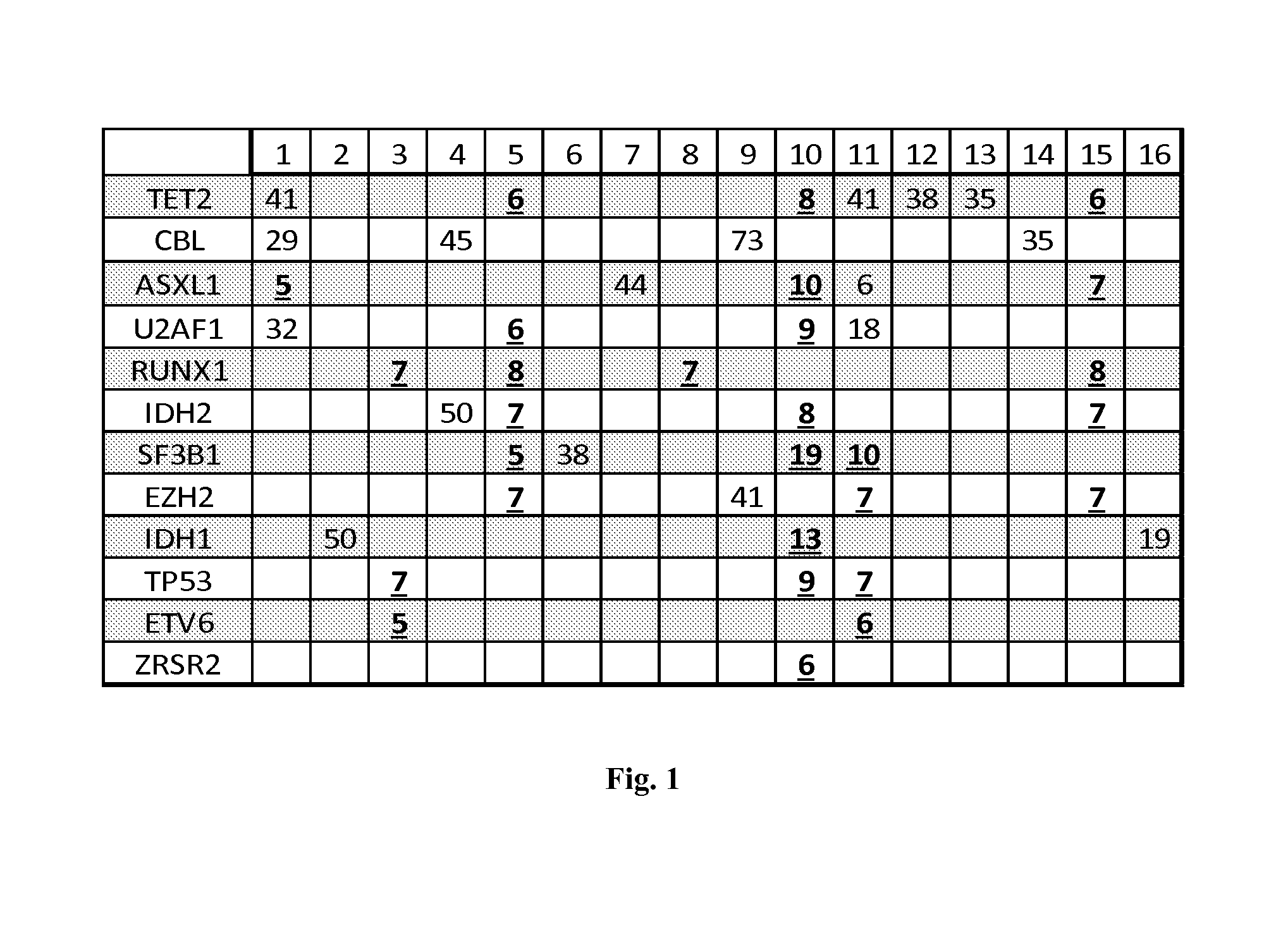
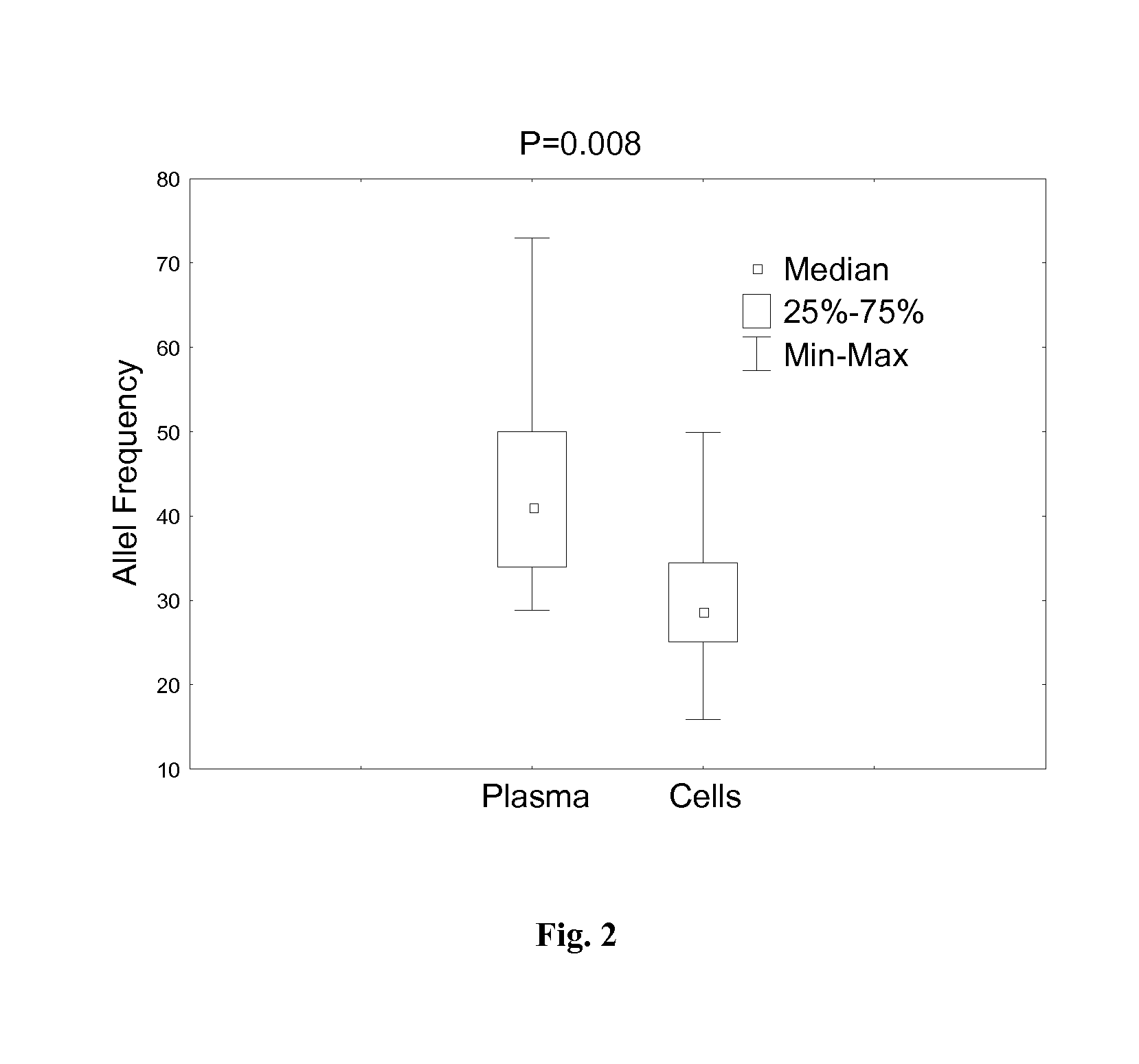
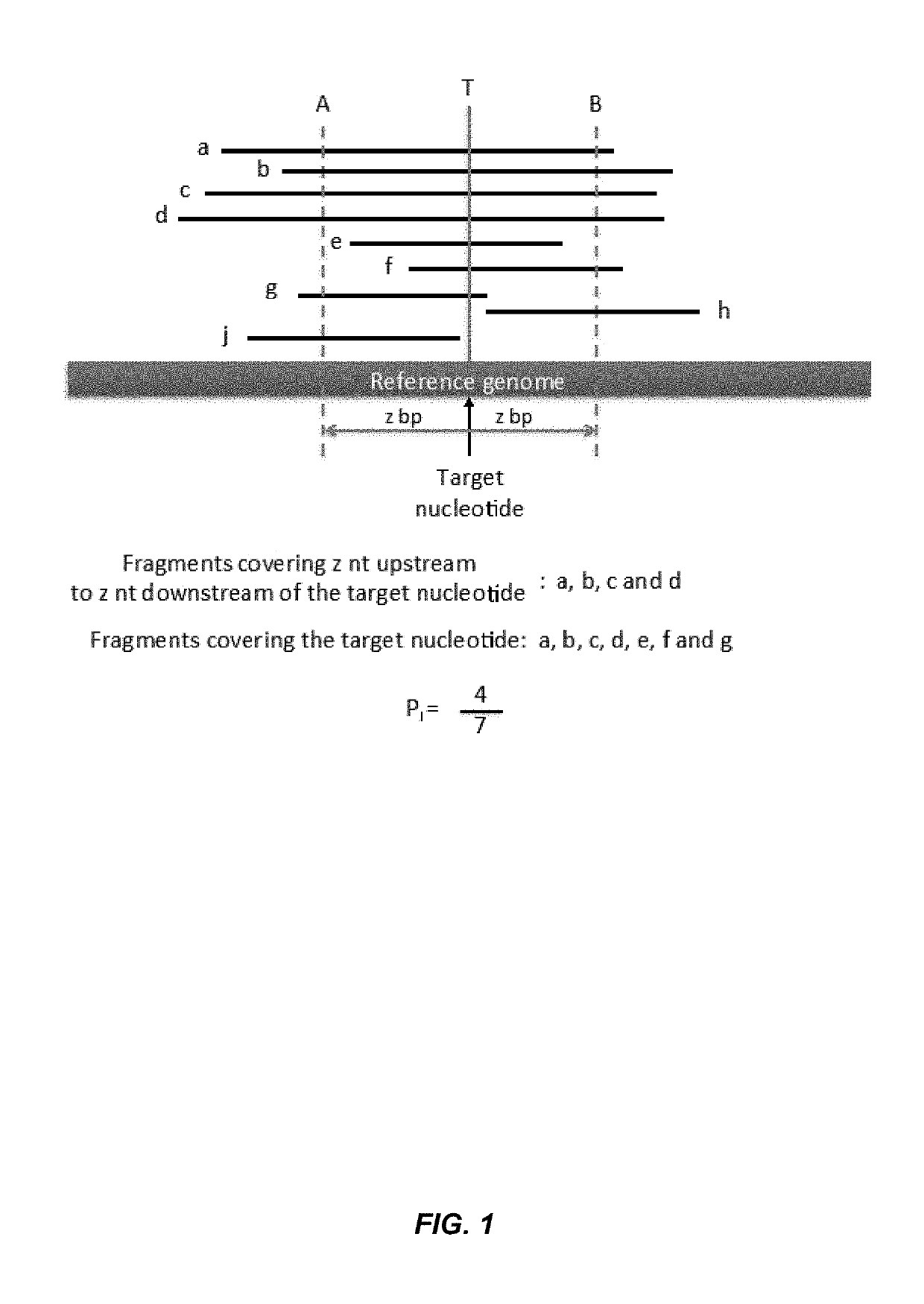
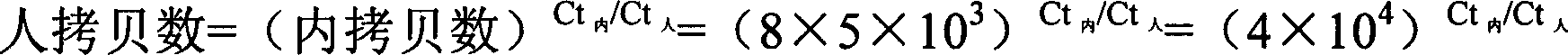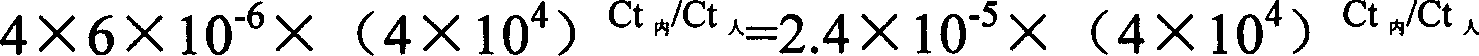Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Plasma dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
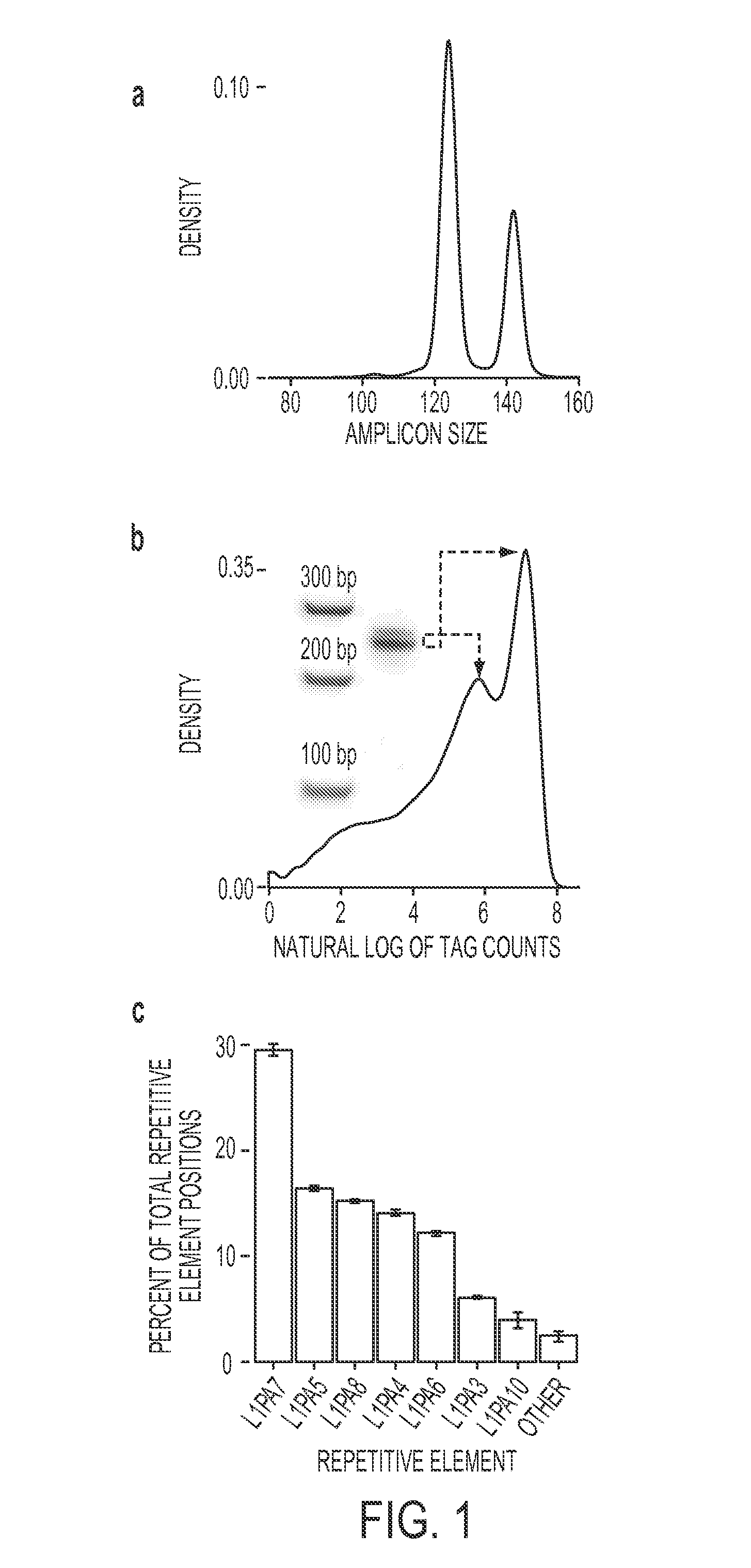
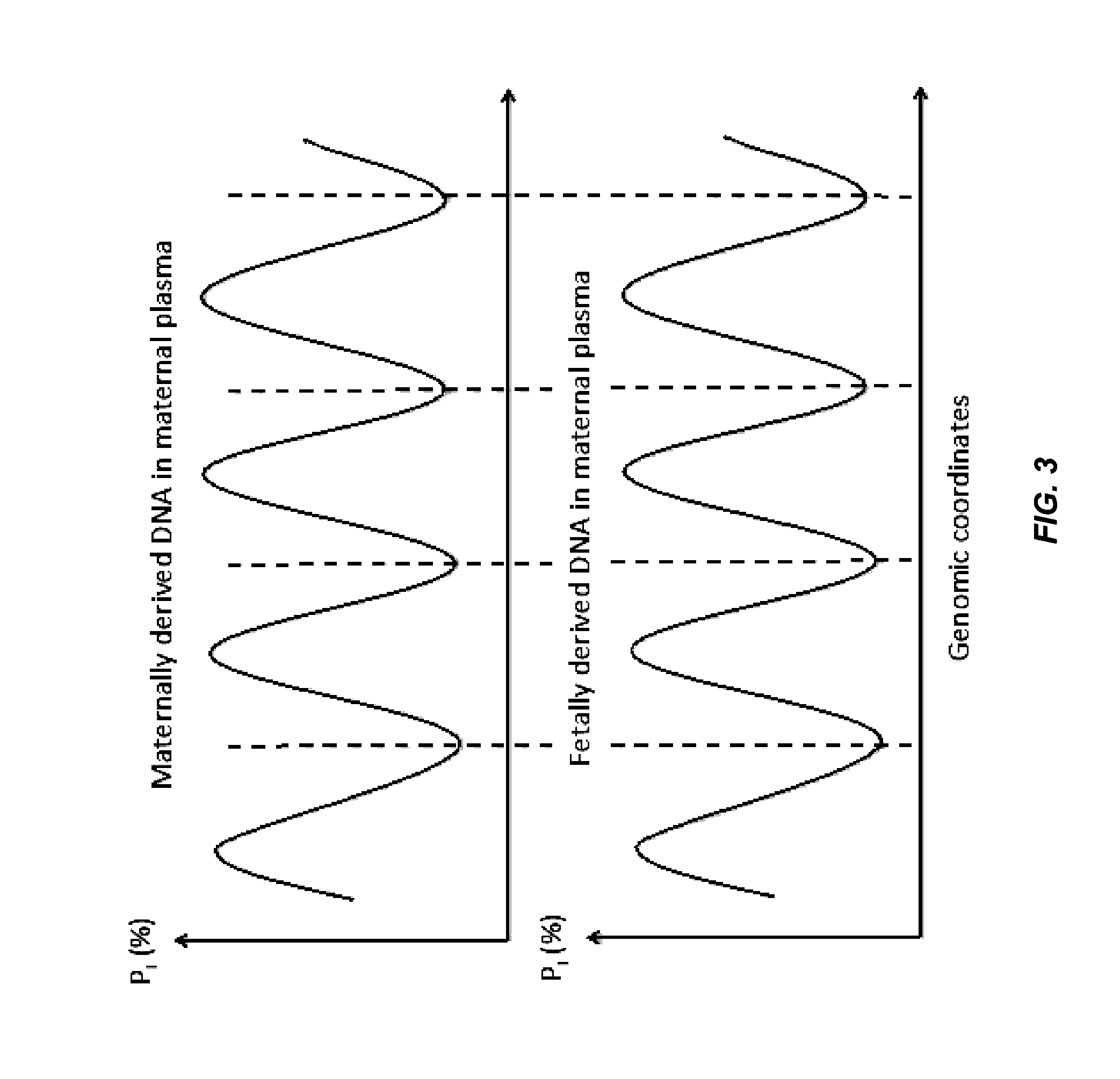
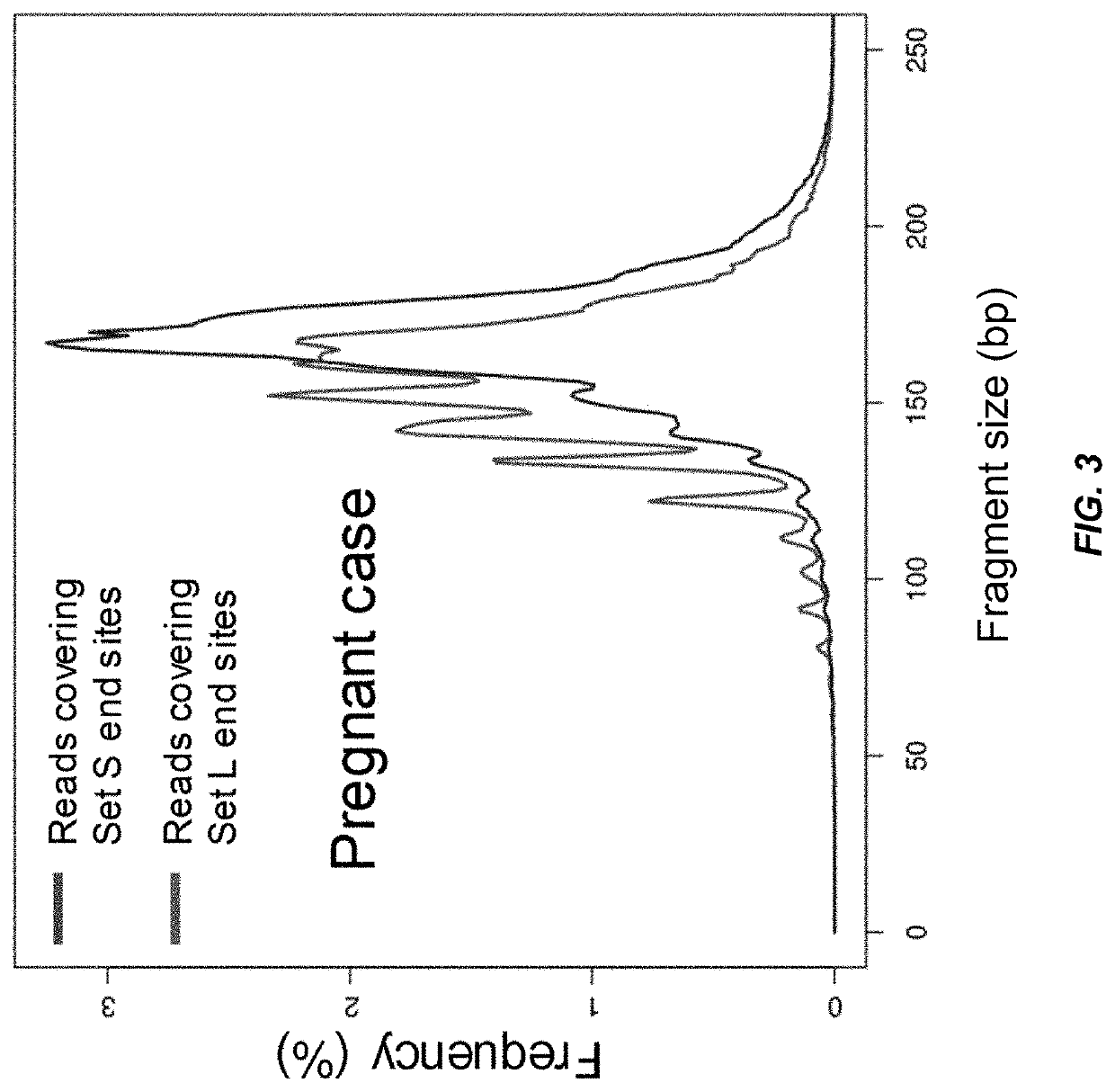
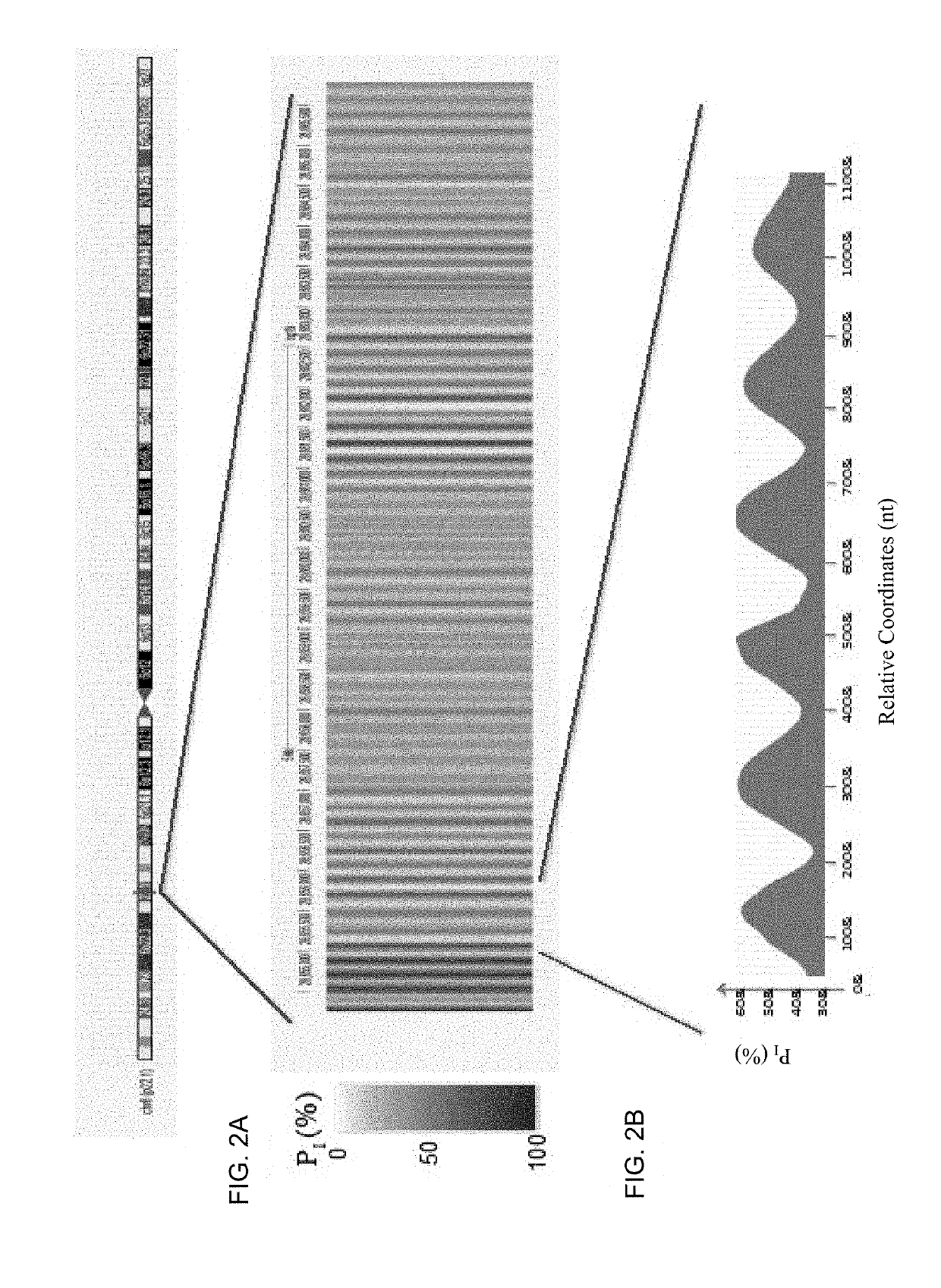
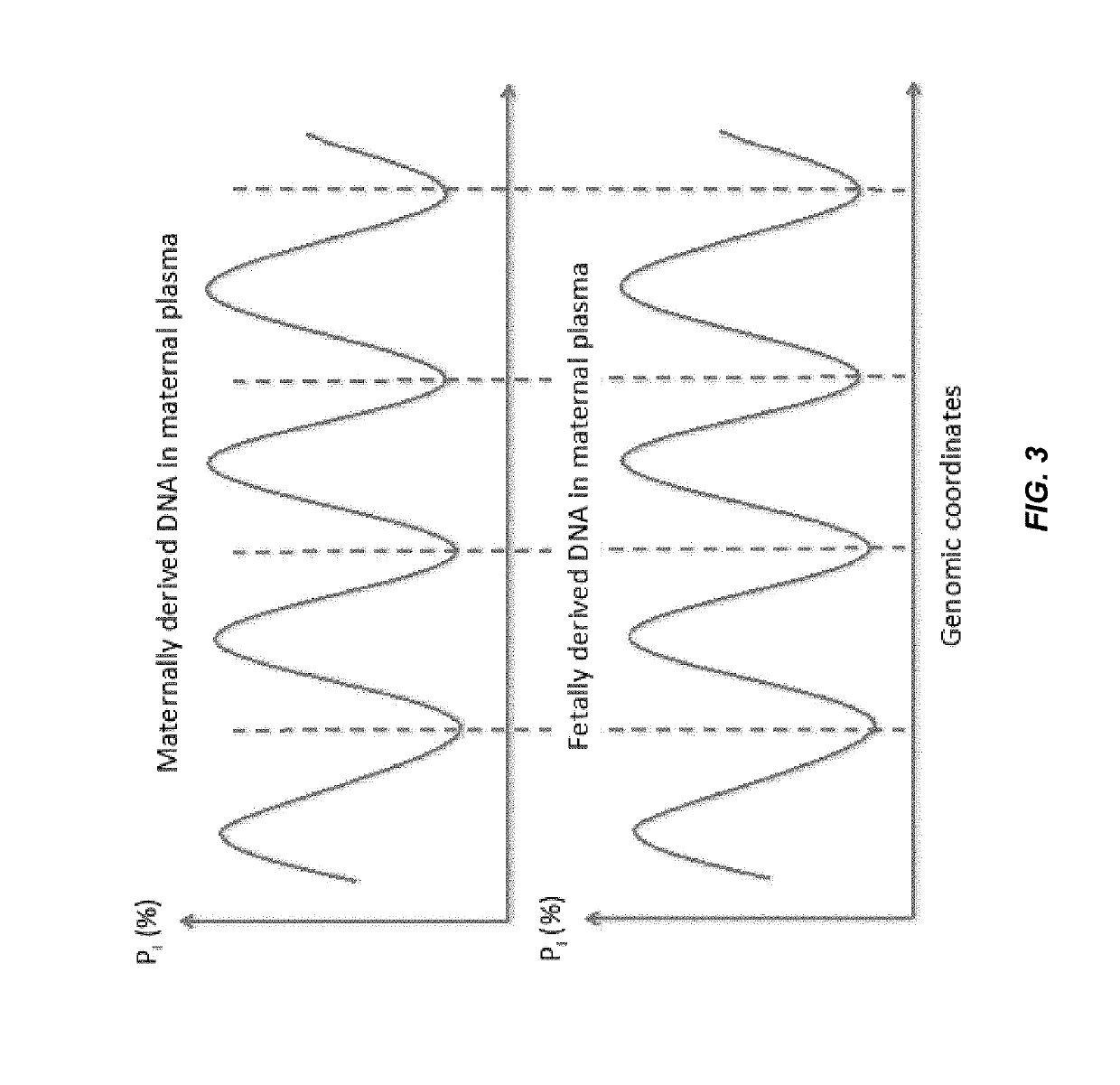
Plasma consists of DNA released from multiple tissues within the body. Using genome-wide bisulfite sequencing of plasma DNA, we obtained a bird’s eye view of the identities and contributions of these tissues to the circulating DNA pool.
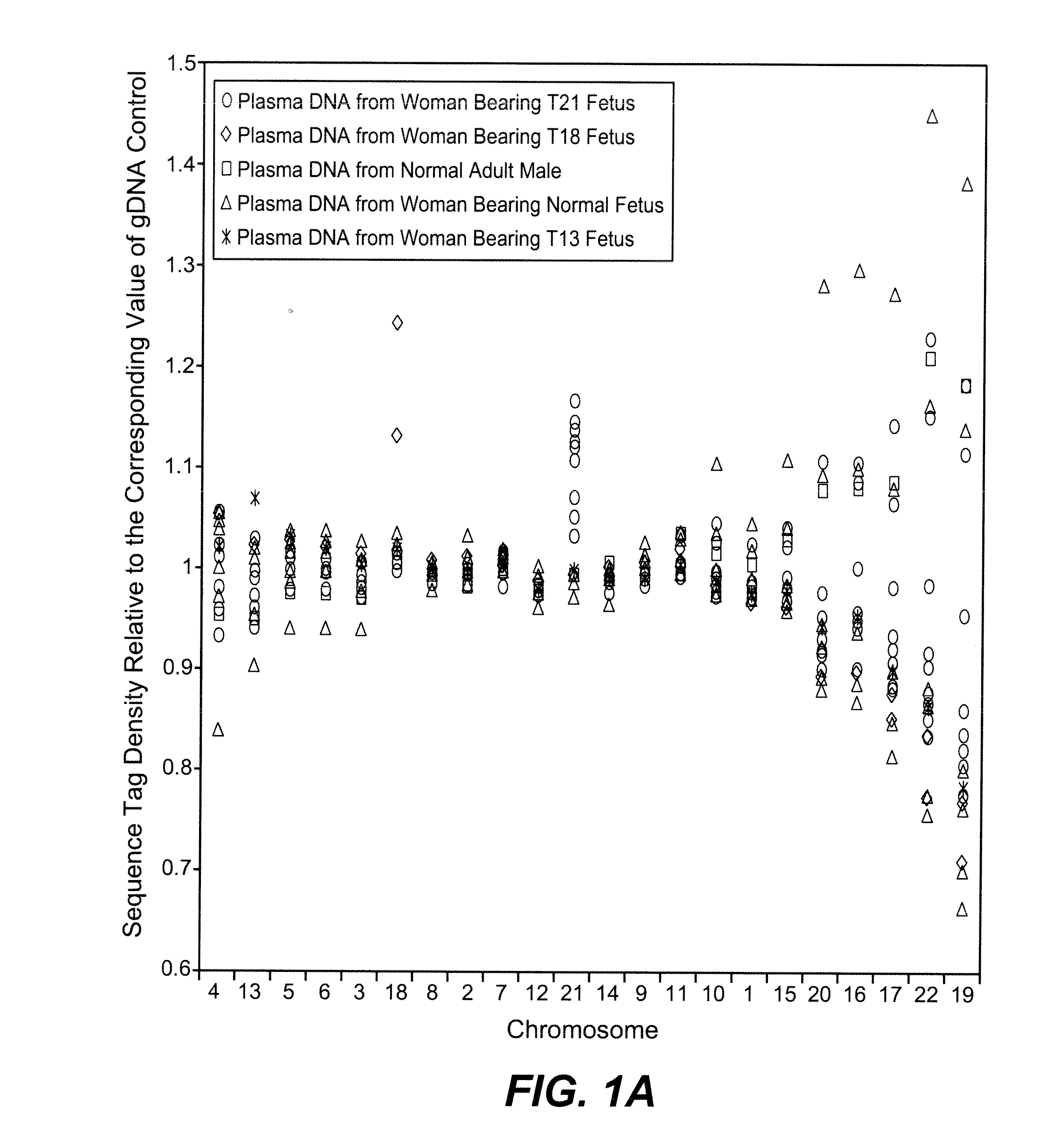
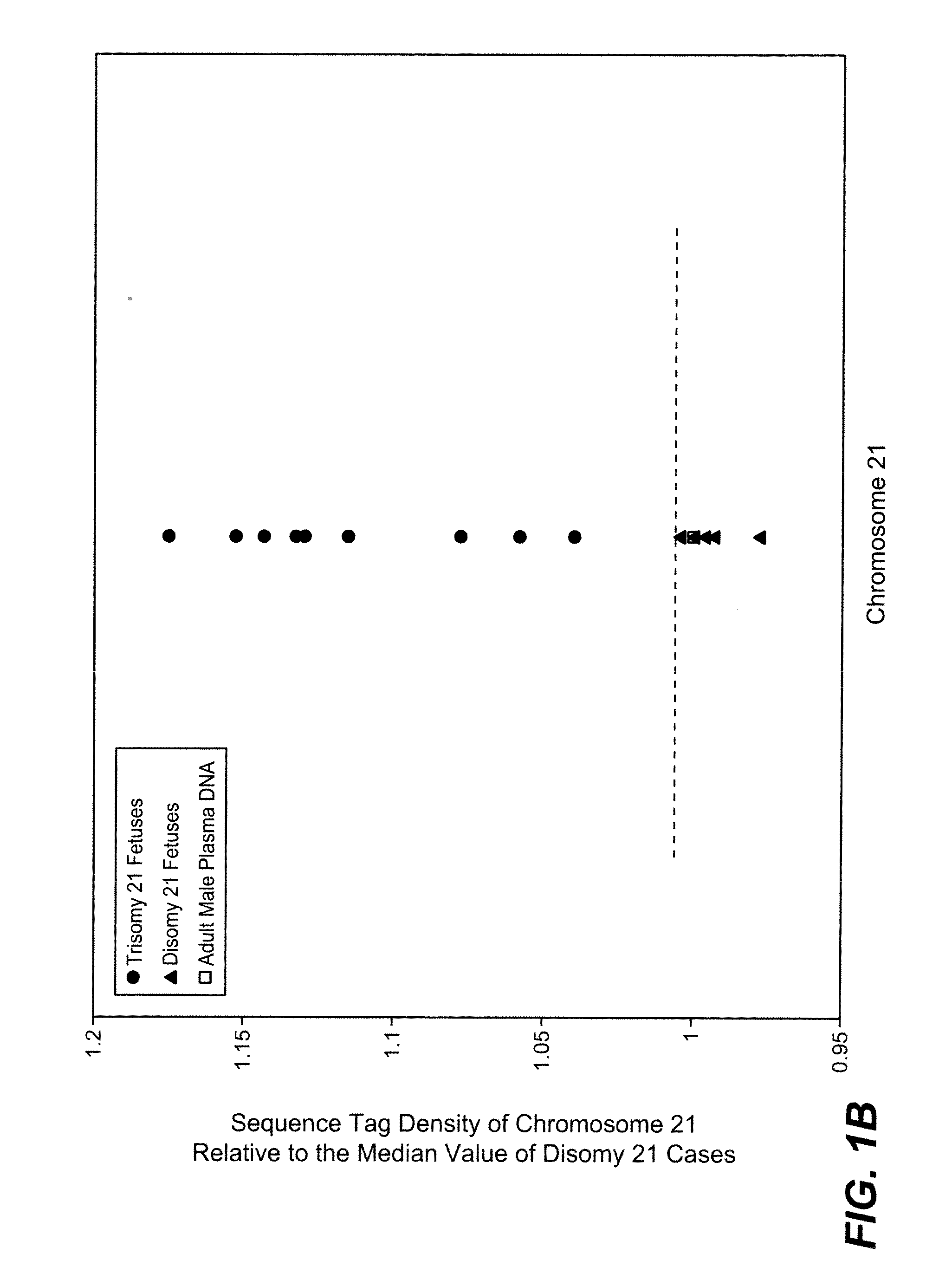
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
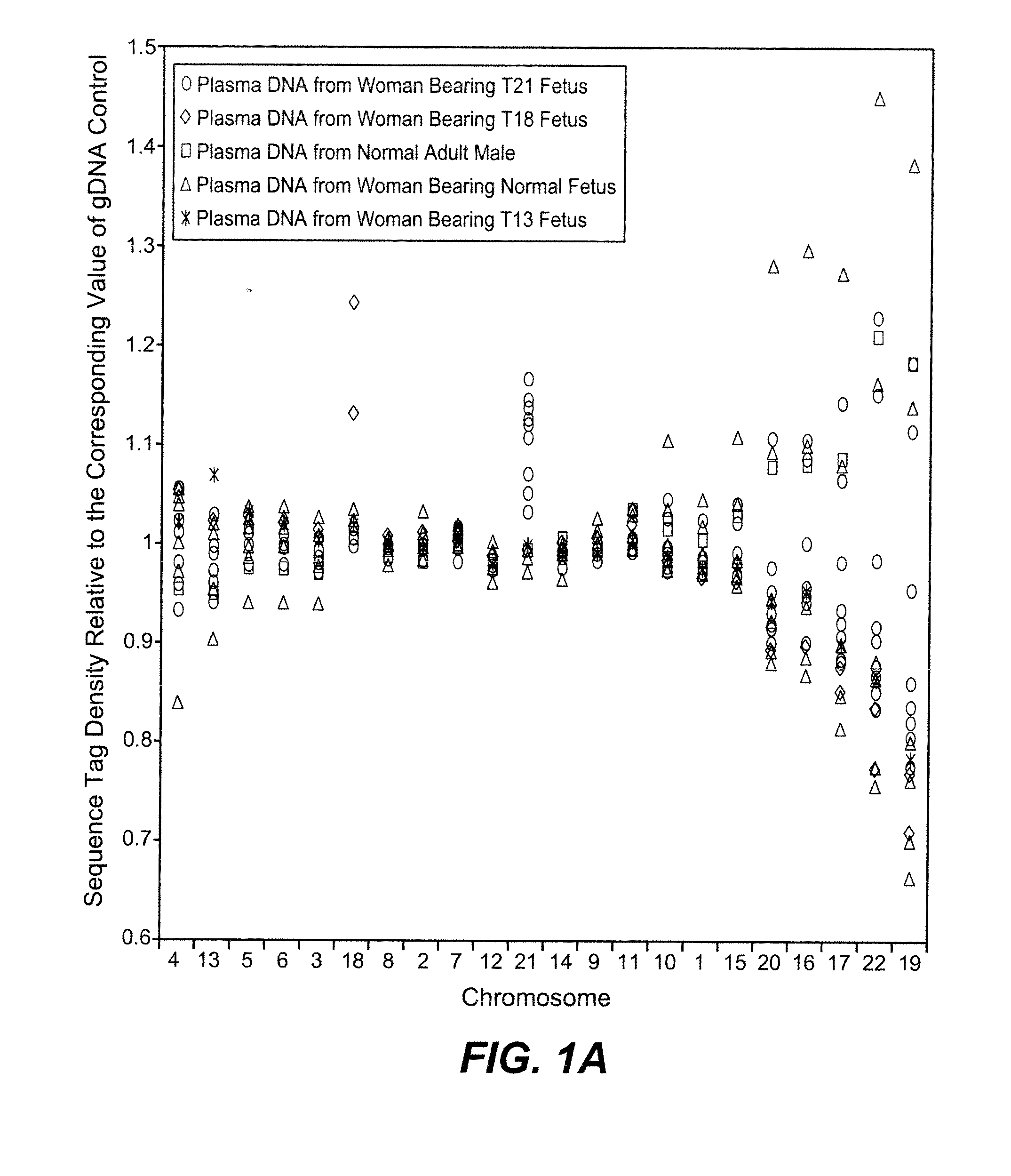
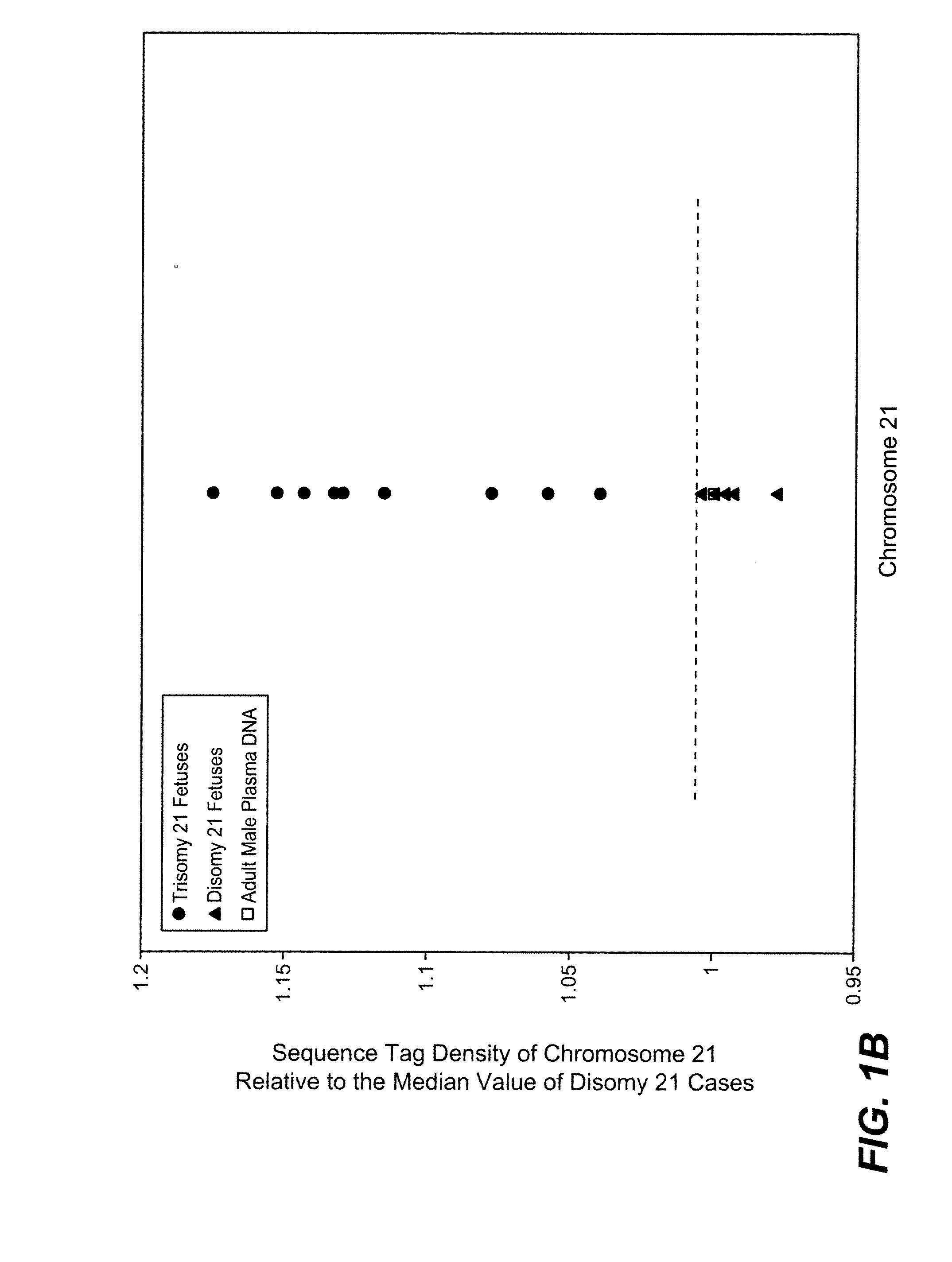
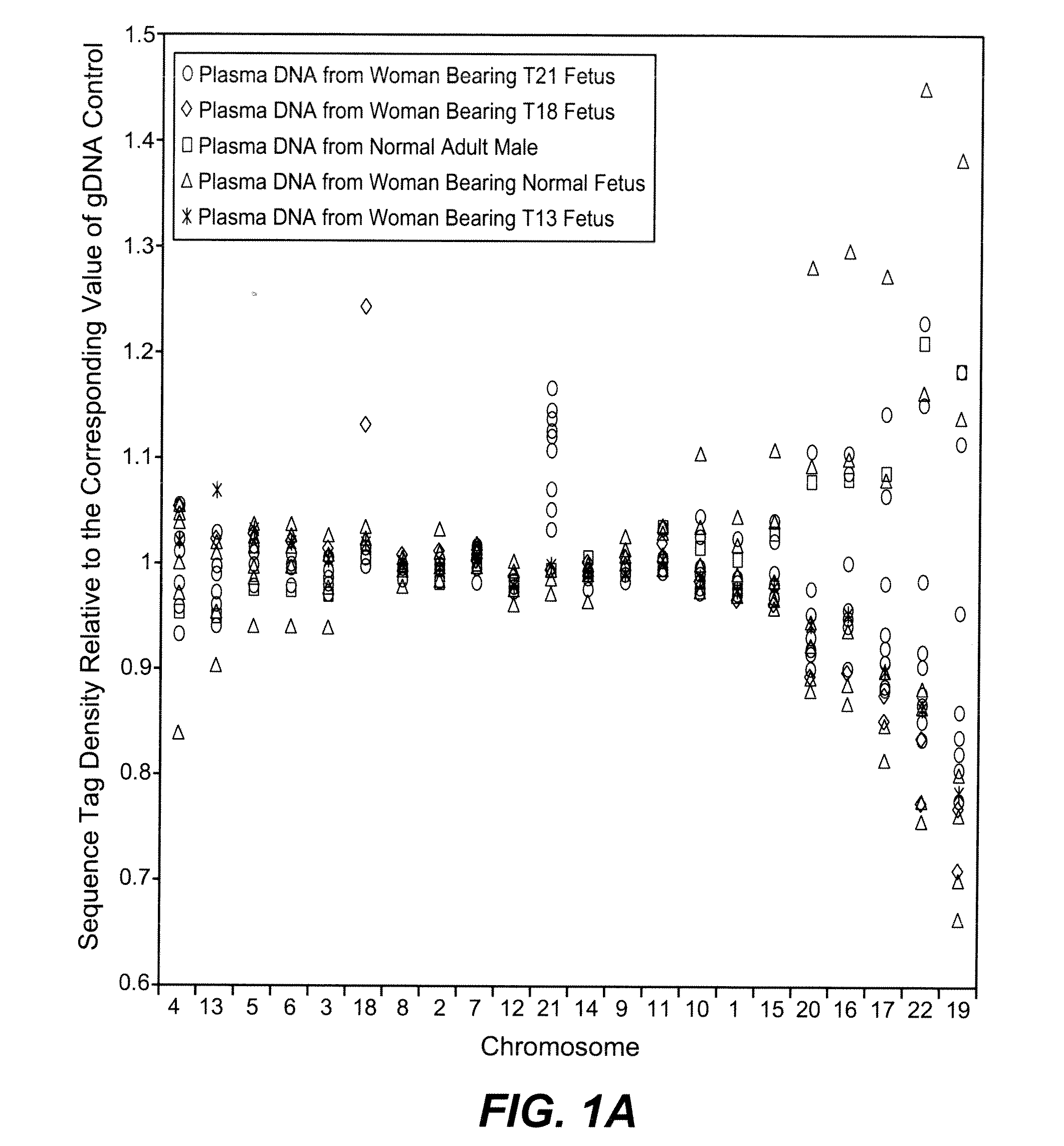
InactiveUS20100112575A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
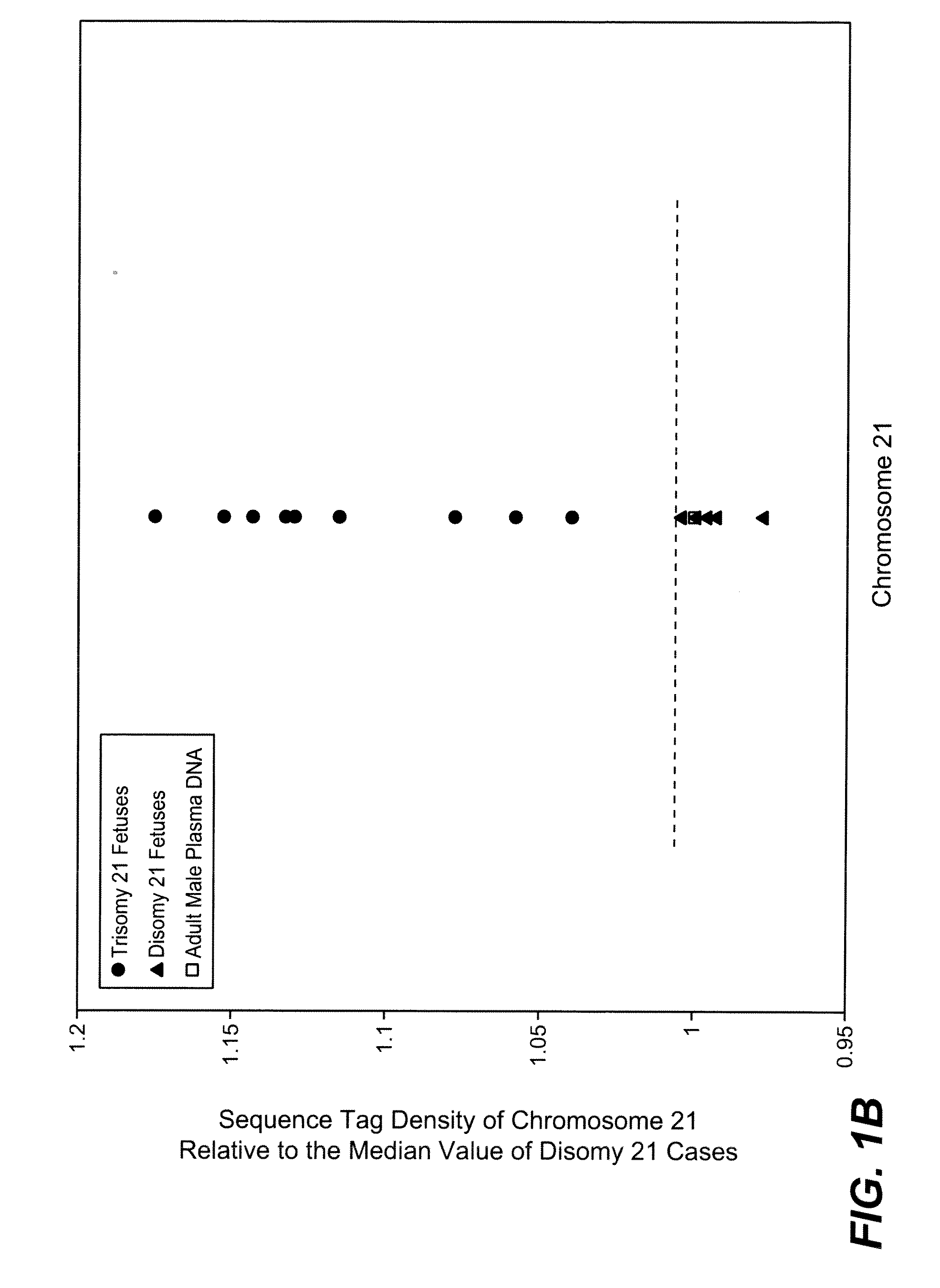
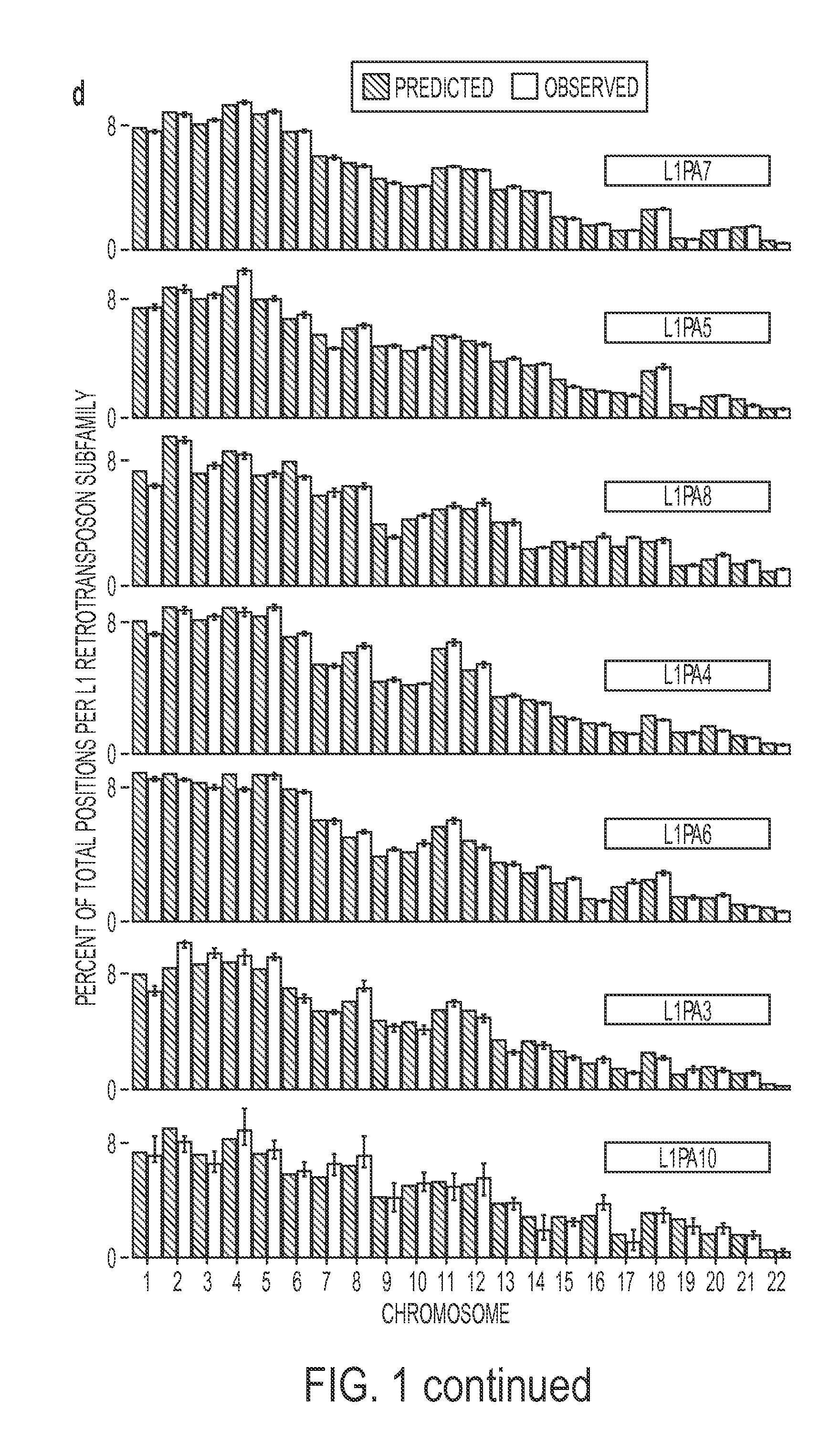
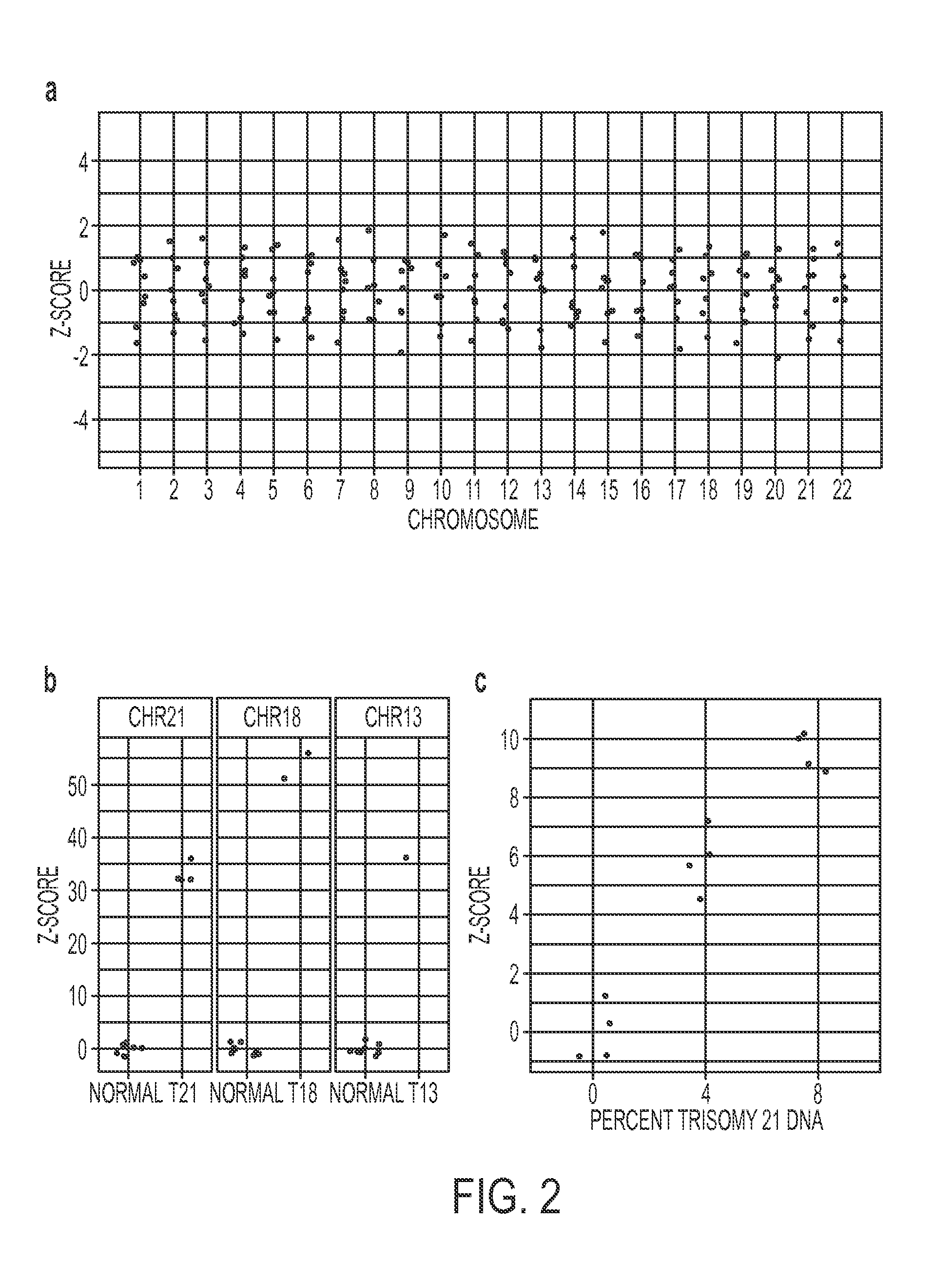
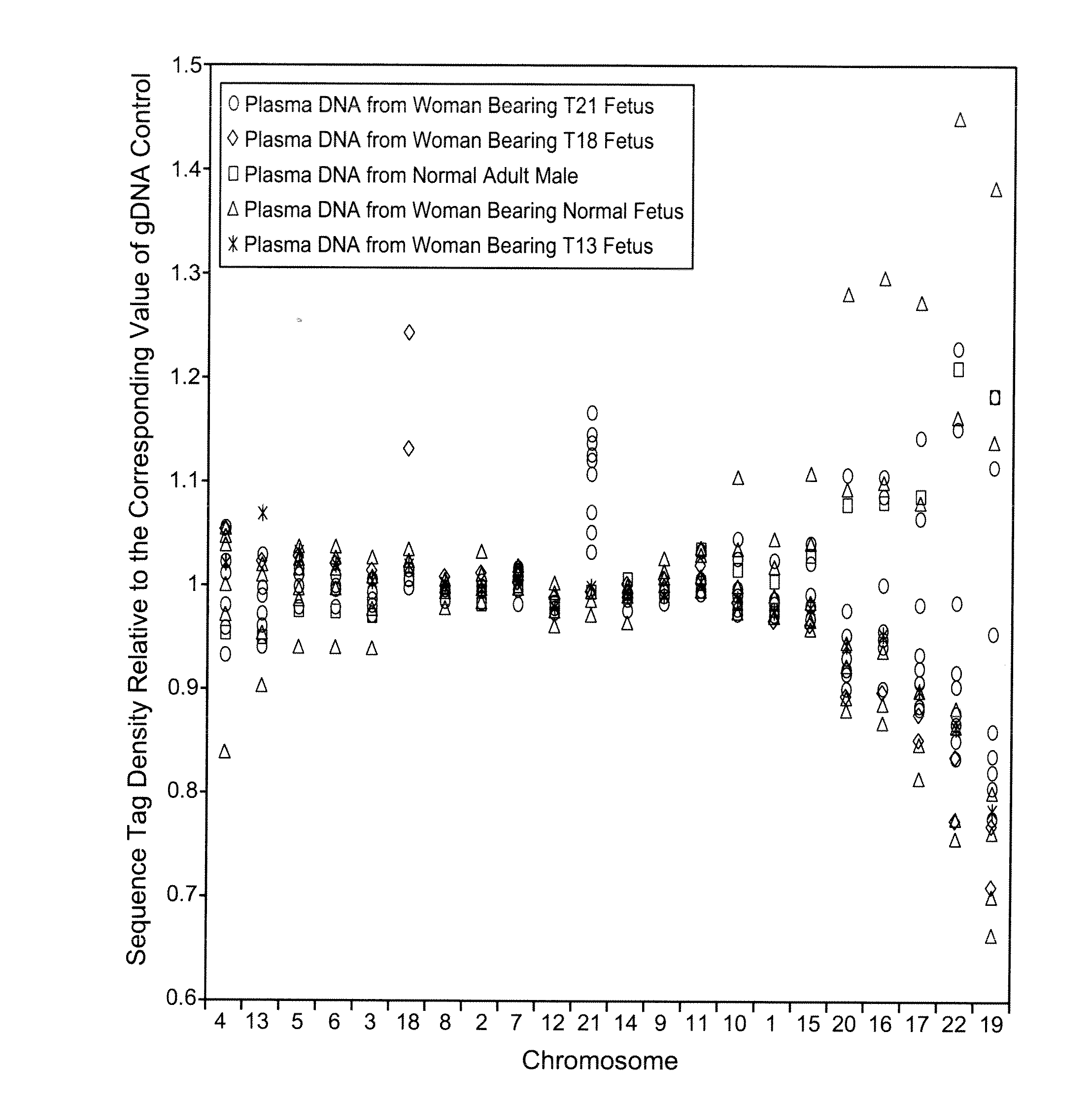
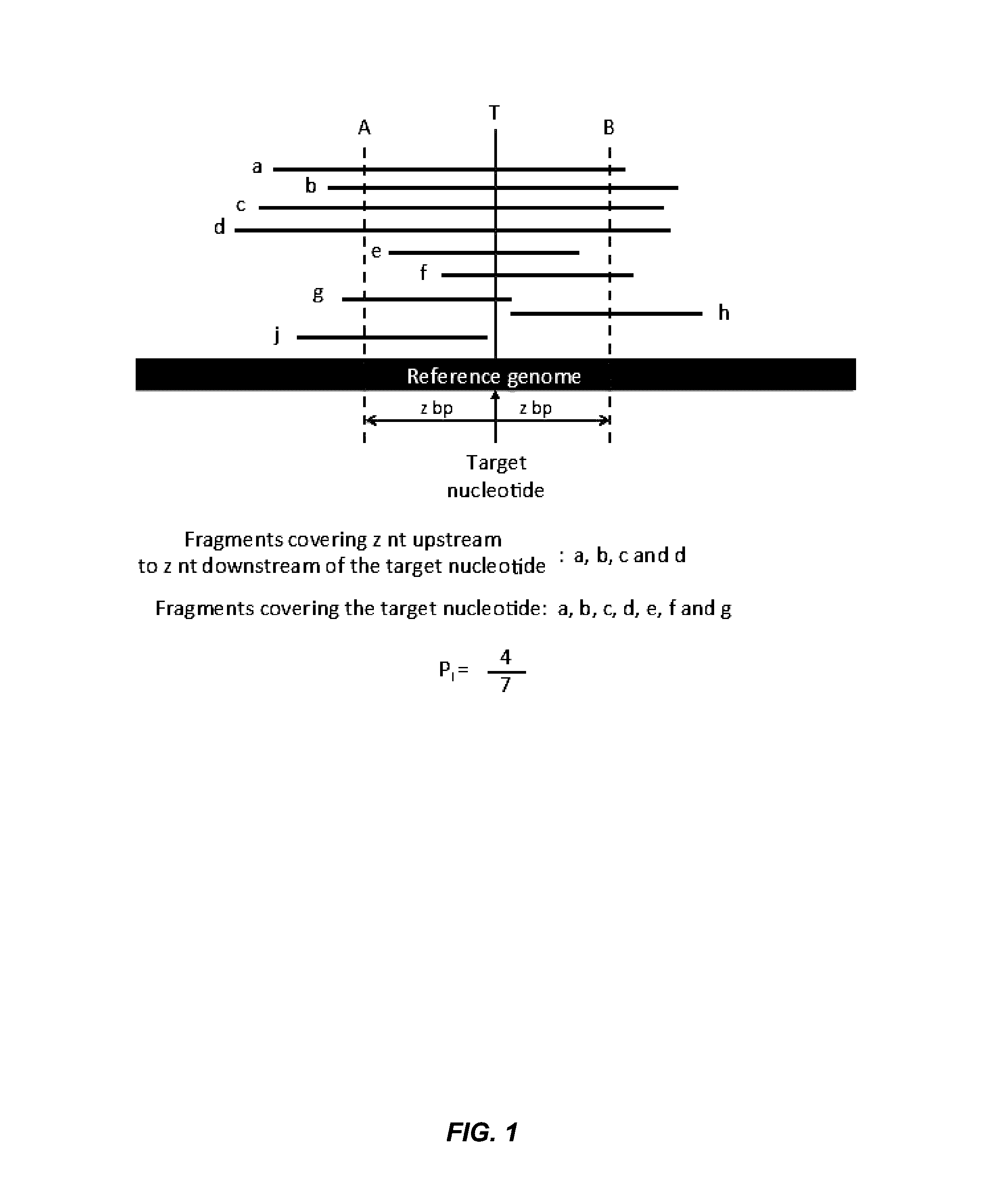
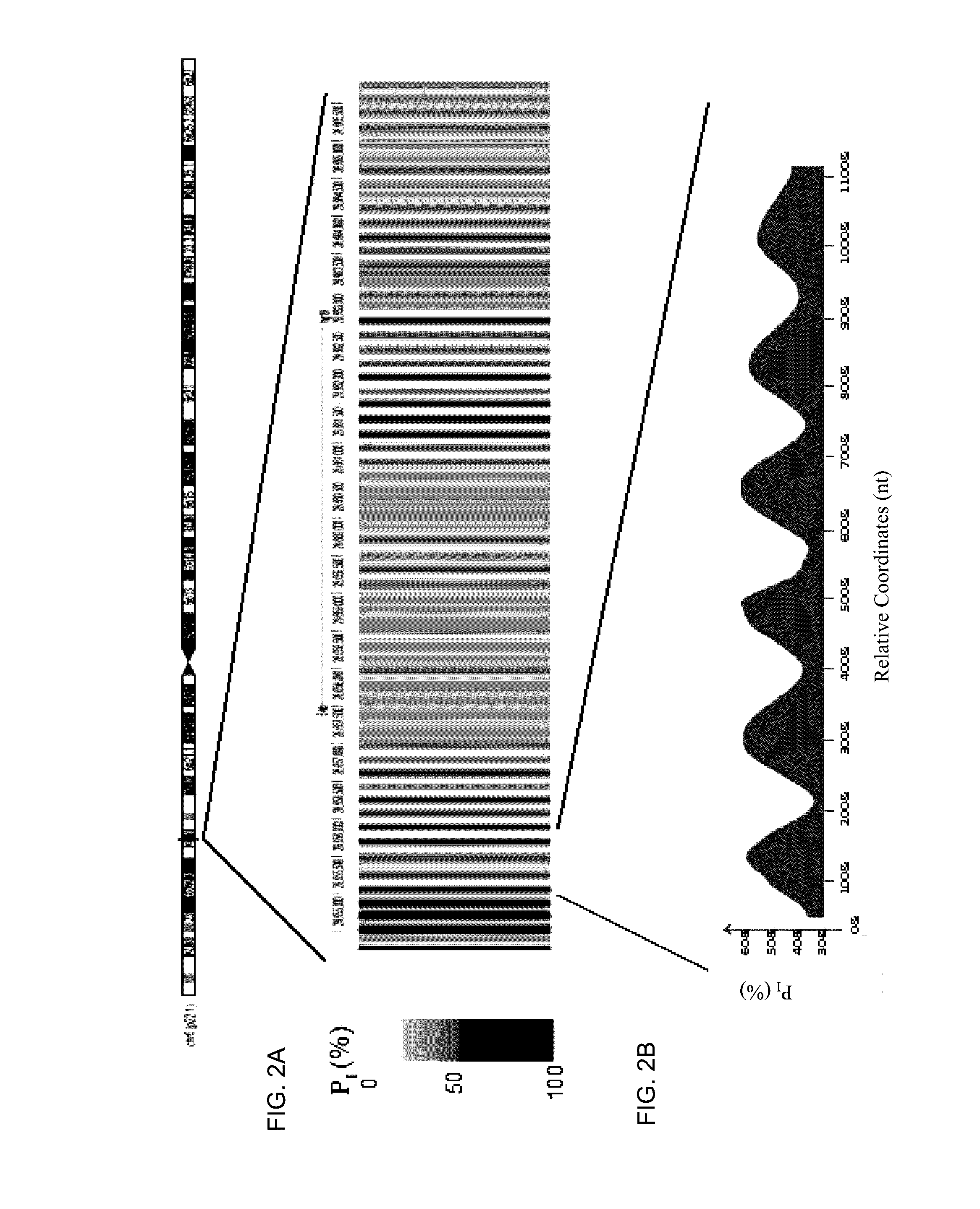
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20100138165A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mutational analysis of plasma DNA for cancer detection
ActiveUS20140100121A1Accurate parameterLevel of heterogeneity of tumorsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation frequencyBlood plasma
