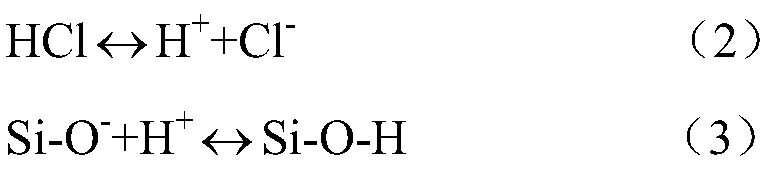Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Isotopes of hydrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
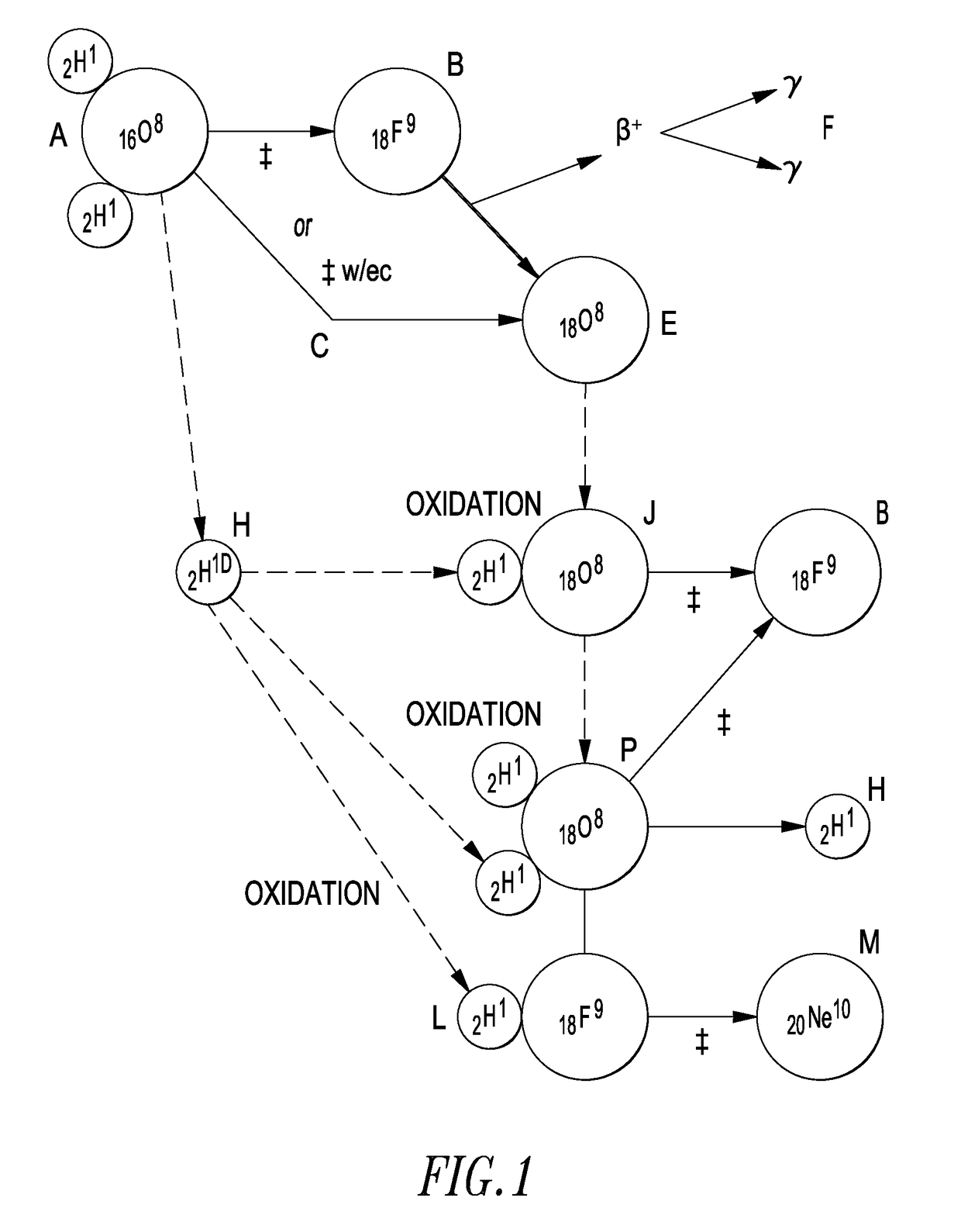
Hydrogen (₁H) has three naturally occurring isotopes, sometimes denoted ¹H, H, and ³H. The first two of these are stable, while ³H has a half-life of 12.32 years. There are also heavier isotopes, which are all synthetic and have a half-life less than one zeptosecond (10⁻²¹ second). Of these, H is the most stable, and ⁷H is the least.
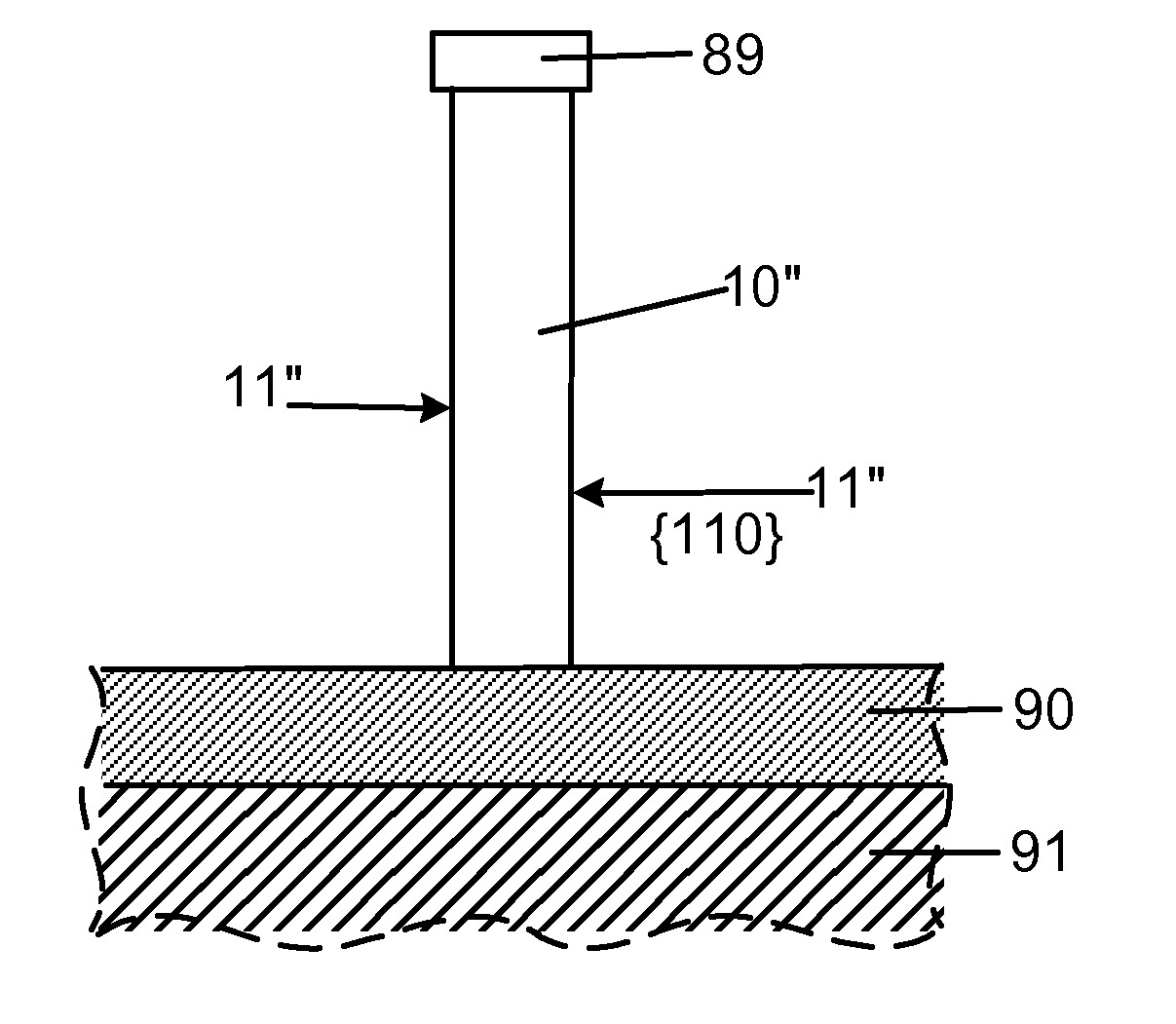
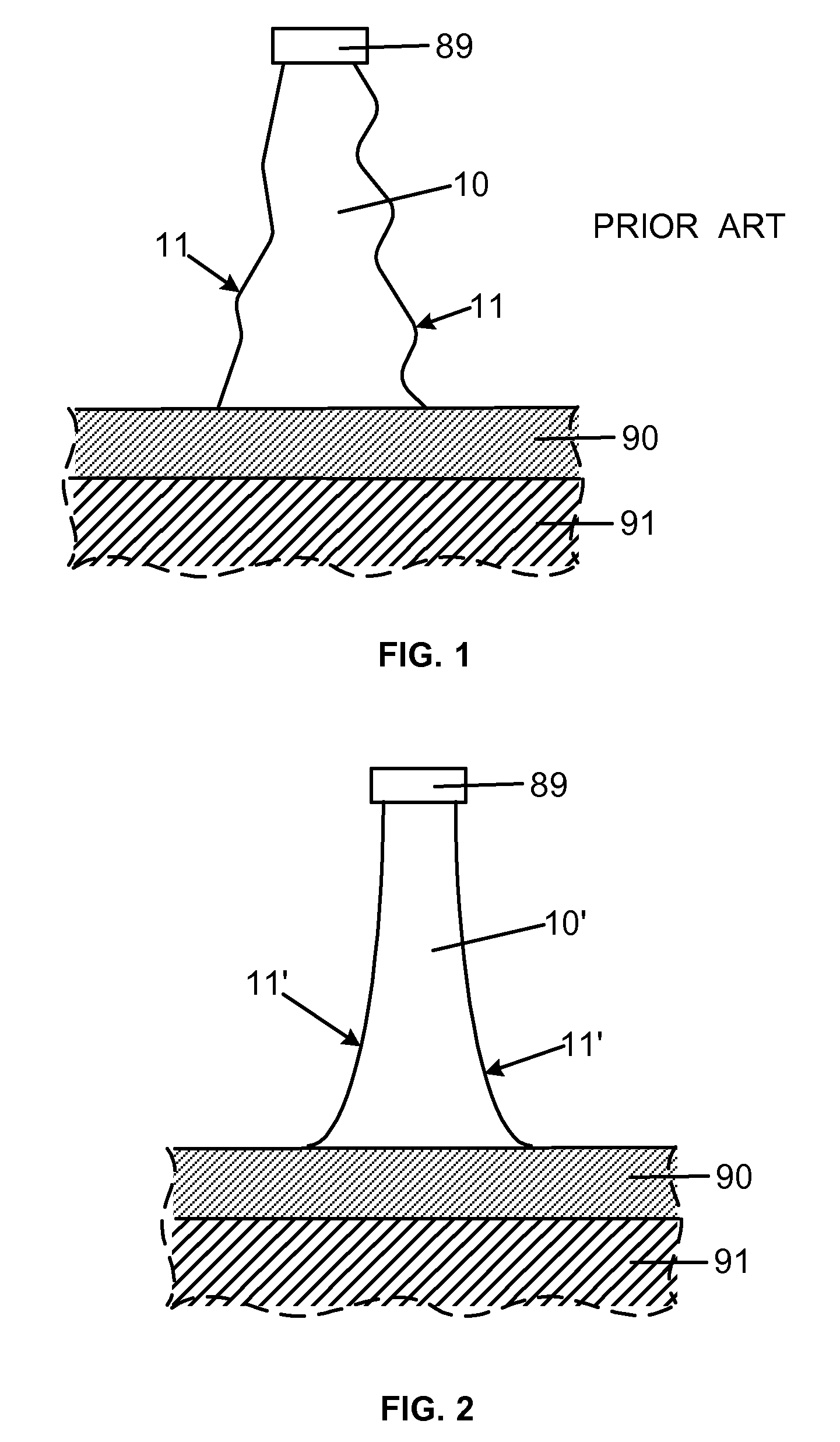
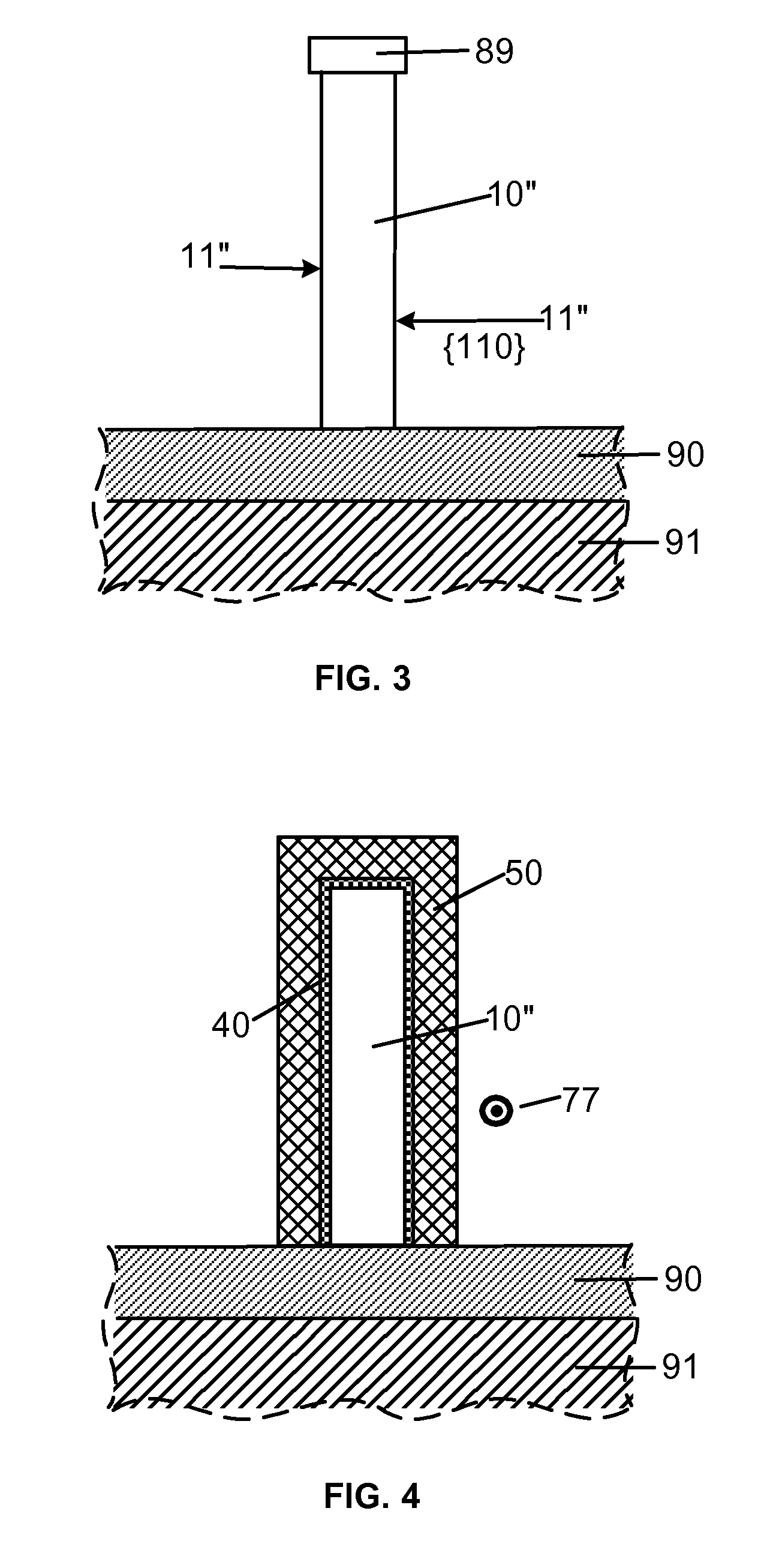
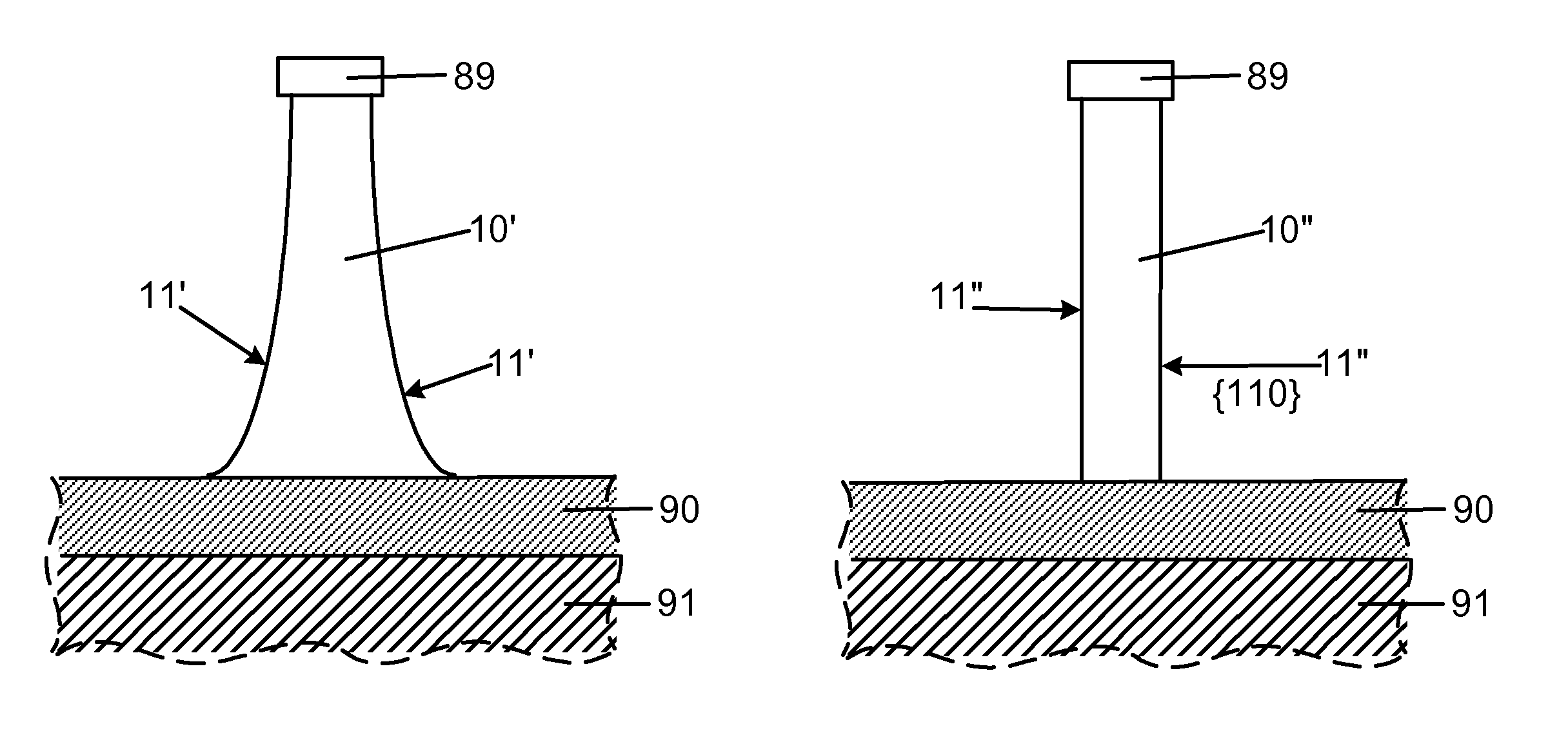
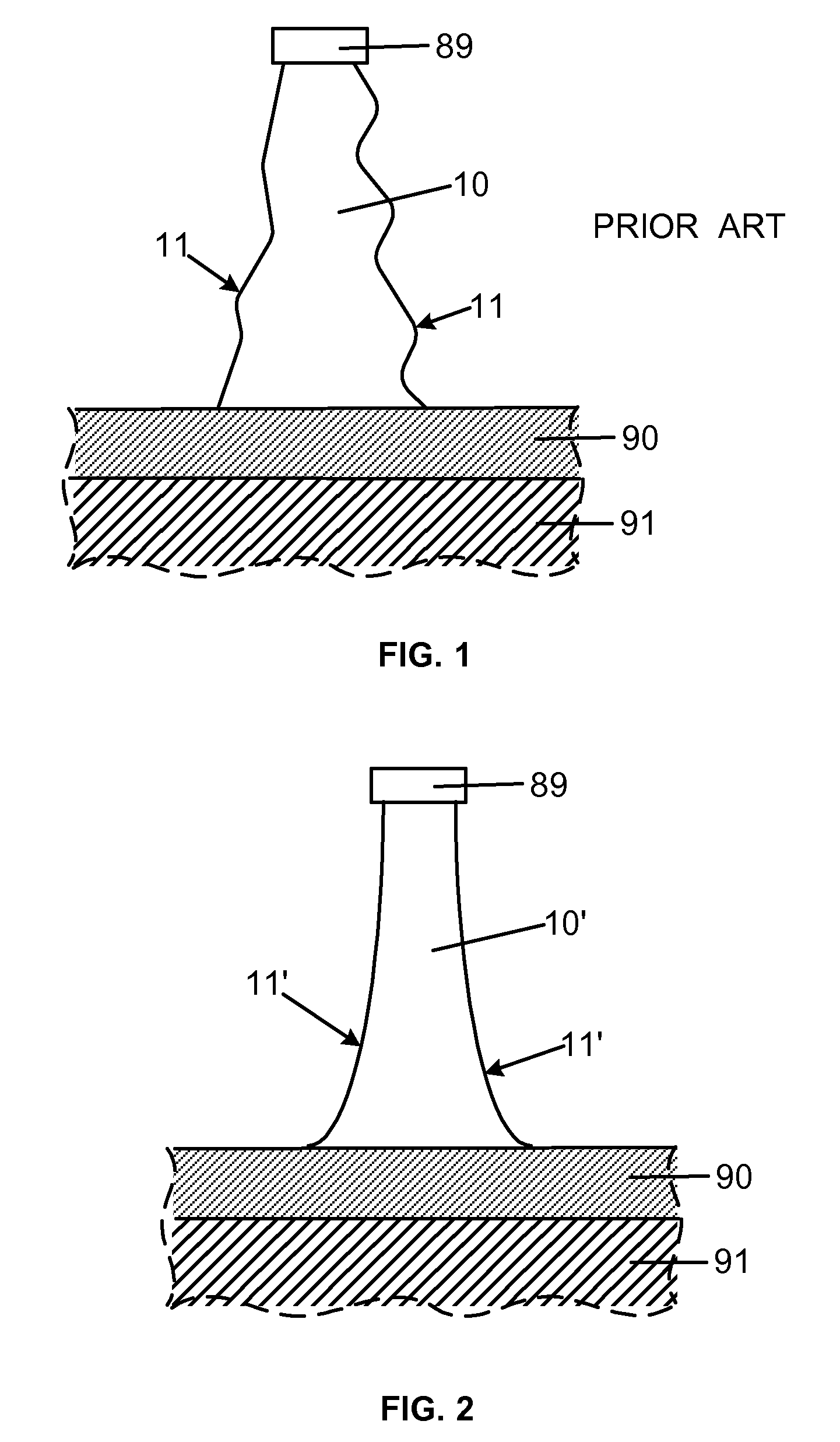
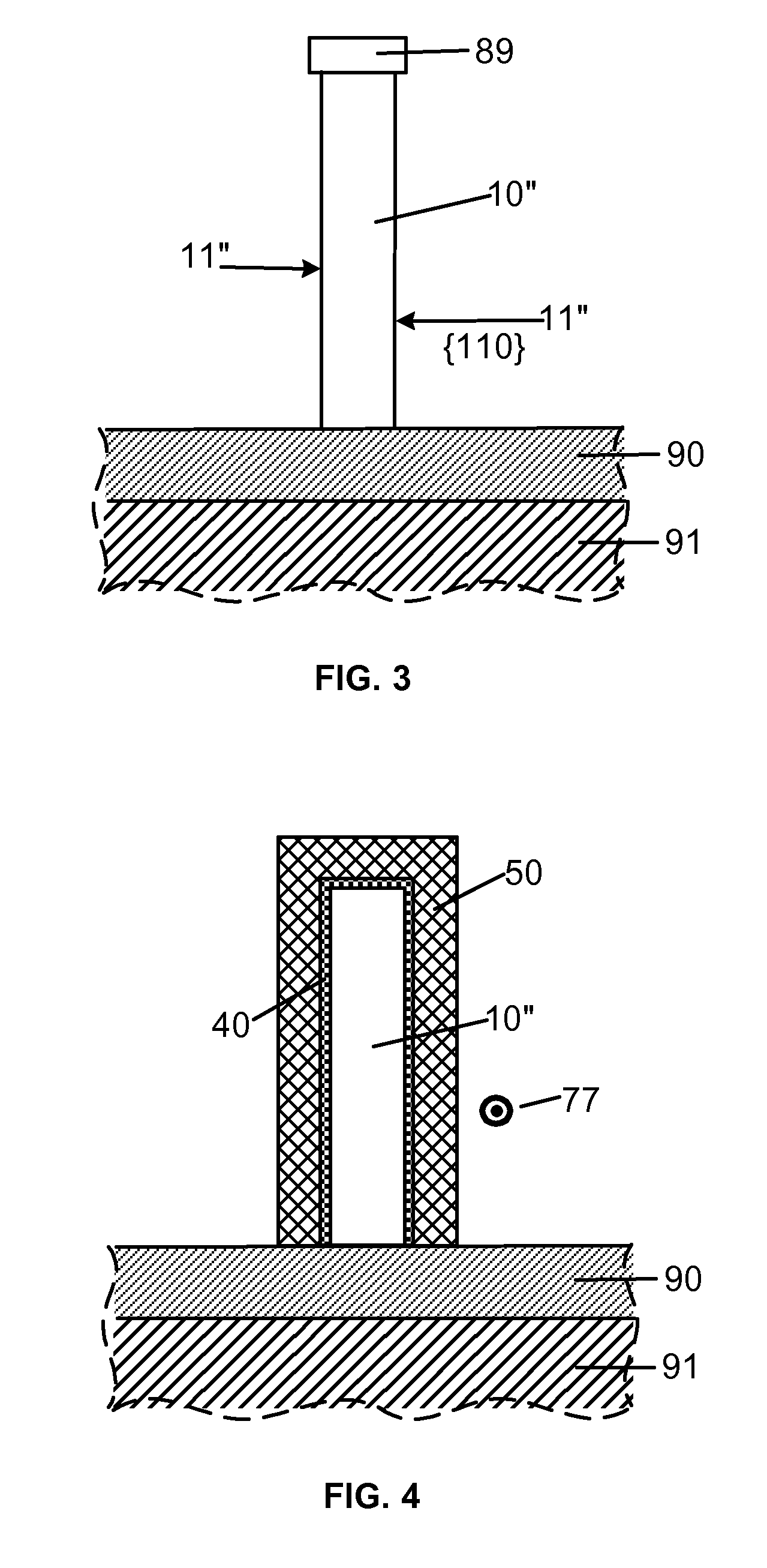
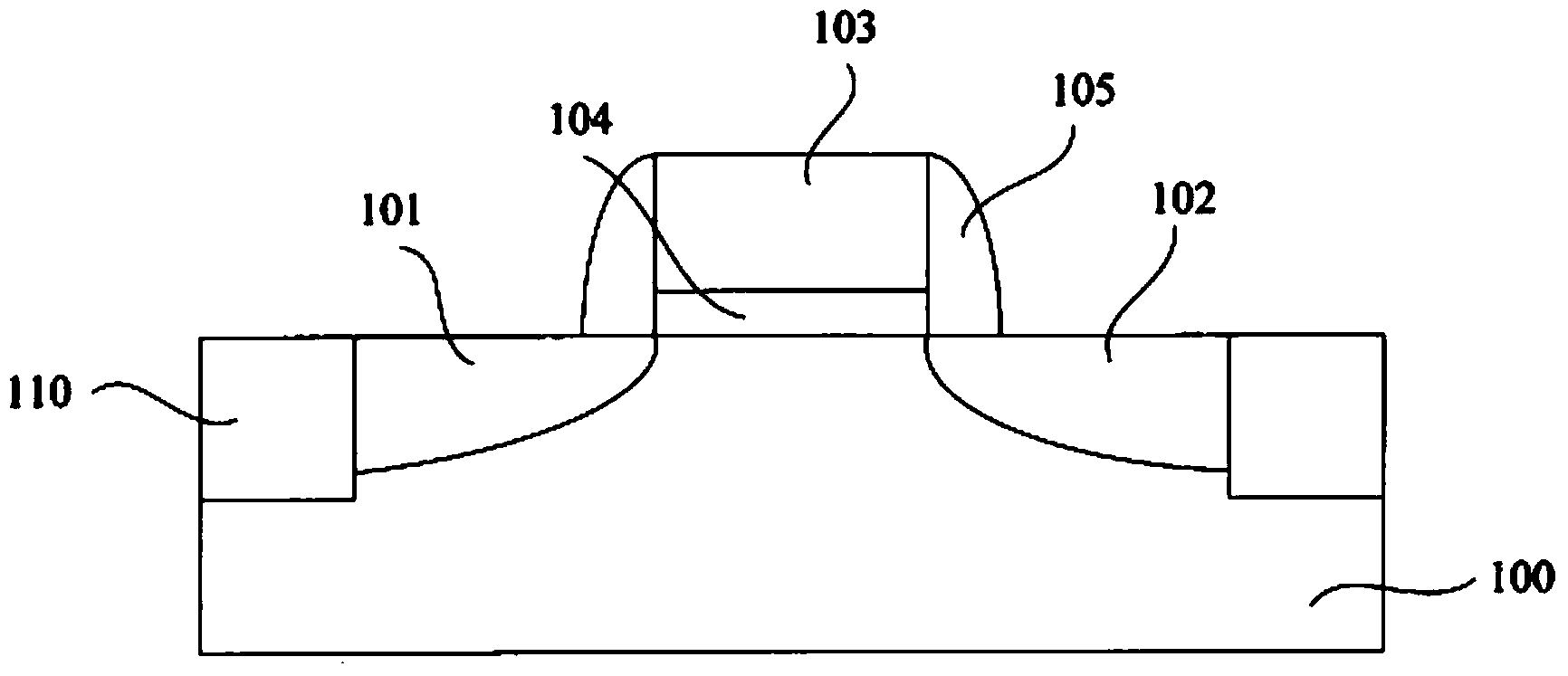
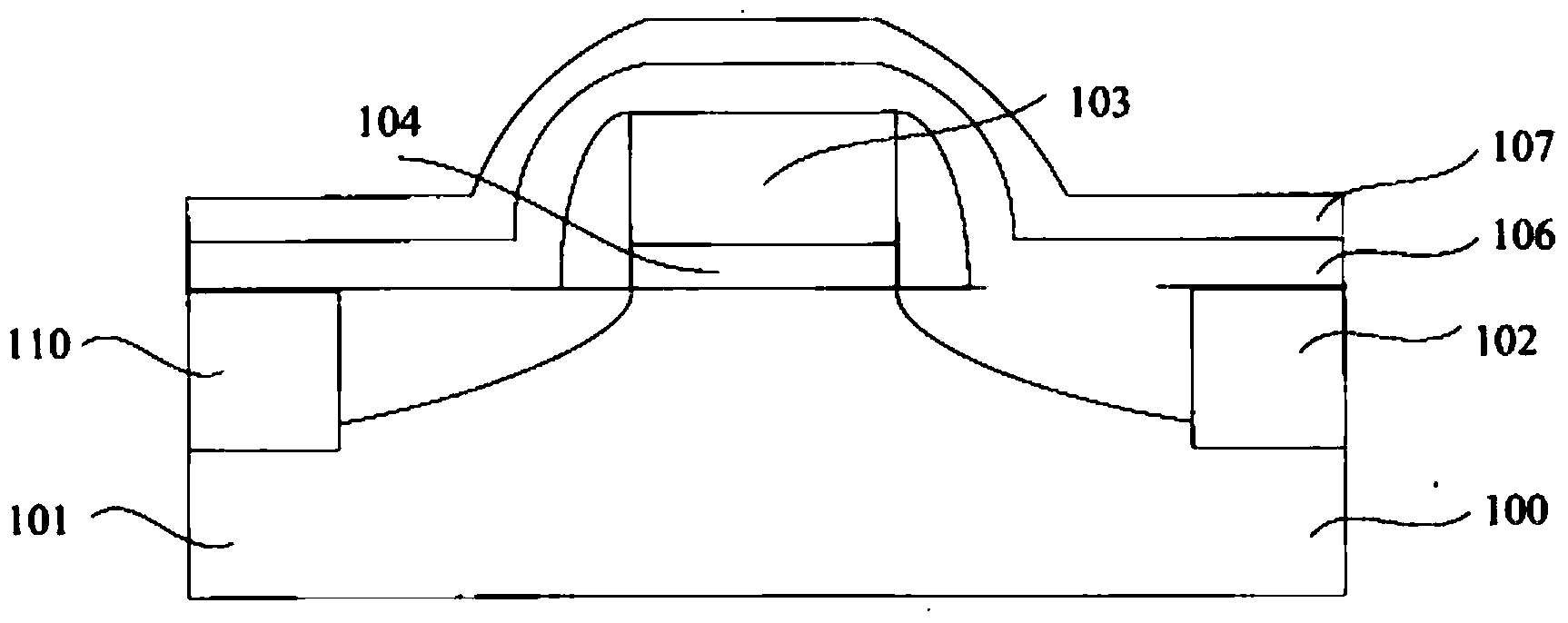
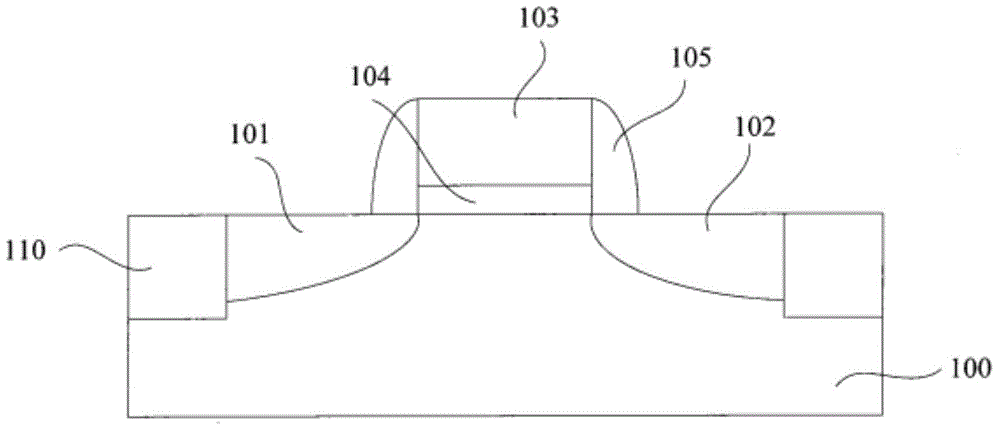
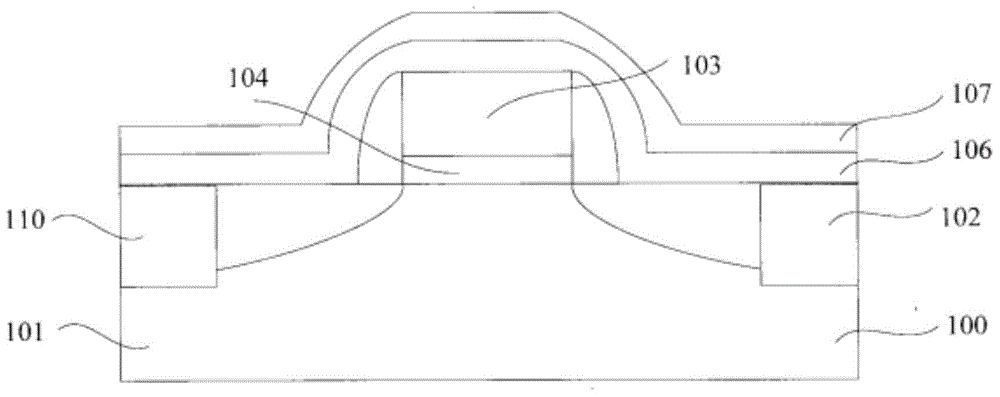
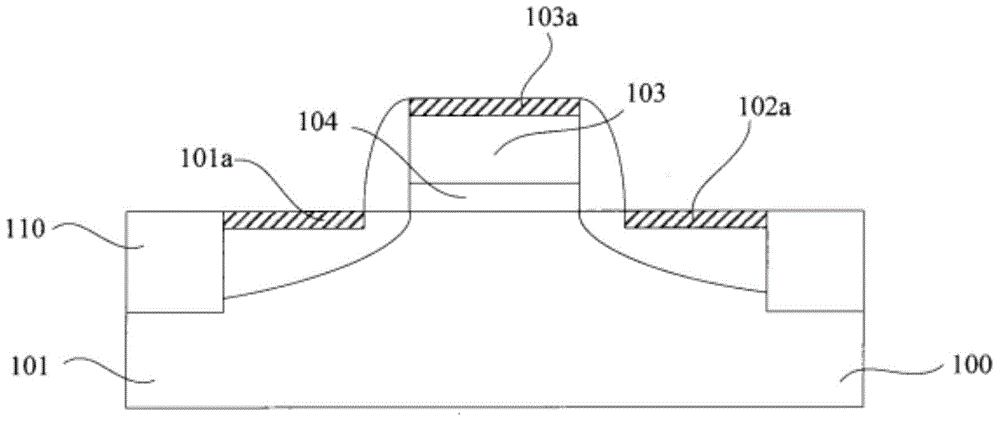
Smooth and vertical semiconductor fin structure
InactiveUS20100048027A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingCrystal orientation
A method for processing a semiconductor fin structure is disclosed. The method includes thermal annealing a fin structure in an ambient containing an isotope of hydrogen. Following the thermal annealing step, the fin structure is etched in a crystal-orientation dependent, self-limiting, manner. The crystal-orientation dependent etch may be selected to be an aqueous solution containing ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). The completed fin structure has smooth sidewalls and a uniform thickness profile. The fin structure sidewalls are {110} planes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
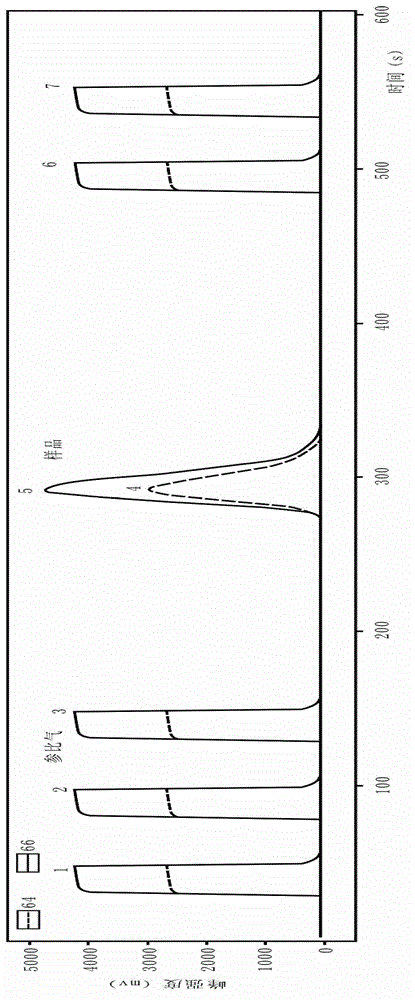
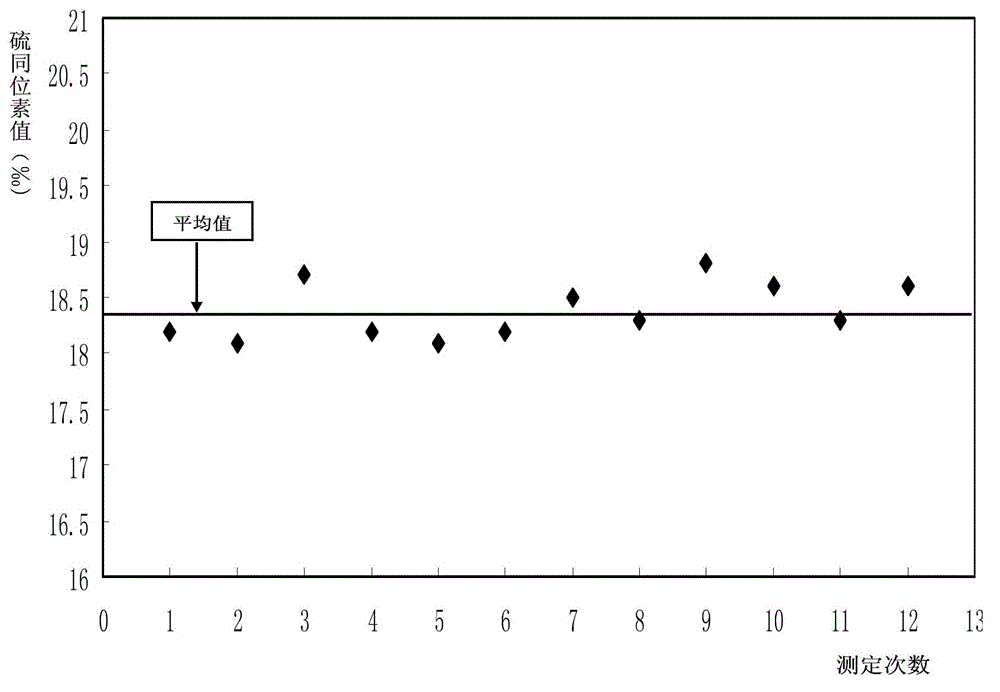
Online analysis method for sulfur isotope of hydrogen sulfide gas in natural gas
ActiveCN102749382ARealize direct and automatic conversionEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElement analysisContinuous flow
The invention relates to an online analysis method for sulfur isotope of hydrogen sulfide gas in natural gas. The method comprises the steps of collecting a natural gas sample; heating oxidation furnace of an elemental analyzer to 1,020 DEG C; heating a chromatographic column box to 50 DEG C; introducing reference gas into a stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer, adjusting center magnetic field of the peak with mass / charge ratio of 66, and storing