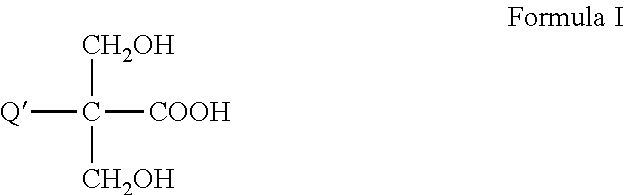Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Dynamic mechanical analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
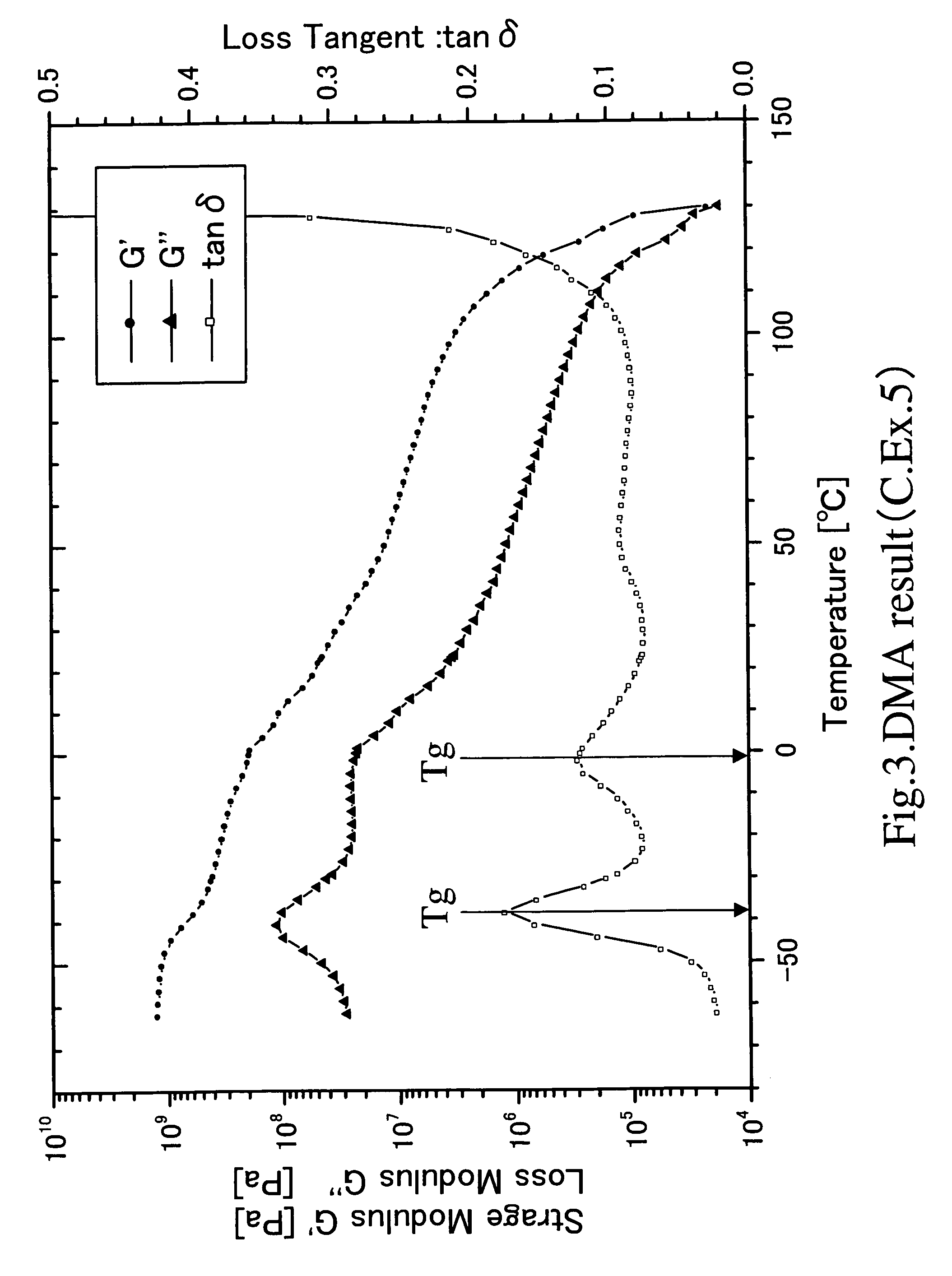
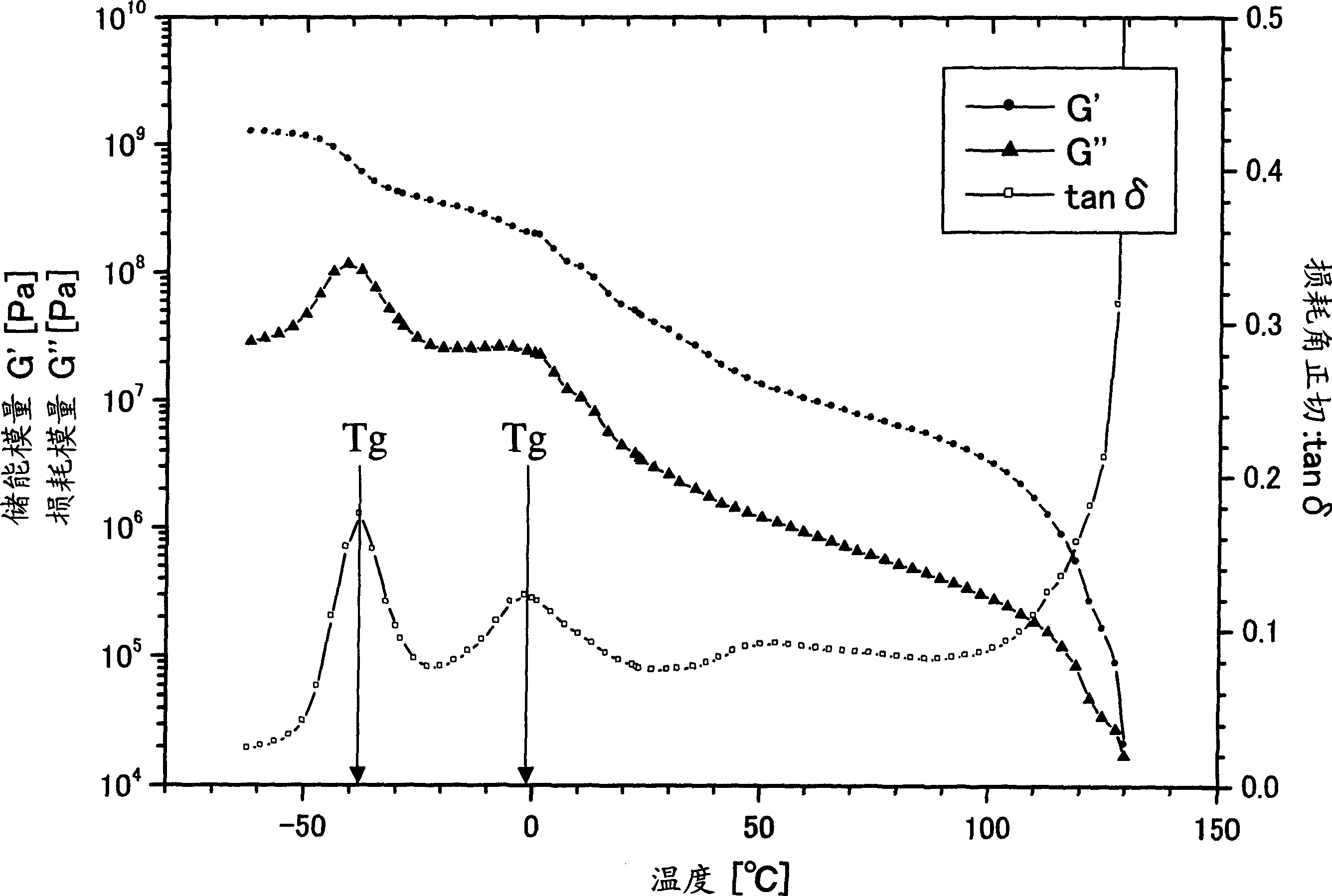
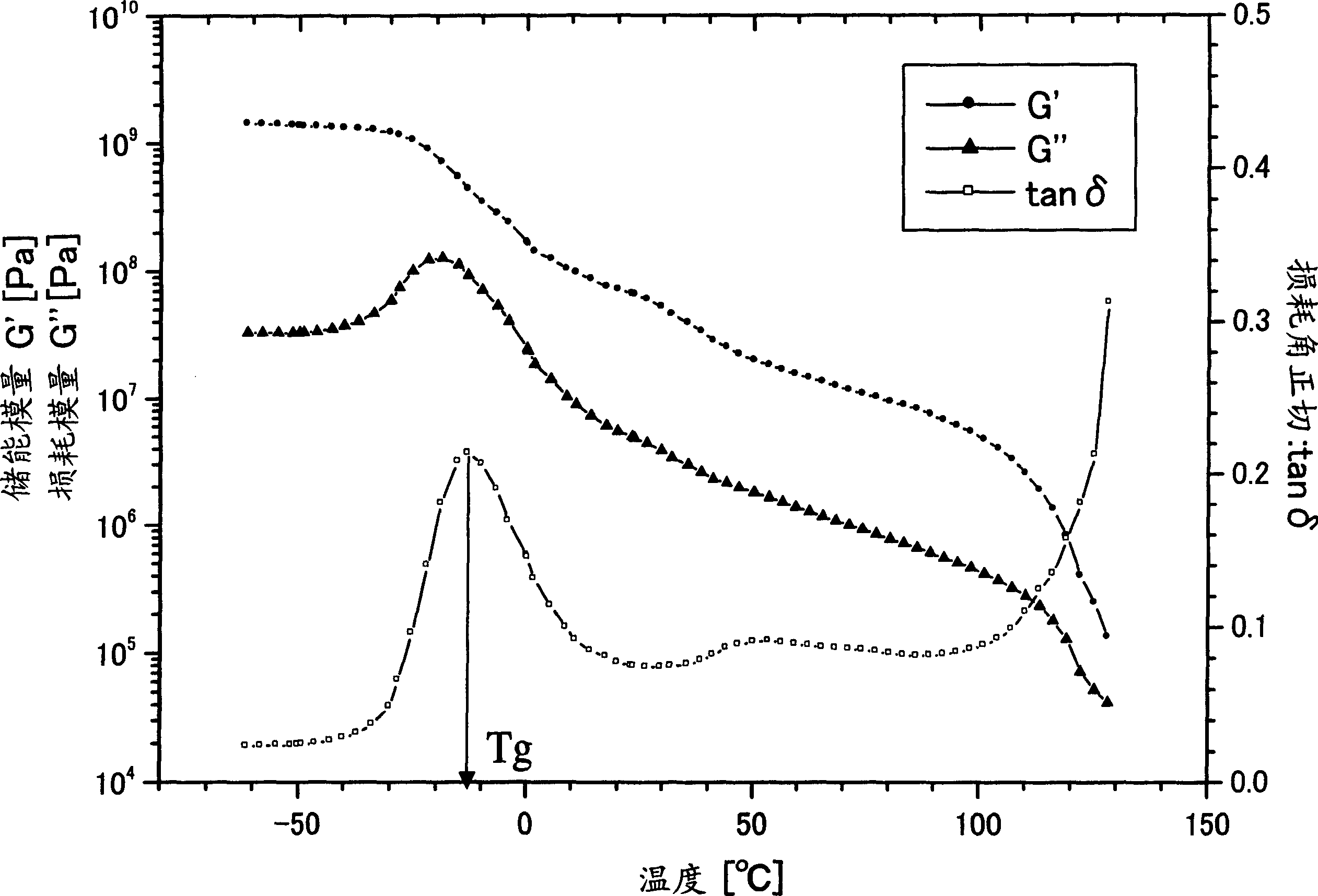
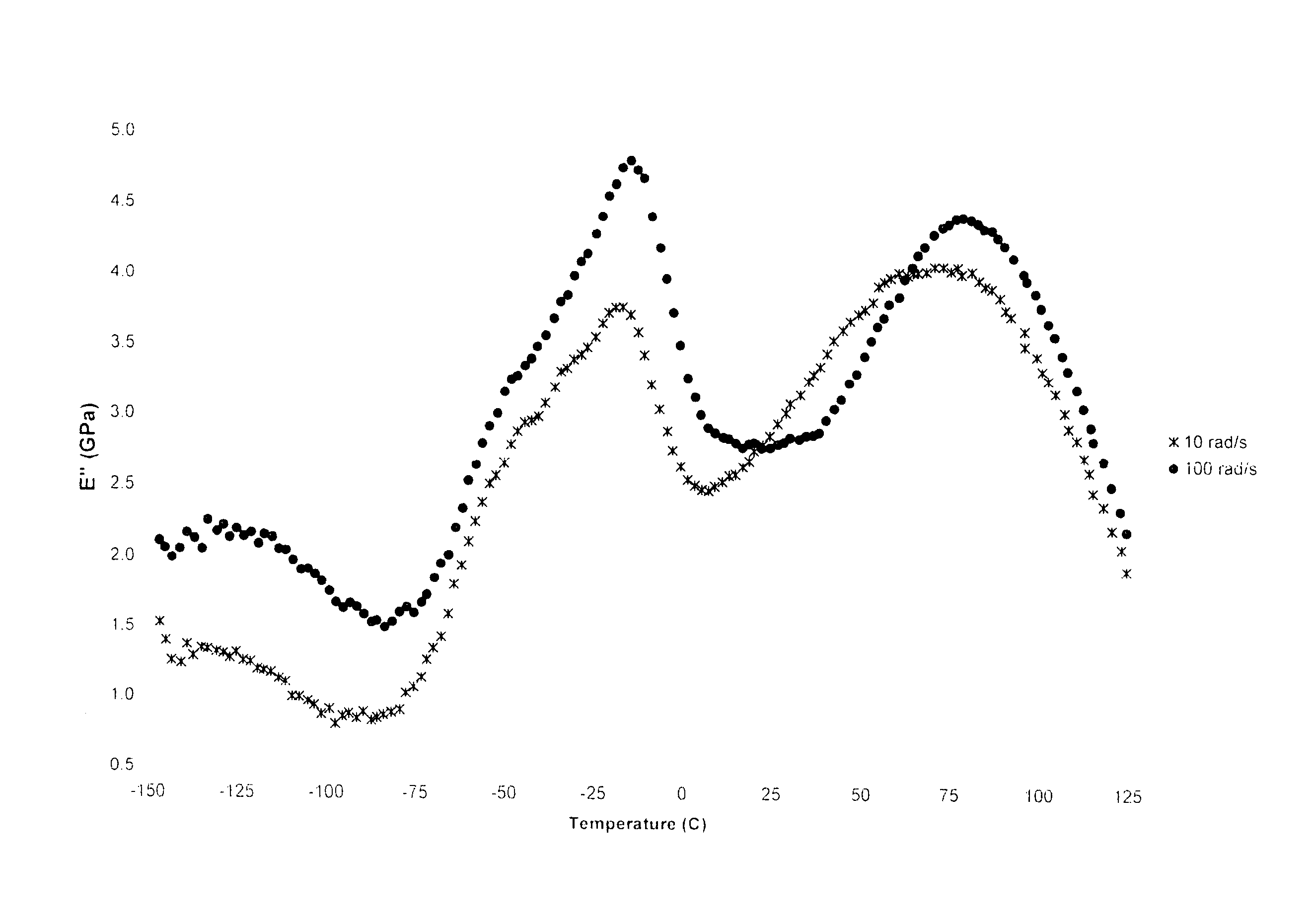
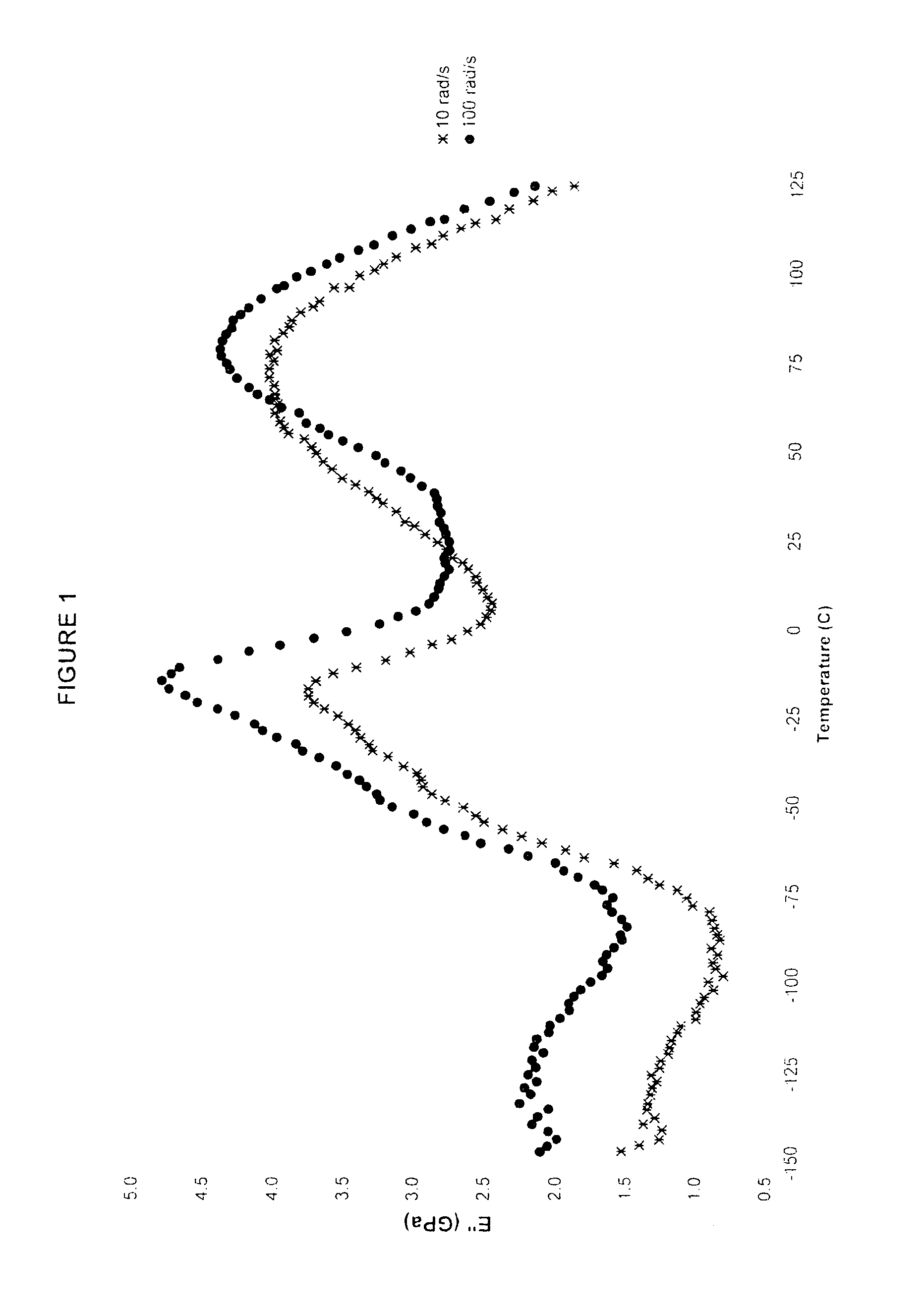
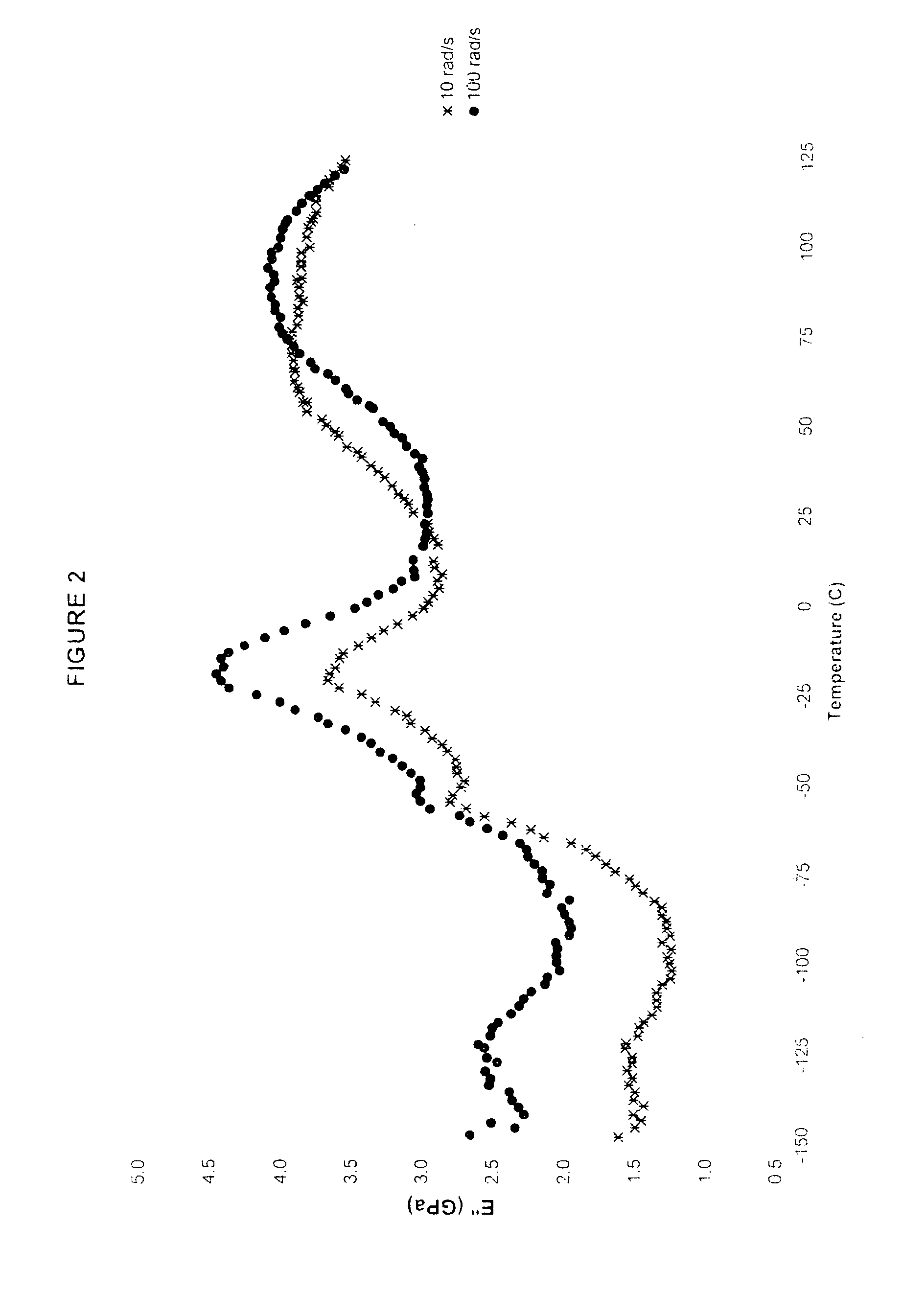
Dynamic mechanical analysis (abbreviated DMA, also known as dynamic mechanical spectroscopy) is a technique used to study and characterize materials. It is most useful for studying the viscoelastic behavior of polymers. A sinusoidal stress is applied and the strain in the material is measured, allowing one to determine the complex modulus. The temperature of the sample or the frequency of the stress are often varied, leading to variations in the complex modulus; this approach can be used to locate the glass transition temperature of the material, as well as to identify transitions corresponding to other molecular motions.
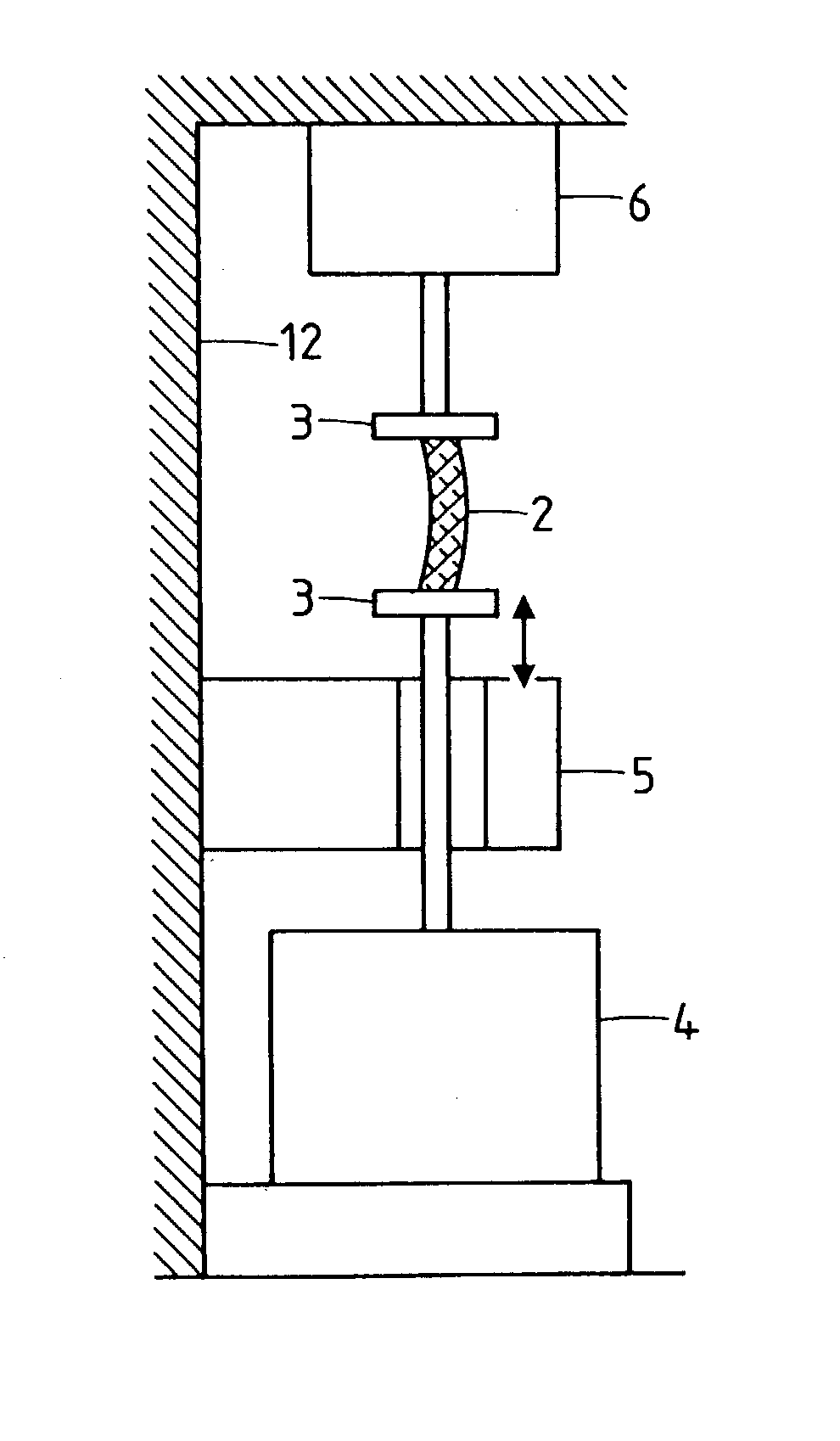
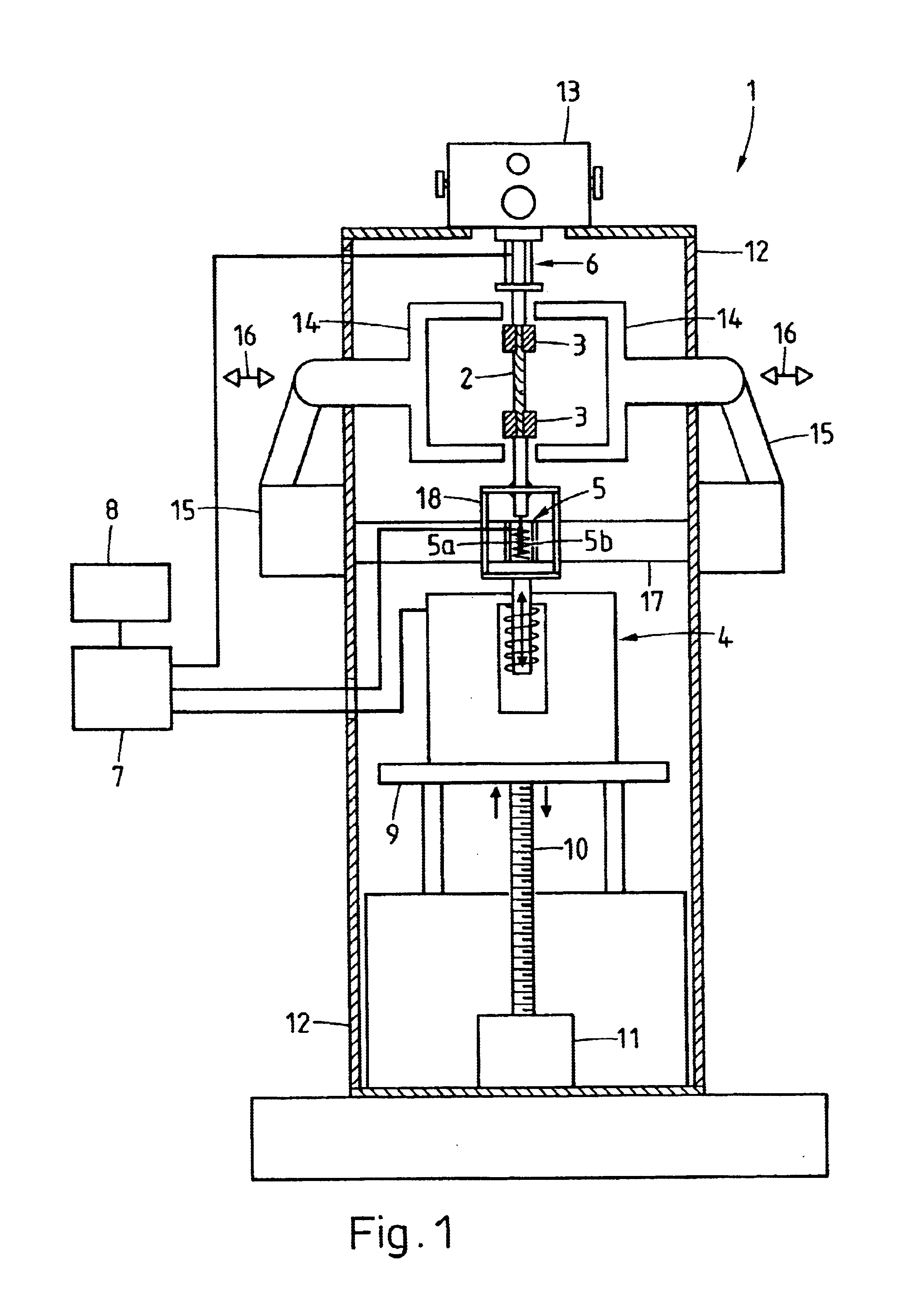
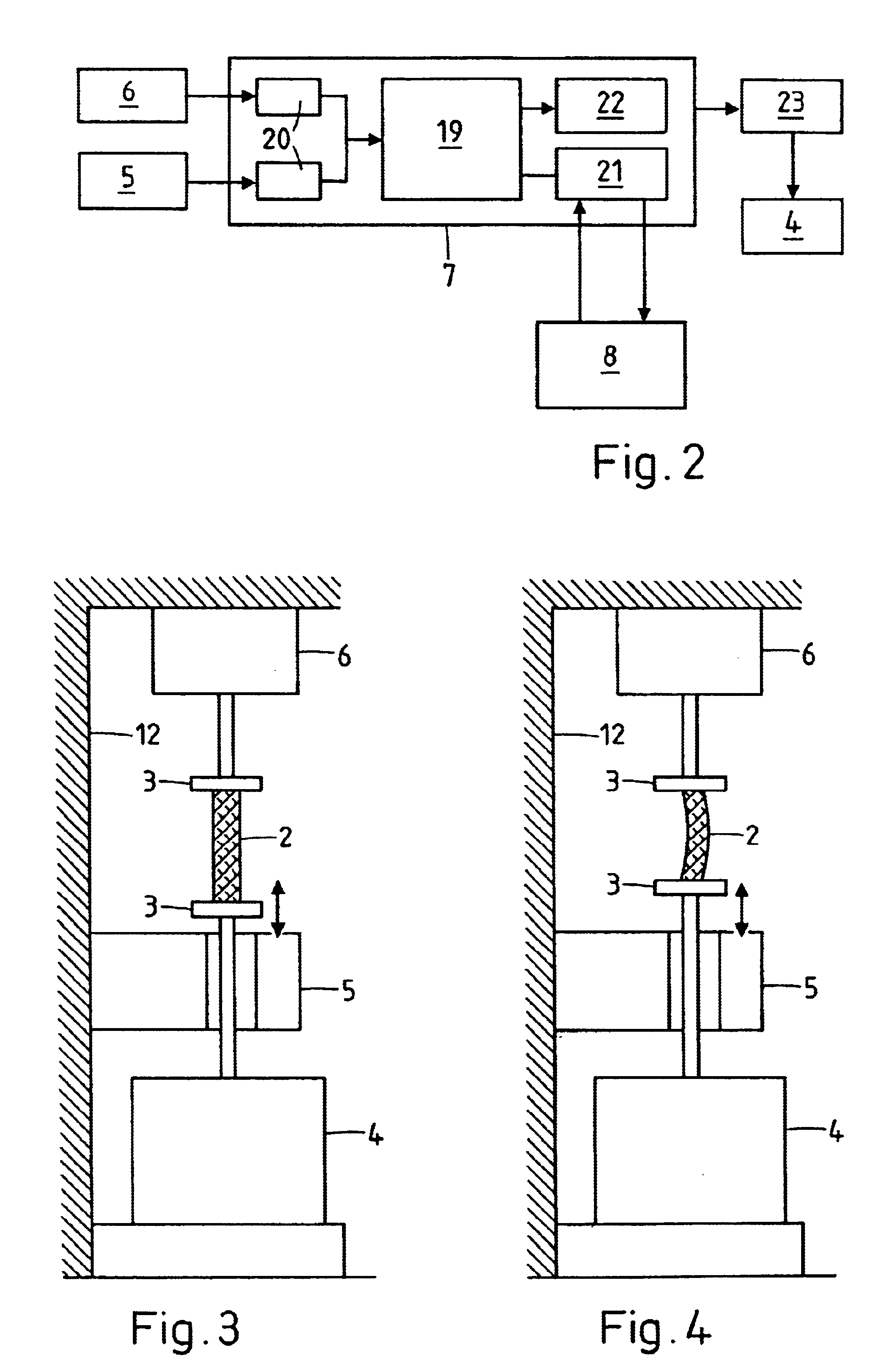
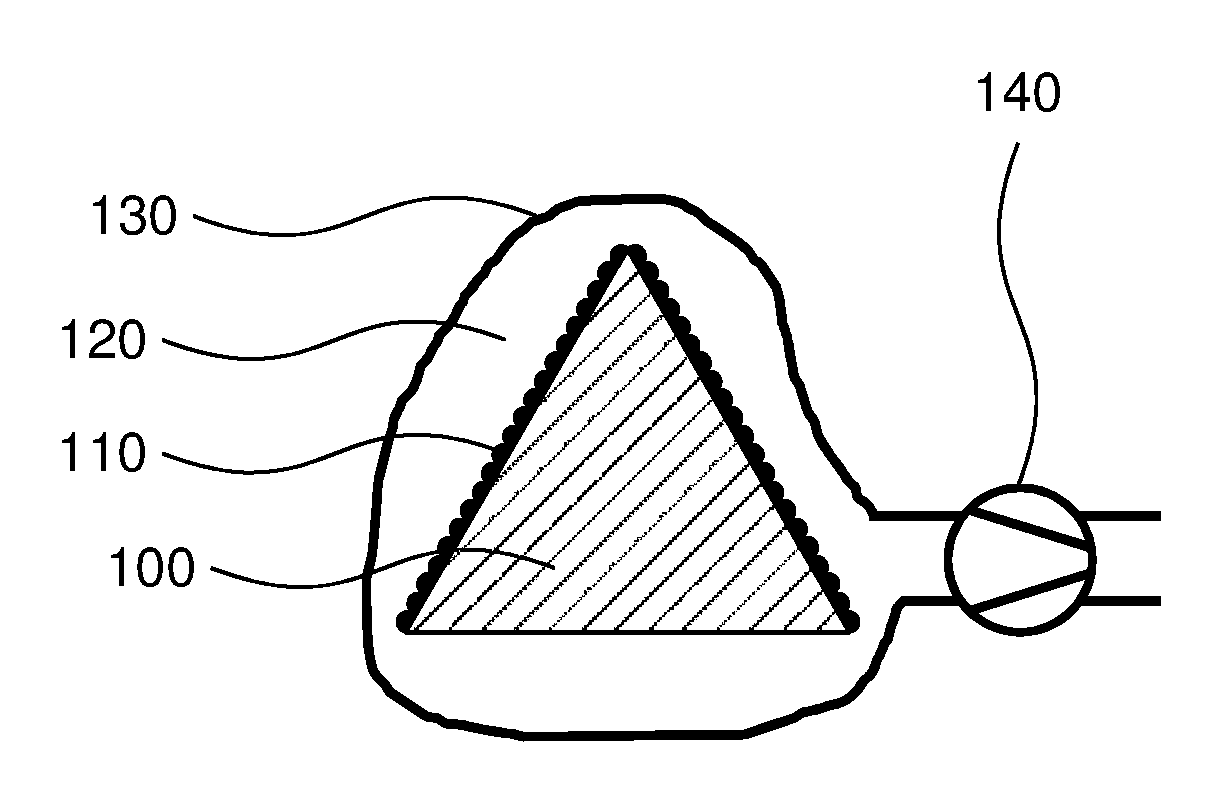
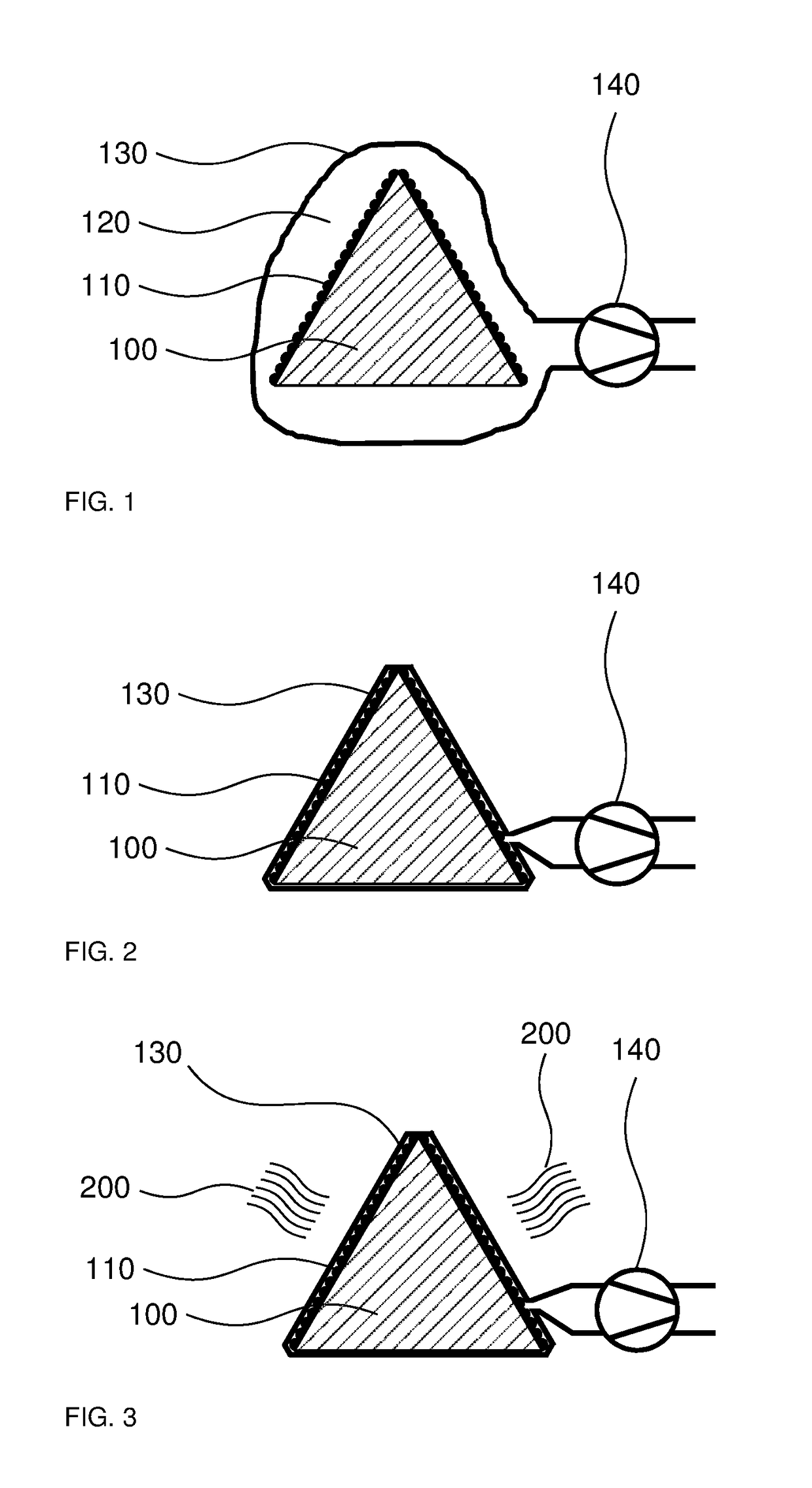
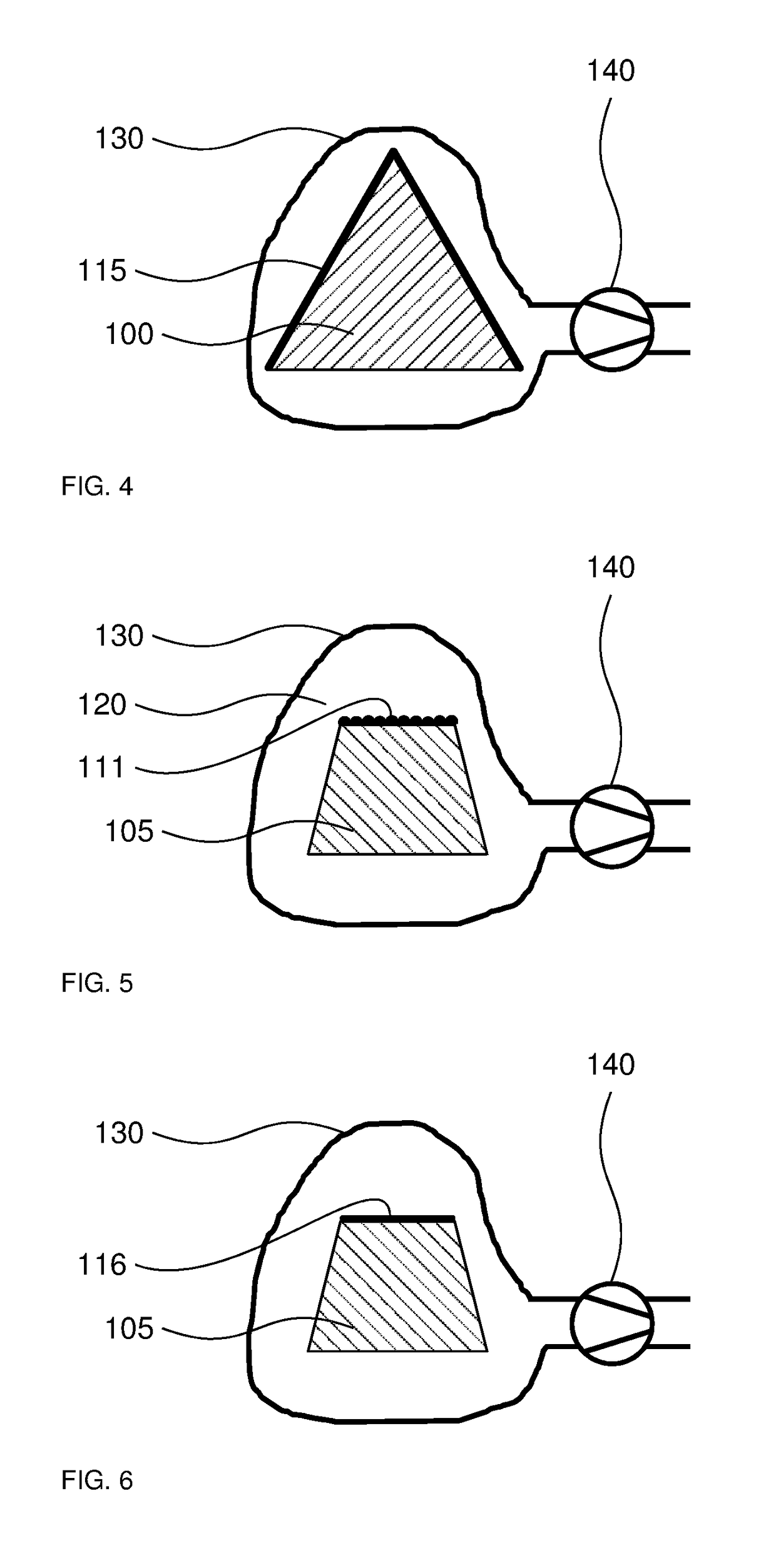
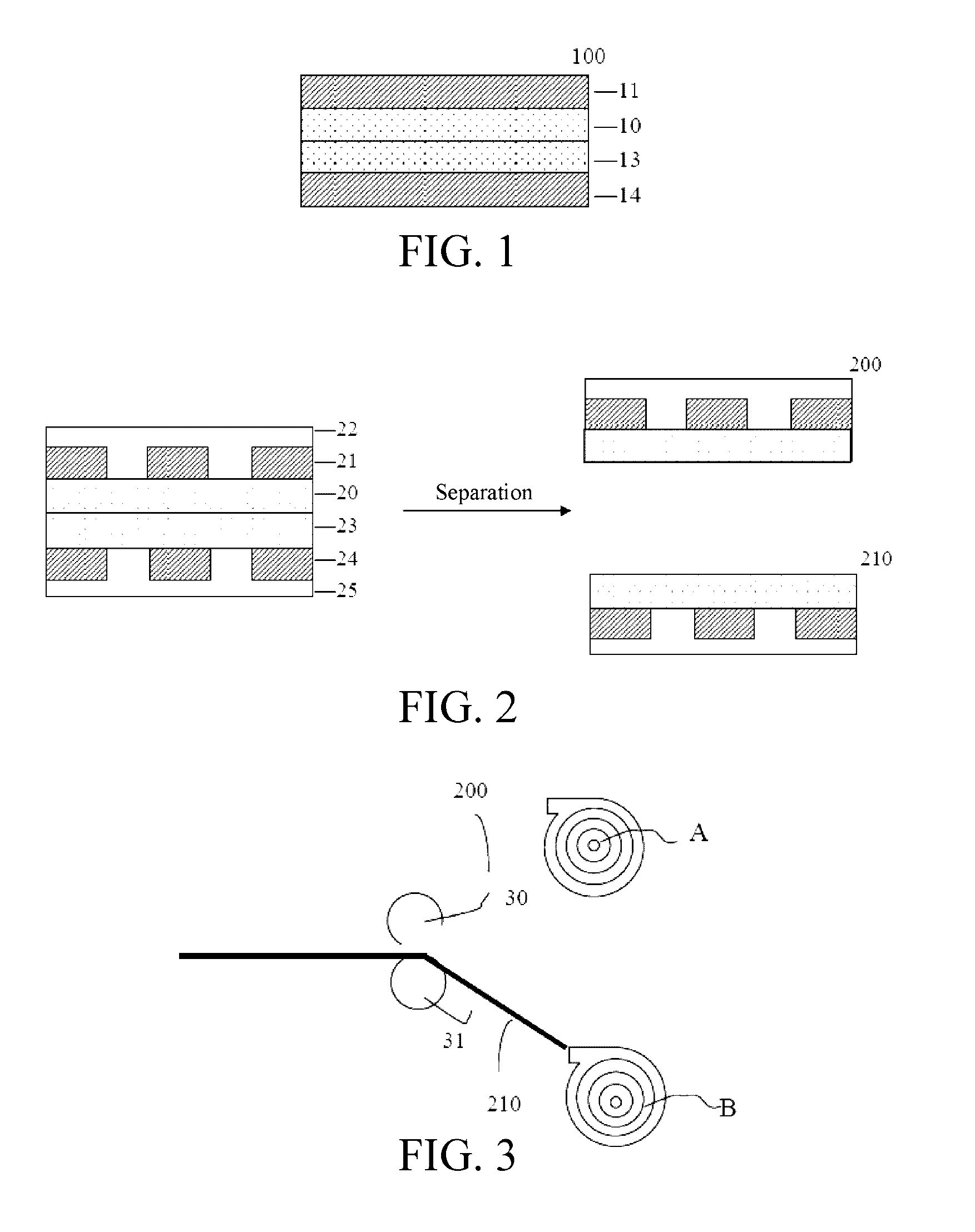
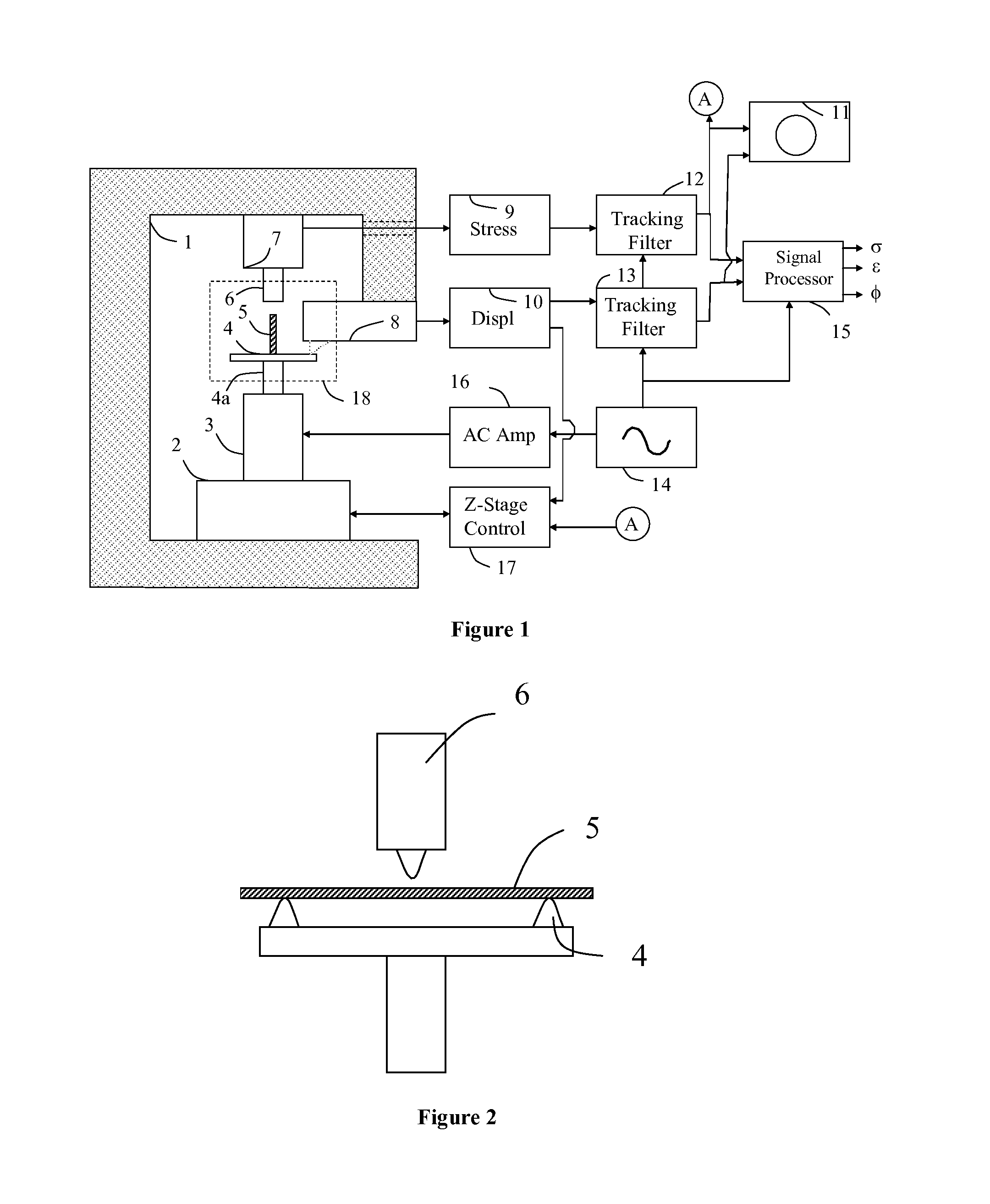
Method and apparatus for performing dynamic mechanical analyses
InactiveUS20030188585A1Error freeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesClassical mechanicsDynamic mechanical analysis
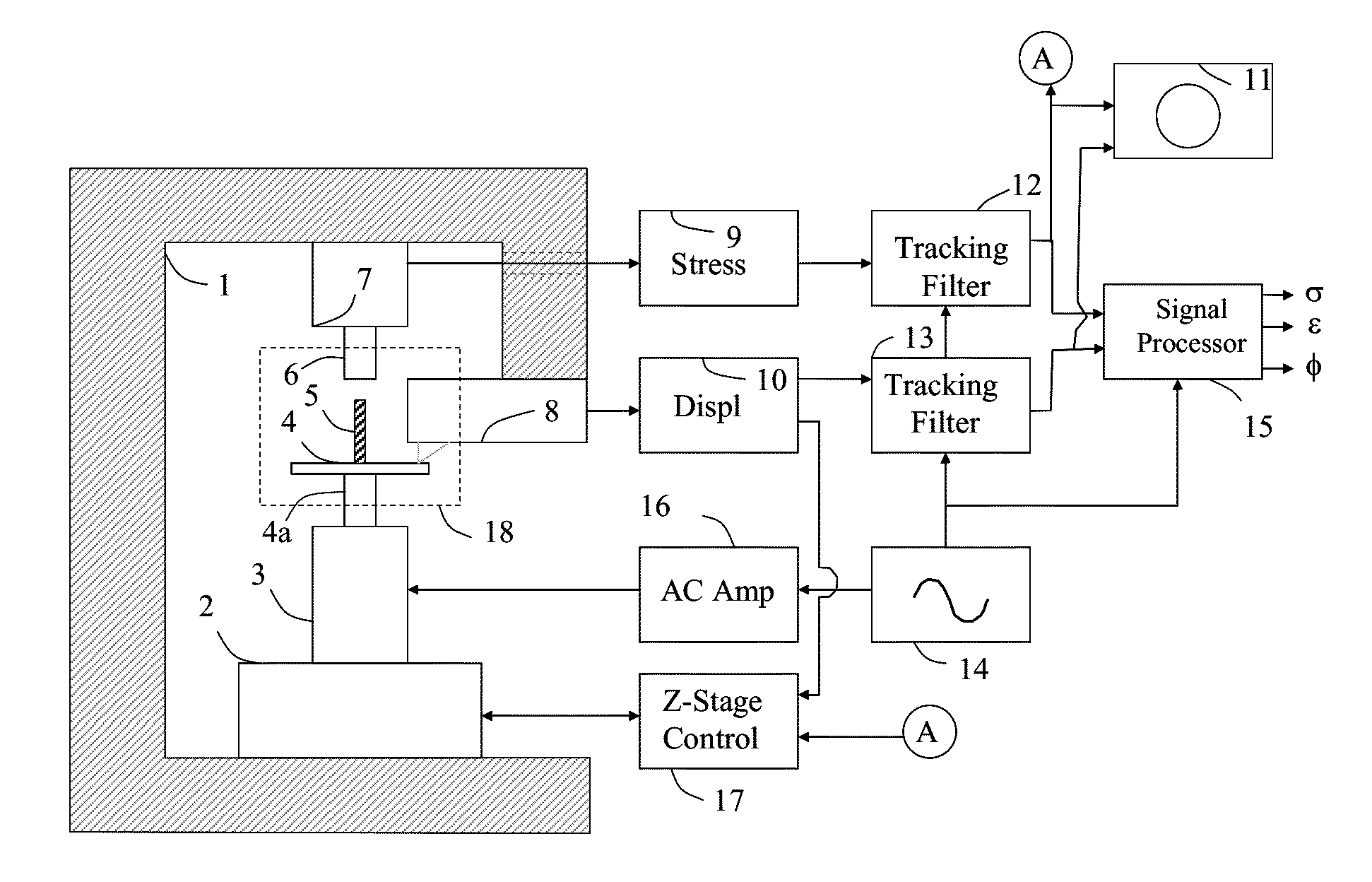
