Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Glomus mosseae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, and all species form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizas) with plant roots. Glomus is the largest genus of AM fungi, with ca. 85 species described, but is currently defined as non-monophyletic.
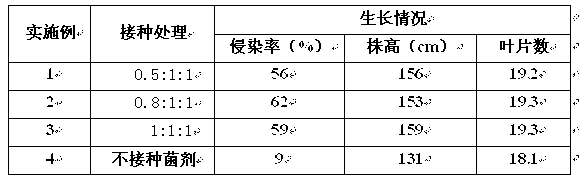
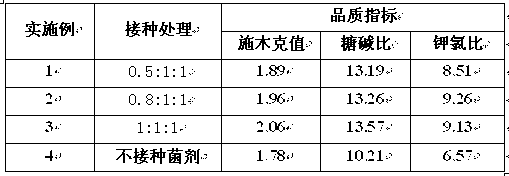
Application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation
InactiveCN103125251AImprove qualityImprove mineral nutritionHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
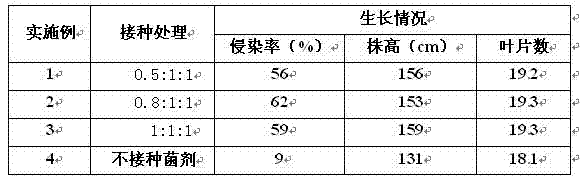
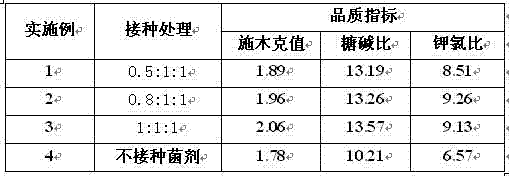
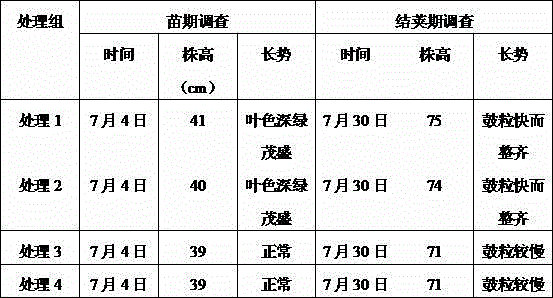
The invention relates to an application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation. A primary arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide is inoculated and propagated separately, and propagule spore density of an arbuscular mycorrhiza of each fungi after the propagation is 30 pieces per gram of dry soil. A float breeding method is adopted to conduct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide combinedinoculation to tobacco, mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are obtained, and the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are directly applied to field production. When being transplanted, the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are conducted with a two-step inoculation, and the mixed fungicide is mixed by propagated acaulospora mellea, glomus mosseae and glomus intraradices at a proportion of 0.5-1: 1:1. A colony formed by the propagation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is close to a natural state, and fungus cooperate and play a better role of growth promoting and quality improving. According to the application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation, by means of the two times of inoculations of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, the proportion of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the tobacco in a symbiotic system built during a seedling stage of the tobacco is guaranteed, and the beneficial effects of the symbiotic system to the development of the tobacco seedlings are ensured. The application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation is simple and practical in method and environment friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
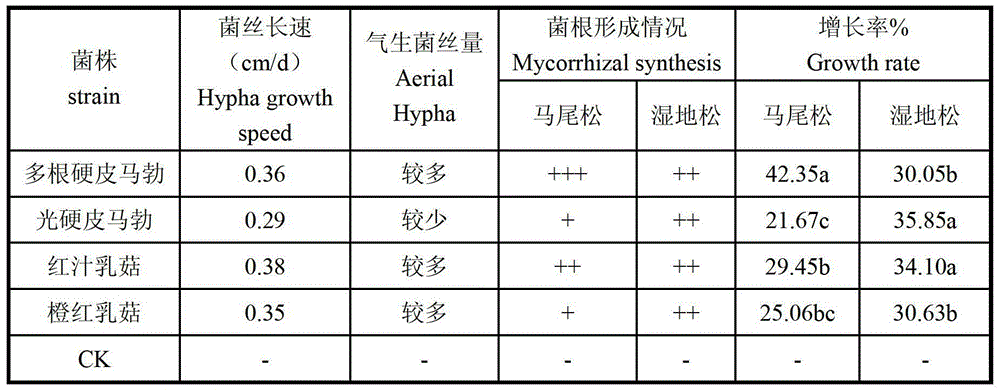
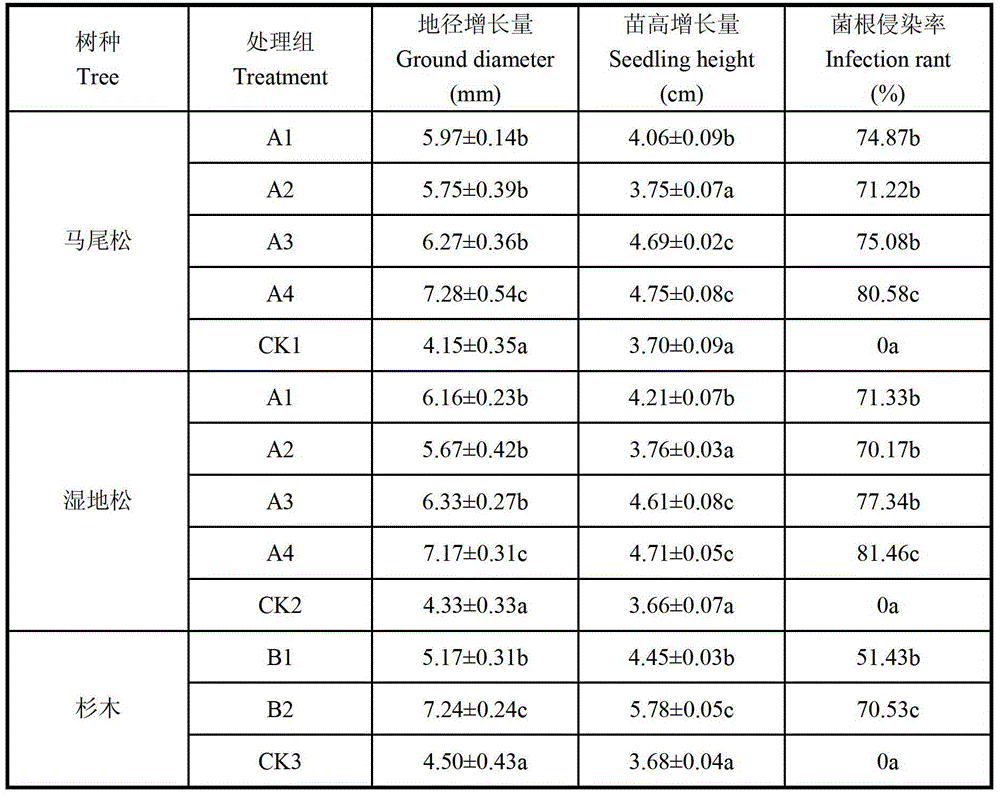
Pine or fir artificial forest stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN103329941AImprove survival rateIncrease growth ratePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyLactarius alnicola
The invention discloses a stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant for a pine or fir artificial forest, and a preparation and application methods thereof. The composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant is compounded from an endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant and an exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant, wherein the endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant is obtained by culturing Glomus mosseae or Glomus intraradices in pots in a greenhouse; and the exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant is obtained by fermenting Lactarius hatsudake Tanaka and Scleroderma polyrhizum Pers. in a liquid fermentation medium. In the forestation process, the seedling root system is subjected to slurry dipping treatment or embedded in pine or fir forest soil, thereby promoting rootage and growth of pines or cedars, improving the tree vigor, enhancing the stress tolerance, increasing the absorptivity of P, and preventing the pine leaf cast, fir anthracnose, pine seedling blight and cataplexis.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strain and application thereof to resisting root-knot nematode
ActiveCN101705192APromote absorptionHarm reductionBiocideFungiBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
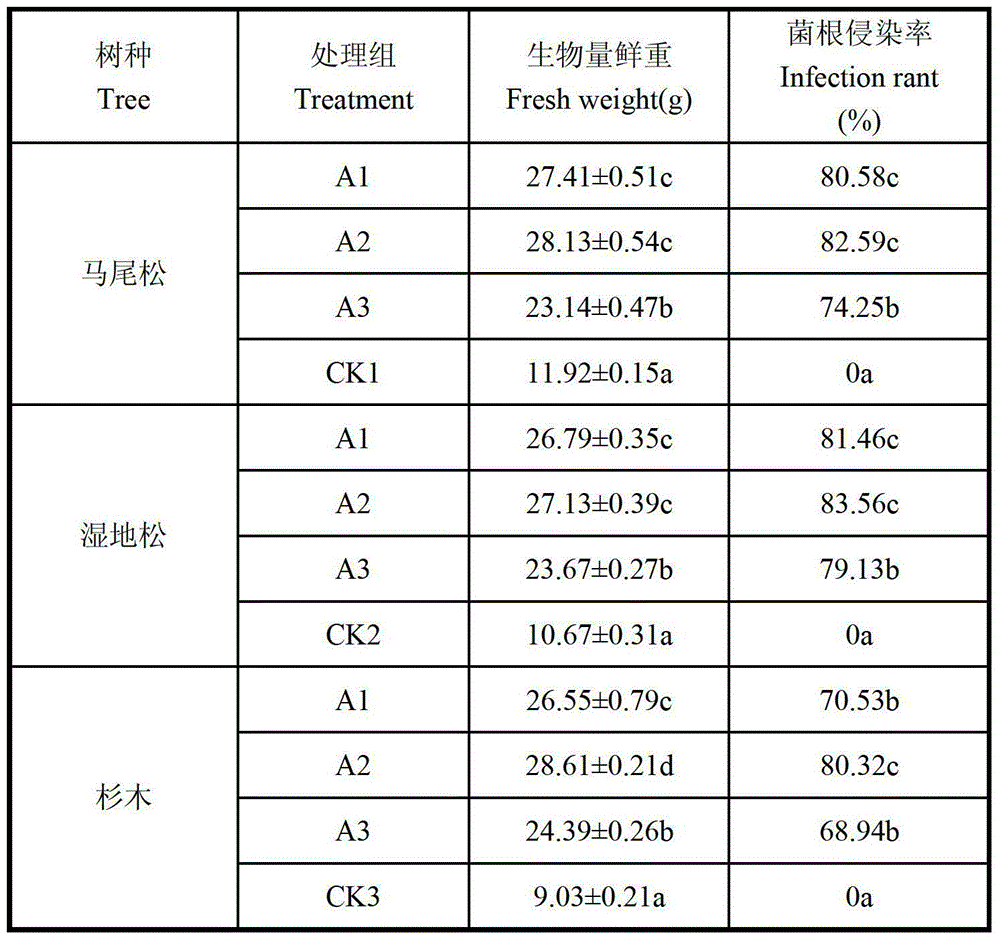
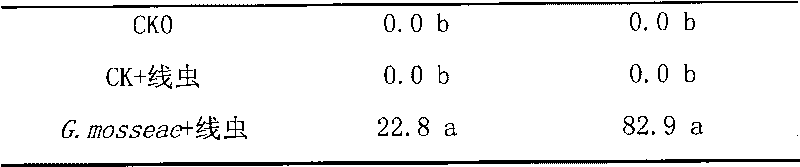
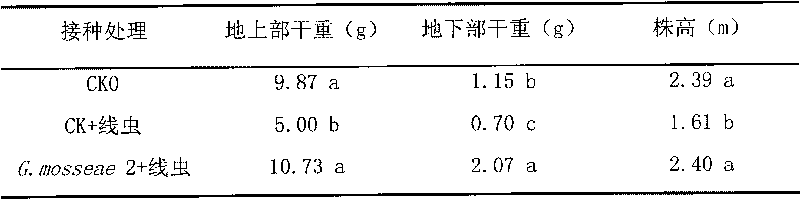
The invention discloses an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strain and application thereof to resisting root-knot nematode. The strain is arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strain Glomus mosseae 96022CGMCC No.3451. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strain Glomus mosseae 96022 can be applied to preventing and curing diseases caused by plant root-knot nematode. Proved by pot experiment results, the inoculation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus strain Glomus mosseae can obviously inhibit damages to cucumber roots of the root-knot nematode so as to have a certain preventing and curing effect, and the preventing and curing efficiency reaches 41 percent.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
