Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
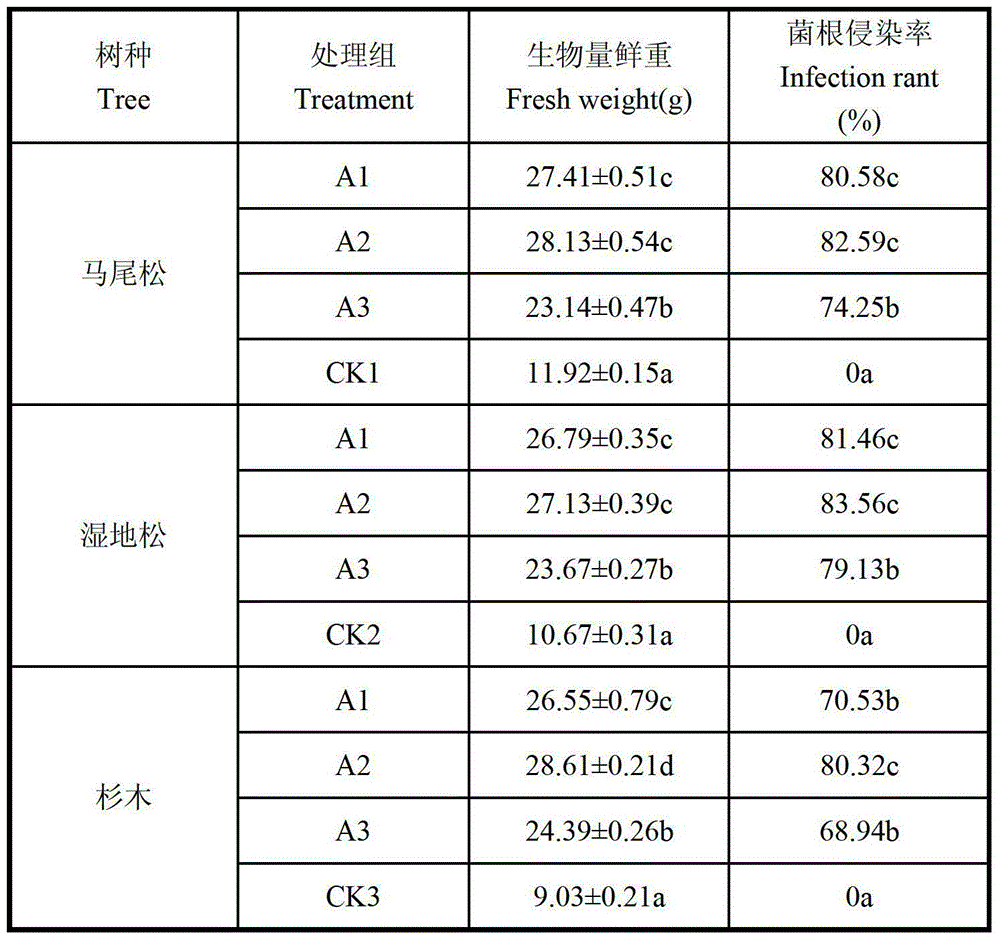
36 results about "Glomus intraradices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glomus intraradices is an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture. In addition, it is one of the best mycorrhizal varieties of fungi available to mycoforestry, but it "has virtually no market value as an edible or medicinal mushroom" Glomus intraradices is also commonly used in scientific studies of the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant and soil improvement. Mycorrhizal Fungi Endomycorrhizal Fungi Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Glomus intraradices Recent molecular analysis of Ribosomal DNA suggests that Glomus intraradices is not in fact in the genus Glomus at all, and should be renamed Rhizophagus intraradices.
Application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation
InactiveCN103125251AImprove qualityImprove mineral nutritionHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
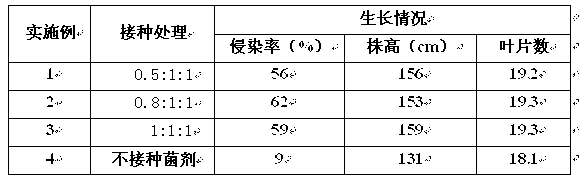
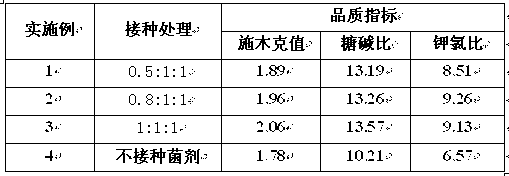
The invention relates to an application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation. A primary arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide is inoculated and propagated separately, and propagule spore density of an arbuscular mycorrhiza of each fungi after the propagation is 30 pieces per gram of dry soil. A float breeding method is adopted to conduct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide combinedinoculation to tobacco, mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are obtained, and the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are directly applied to field production. When being transplanted, the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are conducted with a two-step inoculation, and the mixed fungicide is mixed by propagated acaulospora mellea, glomus mosseae and glomus intraradices at a proportion of 0.5-1: 1:1. A colony formed by the propagation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is close to a natural state, and fungus cooperate and play a better role of growth promoting and quality improving. According to the application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation, by means of the two times of inoculations of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, the proportion of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the tobacco in a symbiotic system built during a seedling stage of the tobacco is guaranteed, and the beneficial effects of the symbiotic system to the development of the tobacco seedlings are ensured. The application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation is simple and practical in method and environment friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil
InactiveCN101947545AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBioremediation
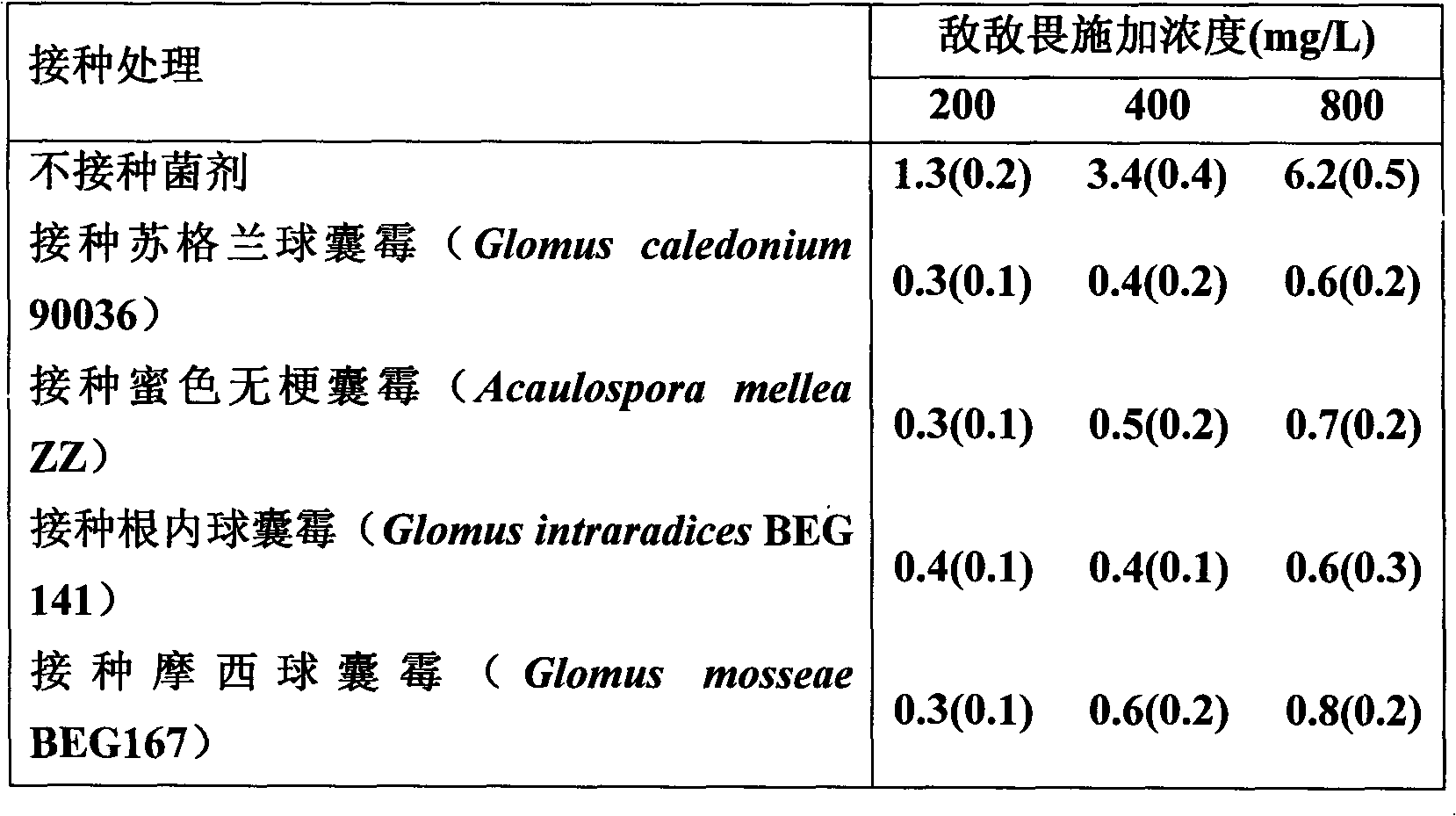
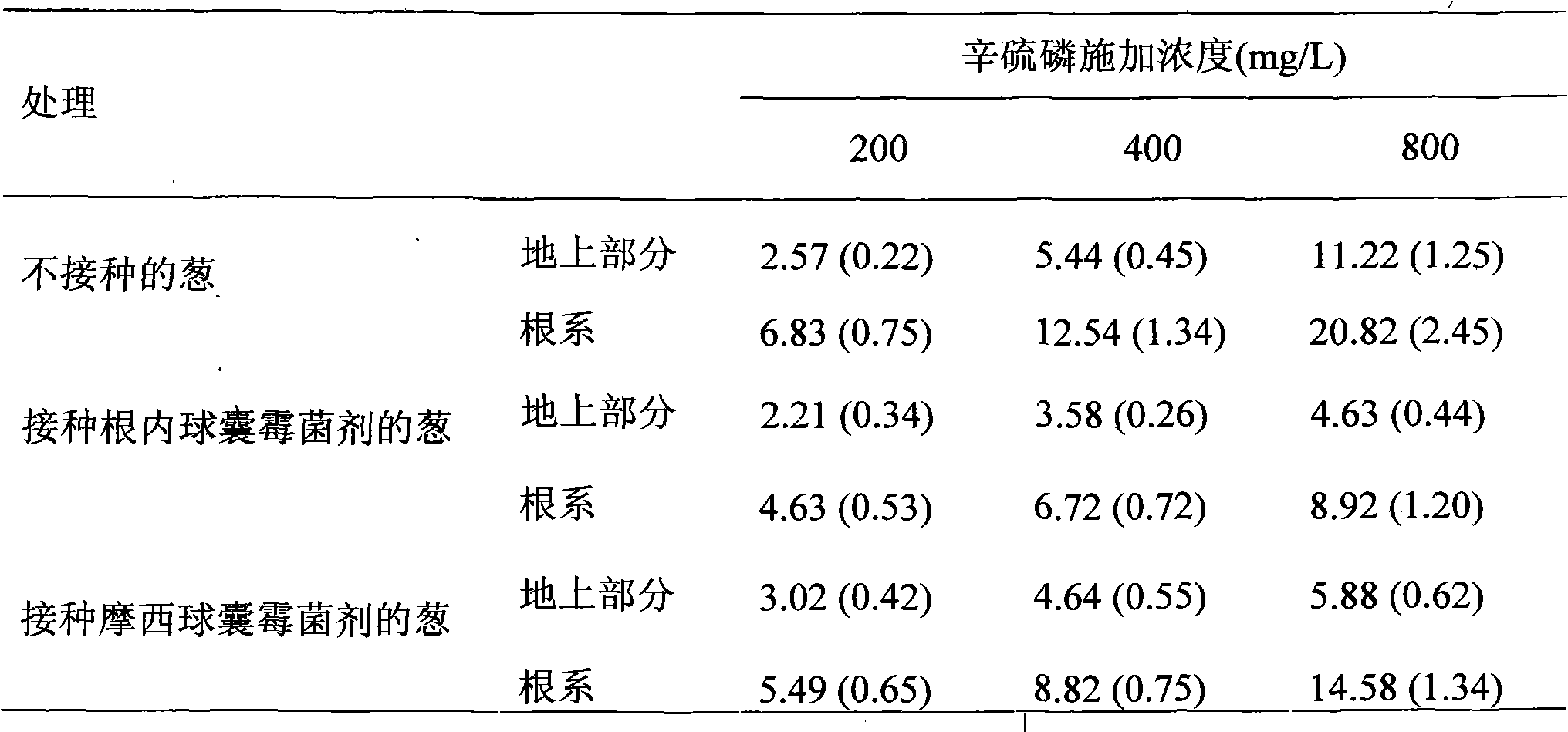
The invention discloses a method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant symbiotic system is used for accelerating the recovery of the organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent; (2) inoculating the fungi agent to the soil to be restored, and planting quick growth plants, or transplanting the plants after mycorrhizal seedling culture; and (3) managing the plants to grow 2 to 3 months. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent comprises Glomus caledonium 90036, Acaulospora mellea ZZ, Glomus mosseae BEG167 and Glomus intraradices BEG 141). The host plant is selected from quick growth plants such as Sudan grass, alfalfa, corn, broomcorn and the like. The method can reduce the pesticide residue in agricultural products, reduce environment transfer to water, atmosphere and the like and reduce harm to human health, and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for reducing vegetable phoxim residue by utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices
InactiveCN102057826AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthFungiHorticultureGlomus intraradicesGourd
The invention relates to a method for reducing vegetable phoxim residue by utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices. Arbuscular mycorrhiza homobium is formed by mainly utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices and a vegetable crop to reduce phoxim residue in a vegetable. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of: propagating the glomus mosseae or the glomus intraradices; using a glomus mosseae microbial inoculum or a glomus intraradices microbial inoculum on vegetables; and applying phoxim and managing the vegetable until the growth period of the vegetable crop is finished. The method of the invention is suitable for vegetable crops easy to form arbuscular mycorrhiza of a potato family, a lily family, a gourd family, a bean family, and the like. The method of the invention can reduce phoxim residue in soil and vegetables, prevent pesticide from being transferred to environments of water bodies, atmosphere, and the like and lessen harm to the health of human bodies and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore
ActiveCN101565689ALow costLow nutritional requirements for growthMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologyMicrobial culture technique
The invention discloses a production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism culturing, and comprises the following technical steps of: 1) culturing carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA; 2) culturing the carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA and glomus intraradices together in an improved synthetic culture medium; 3) taking a culture containing the root, hypha and spore infected by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and transplanting the culture to a special culture box for culturing; 4) collecting the spore and mycelium; and 5) storing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore. Compared with the prior art, the production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore has the advantages that: 1, the culture medium is an asepsis environment with low cost, which not only can meet the growing of a host plant, but also is suitable for the growing of AM epiphyte; 2, the nutrition requirements for the growing of the host plant are low and the host plant can grow and be cultured on the synthetic culture medium; 3, the spore cultured by the method is a non-pollution pure culture; and 4, the produced spore is stored in liquids and the activity can be maintained by above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
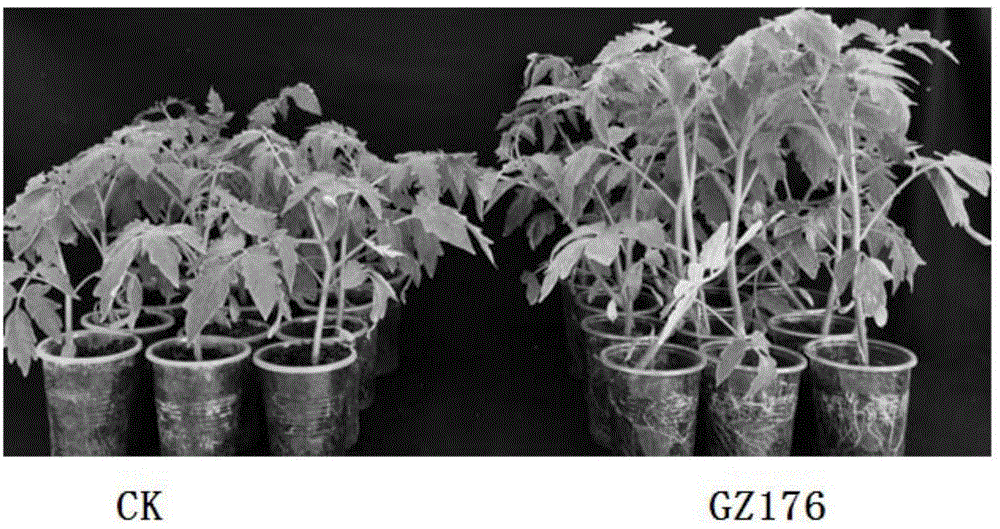
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 for disease prevention, growth promotion and adverse resistance of herbaceous plants and microbial inoculums and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176
The invention discloses arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 for disease prevention, growth promotion and adverse resistance of herbaceous plants and microbial inoculums and application of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 is rhizophagus intraradices and can be made into powder with concentration being 40-60 spores per gram, herbaceous plant disease prevention rate is up to 71.3% after the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 powder is subjected to seed dressing under normal management conditions of greenhouses, and herbaceous plant growth promotion rate is higher than 16.19%; in the field, disease prevention and control rate reaches 75.27%, and yield increasing rate exceeds 36.17%; adverse resistance of the herbaceous plants can be improved remarkably.