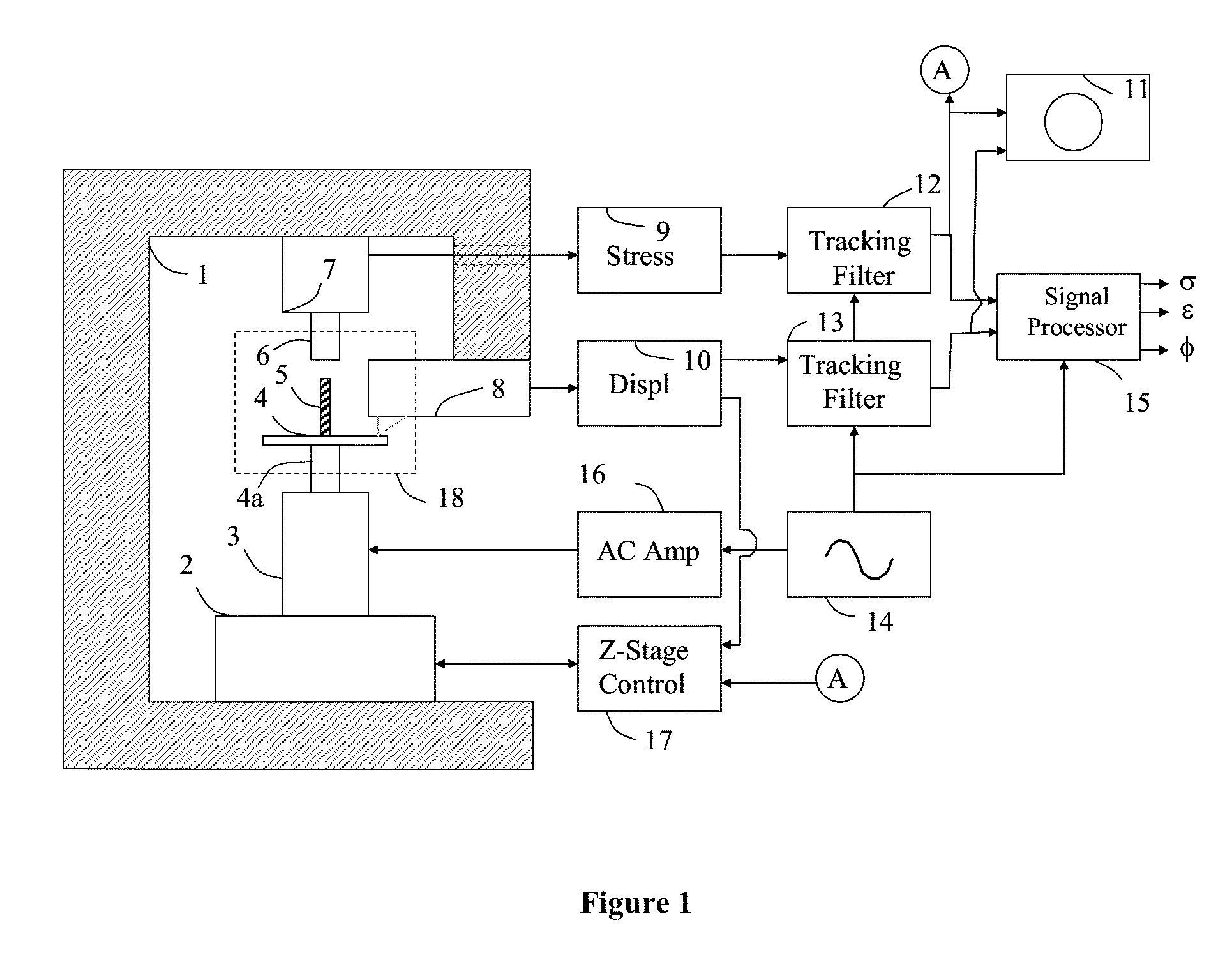
In a dynamic mechanical analysis, a test specimen (2) is coupled to an excitation device (4) by means of a holder device (3). The excitation device (4) applies an excitation force comprised of a static pre-tensioning force component and a time-variable force component to the test specimen, and a deformation of the test specimen (2) is measured by means of one or more displacement sensors (5). The method includes a test phase with the steps: applying the excitation force to the test specimen; while said excitation force is in effect, determining at least one decision parameter, said decision parameter being indicative of a degree of slack in said coupling of the test specimen; comparing said decision parameter to at least one reference value; based on said comparison, determining whether or not the test specimen is coupled to the excitation device in a completely slack-free state, so that physical values derived from said measurements of the deformation will not be subject to errors caused by an insufficient amount of said pre-tensioning force component.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Geocell for load support applications
ActiveUS20100080659A1Rigid enoughAccept high stressPaving reinforcementsArtificial islandsGeocellsThermal expansion
A geocell is disclosed that has high strength and stiffness, such that the geocell has a storage modulus of 500 MPa or greater at 23° C.; a storage modulus of 150 MPa or greater at 63° C. when measured in the machine direction using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) at a frequency of 1 Hz; a