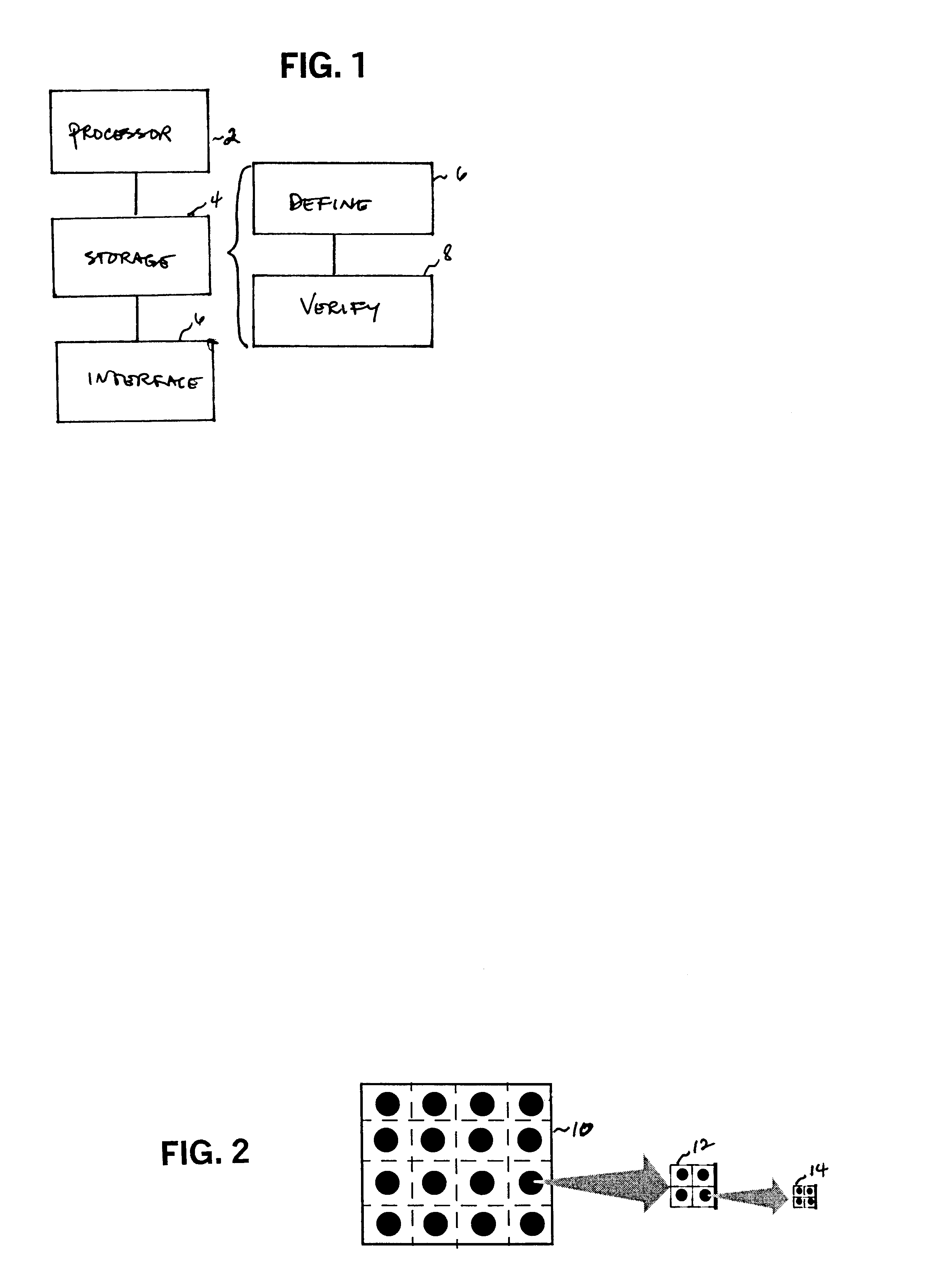
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
264 results about "Place and route" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
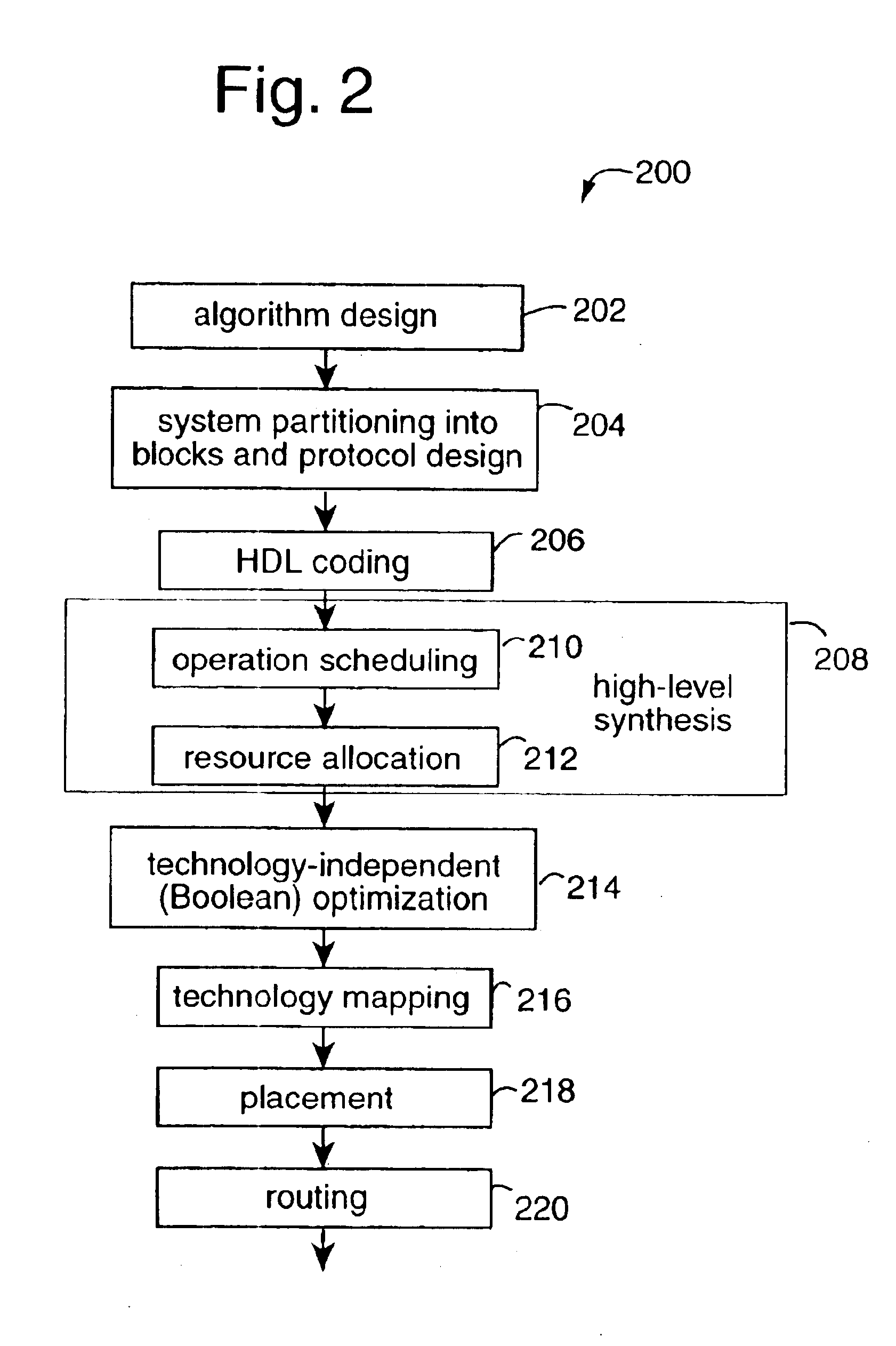
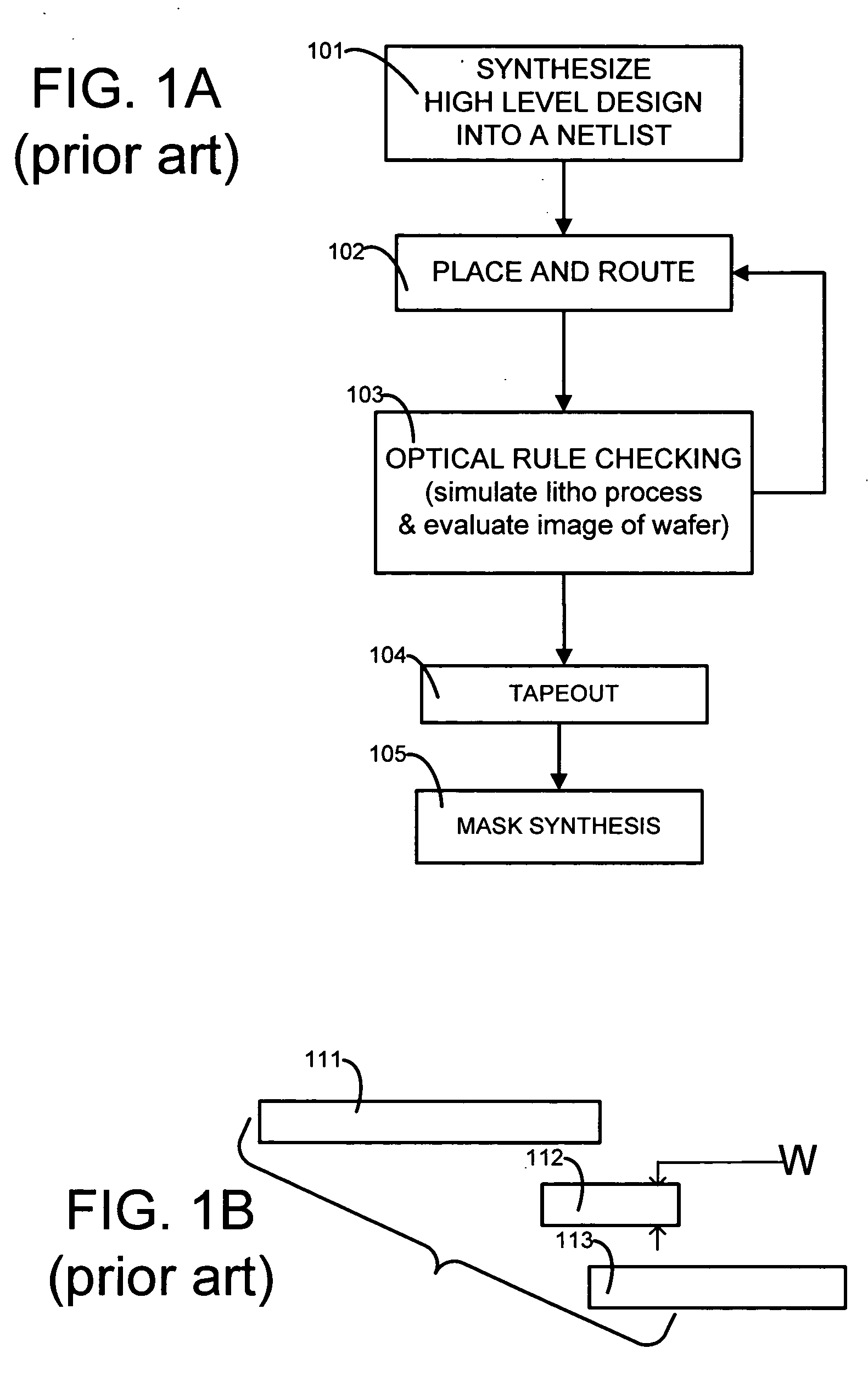
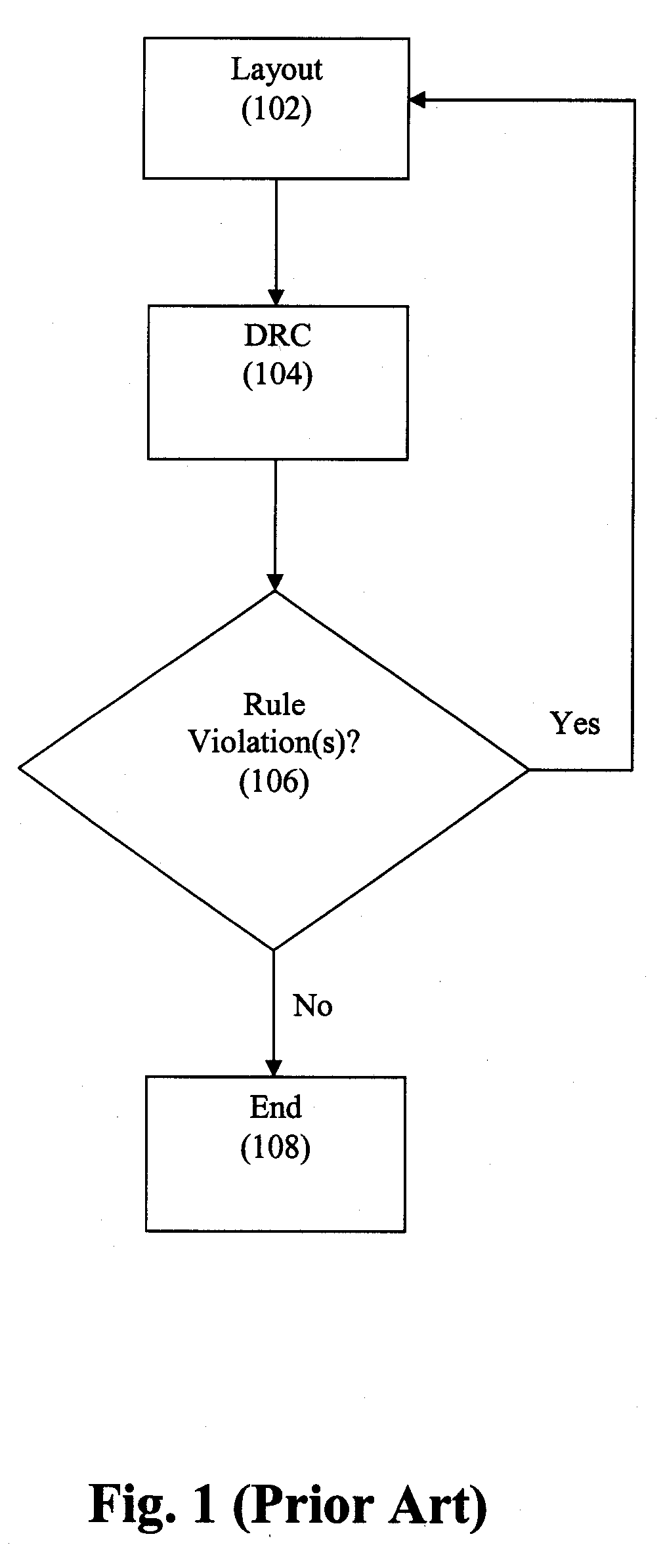
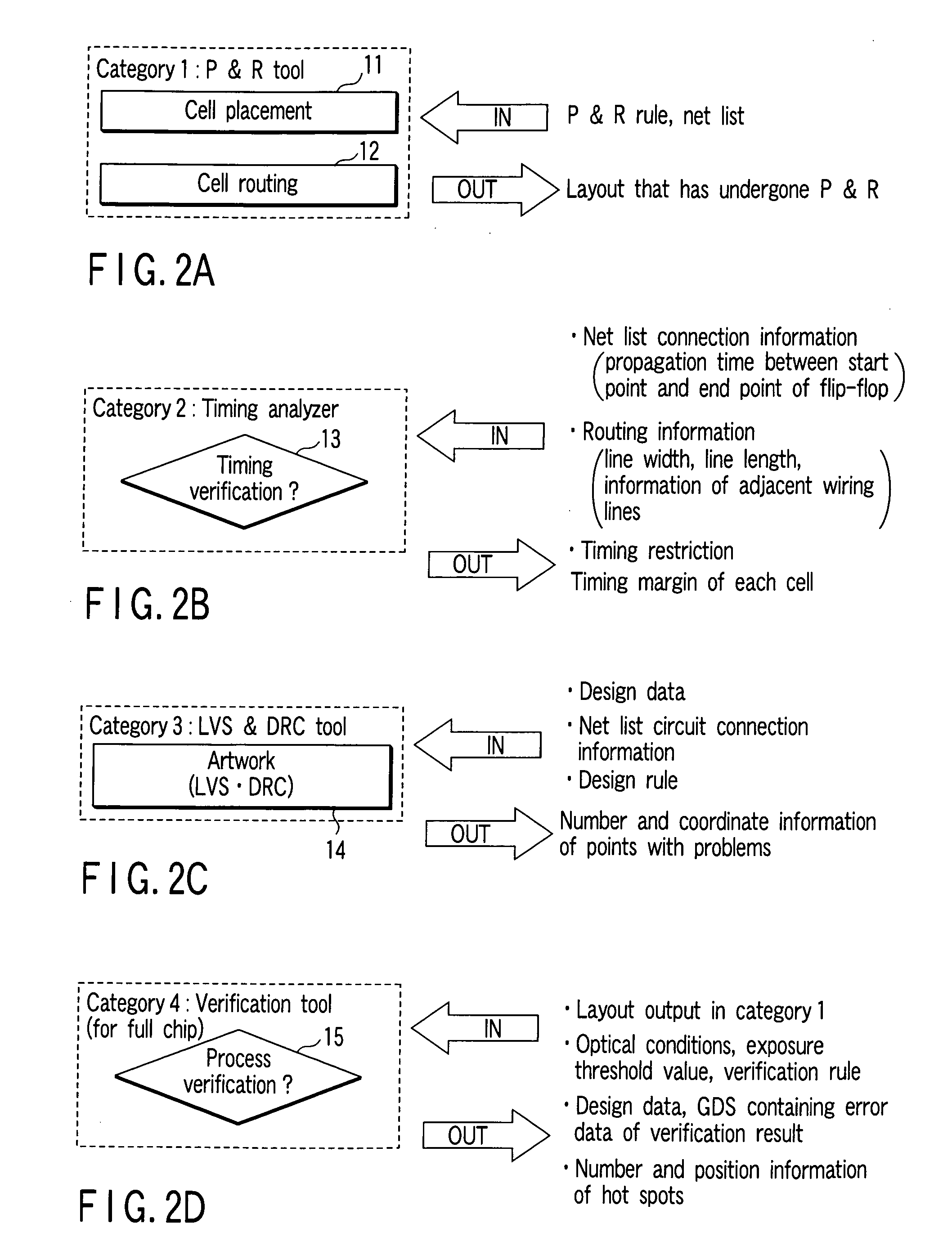
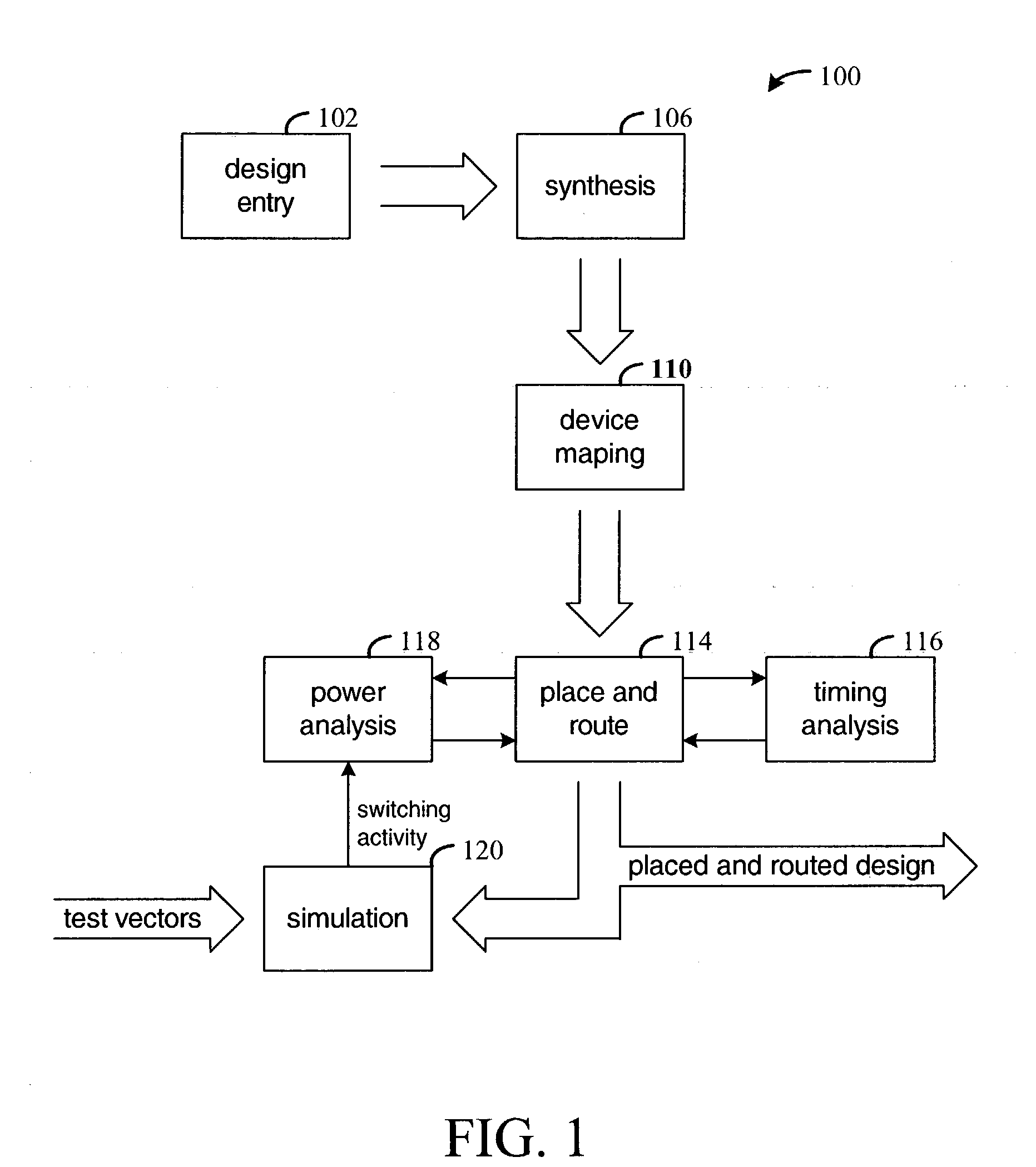
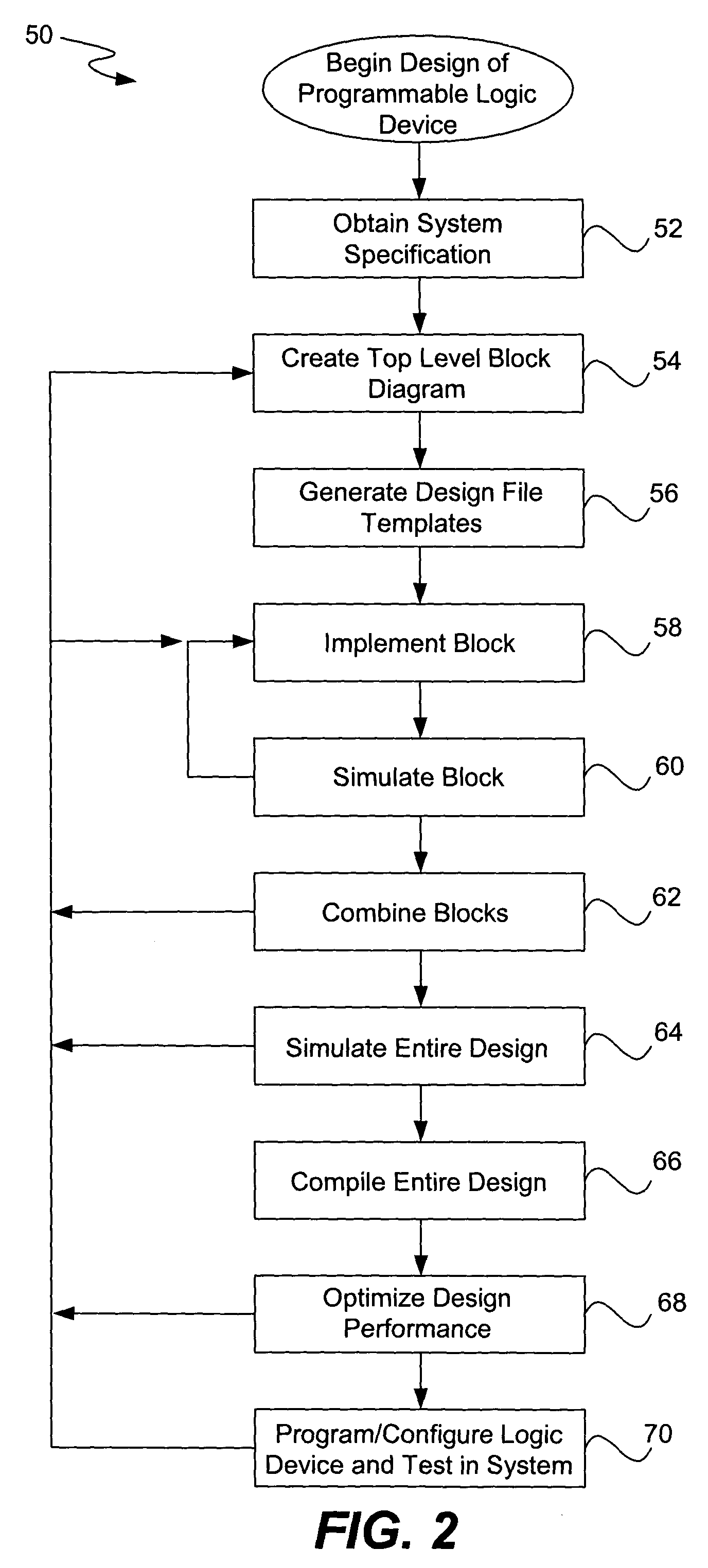
Place and route is a stage in the design of printed circuit boards, integrated circuits, and field-programmable gate arrays. As implied by the name, it is composed of two steps, placement and routing. The first step, placement, involves deciding where to place all electronic components, circuitry, and logic elements in a generally limited amount of space. This is followed by routing, which decides the exact design of all the wires needed to connect the placed components. This step must implement all the desired connections while following the rules and limitations of the manufacturing process.
