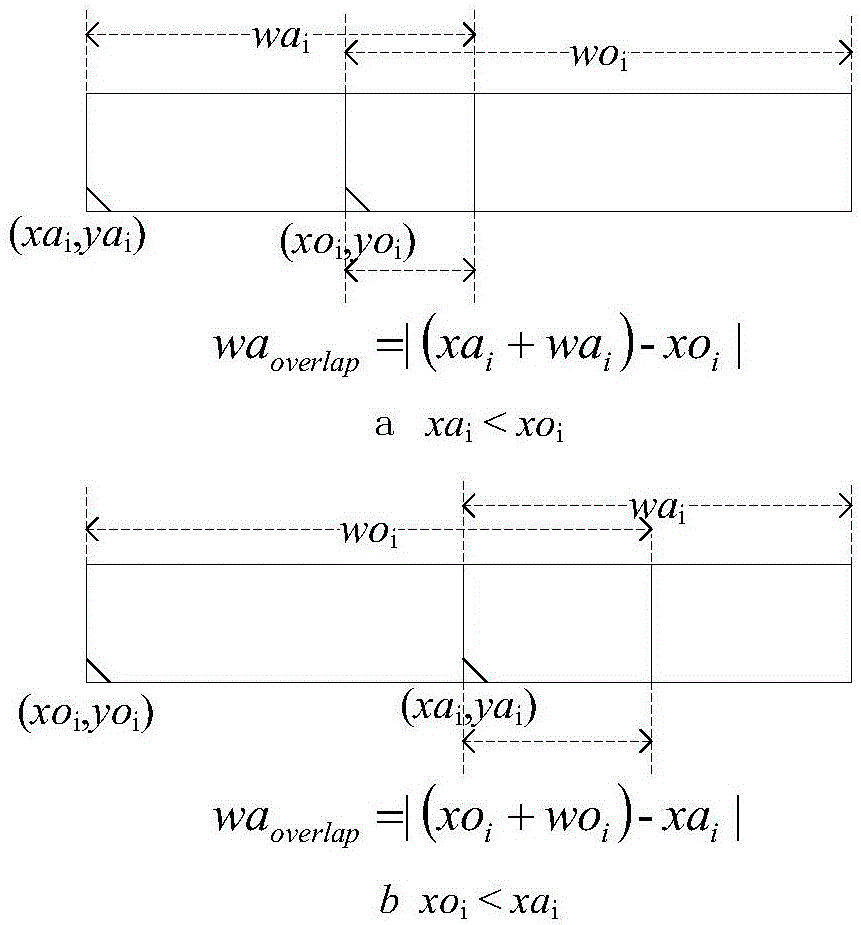Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Engineering change order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
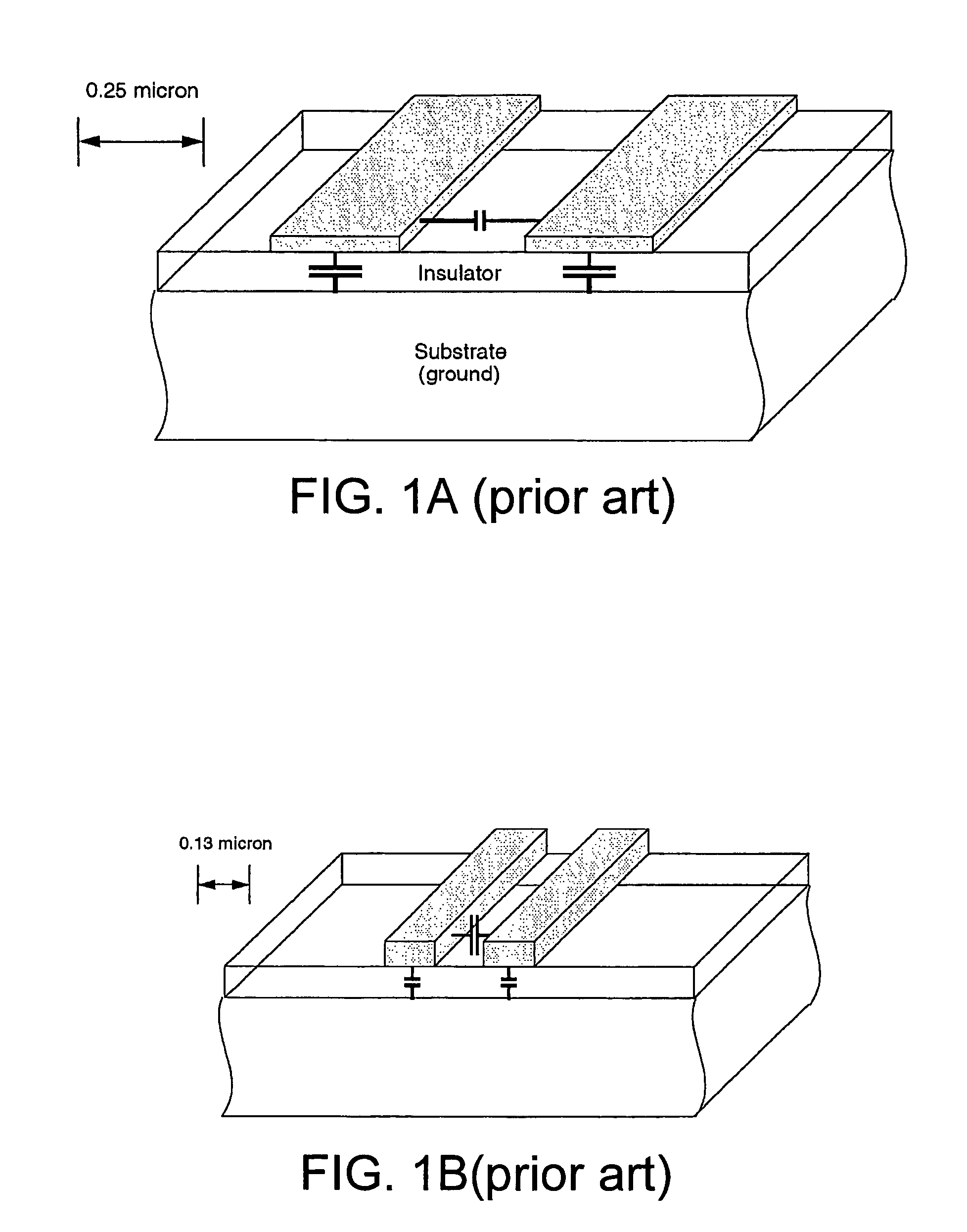
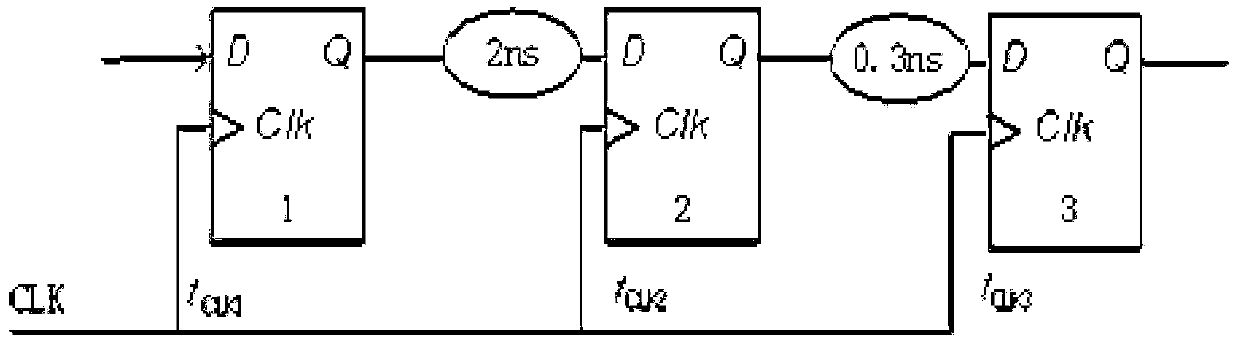
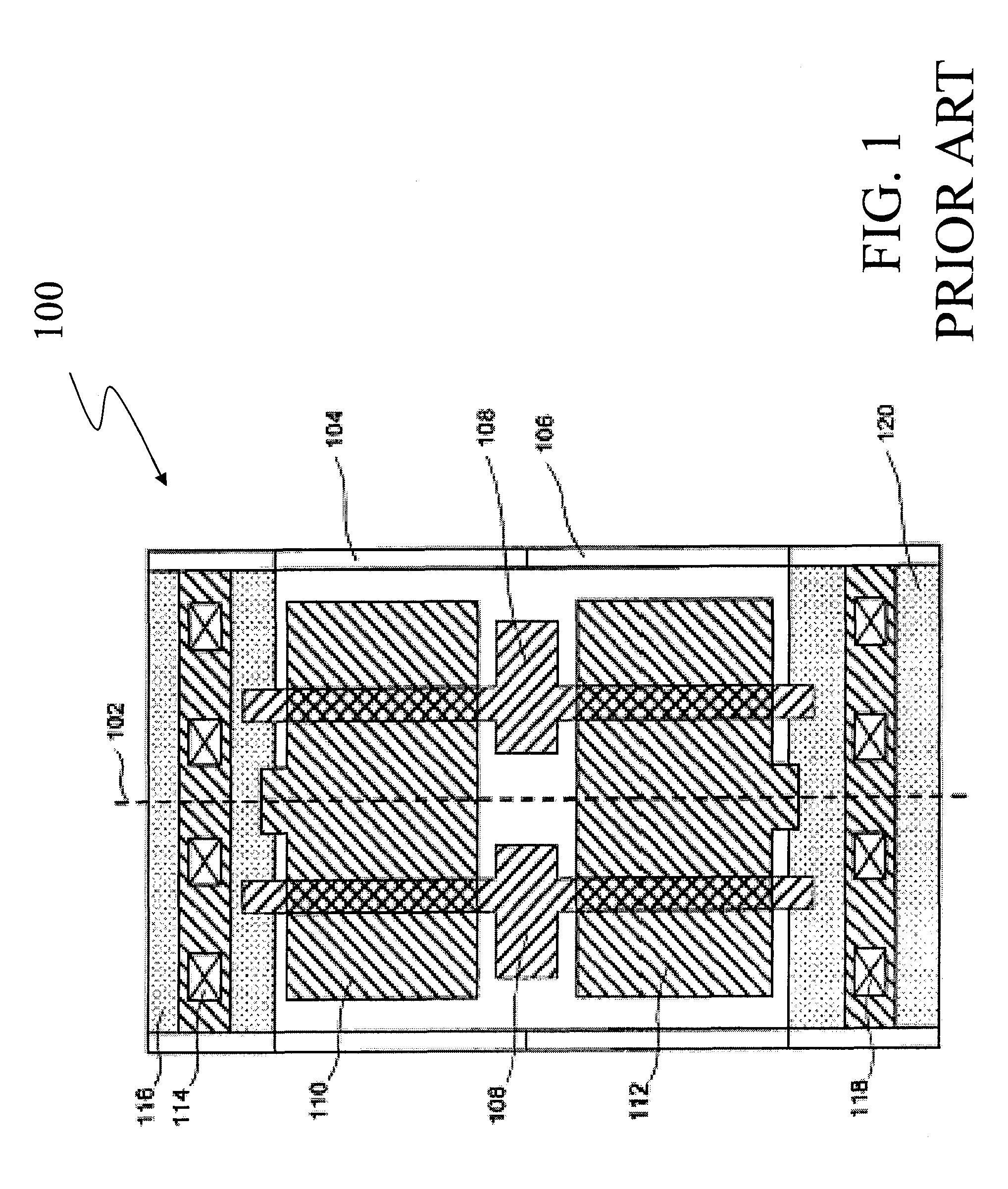
Engineering change orders (ECO) are used for changes in components, assemblies, or documents such as processes and work instructions. They may also be used for changes in specifications. Lastly, it can be "a modification that will have an effect on a manufactured product or manufacturing process."
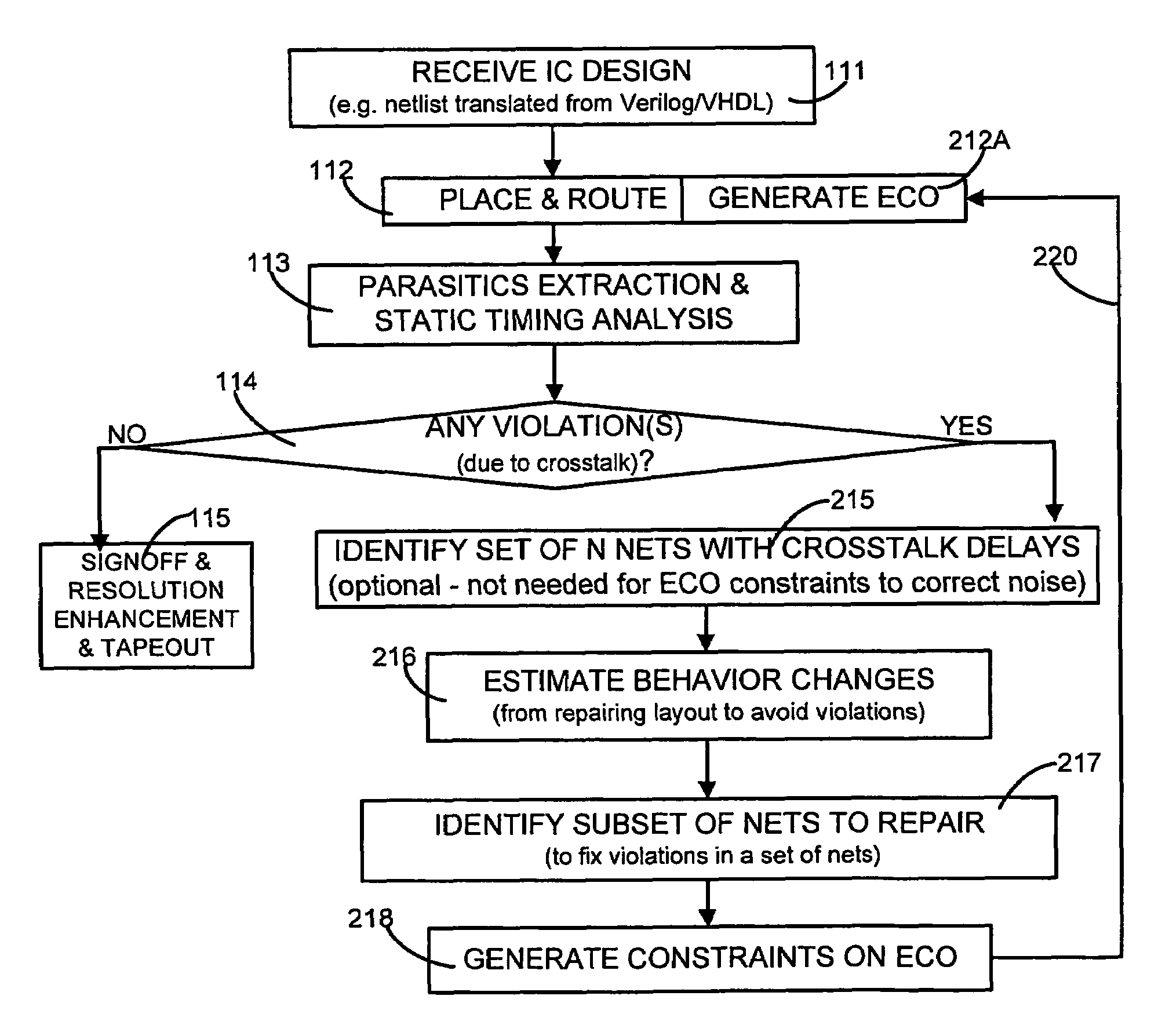
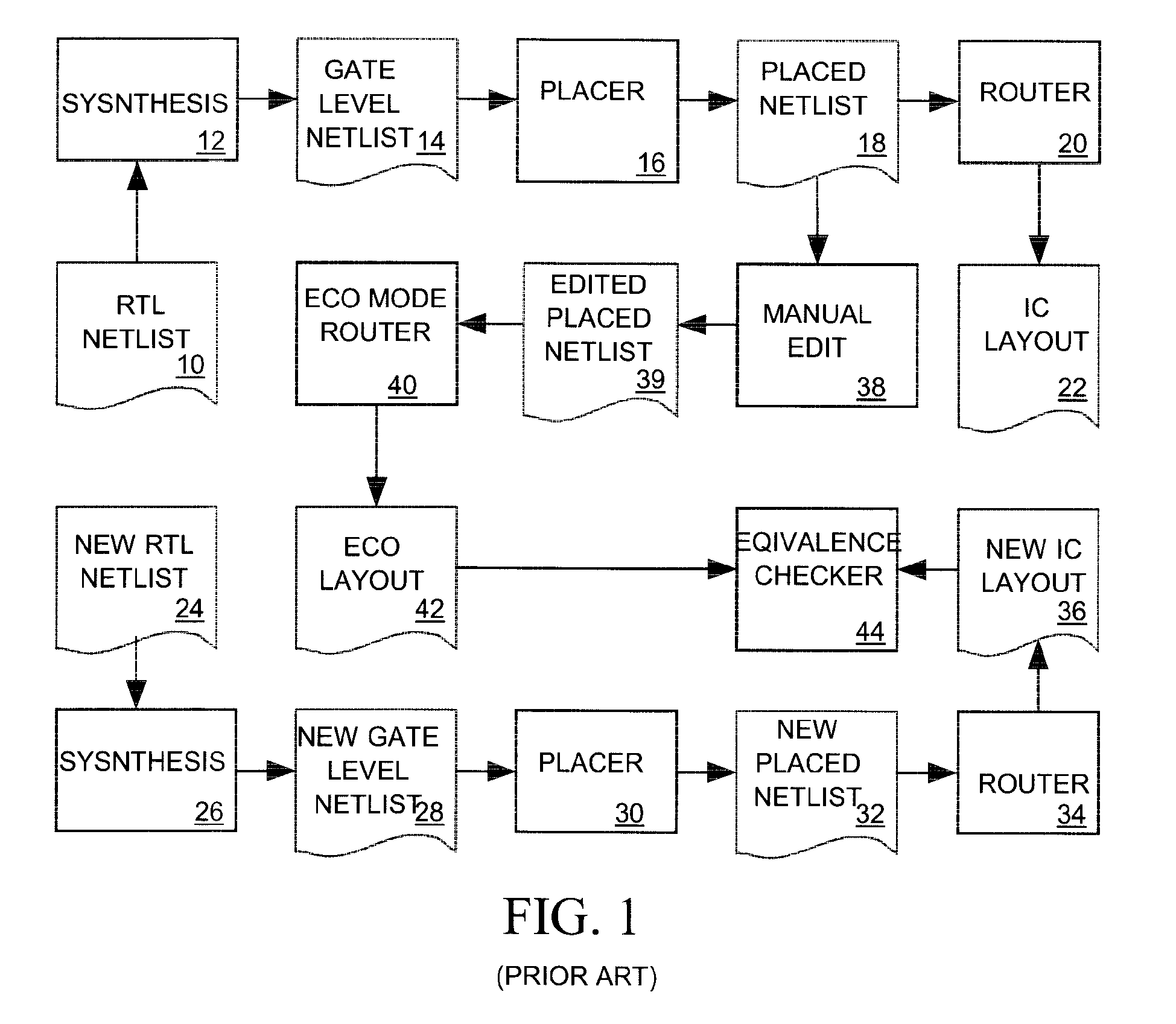
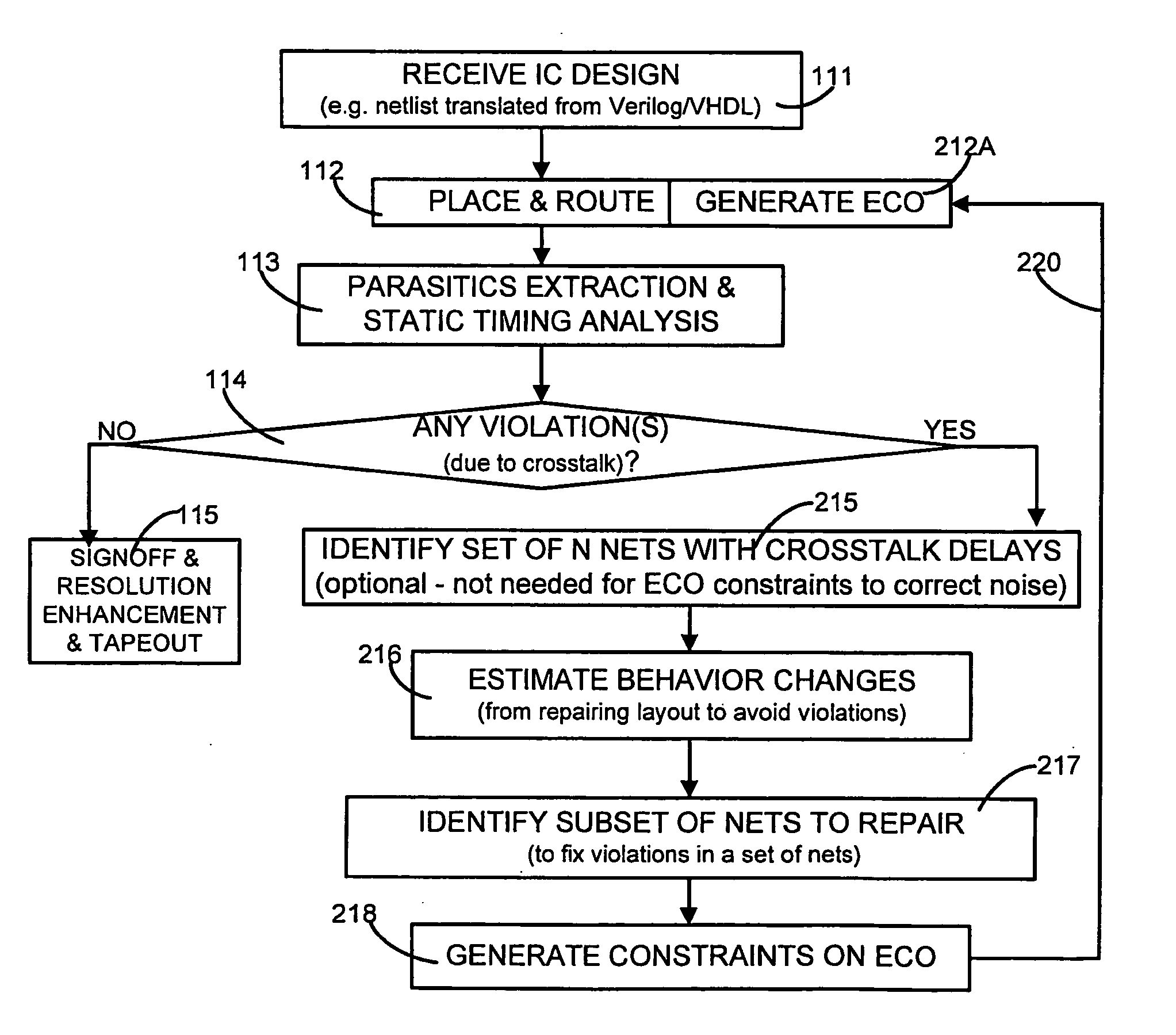
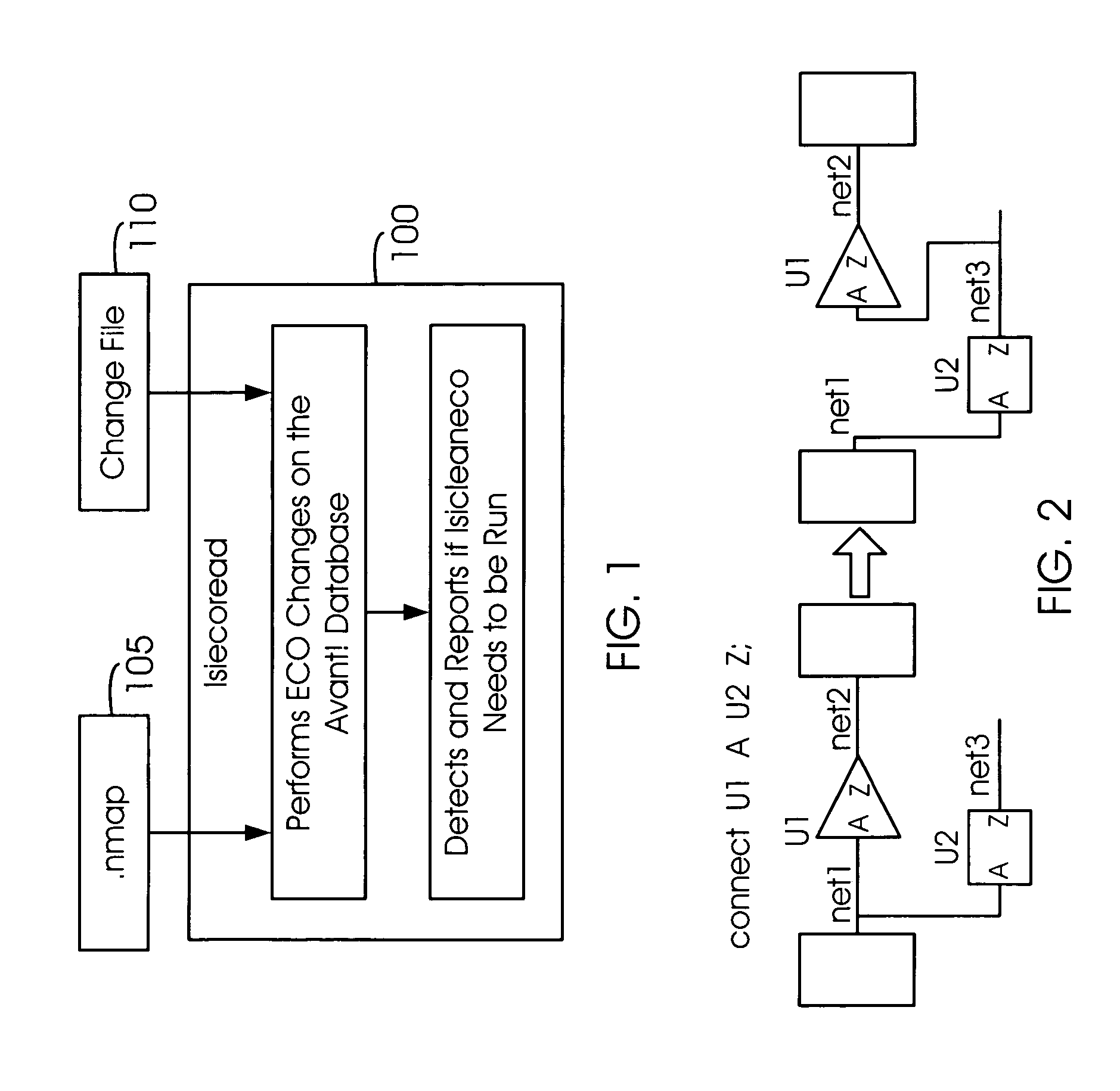
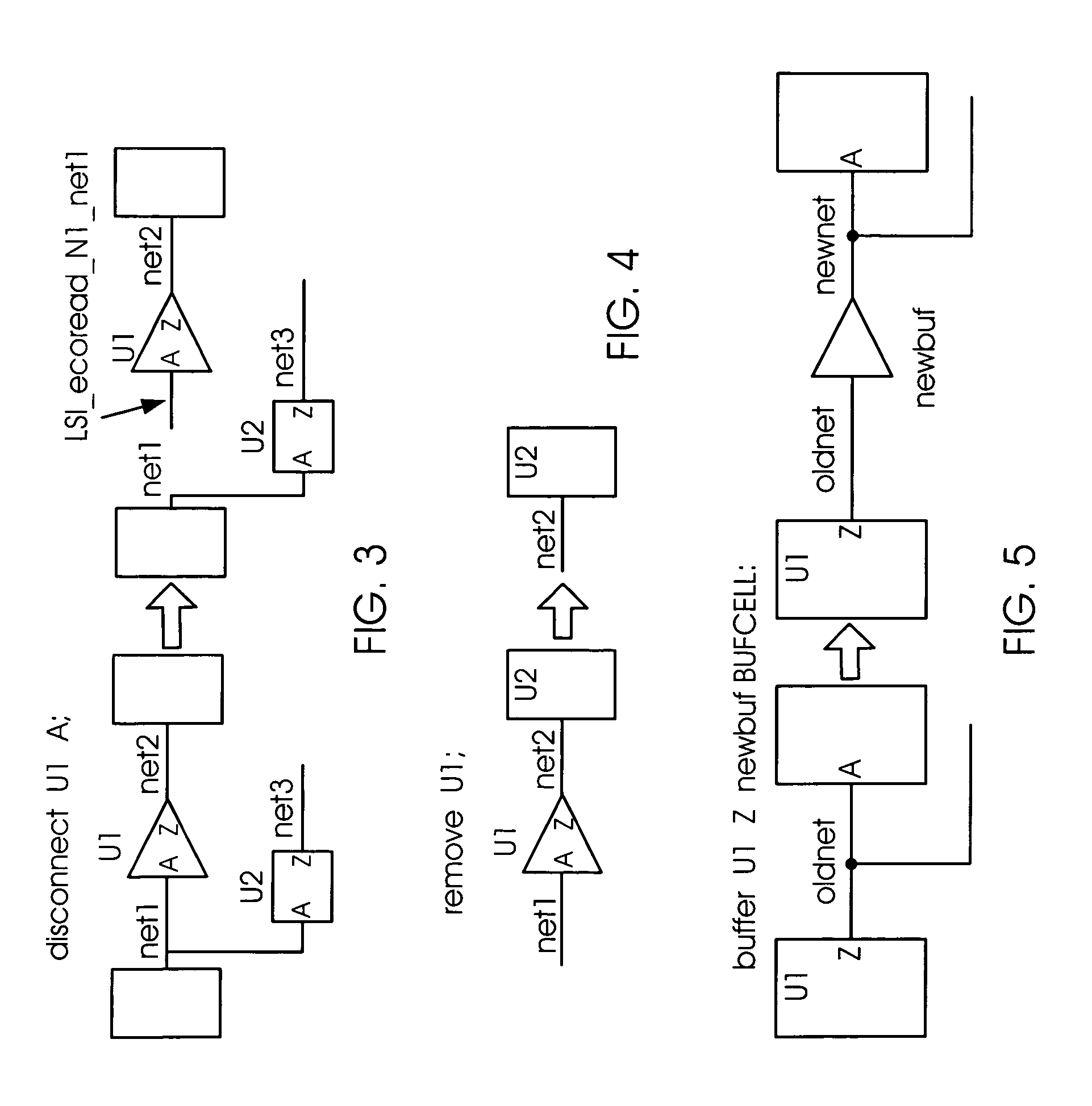
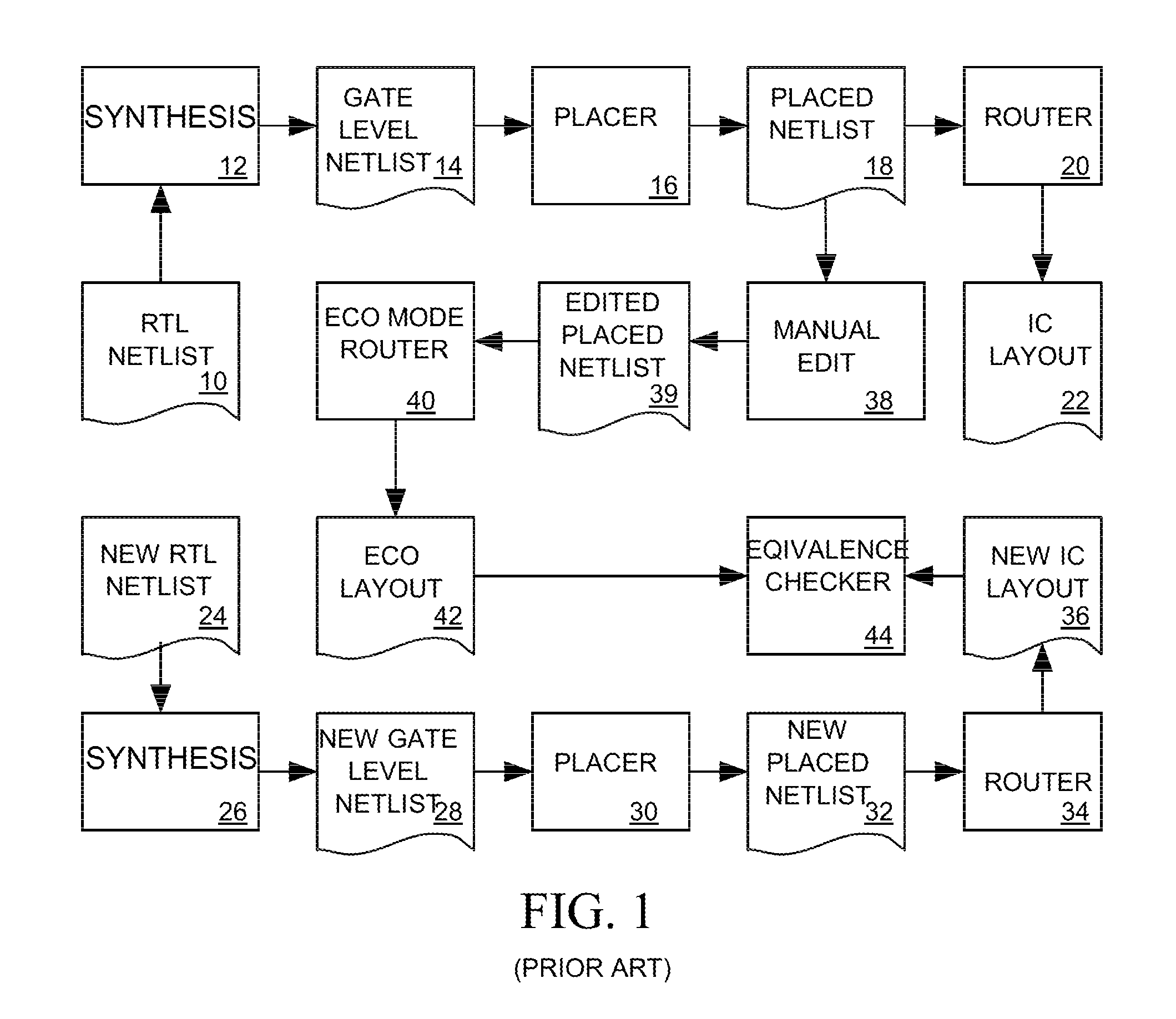
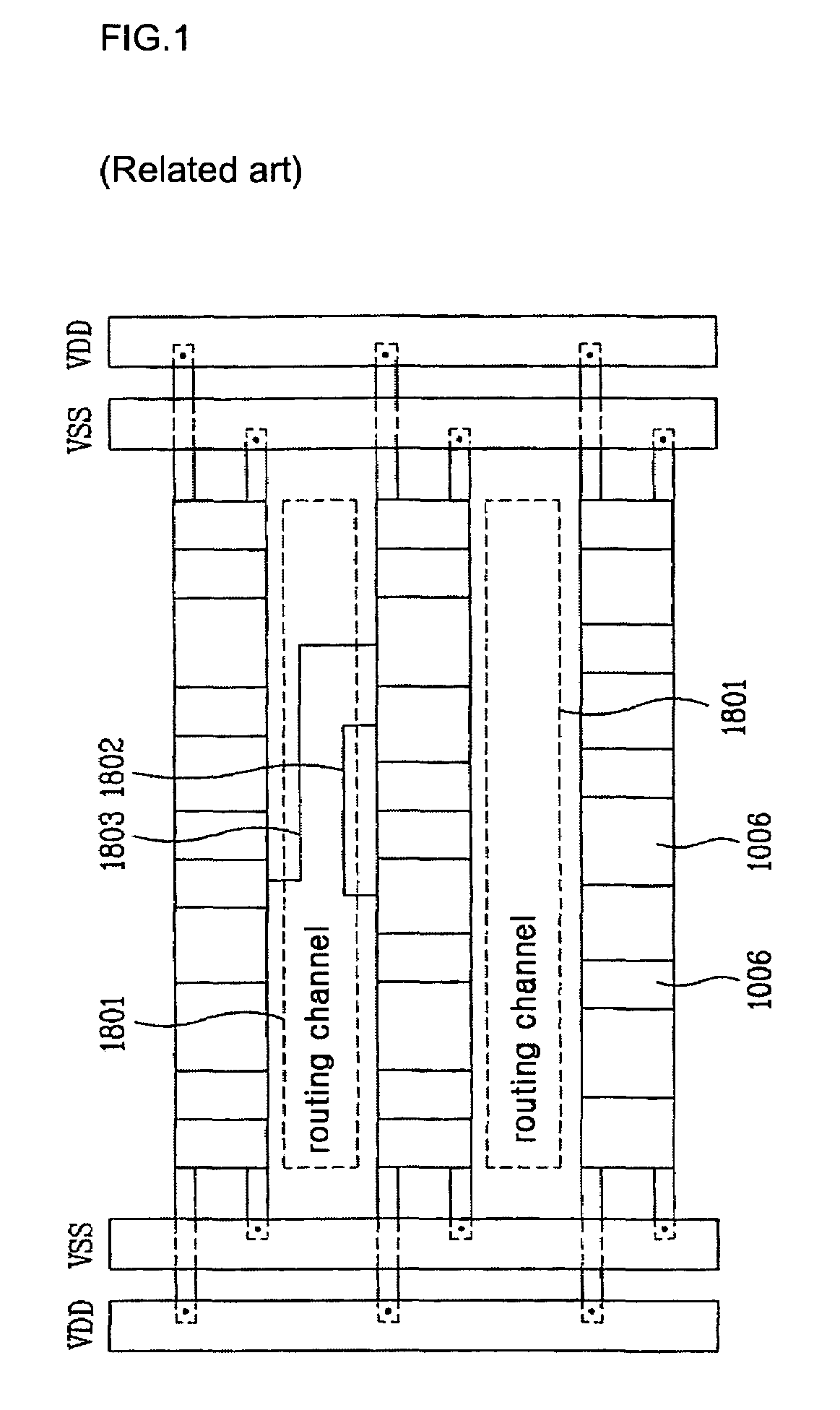
Generation of engineering change order (ECO) constraints for use in selecting ECO repair techniques
ActiveUS7454731B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLayoutEngineering change order
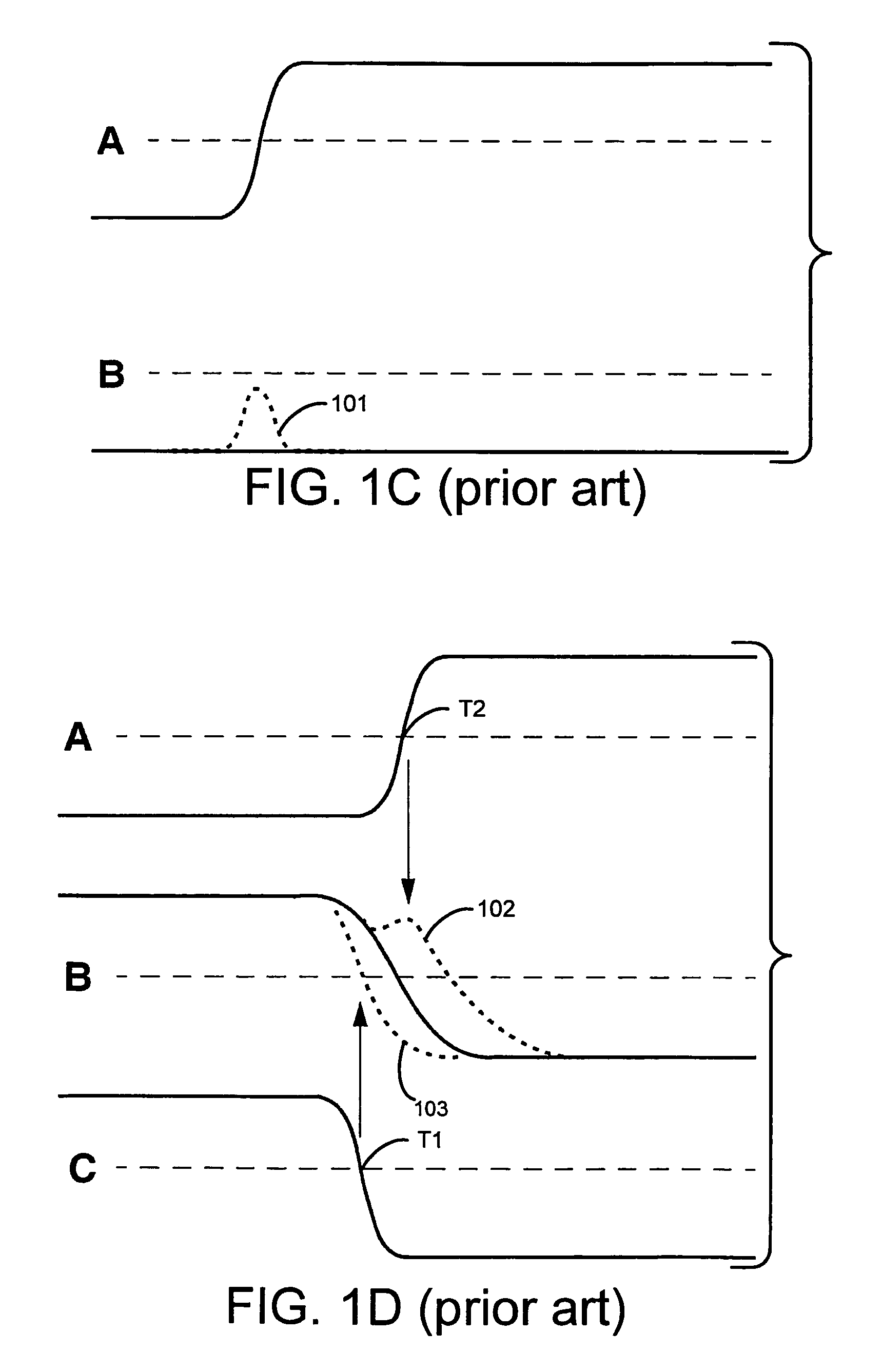
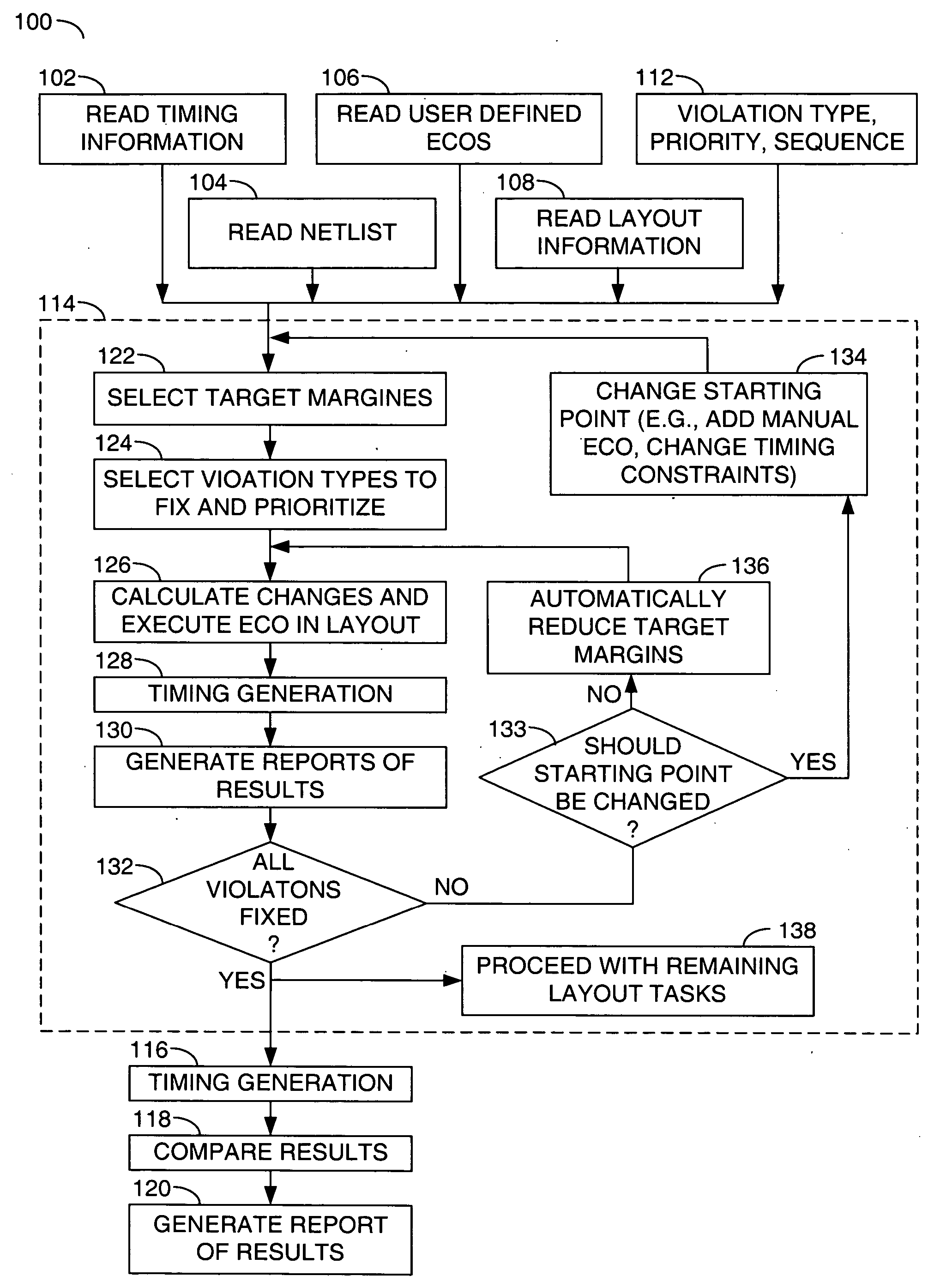
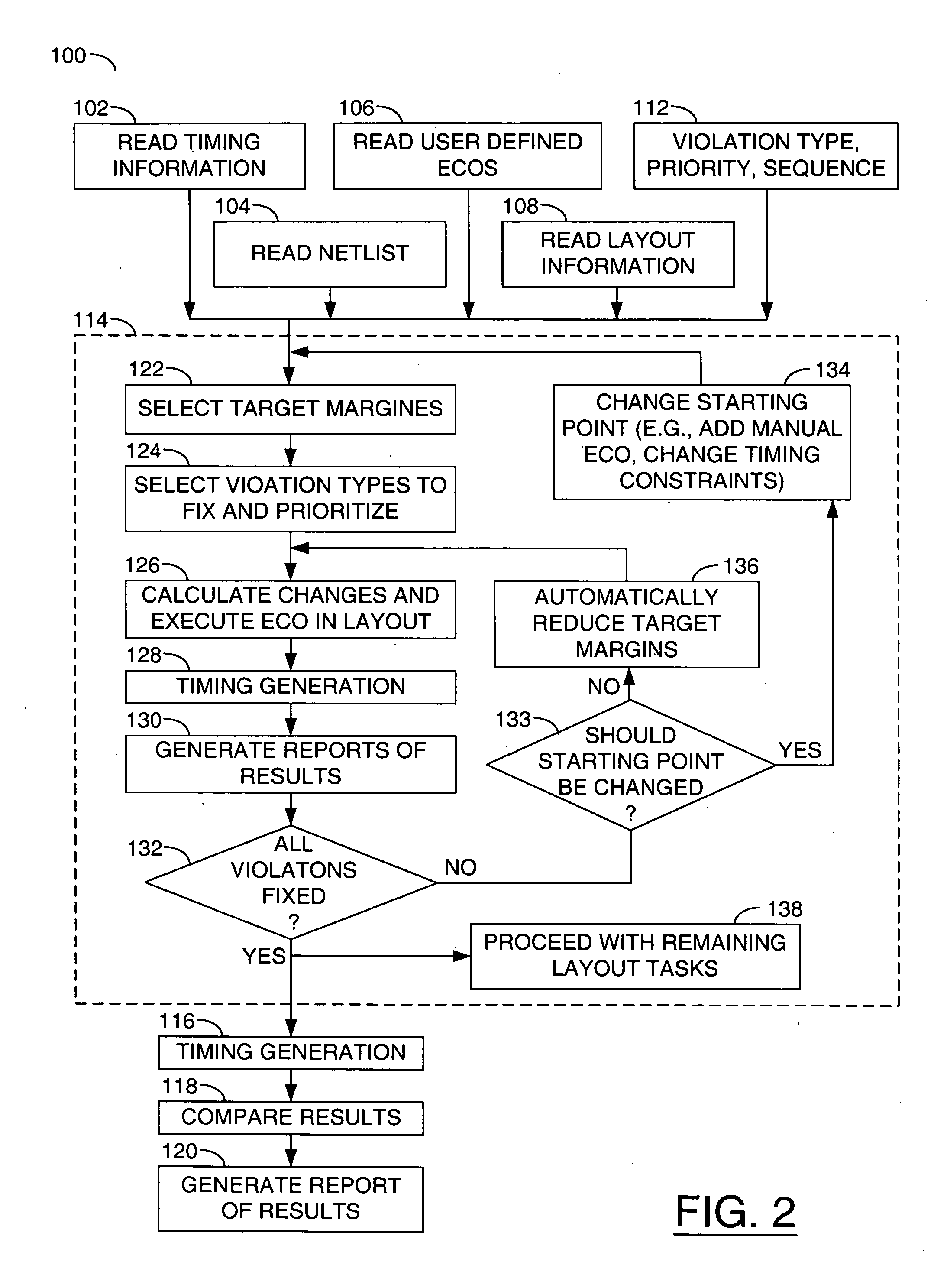
Static timing and / or noise analysis are performed on a netlist of an integrated circuit, to estimate behavior of the netlist and to identify at least one violation by said behavior of a corresponding requirement thereon, such as setup time, hold time or bump height in a quiescent net. Thereafter, effect of engineering change order (ECO) to correct the violation are automatically analyzed, based on the layout, the parasitics, the timing and / or noise behavior, and the violation, followed by generation of a constraint on the behavior (called “ECO” constraint), such as a timing constraint and / or a noise constraint. Next, the ECO constraint is automatically used, e.g. in a place and route tool, to select an ECO repair technique, from several ECO repair techniques that can overcome the violation. The selected ECO repair technique is automatically applied to the layout, to generate a modified layout which does not have the violation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
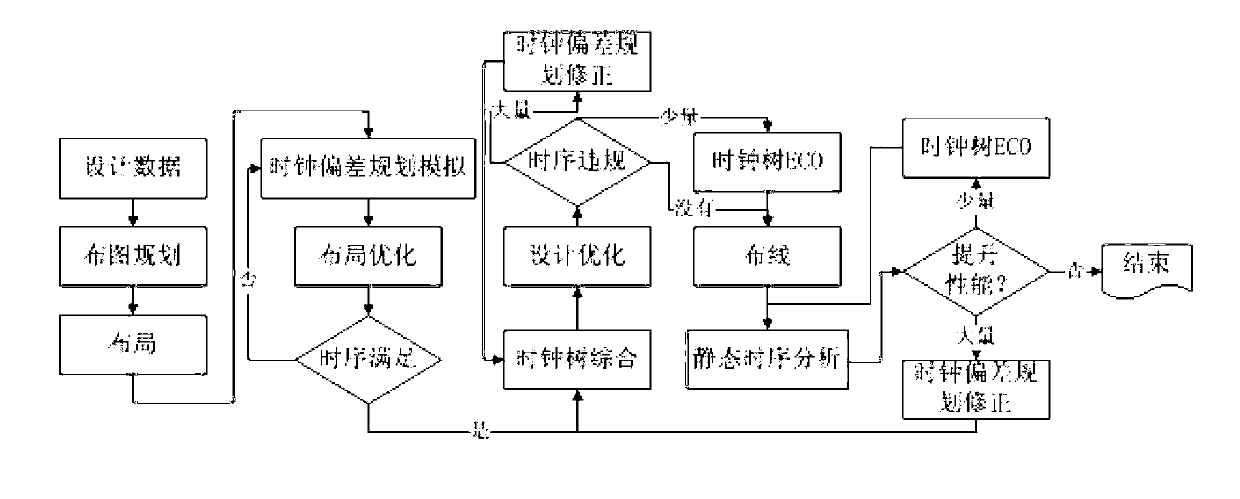
Processor performance optimization method based on clock planning deviation algorithm
InactiveCN103324774AHigh frequencySpecial data processing applicationsLayout planningStatic random-access memory
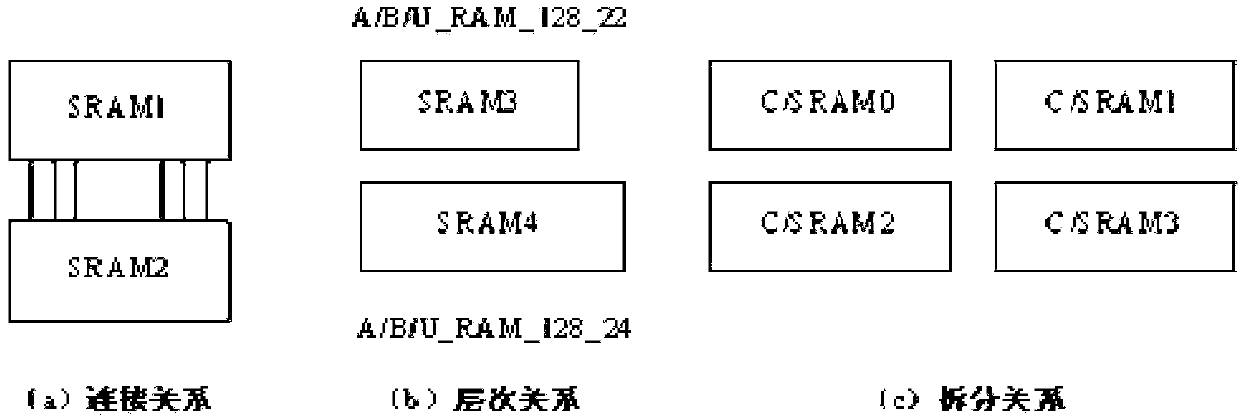
