Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Standard normal variate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
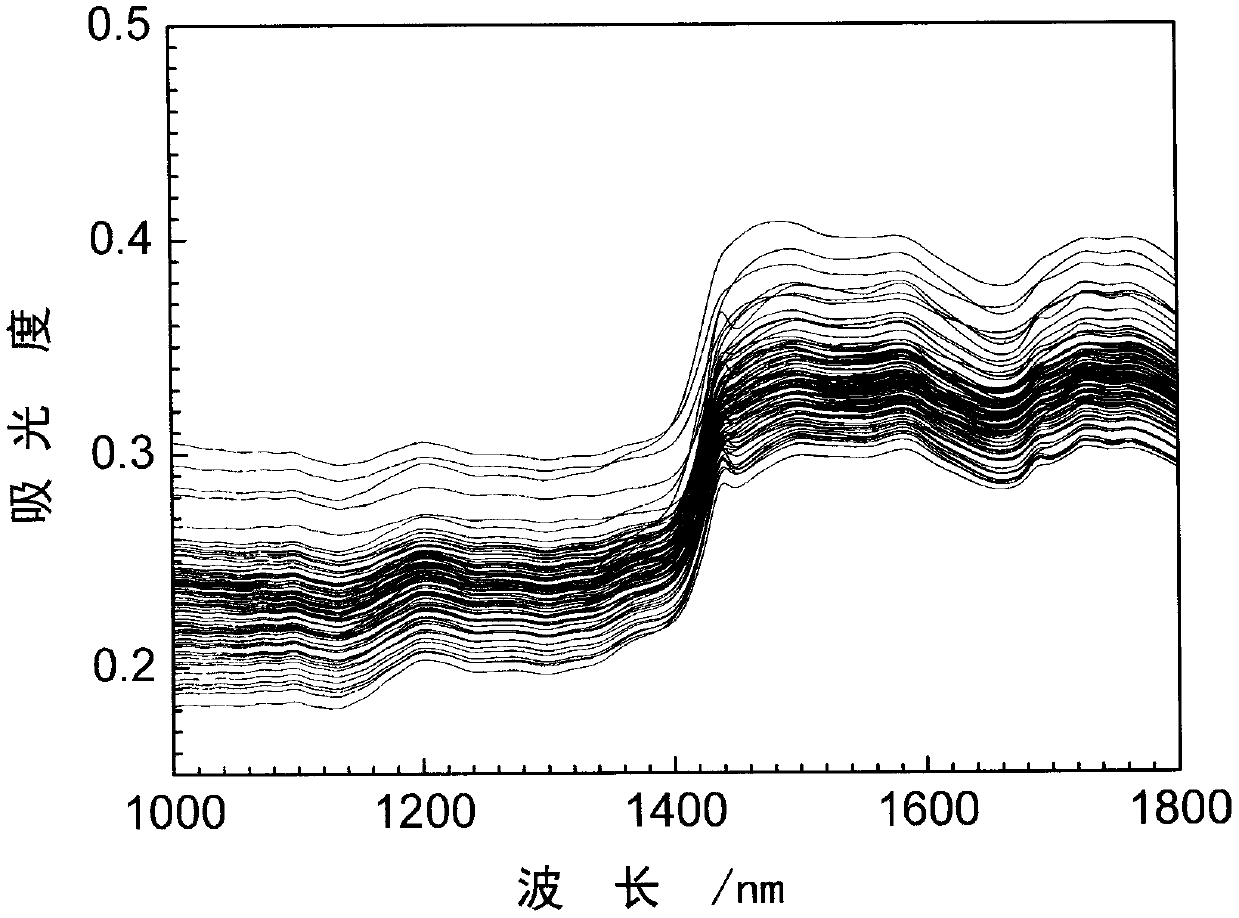
A standard normal variate is a normal variate with mean µ=0 and standard deviation σ =1 with a probability density function is The probability that the variate would take is denoted by the shaded area in the figure.The variate would take a value between 0 and z.
Method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology
InactiveCN104020129ADiscrimination scienceAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis by optical meansBlack teaAmino acid content
The invention discloses a method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on a near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology. The method comprises: selecting a sample and performing pre-processing; using high performance liquid chromatograph to determine the content of amino acids in the sample; acquiring the spectrum of the sample, utilizing synergy interval partial least square to establish a near-infrared-spectroscopy quantitative discrimination model for amino acids, finding amino acid variation distribution, and discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea. According to the method for discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea based on the near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology, pretreatment is performed on an acquired original spectrum by utilizing standard normal variable transformation (SNVT), and the amino acid near-infrared discrimination model is constructed by employing synergy interval partial least square (SiPLS). The invention provides the quantitative determining method for scientifically accurately discriminating the fermentation quality congou black tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying quality of Congou black tea based on near infrared spectrum combined with catcchins analysis technology
InactiveCN104034692ADiscrimination scienceAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredBlack tea
The invention discloses a method for identifying the quality of Congou black tea based on the near infrared spectrum combined with a catcchins analysis technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a sample and carrying out pretreatment; measuring the content of catcchin in the sample by a high-performance liquid chromatograph; acquiring the spectrum of the sample, building a catcchin near infrared spectrum quantitative judgment model by use of the synergy interval partial least squares, finding the catcchin change distribution and identifying the quality of the Congou black tea. According to the method, standard normal variable type (SNVT) is utilized to perform treatment on the acquired original spectra and the SiPLS synergy interval partial least squares (Synergy Interval Partial Least Square) is adopted to construct the catcchin near infrared spectrum quantitative judgment model, thereby providing a scientific and accurate quantitative judgment method for the fermentation quality of the Congou black tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly detecting yellow pigment content in wheat grain
InactiveCN103149174AReduce distractionsSimple processing methodColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrum analyzerFt ir spectra
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting yellow pigment content in a wheat grain. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out preprocessing on near infrared spectrum data through a first-order derivative and a standard normal variable quantity transition method by taking chemical quantitative determination as foundation and utilizing a near infrared spectrum analyzer and an analysis software; and establishing a calibration model and carrying out optimizing process by adopting a partial least squares method and a multiple linear regression algorithm, embedding the optimized model in the near infrared spectrum analyzer, and rapidly predicating the yellow pigment content of the wheat grain by utilizing a near infrared spectrum to scan. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the purpose of simple, rapid, efficient, high-throughput, low-cost, pollution-free, sample-destroying-free and multiple-components simultaneous measurement for mass materials at wheat breeding early stage is realized, and a new method is provided for rapidly screening the wheat new variety (system) with high yellow pigment content or low yellow pigment content of wheat breeding.
Owner:ZHOUKOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for quickly determining rutin content in flos sophorae processed product through near infrared spectrum
InactiveCN107449753ANon-destructive testingNIR Quantitative Calibration Model StabilizationMaterial analysis by optical meansFlosPretreatment method
The invention discloses a method for quickly determining a rutin content in a flos sophorae processed product through near infrared spectrum. The method comprises the following steps of S1, acquiring spectroscopic data; S2, determining a reference value; S3, determining a characteristic spectrum band: removing a band influenced by temperature, humidity and sample moisture, and combining a rutin reference substance near infrared spectrogram to determine a modeling band; S4, establishing a correction model: adopting a partial least squares method, standard normal variate and first derivative spectrophotometry as spectral pretreatment methods, and establishing the correction model through model evaluation parameters; S5, verifying the correction model: predicting flos sophorae samples which do not participate in modeling so as to verify the correction model; S6, determining a content of an unknown sample. Compared with HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography), the near infrared spectroscopy is simple, fast, stable in model, and high in accuracy, and can be applied in predicting the rutin content in different flos sophorae processed products at the same time. The invention provides a new evaluation method for determining and checking the flos sophorae quality, and provides a scientific basis for quality supervision of flos sophorae processed products on the market.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
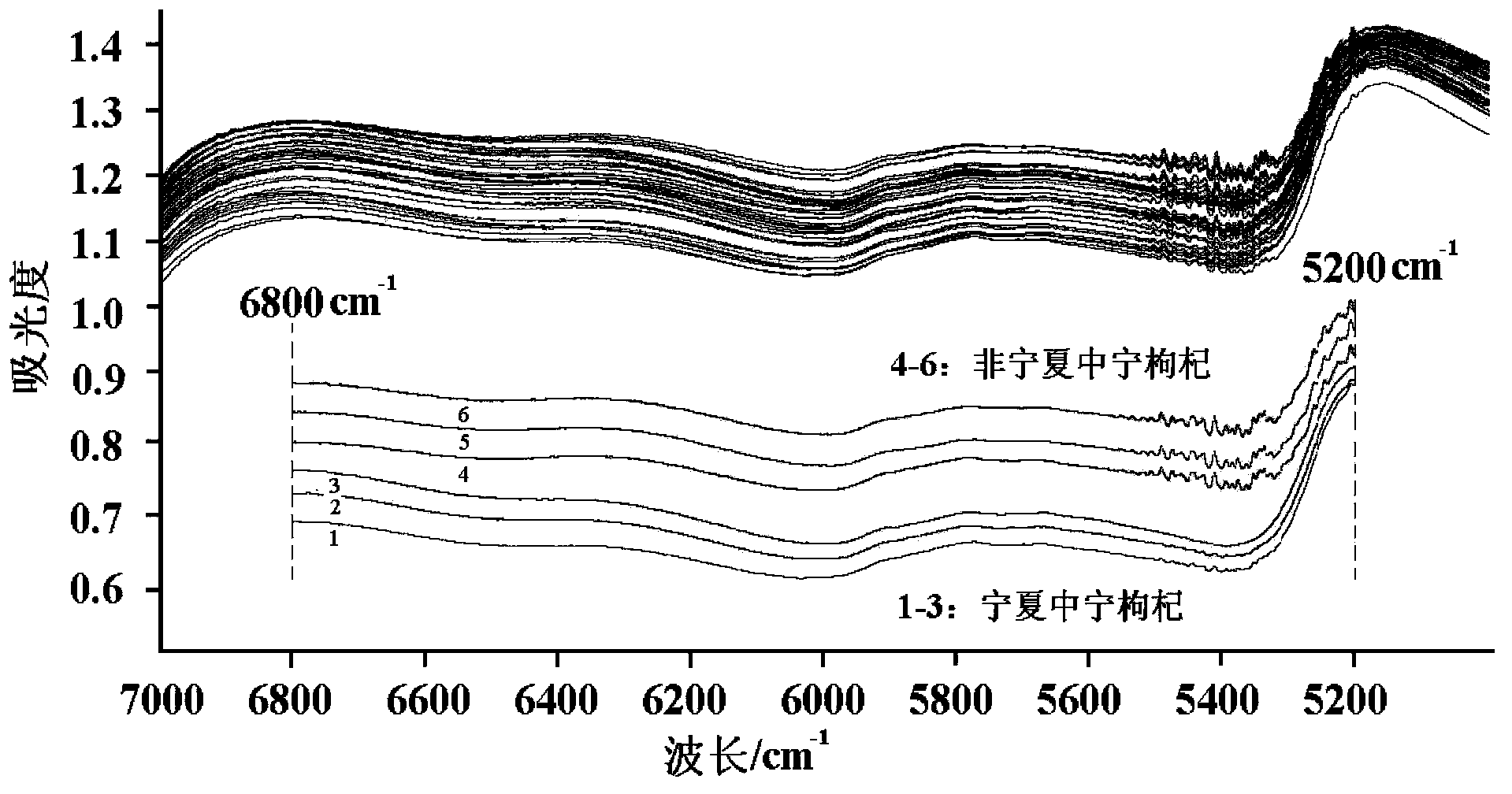
Near infrared spectrum based discrimination method for Zhongning fructus lycii
InactiveCN103353443ANo pollutionNo harmColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredPretreatment method
The invention discloses a near infrared spectrum based discrimination method for Zhongning fructus lycii. The method includes: taking a near infrared spectrometer as a detecting tool, scanning the near infrared spectrum of a fructus lycii sample, conducting distance discriminant analysis on the near infrared spectrum of the fructus lycii sample, in a spectral wavelength range of 6500-5200cm<-1>, by adopting a pretreatment method combining an original spectrum with a multiplicative scatter correction method and the original spectrum with a standard normal variate transformation method, establishing a fructus lycii production place discriminant analysis model and carrying out discriminant analysis on the production place of the fructus lycii sample. The method can reach a recognition rate up to over 90%. During operation, the fructus lycii sample has no need for any treatment. Being nondestructive, rapid and real-time, the method does not employ any reagent, has no harm to human body and environment, and can replace traditional high cost, time-consuming, and laboursome production place discrimination method, thus being a near infrared spectrum based new method for rapid discrimination of the fructus lycii production place.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for detecting moisture content of dry powder extinguishing agents based on near infrared spectroscopy analysis
ActiveCN103175806ANo pollutionQuick analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsPre treatmentFunctional relation
The invention provides a method for detecting the moisture content of dry powder extinguishing agents based on near infrared spectroscopy analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) establishing a calibration set and a validation set sample spectrum; 2) preprocessing original spectral information through a second derivative, standard normal variate and Karl Norris derivate smoothing filter; 3) establishing a calibration model for the functional relation between a near infrared spectrum of the calibration set and the true value of the moisture content of a corresponding dry powder extinguishing agent sample by using a partial least squares method; 4) validating and optimizing the calibration model; and 5) inputting the near infrared spectrum of the dry powder extinguishing agent sample to be detected into the optimized calibration model, so as to obtain the moisture content value. The method is a method for quickly detecting the moisture content of the dry powder extinguishing agents based on the near infrared spectroscopy analysis, is established based on the analysis of the near infrared spectrums of the moisture content values of different dry powder extinguishing agents; and the detection method has the advantages of being quick in analysis, high in efficiency, simple and convenient to operate, low in cost, and free from pollution to the environment.