the magnetic field value; connecting a steel cylinder filled with the natural gas sample with a sampling valve, placing in a ventilating hood, and switching on the ventilating hood; taking the natural gas sample with an airtight sample injector; injecting the natural gas sample into a sample inlet; introducing the natural gas sample into a high-temperature oxidation tube with carrier gas, to be oxidized into carbon dioxide, water and sulfur dioxide gas, carrying the mixed gas with carrier gas through a dewatering tube for water removal; separating the dewatered mixed gas with a gas chromatographic column, sequentially introducing into a stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer through a continuous flow interface, measuring sulfur isotope composition, and generating spectrogram.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
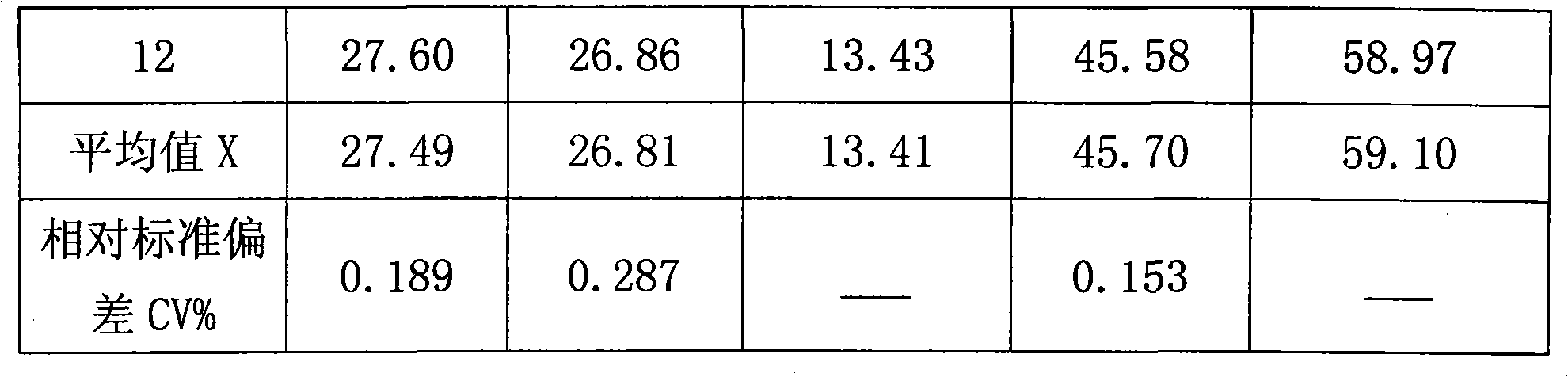
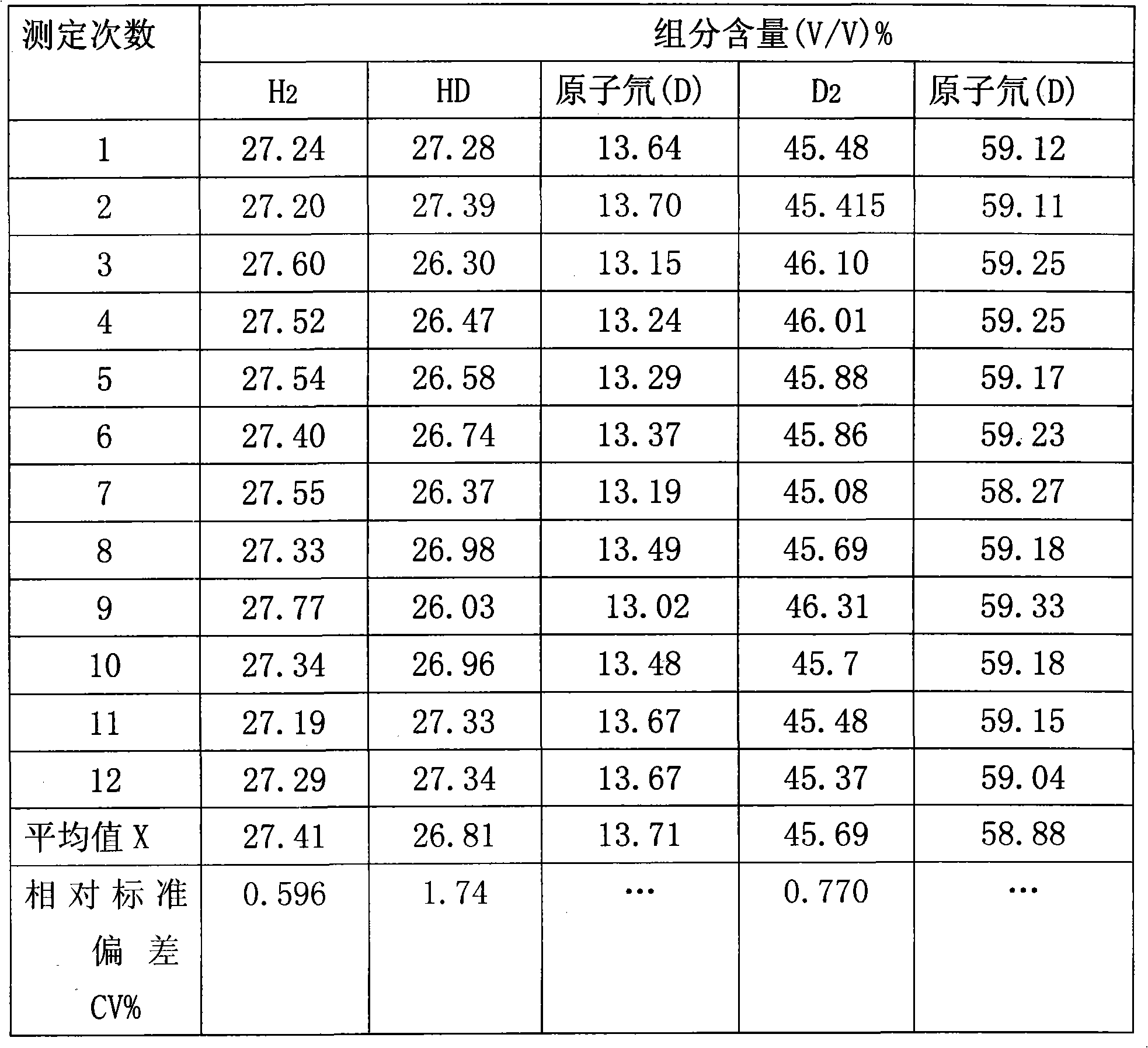
Method for quantitatively measuring hydrogen, deuteration hydrogen and deuterium hydrogen isotope element
The invention relates to an quantitative determination method of the isotope of hydrogen, hydrogen deuteride and hydrogen deuterium, which comprises using neon gas to be carrier gas, leading a gas chromatograph to adopt a double-strut double-temperature system, choosing 50 DEG C sampling temperature, sampling through an injector or a gas sampling valve, and the sampling quantity is 0.1-2.2mL, sample gas which is separated by a gas-chromatography column generates electrical signals through a detector, recording the pear areas of hydrogen, hydrogen deuteride and deuterium gas of chromatogram peaks through a chromatogram working station after the electrical signals are magnified through a front magnifier, adopting a volume correction factor normalization method or an external standard method to measure the content of hydrogen (H2), hydrogen deuteride (HD) and deuterium (D2), and getting detection results. The invention has the advantages of excellent separation effect of hydrogen isotope and high detection sensitivity, the detection of the pureness of deuterium gas can reach more than 99.99%, hydrogen deuteride (HD) and deuterium (D2) are sampled in big dosage, the peaks are not overlapped, thereby guaranteeing the quantitative detection of high-purity deuterium gas, and standard gas is not needed to be prepared in the process of detecting. The method simplifies the operation process, which is convenient for on-line detection of deuterium gas in the process of producing.