The invention discloses a processor performance optimization method based on the clock planning deviation algorithm, which comprises the following steps: the layout planning phase, the layout phase and the follow-up phase, wherein in the layout planning phase, grouping SRAM (static random access memory) according to the path relation between an SRM (shared resource module) preceding-stage or backward-stage register and multiple SRM; clock deviation planning is performed in the layout phase, and the layout phase is divided into two phases, namely before clock tree synthesis and after clock tree synthesis; before clock tree synthesis, SRAM clock delay is adjusted according to the average surplus capacity between SRAM and multiple paths of the preceding-stage or backward-stage register, and planning the clock jitter of the register by adopting the partial surplus capacity borrowing algorithm; after clock tree synthesis, handling a large number and few time sequence violations respectively by adopting the clock tree algorithm correction and the engineering change; in the follow-up phase, to handle the storage time violation after wiring, the restoring scheme based on distributed multi-scenario time sequence analysis, and combining an ECO (engineering change order) and a script is adopted.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
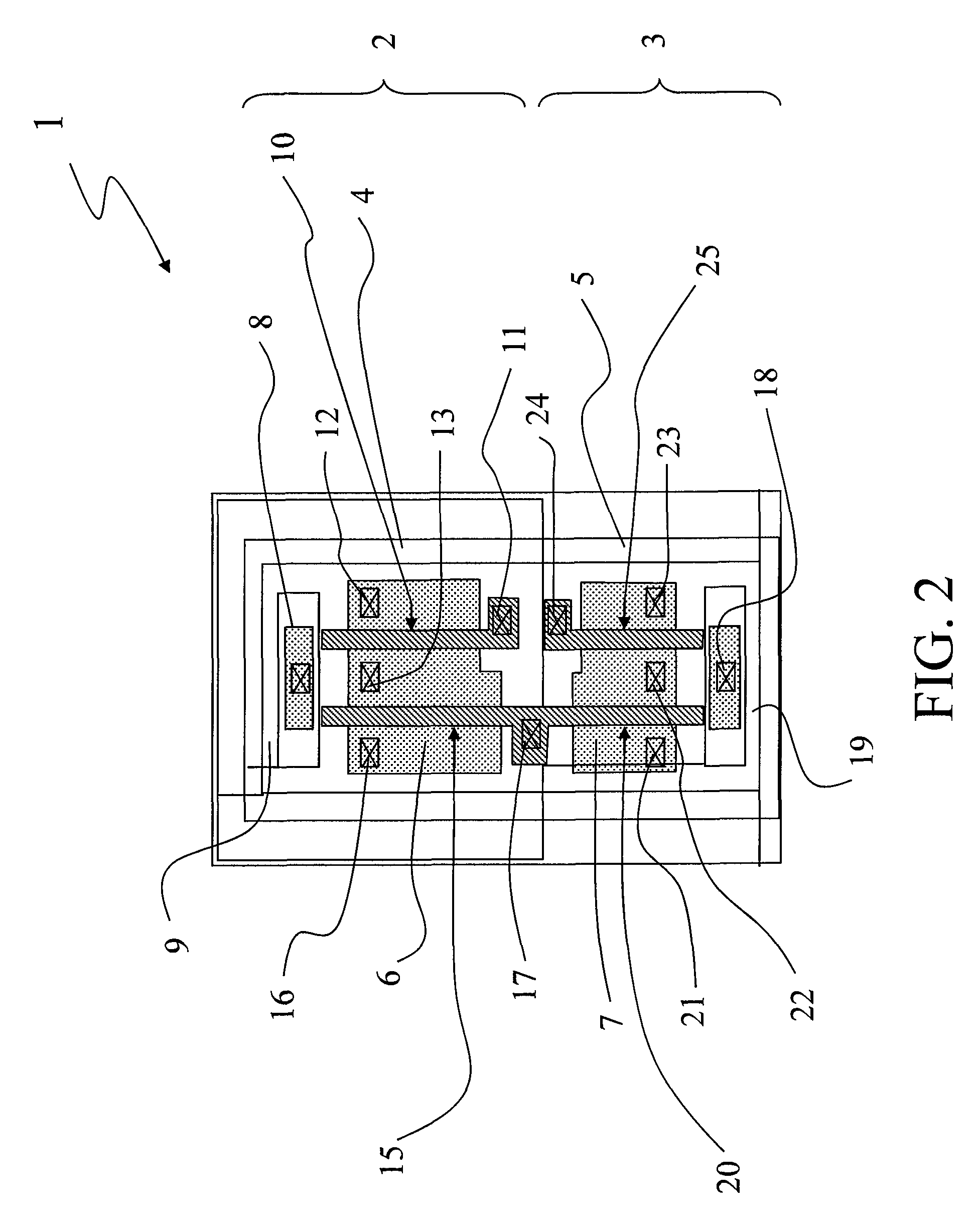
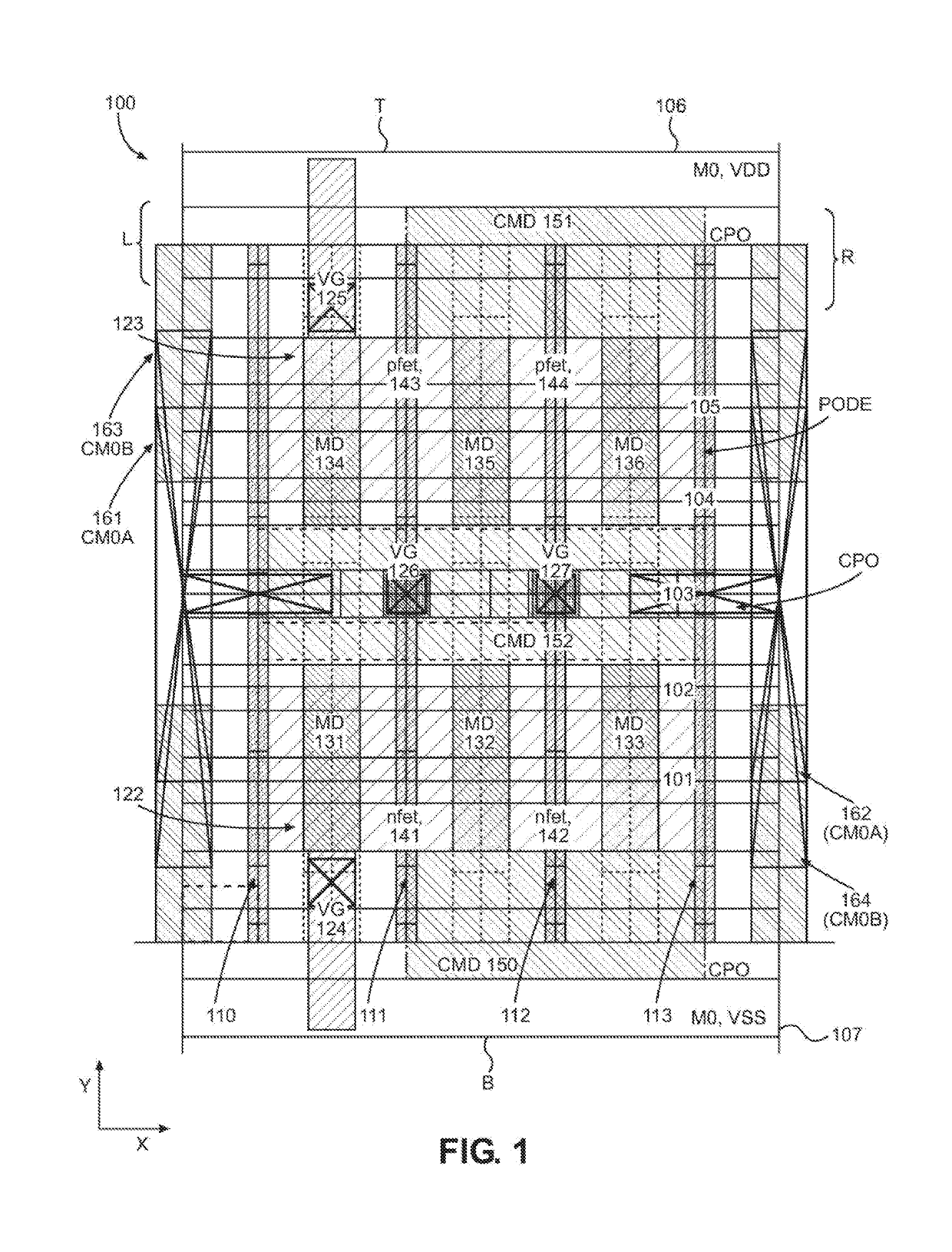
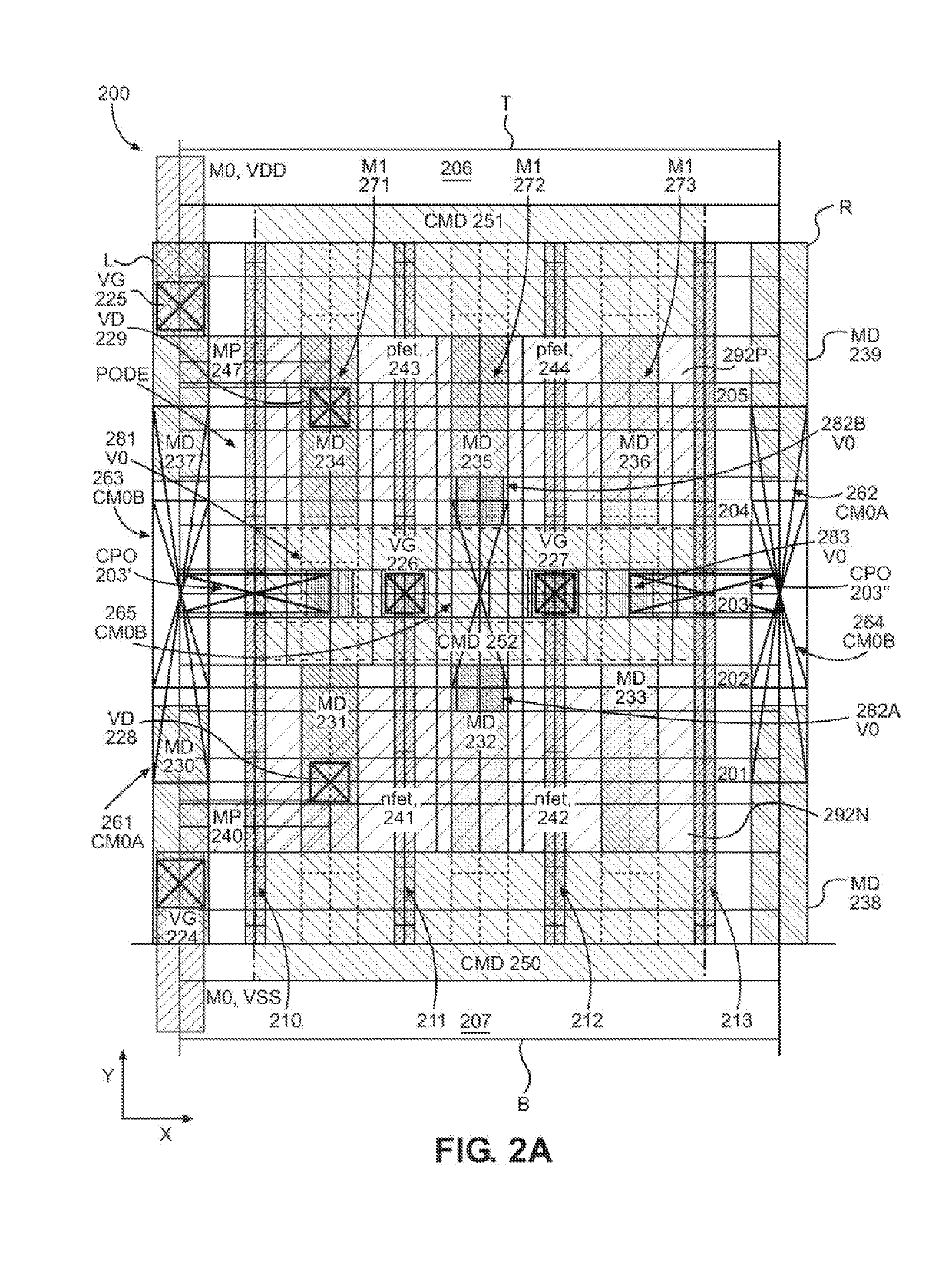
Reconfigurable engineering change order base cell
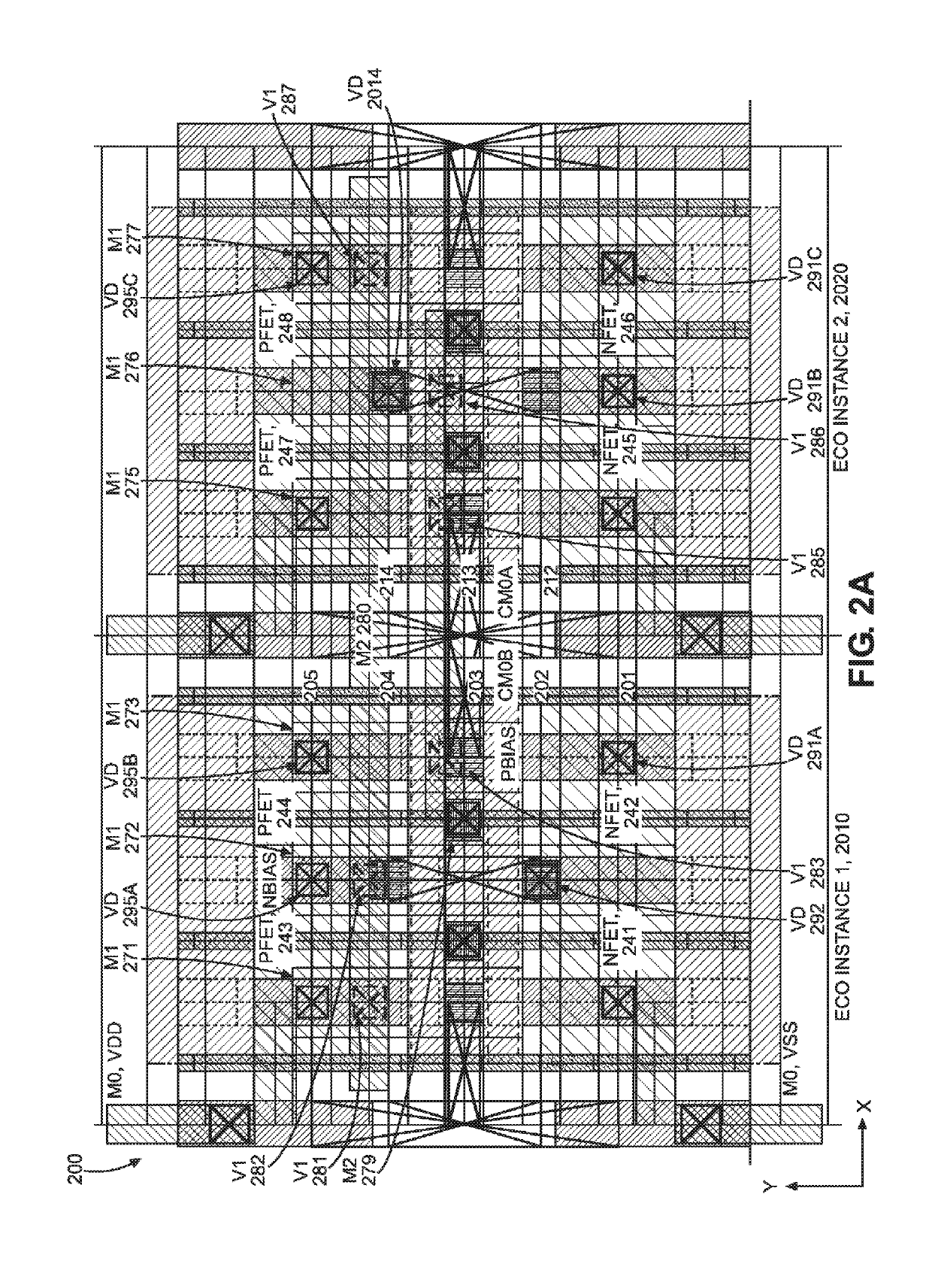
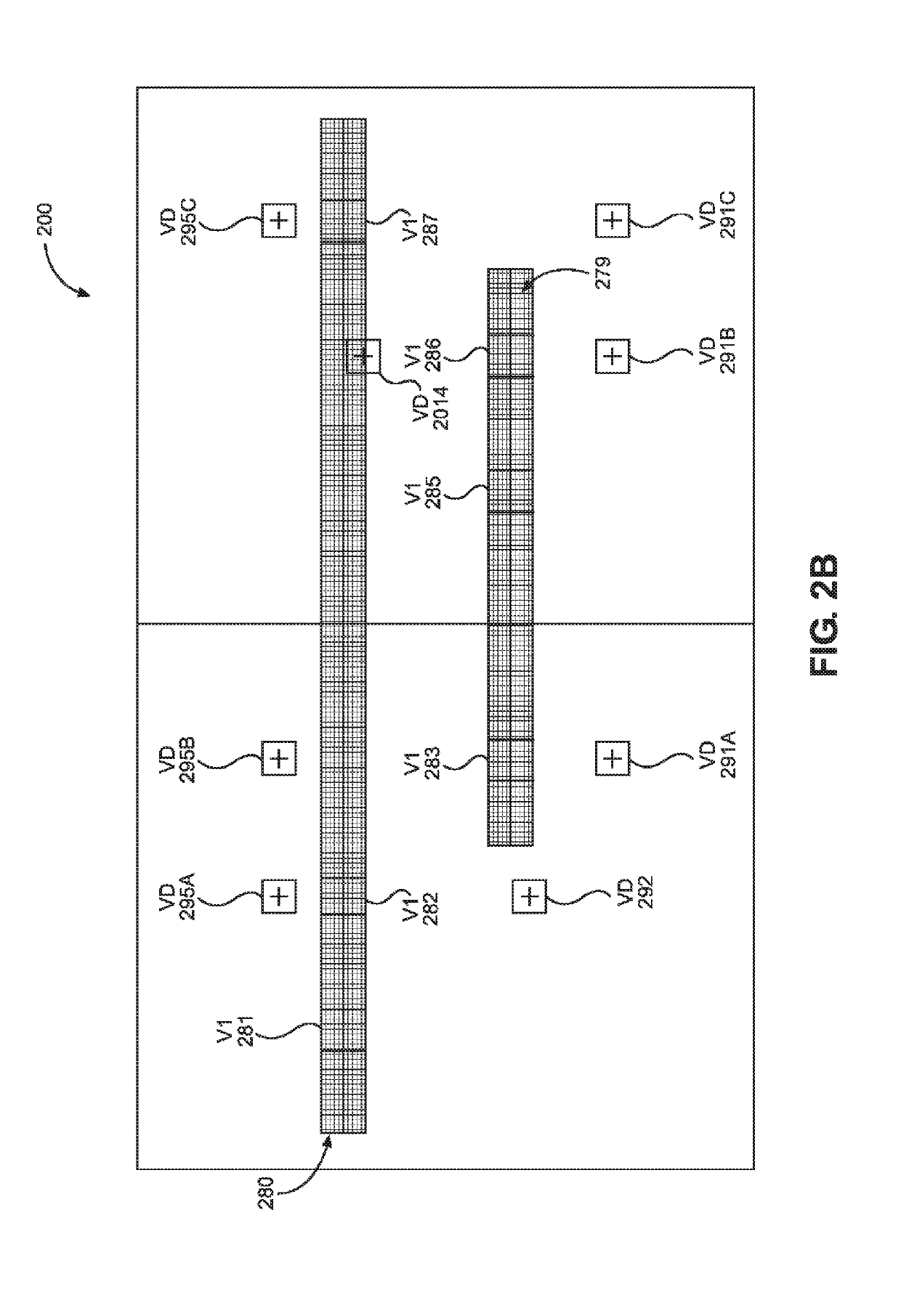
ActiveUS8446176B1TransistorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectricityElectrical conductor
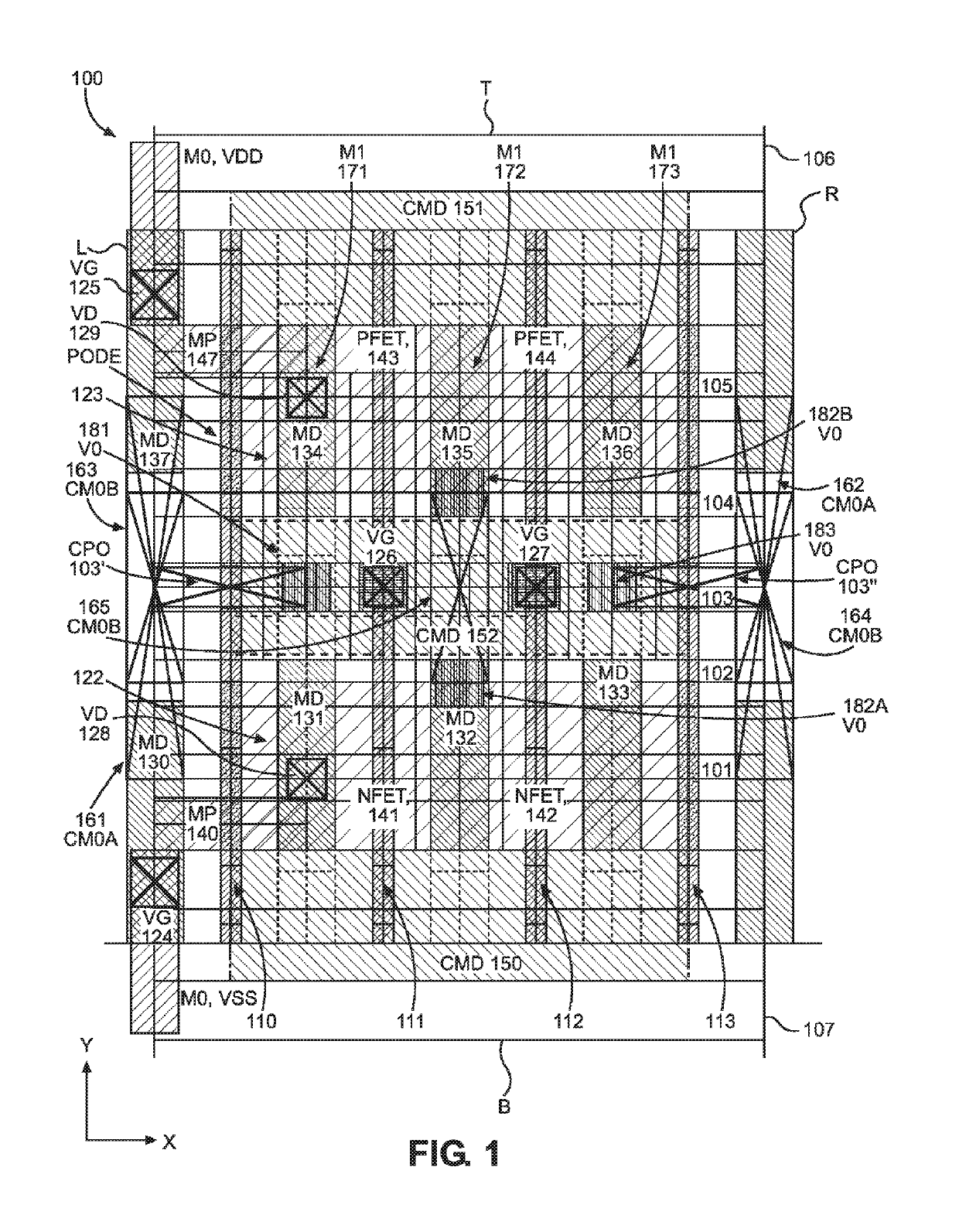
An integrated circuit ECO base cell module is formed with PMOS and NMOS gate electrode structures and power supply lines that are electrically separated from one another up to the second metal (M2) layer in a fixed circuit structure that may be reconfigured with one or more conductor elements formed above the M2 layer to form a predetermined circuit function.
Owner:NXP USA INC
System for implementing post-silicon IC design changes
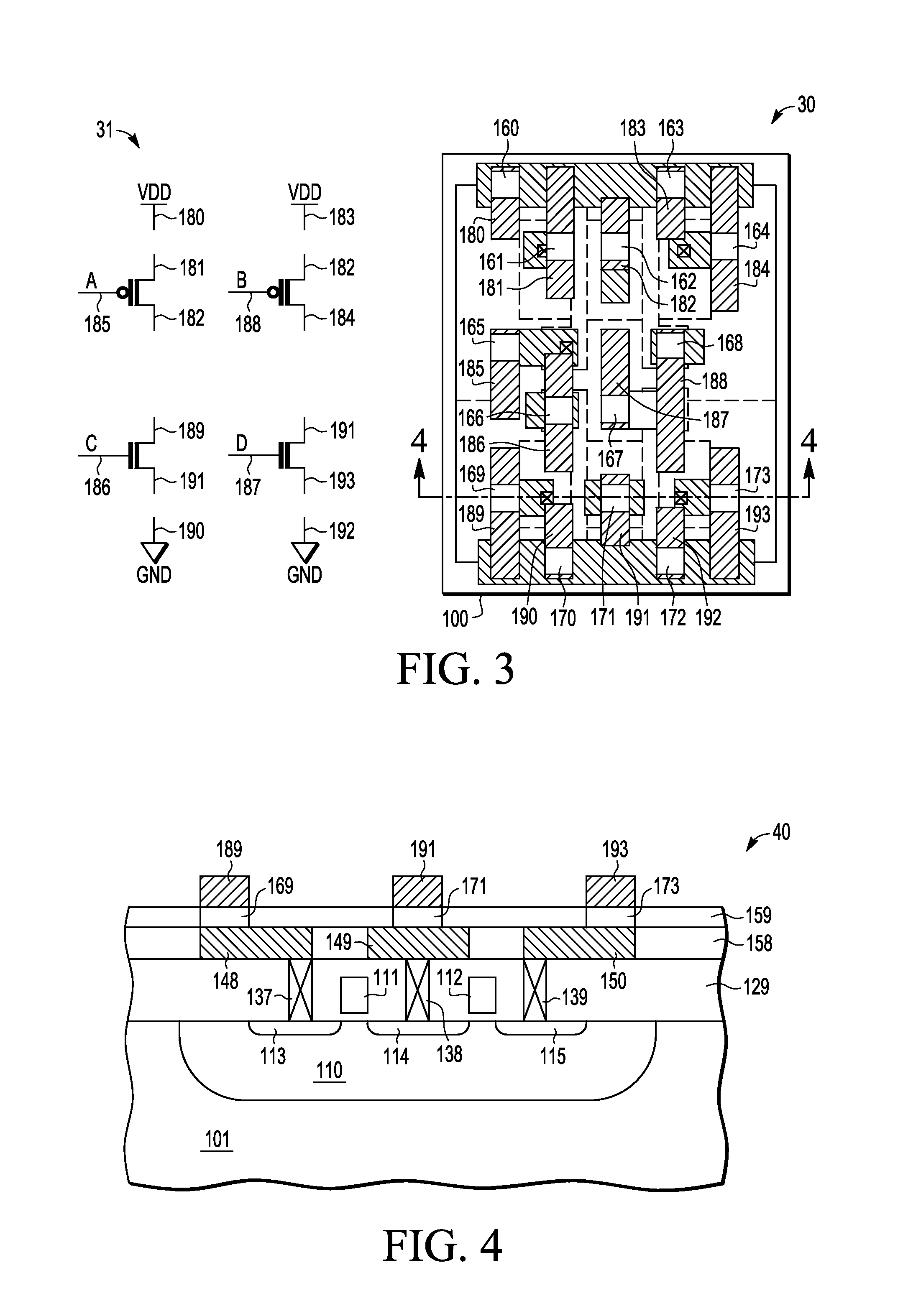
ActiveUS20090178013A1Improve routeablityCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationEngineeringActive cell
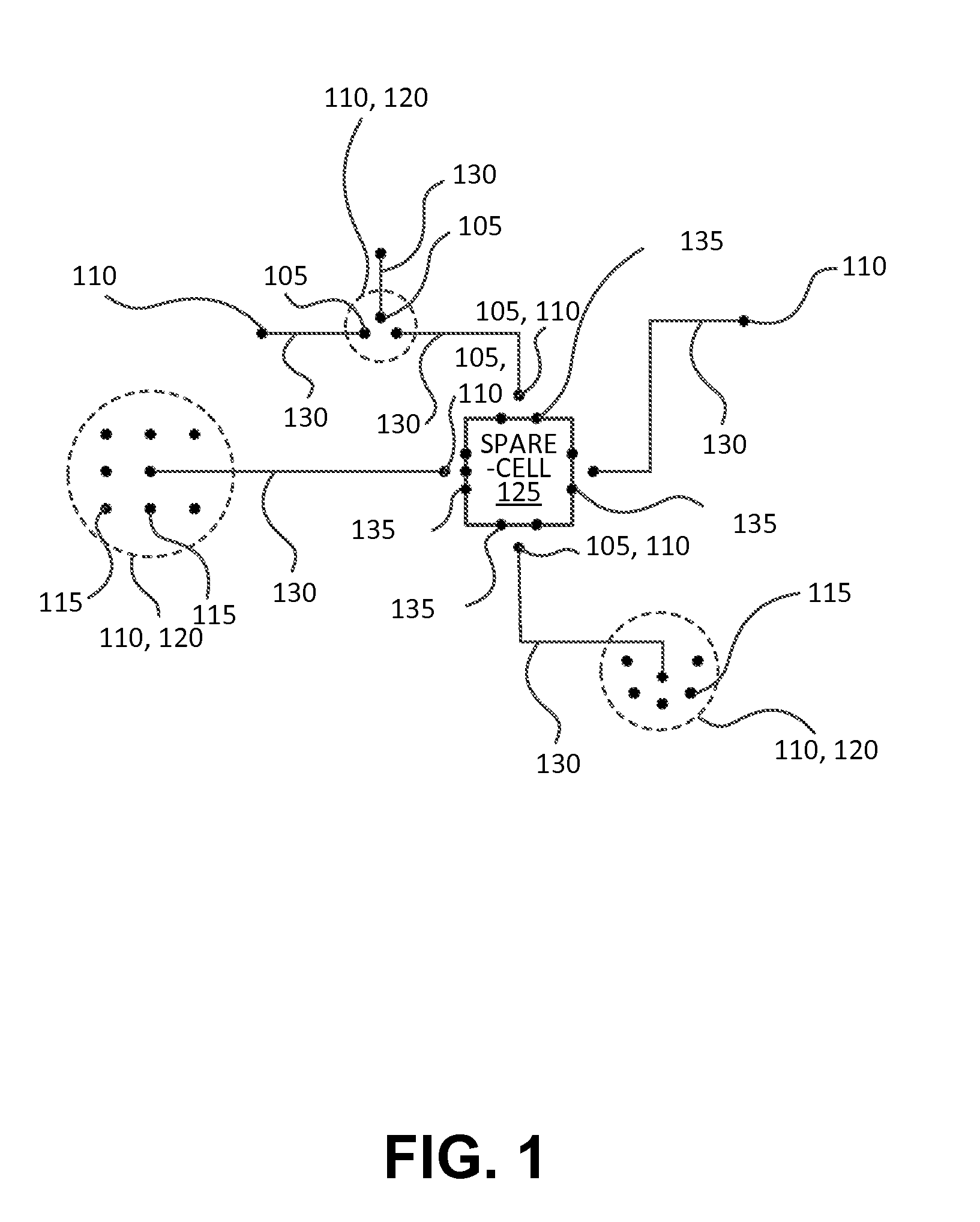
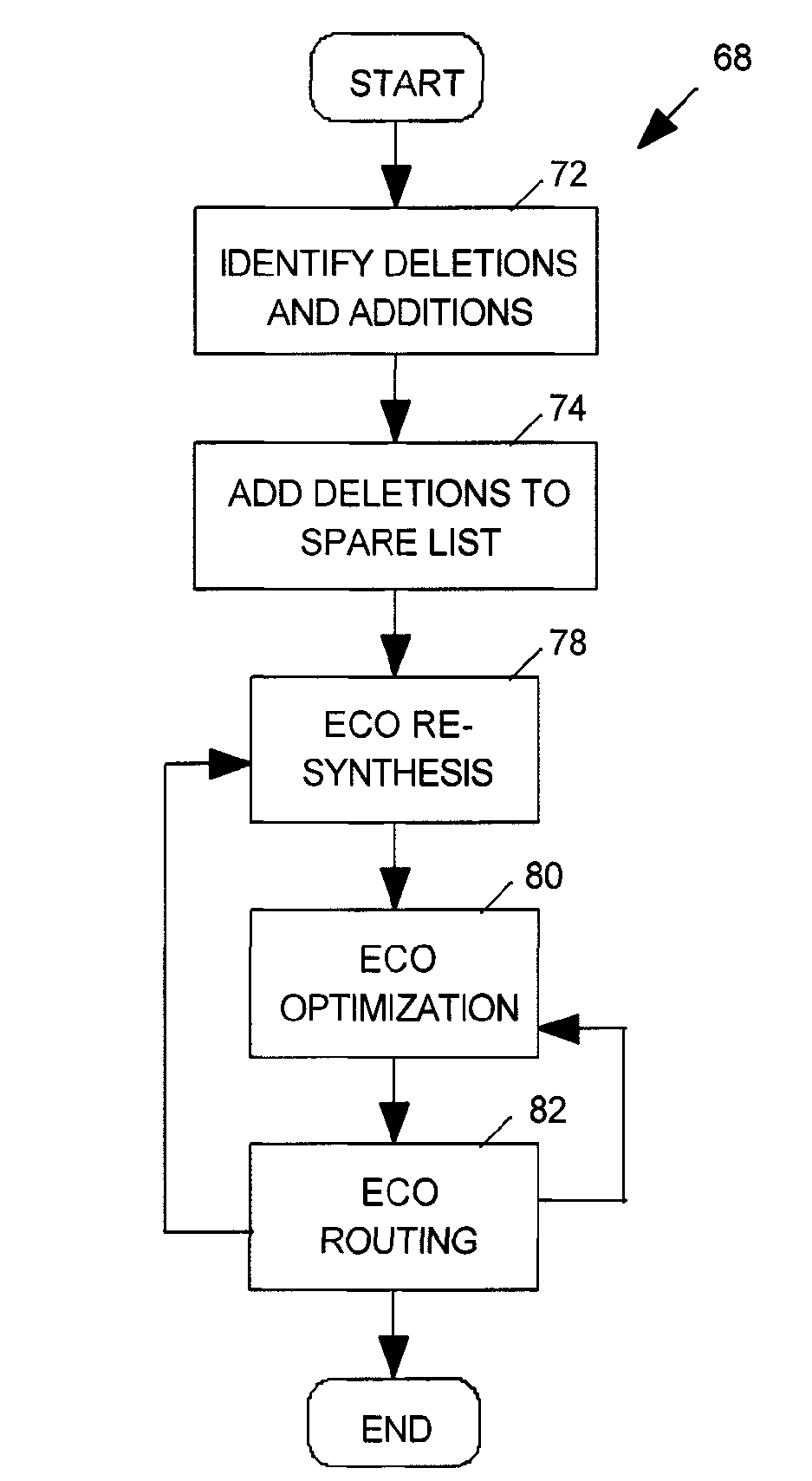
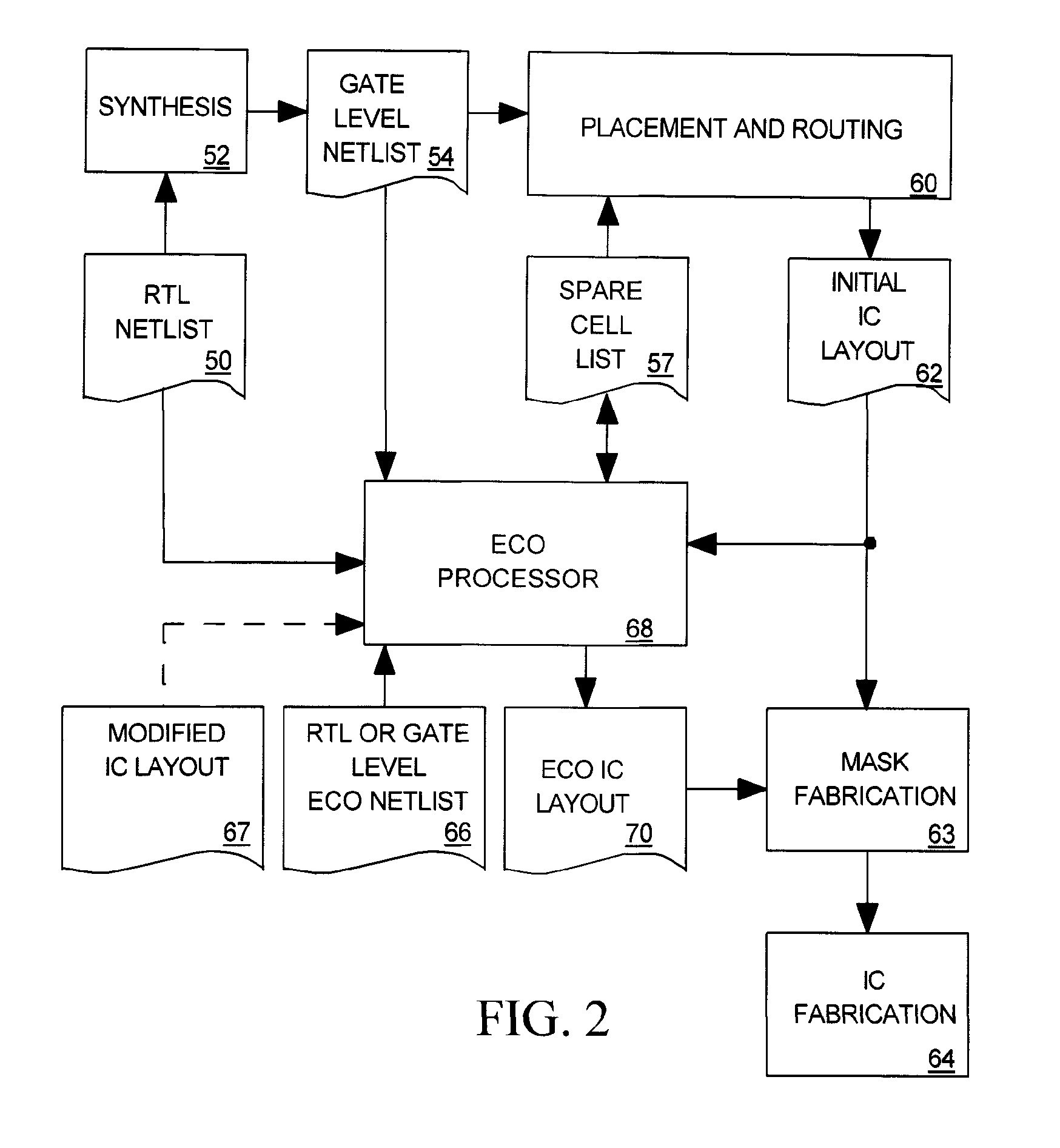
An engineering change order (ECO) modifying an IC having spare cell instances is implemented by converting active cell instances implementing portions of the IC to be deleted into additional spare cell instances, by creating a technology independent behavioral model of portions of the IC to be added, by selecting spare cell instances to implement the behavior model, and by routing nets to the selected spare cell instances in a way that minimizes a number of metal layers of the IC that are modified.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Generation of engineering change order (ECO) constraints for use in selecting ECO repair techniques