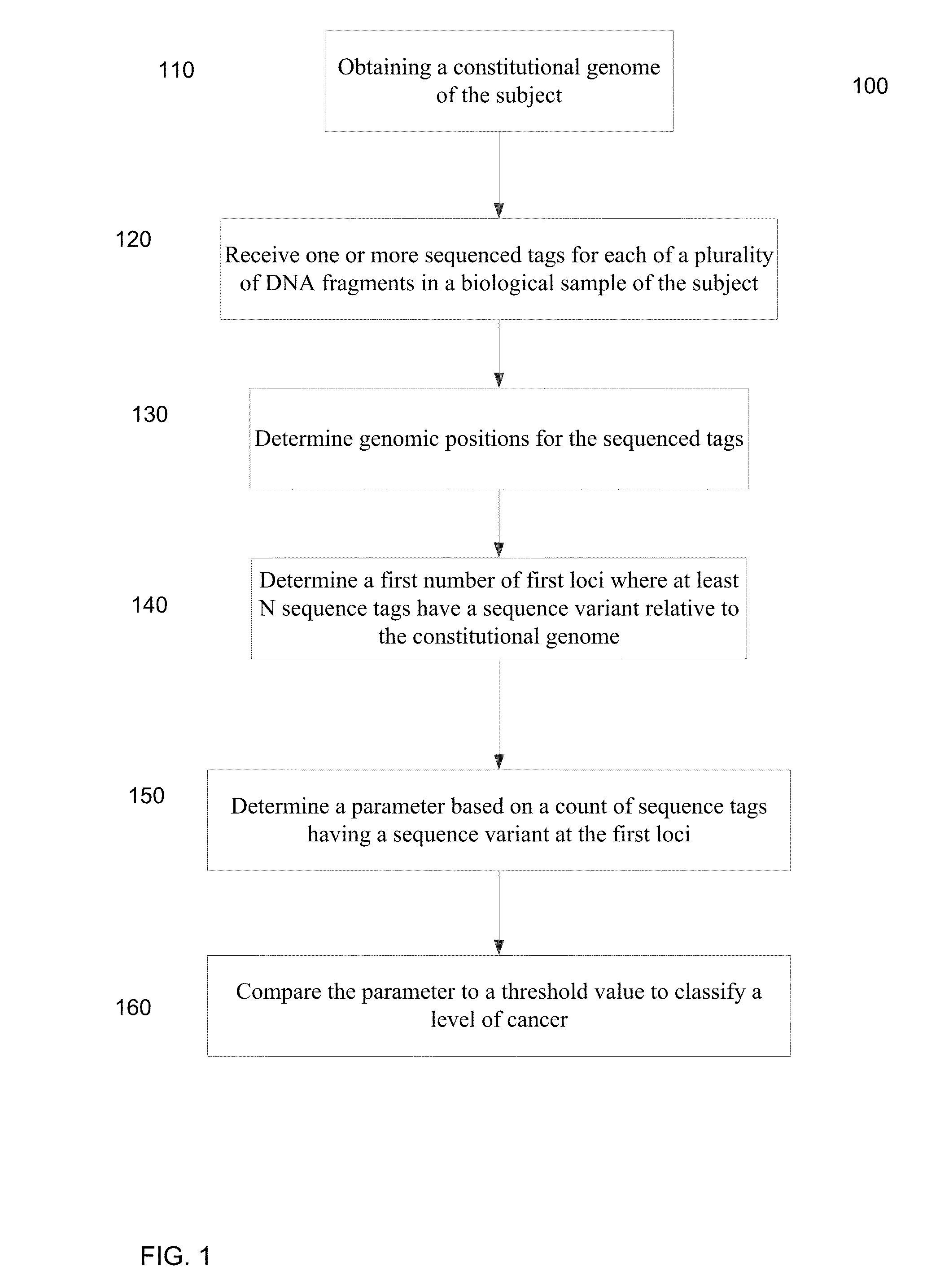
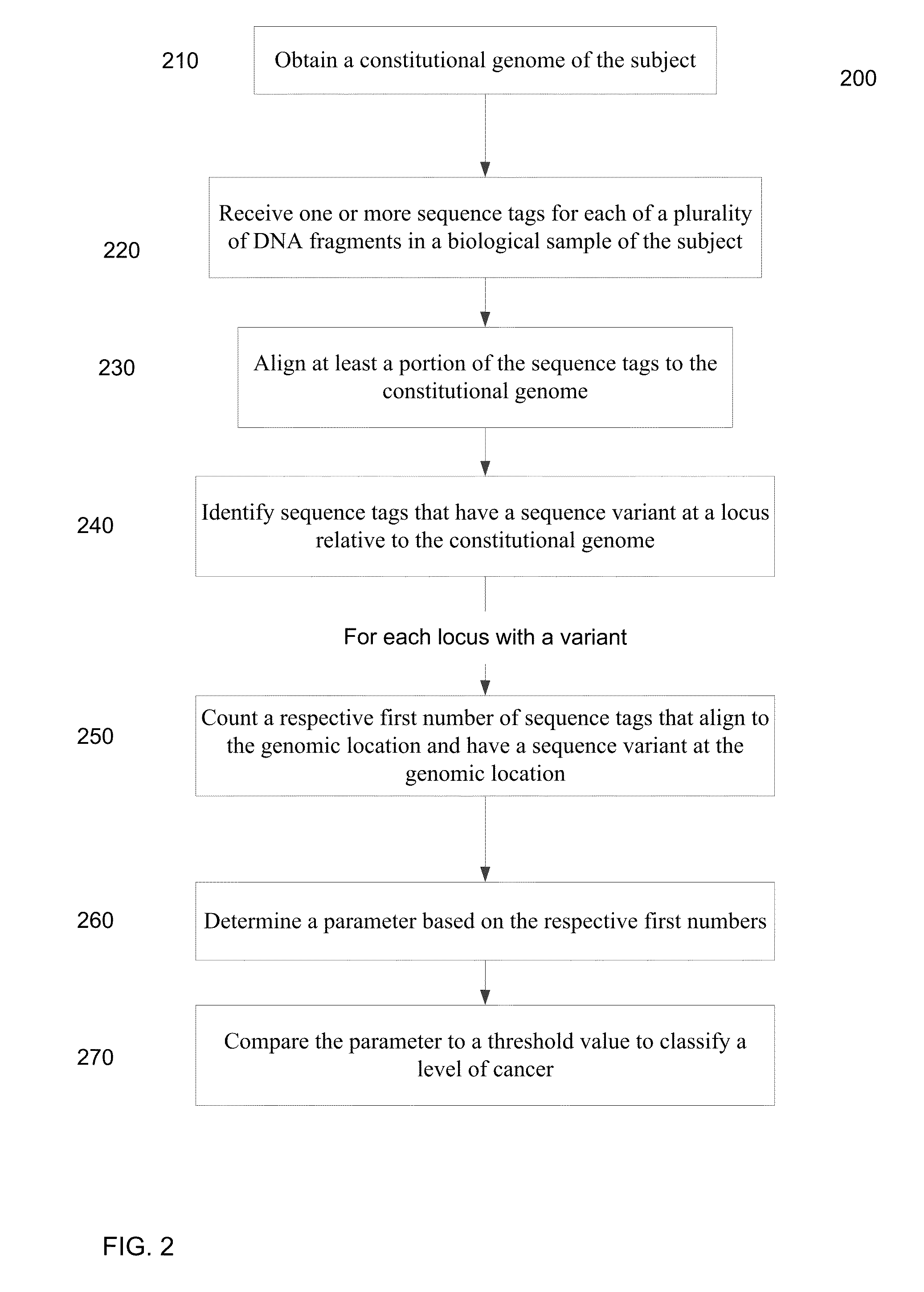
A frequency of somatic mutations in a biological sample (e.g., plasma or serum) of a subject undergoing screening or monitoring for cancer, can be compared with that in the constitutional DNA of the same subject. A parameter can derived from these frequencies and used to determine a classification of a level of cancer. False positives can be filtered out by requiring any variant locus to have at least a specified number of variant sequence reads (tags), thereby providing a more accurate parameter. The relative frequencies for different variant loci can be analyzed to determine a level of heterogeneity of tumors in a patient.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Rapid aneuploidy detection
ActiveUS20150051085A1Assessing genomic copy number sensitively and rapidlyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell freeTrisomy
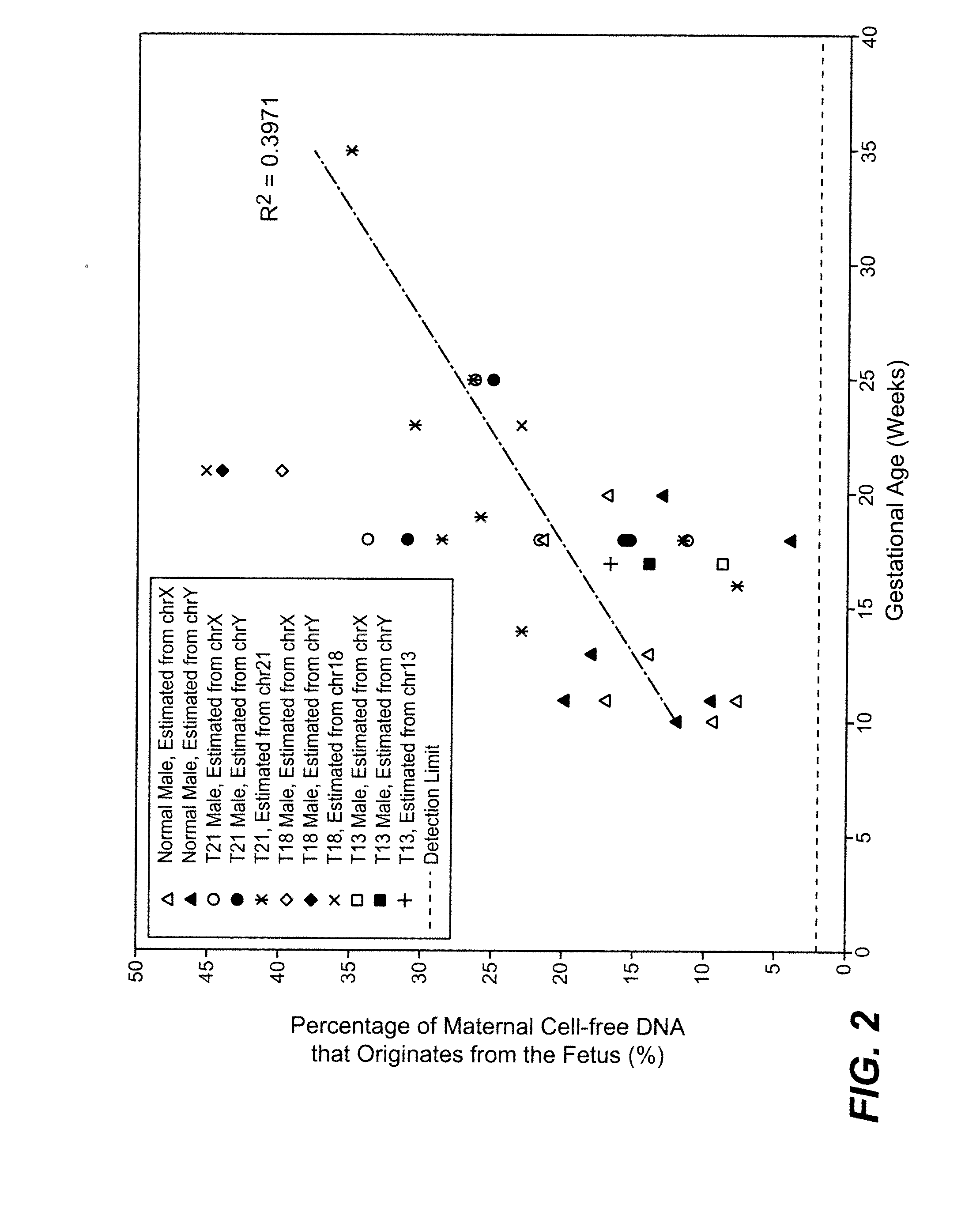
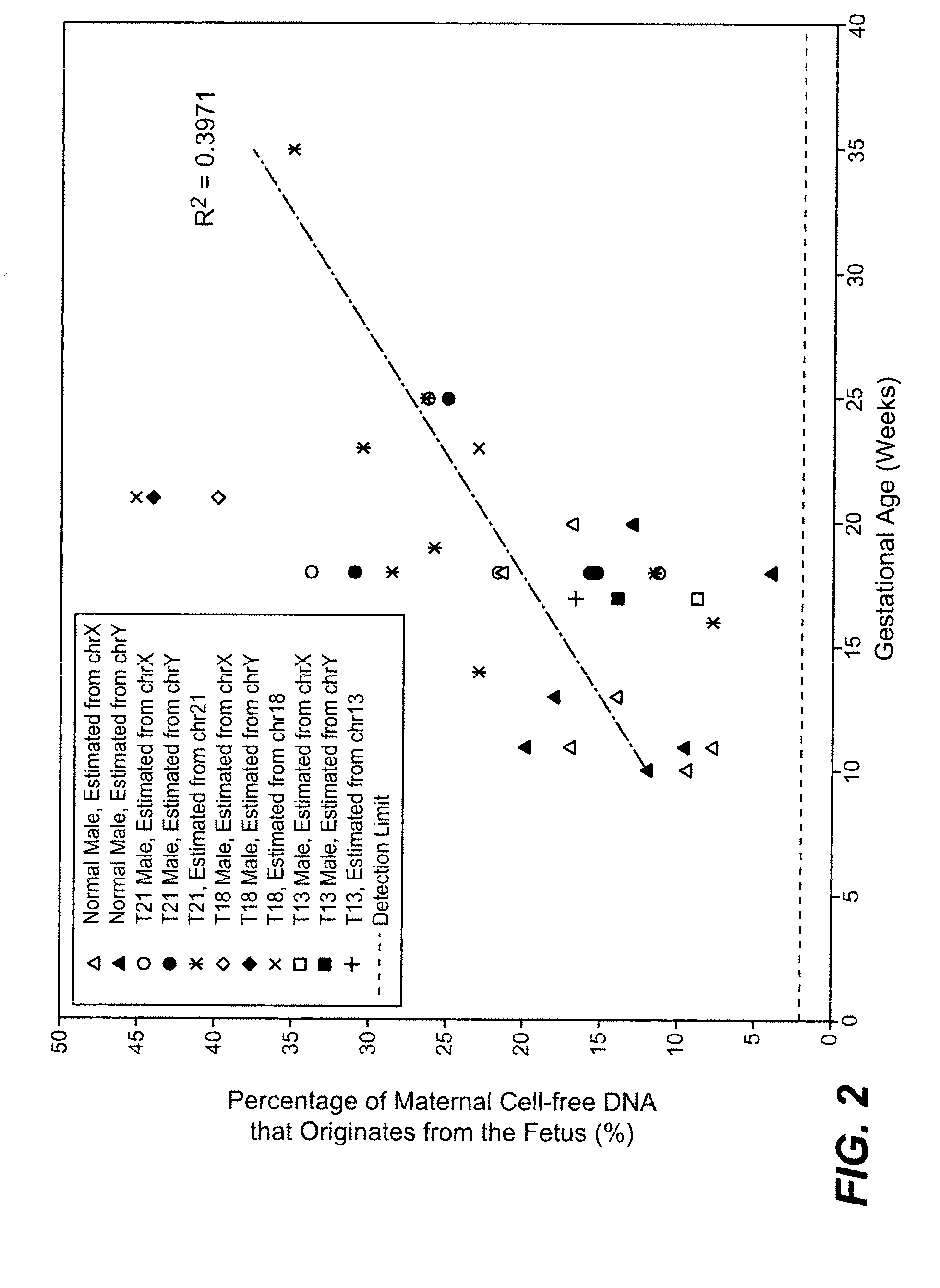
Massively parallel sequencing of cell-free, maternal plasma DNA was recently demonstrated to be a safe and effective screening method for fetal chromosomal aneuploidies. Here, we report an improved sequencing method achieving significantly increased throughput and decreased cost by replacing laborious sequencing library preparation steps with PCR employing a single primer pair. Using this approach, samples containing as little as 4% trisomy 21 DNA could be readily distinguished from euploid samples.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
ActiveUS20110246083A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