Owner:南京本源生态农业科技有限公司
Complex bacterium preparation for fixing nitrogen, solubilizing phosphorus and potassium and rooting and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a complex bacterium preparation for fixing nitrogen, solubilizing phosphorus and potassium and rooting and a preparation method thereof. The preparation is mainly prepared by mixing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-20 parts of azotobacter vinelandii, 10-30 parts of bacillus megatherium, 10-30 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, 5-15 parts of azotobacter chroococcum, 10-15 parts of glomus intraradices and 10-25 parts of glomus mosseae. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out high-density culture on each strain; grafting to a shake flask filled with a culture medium in a volume ratio of 15-30 percent for activated culture; grafting the cultured strains into a fermentation tank for fermentation culture expansion; dehydrating and drying the culture expanded single strains to prepare hypopus microorganism dried powder; and mixing to obtain the complex bacterium preparation for fixing nitrogen, solubilizing phosphorus and potassium and rooting. The complex bacterium preparation is used for industrial crops, fruit trees, food crops and the like, has the advantages of biological property, environmental friendliness, high yield and high quality in comparison with existing products, and cannot pollute soil.
Owner:SHANDONG SUKAHAN BIO TECH
Pine or fir artificial forest stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, and preparation and application methods thereof
InactiveCN103329941AImprove survival rateIncrease growth ratePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyLactarius alnicola
The invention discloses a stress-tolerant growth-promoting composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant for a pine or fir artificial forest, and a preparation and application methods thereof. The composite mycorrhizal fungi inoculant is compounded from an endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant and an exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant, wherein the endomycorrhizal fungi inoculant is obtained by culturing Glomus mosseae or Glomus intraradices in pots in a greenhouse; and the exotrophic mycorrhiza fungi inoculant is obtained by fermenting Lactarius hatsudake Tanaka and Scleroderma polyrhizum Pers. in a liquid fermentation medium. In the forestation process, the seedling root system is subjected to slurry dipping treatment or embedded in pine or fir forest soil, thereby promoting rootage and growth of pines or cedars, improving the tree vigor, enhancing the stress tolerance, increasing the absorptivity of P, and preventing the pine leaf cast, fir anthracnose, pine seedling blight and cataplexis.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Medium prescription for production of fungus-treated tobacco rooted seedlings by floating nursery
InactiveCN101297632AWide variety of sourcesE-buyCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationBiotechnologySnow mold
The invention relates to a special matrix formula suitable for culturing mycorrhizal tobacco seedling in the condition of flue-cured tobacco seedling by floating system; all the constituents and the volume thereof are as follows: 60 percent of peat, 20 percent of perlite and 20 percent of vermiculite. The formula can improve the comprehensive quality of the tobacco seedling, cultures sound seedlings and has the advantages of wide material sources, easy acquisition, easy matrix preparation, simple production, simple inoculating operation, little fungicide dosage and easy promotion, etc. The culture medium, the inoculating technique and the corresponding Glomus intraradices Smith and Schenck are combined together, infection rate of mycorrhiza is up to over 40 percent and the effect of the mycorrhiza is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
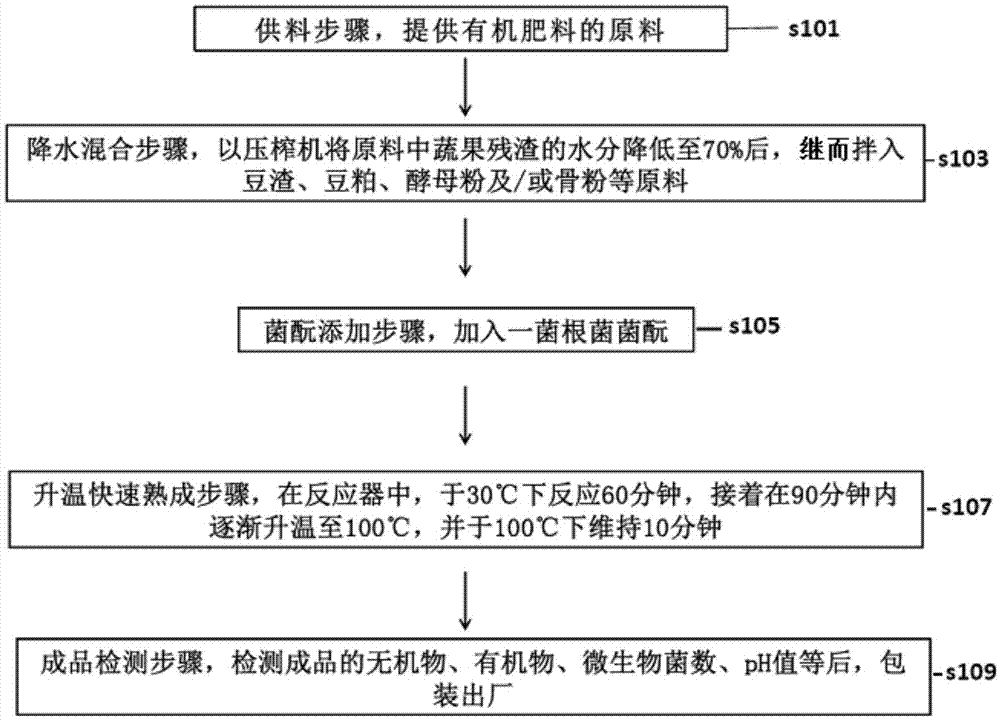
An organic fertilizer increasing trace element contents of crops and a preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107043282AManganese increaseBioloigcal waste fertilisersHorticultureAcaulospora morrowiaeWater content
The invention relates to an organic fertilizer increasing trace element contents of crops. The fertilizer includes fruit and vegetable dregs the water content of which is less than 70%, bean dregs, bean meal and a mycorrhizal fungi. The mycorrhizal fungi is one or more selected from a group consisting of glomus mosseae, glomus etunicatum, glomus intraradices, glomus claroideum, glomus spurcum, entrophospora kentinensis, acaulospora morrowiae and scutelospora nigra. The organic fertilizer can be applied for leaf vegetable type, fruit type, cereal type, and tuber type crops, and can obviously increase growth and weights of the crops.
Owner:BIOZYME BIOBTECH CORP
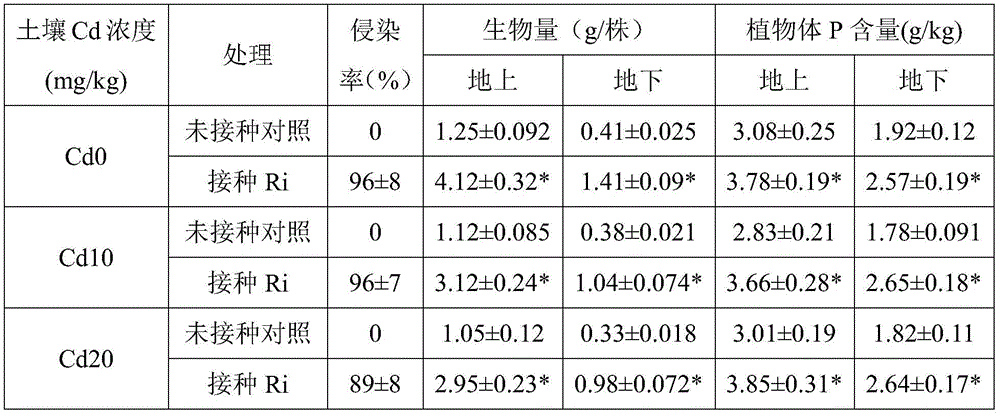
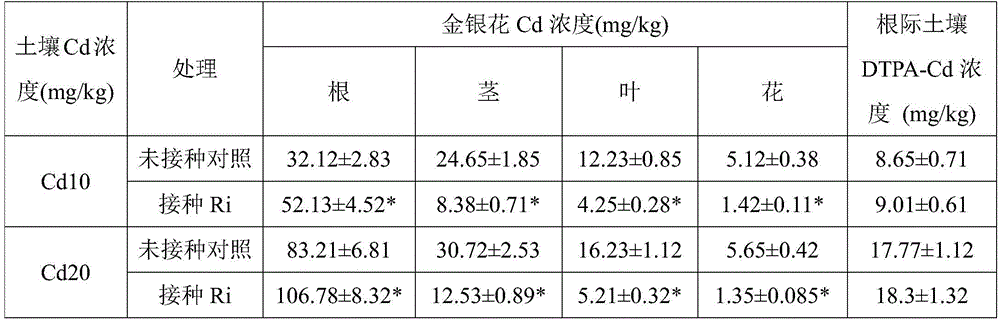
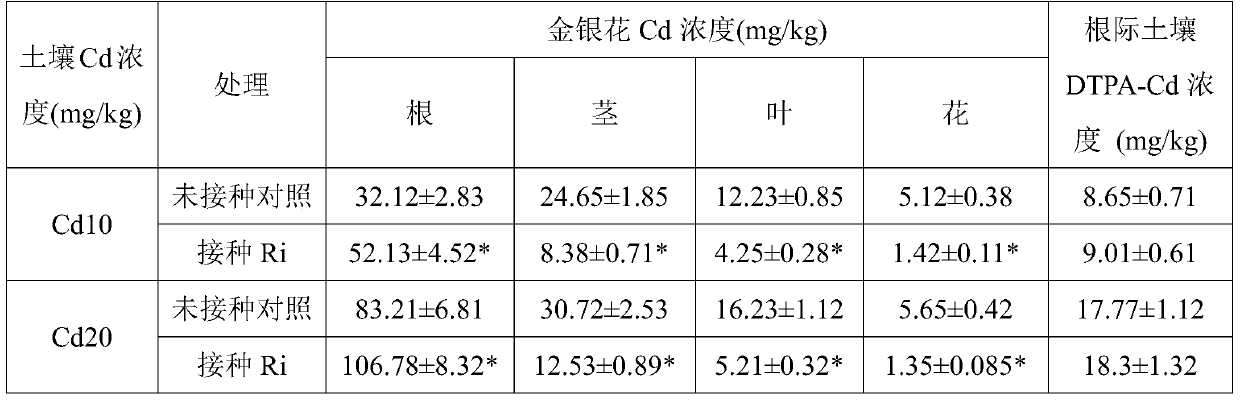