tensile stress at 12% strain of 14.5 MPa or greater at 23° C.; a coefficient of thermal expansion of 120×10−6 / ° C. or less at 25° C.; and / or a long term design stress of 2.6 MPa or greater. The geocell is suitable for load support applications, especially for reinforcing base courses and / or subbases of roads, pavement, storage areas, and railways.
Owner:GEOTECH TECHNOLOGIES LTD
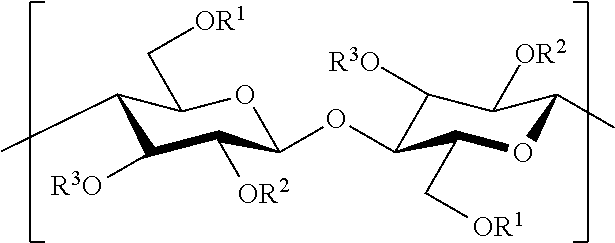
Propylene-ethylene random block copolymer and biaxially oriented multi-layer film using the same as a surface layer
ActiveUS20050113517A1High transparencyIncrease flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A polyolefin based biaxially oriented multi-layer film having at least one surface layer comprise of the propylene-ethylene random block copolymer; The propylene-ethylene random block copolymer obtained through sequential polymerization catalyzed by a metallocene component which is composed of 30 to 70 wt % of a propylene-ethylene random copolymer component having an ethylene content of 1 to 7 wt % produced in the first step of the polymerization and from 70 to 30 wt % of a low crystallinity or an amorphous propylene-ethylene random copolymer component produced in the second step of the polymerization having an ethylene content of 6 to 15 wt % higher than that of the polymer component obtained in the first step, wherein that shows a single peak at 0° C. or lower in the temperature-loss tangent (tanδ) curve obtained by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA).
Owner:JAPAN POLYPROPYLENE CORP
Cellulose esters in highly-filled elastomaric systems
An elastomeric composition is provided comprising at least one primary elastomer, one or more fillers, and at least one non-fibril cellulose ester, wherein the elastomeric composition exhibits a dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) strain sweep modulus as measured at 5% strain and 30° C. of at least 1,450,000 Pa and a molded groove tear as measured according to ASTM D624 of at least 125 lbf / in.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Propylene-ethylene random block copolymer and biaxially oriented multi-layer film using the same as a surface layer
ActiveUS7390575B2Improved transparency and flexibilityNo stickinessSynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersPolyolefinSurface layer
A polyolefin based biaxially oriented multi-layer film having at least one surface layer comprise of the propylene-ethylene random block copolymer;The propylene-ethylene random block copolymer obtained through sequential polymerization catalyzed by a metallocene component which is composed of 30 to 70 wt % of a propylene-ethylene random copolymer component having an ethylene content of 1 to 7 wt % produced in the first step of the polymerization and from 70 to 30 wt % of a low crystallinity or an amorphous propylene-ethylene random copolymer component produced in the second step of the polymerization having an ethylene content of 6 to 15 wt % higher than that of the polymer component obtained in the first step, wherein that shows a single peak at 0° C. or lower in the temperature-loss tangent (tan δ) curve obtained by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA).