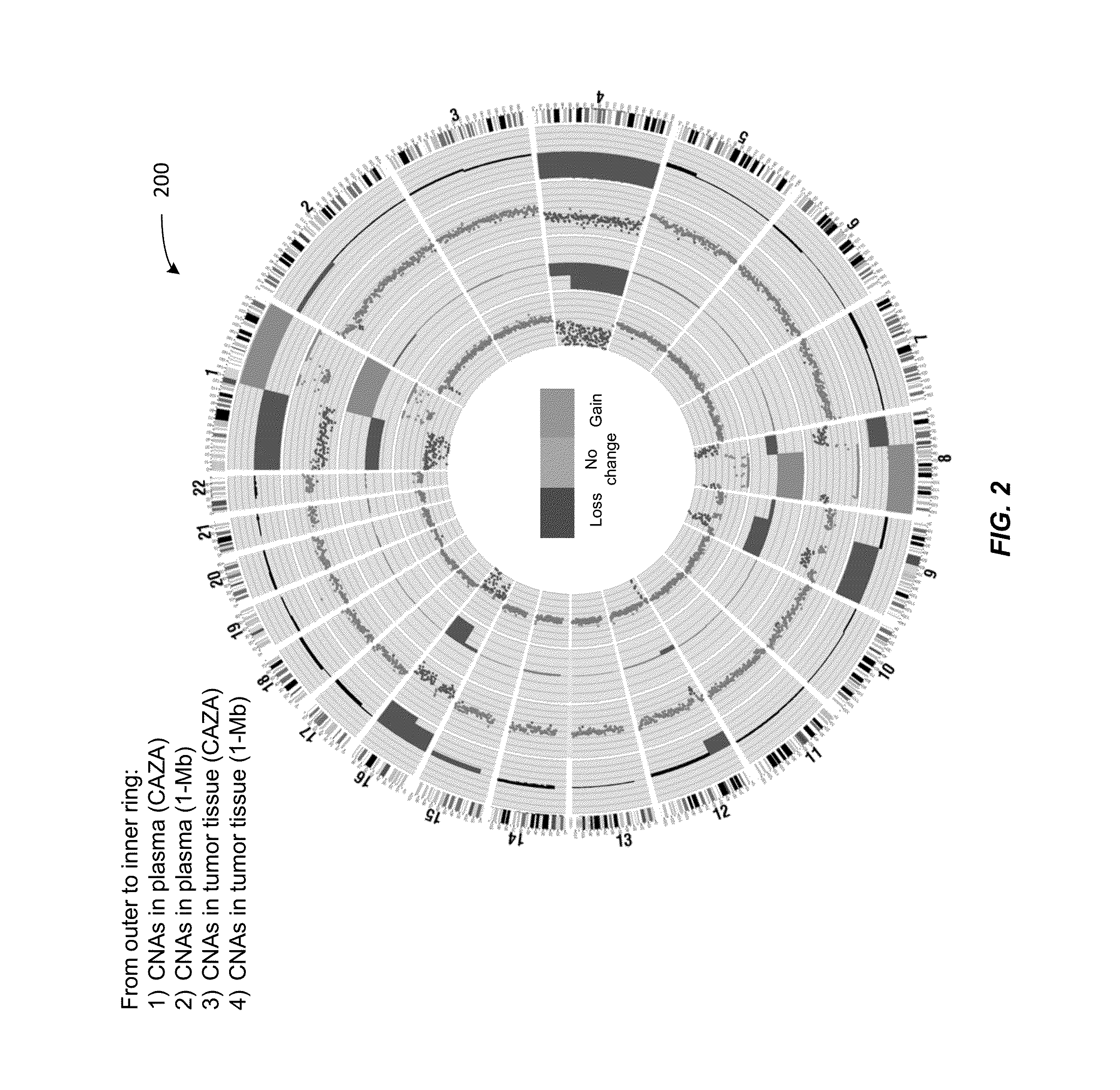
Using size and number aberrations in plasma DNA for detecting cancer
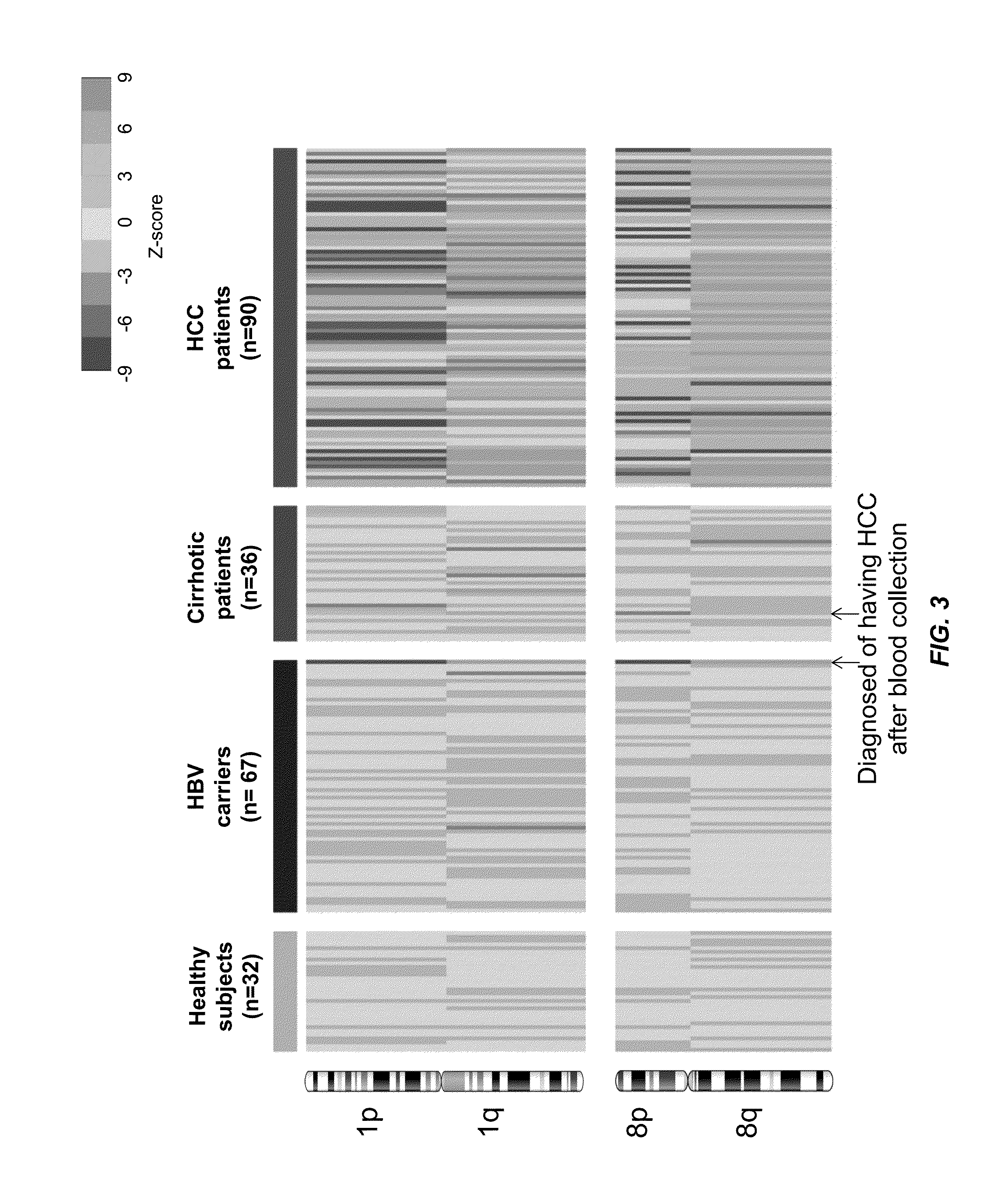
Analysis of tumor-derived circulating cell-free DNA opens up new possibilities for performing liquid biopsies for solid tumor assessment or cancer screening. However, many aspects of the biological characteristics of tumor-derived cell-free DNA remain unclear. Regarding the size profile of plasma DNA molecules, some studies reported increased integrity of tumor-derived plasma DNA while others reported shorter tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules. We performed an analysis of the size profiles of plasma DNA in patients with cancer using massively parallel sequencing at single base resolution and in a genomewide manner. Tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules were further identified using chromosome arm-level z-score analysis (CAZA). We showed that populations of aberrantly short and long DNA molecules co-existed in the plasma of patients with cancer. The short ones preferentially carried the tumor-associated copy number aberrations. These results show the ability to use plasma DNA as a molecular diagnostic tool.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for retarding unhealth manifestations brought by ageing of human beings
InactiveUS20090053200A1Reduce functionReduced stress resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDna antibodyBlood plasma
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Kit, primers, probe sequence and method for detecting fetus chromosome aneuploid
