Microbial agent and application for treating cultivating wastes
A microbial agent and animal feces technology, applied in the treatment of biological organic parts, methods based on microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of unstable quality of the agent, high preparation cost, and different requirements for the growth environment of different microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The production of embodiment 1 microbial bacterial agent
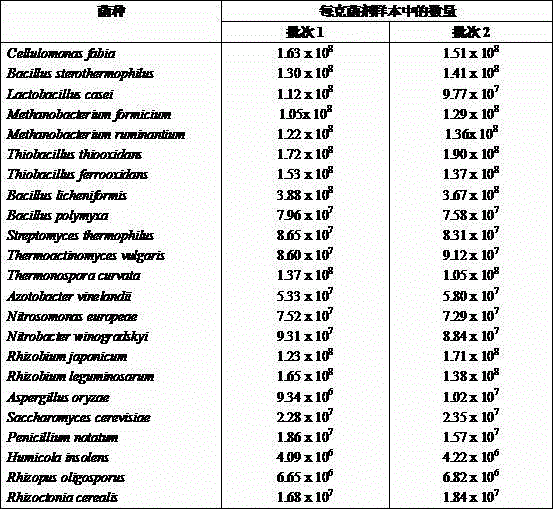
[0054] The present embodiment uses the following strains to prepare microbial inoculum: (1) Cellulomonas faeci ( Cellulomonas fabia ), (2) Bacillus stearothermophilus ( Bacillus sterothermophilus ), (3) Lactobacillus casei ( Lactobacillus casei ), (4) Methanobacter ants ( Methanobacterium formicium ), (5) Methanobacter ruminantum ( Methanobacterium ruminantium ), (6) Thiobacillus thiooxidans ( Thiobacillus thiooxidans ), (7) Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ( Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ), (8) Bacillus licheniformis ( Bacillus licheniformis ), (9) Bacillus polymyxa ( Bacillus polymyxa ), (10) Streptomyces thermophilus ( Streptomyces thermophilus ), (11) common high temperature actinomycetes ( Thermoactinomyces vulgaris ), (12) Thermomonospora curved ( Thermonospora curvata ), (13) brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria ( Azotobacter vinelandii ), (14) Nitrosomonas europeanum ( Nitrosomonas europeae ), (...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Production of Organic Fertilizer
[0058] Take cow dung with a water content of 65% (weight ratio) (if the water content is insufficient, you can add water) and crushed rice bran with particles smaller than 5mm, mix them evenly at a mass ratio of 85:15, and make the mixed cow dung and rice bran There is no agglomeration above 40mm.
[0059] Then, the mixture of 1 ton of above-mentioned cow dung and rice bran is mixed with the microbial inoculant produced in 1kg of Example 1, and heaped into the fermenter to form a compost heap. During the compost heap placement period, along with the fermentation process, the compost heap can naturally heat up. This fermentation heating process usually takes 2-3 days, and the compost heap can be turned 1-2 times during this period. Then, when the temperature of the compost heap rises to 65°C, turn on the turner to turn the compost heap to dissipate the heat generated by fermentation to ensure that the temperature does not e...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 Effect of Organic Fertilizers on Soybeans with Stubble
[0062] This example describes the stubble yield analysis in the continuous soybean planting experiment conducted by the National Soybean Engineering Technology Research Center commissioned by the inventor in 2009 in Acheng District, Harbin City, Heilongjiang Province.
[0063] 1. Test materials and design
[0064] 1.1 Test material
[0065] Bio-organic fertilizer: the organic fertilizer produced by the same method as in Example 2
[0066] Soybean variety: Heinong 48.
[0067] 1.2 Experimental design
[0068] The crop planted in the previous crop is corn, and the soybeans planted in this round are facing soybeans.
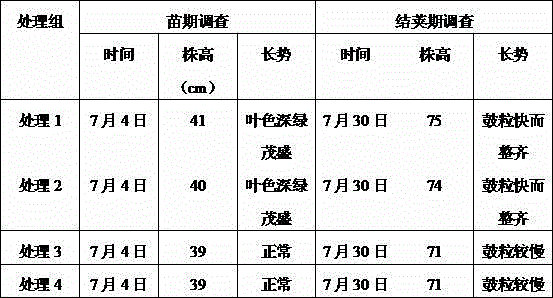
[0069] The experiment consisted of four treatments:
[0070] (1) Treatment 1: Apply 20kg of western compound fertilizer per mu + 50kg of bio-organic fertilizer of the present invention as base fertilizer once.
[0071] (2) Treatment 2: Apply 20kg of western compound fertilizer per mu +...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com