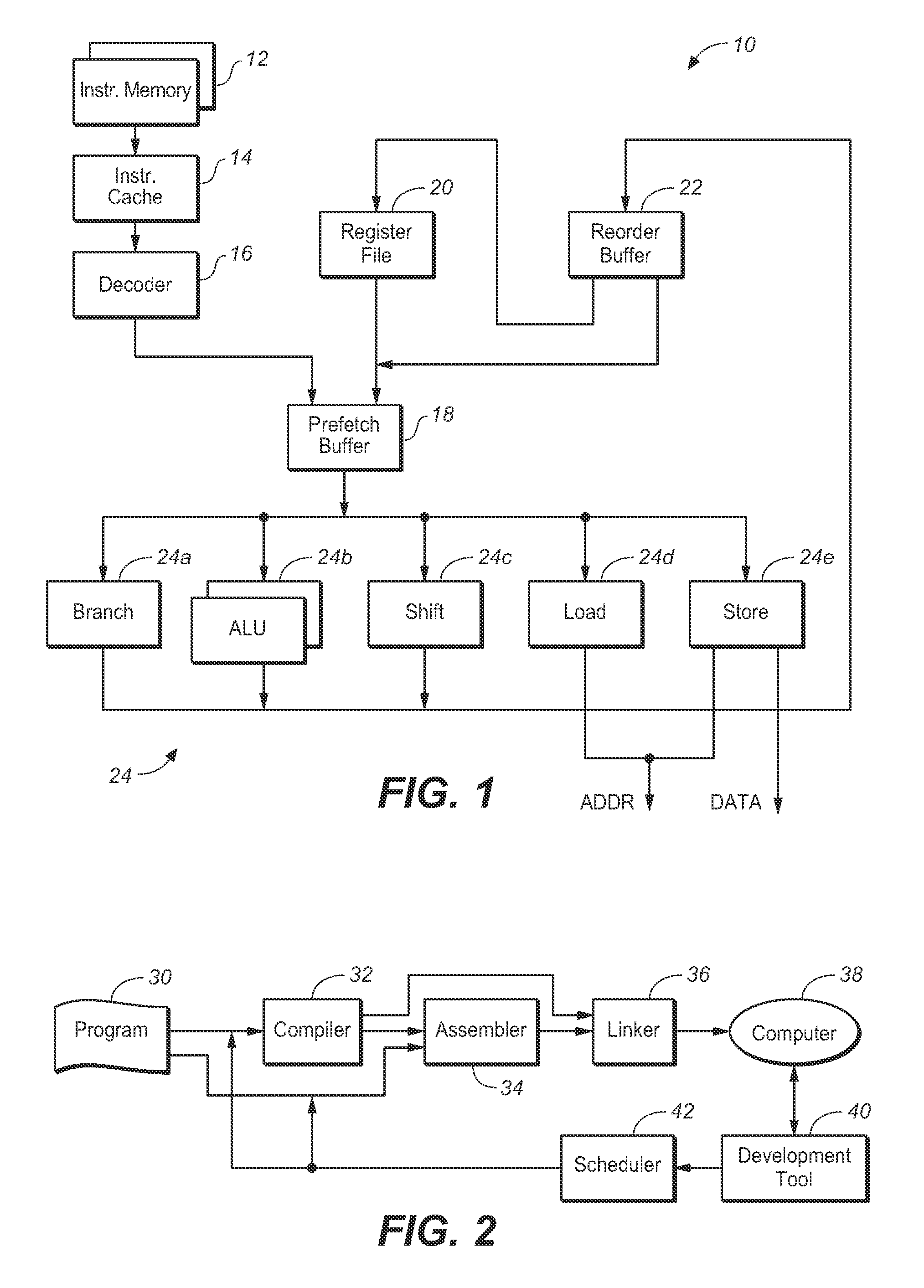
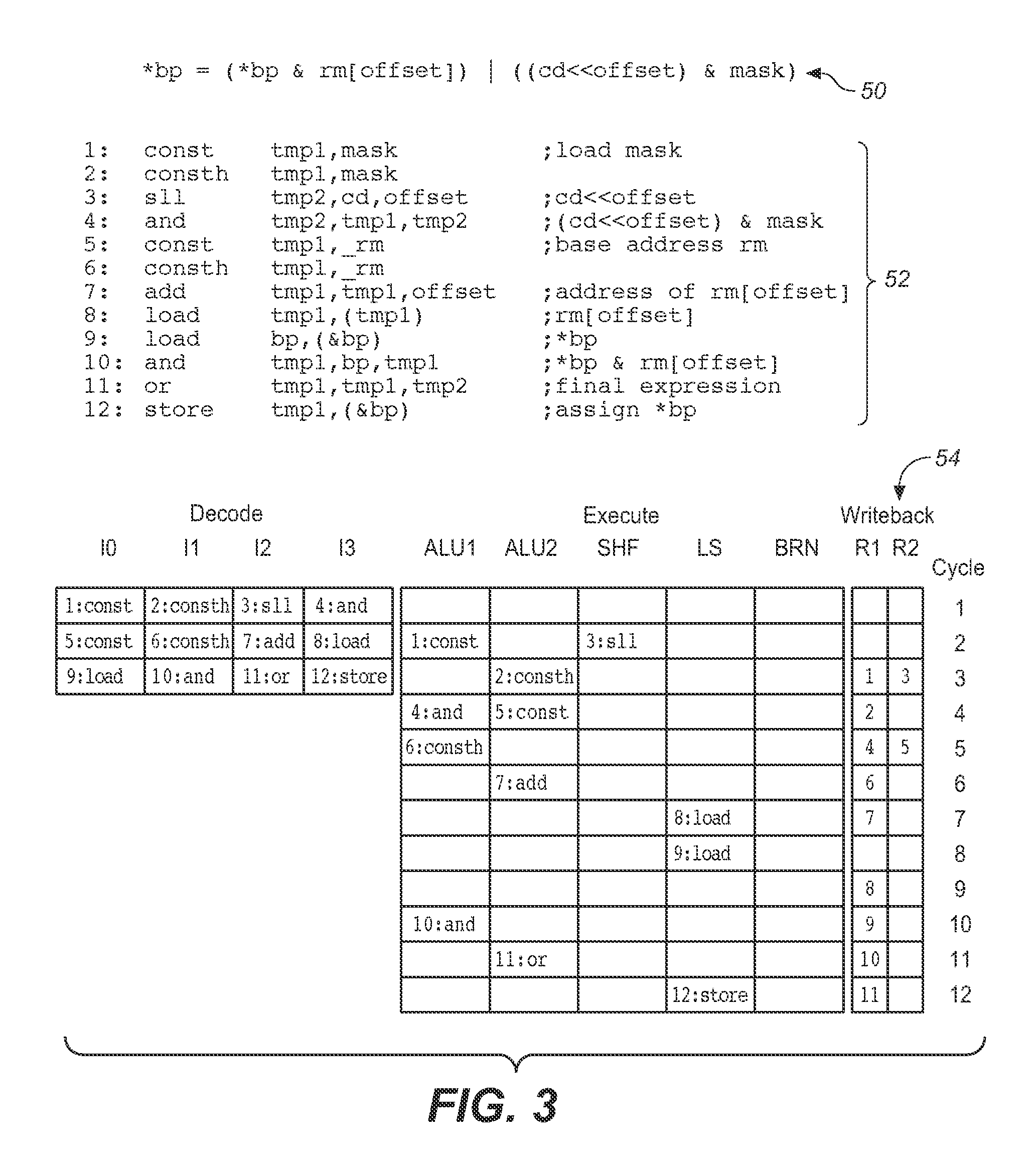
Multi-pipe dispatch and execution of complex instructions in a superscalar processor
ActiveUS7085917B2Performance maximizationImprove performanceCooking-vessel materialsRuntime instruction translationScalar processorControl signal
In a computer system, a method and apparatus for dispatching and executing multi-cycle and complex instructions. The method results in maximum performance for such without impacting other areas in the processor such as decode, grouping or dispatch units. This invention allows multi-cycle and complex instructions to be dispatched to one port but executed in multiple execution pipes without cracking the instruction and without limiting it to a single execution pipe. Some control signals are generated in the dispatch unit and dispatched with the instruction to the Fixed Point Unit (FXU). The FXU logic then execute these instructions on the available FXU pipes. This method results in optimum performance with little or no other complications. The presented technique places the flexibility of how these instructions will be executed in the FXU, where the actual execution takes place, instead of in the instruction decode or dispatch units or cracking by the compiler.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for predicting a first microcode instruction of a cache line and using predecode instruction data to identify instruction boundaries and types
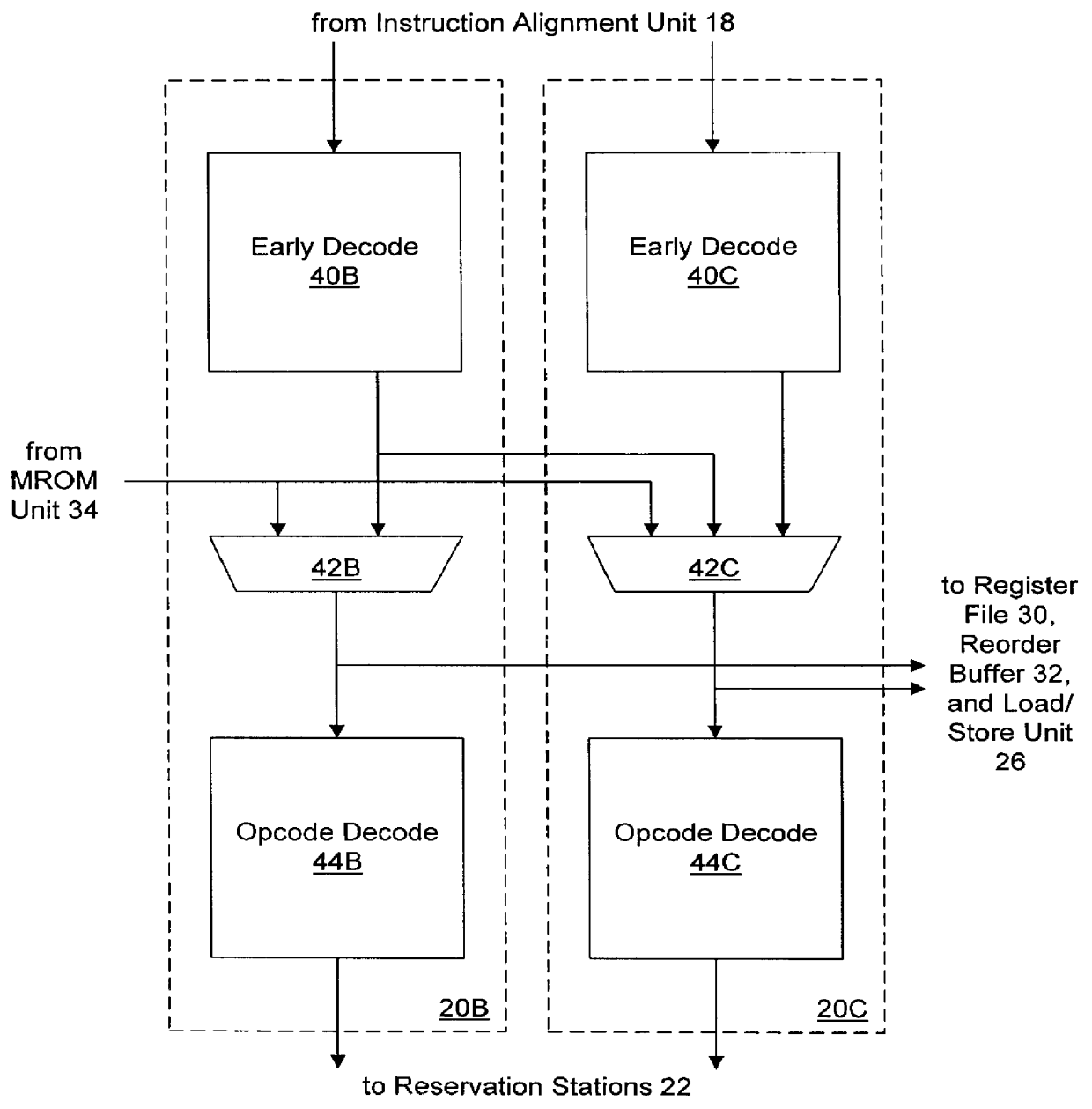
A superscalar microprocessor predecodes instruction data to identify the boundaries of instructions and the type of instruction. To expedite the dispatch of instructions, when a cache line is scanned, the first scanned instruction is predicted to be a microcode instruction and is dispatched to the MROM unit. A microcode scan circuit uses the microcode pointer and the functional bits of the predecode data to multiplex instruction specific bytes of the first microcode instruction to the MROM unit. If the predicted first microcode instruction is not the actual first microcode instruction, then in a subsequent clock cycle, the actual microcode instruction is dispatched the MROM unit and the incorrectly predicted microcode instruction is canceled.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System and method for handling load and/or store operations in a superscalar microprocessor
InactiveUS6957320B2Runtime instruction translationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationExecution unitByte
The present invention provides a system and method for managing load and store operations necessary for reading from and writing to memory or I / O in a superscalar RISC architecture environment. To perform this task, a load store unit is provided whose main purpose is to make load requests out of order whenever possible to get the load data back for use by an instruction execution unit as quickly as possible. A load operation can only be performed out of order if there are no address collisions and no write pendings. An address collision occurs when a read is requested at a memory location where an older instruction will be writing. Write pending refers to the case where an older instruction requests a store operation, but the store address has not yet been calculated. The data cache unit returns 8 bytes of unaligned data. The load / store unit aligns this data properly before it is returned to the instruction execution unit. Thus, the three main tasks of the load store unit are: (1) handling out of order cache requests; (2) detecting address collisions; and (3) alignment of data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Superscalar microprocessor having multi-pipe dispatch and execution unit
InactiveUS7082517B2Performance maximizationImprove performanceRuntime instruction translationDigital computer detailsControl signalScheduling instructions
In a computer system for use as a symetrical multiprocessor, a superscalar microprocessor apparatus allows dispatching and executing multi-cycle and complex instructions Some control signals are generated in the dispatch unit and dispatched with the instruction to the Fixed Point Unit (FXU). Multiple execution pipes correspond to the instruction dispatch ports and the execution unit is a Fixed Point Unit (FXU) which contains three execution dataflow pipes (X, Y and Z) and one control pipe (R). The FXU logic then execute these instructions on the available FXU pipes. This results in optimum performance with little or no other complications. The presented technique places the flexibility of how these instructions will be executed in the FXU, where the actual execution takes place, instead of in the instruction decode or dispatch units or cracking by the compiler.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pipelined instruction dispatch unit in a superscalar processor