ActiveCN105695567AAccurate detectionAvoid detection errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceWeeks pregnant
The invention provides a kit, primers, probe sequences and a method for detecting fetus chromosome aneuploid. The kit comprises the multiple pairs of specific primers and a plurality of specific Taqman probes all of which are designed according to 13#, 18# and 21# chromogene sequences of the human, and further comprises a reaction system used for digital PCR, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the specific primers and the specific Taqman probes is SEQ ID NO: 1-90. The detection method comprises the steps that firstly, the specific primers and the specific Taqman probes are designed according to the 13#, 18# and 21# chromogene sequences of the human; secondly, peripheral blood of a (12-23)-week pregnant woman is collected for plasma DNA extracting; thirdly, the reaction system of the digital PCR amplification gene sequence is prepared; fourthly, the numbers of 13#, 18# and 21# chromosomes of a fetus are calculated through digital PCR detection for the number of the chromosomes, digital PCR is used for detecting FAM and VIC fluorescence of all reaction units of a chip, and the copy number of the 13# chromosome, the copy number of the 18# chromosome and the copy number of the 21# chromosome are calculated respectively. By means of the kit and the method, the number of the 13# chromosome, the number of the 18# chromosome and the number of the 21# chromosome of the fetus can be efficiently, quickly and accurately detected without invasion, and the kit and the method are beneficial to clinic application and popularization.