Owner:柯香文
System and method for separating heavy isotopes of hydrogen oxide from water
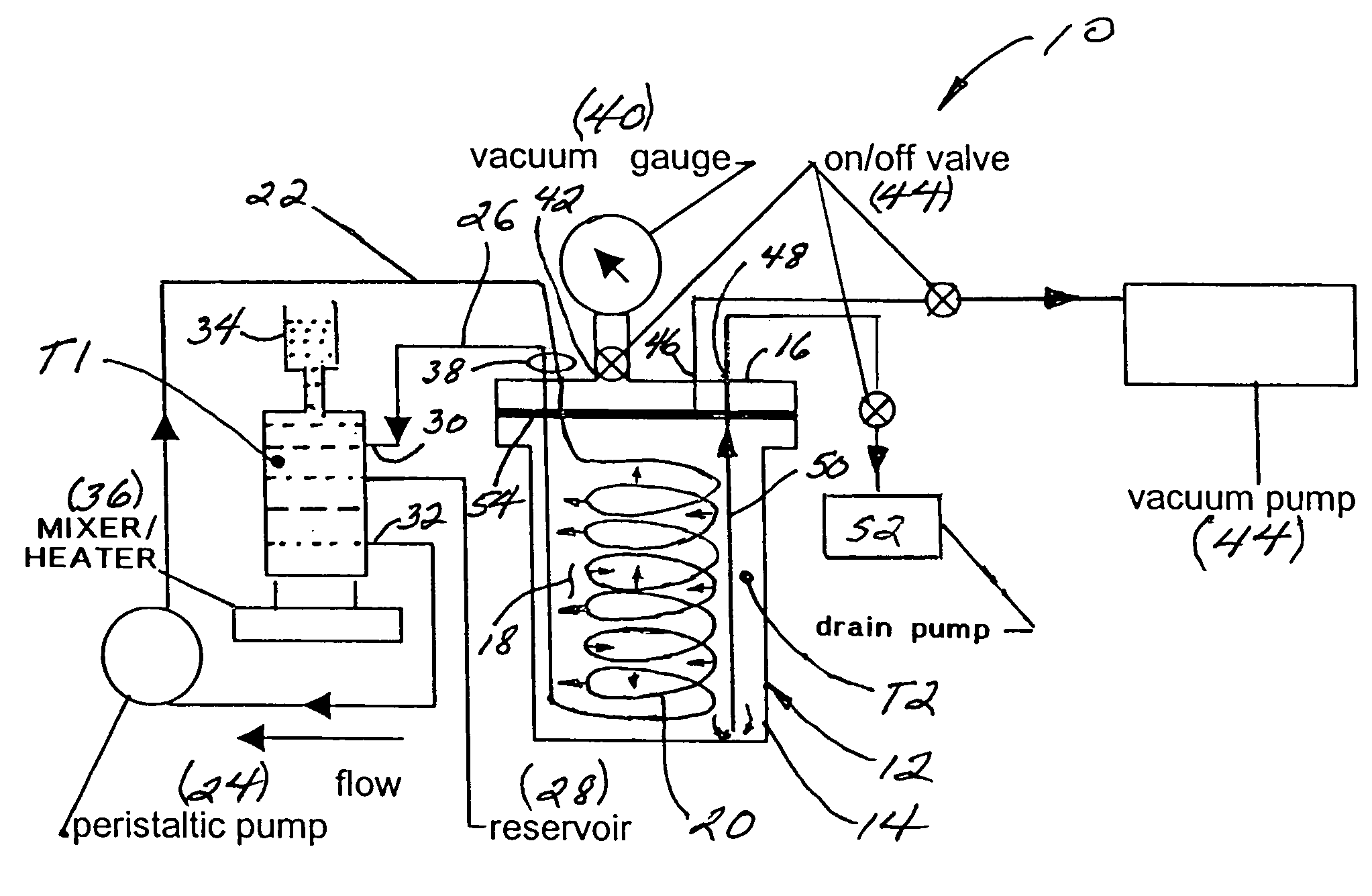
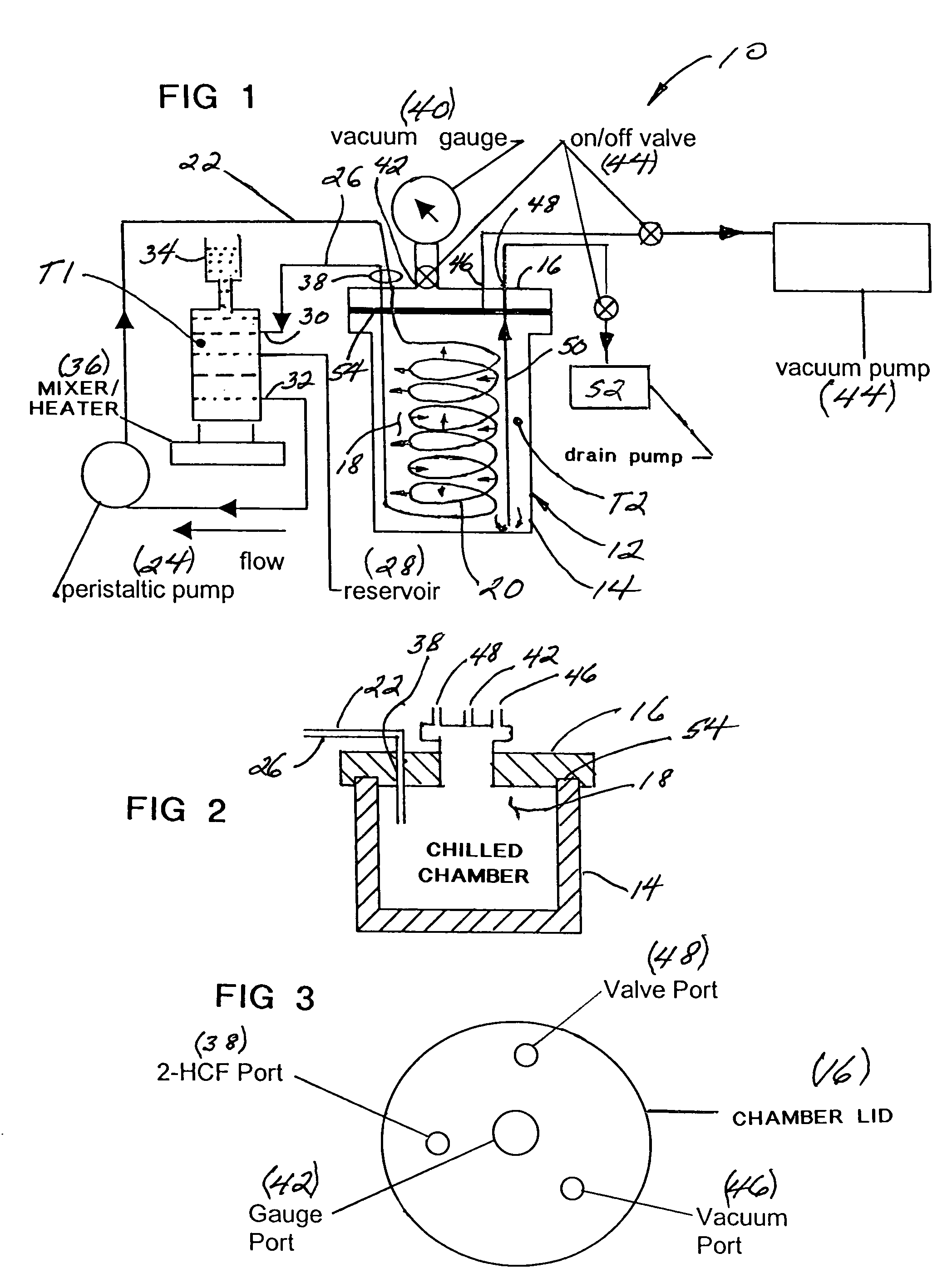
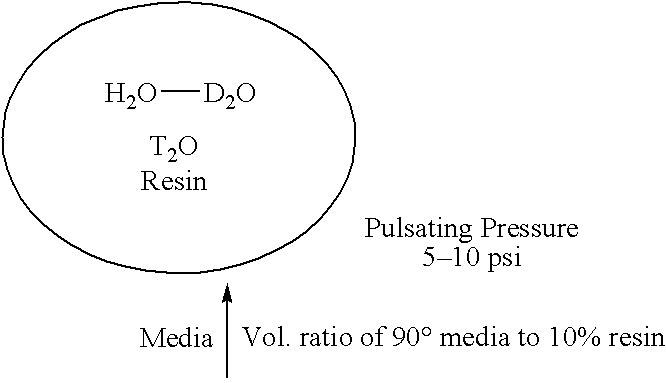
An apparatus and method for separating heavy isotopes of hydrogen from contaminated water. The apparatus includes a treatment chamber with an elongated hollow core fiber (HCF) extending within the chamber. A reservoir holds contaminated water mixed with beads formed of an exchange resin, the mixture of contaminated water and beads forming a flowable slurry. The slurry is continuously circulated through the hollow core fiber and the reservoir preferably by a pulsating peristaltic pump. The beads absorb a portion of the heavy isotopes from the slurry by exchange with waters of hydration of the beads while the hollow core fiber allows permeation of only light water from said slurry outwardly through the HCF wall as a permeate.
Owner:PATTERSON LEGACY
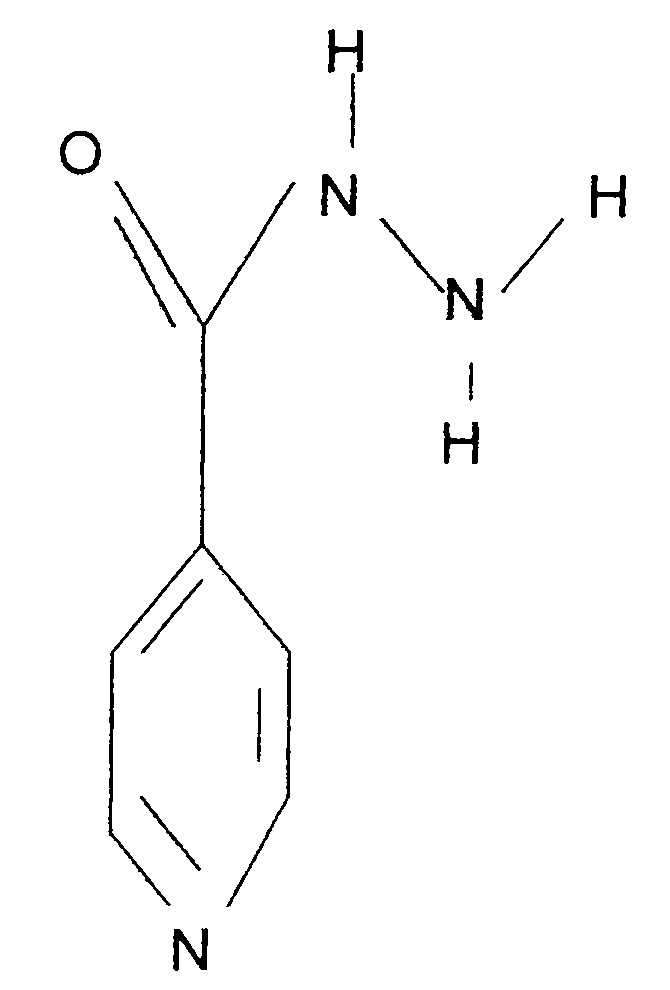
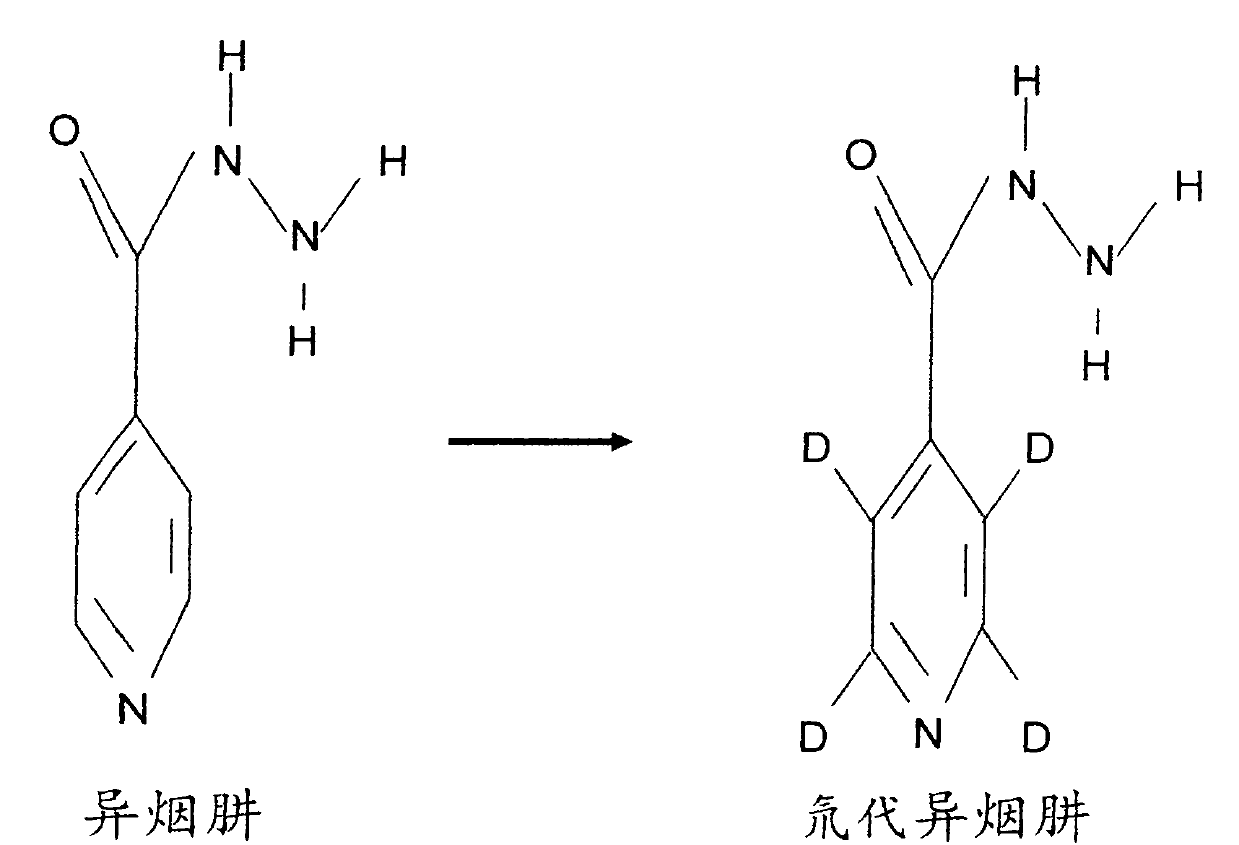
Preparation method and application of deuterated drugs
InactiveCN102020522AReduce toxicity and side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBond energy
A carbon hydrogen structure (C: H) is one of the basic structures in the pharmaceutical chemistry structure and a formed C-H bond is the basic chemical bond. The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of deuterated drugs which can change the chemical bond energy and the hydrogen bond energy in the structure of pharmaceutical compound. The hydrogen atom (H) in pharmaceutical compound structure is substituted by the A deuterium atom (D) which is the isotope of hydrogen, therefore changing the molecular structure and the bond energy of the substituted pharmaceutical compound so as to form a new deuterated drug. The deuterated drugs can be used for pharmacokinetics research, can obviously enhance the disease-preventing or treating function of the drugs, and can reduce the toxic and side effect of the drugs.
Owner:陈松源
Isotope based surface water pollution source analytical method
InactiveCN103808790AImprove accuracyImprove work efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInternational standardIsotopes of carbon
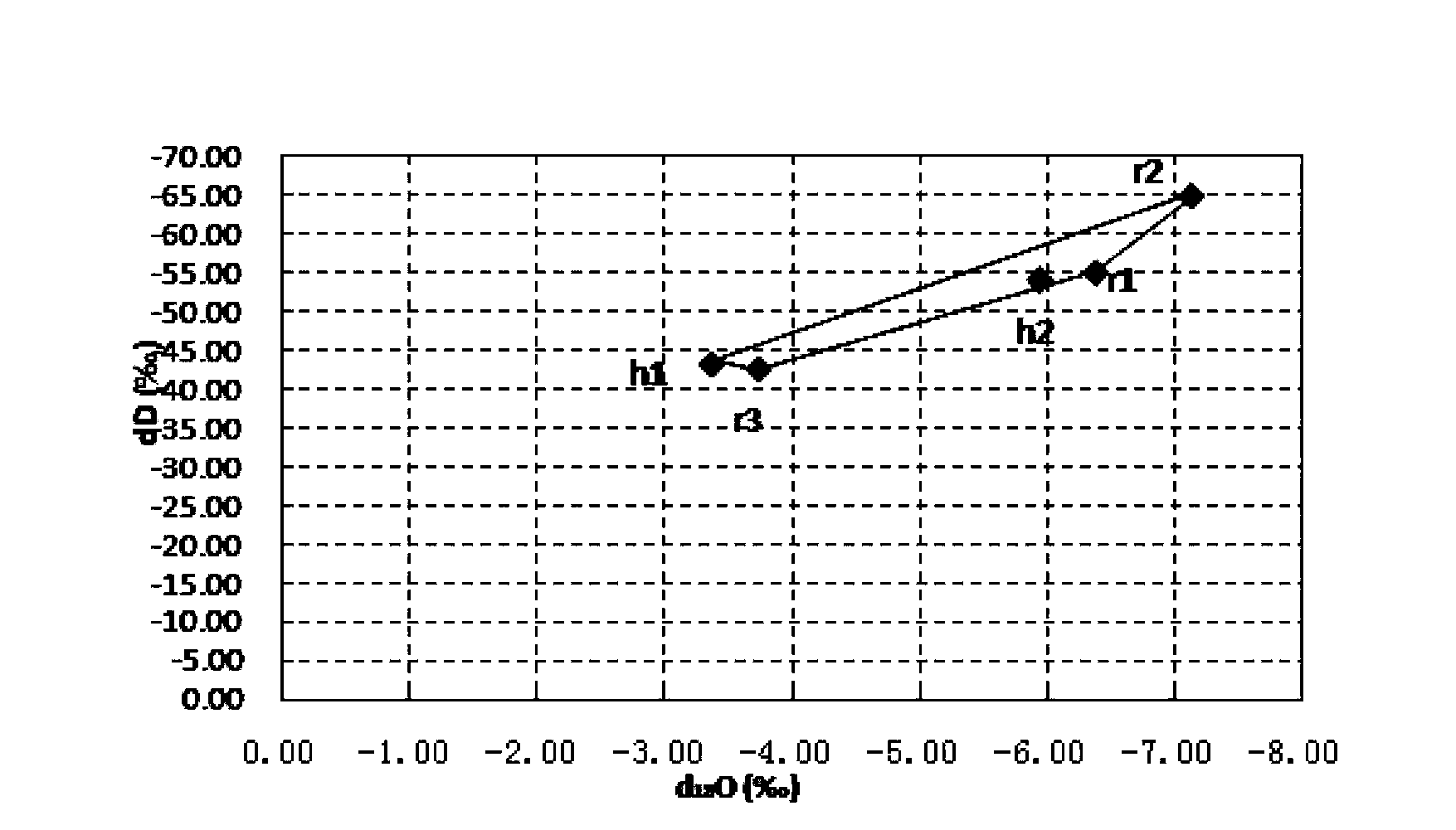
The invention relates to an isotope based surface water pollution source analytical method, which comprises the steps of: 1) sampling: laying sampling points and conducting sampling according to industry standards; 2) isotope detection: taking isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen, namely D, <18>O, <13>C, and <15>N as the indexes; employing an isotope ratio mass spectrometer to detect the ratios of isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen, namely D, <18>O, <13>C, and <15>N in samples, and conducting comparison with international standard substances, and working out isotope ratios of the samples; and 3) data analysis: drawing a hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio diagram according to the ratios of isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen, namely D and <18>O in source and convergence samples; selecting analysis nodes, calculating a pollution source contribution rate through a source convergence isotope ratio of the nodes, and determining a new pollution source by judging whether the source convergence isotope ratio of outflow nodes is balanced, and then making use of analysis of the isotopes of carbon and nitrogen, namely <13>C and <15>N to verify the accuracy of the result. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of improving the accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
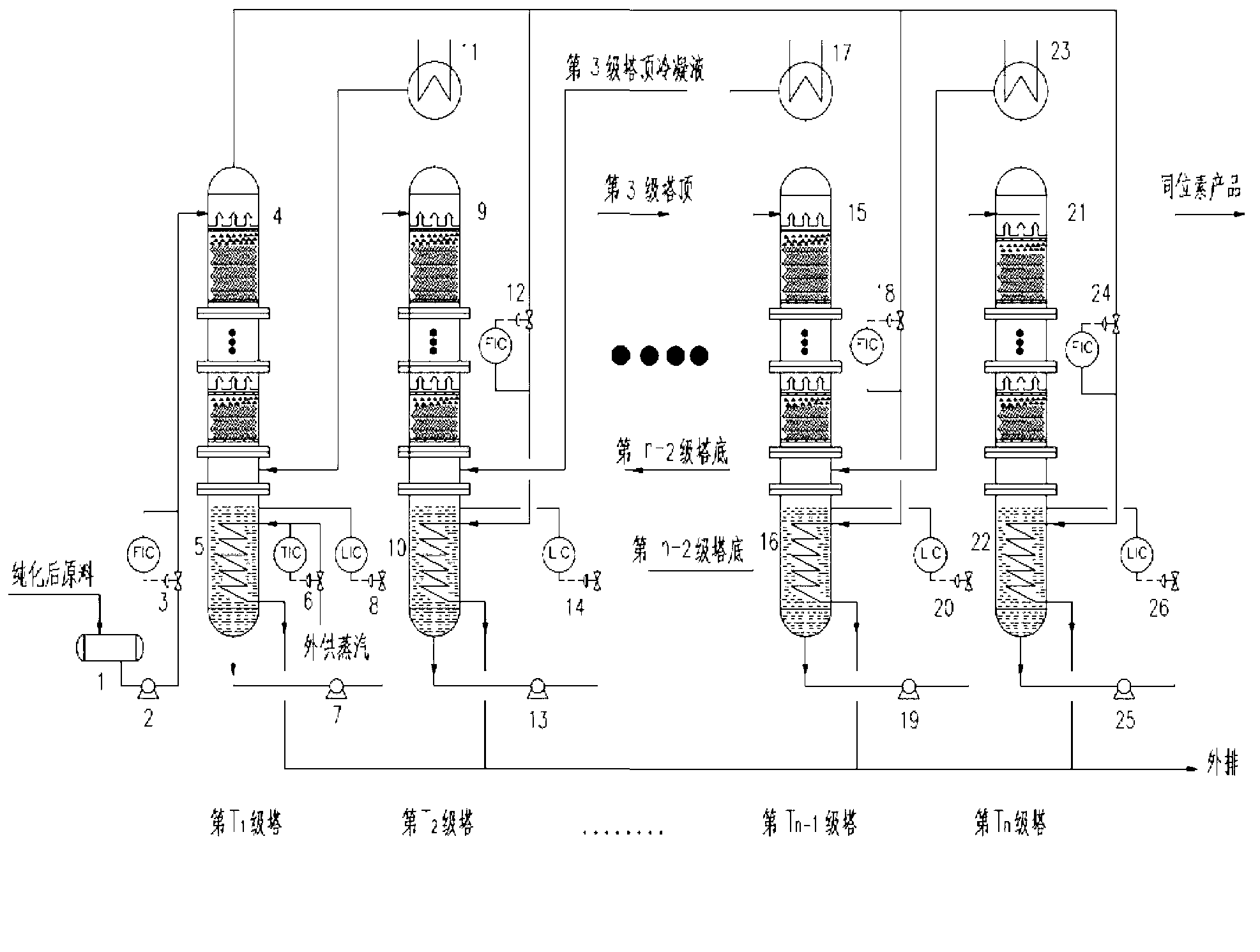
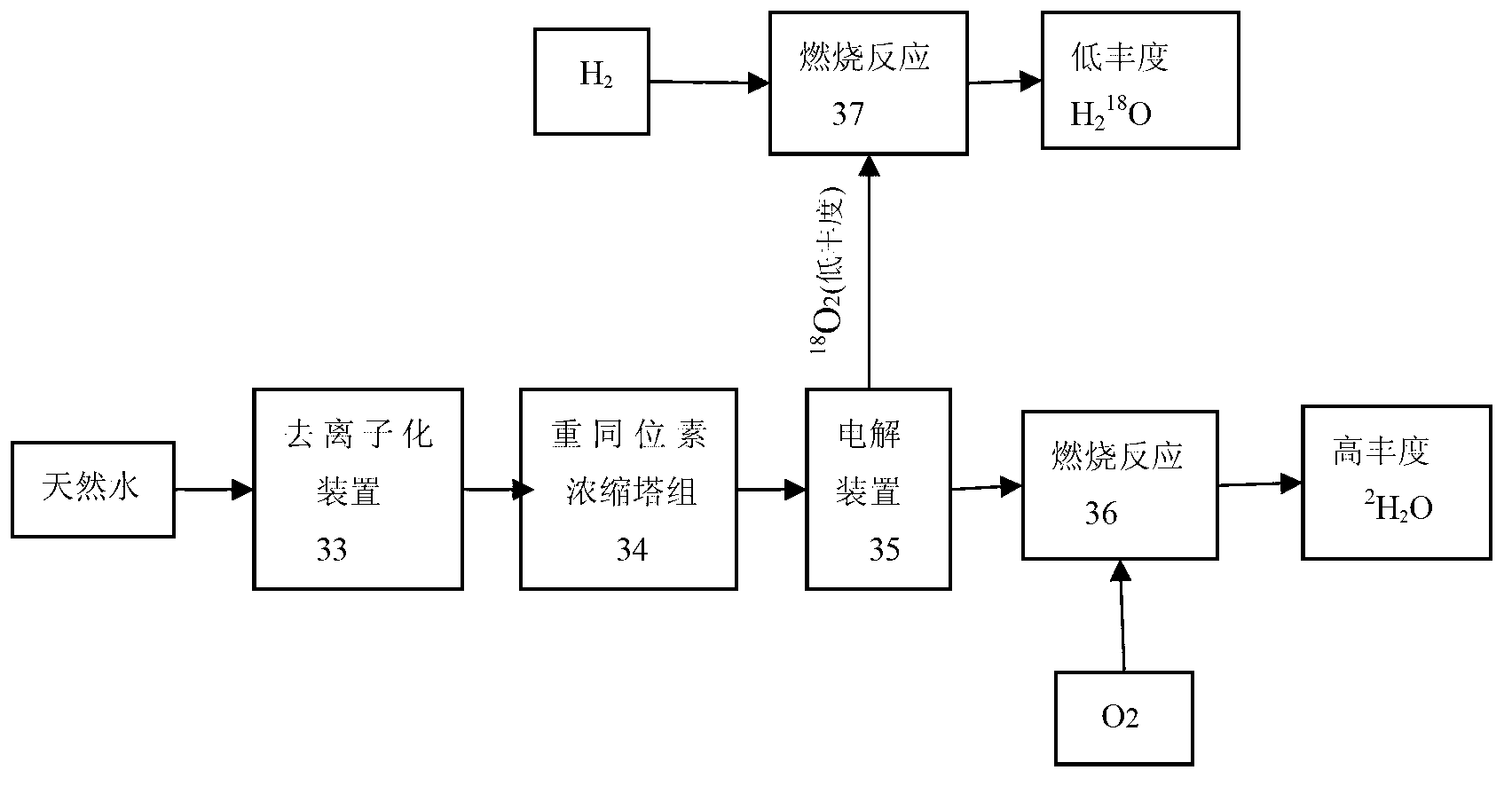
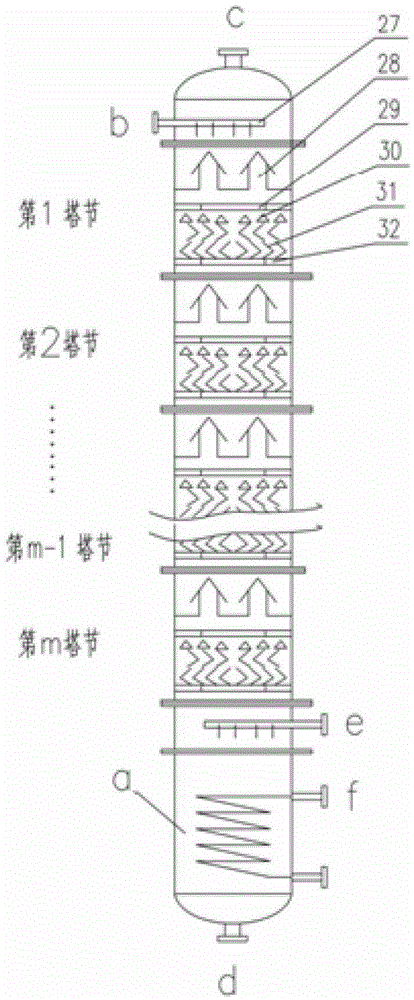
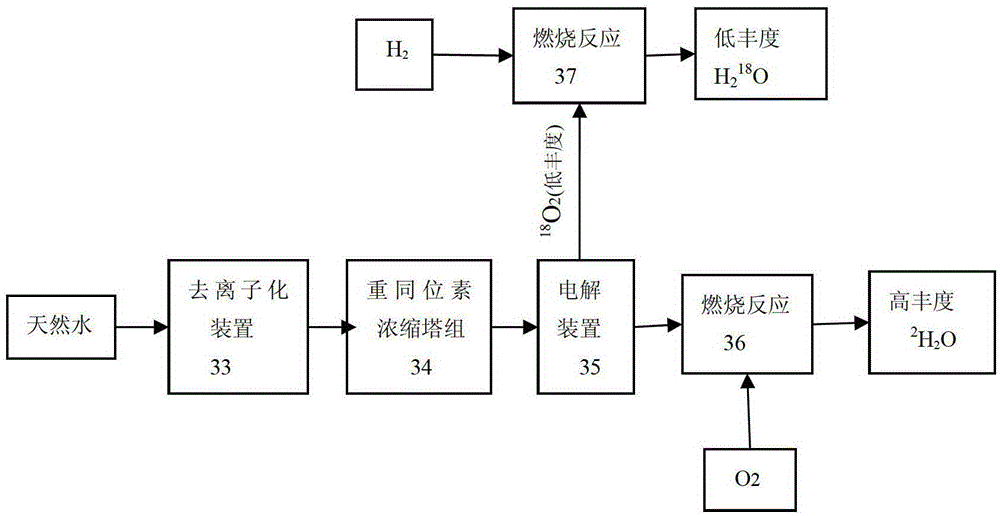
Method and device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C