InactiveUSRE38599E1Avoid complex processDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionScalar processorScheduling instructions
A pipelined instruction dispatch or grouping circuit allows instruction dispatch decisions to be made over multiple processor cycles. In one embodiment, the grouping circuit performs resource allocation and data dependency checks on an instruction group, based on a state vector which includes representation of source and destination registers of instructions within said instruction group and corresponding state vectors for instruction groups of a number of preceding processor cycles.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
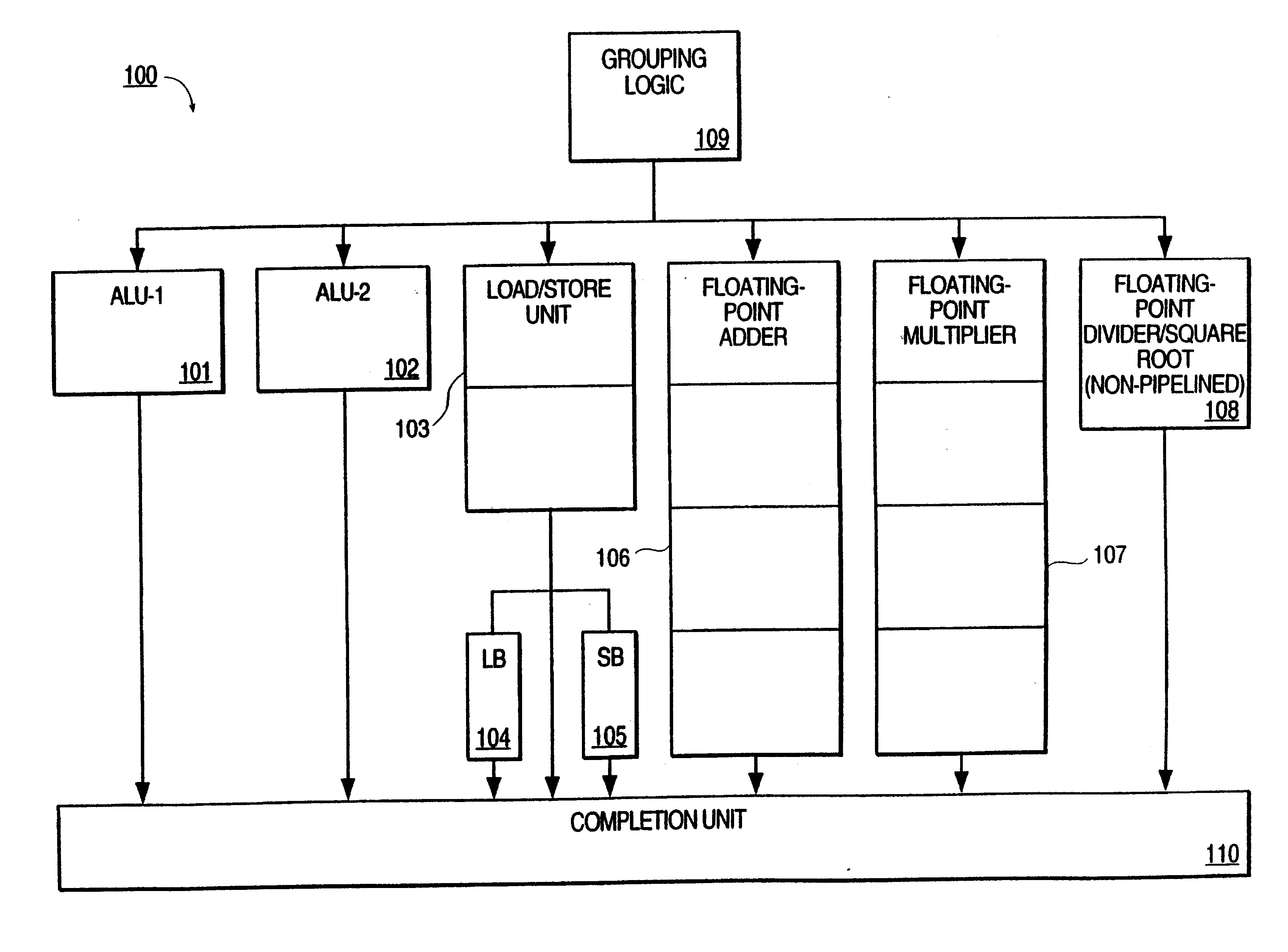
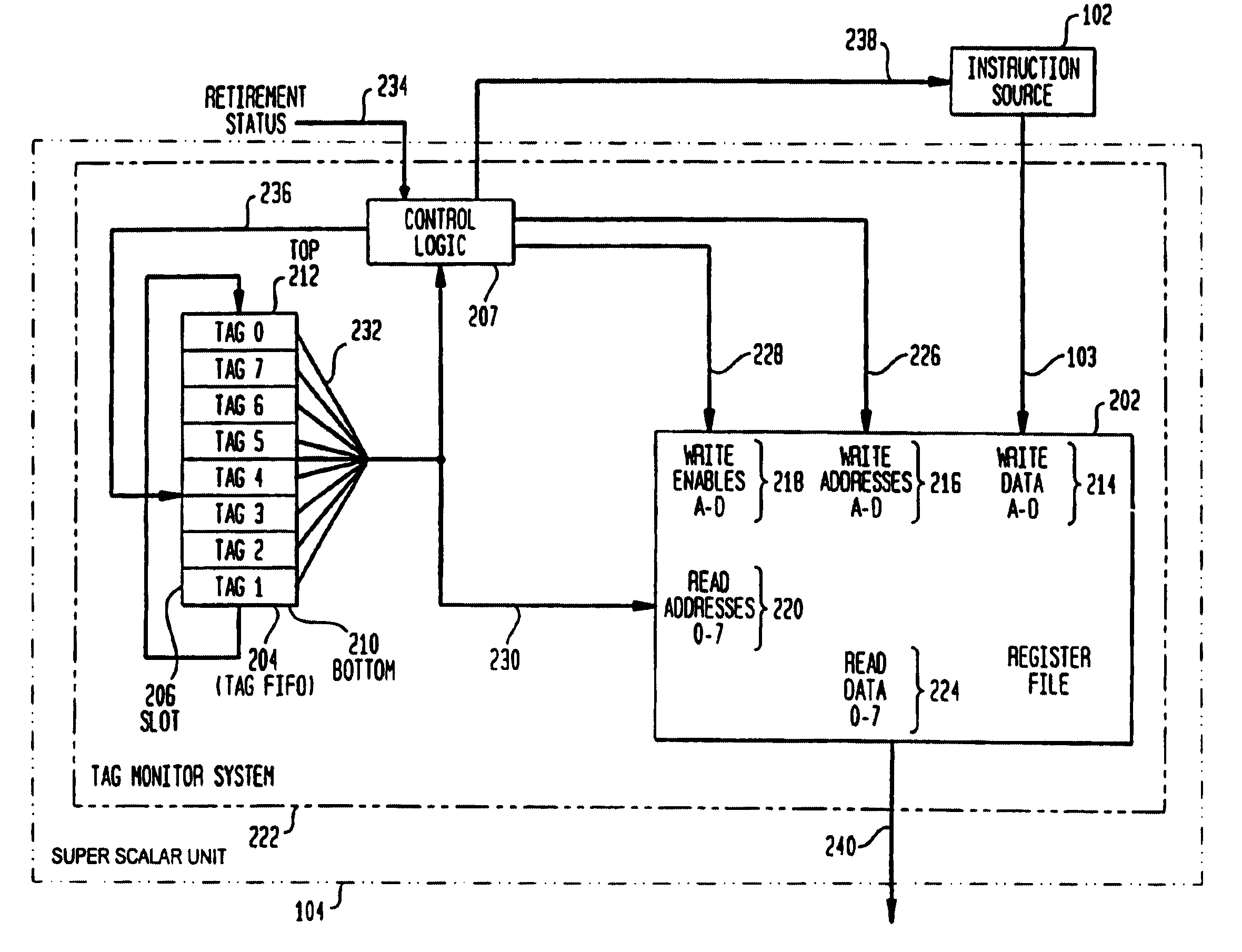
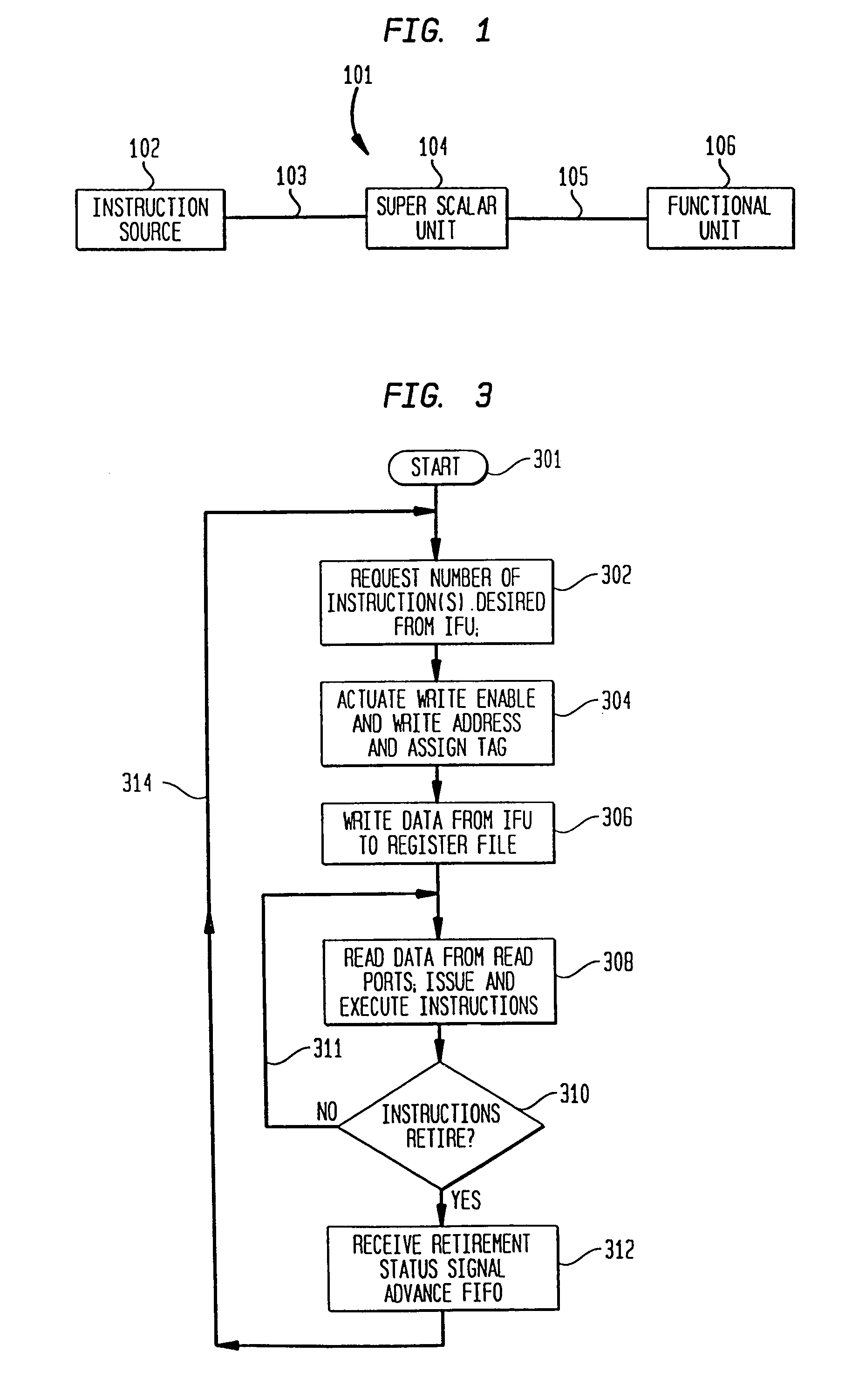
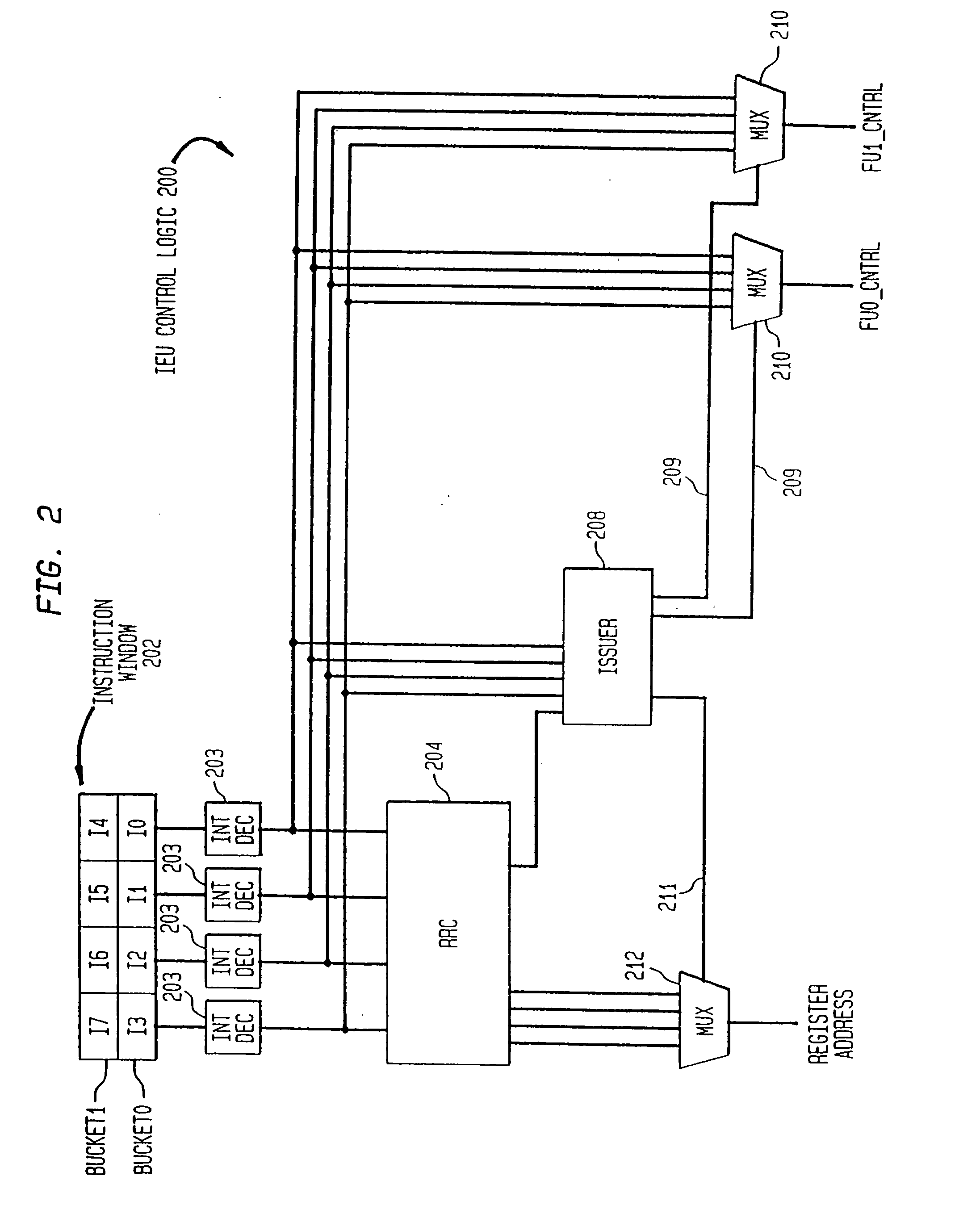
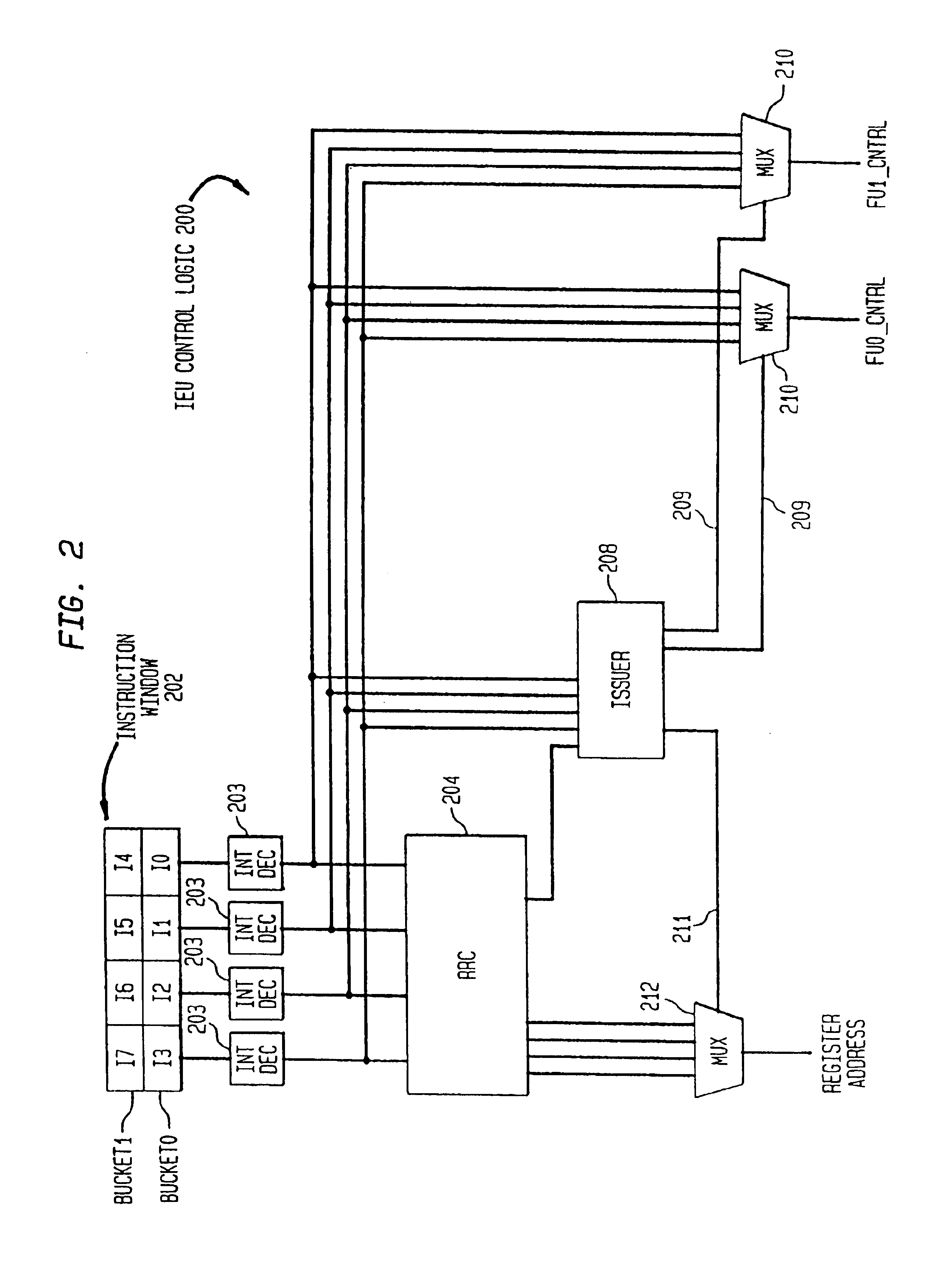
System and method for assigning tags to control instruction processing in a superscalar processor
InactiveUS7043624B2Simple designImprove operational flexibilityGeneral purpose stored program computerConcurrent instruction executionScalar processorProcessor register
A tag monitoring system for assigning tags to instructions. A source supplies instructions to be executed by a functional unit. A register file stores information required for the execution of each instruction. A queue having a plurality of slots containing tags which are used for tagging the instructions. The tags are arranged in the queue in an order specified by the program order of their corresponding instructions. A control unit monitors the completion of executed instructions and advances the tags in the queue upon completion of an executed instruction. The register file stores an instruction's information at a location in the register file defined by the tag assigned to that instruction. The register file also contains a plurality of read address enable ports and corresponding read output ports. Each of the slots from the queue is coupled to a corresponding one of the read address enable ports. Thus, the information for each instruction can be read out of the register file in program order.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for handling load and/or store operations an a supperscalar microprocessor
InactiveUS20050188184A1Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsExecution unitTerm memory
The present invention provides a system and method for managing load and store operations necessary for reading from and writing to memory or I / O in a superscalar RISC architecture environment. To perform this task, a load store unit is provided whose main purpose is to make load requests out of order whenever possible to get the load data back for use by an instruction execution unit as quickly as possible. A load operation can only be performed out of order if there are no address collisions and no write pendings. An address collision occurs when a read is requested at a memory location where an older instruction will be writing. Write pending refers to the case where an older instruction requests a store operation, but the store address has not yet been calculated. The data cache unit returns 8 bytes of unaligned data. The load / store unit aligns this data properly before it is returned to the instruction execution unit. Thus, the three main tasks of the load store unit are: (1) handling out of order cache requests; (2) detecting address collisions; and (3) alignment of data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
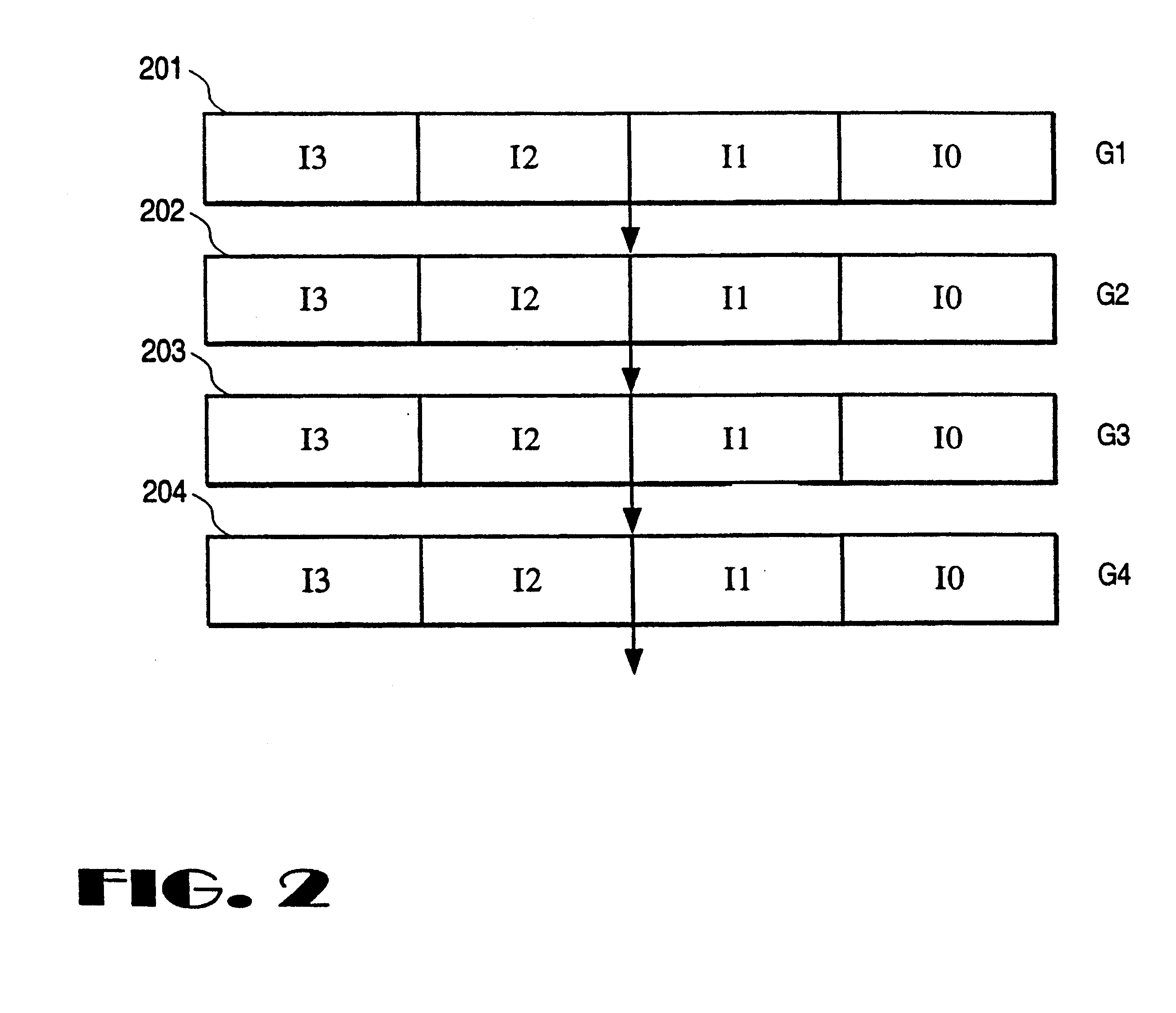
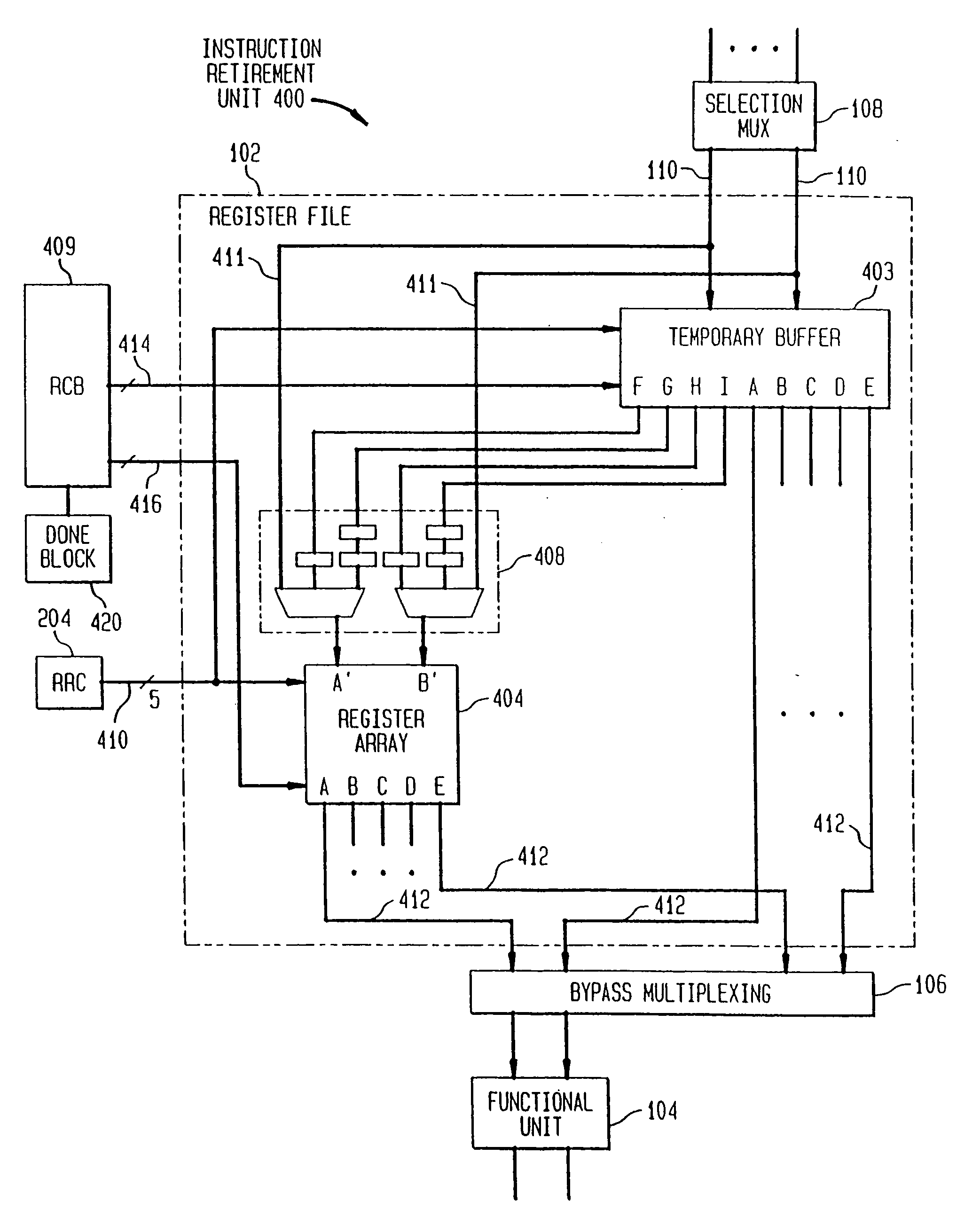
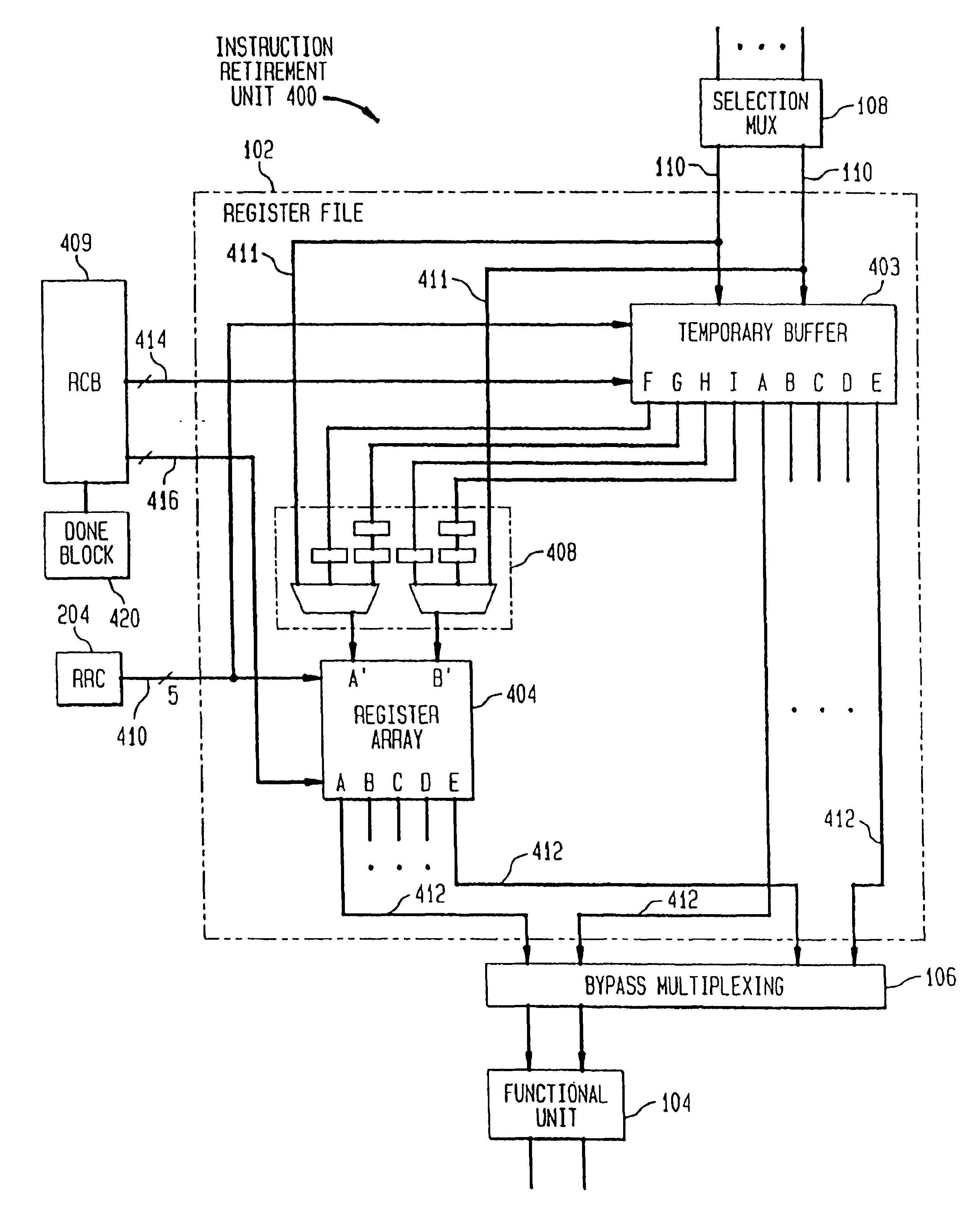
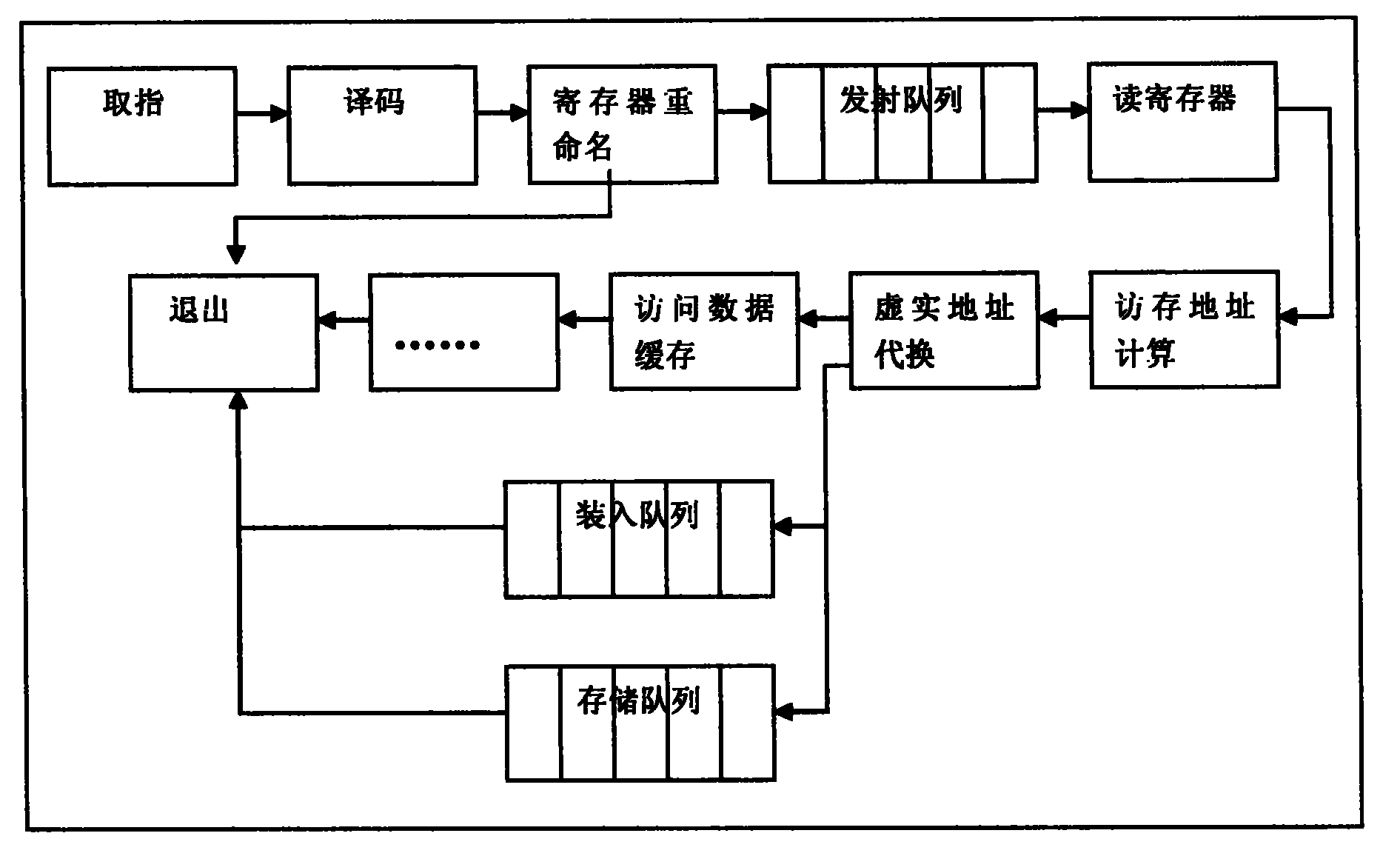
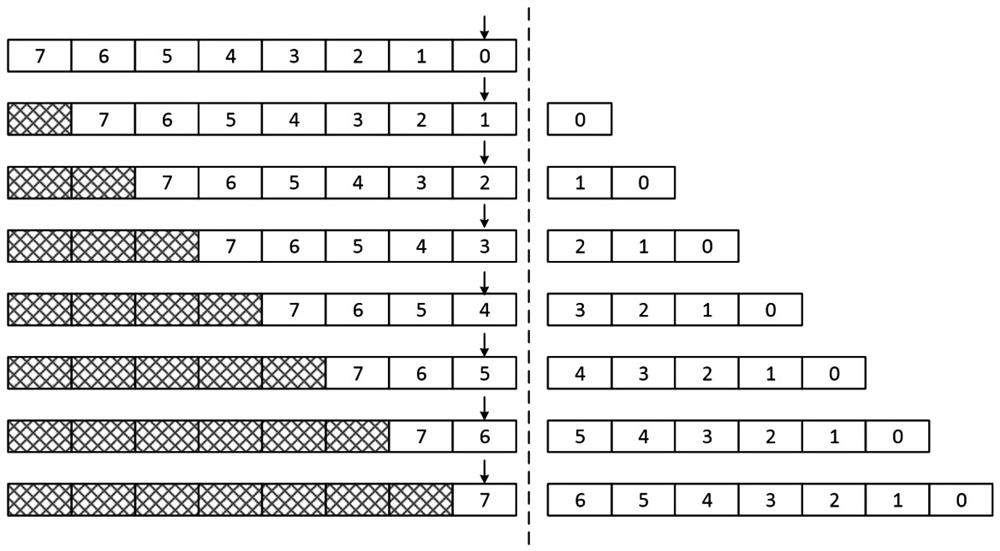
System and method for retiring approximately simultaneously a group of instructions in a superscalar microprocessor
InactiveUS20050228973A1Quick and efficient in handlingMaintain integrityRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsSuperscalar microprocessorInstruction set
An system and method for retiring instructions in a superscalar microprocessor which executes a program comprising a set of instructions having a predetermined program order, the retirement system for simultaneously retiring groups of instructions executed in or out of order by the microprocessor. The retirement system comprises a done block for monitoring the status of the instructions to determine which instruction or group of instructions have been executed, a retirement control block for determining whether each executed instruction is retirable, a temporary buffer for storing results of instructions executed out of program order, and a register array for storing retirable-instruction results. In addition, the retirement control block further controls the retiring of a group of instructions