Owner:内蒙古因诺生物技术有限公司
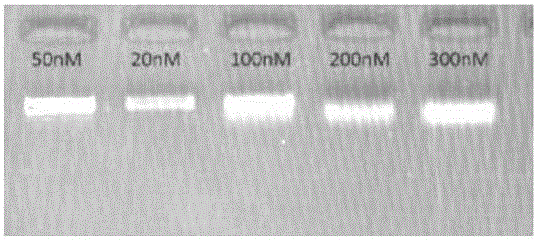
Blood plasma DNA library building method and kit
ActiveCN109971827AImprove the efficiency of database constructionIncrease the amount of effective dataMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBlood plasmaEmbryo tail
The invention provides a blood plasma DNA library building method and kit. The library building method comprises the following steps: repairing the tail end of blood plasma DNA and adding A to obtainrepaired DNA; and sequentially carrying out joint connection and PCR amplification on the repaired DNA by adopting a joint with a unique tag sequence to obtain a sequencing library of the blood plasmaDNA. The sequencing library of the blood plasma DNA is constructed by joint connection of the blood plasma DNA with unique tag sequence after repairing and A addition. By the formed library, repeatsgenerated by library-building amplification or sequencing amplification according to the unique tag sequence are conveniently distinguished from real repeat sequences in the blood plasma DNA when sequencing data are analyzed at a later stage, then amplification repeats are removed, repeats exist in blood plasma fragments DNA retains, thus, the effective data size of blood plasma-derived DNA is increased, and the blood plasma DNA library building efficiency is improved to a certain extent.
Owner:NANODIGMBIO (NANJING) BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Single-molecule sequencing of plasma DNA
ActiveUS20170044606A1Improve efficiencyEfficient readingMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDNA fragmentationNucleic acid sequencing
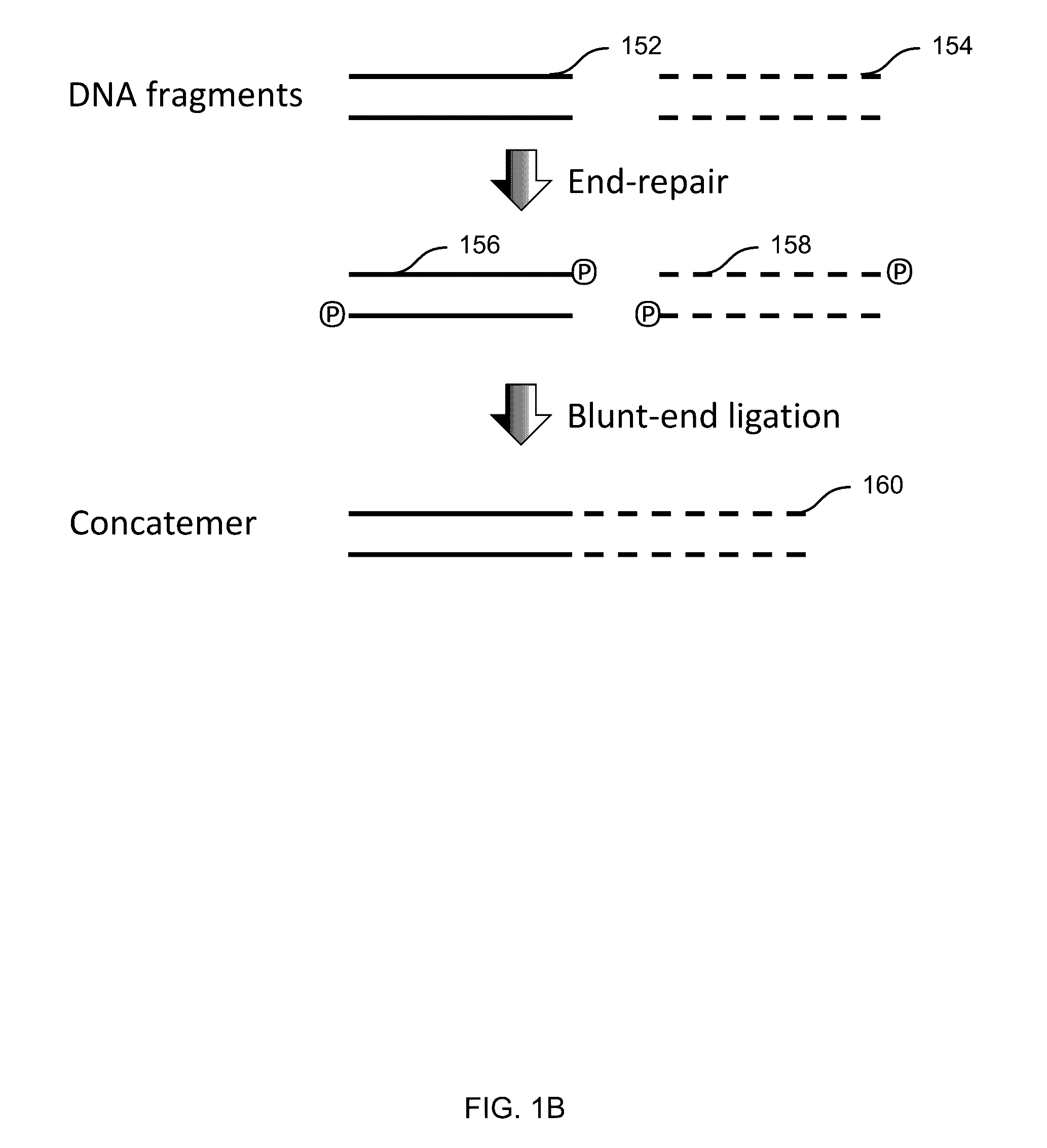
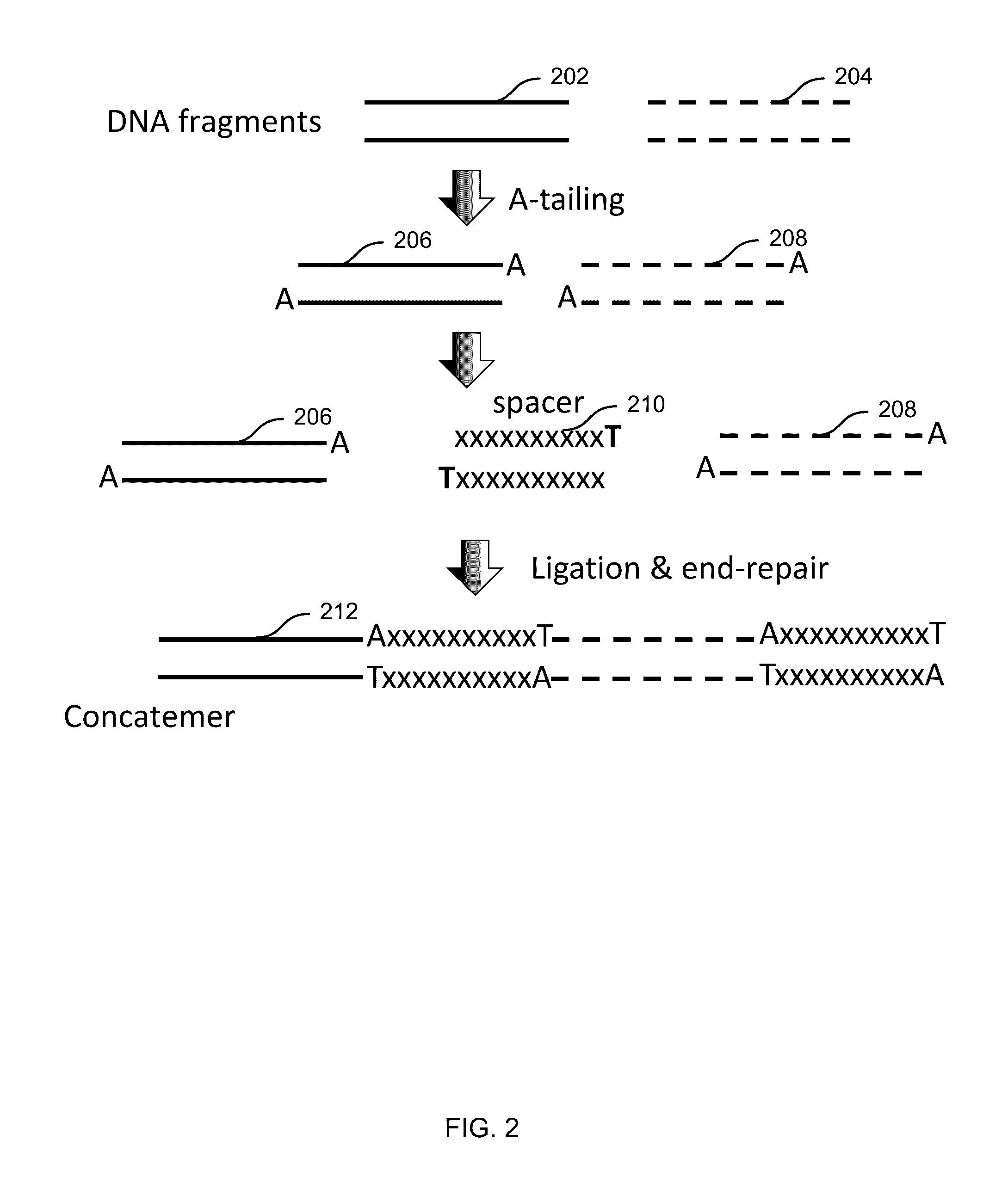
Embodiments may include a method of determining a nucleic acid sequence. The method may include receiving a plurality of DNA fragments. The method may also include concatemerizing a first set of the DNA fragments to obtain a concatemer. The method may include performing single-molecule sequencing of the concatemer to obtain a first sequence of the concatemer. In some embodiments, single-molecule sequencing may be performed using a nanopore, and the method may include passing the concatemer through a nanopore. A first electrical signal may then be detected as the concatemer passes through the nanopore. The first electrical signal may correspond to a first sequence of the concatemer. In addition, the method may include analyzing the first electrical signal to determine the first sequence. Subsequences of the first sequence may be aligned to identify sequences corresponding to each of the first set of the DNA fragments.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Size-tagged preferred ends and orientation-aware analysis for measuring properties of cell-free mixtures
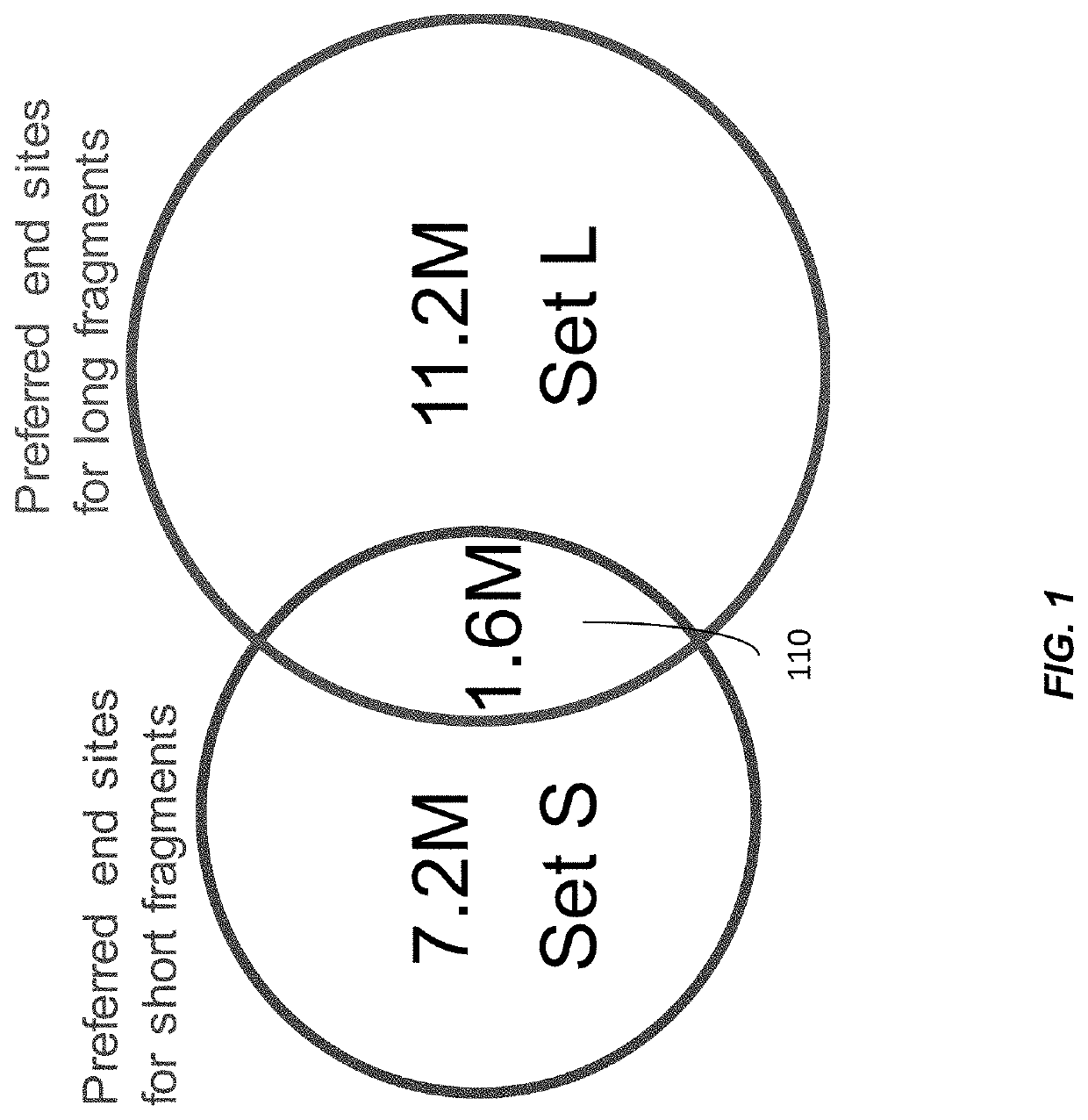
Various applications can use fragmentation patterns related of cell-free DNA, e.g., plasma DNA and serum DNA. For example, the end positions of DNA fragments can be used for various applications. The fragmentation patterns of short and long DNA molecules can be associated with different preferred DNA end positions, referred to as size-tagged preferred ends. In another example, the fragmentation patterns relating to tissue-specific open chromatin regions were analyzed. A classification of a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type can be determined in a mixture of cell-free DNA from different tissue types. Additionally, a property of a particular tissue type can be determined, e.g., whether a sequence imbalance exists in a particular region for a tissue type or whether a pathology exists for the tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
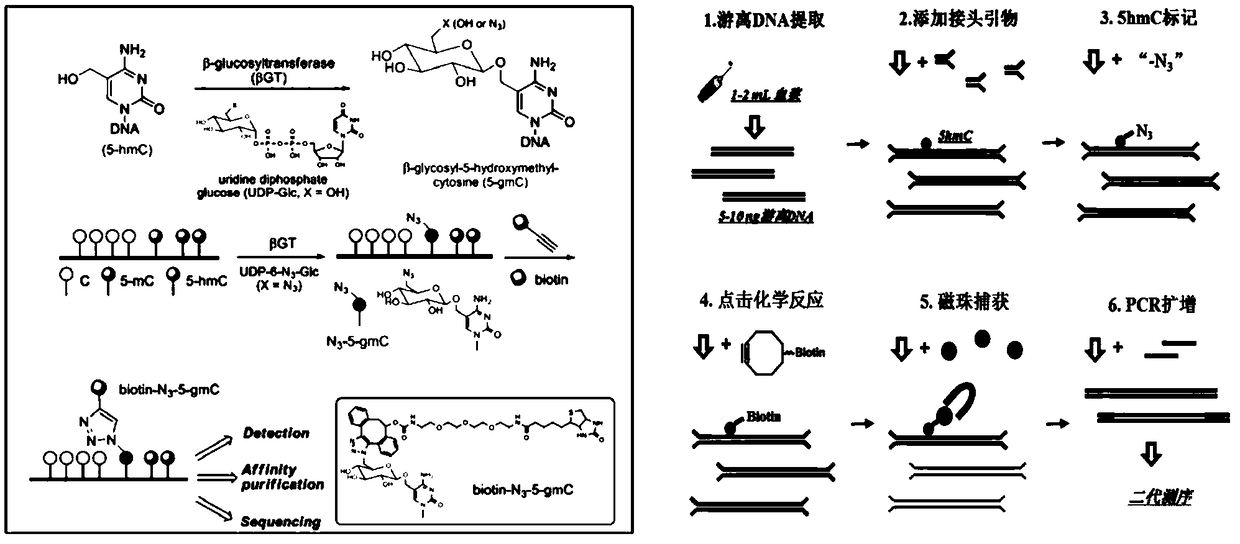
Superficial modification based 5hmC (5-hydroxymethylcytosine) polymolecular marker and CRC (colorectal cancer) early diagnosis model
ActiveCN109504778AImprove complianceEasy and fast detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisStool occult bloodMolecular diagnostic techniques
The invention relates to the technical field of clinical molecular diagnosis, in particular to a superficial modification based 5hmC (5-hydroxymethylcytosine) polymolecular marker and a CRC (colorectal cancer) early diagnosis model. With the adoption of a 5-hmC high throughput sequencing technology, 5-hmC expression quantities of peripheral blood plasma DNA whole genomes of a CRC patient and a healthy person are checked, 5-hmC differential expression of genetic loci of the whole genomes of the two groups of samples are compared, the genetic locus of the part with the most obvious differentialexpression is screened as the gene marker of the diagnosis model, and then the CRC early diagnosis model is constructed. Verification proves that the diagnosis sensitivity and specificity are both higher, and compared with a stool occult blood detection kit and a spetin9 kit in the market currently, sensitivity and specificity are improved by about 20% and 8% respectively. The diagnosis method hasthe advantages of being noninvasive in detection and convenient, can be applied to the first-line clinic and is used for early screening of CRC.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Method and kit for non-invasive measurement on fetus deaf pathogenic gene mutation
PendingCN105087756AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNon invasiveHigh throughput sequence
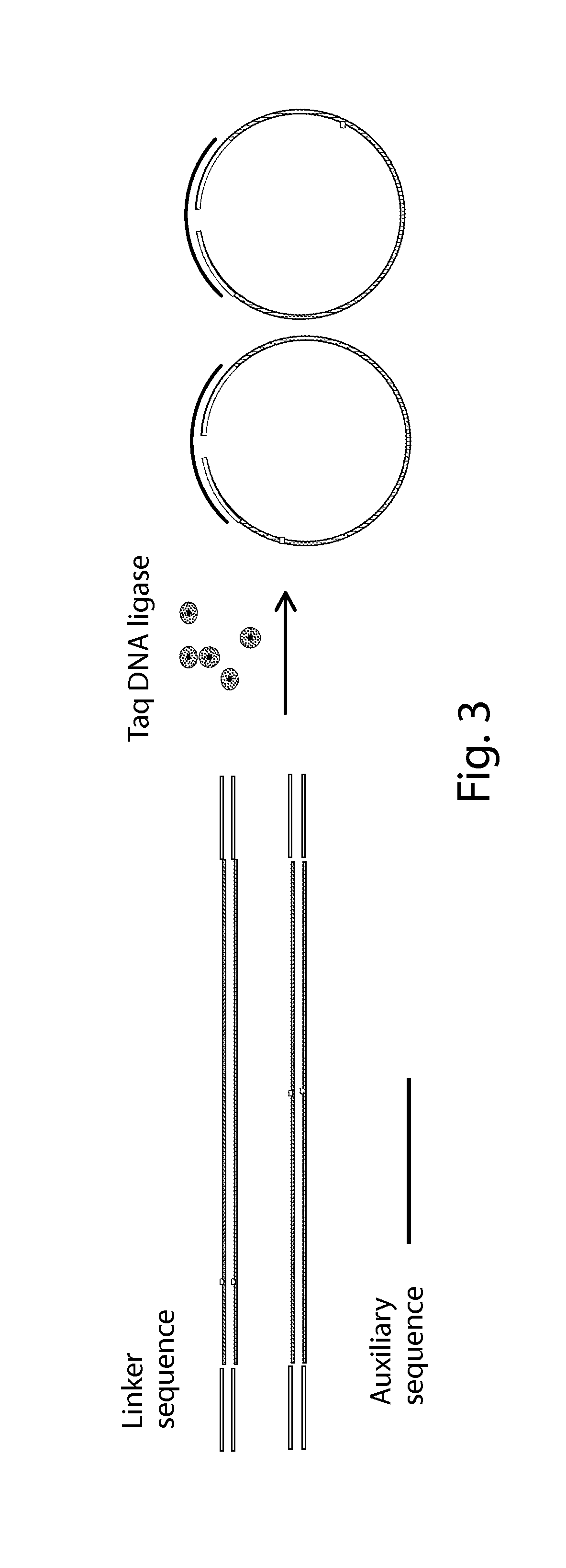
The present invention is directed to a method, kit and primers for detecting fetal deafness pathogenic gene mutations. The method of the invention comprises: (a) designing primers according to the pre-determined mutation loci of deafness pathogenic genes; (b) extracting plasma DNAs in a pregnant woman; (c) connecting the extracted plasma DNAs with pre-amplification linkers to obtain connected products; (d) PCR pre-amplifying the connected product to obtain pre-amplified products; (e) cyclizing the pre-amplified products to obtain cyclised DNAs; (f) PCR amplifying the cyclised DNAs using the designed primers to obtain amplified products; and (g) high throughput sequencing the amplified products and analyzing the mutations of the fetal deafness pathogenic genes. The invention can effectively determine whether the pre-determined loci on deafness pathogenic genes have been mutated as well as the mutation type.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
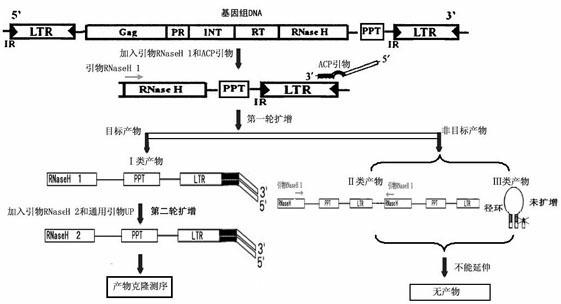
Method for separating long terminal repeats of retrotransposons
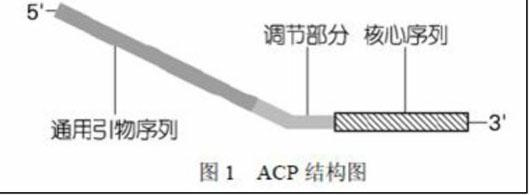
InactiveCN102140450AStrong specificityReduce generationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLong terminal repeatGenomic clone
The invention discloses a method for separating long terminal repeats of retrotransposons. Genome DNA is taken as a template, an RNaseH1 primer is respectively combined with different annealing control primers for first polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction, the first PCR product is diluted to serve as a template, an RNaseH2 primer and a universal primer UP are subjected to secondary PCR reaction amplification, conversion and extraction of plasma DNA are performed, and a sequence is subjected to sequencing to obtain an amino acid sequence of RNaseH enzyme, and proteins are encoded. Compared with the common PCR technology, the method has the advantages that: the operation is simple, long terminal repeat regions of the retrotransposons are easily aligned, and the pertinence is high; compared with a flow type magnetic microbead inverse hybrid method, the method has the advantages of saving hybrid, eluting, screening and other processes, simplifying the flow and having high efficiency;and compared with other separation methods, the method has the advantages of reducing time consumption, quickly obtaining target segments, cloning the long terminal repeats in short time, and reducing false positive rate.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Huaman plasma DNA quantitative analyser
InactiveCN1811387AAccurate quantitative detectionOvercoming Extraction EfficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to a quantitative detection analysis method of human plasma DNA level. Said method includes the following steps: selecting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA series whose extraction efficiency is identical to or similar to that of human plasma DNA, but they are non-homologous, selecting housekeeping gene beta actin as determination gene, inserting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA into carrier pMD18T and placing it in the bacteria to make culture, making blue and white spot screening, colony PCR identification, enzyme-cutting into linearity, placing the above-mentioned material into plasma, adopting double fluorescent quantitative gene amplification, fluorescent groups are respectively FAM and HEX, extracting known exogenous positive plasmid recovery efficiency, using computation formula to make computation so as to obtain the quantity of plasma DNA.