Owner:JAPAN POLYPROPYLENE CORP
Thermotropic crosslinking type shape memory polyurethane material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a thermotropic crosslinking type shape memory polyurethane material obtained by thermal crosslinking of thermoplastic polyurethane with a side-chain double bond, a bifunctional crosslinking agent and an initiator; in a bending mode, the shape fixed rate is more than or equal to 95%, and the shape recovery rate is more than or equal to 90%; in a dynamic mechanical analysis tensile mode, the shape fixed rate is more than or equal to 95%, and the shape recovery rate is more than or equal to 90%. A preparation method disclosed by the invention is a second-step method and comprises the steps: firstly preparing the thermoplastic polyurethane with the side-chain double bond, then carrying out melting mixing or solution mixing with the bifunctional crosslinking agent under a condition with addition of the initiator, and carrying out thermal crosslinking to prepare the product. The polyurethane material disclosed by the invention has excellent shape memory properties and mechanical properties, the transition temperature is close to a body temperature, and the raw materials have good biological compatibility and no toxicity and can be degraded; the polyurethane material can be used as in-vivo implant materials and clinical surgical materials, also can be used for wire and cable casings and building pipe connecting sleeves, moreover, can be used for buffer sole protection devices, deformation toys and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:眉山尤博瑞新材料有限公司
Crack resistant solar cell modules
ActiveUS9035172B2Less development riskPV power plantsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyolefinSide chain
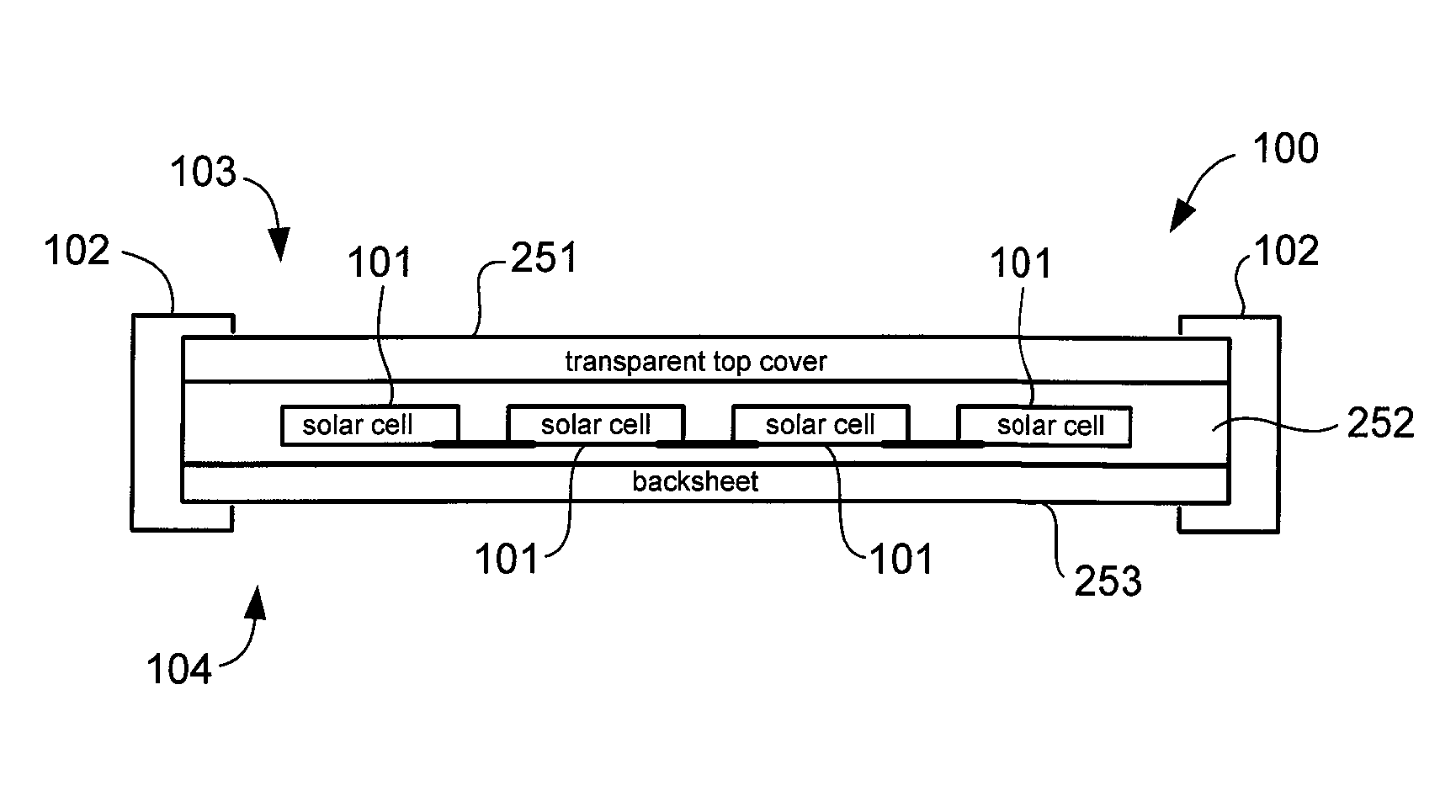
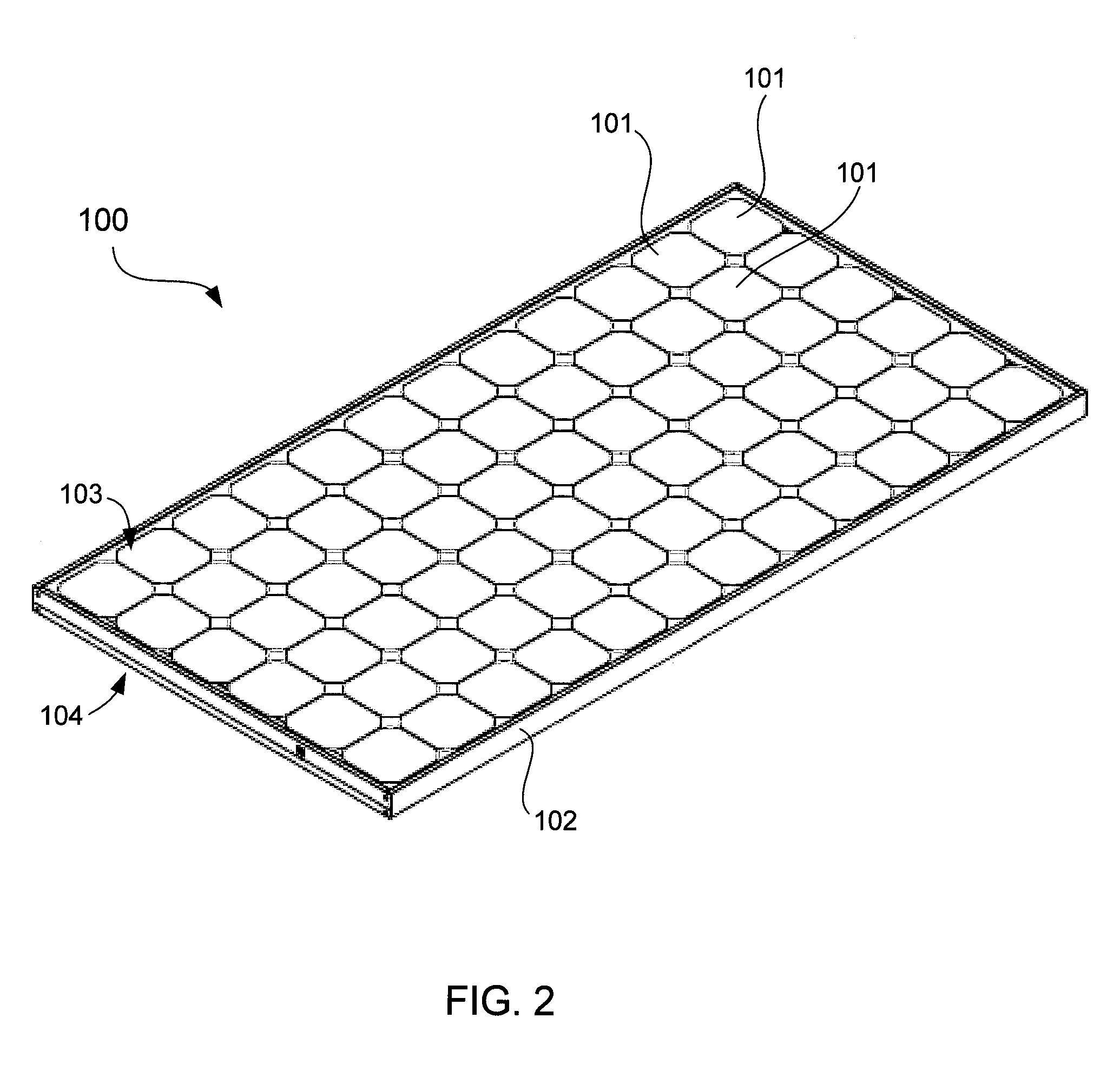
A crack resistant solar cell module includes a protective package mounted on a frame. The protective package includes a polyolefin encapsulant that protectively encapsulates solar cells. The polyolefin has less than five weight percent of oxygen and nitrogen in the backbone or side chain. In other words, the combined weight percent of oxygen and nitrogen in any location in the molecular structure of the polyolefin is less than five. The polyolefin also has a complex viscosity less than 10,000 Pa second at 90° C. as measured by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) before any thermal processing of the polyolefin. The protective package includes a top cover, the encapsulant, and a backsheet. The solar cell module allows for shipping, installation, and maintenance with less risk of developing cracks on the surfaces of the solar cells.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD
Smear resistant inkjet inks
ActiveUS9090734B2Good smear-fastnessHigh optical densityInksPrintingPolyurethane dispersionDynamic mechanical analysis
Owner:DUPONT ELECTRONICS INC
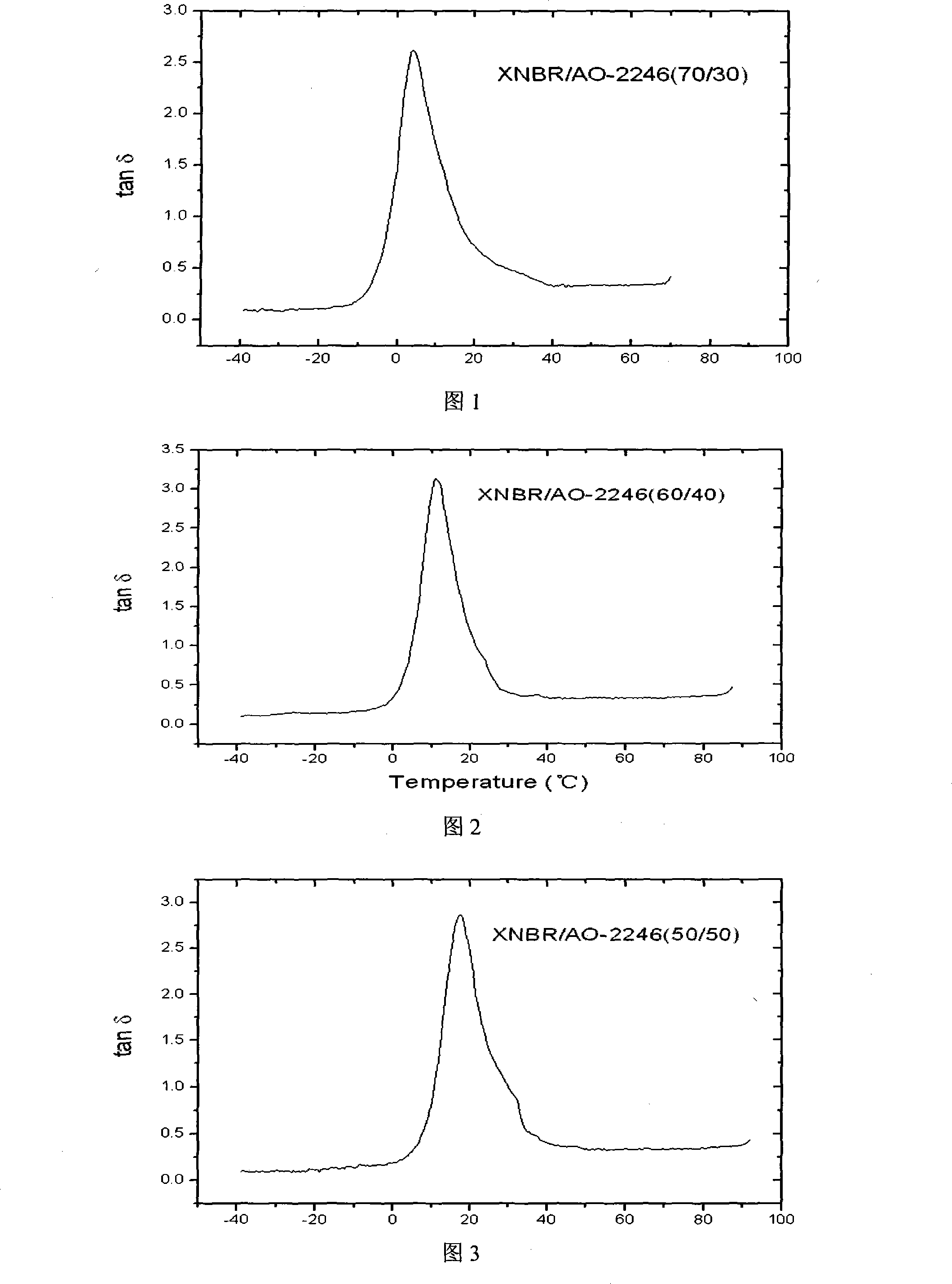
Carboxy nitrile rubber high-performance damping material and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101173066AImprove loss factorWide effective damping temperature rangeNitrile rubberPhenolic antioxidant
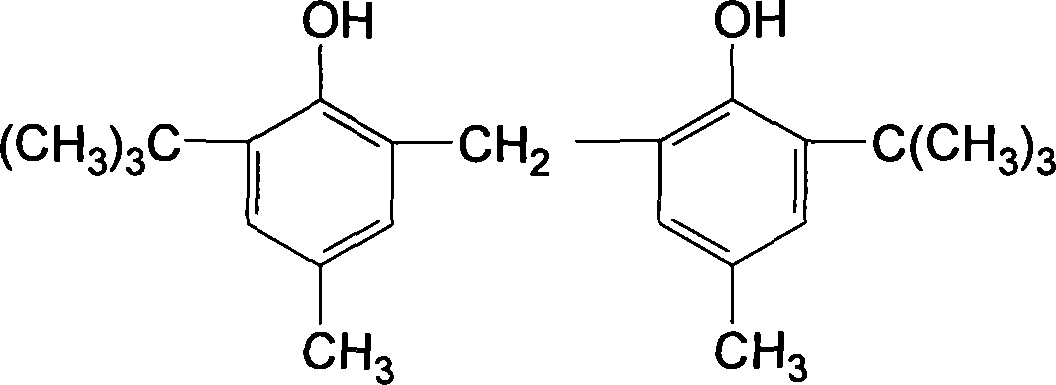
The invention relates to a carboxylated nitrile rubber-based high-performance damping material and a preparation method thereof. The material uses carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) as a matrix and a hindered phenolic antioxidant 2,2'-methylene bis( 4-methyl-6-tert-butylphenol) is a damping additive obtained by blending and tableting; preparation: (1) Blending a certain proportion of carboxylated nitrile rubber and damping additives on a double-roller mixer Making a mixed film; (2) hot pressing the mixed film on a flat vulcanizing machine to obtain a thin sheet sample; (3) using a dynamic mechanical analyzer to perform a dynamic mechanical test on the sample to characterize its damping performance. The damping material of the present invention is characterized by a large loss factor, a wide effective damping temperature range, and the position of the damping peak can be regulated by adjusting the content of the damping additive, thereby obtaining a high-performance damping material suitable for use at different temperatures.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Biaxially oriented multi-layer film using propylene-ethylene random block copolymer as a surface layer
A polyolefin based biaxially oriented multi-layer film having at least one surface layer comprise of the propylene-ethylene random block copolymer; The propylene-ethylene random block copolymer obtained through sequential polymerization catalyzed by a metallocene component which is composed of 30 to 70 wt % of a propylene-ethylene random copolymer component having an ethylene content of 1 to 7 wt % produced in the first step of the polymerization and from 70 to 30 wt % of a low crystallinity or an amorphous propylene-ethylene random copolymer component produced in the second step of the polymerization having an ethylene content of 6 to 15 wt % higher than that of the polymer component obtained in the first step, wherein that shows a single peak at 0 DEG C. or lower in the temperature-loss tangent (tandelta) curve obtained by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA).