Owner:应急管理部天津消防研究所
Probabilistic reliability estimation method and device of active power distribution network
The present invention provides a probabilistic reliability estimation method and device of an active power distribution network. The method includes the following steps that: the load power and / or power supply power at each node of a power distribution network system are obtained; random variables composed of the load power and / or power supply power are transformed into first standard normal variables which are unrelated to one another; a point estimation method is adopted to construct a sample matrix corresponding to a random variable space based on the first standard normal variables; and failure mode influence analysis is carried out for the sample matrix, so that the probability density function of a reliability index is obtained. According to the method and device of the invention, a condition that the point estimation method can convert influences on reliability caused by the power supply power of DG (distributed generation) and the load power at each node into a deterministic problem so as to solve the deterministic problem is considered, and therefore, calculation is simple; a condition that Nataf transformation is not limited by the type of input variables, so that the relativity problem of the random variables can be effectively processed; and the point estimation method and the Nataf transformation are combined together, and therefore, the accurate estimation of the probabilistic reliability of the active power distribution network can be realized.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
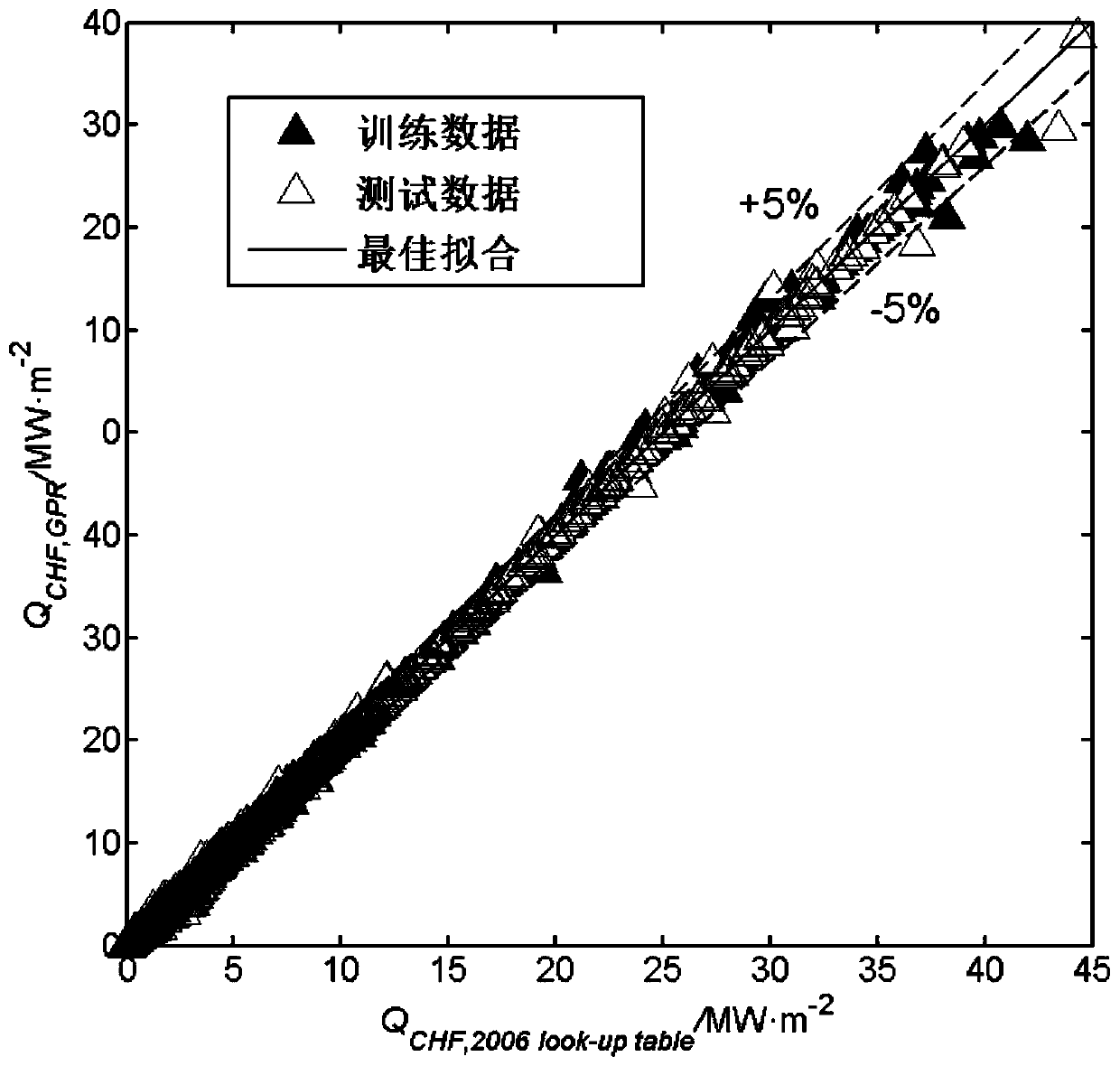
Gaussian process regression-based critical heat flux density prediction method
PendingCN109871602AAccurate predictionImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsData setHeat flow
The invention discloses a Gaussian process regression-based critical heat flux density prediction method, which is specifically implemented according to the following steps of: 1, dividing a collecteddata set into two parts, namely 70% of data as a training set and the balance of 30% of data as a test set, and recording D * = [(X *, y *)}; 2, preprocessing the training set data and the test set data by adopting a standard normal variable method to enable the mean value of the training set D and the test set D * to be 0 and the standard deviation to be 1; 3, inferring the relation between thetraining input variable and the training target output by using Gaussian process regression to obtain a critical heat flux prediction model; And 4, predicting the critical heat flux density through the system pressure P, the mass flow rate G and the balanced steam content Xe by using the obtained critical heat flux density prediction model. The method can accurately and effectively predict the critical heat flux density.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Near-infrared spectral discrimination method for mutton adulterated with duck meat
InactiveCN105092525AQuick DiscriminationStable discriminantMaterial analysis by optical meansCoomassie blue GScattering correction
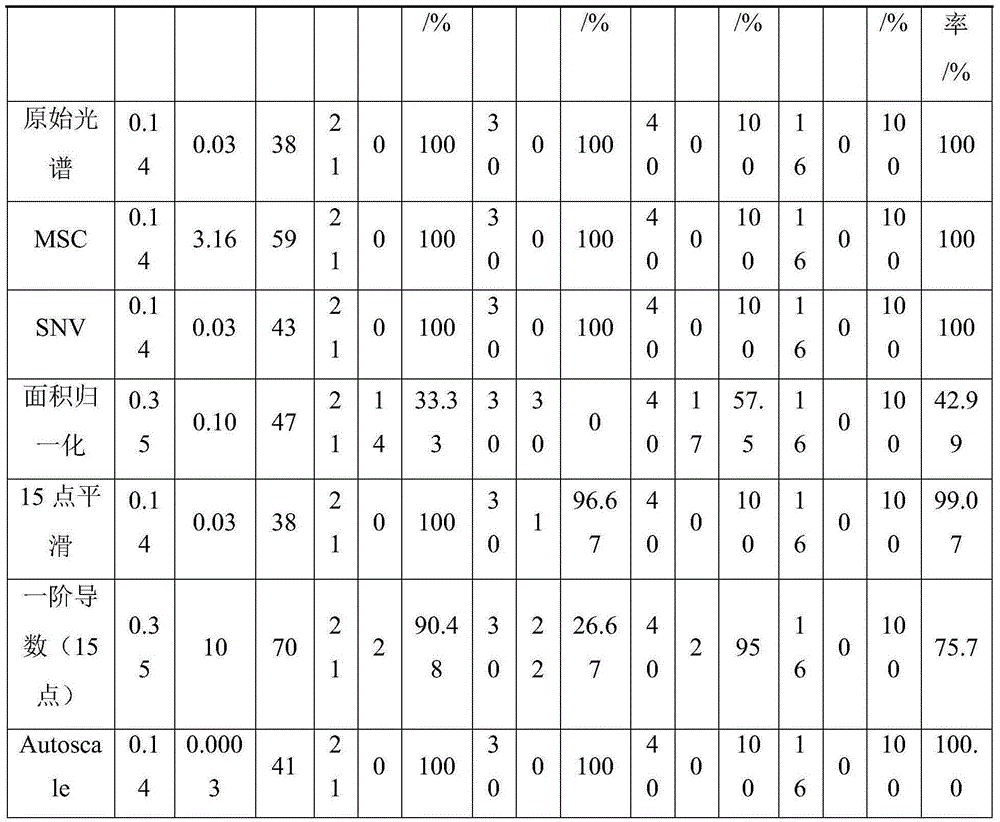
The invention provides a near-infrared spectral discrimination method for mutton adulterated with duck meat and belongs to the technical field of food safety inspection. The invention provides a method for quickly discriminating mutton adulterated with duck meat. The method comprises the following steps: (1) respectively preparing samples of mutton, duck meat and adulterated mutton, and a to-be-tested sample of unknown meat; (2) preparing Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 solution; (3) respectively taking and adding the samples into Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 solution, performing pulping and then sampling near-infrared spectrums of the samples as original spectrums; (4) performing optimized selection of modeling wave bands to the original spectrums, and respectively performing multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), standardized normal variate (SNV), area normalization, Autoscale, smoothing processing, first-order derivative processing and the like to the selected modeling bands to preprocess the original spectrums; (5) establishing adulterated mutton discrimination model by adopting a support vector machine regression modeling method. The method can realize quick, accurate and stable discrimination of mutton adulterated with duck meat.
