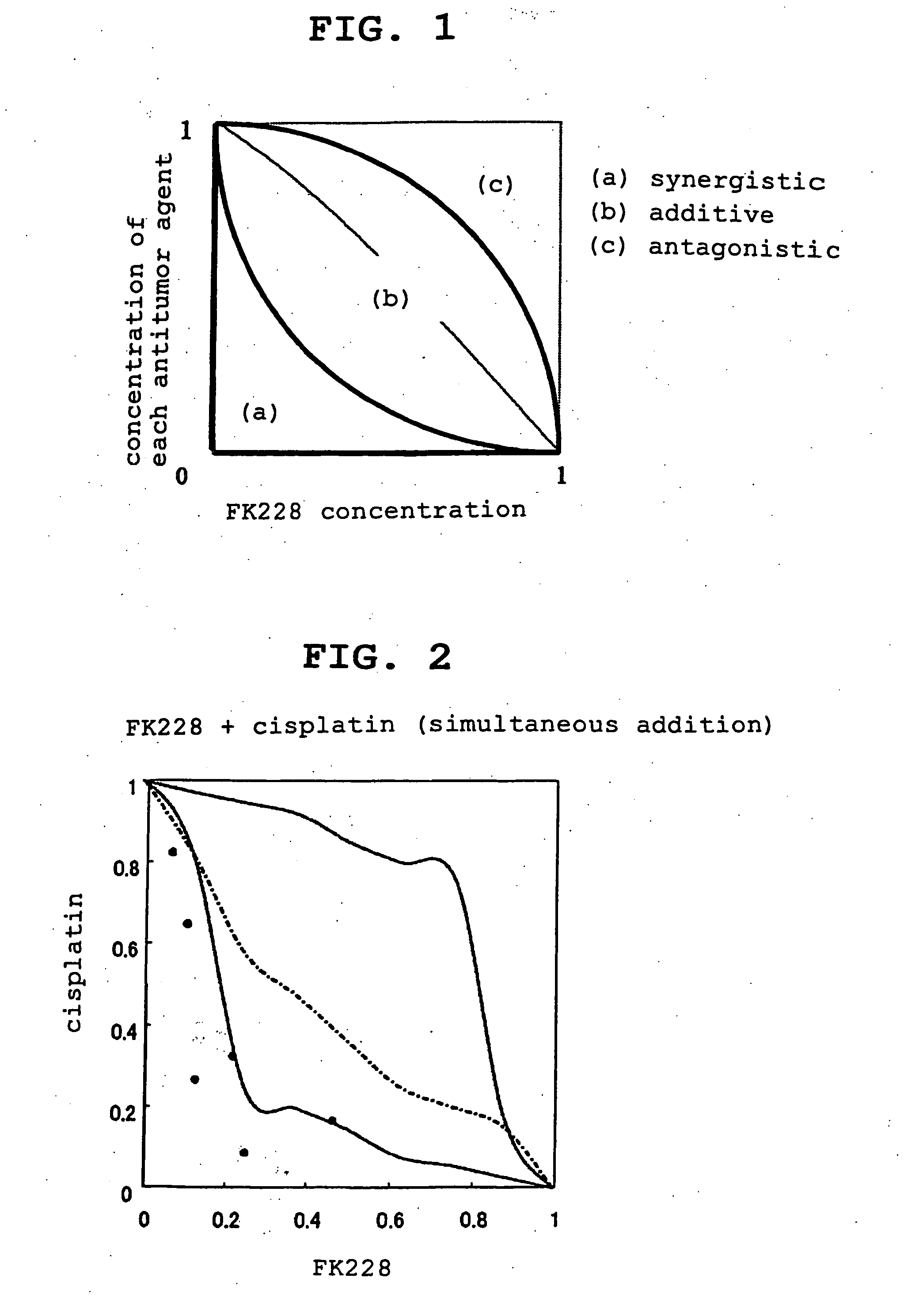
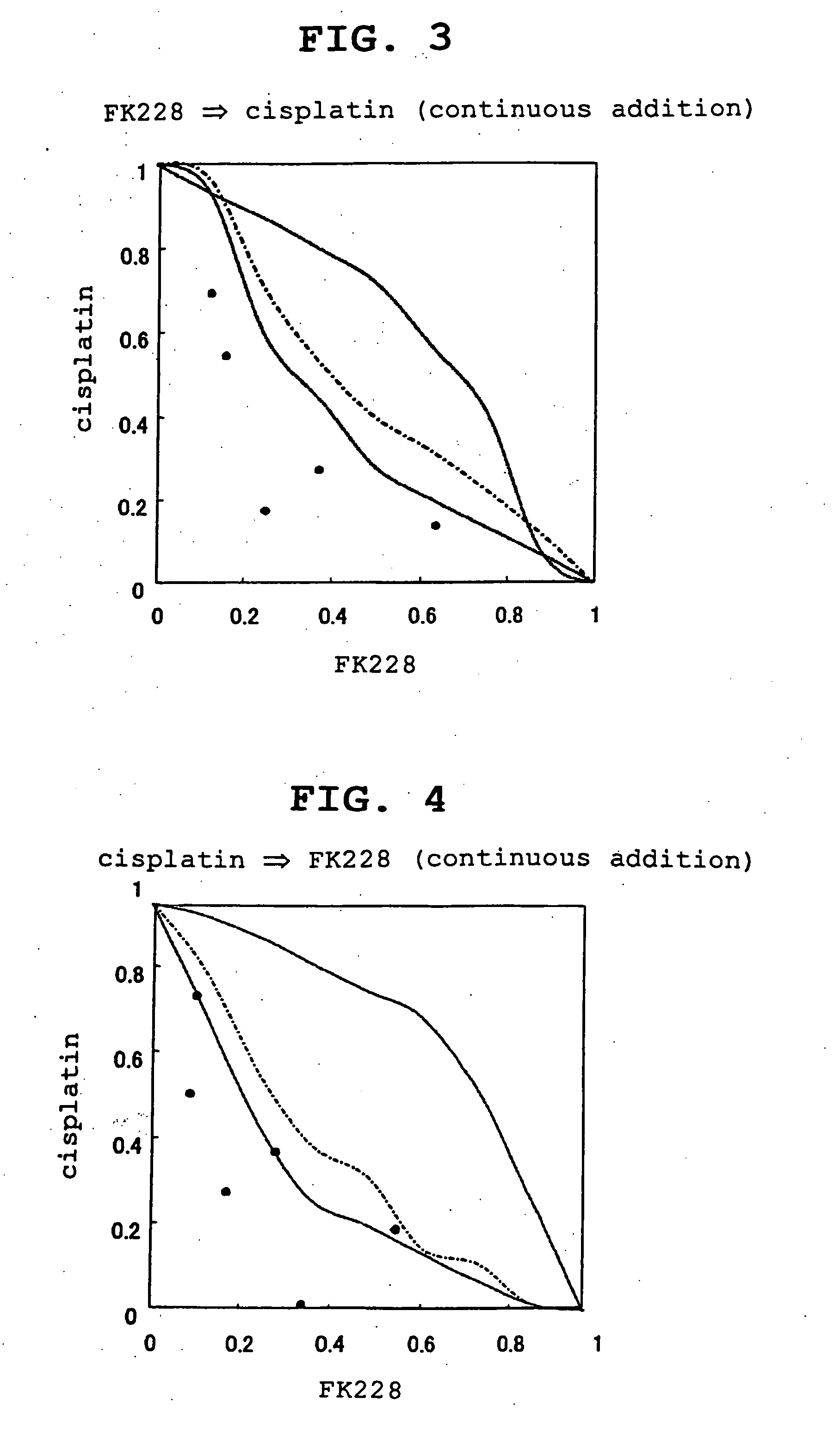
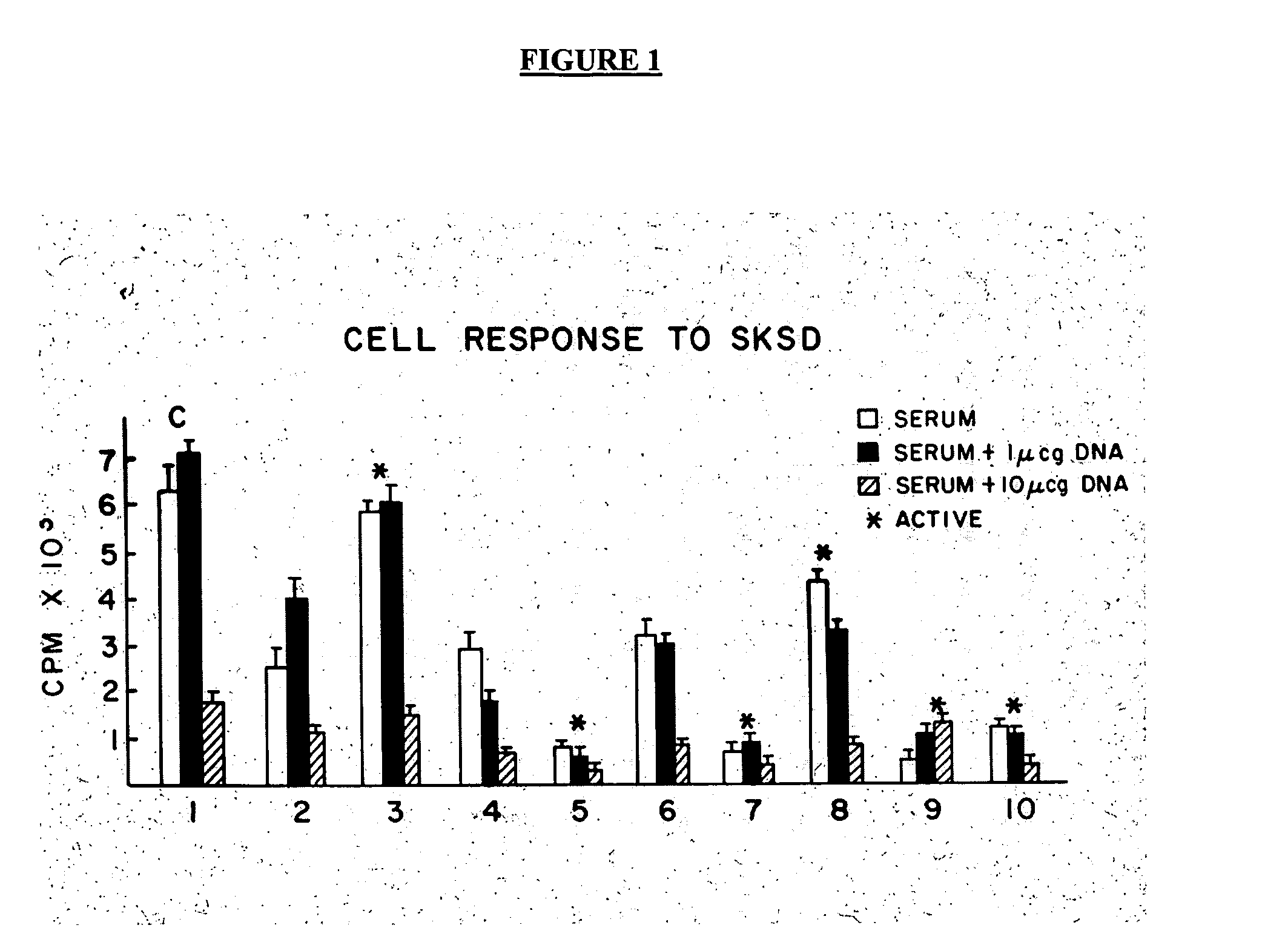
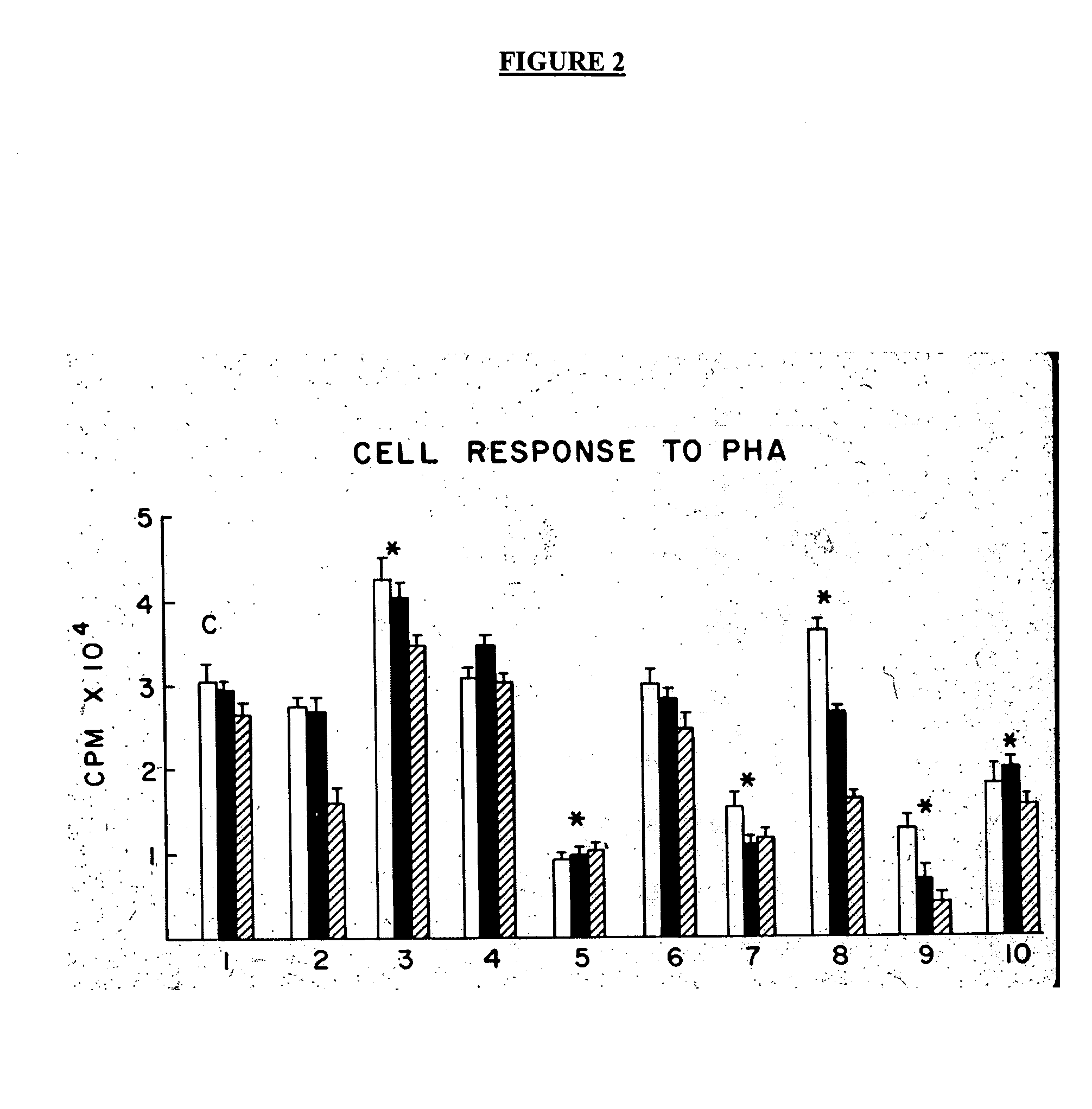
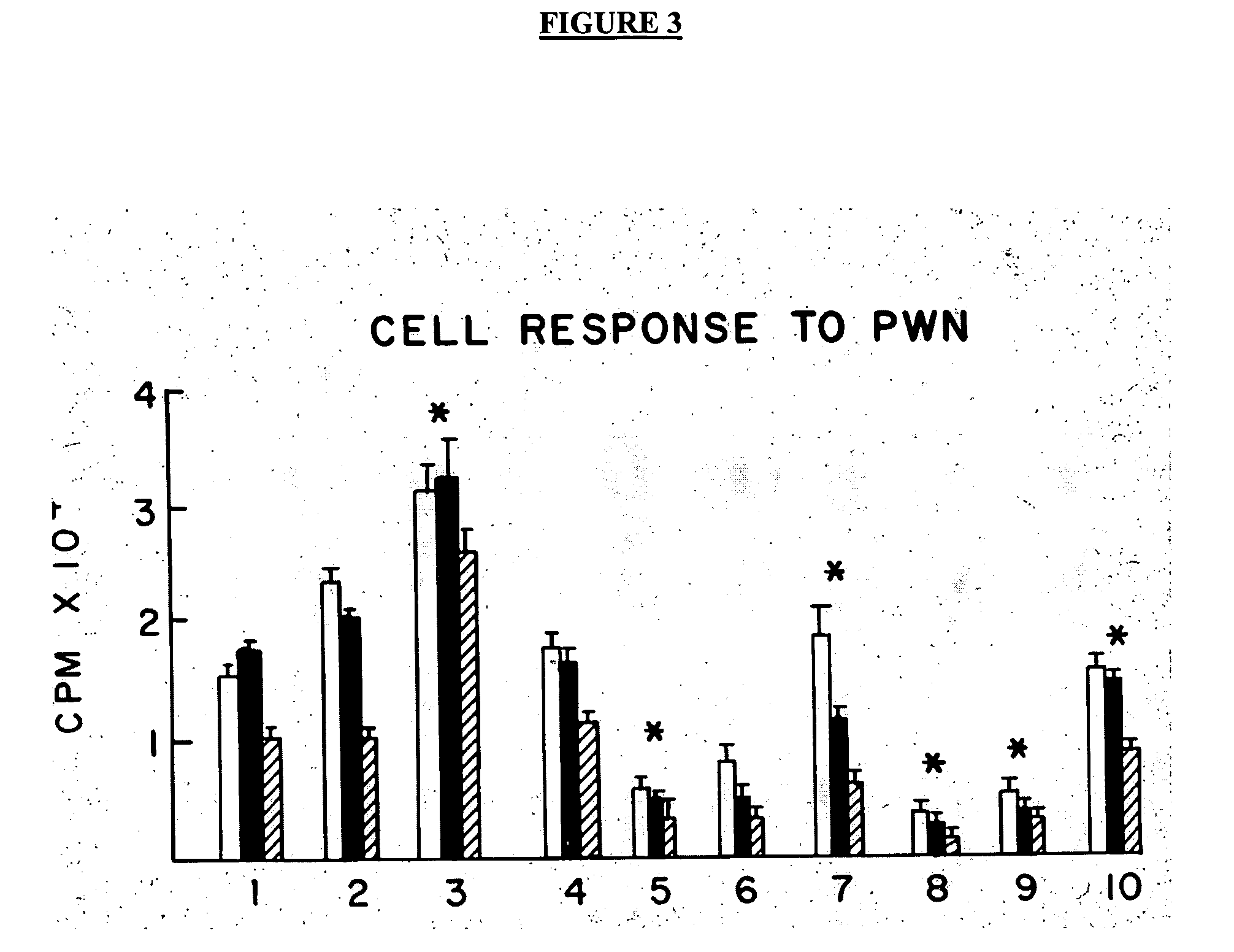
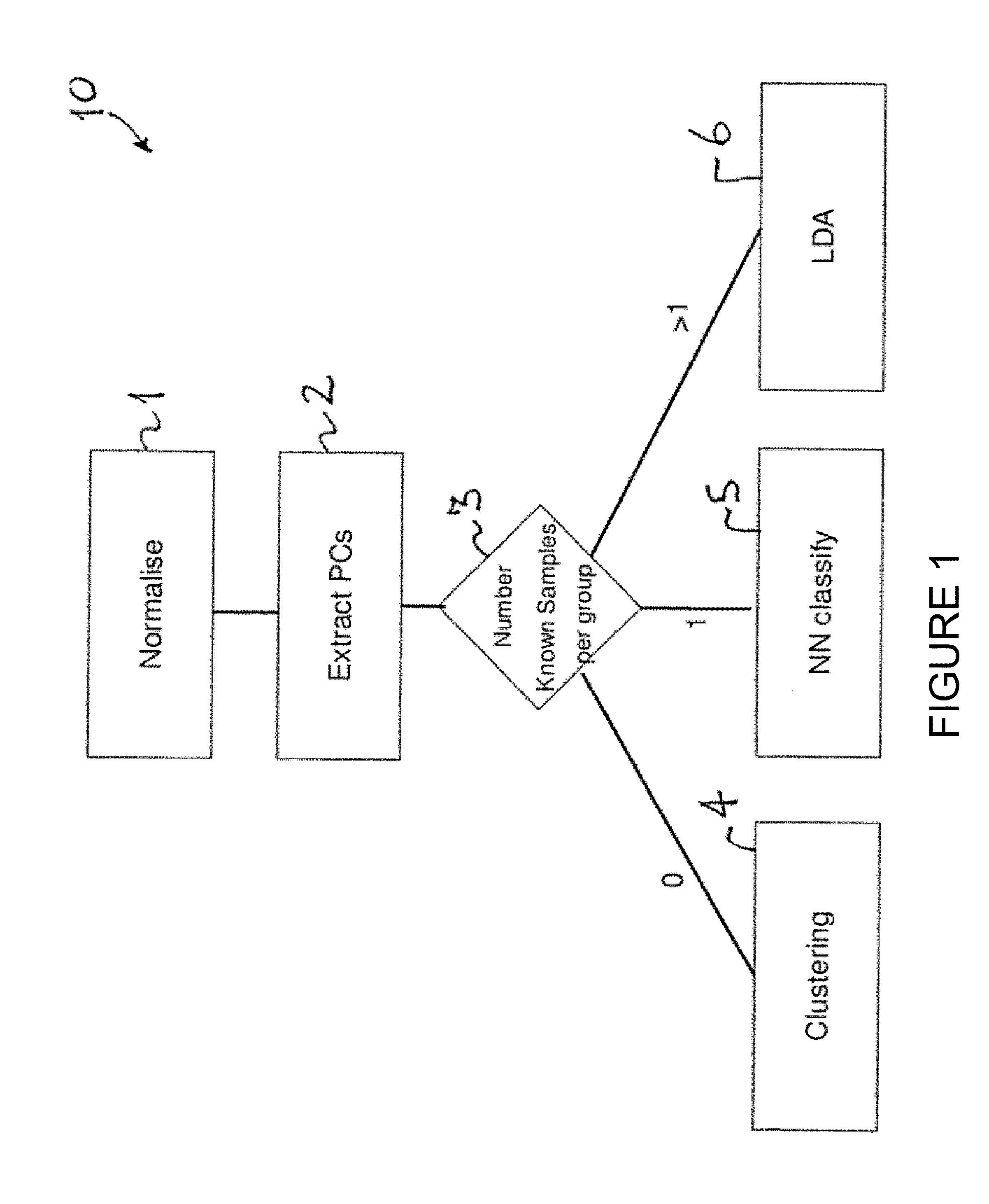
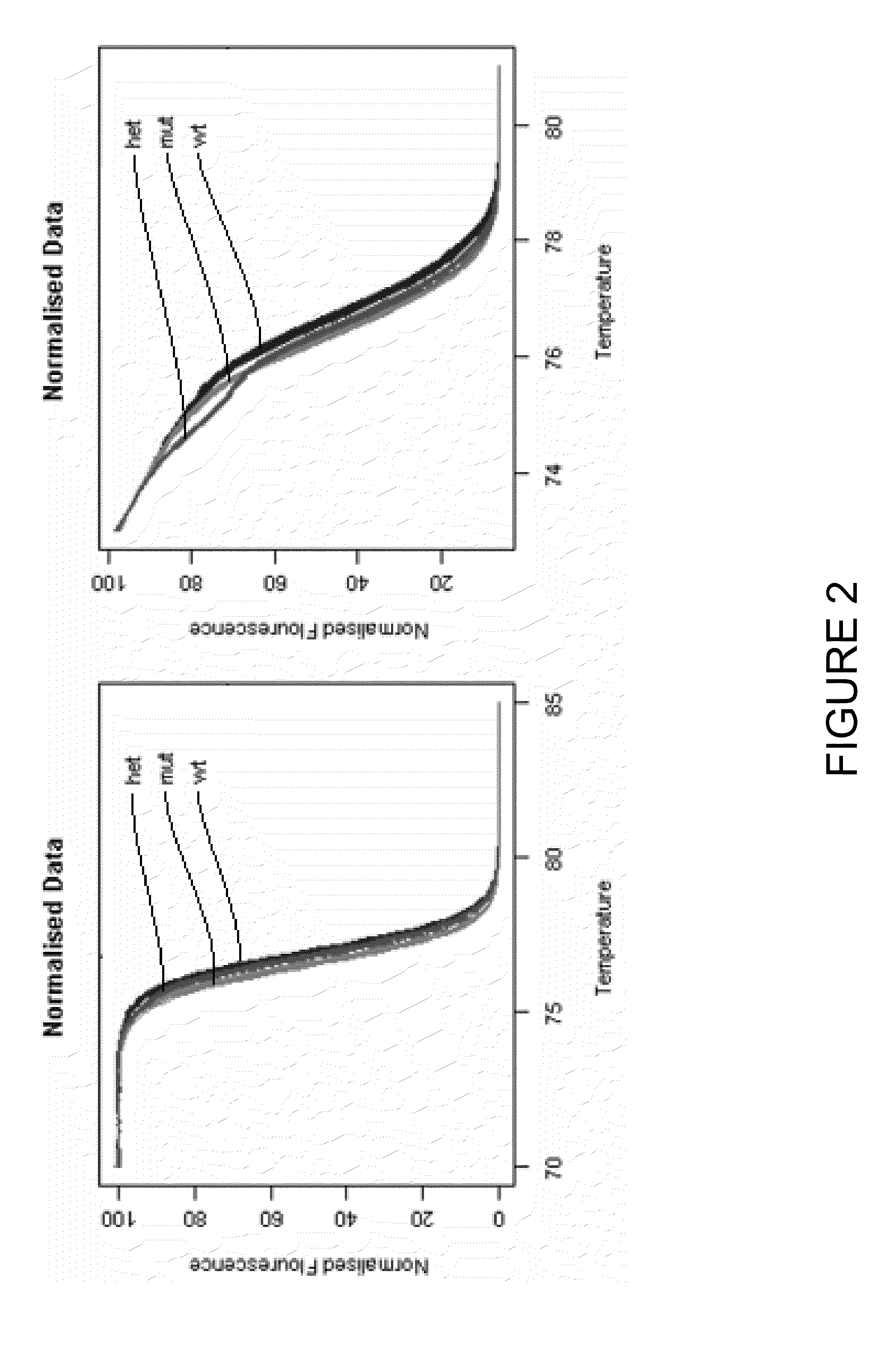
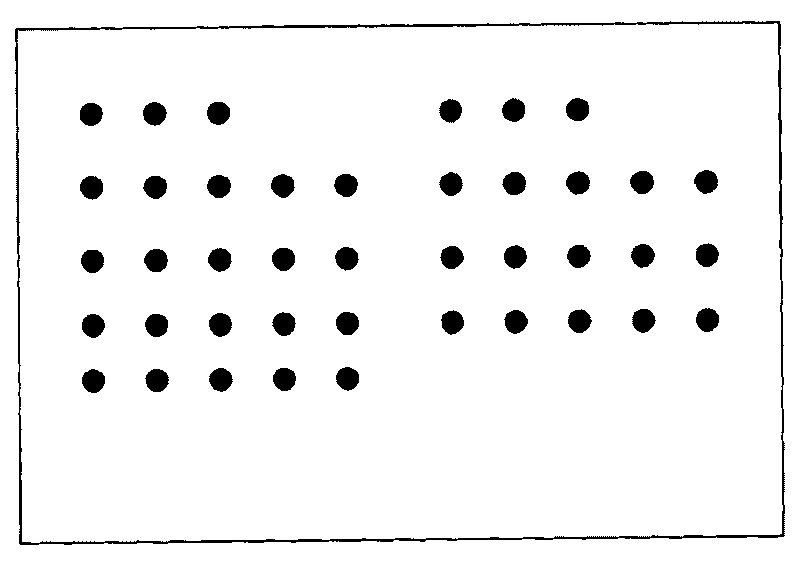
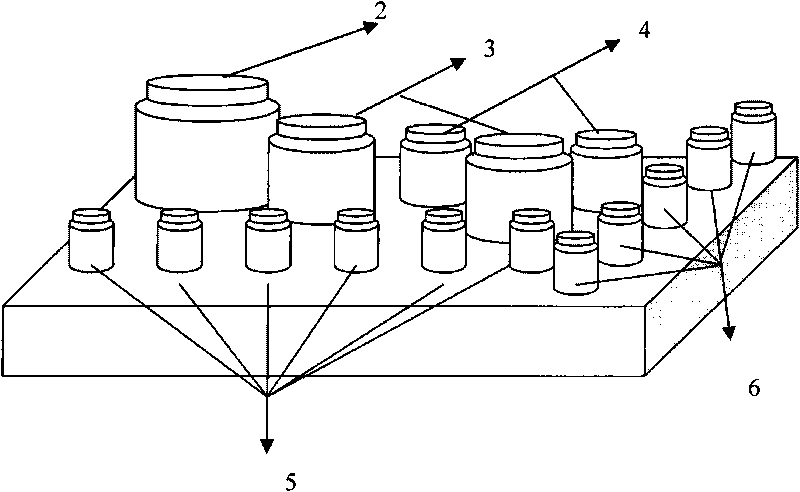
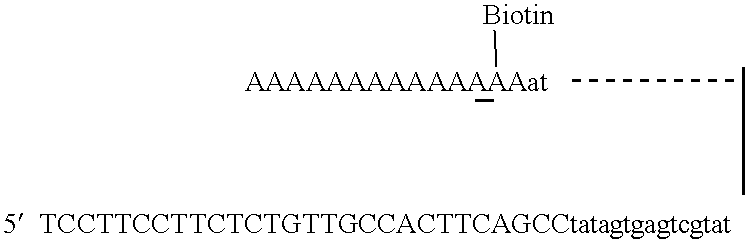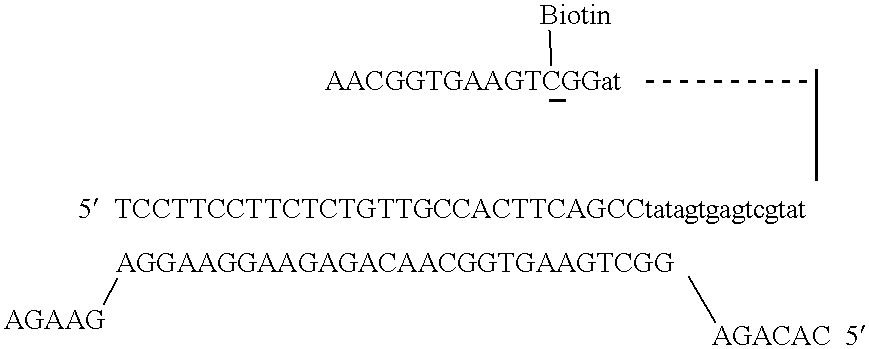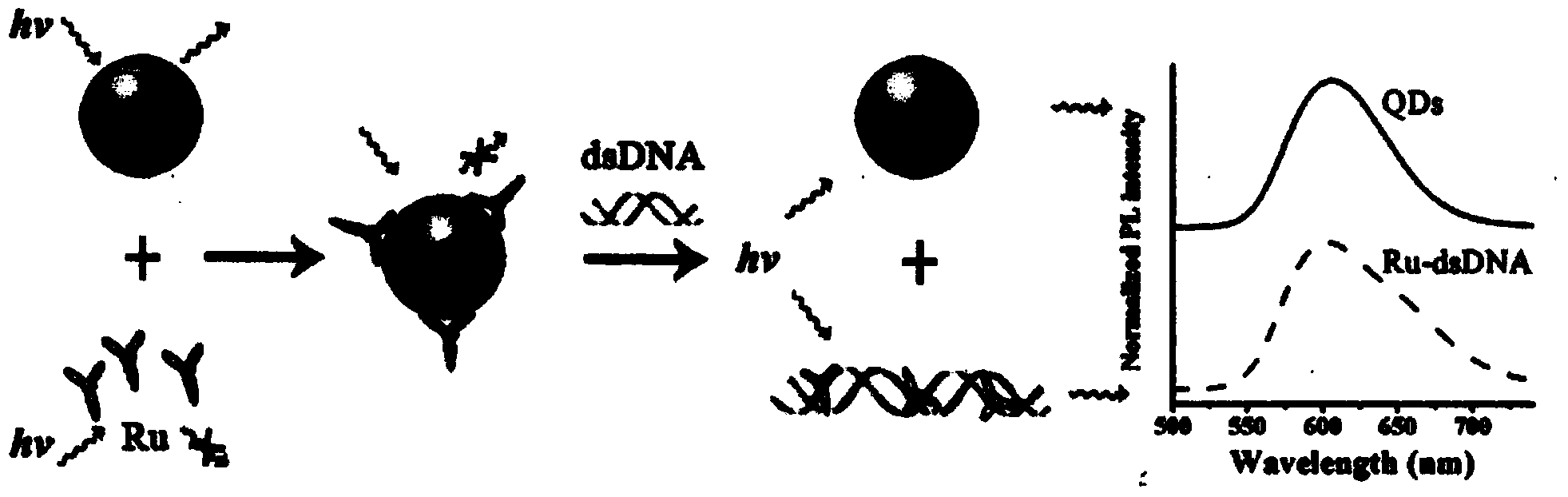Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "DNA formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
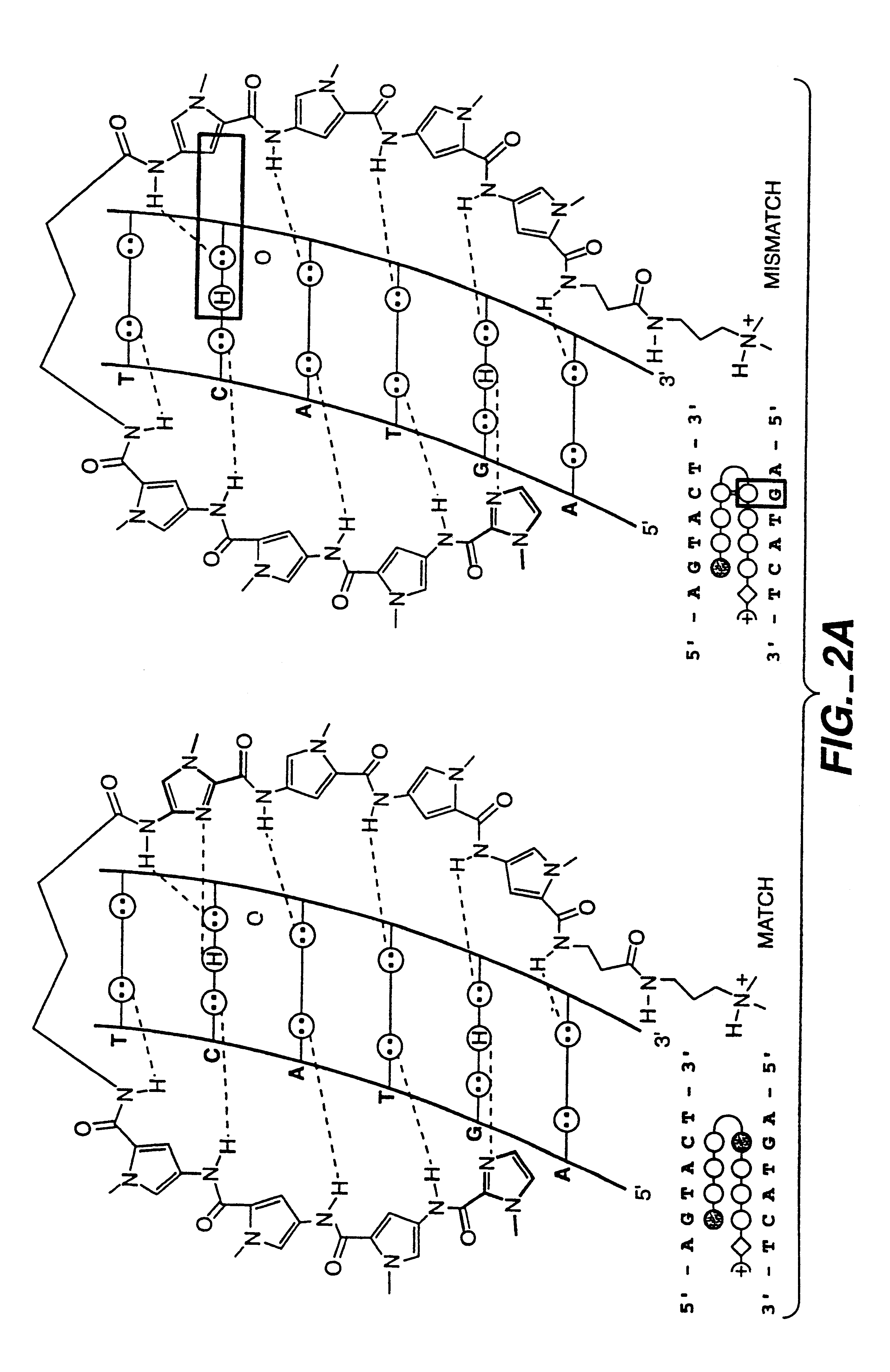
The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). These four bases are attached to the sugar-phosphate to form the complete nucleotide, as shown for adenosine monophosphate. Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.
Method for Accurate Sequencing of DNA
ActiveUS20150275289A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDNA formationComputational biology
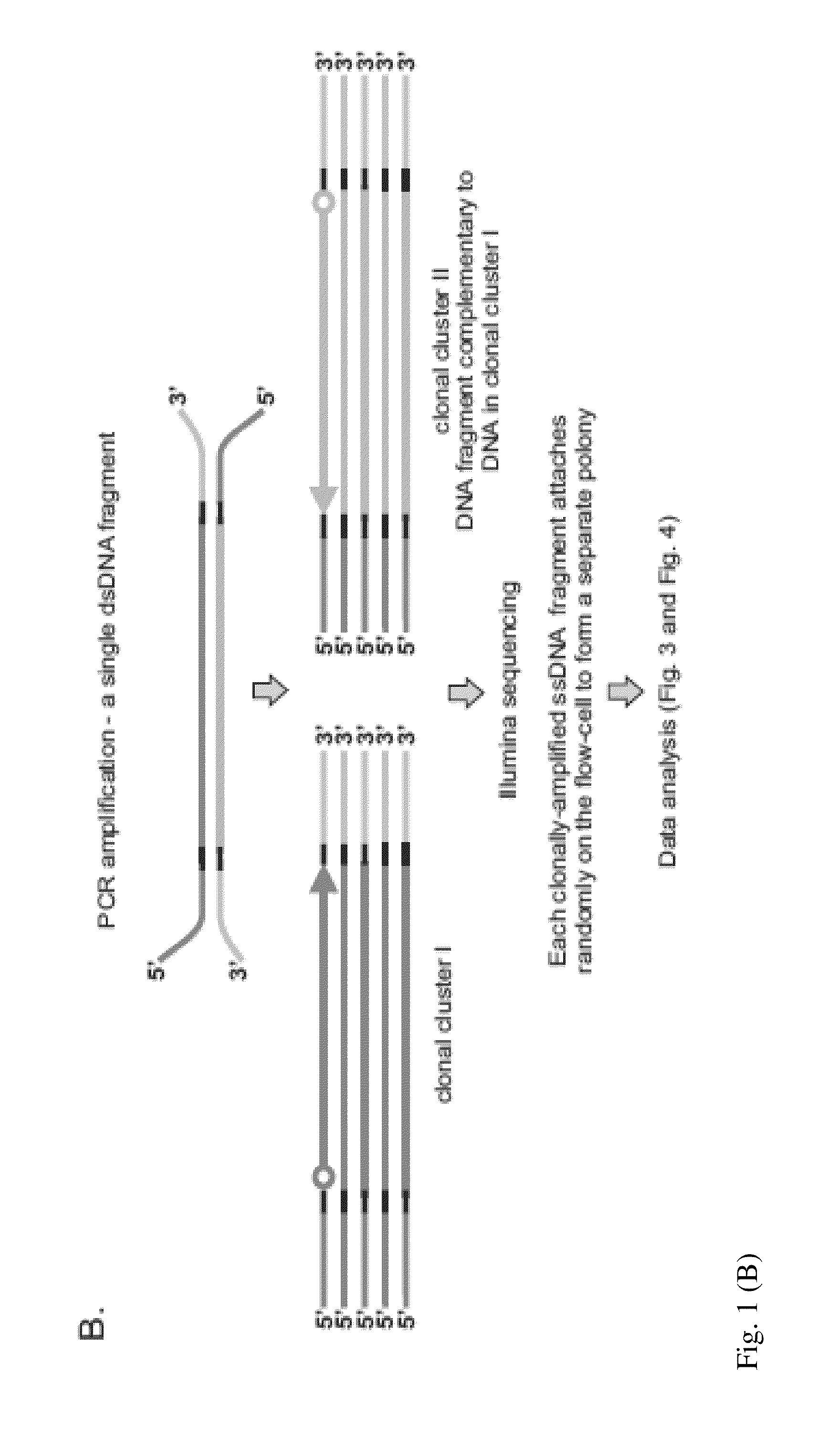
DNA is sequenced by (a) independently sequencing first and second strands of a dsDNA to obtain corresponding first and second sequences; and (b) combining the first and second sequences to generate a consensus sequence of the dsDNA. By independently sequencing first and second strands the error probability of the consensus sequence approximates a multiplication of those of the first and second sequences.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and Compositions for Use in Preparing Hairpin Rnas
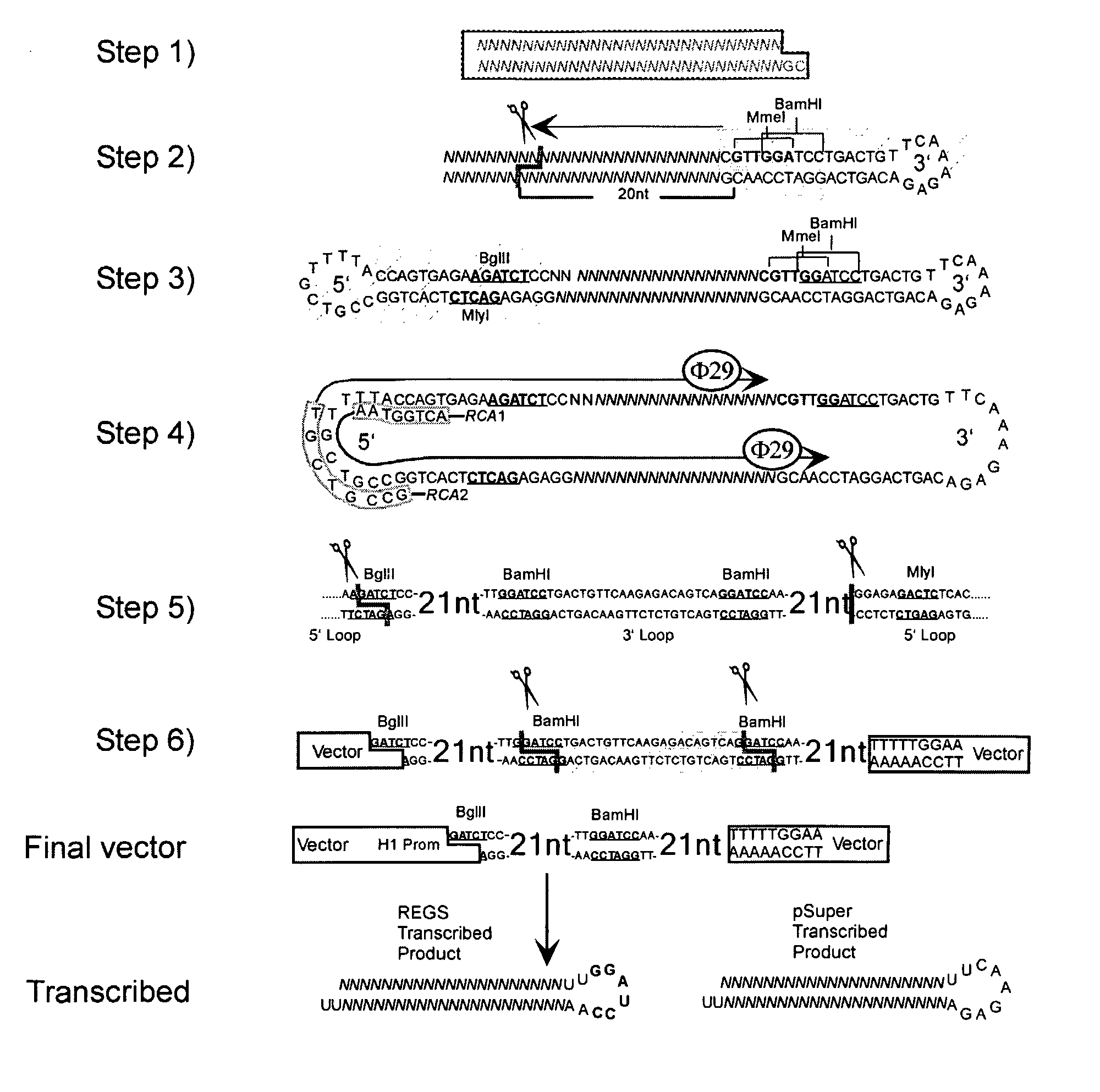
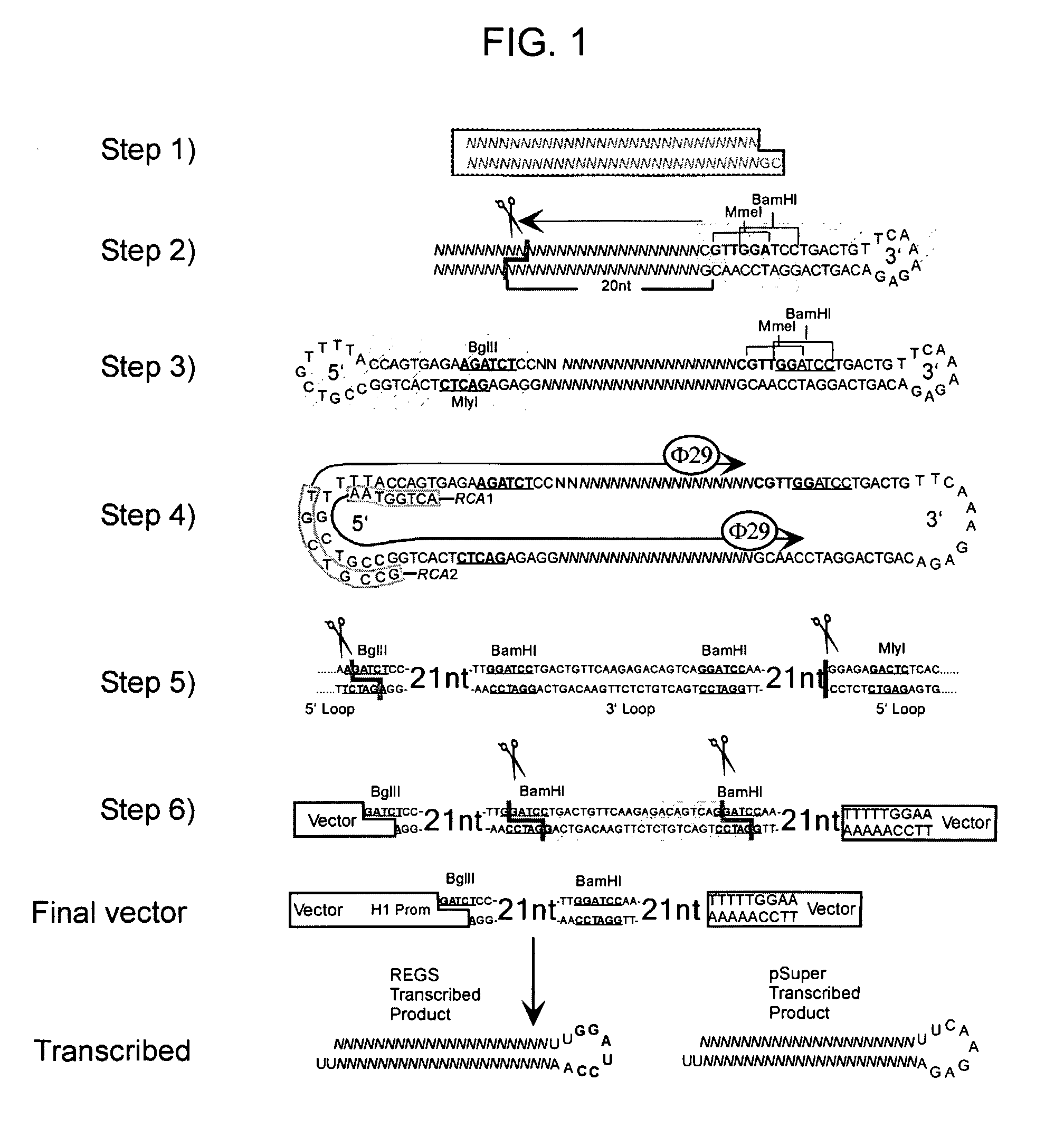
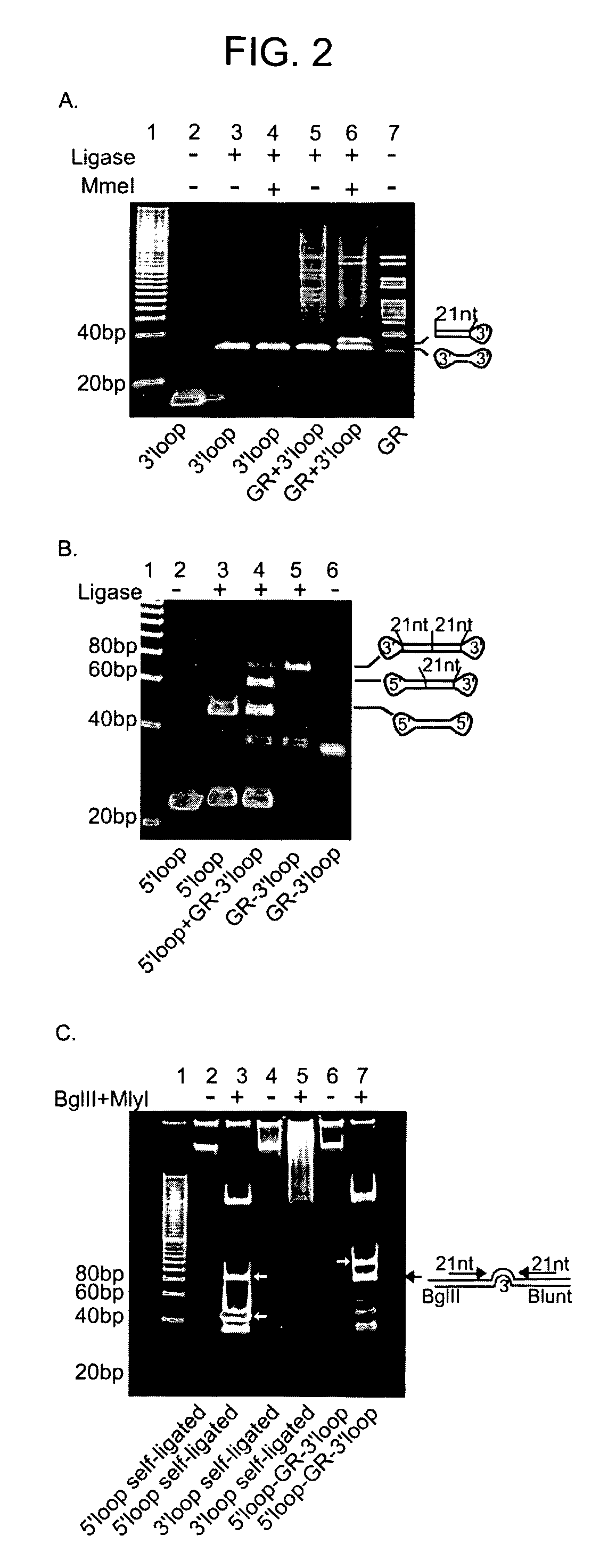