Owner:JAPAN POLYPROPYLENE CORP
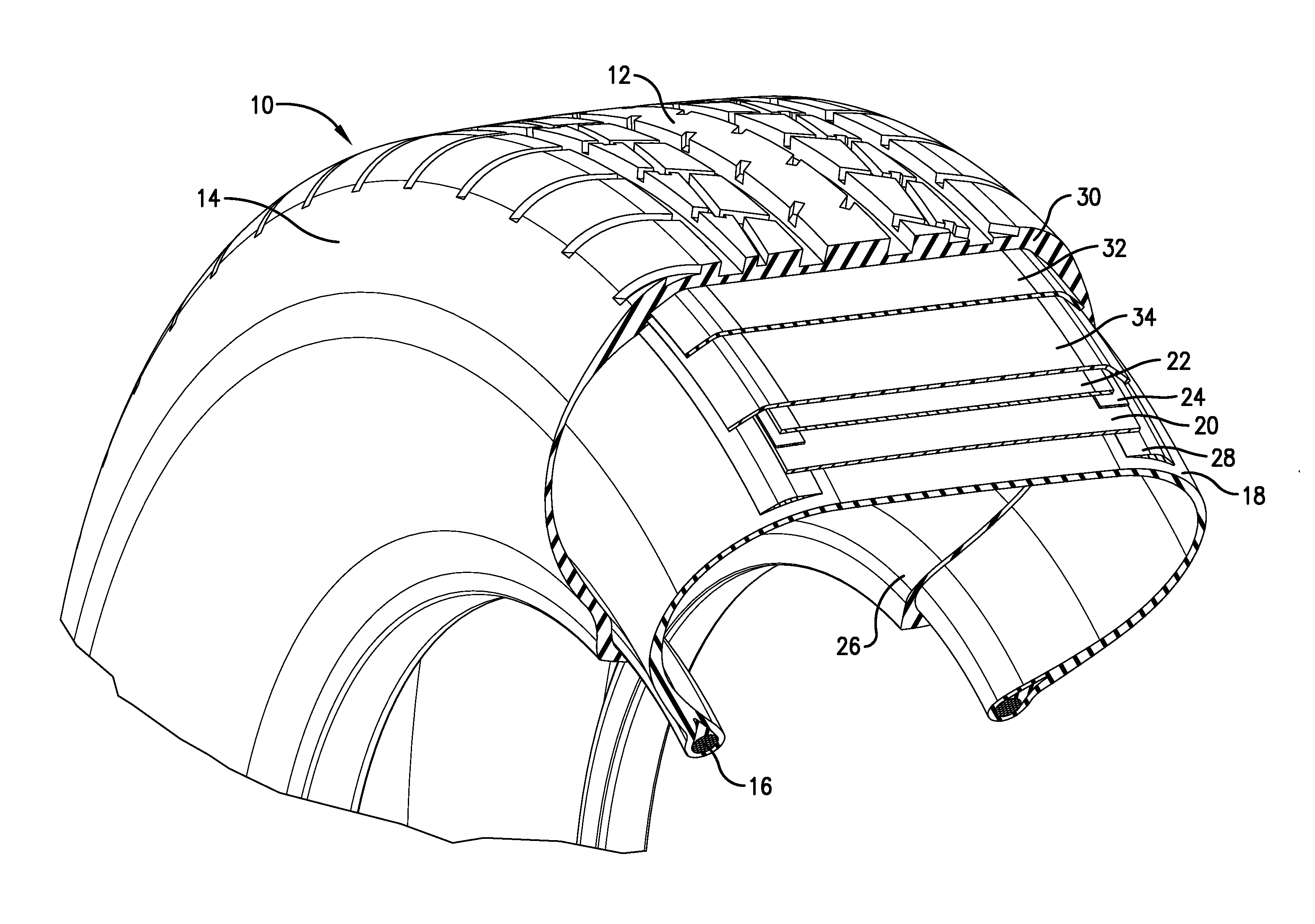
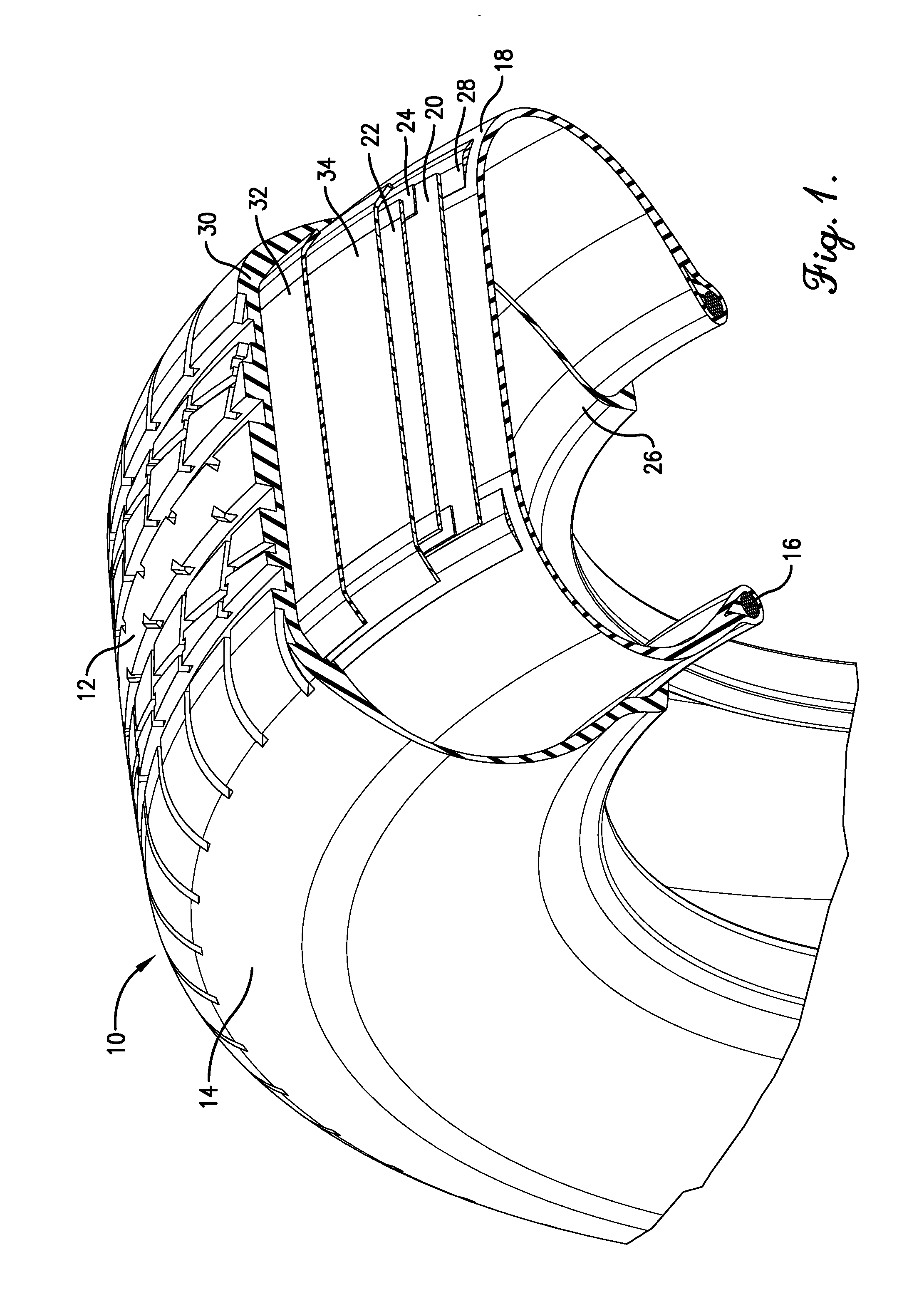
Cellulose esters in pneumatic tires
A tire component is provided comprising an elastomeric composition containing at least one non-fibril cellulose ester, at least one primary elastomer, and one or more fillers, wherein said composition exhibits a dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) strain sweep modulus as measured at 5% strain and 30° C. of at least 1,450,000 Pa and a molded groove tear as measured according to ASTM D624 of at least 120 lbf / in.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Epoxide resin based piezoelectric damping composite material and method for preparing the same
The invention discloses an epoxide resin based piezoelectricity damping composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material consists of piezoelectric ceramics, graphitized carbon black and epoxide resins, wherein the components are integrated into one whole body by the secondary casting; the introduced piezoelectric ceramics is centralized on the upper part and the lower part of the composite material respectively, naturally settled in the process of forming and finally forms a sandwich structure with graded distribution. The invention utilizes the secondary casting forming process to prepare the epoxide resin based piezoelectricity damping composite material with the gradient sandwich structure, on the basis of realizing the piezoelectricity damping by the three-phase cooperation effect, the composite material also has the advantages of the sandwich structure, thereby greatly improving the damping performance of the composite material; through the dynamic mechanical analysis of a sample, the max. damping factor (tan delta max) is increased by more than 20 percent, the damping temperature zone delta T (the temperature zone where tan delta is more than 0.3)) is increased by more than 33 percent, and the area TA included under the tan delta-T curve is increased by more than 19 percent.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Geocell for load support applications
A geocell is disclosed that has high strength and stiffness, such that the geocell has a storage modulus of 500 MPa or greater at 23 DEG C; a storage modulus of 150 MPa or greater at 630C when measured in the machine direction using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) at a frequency of 1 Hz; a tensile stress at 12% strain of 14.5 MPa or greater at 230C; a coefficient of thermal expansion of 120 x 10'6 / 0C or less at 250C, and / or a long term design stress of 2.6 MPa or greater. The geocell is suitable for load support applications, especially for reinforcing base courses and / or subbases of roads, pavement, storage areas, and railways.
Owner:PRS MEDITERRANEAN
Thermoset dampener material
Thermoset compositions useful for dampening vibrations at elevated temperatures are disclosed. The thermoset compositions may have a glass transition temperature of 150 DEG C or greater, a tan d peak of 0.2 or greater, and a tan delta peak width measured at half-height larger than about 40 DEG C, each as measured by dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA) at a frequency of 1 Hz. The thermoset compositions may be used to dampen vibrations at temperatures in excess of 100 DEG C.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
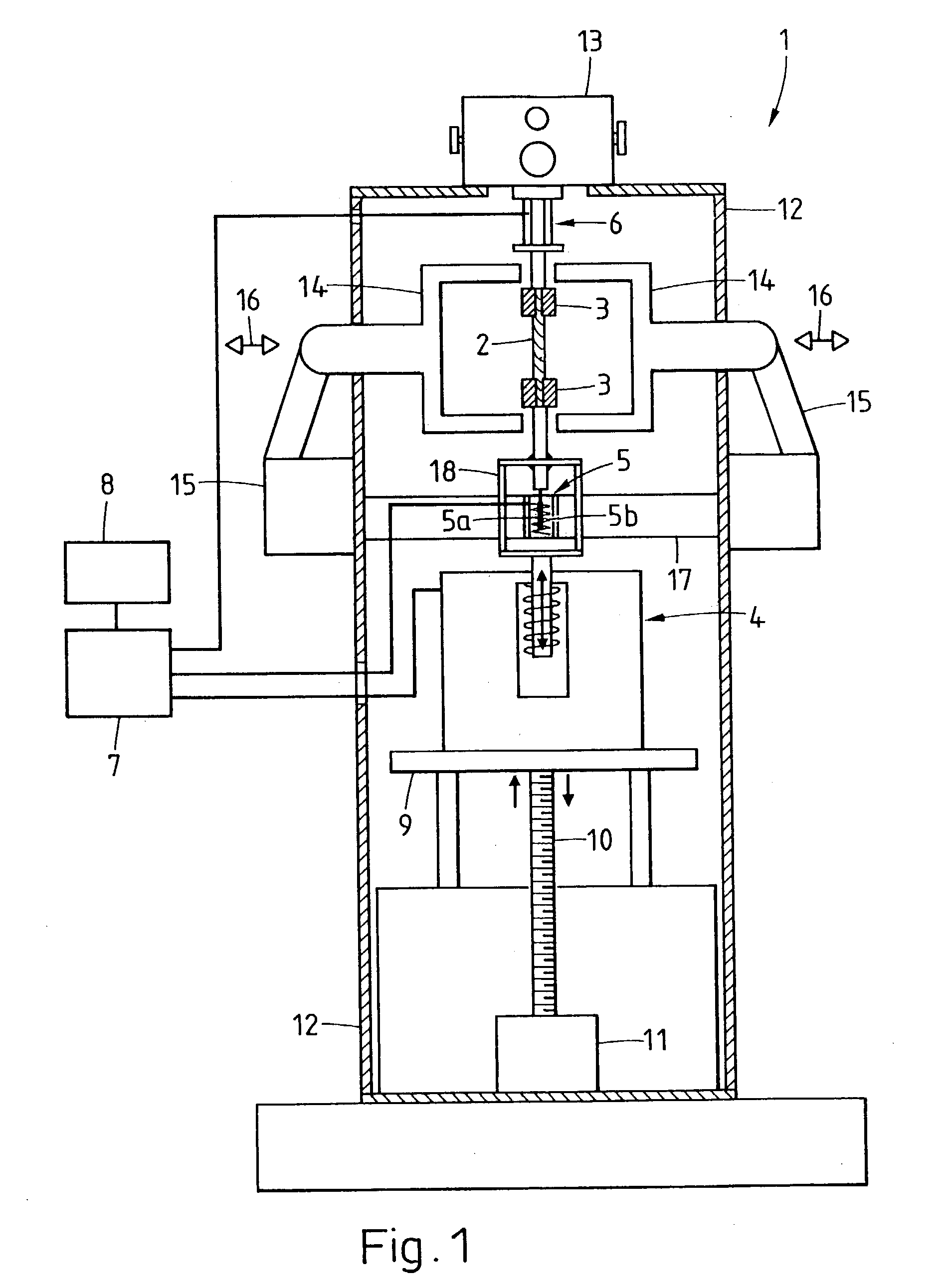
Method and Apparatus for Direct-Acting Wide Frequency Range Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Materials
InactiveUS20130047741A1Force measurement by measuring frquency variationsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDynamic mechanical analysisMechanical engineering
An improved method and apparatus for direct acting dynamic mechanical analysis capable of accurate data at high frequencies where during temperature ramping, the sample is not in contact with both of 1) the strain excitation means and 2) the stress sensing means, thus providing numerous advantages and allowing additional analysis of sample dimension data and zero strain state.