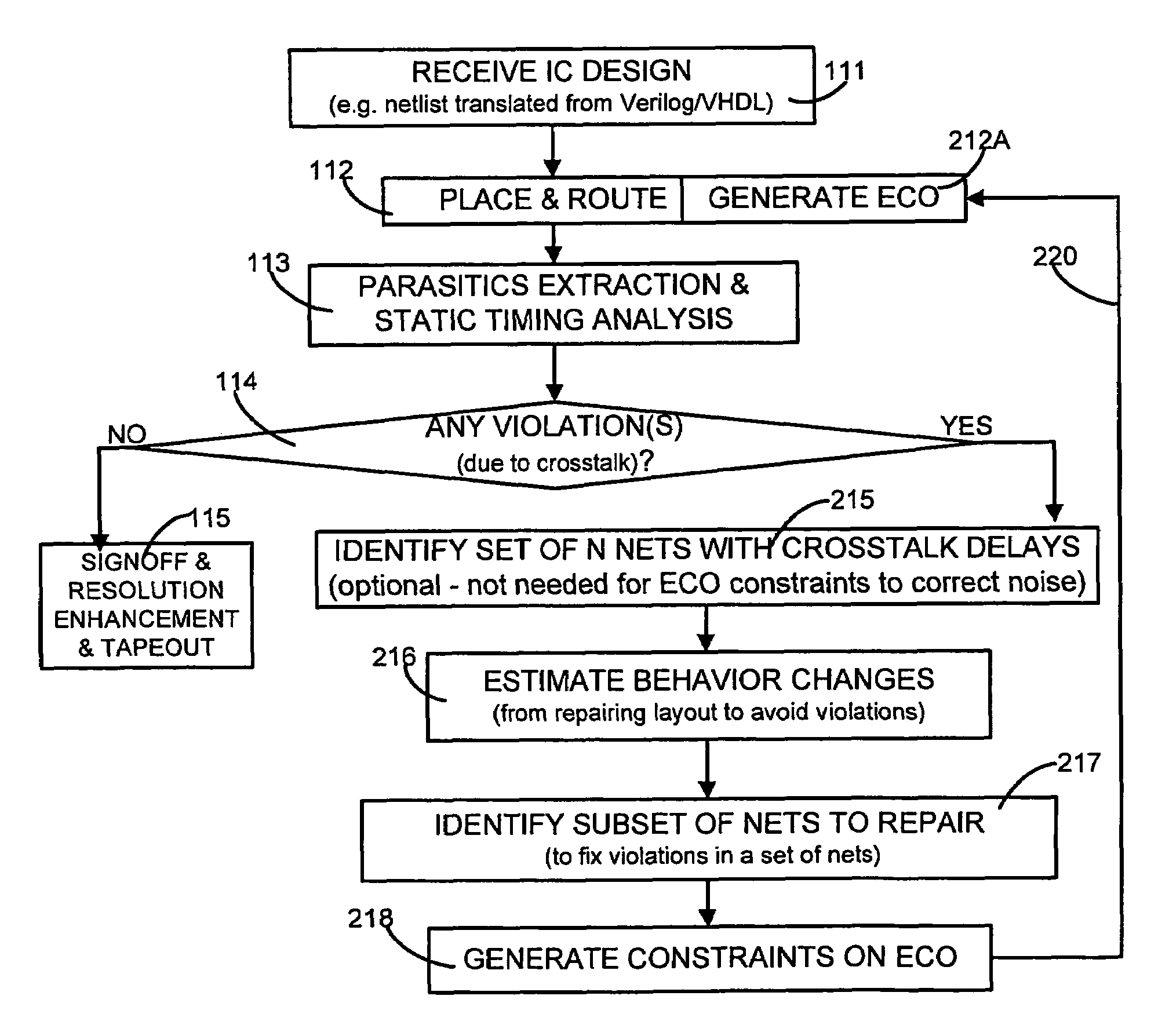
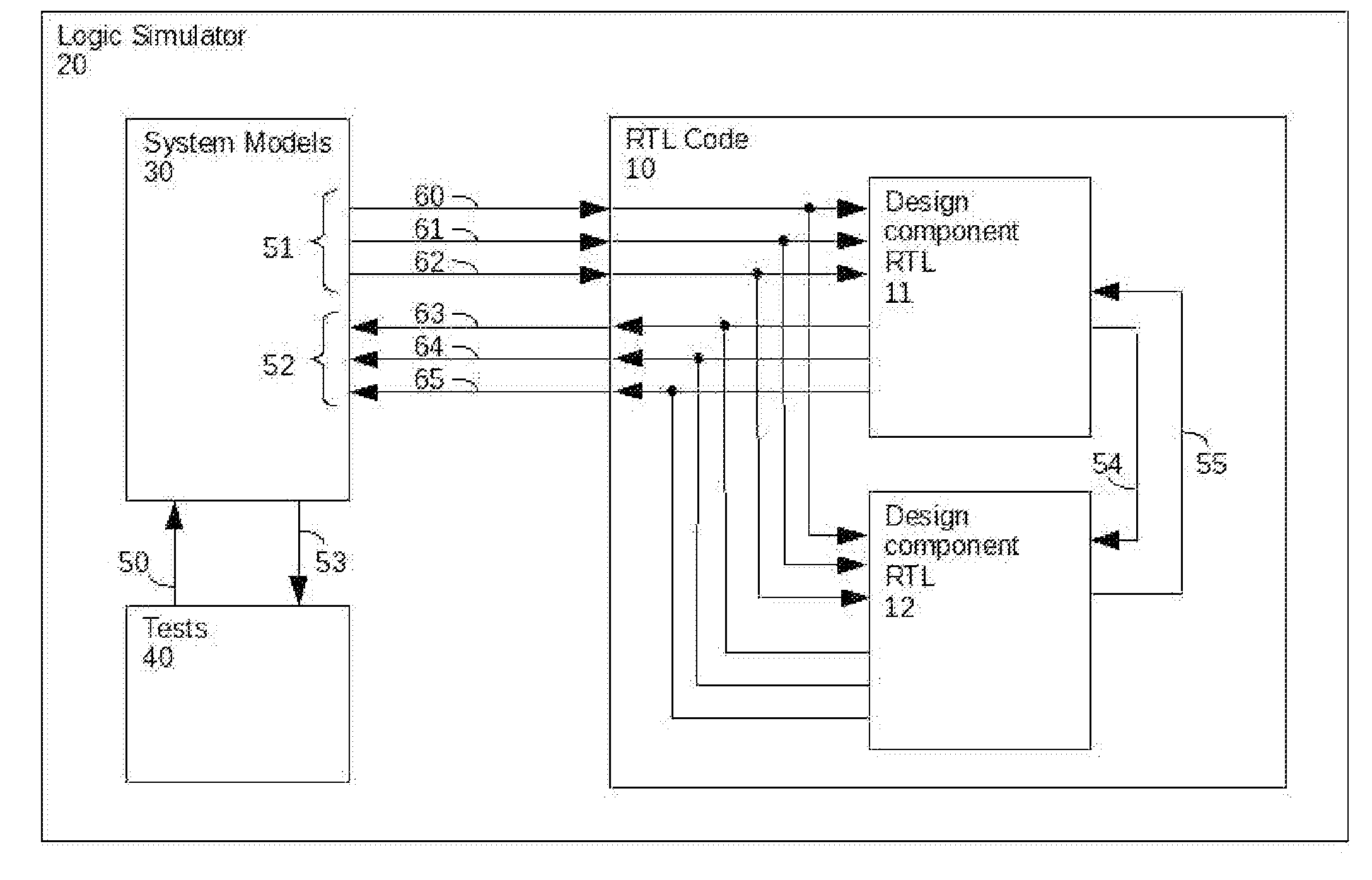
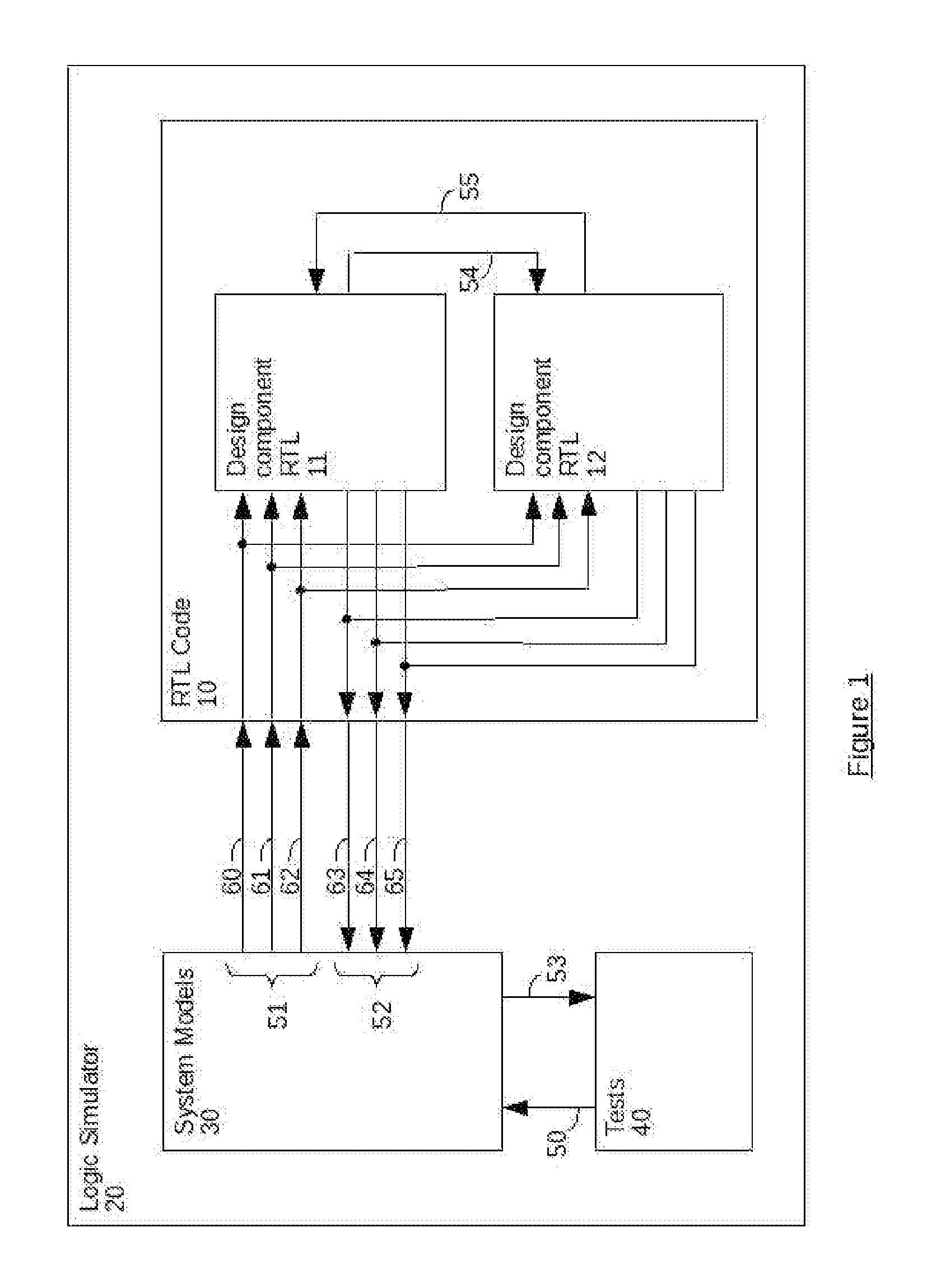
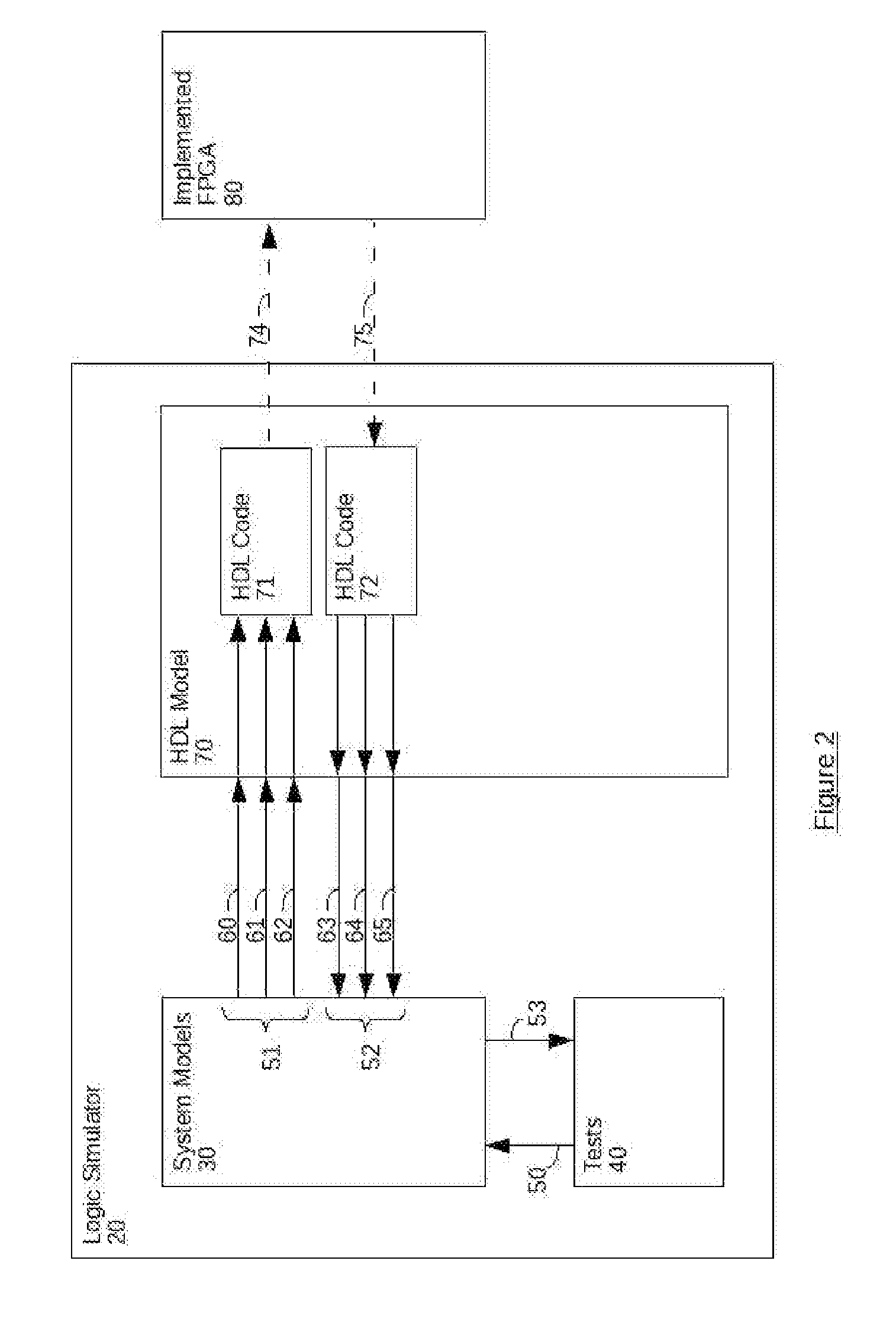
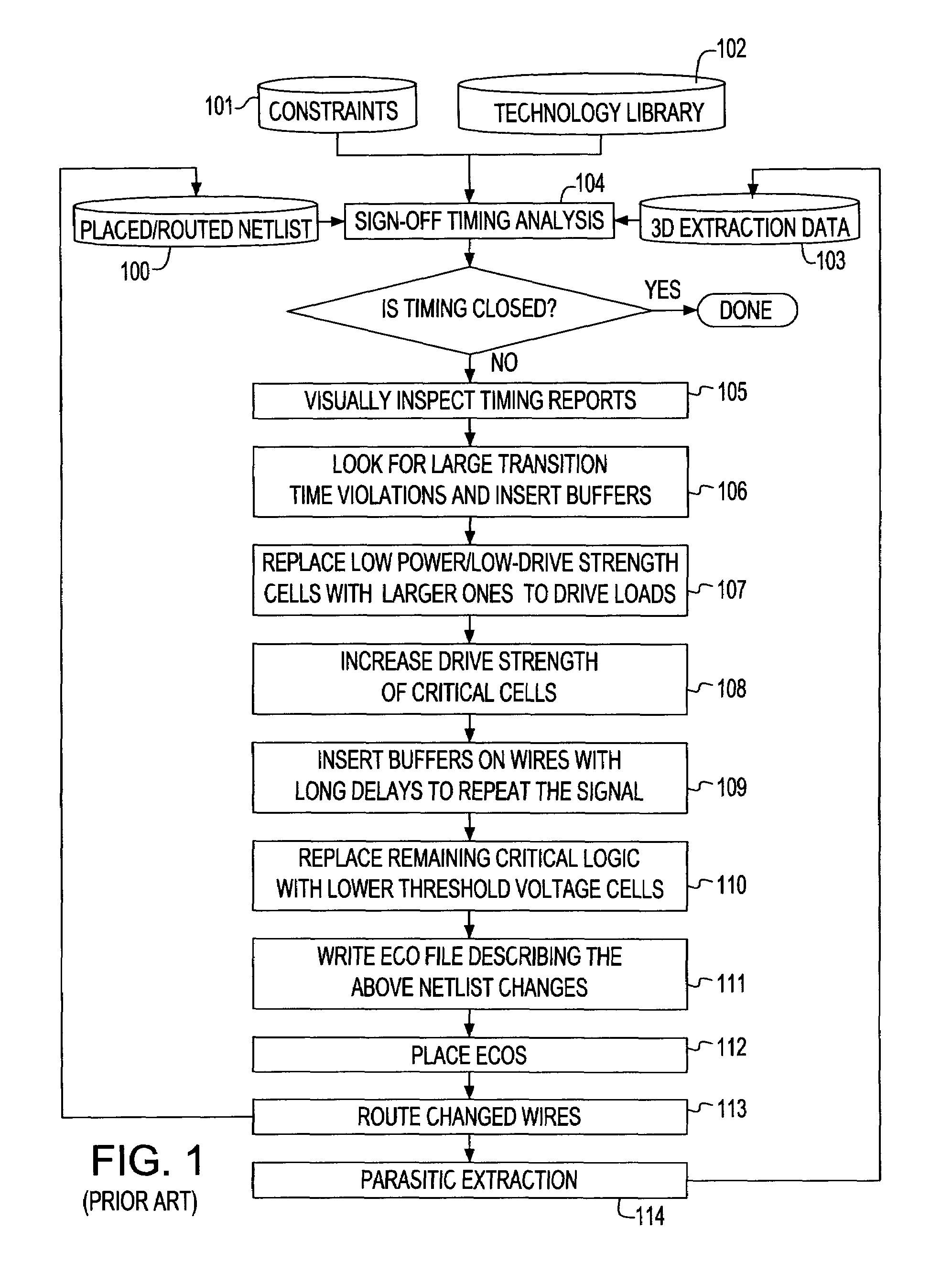
Generation of engineering change order (ECO) constraints for use in selecting ECO repair techniques
ActiveUS7454731B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLayoutEngineering change order
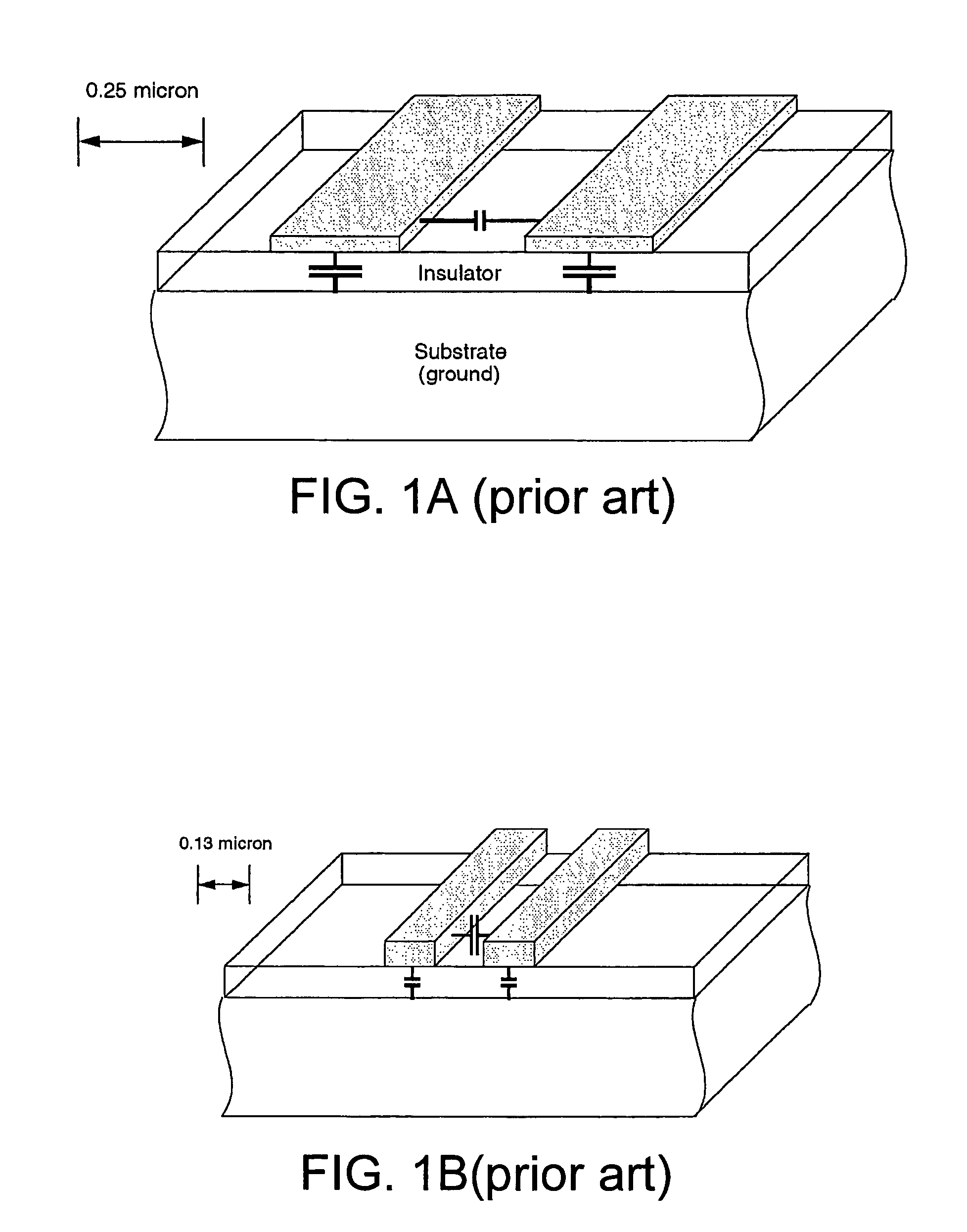
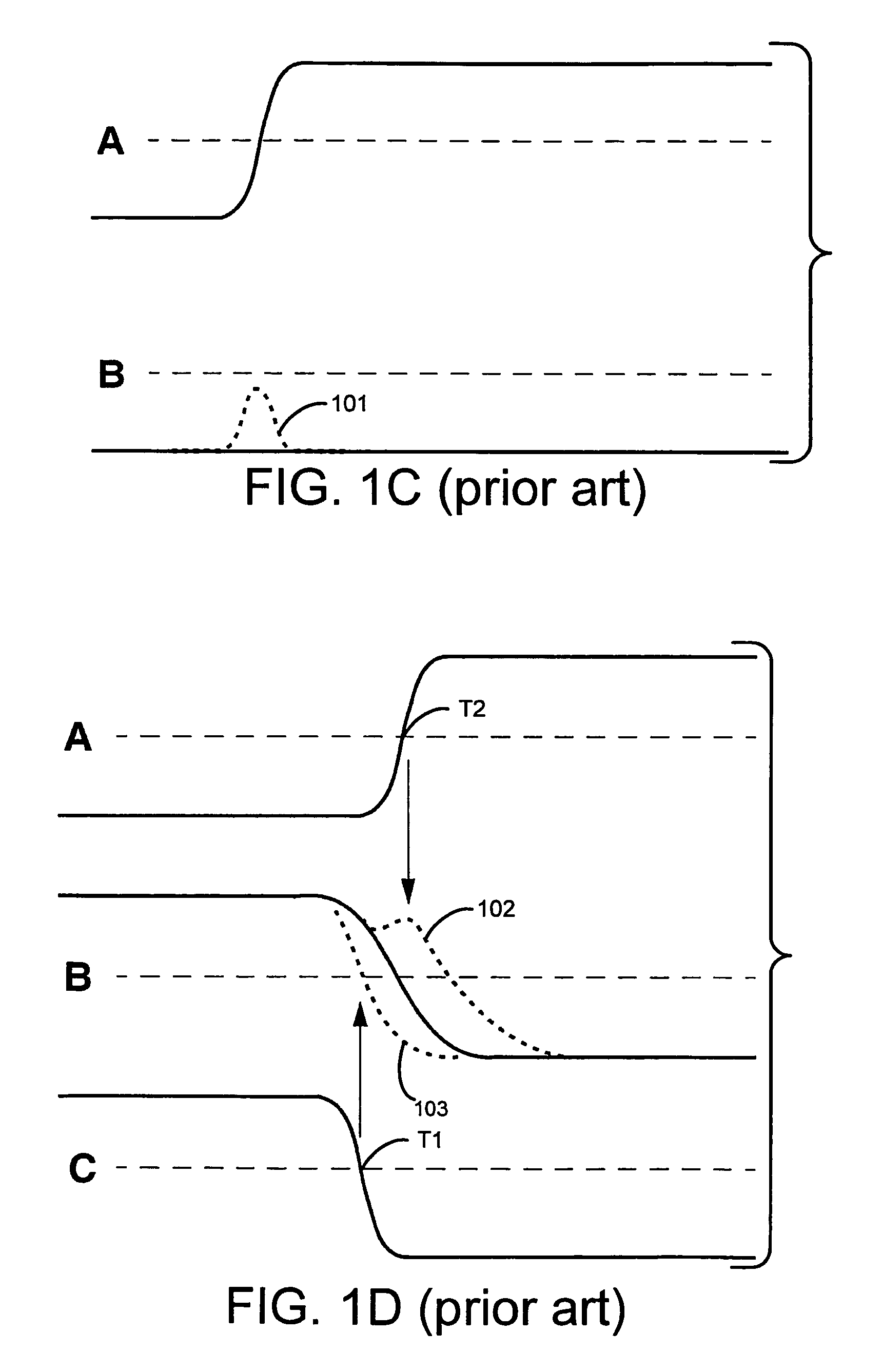
Static timing and / or noise analysis are performed on a netlist of an integrated circuit, to estimate behavior of the netlist and to identify at least one violation by said behavior of a corresponding requirement thereon, such as setup time, hold time or bump height in a quiescent net. Thereafter, effect of engineering change order (ECO) to correct the violation are automatically analyzed, based on the layout, the parasitics, the timing and / or noise behavior, and the violation, followed by generation of a constraint on the behavior (called “ECO” constraint), such as a timing constraint and / or a noise constraint. Next, the ECO constraint is automatically used, e.g. in a place and route tool, to select an ECO repair technique, from several ECO repair techniques that can overcome the violation. The selected ECO repair technique is automatically applied to the layout, to generate a modified layout which does not have the violation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
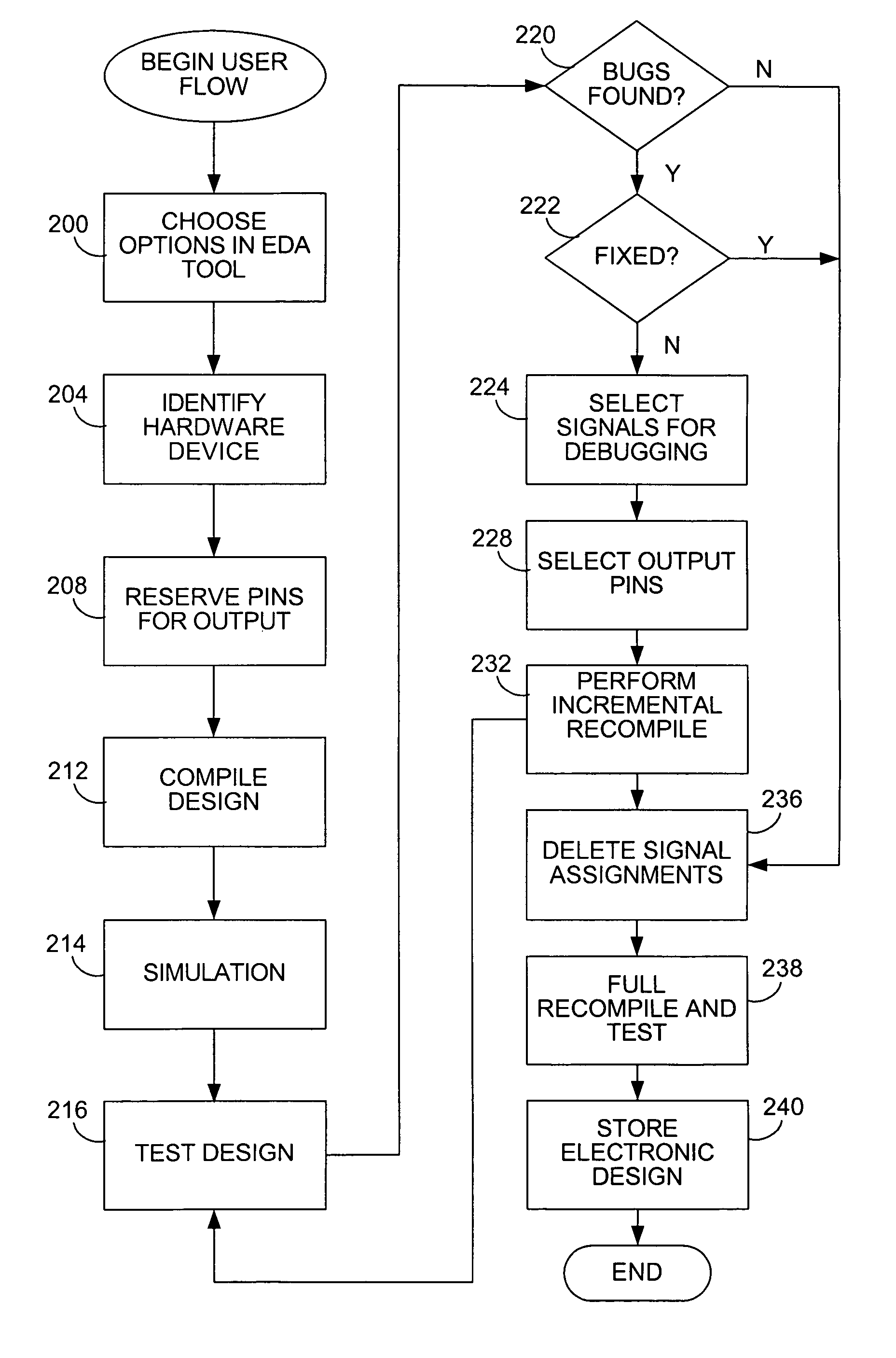
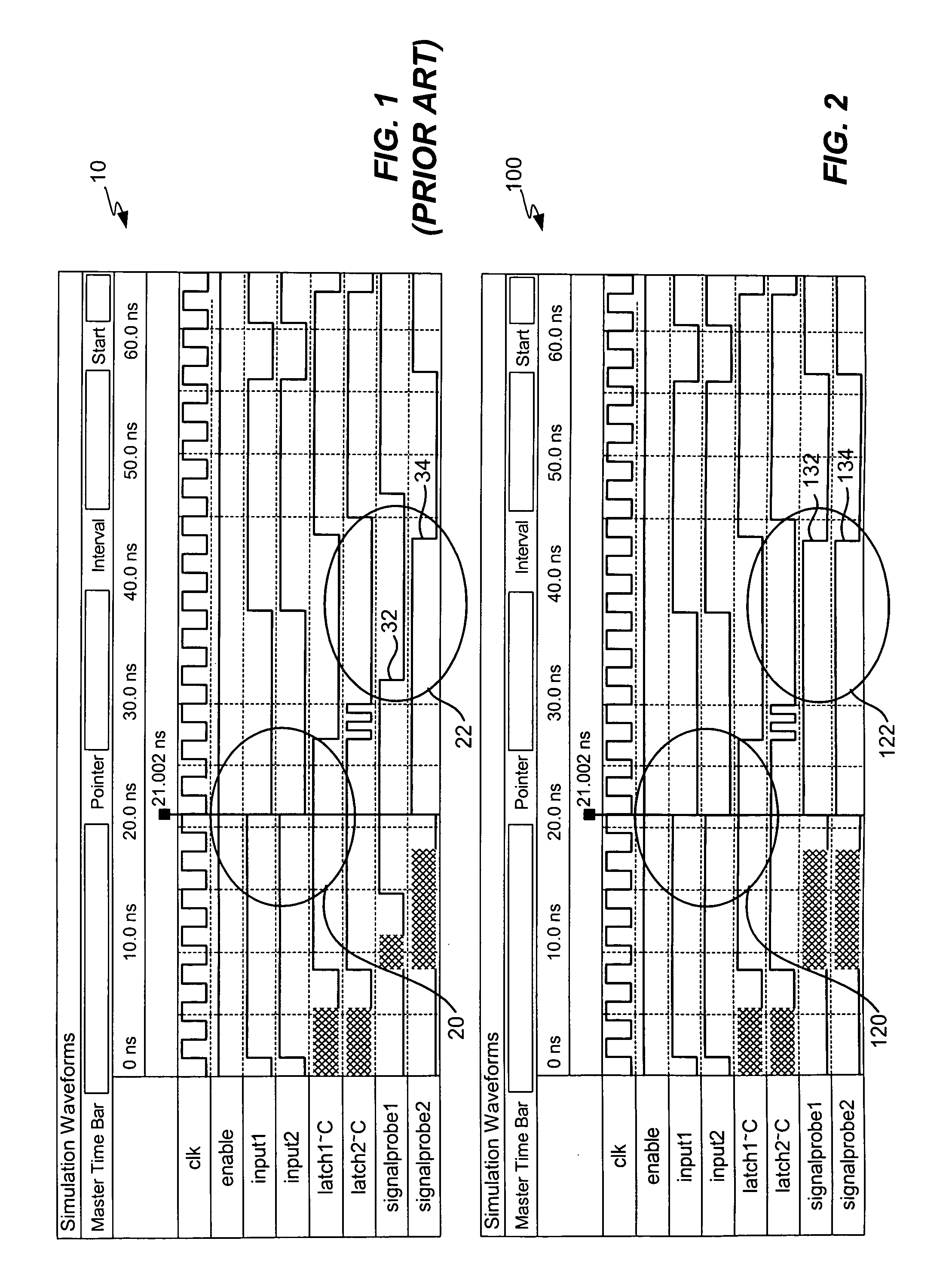
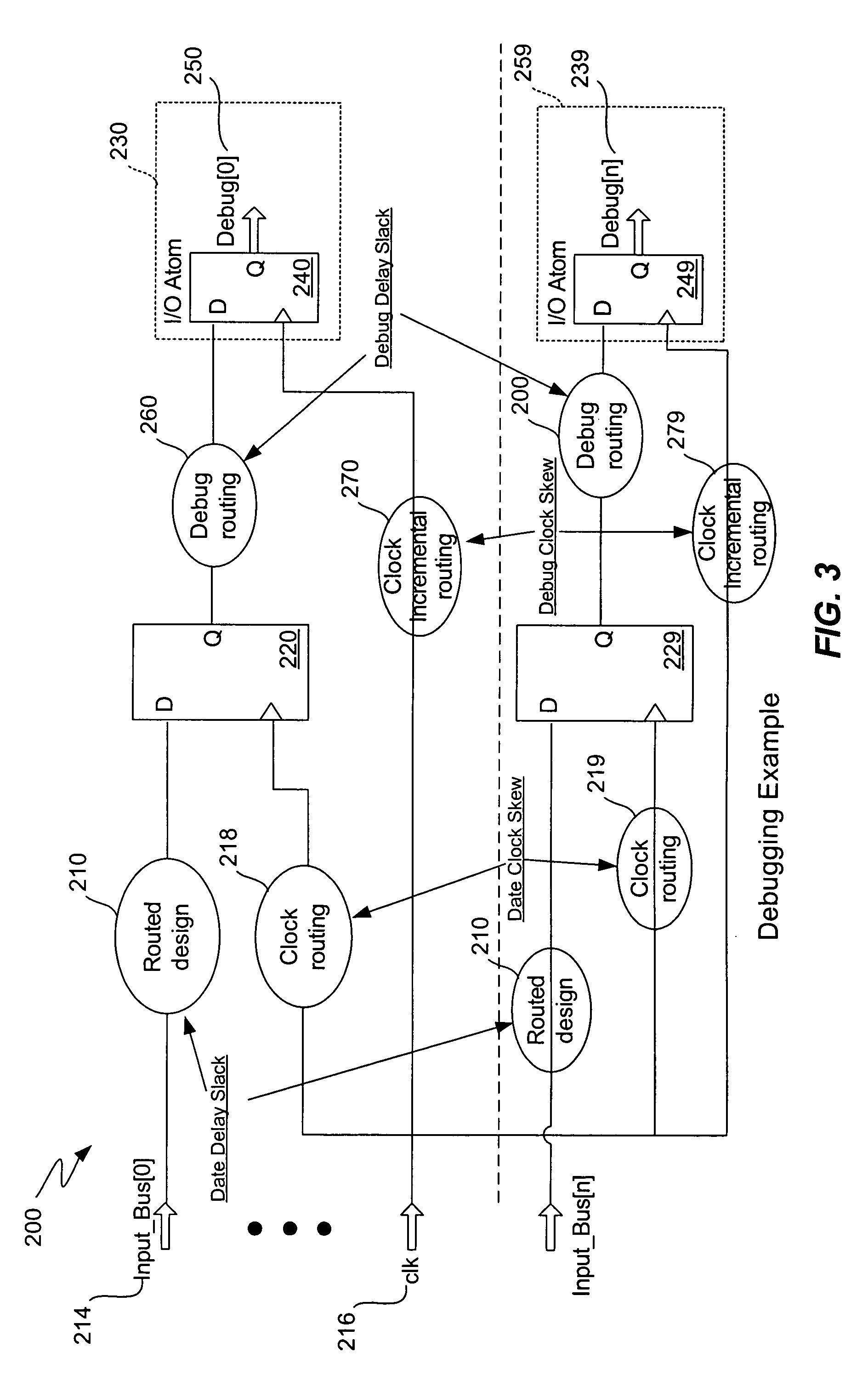
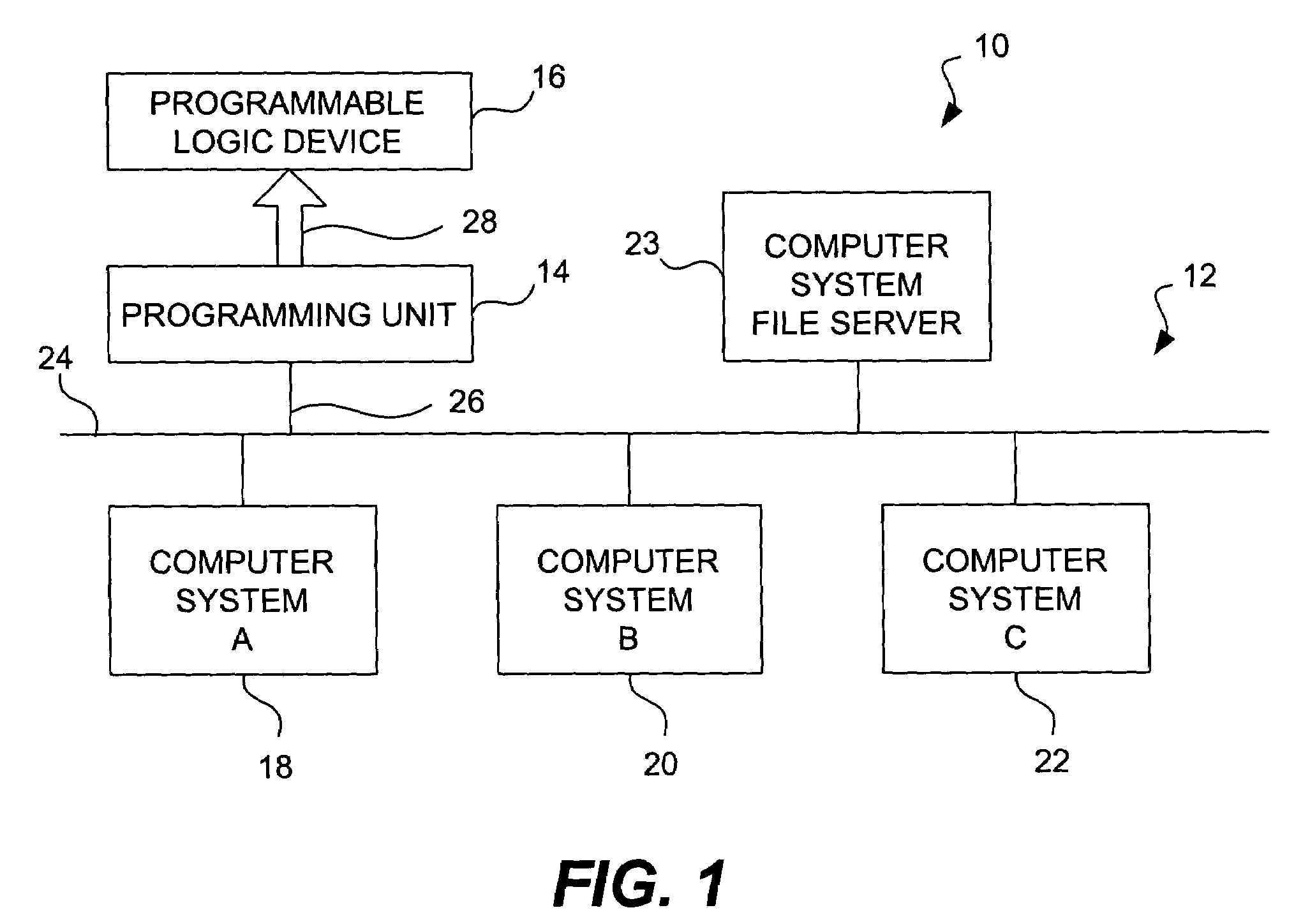
Chip debugging using incremental recompilation and register insertion
InactiveUS7206967B1Efficient solutionError detection/correctionElectrical testingComputer architectureProcessor register
While debugging, a user chooses an incremental recompile. Internal signals of interest and output pins are selected, and a number of additional registers are chosen to insert in the path of each internal signal. A clock is selected for the registers. An incremental recompile of the compiled design compiles a routing from each internal signal to an output pin via the added registers. The database building and logic synthesis stages are skipped. The post-fitting logical netlist and routing netlist are retrieved. The new registers are created and the internal signal is connected to the output pin atom in the logical netlist. The fitter places and routes the connections to create a new routing netlist and then the new routing netlist is output into a programming output file (POF) in a form suitable for programming the PLD. The original routing netlist is undisturbed. The user views the internal signals at the output pins chosen. The user may iterate through this process many times in order to debug the PLD. The debugging assignments may be deleted.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
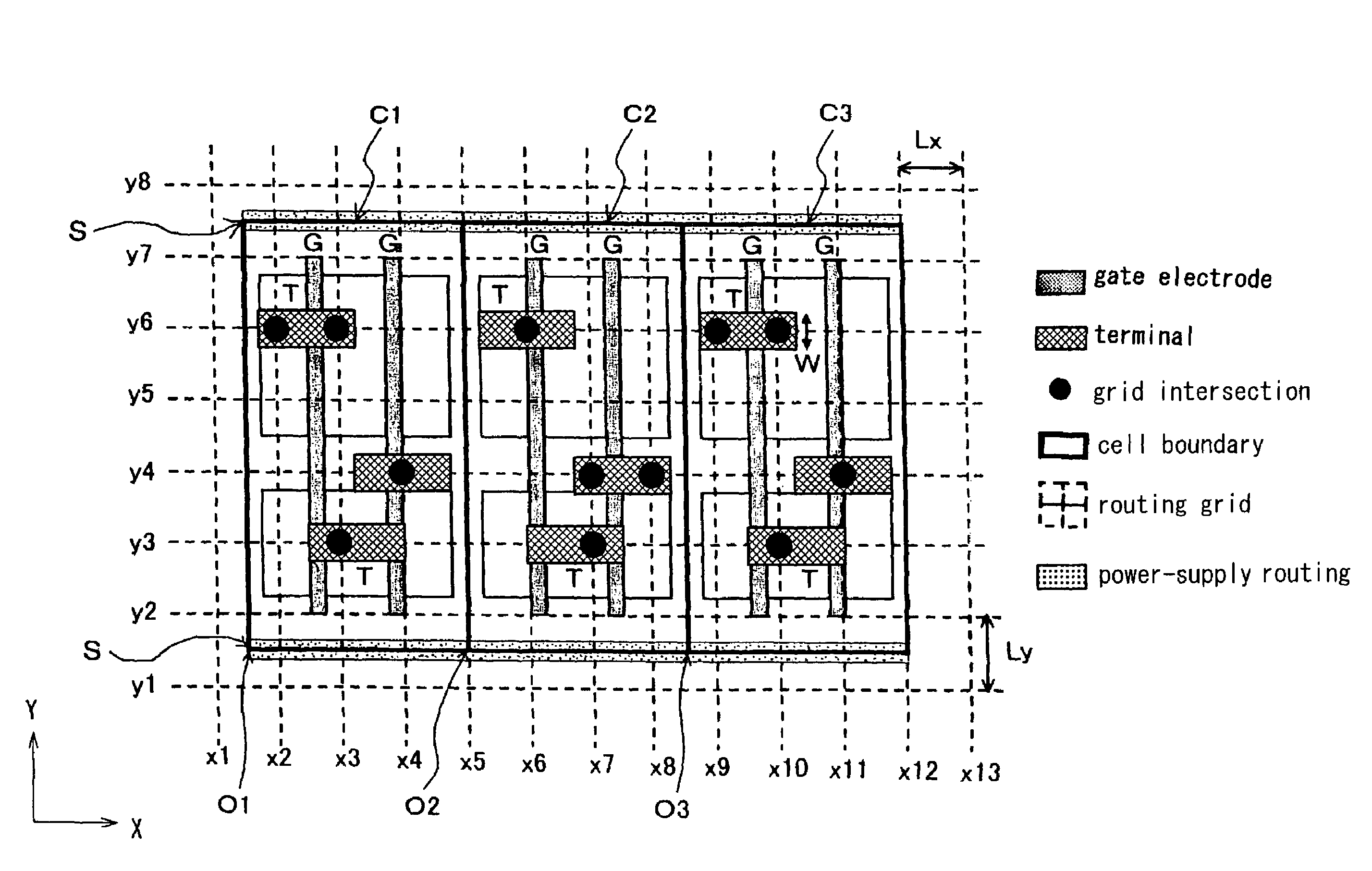
Cell, standard cell, standard cell library, a placement method using standard cell, and a semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS7503026B2Reducing cell area and chip areaHigh precisionSolid-state devicesComputer aided designElectrical batteryEngineering
A cell according to the present invention comprises a plurality of terminals capable of transmitting an input signal or an output signal and serving as a minimum unit in designing a semiconductor integrated circuit, wherein the plurality of terminals is located on routing grids lined in a Y direction which is a direction vertical to a power-supply wiring of the cell used in automatic placement & routing and has a shape extended in an X direction which is a direction in parallel with the power-supply wiring, more specifically such a shape that, for example, a longer-side dimension of the terminal is equal to “a routing grid interval in the X direction+a wiring width. According to the constitution, a cell area is reduced, which advantageously leads to the reduction of a chip area.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