Owner:HENAN PROVINCE PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION & INSPECTION CENT
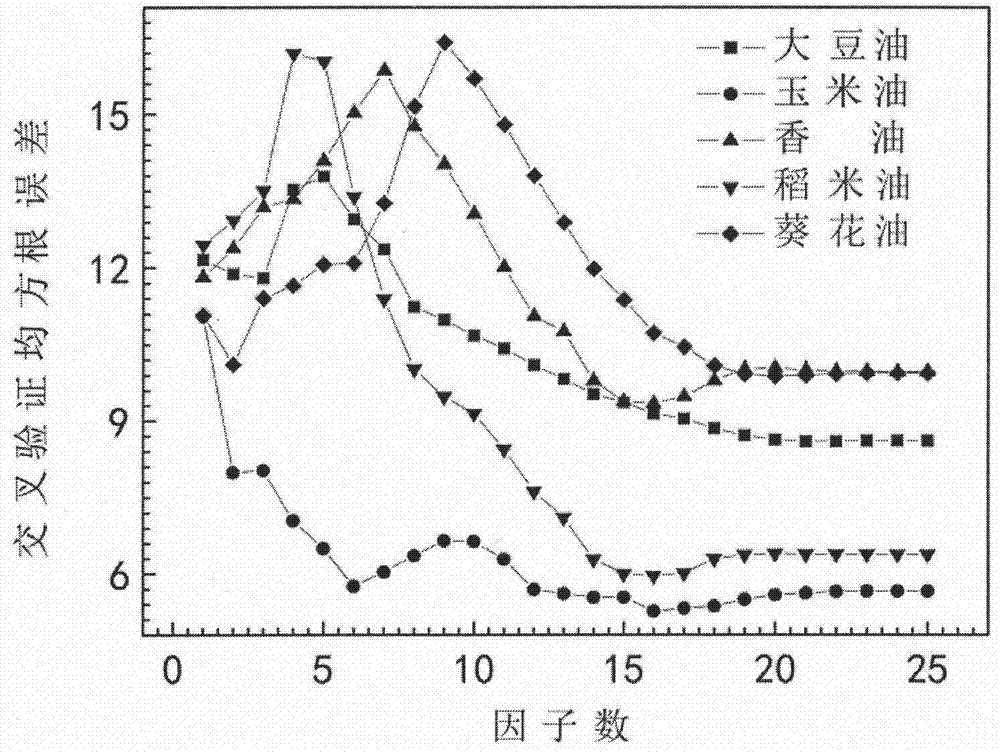
Quantitative analysis method based on near infrared spectrum and chemometrics and used for five-element blend oil
InactiveCN107036999AImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredPretreatment method
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Agricultural product element quantitative detection model building method based on X-ray fluorescence analysis
InactiveCN104897709AHigh precisionAccurate NDTMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPrincipal component analysisPeak value
The invention discloses an agricultural product element quantitative detection model building method based on X-ray fluorescence analysis. The method comprises the following steps: first, conducting pre-processing on an obtained sample spectrogram to obtain a standard spectrogram, wherein the pre-processing particularly comprises differential processing, normalization, multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), centralization, standard normal variable exchange (SNV), light spectrum smoothing and the like; then, carrying out sample set partition and abnormal sample rejecting through a principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS ) data processing method, so as to obtain a calibration set and a forecast set; finally, conducting calibration of indexes to be detected on agricultural products through principal component analysis and artificial neural network (PCA+ANN), as well as partial least squares and artificial neural network (PLS+ANN). The method adopts a peak value method in model building, so as to solve the problem of overlapping in application of the conventional peak area model building method, and improve the accuracy of a sample calibration model.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Scheme based on near infrared technology and used for detecting phosphorous in water
InactiveCN105092523ANon-destructiveEasy to operateMaterial analysis by optical meansCorrection algorithmInfrared
Disclosed is a scheme based on near infrared technology and used for detecting phosphorous in water. The scheme includes: utilizing near infrared spectroscopy to measure 0mg / L-50mg / L of phosphorous solutions different in concentration by utilizing NIR equipment to acquire spectra, and storing the spectra as CSV data; utilizing TQ analyst for primary analysis; utilizing a derivative algorithm (Derivatives norris gap), a multiplicative scatter correction (Multiplicative scatter correction, MSC) algorithm, a smoothing (Smoothing) algorithm and a standard normal variate transformation (Standard normal variate transformation, SNV) method to pre-process near infrared spectrum data respectively; utilizing MATLAB for simulation, selecting a simulation model PLSR, utilizing a concentration gradient classifying method for simulation, and building a mathematic model; acquiring simulation results, optimizing the same, and integrating to acquire a final result. By the scheme, quick, environment-friendly, nondestructive and online detection of the phosphorous solutions different in concentration can be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction method of effective component prediction model for silage corn and application thereof
PendingCN110346322AFast detection methodNo consumptionMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingMathematical model
The invention discloses a construction method of an effective component prediction model for silage corn and application thereof, thereby solving technical problems of resource wasting and low economic benefit. The method comprises: taking a sample, drying the sample and pulverizing the dried sample; analyzing crude protein, moisture, neutral detergent fiber, acid detergent fiber and starch content values; carrying out near-infrared spectrometer scanning and collecting on the sample by means of grating continuous spectroscopy of an near-infrared spectroscopy; and carrying out detrending correction and standard normal variable transformation preprocessing on an original spectrum of diffuse reflection of obtained data, and then establishing a corresponding prediction model by using a partialleast squares method and detecting content of nutrients in silage corn by using the model. According to the invention, on the basis of combination of the near-infrared spectroscopy technology with chemometrics method, a qualitative and quantitative calibration mathematical model between chemical values of main components of silage corn and near-infrared spectroscopy data is established by using multivariate data analysis software, thereby establishing a rapid component of the main components of silage corn and laying a foundation for precise feeding.
Owner:河南省饲草饲料站
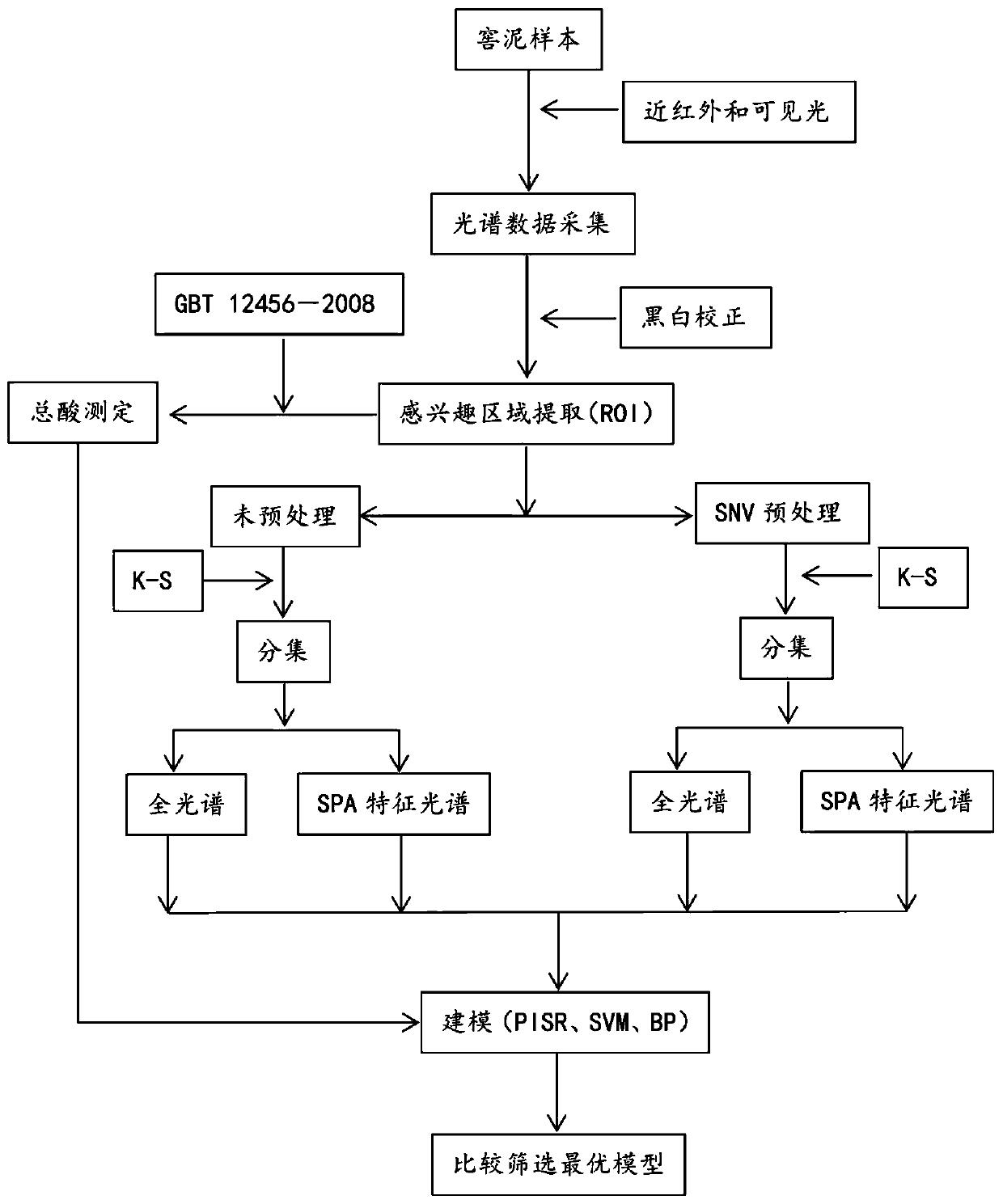
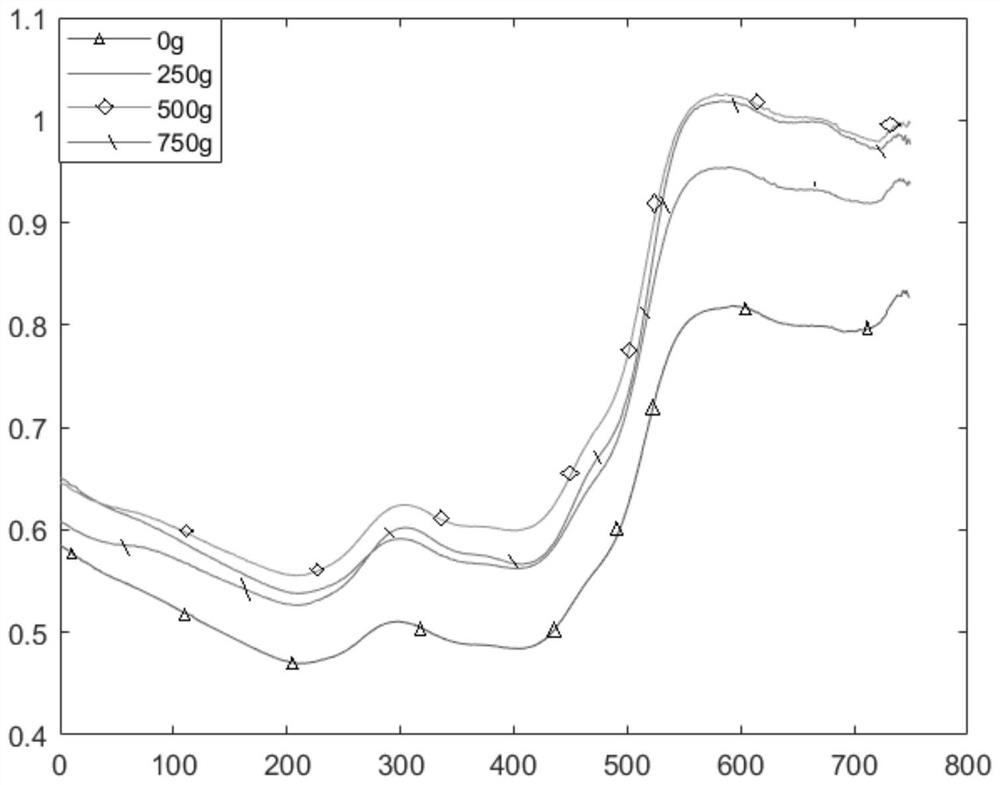
Pit mud total acid prediction model building method based on hyperspectral image technology
ActiveCN110441249ARapid Total Acid Detection MethodEfficient Total Acid Detection MethodData processing applicationsColor/spectral properties measurementsFull waveRoot mean square