The invention relates to a method and a device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C. The method comprises the steps of: by taking compounds respectively containing stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C as materials, carrying out purification treatment, adding to a heavy isotope concentration tower group formed by a plurality stages of gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series; continuously and partially vaporizing and partially condensing in the gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series by weak vapor pressure difference between light and heavy isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon elements, and gradually concentrating and purifying corresponding heavy isotope. Each tower disclosed by the invention adopts different operation pressures and coupling utilization of heat between the towers; over 30-40% of energy consumption can be saved; a composite structure mass transfer component composed of a liquid collecting distributer, a Dixon mass transfer component, a corrugated mass transfer component and the like is adopted inside the tower; the device is easy to amplify; the device of producing heavy 2H, 18O or 13C isotope at a large scale just needs to be connected with 2-8 gas-liquid mass transfer towers in series; over 50% of investment is saved in comparison with the same scale of device, and the towers adopt a single tandem cascade technology; and the method is simple in flow and easy to control and operate.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHENGNENG ISOTOPE
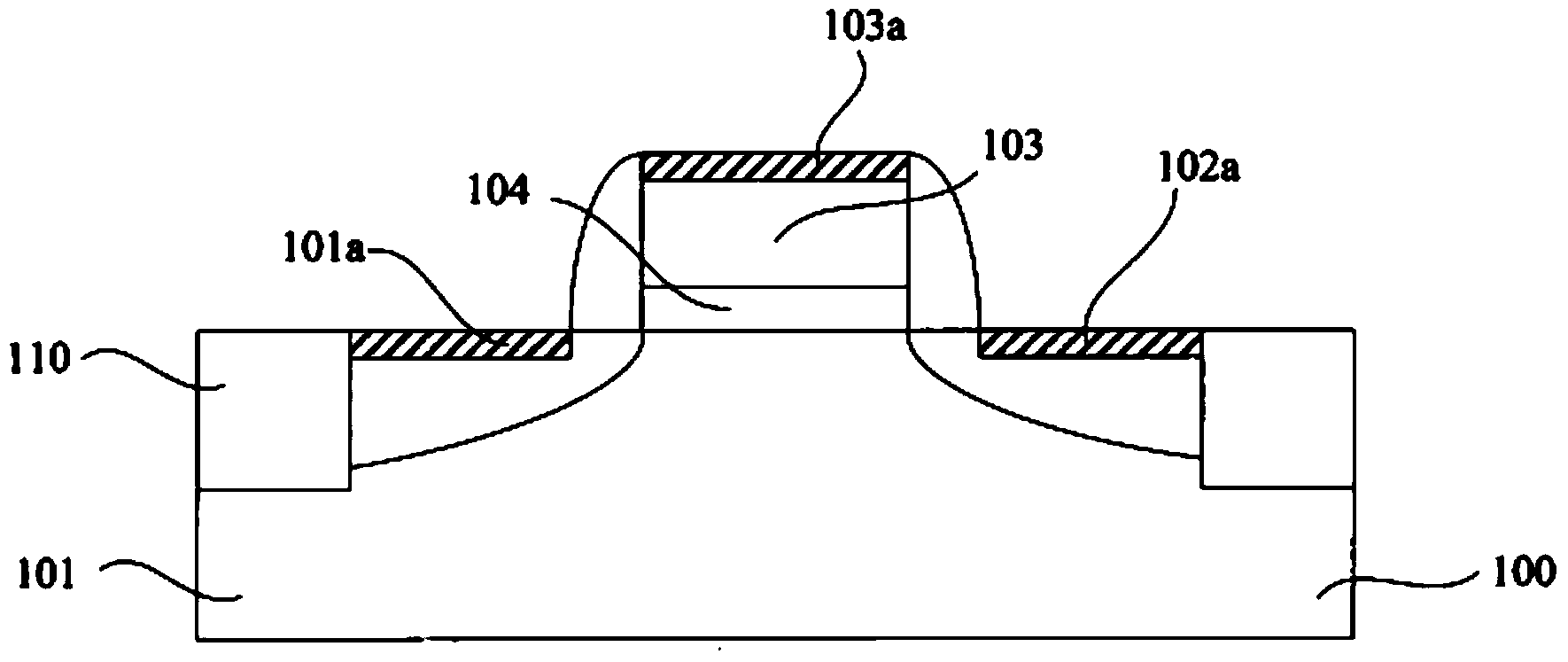
Smooth and vertical semiconductor fin structure
InactiveUS8268729B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSelf limitingCrystal orientation
A method for processing a semiconductor fin structure is disclosed. The method includes thermal annealing a fin structure in an ambient containing an isotope of hydrogen. Following the thermal annealing step, the fin structure is etched in a crystal-orientation dependent, self-limiting, manner. The crystal-orientation dependent etch may be selected to be an aqueous solution containing ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). The completed fin structure has smooth sidewalls and a uniform thickness profile. The fin structure sidewalls are {110} planes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
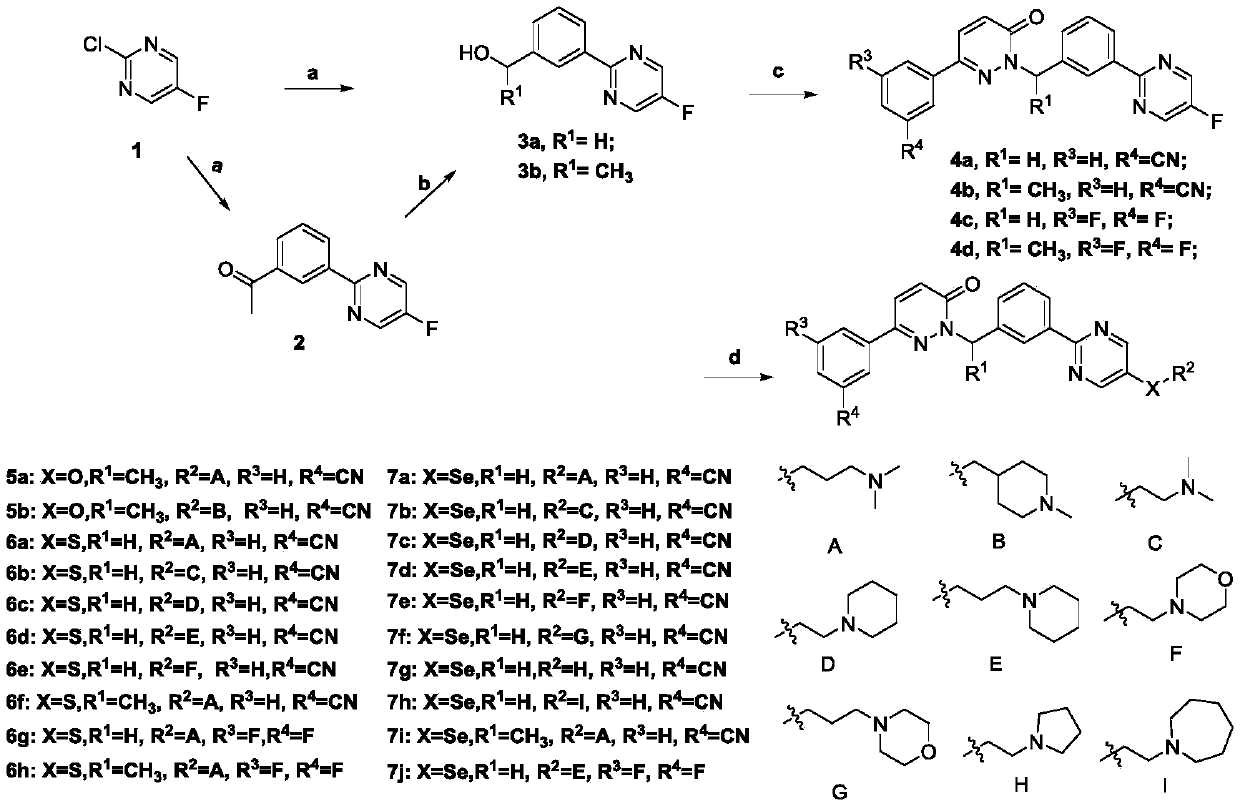
Novel Tepotinib derivative and preparation method thereof and application of derivative in antitumor drug
InactiveCN108752322AImprove bioavailabilityGood antitumor activityIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsSulfurC-Met
The invention discloses a novel Tepotinib derivative and a preparation method thereof and an application of the derivative in an antitumor drug. According to the invention, a chiral structure is introduced in molecules, a hydrogen isotope deuterium is introduced in an easily metabolical part in the molecules, and atoms of sulfur, selenium and sulfoxide or groups are introduced in the molecules. The antineoplastic active experiments (having c-Met-expressed tumor cells) on a cell level proves that the compound has excellent antineoplastic activity, and the stability of the antineoplastic compound is obviously increased.
Owner:SYMEPILIN PHARMA CO LTD
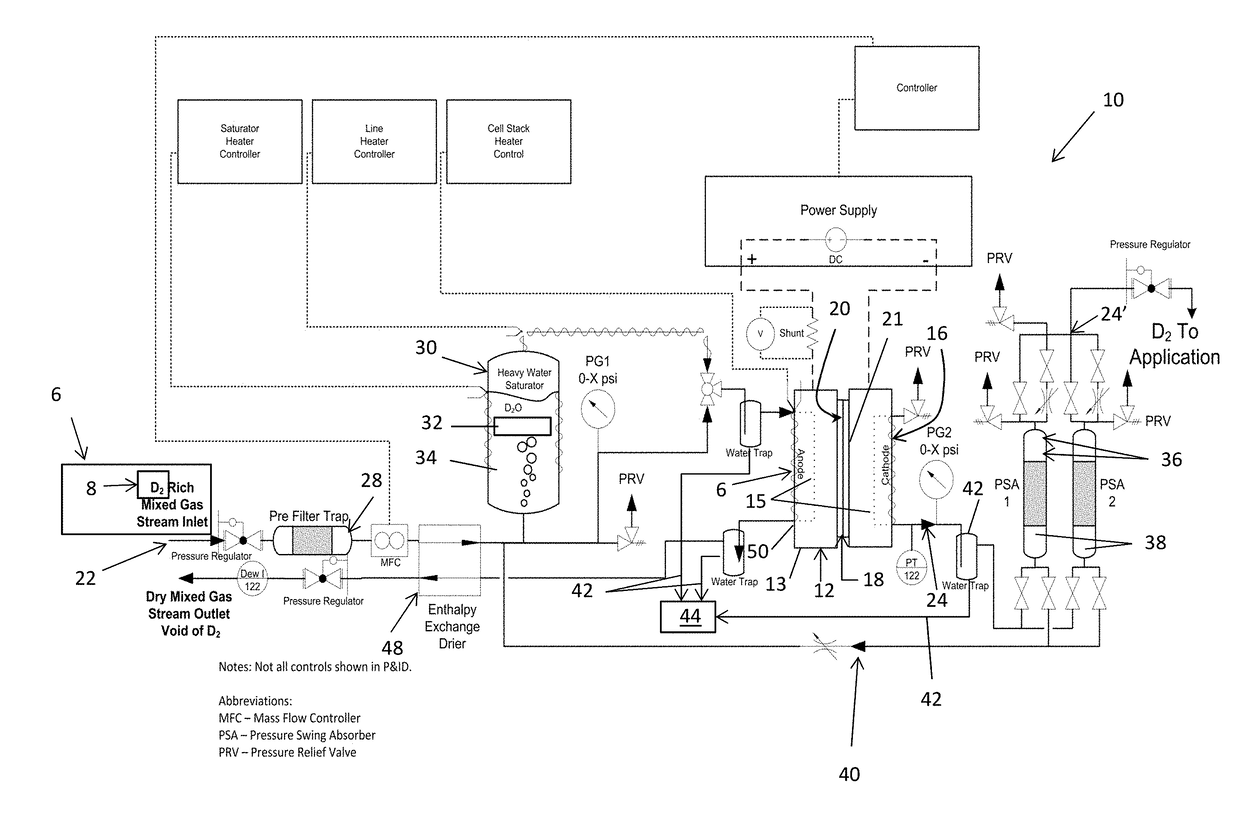
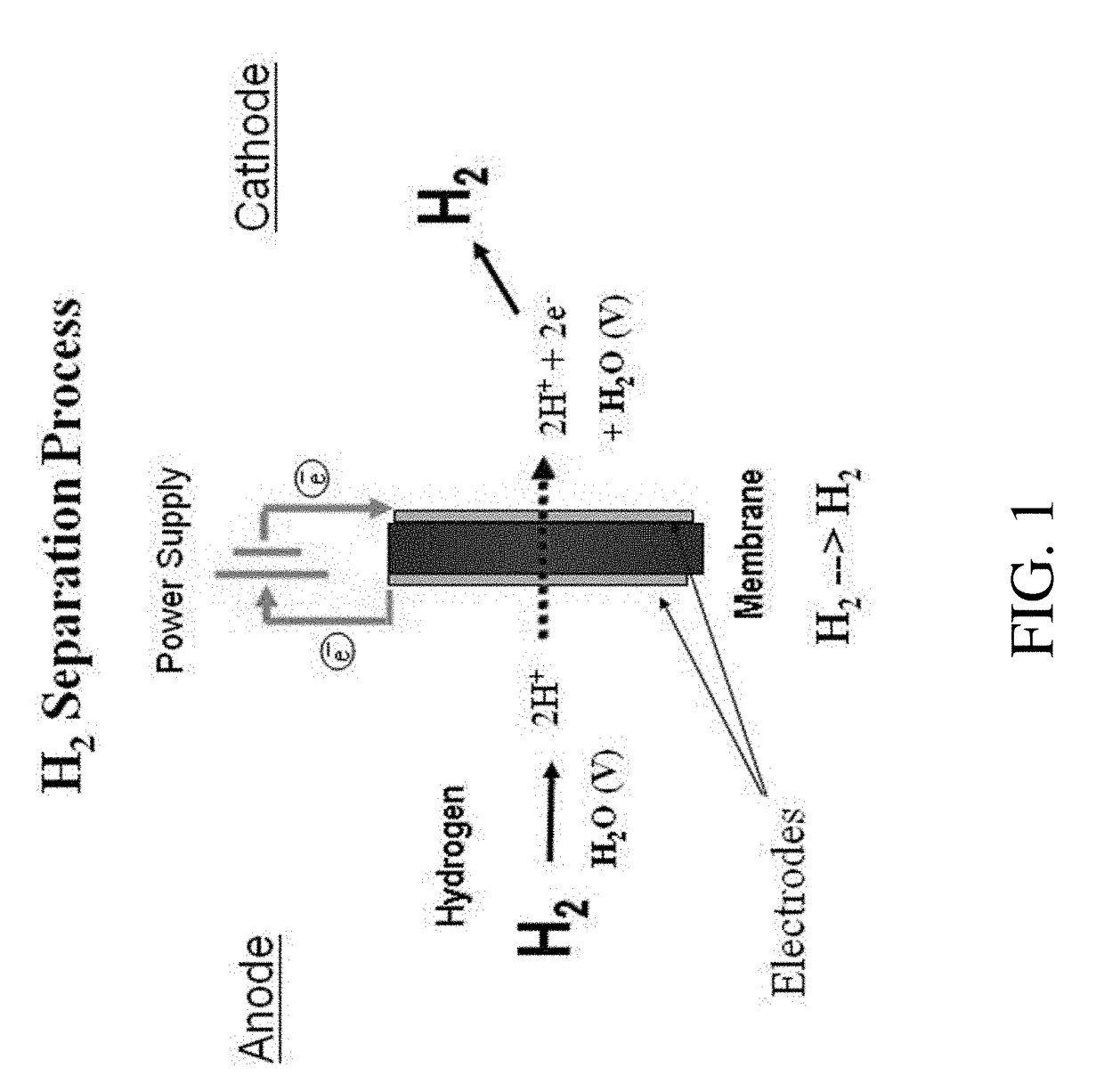
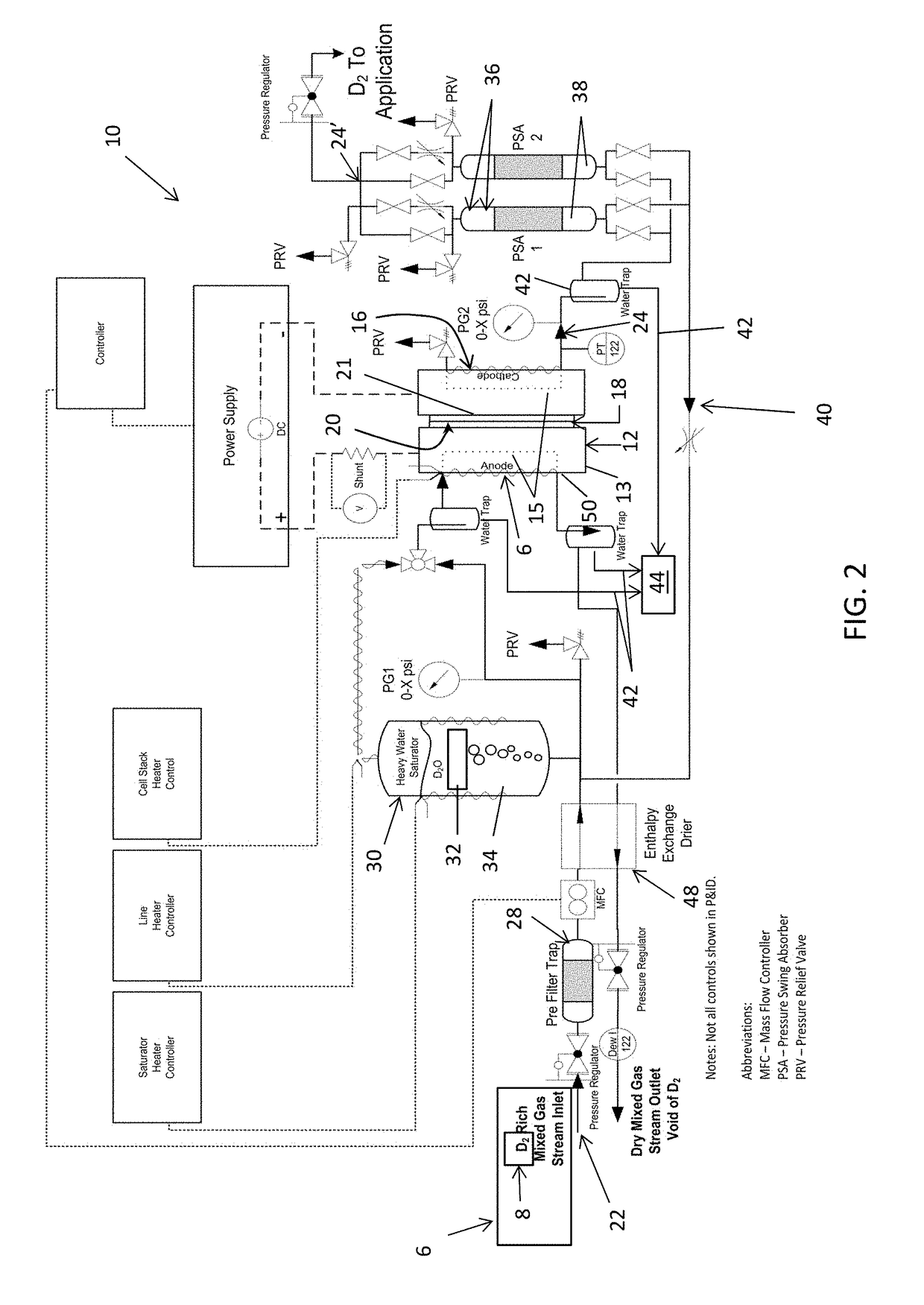
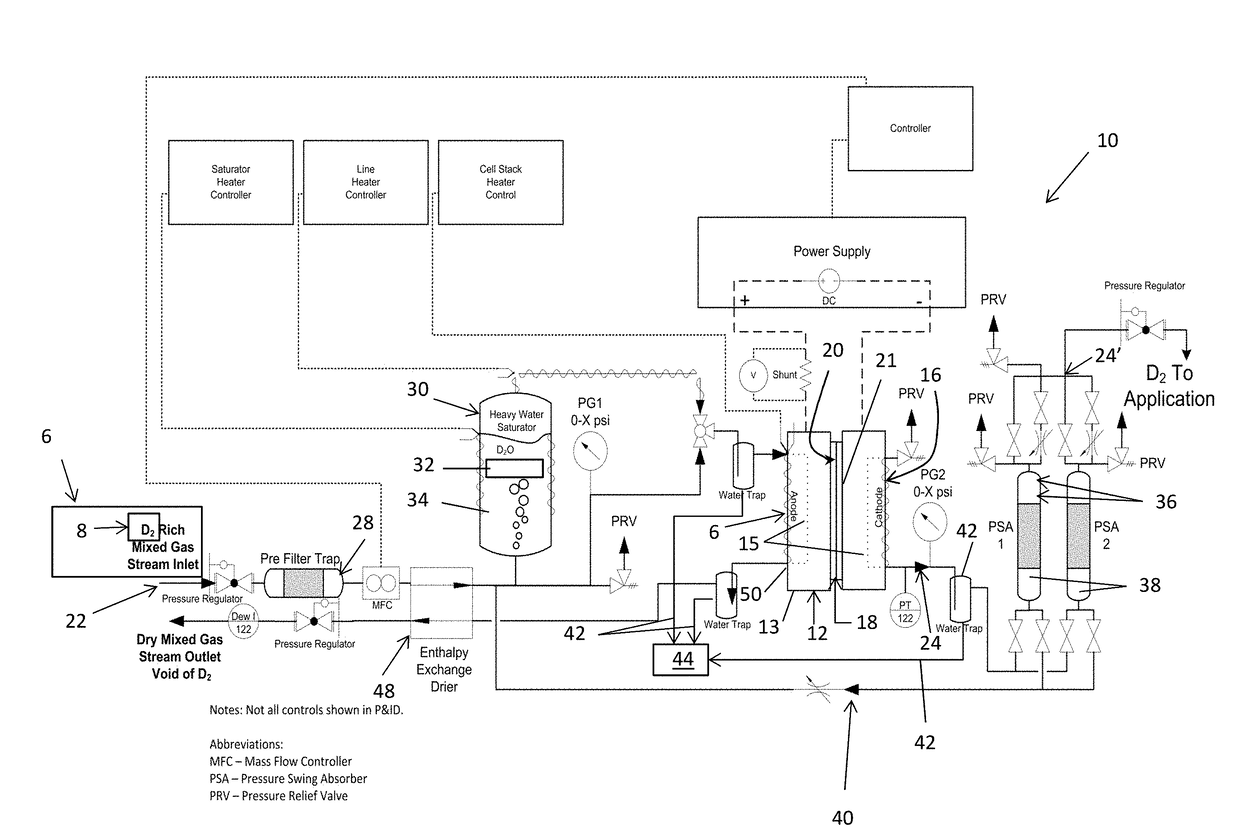
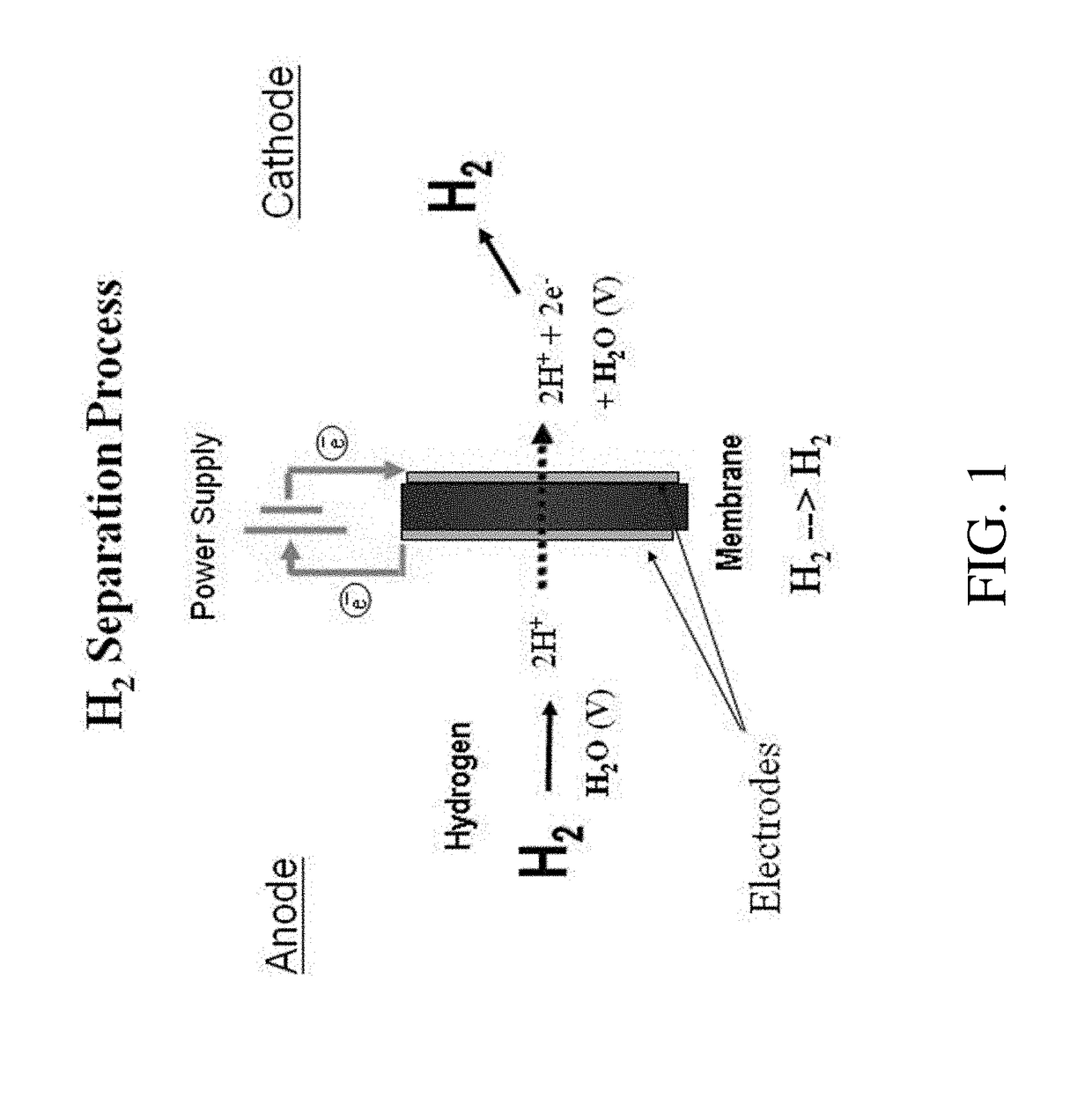
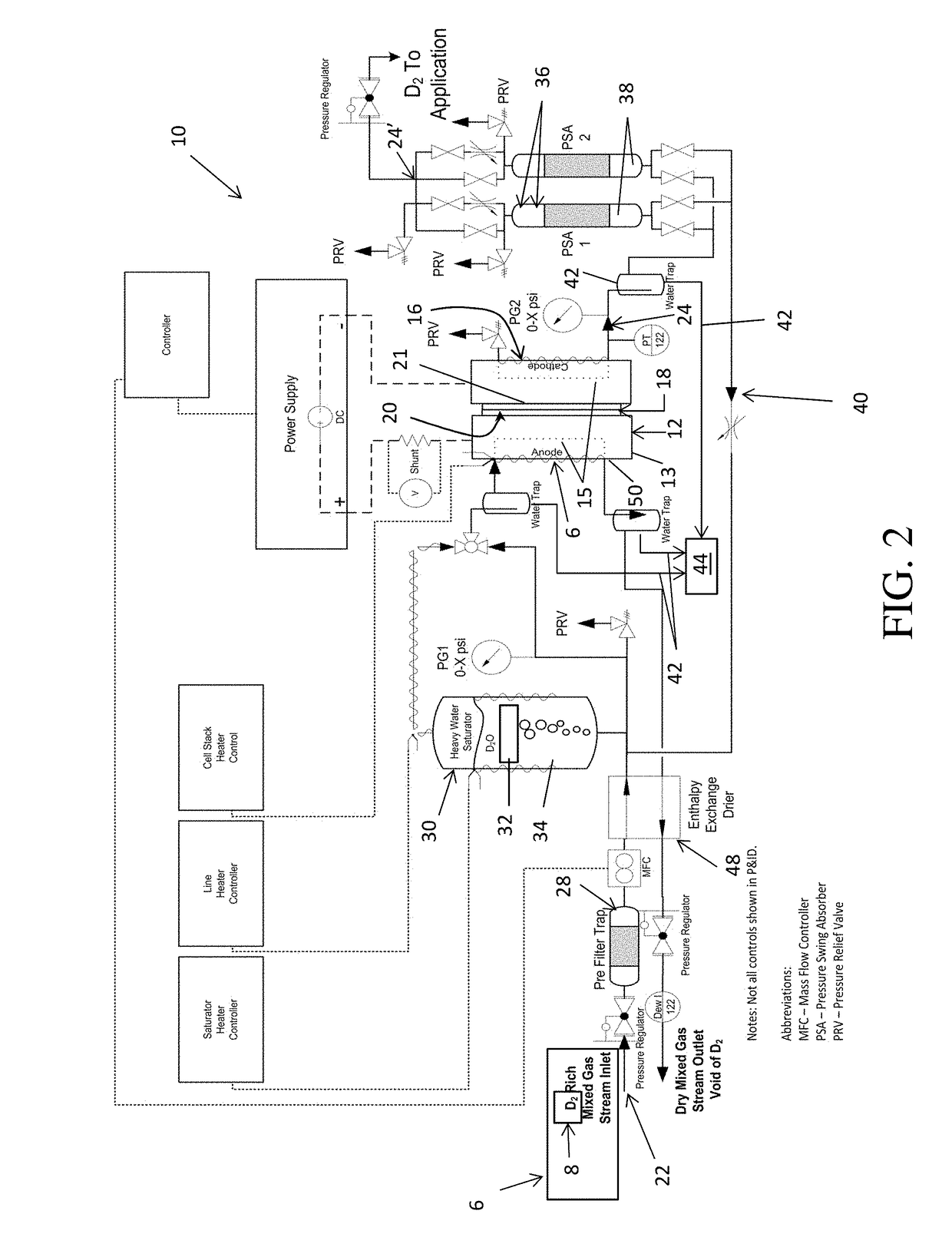
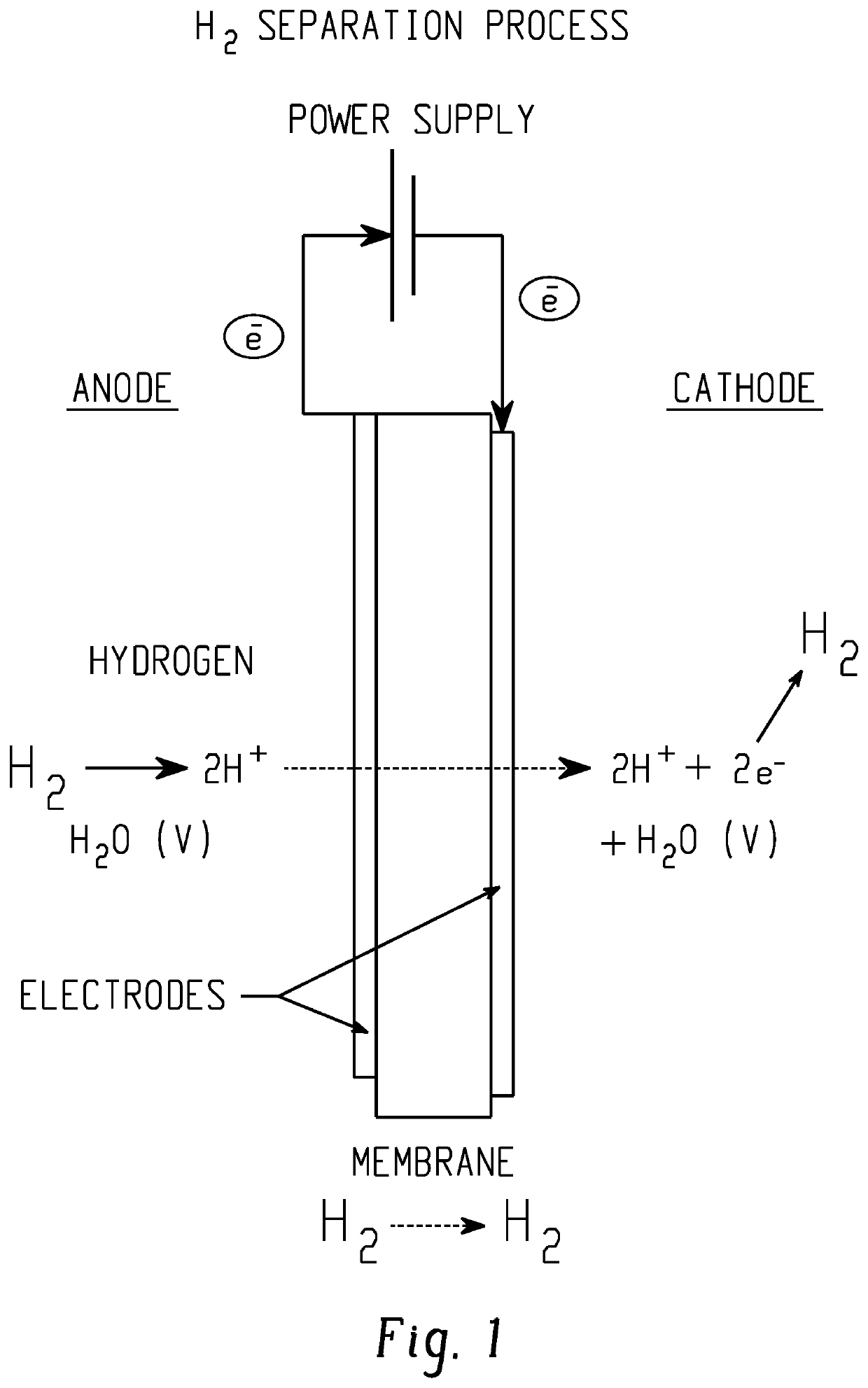
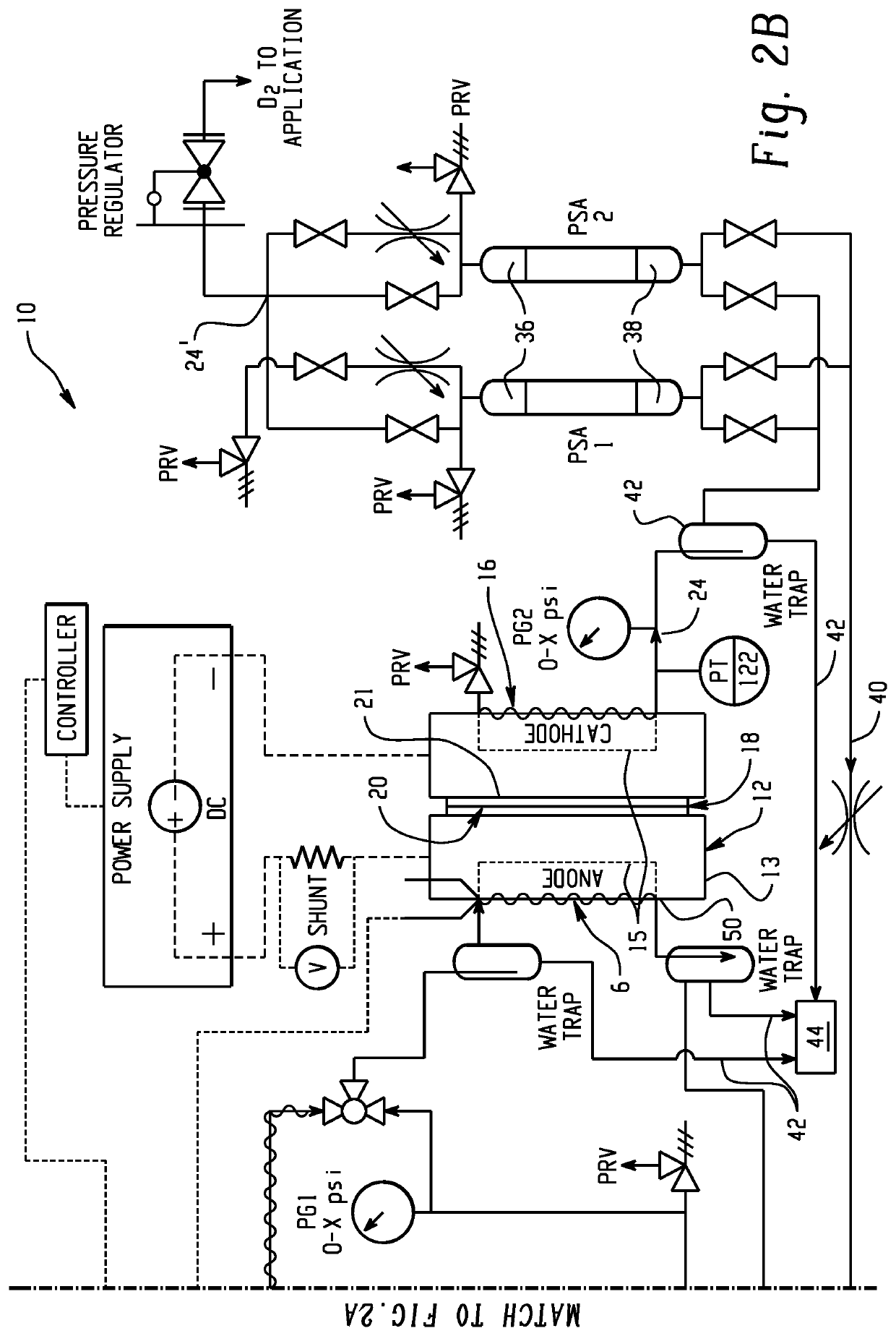
Method and apparatus providing high purity diatomic molecules of hydrogen isotopes