determined to be retirable, by simultaneously transferring their results from the temporary buffer to the register array, and retires instructions executed in order by storing their results directly in the register array. The method comprises the steps of monitoring the status of the instructions to determine which group of instructions have been executed, determining whether each executed instruction is retirable, storing results of instructions executed out of program order in a temporary buffer, storing retirable-instruction results in a register array and retiring a group of retirable instructions by simultaneously transferring their results from the temporary buffer to the register array, and retiring instructions executed in order by storing their results directly in the register array.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for retiring approximately simultaneously a group of instructions in a superscalar microprocessor
InactiveUS6920548B2Quick and efficient in handlingMaintain integrityRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsSuperscalar microprocessorInstruction set
An system and method for retiring instructions in a superscalar microprocessor which executes a program comprising a set of instructions having a predetermined program order, the retirement system for simultaneously retiring groups of instructions executed in or out of order by the microprocessor. The retirement system comprises a done block for monitoring the status of the instructions to determine which instruction or group of instructions have been executed, a retirement control block for determining whether each executed instruction is retirable, a temporary buffer for storing results of instructions executed out of program order, and a register array for storing retirable-instruction results. In addition, the retirement control block further controls the retiring of a group of instructions determined to be retirable, by simultaneously transferring their results from the temporary buffer to the register array, and retires instructions executed in order by storing their results directly in the register array. The method comprises the steps of monitoring the status of the instructions to determine which group of instructions have been executed, determining whether each executed instruction is retirable, storing results of instructions executed out of program order in a temporary buffer, storing retirable-instruction results in a register array and retiring a group of retirable instructions by simultaneously transferring their results from the temporary buffer to the register array, and retiring instructions executed in order by storing their results directly in the register array.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A device for extending the capacity of access queue by distribution control
ActiveCN101447911BLarge capacityIncrease the number ofConcurrent instruction executionProduction lineDistribution control
The invention discloses a device for extending the capacity of access queue by distribution control in the superscalar microprocessor, namely, in the instruction production line of the microprocessor, an access queue distributor is arranged at a register renaming station, and an access instruction transmission controller is arranged at an instruction transmission station. The access queue distributor checks whether the current new entry numbers to be distributed are matched with the access queue entry numbers loaded by access instructions in the transmission queue, when distributing the access queue entry numbers to each access instruction, if not, distributes new entry and sends the access instructions to the transmission queue; if so, does not distribute new entry and blocks the access instructions at the register renaming station. The access instruction transmission controller adds an judgement condition based on the normal instruction transmission condition when ready to transmit the access instructions, namely checks whether the access queue entry numbers loaded by the access instructions are matched with the access queue entry numbers loaded by the access instructions transmitted but not exited, if not, the transmission is allowed to transmit the access instruction to the executive parts; if so, the transmission is stopped to keep the access instructions in the transmission in the queue. The device pre-distributes the access queue occupied by these access instructions to the new access instructions prior to the exit of the access instructions, and the cache is in theexisting transmission queue, and on the premise of no coverage of access queue information, the number of the access instruction on the stream line is increased to indirectly extend the capacity of the access queue and make up the performance loss of the common access queue control methods.