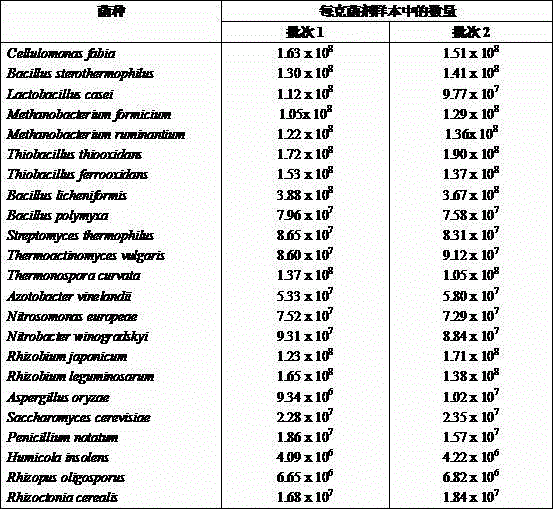
Microbial agent and application for treating cultivating wastes
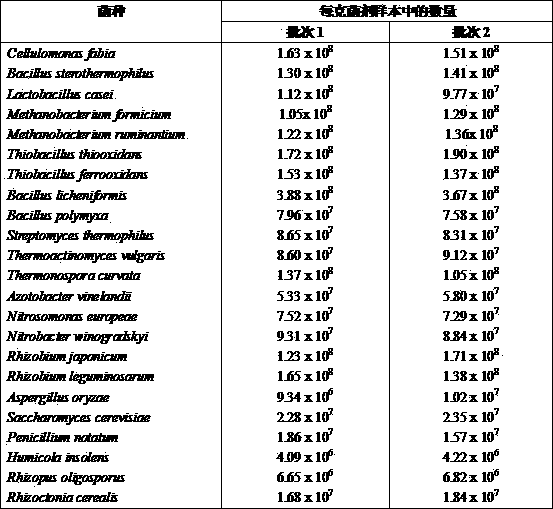
The invention provides a live microbial composition for fermentation treatment of cultivating wastes. The composition is characterized by consisting of bean fiber monad, bacillus stearothermophilus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus polymyxa, streptomycete, thermoactinomycete, thermomonospora, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, nitrated monad, nitrobacteria, rhizobium, Aspergillus oryzae, yeasts, moulds, humicola, rhizopus and glomus mosseae. In addition, the invention further provides an organic fertilizer generated by virtue of fermentation of the microbial composition as well as an application and a method thereof. In production of the organic fertilizer, cultivating wastes such as animal wastes are objectively treated.
Owner:宋彦耕
Method for repairing glomus mosseae-contaminated soil through combination of glomus mosseae and nightshade-rice intercropping system
InactiveCN111250539AImprove the ability to absorb and enrich cadmiumTransfer restrictionsContaminated soil reclamationCultivating equipmentsHyperaccumulatorIntercropping
The invention discloses a method for repairing glomus mosseae-contaminated soil through combination of glomus mosseae and a nightshade-rice intercropping system. The method comprises the following steps: propagating to prepare a glomus mosseae inoculant; accelerating germination of the rice and solanum nigrum seeds to obtain rice and solanum nigrum seedlings; transplanting rice and solanum nigrumseedlings into the glomus mosseae-contaminated soil, wherein the intercropping ratio of solanum nigrum to rice is 1: (1-2); and adding the glomus mosseae inoculant into glomus mosseae contaminated soil to form a hyperaccumulator-dry rice-glomus mosseae symbiotic system. By inoculating glomus mosseae, the growth and soil Cd absorption capacity of solanum nigrum can be improved, meanwhile, the content of heavy metal cadmium in rice is remarkably reduced, the effect of repairing Cd-contaminated soil while safe production is achieved is achieved, and the method has the advantages of being efficient, low in cost, easy to operate, free of secondary pollution and the like and has good theoretical and application and popularization value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Repairing material, repairing method and application of ionic rare earth tailing area
InactiveCN112705567AVegetation ecological restoration effect is goodStrong stress resistanceContaminated soil reclamationGlomus intraradicesVegetation
The invention provides a repairing material, a repairing method and application of an ionic rare earth tailing area, and belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration. The invention provides a repairing material for an ionic rare earth tailing area. The repairing material comprises arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pioneer plants, wherein the types of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi comprise one or more of glomus intraradices, glomus mosseae and Paraglomus occultum. The types of the pioneer plants comprise one or more of paspalum, ramie and awn. The repairing material provided by the invention has the characteristics of high plant restoration success rate, excellent effect, capability of obviously reducing the water and soil loss rate and the like when being applied to restoration of the ionic rare earth tailing area, and has a good vegetation ecological restoration effect on the ionic rare earth waste mining area in the rainy region in the south; the invention is suitable for rapid treatment of rare earth tailing waste land in southern rainy regions.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF ECO-ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & PLANNING
Preparation method and application of efficient microbial agent for slope protection
The invention provides a preparation method and application of an efficient microbial agent for slope protection, and relates to the technical field of ecological restoration. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing a bacillus amyloliquefaciens agent, a trichoderma harzianum agent and a glomus mosseae agent according to a mass ratio of 2: 5: 49 to form mixed bacterial powder. The effects of degrading a straw plate and improving the survival rate of slope protection plants are optimal.