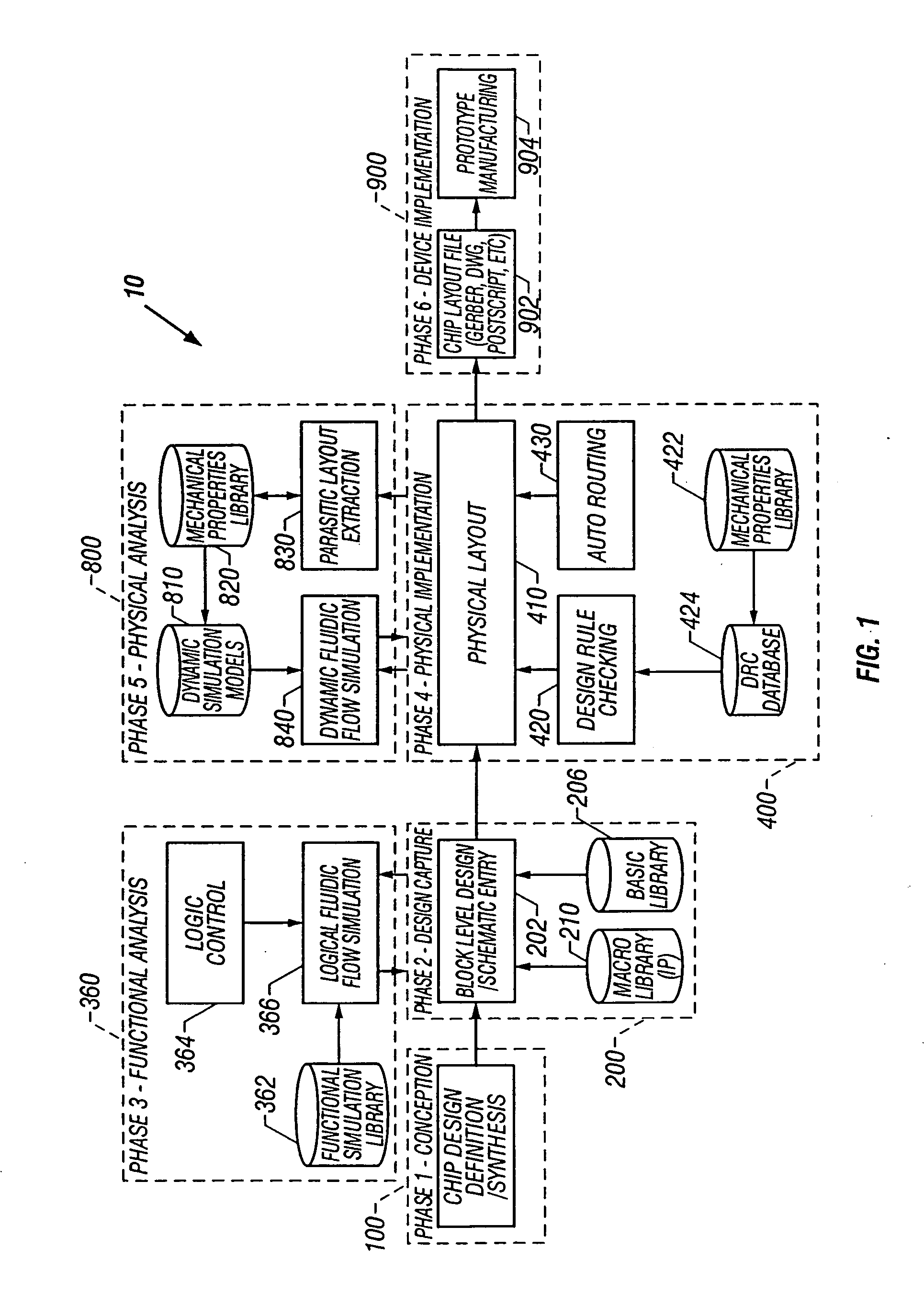
Microfluidic design automation method and system
InactiveUS20050065735A1Shorten the timeEasy placement and routingFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementComputer Aided DesignSystems design
The present invention generally relates to microfluidics and more particularly to the design of customized microfluidic systems using a microfluidic computer aided design system. In one embodiment of the present invention a microfluidic circuit design method is provided. The method includes developing synthesizable computer code for a design. Next, a microfluidic circuit schematic, including a plurality of symbols for microfluidic components, is generated either interactively or using the synthesizable computer code. The microfluidic circuit schematic is then functionally simulated. The microfluidic components are placed and routed on a template to form a physical layout. Then the physical layout is physically simulated using dynamic simulation models of the microfluidic components; and the physical layout is written to a layout file.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
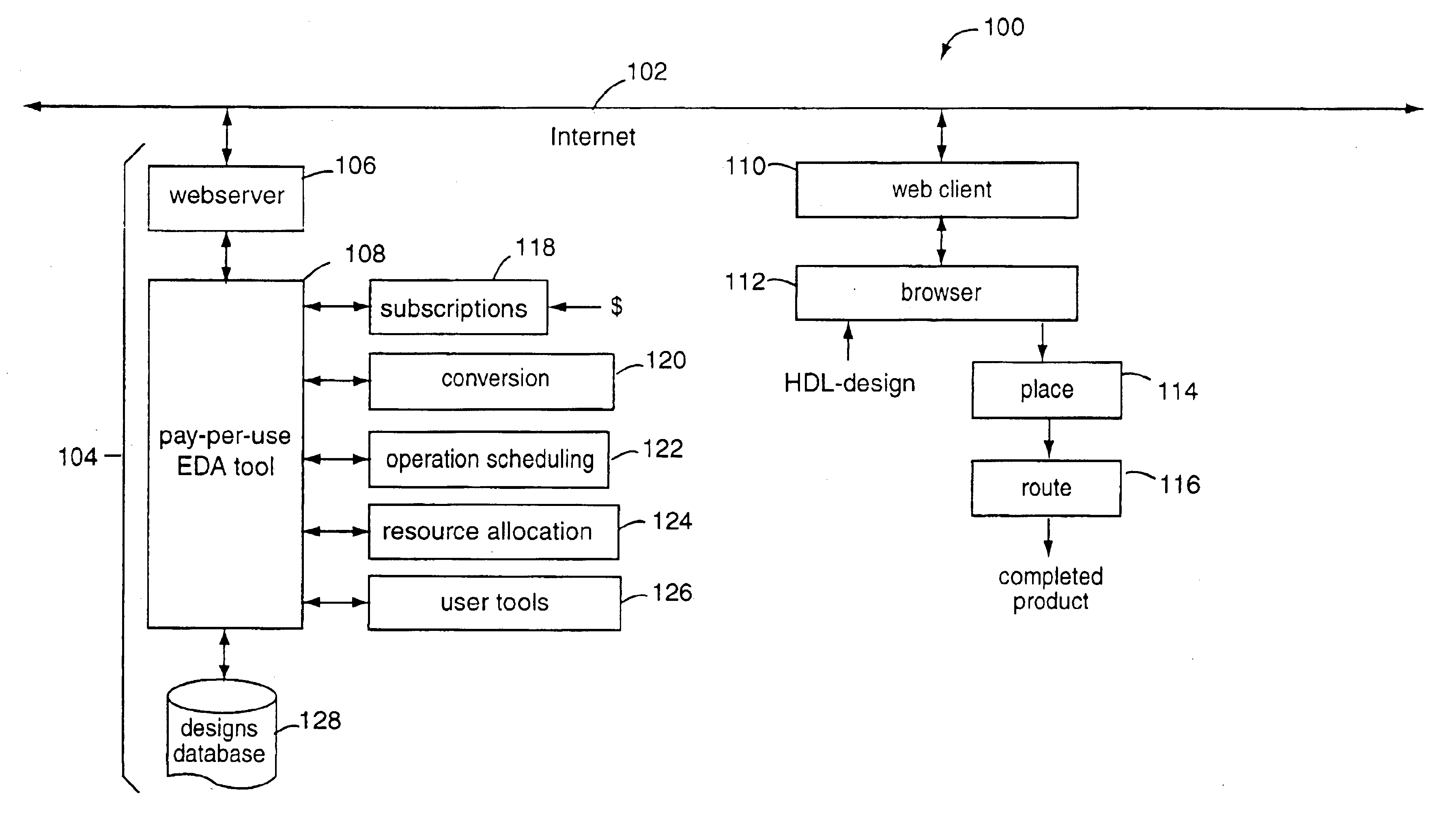
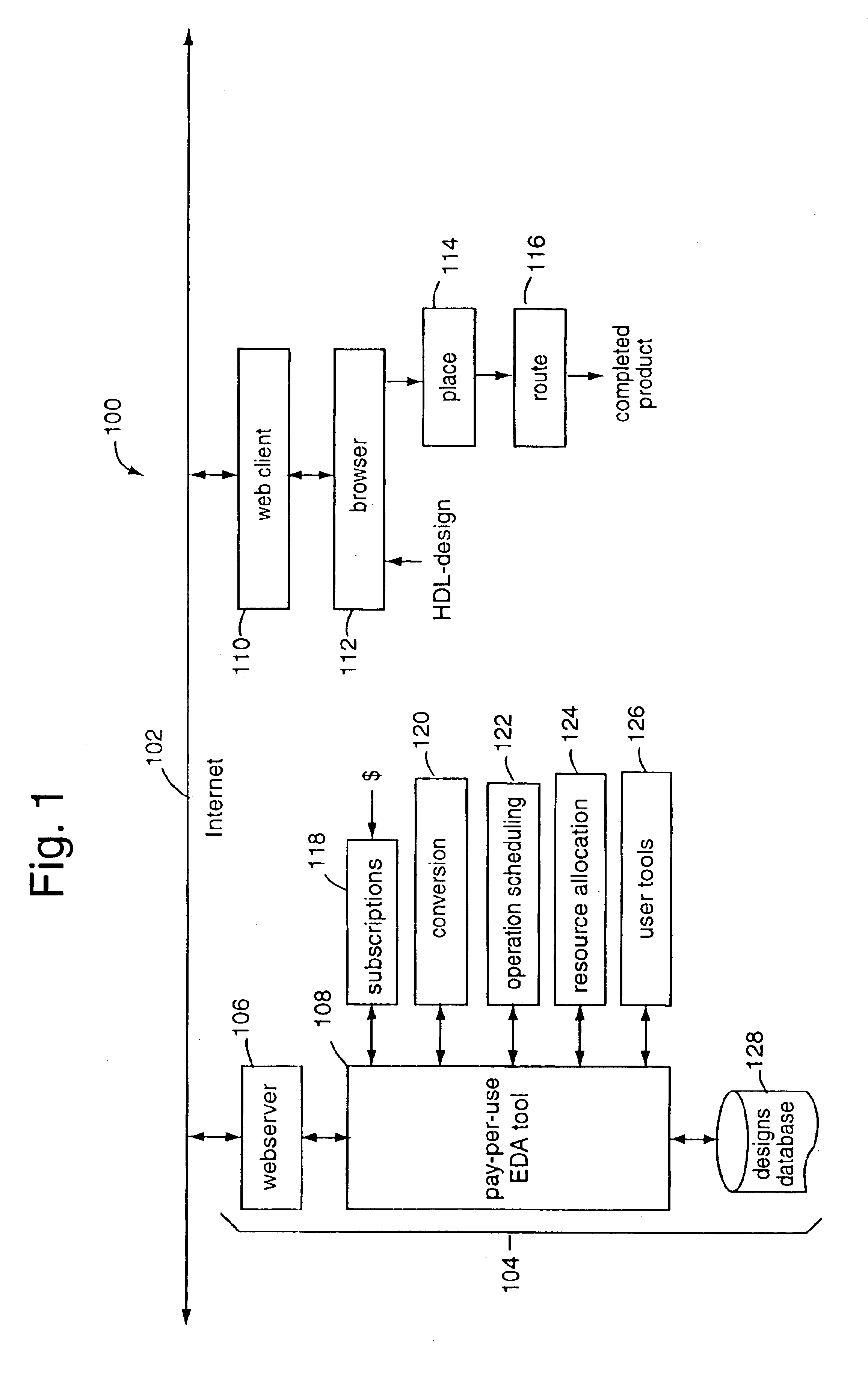
Behavioral-synthesis electronic design automation tool business-to-business application service provider
InactiveUS6782511B1Distributed efficiently and easilyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationWeb serviceIntellectual property
A business-to-business application service provider includes an Internet website and webserver with EDA-on-demand solutions for system-on-a-chip designers. Such website allows electronic designs in hardware description language to be uploaded into a front-end EDA design environment. A behavioral model simulation tool hosted privately on the webserver tests and validates the design. Such tool executes only in the secure environment of the business-to-business application service provider. The validated solution is then downloaded back over the Internet for a pay-per-use fee to the customer, and in a form ready to be placed and routed by a back-end EDA tool. Such validated design solutions are also downloadable to others in exchange for other designs, or available in technology libraries. The intellectual property created can be re-used, sold, shared, exchanged, and otherwise distributed efficiently and easily from a central for-profit clearinghouse.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Apparatus and methods for providing in-chip microtargets for metrology or inspection
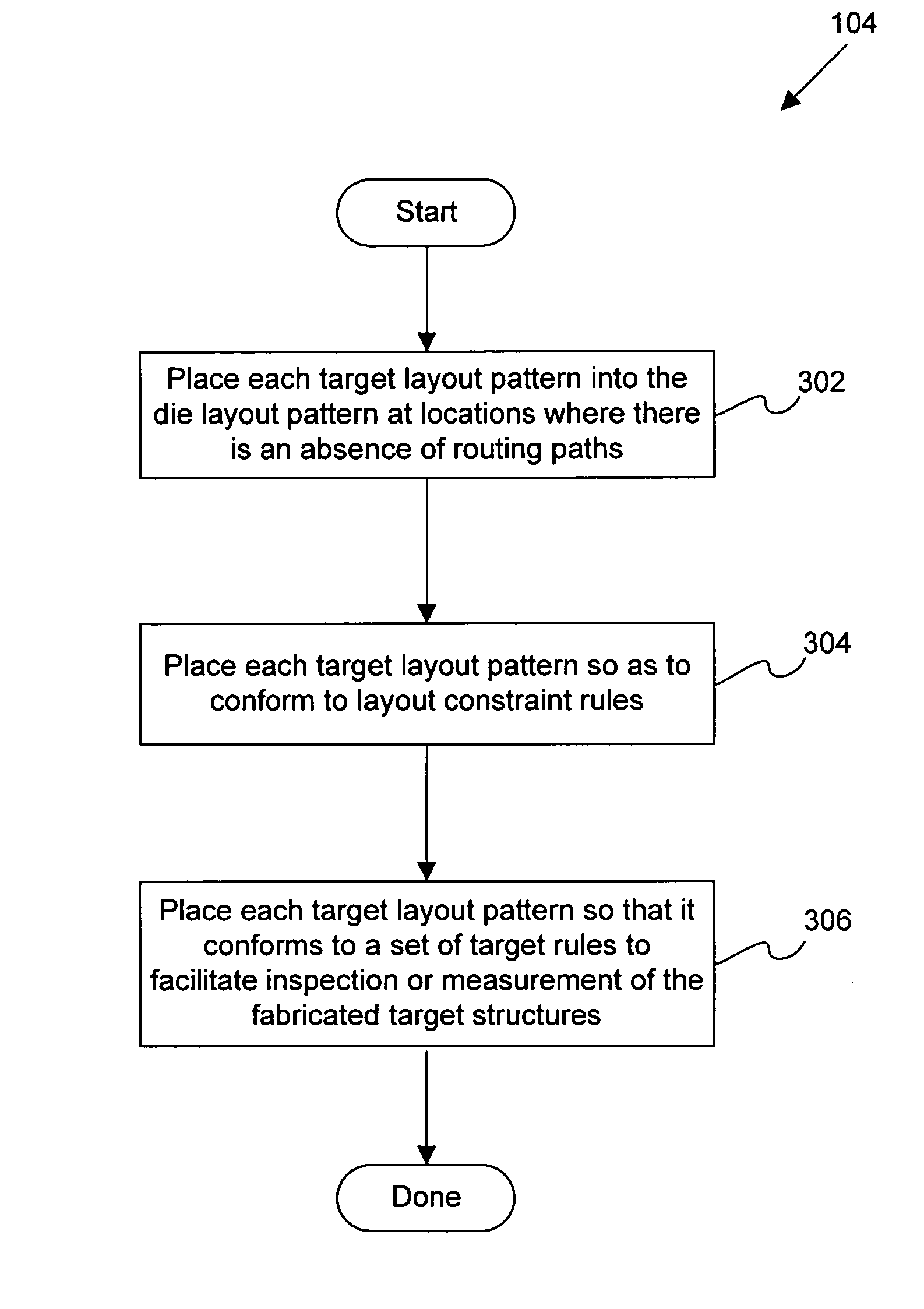
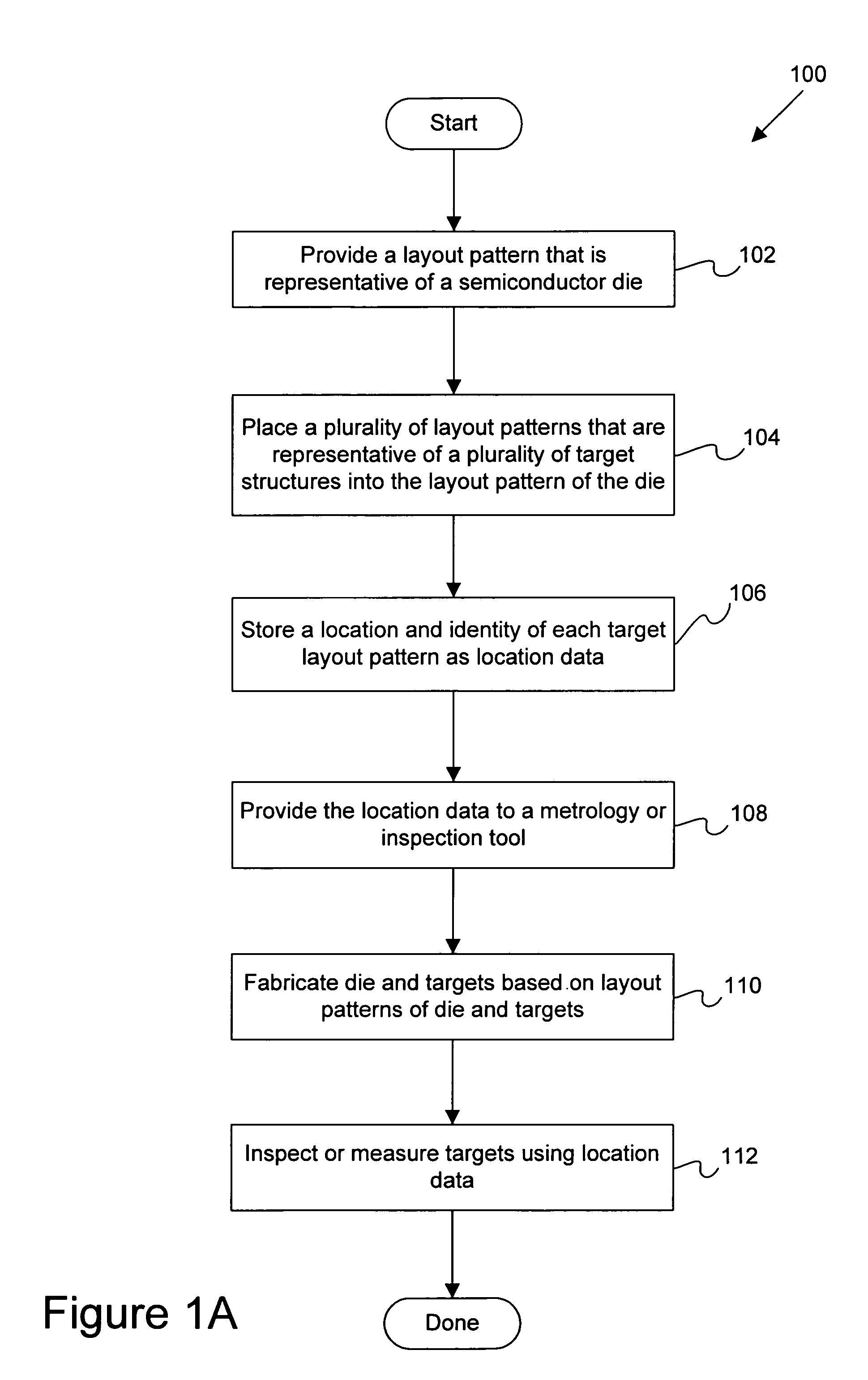
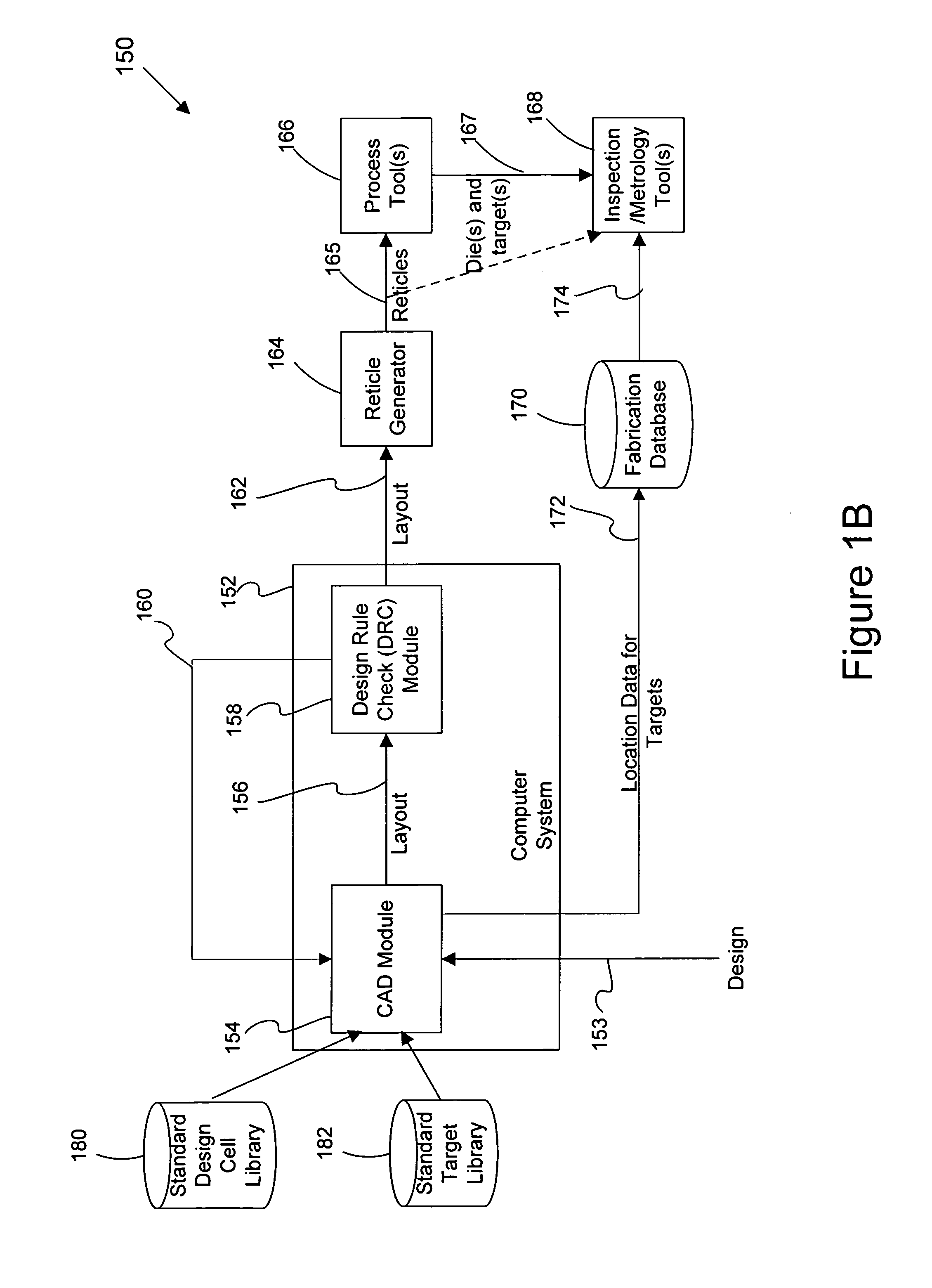
Disclosed are techniques and apparatus for providing metrology or inspection targets in-chip. That is, targets are integrated within the product device or die area. In general terms, the present invention provides techniques for enabling inspection or metrology on targets within the die or active area. Said in another way, target structures are inserted within the die or active area. In one embodiment, a set of rules are provided for integrating test structures within the die. For example, these rules may be implemented by one or more design engineers or by place-and-route tools which automatically generate the die layout pattern and thereafter insert the target structures into the die layout pattern based on these rules. Location data of each target is then retained during the layout generation and provided to one or more inspection or metrology tools and / or metrology engineers so that each target may be found and then inspected or measured.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Automated semiconductor design flaw detection system