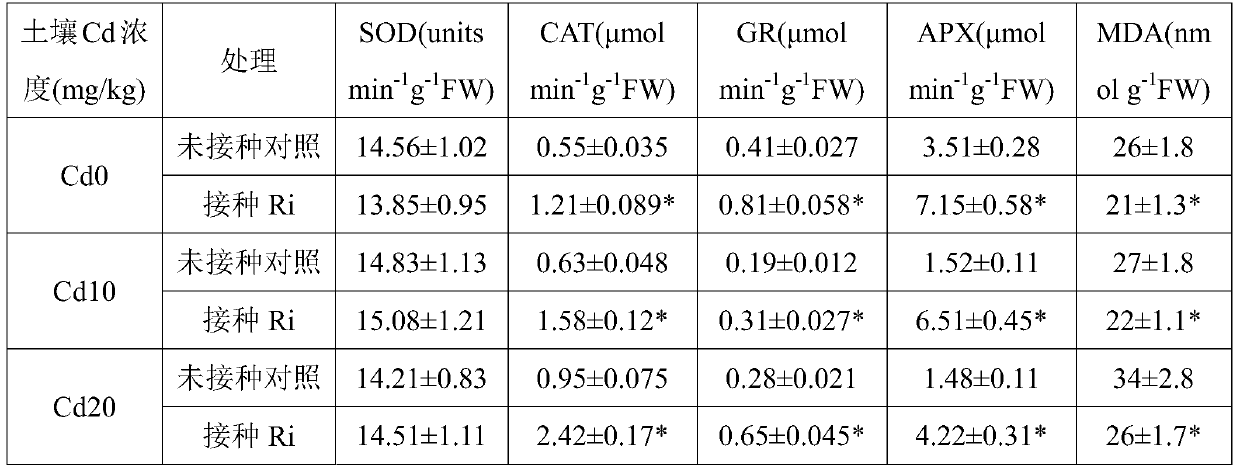
Method for reducing honeysuckle cadmium accumulation and increasing yield of honeysuckle by means of glomus intraradices
InactiveCN105660098AImprove mineral nutritionImprove P nutritionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsGlomus intraradicesSpore
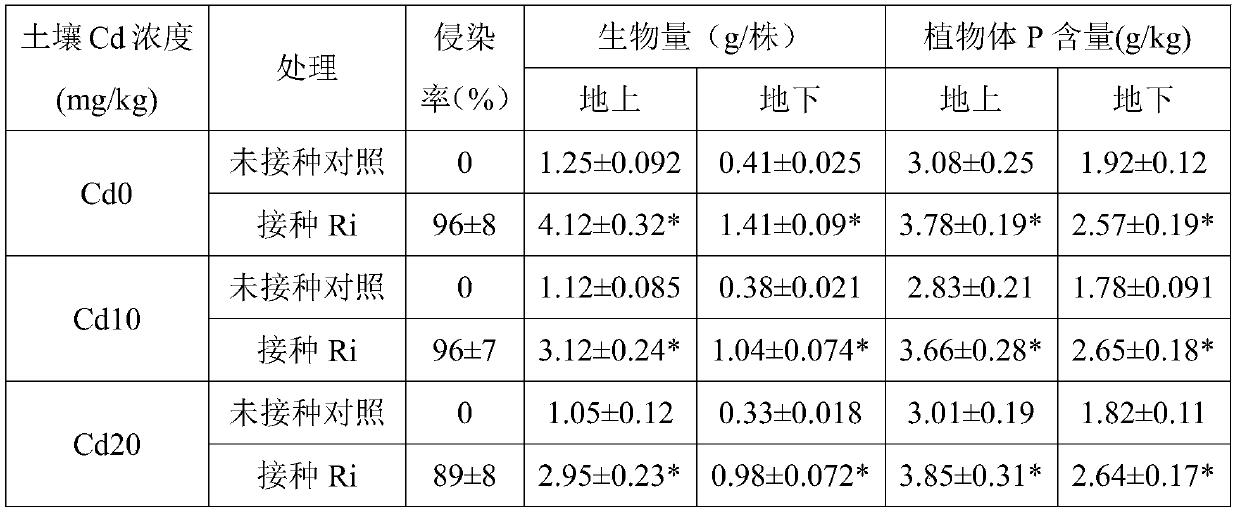
The invention discloses a method for reducing honeysuckle cadmium accumulation and increasing the yield of honeysuckle by means of glomus intraradices. According to the method, glomus intraradices and honeysuckle are used for symbiotic cultivation. Specifically, after glomus intraradices is subjected to propagation cultivation by means of a host plant, a mixture containing host plant root sections, fungus hyphae, mycorrhiza fungal spores and cultivation soil is harvested, namely a glomus intraradices inoculant; then, the glomus intraradices inoculant is inoculated in a culture substrate for honeysuckle cultivation. The method can promote growth of honeysuckle and increase the yield. More importantly, cadmium can be prevented from transferring from the root to the overground portions, and the concentration of cadmium of the overground portions (stems, leaves and flowers) is reduced. A means is provided for safe honeysuckle production in soil polluted by cadmium, and the method plays an important role in honeysuckle production and application. The method is good in effect, free of secondary pollution and low in cost. A new thinking and a new direction are provided for development and utilization of glomus intraradices.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing AMF (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus) capsule fungicide
InactiveCN103814754AProlonged infection timeInfection time increasedHorticultureInfection rateGlycerol
The invention provides a method for preparing AMF (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus) capsule fungicide. The method is characterized in that sodium alga acid is used as a basic carrier, a mixture is obtained by matching and mixing multiple fillers such as chitosan, gelatin, glycerol, rice, peat, coal cinder and malt sprout in the basic carrier, a fungicide mixture can be obtained by embedding the fungicide in the mixture after the mixture is sterilized, a spherical object can be prepared by dripping the fungicide mixture into calcium chloride solution in a physical extrusion way, and the AMF capsule fungicide can be obtained after the spherical object is solidified and cleaned. According to the method disclosed by the invention, spores, mycorrhiza and hypha of inner glomus intraradices fungus are embedded in the sodium alga acid, a complete infection process can be completed when the spores, the mycorrhiza and the hypha are seeded in unpasteurized soil, and the infection rate can be increased with the prolonging of the infection time. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simpleness, low cost and low toxicity; an embedding material of the AMF capsule fungicide prepared by the invention can be easily decomposed by microorganism, the preservation time is longer, and the AMF capsule fungicide can be simultaneously and directly seeded in a big field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Novel method for efficiently planting cold-season type grasses in early spring
InactiveCN102939831AReduce the amount of applicationGrow fastAgriculture gas emission reductionHorticultureCold seasonPropagule
The invention discloses a novel method for efficiently planting cold-season type grasses in early spring and relates to a method for improving the planting capability of the cold-season type grasses. According to the method, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi complex microbial inoculant is applied to soil, wherein the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi complex microbial inoculant is formed by compounding glomus mosseae inoculant with glomus intraradices in the mass ratio of 1:1; the glomus mosseae inoculant and the glomus intraradices are respectively inoculant-soil mixtures obtained by micropropagation of pure spores; the inoculant-soil mixtures contain strain spores and hyphae propagules; and the quantity of the strain spores is 8-13 / g. Due to the use of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi complex microbial inoculant, a mycorrhiza-cold-season type grass mutual-benefit symbiont with high infection rate can be established between the cold-season type grasses and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and can promote the cold-season type grasses to grow more quickly and better and form more-developed root systems at the low-temperature stage in spring and the cold hardiness and physiological functions of the old-season type grasses can be remarkably improved, and thus non-point source pollution substances such as nitrogen and phosphor in the direct surface runoff in early spring are intercepted to the maximum extent and the pollution to receiving rivers is reduced.