Owner:北京航天恒丰科技股份有限公司
Saline-alkali soil improver containing glomus mosseae and improvement method
InactiveCN111117640AIncrease biomassEasy constructionAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesPlant rootsAlkali soil
The invention aims to provide a saline-alkali soil improver containing glomus mosseae and an improvement method, aiming at solving the problems existing in improvement of saline-alkali soil by the existing biotechnology. The saline-alkali soil improver is composed of glomus mosseae, iron tailings and organic soil, the ratio of glomus mosseae liquid to the iron tailings to the organic soil is 2 mL:2-2.5 g: 1.5-1.8 g, and the concentration of the glomus mosseae liquid is 1-9 * 107 CFU / ml. According to the simple saline-alkali soil improvement method, the glomus mosseae infects plant roots to form arbuscular mycorrhizal symbionts, the iron tailings are used as an improver, a synergistic effect is achieved on plants planted in saline-alkali soil, and the plant biomass is improved while the purposes of improving the saline-alkali soil and improving the soil availability of the saline-alkali soil are achieved.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
Saline-alkali soil improvement agent containing composite microbial agents and preparation method and application of saline-alkali soil improvement agent containing composite microbial agents
ActiveCN111088168AHigh activityPromote growthBio-organic fraction processingAgriculture tools and machinesMicroorganismSoil science
The invention aims to solve the problems existing in an existing alkaline soil improvement technique, and provides a saline-alkali soil improvement agent containing composite microbial agents and a preparation method and application of the saline-alkali soil improvement agent containing composite microbial agents. The saline-alkali soil improvement agent disclosed by the invention consists of glomus mosseae, azospirllum brasilense and solid carriers, wherein the mass ratio of total number of effective viable bacteria of the glomus mosseae and the azospirllum brasilense to the solid carriers is1*10<5>-9*10<7> / gram, the ratio of the number of the glomus mosseae to the number of the azospirllum brasilense is 1 to (0.2-5). The saline-alkali soil improvement agent has good effects on plage saline-alkali soil improvement. The application of the saline-alkali soil improvement agent is a method for microorganism ecological improvement of saline-alkali soil, which is simple to operate, low incost and pollution-free.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
Active organic insecticide fertilizer for bacteriostasis and desinsectization and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an active organic insecticide fertilizer for bacteriostasis and desinsectization and a preparation method thereof. The active organic fertilizer comprises 10 to 20 parts of aconite, 5 to 10 parts of ligularia sibirica, 4 to 8 parts of pedicularis verticillata, 10 to 15 parts of radix euphorbiae lantu, 20 to 30 parts of whin, 2 to 3 parts of achnatherum inebrians, 5 to 10 parts of pulsatilla chinensis, 3 to 8 parts of tanacetum vulgare stem, leaf and seed, 50 to 60 parts of spent mushroom compost , 10 to 20 parts of cottonseed meal, and 5 to 10 parts of rice hull. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing raw materials; supplementing water; treating by the solid material microwave technology; adding 80 to 120g / T of active biological compound bacterium, and performing composting fermentation to obtain the bacteriostatic active biological organic insecticide fertilizer, wherein the active biological compound bacterium is prepared by directly mixing bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus megatherium, bacillus subtilis, glomus mosseae and glomus versiforme berch. The organic insecticide fertilizer is the organic insecticide fertilizer containing bacteriostasis and desinsectization components and active organisms and is worthy of wide application.