ActiveUS20100146338A1Shorten the timeLow costError detection/correctionCAD circuit designProgrammable logic deviceSoftware engineering
The process by which a logical simulation model is implemented in a physical device may introduce errors in the resulting implementation. A simulation system enables comparison of a realized physical implementation against the simulation models that produce them, thereby detecting differences between an initial, logical design and the resulting physical embodiment. Errors introduced by an initial design, faulty Intellectual Property blocks, faulty programmable logic device silicon, faulty synthesis algorithms and software, and faulty place and route algorithms and software may be detected. As a result, the simulation system reflects both the accuracy of the actual implemented device with the capacity and performance of a purpose built hardware-assisted solution.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
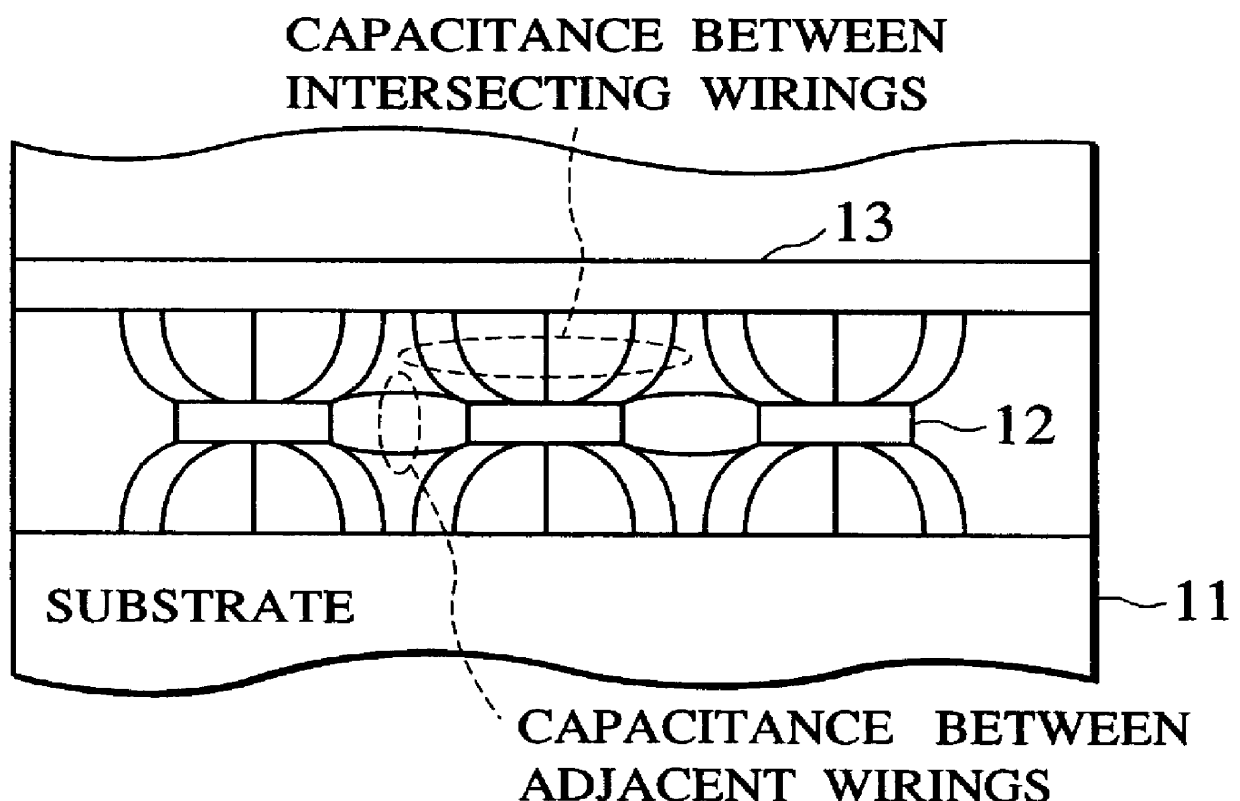
Layout design method and system for an improved place and route
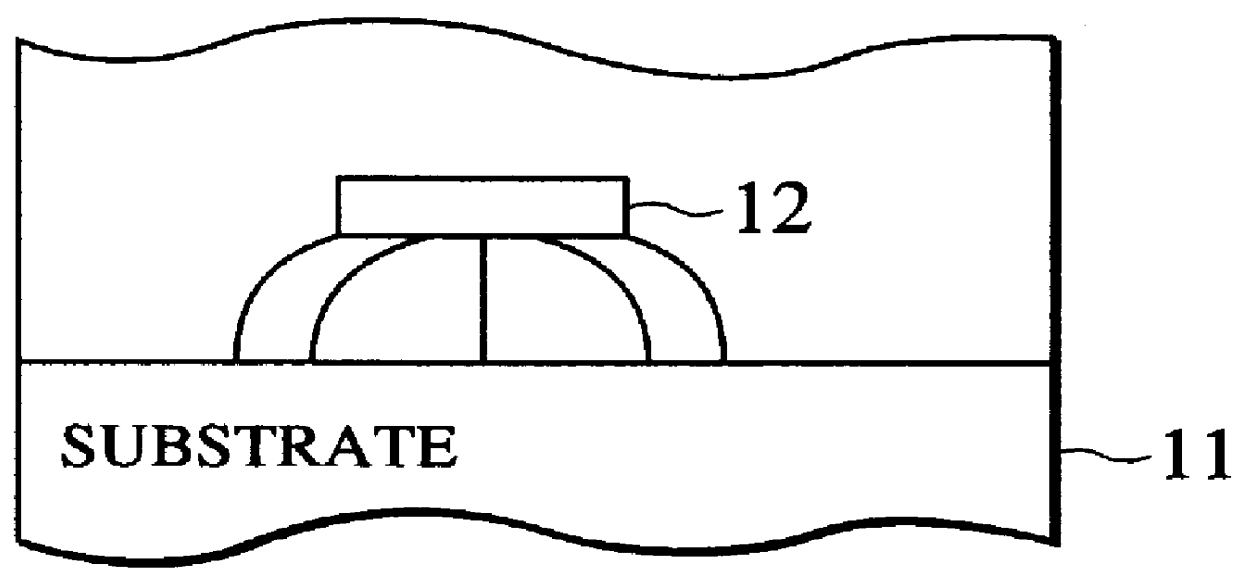
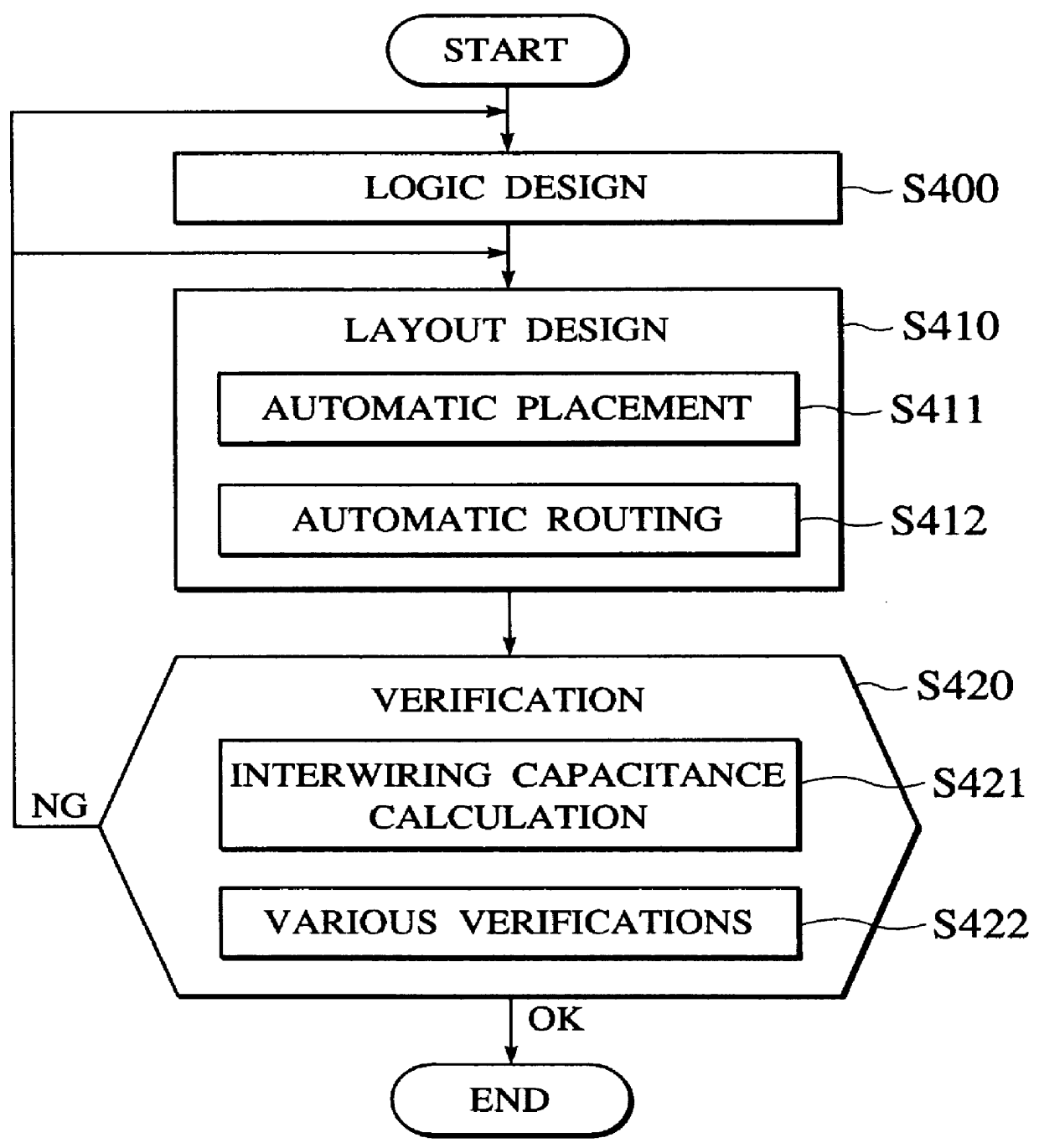
InactiveUS6110222ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer aided designCapacitanceDesign methods
A layout design method and system for a semiconductor integrated circuit improves circuit performances related to operated frequency and power consumption by improved placement and routing. The method features an intersecting wiring predicting step that predicts the number of the intersecting wirings based on predicted wiring routes and an intersecting wiring capacitance calculating step that calculates the capacitances between the intersecting wirings.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Hierarchically-Scalable Reconfigurable Integrated Circuit Architecture With Unit Delay Modules
InactiveUS20120126850A1Significant resiliencyError detection/correctionFail-safe circuitsData operationsTime delays
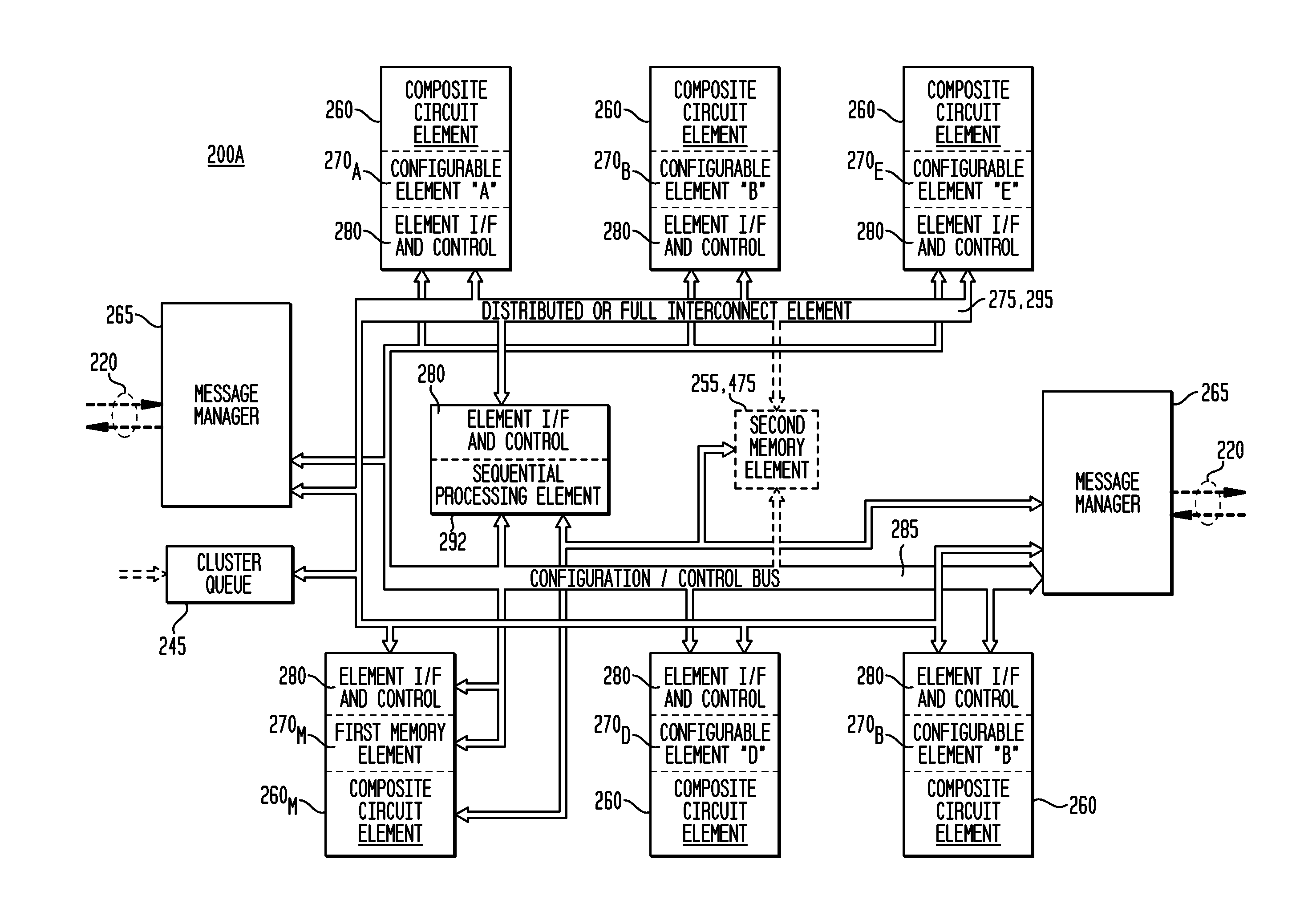
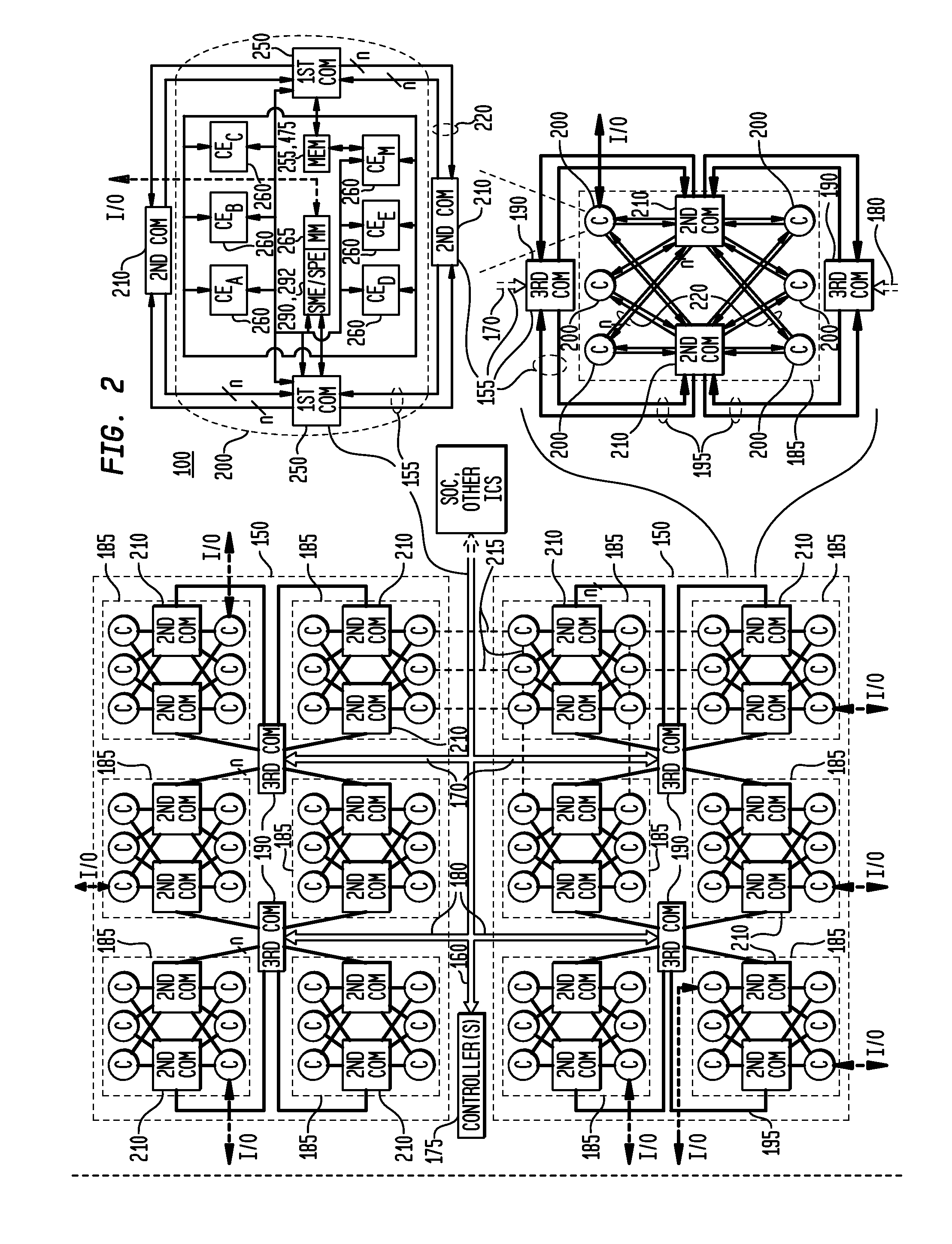
The exemplary embodiments provide a reconfigurable integrated circuit architecture having a predetermined, unit timing increment (or delay) for both data operations and data word transfers within every zone and between zones, which are independent of application placement and routing. An exemplary IC comprises a plurality of circuit zones, with each zone comprising: a plurality of composite circuit elements, a plurality of cluster queues, and a full interconnect bus. Each composite circuit element comprises: a configurable circuit element circuit and an element interface and control circuit, with the element interface and control circuit comprising an input queue and an output queue. Each cluster queue comprises an element interface and control having an input queue and an output queue. The full interconnect bus couples every output queue within the zone to every input queue within the zone. Any data operation performed by a composite circuit element, any data word transfer through a cluster queue, and any data word transfer over the first full interconnect bus, is completed within a predetermined unit time delay which is independent of application placement and application data routing on the reconfigurable IC.