Methods and compositions for producing hRNA, e.g., shRNA, expression modules for specific target nucleic acids are provided. In the subject methods, an initial nucleic acid, e.g., dsDNA, synthetic DNA, etc., corresponding to the target nucleic acid of interest is converted to an intermediate nucleic acid. The resultant intermediate nucleic acid, following an optional size modification step, is then converted to a linear dsDNA that includes at least one copy of the hRNA expression module of interest, or a precursor (i.e., pro-shRNA expression module) thereof, where in certain embodiments conversion may include amplification. Also provided are reagents, systems and kits for use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Intranasal delivery of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050265927A1Suppress gene expressionInhibit expressionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsViral vectorExcipient
Aerosol delivery of nucleic acids to the lungs using viral vectors, polymers, surfactants, or excipients has been described. Compositions for intranasal administration are described that contain nucleic acids without viral or plasmid vectors and with little to no polymers, surfactants, or excipients. In one embodiment, the composition for intranasal delivery consists essentially of at least one nucleic acid and an aqueous solution. Suitable nucleic acids for intranasal delivery include, but are not limited to, dsDNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, ssRNA, short interfering RNA, micro-RNA, and antisense RNA. Methods for treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of at least one symptom or manifestation of a lung disease are also described consisting of administration by intranasal delivery an effective amount of a composition containing a nucleic acid. The composition may be formulated as a liquid or aerosol or other acceptable formulation for intranasal administration.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Isothermal exponential RNA amplification in complex mixtures