The invention discloses a pit mud total acid prediction model building method based on a hyperspectral image technology. Firstly, hyperspectral image information of infrared and visible light wave bands is acquired, average spectral information of an ROI (region of interest) is extracted through ENVI software, errors caused by non-uniform illumination are eliminated through black and white correction, the average spectral reflectivity of each pixel in an image is estimated, quantitative predication models based on full wave bands and characteristic spectra are built respectively through no processing, SNV (standard normal variate) and different modelling methods, and the best model for quantitative predication of pit mud total acid is screened by comparing and analyzing determination coefficients and root-mean-square errors of a training set and a testing set of each fitting model. The method provides powerful technique support for transformation and upgrading of baijiu brewing industrialization and digital and intelligent online real-time monitoring.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Mineral identification method based on laser-induce breakdown spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis
InactiveCN107305187AReal-time measurementHigh sensitivityAnalysis by thermal excitationData acquisitionLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention belongs to the field of geological prospecting and specifically relates to a mineral identification method based on laser-induce breakdown spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting data on the basis of an LIBS (Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) optical system; 2) adopting a cubic spline interpolation algorithm for correcting various spectrogram wavelengths, thereby causing the collected data be consistent; 3) performing standard normal variable correction on the smoothed spectroscopic data, thereby acquiring a spectrum after the standard normal variable correction; 4) utilizing a linear discriminant analysis method to perform feature extraction and clustering analysis on the spectroscopic data after the standard normal variable correction. According to the method, the quick and accurate analysis and discrimination for a mineral sample can be realized in the manner of collecting a certain quantity of analysis samples for forming a training sample and adopting a statistic mode algorithm for acquiring the inherent space structure information of the sample.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Method for nondestructive detection of exogenously doped sucrose in tea leaves based on near infrared spectrum technology
PendingCN111795943AHigh precisionReduce data dimensionalityMaterial analysis by optical meansBiotechnologyInfrared
The invention relates to the technical field of tea quality detection. The invention particularly relates to a method for nondestructive detection of exogenously doped sucrose in tea leaves based on anear infrared spectrum technology. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out near infrared spectrum scanning on black tea samples containing different exogenous sucrose contents; carrying out standard normal variable transformation algorithm processing on the original spectral data obtained by scanning; and carrying out variable screening by adopting a continuous projection algorithm, then carrying out principal component analysis, establishing a detection model by using the optimal principal component, and inputting the near infrared spectrum data of the black tea samples to bedetected into the detection model to realize discrimination and content detection of the exogenously doped sucrose in the black tea. The invention aims to solve the problems of difficulty in manual distinguishing of the sugar-added black tea, time and labor waste in physical and chemical detection and the like, realizes nondestructive, rapid and accurate identification of the sugar-added black teaand quantitative detection of the sugar content, and provides a theoretical method and a scientific basis for qualitative and quantitative detection of exogenous sucrose in the black tea.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
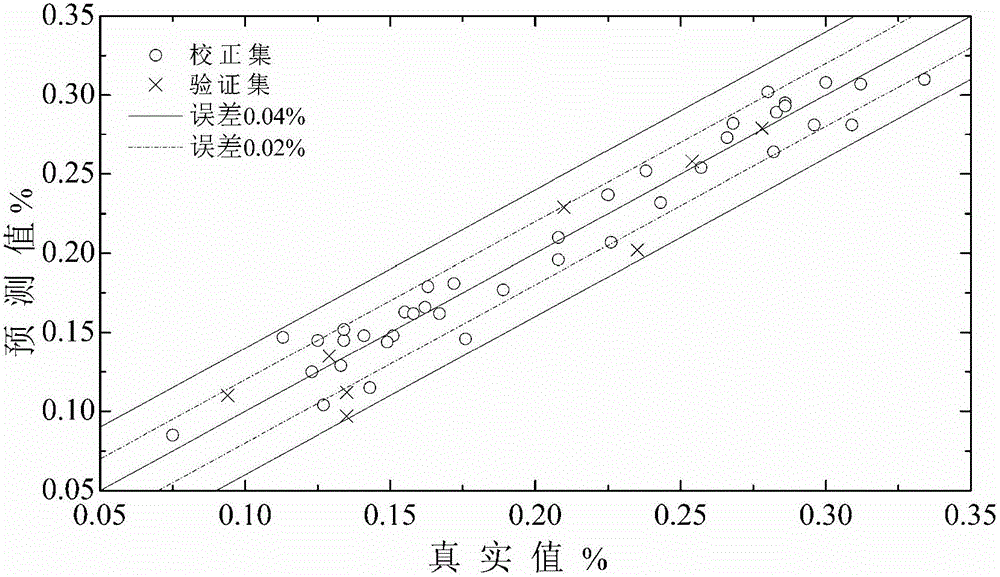
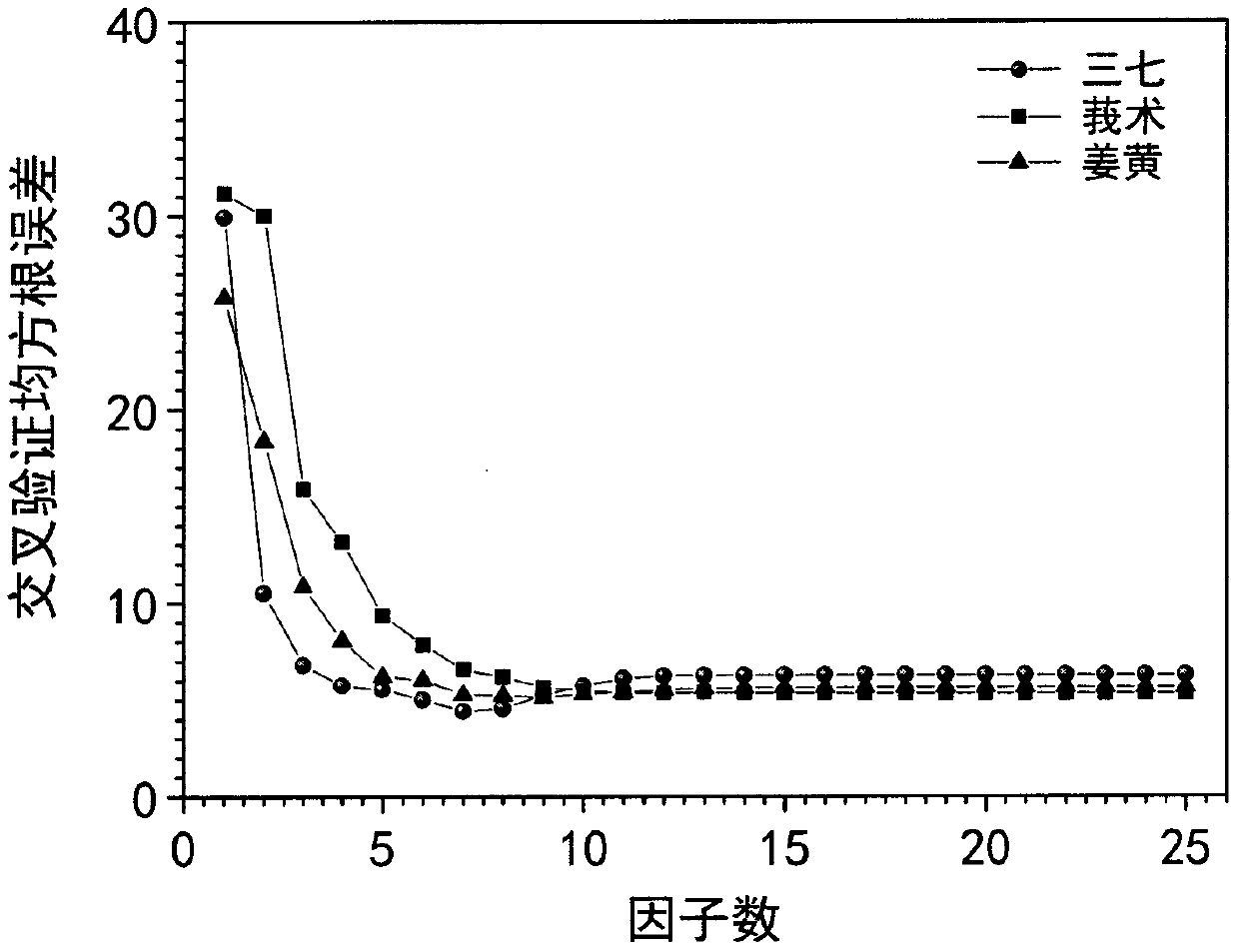
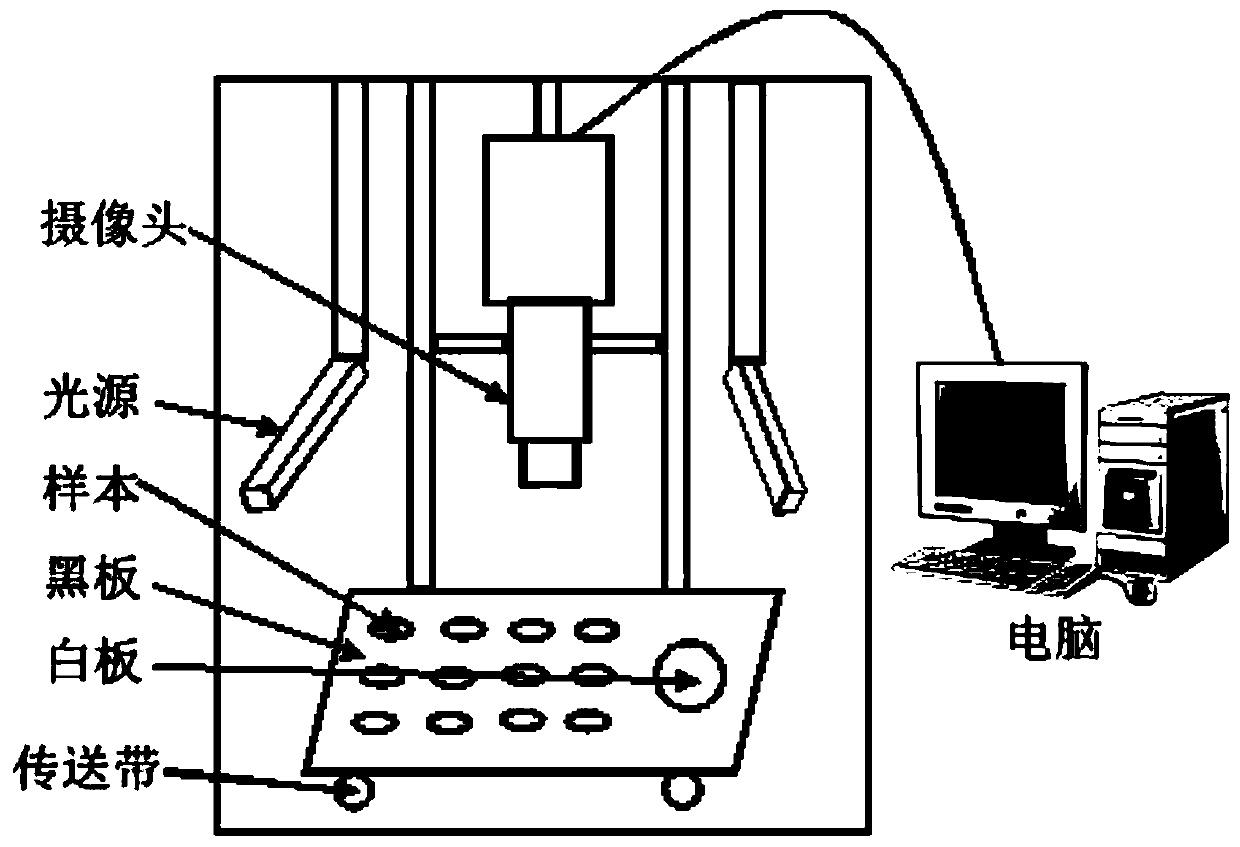
Quantitative analysis method for dual adulterated sanqi based on near infrared spectroscopy and stoichiometry
The invention relates to a quantitative analysis method for dual adulterated sanqi based on near infrared spectroscopy and stoichiometry. The method comprises: preparing an experimental sample and collecting near infrared spectroscopy of the sample; adopting a grouping manner of integral sequence and local random to divide a data set to a training set and a prediction set; determining an optimum factor number according to variation of RMSECV with the factor number; investigating the pretreatment effect of a SG smoothing method, multiplicative scatter correction, standard normal variables, a first derivative, a second derivative, continuous wavelet transform, and a combination thereof, to obtain an optimal pretreatment method; and adopting the optimal pretreatment method to pre-treat the spectrum, establishing a PLSR model, and predicting an unknown sample. Based on the near infrared spectroscopy and stoichiometry, the method is efficient and lossless, and is fast in detection and highin accuracy. The method is suitable for quantitative analysis of a dual adulterated sanqi sample.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
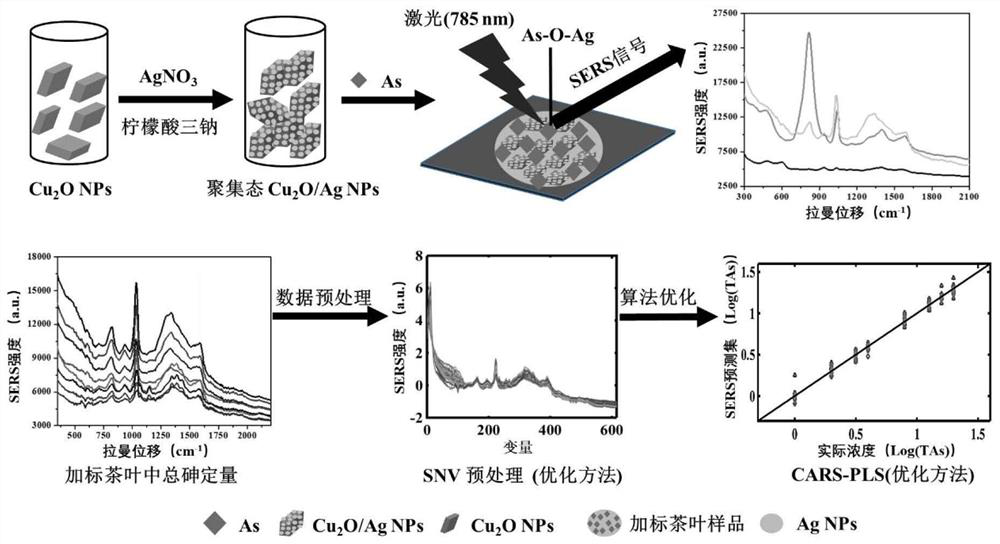
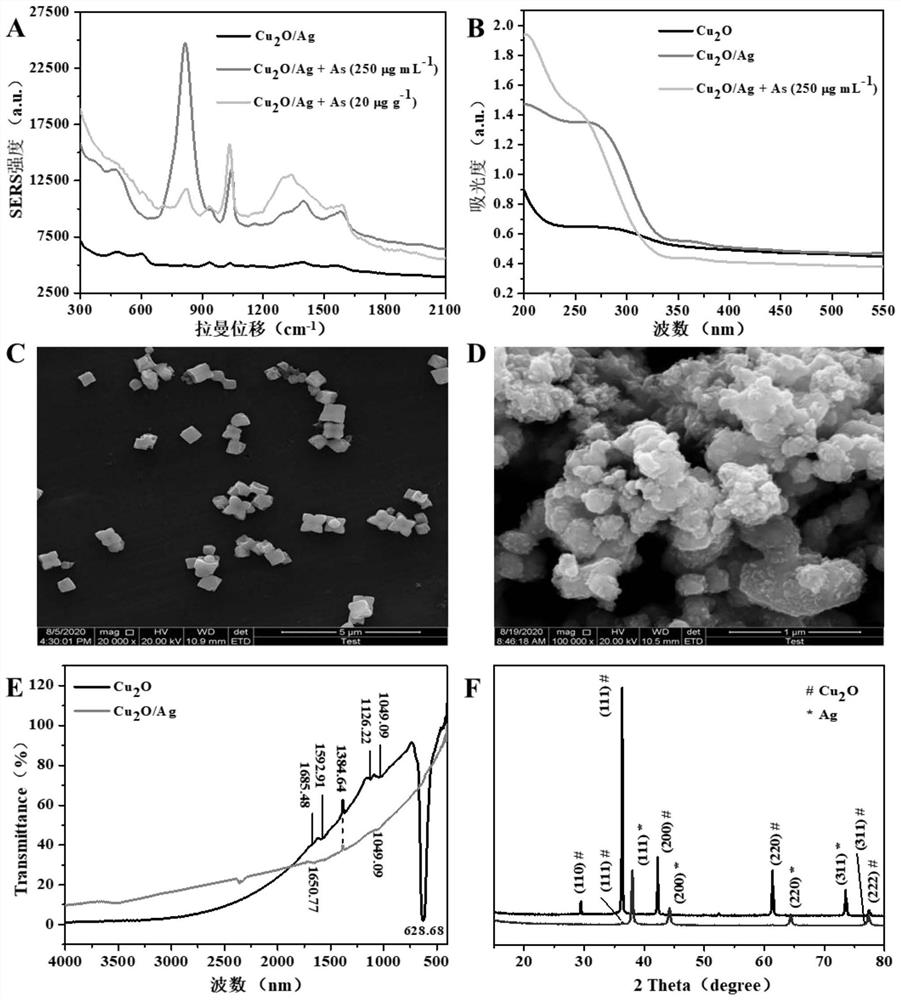
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection method for total arsenic content in food
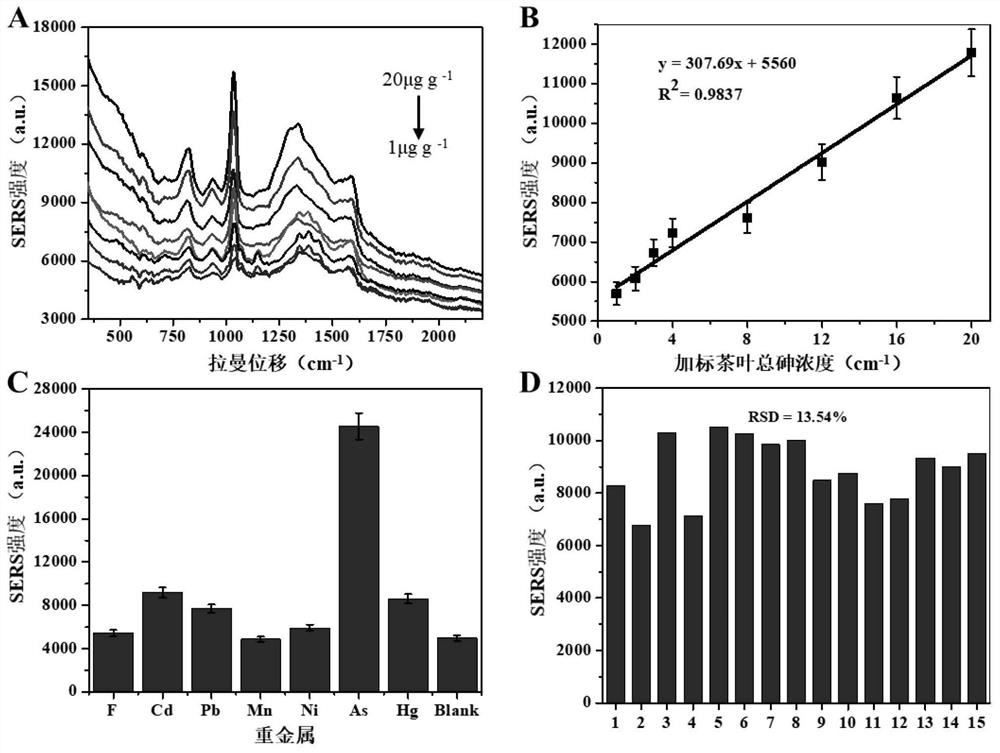