Owner:ELEMENT CXI
Integrated circuit partitioning placement and routing system
InactiveUS6519749B1Improve accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFloor planComputer module
Disclosed herein is a method for dividing an integrated circuit (IC) design into several circuit partitions, each including one or more circuit modules, and then separately carrying out placement and routing for each circuit partition, with each partition being implemented within a separate area of an IC substrate. The method initially generates a whole-chip trial placement that tends to cluster cells of each circuit module together. An IC substrate floor plan assigning modules to various partitions is prepared, with the size, shape and relative position of each partition being determined by size, shape and relative position of areas of the substrate occupied by those modules in the trial floor plan. A trial routing is also performed with information on which to base a pin assignment plan for each module. A detailed placement and routing process is then independently performed for each partition, with placement and routing of cells within each partition constrained by the floor plan and pin assignment plan.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and system for post-routing lithography-hotspot correction of a layout
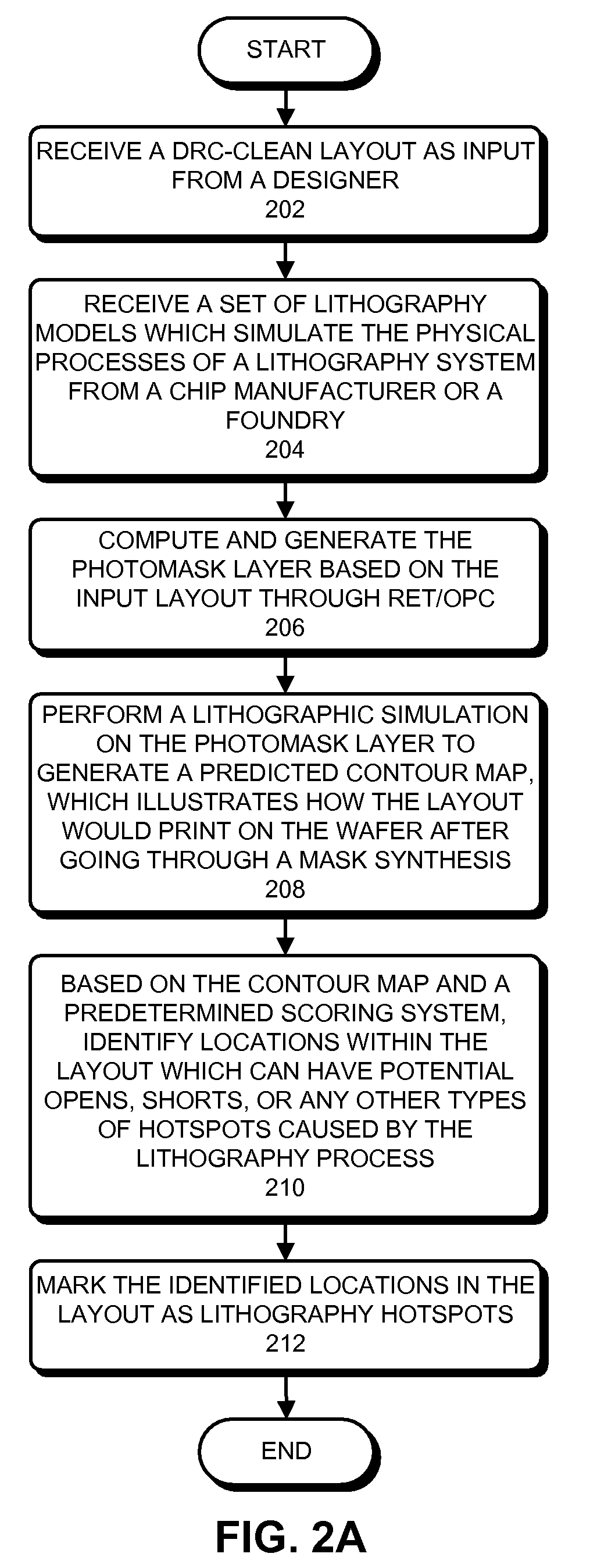
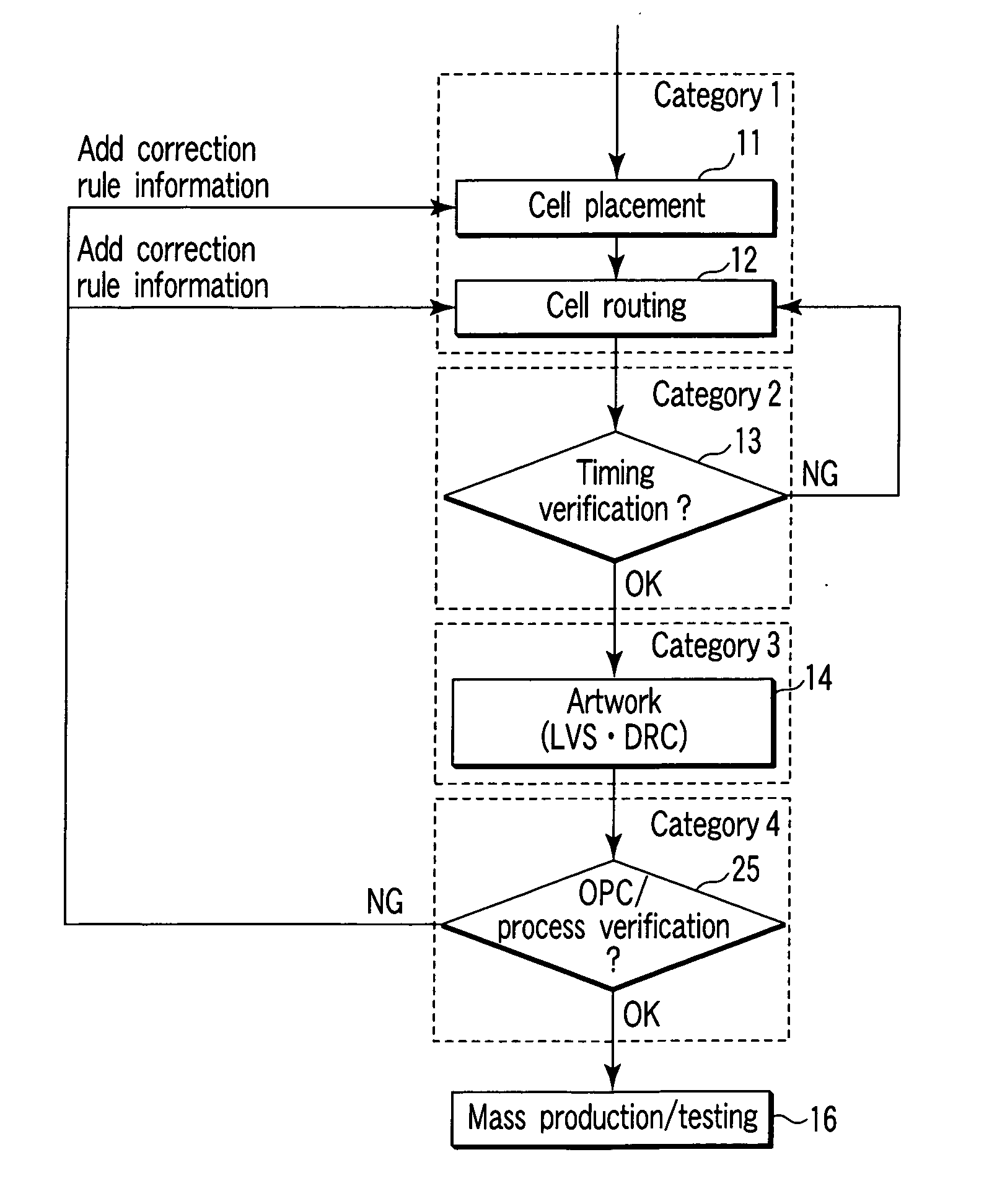
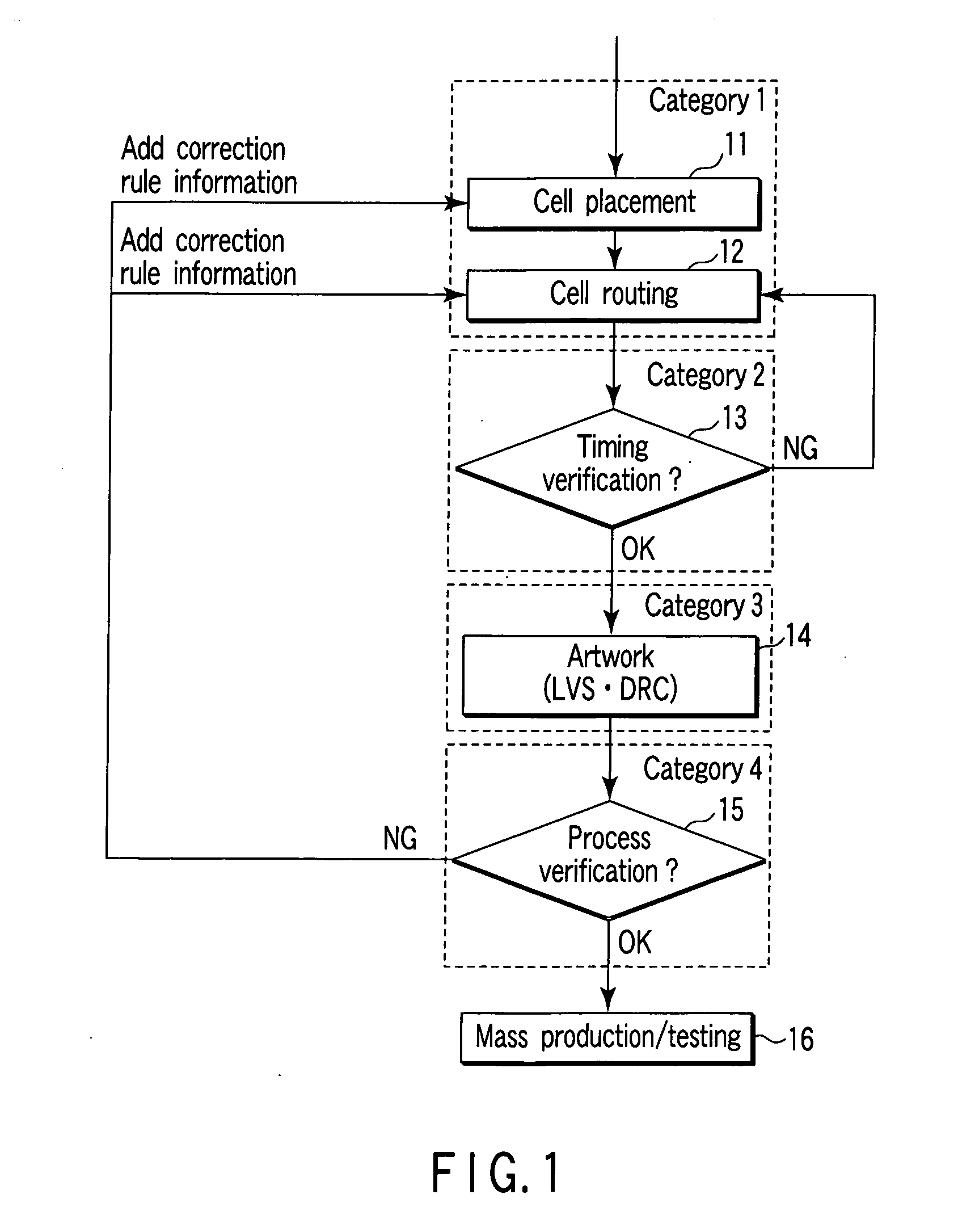
ActiveUS20090300561A1Avoid violationsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designSystem usagePhotolithography
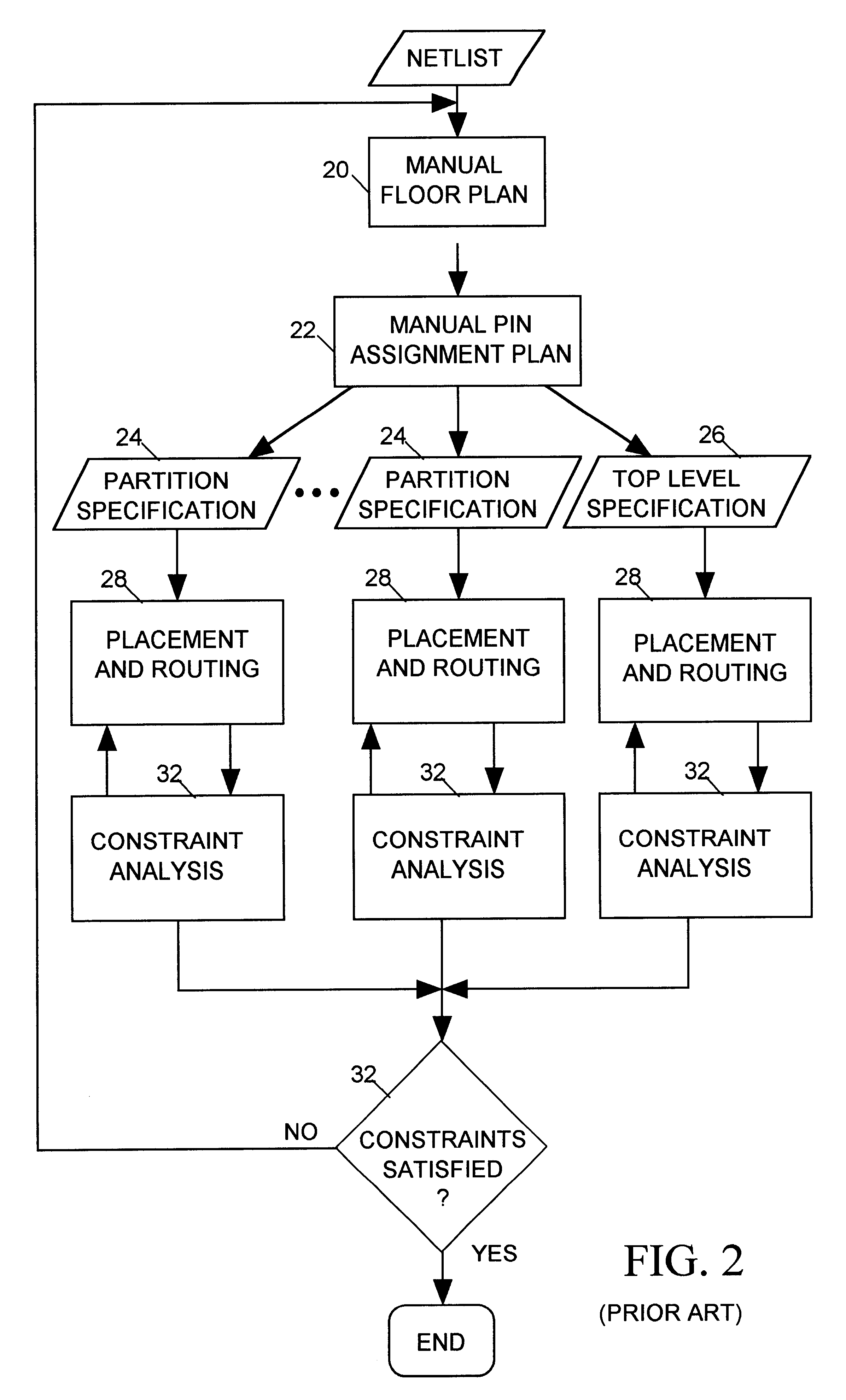
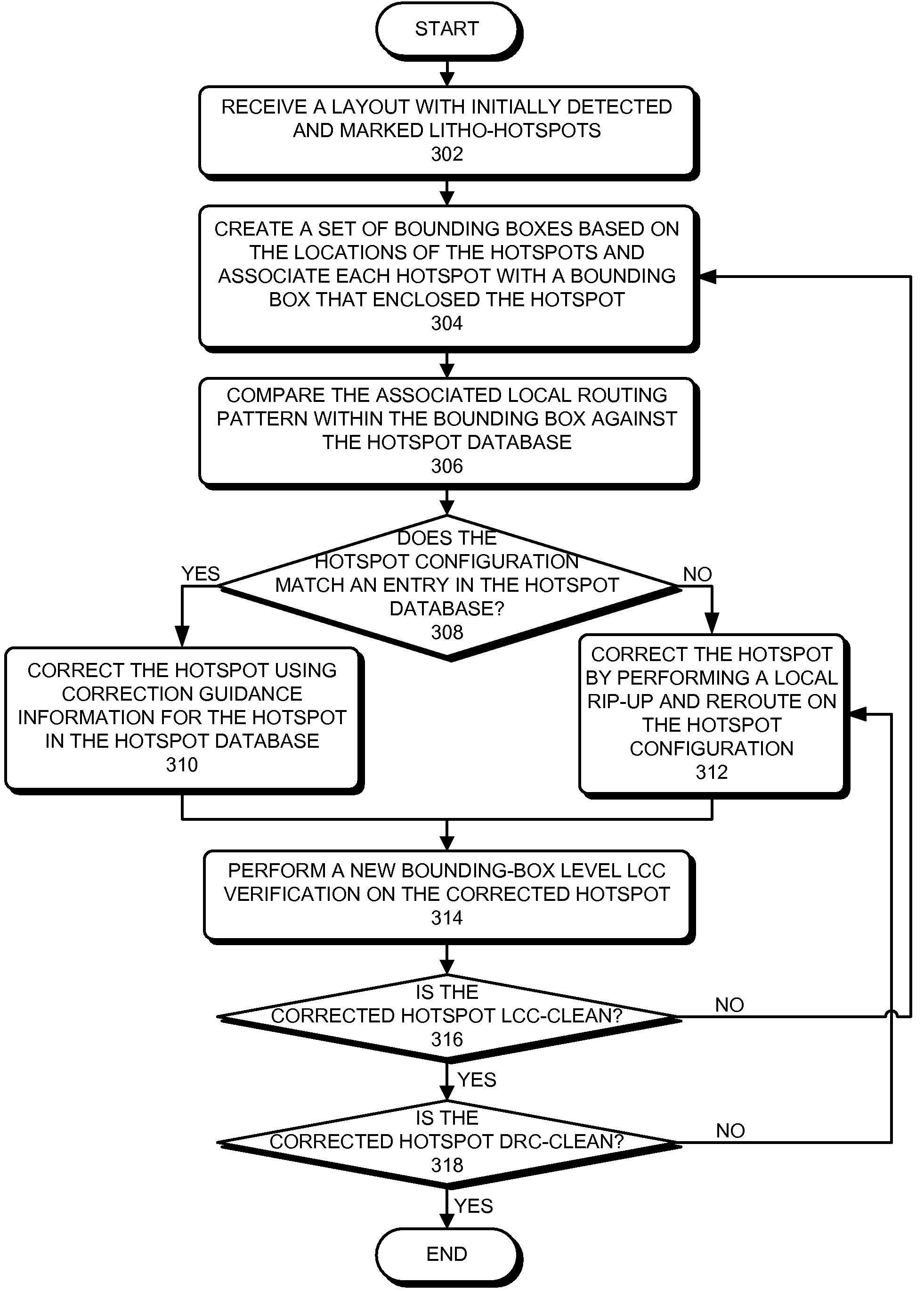
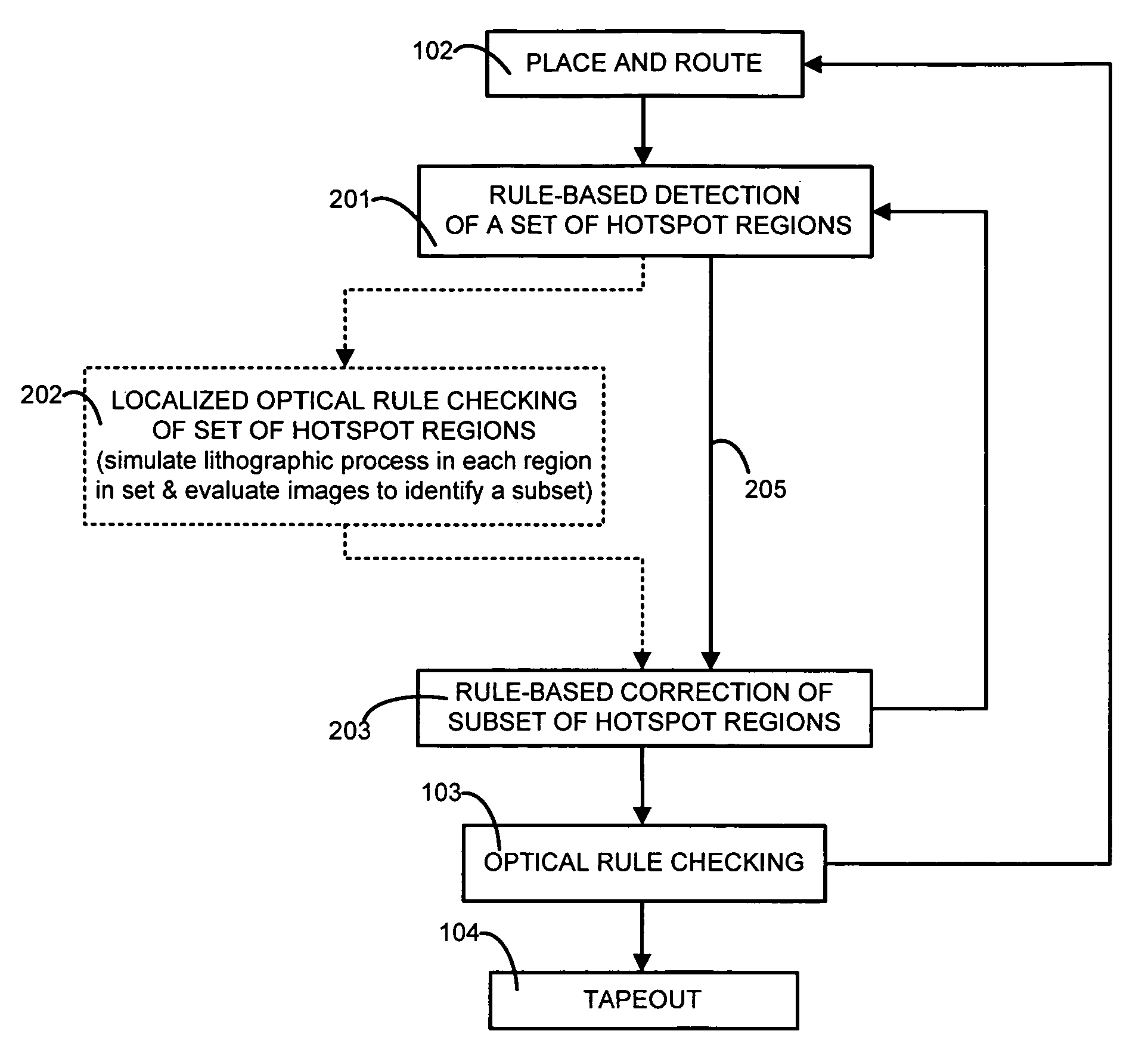
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that verifies an integrated circuit (IC) chip layout. During operation, the system receives a layout of an IC chip after the layout has gone through a place-and-route operation. Next, the system performs a lithography compliance checking (LCC) operation on the layout to detect lithography hotspots within the layout, wherein each lithography hotspot is associated with a local routing pattern around the lithography hotspot. Next, for each detected lithography hotspot, the system compares the associated local routing pattern against a hotspot database to determine if the local routing pattern matches an entry in the hotspot database, which stores a set of known hotspot configurations. If so, the system corrects the lithography hotspot using correction guidance information associated with the hotspot configuration stored in the hotspot database. Otherwise, the system corrects the lithography hotspot by performing a local rip-up and reroute on the local routing pattern, iteratively, until achieving convergence or given number of iterations.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Fast lithography compliance check for place and route optimization
A computer is programmed to use at least one rule to identify from within a layout of an IC design, a set of regions likely to fail if fabricated unchanged. An example of such a rule of detection is to check for presence of two neighbors neither of which fully overlaps a short wire or an end of a long wire. The computer uses at least another rule to change at least one region in the set of regions, to obtain a second layout which is less likely to fail in the identified regions. An example of such a rule of correction is to elongate at least one of the two neighbors. The computer may perform optical rule checking (ORC) in any order relative to application of the rules, e.g. ORC can be performed between detection rules and correction rules i.e. performed individually on each identified region prior to correction.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
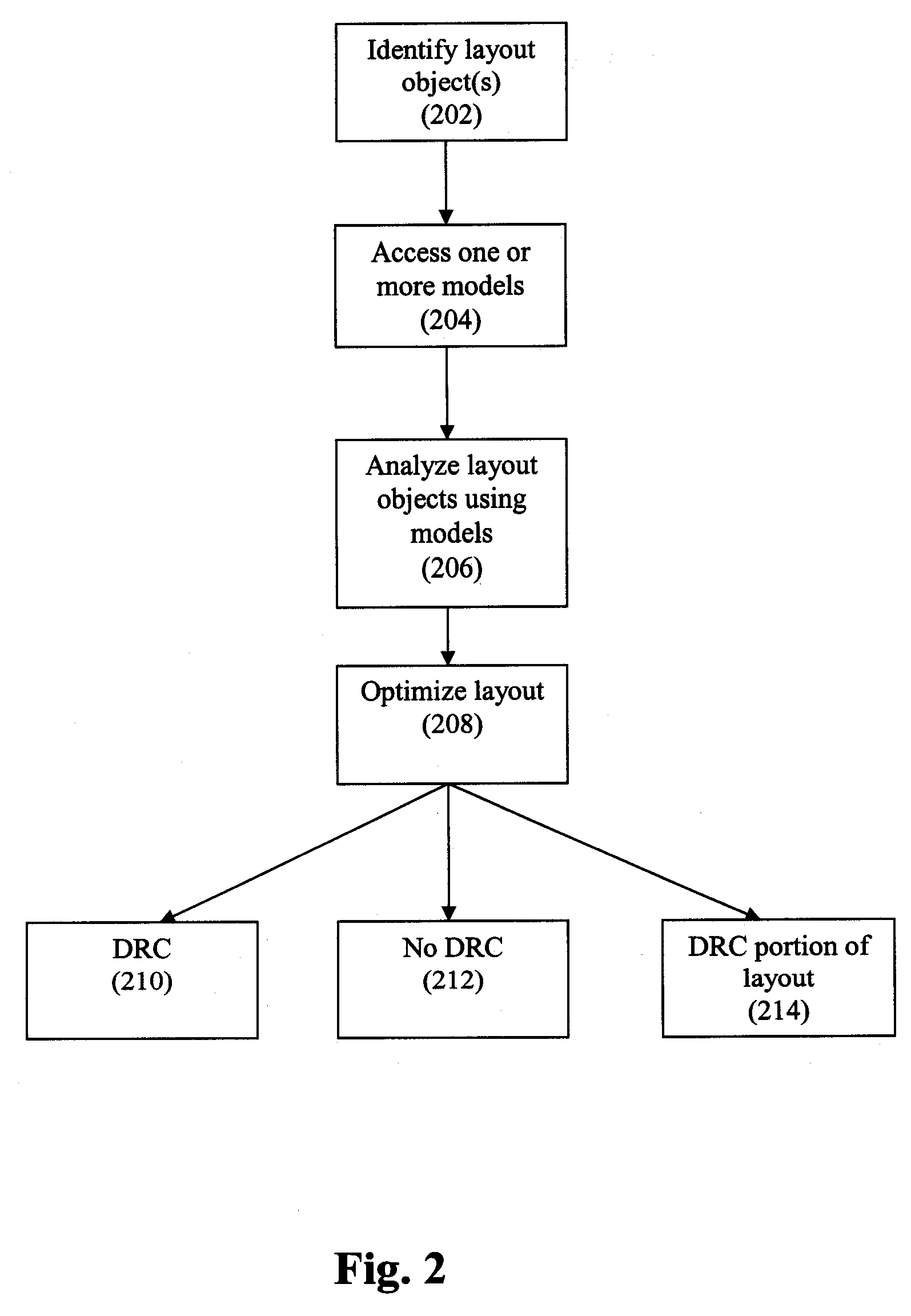
Method and System for Model-Based Routing of an Integrated Circuit
ActiveUS20080163150A1Minimize changesSignificant changeComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringManufacturing variation