ActiveUS20080077900A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringEngineering change order
Static timing and / or noise analysis are performed on a netlist of an integrated circuit, to estimate behavior of the netlist and to identify at least one violation by said behavior of a corresponding requirement thereon, such as setup time, hold time or bump height in a quiescent net. Thereafter, effect of engineering change order (ECO) to correct the violation are automatically analyzed, based on the layout, the parasitics, the timing and / or noise behavior, and the violation, followed by generation of a constraint on the behavior (called “ECO” constraint), such as a timing constraint and / or a noise constraint. Next, the ECO constraint is automatically used, e.g. in a place and route tool, to select an ECO repair technique, from several ECO repair techniques that can overcome the violation. The selected ECO repair technique is automatically applied to the layout, to generate a modified layout which does not have the violation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
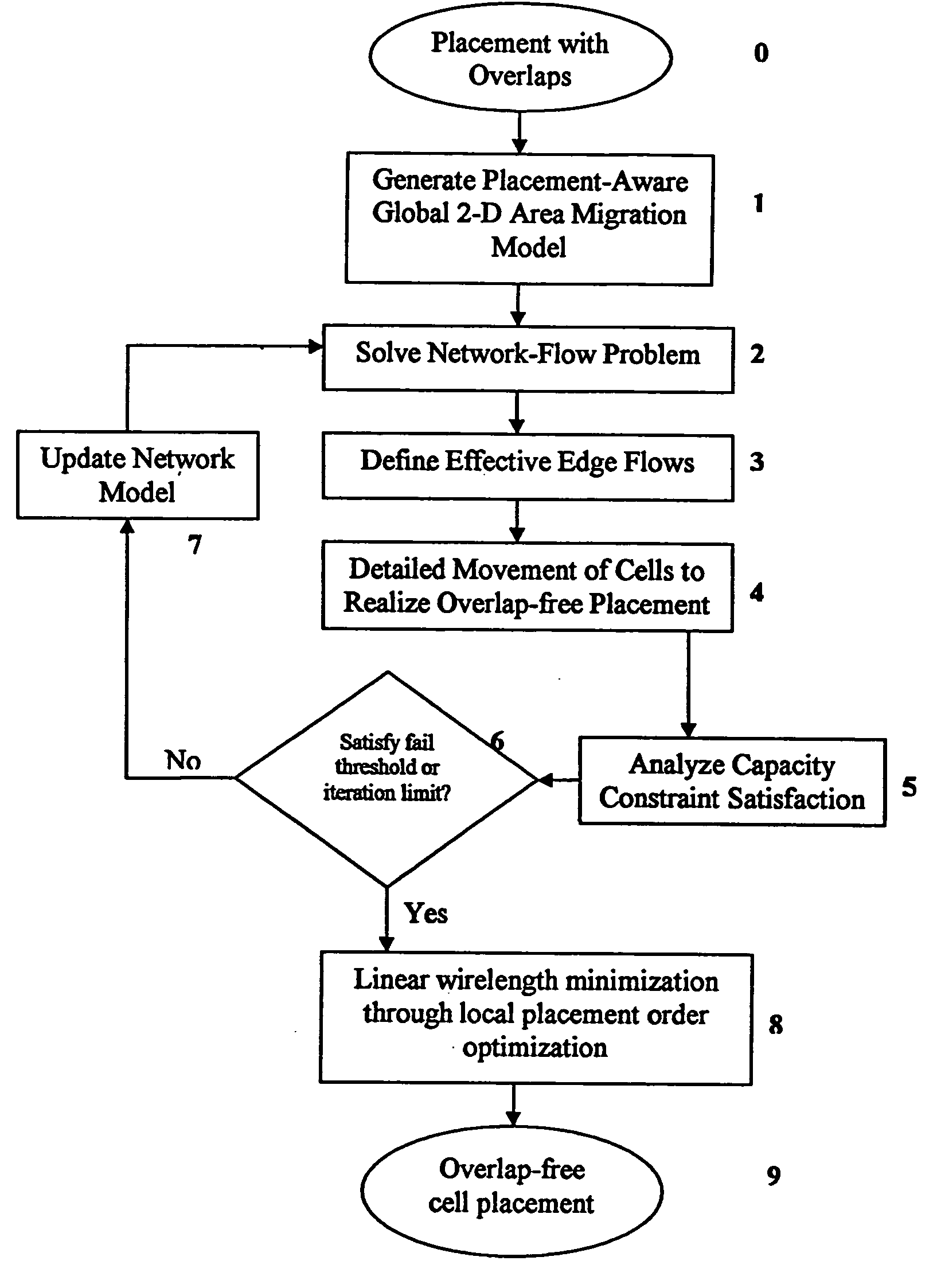
Method for legalizing the placement of cells in an integrated circuit layout
InactiveUS20050166169A1Maintain qualityAutomatically resolve cell overlapsComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationHigh cellIntegrated circuit layout
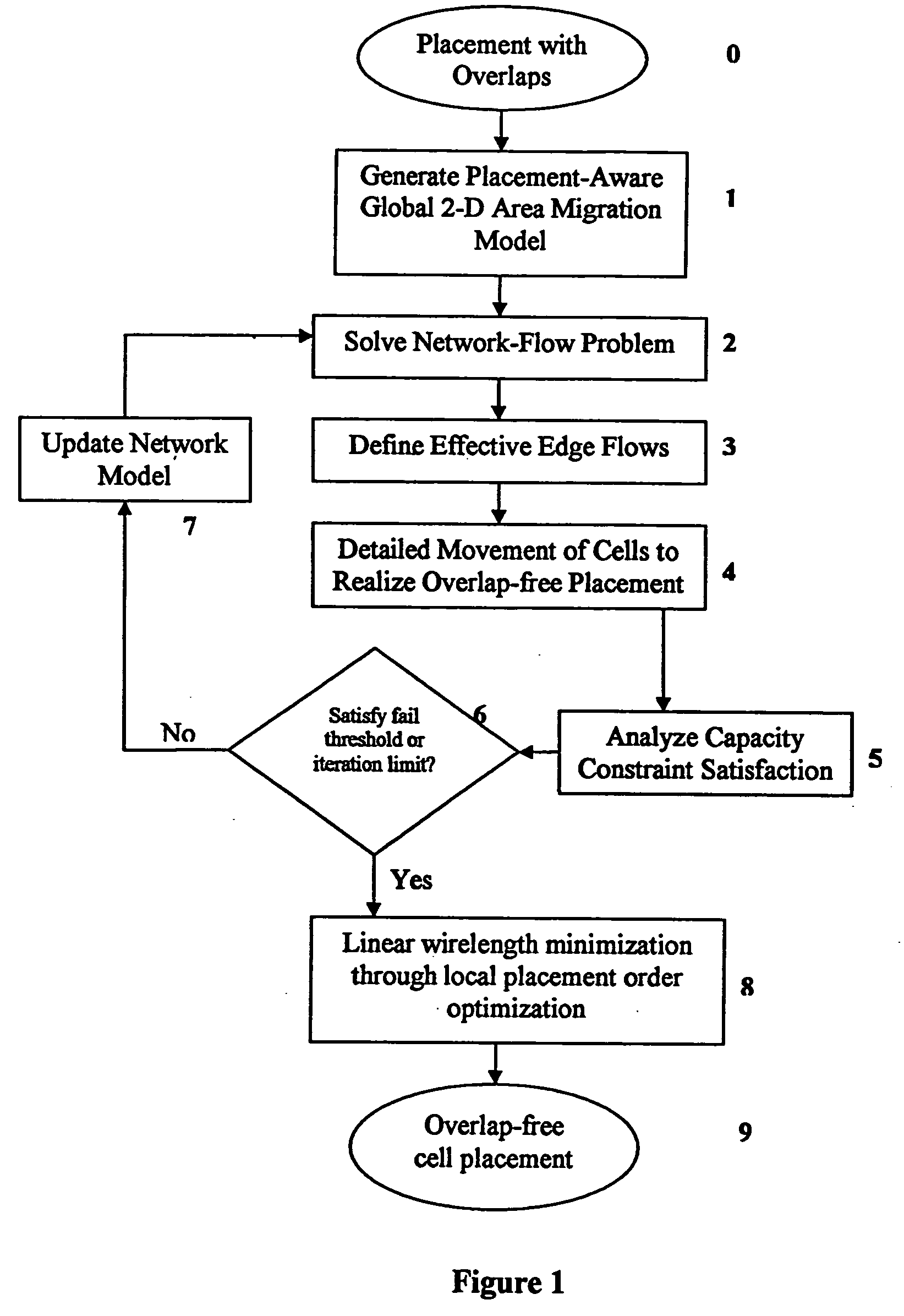
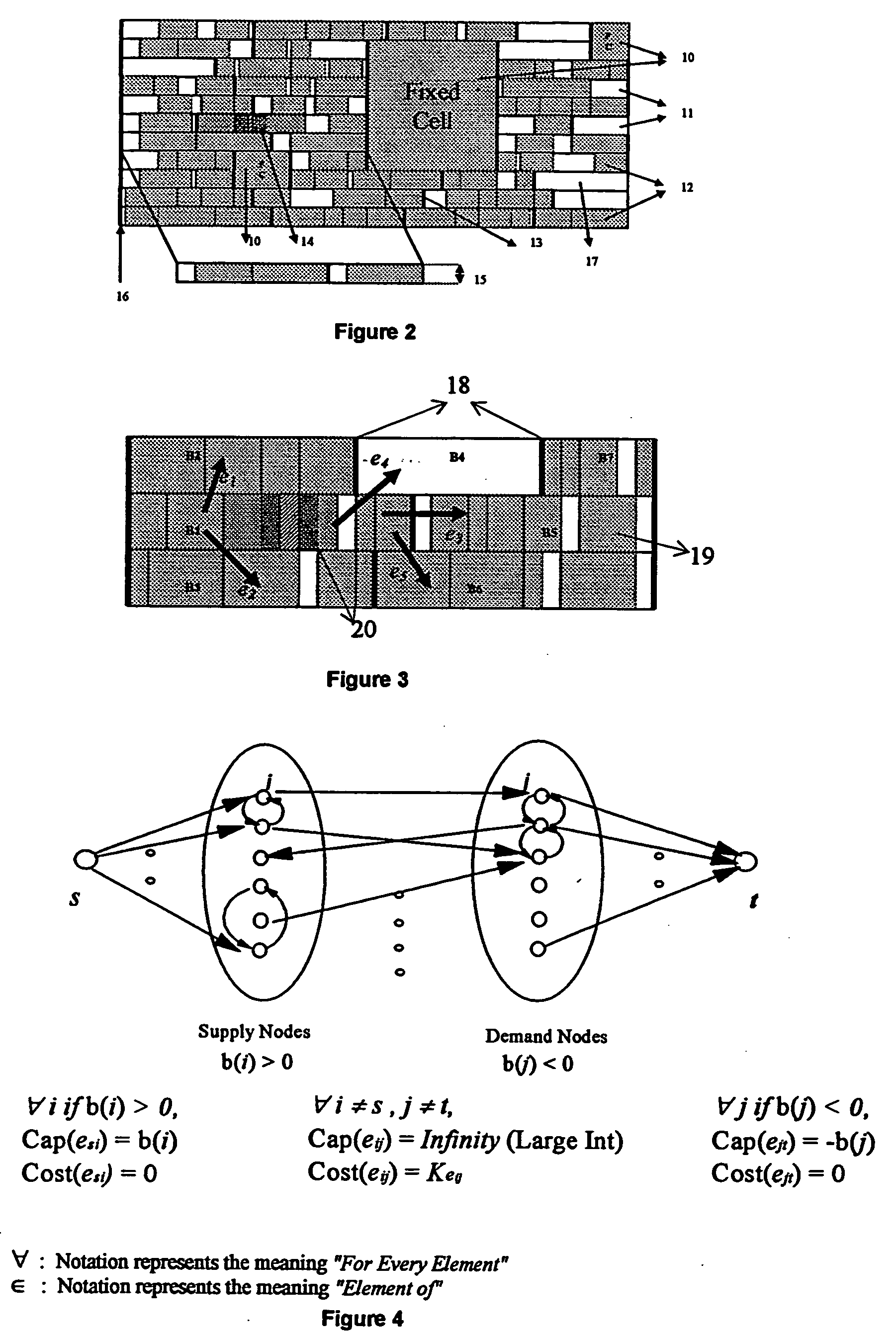
A method for resolving overlaps in the cell placement (placement legalization) during the physical design phase of an integrated chip design is described. This problem arises in several contexts within the physical design automation area including global and detailed placement, physical synthesis, and ECO (Engineering Change Order) mode for timing / design closure The method involves capturing a view of a given placement, solving a global two-dimensional area migration model and locally perturbing the cells to resolve the overlaps with minimal changes to the given placement. The method first captures a two-dimensional view of the placement including blockage-space, free-space and the given location of cells by defining physical regions. The desired global area migration across the physical regions of the placement image is determined such that it satisfies area capacity-demand constraints. The method also provides moving the cells between physical regions along previously computed directions of migration to minimize the movement cost. Also provided is an approximate method to model the movement of multi-row high cells.