PendingCN112798573AImprove accuracyRealize highly sensitive quantitative detectionRaman scatteringSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection method for total arsenic content in food. The surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection method comprises the following steps of: preparing Cu2O nanoparticles; synthesizing Cu2O / Ag nanoparticles; establishing a total arsenic content detection standard curve; preprocessing original SERS spectral data through standard normal variable transformation (SNV), and establishing a quantitative detection model on the basis of partial least squares (PLS); and after pretreating a to-be-detected food sample, adding the to-be-detected food sample into a Cu2O / Ag surface enhanced Raman substrate, performing uniform mixing so as to obtain a mixed solution, measuring a Raman spectrum after the mixed solution is dried, and calculating the total arsenic content in the to-be-detected food sample through the quantitative detection model. The Cu2O / Ag surface enhanced Raman substrate prepared by the invention can realize label-free, rapid and high-sensitivity detection of total arsenic in food based on an SERS technology. The quantitative detection model is established based on the standard normal variable transformation pretreatment and the partial least square method, so that the total arsenic content in the food is accurately predicted, and rapid evaluation of heavy metals in the food is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Non-destructive testing method for plum hardness based on visible/near-infrared spectroscopy
InactiveCN109342331AReduce distractionsGood for deep diggingColor/spectral properties measurementsPattern recognitionPrincipal component regression
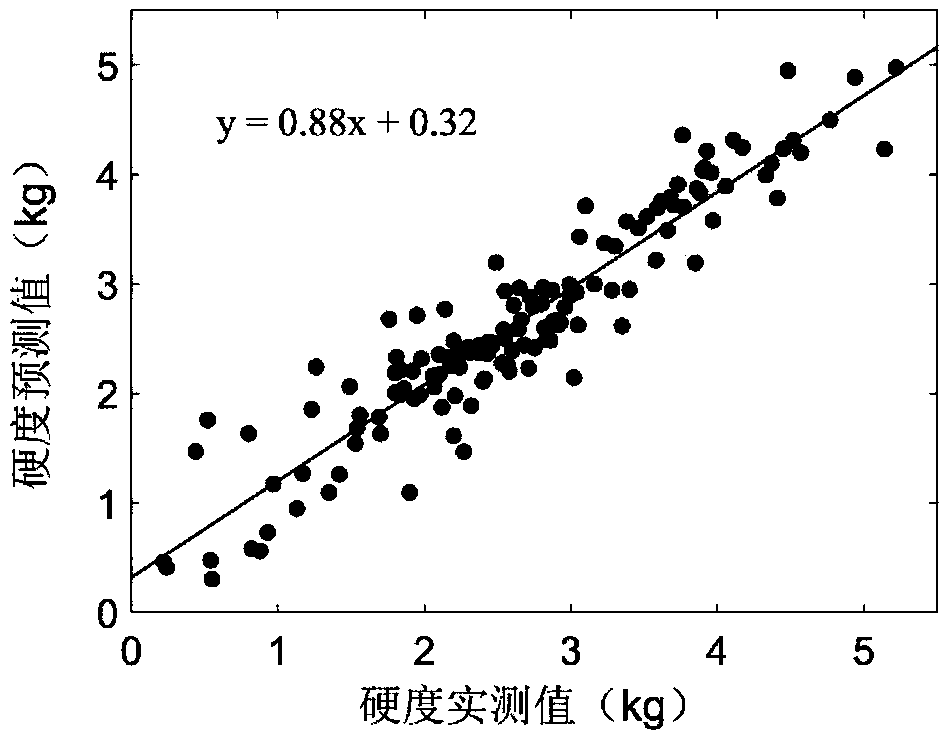
The invention discloses a non-destructive testing method for plum hardness based on a visible / near-infrared spectroscopy. The method comprises the following steps: collecting different varieties of fresh plum samples, and using a hyperspectral image collecting system to collect hyperspectral images of plum samples; performing a black-and-white correction on hyperspectral images, and using median filtering and mathematical morphology processing method to construct mask images to extract an average spectral reflectance of the whole fruit region of plums; using an SPXY algorithm to divide the acquired spectral data into a calibration set and a testing set, preprocessing the spectral data by Standard Normal Variate (SNV) to obtain a spectral database of a calibration and test sample set; usinga digital fruit hardness tester to measure and calibrate and test the hardness values of the plum samples in the sample set; combining the Principal Component Regression method (PCR) with stoichiometry to establish a prediction model of plum hardness. The non-destructive testing method for the plum hardness based on the visible / near-infrared spectroscopy is capable of detecting plum hardness quickly and non-destructively based on the visible / near infrared spectroscopy.
Owner:GUIYANG UNIV
Construction and application of prediction model for effective components of alfalfa hay
PendingCN110208210ANo consumptionRapid determinationMaterial analysis by optical meansAlfalfa hayEconomic benefits
The invention discloses construction and application of a prediction model for effective components of alfalfa hay. The technical problems of resource waste and low economic benefit are solved. A method comprises the steps: samples are taken to be dried and smashed; content values of crude proteins, water, neutral detergent fibers, acid detergent fibers and crude ash are analyzed and chemically examined; alfalfa hay powder is taken, and all the alfalfa hay powder samples are subjected to near infrared spectrum scanning collecting in a grating continuous spectrum mode of a near infrared spectrometer; and a diffuse reflection original spectrum of obtained data is subjected to derivative processing, standard normal variate transformation and de-trending correction, and the corresponding prediction model is established through a partial least squares method. The content of the effective components of the alfalfa hay is detected through the model; and the quick detecting method of the maincomponents of the alfalfa hay lays a foundation for accurate feeding.
Owner:河南省饲草饲料站
Method for detecting microorganism content in complex solution based on ultraviolet-visible spectrum
InactiveCN110174365AAvoid influenceImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsEscherichia coliBiological activation
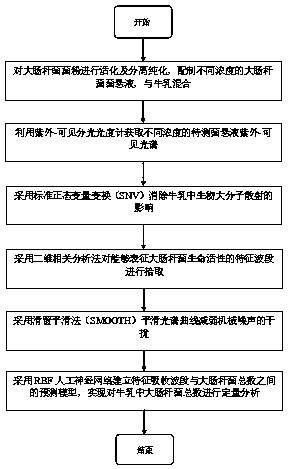
The invention provides a method for detecting the microorganism content in a complex solution based on an ultraviolet-visible spectrum, for effectively solving the problems of red shift of a characteristic spectrum peak of a microorganism in the spectrum caused by complex detection background components, overlap of the spectrum peaks between a medium component and the microorganism, and spectral noise interference and the like. According to the method provided by the invention, cow milk is used as a detection background, the Escherichia coli is used as a detection object, and the method comprises the steps of: firstly performing activation, separation and purification on Escherichia coli powder to obtain bacterial suspension of Escherichia coli; obtaining the ultraviolet-visible spectra ofbacterial suspension to be detected with different concentrations in the cow milk by using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer; eliminating baseline drift, spectral noise interference and otherproblems caused by the scattering of macromolecules such as protein, fat and the like in the cow milk by using standard normal variable transformation; separating an overlapping spectrum of the cow milk and the Escherichia coli by using a two-dimensional correlation analysis method; and establishing a prediction model based on an RBF neural network to realize the quantitative detection of the total number of the Escherichia coli in the cow milk.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An apple variety identification method based on fuzzy clustering of spectral band optimization