Disclosed is a method, system, and computer program product for implementing model-based floorplanning, layout, placement, and routing. Models are used to guide the placement and routing of polygons on the IC layout based upon predictions of manufacturing variations.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
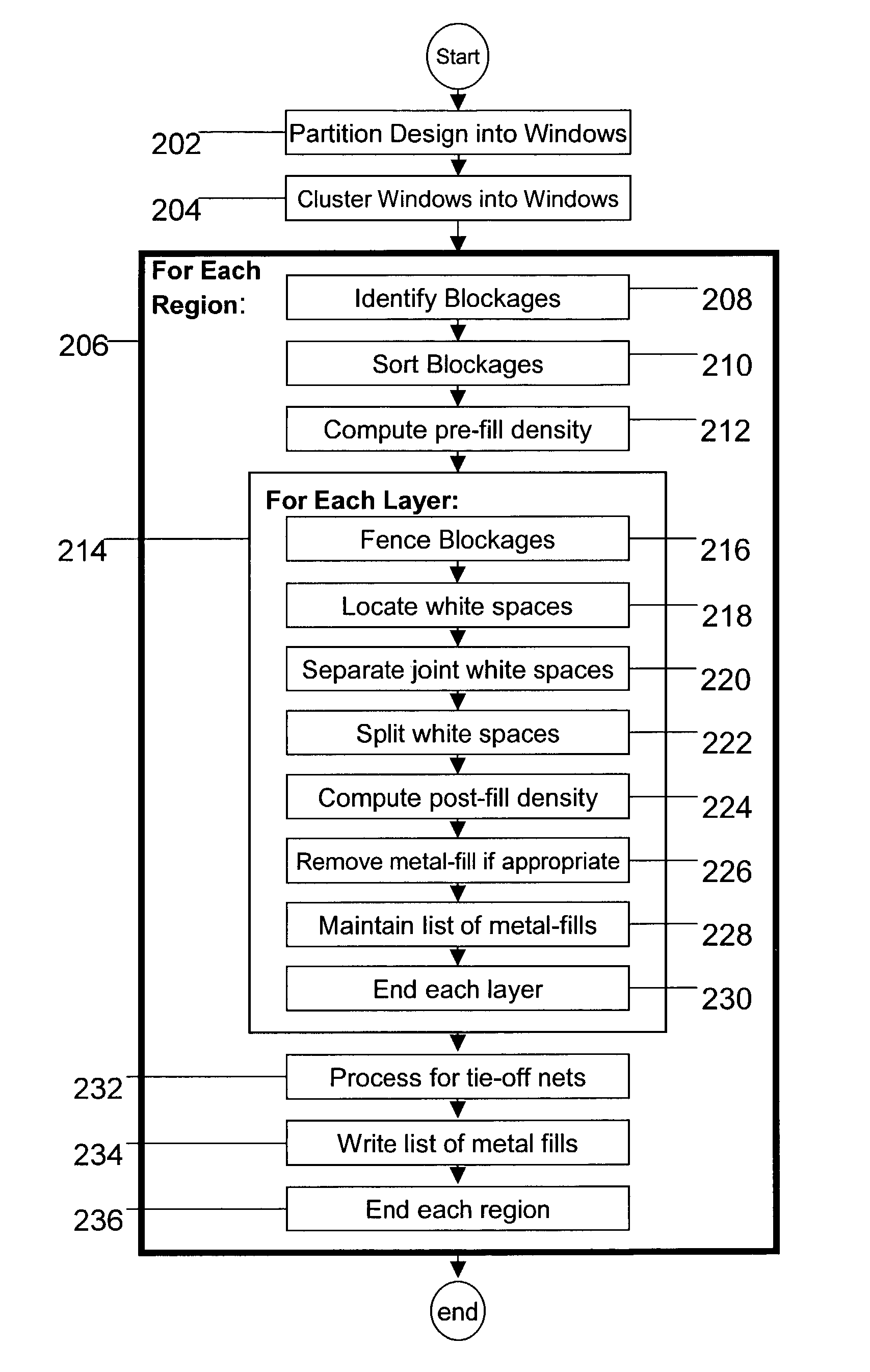
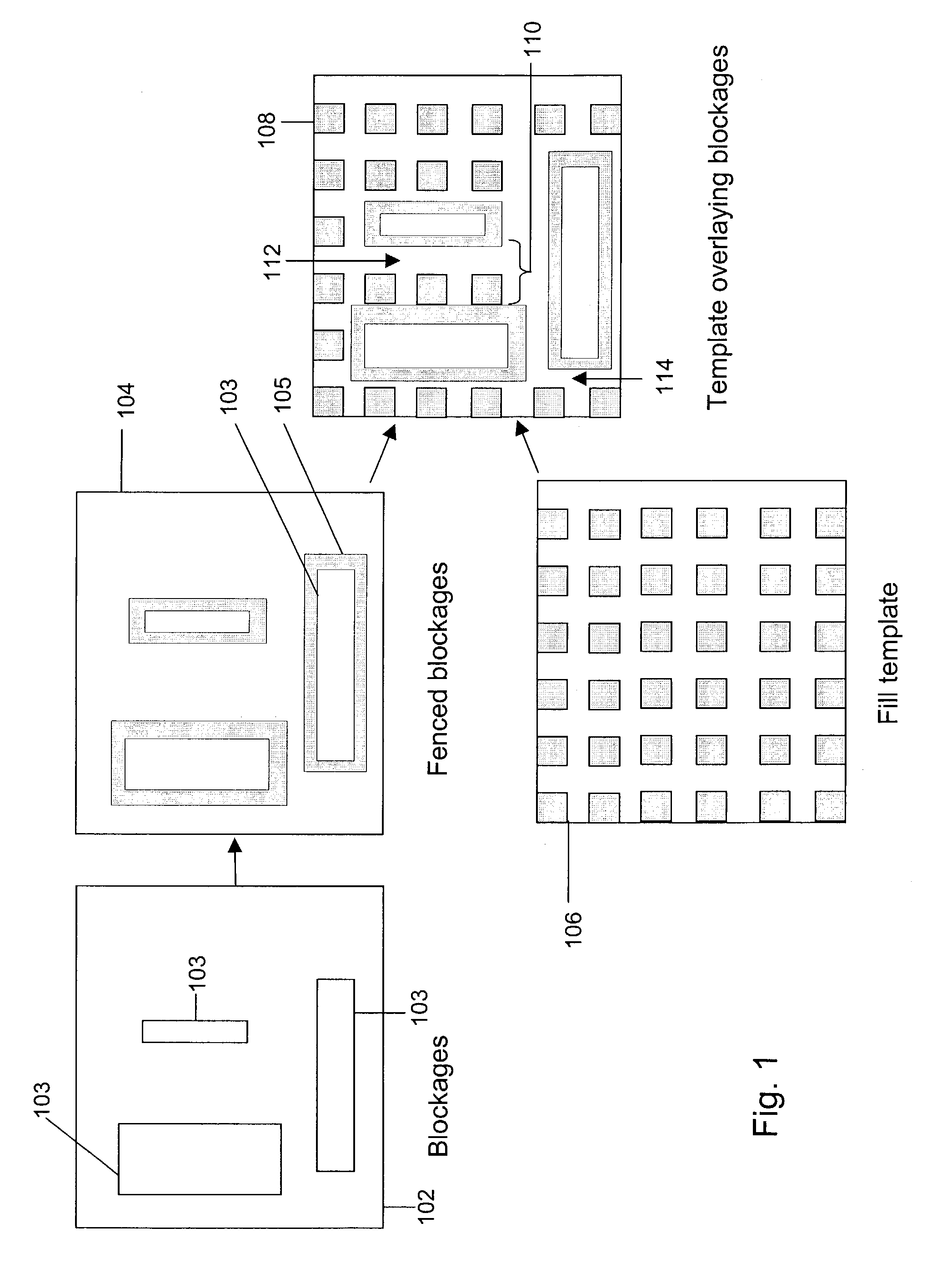
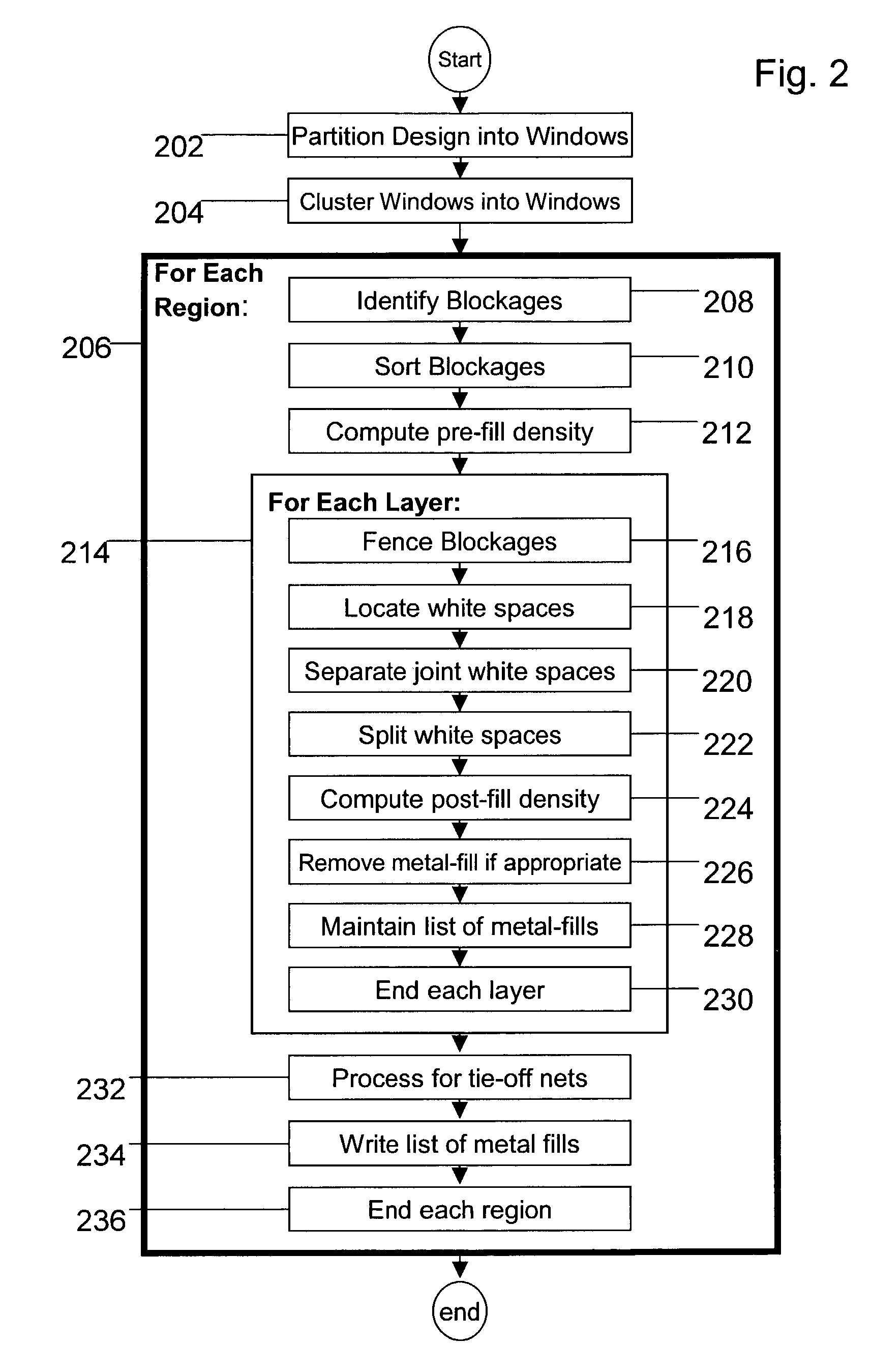
Place and route tool that incorporates a metal-fill mechanism
InactiveUS7328419B2Not be addCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcess engineeringIndustrial engineering
Disclosed is a method, system, and article of manufacture for a one-pass approach for implementing metal-fill for an integrated circuit. Also disclosed is a method, system, and article of manufacture for implementing metal-fill that is coupled to a tie-off connection. An approach that is disclosed comprises a method, system, and article of manufacture for implementing metal-fill having an elongated shape that corresponds to the length of whitespace. Also disclosed is the aspect of implementing metal-fill that matches the routing direction. Yet another disclosure is an implementation of a place & route tool incorporating an integrated metal-fill mechanism.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
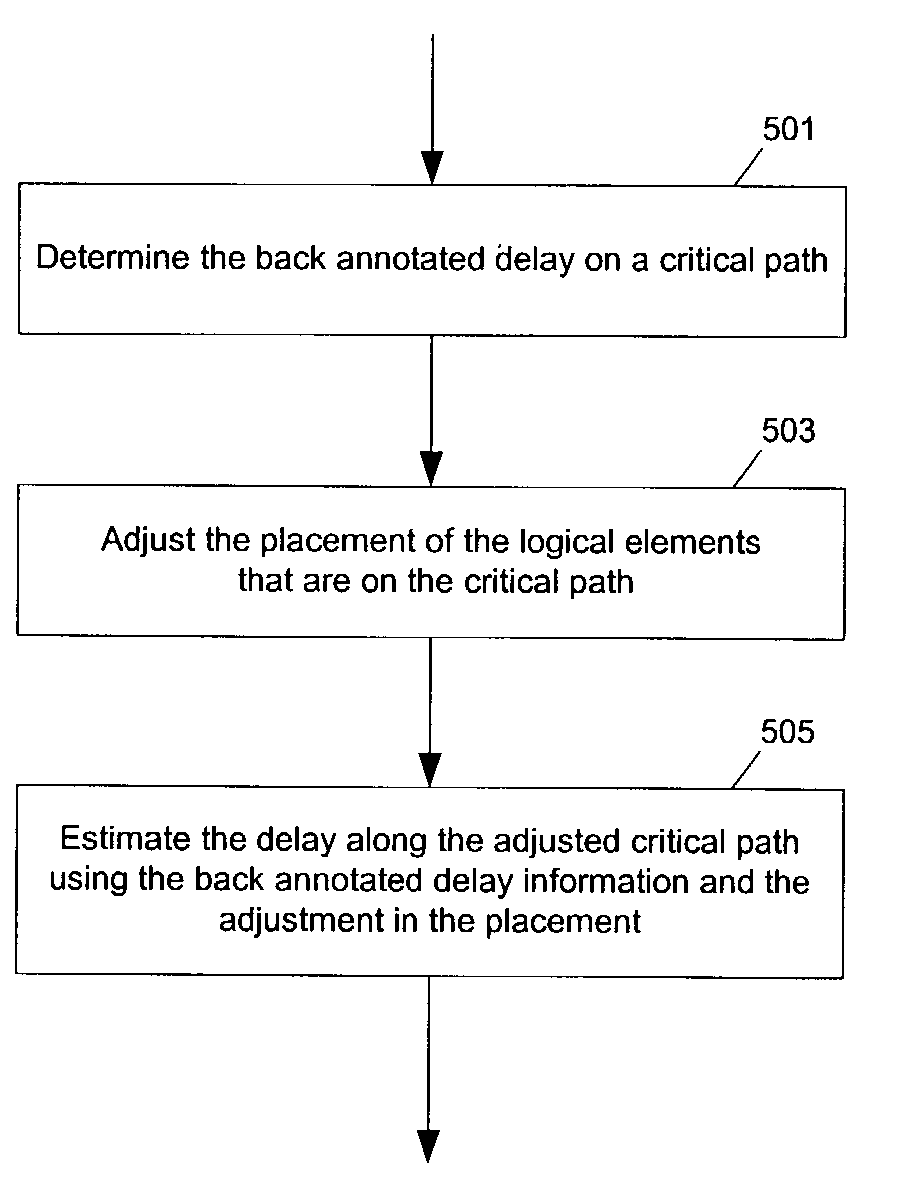
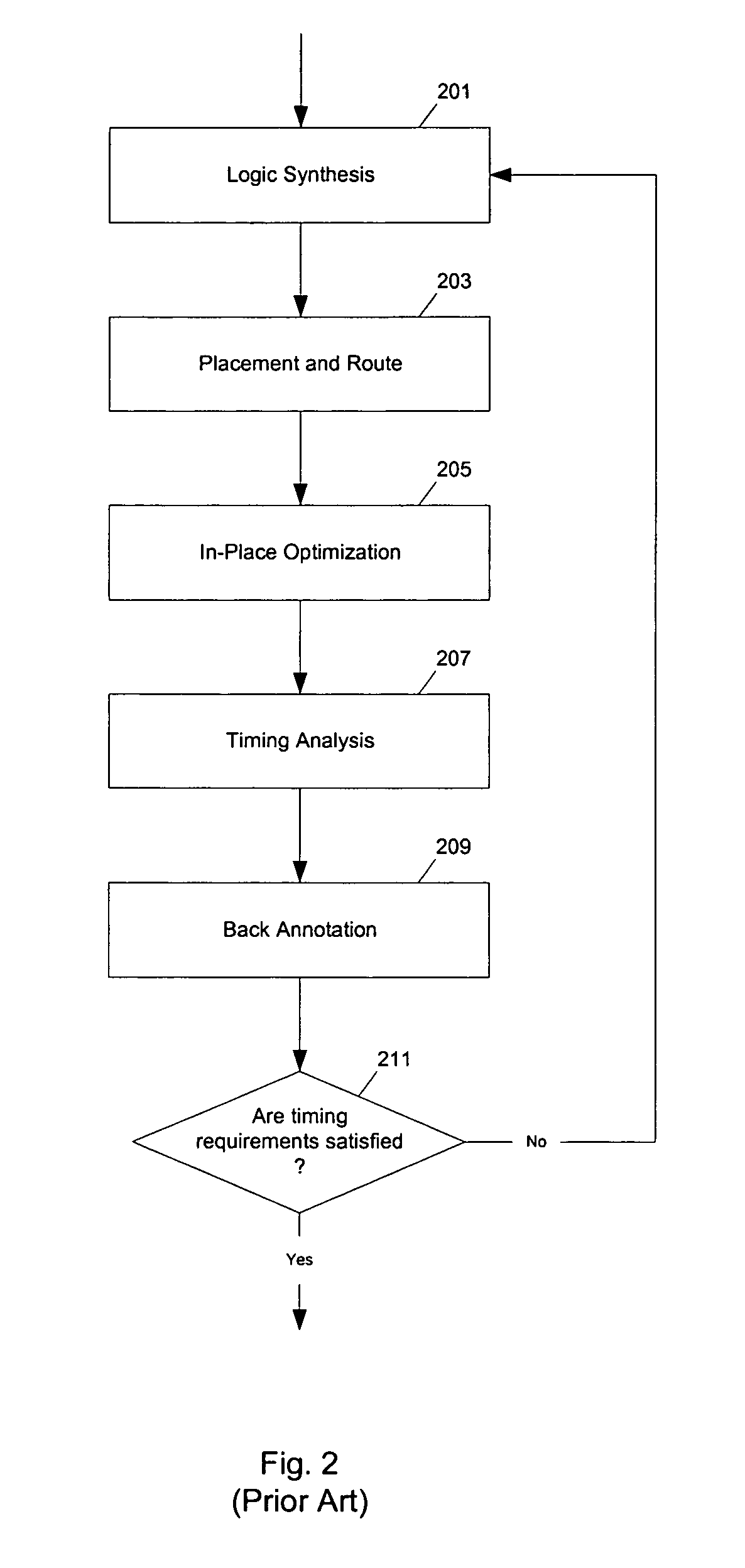
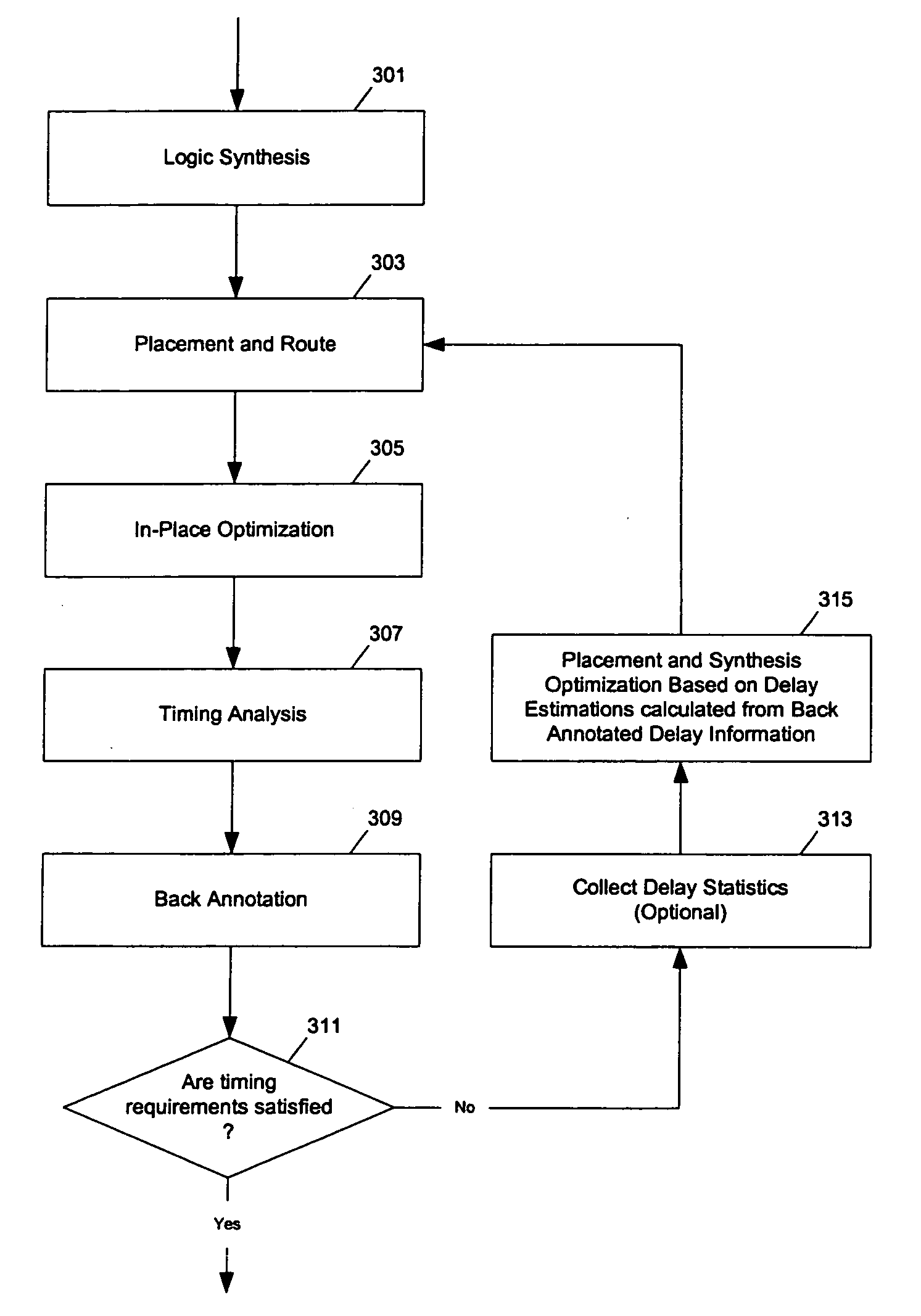
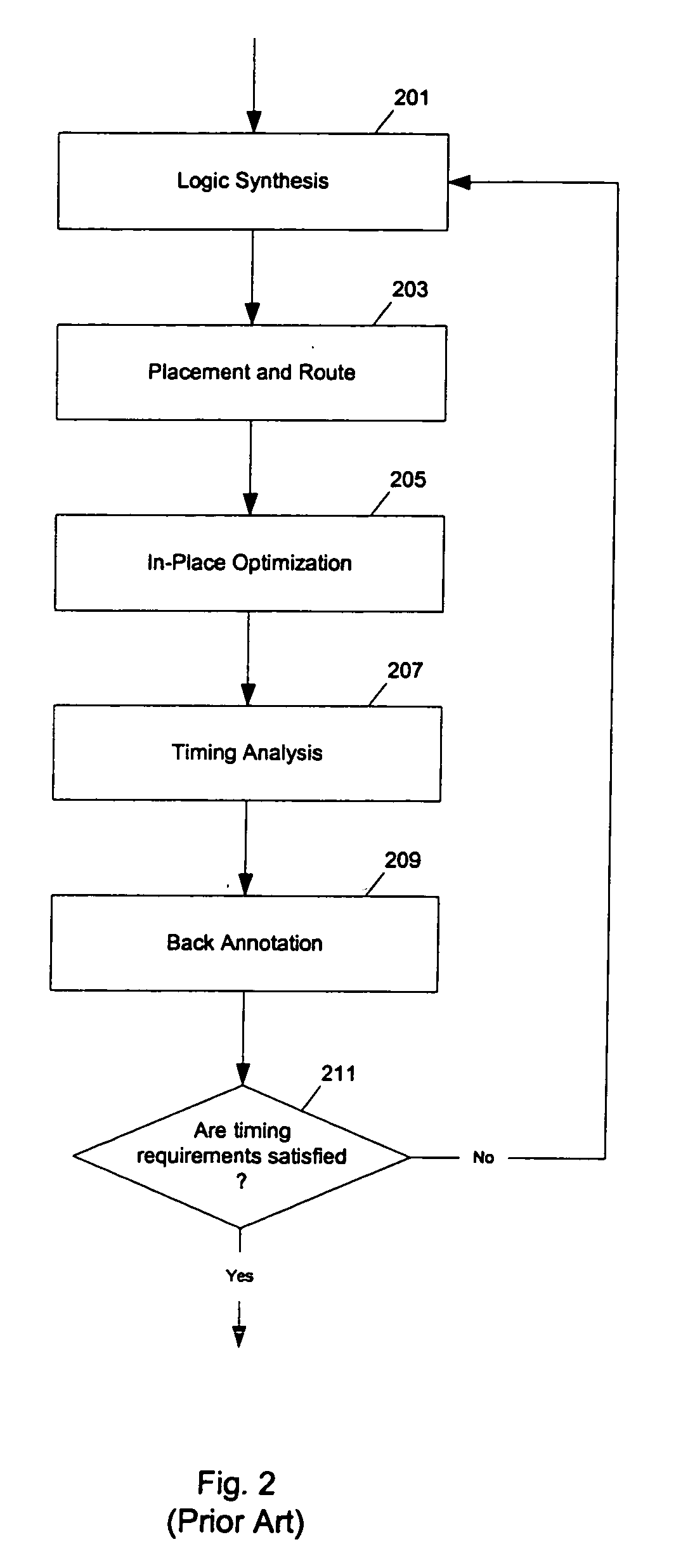
Method and apparatus to estimate delay for logic circuit optimization
InactiveUS6973632B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic optimizationLogic circuitry
Methods and apparatuses to estimate delay for logic circuit optimization using back annotated placement and delay data. In one aspect of the invention, a method to design a logic circuit, the method includes: modifying a first path that is back annotated with first placement information and first delay information to generate a second path; and calculating a signal delay on the second path from second placement information for the second path, the first placement information and the first delay information (or, computing an adjustment to the first delay information from second placement information for the second path and the first placement information). In one example according to this aspect, the first placement information and the first delay information are back annotated from a timing analysis based on placing and routing at least the first path. An actual route is determined from the first placement information in calculating the signal delay.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
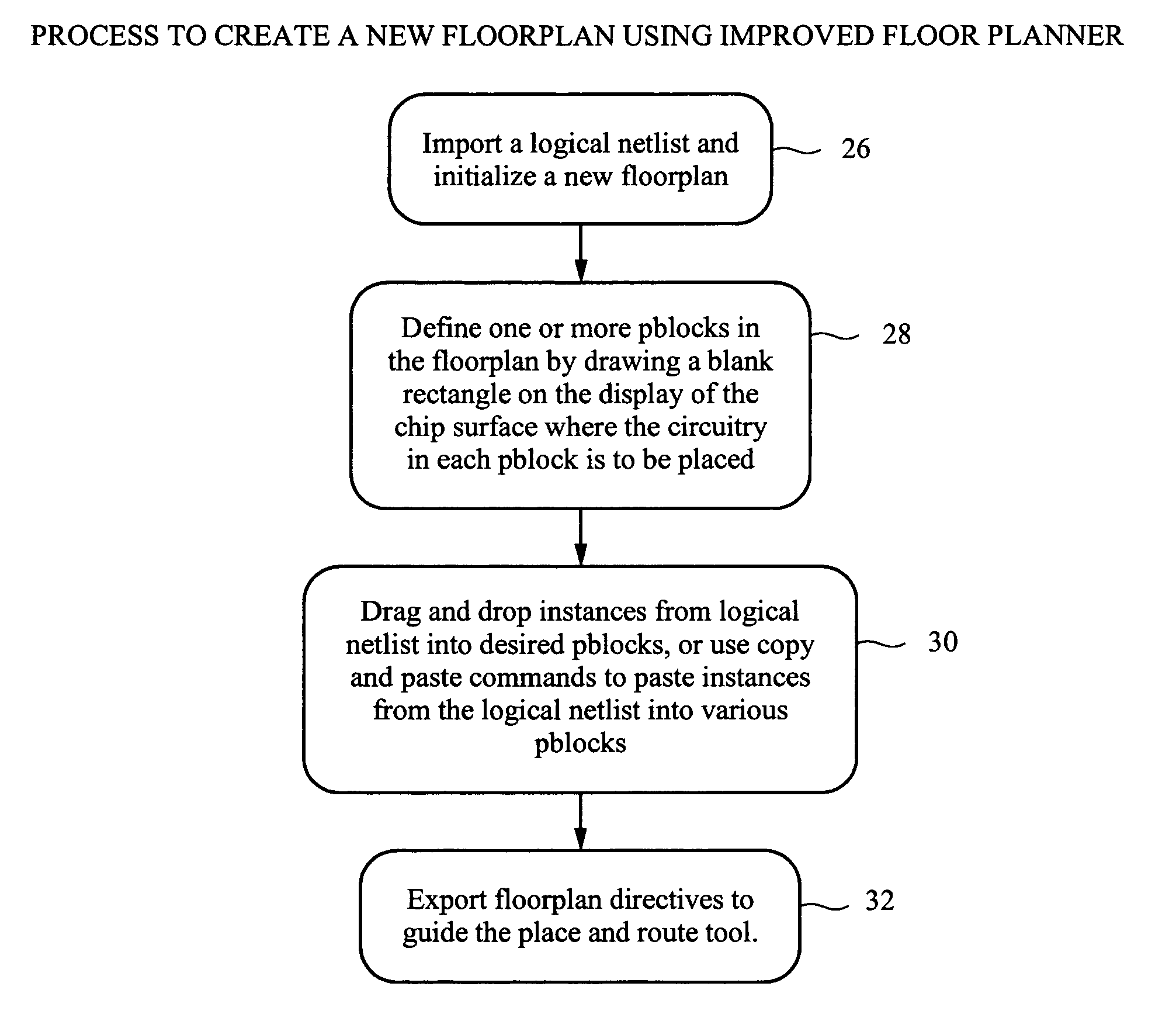
Data structures for representing the logical and physical information of an integrated circuit
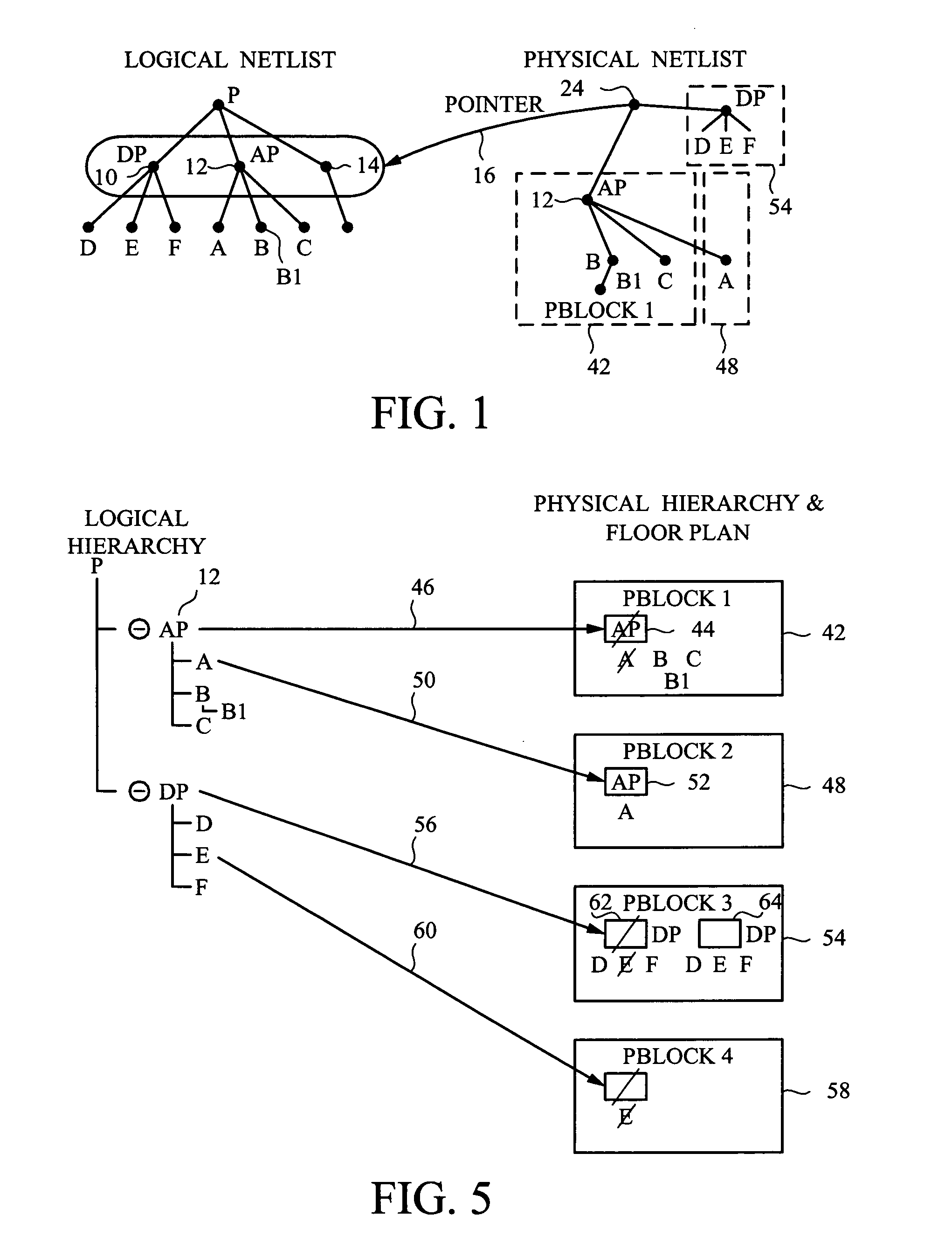
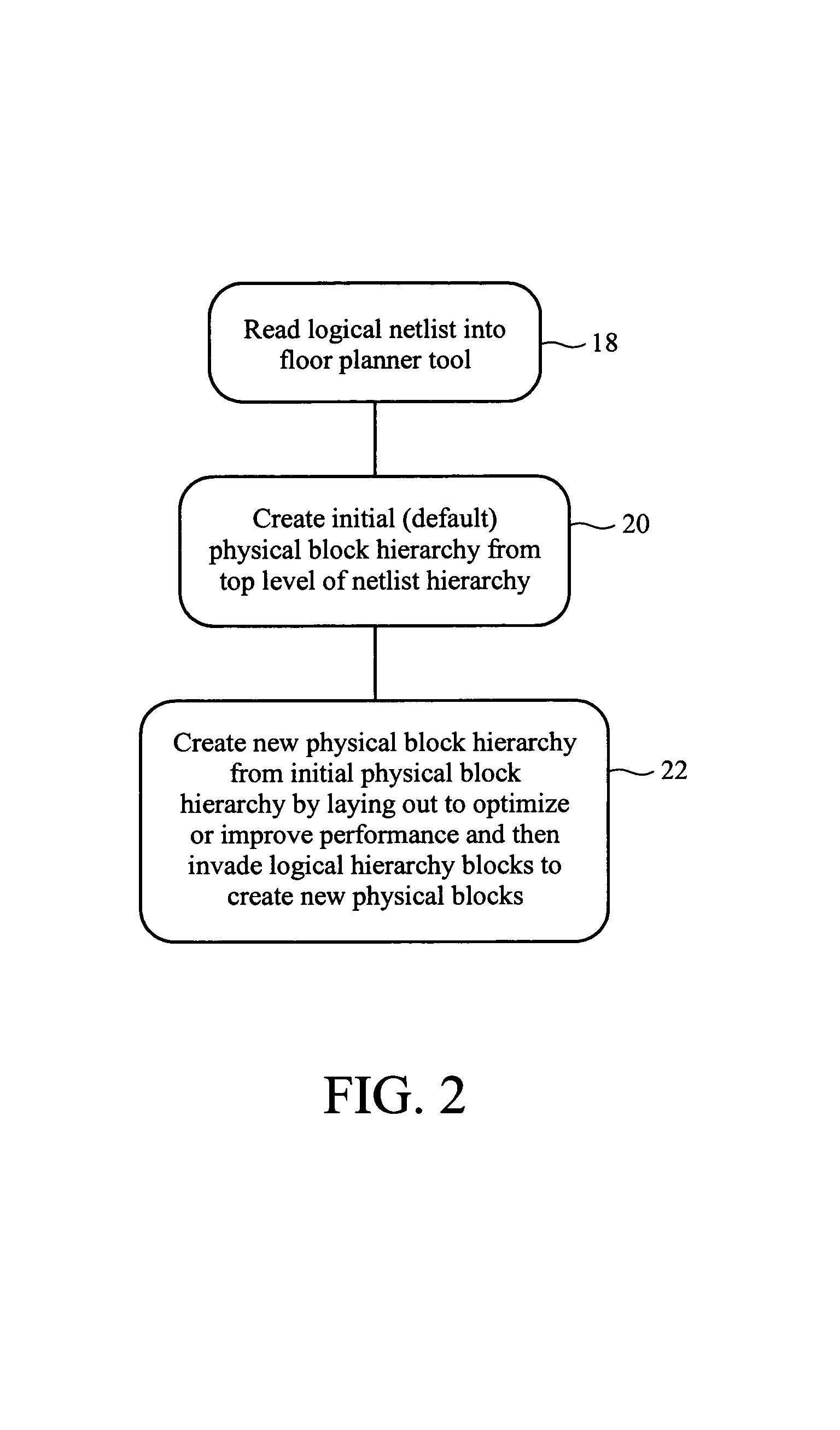
ActiveUS20050204315A1Improve performanceMeet constraintsComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionProgram controlArray data structureDisplay device
A floor planner tool for integrated circuit design which provides tools and displays for a designer to create a floor plan to define desired placement of circuits defined in a logical netlist by creating a physical hierarchy comprised of nested pblocks. Each pblock is a data structure which contains data which defines which circuits from the logical netlist are assigned to it. Each pblock stands alone and can be input to a place and route tool without the rest of the physical hierarchy. Each pblock data structure contains pointers to the circuits on the netlist assigned to that plbock, identifies other pblocks nested within it and contains at least a list of boundary pins for that pblock. Net data structures in the physical hierarchy define which nets are connected to which pins. PCellview data structures define the internal structure of each pblock.