Methods and compositions are provided for performing isothermal amplification of a nucleic acid target employing probes characterized by having a masked RNA polymer promoter unable to bind to a complementary initiator oligonucleotide and RNA polymerase and initiate transcription, a dsDNA sequence which when invaded by the target nucleic acid exposes the masked promoter to initiate transcription, and a template sequence, a portion of which is normally included in the dsDNA region, which when copied produces a product that can reinitiate the process of invading the dsDNA region and initiating transcription of another copy.
Owner:DISCOVERX INC
Antitumor agent
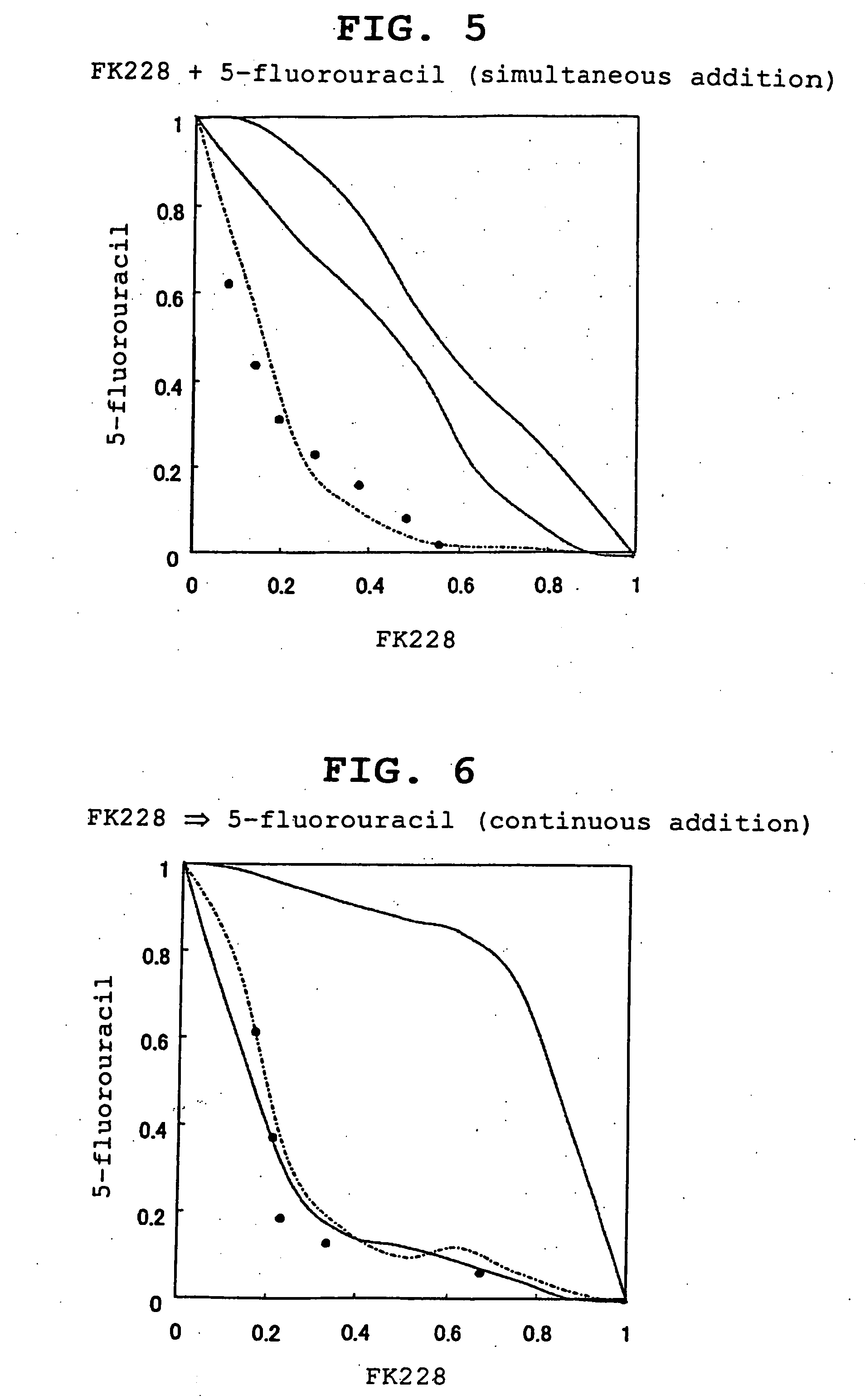
ActiveUS20050187149A1Improve anti-tumor effectEliminate side effectsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkMetabolite
An antitumor agent containing, in combination, at least one kind of antitumor agent selected from the group consisting of an antitumor agent that forms a cross-link with DNA and shows an antitumor effect, an antimetabolite antitumor agent and a taxane antitumor agent, and a histone deacetylase inhibitor. According to the present invention, an antitumor agent causing reduced side effects and having a superior antitumor activity can be provided.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Method to produce single stranded DNA of defined length and sequence and DNA probes produced thereby
ActiveUS20080026393A1Convenient lengthSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical synthesisSingle strand