Owner:IBM CORP
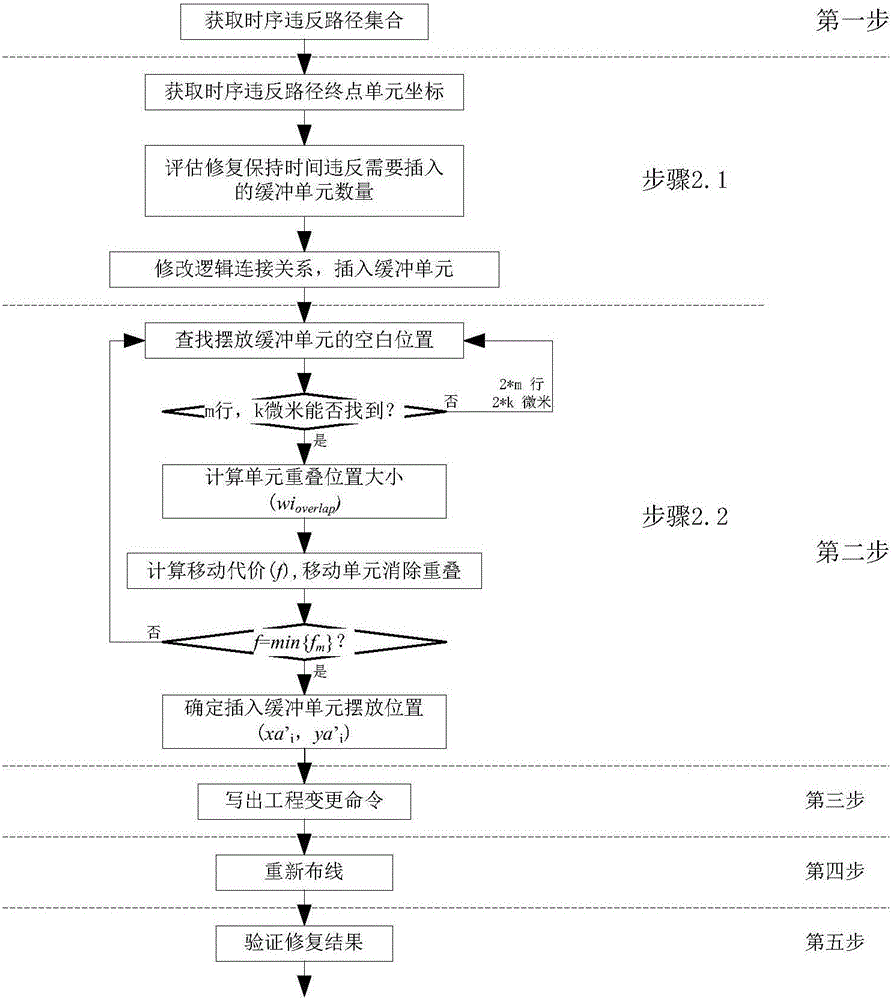
Repairing method of retention time violation
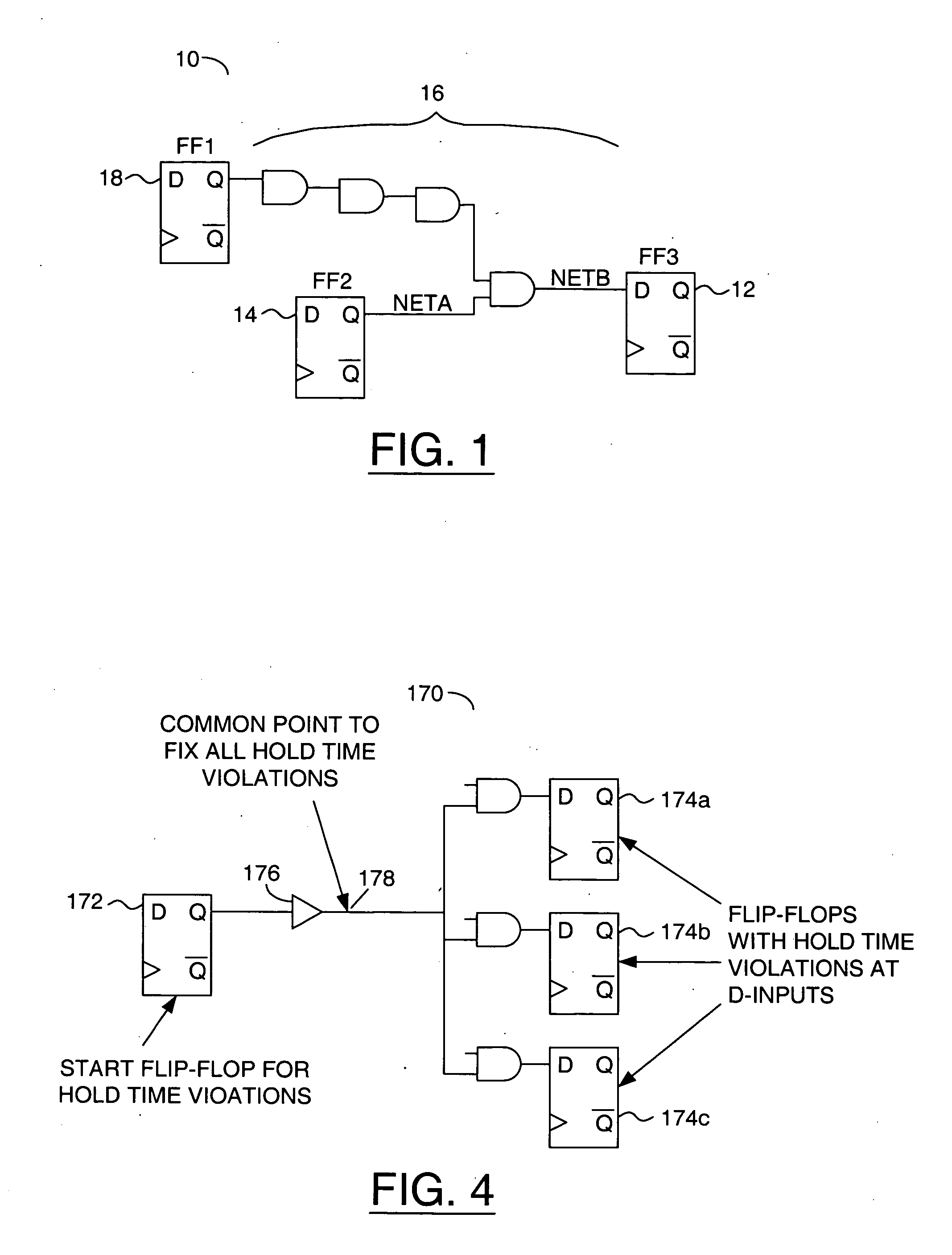
ActiveCN105787213ARemove overlapFix hold time violationSpecial data processing applicationsStatic timing analysisRetention time
The invention relates to a repairing method of retention time violation.The method includes: acquiring the starting point, ending point and violation value of a path with the retention time violation from the result of static time sequence analysis; secondly, selecting the ending point of the path with the retention time violation as the to-be-inserted node of a repairing unit, and inserting one buffer unit or delay unit at the to-be-inserted node during each repairing so as to reduce the influence of the repairing unit insertion on the time sequence of other paths; thirdly, search the physical position for unit placing near the node with the inserted repairing unit, releasing the space required by the repairing unit through the position of the original unit in mobile design, and setting a target function to allow the total cost of the mobile unit to be the lowest so as to achieve low disturbance to the original design; fourthly, generating corresponding repairing logic, placing units and the engineering change order of mobile unit positions; fifthly, rewiring the connection relation with the logic being modified, extracting parasitic parameters, and performing static time sequence analysis to guarantee that the retention time is repaired completely.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
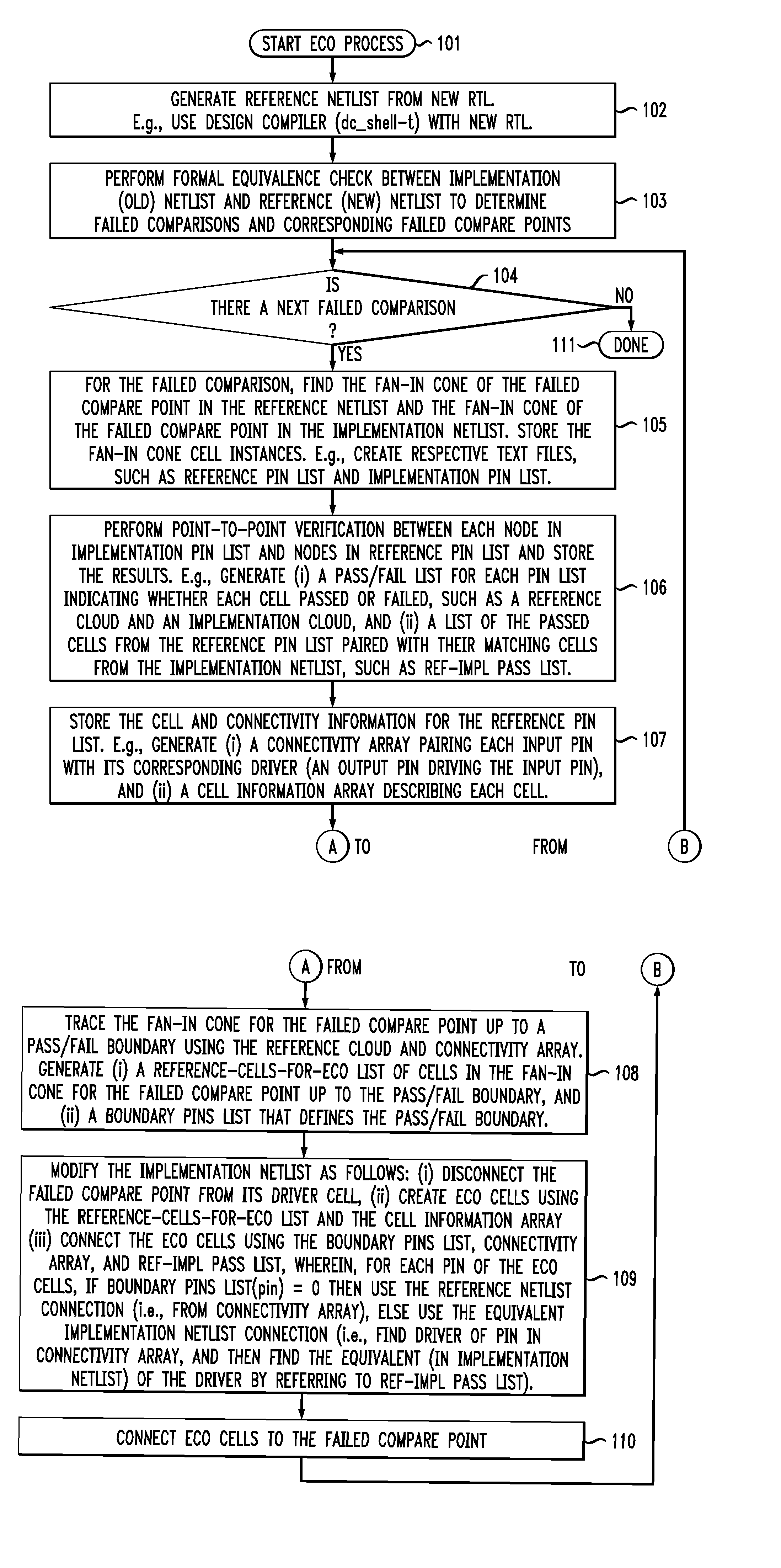
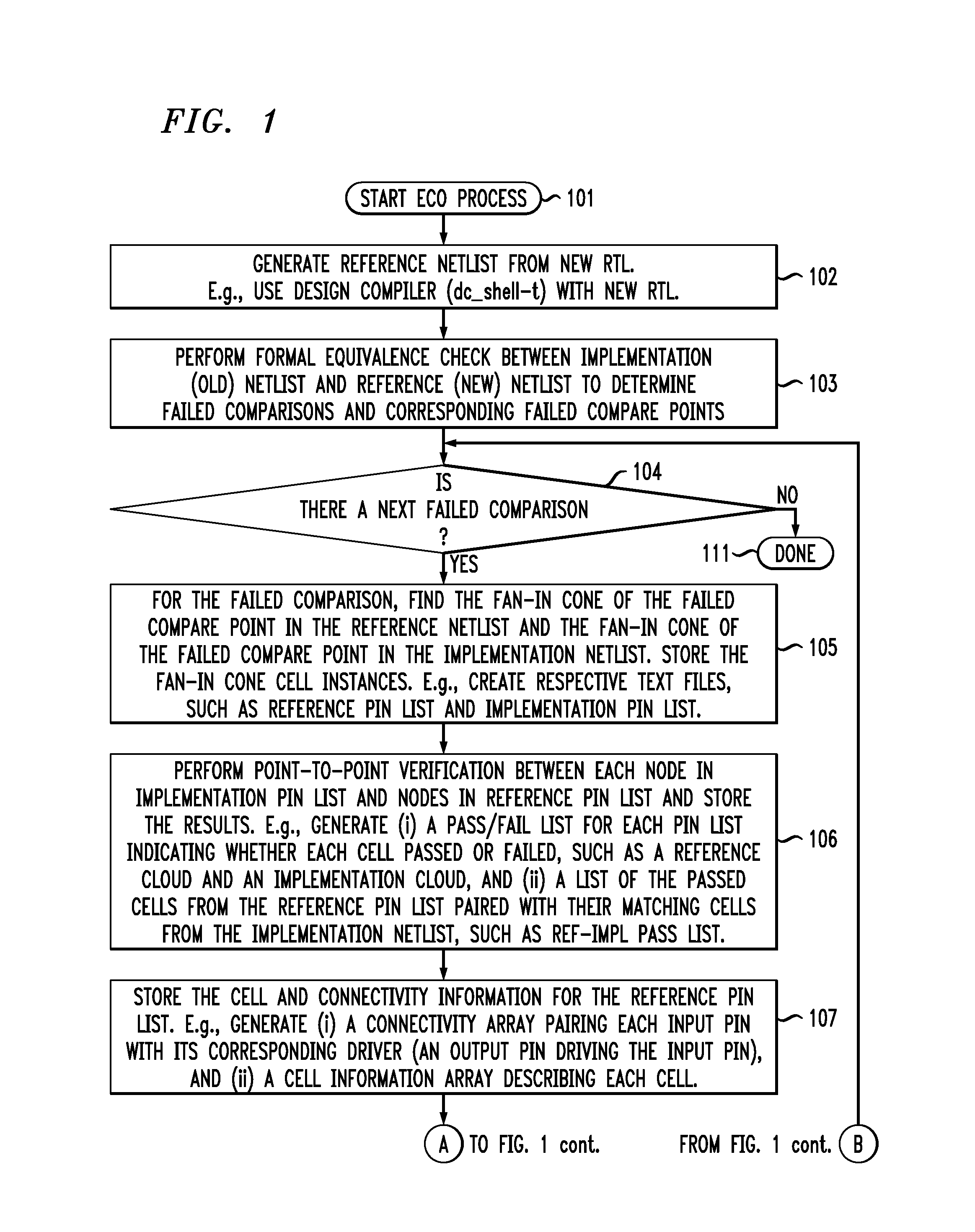
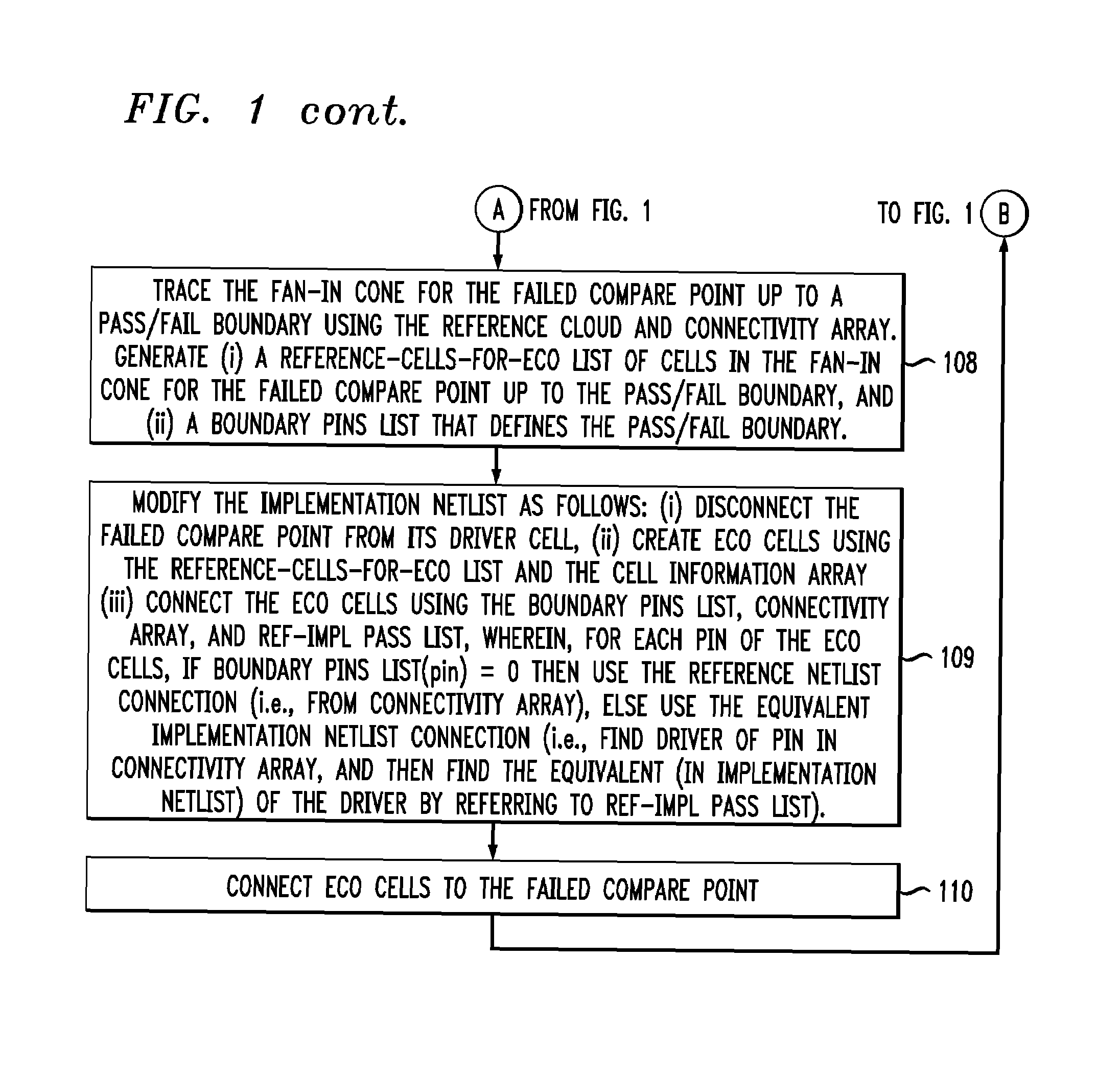
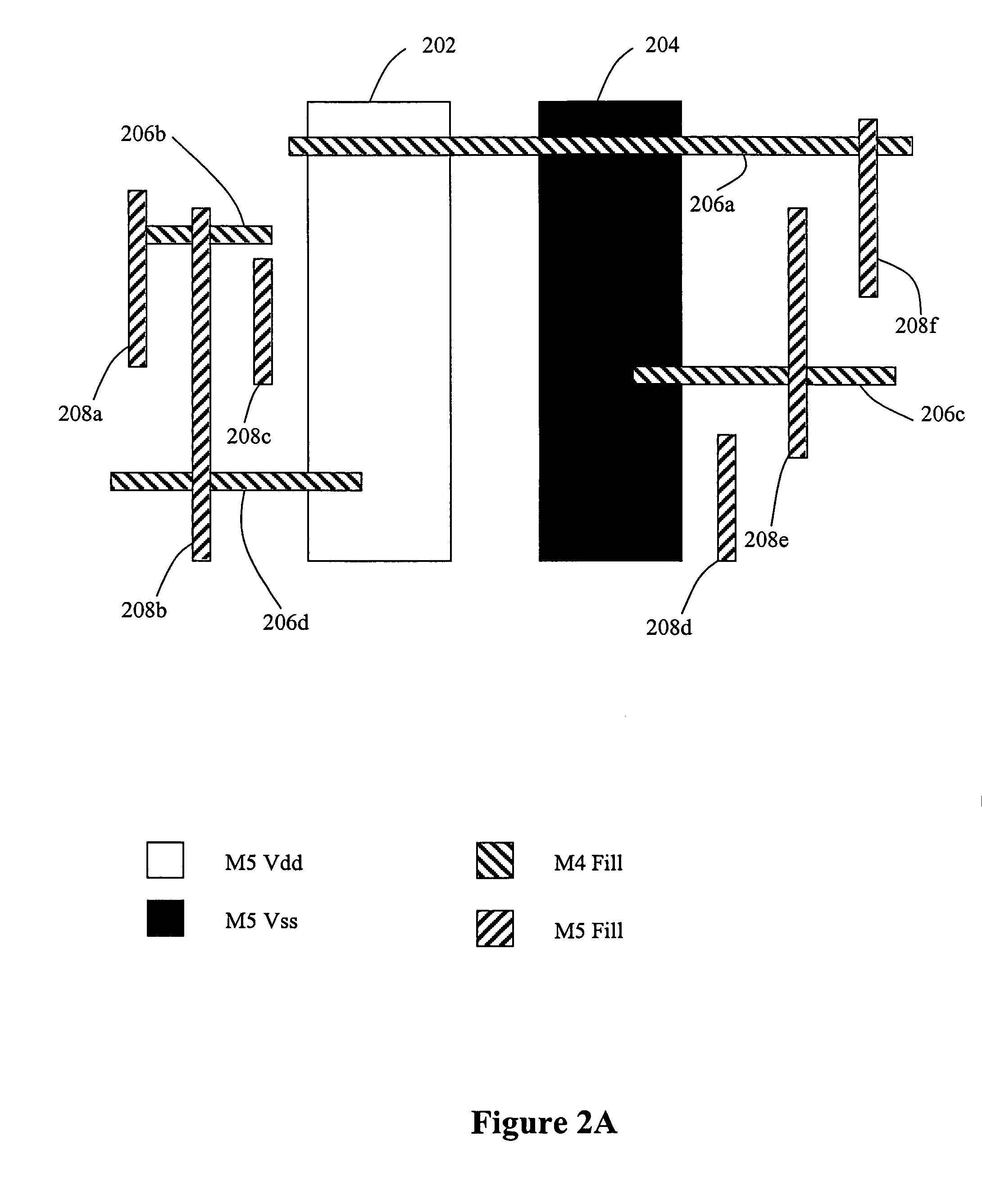
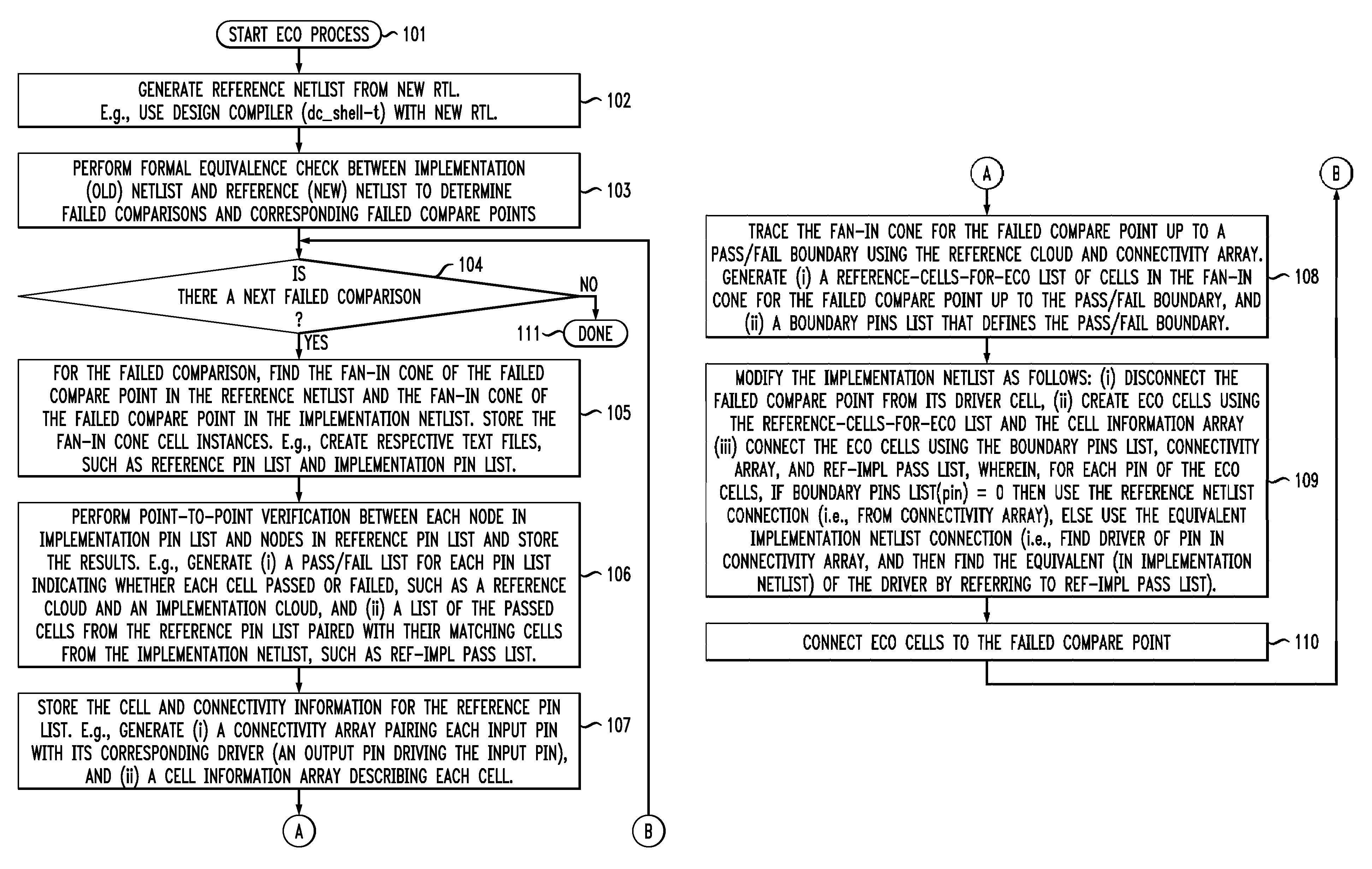
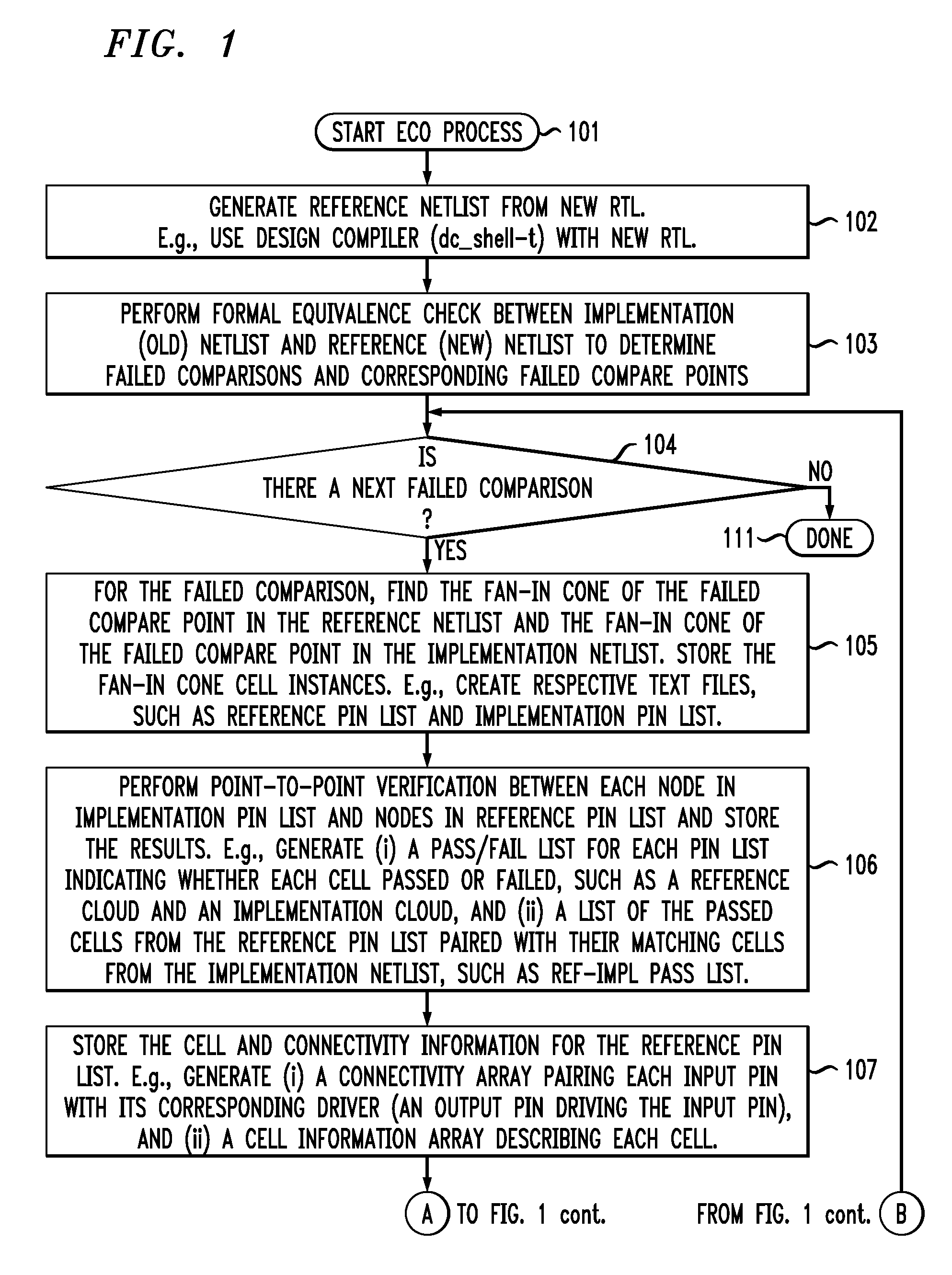
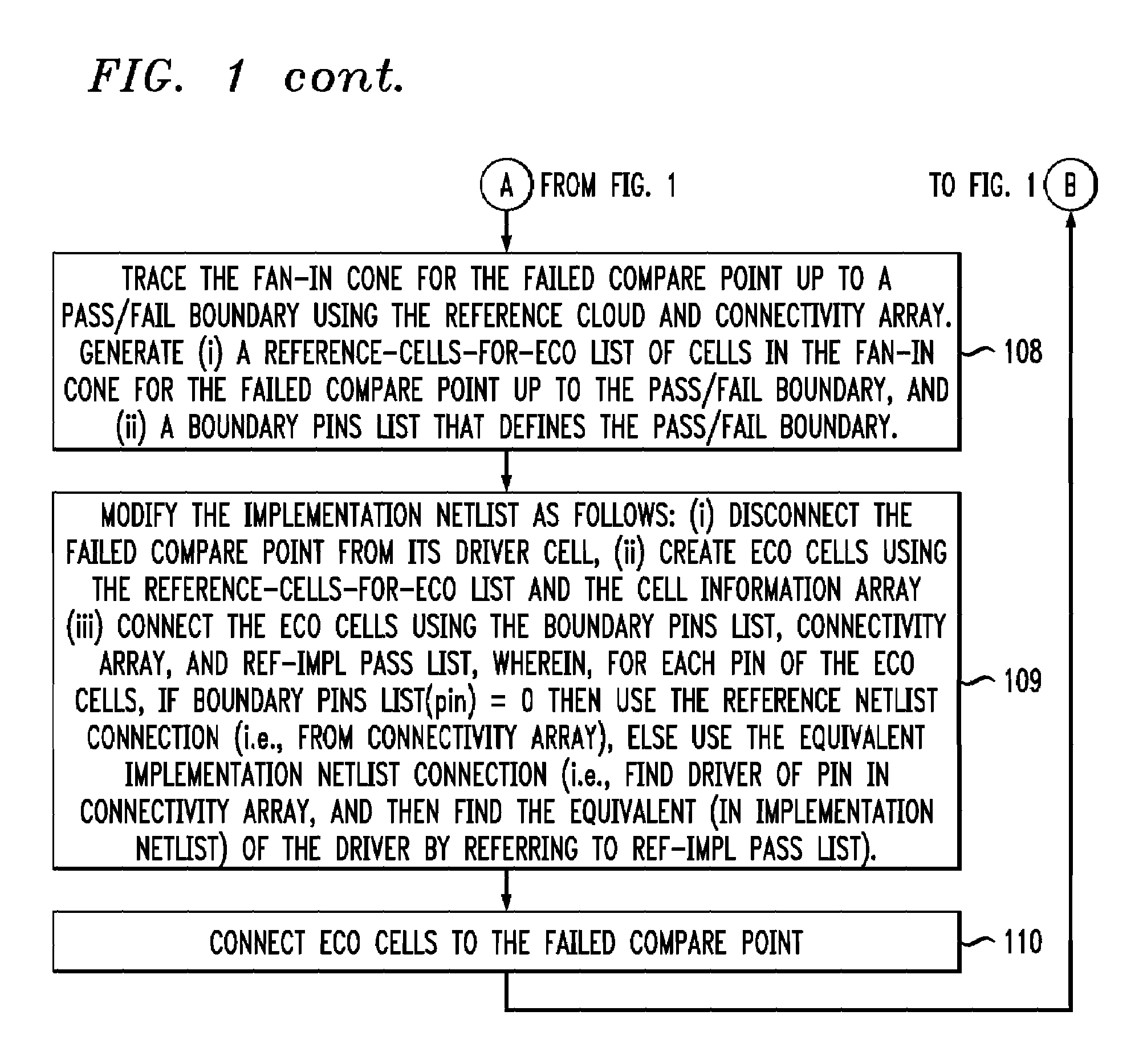
Command-language-based functional engineering change order (ECO) implementation
InactiveUS20070271537A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureCommand language
In one implementation, the invention can be a computer-implemented method for generating an engineering change order (ECO) netlist for an integrated circuit (IC). The method includes performing a formal equivalence check between an implementation netlist and a reference netlist to identify one or more corresponding failed compare points in the implementation and reference netlists. The method further includes, for at least one failed comparison: (i) performing equivalence verifications based on fan-in cones for the failed compare points, to generate pin pass / fail information, (ii) tracing the fan-in cone for the reference netlist to generate ECO pin and cell information, and (iii) modifying the implementation netlist, based on (1) the pin pass / fail information, (2) cell connectivity information, (3) cell description information, and (4) the ECO pin and cell information, to generate the ECO netlist by adding one or more new ECO cells to the implementation netlist and appropriately connecting them.