Owner:上海高性能集成电路设计中心
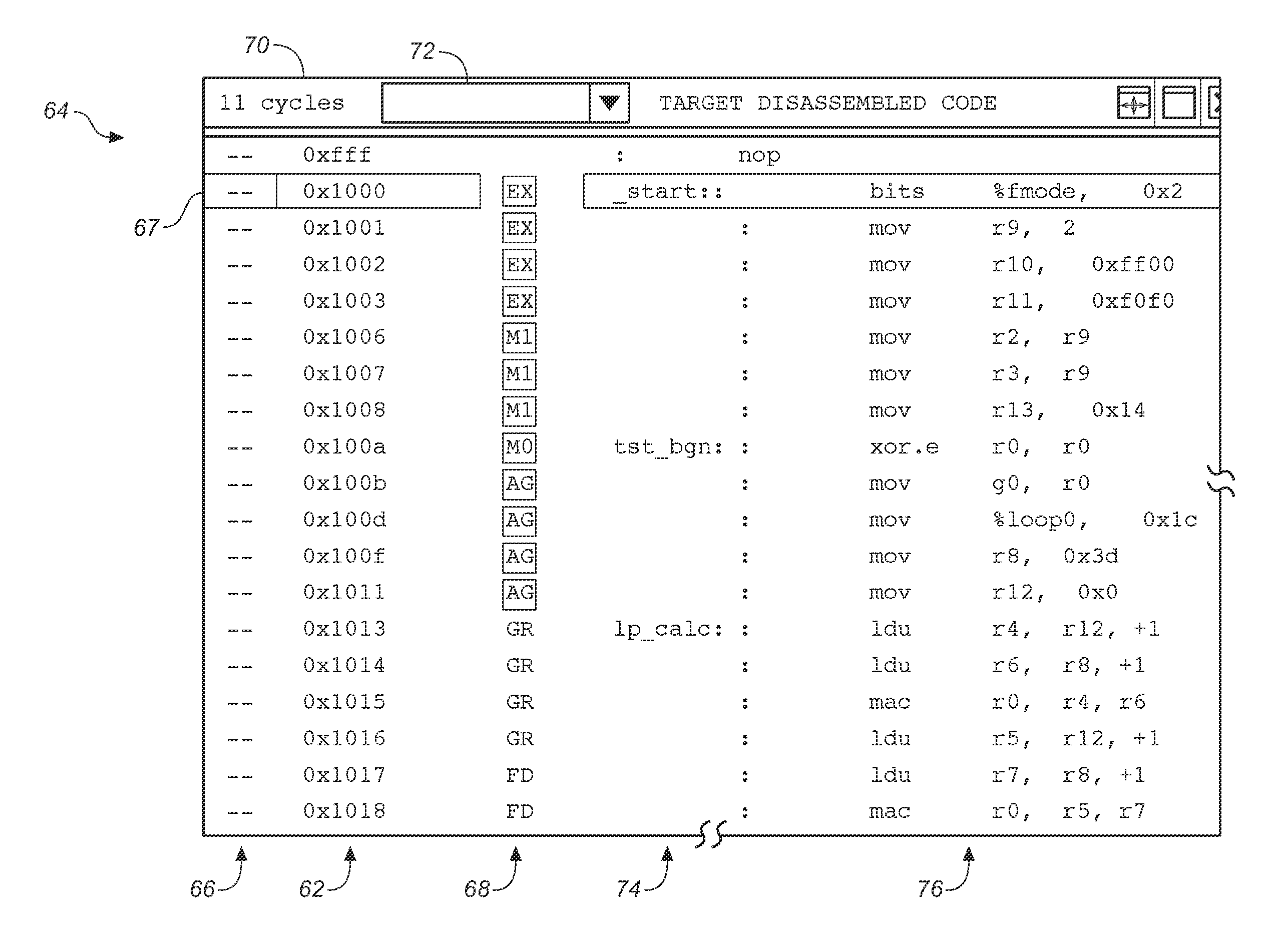
User interface software development tool and method for enhancing the sequencing of instructions within a superscalar microprocessor pipeline by displaying and manipulating instructions in the pipeline
InactiveUS7703076B1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsScalar processor
A graphics rendering engine within a software development tool is used to perform software debug operations by analyzing the status of instructions within various stages of a superscalar processor pipeline. The debug operations are carried out using code breakpoints selected by a user through a graphical user interface. Once a line of code is selected, the processor pipeline can be examined by designating a highlighted color, for example, for certain stages and corresponding instructions that will proceed to the next stage, and not designating stages and corresponding instructions that will not proceed. This allows a user to visually examine the efficiency of the instruction throughput at select regions in the sequence of instruction addresses. Armed with the information, a user can then modify the sequence if desired.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
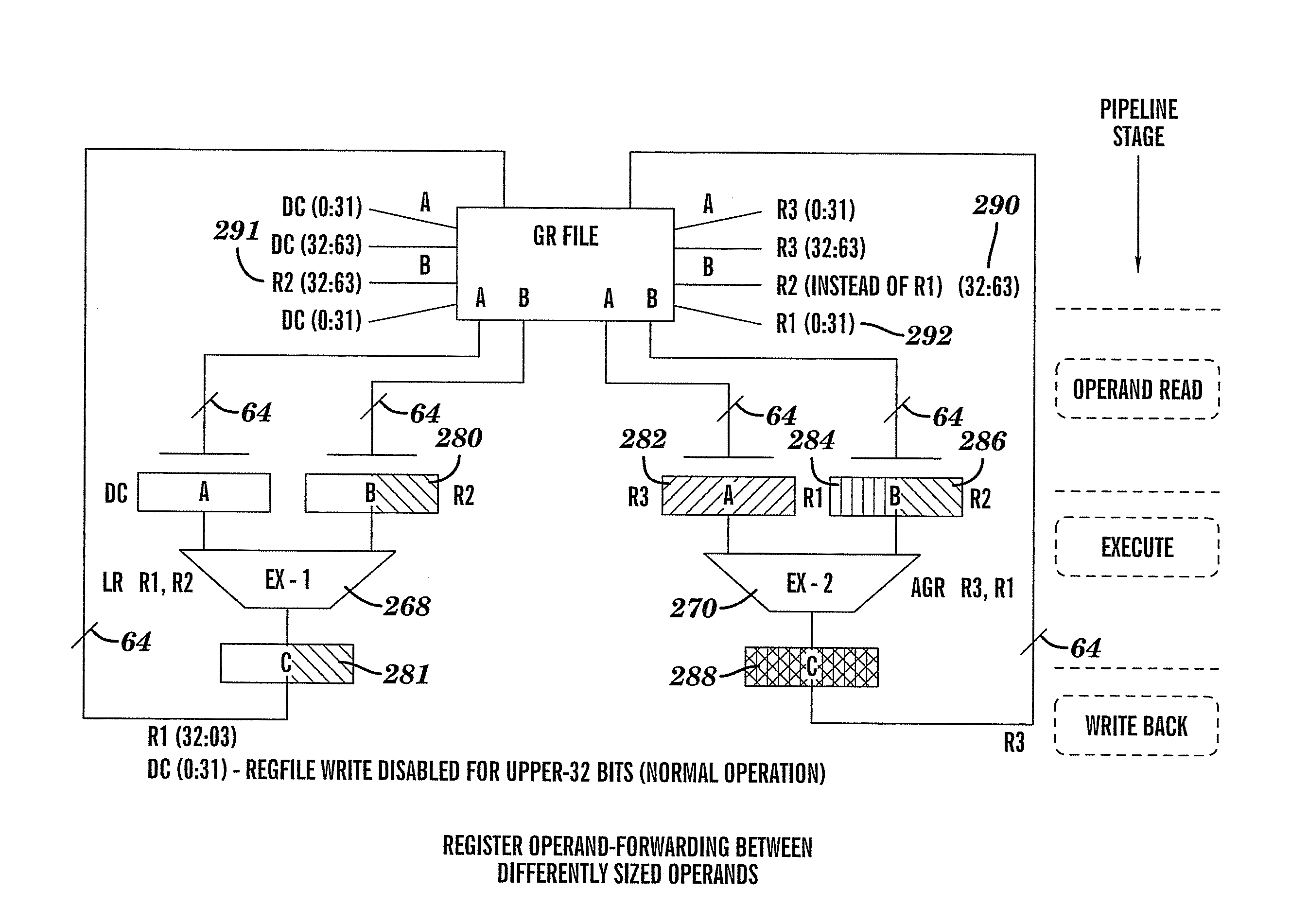
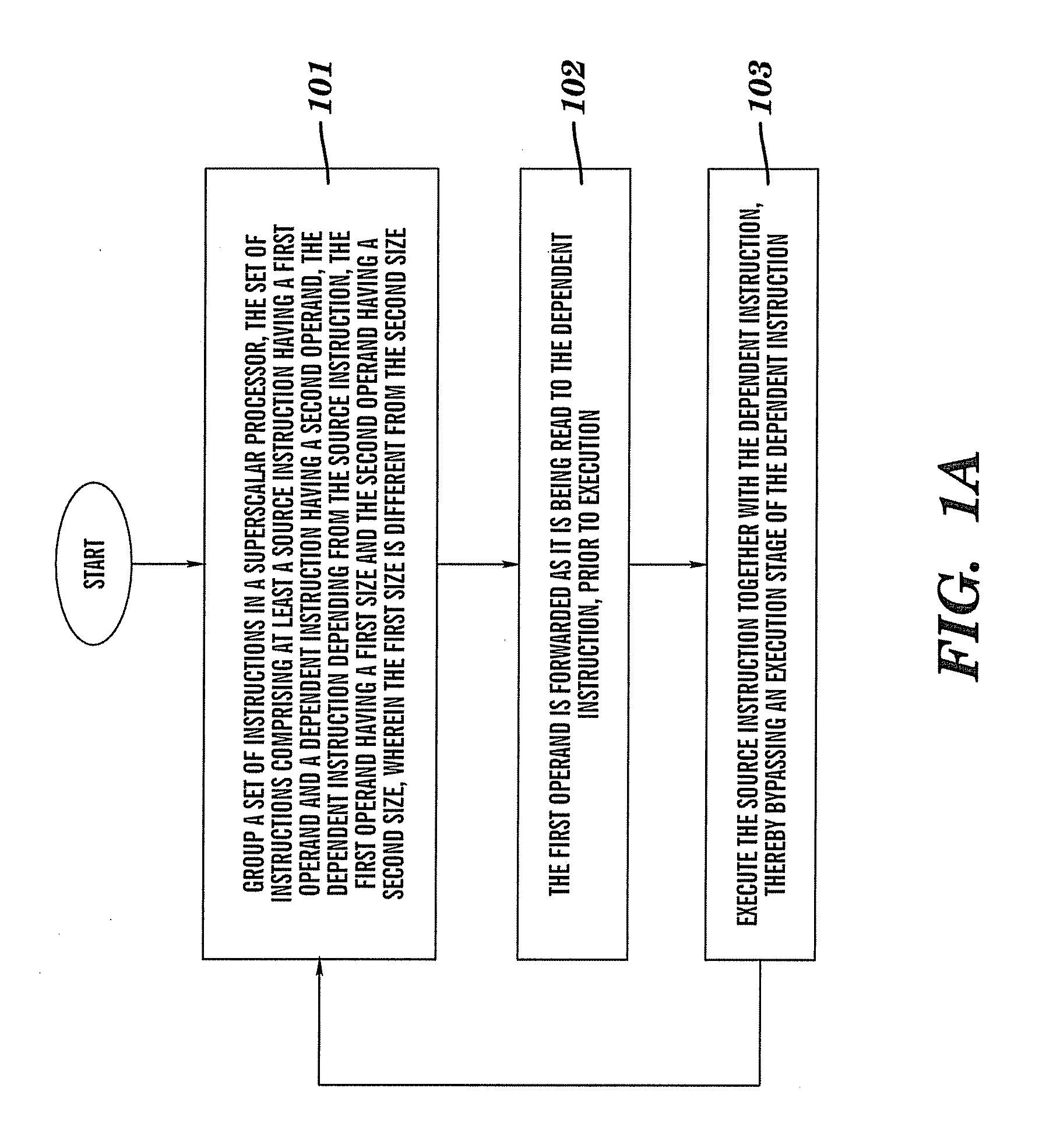
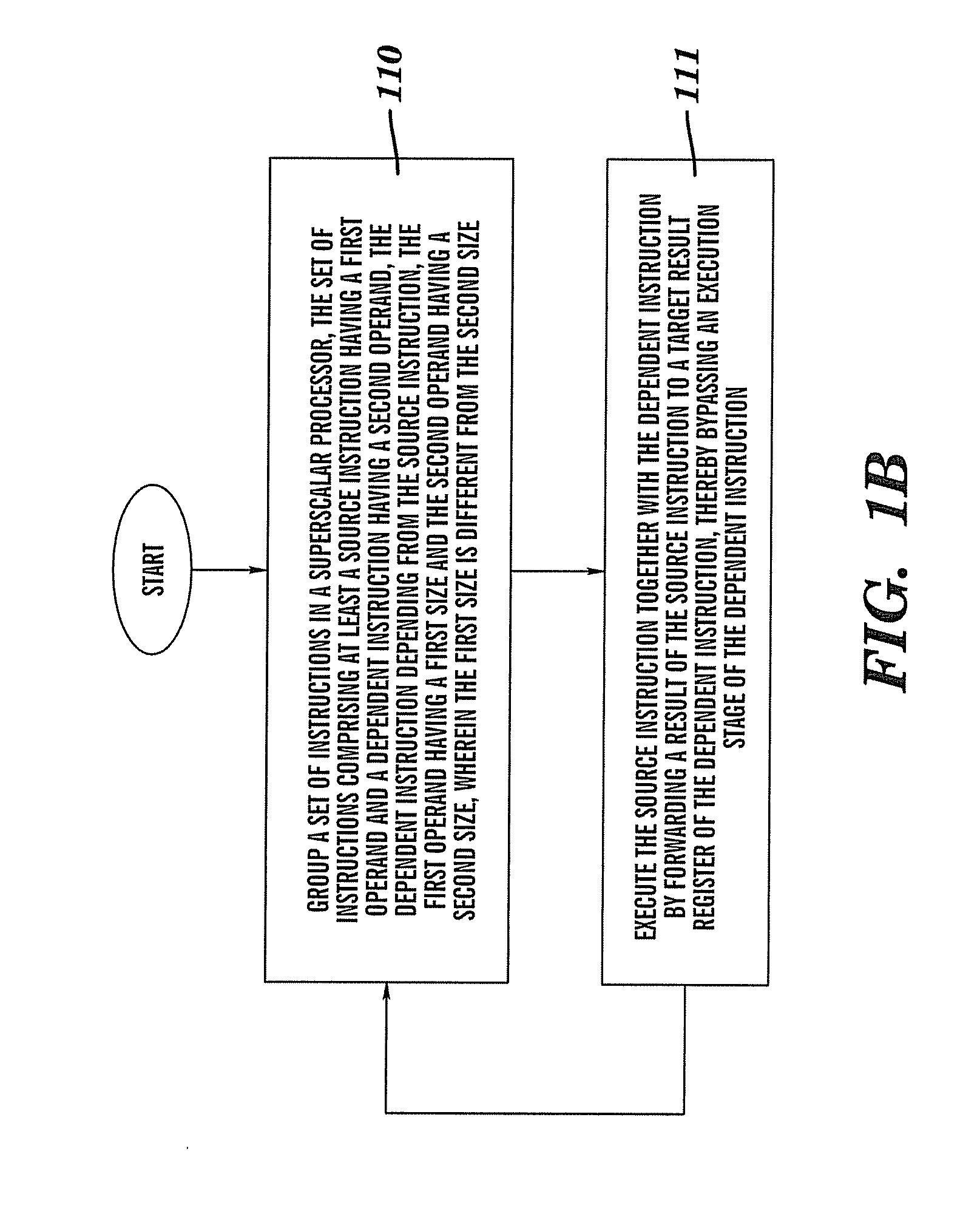
Method, system, computer program product, and hardware product for implementing result forwarding between differently sized operands in a superscalar processor
Result and operand forwarding is provided between differently sized operands in a superscalar processor by grouping a first set of instructions for operand forwarding, and grouping a second set of instructions for result forwarding, the first set of instructions comprising a first source instruction having a first operand and a first dependent instruction having a second operand, the first dependent instruction depending from the first source instruction; the second set of instructions comprising a second source instruction having a third operand and a second dependent instruction having a fourth operand, the second dependent instruction depending from the second source instruction, performing operand forwarding by forwarding the first operand, either whole or in part, as it is being read to the first dependent instruction prior to execution; performing result forwarding by forwarding a result of the second source instruction, either whole or in part, to the second dependent instruction, after execution; wherein the operand forwarding is performed by executing the first source instruction together with the first dependent instruction; and wherein the result forwarding is performed by executing the second source instruction together with the second dependent instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for realizing streamline retiring of store instruction in superscalar microprocessor
ActiveCN104391680AIncrease profitImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionInterface protocolSuperscalar microprocessor
The invention relates to a method for realizing streamline retiring of a store instruction in a superscalar microprocessor. The method is characterized in that the automatic sequencing function of buffer of three types is utilized, the interface protocol of the buffer of the three types is improved, the executing conditions of the store instruction are weakened, and therefore, the retiring of the store instruction is sped up. According to the method, the quantity of instructions retired in each clock period and the quantity of the store instruction of writing first-stage data cache in each clock cycle are properly allocated, thus the store instruction streamline retiring function can be realized under the condition that the store address hits the first-stage data cache and the writing is authorized when executing the continuous store instruction sequence, and as a result, the performance of the microprocessor can be obviously improved.