Owner:乌鲁木齐木易联华生物科技有限公司
Cultivating method for solanaceous plants
InactiveCN103703986AImprove drought resistanceImprove frost resistanceHorticulturePseudomonadaceaeDisease resistant
The invention provides a cultivating method for solanaceous plants. The method comprises the following steps of implanting rooted seedlings obtained through seeds or tissue culture into solid substrates, inoculating Glomus mosseae to the substrates, inoculating pseudomonadaceae to the substrates after the plantules of seeds germinate and are exposed out of the substrates to form seedlings, inoculating pseudomonadaceae to the substrates while the rooted seedlings are implanted to the substrates and when the rooted seedlings obtained through the tissue culture are cultivated, obtaining the seedlings with the fungi after the pseudomonadaceae is inoculated, and cultivating the seedlings to ripe. According to the method, in the cultivating process of the solanaceous plants, the Glomus mosseae and the pseudomonadaceae are inoculated to the seedlings successively, the cultivated solanaceous plants are made to show excellent drought resistance, frost resistance, disease resistance and other resistance performance in a seedling stage, and meanwhile, the grow rate of the seedlings of the solanaceous plants is improved greatly under the synergistic effects of the two symbiotic fungi.
Owner:魏晓辰
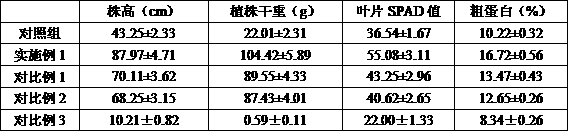
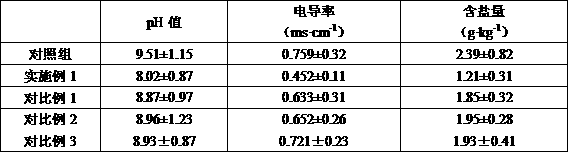
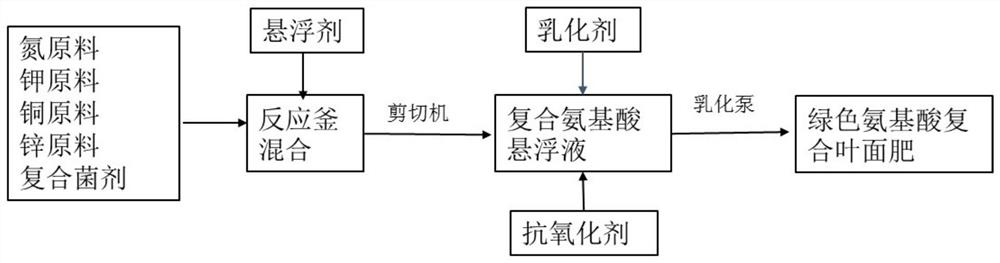
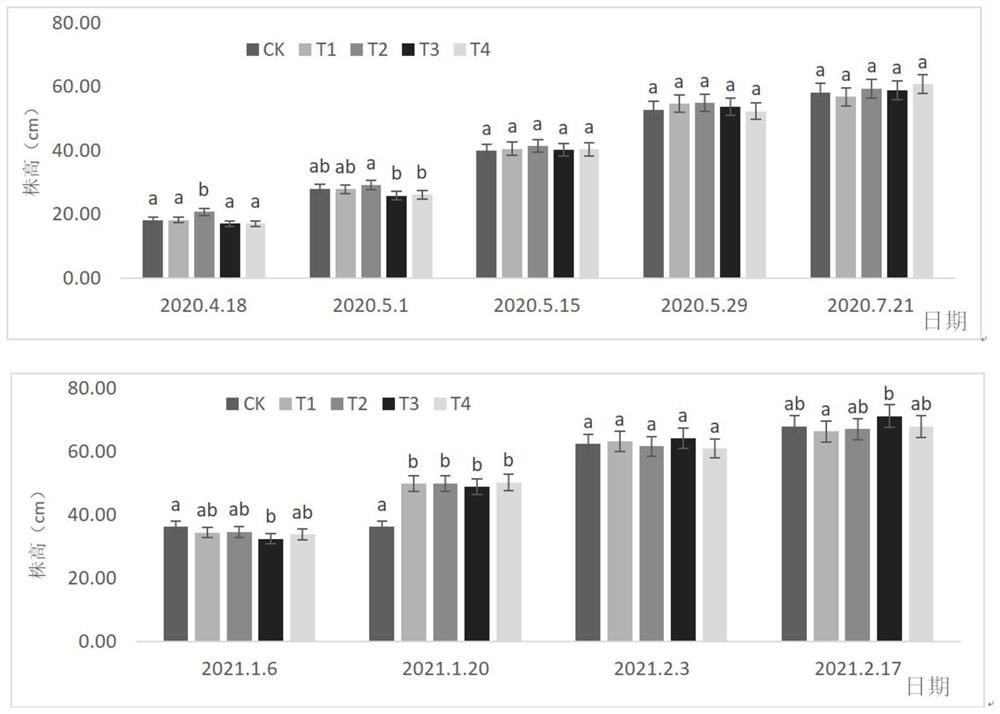
Amino acid compound foliar fertilizer and application thereof
InactiveCN114230405AEasy to get materialsEasy to implementAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSulfate zincBacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses an amino acid compound foliar fertilizer, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 150 to 220 parts of urea, 1170 to 1275 parts of 50 percent plant source enzymolysis compound amino acid concentrated solution, 150 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 20 parts of copper sulfate pentahydrate, 20 parts of zinc sulfate heptahydrate and 15 parts of compound bacteria consisting of glomus mosseae and bacillus thuringiensis. The foliar fertilizer is convenient in raw material taking, simple and convenient in process operation, safe, environment-friendly and pollution-free in preparation process, contains nutrient elements and nutrient coordination substances required in celery growth, improves the celery yield, promotes celery quality improvement, and provides powerful support for green and sustainable development of the celery industry.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
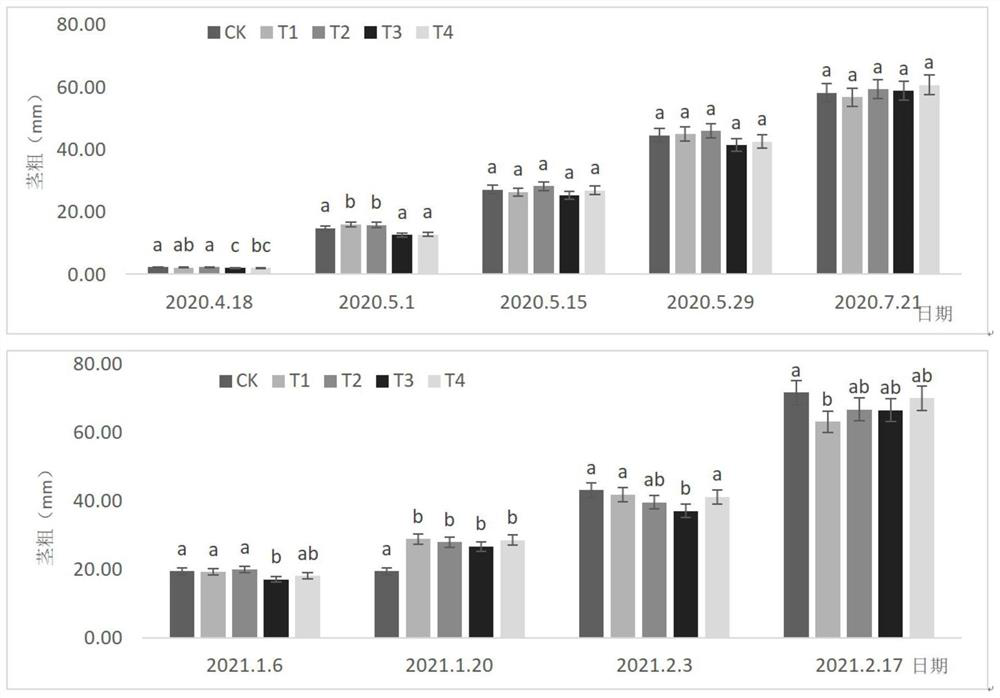
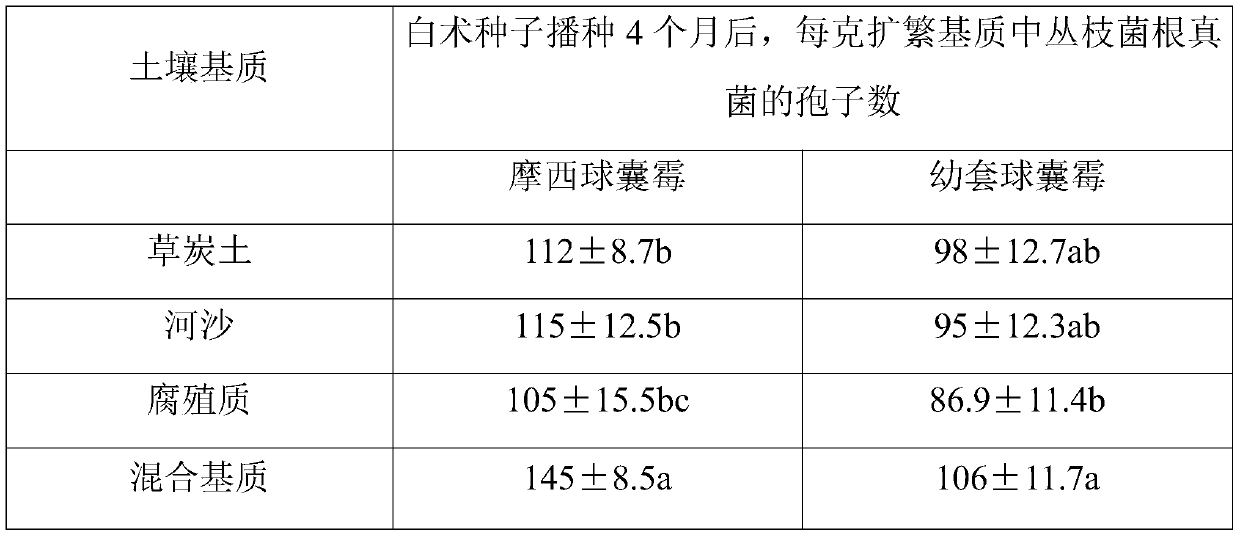
A method for improving the growth and drought resistance of Atractylodes macrocephala seedlings
ActiveCN108651195BPromote growthImprove drought resistanceCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAtractylodes macrocephalaSeedling
The invention relates to a method for improving the growth and drought resistance of Atractylodes atractylodes seedlings, which belongs to the field of processing Atractylodes rhizomes. The method adopts Glomus mosesi as the first strain and Glomus tetus as the second strain, and treats The first strain and the second strain are mixed after a unique propagation work, and the obtained arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus propagation mixture is applied to the Atractylodes macrocephala seedling substrate added with dry chicken manure, and the cerium chloride solution is used to Treat Atractylodes macrocephala seeds, and spray Atractylodes atractylodes seedlings with special spraying water, thus overcoming the problems in the prior art that Atractylodes atractylodes is severely degraded after multiple generations of reproduction, resulting in weakened resistance, reduced quality, and high seedling mortality. Further, the growth ability and drought resistance ability of Atractylodes macrocephala seedlings are significantly improved, and seedlings with strong growth ability and drought resistance ability can be provided for Atractylodes rhizome production, thereby expanding the development of Atractylodes rhizome production and expanding the development and utilization of Atractylodes rhizome resources.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
