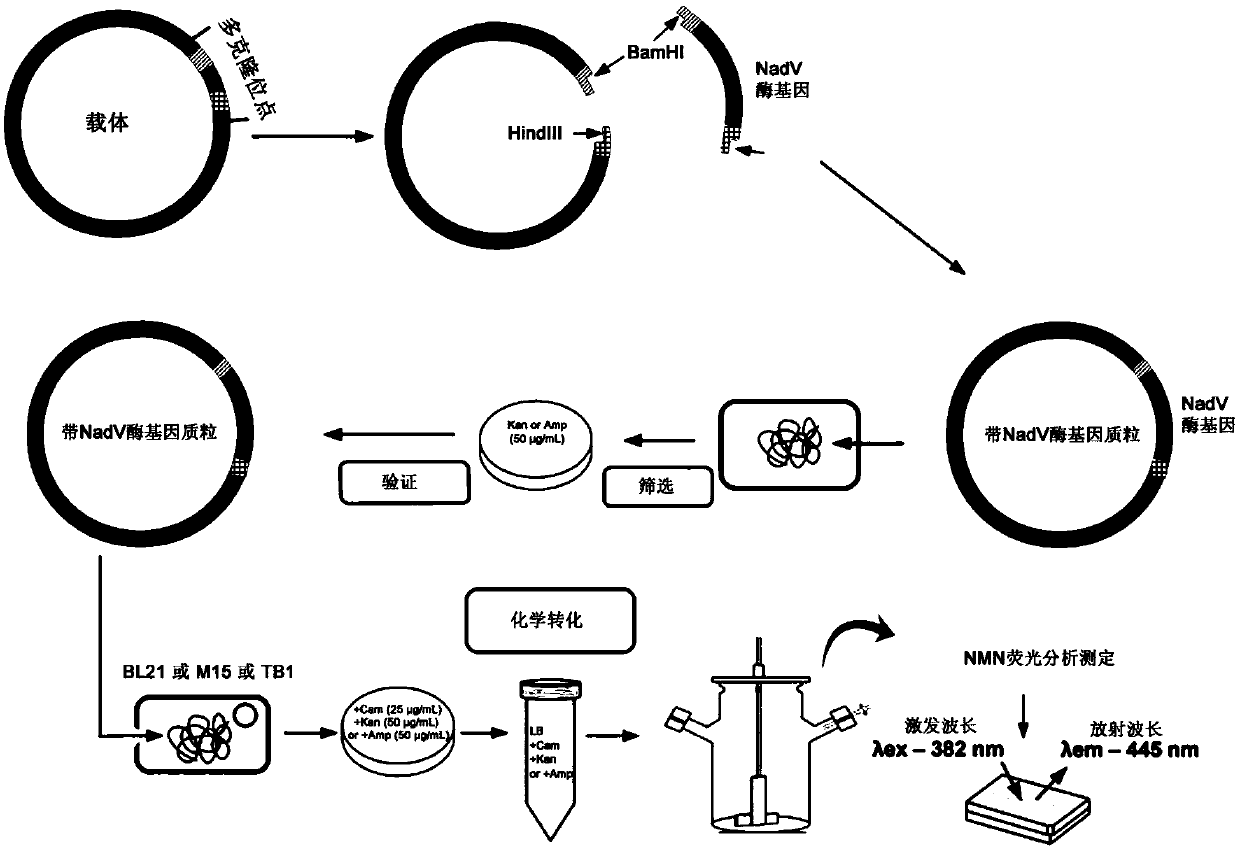
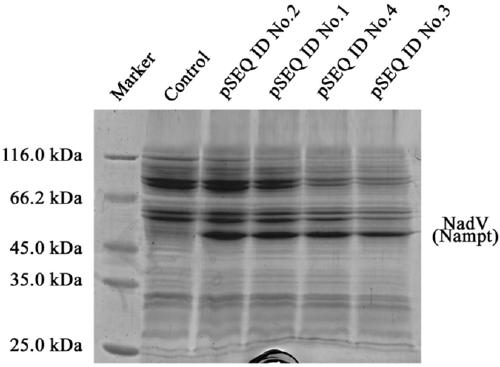
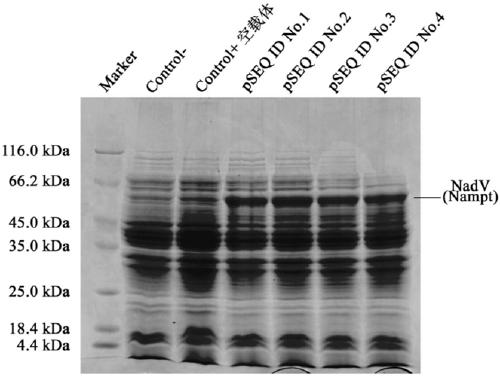
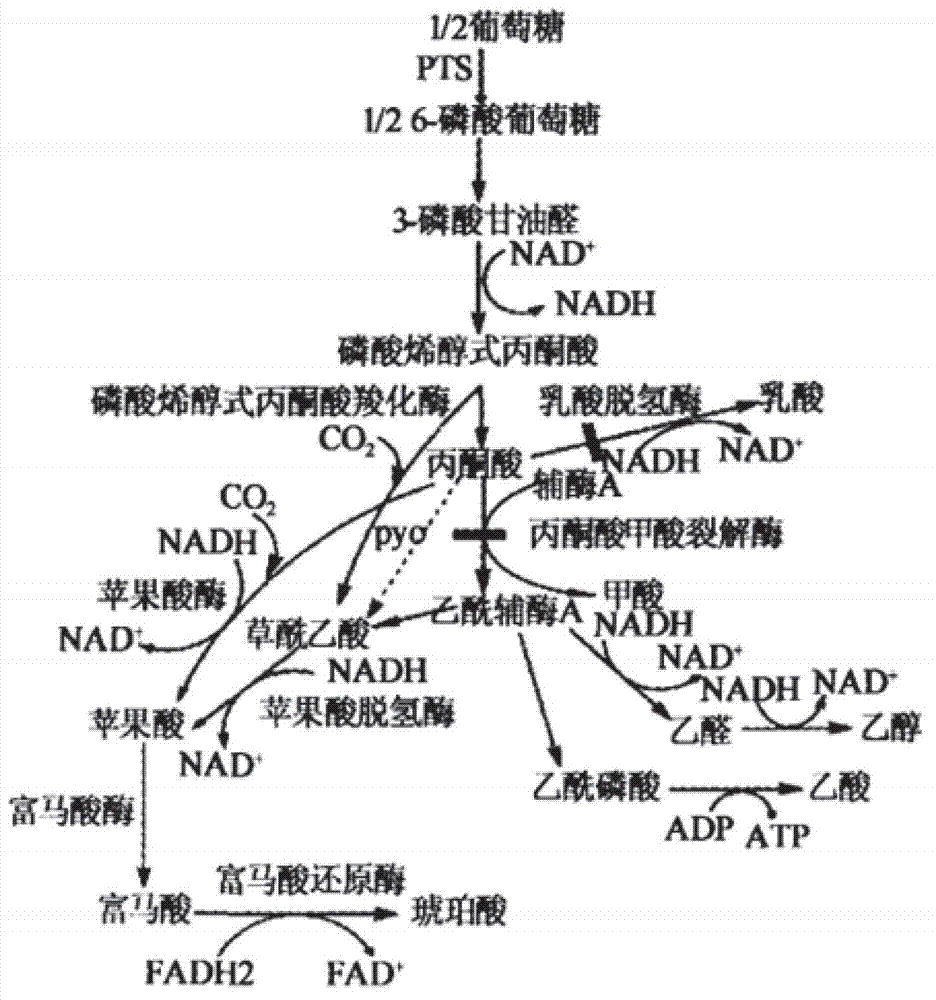
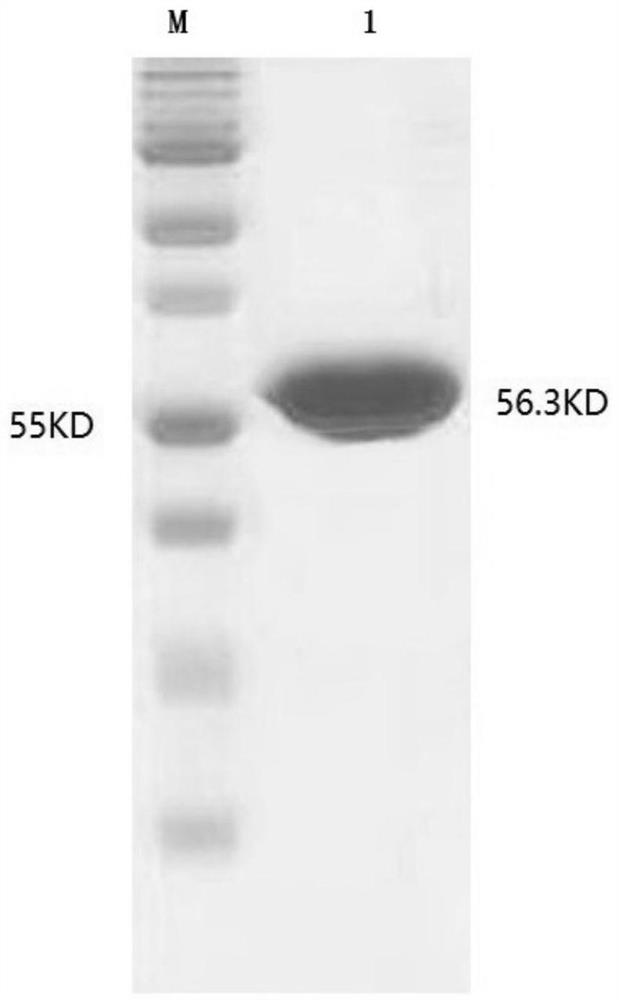
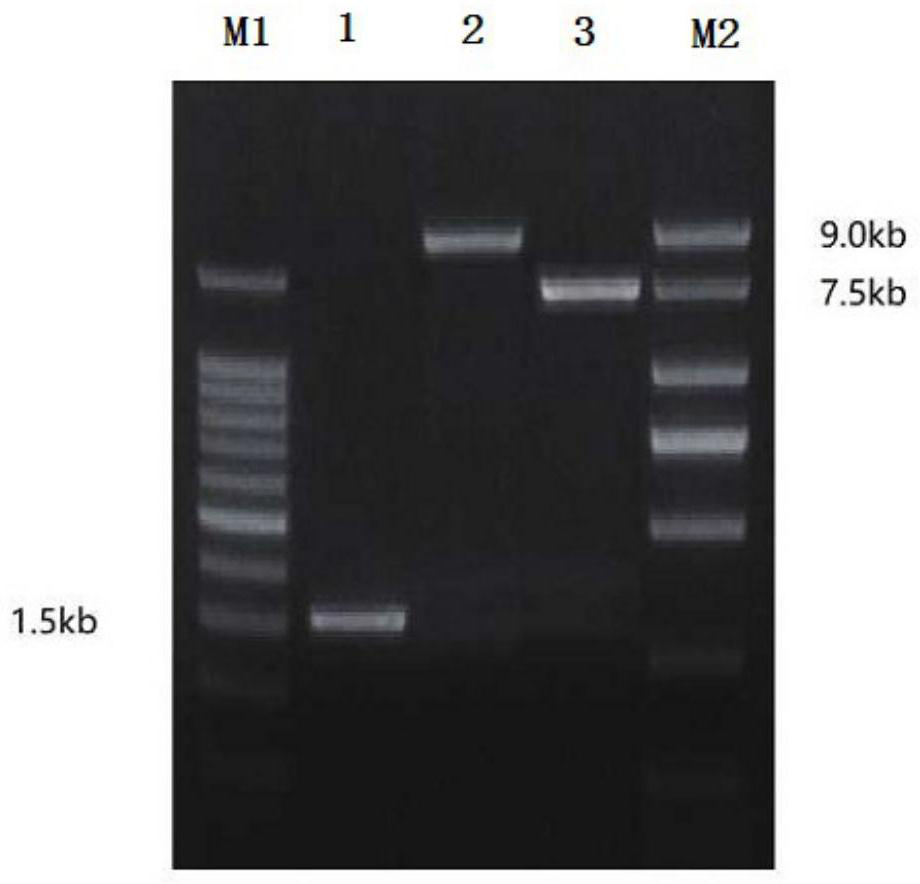
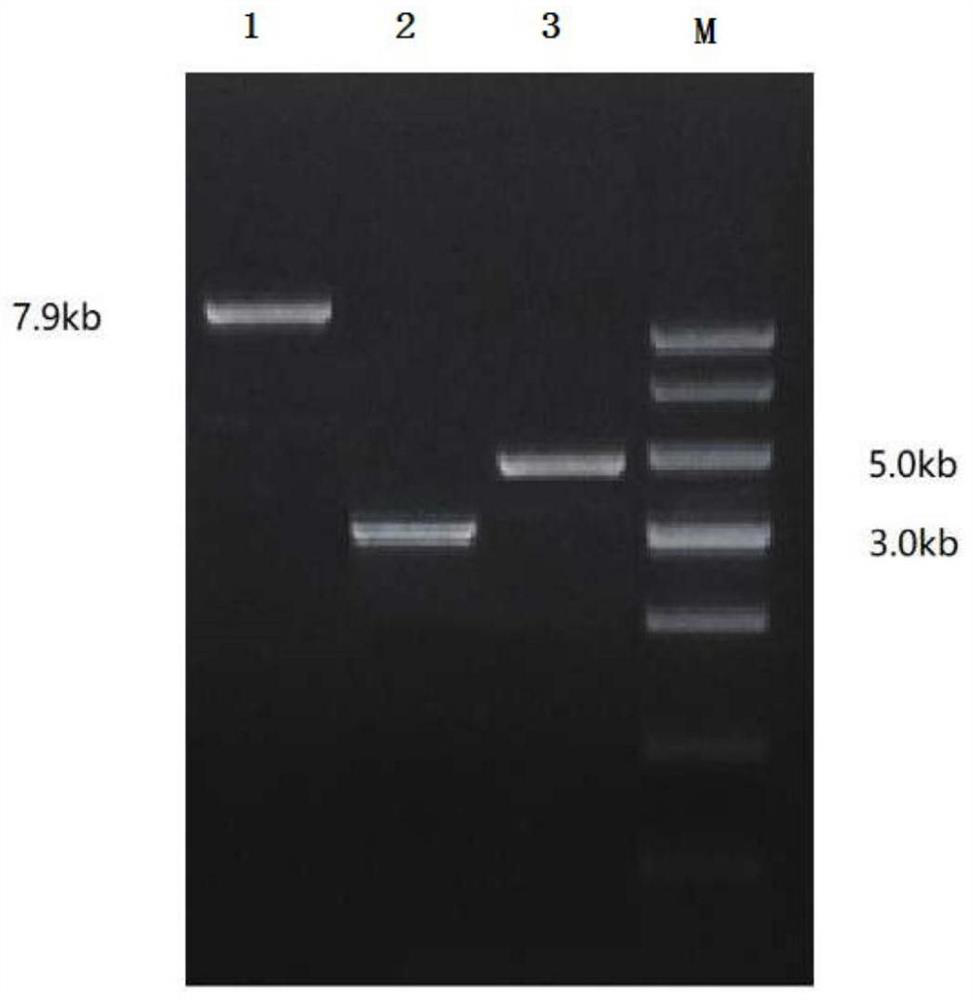
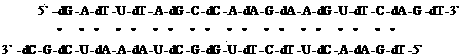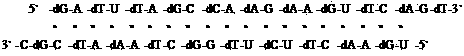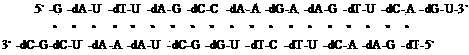Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
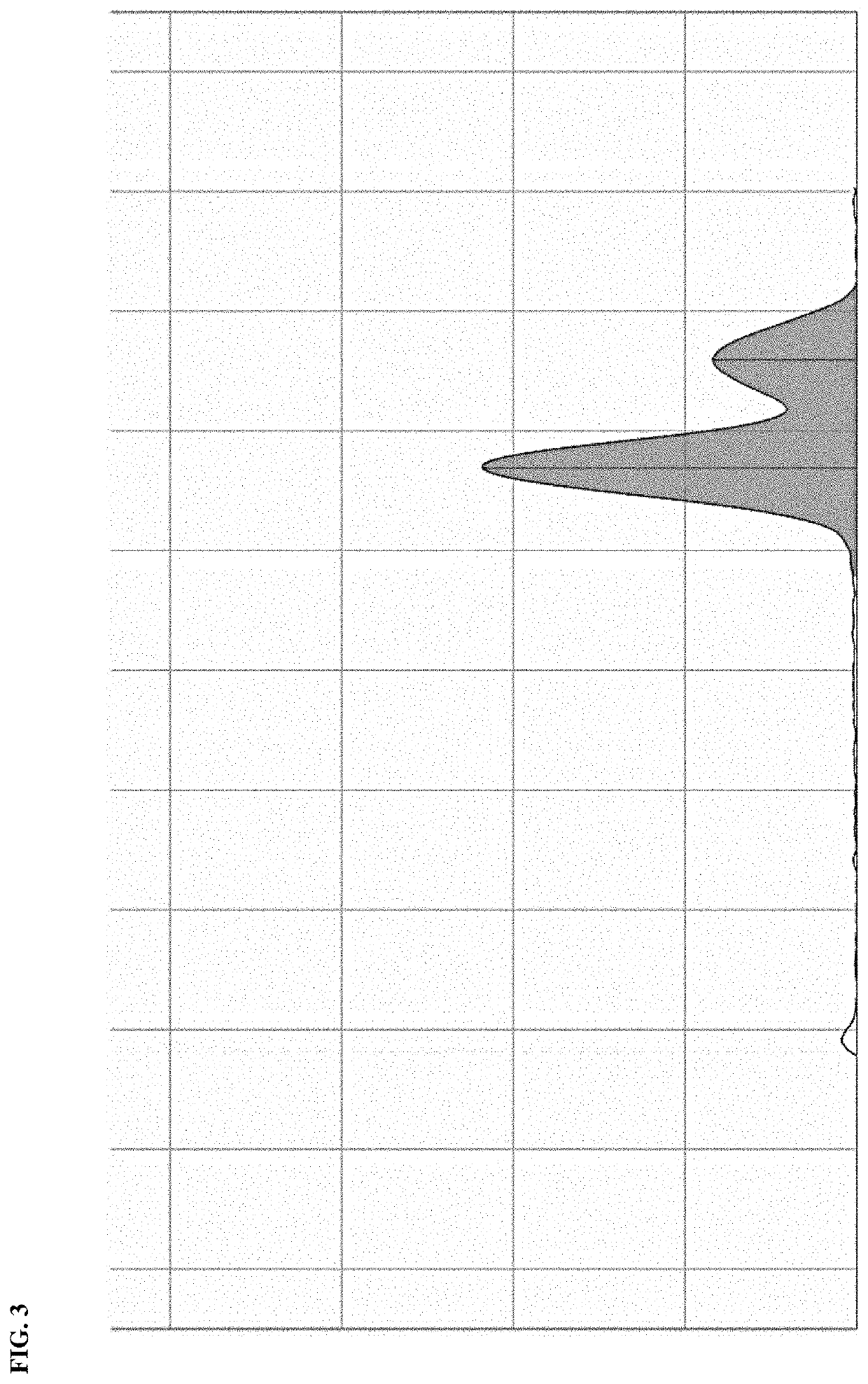