Owner:WOO LECON
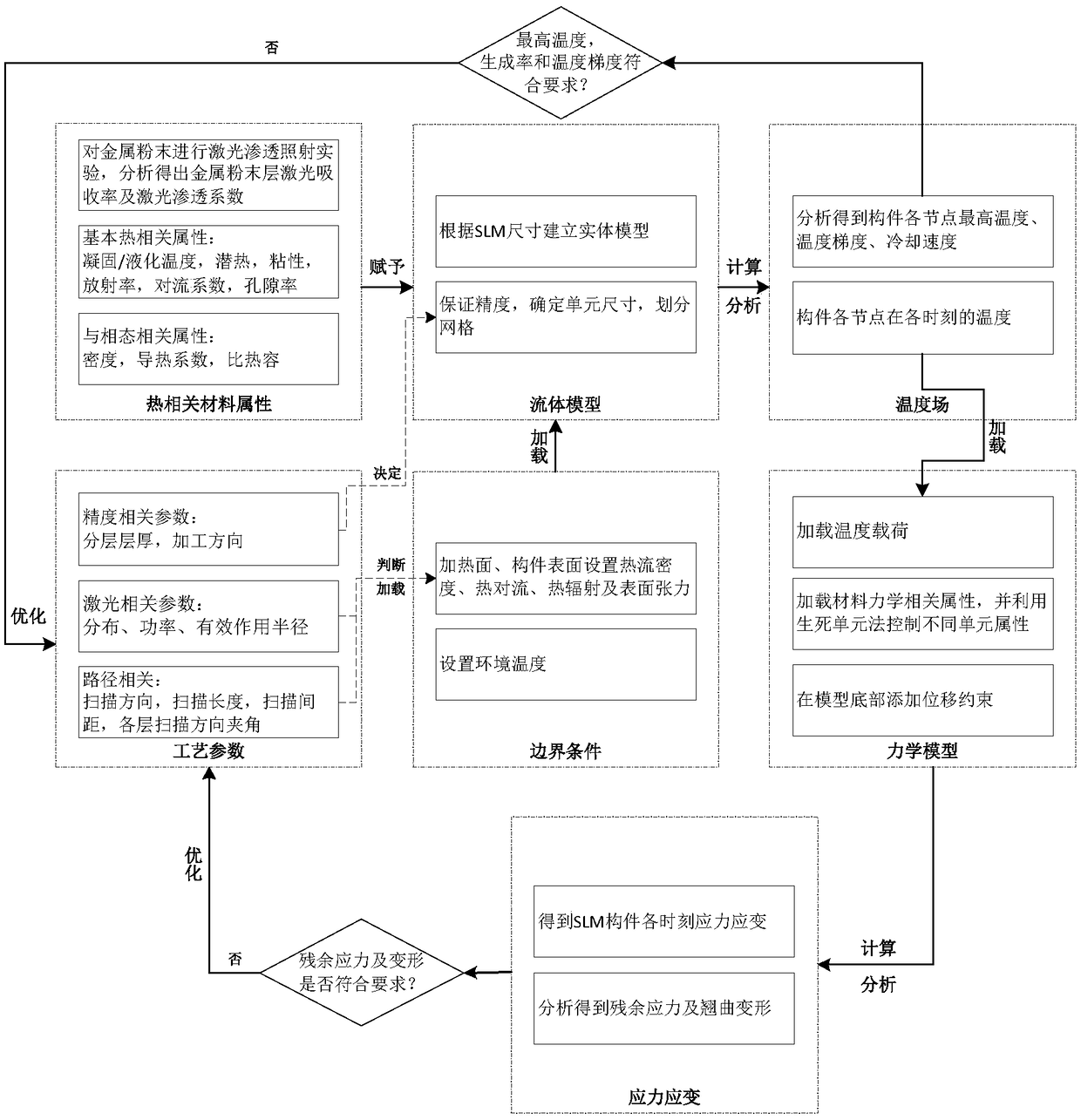
Prediction method for temperature distribution and warping deformation in selective laser melting process
ActiveCN108717481AReduce warpageOptimizing Process ParametersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSelective laser meltingTransient analysis
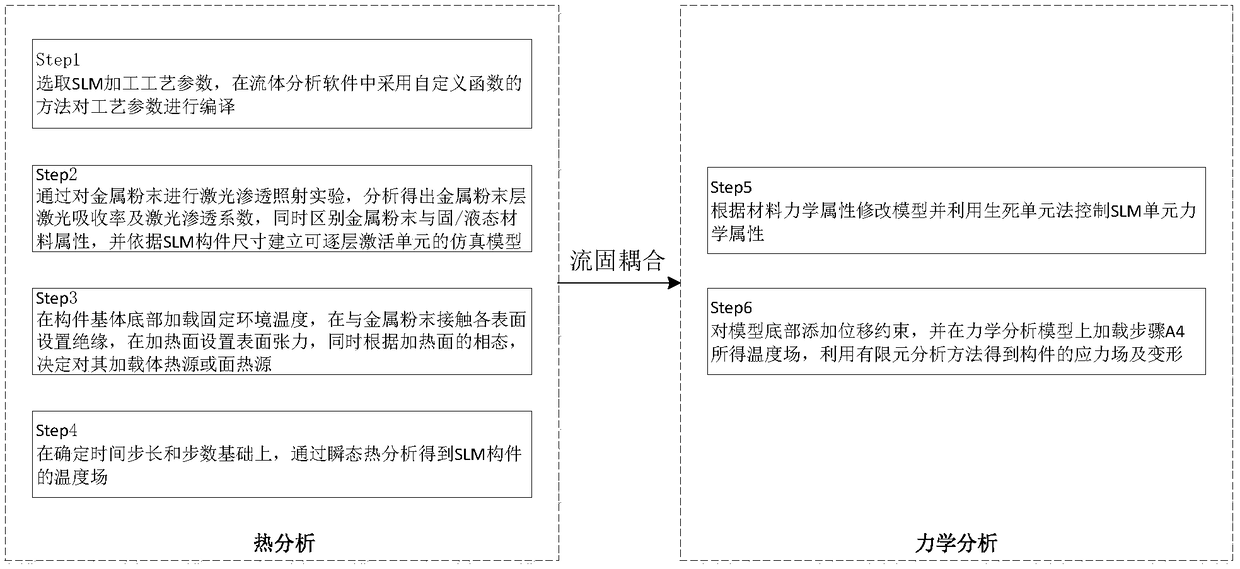
The invention discloses a prediction method for temperature distribution and warping deformation in a selective laser melting process. The method is mainly composed of thermal analysis and mechanicalanalysis. Thermal analysis comprises the steps that Step1, processing parameters are determined, and technological planning is performed; Step2, metal material heat relevant properties are acquired, and a model is established according to the dimensions of an SLM component; Step3, temperature boundary conditions are loaded; and Step4, transient analysis is performed to obtain a temperature field of the SLM component. Mechanical analysis comprises the steps that Step5, the model is modified according to material mechanical properties; and Step6, the boundary conditions are added, and the temperature field obtained through analysis in Step4 is used as a load to obtain a stress field and deformation of the component through analysis. According to the method, through thermoset coupling, thermal analysis and mechanical analysis are combined to establish a temperature and deformation prediction system, and technical support is provided for optimizing technological parameters and reducing warping deformation of the SLM component.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
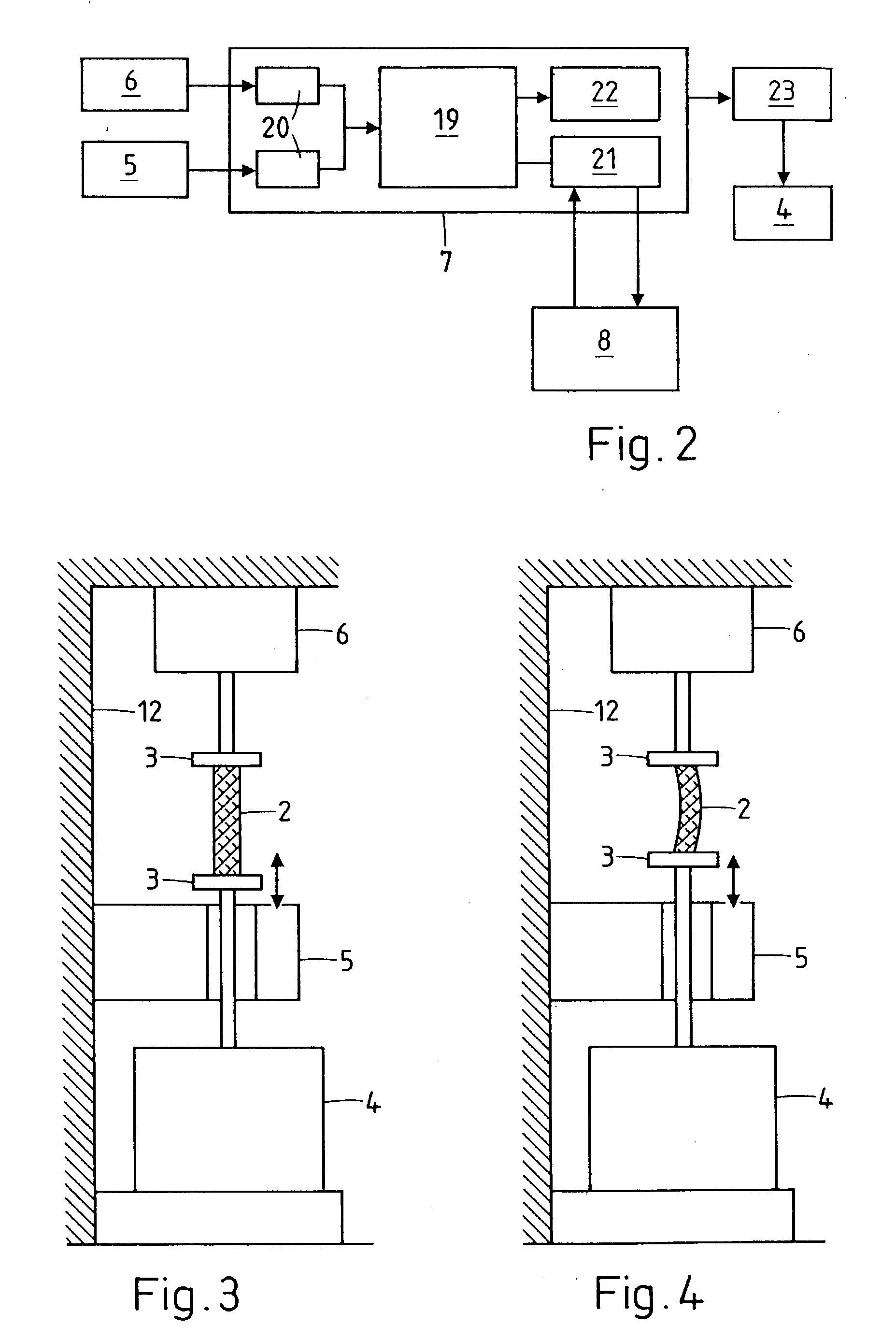
Method and apparatus for performing dynamic mechanical analyses
InactiveUS6880385B2Error freeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesTest sampleCoupling
In a dynamic mechanical analysis, a test specimen is coupled to an excitation device by a holder device. An excitation force made up of a static pre-tensioning force component and a time-variable force component is applied to the test specimen, and a deformation of the test specimen is measured by one or more displacement sensors. In a test phase an excitation force is applied to the test specimen, while at least one decision parameter is determined. The decision parameter is indicative of a degree of slack in the coupling of the test specimen. Based on the comparison between the decision parameter and at least one reference value it is determined whether or not the test specimen is coupled to the excitation device in a completely slack-free state, so that any measured physical values will not be subjected to errors caused by an insufficient amount of the pre-tensioning force.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Method of treating at least part of the surface of a 3d-printed article
ActiveUS20180111315A1Fine surfaceEasy to demonstrateAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structures3d printPolymer science
A method of treating at least part of a surface (110) of an article (100) in which an article (100) is treated, at least part of a surface (110, 111) of the article having been produced by an additive manufacturing method from a construction material, and the construction material provides a temperature TG′ at which the storage modulus G′ of the construction material (determined by dynamic-mechanical analysis according to ISO 6721 at a shear rate of 1 / s) is 10 MPa. The article is preferably placed into an evacuable volume and the volume is evacuated. By heating and exerting pressure, the surface is plastically deformed and can be smoothed thereby.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
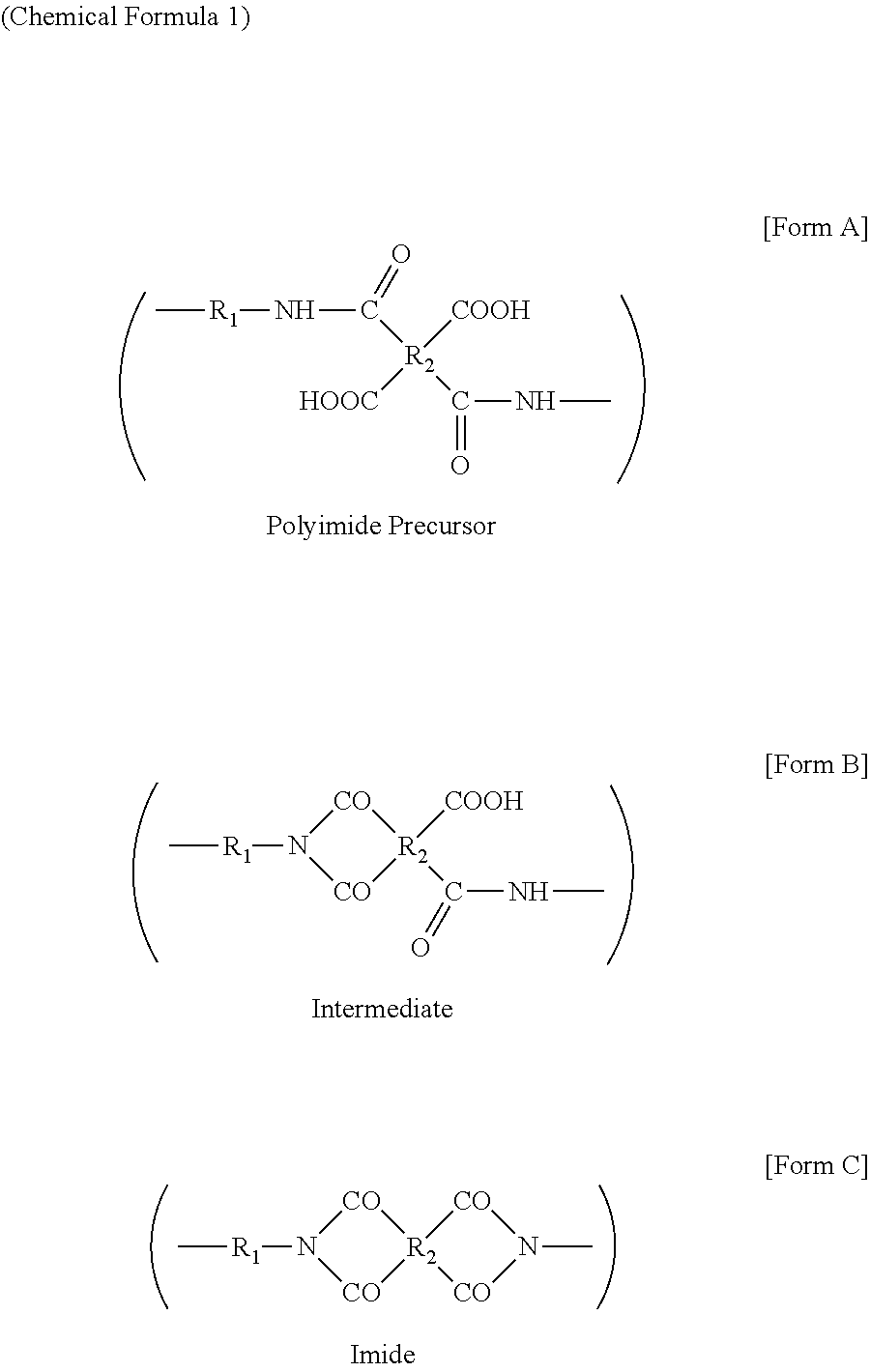
Polyimide resin and metal-clad laminate comprising the same
ActiveUS20160369053A1Avoid warpingSimple processPrinted circuit aspectsSynthetic resin layered productsVitrificationDynamic mechanical analysis
The present disclosure provides a polyimide resin having at least two glass transition temperatures measured by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). Also, a metal-clad laminate including the polyimide resin.
Owner:ETERNAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Direct-Acting Wide Frequency Range Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Materials
InactiveUS20160018306A1Accurate analysisFlow propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringDynamic mechanical analysis
An improved method and apparatus for direct-acting dynamic mechanical analysis that accomodates sample distortion due to environmental (e.g., temperature) variation.