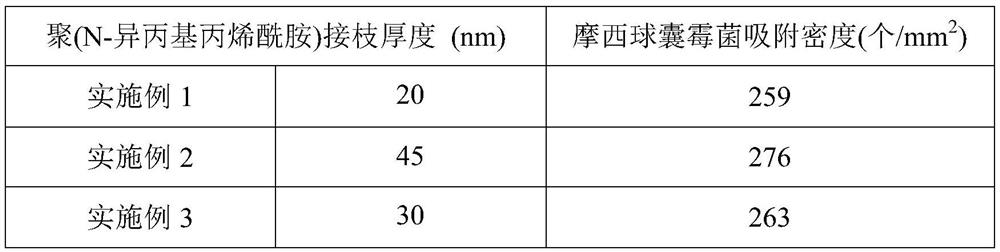
A kind of preparation method of solid bacterial agent for rice crops
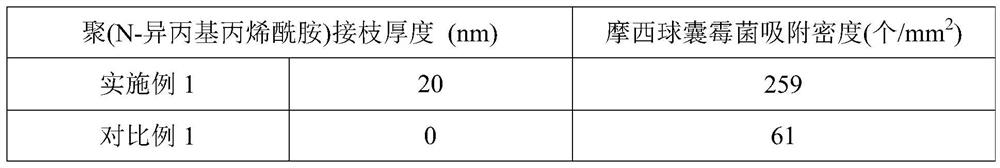
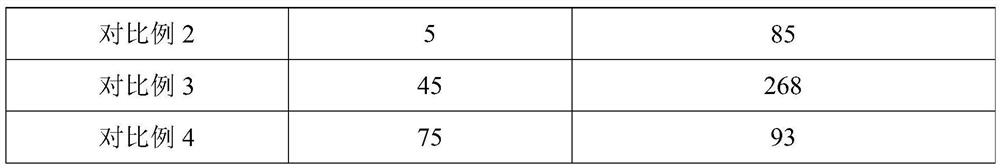
ActiveCN109182139BImprove adsorption capacityFungiMicroorganism based processesFungicidePolyvinyl alcohol
The present invention relates to the field of biological bacterial fertilizer and bacterial agent, in particular to a preparation method of solid bacterial agent for rice crops, comprising the following steps: 1) grinding the fertilizer into fine powder; 2) dissolving sodium alginate and polyvinyl alcohol Fully dissolve in water, add CaCO to the resulting mixture 3 ; Then drop into the cross-linking agent to solidify to form gel balls; 3) Wash the gel balls with an acidic solution to obtain a porous gel material; 4) Graft N-isopropylacrylamide on the surface of the porous gel material ; 5) Mixing and culturing the fungus liquid of Glomus moses and the obtained porous gel material to obtain a solid gel bacterial preparation. The present invention uses sodium alginate / polyvinyl alcohol porous gel material as a carrier, and the pore wall in the porous gel material is covered with fertilizer fine powder, and a large amount of Glomus moses mold is adsorbed on the surface of the pore wall, and the material is Biodegradable materials, will not remain in the soil, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SEGA SCI & TECH
Method for improving total flavonoid content and yield of clematis plants by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
ActiveCN107821023BPromote accumulationIncrease contentFungiGrowth substratesBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
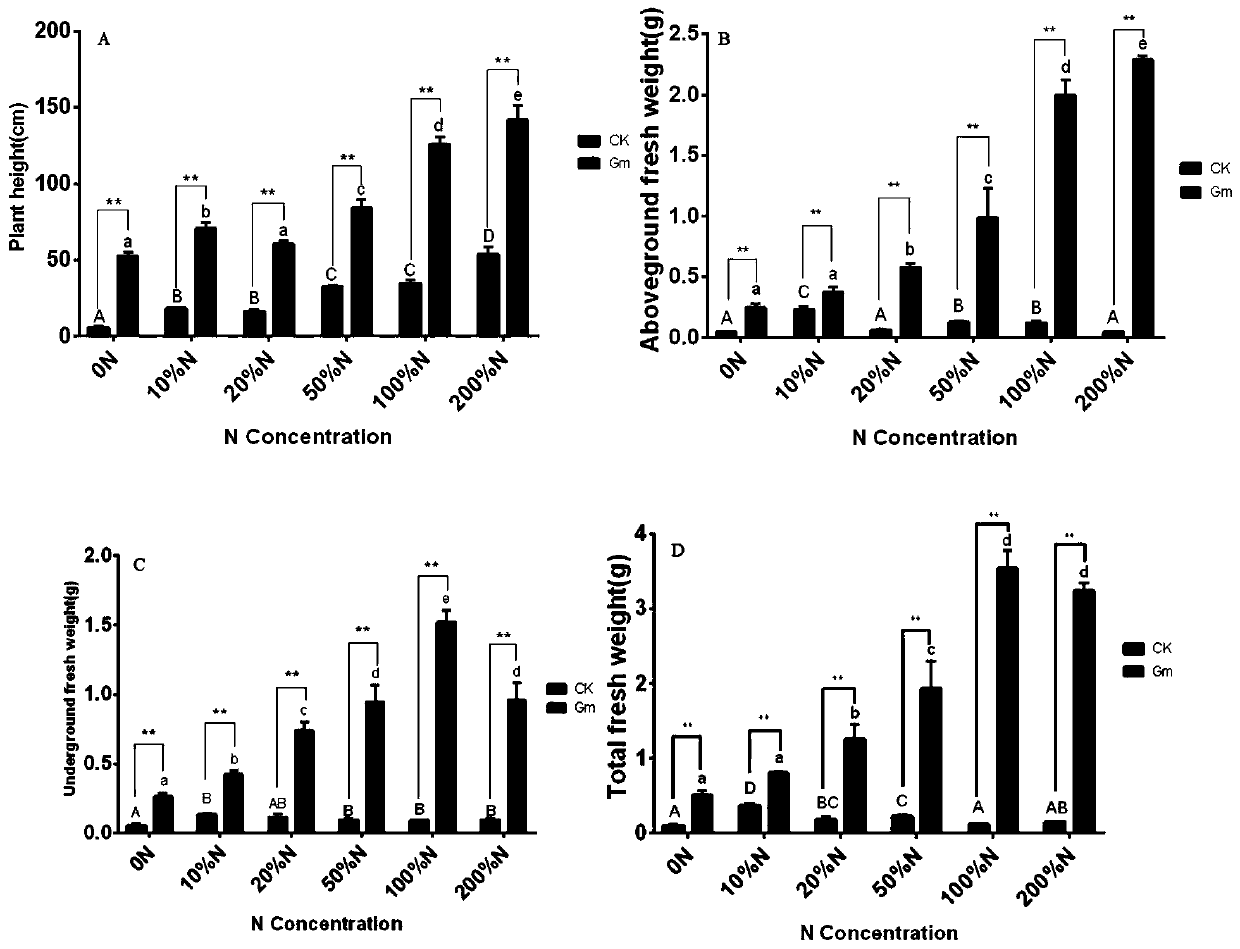
The invention belongs to the field of fungi for plants, and particularly relates to a method for improving the content and yield of total flavonoid of clematis plants by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. By inoculating the clematis plants with glomus mosseae under different contents of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), the growth, the physiological and biochemical characteristics and accumulationof total flavonoid of the clematis plants are influenced, and by utilizing a qRT-PCR technology, the expression characteristics of responses of key enzyme genes to different contents of N and P in the synthesis pathway of flavonoid biomass are analyzed, so that influence mechanisms of the fungi on the growth of the clematis plants and accumulation of active ingredients are found, and a basis is provided for the application of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the cultivation, resource development and utilization and other aspects of medicinal plants.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MEDICAL UNIV
A substrate for maple cuttings
ActiveCN108990571BIncrease resistancePromote absorptionGrowth substratesCulture mediaPlant regulatorsAzotobacter chroococcum
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant seedling propagation, and discloses a matrix for maple cuttage. The matrix comprises glomus mosseae, trichoderma asperellum, azotobacter chroococcum and bacillus megatherium. When the matrix is adopted for cuttage, cutting slips do not need to be disinfected and do not need to be soaked by a plant conditioning agent, the process is shortened, manpower and material resources are saved, efficiency is improved, and the rooting rate is high.