38 results about "Ribose phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
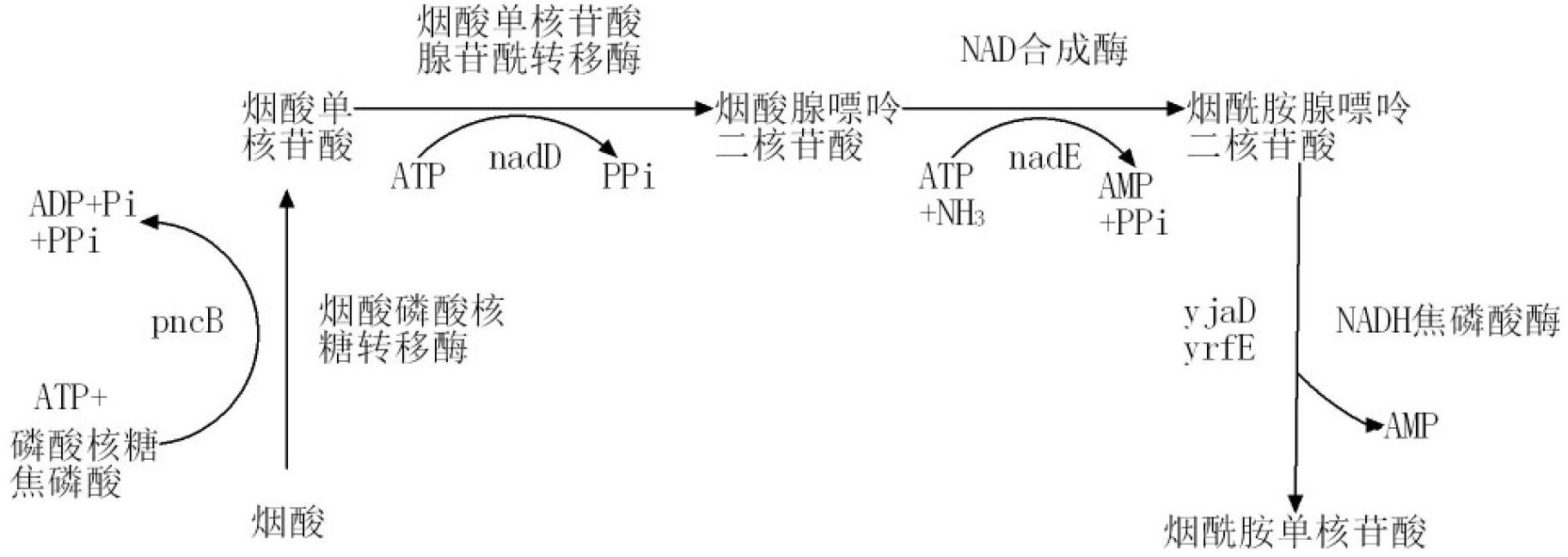
Ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) is both a product and an intermediate of the pentose phosphate pathway. The last step of the oxidative reactions in the pentose phosphate pathway is the production of ribulose 5-phosphate. Depending on the body's state, ribulose 5-phosphate can reversibly isomerize to ribose 5-phosphate.