Owner:WOO LECON
Polyurethaneurea segmented copolymers
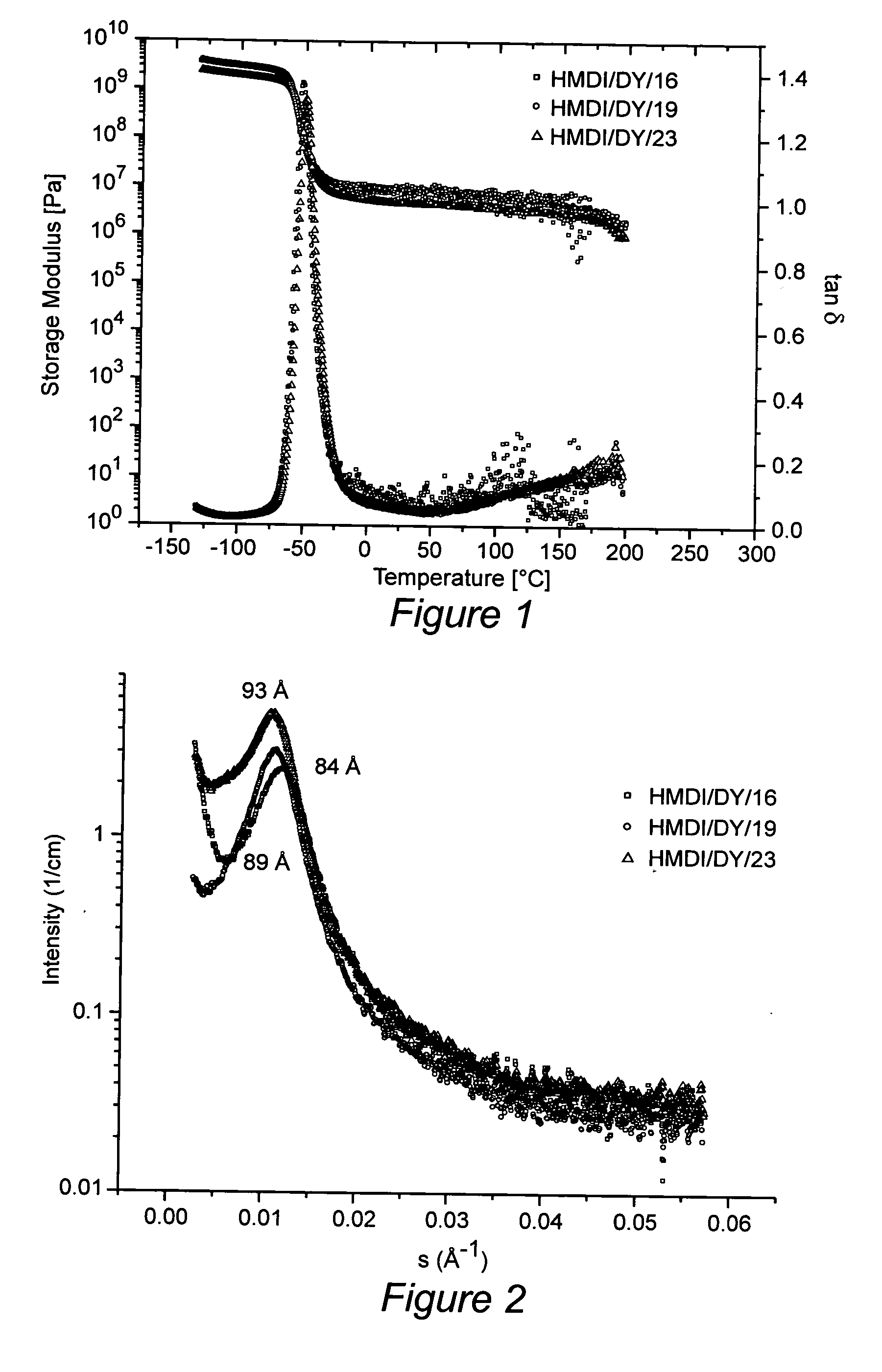
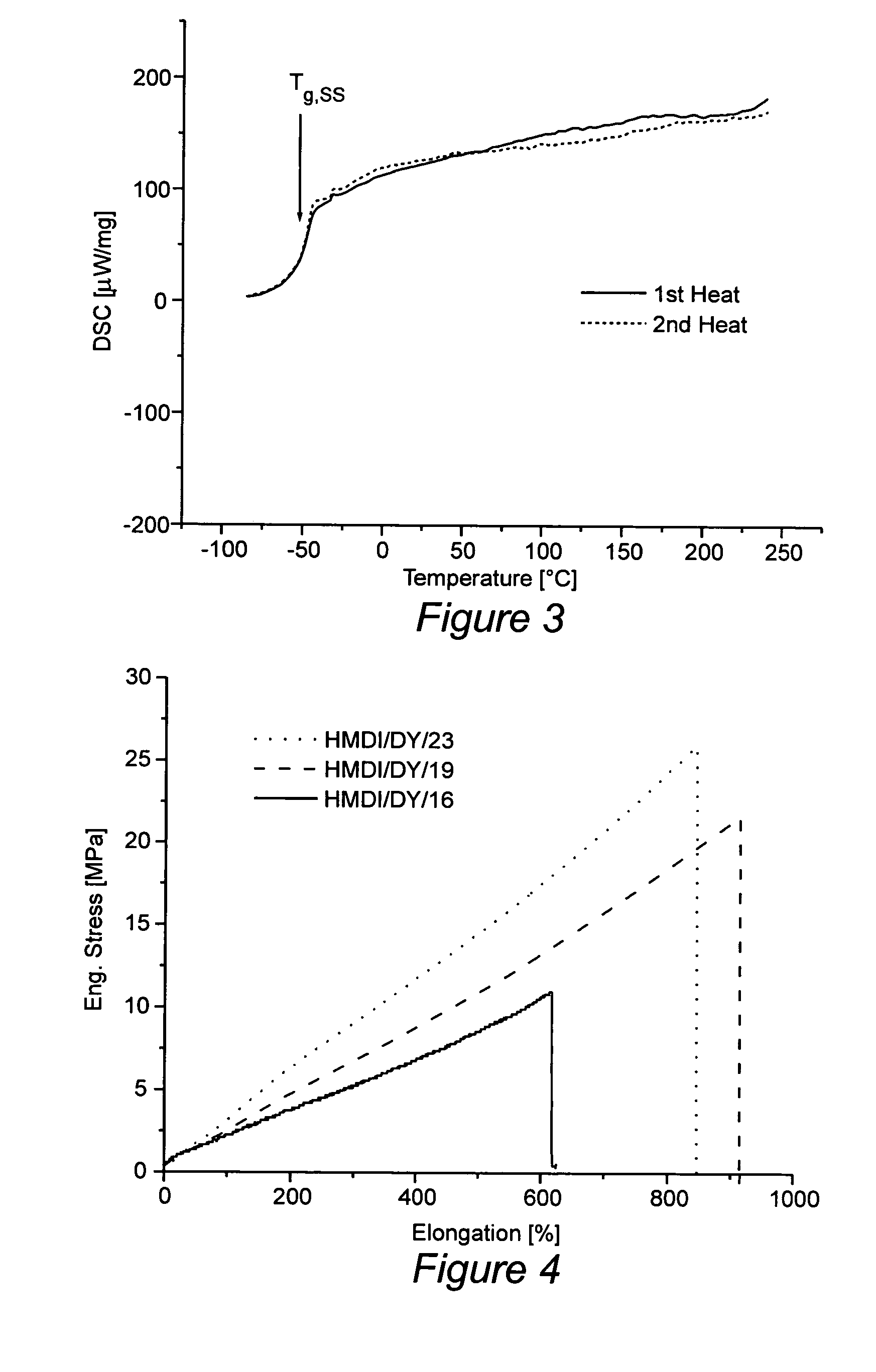
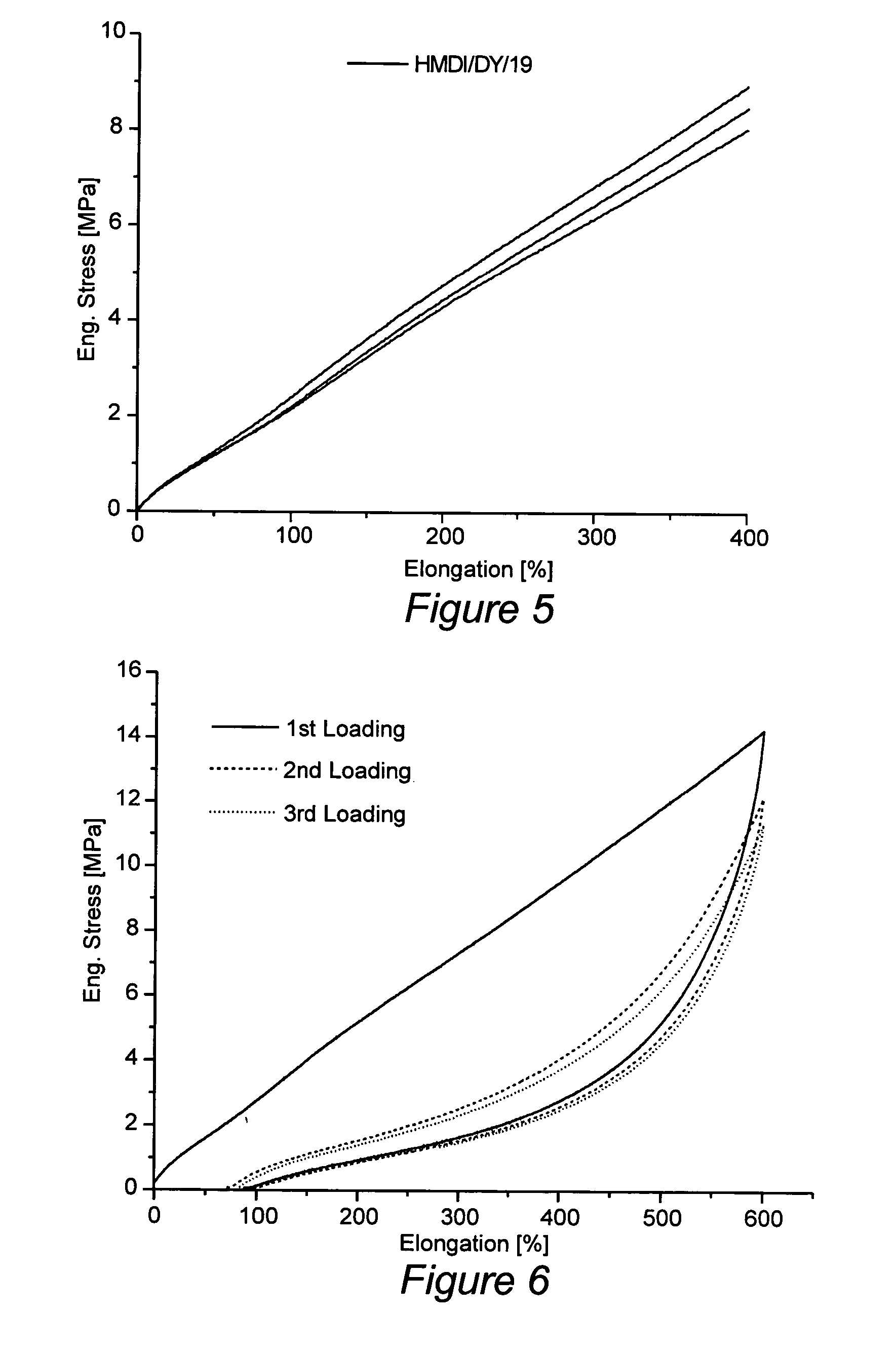
Novel segmented polyurethaneurea copolymers were synthesized using a poly(ethylene-butylene)glycol based soft segment. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) established the presence of a microphase-separated structure in which hard microdomains are dispersed throughout a soft segment matrix. Wide angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) results suggest the materials are amorphous. Samples that are made with HMDI / DY and have hard segment contents in the range of 16-23 wt % surprisingly exhibit near-linear mechanical deformation behavior in excess of 600% elongation. They also show very high levels of recoverability even though their hysteresis is also considerable. The materials are both melt processable and solution processable.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Cellulose esters in pneumatic tires
A process for producing a tire component is provided. The process comprises blending an elastomeric composition containing at least one non-fibril cellulose ester, at least one primary elastomer, and one or more fillers, wherein the elastomeric composition exhibits a dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) strain sweep modulus as measured at 5% strain and 30° C. of at least 1,450,000 Pa and a molded groove tear as measured according to ASTM D624 of at least 120 lbf / in.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Radiation curable inkjet printing methods
InactiveUS20100309268A1Economical and versatileDuplicating/marking methodsInksPolymer substrateEngineering
A radiation curable inkjet printing method for producing printed flexible foils and plastic bags includes the steps of a) providing a web-like polymeric substrate having a maximum value for Tan δ between 40° C. and 110° C.; b) providing a single pass inkjet printer having at least one page-wide printhead or at least one set of staggered printheads, a transporting device arranged to transport the web-like recording medium, and a curing device; c) jetting onto the web-like polymeric substrate having a surface energy Ssub, a non-aqueous radiation curable inkjet liquid having a surface tension SLiq, wherein SLiq is smaller than SSub by at least 4 mN / m; and d) curing the radiation curable liquid on the substrate at a surface temperature equal or higher than the temperature of the maximum value for Tan δ and smaller than the melting point of the polymeric recording medium. The maximum value for Tan δ is determined by dynamic mechanical analysis at a temperature ramp of 3° C. / min using forced oscillation with a cycle of 1 second and an amplitude of 100 μm. Also, a single pass inkjet printer for performing the method.
Owner:AGFA NV
Drawn gel-spun polyethylene yarns
Drawn multi-filament polyethylene yarns and articles thereof having unique signatures in dynamic mechanical analysis reflective of unique microstructures, and having superior ballistic resistant properties.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Geocell for load support applications
A geocell is disclosed that has high strength and stiffness, such that the geocell has a storage modulus of 500 MPa or greater at 23° C.; a storage modulus of 150 MPa or greater at 63° C. when measured in the machine direction using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) at a frequency of 1 Hz; a tensile stress at 12% strain of 14.5 MPa or greater at 23° C.; a coefficient of thermal expansion of 120×10−6 / ° C. or less at 25° C.; and / or a long term design stress of 2.6 MPa or greater. The geocell is suitable for load support applications, especially for reinforcing base courses and / or subbases of roads, pavement, storage areas, and railways.
Owner:GEOTECH TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Process for dispersing cellulose esters into elastomeric compositions
An elastomeric composition is provided comprising at least one non-fibril cellulose ester, at least one carrier elastomer, and at least one primary elastomer, wherein the elastomeric composition exhibits a dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) strain sweep modulus as measured at 5% strain and 30° C. of at least 1,450,000 Pa and a molded groove tear as measured according to ASTM D624 of at least 120 lbf / in.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polymeric compositions with improved noise suppression
InactiveUS20160075891A1Non-rotating vibration suppressionLaminationEngineeringDynamic mechanical analysis
Disclosed is a method for improving vibration damping of a substrate, such as the underbody of an automobile. The method comprises applying a plastisol which comprises a polymeric component and a plasticizer. The fused plastisol has improved damping behavior as determined using Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis. Novel plastisols and novel plasticizers are also disclosed.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Transparent electrode
InactiveUS20110171445A1Improve heat resistanceImprove conductivityGas discharge electrodesLayered productsHeat resistanceConductive materials
Disclosed herein is a transparent electrode, including: a polyimide film having an average linear thermal expansion coefficient of 50.0 ppm / ° C. or less, which is measured by thermo-mechanical analysis based on a film thickness of 50˜100 μm at a temperature of 50˜250° C., and a yellowness of 15 or less; and an electrode layer including a conductive material and a polyimide resin having an average linear thermal expansion coefficient of 50.0 ppm / ° C. or less, which is measured by thermo-mechanical analysis based on a film thickness of 50˜100 μm at a temperature of 50˜250° C., and a yellowness of 15 or less. The transparent electrode is advantageous in that a problem of a short circuit does not occur even when apparatuses including this transparent electrode are over-heated because it has excellent heat resistance, and in that it is transparent and has high electroconductivity.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Aqueous multi-stage copolymer compositions for use in leather topcoats
ActiveUS10100377B2Keep the lookMaintain softnessSpecial leathers manufacturePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolymer scienceTotal solid content
The present invention provides aqueous composition comprising a multi-stage acrylic emulsion polymer having a first stage polymer of from 0.5 to 4 wt. %, based on the total weight of monomers used to make the first stage polymer, of a copolymerized carboxylic acid or salt group containing monomer, and having 10 to 30 wt. %, on total solids of the multi-stage acrylic emulsion polymer, of a second stage polymer of from 3 to 15 wt. % of a copolymerized hydroxyl group containing monomer, the first stage polymer having a glass transition temperature (Tg) by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) of less than −10° C. and the second stage polymer having a Tg (DMA) of greater than 80° C.; and (ii) from 25 to 75 wt. %, based on the total solids weight of the multi-stage acrylic polymer, of a polyurethane.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Side amino polysiloxane-modified polyurethane coating agent
InactiveCN108084397AObvious microphase separation structureImprove performanceLiquid repellent fibresPropanoic acidPolyethylene glycol
A side amino polysiloxane-modified polyurethane coating agent is disclosed. Side aminopolysiloxane (SAPDMS), polytetrahydrofuran glycol and polyethylene glycol as mixed soft segments, dimethylol propionic acid as a hydrophilic chain extender, and 1,4-butanediol as a hard segment regulator are reacted with isophorone diisocyanate to synthesize a waterborne silicone modified polyurethane (WSSPU), and the waterproof and moisture-permeable fabric coating agent is prepared based on the WSSPU. The composition and microstructure of a WSSPU film can be characterized by an infrared spectroscopy, a differential scanning calorimeter, a dynamic mechanical analyzer, a positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy, and the like. The mechanical properties of the WSSPU film and the waterproof and moisture-permeable properties of a coated fabric are investigated. Results show that a stable emulsion can be obtained when the dosage of the side aminopolysiloxane (mass ratio) is less than 15%. After polysiloxane modification, the internal micro-phase separation structure of the film is more obvious, the free volume cavity becomes larger, and the moisture-permeable properties are improved.
Owner:韩会义
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com