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
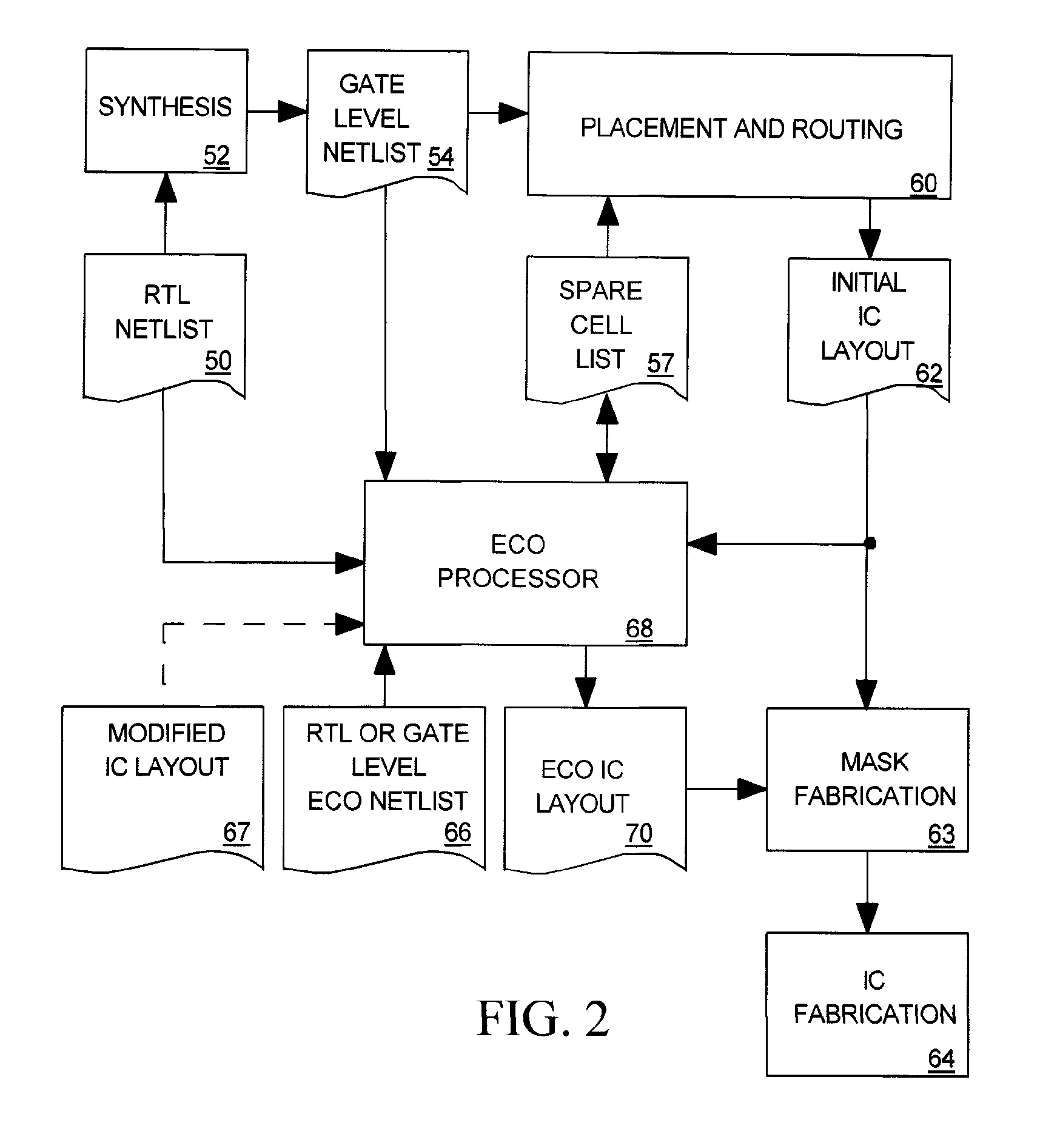
Spatially aware drive strength dependent die size independent combinatorial spare cell insertion manner and related system and method
InactiveUS20080237644A1Raise countIncrease design areaSolid-state devicesComputer aided designReserve CellChip size
A design method for an integrated circuit adds spare cells in a System-on-Chip to allow for Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) to be performed at a later stage in the design. This method can be used to provide a second version of the chip having minimal alterations performed in a short cycle time. The spare cells can be divided into combinational and sequential cells. There is an optimum spread of combinational cells in the design for post placement repairs of the chip with just metal layer changes. The method takes into account the drive strength of the spare cells as the main factor in their placement on the chip.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
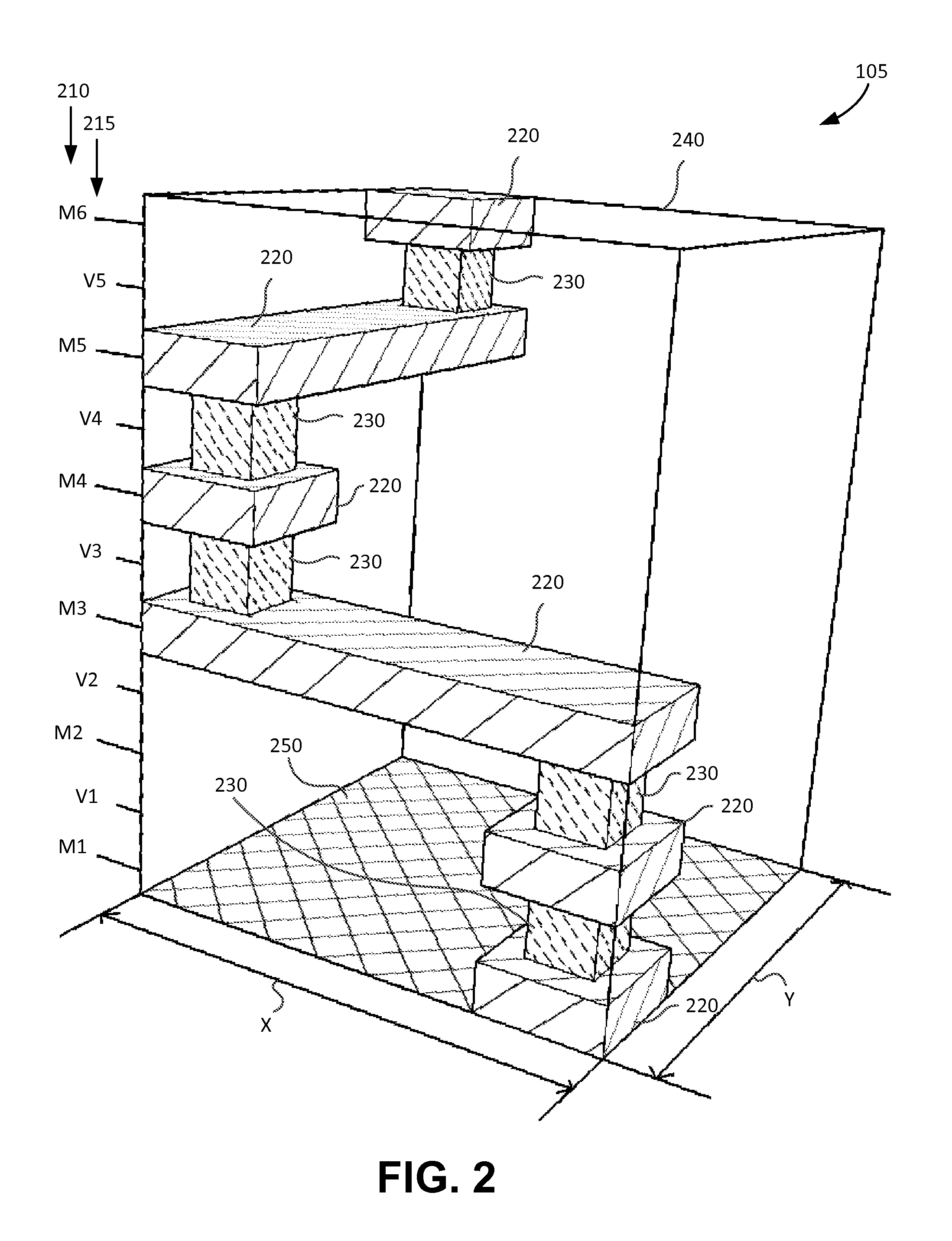
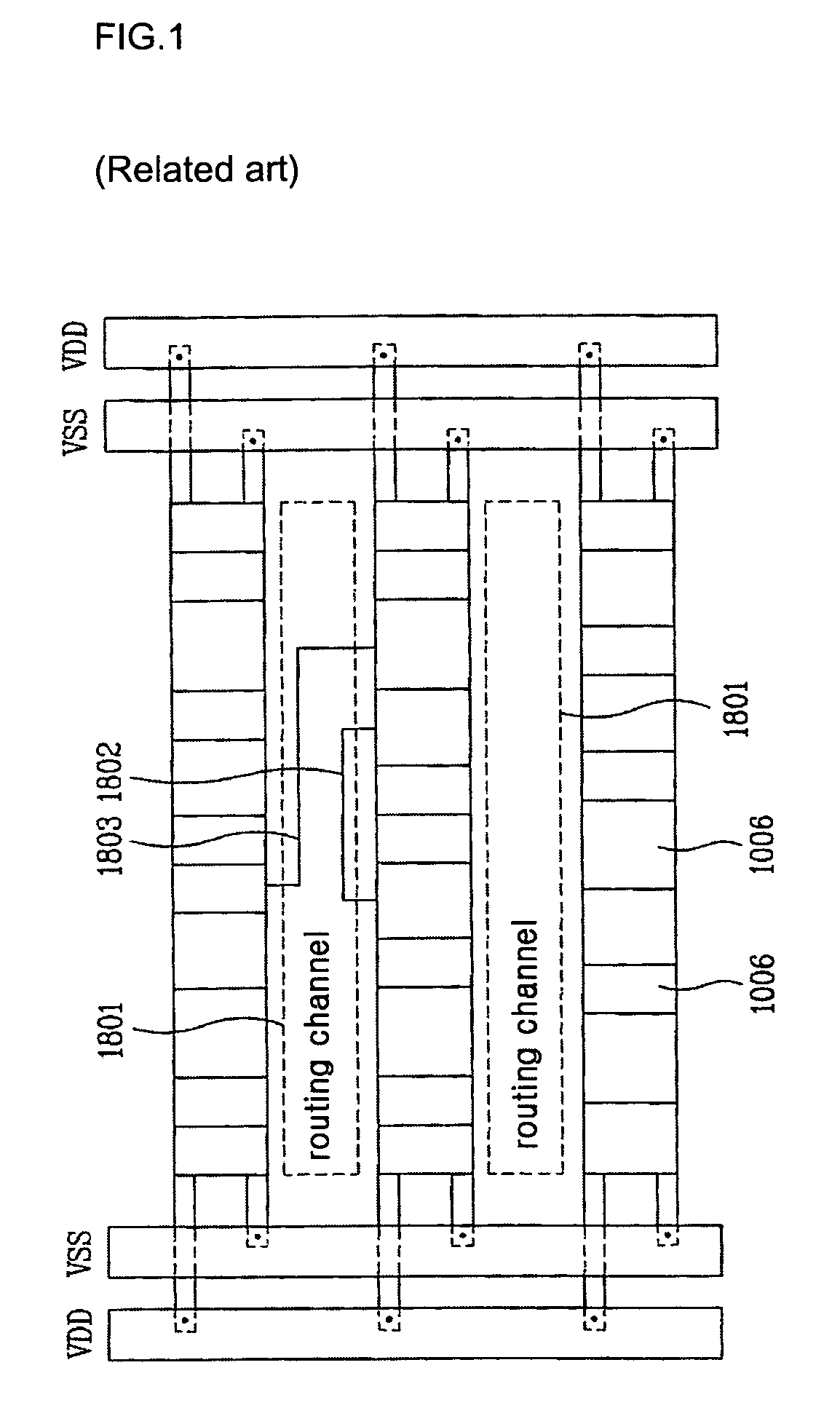
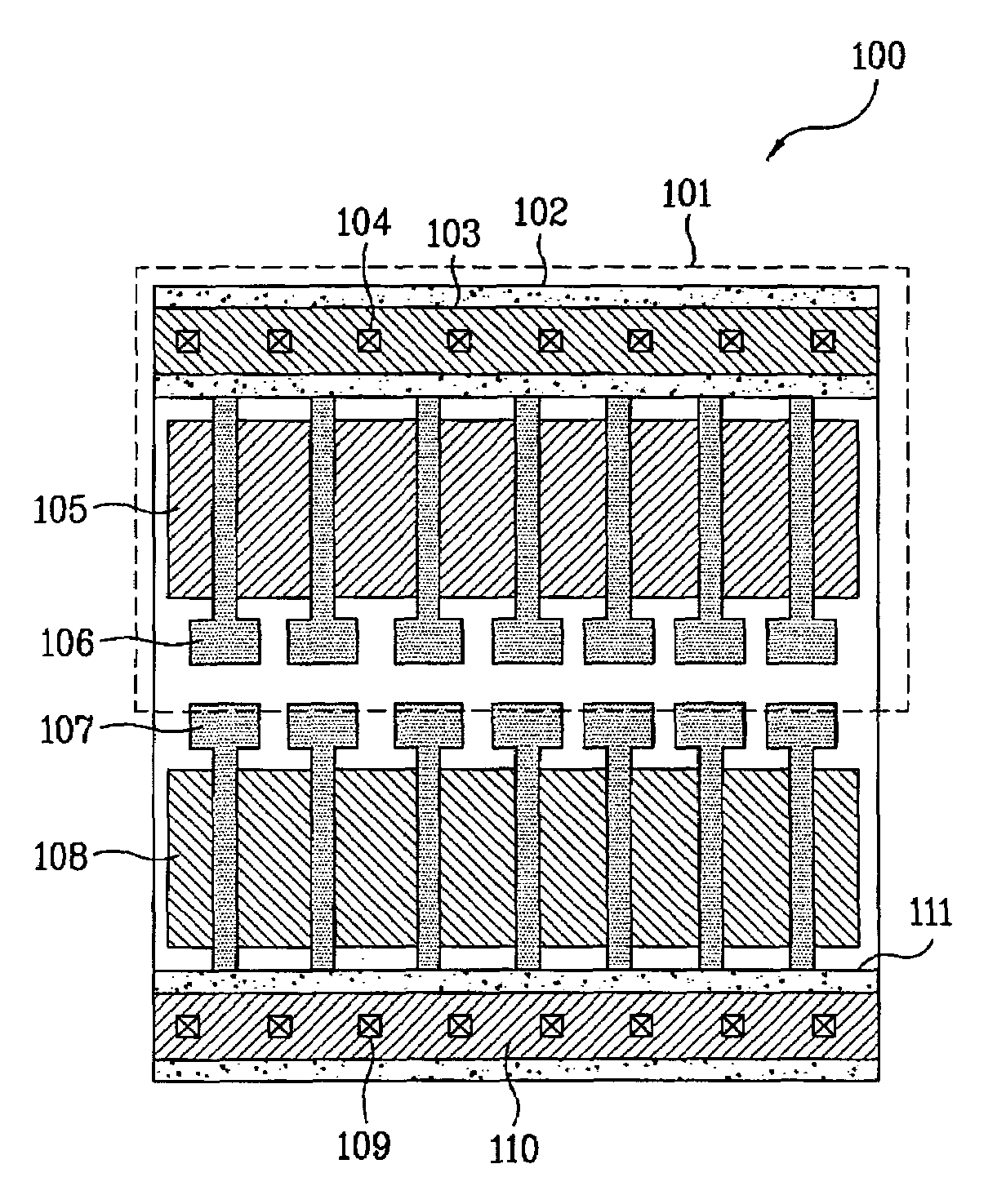
Architecture of Spare Wiring Structures for Improved Engineering Change Orders
InactiveUS20140332979A1Reduce complexitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineering change orderIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit includes a substrate having a plurality of electronic devices, a plurality of interconnect layers disposed on one or both sides of the substrate, and a plurality of active electrically conductive interconnect layer structures. The plurality of interconnect layers include horizontal interconnect and vertical-interconnect-access (VIA) layers. The plurality of active electrically conductive interconnect layer structures are disposed on at least one of the plurality of interconnect layers and electrically coupled with at least one of the plurality of electronic devices. The integrated circuit also includes a plurality of spare electrically conductive interconnect layer structures disposed on at least one of the plurality of interconnect layers and electrically isolated from the plurality of active electrically conductive interconnect layer structures.