Owner:上海高性能集成电路设计中心
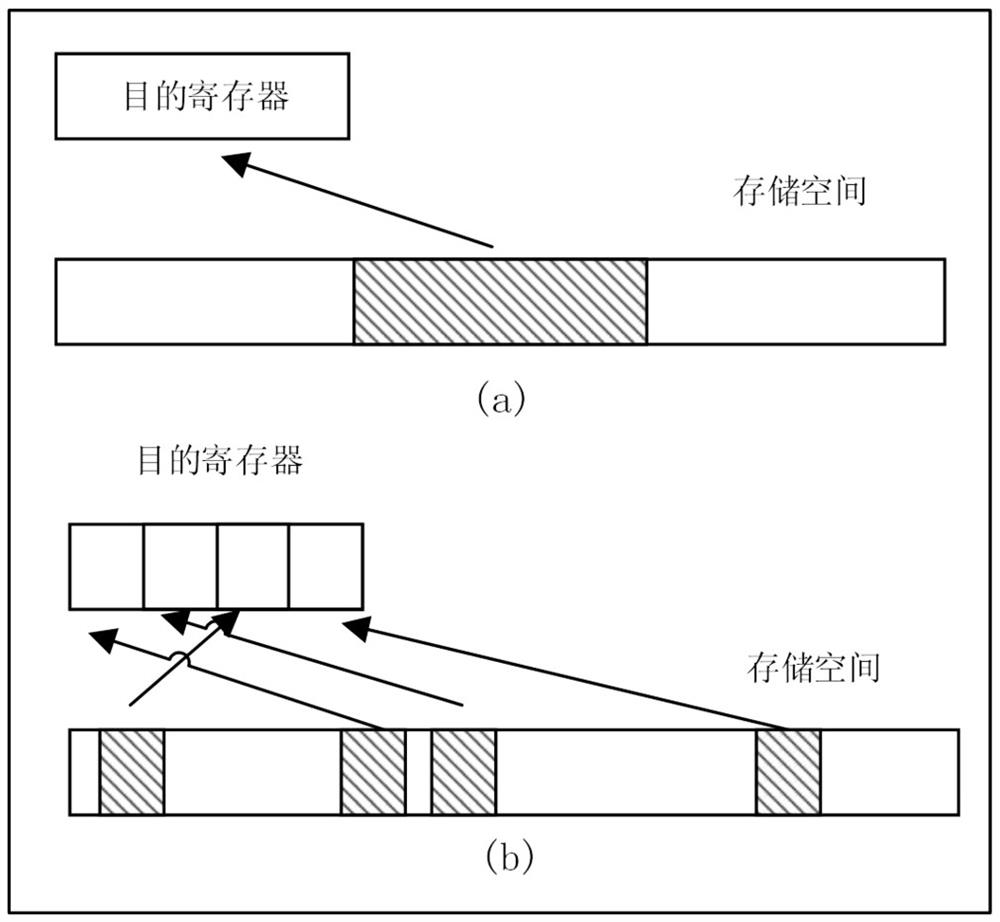
Implementation method of vector aggregation loading instruction
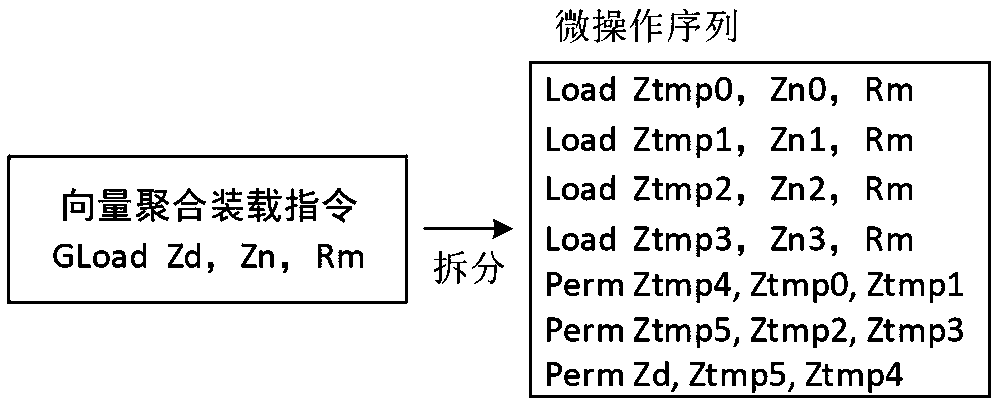
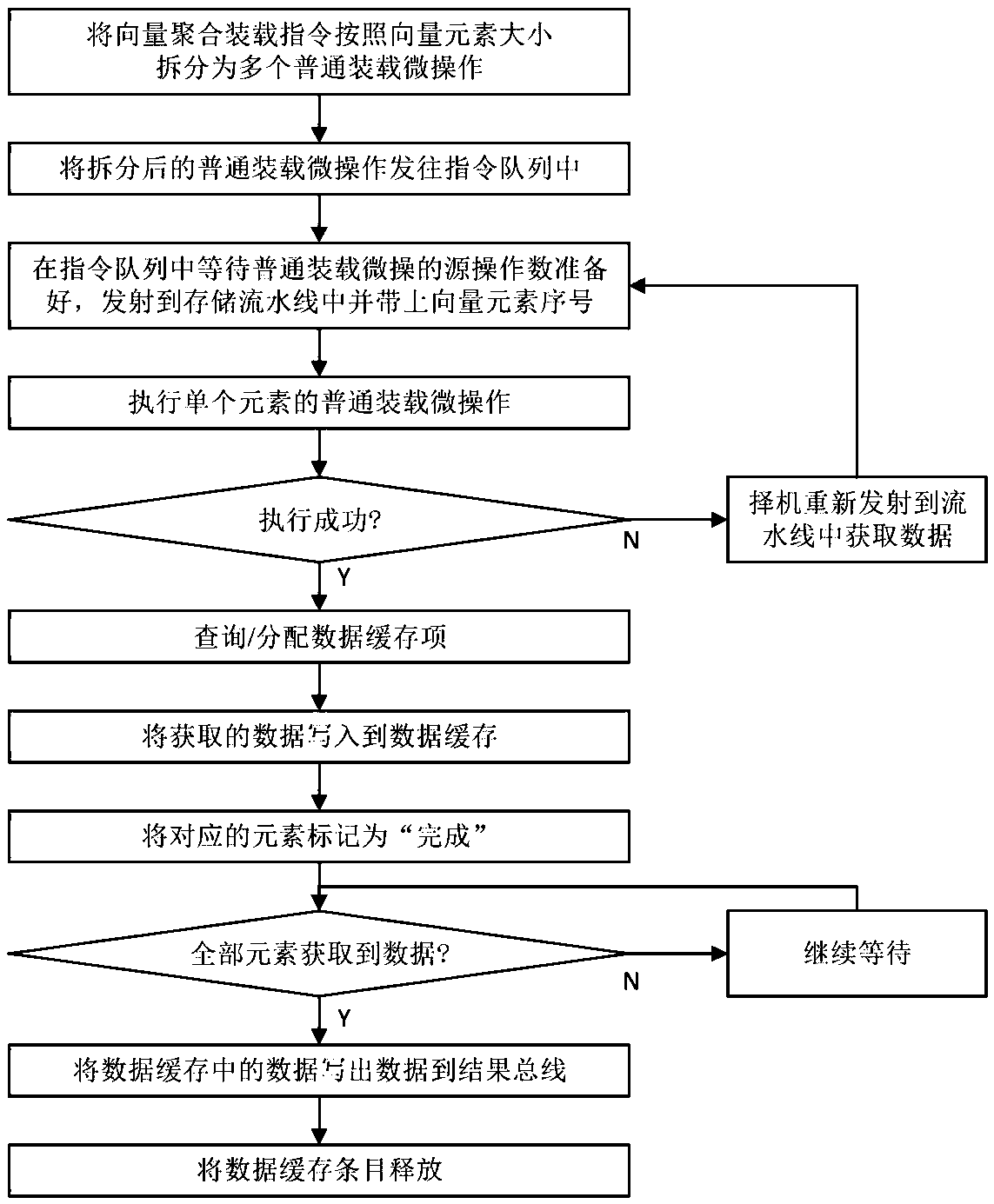
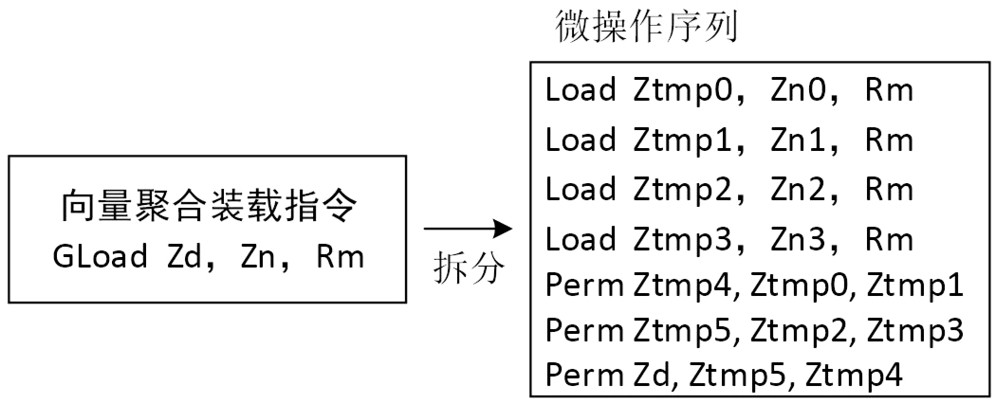
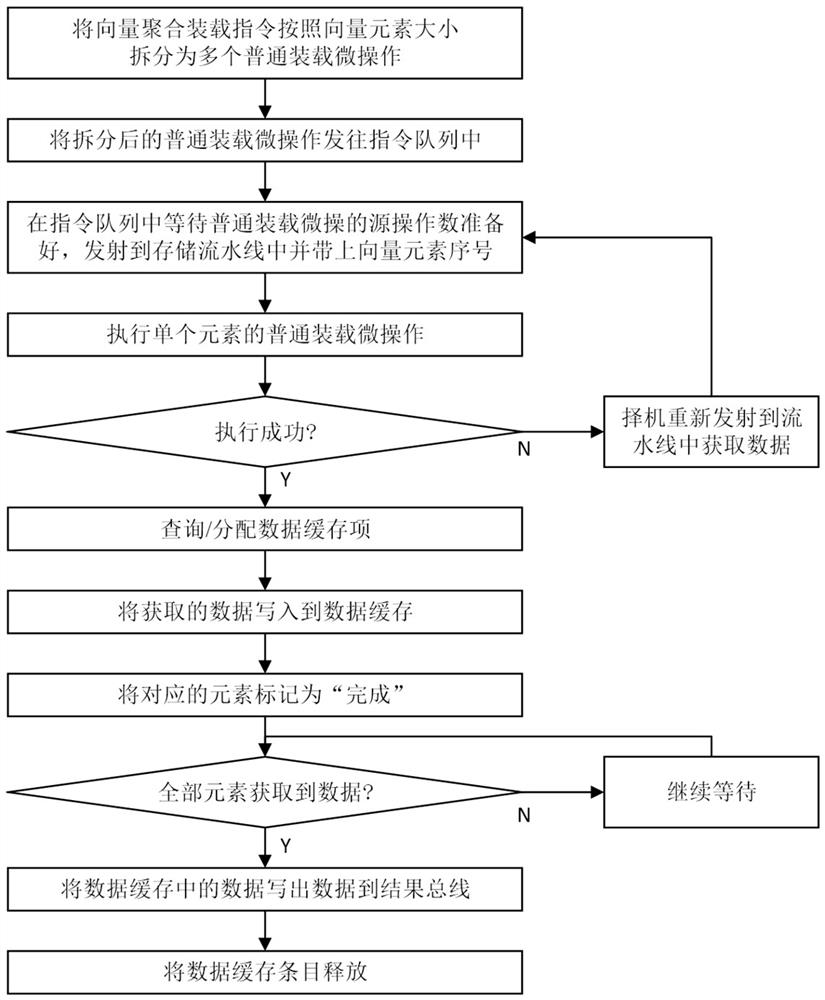
ActiveCN110908716ALower latencyImprove concurrencyConditional code generationConcurrent instruction executionMicro-operationTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to the technical field of microprocessor design, in particular to a method for realizing a vector aggregation loading instruction, which comprises the following steps of: splitting the vector aggregation loading instruction into a plurality of single-element common loading microoperations; sending the split micro-operation and the corresponding element serial number to an instruction queue; after the operands are prepared, sending the single-element loading microoperation to a storage pipeline to obtain data; writing the obtained data into corresponding elements of the corresponding data cache items; and after all element data of the data cache item is written in, writing result data to a result bus from the data cache, and finishing the execution of the vector aggregation loading instruction. The method can effectively improve the execution performance of the vector aggregation loading instruction, can utilize the path of a common loading instruction to the maximum extent, is suitable for a high-performance out-of-order superscalar microprocessor, and has the advantages of being simple to implement and high in performance.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
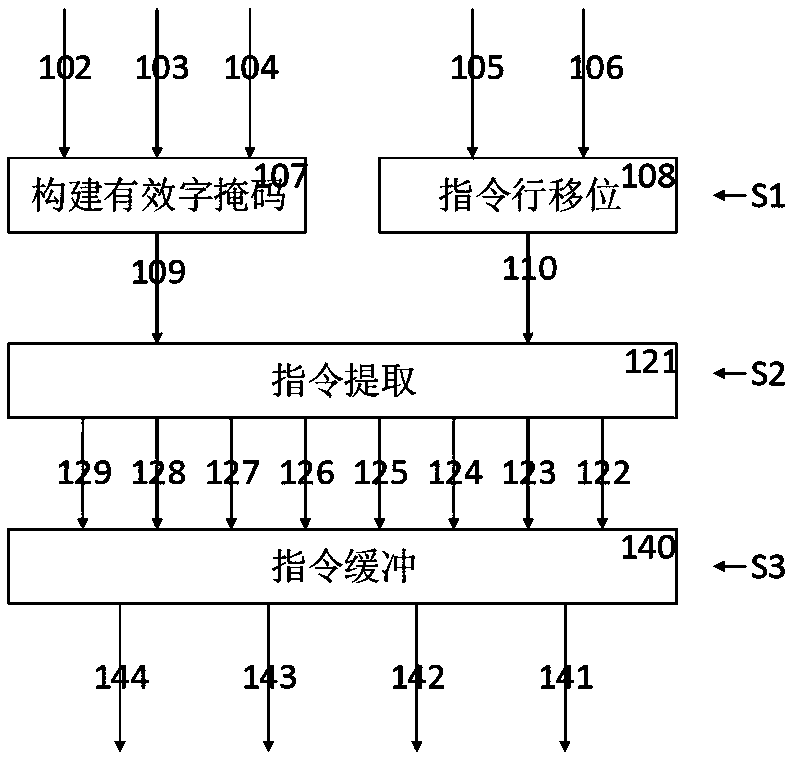
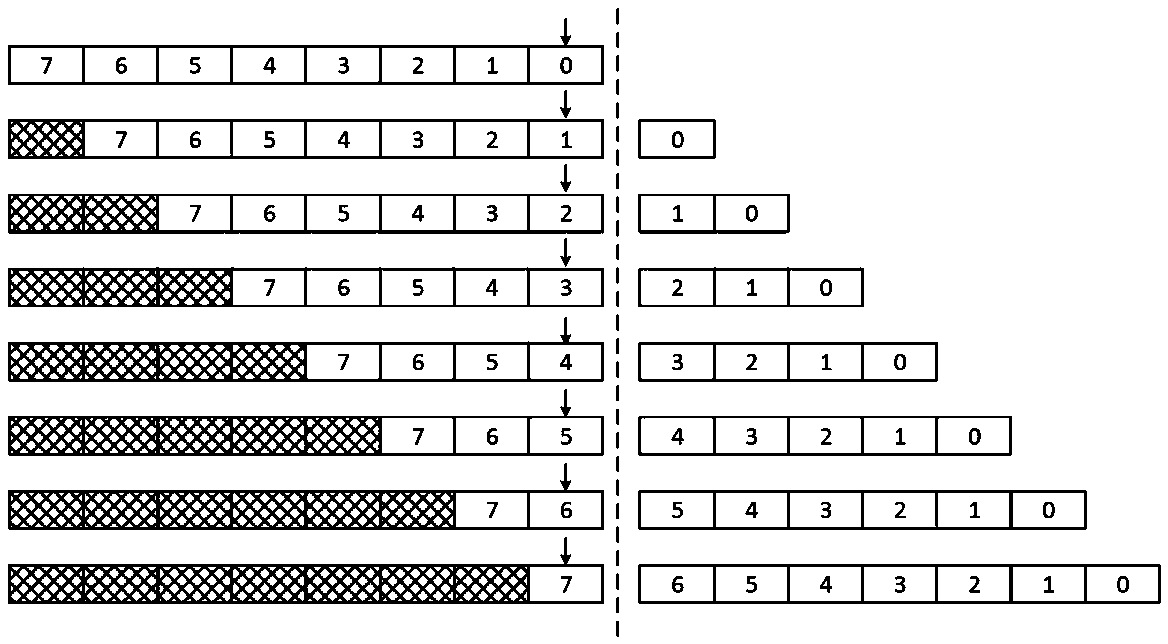
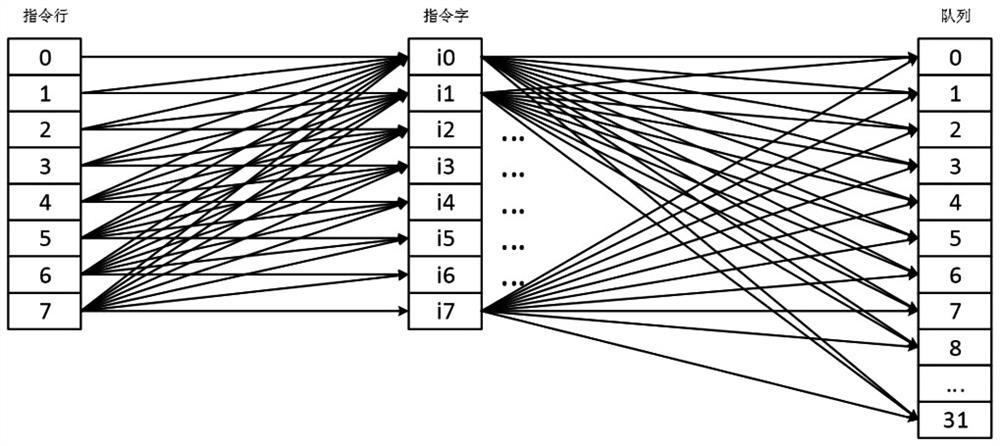
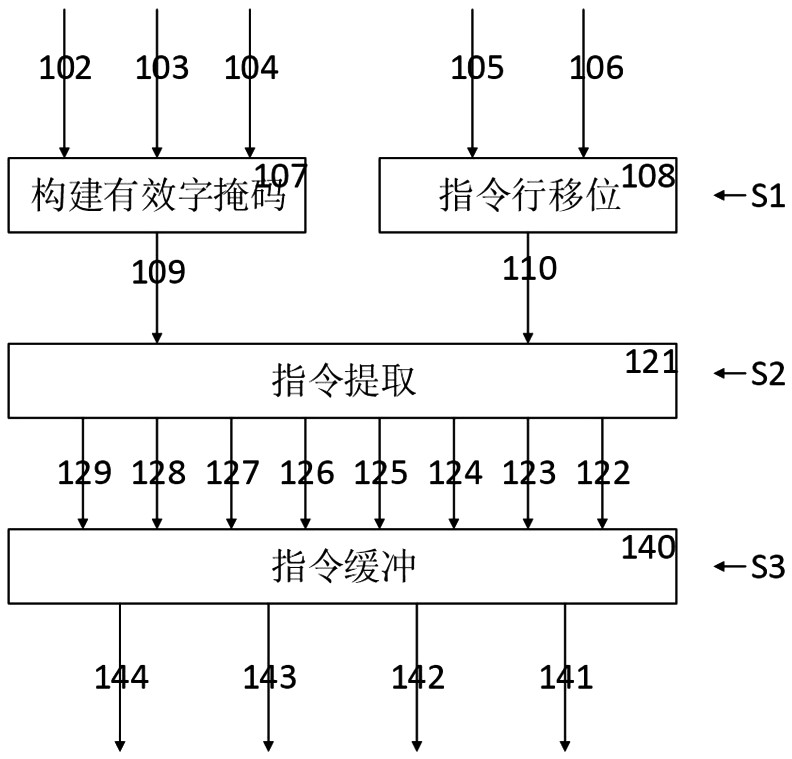
A shift-based instruction extraction and buffering method and superscalar microprocessor
ActiveCN109101275AReduce overheadSimple extraction logicConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsSuperscalar microprocessorWrite buffer
Owner:飞腾技术(长沙)有限公司 +1
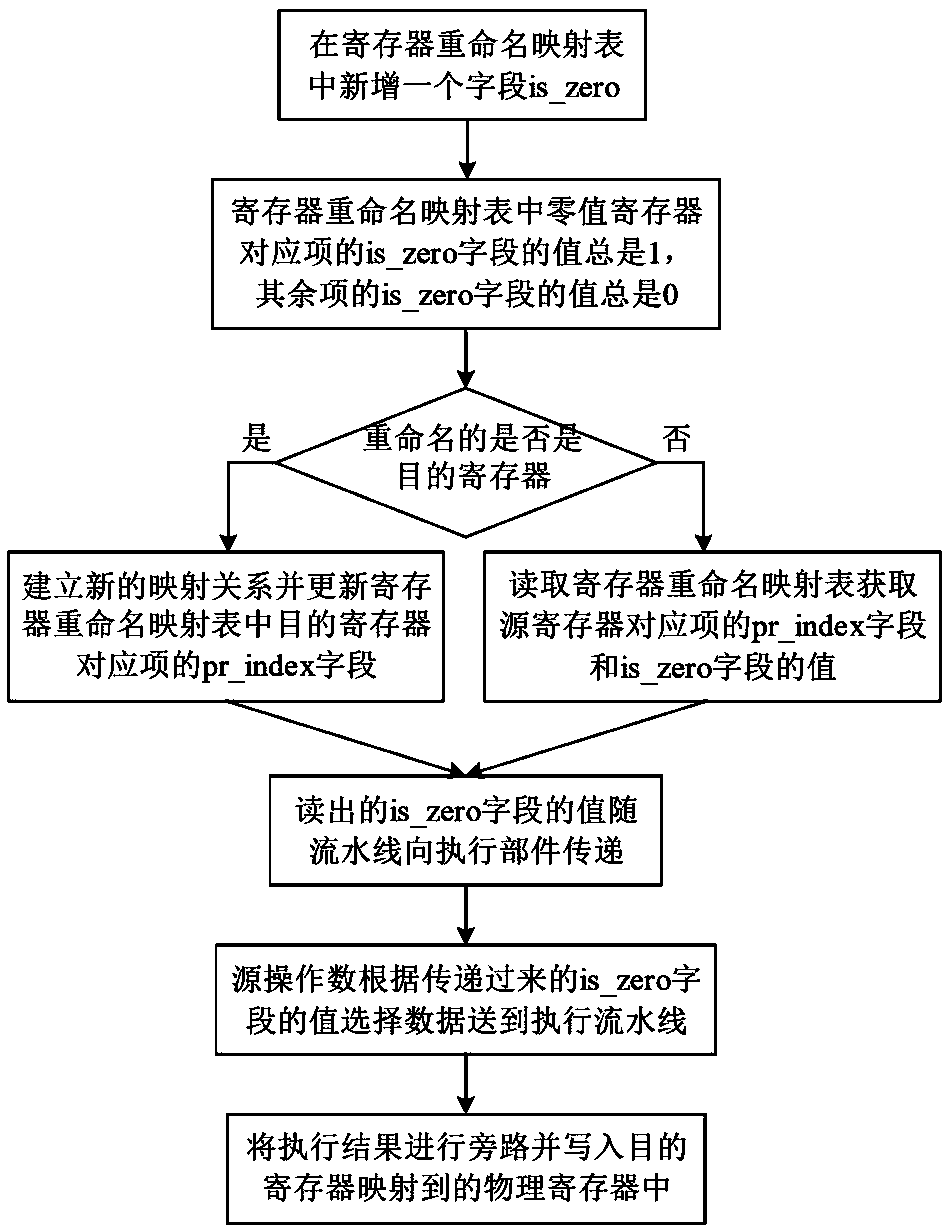
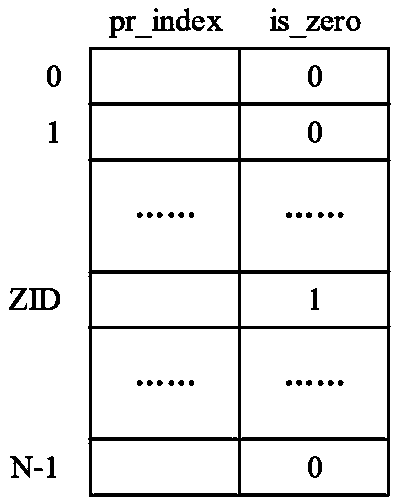
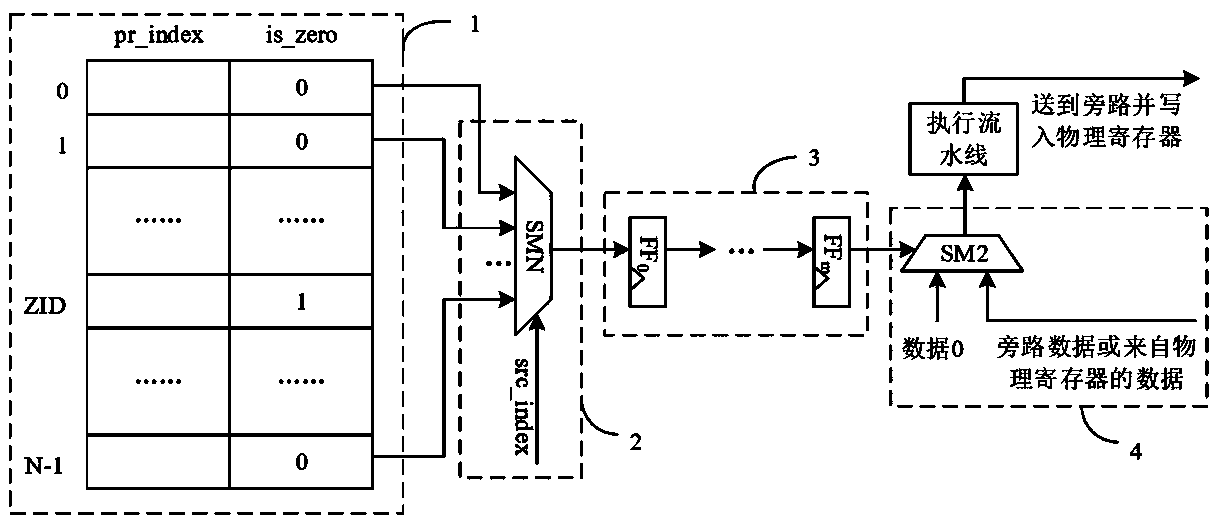
Zero-value register implementation method and device
The invention relates to an out-of-order superscalar microprocessor design technology, in particular to a zero-value register implementation method and device. The method comprises the following stepsof: adding an identification field is_zero in a register renaming mapping table, wherein the identification field is_zero represents whether the register is a zero value register or not; and readingand transmitting the field in the register renaming stage to an execution component step by step along with an assembly line, wherein the identification field is_zero is used as a selection signal, data 0 is directly selected when a source operand comes from a zero value register, and data does not need to be obtained from a bypass or a physical register. According to the method, the complexity ofregister renaming, physical register writing and data bypass logic is reduced, and the zero-value register implementation method and device are suitable for the advantage of simple logic implementation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