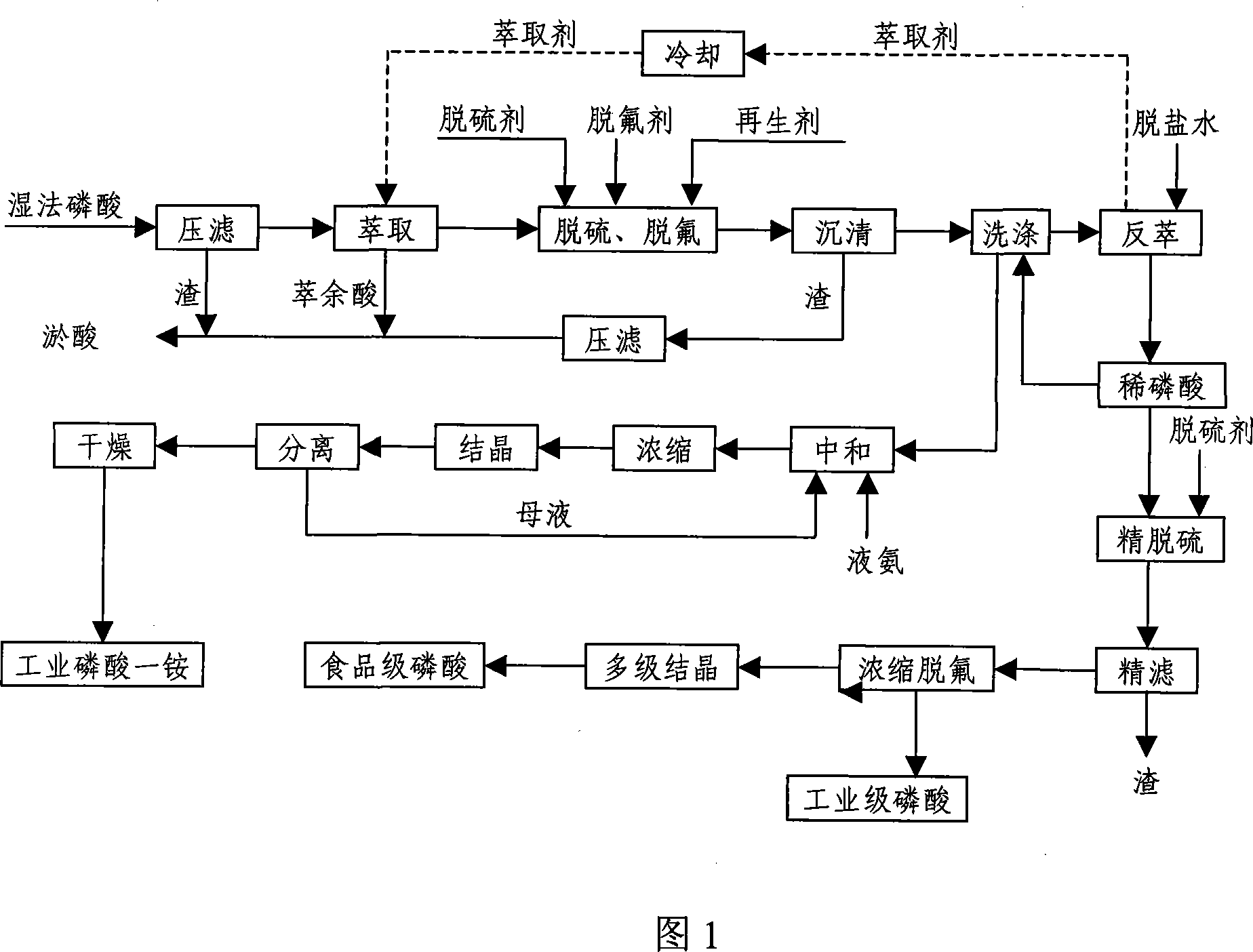
Method for producing technical grade ribose phosphate, food grade ribose phosphate and industry ammonium diacid phosphate using wet-process ribose phosphate
The invention discloses a method of using wet phosphoric acid to prepare industrial grade phosphoric acid, food grade phosphoric acid and industrial ammonium diacid phosphate, which is characterized in using wet phosphoric acid as the material, and preparing industrial grade phosphoric acid and food grade phosphoric acid respectively by using a series of compound purifying technologies such as chemical sedimentation and extracting by organic solvent and concentration and recrystallization and other technologies; meanwhile, the invention uses a part of purified diluted phosphoric acid to prepare industrial ammonium diacid phosphate. The invention has the advantages of reasonable cascade utilization of the wet phosphoric acid, high additional value of phosphorus, and further exploitation of the lower industrial and food grades phosphate.
Owner:中化重庆涪陵化工有限公司
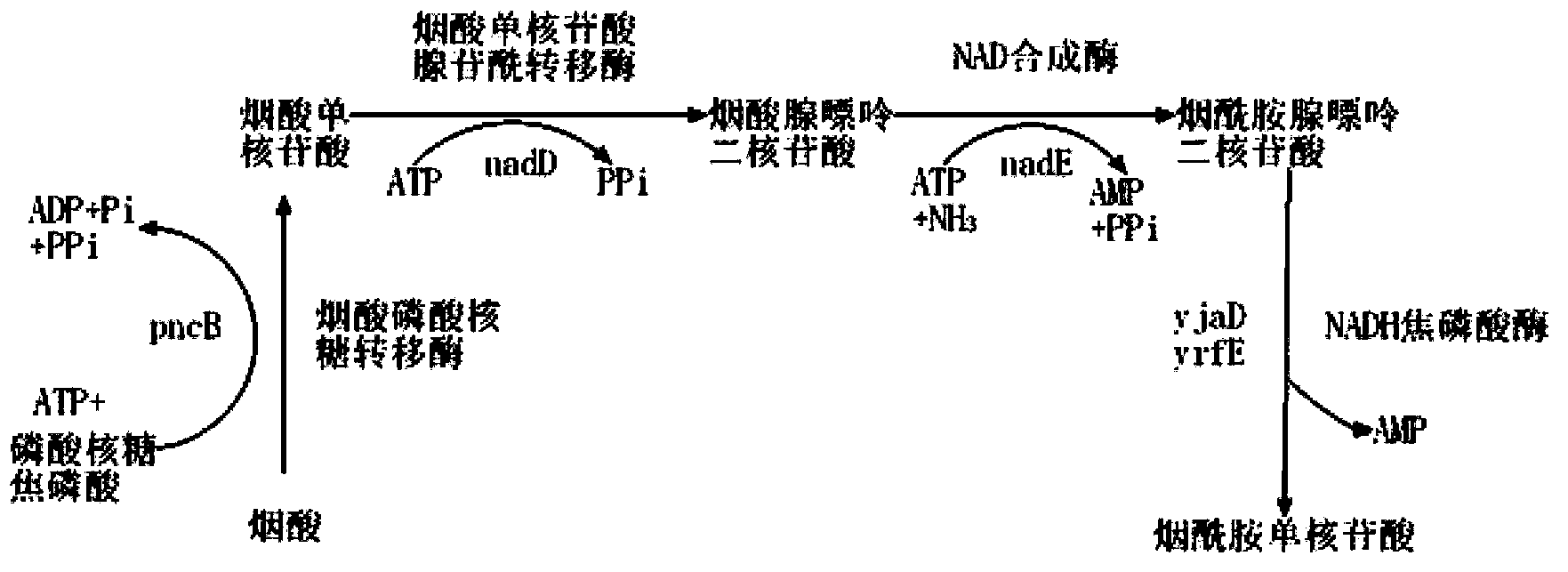
Catalytic preparation of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide by immobilized whole-cell one-step enzymatic reaction
InactiveCN108949865ALow costSimple production processFermentationNicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferaseNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide (beta-NMN). According to the method, D-5-ribose phosphate, ATP and nicotinamide are used as raw materials, beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide can be efficiently and biologically synthesized by catalysis of immobilized whole-cell containing phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, and the concentration of the synthesized beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide can be 13.3g / L, so that the synthetic amount and conversion rate of beta-NMN enzymatic reaction can be increased, the immobilized whole-cell can be used repeatedly, and the reaction complexity and production cost can be reduced.