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
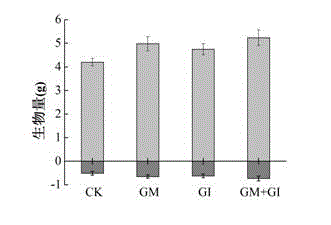
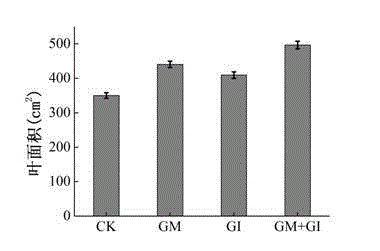
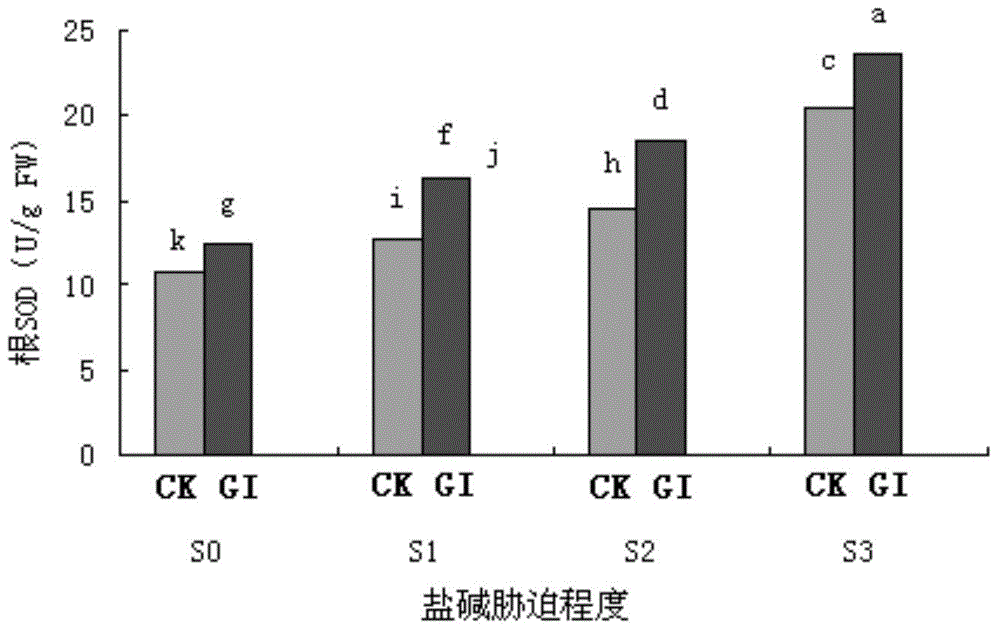
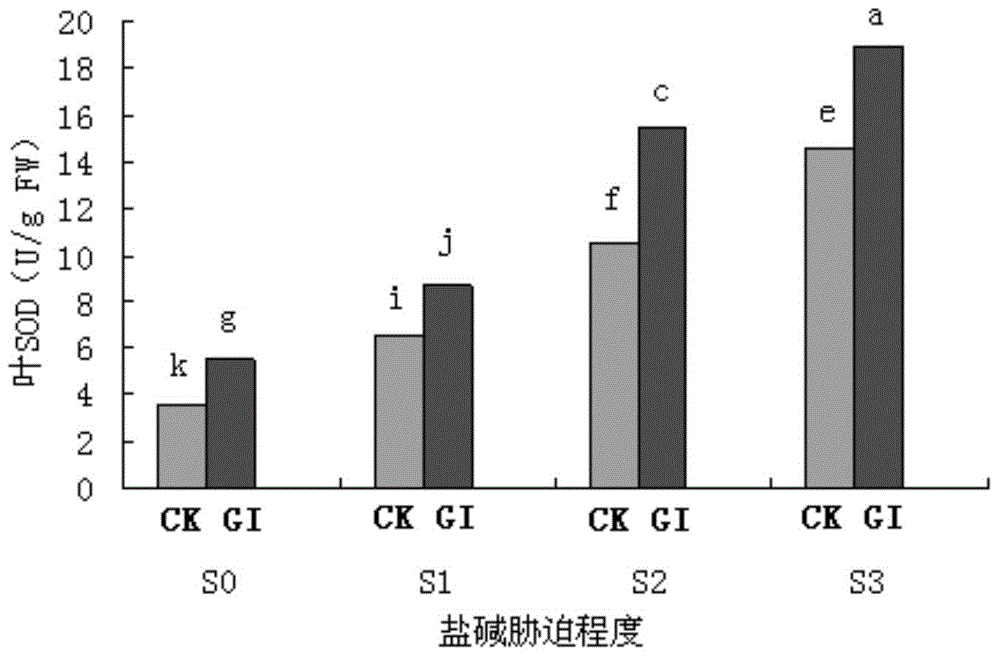
Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus capable of improving saline-alkali tolerance of Elaeagnus angustifolia
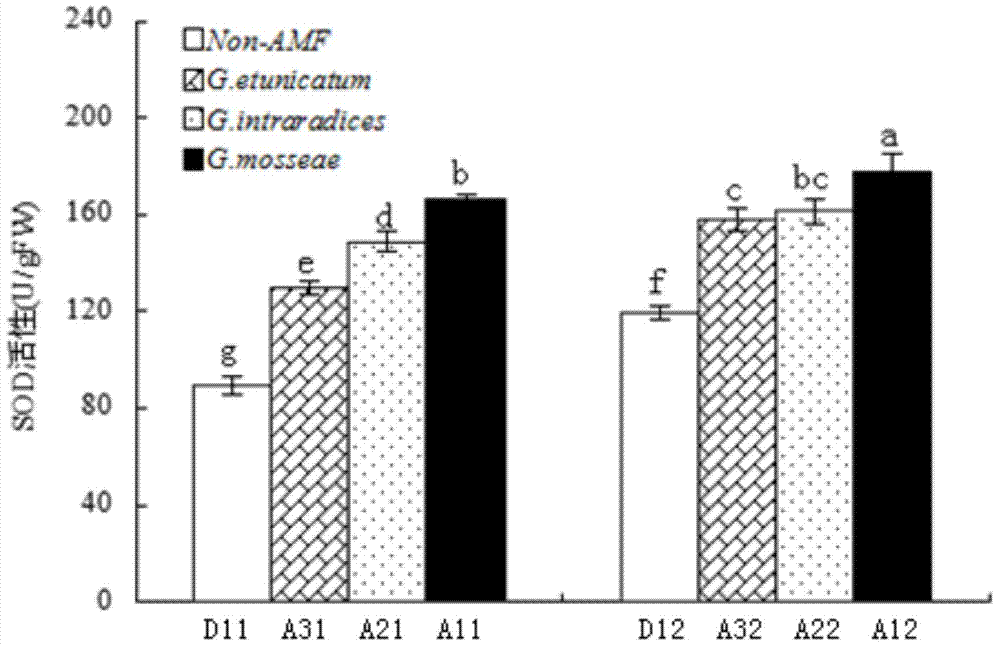
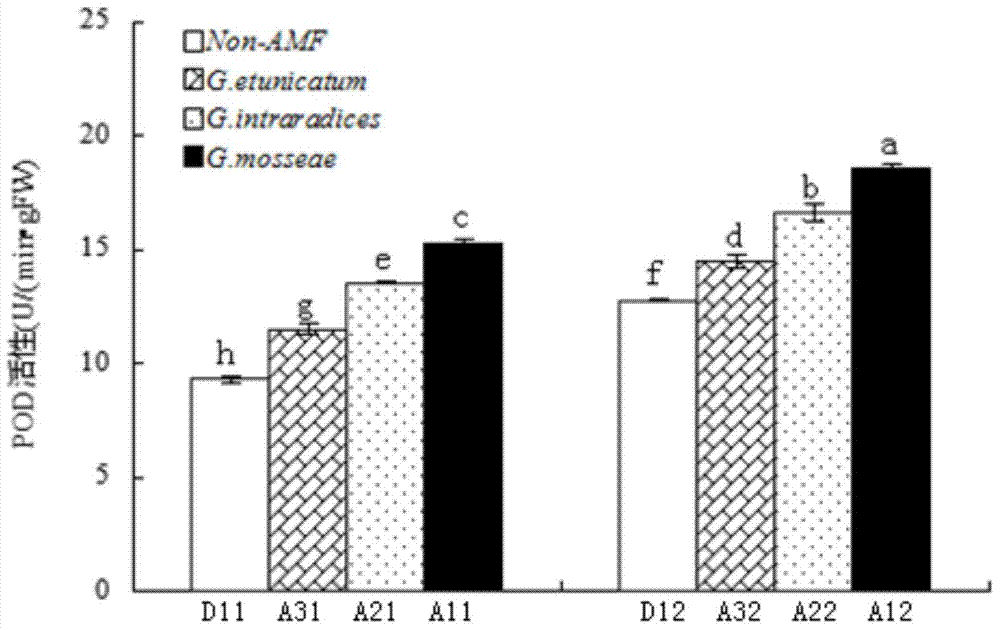
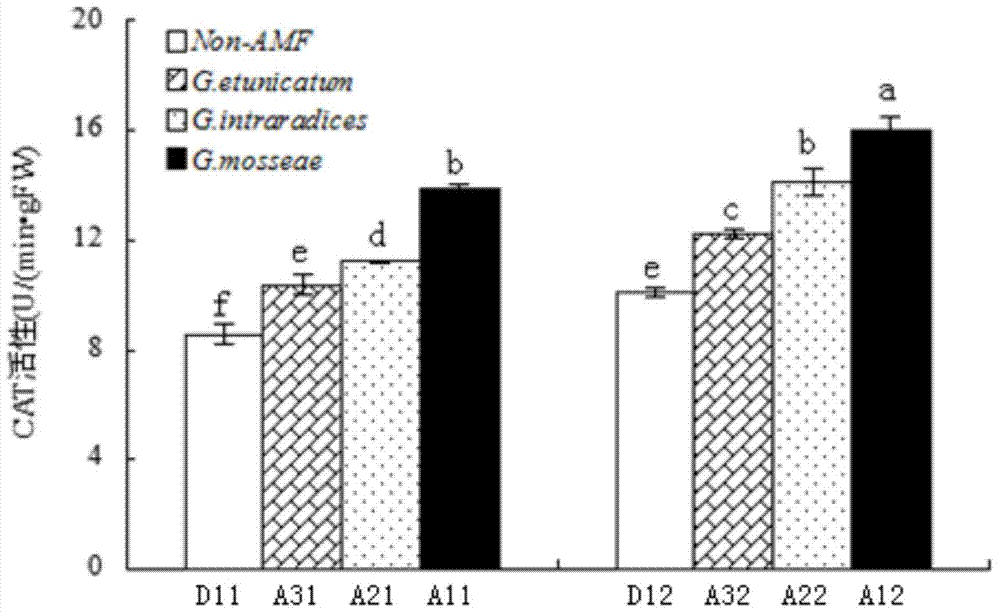
The invention provides an Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus capable of improving saline-alkali tolerance of Elaeagnus angustifolia and relates to an Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus. The Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus provided by the invention has a higher capacity of tolerating saline-alkali stress and provides a theoretical basis for remediation of saline-alkali soil by jointly using mycorrhiza and plants. The Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus capable of improving saline-alkali tolerance of Elaeagnus angustifolia provided by the invention is Glomus intraradices HDSF5 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the date of preservation is March 11, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.10607. By inoculating Glomus intraradices HDSF5, the growth of Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings under saline-alkali stress is obviously promoted, and the content of chlorophyll, photosynthetic physiological characteristic and the activity of SOD, CAT and POD in leaf and root tissues are improved. The Glomus intraradices HDSF5 provided by the invention can tolerate the saline-alkali inhibiting effect and can promote the growth of the Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Embedding for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent and preparation of capsule fungi agent
The invention discloses an embedding method of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a preparation method of a capsule fungus. The invention uses sodium alginate as a basic carrier to spore, mycorrhizal and hyphae of the fungus Glomus intraroote Embedded in gel particles, the complete infection process can be completed when sown in non-sterilized soil, and the infection rate has a certain increase with the extension of the infection time. Chitosan, gelatin, glycerin, rice, peat, coal cinder, and malt root added different nutrients, so that the infection rate of the bacterial agent was different, and the infection rate of rice was the highest, reaching 42.9% after 25 days.
Owner:TONGLING DONGSHENG ECOLOGICAL AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore
ActiveCN101565689BLow costLow nutritional requirements for growthMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologyMicrobial culture technique
The invention discloses a production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism culturing, and comprises the following technical steps of: 1) culturing carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA; 2) culturing the carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA and glomus intraradices together in an improved synthetic culture medium; 3) taking a culture containing the root, hypha and spore infected by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and transplanting the culture toa special culture box for culturing; 4) collecting the spore and mycelium; and 5) storing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore. Compared with the prior art, the production method for high-densitypure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore has the advantages that: 1, the culture medium is an asepsis environment with low cost, which not only can meet the growing of a host plant, but also is suitable for the growing of AM epiphyte; 2, the nutrition requirements for the growing of the host plant are low and the host plant can grow and be cultured on the synthetic culture medium; 3, the spore cultured by the method is a non-pollution pure culture; and 4, the produced spore is stored in liquids and the activity can be maintained by above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Repairing material, repairing method and application of ionic rare earth tailing area
InactiveCN112705567AVegetation ecological restoration effect is goodStrong stress resistanceContaminated soil reclamationGlomus intraradicesVegetation
The invention provides a repairing material, a repairing method and application of an ionic rare earth tailing area, and belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration. The invention provides a repairing material for an ionic rare earth tailing area. The repairing material comprises arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pioneer plants, wherein the types of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi comprise one or more of glomus intraradices, glomus mosseae and Paraglomus occultum. The types of the pioneer plants comprise one or more of paspalum, ramie and awn. The repairing material provided by the invention has the characteristics of high plant restoration success rate, excellent effect, capability of obviously reducing the water and soil loss rate and the like when being applied to restoration of the ionic rare earth tailing area, and has a good vegetation ecological restoration effect on the ionic rare earth waste mining area in the rainy region in the south; the invention is suitable for rapid treatment of rare earth tailing waste land in southern rainy regions.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF ECO-ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & PLANNING
Method for promoting sprouting of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi spore and growth of hypha
InactiveCN103981100APromote germinationPromote growthFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlomus intraradices