ActiveCN109685099AAvoid accuracyThe detection process is fastMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionInfraredSpectral bands
The invention discloses an apple variety identification method based on optimal fuzzy clustering of a spectral band. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring Fourier near-infrared spectrums of different varieties of apple samples: for the different varieties of apple samples, detecting the apple samples by using a Fourier near-infrared spectrometer, obtaining Fourier near-infrared spectrum data of the apple samples, and storing the data in a computer; And S2, preprocessing the near infrared spectrum of the apple sample in the step S1 by using a standard normal variable change (SNV). And S3, carrying out waveband optimization on the near infrared spectrum in the step S2 by using BIPLSDA (Binary Interval Least Squares Analysis). S4, carrying out dimension reduction processingand identification information extraction on the apple near-infrared spectrum: compressing the apple near-infrared spectrum data in the step S3 by utilizing principal component analysis (PCA); And then utilizing linear discriminant analysis (LDA) to extract the identification information of the data. And S5, identifying the apple variety of the test sample containing the identification informationin the step S4 by using an improved fuzzy C-means clustering method.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Electronic nose vinegar variety identification method through fuzzy covariance learning network
InactiveCN107886056AImprove classification accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisData compression
The invention discloses an electronic nose vinegar variety identification method through a fuzzy covariance learning network. The method concretely comprises the following steps that firstly the electronic nose is applied to acquire different varieties of vinegar data, then the acquired vinegar data are preprocessed through a standard normal variable transformation (SNV), then data compression isperformed by using principal component analysis (PCA) and the identification information of training samples is extracted by using linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and finally the vinegar variety is identified according to the fuzzy covariance learning network method. The electronic nose vinegar variety identification method through the fuzzy covariance learning network is high in classification accuracy, simple and convenient, lossless, low in cost and easy to implement and popularize and use.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Binary adulterate angelica sinensis quantitative analysis method based on near infrared spectrum and chemometrics
InactiveCN109765200AAccurate identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansPretreatment methodData set
The invention discloses a binary adulterate angelica sinensis quantitative analysis method based on near infrared spectrum and chemometrics. The method comprises the specific steps of purchasing someangelica sinensis and similar products, and preparing a certain number of angelica sinensis adulterate samples; collecting near infrared diffuse reflection spectrum of the adulterate samples; dividinga data set into a training set and a prediction set in a KS grouping mode; determining the number of factors of a partial least squares regression model; inspecting preprocessing effects of an SC smoothing method, a multiplicative scatter correction method, a standard normal variable method, a first-order derivative method, a second-order derivative method, a continuous wavelet transform method and combinations of the methods, thereby obtaining the optimum preprocessing method; and carrying out quantitative analysis on binary adulterate angelica sinensis through adoption of the optimum preprocessing-PLSR modeling method. On the basis of the near infrared spectrum and the chemometrics, the method is rapid, simple and convenient, and the samples are not damaged. The method is applicable tothe quantitative analysis of the binary adulterate angelica sinensis.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for detecting moisture content of dry powder extinguishing agents based on near infrared spectroscopy analysis
ActiveCN103175806BNo pollutionQuick analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansFunctional relationMoisture
The invention provides a method for detecting the moisture content of dry powder extinguishing agents based on near infrared spectroscopy analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) establishing a calibration set and a validation set sample spectrum; 2) preprocessing original spectral information through a second derivative, standard normal variate and KarlNorris derivate smoothing filter; 3) establishing a calibration model for the functional relation between a near infrared spectrum of the calibration set and the true value of the moisture content of a corresponding dry powder extinguishing agent sample by using a partial least squares method; 4) validating and optimizing the calibration model; and 5) inputting the near infrared spectrum of the dry powder extinguishing agent sample to be detected into the optimized calibration model, so as to obtain the moisture content value. The method is a method for quickly detecting the moisture content of the dry powder extinguishing agents based on the near infrared spectroscopy analysis, is established based on the analysis of the near infrared spectrums of the moisture content values of different dry powder extinguishing agents; and the detection method has the advantages of being quick in analysis, high in efficiency, simple and convenient to operate, low in cost, and free from pollution to the environment.