Owner:XILINX INC
Semiconductor circuit pattern design method for manufacturing semiconductor device or liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060271907A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid-crystal displayDevice material
A semiconductor circuit pattern design method includes the following operations. A design pattern is created by placing a plurality of cells in each functional block as a unit of the semiconductor circuit and executing routing among the plurality of placed cells. Mask pattern data based on the design pattern is created. A predictive pattern to be formed on the substrate by the mask pattern data is predicted. A difference amount between the predictive pattern and a target pattern to be formed on the substrate by the mask pattern data is checked. The difference amount is compared with a predetermined allowable variation amount. If the difference amount is larger than the allowable variation amount in the comparison, at least one of placement and routing of the cells in the design pattern corresponding to the mask pattern data used to predict the predictive pattern is corrected.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050104133A1Cell height can be increasedRestricted degrees of freedomTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringSemiconductor
In a low power consumption mode in which prior data is retained upon power shutdown, the return speed thereof is increased. While use of an existent data retaining flip-flop may be considered, this is not preferred since it increases area overhead such as enlargement of the size of a cell. A power line for data retention for power shutdown is formed with wirings finer than a usual main power line. Preferably, power lines for a data retention circuit are considered as signal lines and wired by automatic placing and mounting. For this purpose, terminals for the power line for data retention are previously designed by providing the terminals therefor for the cell in the same manner as in the existent signal lines. Additional layout for power lines is no longer necessary for the cell, which enables a decrease in the area and design by an existent placing and routing tool.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus to estimate delay for logic circuit optimization
InactiveUS20060095879A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSignal delayLogic circuitry
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
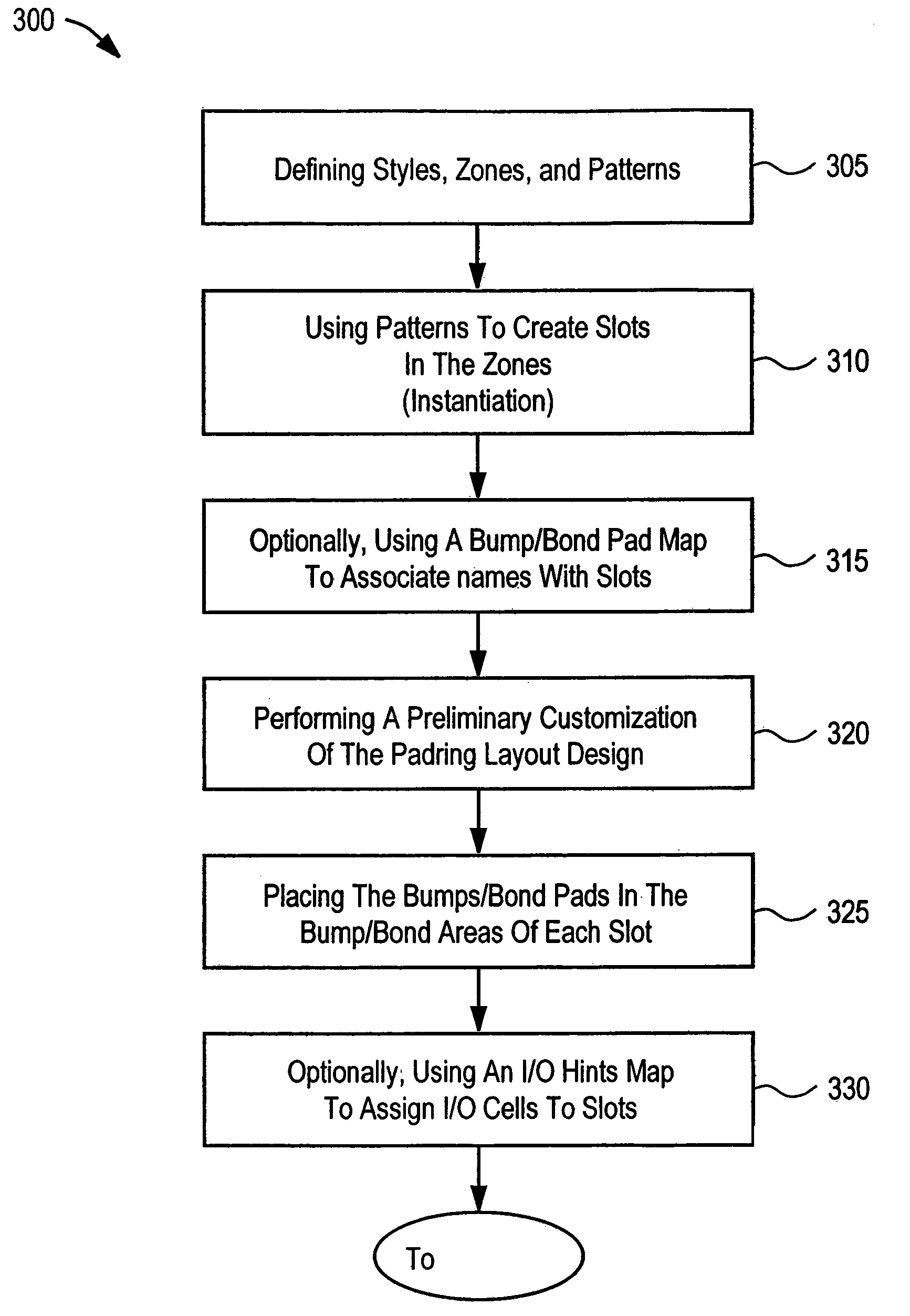
Method of optimizing placement and routing of edge logic in padring layout design
ActiveUS7117469B1Many timesQuick buildComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designRegular patternLogic cell
Methods for generating a padring layout design are described. These methods utilize automation while still allowing customization. Automation is emphasized as much as possible so that more time can be used to solve the various problems that make each padring layout design unique. A framework in which regular patterns can be described, replicated, and tailored is provided. The padring is broken down into zones in which slots having bumps / bond pads areas, I / O cell areas, and / or edge logic cell areas are laid out in a regular pattern through an instantiation process. Edge logic, which is comprised of standard cells, is pulled from the core of the chip because these cells couple directly to I / O cells and are critical for timing. The framework allows the bumps / bond pads, I / O cells, and edge logic cells to be laid out in respective bumps / bond pads areas, I / O cell areas, and / or edge logic cell areas according to algorithms associated with the patterns and using a variety of maps which associate the logical netlist with the physical layout design.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Process for adjusting data structures of a floorplan upon changes occurring
ActiveUS7120892B1Improve performanceMeet constraintsComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionProgram controlArray data structureDisplay device
A floor planner tool for integrated circuit design which provides tools and displays for a designer to create a floor plan to define desired placement of circuits defined in a logical netlist by creating a physical hierarchy comprised of nested pblocks. Each pblock is a data structure which contains data which defines which circuits from the logical netlist are assigned to it. Each pblock stands alone and can be input to a place and route tool without the rest of the physical hierarchy. Each pblock data structure contains pointers to the circuits on the netlist assigned to that plbock, identifies other pblocks nested within it and contains at least a list of boundary pins for that pblock.
Owner:XILINX INC
Method for realizing full three-dimensional intelligent virtual computer room
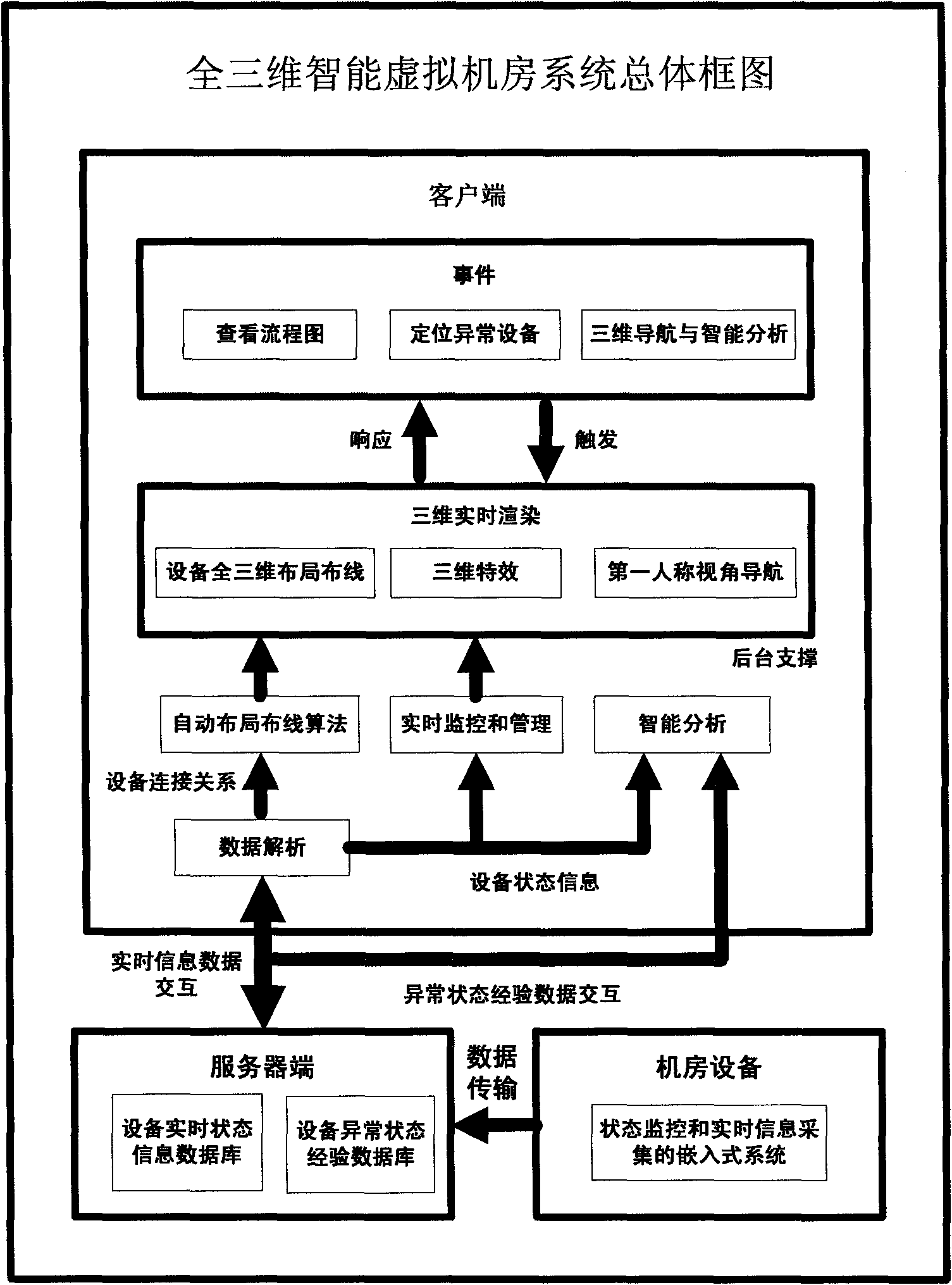
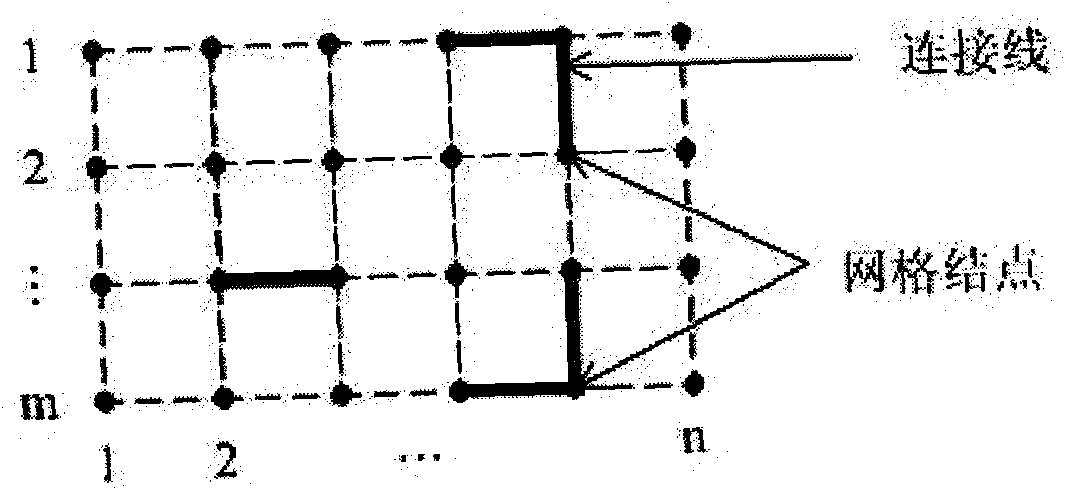
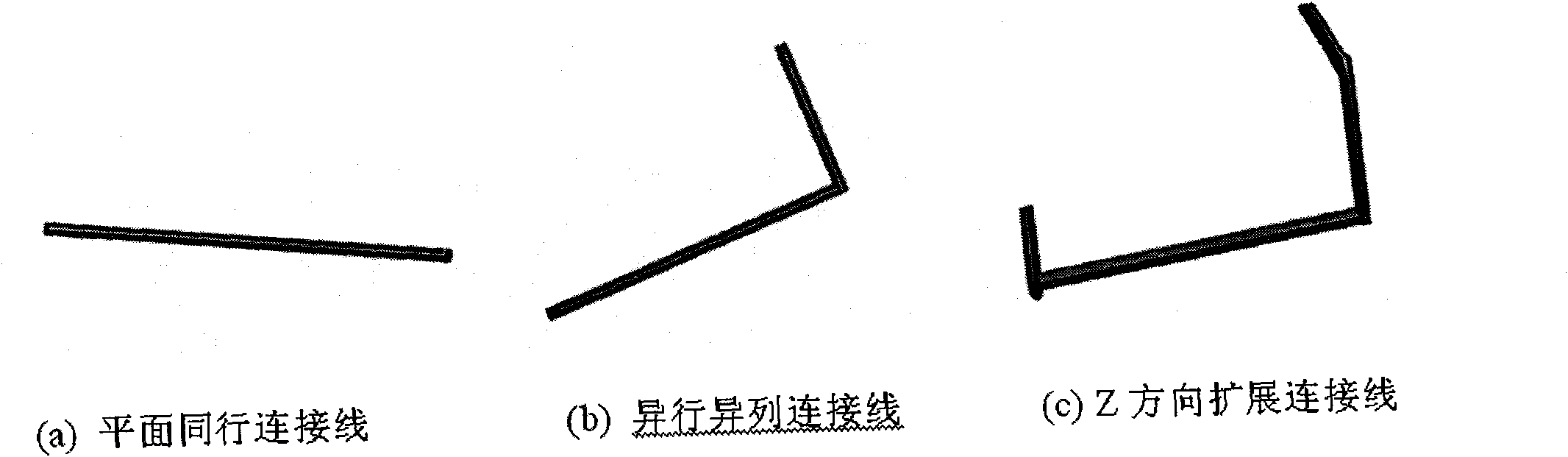
InactiveCN101820532ARapid positioningEffective judgmentClosed circuit television systemsSteroscopic systemsThree-dimensional spaceSimulation
The invention relates to a method for realizing a full three-dimensional intelligent virtual computer room, and belongs to the fields of computer graphics and virtual reality. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) simulating a full three-dimensional system structure and state; (2) monitoring and managing the running states of multiple kinds of large computer room equipment in real time; (3) performing monitoring, transmission and three-dimensional display on signals in real time based on a C / S architecture; (4) automatically laying out and wiring in a three-dimensional space system in real time; and (5) in a three-dimensional space, performing quick positioning, three-dimensional navigation and intelligent analysis on exceptional equipment. In the method, after a two-dimensional sketch map is changed into a full three-dimensional real-time intelligent layout map, according to equipment connection information updated by a server, all equipment is subjected to real-time layout and wiring at a client, the connection relationships of the multiple kinds of equipment are more clear and intuitively, the concept of layout is added, and a phenomenon that a flow chart only has a single function of the connection relationships is improved, so each equipment comprises definite real-time position information, the exceptional equipment is quickly positioned, and the navigation display and intelligent analysis in the three-dimensional space assist users to more effectively judge problems and solve problems.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
System and method for estimating capacitance of wires based on congestion information
InactiveUS6519745B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
A system for calculating interconnect wire lateral capacitances in an automated integrated circuit design system subdivides the chip area of a circuit design to be placed and routed into a coarse grid of buckets. An estimate of congestion in each bucket is computed from an estimated amount of routing space available in the bucket and estimated consumption of routing resources by a global router. This congestion score is then used to determine the spacing of the wires in the bucket which is in turn used to estimate the capacitance of the wire segment in the bucket.
Owner:MAGMA DESIGN AUTOMATION