The invention discloses a method for promoting sprouting of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi spore and growth of hypha. The method comprises the steps: screening arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi spores, sterilizing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi spores, sucking the sterilized spores by utilizing a sterile gun head under the microscope, transferring the spores onto a culture medium in a culture dish, inoculating 50 spores in each culture dish, culturing in a dark box, and culturing the spores for 20 days under the condition of 26 DEG C. The method has beneficial effects that the glomus intraradices spore sprouting and hypha growth are promoted by adopting 50ml / L root secreted liquid of RiT-DNA transgenic carrot root, glucose and an appropriate nitrogen source. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, use of cheap materials and environmental friendliness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Field fast production method of lawn grass strengthening biological fertilizers
The invention provides a field fast production method of lawn grass strengthening biological fertilizers and relates to the field fast production method of the lawn grass strengthening biological fertilizers. The field fast production method aims at solving the problems that the preparation method of the existing lawn grass strengthening biological fertilizers is complicated, the time consumption is long, the cost is high, the yield is low, and the wide application and popularization is difficult. The method comprises the following steps that matrixes and flowerpots are sterilized; white clover glass seeds are sprouted; Glomus mosseae and Glomus intraradices are inoculated into the matrixes, and the white clover glass seeds are spread; after white clover leaves are grown, the watering is carried out, the culture is carried out for 20 to 30 days, water is not added until the leaves are withered, soil and roots are recovered, and composite microbial inoculums are obtained; formalin is adopted to sterilize field soil, the composite microbial inoculums and the white clover glass seeds are mixed, and the sowing is carried out; and after the white clover glass grows for 20 to 30 days, the water is not added until the glass is withered, the soil and the roots are recovered, the natural air drying is carried out, the soil and the roots are stored in ventilating drying places, and the lawn grass strengthening biological fertilizers are obtained. The field fast production method has the advantages that the method is simple, the speed is high, the cost is low, and the operation is easy. The field fast production method is used in the field of biological fertilizers.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Drought-resistant blueberry and cultivation method thereof
InactiveCN104823739AImprove drought resistanceStrong drought resistanceHorticulture methodsGlomus intraradicesBlueberry Plants
The invention discloses a drought-resistant blueberry and a cultivation method thereof. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: a, inoculating to-be-inoculated blueberry plants with fungi; and b, subjecting inoculated blueberry plants to drought stress treatment, wherein the fungi are one or more selected from the group consisting of Glomus mosseae, Glomus versiforme, Glomus intraradices and Glomus etunicatum. The blueberry cultivated by using the method provided by the invention has excellent drought resistance.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of compound microbial fertilizer for peony root drenching
ActiveCN106116883AImprove self-resiliencePromote vegetative growthAnimal corpse fertilisersExcrement fertilisersBacillus megateriumNutrition
The invention relates to a preparation method of a compound microbial fertilizer for peony root drenching. The method includes steps: adopting candida tropicalis for fermenting sweet potato residues and fruit wastes to obtain a fermented product I; mixing chicken manure, cow dung, biogas digester residues and wheat straws to realize natural fermentation to obtain a fermented product II; proportionally mixing the fermented product I and the fermented product II, performing inoculation of geotrichum candidum, bacillus megaterium and bacillus mucilaginosus, and fermenting to obtain a fermented product III; adding appropriate amount of a mixture containing mycorrhizal fungi spores of glomus intraradices and glomus mosseae, root internal and external hyphae and infected plant root segments, fish meal, zinc sulfate and bacillus subtilis HS5B5 bacterial liquid, and well mixing to obtain the compound microbial fertilizer for peony root drenching. According to peony growth nutritional and environmental demands, agricultural by-products are used as raw materials, and the prepared compound microbial fertilizer is capable of protecting peony roots and inhibiting pathogenic microorganisms and provides comprehensive nutrition for peony growth to promote growth and prolong flowering phase.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil
InactiveCN101947545BImprove nutritional statusPromote growthContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBioremediation
The invention discloses a method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant symbiotic system is used for accelerating the recovery of the organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) propagating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent with strains respectively of Glomus caledonium 90036, Acaulospora mellea ZZ, Glomus mosseae BEG167, Glomus intraradices BEG 141; (2) applying the propagated fungi agent to the soil to berestored, and planting sudan grass or alfalfa grass, or quick growth plants, or corn, or broomcorn, or transplanting the plants after mycorrhizal seedling culture; and (3) managing the plants to grow 2 to 3 months. The host plant is selected from quick growth plants such as Sudan grass, alfalfa, corn, broomcorn and the like. The method can reduce the pesticide residue in agricultural products, reduce environment transfer to water, atmosphere and the like and reduce harm to human health, and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cold-resistant blueberry plants and cultivation method thereof