An electrochemical hydrogen isotope recycling apparatus for recycling an isotope of hydrogen includes an electrochemical recycling unit, the unit comprising: an anode; a cathode; and an isotope-treated, proton exchange membrane operatively disposed between the anode and cathode, the isotope-treated, proton exchange membrane having heavy water containing the isotope of hydrogen therein, the device configured to receive a feedstream containing the isotope of hydrogen. A process by which high purity hydrogen isotope products are produced using an electrochemical membrane process in which all conventional water containing components are pre-processed using a heavy water containing the isotope of hydrogen.
Owner:SKYRE INC
In situ apparatus and method for providing deuterium oxide or tritium oxide in an industrial apparatus or method
An electrochemical hydrogen isotope recycling apparatus for recycling an isotope of hydrogen includes an electrochemical recycling unit, the unit comprising: an anode; a cathode; and an isotope-treated, proton exchange membrane operatively disposed between the anode and cathode, the isotope-treated, proton exchange membrane having heavy water containing the isotope of hydrogen therein, the device configured to receive a feedstream containing the isotope of hydrogen. A process by which high purity hydrogen isotope products are produced using an electrochemical membrane process in which all conventional water containing components are pre-processed using a heavy water containing the isotope of hydrogen.An industrial apparatus 10 and / or method, such as an electrochemical hydrogen isotope recycling apparatus and / or method, includes an apparatus 49 and / or process by which gaseous D2 is recovered in a reactor 3 from a gas stream via a reaction in the reactor with another molecule to form a useful chemical compound containing D.
Owner:SKYRE INC
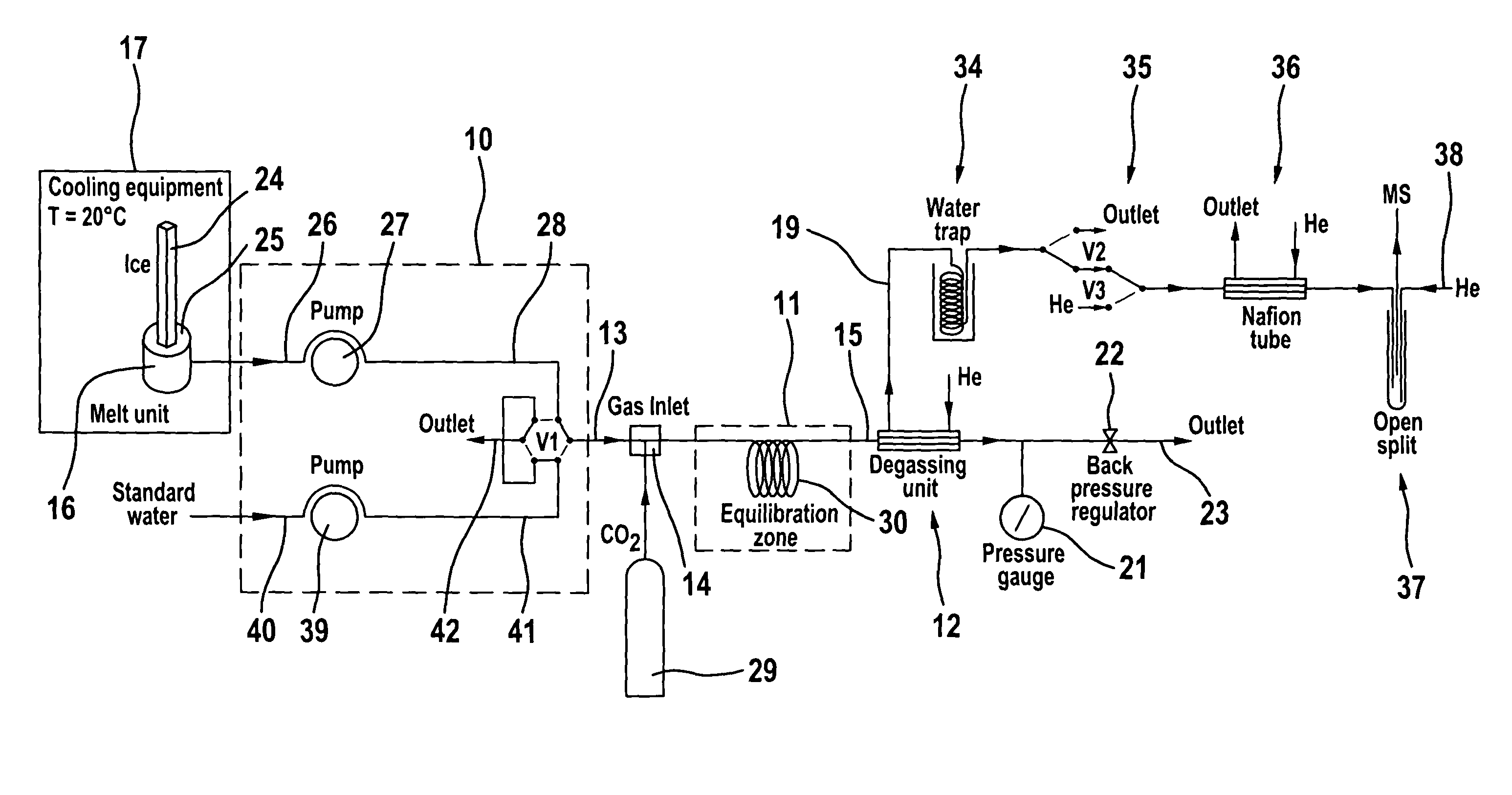
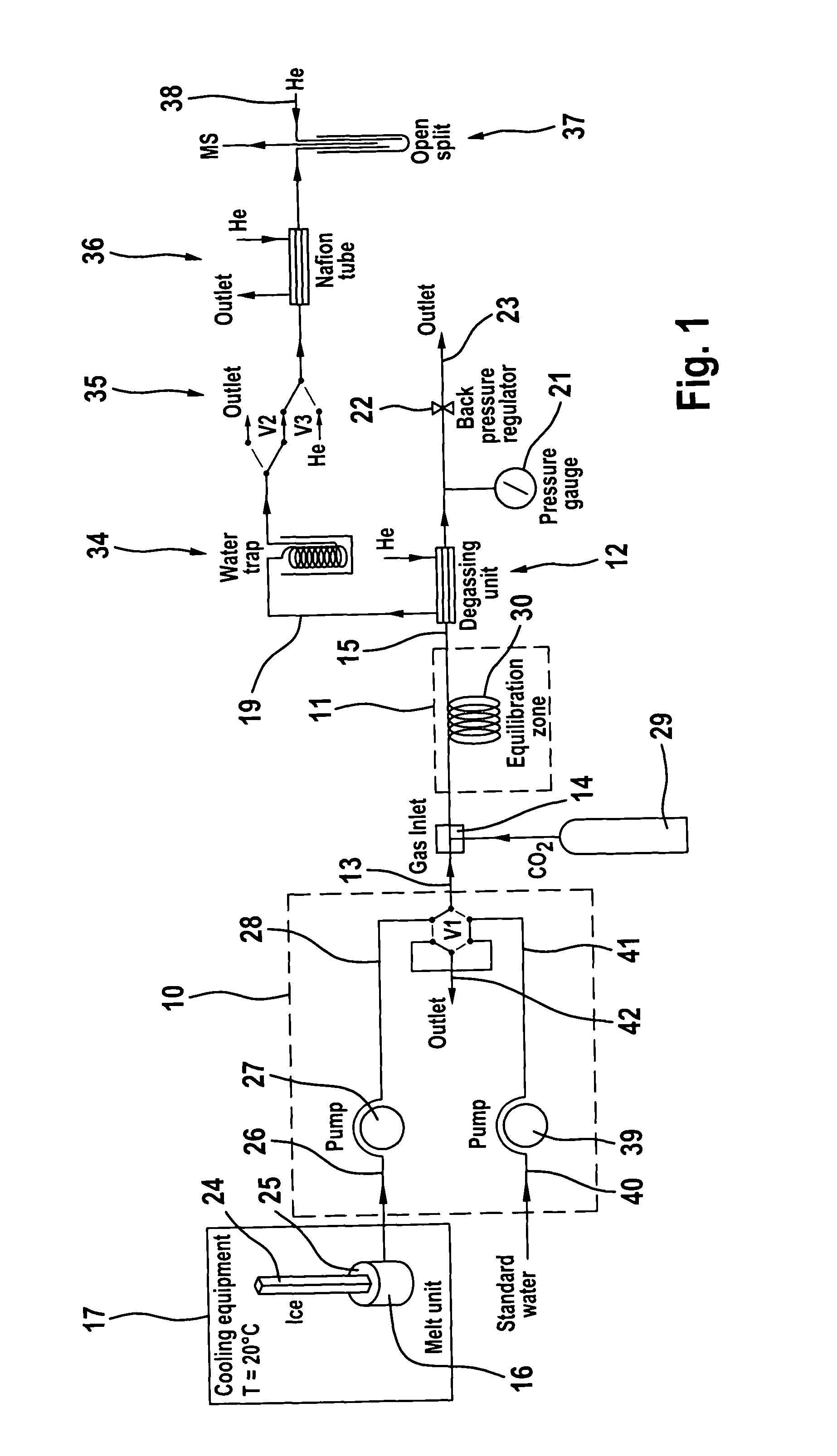
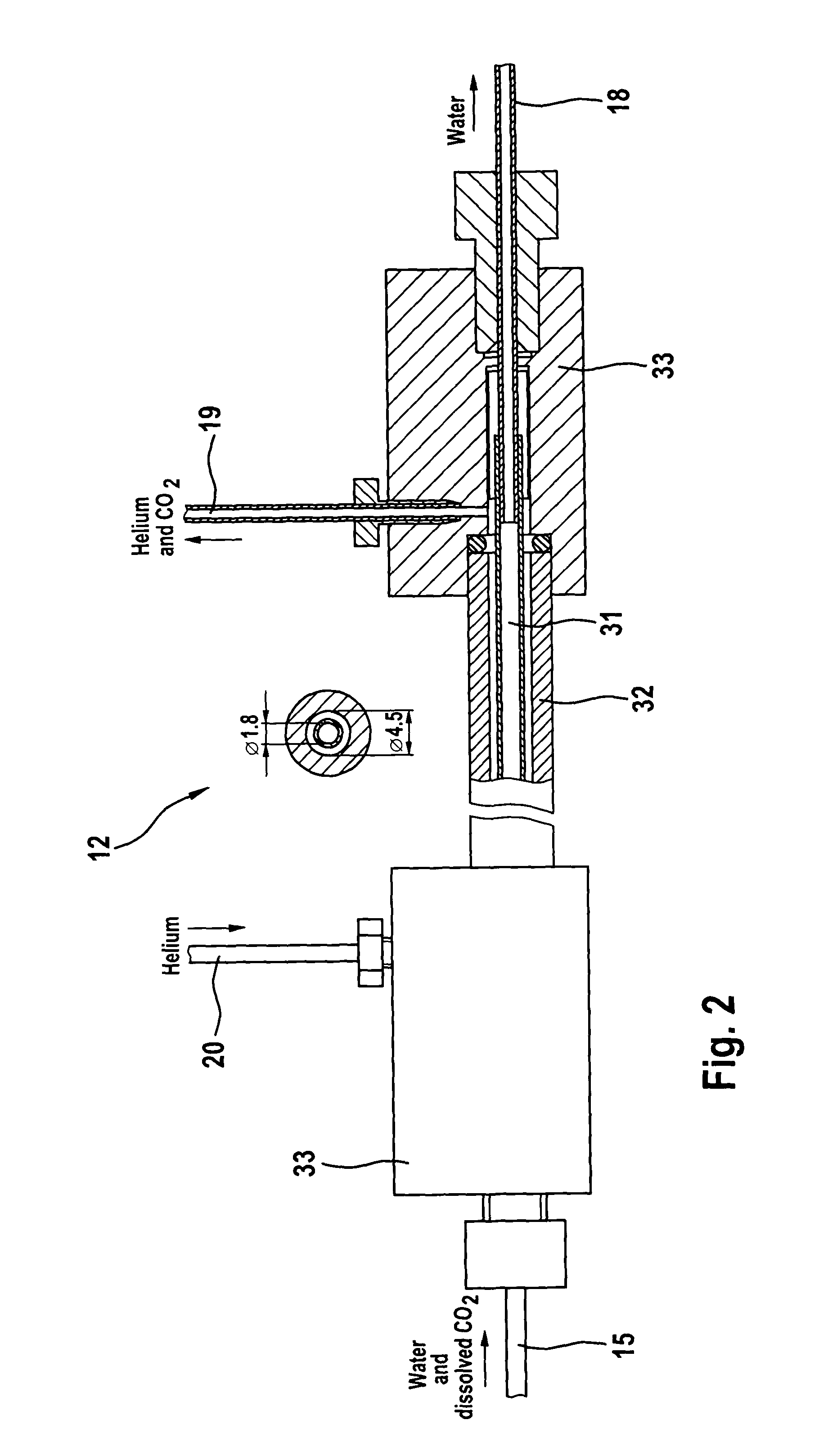
Process and apparatus for providing a gaseous substance for the analysis of chemical elements or compounds
The invention relates to a process and to an apparatus for providing a gaseous substance for the analysis of chemical elements or compounds. In one embodiment, a starting substance is continuously admixed with a reagent substance. This results in a gaseous reaction product which contains information about the elements of the starting substance, and a residual substance. The gaseous reaction product is separated from the residual substance and removed for analysis. One application is the isotopic analysis of oxygen or hydrogen from water.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN
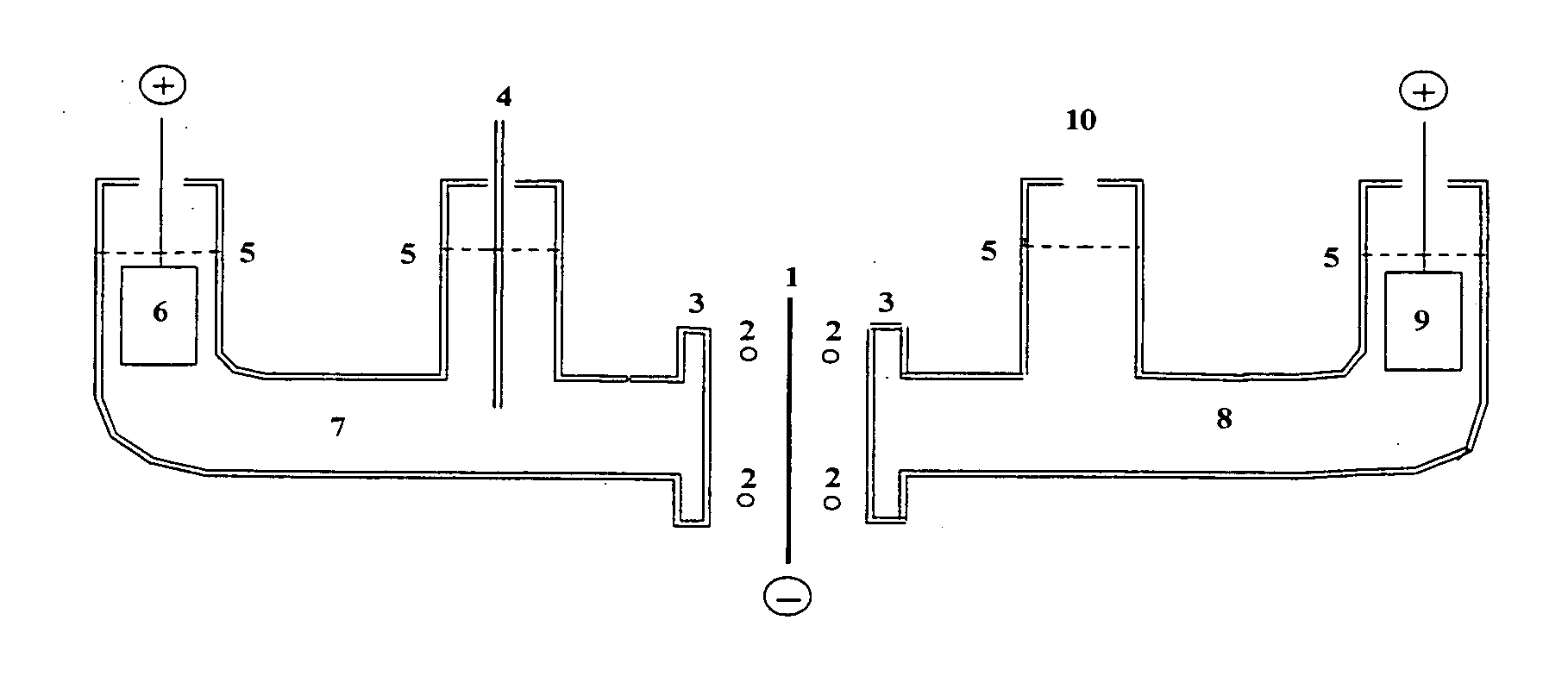
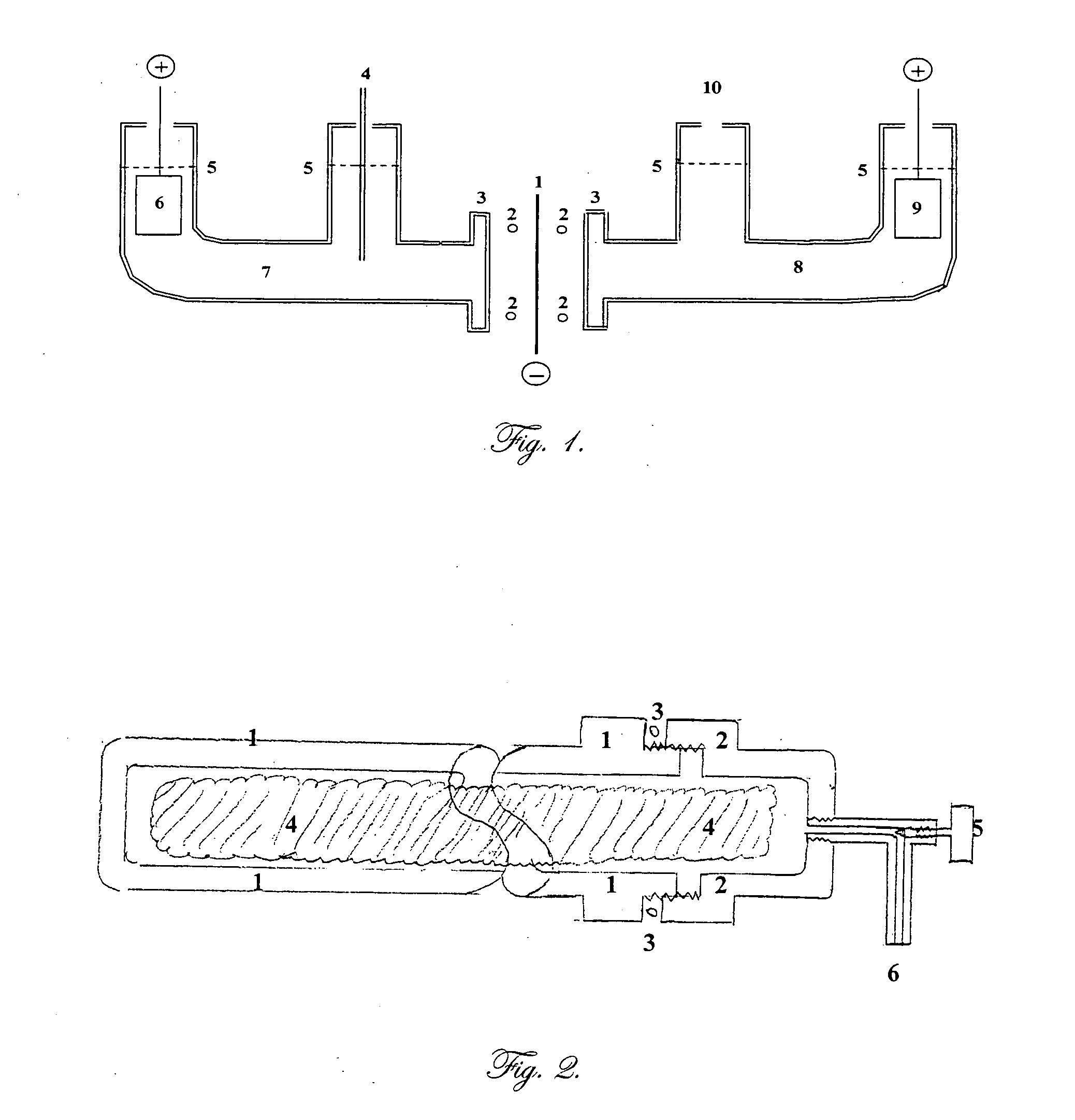
Chamber for reaction of lithium and deuterium
An electrochemical device is described which consists of two electrolyte chambers separated by a common electronically conducting cathode, such as a metal foil. On one side of the common cathode is a non-aqueous electrolyte which does not react with lithium metal and from which lithium metal may be plated. On the other side of the common cathode is an aqueous electrolyte from which isotopes of hydrogen may be electrochemically reduced on the common cathode. The cathode is impervious to either electrolyte. The anode on the non-aqueous side contains lithium metal, and on the aqueous side, the anode is an electronically conductive material which will not react with the electrolyte during the electrochemical release of oxygen. The purpose of the common cathode is to bring elemental lithium and elemental hydrogen together by diffusion within a metallic matrix, free of either electrolyte. Additionally, a non-electrochemical device is described which allows isotopes of lithium and hydrogen to interact within an alloy capable of absorbing both elements in a condensed phase.
Owner:SCHLAIKJER CARL R
Separating method of hydrogen isotope mixed gas
InactiveCN107261845AEasy to separateReduce demandIsotope separationPositive pressureChromatography column