Owner:应急管理部天津消防研究所
Method for quantitative analysis of ternary adulterated pseudo-ginseng based on integrating sphere diffuse reflection UV-visible spectroscopy
InactiveCN107727591AEnables direct measurementFast analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsMetrologyData set
The invention relates to a method for quantitative analysis of ternary adulterated pseudo-ginseng based on integrating sphere diffuse reflection UV-visible spectroscopy. The method comprises scanninga ternary adulterated pseudo-ginseng sample through an integrating sphere diffuse reflection UV-visible spectrophotometer, dividing a data set into a training set and a prediction set, inspecting pretreatment effects of centralization, scaling, maximum / minimum normalization, standardization, standard normal variation, multiplicative scatter correction, first-order derivation, second-order derivation, continuous wavelet transform and SG smoothing, selecting an optimal pretreatment method, processing a spectrum through the optimal pretreatment method, building a least squares model and forecasting an unknown sample. Through use of integrating sphere diffuse reflection, sample pretreatment is avoided and non-destructive direct measurement of the sample is realized. The UV-visible spectroscopydetection is fast. The spectrum is processed by stoichiometry and a model is built by stoichiometry so that prediction accuracy is high. The method is suitable for quantitative analysis of ternary adulterated pseudo-ginseng.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Classification method and device for selecting high spectral wavelength based on single factor variance analysis
InactiveCN110020679AReduce modeling timeImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingClassification methods
The invention provides a classification method and device for selecting hyperspectral wavelengths based on single-factor variance analysis, and belongs to the technical field of image processing and spectroscopy. The classification method for selecting the hyperspectral wavelength based on the single factor variance analysis comprises the following steps: acquiring a hyperspectral image of a to-be-classified sample; carrying out image processing on the hyperspectral image of the sample to obtain the spectral information of the sample; correcting the spectral information of the sample by adopting standard normal variable transformation; calculating the characteristic wavelength in the spectral information of the sample by adopting single-factor variance analysis; extracting the spectral information of the sample corresponding to the characteristic wavelength from the corrected spectral information of the sample; dividing spectral information of samples corresponding to the characteristic wavelengths into a training set, a verification set and a test set; obtaining a sample classifier according to the spectral information training set and the verification set of the sample; and adopting a sample classifier to classify the spectral information test set of the samples. According to the method, the classification accuracy can be improved, and the classification modeling time is shortened.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
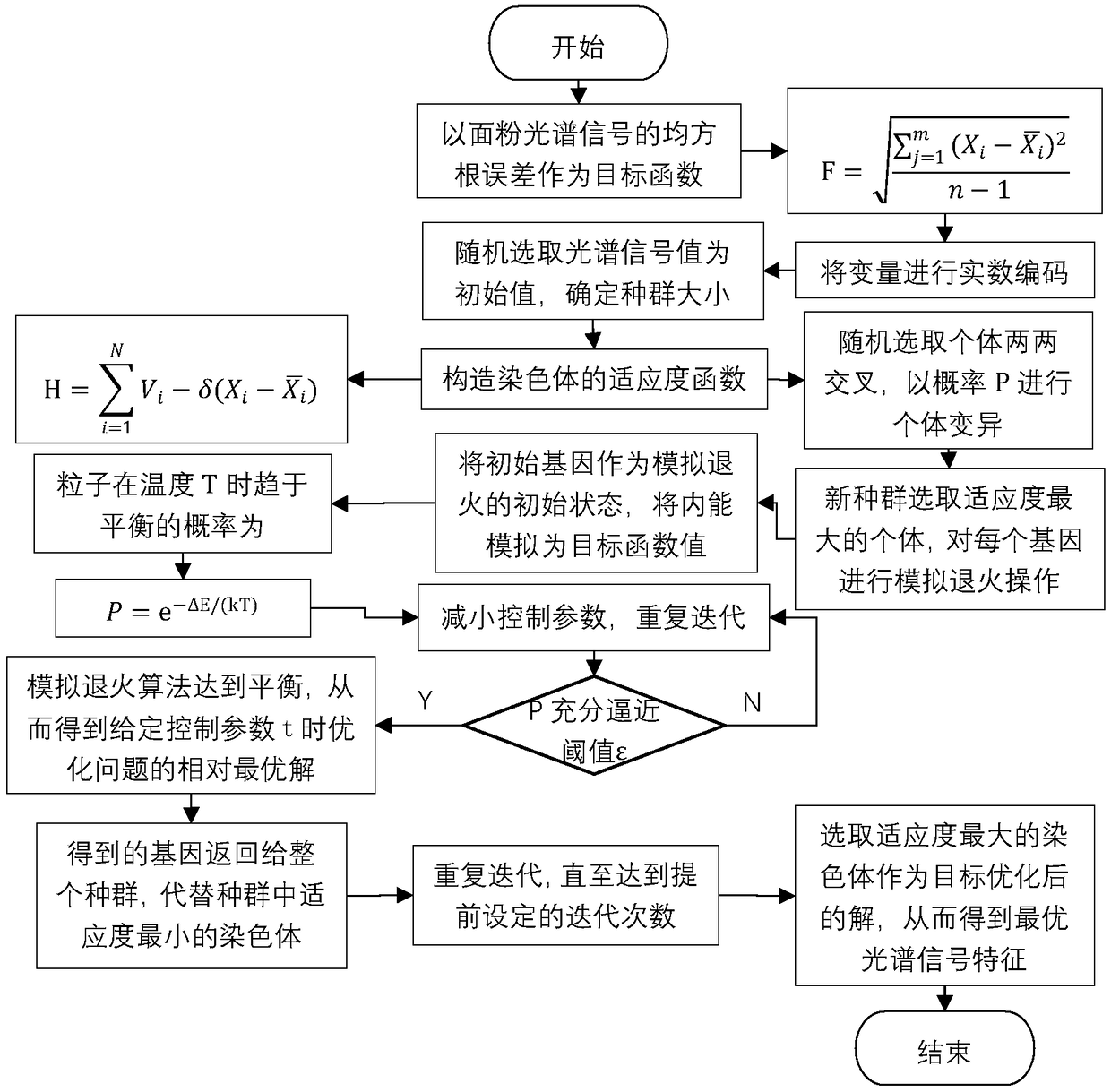
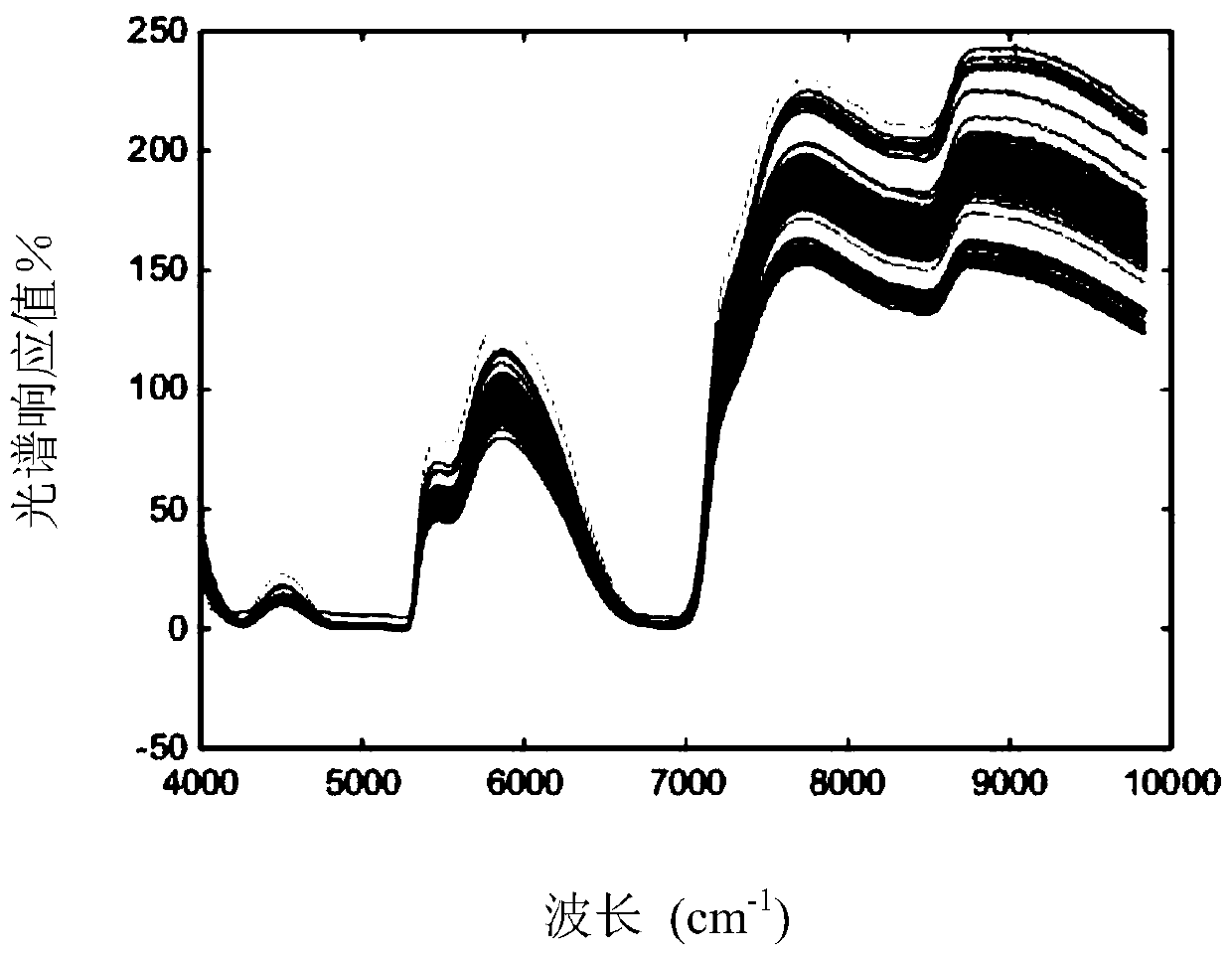
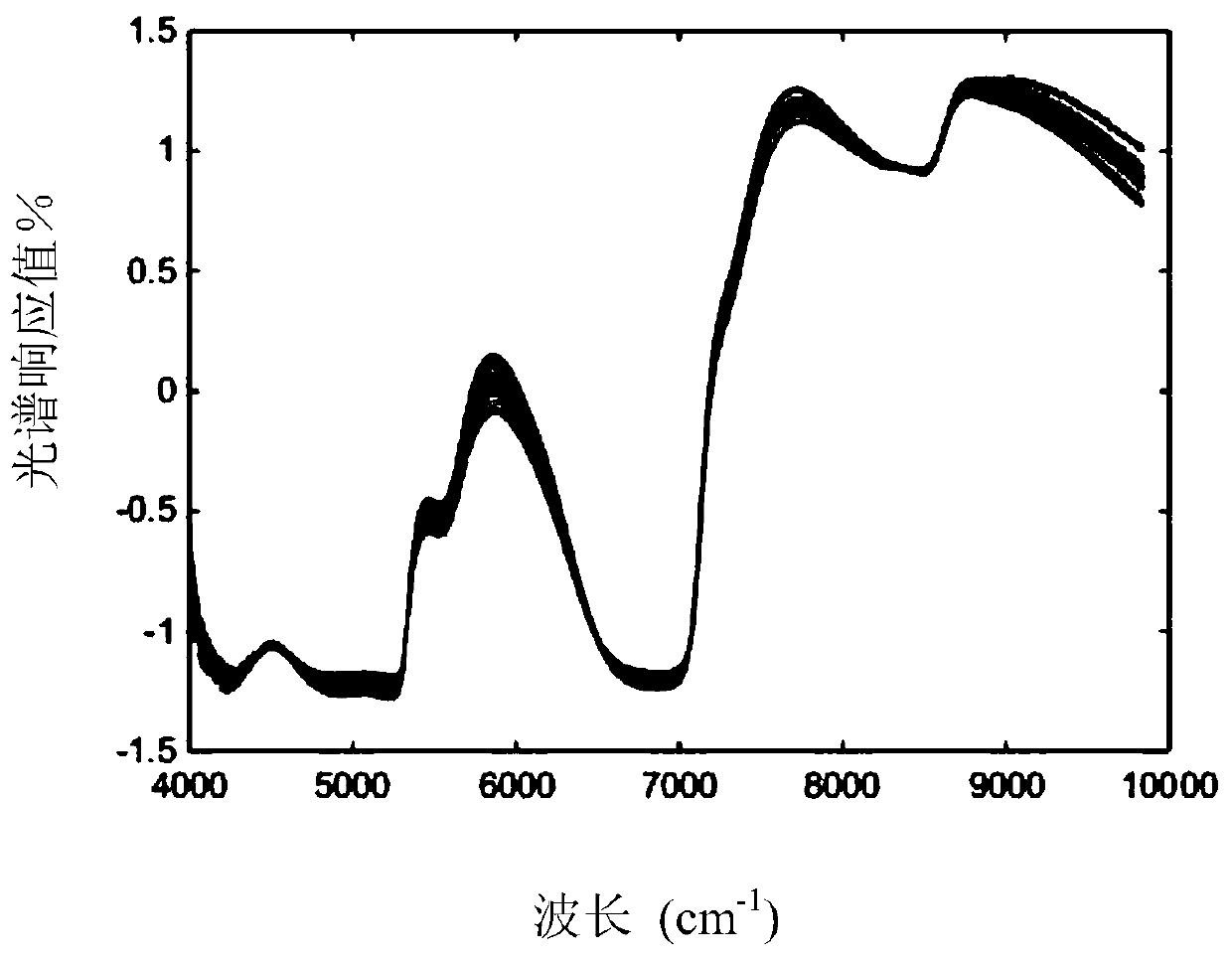
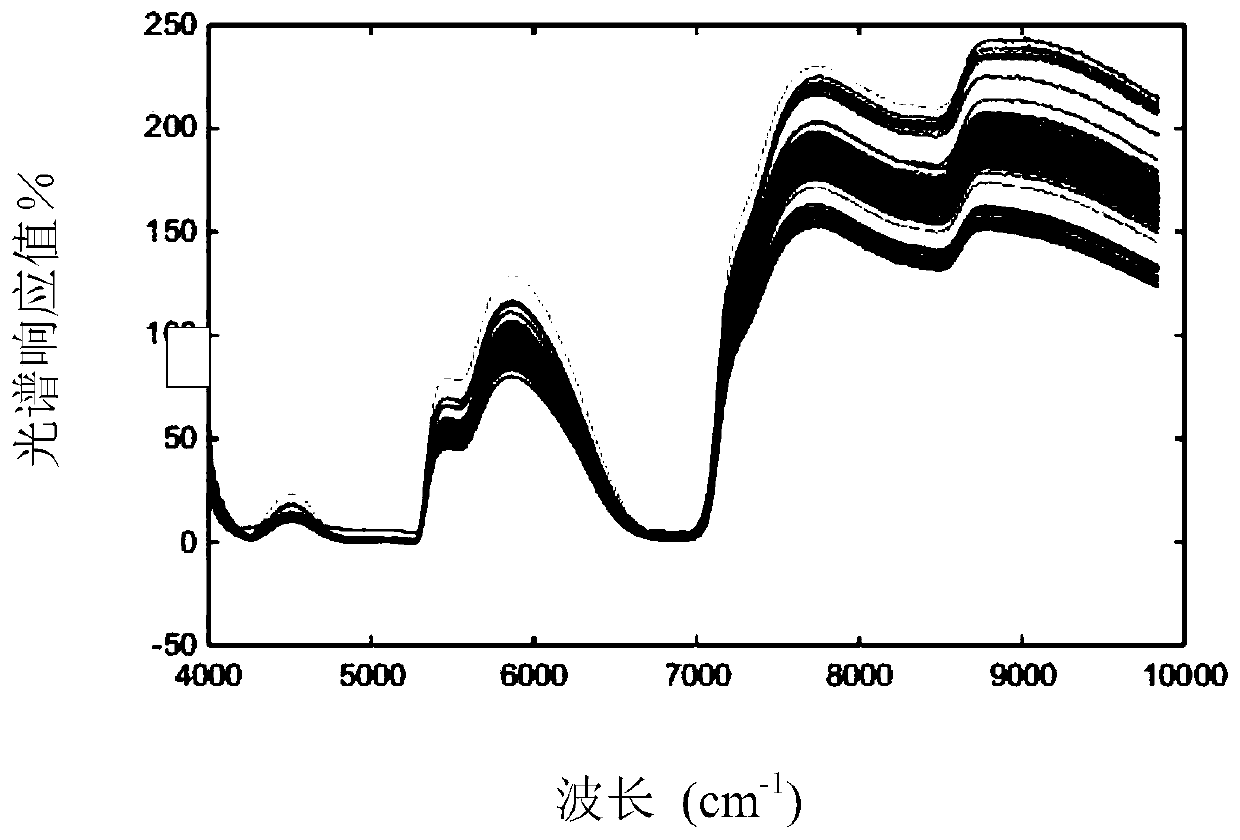
Flour quality detection method based on hybrid simulated annealing and genetic algorithms
InactiveCN109342352AImprove accuracyReduce complexityMaterial analysis by optical meansGenetic algorithmSolid particle