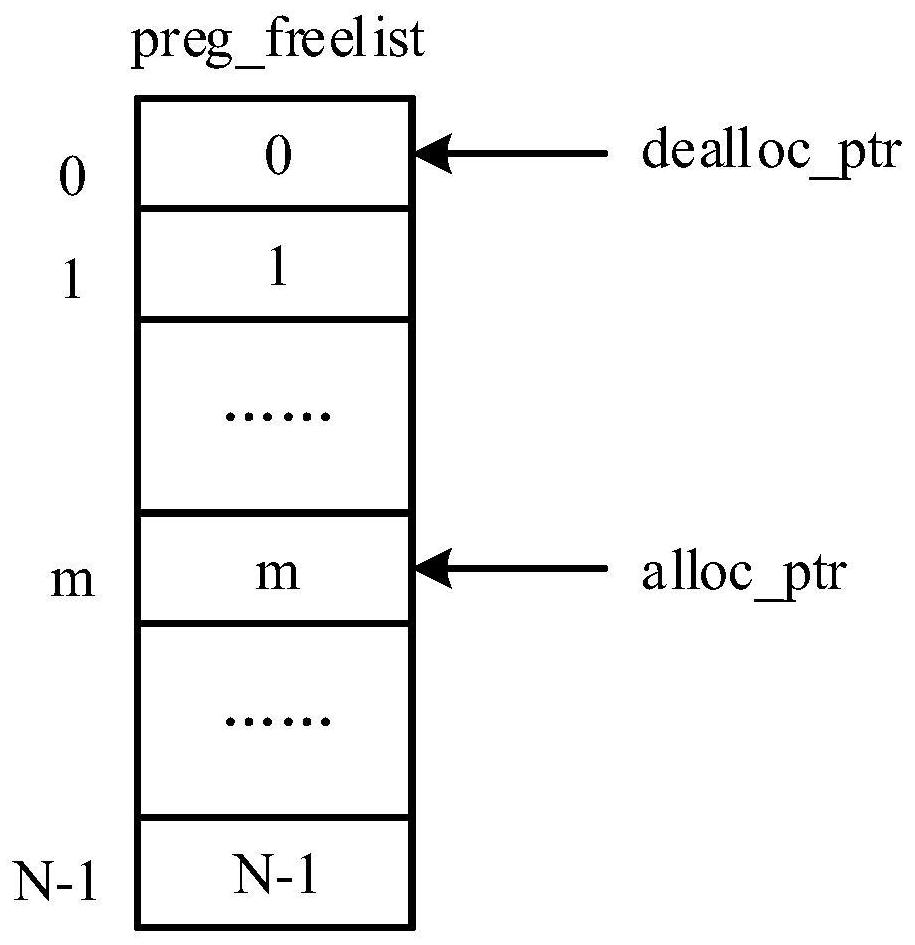
A method and device for acquiring free physical registers
ActiveCN110647361BOptimize timingReduce overheadConcurrent instruction executionAccess methodSuperscalar microprocessor
The present invention relates to out-of-sequence superscalar microprocessor design technology, in particular to a method and device for obtaining free physical registers. The method of the present invention includes initializing a physical register free list for recording all physical registers that can be used for renaming , the physical register free list has an allocation pointer and a recovery pointer, initially the number of the free physical register recorded in the nth item of the physical register free list is n, the recovery pointer points to the 0th item, and the allocation pointer points to the mth item, The m registers used to save the numbers of the free physical registers to be used by the register renaming pipeline station are allocated to the renamed instructions in sequence from 0 to m-1; how to update the m registers and Allocate pointers. The invention has the advantages of good timing and small hardware overhead.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
A Realization Method of Vector Aggregate Load Instruction
ActiveCN110908716BLower latencyImprove concurrencyConditional code generationConcurrent instruction executionMicro-operationOperand
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Register renaming system and method for managing rename registers
InactiveCN102566976BEasy to determineProcessing speedConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureTime cost
The invention relates to a register renaming system and method for managing and renaming registers. The invention specifically provides the register renaming system for managing and renaming the registers by adopting multiple renamed register queues, and the system comprises a physical register group, a register alias table (RAT), an architecture register mapping table (ARMT), a select finger of the renamed register queues, a decoder, a logic register renaming device, an RAT modifying device and an updating device of the renamed register queues. In addition, the invention further provides the method for managing and renaming the registers by adopting the multiple renamed register queues. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, renaming operation can be simultaneously performed on the multiple registers within a same period, the implementation method is simple, the time cost is small, and the register renaming system and method are suitable for superscalar microprocessors with higher transmission width.