Owner:SYNCOZYMES SHANGHAI
Niacinamide ribose phosphate transferase for preparing NMN, coding gene, recombinant vector and application
ActiveCN109666658ASimple processReduce investmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNiacinamide
Owner:成都及禾生物科技有限公司
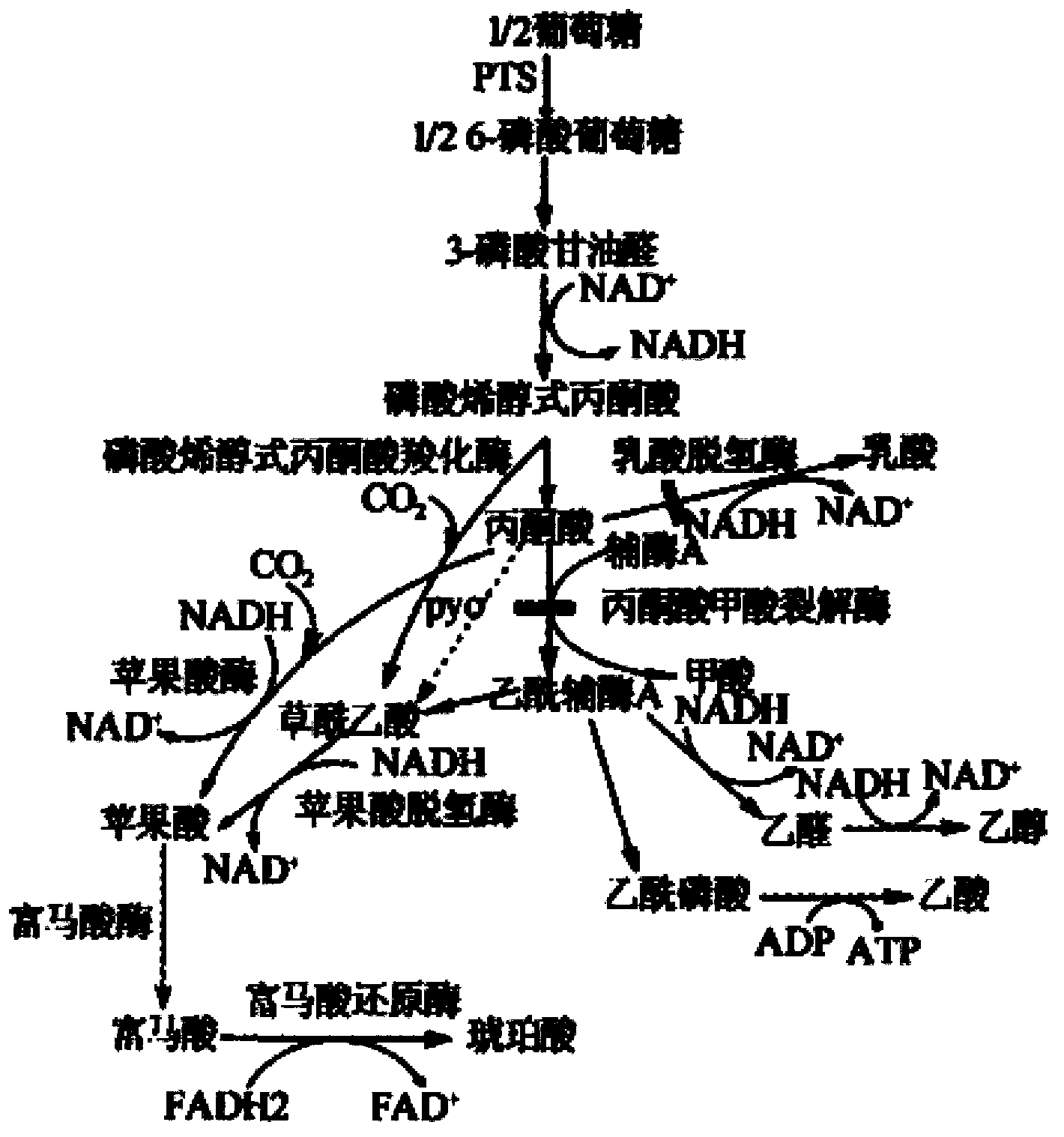
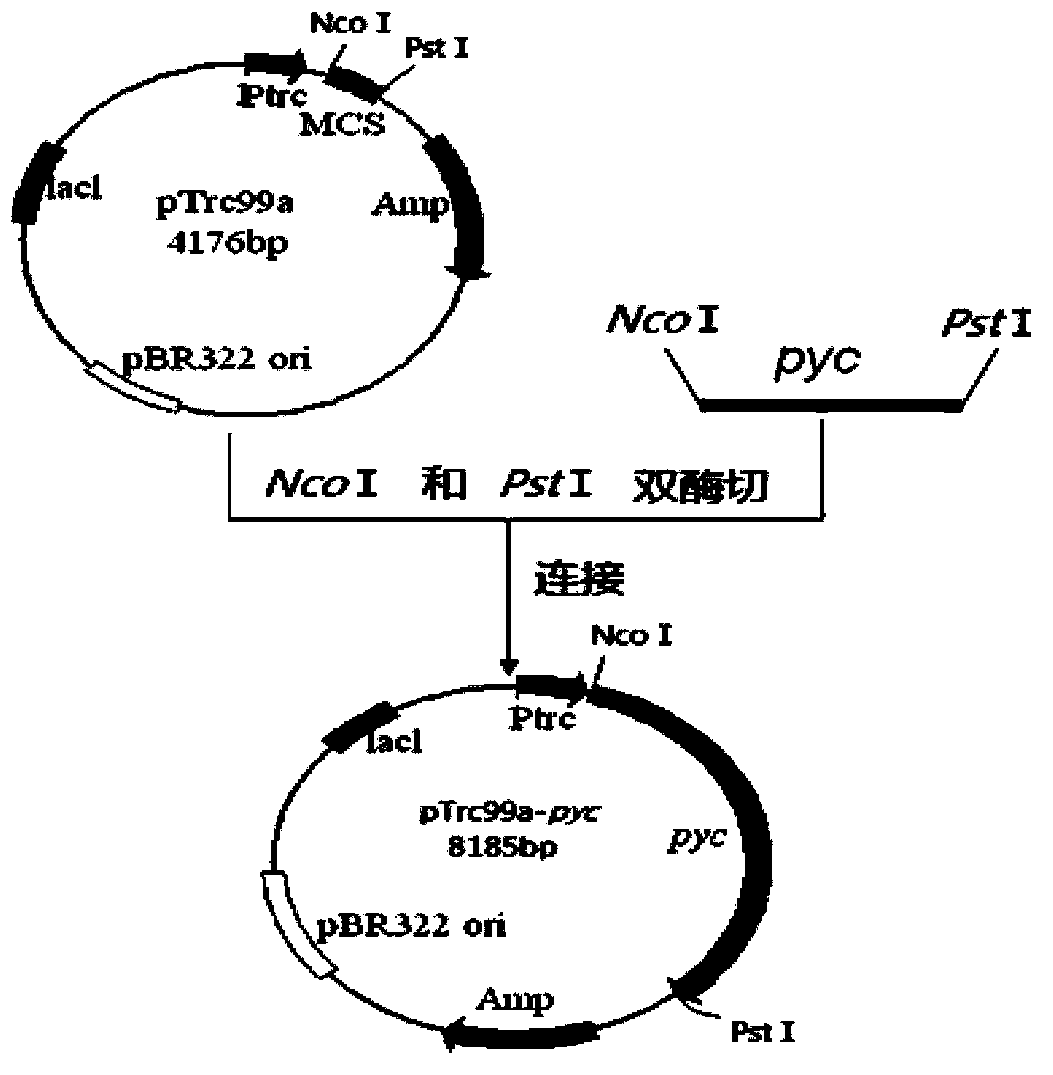
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN102864116AEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
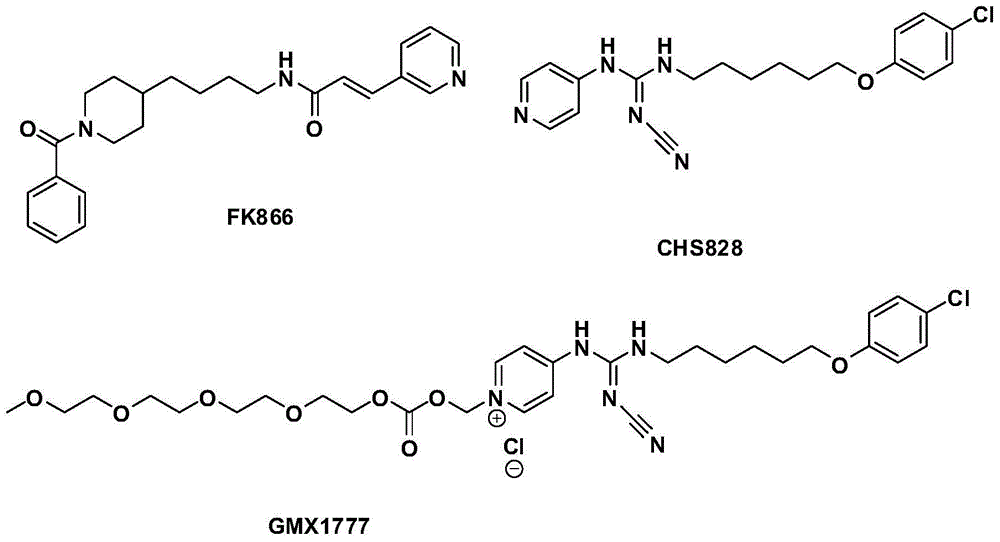
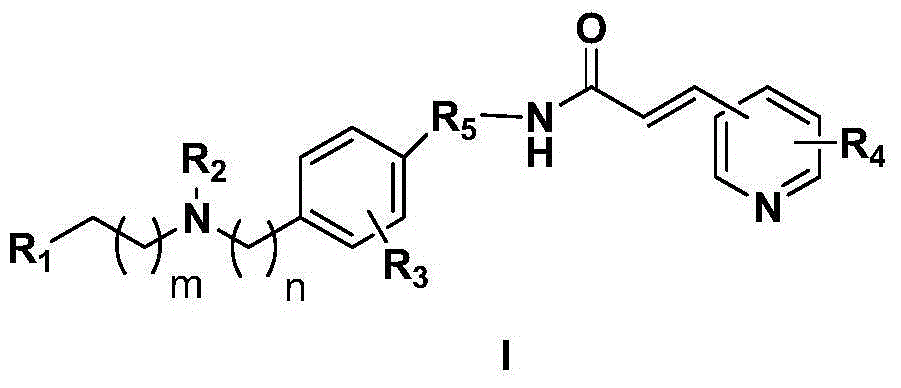
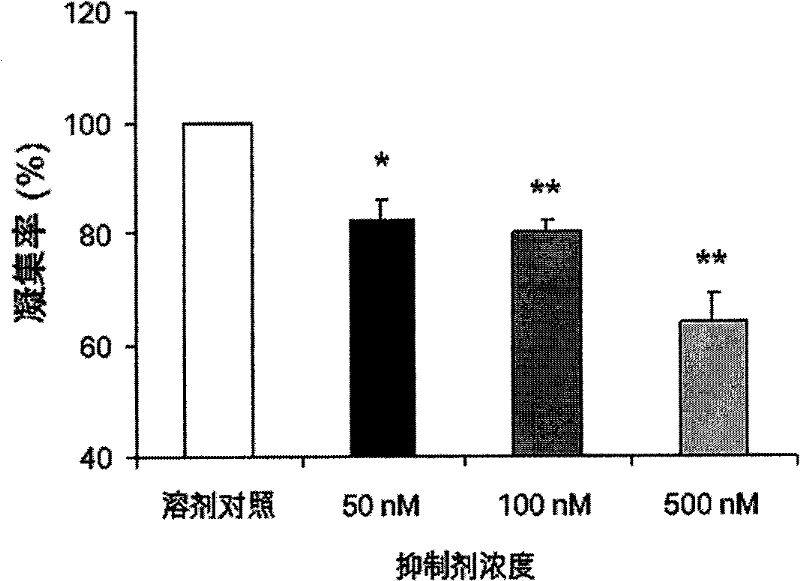
Novel nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor as well as synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN104557863ASynthetic raw materials are cheapEasy to routeOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTransferase inhibitorStructural formula
The invention discloses a novel nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor as well as a synthetic method and application thereof. The novel nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor is a compound or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof shown in the structural formula I in the specification. The novel nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor is prepared from cheap synthetic raw materials, concise in route, simple in operation and suitable for industrial production; the obtained compound is excellent in antitumor activity and is expected to be developed as a new antitumor drug.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and method for fermenting and producing succinic acid
InactiveCN102643774AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and a method for fermenting and producing succinic acid. Bacterial strains of the succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium are classified and named as Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) BA306 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012103. A construction process mainly comprises inactivating or knocking phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase genes and ptsG genes in a phosphoric acid movement system, conducting excessive coexpression on phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase and niacin ribose phosphate transferring enzyme, enabling recombination of colon bacillus to be capable of efficiently using monosaccharide of glucose, xylose, arabinose, fructose and the like, simultaneously efficiently using mixed sugar and cellulose hydrolysate in various proportions for growth, and substantially improving combined efficiency of the succinic acid. A fermentation process adopts a two-stage fermentation mode, biomass liveweight is improved in an aerobic stage, and fermentation and acid production are carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
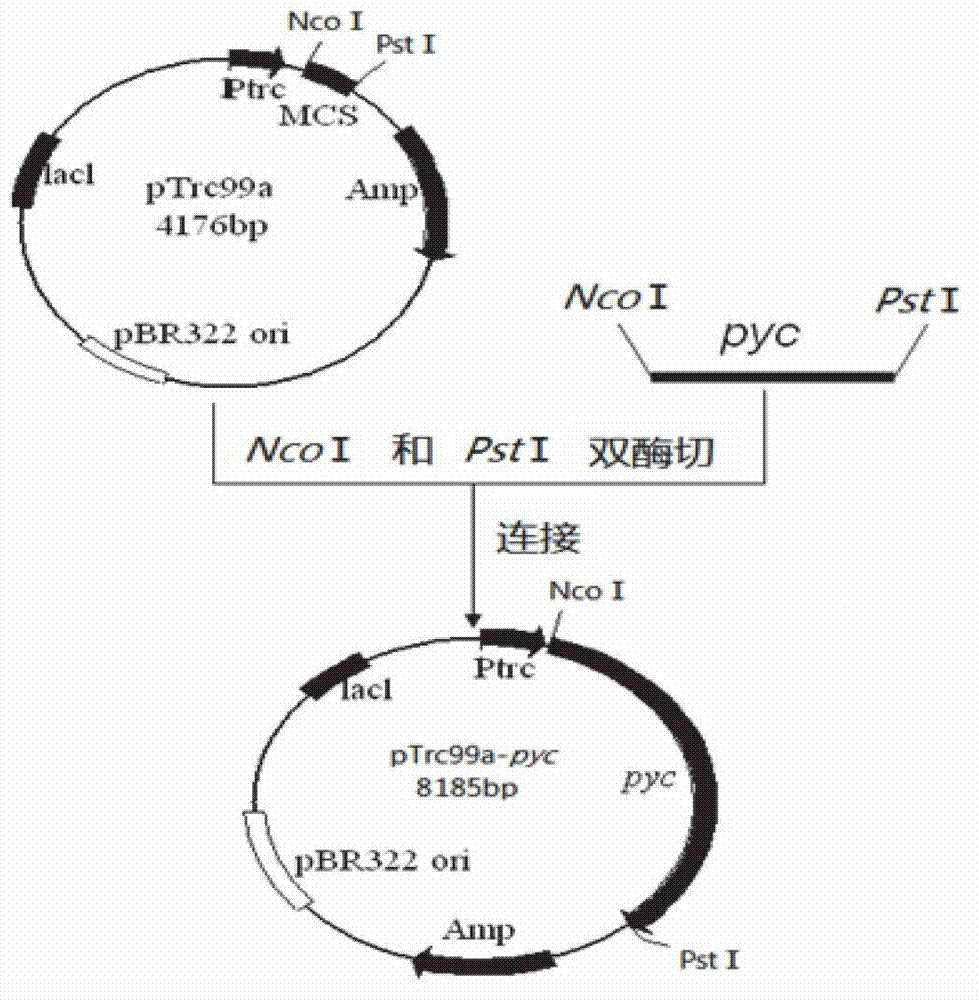
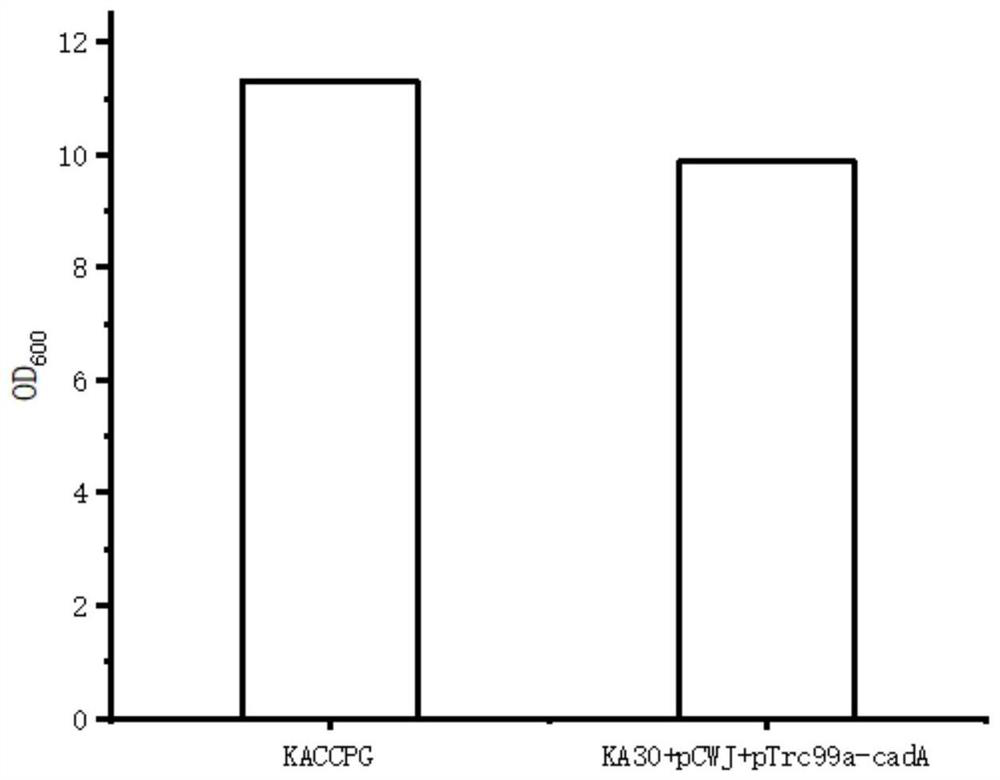
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of recombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for producing pentamethylene diamine and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. A ribulose diphosphate carboxylase gene in rhodospirillum, a ribose phosphate kinase gene and a lysine decarboxylase gene in spinach are synthesized from the beginning, PCR copy an escherichia coli molecular chaperone gene to construct a plasmid pTrc99a-cadA-cbbM and a plasmid pCWJ-prkA-GroEL / GroES, the double-plasmid recombinant bacteria grow well in a specific culture medium, and glucose is efficiently utilized. According to the recombinant escherichia coli, inducers arabinose and IPTG are respectively added in different time periods, the heterologous gene expression is stable, the reaction system is simple, the condition is mild, the period is short, few byproducts are produced, the method is clean and pollution-free, the method is a simple, rapid and efficient production way, and the fermentation result shows that the yield of the recombinant escherichia coli KACCPG is obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
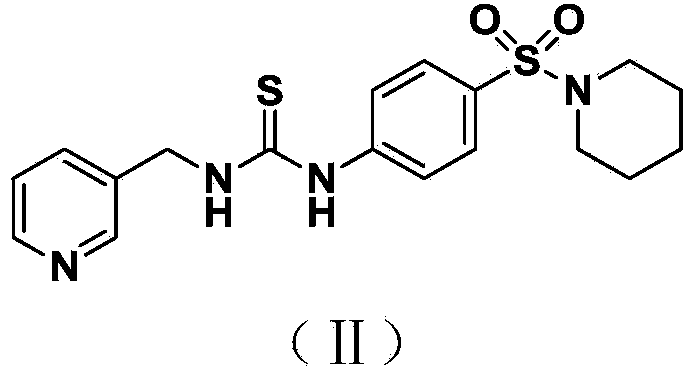