Owner:BLACKCOMB DESIGN AUTOMATION
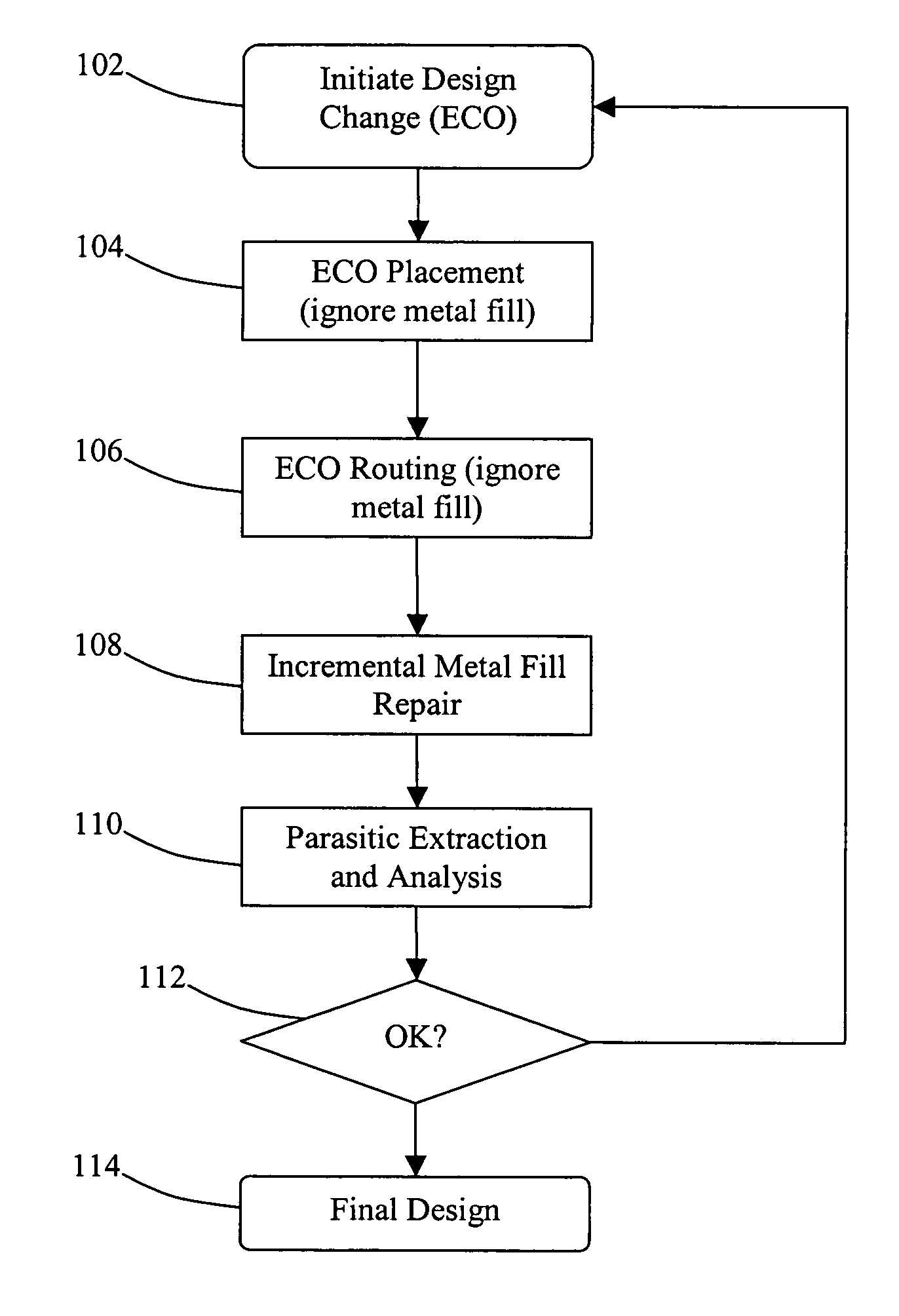
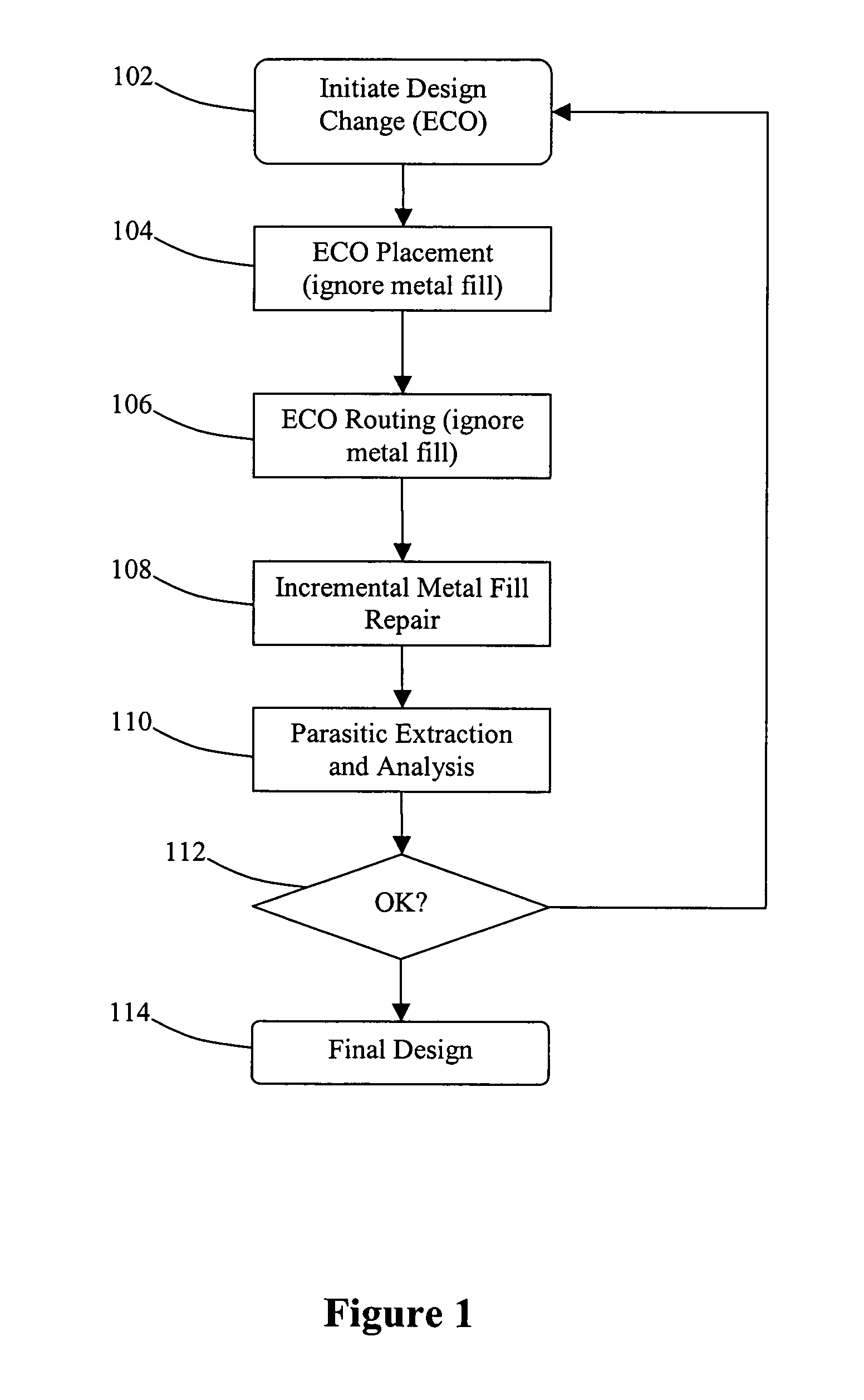
Method and system for implementing metal fill
ActiveUS7661078B1Reducing local step heightReduce yieldDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designEngineeringImproved method
Disclosed is an improved method and system for implementing metal fill for an integrated circuit design. When an engineering change order is implemented, the existing dummy metal fill geometries are initially ignored when modifying the layout, even if this results in shorts and / or other DRC violations. Once the ECO changes have been implemented, those violations caused by interaction between the changes and the metal fill are repaired afterwards.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Command-language-based functional engineering change order (ECO) implementation
InactiveUS7644382B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureCommand language
In one implementation, the invention can be a computer-implemented method for generating an engineering change order (ECO) netlist for an integrated circuit (IC). The method includes performing a formal equivalence check between an implementation netlist and a reference netlist to identify one or more corresponding failed compare points in the implementation and reference netlists. The method further includes, for at least one failed comparison: (i) performing equivalence verifications based on fan-in cones for the failed compare points, to generate pin pass / fail information, (ii) tracing the fan-in cone for the reference netlist to generate ECO pin and cell information, and (iii) modifying the implementation netlist, based on (1) the pin pass / fail information, (2) cell connectivity information, (3) cell description information, and (4) the ECO pin and cell information, to generate the ECO netlist by adding one or more new ECO cells to the implementation netlist and appropriately connecting them.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
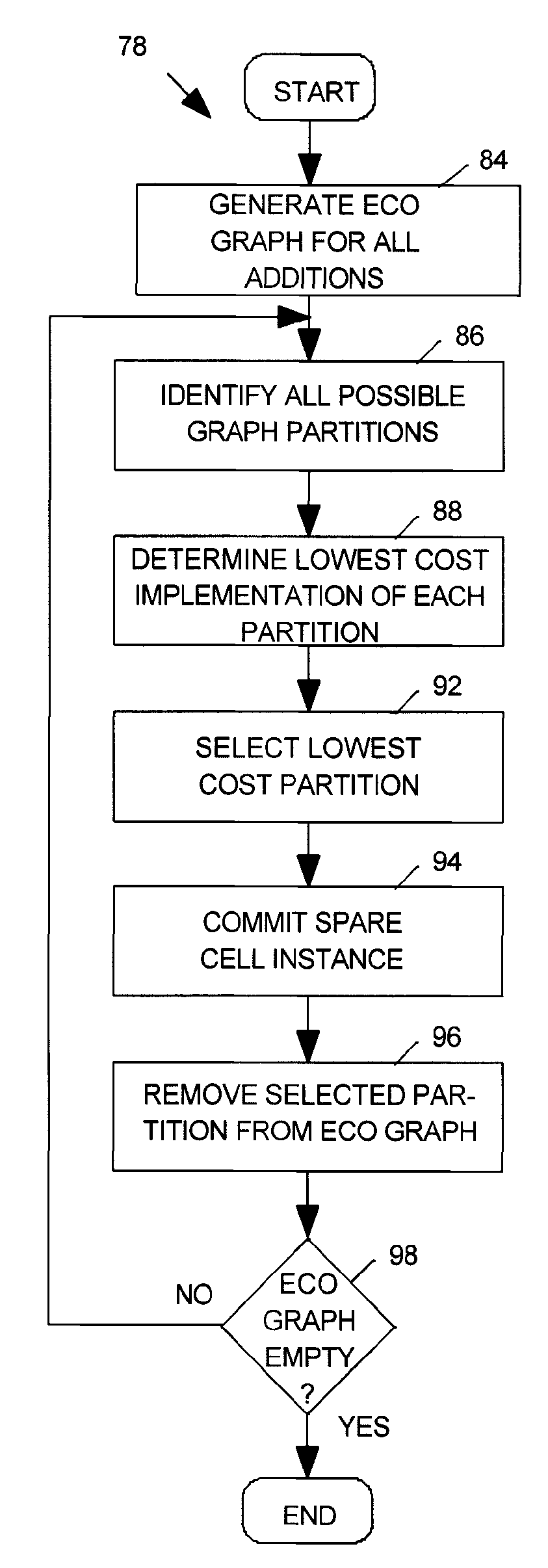
Engineering change order scenario manager
InactiveUS20060026546A1Reduce in quantityComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designEngineering change orderCircuit design
A method and apparatus for managing a plurality of change orders for a circuit design is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) receiving the change orders generated manually by a user, (B) analyzing the circuit design with all of the change orders implemented and (C) generating a report suitable for the user to understand based on a result of the analyzing.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
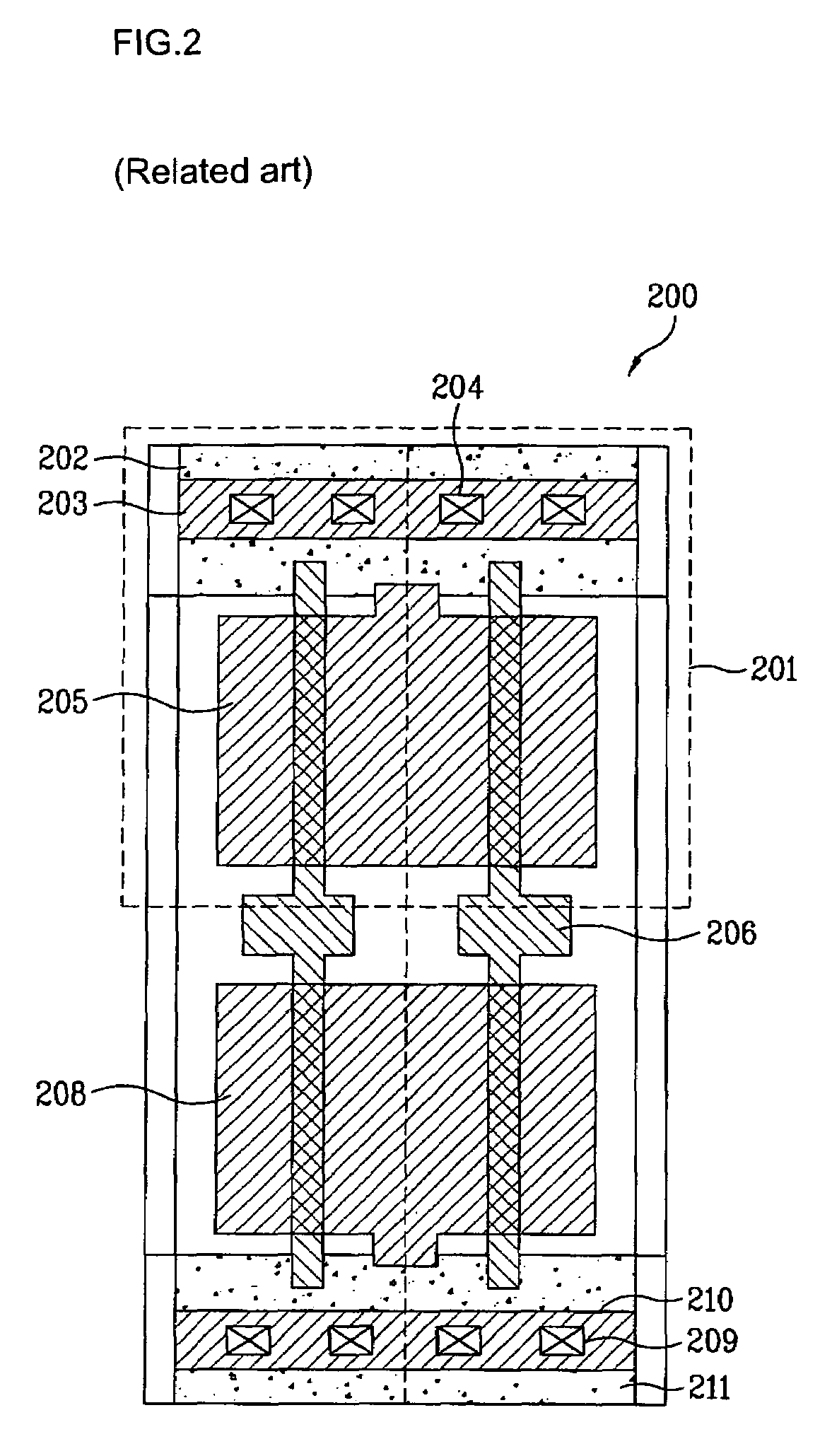
Base cell for engineering change order (ECO) implementation
ActiveUS7965107B2Easy to implementReliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering change order
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
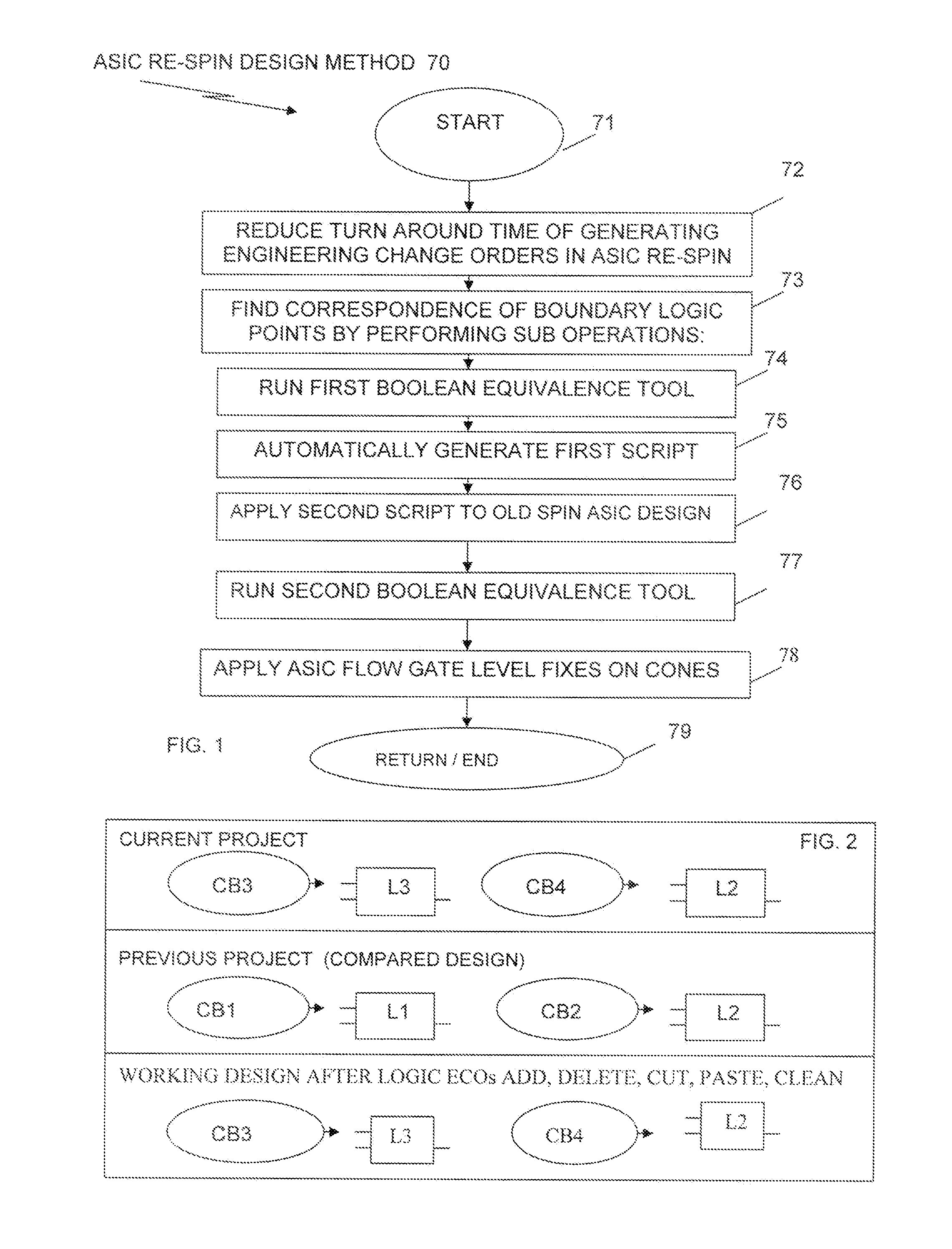
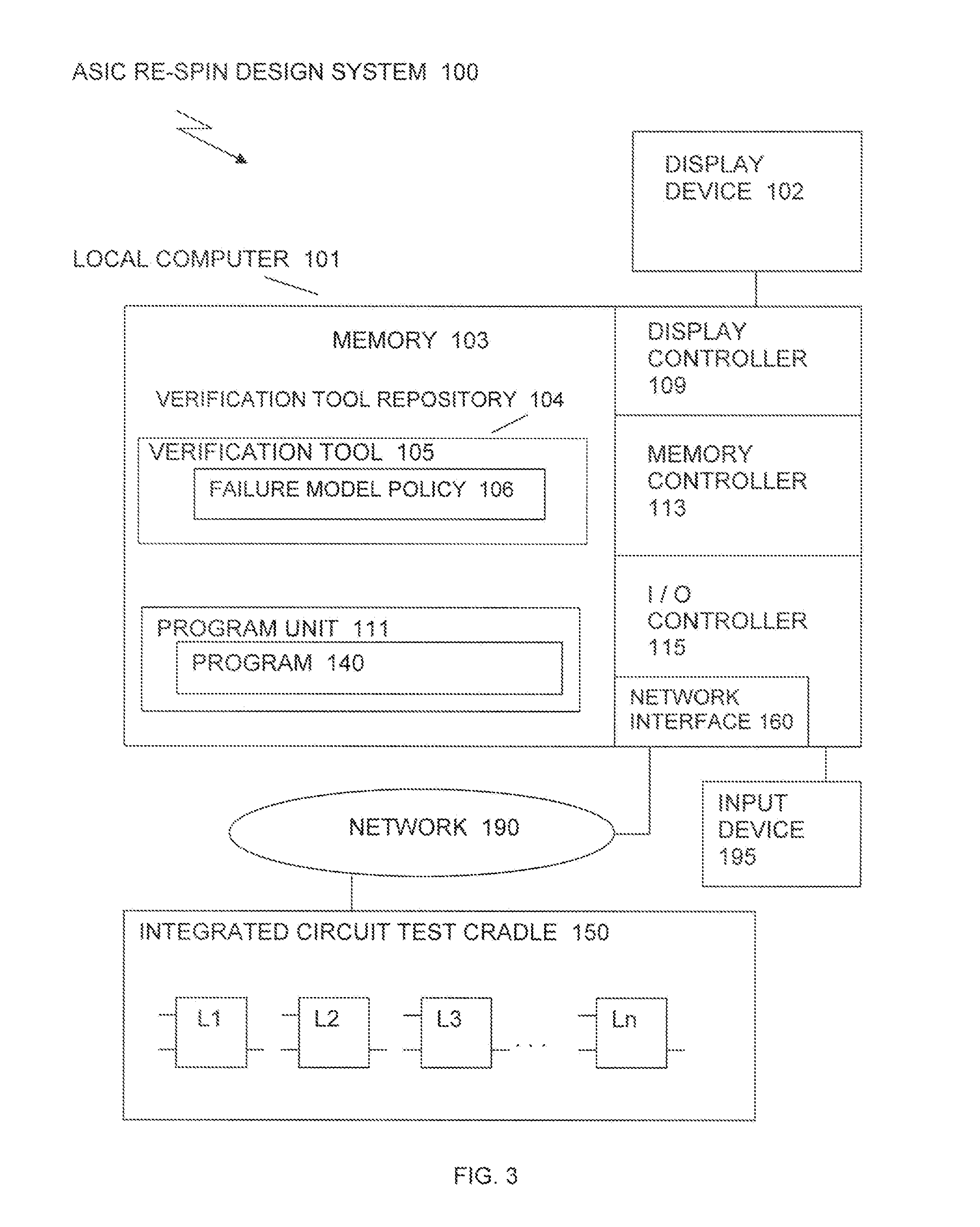
Method and system for reducing turn around time of complicated engineering change orders and asic design reutilization
InactiveUS20090178015A1Reduce turnaround timeTest may passCAD circuit designProgram controlEngineering change orderLogic gate
Reducing turn around time of engineering change orders in ASIC re-spin design includes finding, on the fly, all corresponding boundary points of storage gate elements indicated by engineering change orders to be either added, deleted or renamed. Boolean equivalence tools are used between an old spin ASIC design and a new ASIC design netlist, as well as between the new ASIC design netlist and a new re-spin ASIC design to obtain failing boundary storage gate elements and perform one or more of adding, deleting or modifying or renaming all failing boundary storage gate elements, so they pass correspondence tests. Engineering change order scripts are automatically generated to indicate which storage logic gate elements are to be added, deleted or modified and the scripts are applied to the old ASIC design to obtain the new re-spin ASIC design, after which ASIC flow gate level fixes are applied to synthesized storage gate elements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
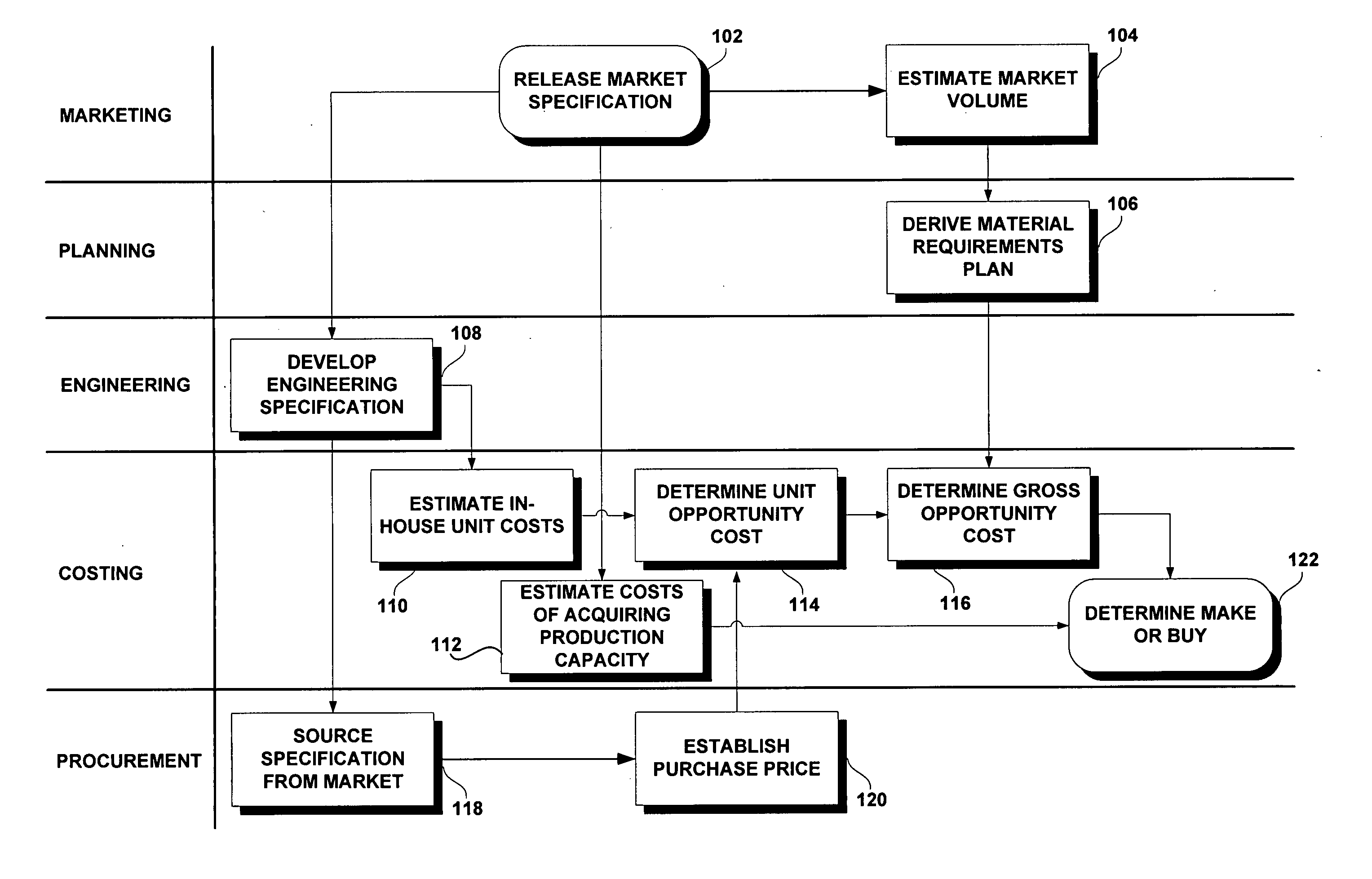
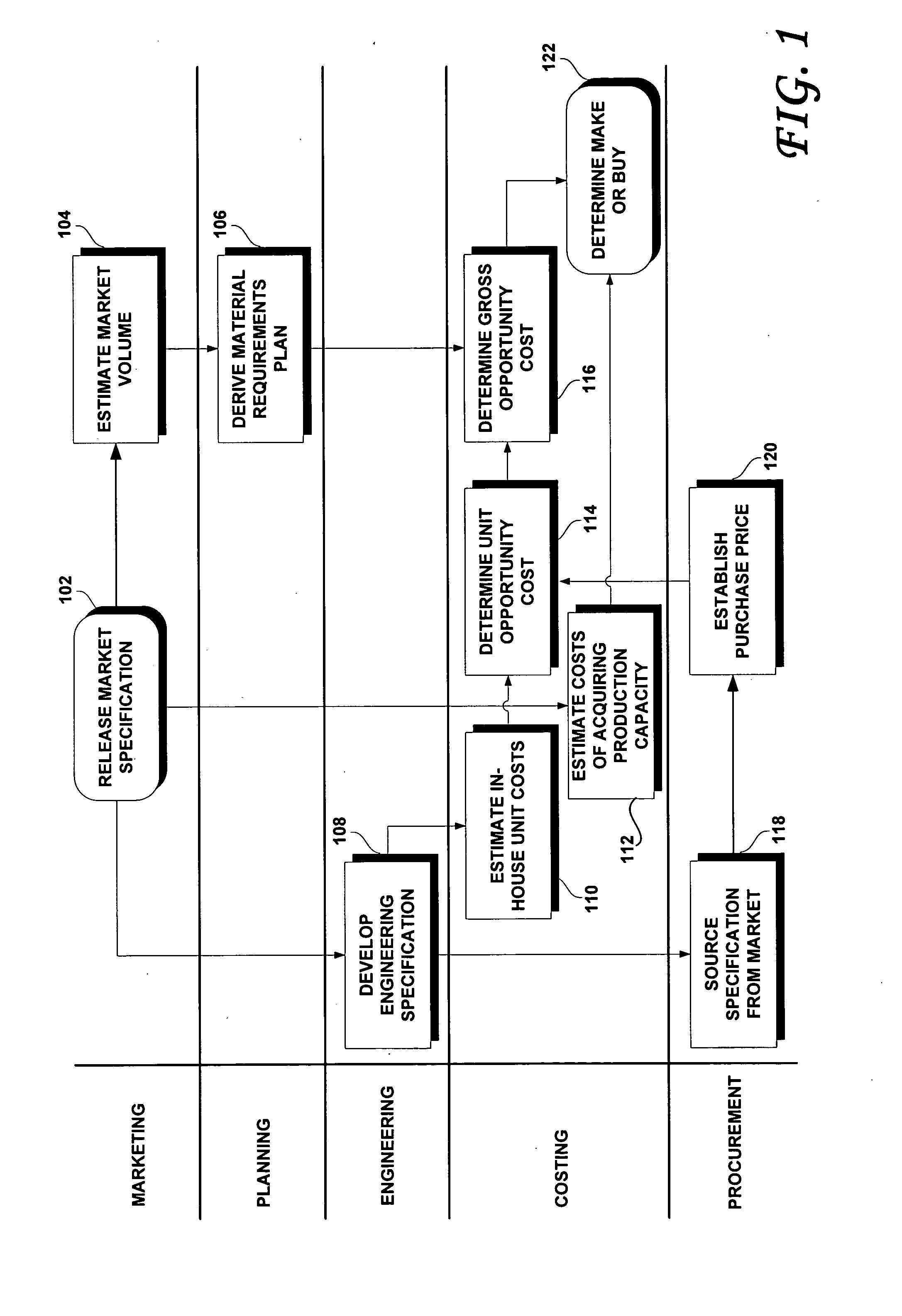
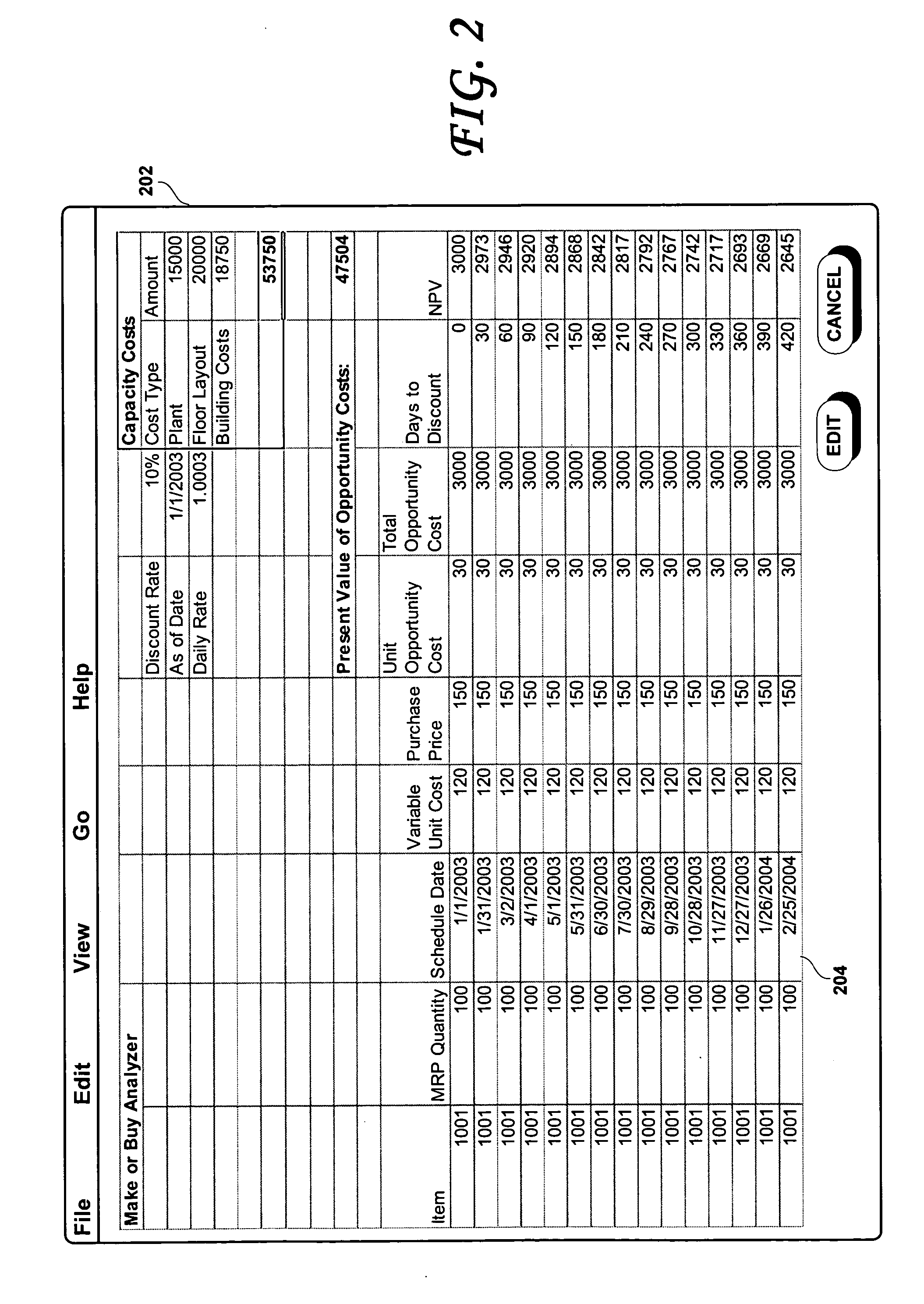
Methods and systems for investment appraisal for manufacturing decisions
ActiveUS20050228759A1Buying/selling/leasing transactionsElectric/magnetic computingEngineering change orderComputer science
A computer implemented method for deciding and justifying make or buy decisions in which it is determined whether to make an item in-house or to buy the item from outside suppliers. Also disclosed are computer implemented methods of determining and justifying an optimal timing to implement an engineering change order in which a more expensive item is replaced with a less expensive item.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
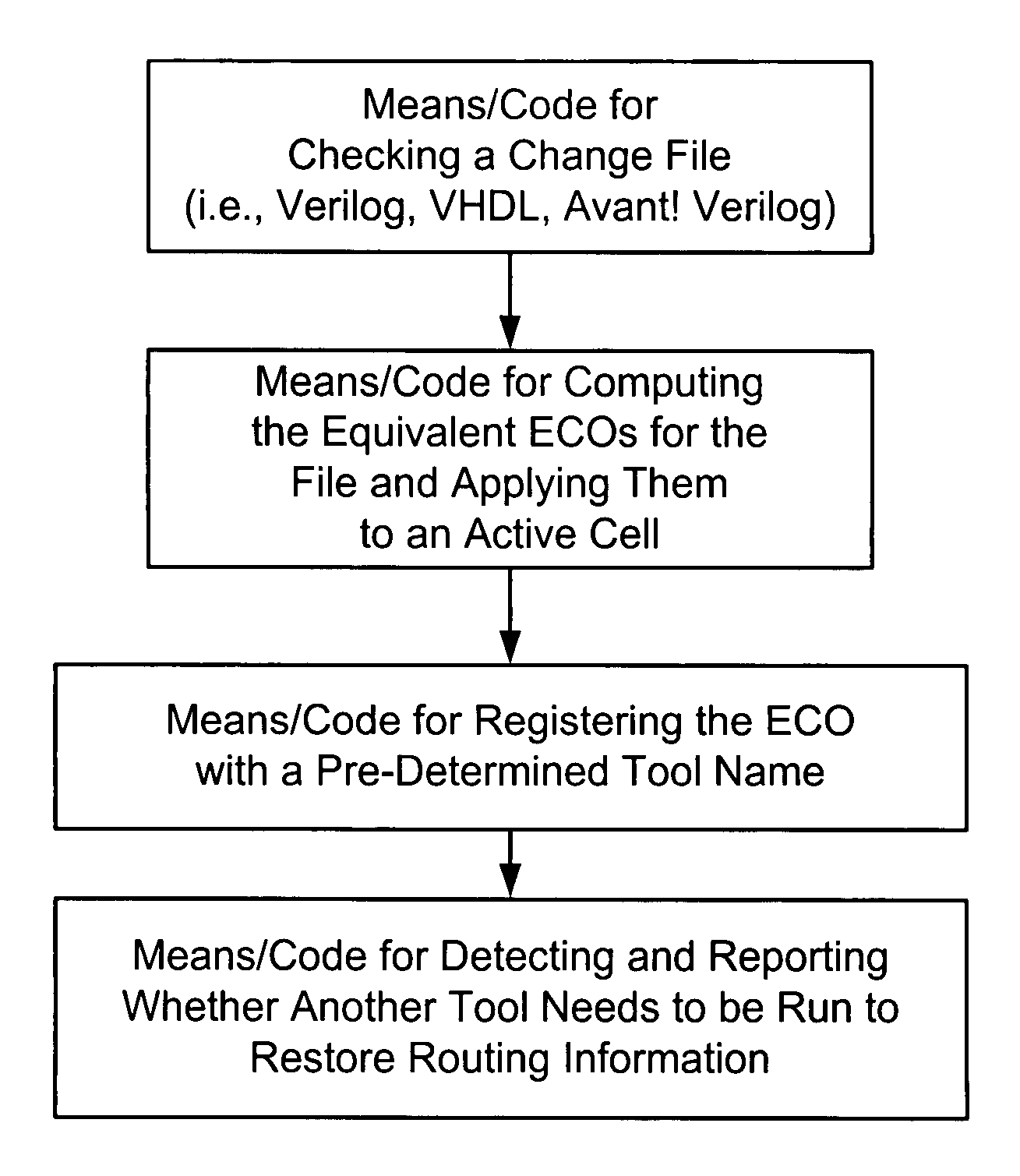
Method and apparatus for implementing engineering change orders
ActiveUS7007248B2Easy to learnEasy maintenanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsApplication engineeringActive cell
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Engineering change order (ECO) cell architecture and implementation
InactiveUS20190138682A1Easy to modifyConvenient power supplySolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringEngineering change order
Engineering change order (ECO) cell architecture and implementation is disclosed. In particular, exemplary aspects disclosed herein provide a generic cell structure that may be readily modified to effect an ECO without requiring extensive mask changes beyond one or two levels including the level in which the cell is located. Further, this generic cell structure can be “parked” fairly deep in the manufacturing process, such as in the middle-end-of-line (MEOL), so that fewer changes to other masks are needed in the event of a change. The generic cell may further act as a filler cell for pattern density. Inclusion of such a generic cell in a circuit design can help alleviate the need for extensive mask redesign and accompanying delays in the production of finished silicon.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