A method for producing a single stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecule of a defined length and sequence is disclosed. This method enables the preparation of, inter alia, probes of greater length than can be chemically synthesized. The method starts with a double stranded molecule, such as genomic, double stranded DNA (dsDNA) from any organism. A fragment of the starting molecule (dsDNA) is amplified by specific primers engineered to introduce cleavage sites on either side of the desired sequence. Cleavage steps on the amplified, engineered fragment are combined with a phosphate removal step, thereby creating a construct that can be digested with an exonuclease without damage to the desired ssDNA. Probes, which hybridize with large gaps between the ends of the probes, are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Treatment of inflammatory, non-infectious, autoimmune, vasculitic, degenerative vascular, host-v-graft diseases, Alzheimers disease, and amyloidosis using mammalian, dsDNA vaccination
The present invention relates generally to compositions and methods using mammalian, dsDNA (Double Stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid) vaccination for the induction and maintenance of regulator suppressor T cells resulting in suppression of non infectious, and post infectious, inflammatory, allergic, auto-immune, vasculitic, certain degenerative vascular, and graft versus host diseases, with or without the use of IL-10, and with or without the use or TGFβ, with or without the use of anti-IL 6 receptor antibody, anti TNF antibody and or Plasmapheresis, IVIG, Corticosteroids, Methotrexate, Bromocriptine, and or vitamin D analogues.