Urea type derivative used as nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines. The invention provides a urea type derivative and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The general structural formula of the compound is as shown in formula (I) in the specification. As proved by pharmacological experiments, the compound or salt mentioned in the invention not only has quite high inhibition activity on nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase but also has high antitumor activity in vitro. The invention further provides a preparation method of the derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, as well as an application of the derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to preparation of a nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor or antitumor drugs.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Nutrition agent for increasing yield of grain crops, and preparation and application method thereof
InactiveCN102898226AWide variety of sourcesLow priceFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesNutritionPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a nutrition agent for increasing yield of grain crops and a preparation method. The nutrition agent is composed of nucleotides, 5-ribose phosphate, boron and a diffusion agent. The preparation method comprises mixing the nucleotides, the 5-ribose phosphate and the boron with stirring, and then adding the diffusion agent under normal temperature to prepare the agent. The nutrition agent has advantages of good water-solubleness, easy absorption and utilization for the crops, simple usage, small application amount, stable performance and long shelf-life, can not only provide nucleic acids, trace element boron and other nutrients necessary for rice and other main food crops after flowering, but also inhibit photorespiration consumption of the crops, and is remarkable in yield increasing for the rice and other food crops and good in economic benefit.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Nucleic acid mediated electron transfer
InactiveUS7851146B2Fast electron transfer rateFaster rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical conductorElectron donor
The present invention provides for the selective covalent modification of nucleic acids with redox active moieties such as transition metal complexes. Electron donor and electron acceptor moieties are covalently bound to the ribose-phosphate backbone of a nucleic acid at predetermined positions. The resulting complexes represent a series of new derivatives that are bimolecular templates capable of transferring electrons over very large distances at extremely fast rates. These complexes possess unique structural features which enable the use of an entirely new class of bioconductors and photoactive probes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN113106080AIncrease enzyme activityEfficient catalytic conversionGenetic engineeringFermentationRiboseValine
The invention discloses a nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase mutant and application thereof. In the first aspect of the application, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase mutant is provided, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase mutant comprises an amino acid sequence obtained after an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 is mutated, and mutation comprises at least one of the facts that valine at the position 202 is mutated into alanine and leucine at the position 364 is mutated into proline. According to the embodiment of the invention, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase at least has the following beneficial effects: compared with the existing nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase provided by the embodiment of the invention has higher enzyme activity than the conventional wild type nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase, and the substrate containing nicotinamide and 5-phosphoribose-1-pyrophosphoric acid can be efficiently catalytically converted into NMN.