Owner:北京国睿中数科技股份有限公司
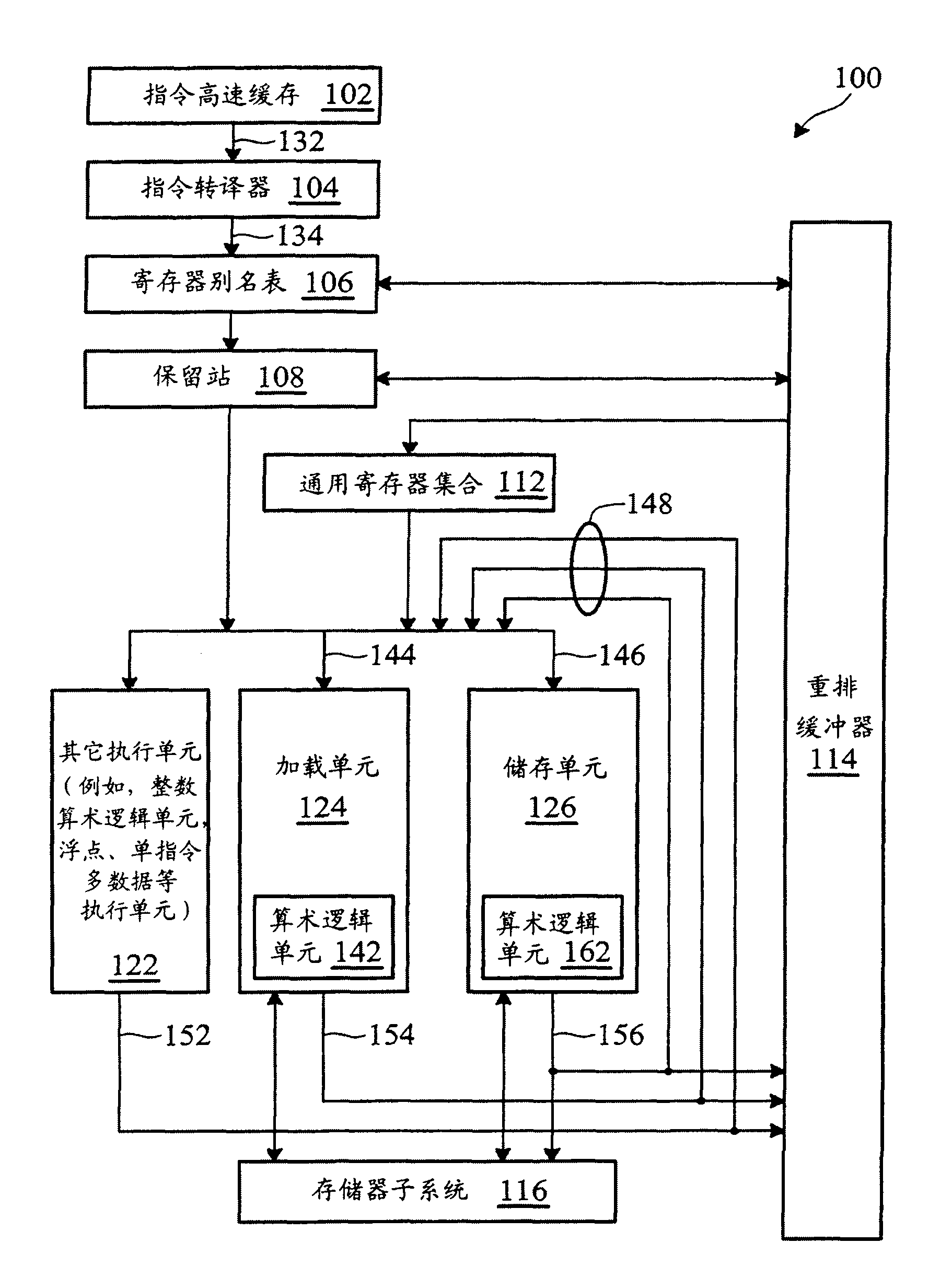
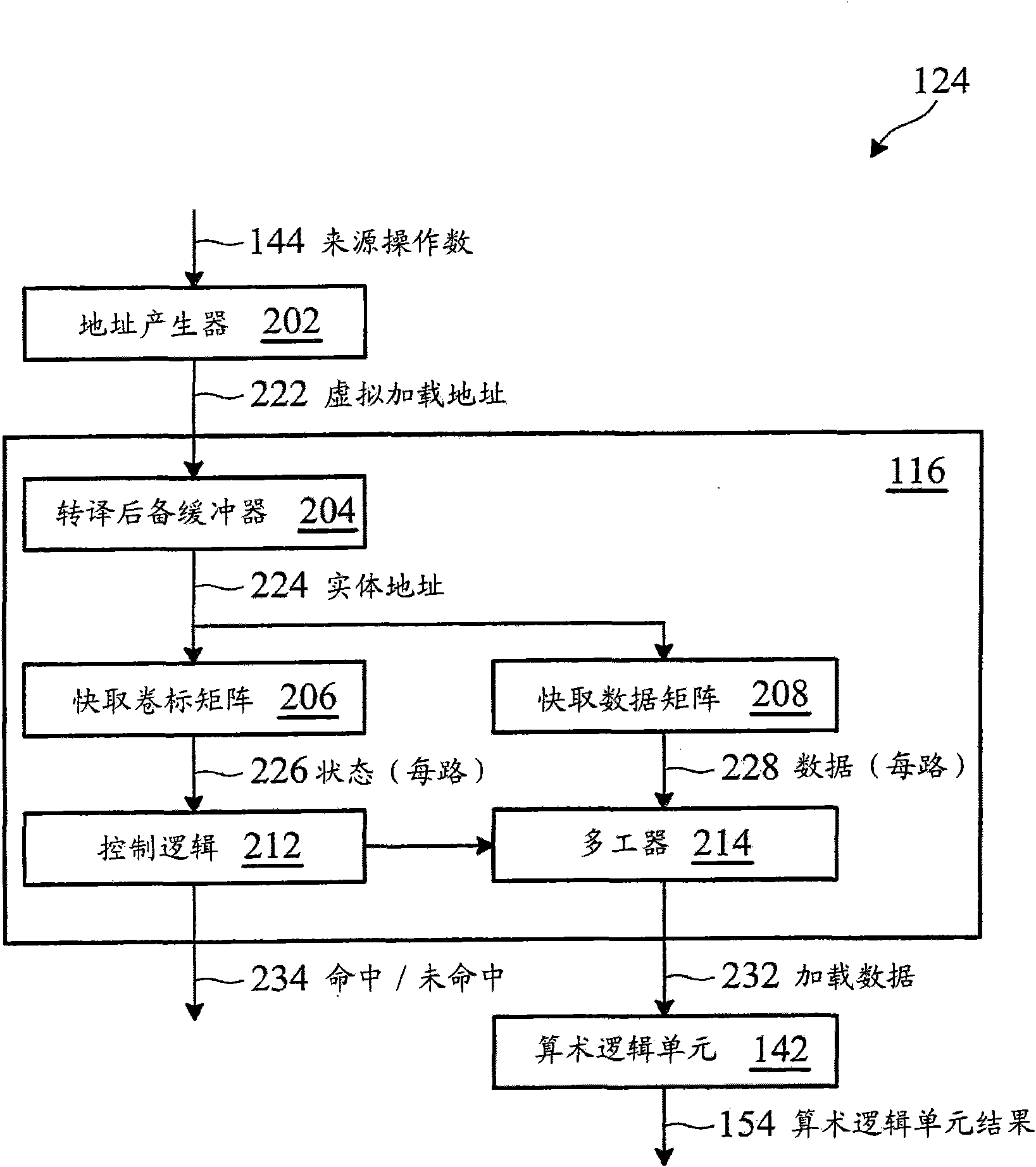
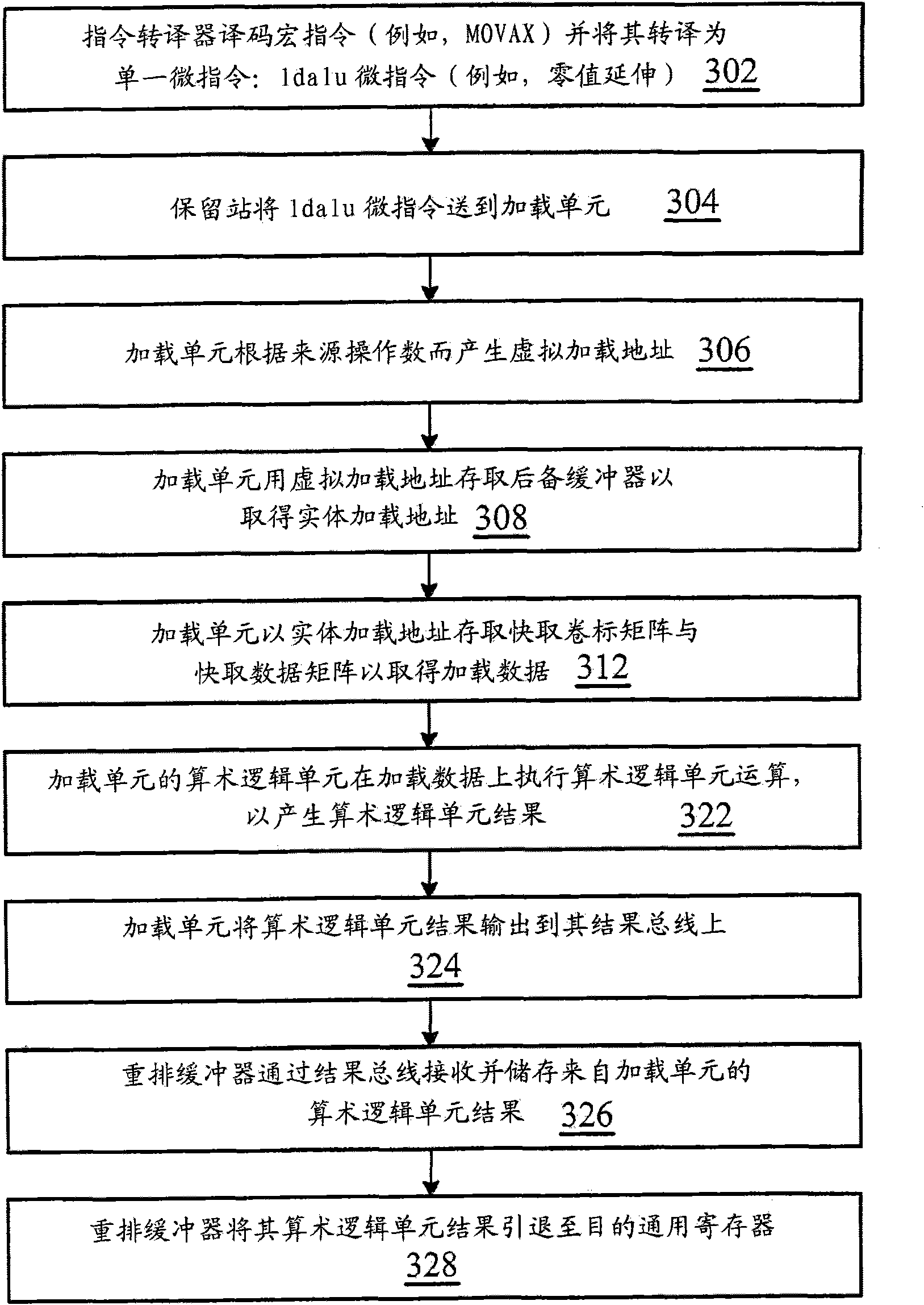
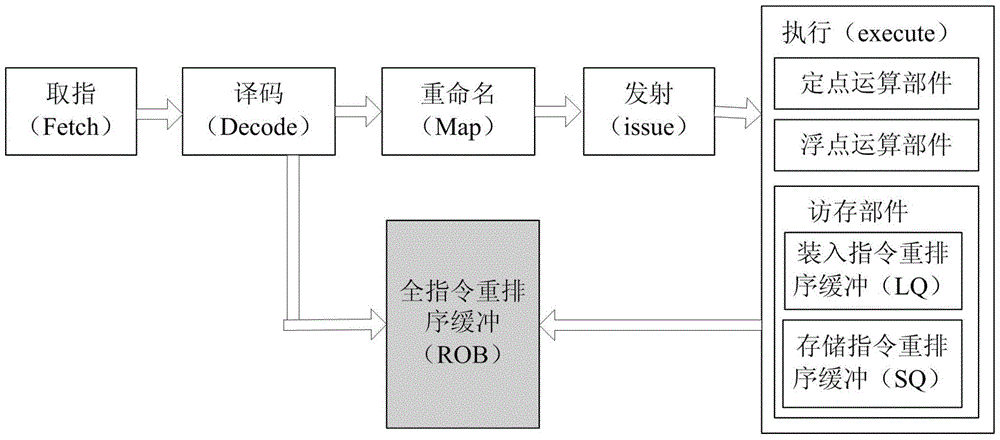
Instruction processing method and its applicable superscalar pipeline microprocessor
ActiveCN101907984BAdded lookahead capabilityTake advantage of instruction-level parallelizationConcurrent instruction executionArithmetic logic unitProcessor register
A super-scale pipeline microprocessor and command processing method. The super-scale pipeline microprocessor has a register aggregation, a high speed cache, a performing unit and a load application unit coupled to the high speed cache, that are defined by the command set framework of the super-scale pipeline microprocessor. The load application unit is different from other performing units of the super-scale pipeline microprocessor, and the load application unit includes an arithmetic logic unit. The load application unit receiving a first command, the first command designates the first storage address of the first origin operand, operation performed on the first origin operand and generating result, and a first destination register in the register aggregation to store the result. The load application unit reads the first origin operand from the high speed cache. The arithmetic logic unit performs operation on the first origin operand to generate result, rather than forwarding the first origin operand to anyone of the other performing units to perform operation on the first origin operand to generate result. The load application unit further outputs the result for subsequent fallback to the first destination register.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
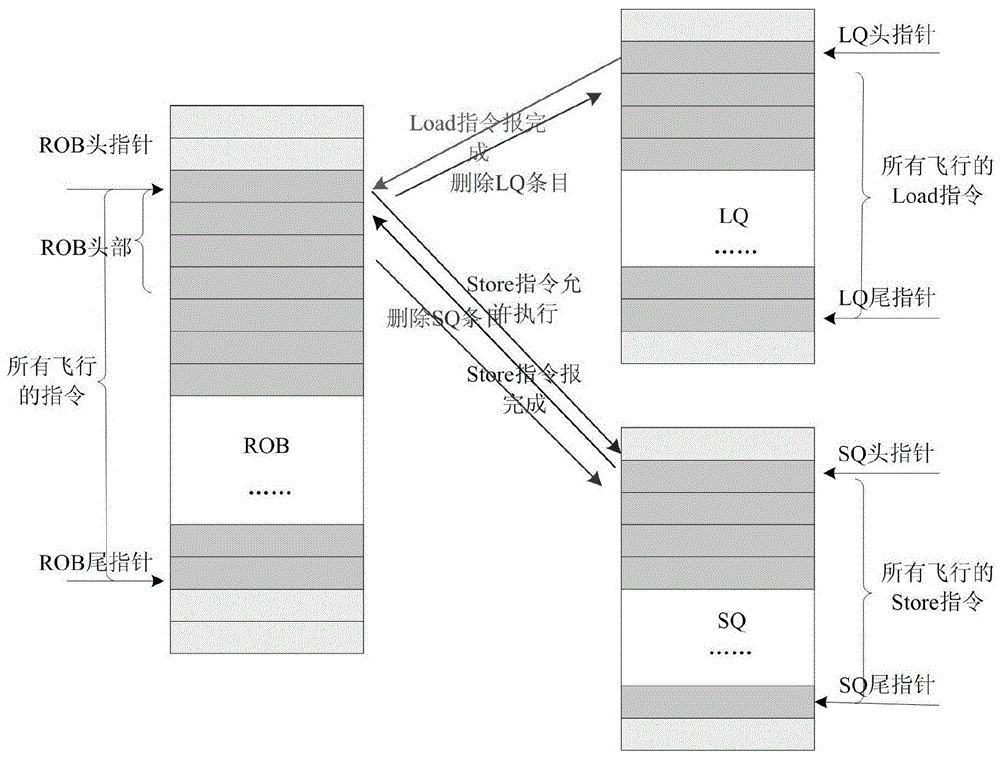
Retransmission self-trapping immediate processing method in superscalar microprocessor
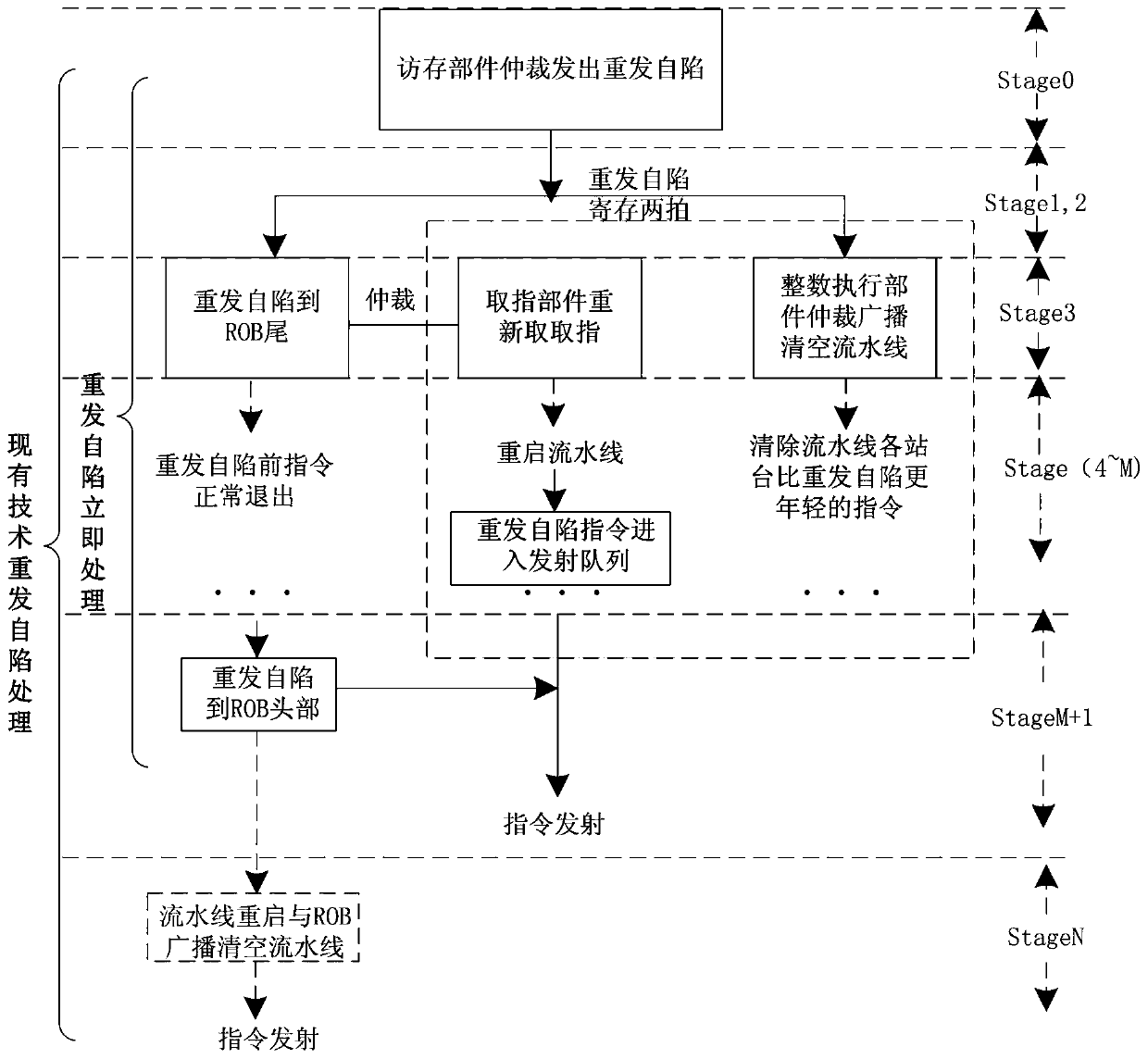
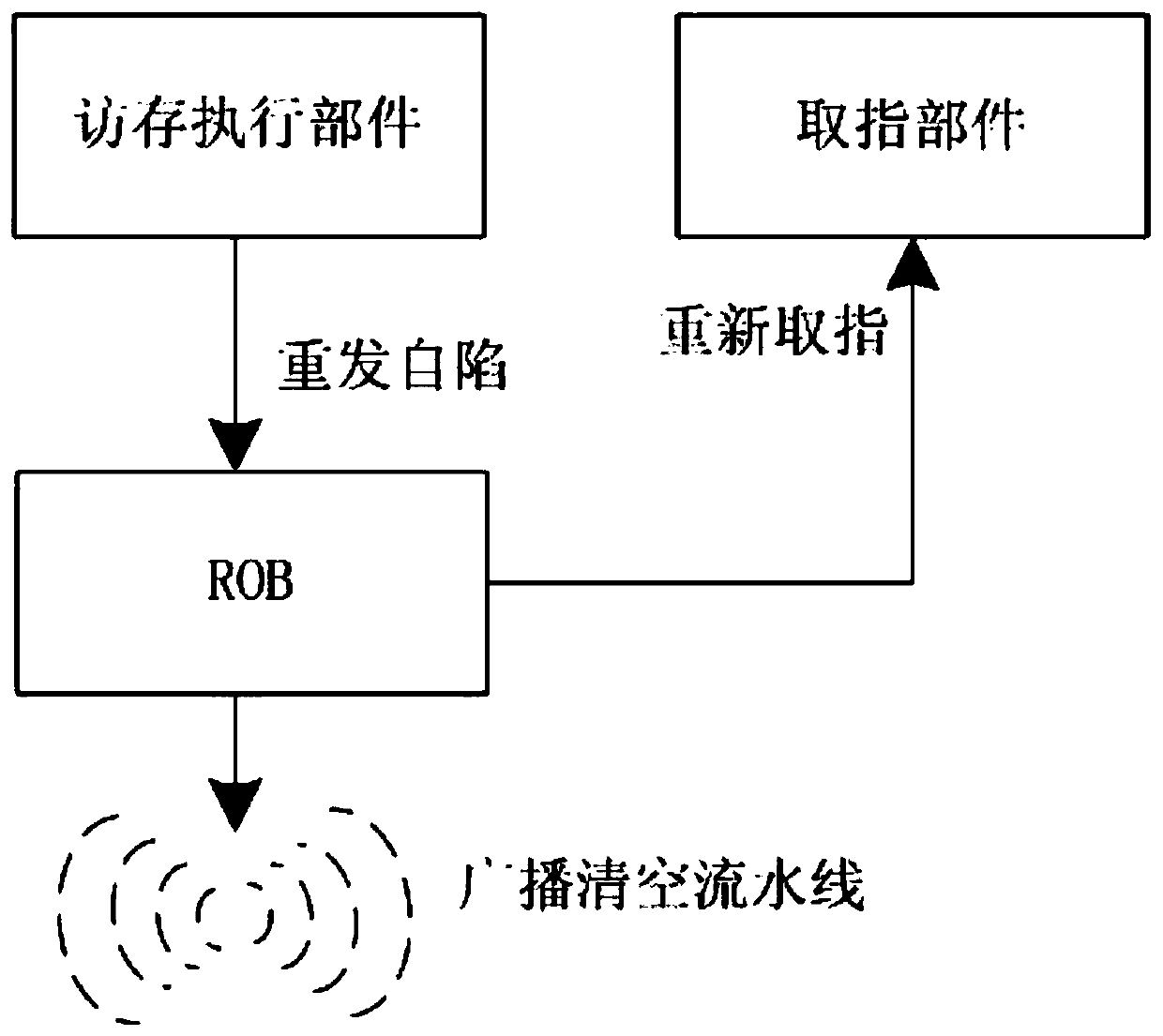
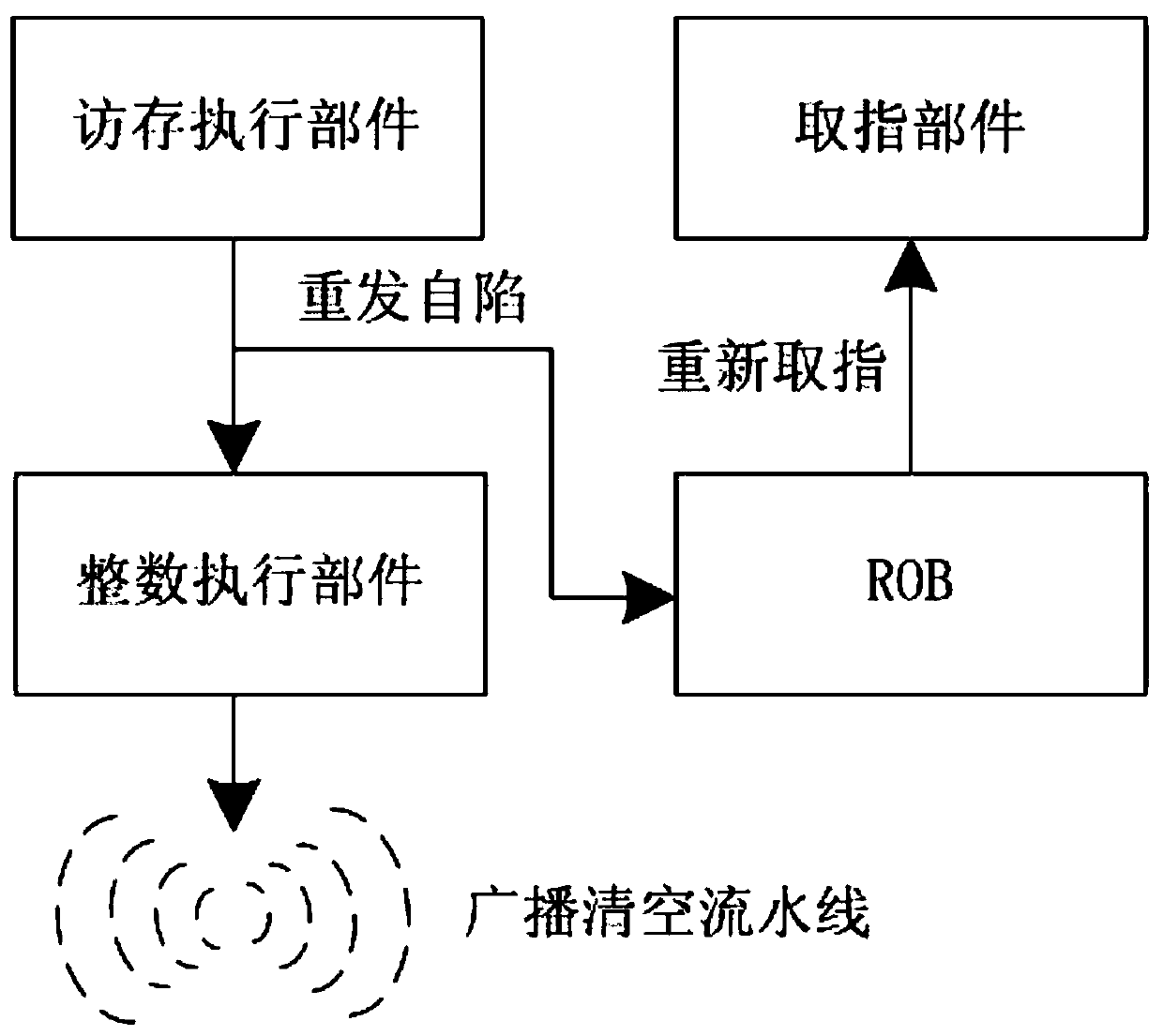
ActiveCN110609709AReduce waiting timeReduce the presence of air bubblesConcurrent instruction executionEnergy efficient computingTrappingAssembly line
The invention relates to a retransmission self-trapping immediate processing method in a superscalar microprocessor. The method comprises the following steps of after arbitration in a memory access component, reporting the retransmission self-trapping to a reordering buffer and an integer execution component; using the reordering buffer to register the received retransmission self-trapping information into a reordering buffer entry after carrying out fixed registration for two beats; after the retransmission self-trapping information received by the integer execution part is fixedly registeredfor two beats, arbitrating and sending the broadcast emptying assembly line information; using the reordering buffer to send a retransmission self-trapping request and an instruction fetching addressto the value fetching component at the next beat of receiving the retransmission self-trapping, and restarting the assembly line platform; and after the retransmission self-trapping in the reorderingbuffer entry reaches the header, deleting the retransmission self-trapping from the entry, and recovering the transmission of the retransmission self-trapping instruction. According to the method, the processing time of retransmission self-trapping is shortened, so that the instruction pipeline can be recovered and restarted more quickly.
Owner:上海高性能集成电路设计中心
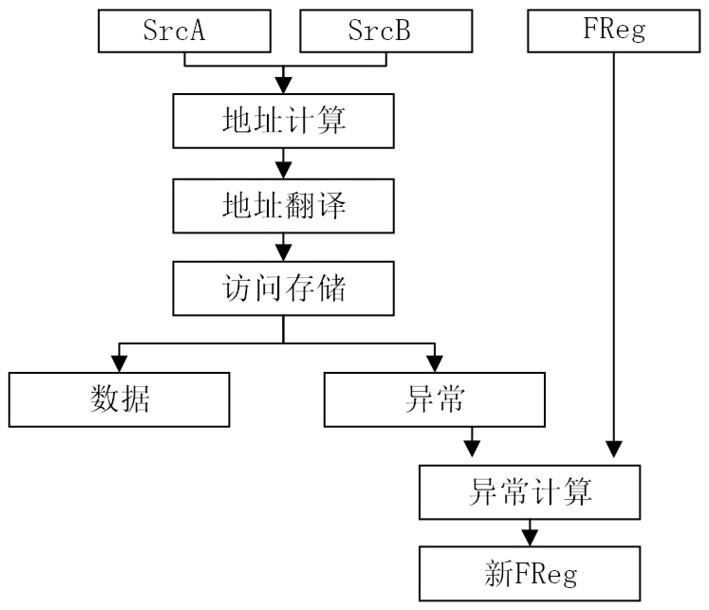
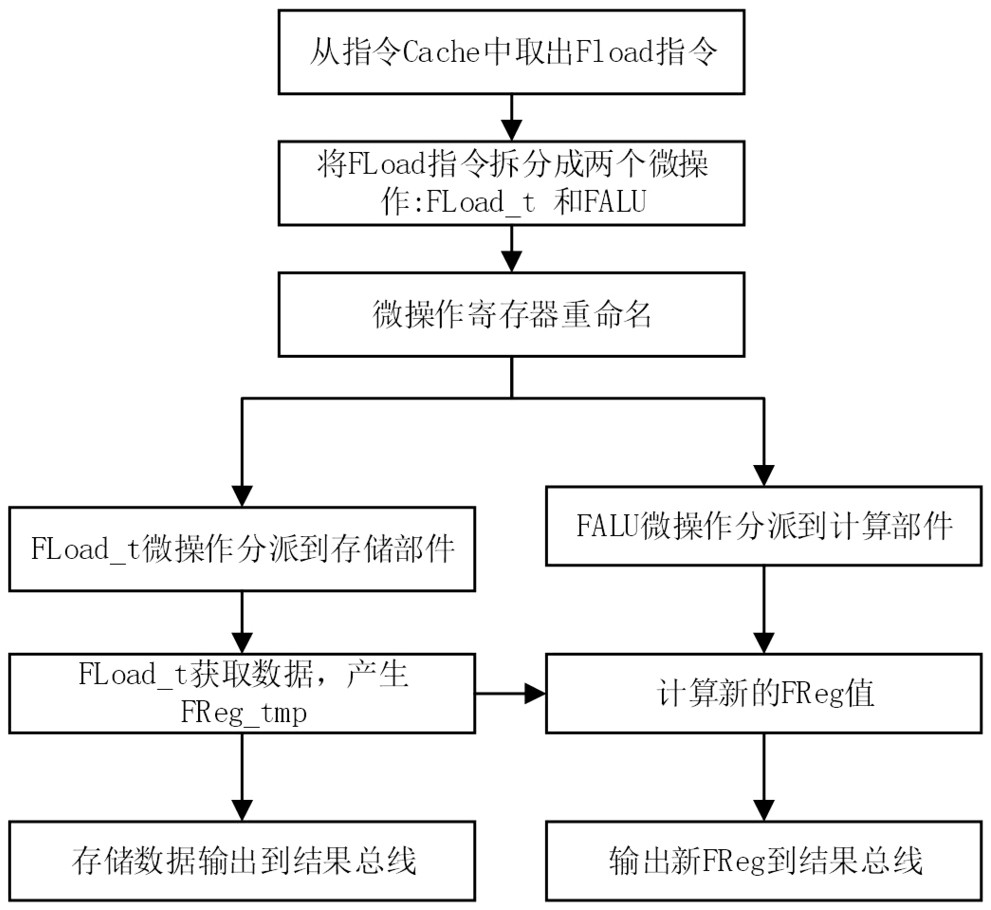
A Method of Execution of Vector Storage Instruction with Abnormal Return
ActiveCN110928577BImprove performanceImprove execution efficiencyRegister arrangementsComputer architectureMicro-operation