Owner:LAWLESS OLIVER J
Self-immunity hepatitis detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101750492AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMaterial analysisProtein markersHepatitis
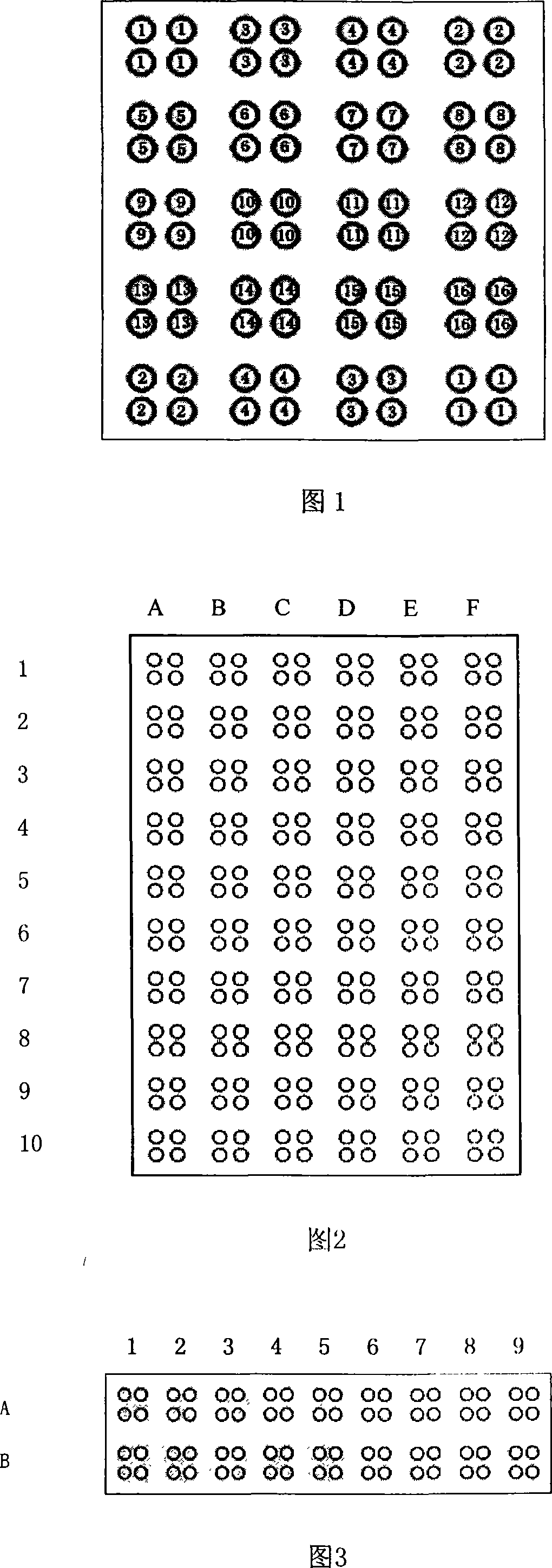
The invention discloses a self-immunity hepatitis detection protein chip and a kit thereof. The chip and the kit can be used for simultaneously detecting 12 immunity protein markers: ANA (dsDNA, RNP, Sm, SS-A / Ro, SS-B / La, Sc1-70, Jo-1), SMA, LKM-1, SLA / LP, F-actin and AMA. The invention overcomes the shortcomings of the current products that the detection index is single and incomplete. The invention provides a detection method which has a complete diction result and a simpler process.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
NF-KB detection double-stranded DNA micro array chip and preparation
InactiveCN1580278AHigh affinityInhibit bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological studiesRegulation of gene expression
The invention can prepare the microarray of double -stranded DNA(ds DNA) on the surface of solid substrates. By this method, the probes of ds DNA can engomphosised in the nuclear factor kappa B(NF-kappa B) to high-throughpput detect NF-kappa B inside of caryon and screen ds DNA / NF-kappa B molecules interfering dsDNA / NF-kappa B interaction. First, depending on patent technic and others methods of this invention, the invention prepare the microarray of double -stranded DNA(ds DNA) on the surface of solid substrates to allow mounts of dsDNA explorer on the dsDNA micro embattle to link with locus. Second, allow dsDNA micro embattle to across and link with specifically cell nuckoproteides or NF-kappa pure albumen. Third, do qualitative determination or quantiative determination to NF-kappa albumen in special caryon by reaction of NF-kappa B with dsDNA as micro embattle butt.
Owner:王进科 +3
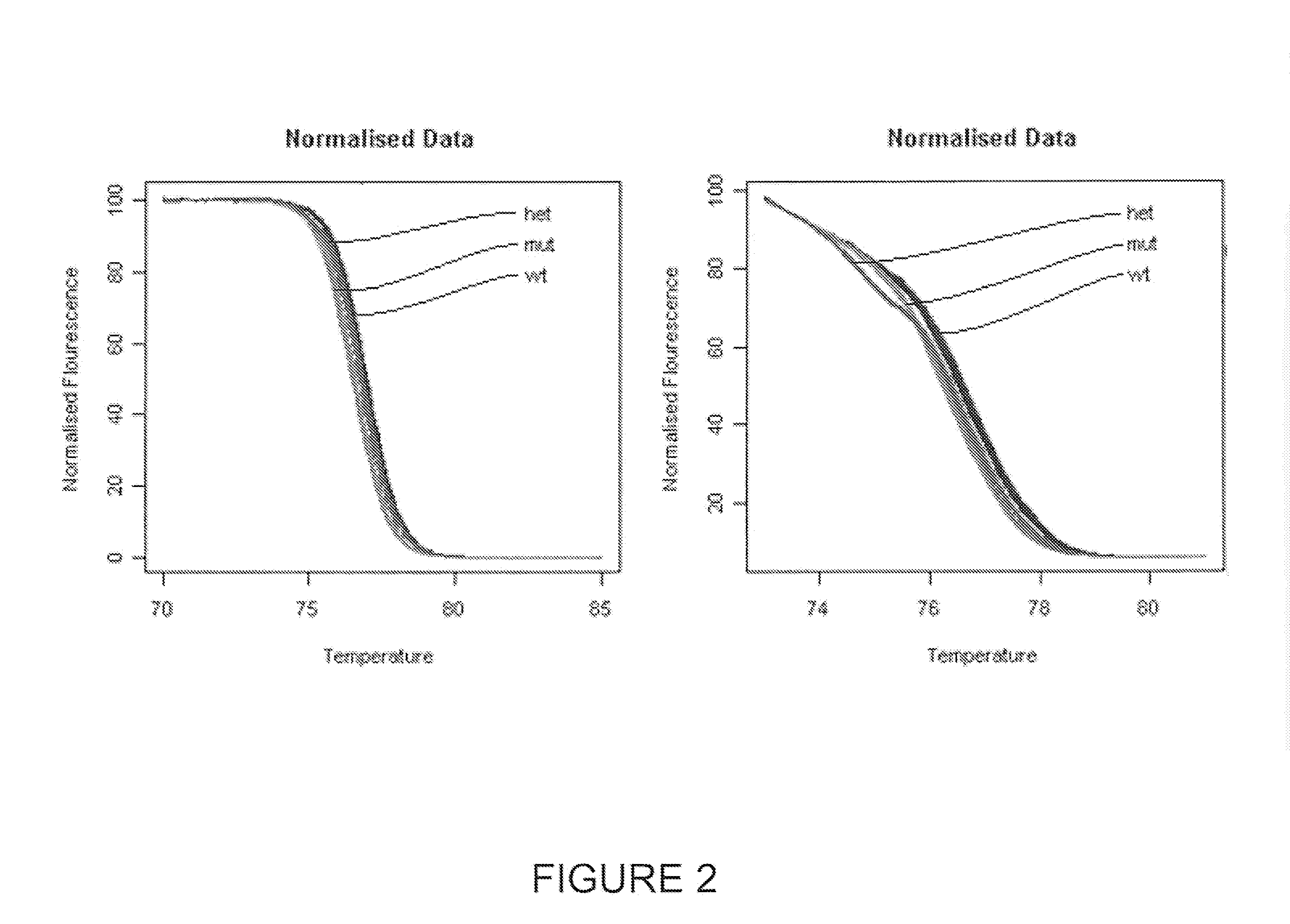
Method and system for analysis of melt curves, particularly dsDNA and protein melt curves
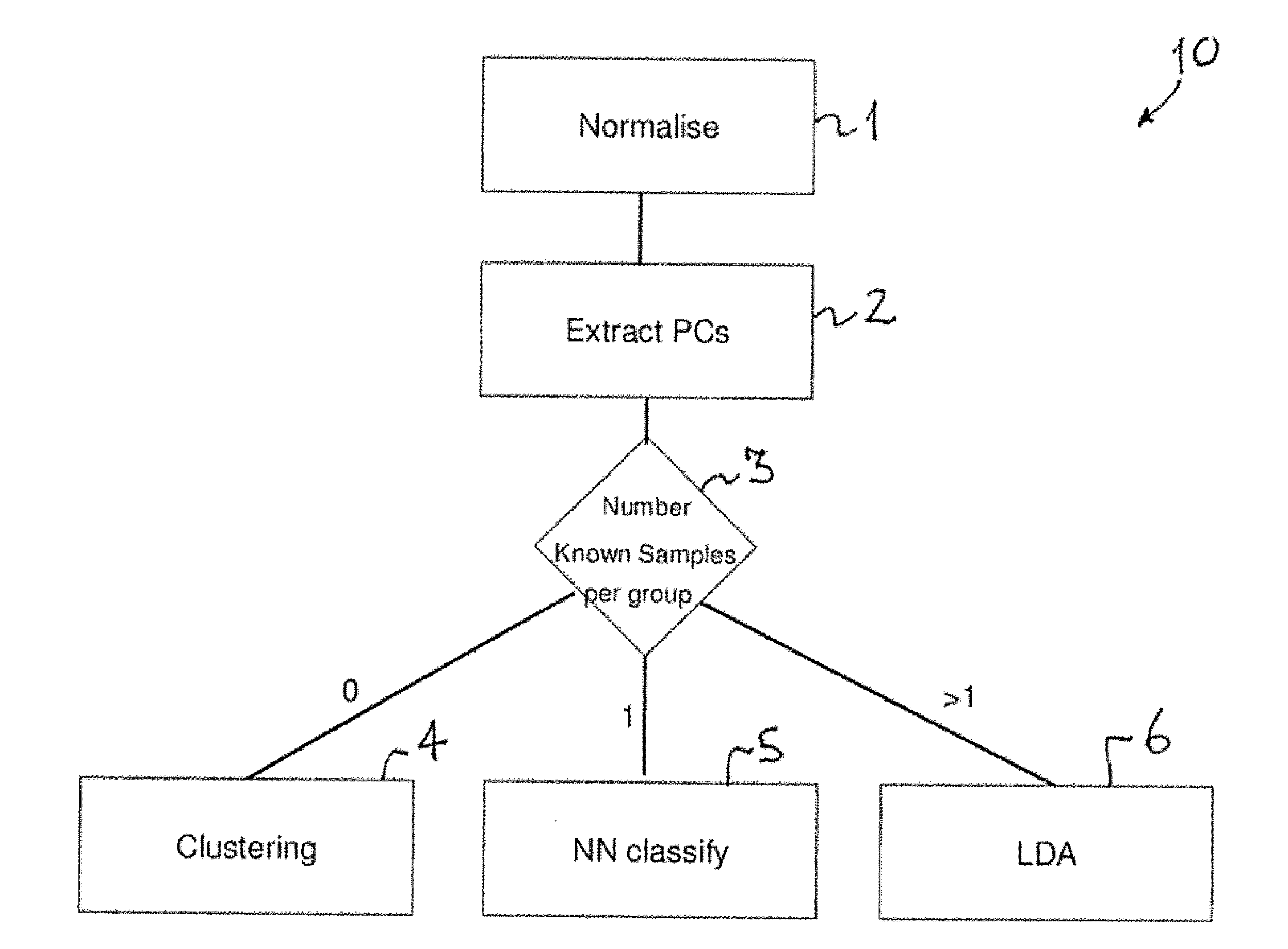
ActiveUS8271205B2Efficient analysisEasy to identifyComputer controlMicrobiological testing/measurementKernel principal component analysisData set
A computer-implemented method of analysis of melt curve data comprising the steps of: (a) parameter model fitting the melt curve data; (b) performing a principal component analysis of the melt curve data; and (c) utilizing the principal components for clustering the melt curve data into groups. Such a method allows an efficient analysis of variations in melt curve shape and position and allows to statistically quantify these variations for both supervised and unsupervised data sets. Current melt analysis methods neither allow for statistical measures of each unknown nor do they allow for the determination of unsupervised data sets (i.e., unknown number of groups present). Particularly, the method according to the invention can be advantageous for identifying a specific sequence of dsDNA in a sample after performing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Complex formation between dsDNA and oligomer of cyclic heterocycles