Owner:富蓝农业科技(广东)有限公司
Active coke-based saline-alkali soil improver and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112876320AImprove fertilityImprove macroporous microporous structureSuperphosphatesExcrement fertilisersAlkali soilGlomus versiforme
The invention belongs to the field of soil improvement, and particularly relates to an active coke-based saline-alkali soil improver and a preparation method thereof. The improver is composed of a porous biological fertilizer and a strain inoculant which are independently packaged, wherein the porous biological fertilizer is obtained by mixing, aging and fermenting an active coke mixture, vinegar residues and chicken manure according to the weight ratio of 1: (0.2-5): (0.2-1); the active coke mixture is obtained by fully mixing active coke screen underflow subjected to homogenization pretreatment and acidification impurity removal with a calcium superphosphate saturated solution and a silicon fertilizer according to the solid weight ratio of 1: (0.5-5): (0.2-1) by utilizing alternating-frequency magnetic coupling ultrasonic grading mechanical stirring; and the strain fungicide is composed of mycorrhizal fungi and a water-retaining agent according to the weight ratio of (0.1-1): (1-5), the mycorrhizal fungi are obtained by compounding glomus mosseae, glomus intraradices and glomus versiforme according to the weight ratio of 1: (0.2-2): (0.5-5) and propagating in local soil, and the inoculated product is a rhizosphere mixture composed of spores, hyphae and mycorrhizal fragments.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Microbial preparation for greenhouse planting and application thereof
PendingCN110964648AAvoid damageImprove qualityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyGlomus intraradices
The invention relates to a microbial preparation and application thereof, in particular to a microbial preparation for greenhouse planting and an application thereof. The method aims at solving the problems that in the greenhouse planting process, a chloroplast base grain structure is damaged, so that the crop yield is reduced, and the quality becomes poor. The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention is composed of glomus mosseae HDSF1 and glomus intritus HDSF5. The microorganism is applied to greenhouse planting. The microbial preparation is applied to greenhouse planting, particularly to greenhouse soil subjected to pesticide damage and salinization stress, damage of the pesticide damage and salinization to the base grain structure of chloroplast is relieved, normal production of crops is guaranteed, and by means of the microbial preparation, the crops are high in yield and good in quality.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Dioscorea composita compound mycorrhizal fungus growth promoting agent and agricultural light complementary planting method for Dioscorea composita
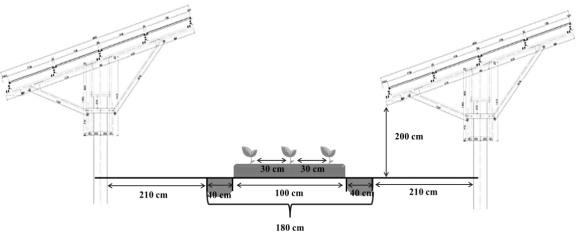
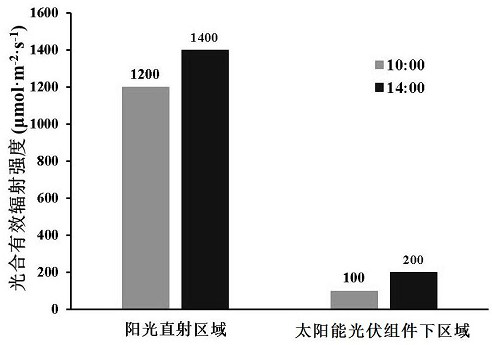
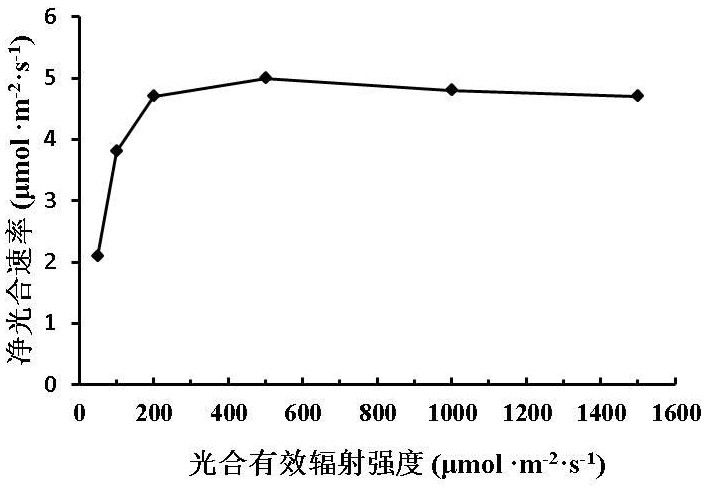
ActiveCN114540259AImprove growth performancePromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyCrop cultivation
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganism and crop cultivation, in particular to a compound mycorrhizal fungus growth promoting agent for dioscorea composita and an agricultural light complementary planting method for dioscorea composita. The compound mycorrhizal fungus growth-promoting agent for the dioscorea composita comprises glomus mosseae, streptomyces azofixing and plant rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria, and can greatly improve the photosynthesis of the dioscorea composita under a photovoltaic panel and promote the growth and development of the dioscorea composita. By adopting the compound mycorrhizal fungus growth promoting agent, the unoccupied land under a solar photovoltaic panel is utilized, and solar photovoltaic and dioscorea composita planting are combined in a high-ridge close planting mode; the whole planting process is easy to operate and low in cost, and three-dimensional value-added utilization of the land is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Method for enhancing petroleum-contaminated soil remediation capacity of phytolacca americana
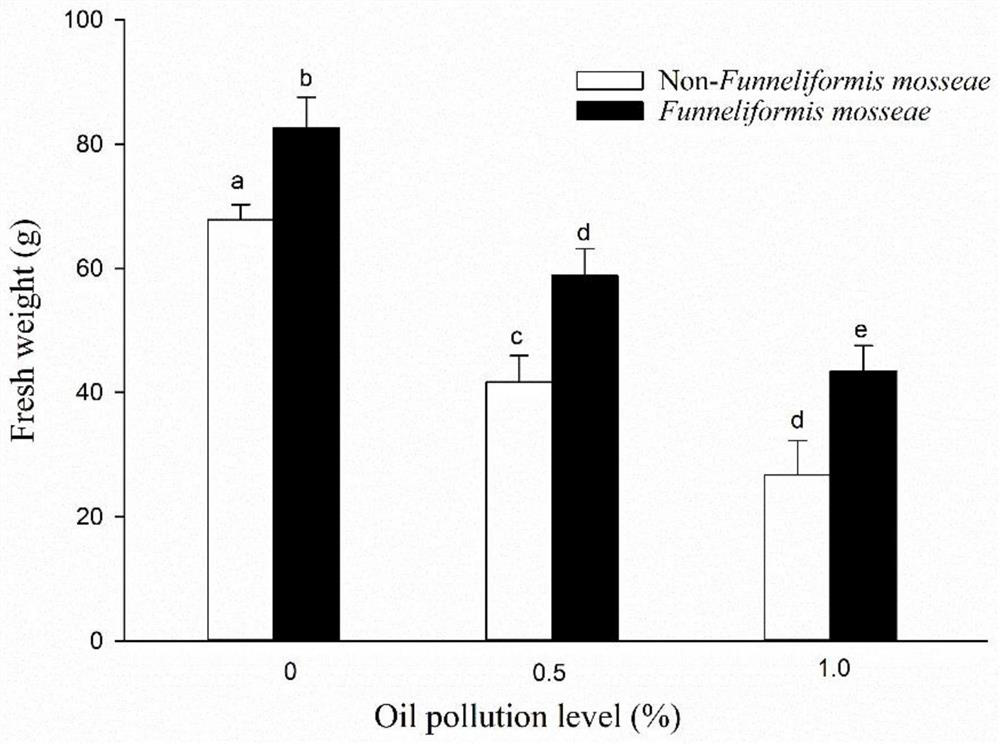
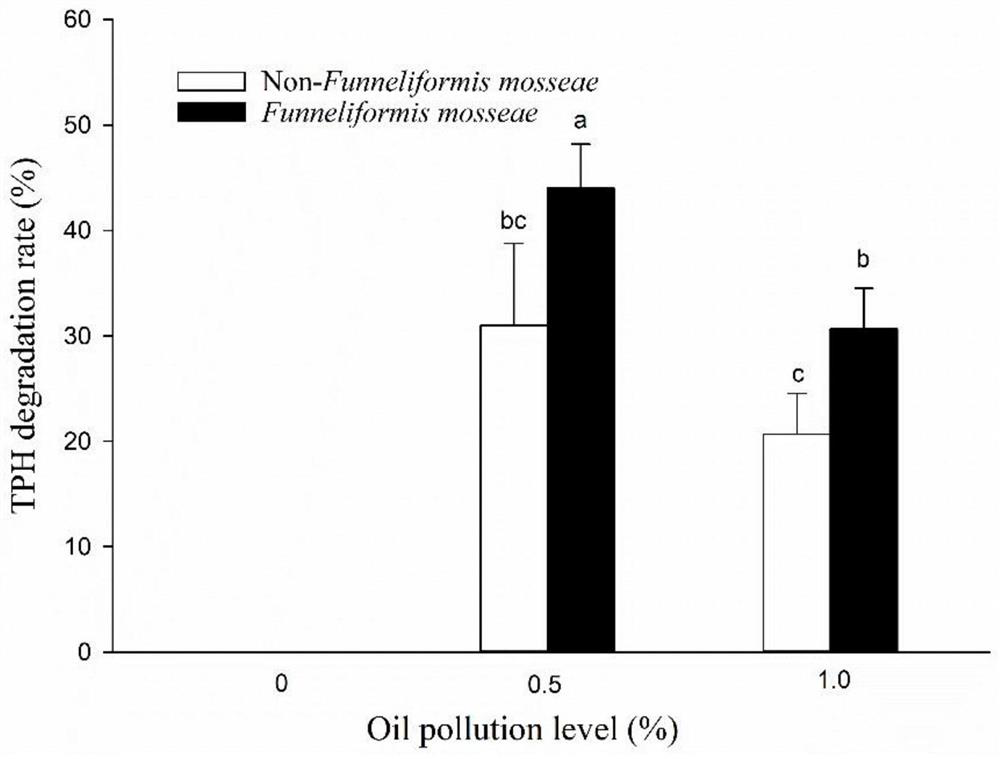
InactiveCN112264460AEnhance the ability to degrade soil oil pollutionLarge biomassContaminated soil reclamationPetroleum oilEnvironmental chemistry
The invention relates to the technical field of remediation of soil-contaminated environments, in particular to a method for enhancing the petroleum-contaminated soil remediation capacity of phytolacca americana. Specifically, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant is inoculated into a phytolacca americana growth substrate to enhance the petroleum-contaminated soil remediation capacity of phytolacca americana. Preferably, the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant is a glomus mosseae inoculant. According to the invention, glomus mosseae plays a role in promoting the mineral nutrient absorption, growth and development of phytolacca americana, and enhances the capacity of the phytolacca americana in degrading petroleum pollution in soil. Specifically, after glomus mosseae is inoculated,the biomass of phytolacca americana is increased by 38.55%, and a petroleum degradation rate is increased by 50.00%. By inoculating glomus mosseae, the biomass of phytolacca americana in petroleum-contaminated soil can be remarkably improved, and the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation rate of phytolacca americana in the petroleum-contaminated soil remediation process is remarkably increased. Moreover, the method has the advantages of no negative influence on the environment, no secondary pollution, good remediation effect and low cost.
Owner:青岛斯坦德衡立环境技术研究院有限公司
A kind of plant cultivation method of Solanaceae
The invention provides a method for cultivating Solanaceae plants, comprising the following steps: implanting seeds or rooted seedlings obtained by tissue culture into a solid substrate, and inoculating the substrate with Glomus mosei; the germs of the seeds germinate and are exposed outside the substrate to form seedlings Afterwards, inoculate Pseudomonas to matrix; When cultivating the rooted shoots that tissue culture obtains, then inoculate Pseudomonas to matrix simultaneously when implanting matrix; After inoculating Pseudomonas, obtain the seedling of bacterialization; Seedlings are grown to maturity. The present invention proposes to inoculate Glomus mosei and Pseudomonas successively to its seedlings during the cultivation process of Solanaceae plants, The cultivated Solanaceae plants exhibit excellent stress resistance characteristics such as drought resistance, frost resistance, and disease resistance at the seedling stage, and at the same time, under the synergistic effect of the two symbiotic bacteria, the growth rate of the Solanaceae plant seedlings is also greatly improved .
Owner:魏晓辰
Pine or fir artificial forest stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN103329941BImprove survival rateIncrease growth rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyLactarius alnicola