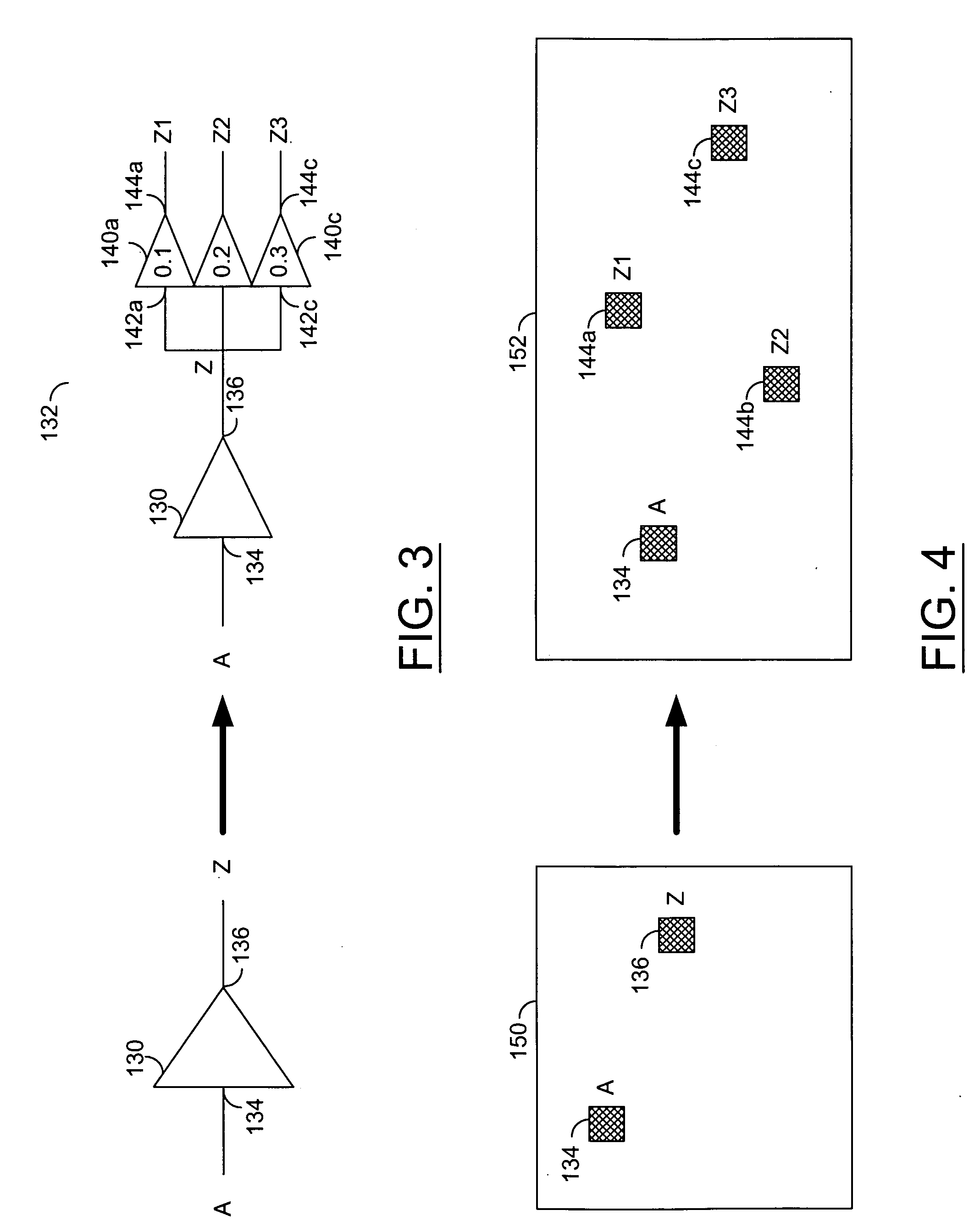
Engineering change order cell and method for arranging and routing the same
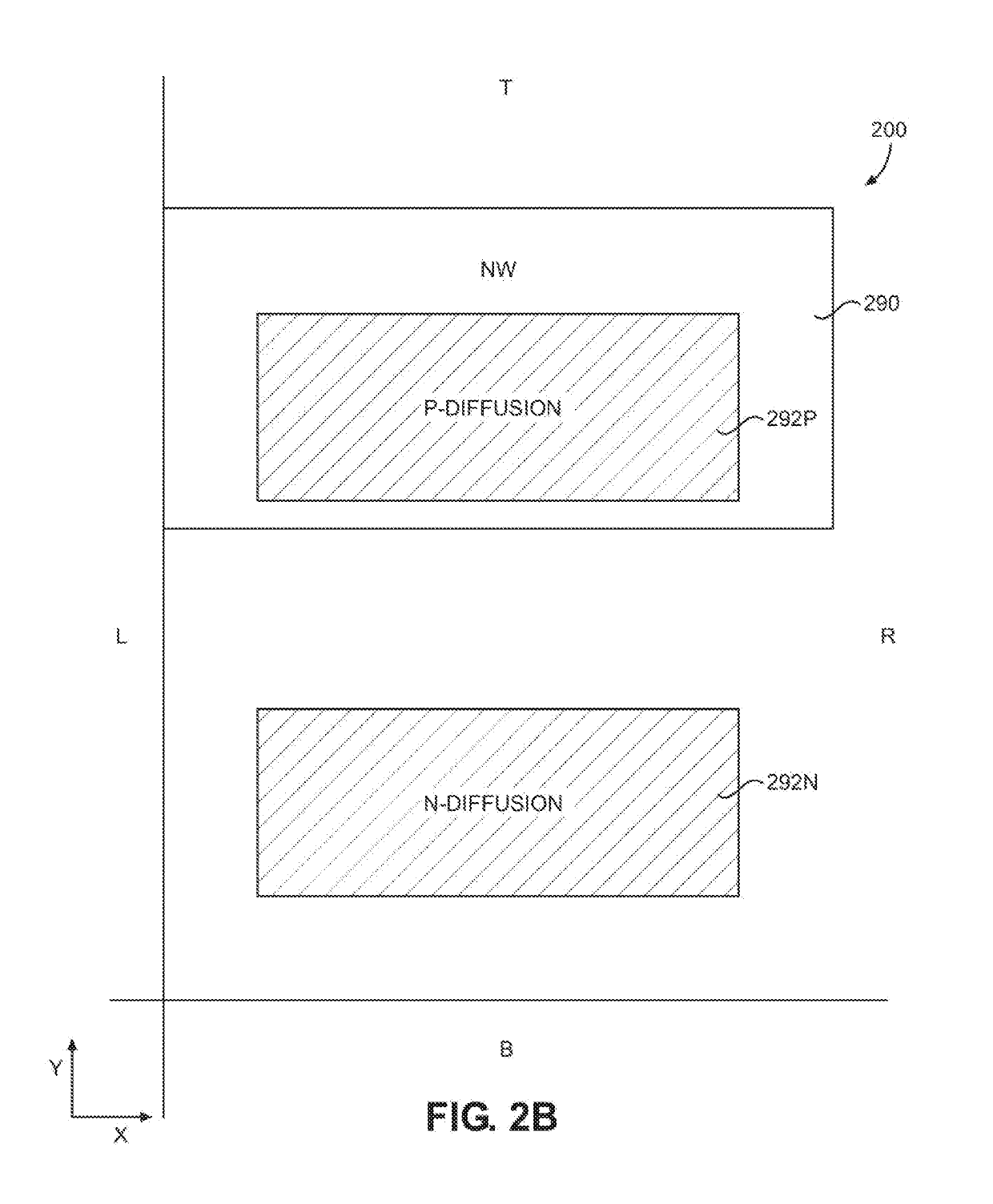
InactiveUS20070157151A1Lower junction capacitanceObtain flexibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineering change orderDiffusion layer
There is provided an engineering change order (ECO) cell, which includes: a function circuit including at least one PMOS transistor with a P-diffusion layer and a first poly gate, at least one NMOS transistor with an N-diffusion layer and a second poly gate; a first power layer supplying the at least one PMOS transistor with a first power voltage; and a second power layer supplying the at least one NMOS transistor with a second power voltage. The first poly gate of the PMOS transistor is isolated from the second poly gate of the NMOS transistor.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Timing violation debugging inside place and route tool
InactiveUS20080077903A1Reduce turnaround timeComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designUser inputDisplay device
A storage medium for use in a computer to develop a circuit design. The storage medium recording a software tool that may be readable and executable by the computer. The software tool generally includes the steps of (A) receiving a first user input that identifies a specific cell of a plurality of existing cells in the circuit design, the specific cell having a timing characteristic, (B) generating a replacement display corresponding to the specific cell, the replacement display comprising a plurality of alternate cells suitable to replace the specific cell, each of the alternate cells having a different value associated with the timing characteristic of the specific cell, (C) receiving a second user input that identifies a replacement cell of the alternate cells and (D) automatically generating a first engineering change order to replace the specific cell with the replacement cell.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
System for implementing post-silicon IC design changes
ActiveUS8015522B2Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designActive cellEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Engineering change order cell and method for arranging and routing the same
InactiveUS7698680B2Obtain flexibilityLower junction capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringEngineering change order
There is provided an engineering change order (ECO) cell, which includes: a function circuit including at least one PMOS transistor with a P-diffusion layer and a first poly gate, at least one NMOS transistor with an N-diffusion layer and a second poly gate; a first power layer supplying the at least one PMOS transistor with a first power voltage; and a second power layer supplying the at least one NMOS transistor with a second power voltage. The first poly gate of the PMOS transistor is isolated from the second poly gate of the NMOS transistor.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
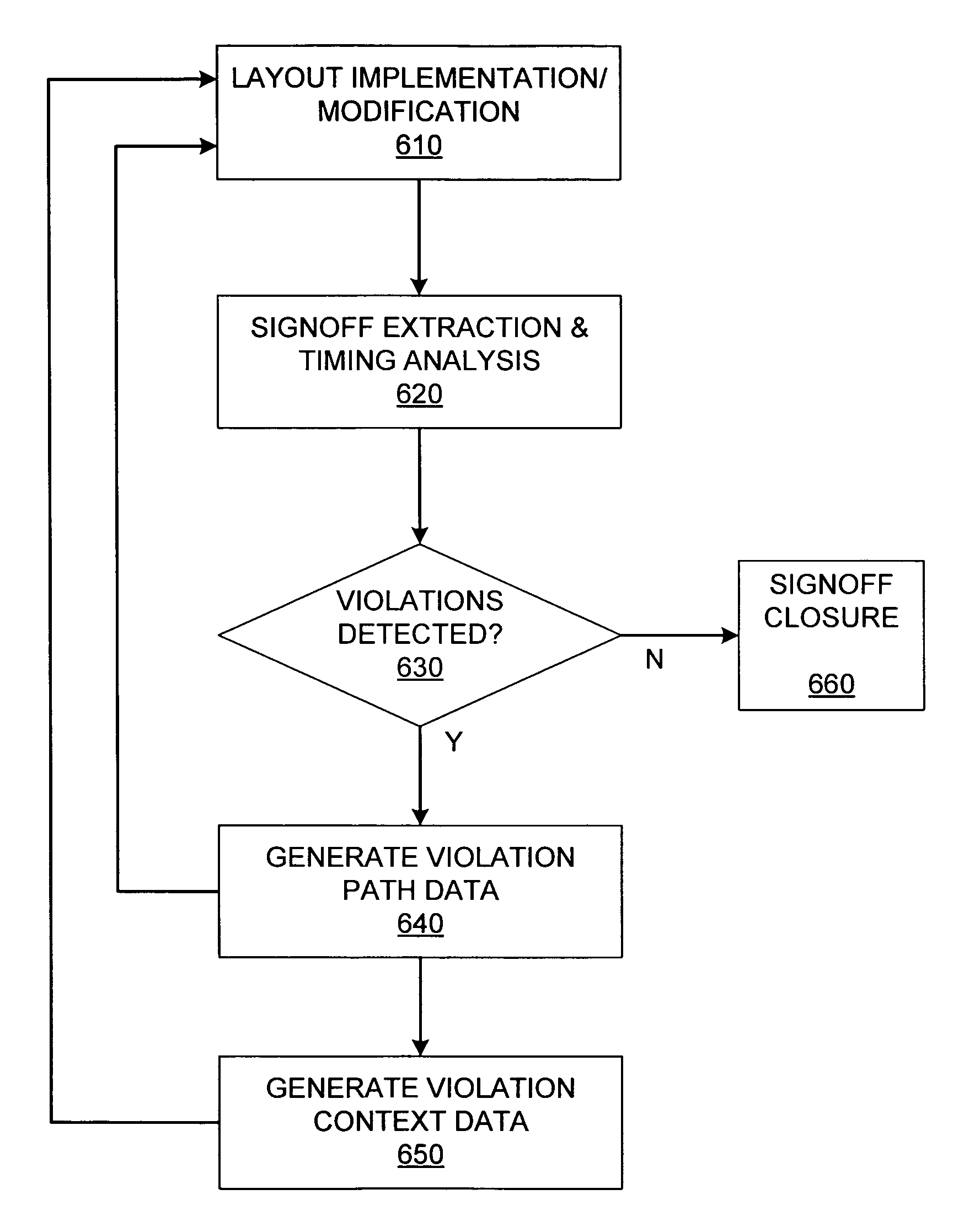
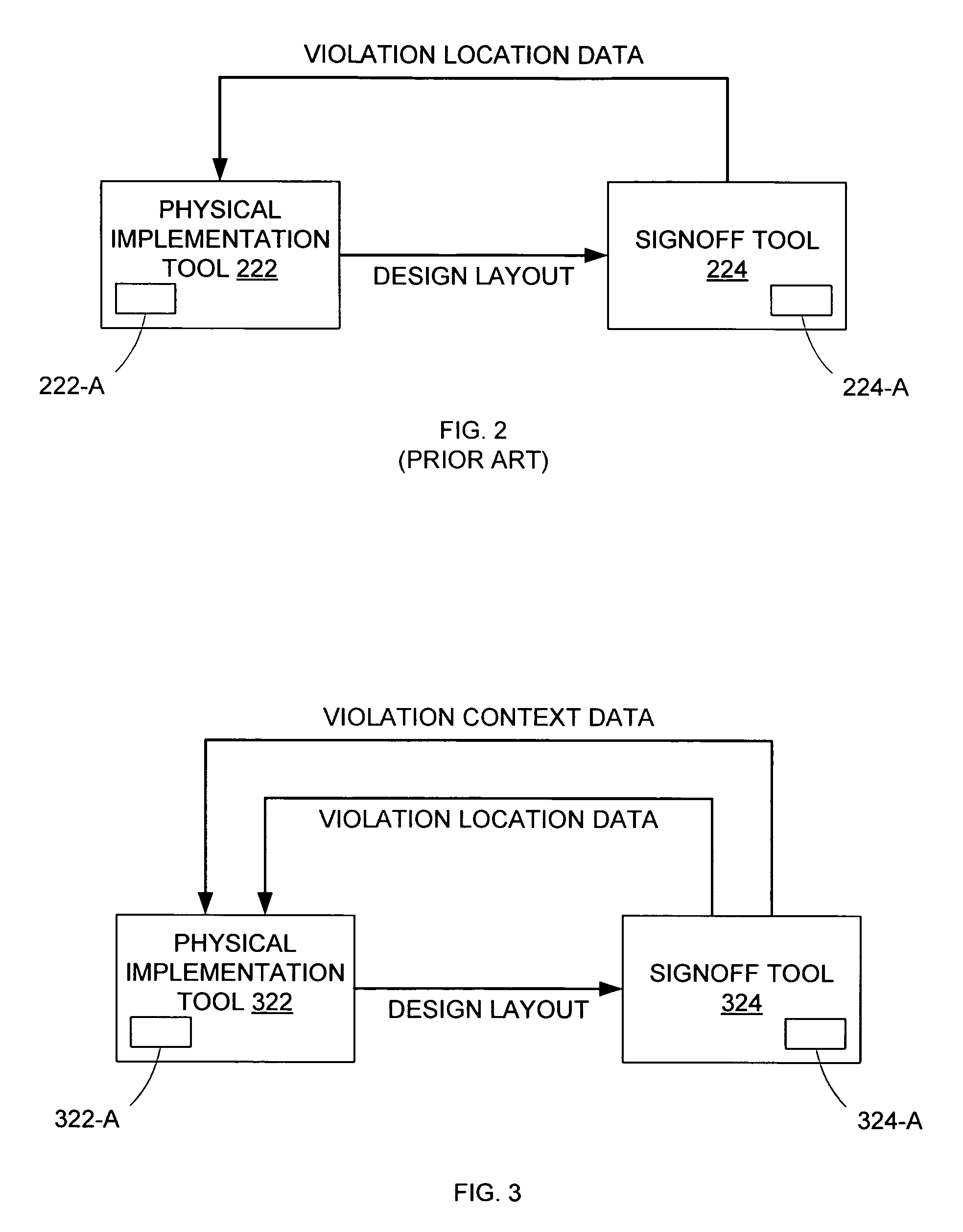
Engineering change order process optimization
ActiveUS7552409B2Less preciseGenerate efficientlyComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designProcess optimizationImplementation analysis
A method for reaching signoff closure in an ECO (engineering change order) process involves the use of violation context data from the signoff tool as the basis for design layout modifications in an implementation tool. The violation context data includes violation information other than violation location / path information. Because the signoff tool, and more specifically, the signoff algorithm used by that tool is the most accurate model of actual IC behavior, the use of violation context data generated by the signoff tool to implement changes to the design layout will generally produce appropriate and effective results. By accessing this violation context data from the signoff tool, an implementation tool need not rely on its less accurate implementation analysis to determine the optimal design layout modifications for correcting violations detected by the signoff tool.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
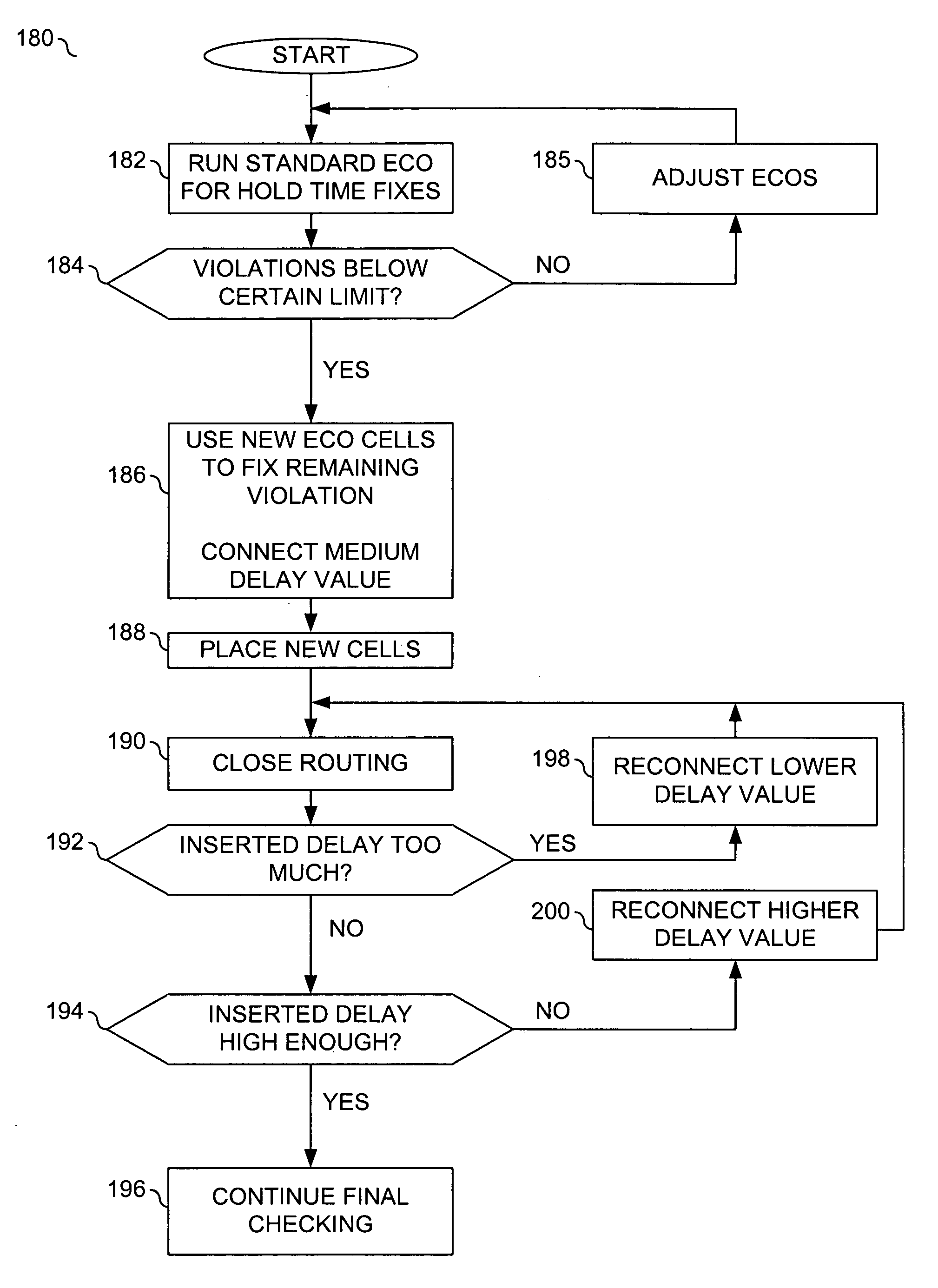
Special engineering change order cells
InactiveUS20060031798A1Impact signal timingMinimize signal integrityComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designEngineeringEngineering change order
A method for correcting a plurality of violations in a circuit design and new cells used in the method are disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) implementing a first engineering change order in the circuit design to correct a first of the violations, (B) implementing a second engineering change order with a special cell to correct a second of the violations, the special cell having a plurality of interfaces available for a signal path associated with the second violation, each of the interfaces having a characteristic appropriate to correct the second violation, each of the characteristics having a different performance and (C) routing the signal path to one of the interfaces to fix the second violation.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
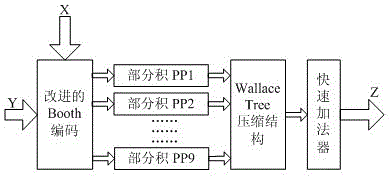
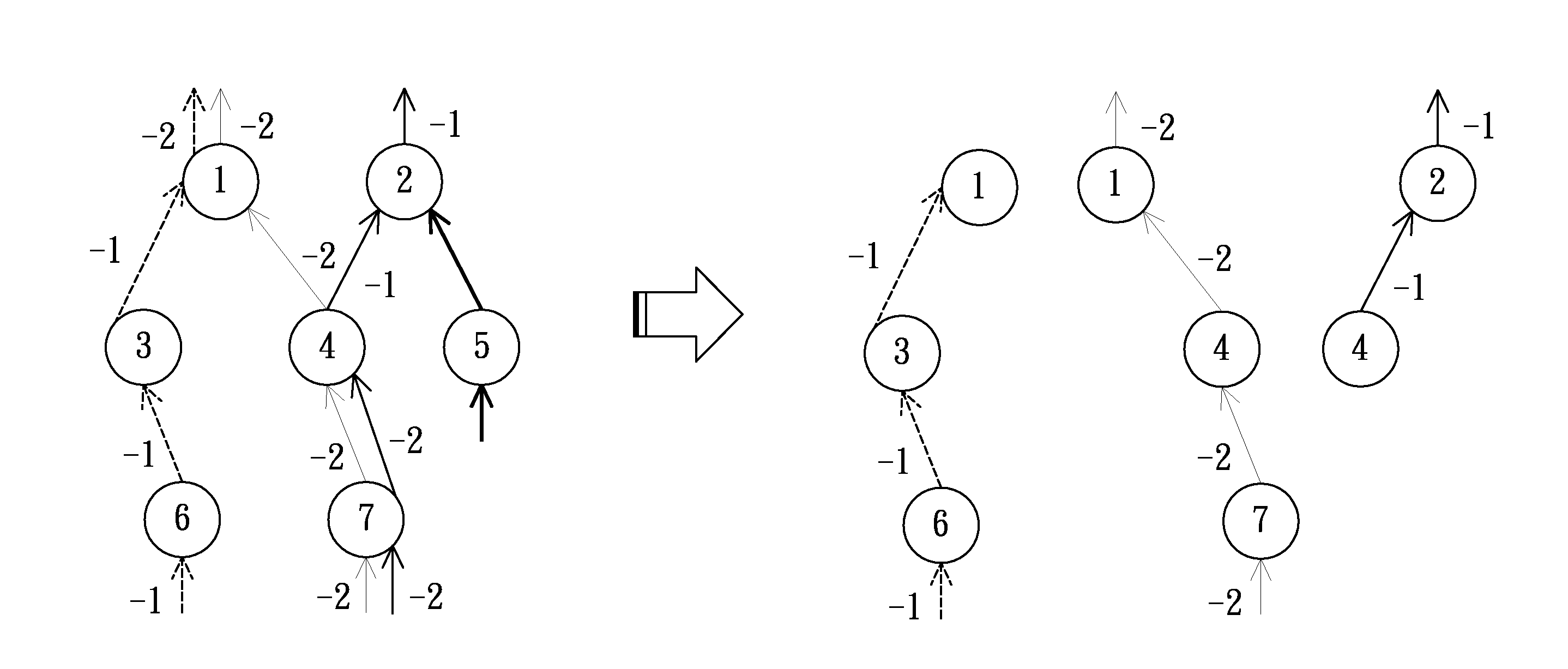
ECO (Engineering Change Order) optimization method of multiplier based on standard cell library extension
InactiveCN102622466AImprove performanceAutomate your designSpecial data processing applicationsPerformance functionCapacitance