Methods and compositions are provided for forming complexes intracellularly between dsDNA and oligomers of heterocycles, aliphatic amino acids, particularly omega-amino acids, and a polar end group. By appropriate choice of target sequences and composition of the oligomers, complexes are obtained with low dissociation constants. The formation of complexes can be used for modifying the phenotype of cells, either prokaryotic or eukaryotic, for research and therapy.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Western blot kit for detecting antibody of autoimmune disease and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103105489AOvercome the cumbersome operation of individual detection one by oneImprove accuracyMaterial analysisAntigenAnti-mitochondrial antibody
The invention provides a western blot kit for detecting the antibody of autoimmune disease and a preparation method of the western blot kit, and relates to a western blot kit for detecting related antibodies of various autoimmune diseases, aiming at overcoming the technical defect that a western blot product is unavailable for testing and screening various autoimmune diseases in the prior art. The nitrocellulose membrane or the nylon membrane contains at least two parallel detection lines coated by at least two of ten natural antigens or recombinant antigens, i.e. dsDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), Sm / RNP (ribonucleoprotein), CCP (critical compression pressure), SSA (sulfosalicylic acid), SSB (single-strand binding protein), GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase), ICA (islet cell antibody), IA-2A (islet cell), TG (triglyceride) and AMA-M2 (anti-mitochondrial antibody), a high-concentration quality control band, a median-concentration quality control band and a low-concentration quality control band. The deficiency of the detection sensitivity and the specificity of the single autoantibody can be overcome, the operating complexity for independently detecting the related autoantibody of various diseases one by one can be overcome, and the detection efficiency and the result judging accuracy degree can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YHLO BIOTECH
Microbial production of pure single stranded nucleic acids
Methods and compositions for bacterial production of pure single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) composed of custom sequence and size have been developed. The methods enable scalability and bio-orthogonality in applications of scaffolded DNA origami, offering one-step purification of large quantities of pure ssDNA amendable for immediate folding of DNA nanoparticles. The methods produce pure ssDNA directly from bacteria. In some embodiments the E. coli helper strain M13cp combined with a phagemid carrying only an f1 -origin allows for, without the need for additional purification from contaminating dsDNA. This system is useful for generalized circular ssDNA synthesis, and here is applied to the assembly of DNA nanoparticles folded both in vitro and direct from phage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ANALYSIS OF MELT CURVES, PARTICULARLY dsDNA AND PROTEIN MELT CURVES
ActiveUS20100076690A1Efficient executionEfficient analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDigital computer detailsKernel principal component analysisData set
A computer-implemented method of analysis of melt curve data comprising the steps of: (a) parameter model fitting the melt curve data; (b) performing a principal component analysis of the melt curve data; and (c) utilizing the principal components for clustering the melt curve data into groups. Such a method allows an efficient analysis of variations in melt curve shape and position and allows to statistically quantify these variations for both supervised and unsupervised data sets. Current melt analysis methods neither allow for statistical measures of each unknown nor do they allow for the determination of unsupervised data sets (i.e., unknown number of groups present). Particularly, the method according to the invention can be advantageous for identifying a specific sequence of dsDNA in a sample after performing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Lupus erythematosus detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101726586AThe detection indicators are comprehensive and appropriateImprove detection efficiencyBiological testingDiseaseProtein markers