The invention discloses an execution method of a vector storage instruction with abnormal return, the steps include taking out the instruction from the instruction buffer; splitting the vector storage instruction with abnormal return into two micro-operations: the first micro-operation is a storage operation, The second micro-operation is an exception information calculation operation; decoding, register renaming, dispatching and execution are performed in units of micro-operations. The first micro-operation is executed in the storage unit, retrieves the corresponding data from the storage, and outputs memory access exception information. The second micro-operation is executed in the calculation unit, receives the exception information of the first micro-operation and calculates a new exception register value. The invention can be used for the execution of vector storage instructions with abnormal return in the design of out-of-order superscalar microprocessors, can improve the parallelism between the vector storage instructions with abnormal return, improve processor performance, and reduce source registers of instruction execution paths number, reducing the implementation cost.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
A Shift-Based Instruction Fetching and Buffering Method and Superscalar Microprocessor
ActiveCN109101275BReduce overheadEasy to implementConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsComputer architectureEngineering
The invention discloses a shift-based instruction extraction and buffering method and a superscalar microprocessor. The implementation steps of the extraction and buffering method include constructing an effective word mask for the instruction word, and right-aligning the instruction line according to the instruction word offset According to the effective word mask, split the shifted instruction line according to the word width and extract the effective words, sort the effective words into the buffer block sequence, and write the buffer block sequence into the buffer queue according to the write enable control of the buffer item ; The superscalar microprocessor includes an instruction fetch and buffer logic unit programmed to perform the aforementioned instruction fetch and buffer method. The invention adopts the design of command line shifting, command word sorting and buffer block sequence writing into the buffer queue, which is simpler and easier to implement than the traditional logic, can ensure the high efficiency of fetching, and also makes the extraction logic and buffer logic more efficient. For simplicity, the hardware overhead is reduced.
Owner:飞腾技术(长沙)有限公司 +1
A Pipeline Commitment Method for Store Instructions in a Superscalar Microprocessor
ActiveCN104391680BIncrease profitImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionInterface protocolInstruction pipeline
The invention relates to a method for realizing streamline retiring of a store instruction in a superscalar microprocessor. The method is characterized in that the automatic sequencing function of buffer of three types is utilized, the interface protocol of the buffer of the three types is improved, the executing conditions of the store instruction are weakened, and therefore, the retiring of the store instruction is sped up. According to the method, the quantity of instructions retired in each clock period and the quantity of the store instruction of writing first-stage data cache in each clock cycle are properly allocated, thus the store instruction streamline retiring function can be realized under the condition that the store address hits the first-stage data cache and the writing is authorized when executing the continuous store instruction sequence, and as a result, the performance of the microprocessor can be obviously improved.
Owner:上海高性能集成电路设计中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com