Owner:深圳希吉亚生物技术有限公司
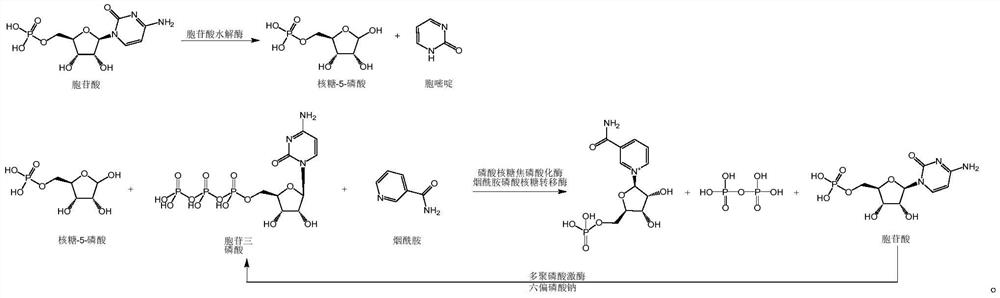
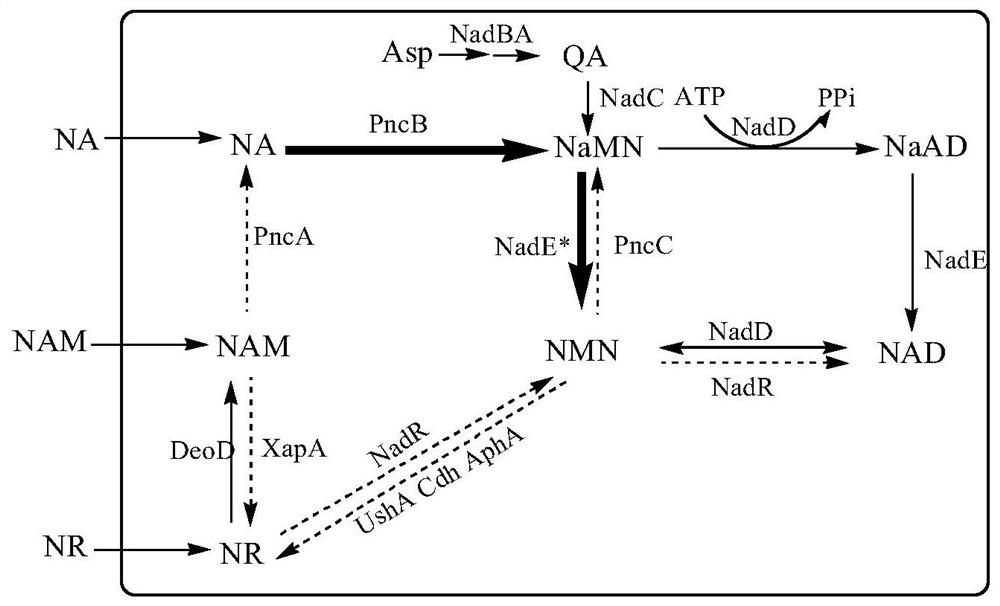
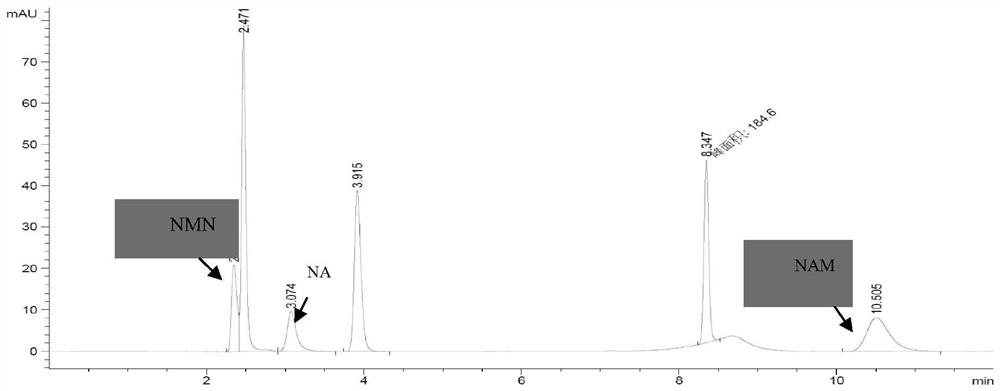
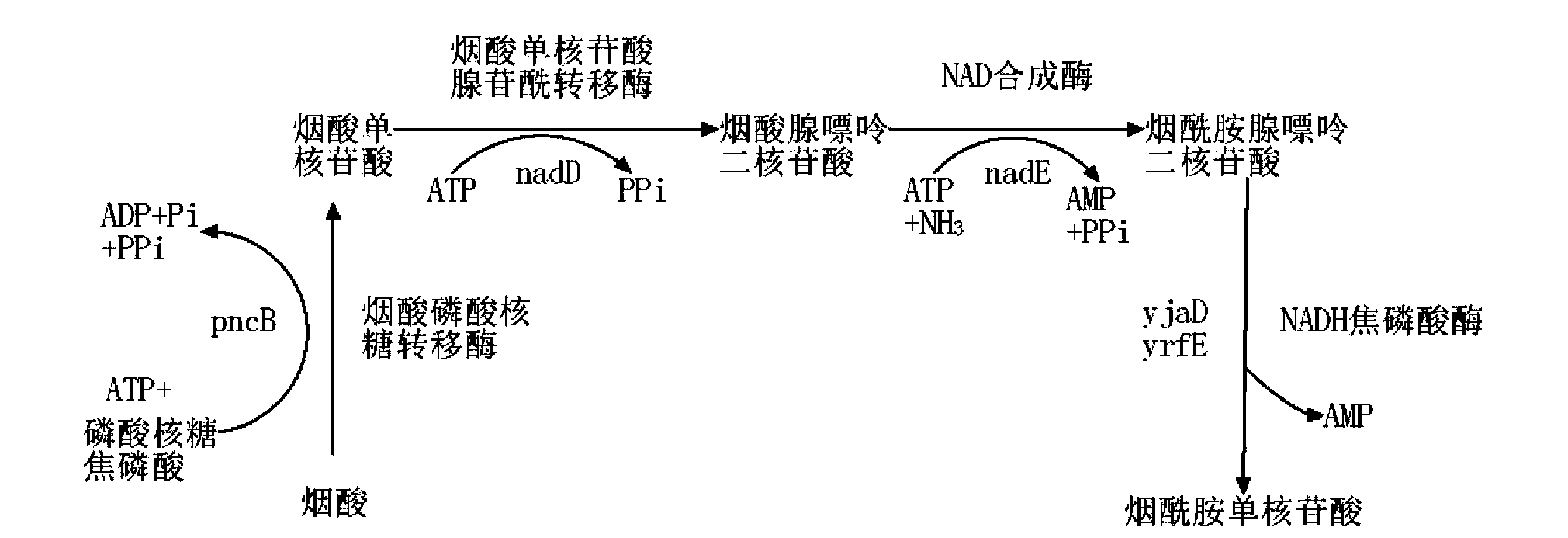
Enzymatic synthesis method of nicotinamide mononucleotide
ActiveCN112961890AGood removal effectAvoid expensiveFermentationBulk chemical productionEnzymatic synthesisNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses an enzymatic synthesis method of nicotinamide mononucleotide. The enzymatic synthesis method comprises the following steps: S1, taking ribose-5-phosphate, cytidine monophosphate, polyphosphate and nicotinamide as raw materials, and generating nicotinamide mononucleotide under the catalytic action of ribose phosphate pyrophosphorylase, polyphosphate kinase and nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase. The applicant uses polyphosphate kinase to catalyze cytidine monophosphate to cyclically obtain cytidine triphosphate by using a phosphate group provided by the polyphosphate, and the cytidine triphosphate is used as a pyrophosphoric acid donor of the ribose phosphate pyrophosphorylase to promote the enzymatic reaction of the ribose-5 phosphate and the nicotinamide, thereby avoiding the use of expensive ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Besides, the cytidine monophosphate and the cytidine triphosphate in the enzymatic reaction process provided by the invention are almost insoluble in water under an acidic condition, so that impurities in the product can be quickly, simply and conveniently removed by directly adjusting the pH value after the reaction is finished, the purification process is simplified, and the separation and purification difficulty is reduced.
Owner:深圳希吉亚生物技术有限公司
Nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase for preparing NMN
PendingCN112813044ASimple processShort timeFermentationGlycosyltransferasesNucleotideNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase for preparing NMN. The nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase is characterized by comprising an enzyme, wherein the enzyme is an amino-acid-sequence-formed protein which is subjected to substitution, deletion or addition by one or more amino acids or a protein derivative which has activity for catalyzing nicotinamide to obtain beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide. Further, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase also comprises a recombinant expression vector, wherein the recombinant expression vector contains a gene of the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase for preparing the NMN. Further, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase also comprises a genetic-engineered host cell, wherein the host cell contains the recombinant expression vector. The process for preparing the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide NMN, disclosed by the invention, is simple and is short in consumed time, the nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase employed for preparing the NMN is relatively high in activity and can be used for converting a substrate nicotinamide into the NMN at a conversion ratio of 60% or more at a room temperature, reaction conditions are relatively simple and easily achieved, and the production efficiency of the NMN will be increased relatively after the activity of the enzyme is improved.