ActiveCN104737843AImprove cold resistanceReduce contentHorticulture methodsGlomus intraradicesBlueberry Plants
The invention discloses cold-resistant blueberry plants and a cultivation method thereof. The roots of the cold-resistant blueberry plants are infected with fungi, wherein the fungi are selected from one or more of Glomus mosseae, Glomus intraradices and Glomus etunicatum. Because the blueberry plants to be cultivated are inoculated with the Glomus mosseae or the Glomus intraradices or the Glomus etunicatum, the cold resistance of the blueberry plants to be cultivated is improved; even if the blueberry plants are attacked by low temperature in the cultivation process, the content of hazardous substances in plant bodies can be kept low by generating beneficial substances, and then the good cold resistance of the blueberry plants is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method for preventing and treating shallow water system eutrophic lake by virtue of aquatic plants
The invention provides a method for preventing and treating a shallow water system eutrophic lake by virtue of aquatic plants. The method comprises the following steps: (1) with an emergent aquatic plant as a host, inoculating glomus intraradices to a pot culture matrix, and carrying out culturing at 25-30 DEG C for 5-10 days, wherein the mass ratio of zeolite to medical stone to acid-modified argil in the pot culture matrix is 1 to 3 to (0.1-0.3); (2) adding seeds of the emergent aquatic plant into water in a volume ratio of 1 to 2, soaking for 12-24 hours, uniformly scattering the seeds to aculture bed, carrying out culturing at 28-35 DEG C for rooting, covering the culturing bed with a layer of water-immersed silk screen cloth, and transplanting after roots grow to the lengths of 3cm-5cm; (3) fetching adlittoral mud of the eutrophic lake as a soil medium, mixing the adlittoral mud with the pot culture matrix in a mass ratio of (2.5-3) to (1-1.2), carrying out constant-temperature fermentation at 25 DEG C for 24-48 hours, and after the fermentation is finished, transplanting buds of the emergent aquatic plant in the step (2) to the upper part of the mixture; and (4) carrying outculturing by virtue of the culturing bed at 28-35 DEG C for 10-15 days, and externally conveying pots to a shallow water site or an artificial floating island so as to restore an eutrophic water bodyof the shallow water lake when the plant heights are over 8cm, and the infection rates of glomus intraradices at plant roots reach over 95% and the ion concentration of Fe is 4.2mg / L-6.4mg / L throughdetermination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PUTIAN LANDSCAPE & ARCHITECTURE DEV
A method of reducing the accumulation of cadmium in honeysuckle and increasing its yield by using Glomus intrarhizoi
InactiveCN105660098BImprove mineral nutritionImprove P nutritionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsSporeGlomus intraradices
The invention discloses a method for reducing honeysuckle cadmium accumulation and increasing the yield of honeysuckle by means of glomus intraradices. According to the method, glomus intraradices and honeysuckle are used for symbiotic cultivation. Specifically, after glomus intraradices is subjected to propagation cultivation by means of a host plant, a mixture containing host plant root sections, fungus hyphae, mycorrhiza fungal spores and cultivation soil is harvested, namely a glomus intraradices inoculant; then, the glomus intraradices inoculant is inoculated in a culture substrate for honeysuckle cultivation. The method can promote growth of honeysuckle and increase the yield. More importantly, cadmium can be prevented from transferring from the root to the overground portions, and the concentration of cadmium of the overground portions (stems, leaves and flowers) is reduced. A means is provided for safe honeysuckle production in soil polluted by cadmium, and the method plays an important role in honeysuckle production and application. The method is good in effect, free of secondary pollution and low in cost. A new thinking and a new direction are provided for development and utilization of glomus intraradices.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Rice seed seedling raising method based on combination of glomus intraradices and agrobacterium rhizogenes
PendingCN113207587APromote growth and developmentReduce manufacturing costSeed coating/dressingRice cultivationBiotechnologyGlomus intraradices
The invention discloses a rice seed seedling raising method based on combination of glomus intraradices and agrobacterium rhizogenes, relates to a rice seed seedling raising method, and solves the problems that the effect of existing biological fertilizer is only limited to the rice non-flooding period, and the application effect is poor. The method comprises the following steps: accelerating germination of rice seeds, soaking the rice seeds in an agrobacterium rhizogenes agent, filtering, uniformly mixing the rice seeds with the glomus intraradices agent and a rice seedling substrate, and carrying out sowing. According to the seedling raising method, hairy roots generated by agrobacterium rhizogenes induced rice and rice protogenetic root systems can be infected, bacterium and root symbionts can be formed, vitality can be continuously kept after the rice is transplanted to a paddy field, nutrient substances are continuously provided for the rice, growth and development of the rice are promoted, the yield is increased, the blast resistance is enhanced, the application amount of pesticides and chemical fertilizers in the paddy field is reduced, and the ecological agriculture is further developed while the rice production cost is reduced.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Method for reducing vegetable phoxim residue by utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices
InactiveCN102057826BImprove nutritional statusPromote growthFungiHorticultureGlomus intraradicesGourd