Owner:潘世扬
Method and kit for building ALK gene fusion mutation detection library
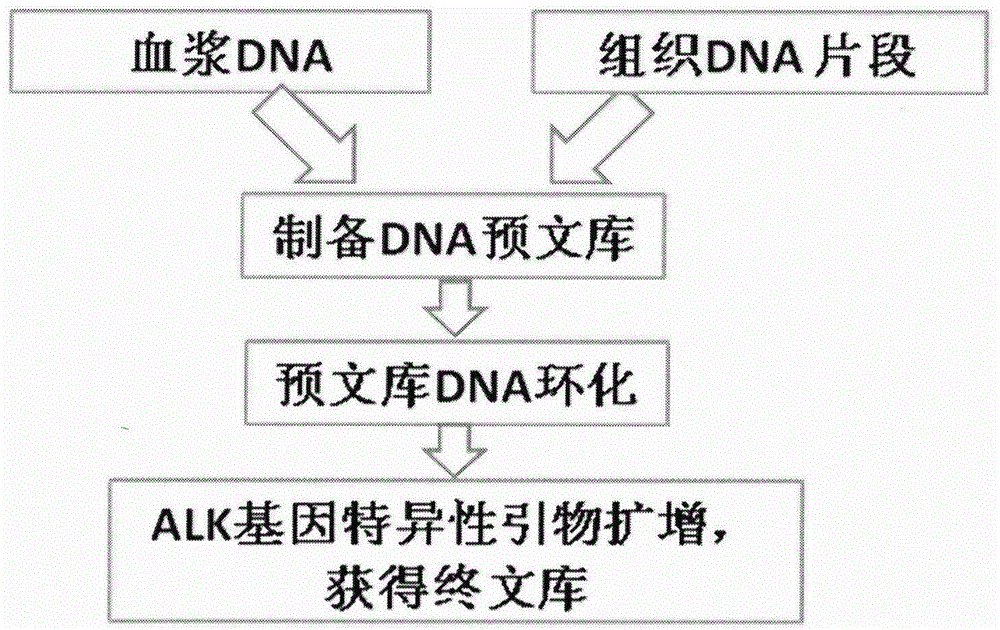
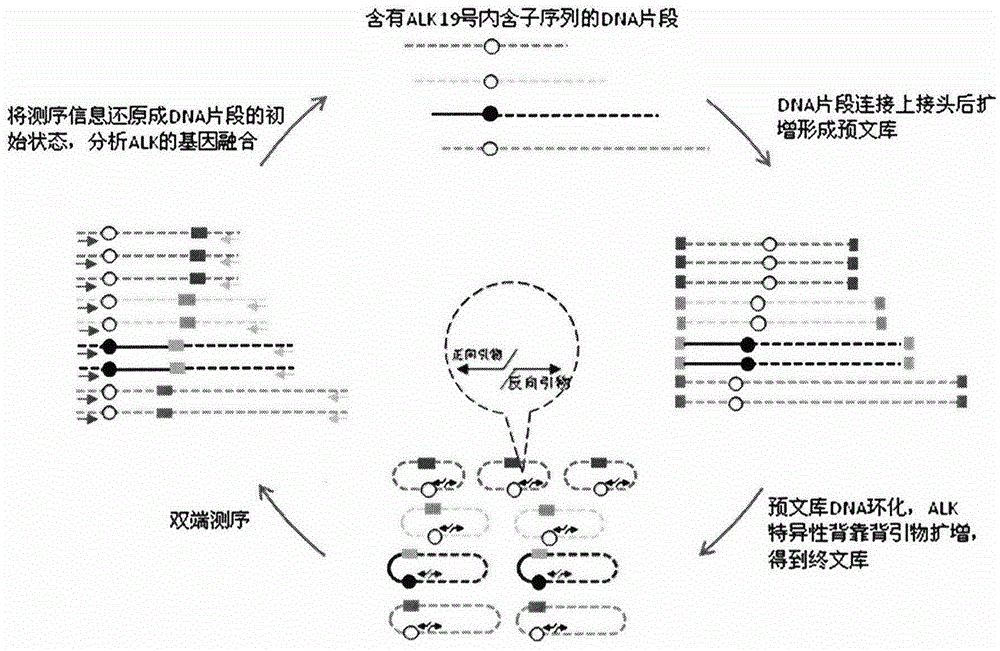
ActiveCN106148323AEfficient amplificationAccurately obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMutation detectionA-DNA
The invention provides a method for building an ALK gene fusion mutation detection library. The method includes the steps of firstly, extracting DNA, and fragmenting the DNA; secondly, building a DNA pre-library; thirdly, cyclizing the DNA; using ALK specific primers to perform PCR amplification, and enriching a target area to generate the final library. The invention further provides a kit for building the ALK gene fusion mutation detection library and a method for detecting ALK gene fusion mutation. The method for building the ALK gene fusion mutation detection library has the advantages that the method targeted at ALK recombination hot spot regions is excellent in sensitivity when being combined with the second-generation high-through sequencing technology, and plasma DNA or tissue DNA can be used as the initial material to accurately detect the information of ALK gene fusion mutation; in addition, when the plasma DNA is used as the initial material, noninvasive detection of ALK gene fusion mutation and crizotinib drug-resistant mutation is achieved.
Owner:BERRY ONCOLOGY CO LTD
Low-frequency mutations enrichment sequencing method for free target DNA in plasma
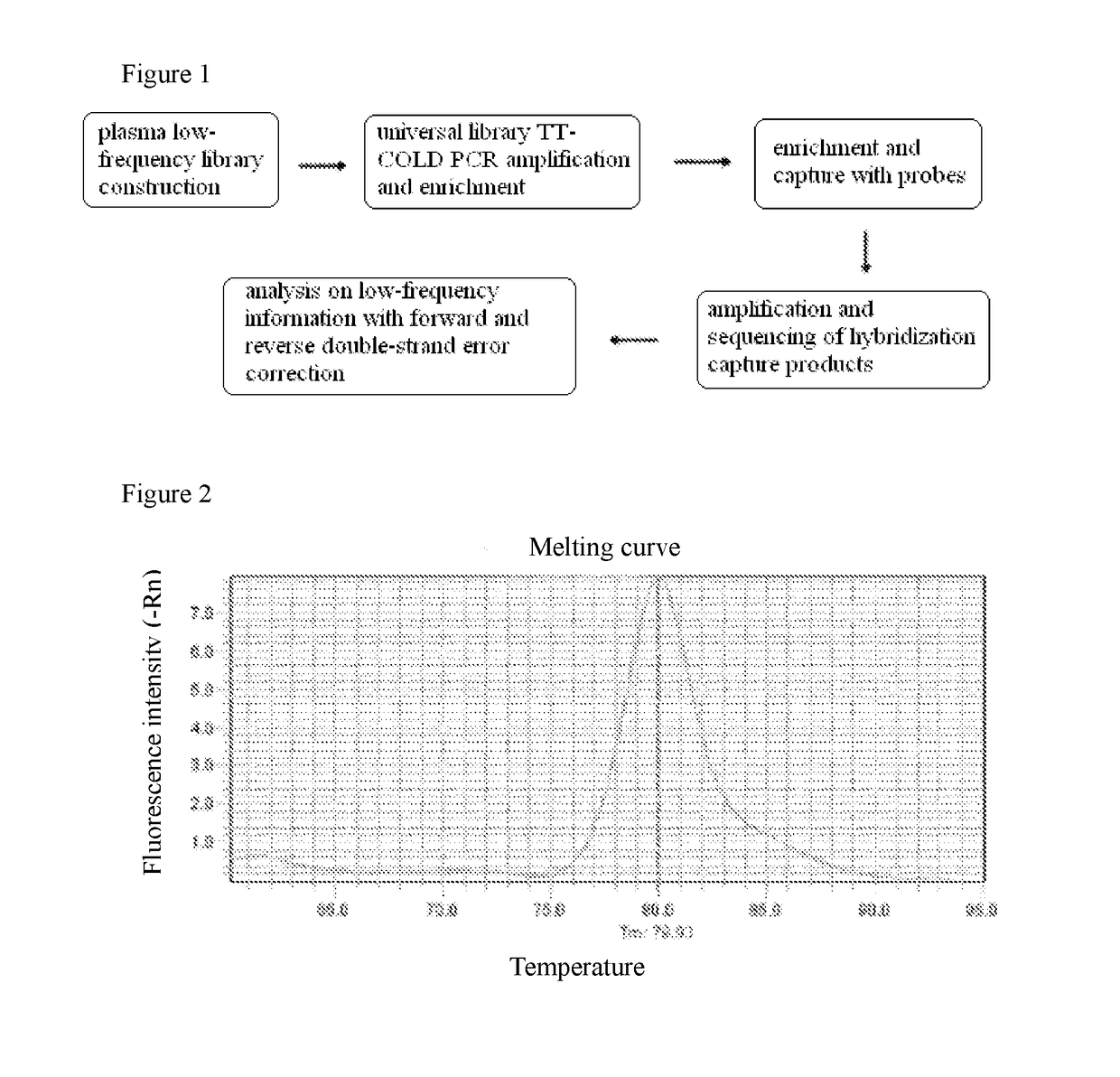
ActiveUS20180371453A1The result is accurateAccurate monitoringDrug and medicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisCOLD-PCR
The present invention provides a low-frequency mutation enrichment sequencing method for free target DNA in plasma, comprising plasma DNA extraction and library construction, general library TT COLD PCR amplification enrichment, probe enrichment capture, PCR and sequencing of captured products, and positive and negatice double-strand error-correction low-frequency information analysis.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH
Method for detecting necrosis degree of hepatic cells through level of plasma free DNA
InactiveCN101955998AReflect the degree of necrosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHepatic inflammationBlood plasma
The invention relates to a method for detecting the necrosis degree of hepatic cells through the level of plasma free DNA, and belongs to the technical field of biology. In the method, through the separation and extraction method and quantification of the plasma free DNA, the necrosis degree of the hepatic cells is reflected by the level of the free DNA. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a primer beta-globin serving as a standard substance; extracting the plasma DNA in a plasma specimen of hepatopath; performing a real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction on the plasma DNA extracted in the plasma specimen; and measuring and calculating the concentration of the plasma free DNA. The method provides a new diagnostic index for the diagnosis of severe hepatitis.
Owner:赵英仁
Methylation quantitative detection method of APC gene in human plasma
InactiveCN101354347AOvercoming the need for electrophoresisOvercoming pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansLoss rateFluorescence
The invention relates to a methylation quantitative test method of APC gene in the DNA of human blood plasma. The methylation quantitative test method obtains venous blood and the blood plasma, prepares a DNA standard curve sample of the blood plasma, extracts the DNA of the blood plasma to be detected, the DNA of a standard curve blood plasma sample and the DNA of healthy human blood plasma, realizes chemical modification of the DNA of the blood plasma to be detected, the standard curve blood plasma sample and the healthy human blood plasma, designs particularity primers and Taqman fluorescent probes according to 707 CpG locus of a 1A sequence in a human APC gene sub-promoter, builds a standard curve according to the augmentation result of the DNA of the standard blood plasma after the augmentation, and implements methylation quantitative result analysis of the sample to be detected. The methylation quantitative test method of the APC gene solves the defects that the blood plasma has less DNA content, high loss rate, DNA degradation and carcinogenic pollutant, etc. The methylation quantitative test method of the APC gene utilizes a primer pair and a Taqman fluorescent probe that aim at the 1A sequence in the APC gene sub-promoter, realizes the detection aiming at the 707 CpG locus in the APC gene sub-promoter with high methylation developing rate, implements quantitative analysis, and can be used in the aspects of cure effect observing as well as prognosis and relapse monitoring of tumor patients.