Owner:浙江嘉杭生物医药有限公司
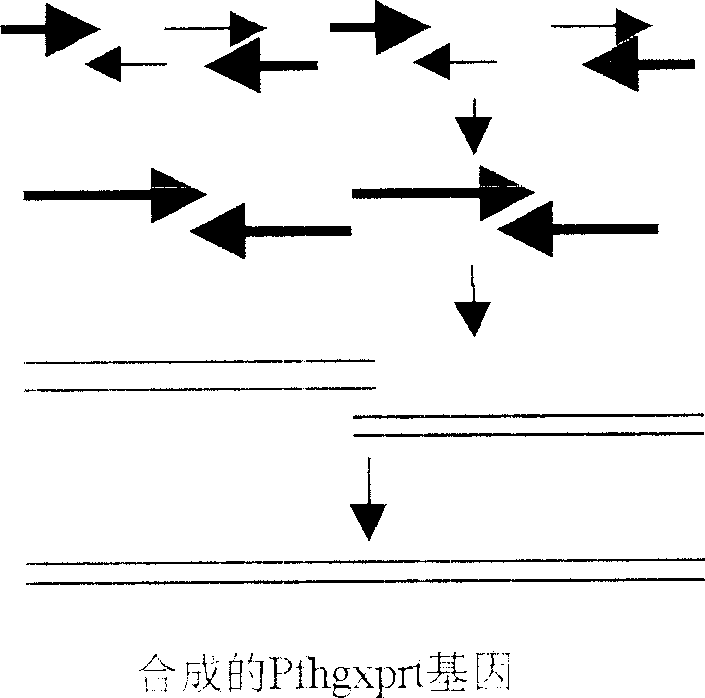
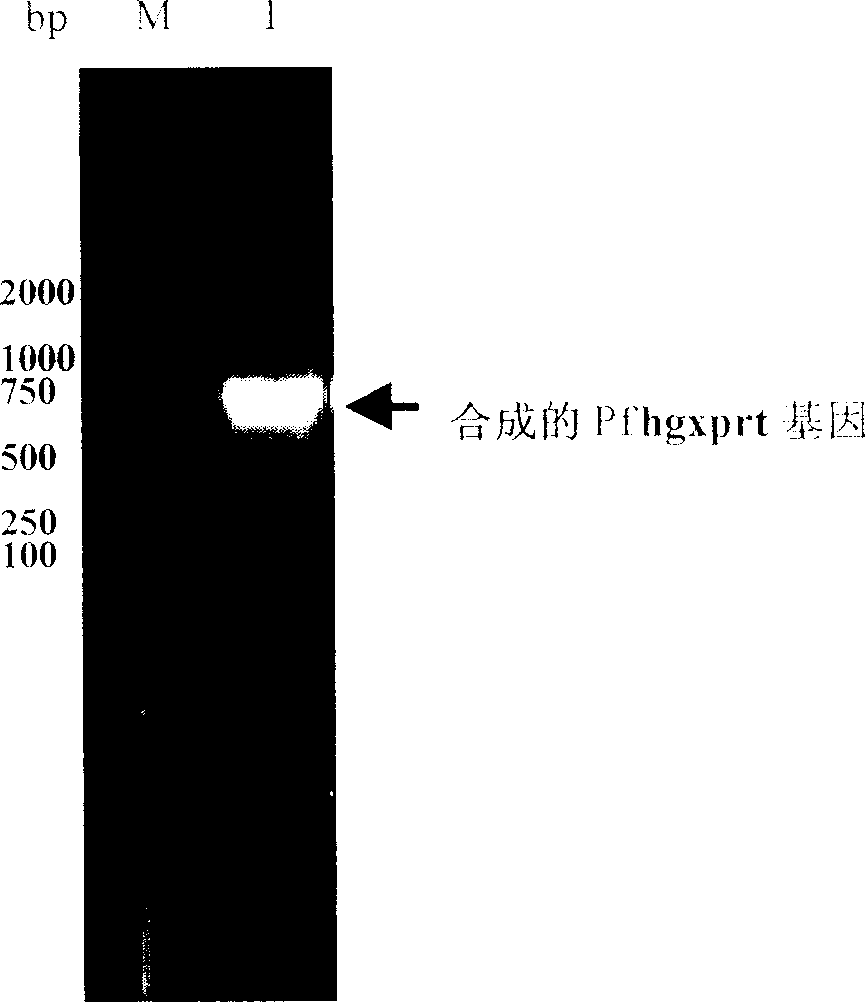
Recombinant malignant malarial parasite hypoxanthine-guanine-xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN1900274AHas ribosyl transfer functionEasy to separate and purifyPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesXanthineEnzyme kinetics
The present invention provides the recombinant protein (HGXPRT) of malignant malarial parasite hypoxanthine-uanine-xanthine ribose phosphate transferase, the recombinant protein coding DNA sequence, vector containing the DNA sequence, host cell containing the vector, gene engineering process for preparing the recombinant protein, and the use of the recombinant protein. The recombinant protein HGXPRT has excellent immunogenicity and excellent enzymic kinetic characteristic, and can induce effective malarial parasite antagonizing immune response in the immunized individual and produce efficient enzymological activity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Novel recombinant microorganism with NMN synthesis path and production method
Owner:SUZHOU BIOSYNTHETICA CO LTD
Method for preparing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide through immobilized whole-cell catalysis by taking modified diatomite as carrier
PendingCN114317515AHigh catalytic efficiencyThe catalytic process is simpleFungiZinc sulatesAmidophosphoribosyltransferaseNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a method for preparing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide through immobilized whole-cell catalysis by taking modified diatomite as a carrier. Modified diatomite subjected to acid and alkali treatment is used as an immobilization carrier, strains respectively containing polyphosphate kinase (Ppk), ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase (RKI1), ribose phosphate pyrophosphate synthase (Prps) and nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase (Nampt) are used as objects to prepare immobilized cells, and then D-ribose, ATP and nicotinamide are used as raw materials to prepare the immobilized cells. The combination of four enzymes including polyphosphate kinase, ribulose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribose phosphate pyrophosphate synthase and nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase is added for catalytic reaction synthesis of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide (beta-NMN), and the conversion rate is high. Not only are the efficiency of synthesizing beta-NMN by an enzyme method and the substrate conversion rate improved, but also the immobilized cells can be repeatedly used for multiple times.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA KINGDOMWAY PHARMA LTD +2
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN102864116BEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Application of nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor
ActiveCN102000079AGood curative effectLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderSide effectNucleotide
The invention discloses an application of a nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor. The nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor can effectively prevent or treat thrombocyte hyperfunction, and blood hypercoagulative state or thrombi, has the advantages of favorable curative effect, small side effect and high safety, and has an important meaning for treating coagulation hyperfunction diseases.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Extraction and purification method of nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase
PendingCN113684193AEasy to separateEfficient separationGlycosyltransferasesPolypeptide with His-tagPhosphoric acidTransferase
The invention discloses an extraction and purification method of nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out fermentation culture on an NAMPT production strain to obtain fermentation liquor, centrifuging, and collecting thalli in the fermentation liquor; (2) adding pure water into the thalli, adjusting the pH value to 7.2-7.4 by using ammonia water, passing through a homogenizer, centrifuging, and separating to obtain supernate; (3) sequentially carrying out activated carbon decoloration and ceramic membrane filtration treatment on the supernate to obtain filtrate; (4) adding a nonionic detergent into the filtrate to remove inclusion bodies so as to obtain crude enzyme liquid; and (5) carrying out affinity chromatography on the crude enzyme liquid by adopting a nickel column, collecting eluent, carrying out electrodialysis desalination on the eluent, concentrating, crystallizing and drying, and extracting and purifying to obtain the NAMPT. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the NAMPT can be effectively extracted and purified from the fermentation liquor containing the nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, and the yield and the purity of the NAMPT are remarkably improved.
Owner:XINTAI JIAHE BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Method for producing nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase by fermentation
ActiveCN113699128AHigh expressionAchieve scaleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for producing nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase by fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating an NAMPT production strain into a culture medium for fermentation culture under the fermentation culture conditions that the fermentation temperature is 32-34 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is 20-40%, and the fermentation culture time is 5-8 hours; and (2) reducing the temperature of the fermentation system to 21-23 DEG C, adding IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), and carrying out induced culture for 20-30 hours to obtain the NAMPT. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, large-scale and industrial production of the NAMPT can be realized.
Owner:XINTAI JIAHE BIOTECH CO LTD +1
A urea derivative as an inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase and its preparation method and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines. The invention provides a urea type derivative and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The general structural formula of the compound is as shown in formula (I) in the specification. As proved by pharmacological experiments, the compound or salt mentioned in the invention not only has quite high inhibition activity on nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase but also has high antitumor activity in vitro. The invention further provides a preparation method of the derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, as well as an application of the derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to preparation of a nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor or antitumor drugs.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
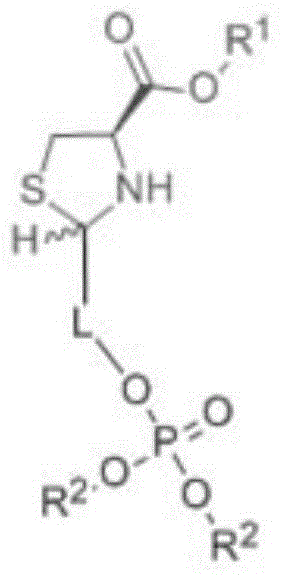
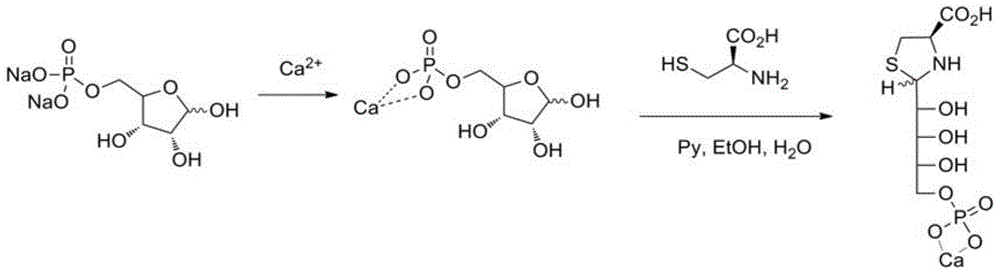
Sugar alcohol phosphate thiazolidine-4-carboxy compound and application thereof
InactiveCN104059107AImprove anti-inflammatory and detoxification abilityIncrease ATP levelsOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticPhosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a sugar alcohol phosphate thiazolidine-4-carboxy compound with the structural formula as the specification. The compound is formed by integrating three groups and can release cysteine and ribose phosphate after being absorbed in vivo. Cysteine can be used for increasing the concentration of glutathione (GSH) in cells, improving the oxidation resistance of the cells and improving the inflammation diminishing and detoxifying capabilities of a human body from inside to outside. Ribose phosphate can be used for replenishing the energy loss caused by wounds or strenuous exercise while rapidly and effectively improving the ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) level in tissues. Bodybuilding and brain-strengthening effects can be synchronously realized through the combination of carboxylate and phosphate groups and different trace elements.