The invention discloses lupus erythematosus detection protein chip and kit thereof. The chip comprises a substrate, protein markers distributed in an array type and control point coatings, wherein the markers and the control point coatings are seven antigen markers, positive controls and negative controls comprising dsDNA (double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid), ssDNA (single stranded deoxyribonucleic acid), Histon, SS-A(Ro60), SS-B(La), Sm (smith) and RNP (ribonucleoprotein) / Sm which are uniformly distributed on the substrate in a dot matrix mode. The invention has comprehensive and appropriate detection indexes and consistent applied reaction conditions, can detect a plurality of indexes at a time, is convenient and quick, greatly improves the detection efficiency and reduces the detection cost. The invention can be suitable for aided diagnosis of suspected lupus erythematosus disease people.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
Colour development protein chip using BCIP/NBT as substrate as well as application in detection of autoantibody thereof
InactiveCN101226192AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingAntigenAutoantibody production
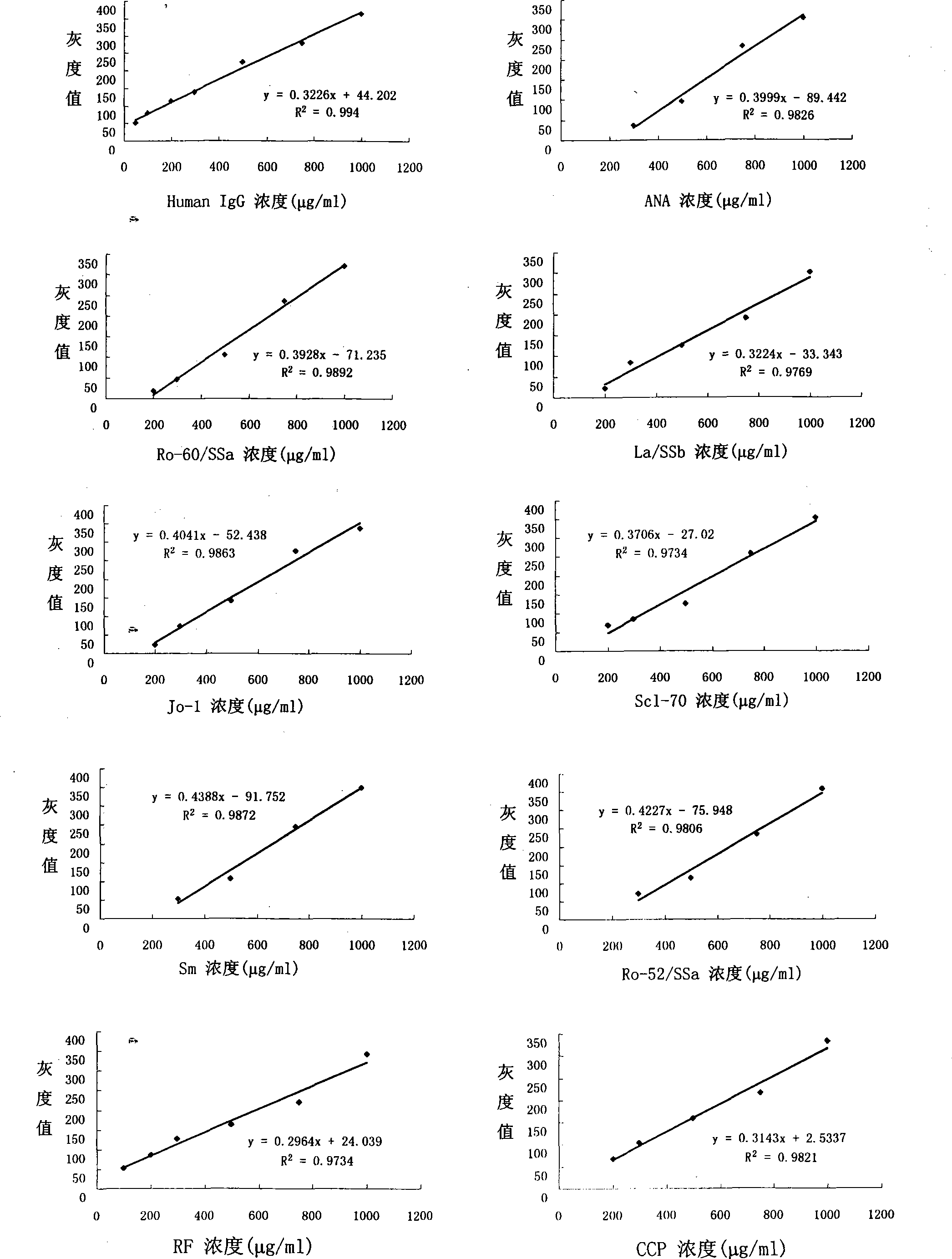
The invention discloses a color protein chip which substrate is BCIP / NBT. The invention is composed of a substrate, an array, 12 antigens coated on the array, negative contrast, positive contrast and blank contrast, wherein the substrate is a glass slide decorated by APES, the kinds and point sample densities of the 12 antigens are 520ug / ml ANA, 465ug / ml Ro-60, 530ug / ml La / SSb, 530ug / ml Jo-1, 525ug / ml Scl-70, 520ug / ml Sm, 615ug / ml Ro-52 / SSa, 340ug / ml RF, 465ug / ml CCP, 410ug / ml u1RNP, 490ug / ml CENP-B, 580ug / ml dsDNA. The invention uses the alkali phosphatase coloring method whose substrate is BCIP / NBT as the final check signal of protein chip to be widely used for self antibody check, while the check sensitivity has higher coincidence rate than prior art, with reduced check cost and time. The invention can be used in clinical check, sanitary supervision, regular sanitary supervision and scientific research or the like.
Owner:SHANDONG MEDICAL BIO TECH RES CENT
Method of high flux screening, capturing and separating target molecule from complex composition matter such as traditional Chinese medicine and chemical mixture
InactiveCN1590560AImprove bindingIncrease transcriptionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipDisease
A process for high-flux screening, capturing and separation of target moleculae from complex substance (Chinese medicine or chemical mixer) includes preparing a ds DNA microarray chip to make its probe have a binding sites of dsDNA bindin, measuring the affinity of the sites, creating the standard affinity parameter system, mixing the microarray chip with said complex substance, reacting, detecting the affinity variation, screening the varied targets, linking them to the surface of chromatographic column, filling the complex substance in it, capturing the effective moleculae by probes, eluting and collecting the effective moleculae.