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Active coke-based saline-alkali soil improver and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112876320AImprove fertilityImprove macroporous microporous structureSuperphosphatesExcrement fertilisersAlkali soilGlomus versiforme
The invention belongs to the field of soil improvement, and particularly relates to an active coke-based saline-alkali soil improver and a preparation method thereof. The improver is composed of a porous biological fertilizer and a strain inoculant which are independently packaged, wherein the porous biological fertilizer is obtained by mixing, aging and fermenting an active coke mixture, vinegar residues and chicken manure according to the weight ratio of 1: (0.2-5): (0.2-1); the active coke mixture is obtained by fully mixing active coke screen underflow subjected to homogenization pretreatment and acidification impurity removal with a calcium superphosphate saturated solution and a silicon fertilizer according to the solid weight ratio of 1: (0.5-5): (0.2-1) by utilizing alternating-frequency magnetic coupling ultrasonic grading mechanical stirring; and the strain fungicide is composed of mycorrhizal fungi and a water-retaining agent according to the weight ratio of (0.1-1): (1-5), the mycorrhizal fungi are obtained by compounding glomus mosseae, glomus intraradices and glomus versiforme according to the weight ratio of 1: (0.2-2): (0.5-5) and propagating in local soil, and the inoculated product is a rhizosphere mixture composed of spores, hyphae and mycorrhizal fragments.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Microbial preparation for greenhouse planting and application thereof
PendingCN110964648AAvoid damageImprove qualityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyGlomus intraradices
The invention relates to a microbial preparation and application thereof, in particular to a microbial preparation for greenhouse planting and an application thereof. The method aims at solving the problems that in the greenhouse planting process, a chloroplast base grain structure is damaged, so that the crop yield is reduced, and the quality becomes poor. The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention is composed of glomus mosseae HDSF1 and glomus intritus HDSF5. The microorganism is applied to greenhouse planting. The microbial preparation is applied to greenhouse planting, particularly to greenhouse soil subjected to pesticide damage and salinization stress, damage of the pesticide damage and salinization to the base grain structure of chloroplast is relieved, normal production of crops is guaranteed, and by means of the microbial preparation, the crops are high in yield and good in quality.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
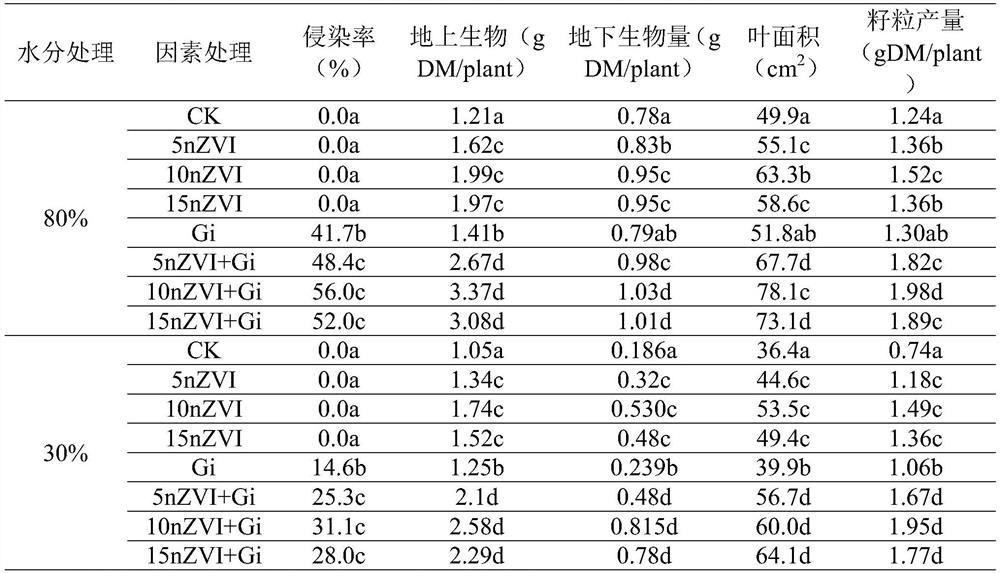
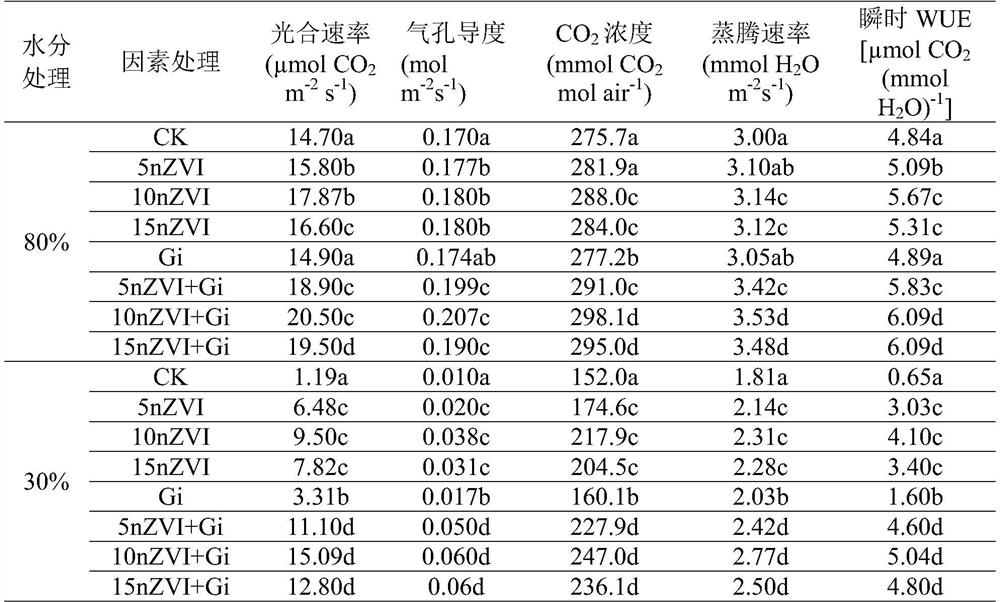
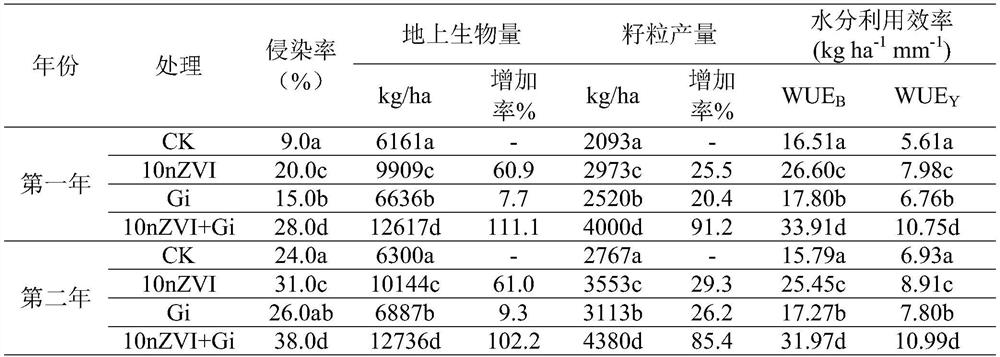
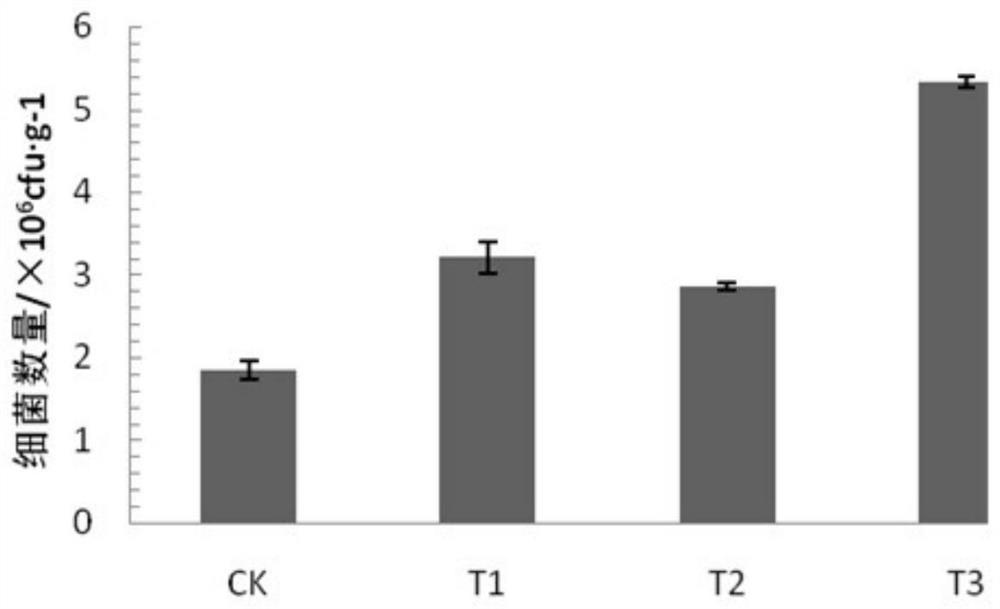
Application and method for water conservation and yield increase of dry land wheat through cooperation of nano elemental iron and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
PendingCN114793793AImprove water use efficiencyImproves drought resilienceSeed and root treatmentGrowth substratesGlomus intraradicesSpore
The invention discloses application and method for water saving and yield increasing of dry land wheat through cooperation of nano elemental iron and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and in the wheat planting process, nZVI and AMF are jointly used for treatment, so that the water utilization efficiency and yield of the dry land wheat can be remarkably improved, and glomus intraradices is adopted as the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; and propagating the glomus intraradices to obtain glomus intraradices inoculum containing 150-200 spores / 10g of dry soil, hyphae inside and outside roots and infected root segments. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out seed soaking treatment by utilizing a solution of nano elemental iron, then adding a glomus intraradices inoculum or an inactivated glomus intraradices inoculum into a culture medium or field soil, and then sowing the wheat seeds subjected to seed soaking treatment. The symbiotic relationship between the AMF and the dry land wheat is enhanced through the nZVI, the growth of the wheat is promoted by utilizing the synergistic effect of the nZVI and the glomus intraradices inoculum, the water utilization efficiency and the drought adaptability of host plants are improved, and the method is beneficial to coping with the drought and changeable climatic environment.
Owner:GANSU ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY
Method for promoting growth of banana seedlings by inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
ActiveCN111642338APromote growth and developmentPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for promoting growth of banana seedlings by inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. According to the method, it is found that an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus mixedstrain (glomus intraradices and glomus manihotis are mixed at a spore ratio of 1:1) has a significant improvement effect on growth and development of banana seedlings as an efficient and safe biological fertilizer and has better ecological economic benefits and environment sustainability effect than other biological fertilizers as a renewable resource for sustainable development through inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus mixed strain into banana roots. The arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus mixed strain has a promotion effect on growth of bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and ammonifiers in a culture substrate, and plays an obvious optimization role in metabolic activity of soil microbial communities of the banana seedlings three months after being inoculated, and growth of banana tissue culture seedlings is significantly promoted by a large number of bacterial metabolic activities.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com