Owner:魏景芬
Application of nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor
ActiveCN102000079BGood curative effectLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderTransferase inhibitorDisease
The invention discloses an application of a nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor. The nicotinamide mononucleotide ribose phosphate transferase inhibitor can effectively prevent or treat thrombocyte hyperfunction, and blood hypercoagulative state or thrombi, has the advantages of favorable curative effect, small side effect and high safety, and has an important meaning for treating coagulation hyperfunction diseases.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Fusion enzyme for producing nicotinamide mononucleotide and application thereof
PendingCN114164190AIncrease productionSimplify the process of production purificationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliIn vitro transformation
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a fusion enzyme for producing nicotinamide mononucleotide and application thereof, the amino acid sequence of the fusion enzyme is formed by combining nicotinamide phosphoribose transferase, ribose phosphate pyrophosphate kinase and a connecting peptide, and combining the nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase and the ribosyl pyrophosphate kinase into a fusion enzyme through a connecting peptide. The fusion enzyme gene can be transformed into escherichia coli or bacillus subtilis, and nicotinamide mononucleotide is produced through fermentation by taking the bacterium as a strain and nicotinamide as a substrate; or after the fusion enzyme is expressed in escherichia coli or bacillus subtilis, the fusion enzyme is extracted and purified, nicotinamide mononucleotide is produced through in-vitro conversion, and the fusion enzyme can remarkably improve the production efficiency of the nicotinamide mononucleotide.
Owner:南宁邦尔克生物技术有限责任公司
Succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and method for fermenting and producing succinic acid
InactiveCN102643774BIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and a method for fermenting and producing succinic acid. Bacterial strains of the succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium are classified and named as Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) BA306 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012103. A construction process mainly comprises inactivating or knocking phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase genes and ptsG genes in a phosphoric acid movement system, conducting excessive coexpression on phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase and niacin ribose phosphate transferring enzyme, enabling recombination of colon bacillus to be capable of efficiently using monosaccharide of glucose, xylose, arabinose, fructose and the like, simultaneously efficiently using mixed sugar and cellulose hydrolysate in various proportions for growth, and substantially improving combined efficiency of the succinic acid. A fermentation process adopts a two-stage fermentation mode, biomass liveweight is improved in an aerobic stage, and fermentation and acid production are carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Method for producing technical grade ribose phosphate, food grade ribose phosphate and industry ammonium diacid phosphate using wet-process ribose phosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing industrial-grade phosphoric acid, food-grade phosphoric acid and industrial monoammonium phosphate with wet-process phosphoric acid. Using wet-process phosphoric acid as raw material, the wet-process phosphoric acid is subjected to a series of chemical precipitation + organic solvent extraction + concentration + recrystallization, etc. Composite purification technology prepares industrial-grade phosphoric acid and food-grade phosphoric acid respectively; at the same time, the present invention uses partially purified dilute phosphoric acid to prepare industrial monoammonium phosphate. The co-production of industrial-grade phosphoric acid, food-grade phosphoric acid and industrial monoammonium phosphate in the present invention enables rational graded utilization of wet-process phosphoric acid, increases the added value of phosphorus, and further develops downstream industrial-grade and food-grade phosphates.
Owner:中化重庆涪陵化工有限公司
A kind of preparation method of phosphoric sugar alcohol tetrahydrothiazole-4-carboxylic acid compound
The invention relates to a preparation method of a sugar alcohol phosphate thiazolidine-4-carboxy compound with the structural formula as the specification. The compound is formed by integrating three groups and can release cysteine and ribose phosphate after being absorbed in vivo. Cysteine can be used for increasing the concentration of glutathione (GSH) in cells, improving the oxidation resistance of the cells and improving the inflammation diminishing and detoxifying capabilities of a human body from inside to outside. Ribose phosphate can be used for replenishing the energy loss caused by wounds or strenuous exercise while rapidly and effectively improving the ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) level in tissues. Bodybuilding and brain-strengthening effects can be synchronously realized through the combination of carboxylate and phosphate groups and different trace elements.
Owner:魏景芬
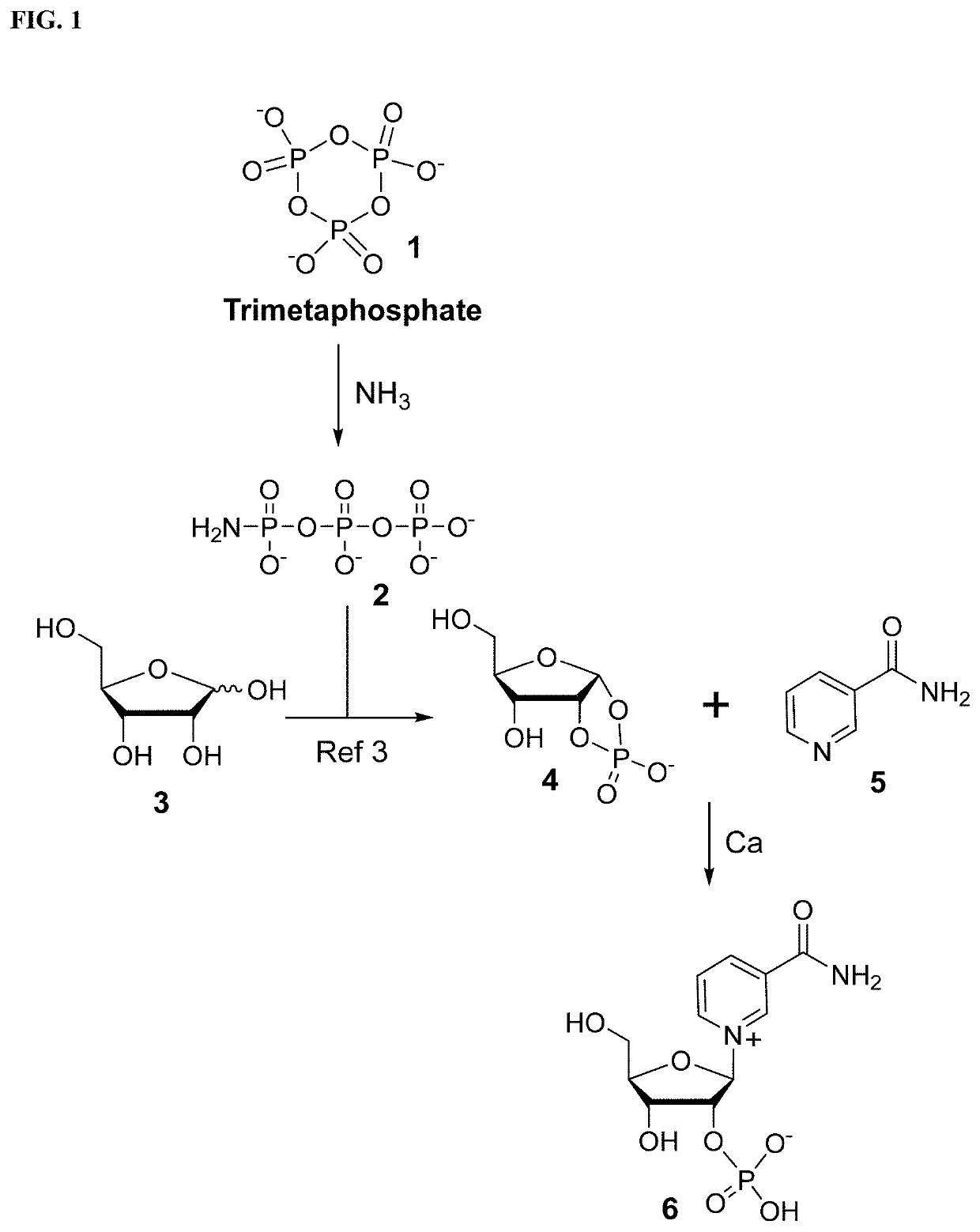
Synthesis and stabilization of nicotinamide ribose and its derivatives
Nicotinamide ribose has many applications, including as a dietary supplement. This invention convers a process to prepare nicotinamide ribose it in its phosphorylated form. The instant invention is based on the discovery that nicotinamide ribose phosphate emerges in stable form by direct reaction of ribose-1,2-cyclic phosphate. It is based on the further conversion of the phosphorylated nicotinamide ribose product to unphosphorylated nicotinamide ribose upon treatment with an enzymatic phosphatase, most preferably in buffer containing borate. It is based on the further discovery that compositions of nicotinamide ribose with borate slow the decomposition of nicotinamide ribose, and therefore is more useful than compositions of nicotinamide ribose without borate.
Owner:KIM HYO JOONG +2
Novel nucleic acid based on small RNA interference principle
The invention relates to an alternating double strand of nucleic acid based on an RNA interference principle. Bases of the sequence of the alternating double-stranded nucleic acid consist of adenine A, guanine G, thymine T, uracil U and cytosine C. The bases are formed by alternately connecting ribose phosphate and desoxyribose phosphate. The double strand can form complete pairing or most of pairing, and each strand is 18 to 30 bases in length. The best base sequence in the first strand is 5'-GAUUUAGCCAAGAAGUUCAGU-3', and the best base sequence in the second strand is 5'-UGAACUUCUUGGCUAAAUCGC-3'. The double strand can interfere with ribonucleotide reductase so as to have an anti-tumor effect, wherein the bases U and T are replaceable.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com