The invention discloses a method for separating a hydrogen isotope mixed gas, which comprises the following steps in sequence: using a positive pressure inert gas to press a transition metal salt solution from one end of a porous layer open-tube chromatographic column; After the other end of the column flows out, the inert gas is purged the porous layer open-tube chromatographic column at room temperature for 12 hours; the porous layer open-tube chromatographic column is put into the chromatographic oven, heated and dehydrated, and cooled to obtain the required porous layer open-tube chromatographic column. The above-mentioned porous layer open-tube chromatographic column is placed in a liquid nitrogen Dewar, neon gas is used as a carrier gas, and the hydrogen isotope mixture gas passes through the porous layer open-tube chromatographic column to realize the separation of hydrogen isotopes. The separation method of the invention has the characteristics of simple method, good separation effect, short separation time and the like.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
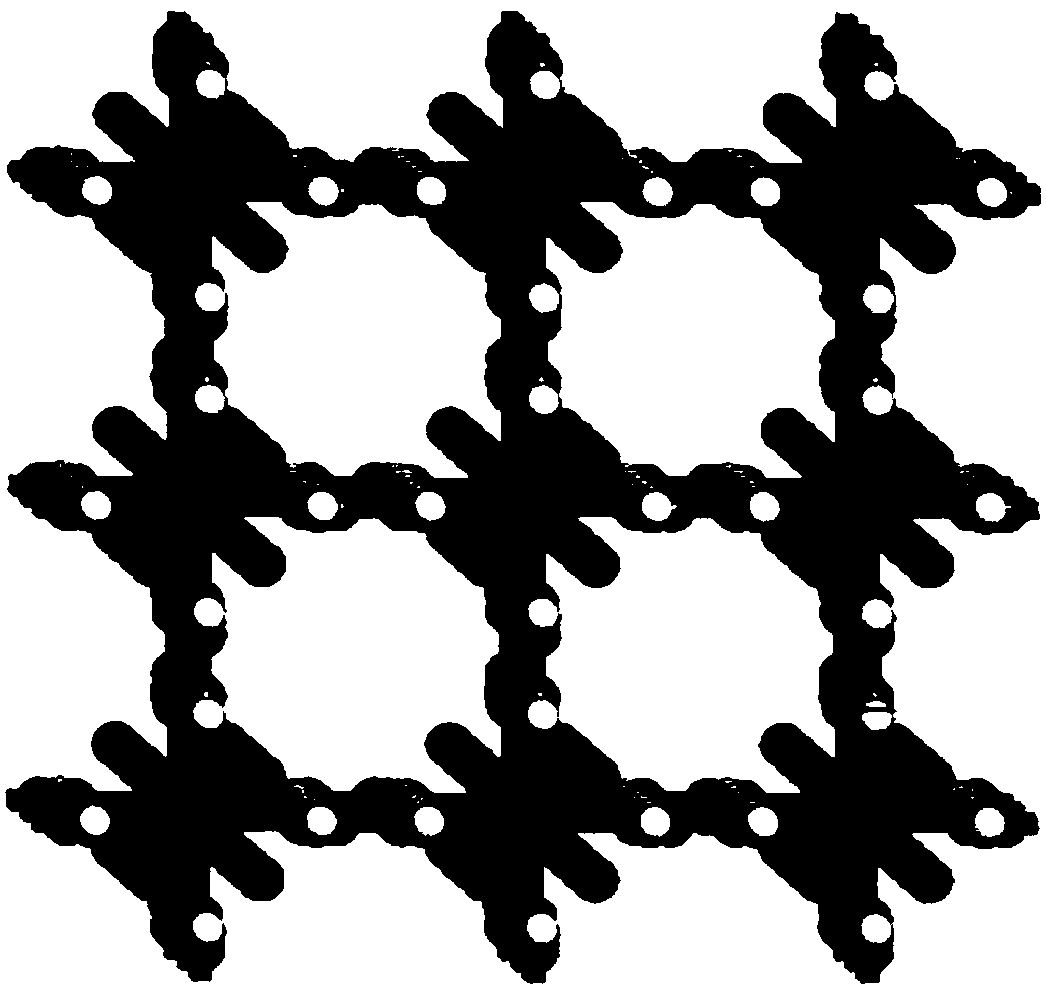
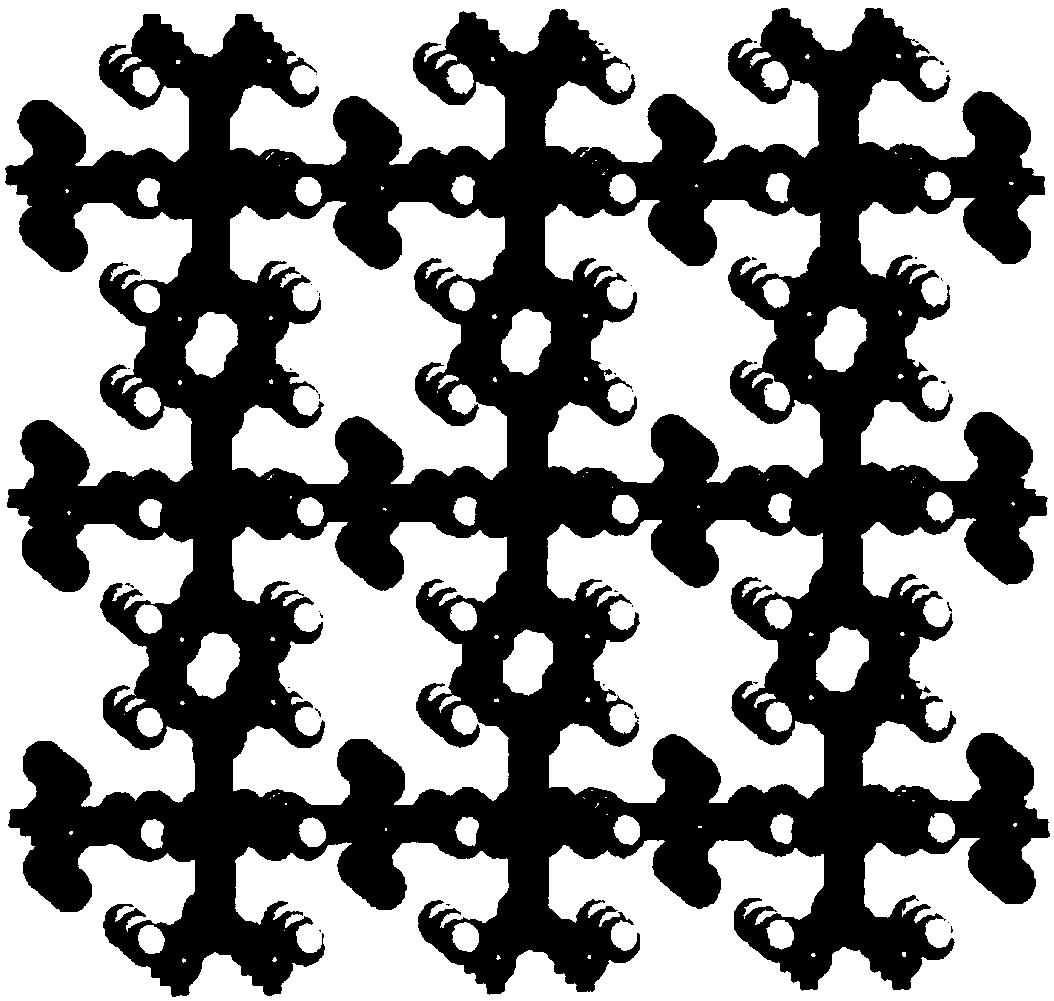
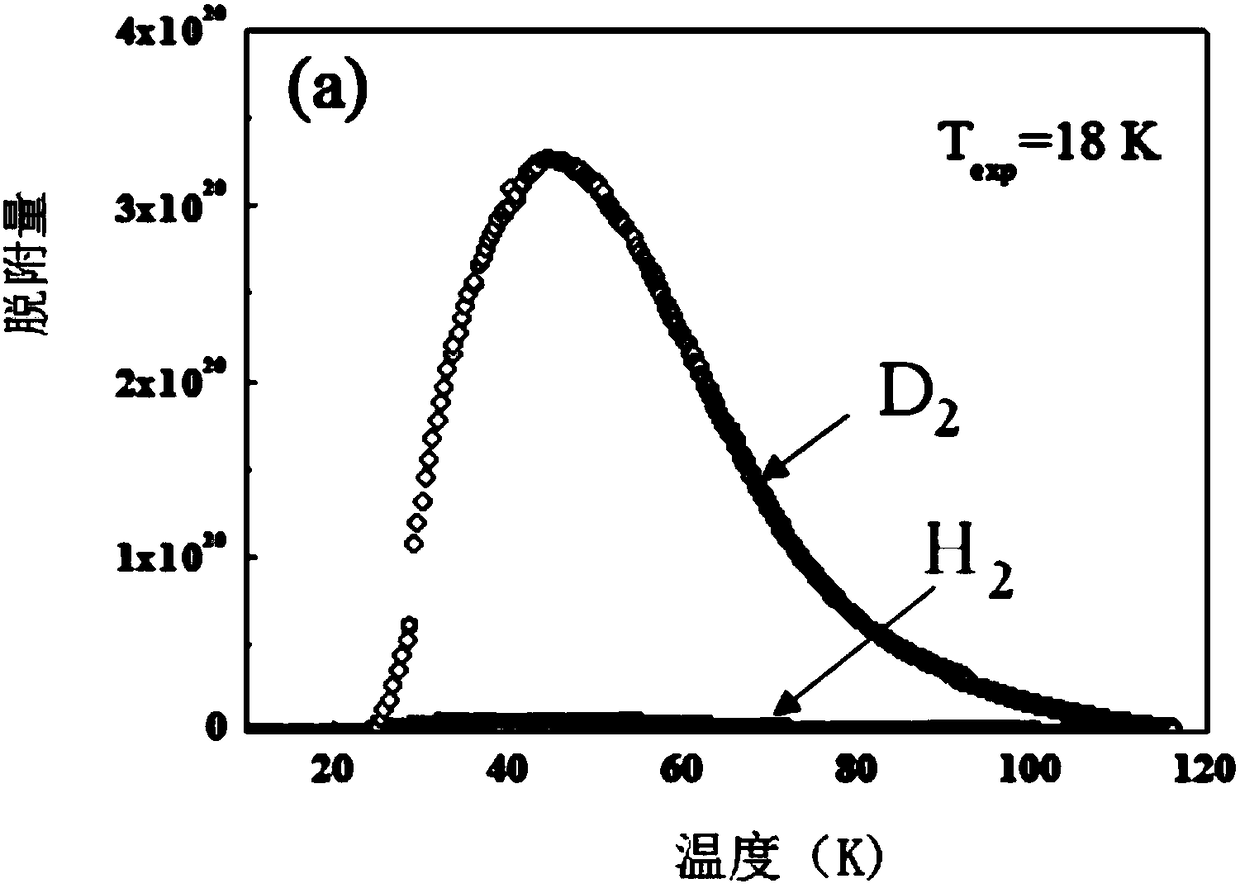
Application of ultra-microporous metal-organic framework materials in isotope separation of hydrogen
ActiveCN108579686AHigh separation selectivitySeparation selectivity overOther chemical processesIsotope separationMetal-organic frameworkMicroporous material
The invention discloses the application of ultra-microporous metal-organic framework materials in isotope separation of hydrogen. The ultra-micro porous metal-organic framework material is SIFSIX-3-Zn, used for the effective separation of hydrogen isotopes at low temperature, and the chemical formula of the SIFSIX-3-Zn is Zn (pyr) 2(SiF6). Application of the ultra-microporous metal-organic framework material in the isotope separation of hydrogen enables the separation and purification of D2, H2 in the hydrogen isotope, and the preparation method of the ultra-microporous metal-organic frameworkmaterial is simple. The material can be synthesized in large volumes, and has the advantages of cheap raw materials and low price, and can be widely applied to the industrial hydrogen isotope separation.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for forming self-alignment metal silicide
InactiveCN104319236AReduce or avoid surface defectsPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideMetal silicide
The invention discloses a method for forming a self-alignment metal silicide. The two times of annealing technologies are adopted, hydrogen isotope gas is introduced in the first time of annealing technology, the hydrogen isotope gas is used for reacting with trace oxygen in the atmosphere to eliminate the oxygen, metal layers such as Ni are prevented from being oxidized, and therefore surface defects (such as a pyramid shape) of the metal silicide are reduced or avoided, and the metal silicide with a flat appearance and good uniformity is formed; isotope atoms in the introduced hydrogen isotope gas can enter the interface of the metal silicide and a silicon substrate and are combined with Si to form a new key which can be hardly fractured, and therefore the defects at the interface are overcome and reduced, and the interface state (Dit) is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Metal oxygen fusion reactor
InactiveUS20170117066A1Reduction of Relative-Rate-of-Change (RRoC)Reduce fusionNuclear energy generationConversion in nuclear reactorNoble gasSulfur
An exothermic fusion reactor is described that uses metal-oxygen transmutation. The process comprises a negatively-charged environment; a moderator comprising at least one noble gas; a metal, including isotopes of hydrogen; and a facilitator comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, selenium, bromine, iodine, or combinations thereof.