Owner:潘世扬
Deep sequencing of peripheral blood plasma DNA as a reliable test for confirming the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome
ActiveUS20160130648A1Increase in bone marrow blastsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGackstroemiaHematologic malignancy
Methods are provided for treating, managing, diagnosing and monitoring myelodysplastic syndrome and other hematologic malignancies. These methods comprise the next generation sequencing analysis conducted on cell-free DNA from peripheral blood plasma or serum.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS LAB
Method for treating diseases associated with changes of qualitative and/quantitative composition of blood extracellular dna
The invention relates to medicine and veterinary science and can be used for treating diseases associated with changes of the qualitative and / quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations. The inventive method for treating diseases associated with modifications of the qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations consists in injecting an agent destroying blood extracellular DNA. DNAse enzyme injected into a systemic blood circulation in doses which modify the electrophoretic profile of the blood extracellular DNA definable by pulse-electrophoresis can be used in the form of an agent destroying said blood extracellular DNA. Said DNAse enzyme can be injected in doses and at regimes ensuring the level of a blood plasma DNA-hydrolytic activity which is measured in the blood plasma and is higher than 150 Kunz units per litre of plasma during a total time higher than 12 hours a day. The inventive method makes it possible to develop a high-efficient and low-toxic method for treating diseases associated with modifications of qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA individually or in combination thereof.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
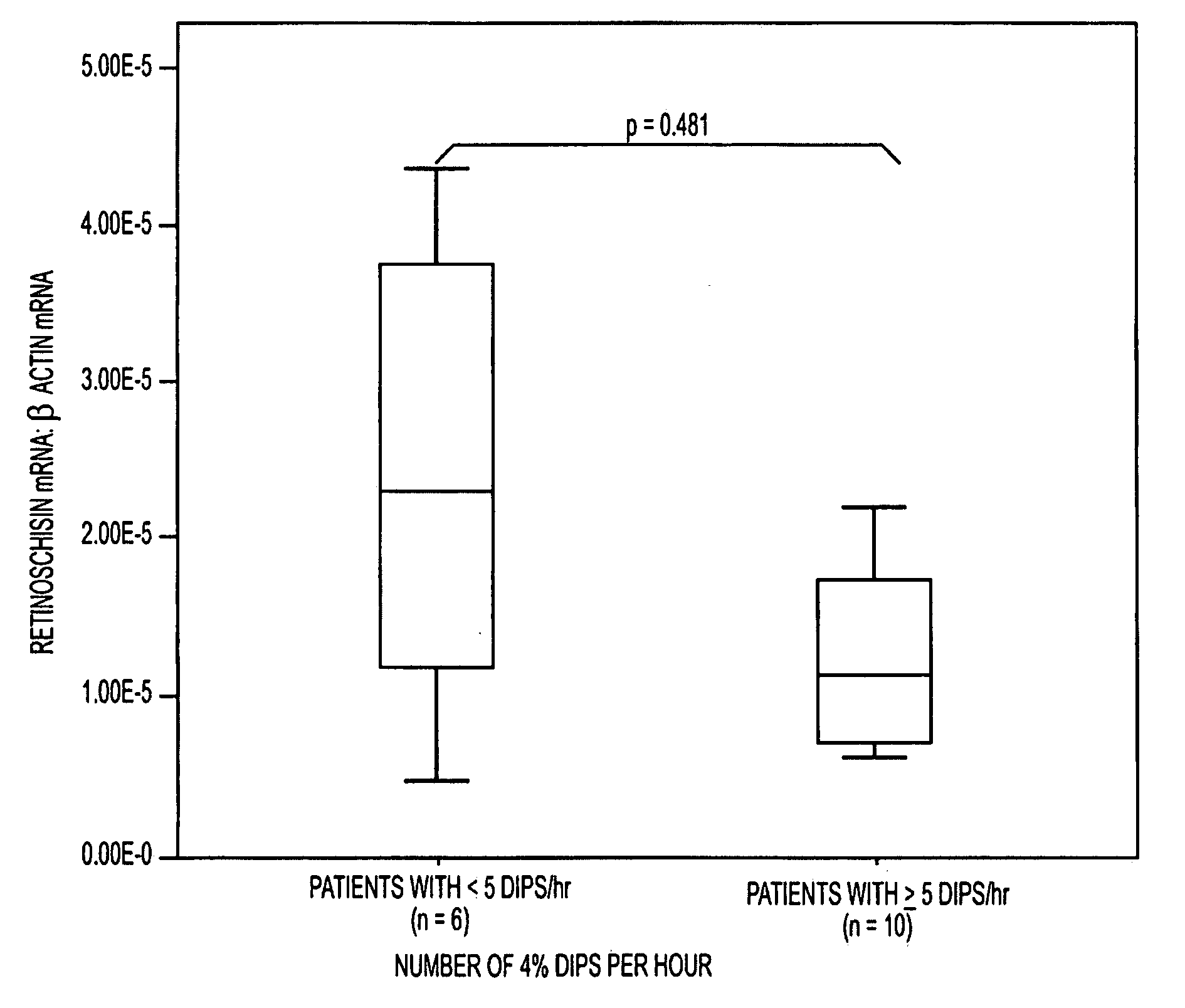
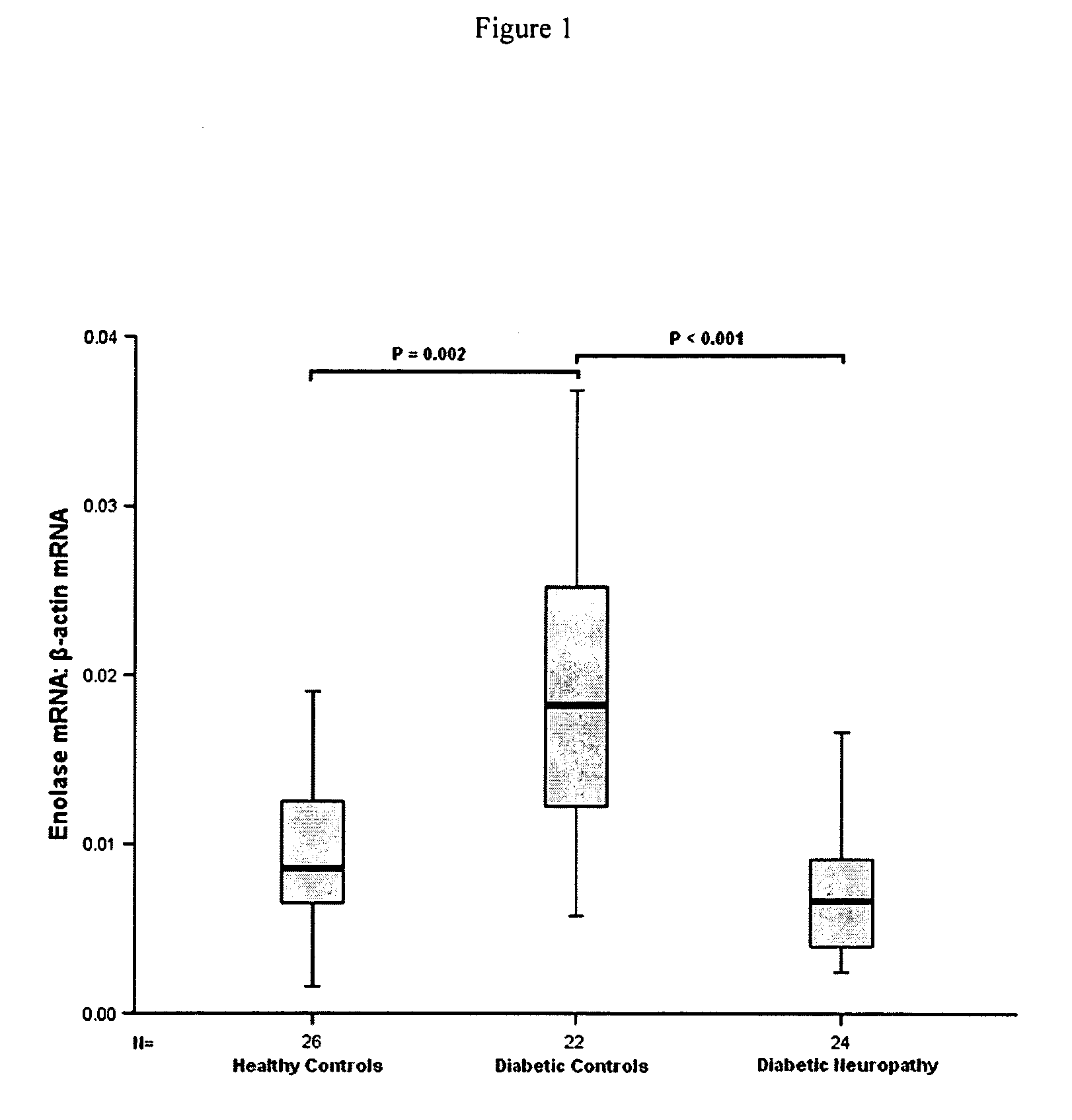
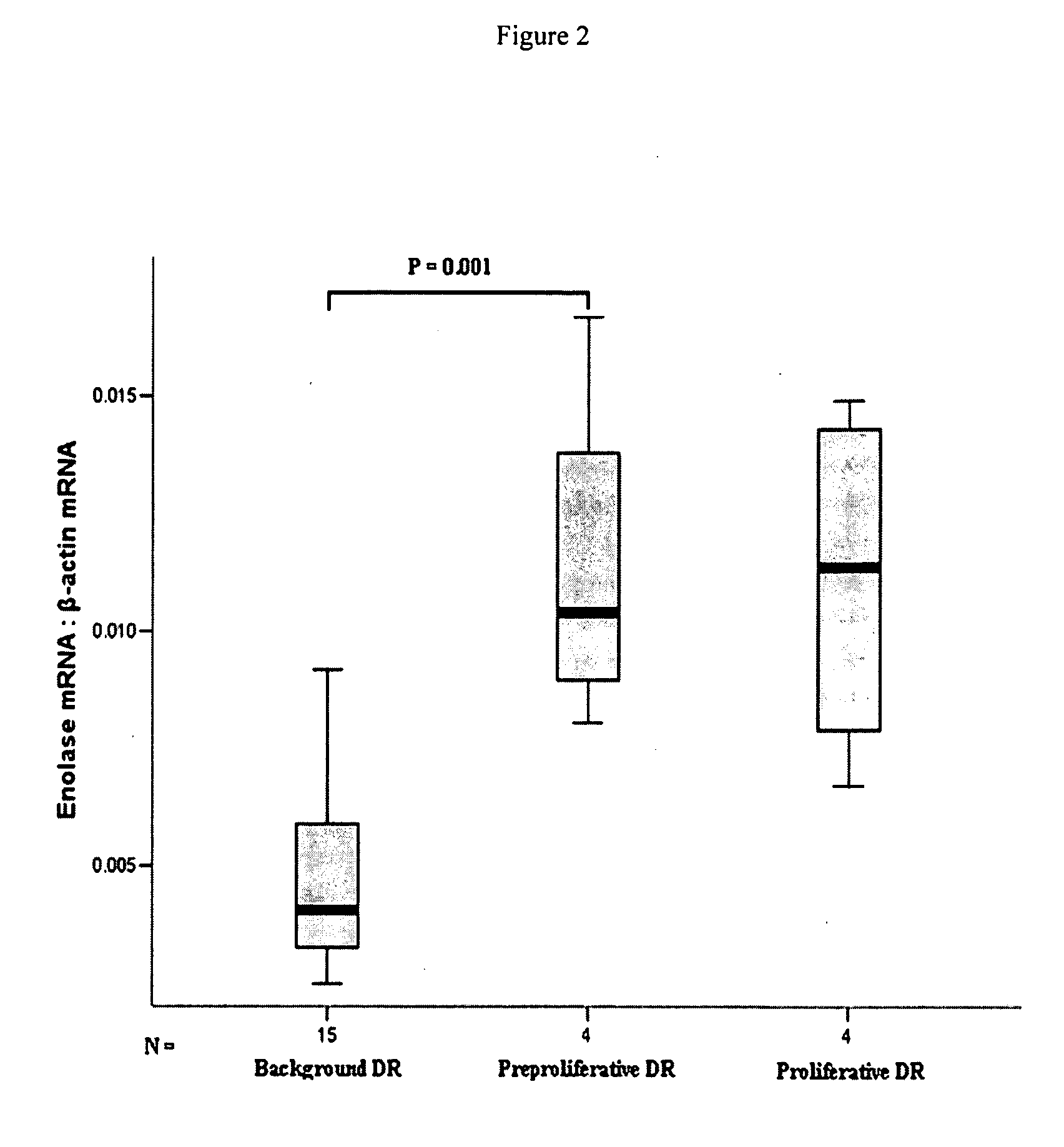
Biomarkers
InactiveUS20100047779A1Rapid and early detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker (petroleum)RETINOSCHISIN
The present invention provides circulating biomarkers for conditions associated with metabolic syndrome, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congestive heart failure. The biomarkers include plasma DNA, neuron-specific enolase, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, rhodopsin, retinoschisin, RPE65 and cardiac troponin T. Methods and kits for detecting these biomarkers in the prediction, monitoring and diagnosing of disease are provided, particularly for determining mRNA levels thereof in a subject's blood.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
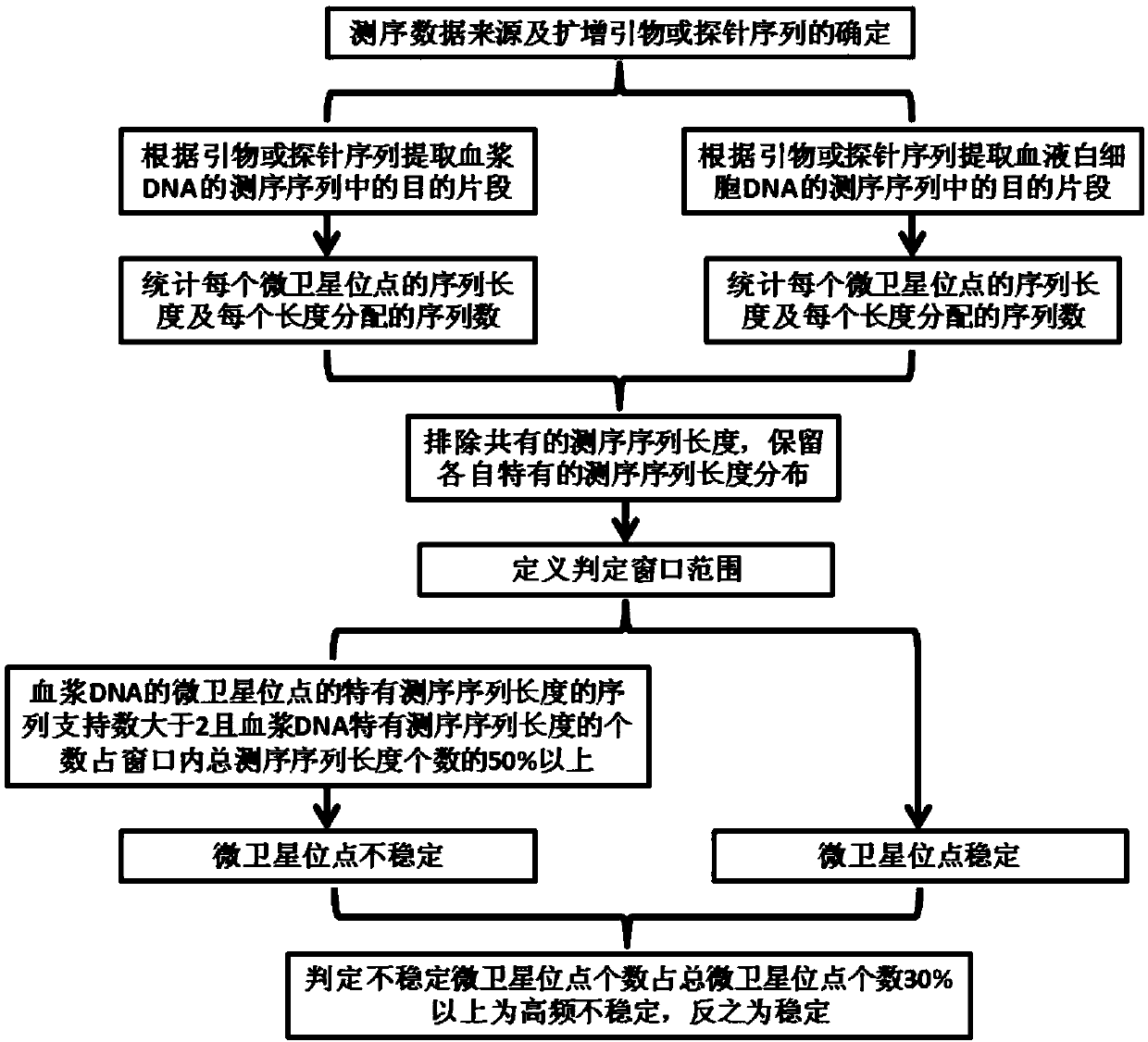
Method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on second generation sequencing technology
InactiveCN109584961AImprove consistencyResolve detectionBiostatisticsSequence analysisMicrosatellite StableTumor tissue
The invention discloses a method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on a second-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps: respectively determining the length and the number of each sequence corresponding to the same microsatellite locus to be detected in second-generation sequencing data of plasma DNA and blood leukocyte DNA, determining the length ofthe sequencing sequence with difference by comparison. Determining the sequence length L corresponding to the primer and / or the probe and the length L'of the corresponding microsatellite locus to bedetected in the known genome, and if the number of sequences with different sequencing sequence lengths is more than 2 in the judgment range window of L-L'(X (L+L'), and accounts for more than 50% ofthe total sequence length in the judgment range window, the microsatellite locus is judged to be unstable, and conversely, the microsatellite locus is judged to be stable. Repeating the process to judge the stability of a plurality of microsatellite loci so as to detect the microsatellite instability of the sample. The method for detecting blood microsatellite instability based on second generation sequencing technology can complete the detection only by extracting the blood of the patient without depending on tumor tissues.
Owner:GENEIS TECH BEIJING CO LTD
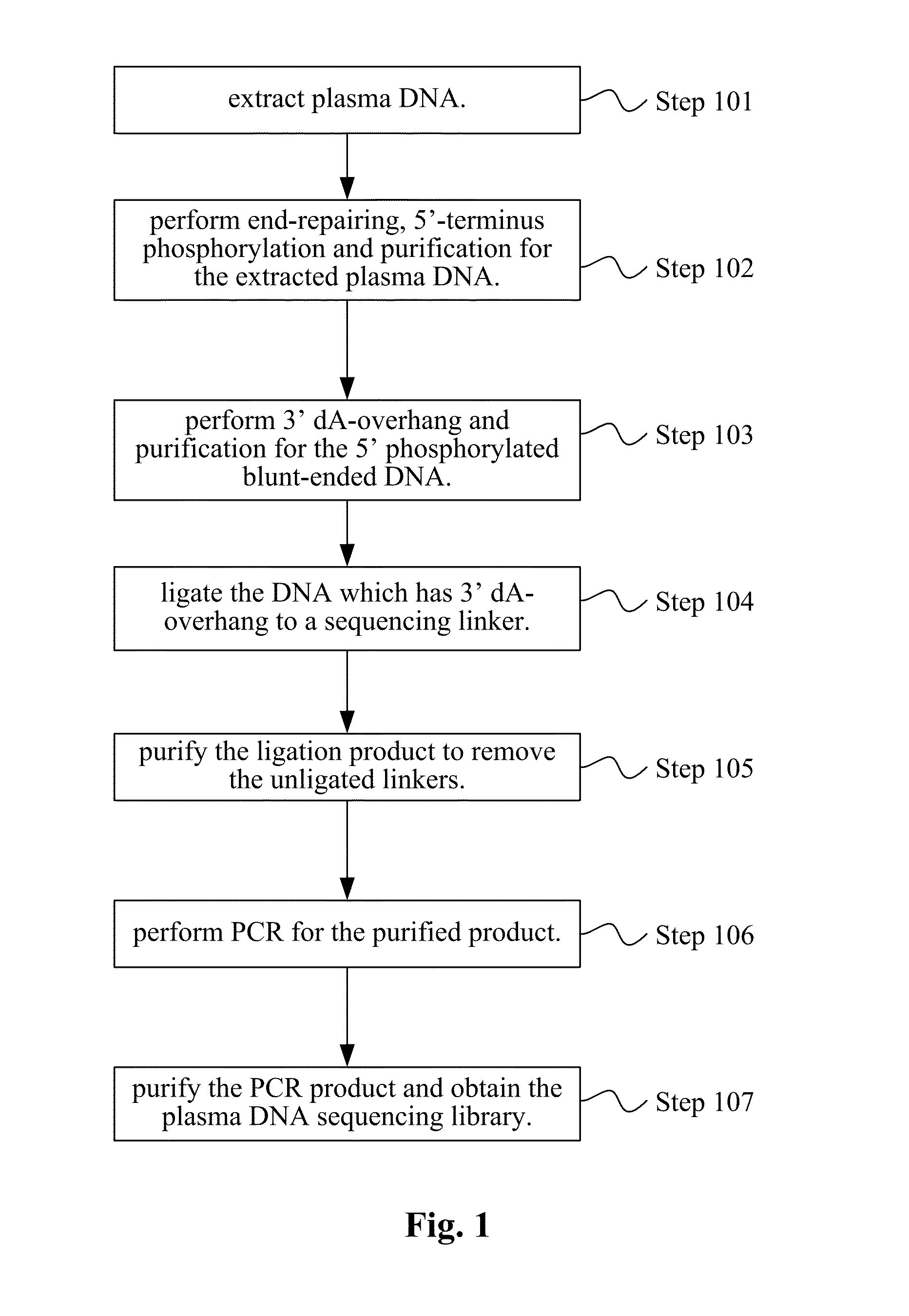
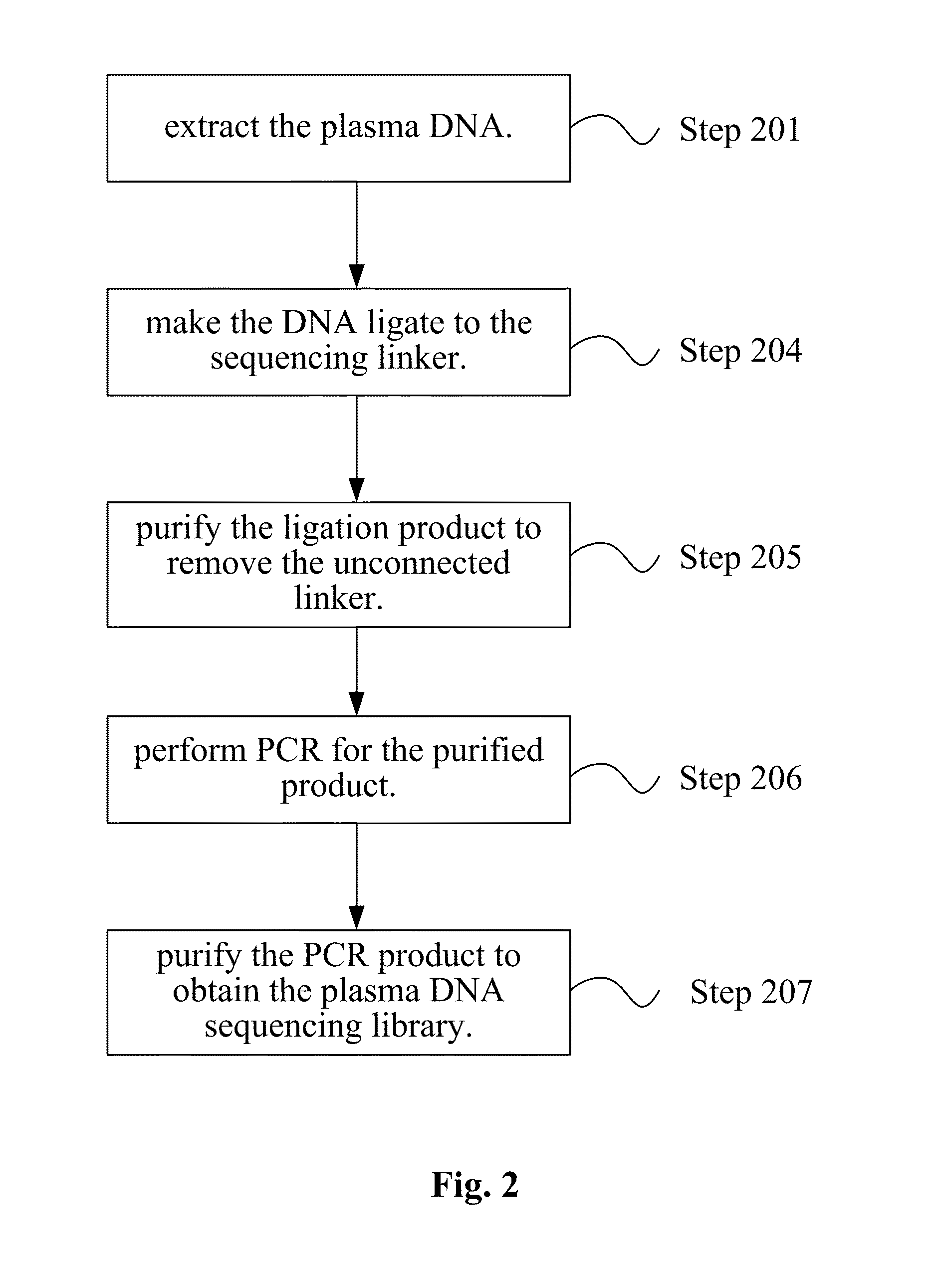
Method and kit for constructing plasma DNA sequencing library
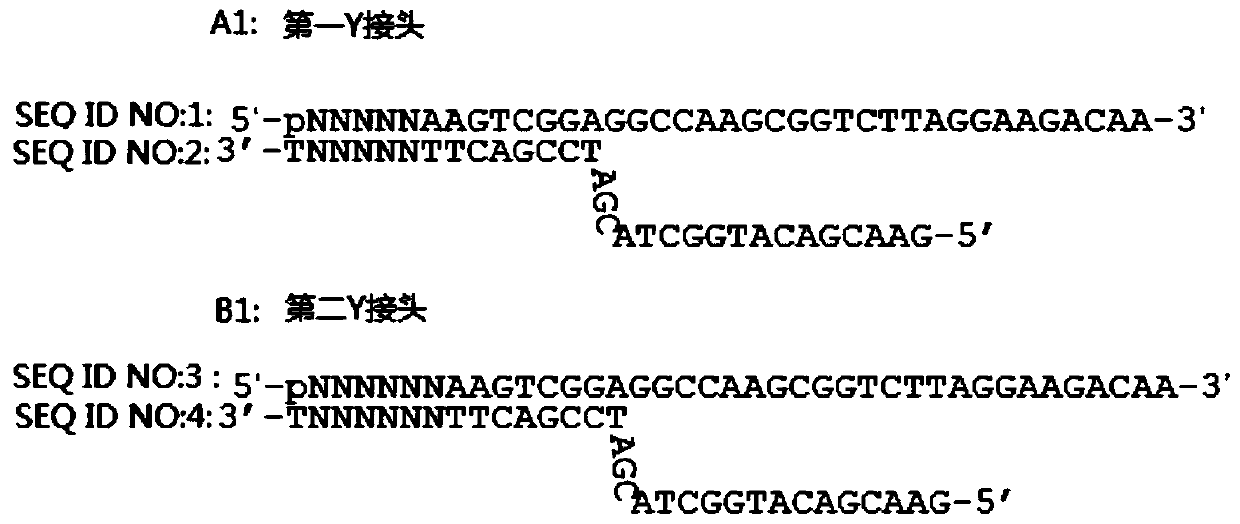
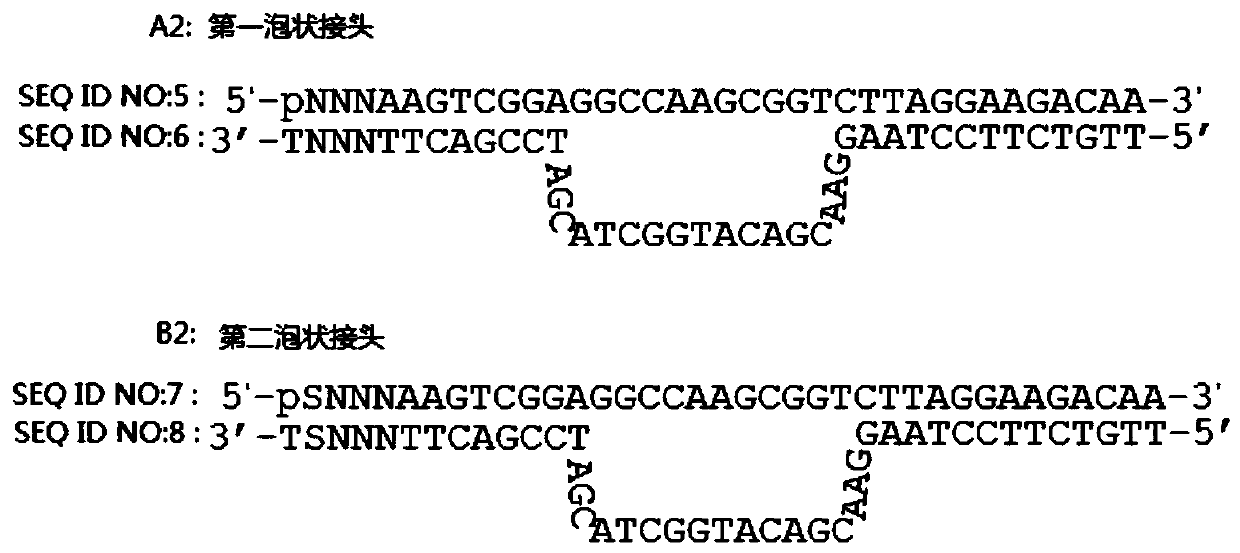
InactiveUS20140228256A1Easy constructionReduce construction costsMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPolymerase chain reactionPlasma dna
The disclosure relates a method and a kit for constructing a plasma Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing library. The method provided by the disclosure includes: extracting a plasma DNA; making the plasma DNA ligate to a sequencing linker, and purifying a ligation product; performing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification for the purified ligation product, purifying the PCR amplification product, and obtaining the plasma DNA sequencing library, wherein, the method does not include the step of performing 5′-terminus phosphorylation for the plasma DNA. The kit provided by the disclosure includes: a reagent which ligates a plasma DNA to a sequencing linker, including the sequencing linker, a ligase and a ligation buffer; and reagents and instruments for purifying the ligation product; a reagent which performs PCR amplification for a purified ligation product, and reagents and instruments for purifying the PCR amplification product; wherein, the kit does not include the reagent which performs 5′-terminus phosphorylation for the plasma DNA. The disclosure simplifies the construction flow of a plasma DNA sequencing library, simplifies the experimental procedures, and makes the construction of the plasma sample library have lower cost, higher efficiency and faster speed, and is convenient for large-scale application.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Method and reagent for enrichment of circulating tumor DNA