The invention discloses a stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant for a pine or fir artificial forest, and a preparation and application methods thereof. The composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant is compounded from an endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant and an exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant, wherein the endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant is obtained by culturing Glomus mosseae or Glomus intraradices in pots in a greenhouse; and the exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant is obtained by fermenting Lactarius hatsudake Tanaka and Scleroderma polyrhizum Pers. in a liquid fermentation medium. In the forestation process, the seedling root system is subjected to slurry dipping treatment or embedded in pine or fir forest soil, thereby promoting rootage and growth of pines or cedars, improving the tree vigor, enhancing the stress tolerance, increasing the absorptivity of P, and preventing the pine leaf cast, fir anthracnose, pine seedling blight and cataplexis.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation
InactiveCN103125251BImprove qualityImprove mineral nutritionHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to an application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation. A primary arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide is inoculated and propagated separately, and propagule spore density of an arbuscular mycorrhiza of each fungi after the propagation is 30 pieces per gram of dry soil. A float breeding method is adopted to conduct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide combinedinoculation to tobacco, mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are obtained, and the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are directly applied to field production. When being transplanted, the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are conducted with a two-step inoculation, and the mixed fungicide is mixed by propagated acaulospora mellea, glomus mosseae and glomus intraradices at a proportion of 0.5-1: 1:1. A colony formed by the propagation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is close to a natural state, and fungus cooperate and play a better role of growth promoting and quality improving. According to the application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation, by means of the two times of inoculations of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, the proportion of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the tobacco in a symbiotic system built during a seedling stage of the tobacco is guaranteed, and the beneficial effects of the symbiotic system to the development of the tobacco seedlings are ensured. The application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation is simple and practical in method and environment friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Microbial agent and application for treating cultivating wastes
ActiveCN103409357BReduce in quantityReduce usageFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides a live microbial composition for fermentation treatment of cultivating wastes. The composition is characterized by consisting of bean fiber monad, bacillus stearothermophilus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus polymyxa, streptomycete, thermoactinomycete, thermomonospora, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, nitrated monad, nitrobacteria, rhizobium, Aspergillus oryzae, yeasts, moulds, humicola, rhizopus and glomus mosseae. In addition, the invention further provides an organic fertilizer generated by virtue of fermentation of the microbial composition as well as an application and a method thereof. In production of the organic fertilizer, cultivating wastes such as animal wastes are objectively treated.
Owner:宋彦耕
Root soil composition and method for improving Fragaria ananassa continuous cropping capability
InactiveCN111684997AImprove the soil environmentSolve some soil problemsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsContinuous croppingFragaria
The invention provides a root soil composition for improving the Fragaria ananassa continuous cropping capability and a method for improving the Fragaria ananassa continuous cropping capability, and relates to the technical field of Fragaria ananassa planting. The root composition provided by the invention comprises a Glomus mosseae root soil mixture and a Glomus versiforme root soil mixture according to a mass ratio of (1.5 to 2.5):(0.8 to 1.2). The method comprises the following steps of (1) performing solar energy sterilization on a greenhouse, and performing high-temperature greenhouse closing at a temperature of 58 DEG C or higher; and (2) within 24 h before fixed planting of the Fragaria ananassa, applicating a root soil composition comprising the Glomus mosseae root soil mixture andthe Glomus versiforme root soil mixture according to the mass ratio of (1.5 to 2.5):(0.8 to 1.2). The root soil composition and method for improving the Fragaria ananassa continuous cropping capability provided by the invention have the advantages that the Fragaria ananassa transplanting survival rate can be improved; the Fragaria ananassa yield can be improved; and the disease incidence of the Fragaria ananassa can be reduced.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Artificial grass carbon prepared from kosteletzkya virginica straws as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103771921BEasy accessAbundant resourcesOrganic fertilisersBiotechnologyKosteletzkya virginica
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to artificial grass carbon prepared from kosteletzkya virginica straws as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The artificial grass carbon prepared from the kosteletzkya virginica straws comprises a kosteletzkya virginica straw self-fermenting product, a Glomus mosseae(Nicol.&Gerd.) microbial agent and furnace slag (the particle diameter is less than or equal to 0.3cm), and the weight ratio of the kosteletzkya virginica straw self-fermenting product to the Glomus mosseae(Nicol.&Gerd.) microbial agent to the furnace slag is 5: 0.05: 1. The preparation method of the artificial grass carbon comprises the steps of fermenting microbial agent preparation, straw pretreatment, straw fermentation and artificial grass carbon preparation. The main nutritive indexes except for humic acid of the artificial grass carbon prepared by using the method are higher than those of a grass carbon matrix. The artificial grass carbon is low in cost, easy to operate and high in yield and can serve as a seedling growing medium or a culture medium to be widely applied to agricultural production.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
A strain of Glomus spp
ActiveCN113388528BHigh retention rateImprove repair effectAgriculture tools and machinesFungiBiotechnologyAlkali soil
The invention provides a strain of Glomus spp., a composition for restoring saline-alkali land, and a method for restoring saline-alkali land, belonging to the technical field of ecological restoration. The surface Glomus fungus provided by the present invention has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 14546, has good root infection ability for pioneer plants in saline-alkali soil with 8 / 1000th salt content, can significantly improve the survival rate of pioneer plants in saline-alkali land, and improves soil Repair effect.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
A special microbial agent for apple trees and its preparation method
ActiveCN110862939BPromote growthIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a special microbial agent for apple trees and a preparation method thereof, comprising the following bacterial species components: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Paenibacillus polymyxa, Bacillus licheniformis, Streptomyces Jingyang, Bacillus coagulans, and Bacillus Veles bacillus and Glomus moesei; the deposit number of Glomus moesei is BGCNM02A. The special microbial agent for apple trees can effectively prevent and treat apple rot disease, and at the same time, can significantly increase apple yield and apple sugar content.