Owner:K ORBITAL LLC
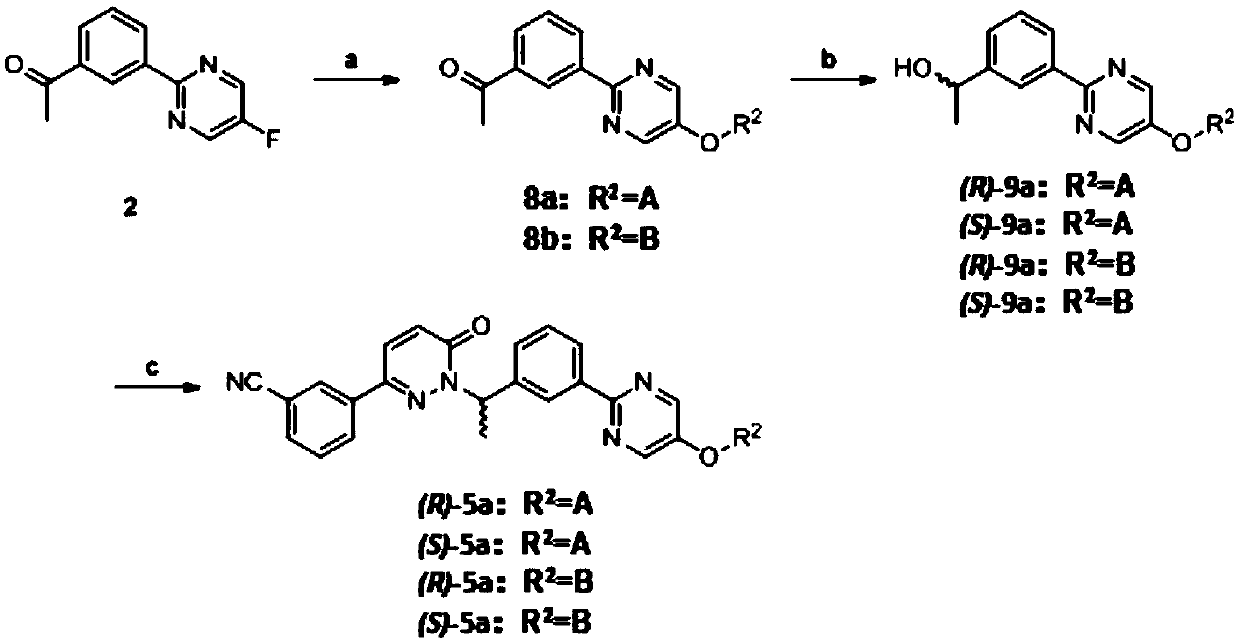
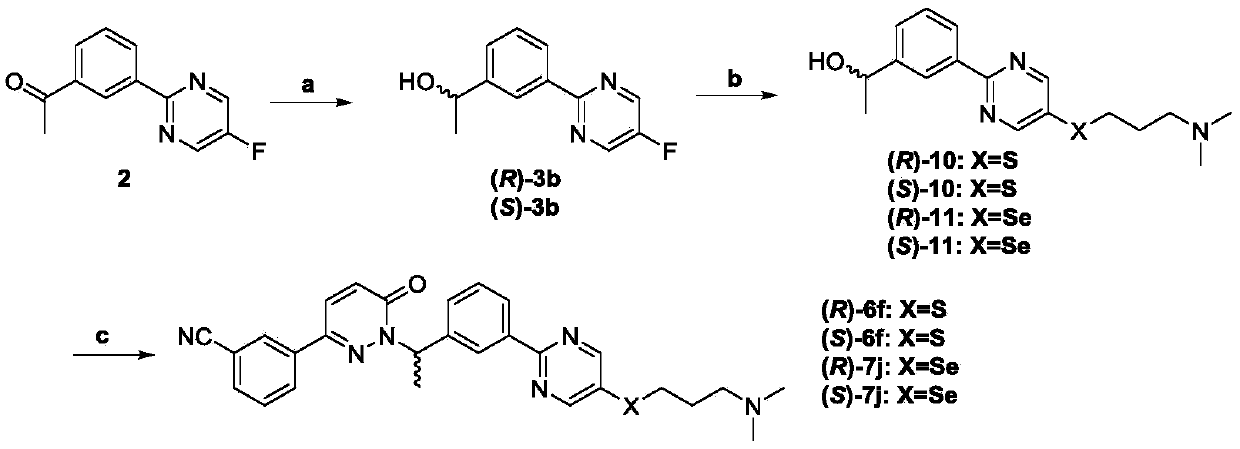
Preparation method of pyrimidine derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN109608442AImprove bioavailabilityGood antitumor activityIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsC-MetSulfur
The invention discloses a novel pyrimidine derivative, a preparation method and application thereof in anti-rumor medicine. A chirality structure is introduced into a molecule, a hydrogen isotope deuterium is introduced to the portion, likely to be metabolized, in the molecule, and sulfur, selenium, sulfoxide and other atoms or perssads are introduced into the molecule. An anti-tumor activity experiment (for tumor cells with c-Met expression) on the cell level proves that the compound has the excellent anti-tumor activity, and the stability of the anti-tumor compound is obviously improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG LEWWIN PHARM RES INST CO LTD +1
Method for forming self-aligned metal silicide
InactiveCN104362087APrevent oxidationReduce or avoid surface defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideMetal silicide
The invention discloses a method for forming self-aligned metal silicide. The method has the advantages that double-step annealing processes are implemented, isotope gas of hydrogen is introduced in the second annealing process, the isotope gas of the hydrogen and trace oxygen in atmosphere react with each other, accordingly, the oxygen can be eliminated, the metal silicide can be prevented from being oxidized, surface defects (such as pyramid shapes) of the metal silicide can be reduced or prevented, and the metal silicide which has flat morphology and is excellent in uniformity can be formed; isotope atoms in the introduced isotope gas of the hydrogen can enter interfaces of the metal silicide and a silicon substrate and can be combined with Si to form new keys which are difficult to break, accordingly, defects at the interfaces can be repaired and reduced, and interface states (Dit) can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
A method and device for enriching and enriching stable isotopes 2h, 18o, 13c
The invention relates to a method and a device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C. The method comprises the steps of: by taking compounds respectively containing stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C as materials, carrying out purification treatment, adding to a heavy isotope concentration tower group formed by a plurality stages of gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series; continuously and partially vaporizing and partially condensing in the gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series by weak vapor pressure difference between light and heavy isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon elements, and gradually concentrating and purifying corresponding heavy isotope. Each tower disclosed by the invention adopts different operation pressures and coupling utilization of heat between the towers; over 30-40% of energy consumption can be saved; a composite structure mass transfer component composed of a liquid collecting distributer, a Dixon mass transfer component, a corrugated mass transfer component and the like is adopted inside the tower; the device is easy to amplify; the device of producing heavy 2H, 18O or 13C isotope at a large scale just needs to be connected with 2-8 gas-liquid mass transfer towers in series; over 50% of investment is saved in comparison with the same scale of device, and the towers adopt a single tandem cascade technology; and the method is simple in flow and easy to control and operate.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHENGNENG ISOTOPE
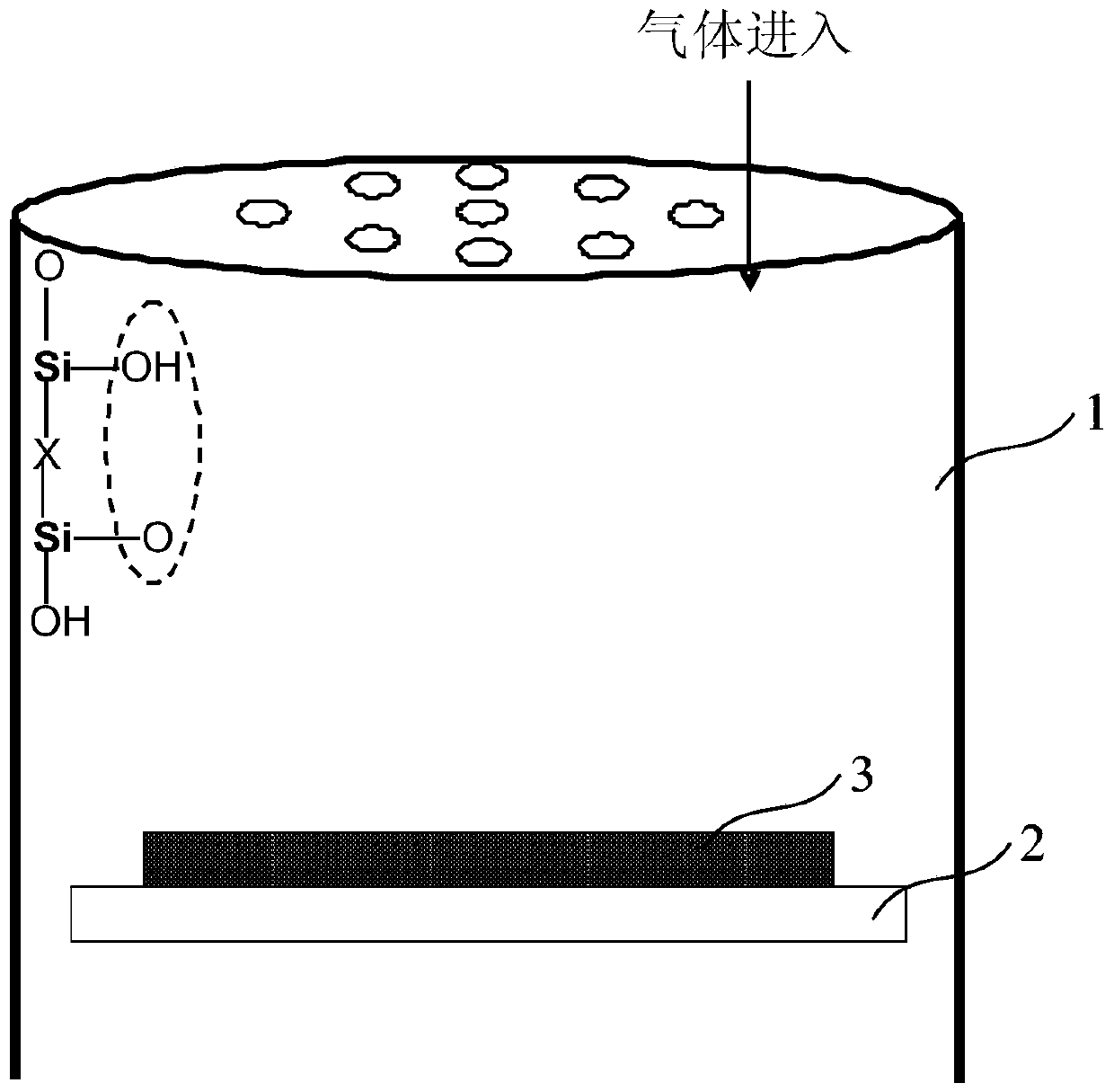
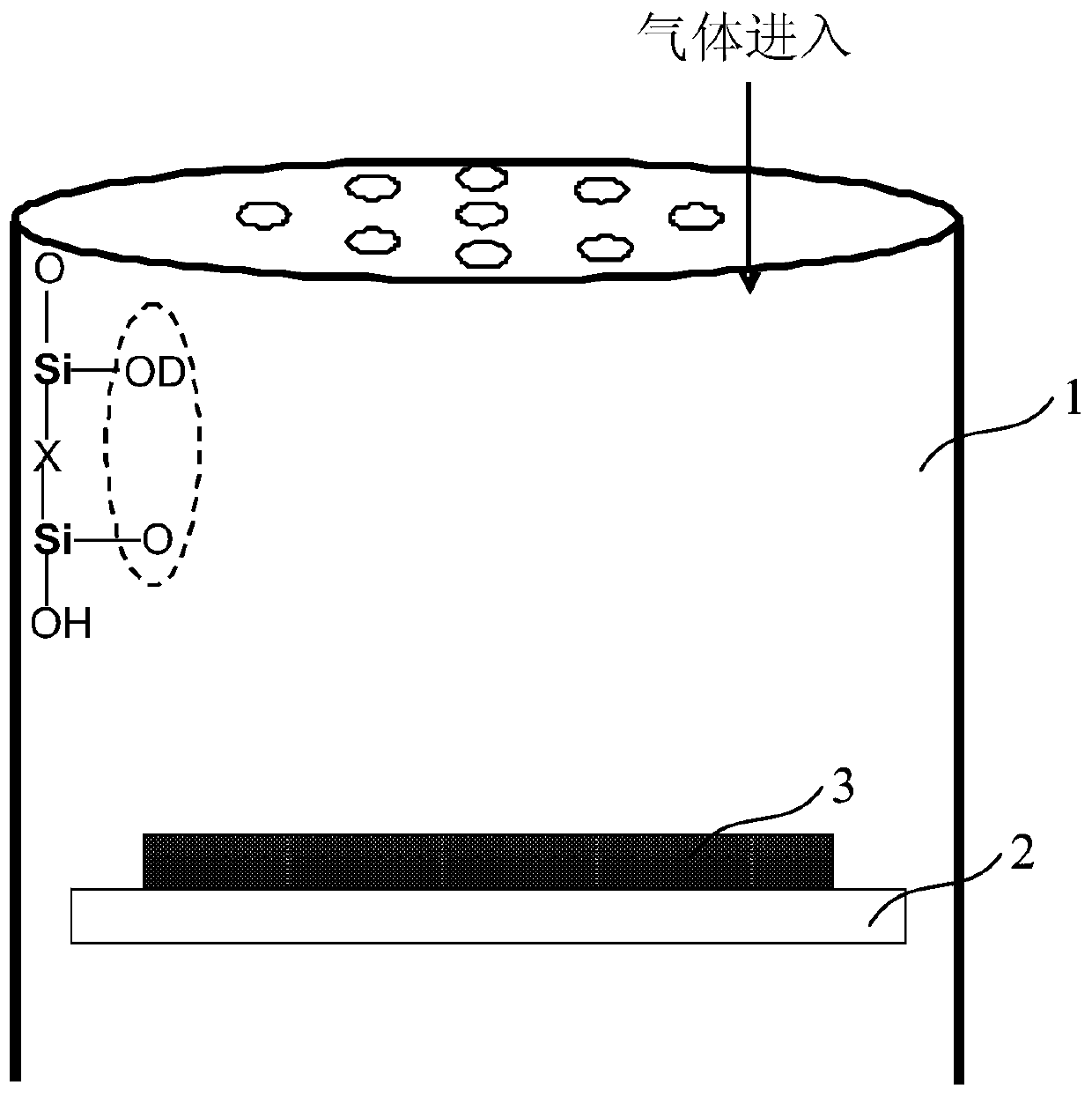
A Method for Improving the Uniformity of Gate Oxide Thickness
ActiveCN105225934BImprove thickness uniformityUniform thicknessSemiconductor devicesChemical reactionDangling bond
The invention provides a method for improving the uniformity of grid oxide thickness. The method is carried out in a quartz tube device, comprising the steps of: introducing a certain flow ratio of deuterium gas and oxygen into the quartz tube, and igniting the deuterium gas React with oxygen to generate D2O, which neutralizes with Si-O-dangling bonds on the wall of the quartz tube to form Si-O-D, thereby avoiding the Si-O-dangling bonds on the wall of the quartz tube from affecting the growth of gate oxide Uniformity of thickness. According to the present invention, the deuterium D2 passed into the quartz tube and the D2O generated by the ignition reaction of oxygen can effectively neutralize the Si-O dangling bonds on the wall of the quartz tube to form a Si-O-D structure. Since the chemical reaction rate of deuterium is lower than that of isotopic hydrogen, the formed Si‑O‑D structure can exist stably in the quartz tube. In the DCE oxidation process of the subsequent gate process, it can avoid breaking the chemical balance of HCl, thereby reducing the activation of Cl-, and making the thickness of the gate oxide generated in the gate oxide oxidation process more uniform.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
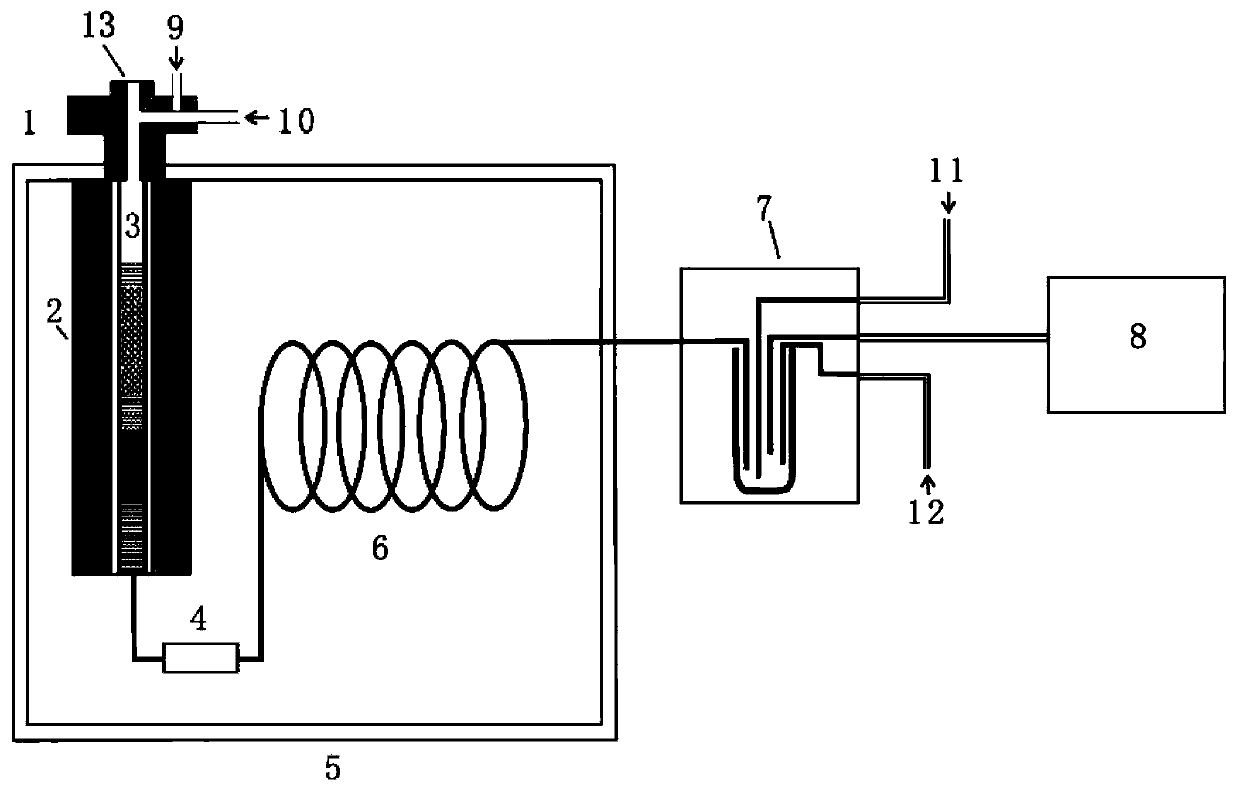
Gas absorbing device for fuel element
InactiveCN104575627AReduced cladding hydrogenationReduce riskOptical rangefindersFuel elementsNuclear engineeringProduct gas
The invention relates to the technical field of fuel elements, and particularly discloses a gas absorbing device for a fuel element. The gas absorbing device for the fuel element comprises a fuel element coating material adopting a cylindrical case structure as well as a gas absorbing structure which is fixed in the fuel element coating material and can absorb hydrogen and isotopes of hydrogen, wherein the gas absorbing structure is located at the upper or lower part of a fuel pellet zone of the whole fuel element. With the adoption of the gas absorbing device for the fuel element, the content of gases such as the hydrogen, the isotopes of the hydrogen and the like in the fuel element can be decreased, risks of hydrogenation and damage to the cladding of the fuel element are reduced, emission of the isotopes of the hydrogen and pollution are reduced, and meanwhile, adverse effects on the performance of the fuel element can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Titanium-based hydrogen storage alloy improved by vanadium-iron alloy and preparation method thereof