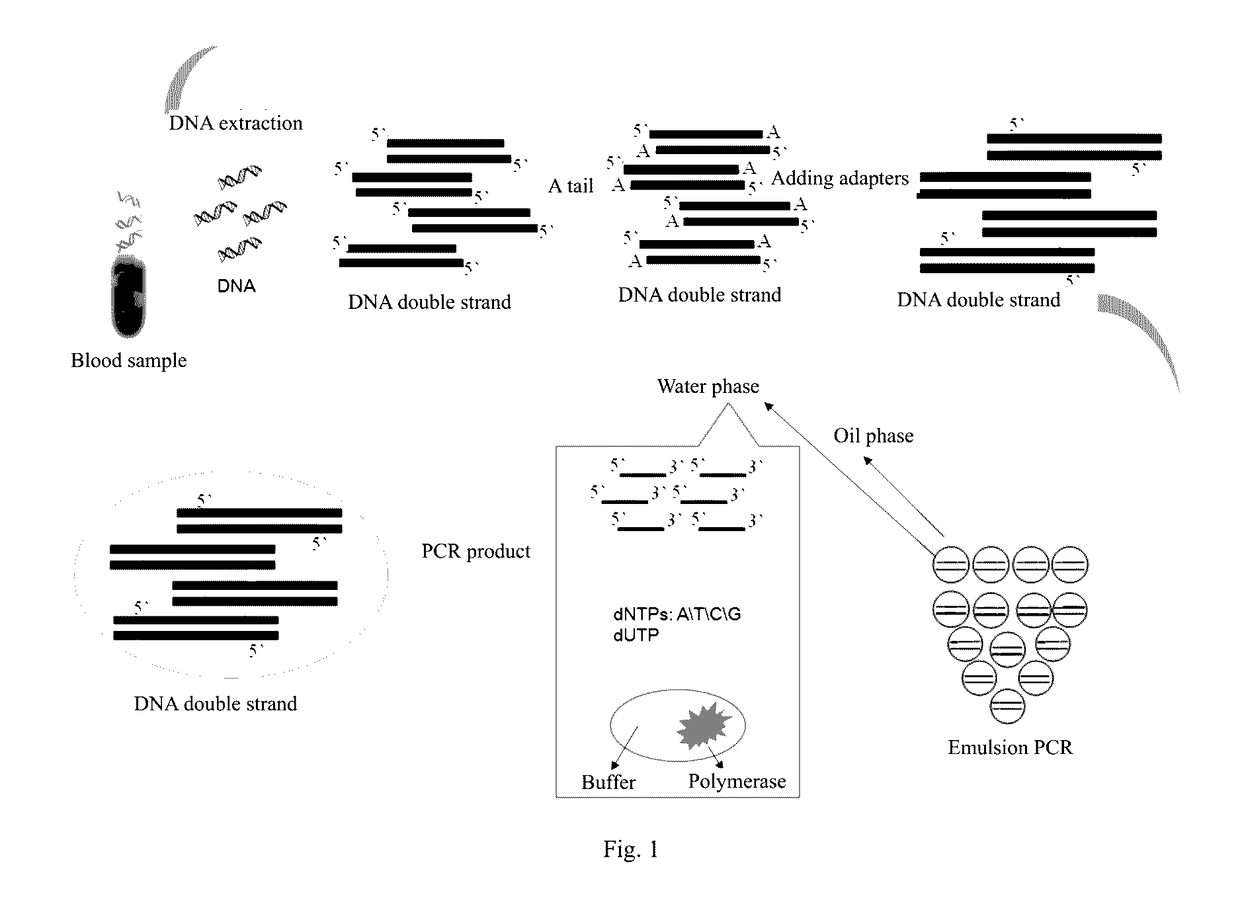
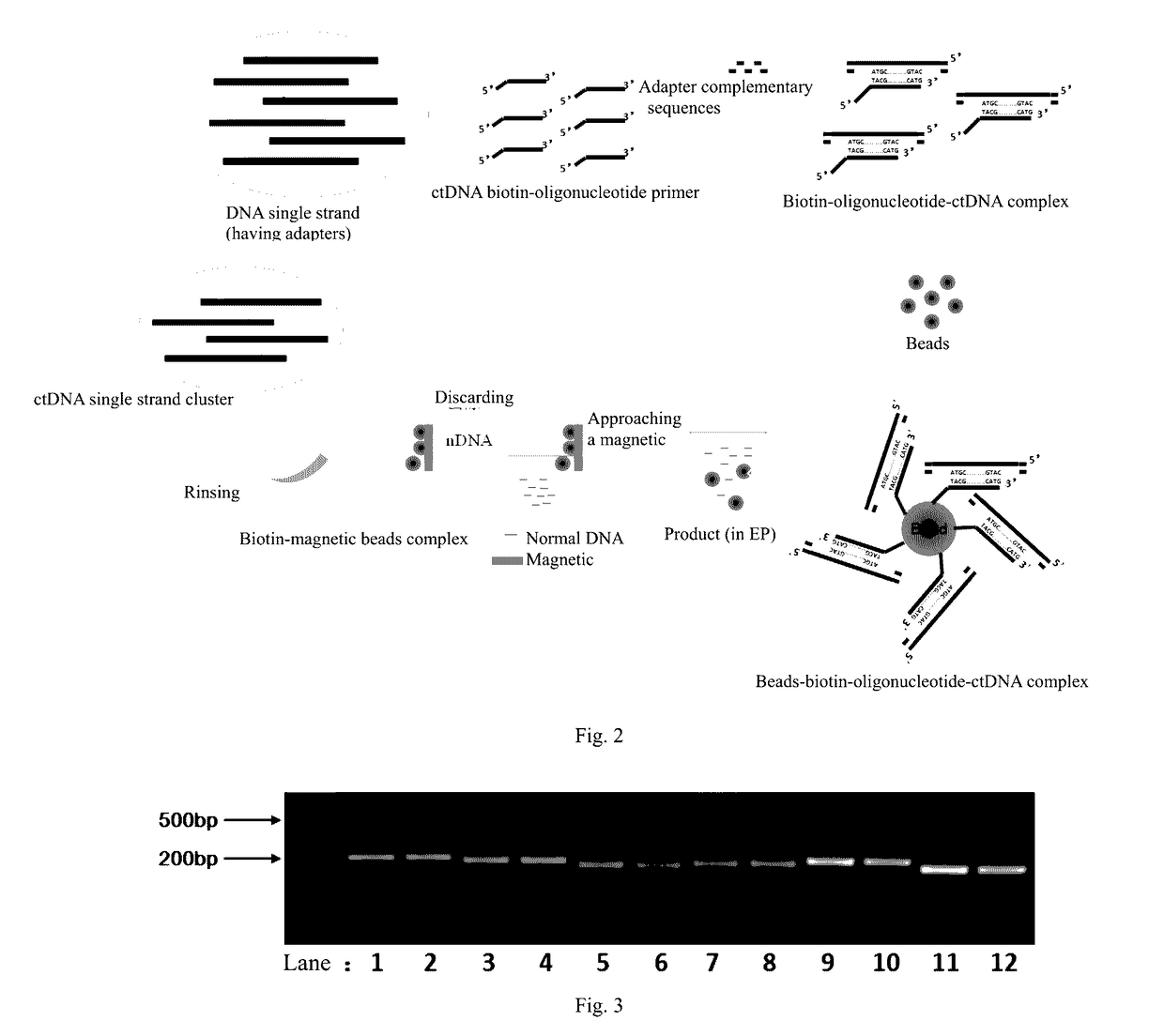
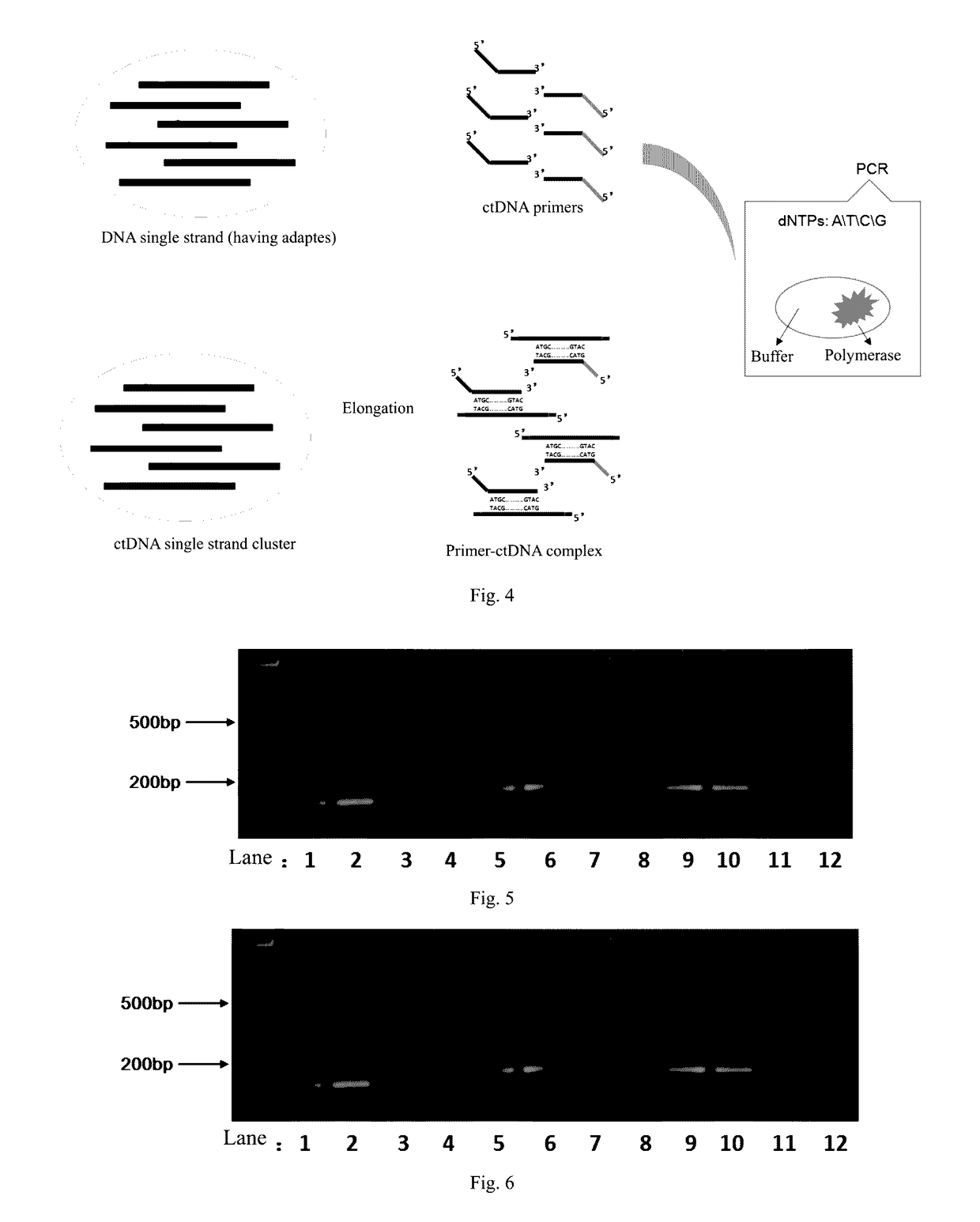
ActiveUS20170067117A1Efficient captureSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerPolymerase L
The present invention provides a method and a reagent for enrichment of circulating tumor DNA, the method comprising the steps of mixing a water phase and an oil phase and shaking the mixture to prepare an emulsion PCR reaction system, and performing emulsion PCR amplification, wherein the water phase comprises peripheral blood plasma DNA as template DNA, a forward primer and a reverse primer, dNTPs, a PCR buffer and a DNA polymerase, the peripheral blood plasma DNA having adapter sequences connected to both ends thereof, and the forward primer and the reverse primer being complementary to the adapter sequences at the two ends respectively; separating the water phase from the oil phase following the emulsion PCR amplification to obtain a PCR amplification product in the water phase; and capturing circulating tumor DNA in the PCR amplification product in the water phase by using a probe sequence that specifically binds to the circulating tumor DNA. The method of the present invention is capable of performing single-molecule high-fidelity ultramicro parallel amplification and effectively capturing peripheral blood plasma ctDNA to provide adequate amount of ctDNA to be used for subsequent sequencing detection.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
Method and a kit for non-invasively detecting fetal deafness pathogenic gene mutations
InactiveUS20150307942A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal DeafnessBlood plasma
The present invention is directed to a method, kit and primers for detecting fetal deafness pathogenic gene mutations. The method of the invention comprises: (a) designing primers according to the pre-determined mutation loci of deafness pathogenic genes; (b) extracting plasma DNAs in a pregnant woman; (c) connecting the extracted plasma DNAs with pre-amplification linkers to obtain connected products; (d) PCR pre-amplifying the connected product to obtain pre-amplified products; (e) cyclizing the pre-amplified products to obtain cyclised DNAs; (f) PCR amplifying the cyclised DNAs using the designed primers to obtain amplified products; and (g) high throughput sequencing the amplified products and analyzing the mutations of the fetal deafness pathogenic genes. The invention can effectively determine whether the pre-determined loci on deafness pathogenic genes have been mutated as well as the mutation type.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Functional oligomer used for non-viral gene vector material and application thereof
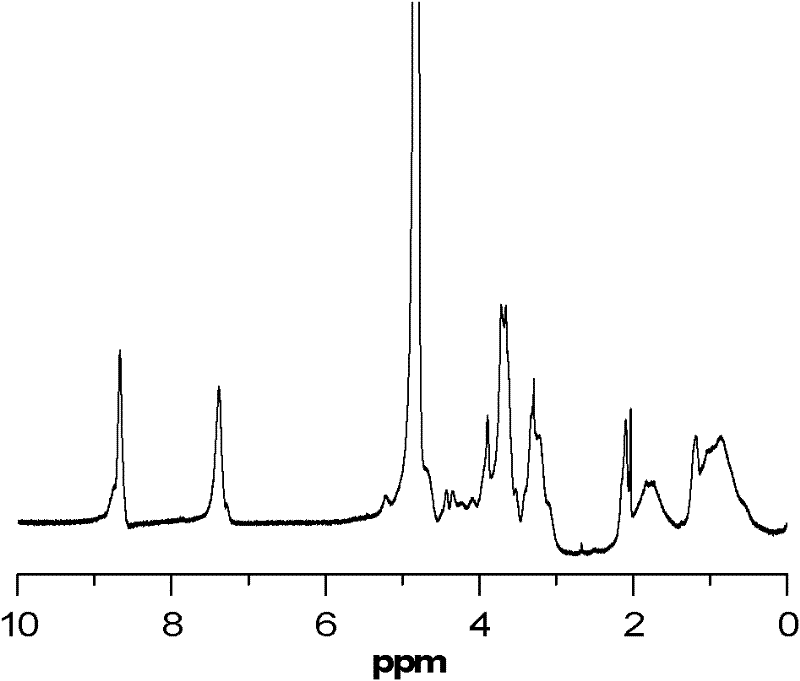
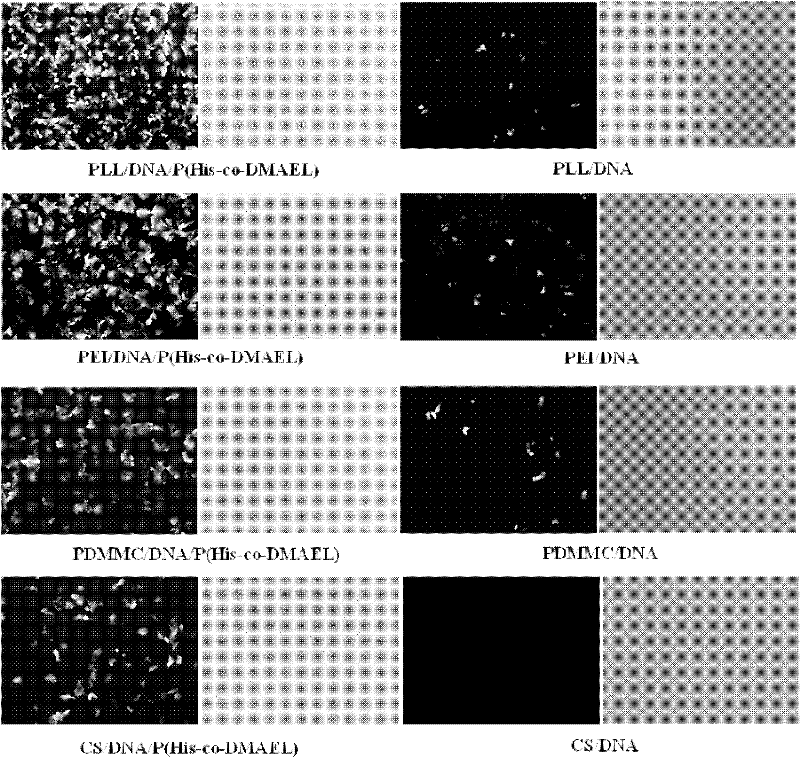
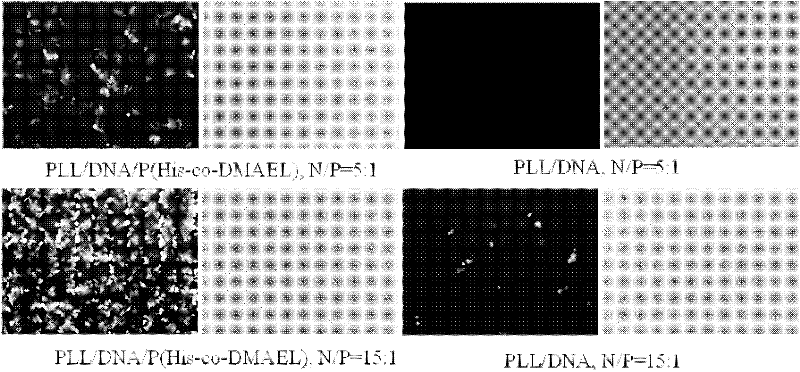
ActiveCN102532411AImprove escape efficiencyImprove protectionOther foreign material introduction processesLysosomeThio-
The invention provides a functional oligomer used for a non-viral gene vector material. The functional oligomer is prepared by free radical polymerization of MA-His-OMe and MAEL through taking water-soluble thio ester as a molecular weight regulating agent. In the preparation method, MA-His-OMe and MAEL are used as monomers, AIBN (2,2-azobisisbutyronitrile) or ACVA (4,4'-azobix(4-cyano valeric acid)) is used as an initiator, and CPADB (4-cyanopentanoic acid dithiobenzoate) is used as a chain transfer agent. According to the invention, the functional oligomer is mixed with a polycation material to prepare a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) composite which is used as the non-viral gene vector material and a cell transfection experiment is carried out. The functional oligomer has the advantages that the functional oligomer has a good protection effect on plasma DNA and can be used for improving the binding action of a complex particle and a cell membrane surface and improving the escape efficiency of the plasma DNA from lysosme / endosome in a cell, thus the transfection efficiency of the complex particle on cells such as HeLa is greatly improved, and the toxicity of the functional oligomer is greatly reduced, therefore the functional oligomer is expected to reach a clinical application level.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Methylation quantitative detection method of RASSFIA gene in human plasma
InactiveCN101354346AStrong specificityEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansVenous bloodDisease course
The invention relates to a methylation quantitative test method of RASSF1A gene in the DNA of human blood plasma. The methylation quantitative test method obtains venous blood and the blood plasma, prepares a DNA standard curve sample of the blood plasma, extracts the DNA of the blood plasma to be detected, the DNA of a standard blood plasma and the DNA of healthy human blood plasma, realizes chemical modification of the DNA of the blood plasma, the standard blood plasma and the healthy human blood plasma, designs a fluorescent quantitative MSP augmenting architecture of particularity primers and Taqman fluorescent probes according to 565 CpG locus in a human RASSF1A gene sub-promoter, builds an external standard curve according to the augmentation result of the DNA of the standard blood plasma, and implements quantitative result analysis of the sample to be detected. The methylation quantitative test method of the RASSF1A gene solves the defects that the disease course of most tumor patients that receive an operation lies in the mid and late periods, and consequently the obtaining damage of operation samples is large and the detectable rate of methylation is relatively lower, etc., has high sensitivity, the lowest detection limit of 1.5 multiplied by 10<2> copy per milliliter, the detection aimed at the 565 CpG locus in the RASSF1A gene sub-promoter, strong particularity, easy obtaining and small damage, and can quantitatively detect the RASSF1A gene methylation in the DNA of the blood plasma.
Owner:潘世扬
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com