The invention relates to an ECO (Engineering Change Order) optimization method of a multiplier based on standard cell library extension. The traditional optimization method is limited in finite drive capability of the standard cells in the library, and cannot realize the shortest path delay. The ECO optimization method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, generating a layout of an extension unit, and characterizing the extension unit to obtain an extension unit library, wherein the characterizing the extension unit comprises characterizing the delay information, characterizing an input port capacitor, characterizing the power consumption, characterizing the area and characterizing a performance function; secondly, performing time series analysis on the multiplier to obtain a key path of the multiplier; and lastly, enabling the gate effects of all stages of the key path of the multiplier to be the same by using the extension unit library so as to obtain the shortest path delay. According to the ECO optimization method, on the premise of not remarkably increasing the design cycle, the key path of the multiplier is analyzed, the shortest path delay is realized, and the performance of the multiplier is improved; in addition, the design automation is conveniently implemented, and the ECO optimization method is also suitable for the rear-end ECO optimization of other digital systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of implementing timing engineering change order
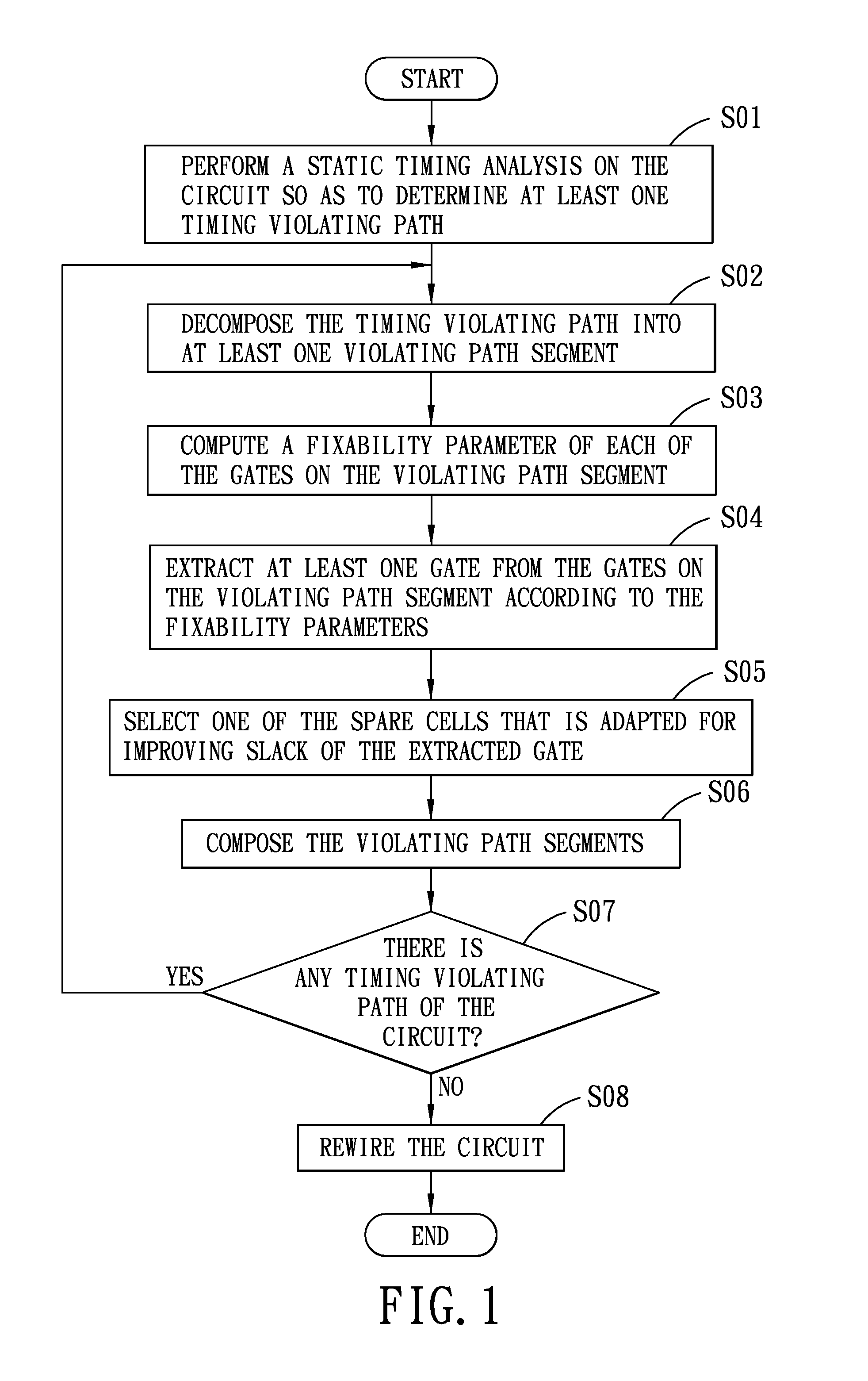
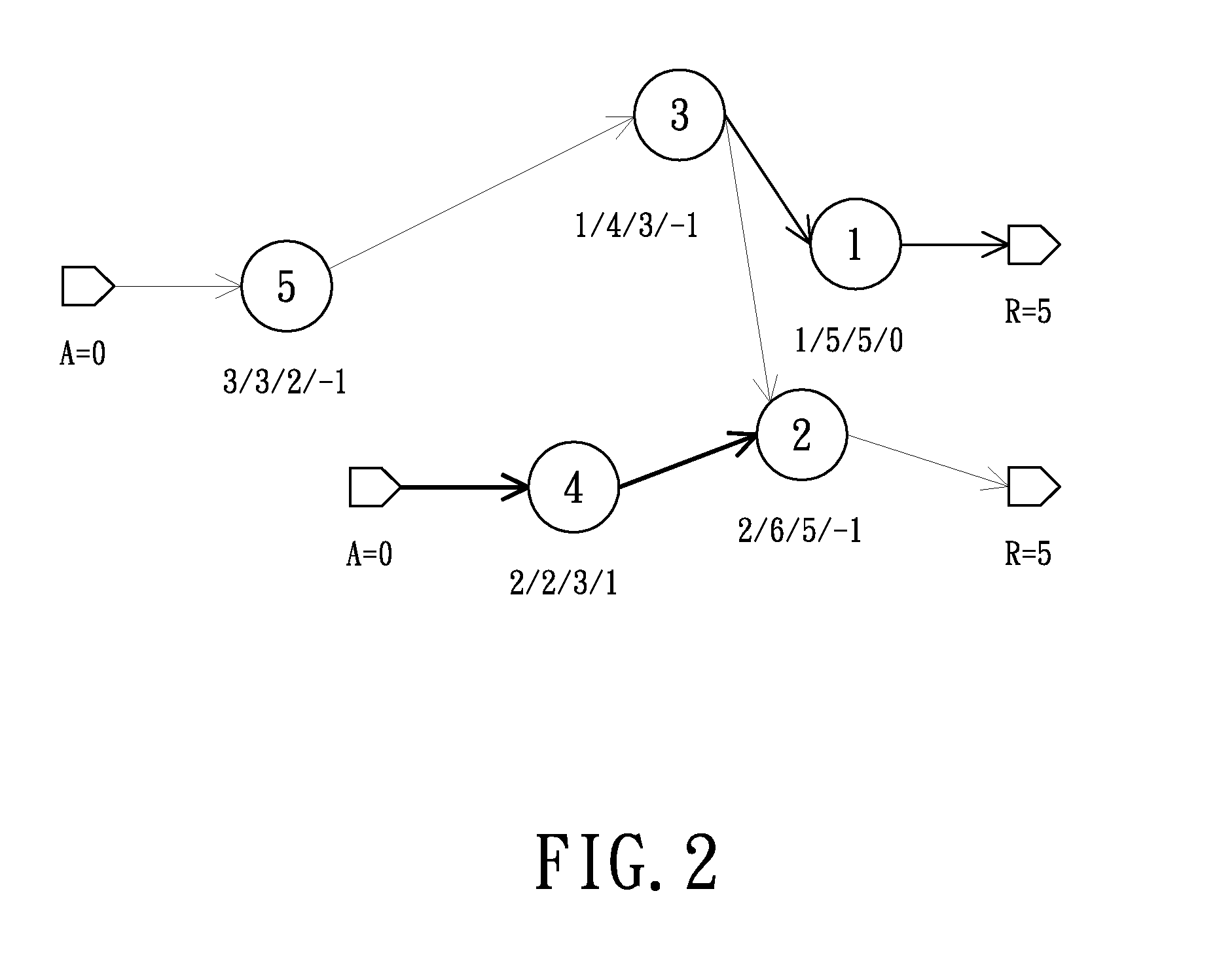
InactiveUS20130298097A1Efficient implementationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisAlgorithm
A method of implementing timing ECO in a circuit includes the steps of performing a static timing analysis on the circuit so as to determine at least one timing violating path of the circuit, decomposing the timing violating path into at least one violating path segment, determining a smooth curve from each timing violating path and determining a plurality of reference points along the smooth curve, computing a fixability parameter of each gate on the violating path segment, extracting at least one gate according to the fixability parameters, and selecting one spare cell and disposing the selected spare cell on the violating path segment.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV +1
Method for realizing automated ECO (Engineering Change Order) netlist in digital IC (Integrated Circuit) design process
ActiveCN102129493AMeet Timing RequirementsImprove processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsProcess efficiencyEngineering change order
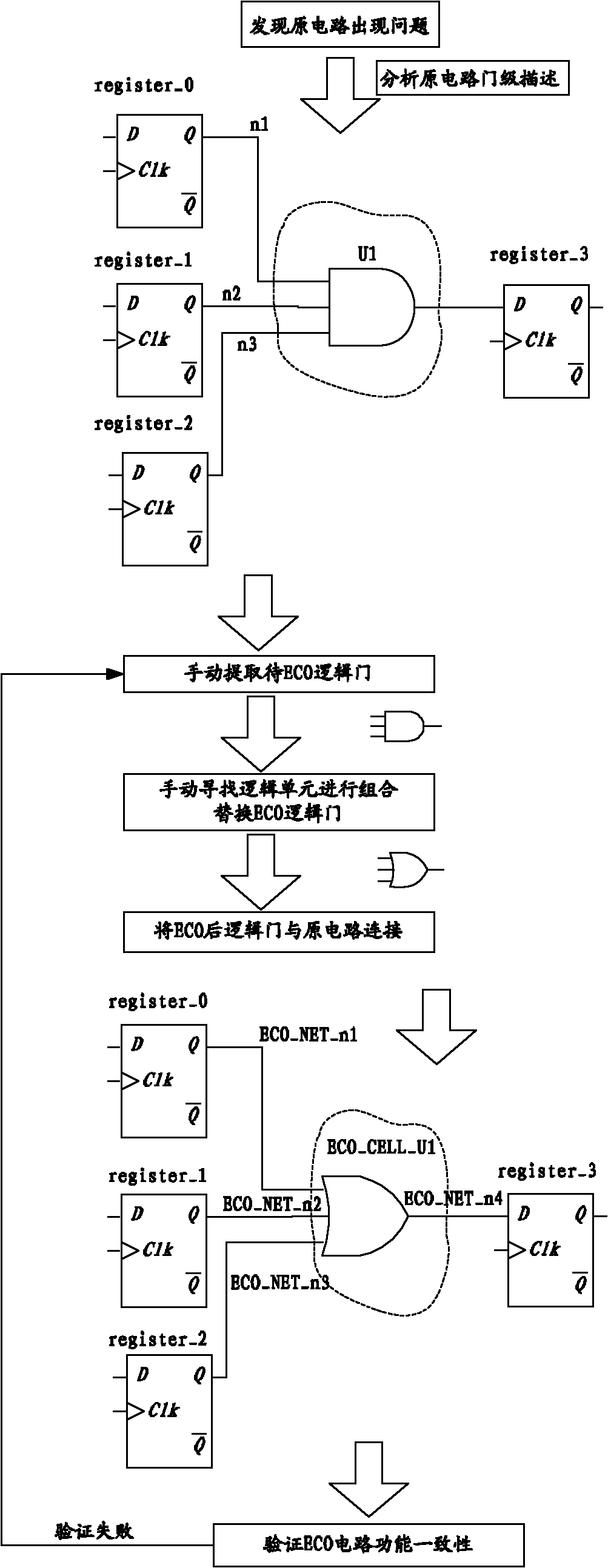
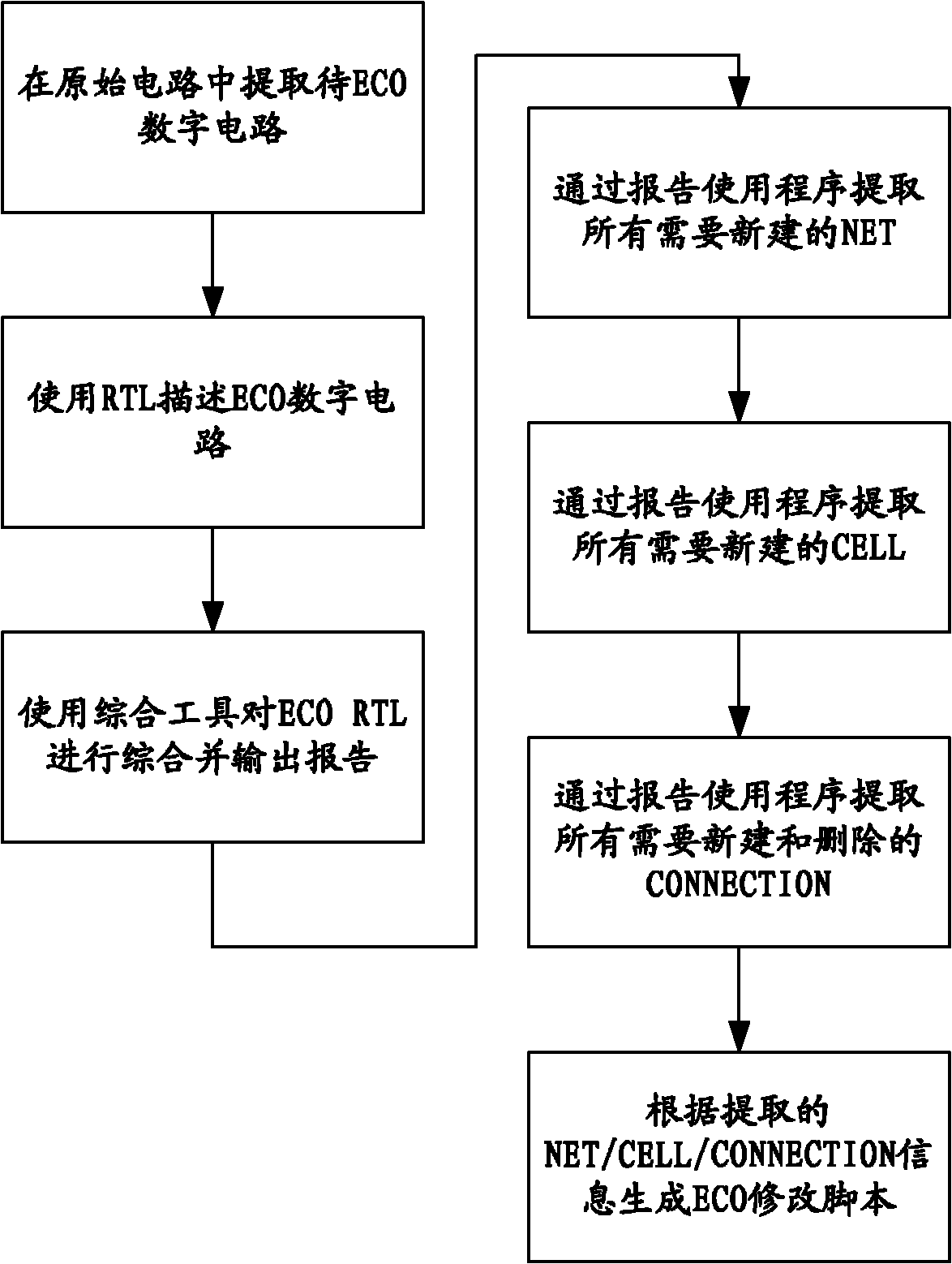
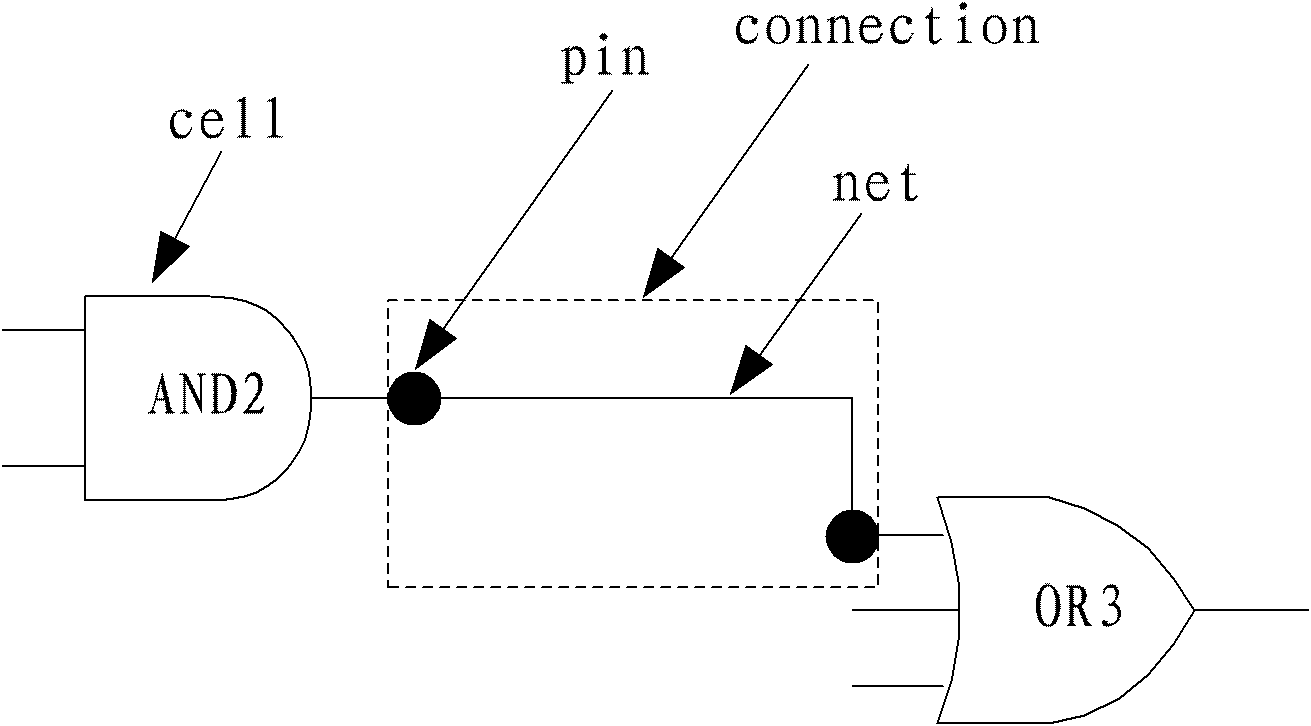
The invention relates to a method for realizing an automated ECO (Engineering Change Order) netlist in a digital IC (Integrated Circuit) design process, comprising the following steps of: extracting an ECO digit circuit in an original circuit, and describing the ECO digit circuit by using RTL (Resistor Transistor Logic); generating a report of an ECO modified script by using the output of an EDA (Electronic Design Automation) tool; and generating the ECO modified script by using an output report of a synthesis tool. In the invention, only the RTL description in the whole process is needed to be modified and few or no ECO modified script is needed to be written, therefore, efficient process, automation realization and difficult error are achieved and temporal constraint can be applied to the ECO process.
Owner:FUZHOU ROCKCHIP SEMICON
Integrated circuit (IC) design methods using engineering change order (ECO) cell architectures
ActiveUS20190188353A1Good flexibilityMinimal disruptionCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsTime criticalEngineering
Aspects disclosed in the detailed description include integrated circuit (IC) design methods using engineering change order (ECO) cell architectures. In particular, exemplary aspects provide a fill algorithm that is both single- and multi-row aware, considers a poly-pitch count, and utilizes metallization of the “empty space” relative to a suite of available fill cells. The algorithm is also aware of timing critical logic elements and may place ECO fill cells in near proximity to such timing sensitive circuits or other margin critical circuits to allow for decoupling or, if there is a logic error, an ECO cell is placed such that the ECO cell is well positioned to be repurposed as a delay circuit or other function to aid in margin control. For maximum flexibility, the algorithm may also address both pre- and post-route applications.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for Implementing Timing Point Engineering Change Orders in an Integrated Circuit Design Flow
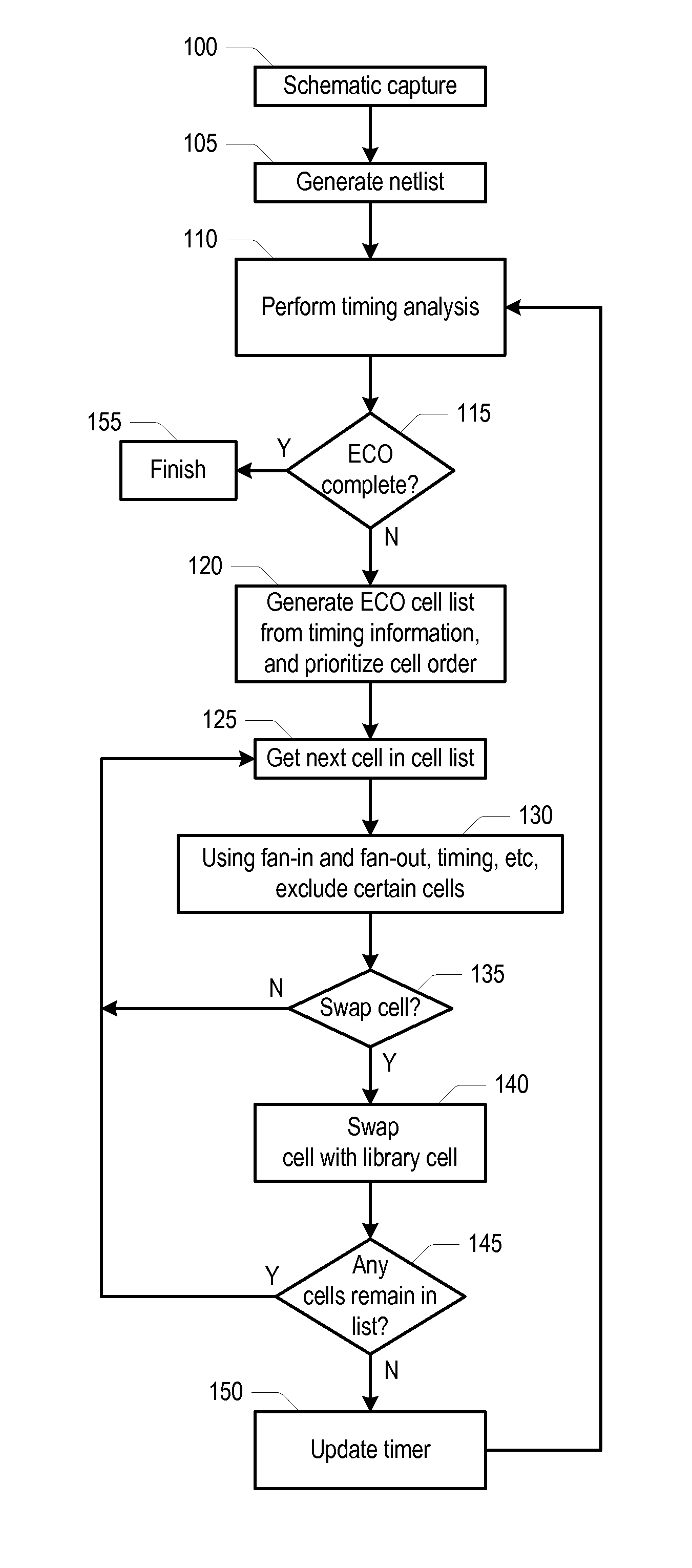
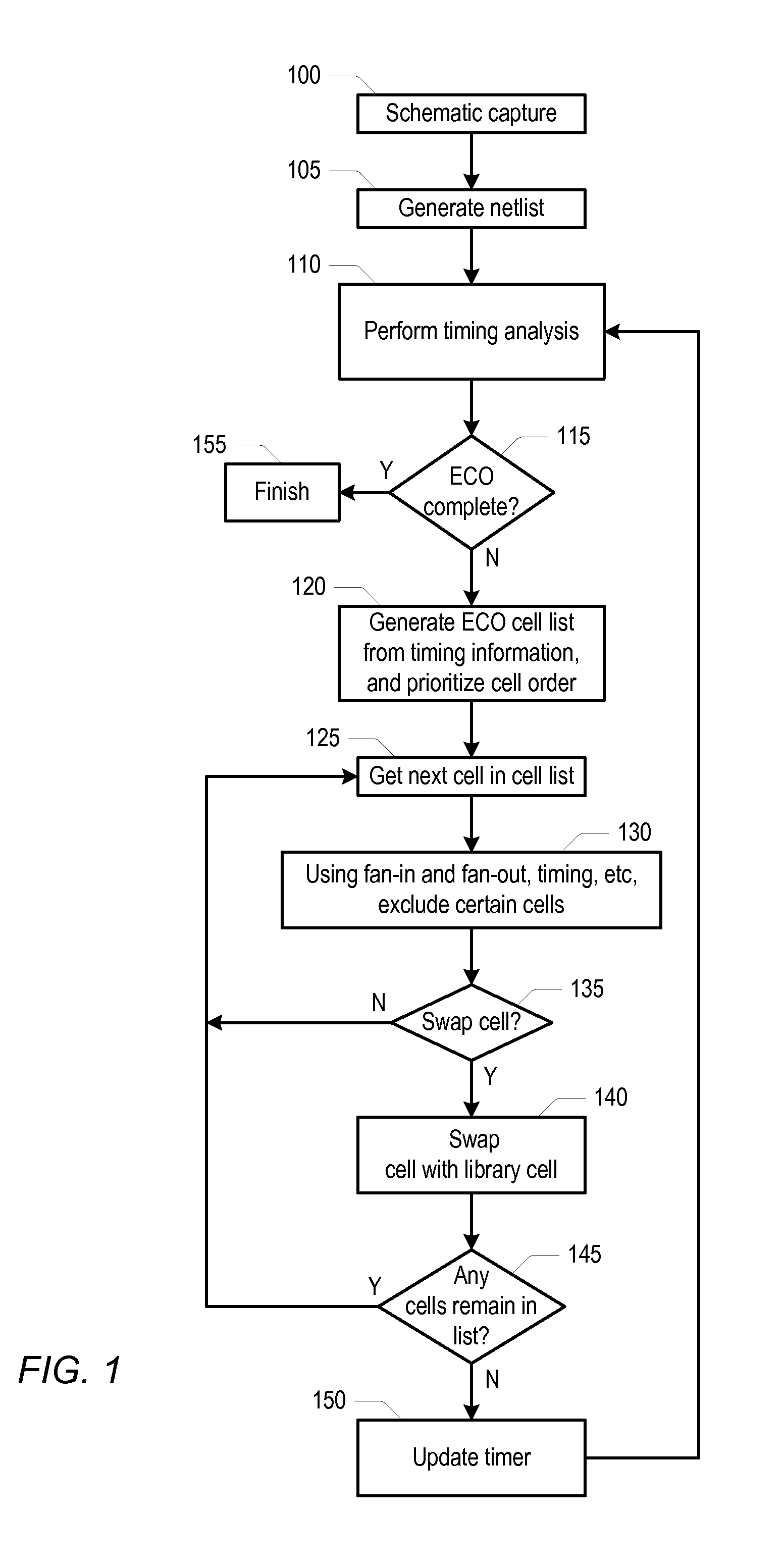
InactiveUS20120144353A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureEngineering change order
A method and system for automatically implementing engineering change order (ECO) corrections in an integrated circuit (IC) include a design tool performing a timing analysis on a netlist of the IC. The method may also include annotating each of the device cells with a worst timing slack through a respective timing point associated with the device cell. In addition, the method may include generating an ECO list of device cells needing ECO correction and prioritizing the ECO correction order of the device cells in the ECO list based upon cell attributes. The method may further include excluding device cells in the ECO list based upon the fan-in or fan-out connection path of other device cells in the ECO list that will be corrected, and the design tool selecting and replacing device cells in the ECO list with different device cells from a design library.
Owner:APPLE INC
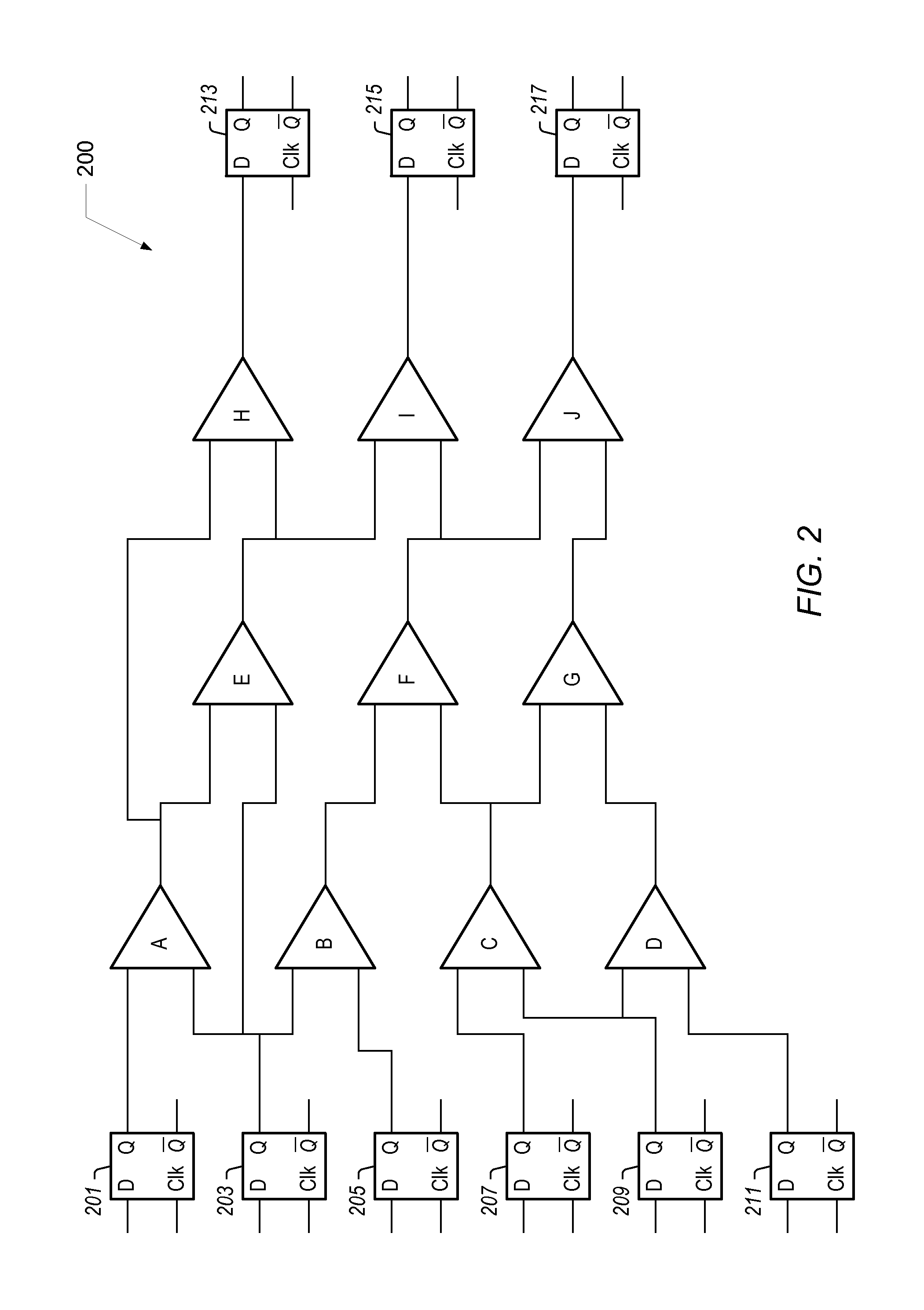
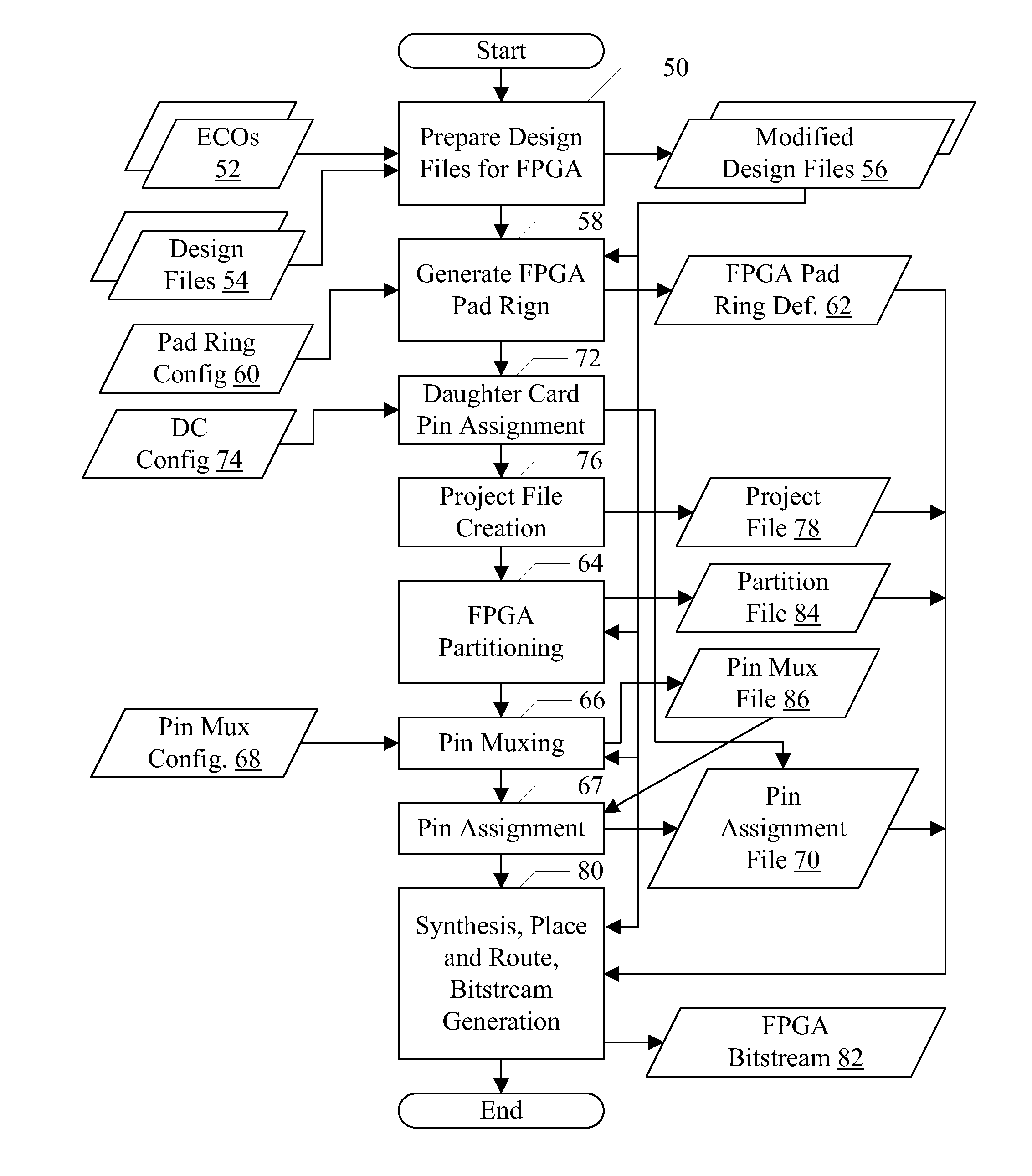
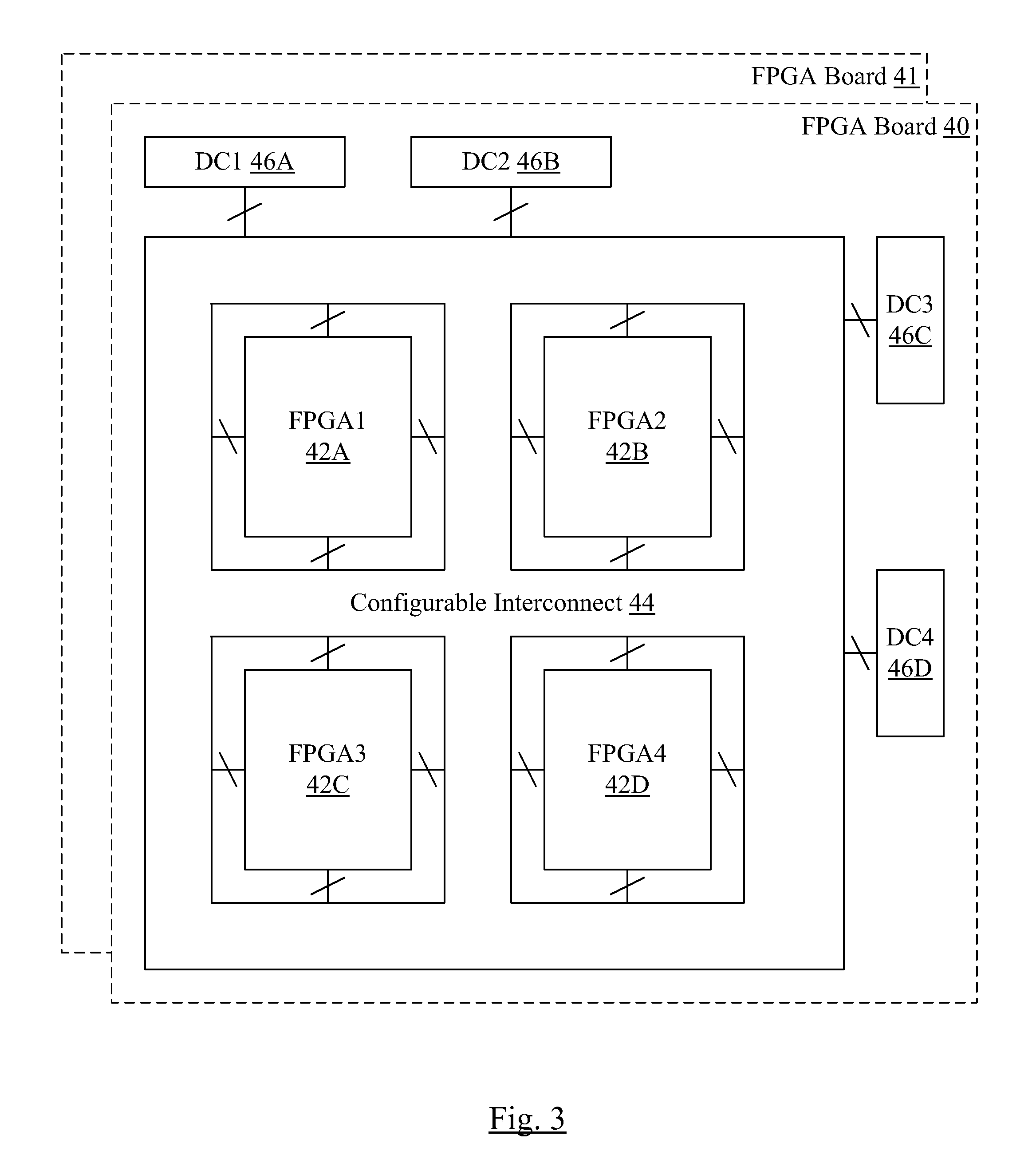
Engineering Change Order Language for Modifying Integrated Circuit Design Files for Programmable Logic Device Implementation
ActiveUS20110145779A1Automatically performAvoid mistakesCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
In an embodiment, a method to automatically process modifications to a set of design files is contemplated. The design files describe at least a portion of an integrated circuit design, and may be coded in a hardware description language. The modifications may be made to prepare the design files for inclusion in a programmable logic device implementation of the integrated circuit (or portion thereof). Specifically, the modifications may be specified using a set of commands which may be assembled by a user.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com