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Online analysis method for sulfur isotope of hydrogen sulfide gas in natural gas
ActiveCN102749382BRealize direct and automatic conversionEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas phaseElement analysis
The invention relates to an online analysis method for hydrogen sulfide gas sulfur isotope in natural gas. The method includes the following steps: collecting natural gas samples; heating the oxidation furnace of the element analyzer to 1020°C; raising the temperature of the chromatographic column box to 50°C; introducing the reference gas into the stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer, and adjusting the mass-to-charge ratio to 66 The magnetic field at the center of the peak, and save the magnetic field value; connect the cylinder containing the natural gas sample to the sampling valve and put it into the fume hood, turn on the power of the fume hood; take the natural gas sample with an air-tight sampling needle; inject the natural gas sample into the In the sample port; the natural gas sample flows into the high-temperature oxidation tube with the carrier gas, and is oxidized into CO2, H2O, SO2 gas, and the mixed gas is carried by the carrier gas and flows through the dehydration tube to remove moisture; the mixed gas after removing moisture flows through the gas phase After the chromatographic column is separated, it enters the stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer through the continuous flow interface to measure the sulfur isotope composition and generate a spectrum to obtain the measurement result.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
In situ apparatus and method for providing deuterium oxide or tritium oxide in an industrial apparatus or method
ActiveUS20200346927A1Loss preventionEasy to separateCellsGas treatmentElectrochemistryNuclear chemistry
In an aspect, an electrochemical hydrogen isotope recycling apparatus for recycling a feedstream comprising a single isotope of hydrogen, comprising: an electrochemical recycling unit, the unit comprising an anode; a cathode; an isotope-treated, cation exchange membrane operatively disposed between the anode and cathode, the isotope-treated, cation exchange membrane having heavy water containing the isotope of hydrogen therein, the unit configured to receive the feedstream containing the single isotope of hydrogen; wherein the single isotope is deuterium or tritium and when the single isotope is deuterium, the heavy water comprises D2O and when the single isotope is tritium, the heavy water is T2O.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE INNOVATIONS INC
Titanium-based hydrogen storage alloy improved by vanadium iron and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-performance low-cost titanium-based hydrogen storage alloy improved by scandium vanadium iron and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of hydrogen storage alloy. The general formula of the titanium-based hydrogen storage alloy improved by the vanadium iron is Ti0.95Sc0.05 (Mn0.7-xCr0.3Mx) 2, wherein M=FeV50 or FeV80, and x is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.7. The reversible hydrogen storage capacity of the hydrogen storage alloy is higher than that of a Ti1-xZrxMnCr series alloy and that of a Ti1-xScxMnCr series alloy; and the cost of the hydrogen storage alloy is lower than that of the two series alloys. The hydrogen storage alloy can be applied to separation of hydrogen, separation and storage of isotopes of hydrogen, catalysts and nickel-hydrogen batteries.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Application of Ultramicroporous Metal-Organic Frameworks in Hydrogen Isotope Separation
ActiveCN108579686BHigh separation selectivitySeparation selectivity overOther chemical processesIsotope separationPhysical chemistryHydrogen isotope
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
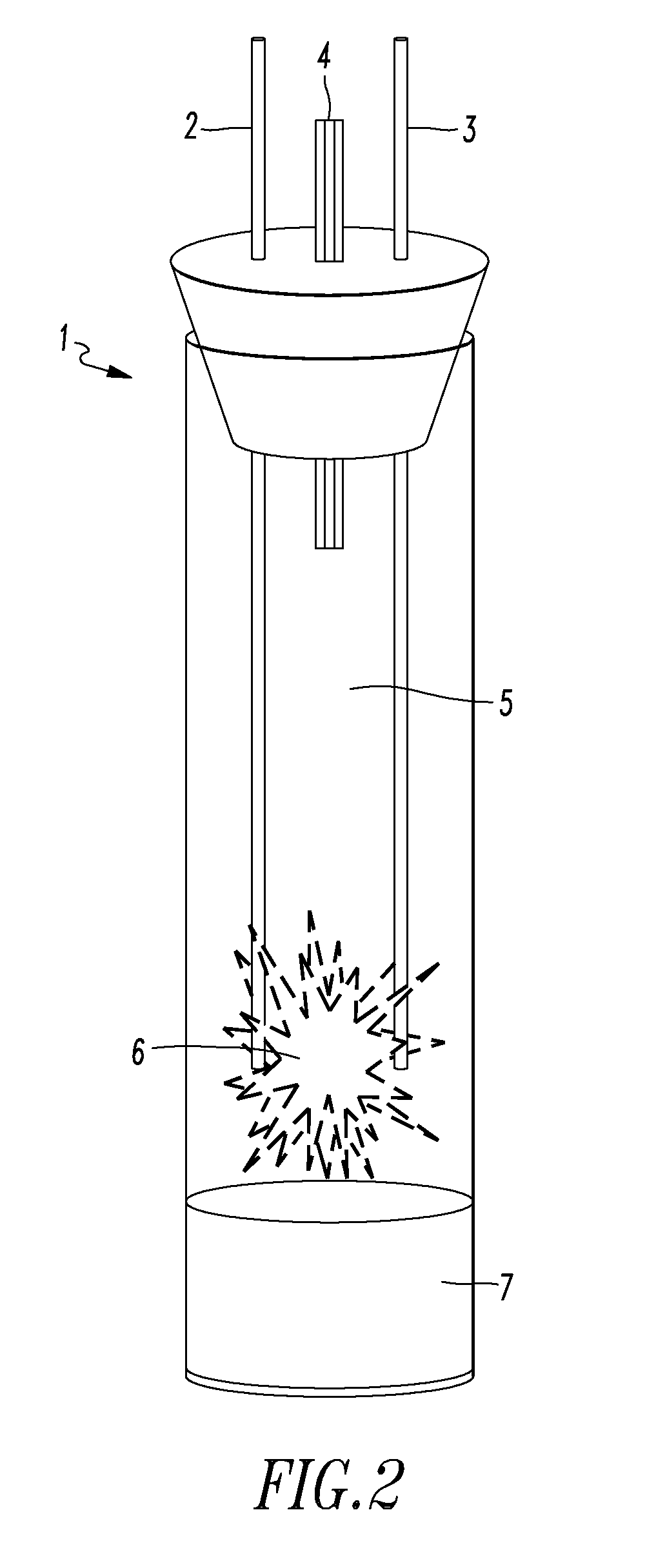
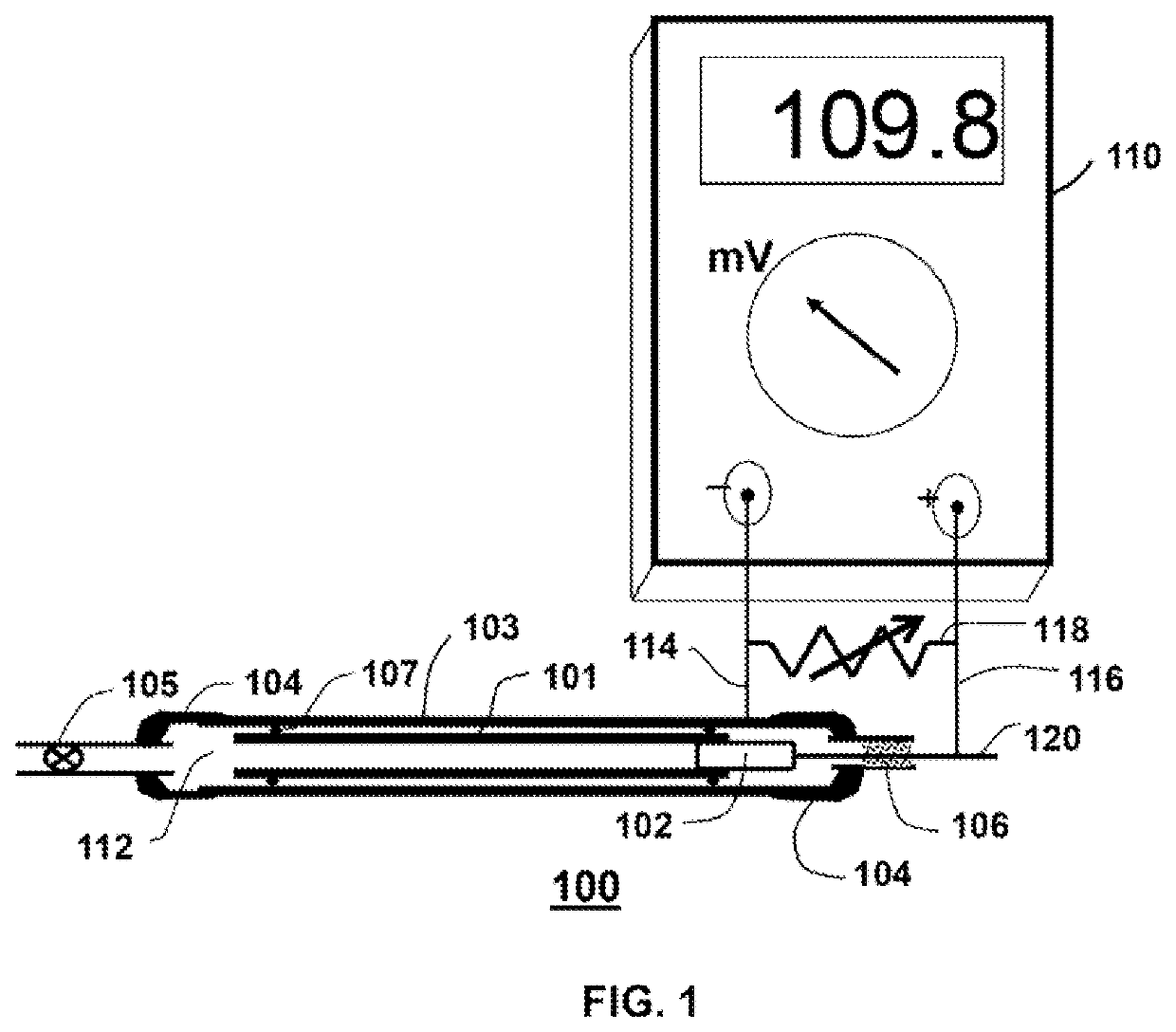
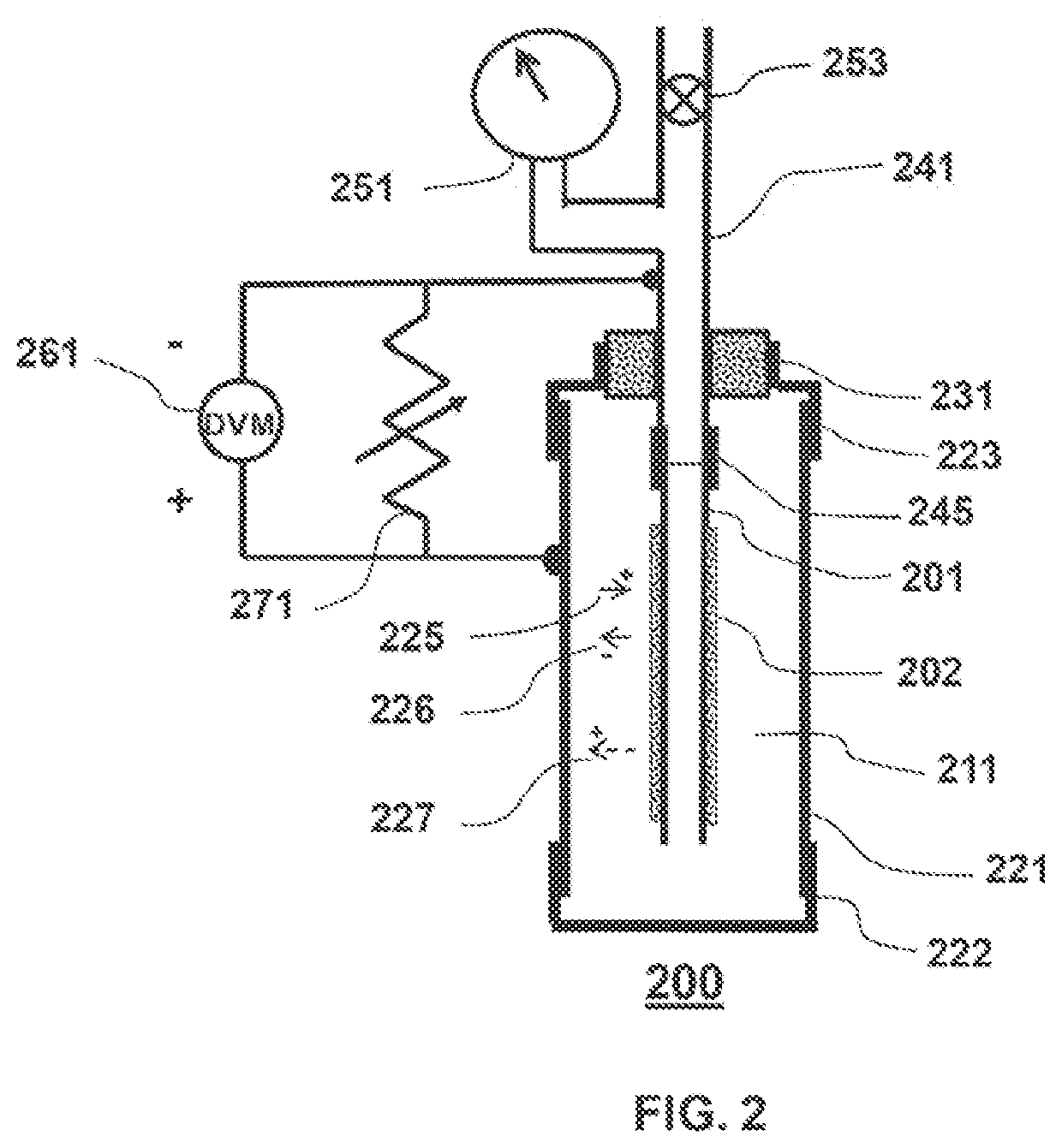
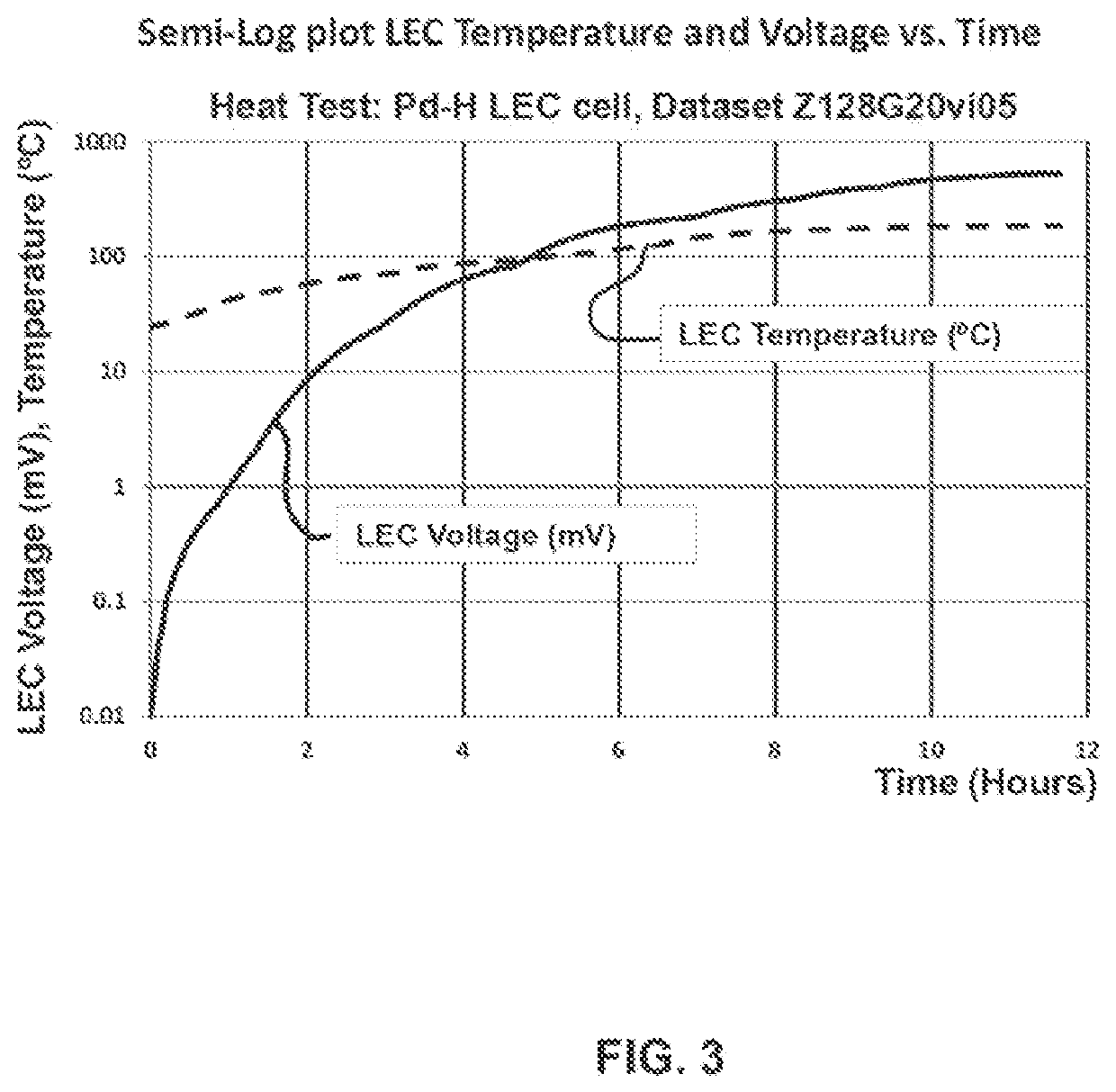
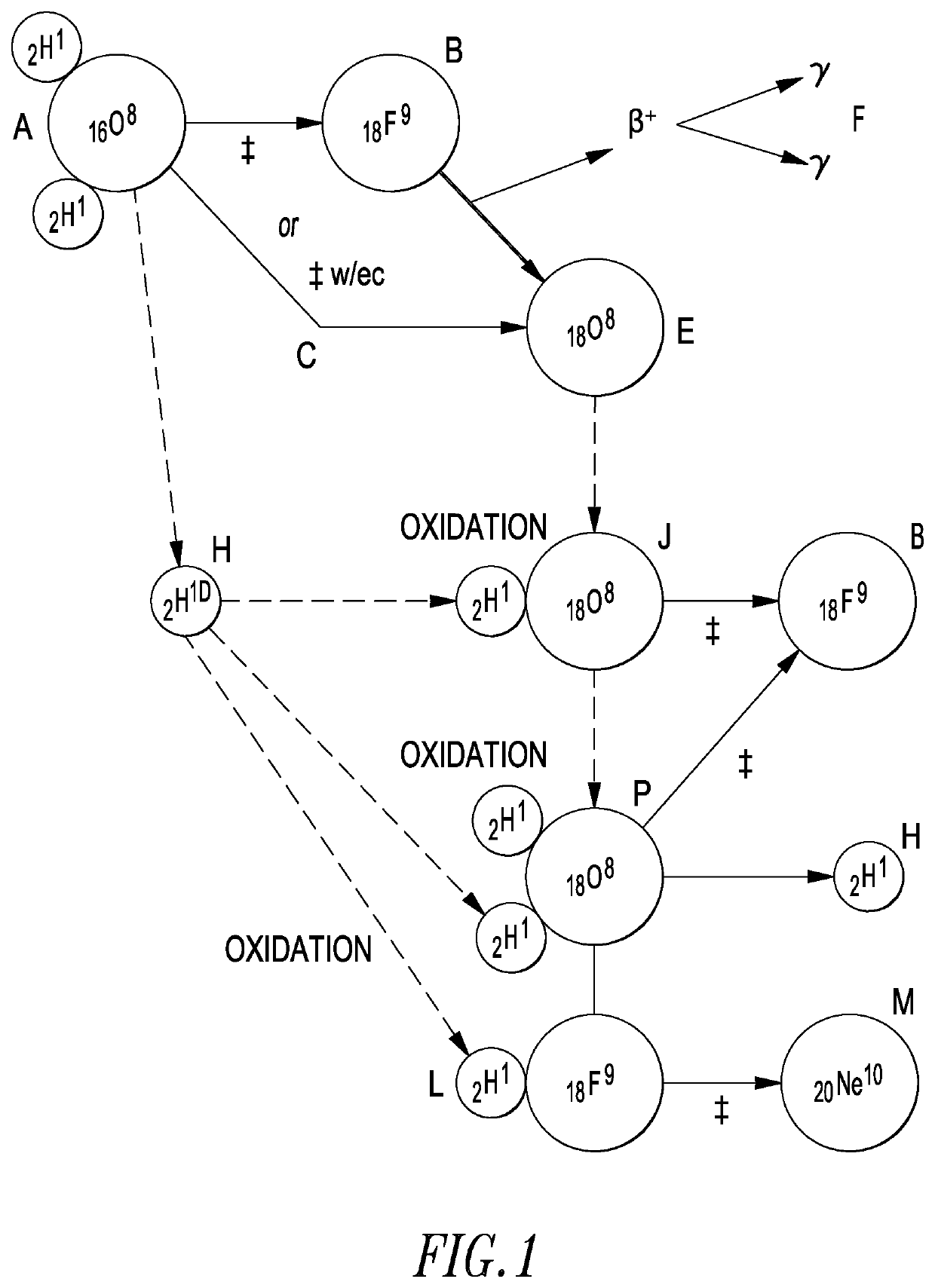
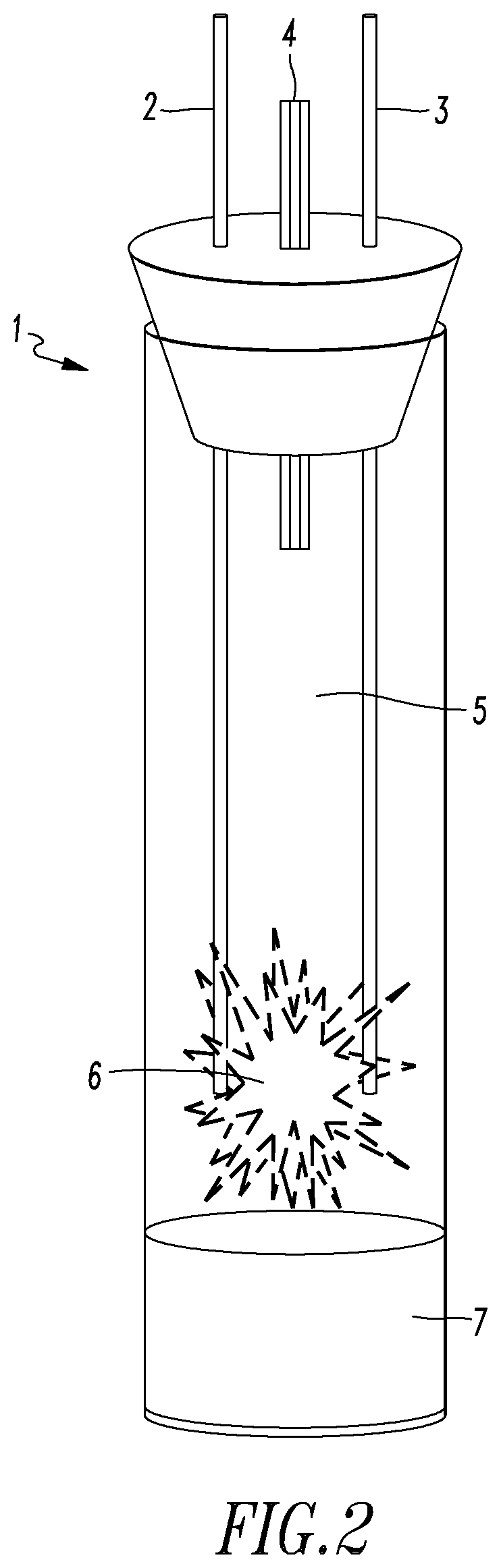
Lattice energy conversion device
A lattice energy converter (LEC) is disclosed that produces ionizing radiation and / or electricity based on the thermal energy in the lattice of a specially prepared working electrode comprised in whole or in part of hydrogen host materials that are occluded with hydrogen or the isotopes of hydrogen and wherein the hydrogen host materials may include vacancies, superabundant vacancies, and other lattice defects. When the hydrogen host material is occluded with hydrogen, the LEC was found to self-initiate the production of ionizing radiation and, when the hydrogen host materials are in fluidic contact with a gas or vapor containing hydrogen or isotopes of hydrogen, the LEC was found to self-sustain the production of ionizing radiation. When the LEC includes one or more additional electrodes or electrode structures, the ionizing radiation was found to be converted to electrical energy. Materials that are normally considered to be radioactive are not required.
Owner:INOVL INC
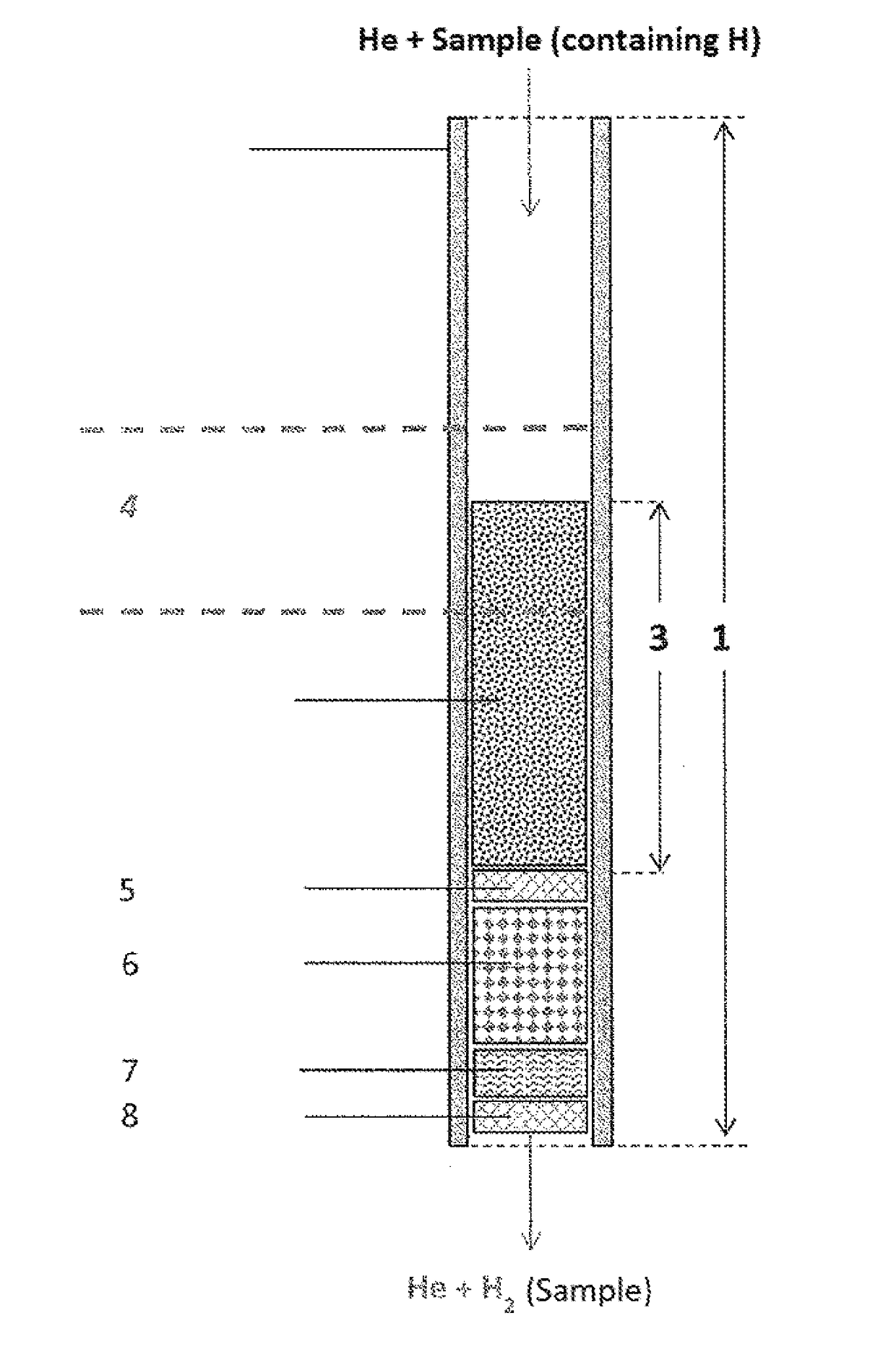
Use of a reactor, methods, and device for quantitatively obtaining molecular hydrogen from substances
ActiveUS20180021746A1Increase productionHydrogenComponent separationCompound specificCompound (substance)
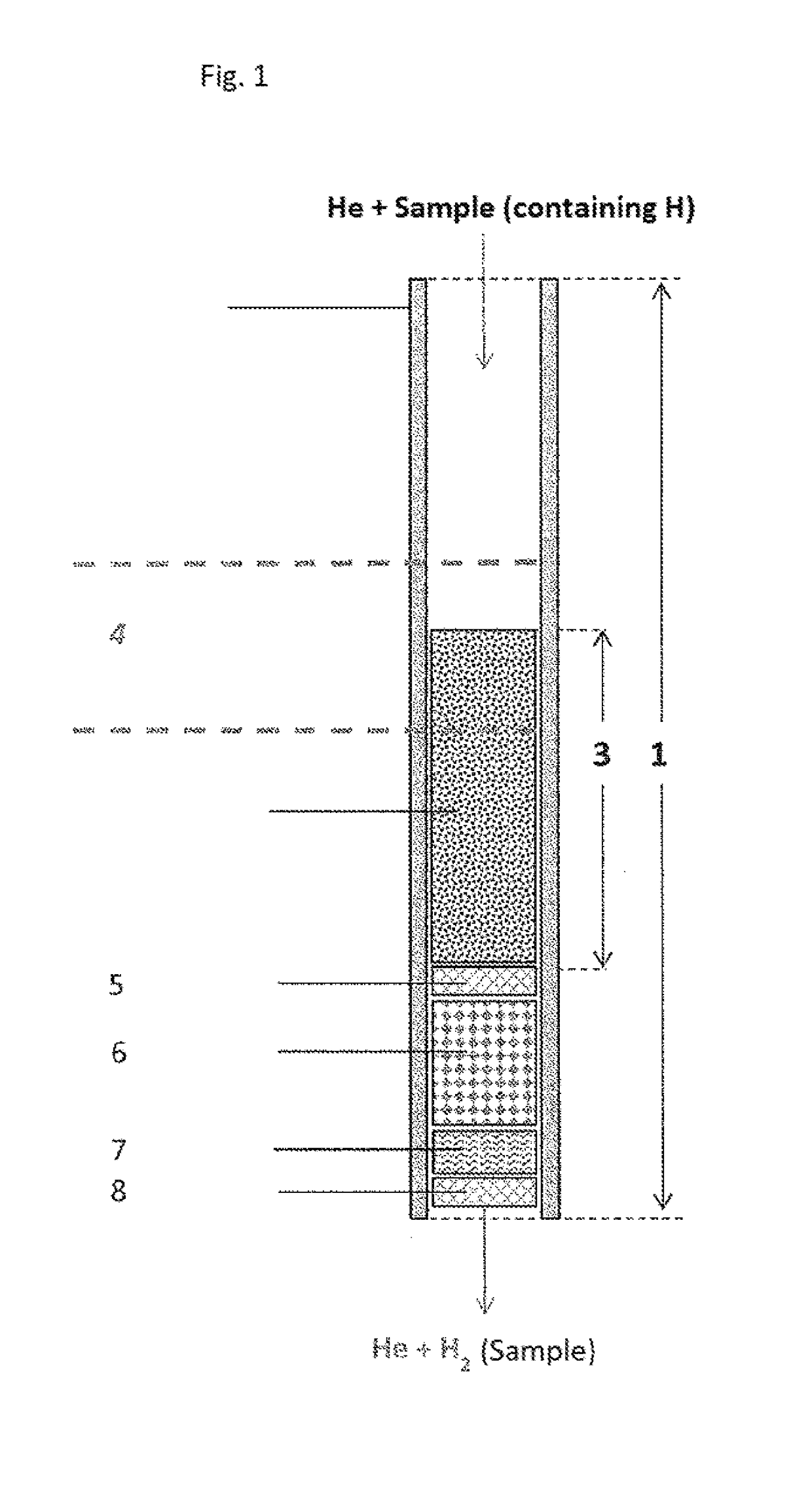
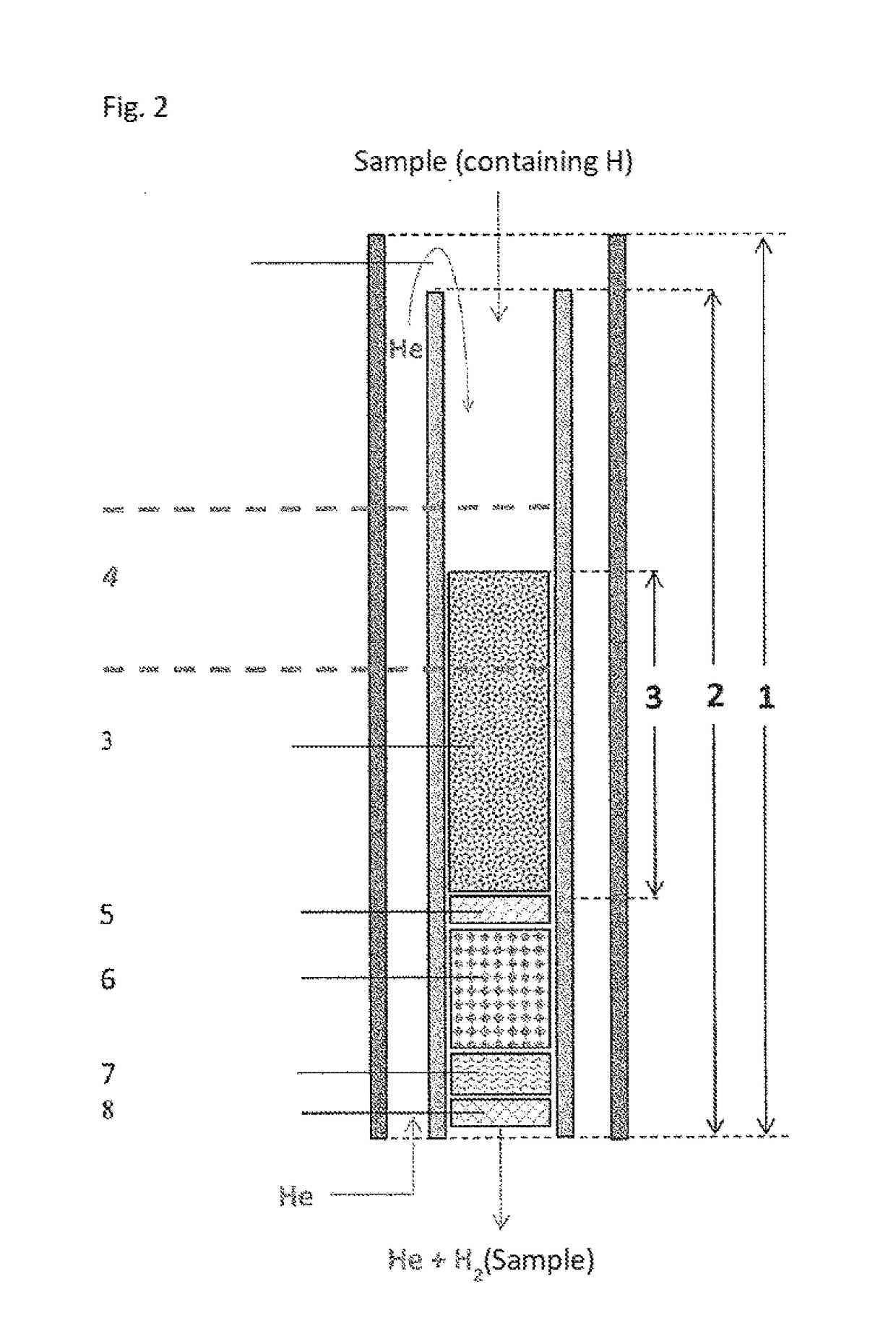
The invention relates to the use of a reactor, methods, and devices for the quantitative recovery of molecular hydrogen from solid, liquid, or gaseous substances which contain hydrogen and which have heteroatoms, as well as to reactors. In this case, the reactors have material containing chromium. The subject matter of the invention also includes the use of the reactor, the method, and the device for the compound-specific or component-specific measurement of the isotope ratio (δ2H) of hydrogen using online apparatuses.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Metal oxygen fusion reactor
An exothermic fusion reactor is described that uses metal-oxygen transmutation. The process comprises a negatively-charged environment; a moderator comprising at least one noble gas; a metal, including isotopes of hydrogen; and a facilitator comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, selenium, bromine, iodine, or combinations thereof.
Owner:K ORBITAL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com