The invention discloses a flour quality detection method based on hybrid simulated annealing and genetic algorithms. The flour quality detection method comprises main steps as follows: scanning flourby an infrared spectrometer to obtain spectral information, performing standard normal variable transformation on a flour spectrum to eliminate solid particles and surface scattering; globally searching the optimal spectral signal characteristic with the genetic algorithm, and searching the optimal individual in the genetic algorithm with the simulated annealing algorithm to realize combination ofglobal search and local search; preprocessing characteristic vectors, and constructing a classifier by a radial neural network to classify the processed characteristic vectors, so as to finish flourquality detection. The method has better robustness, by means of spectral preprocessing, spectral noise is removed, model complexity is reduced, and computation efficiency is improved; by combinationof the genetic algorithm and the simulated annealing algorithm, global and local optimization capabilities of a model are enhanced, accuracy of the flour quality detection is improved by the radial neural network, and nondestructive testing is realized.
Owner:龙口味美思环保科技有限公司
Method for determining yield of gellan gum in gellan gum fermentation liquor by utilizing near infrared spectroscopy
InactiveCN110987863AYield detectionQuick filterMaterial analysis by optical meansBiotechnologyGellan gum
The invention discloses a method for determining the yield of gellan gum in gellan gum fermentation liquor by utilizing near infrared spectroscopy, belongs to the field of microbial fermentation, andrelates to the technical field of near infrared spectroscopy detection. After the fermentation liquid is sampled at different time points, the yield of gellan gum in the fermentation liquid is analyzed by utilizing a traditional method; meanwhile, a near infrared spectrogram of the fermentation liquid is obtained by scanning of a near infrared spectrograph; an original spectrogram is preprocessedthrough methods such as standard normal variable transformation (SNV), multivariate scattering correction (MSC), smooth filtering (S-G), a normalization method and derivative processing, a mathematical model is established by combining an interval partial least squares method (siPLS), and the model is evaluated through parameters such as correlation coefficients and standard root mean square errors. The method is simple and quick to operate and pollution-free, can greatly save the experimental time and cost in the screening of high-yield gellan gum strains, and can also be used for laboratoryor industrial production of gellan gum.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Huangshan Maofeng grade identification method based on fuzzy weighting identification information extraction
PendingCN114384042ACategory performance is excellentCalculation speedMaterial analysis by optical meansAlgorithmPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a Huangshan Maofeng grade identification method based on fuzzy weighting identification information extraction. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out near infrared spectrum acquisition on each grade of Huangshan Maofeng tea; (2) preprocessing the near infrared spectrum of the Huangshan Maofeng by using a standard normal variable; (3) carrying out dimensionality reduction on near infrared spectrum data of the Huangshan Maofeng through principal component analysis; (4) realizing identification information extraction of the near infrared spectrum data by using a fuzzy weighting identification information extraction method; and (5) identifying each grade of Huangshan Maofeng by using a K nearest neighbor method. According to the method, the problem that the effect is not ideal when the traditional discriminant analysis processes the data which does not meet Gaussian distribution is solved, and the influence of outlier data on identification information extraction is reduced. The method can be used for non-destructively, quickly and effectively performing grade identification on the Huangshan Maofeng.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com