Owner:保罗蒂姆汉(潍坊)生物科技有限公司
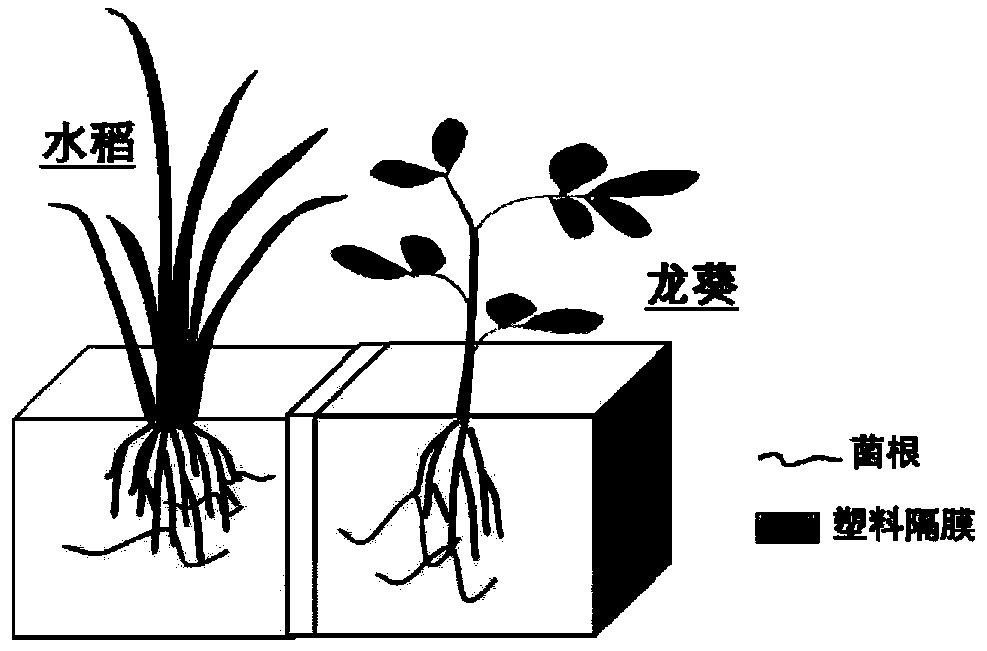
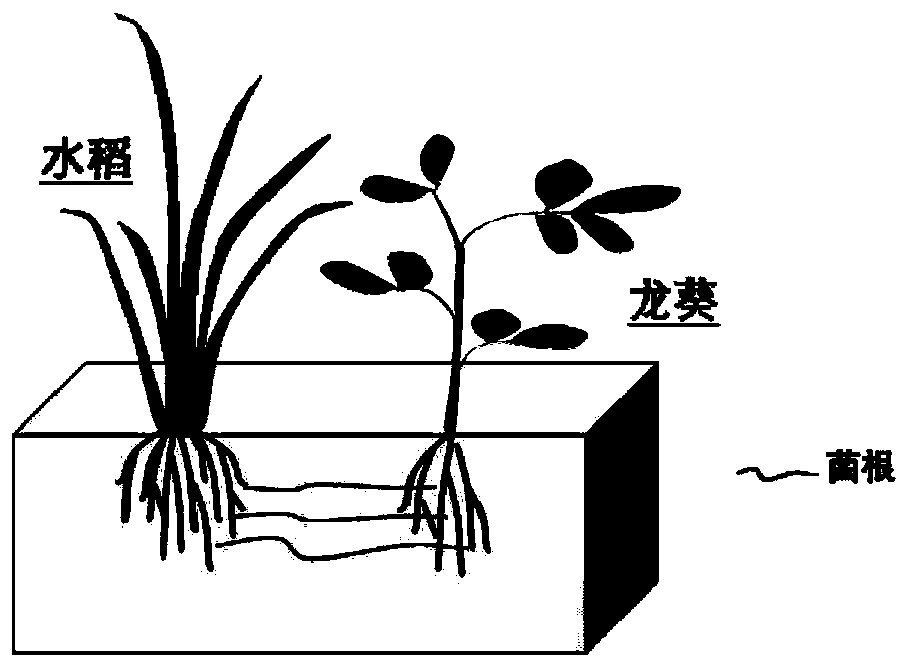
Method for constructing hypha network for transduction of immune signals among plants
ActiveCN113615475AControl contactControl wateringGrowth substratesCulture mediaBiotechnologyPlant roots
The invention discloses a method for constructing a hypha network hypha network for transduction of immune signals among plants. The method comprises the following steps that a corn root system colonized by glomus mosseae is cut into pieces, the corn root system is uniformly mixed with a substrate, the corn root system is cultivated near a cultivated plant root system of potted tobacco for 40 days, and then the corn root system is treated; a donor and a receptor are transplanted into sterilized matrix soil, the donor and the receptor are cultivated together with the cultivated plant with the overground part removed for 40 days, so that the donor plant and the receptor plant establish a hypha network with the cultivated plant along with root growth, and signal exchange is carried out through the hypha network among the root systems of the cultivated plant in the center; and after the donor and the receptor are cultivated for 40 days, methyl jasmonate (MeJA) is sprayed on the donor plant, and a nutrient solution is irrigated once a week in order to prevent root exudates from flowing. According to the invention, the donor plants and the receptor plant are planted in different substrate pots, root contact between the plants is controlled as much as possible, the watering amount of each pot of plants is controlled, and flowing of root exudates is prevented.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biological agent capable of improving soil environment and method for improving soil environment through same
InactiveCN107197635ASolve the problem of continuous croppingRestore activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiologyCulture mediums
The invention discloses a culture method of a biological agent capable of improving the soil environment. The method comprises the following steps that strains of gigasporarosea, gigasporasp, glomus mosseae and glomussp are subjected to treatment respectively, single spore surface sterilization is performed, then, the strains are transferred into a culture dish, and an MES buffer solution and Gel-Gro are added; clover hosts are adopted, a mixture medium with vermiculite and perlite is adopted as a matrix, wherein the volume ratio of vermiculite to perlite is 1:1; the hosts and the medium are transferred to the surface of Gel-Gro medium with germinated spores after growing for two weeks; all the hosts form mycorrhizae with single germination spores respectively; single-cell fungi are obtained; wood bits are packaged into bags made of gauze and put into a bacterium solution with the fungi to be sufficiently soaked; two fungus bags are mixed with one ton of water, the weight of each bag is one kilometer, the fungus bags are placed into a ton bucket and are not dispersed, a circulating pump is used for sufficient convection, the fungus bags are taken out after 6 hours, 50 KG of fermented sheep manure is added, stirring is performed inside the ton bucket with a stirrer, standing is performed after one hour for precipitation, and two thirds of the upper portion is taken out after 24 hours to obtain the finished biological agent.
Owner:徐晨斐
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com