Method and system for progressive clock tree or mesh construction concurrently with physical design
InactiveUS6651232B1Generating/distributing signalsComputer aided designTopology constructionTheoretical computer science
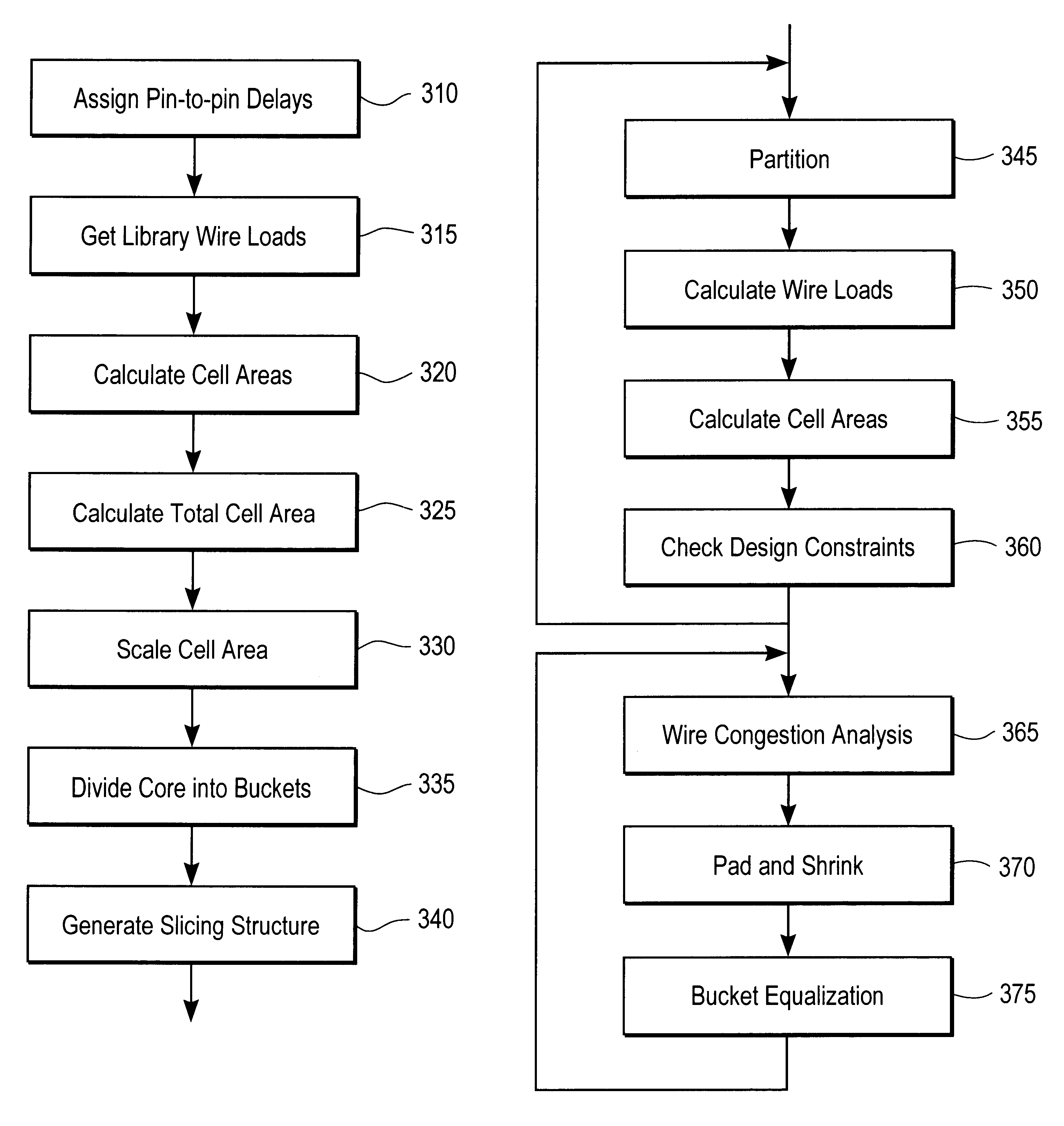
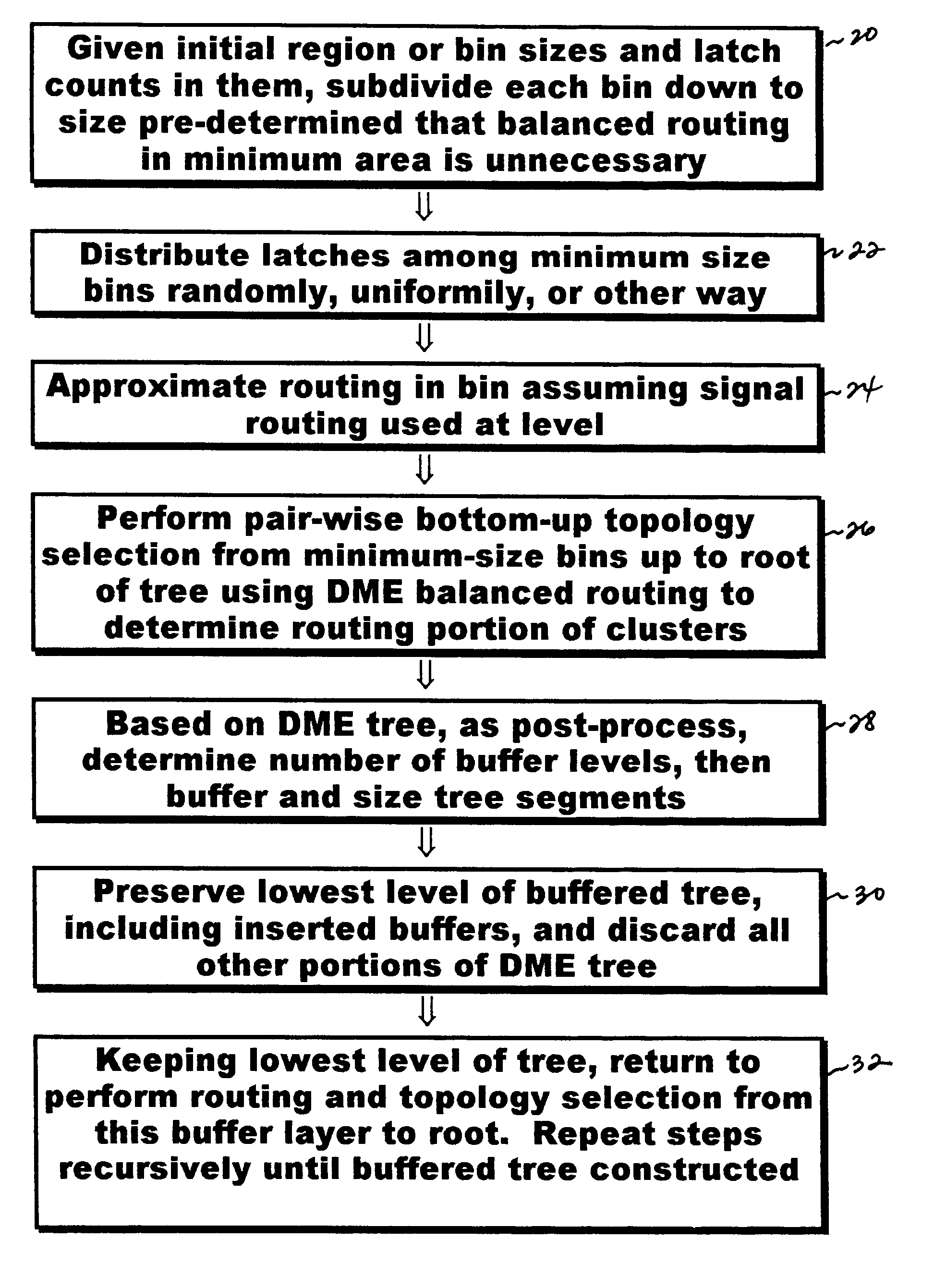
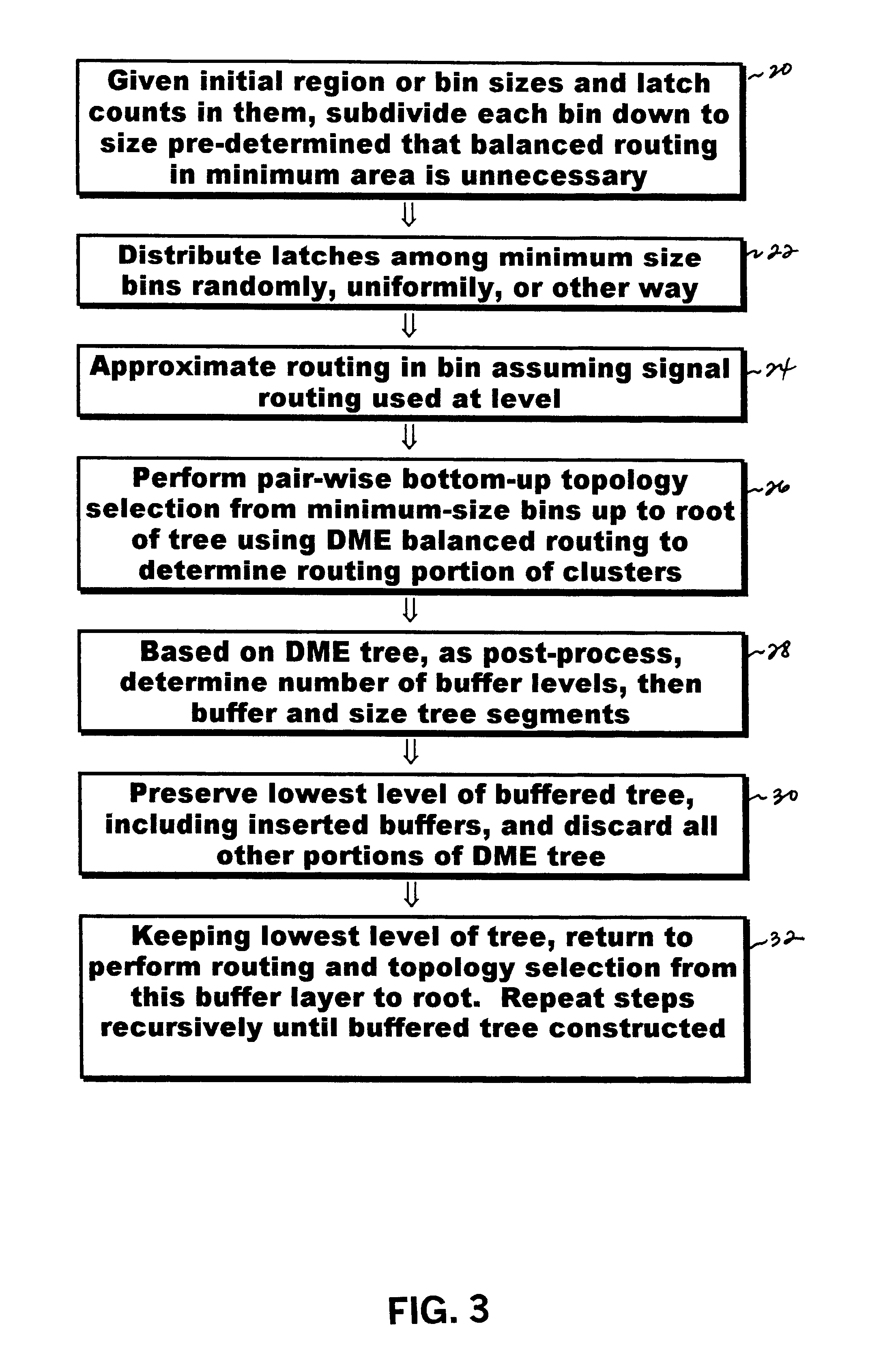
Progressively optimized clock tree / mesh construction is performed concurrently with placement of all remaining objects. Clock tree / mesh is specified loosely for initial placement, then followed by progressive detailed placement. In particular, preferred approach provides automated and reliable solution to clock tree / mesh construction, occuring concurrently with placement process so that clock tree wiring and buffering considers and influences placement and wiring of all other objects, such as logic gates, memory elements, macrocells, etc. Hence, in this concurrent manner, clock tree / mesh pre-wiring and pre-buffering may be based on construction of approximate clock tree using partitioning information only, i.e., prior to object placement. Further, present approach provides modified DME-based clock tree topology construction without meandering, and recursive algorithm for buffered clock tree construction.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for reducing reconfiguration power usage
ActiveUS20130021058A1Low costIncrease costPower consumption reductionCAD circuit designComputer hardwarePower usage
A system and method for reducing power consumption in a reconfigurable integrated circuit. Some embodiments provide placement and routing programs that reduce the number of bits to be reconfigured. Some embodiments provide placement and routing programs that increase the number of groups of circuits that do not need reconfiguration at some times. Some embodiments include circuits that selectively block reconfiguration.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method and apparatus for placement and routing cells on integrated circuit chips
ActiveUS7350173B1Reduce overlapIncrease in sizeComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
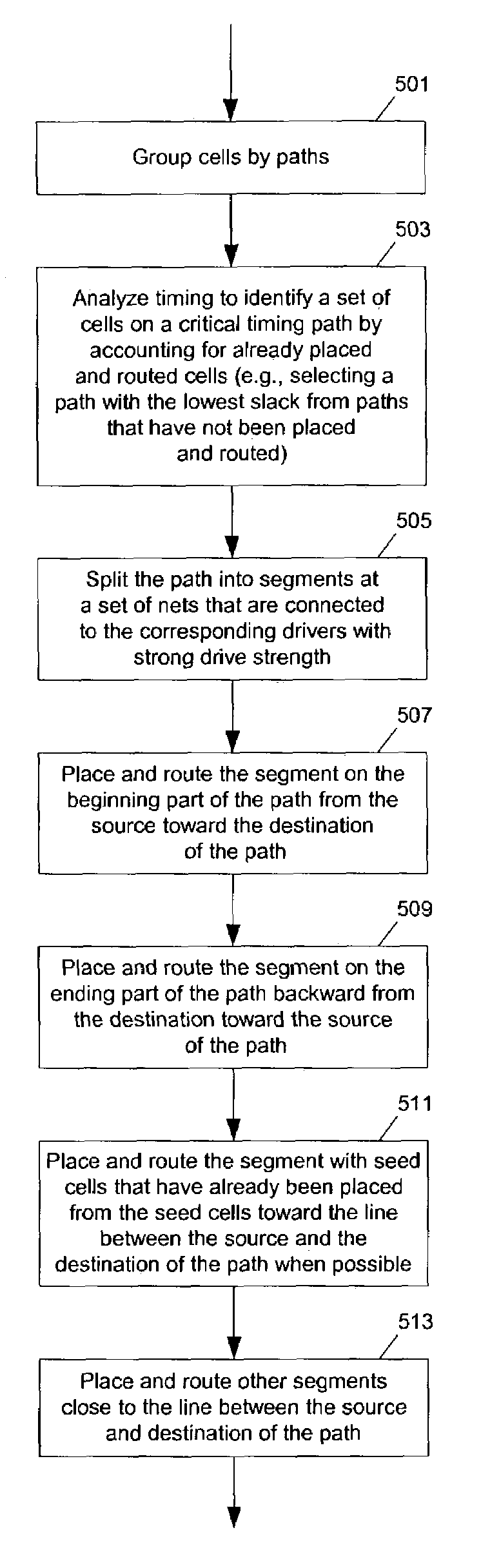
Methods and apparatuses to place and route cells on integrated circuit chips along paths. In one aspect of the invention, methods to layout an integrated circuit are based on placing and routing cells along paths. In one embodiment, a method to layout an integrated circuit including: routing a wire to connect a first cell of the integrated circuit and a second cell of the integrated circuit; and placing a third cell of the integrated circuit after the wire is routed to connect the first cell and the second cell. In one example, the first, second and third cells are on a first path; and, the third cell is connected to one of the first and second cells on the first path by only one net. The first path is selected from a set of paths; and the first and second cells are placed before the wire is routed to connect the first cell and the second cell. Timing is analyzed using a route of the wire connecting the first cell and the second cell to select a second path from the set of paths before a cell is placed on the second path.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
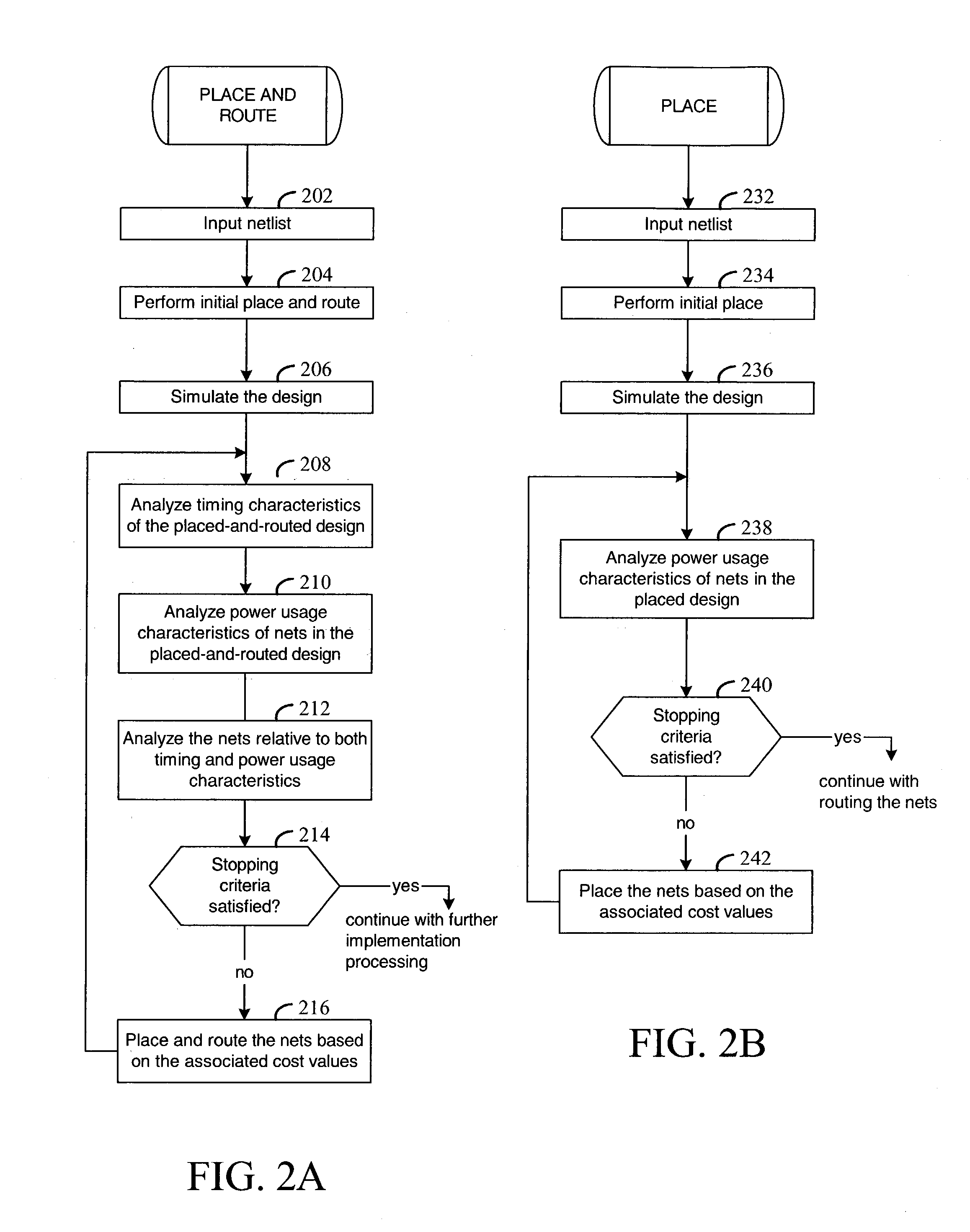
Place-and-route with power analysis
InactiveUS6950998B1Reduce power consumptionTime requiredComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPower analysisEngineering
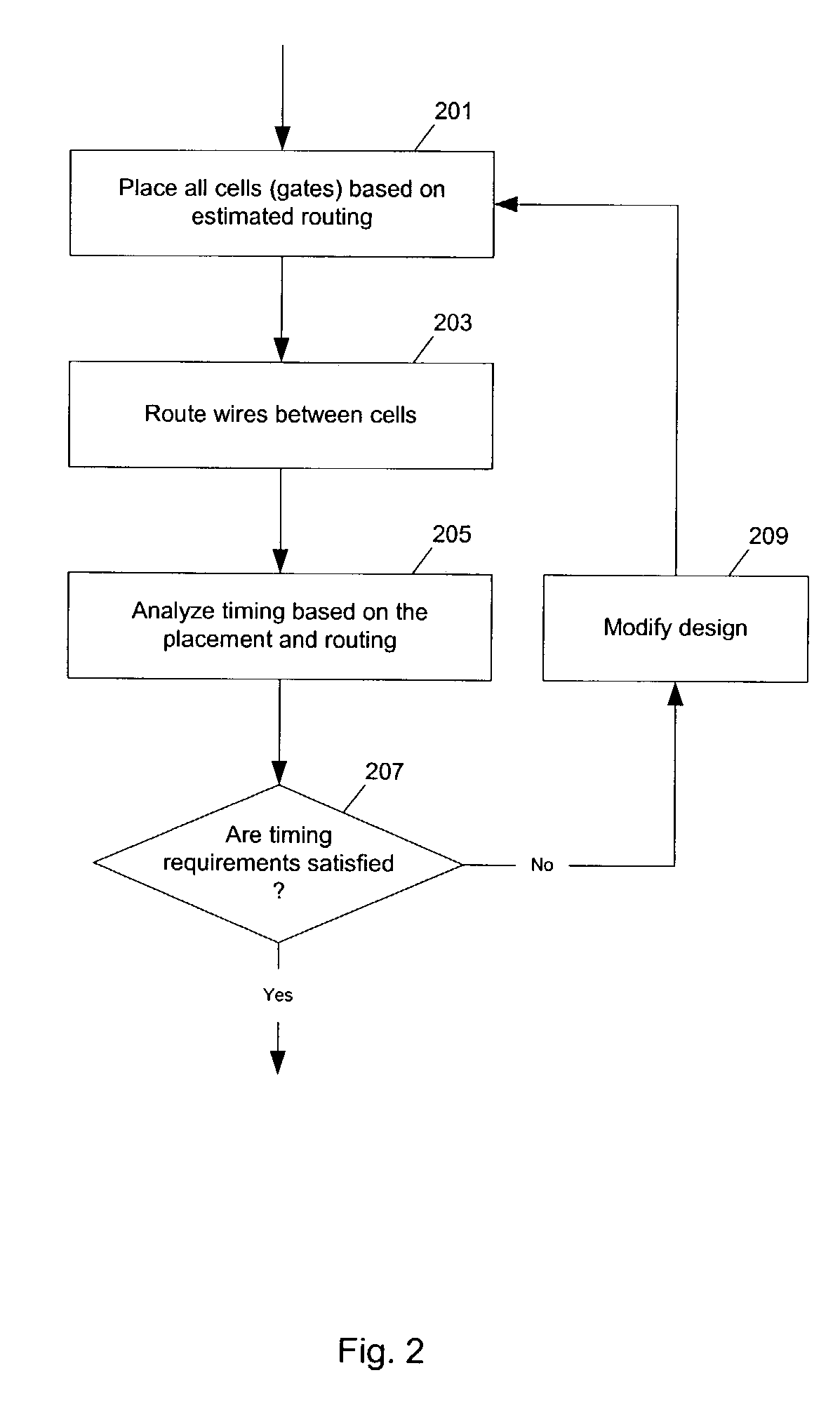
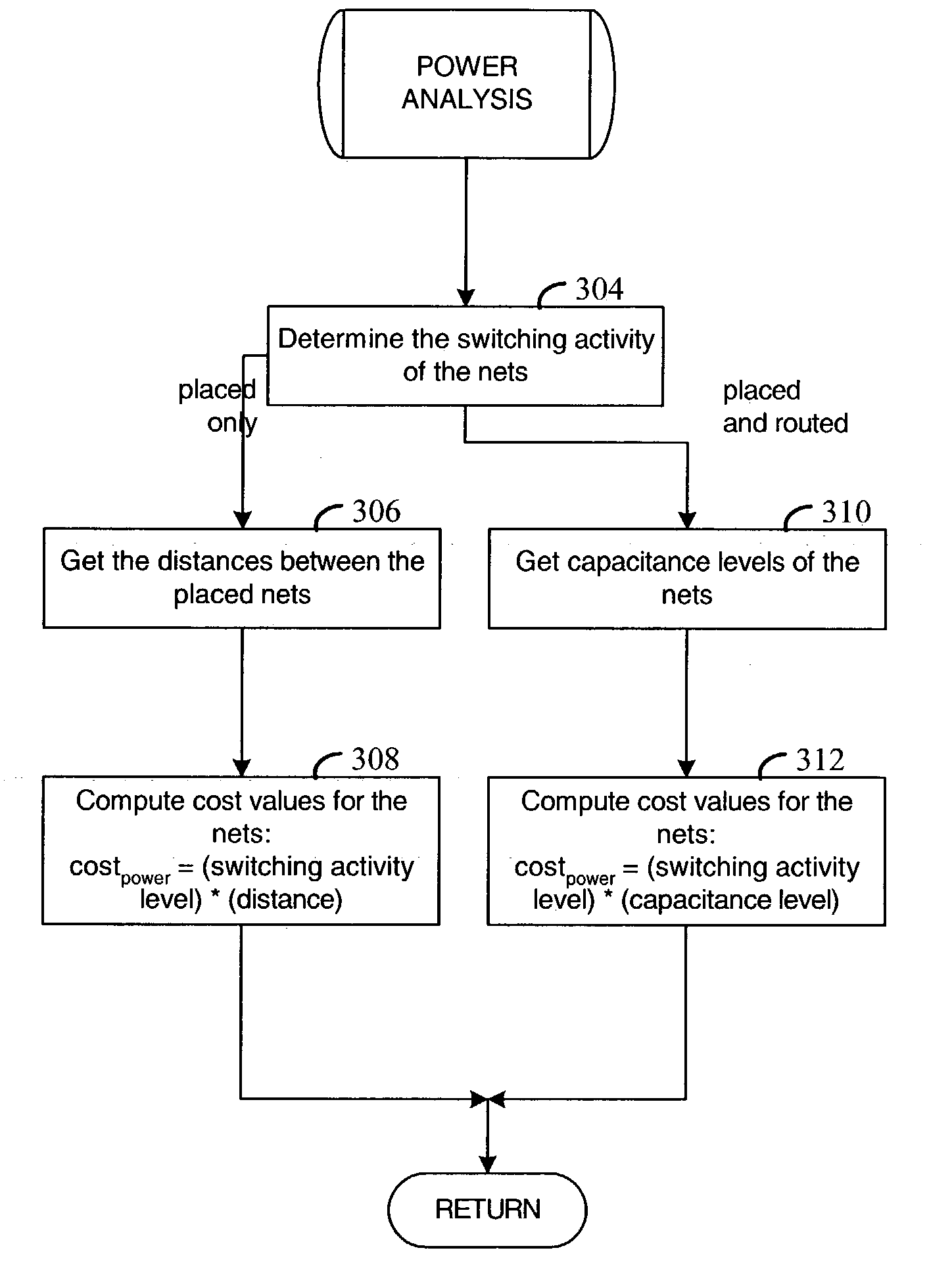
Method and apparatus for placing and routing an electronic circuit design. Various embodiments are disclosed for analyzing placed and / or routed designs for power consumption characteristics and timing characteristics. New designs are iteratively generated in order to reduce power consumption and satisfy timing requirements of the design.
Owner:XILINX INC
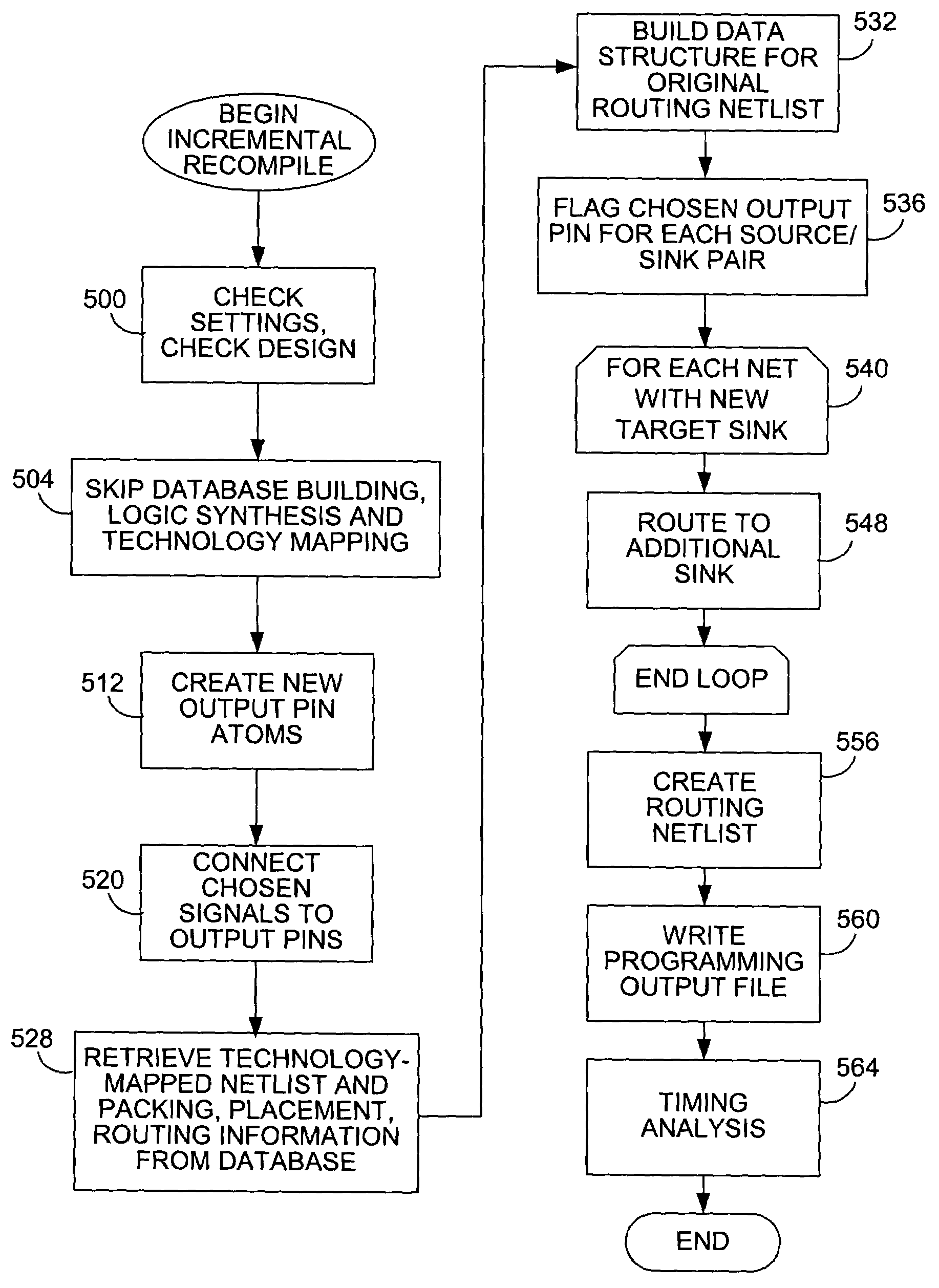
Chip debugging using incremental recompilation
InactiveUS7076751B1Save precious timeCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationIncremental compilerSignal of interest
While debugging, a user chooses an incremental recompile. Internal signals of interest are selected and output pins are optionally reserved. An incremental recompile of the compiled design includes compiling a routing from each internal signal to an output pin. The technology-mapped netlist and placing and routing information corresponding to an original compiled design are saved into a database during full compilation. During debugging, an incremental compiler retrieves this information to build the original routing netlist. The database building, logic synthesis and technology mapping stages may be skipped. New connections are added, fitted to the device, and then the final routing netlist is output into a programming output file (POF) in a form suitable for programming the PLD. The user views the internal signals at the output pins chosen. The user may iterate through this process many times in order to debug the PLD. The debugging assignments may be deleted.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
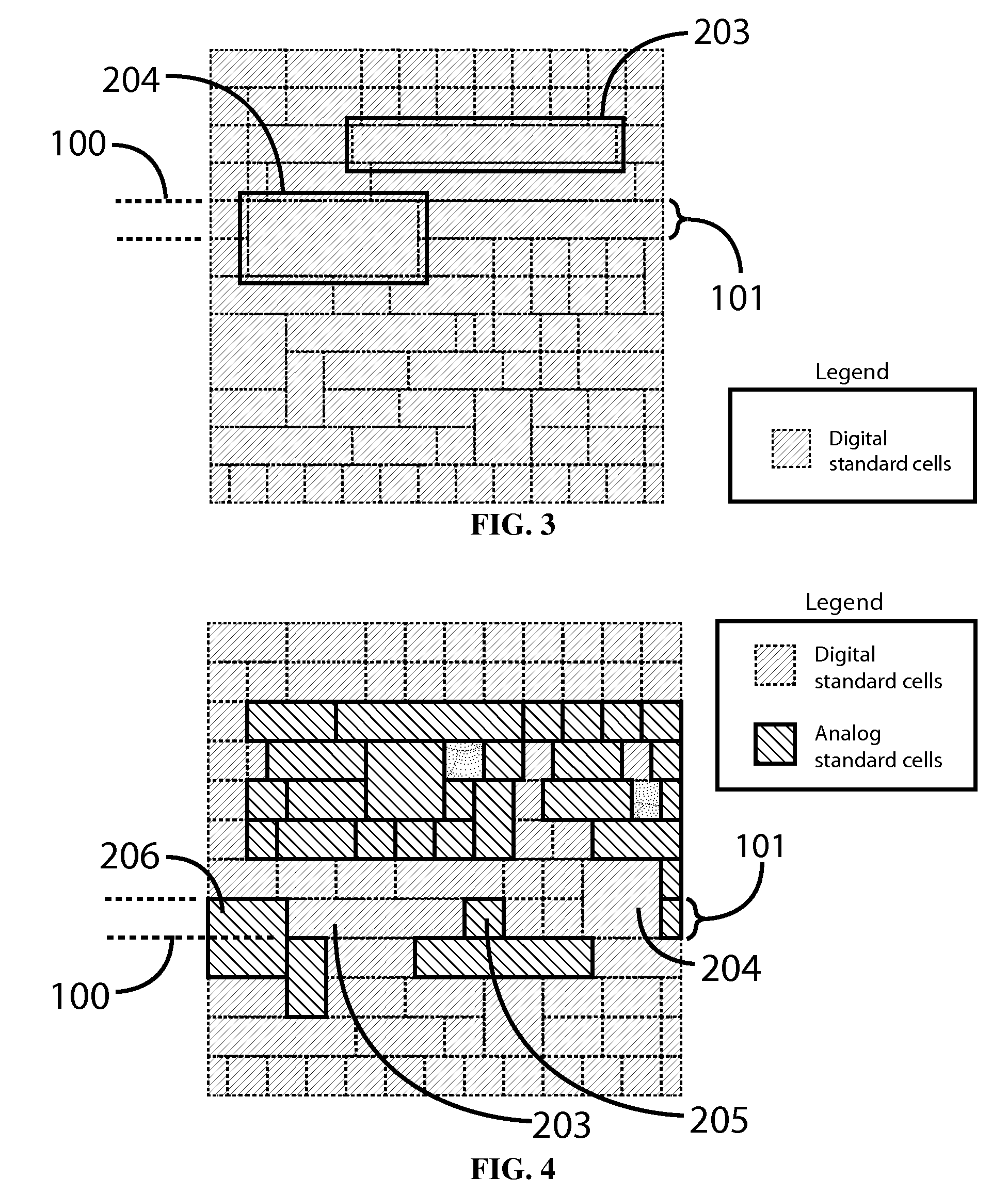
Row Based Analog Standard Cell Layout Design and Methodology
ActiveUS20130042216A1Function increaseCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsStandard cellPlace and route
A system and method of designing the physical layout of an SoC incorporating row-based placement of analog standard cells whose heights are constrained to a predetermined row height or integer multiple thereof. A library of analog standard cells may be utilized by an ECAD tool to map, place, and route analog and mixed signal circuits in a manner similar to how such ECAD tool may utilize a library of digital standard cells to map, place, and route digital circuits. Mapping, placing, and routing of digital, analog, and mixed signal circuits may proceed within a unified ECAD SoC physical design flow. Finally, a general type analog standard cell is taught to further increase the speed and efficiency of analog and mixed-signal SoC layout.
Owner:TOTIC TECH INC
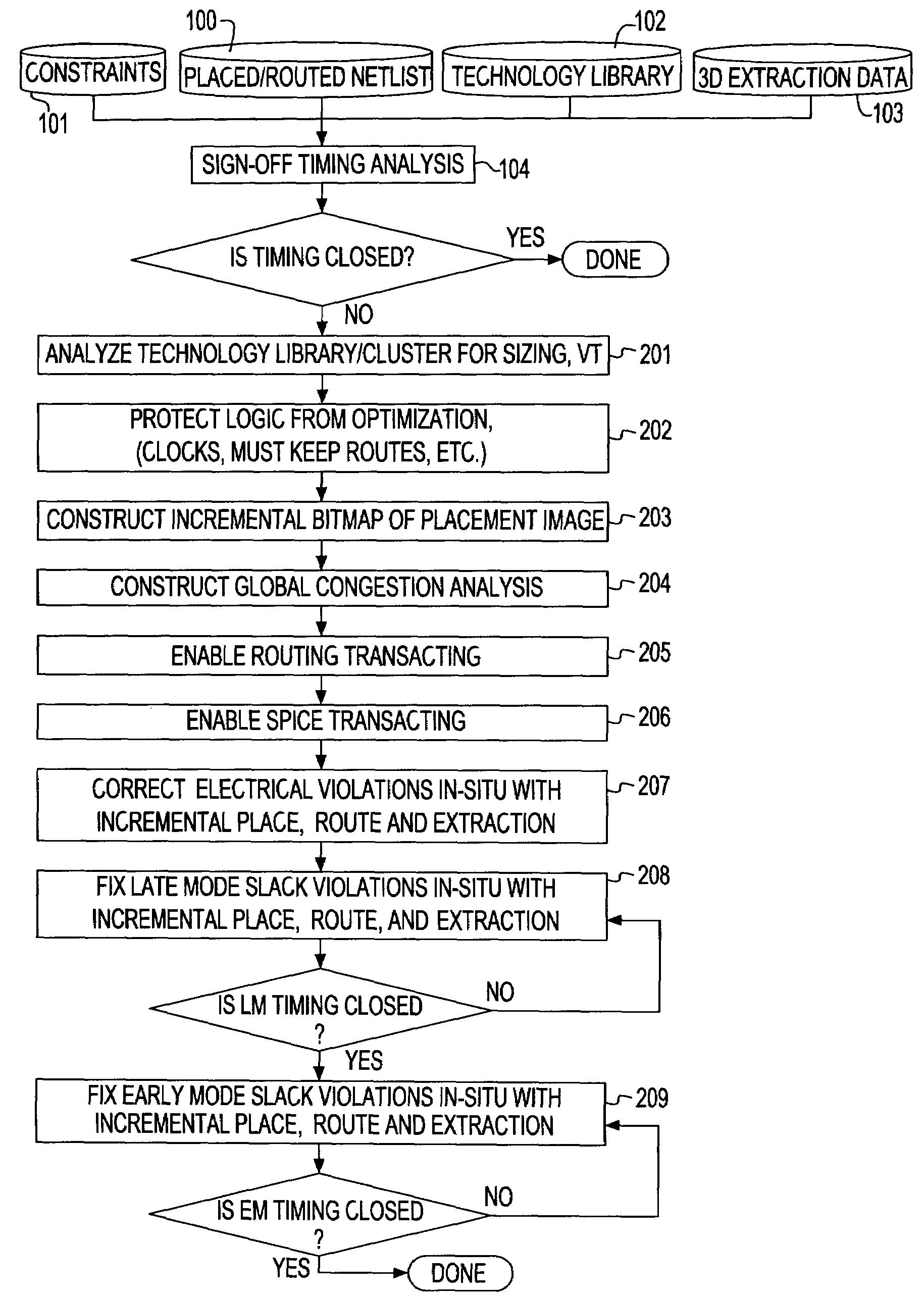
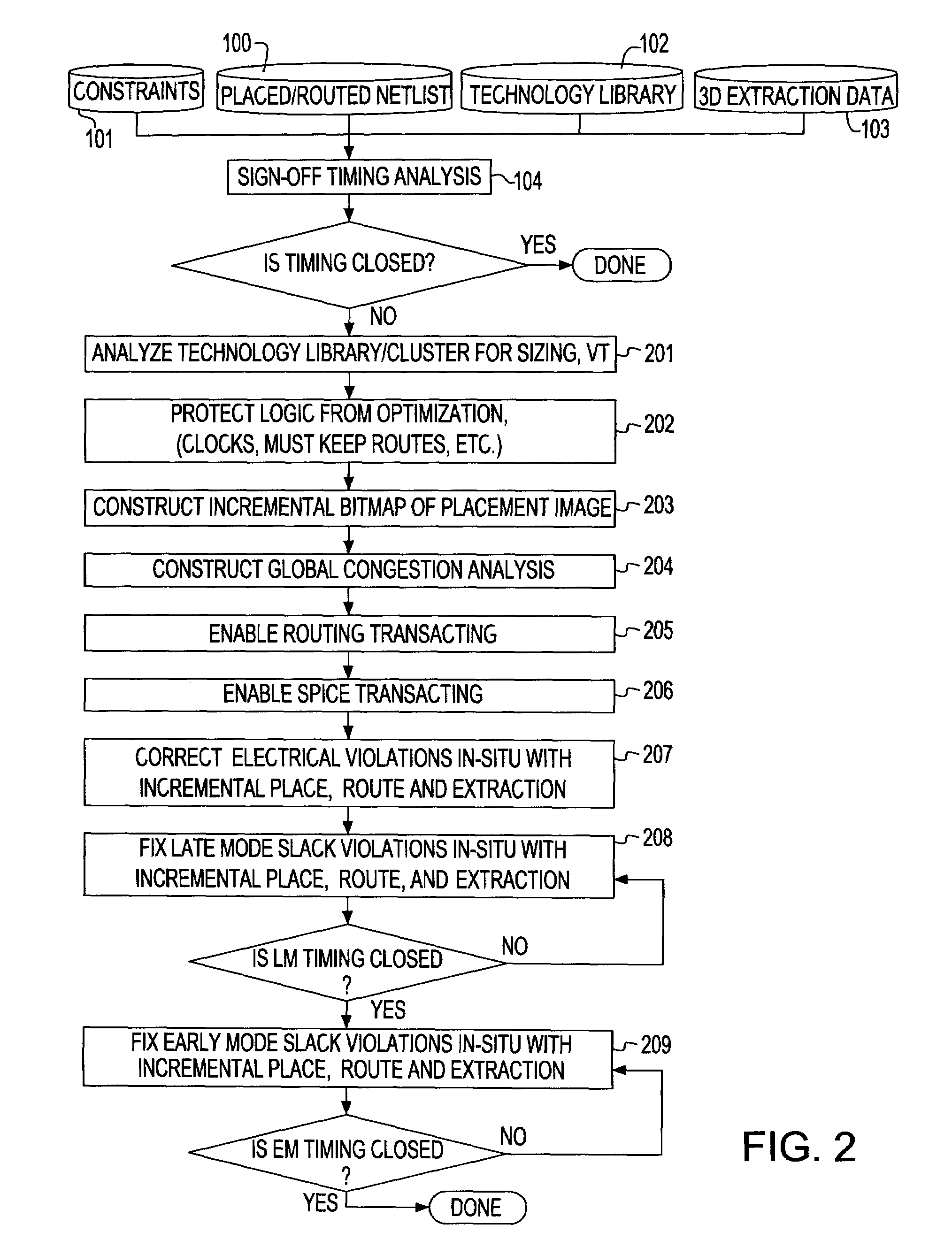
System and method for sign-off timing closure of a VLSI chip
InactiveUS7581201B2Efficiently improve the timing and electrical violationsMinimal placement and routing disruptionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitancePathPing
A method for performing timing optimization of a detail routed netlist, incorporating statistical variability information, common path pessimism reduction, and capacitative coupling information, in a tightly coupled, incremental manner with minimal perturbations to the placement, routing, and asserted parasitic information. The method corrects violations in a placed and routed design of a VLSI circuit chip, where the design is represented by a netlist describing logical and physical characteristics of the design and by a corresponding timing graph, the method including the steps of: identifying violations in the design; iteratively eliminating the violations by incrementally transforming the logical and the physical characteristics of the design, incorporating in the design only legal placements and routes; and applying incremental timing to evaluate the transformations, and updating the existing timing graphs to reflect changes consisting of the legal placements and routes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com