Owner:王进科 +2
Nucleic acid detection method based on surface plasma resonance technology
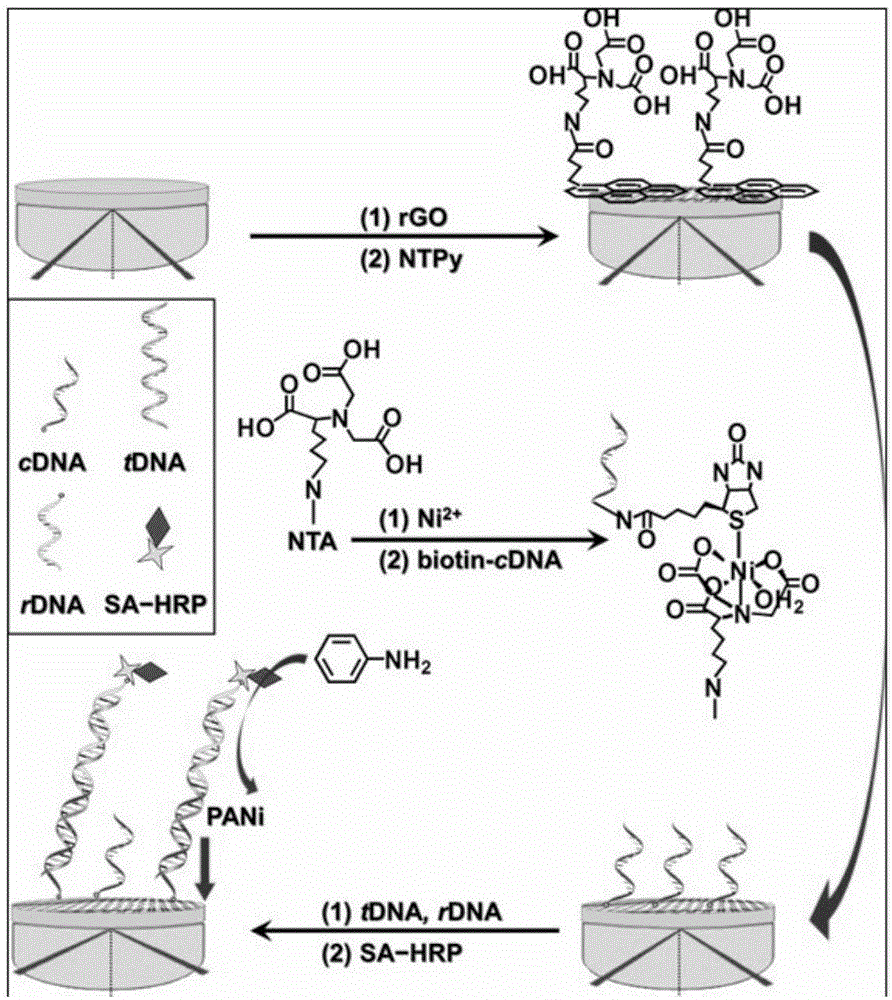
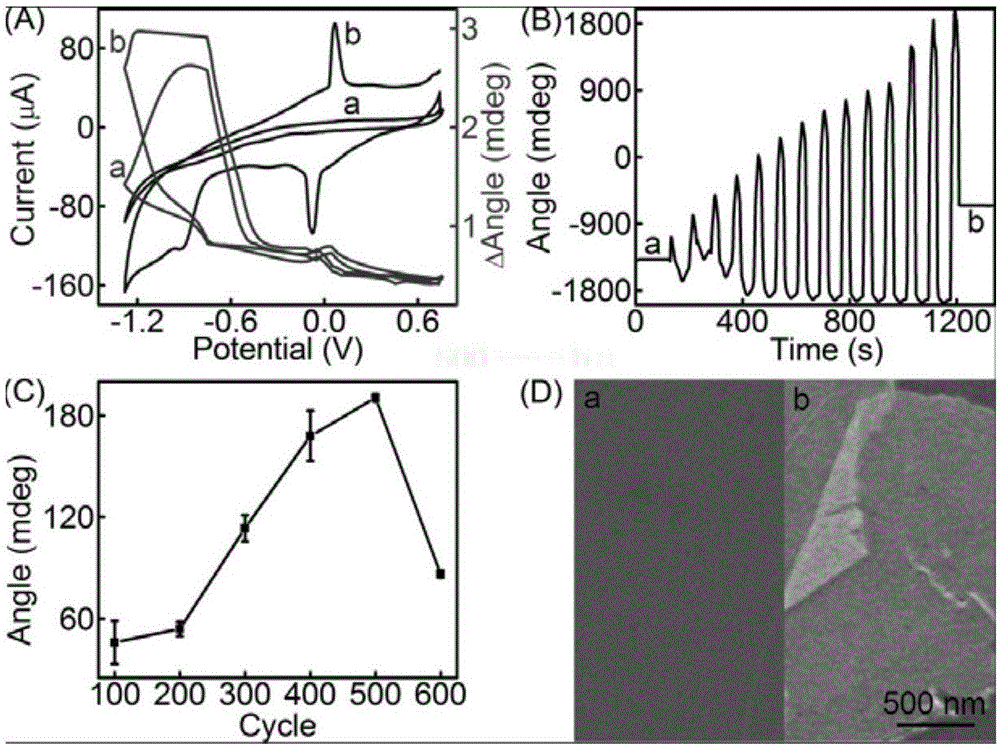
InactiveCN106018349AImplement featuresEasy to detectMaterial analysis by optical meansPeroxidaseBiotin
The invention discloses a nucleic acid detection method based on surface plasmon resonance technology. First, graphene oxide is electrodeposited on the surface of a bare SPR chip, and then the activated molecular layer of perylene derivatives grafted with aminotriacetic acid is adsorbed through conjugation. Assemble the 5′ end biotinylated capture cDNA probe as the sensing interface to detect the target tDNA, and after realizing the binding and capture of tDNA, add the 3′ end biotinylated response rDNA to form a long chain dsDNA and expose its biotin molecules , combined with avidinated horseradish peroxidase to complete the assembly, and finally add aniline and hydrogen peroxide mixed solution, use horseradish peroxidase to catalyze the aniline polymerization deposition reaction to form polyaniline, and realize the detection of target nucleic acid according to the SPR signal. The present invention uses two-dimensional nanomaterials for "bottom-up" construction, and forms an SPR sensing platform with double-sensitized signals with a top-mounted "top-down" gravimetric reactor, which can achieve specificity and sensitivity to target DNA. Sensitive detection, the detection limit can reach femtomolar level.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for probe used for multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
ActiveCN102534004ALower the technical threshold of MLPALower technical barriersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationEnzyme digestion
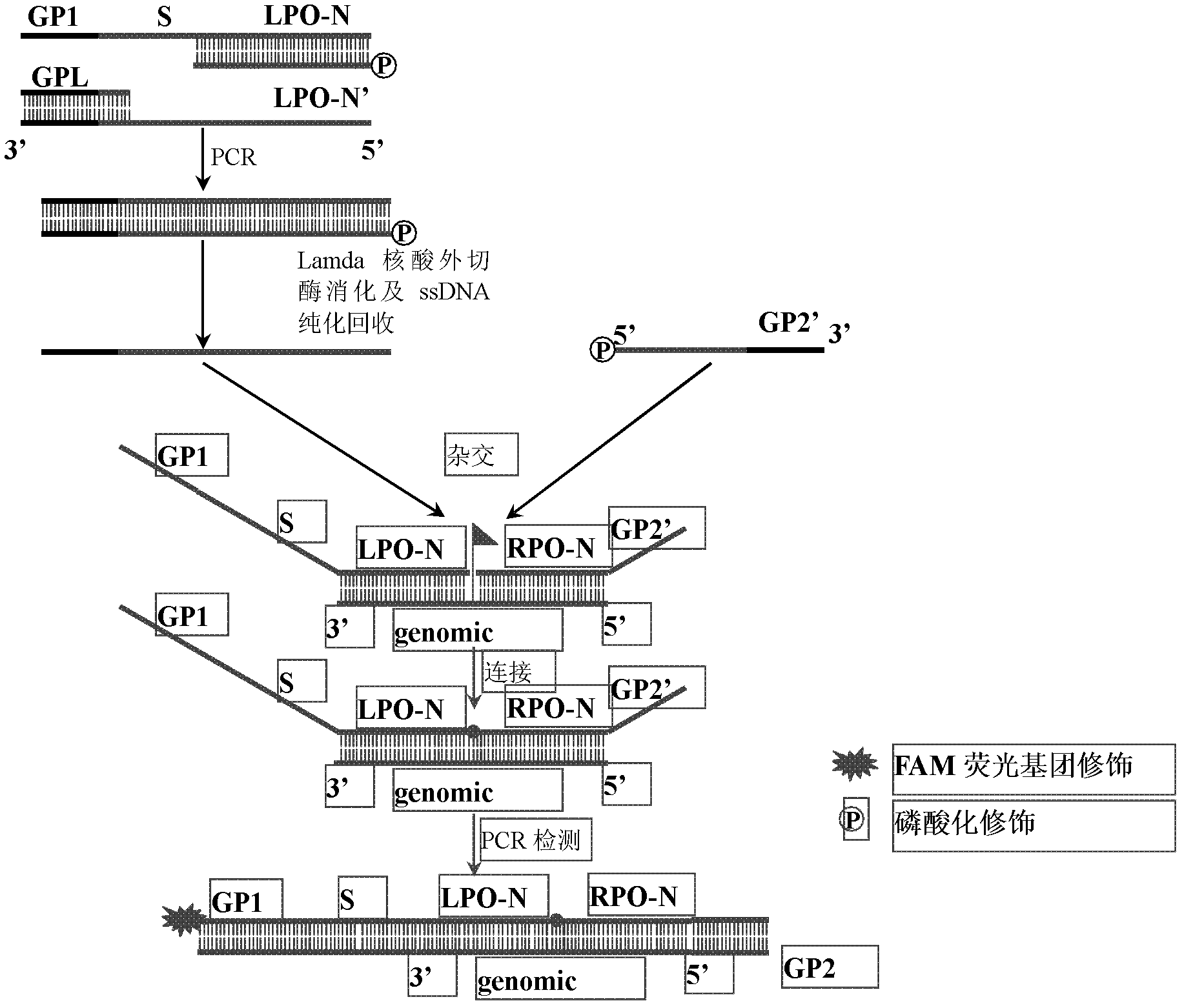
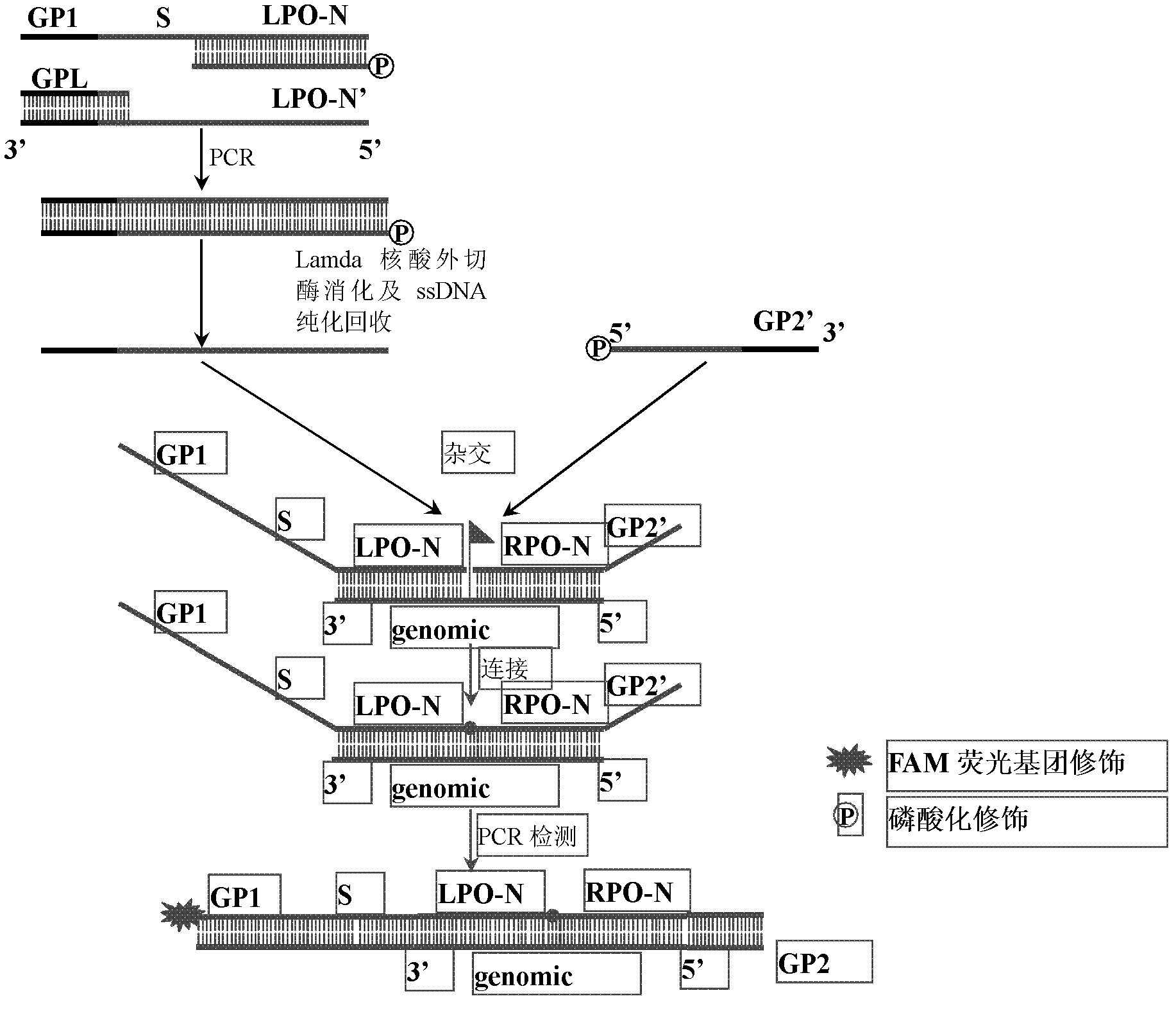
The invention discloses a preparation method for a long probe which can be used for multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a vector which is irrelevant with a target sequence to be tested to serve as a template, and designing a primer according to the length of a target nucleotide sequence and the length of a target probe; (2) artificially synthesizing the primer; (3) performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; (4) purifying and recovering PCR products; (5) digesting the PCR products by using Lambda exonuclease; and (6) recovering single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (ssDNA). The preparation method for the probe for the MLPA is low in cost, and all operations, such as the amplification, enzyme digestion and the like, can be finished only by a PCR instrument; recovery is performed by using a special ssDNA recovery kit after the enzyme digestion is finished, thereby, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and nucleotide which are not completely digested are eliminated, and the hybridization efficiency when an MLPA experiment is conducted is increased; and through full Lambda exonuclease digestion, the dsDNA can be changed into the ssDNA to the maximum degree, and thereby, the preparation efficiency of the probe is increased.
Owner:江西南兴医疗科技有限公司 +1
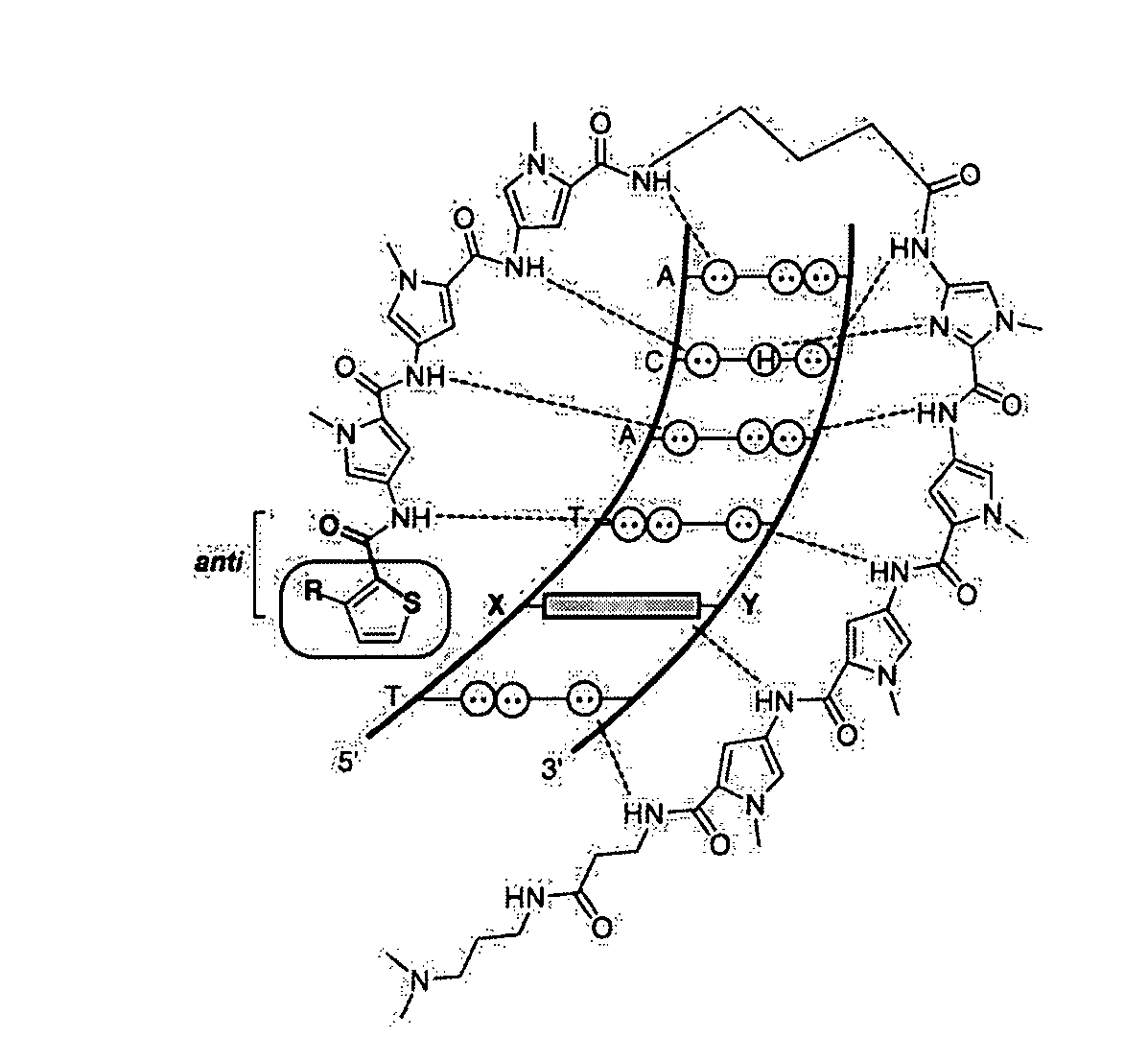
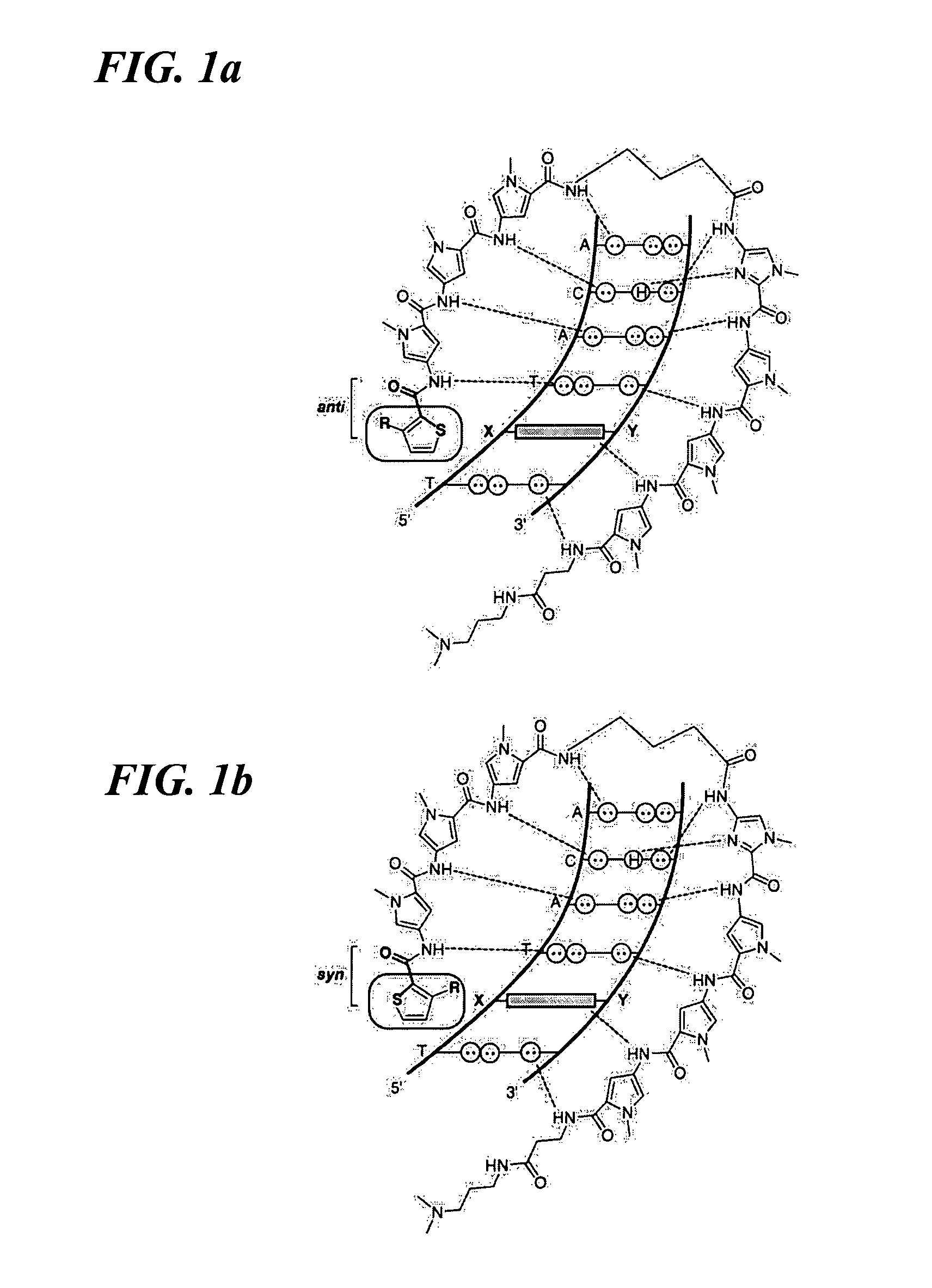
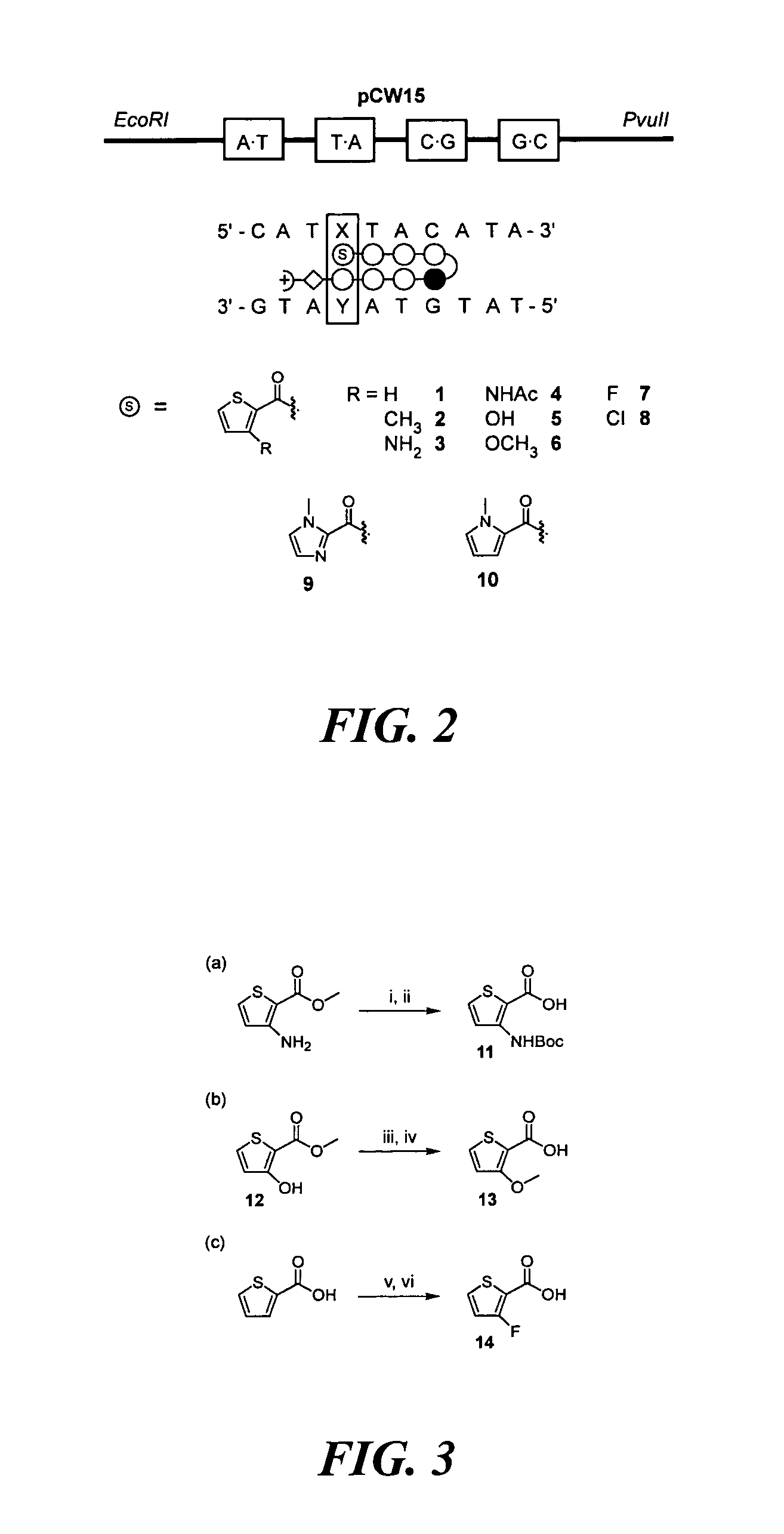
DNA-binding polymers
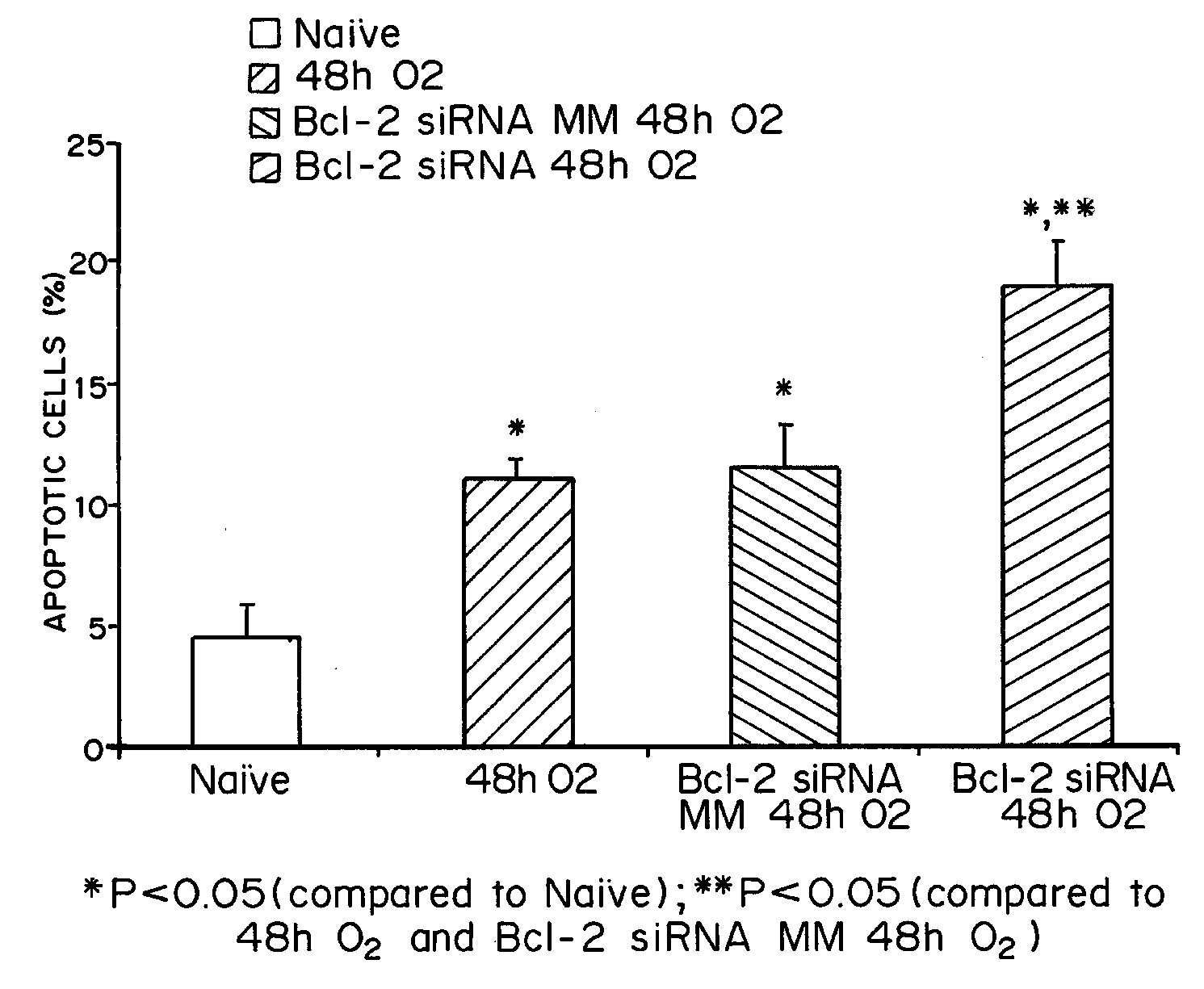
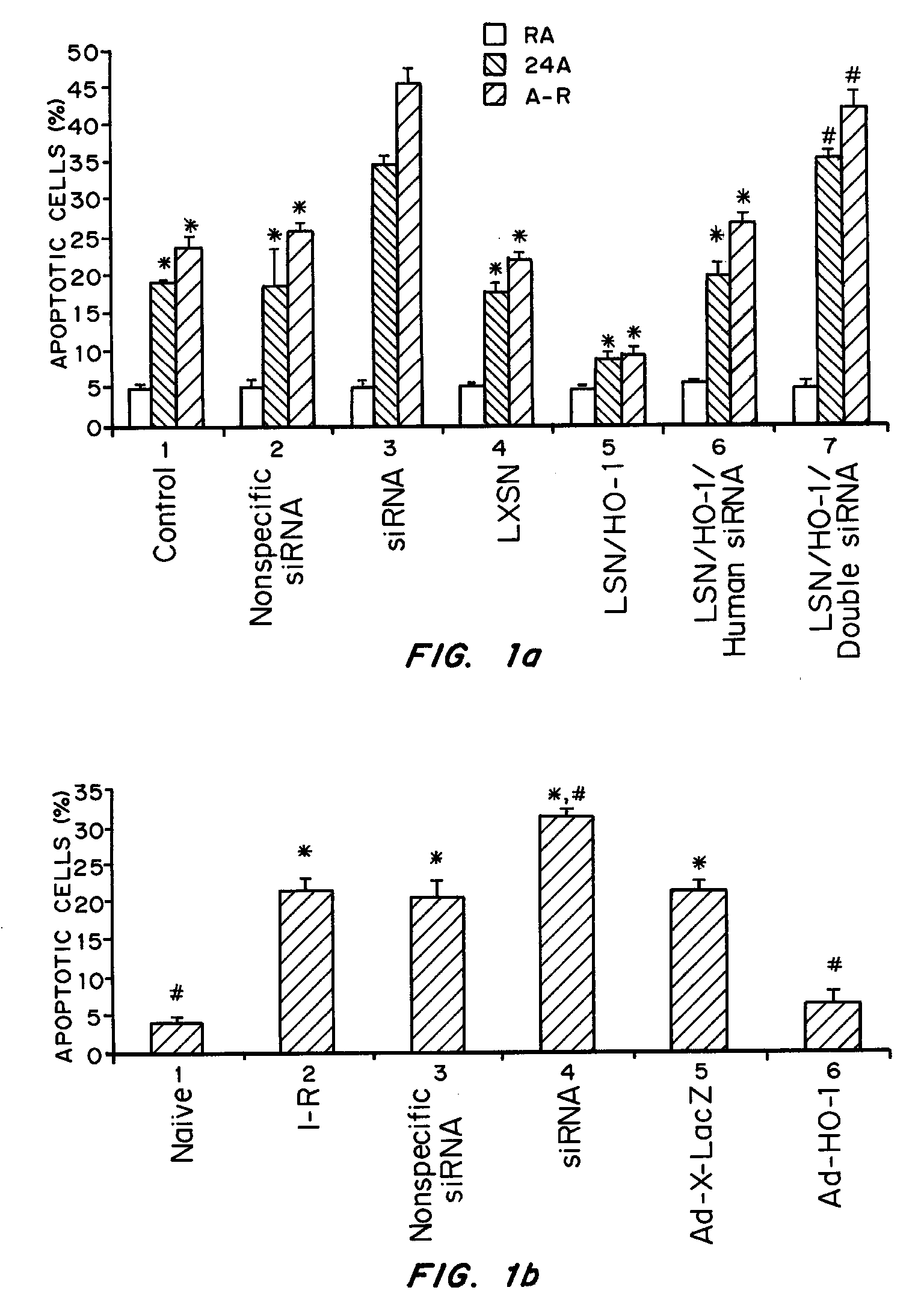
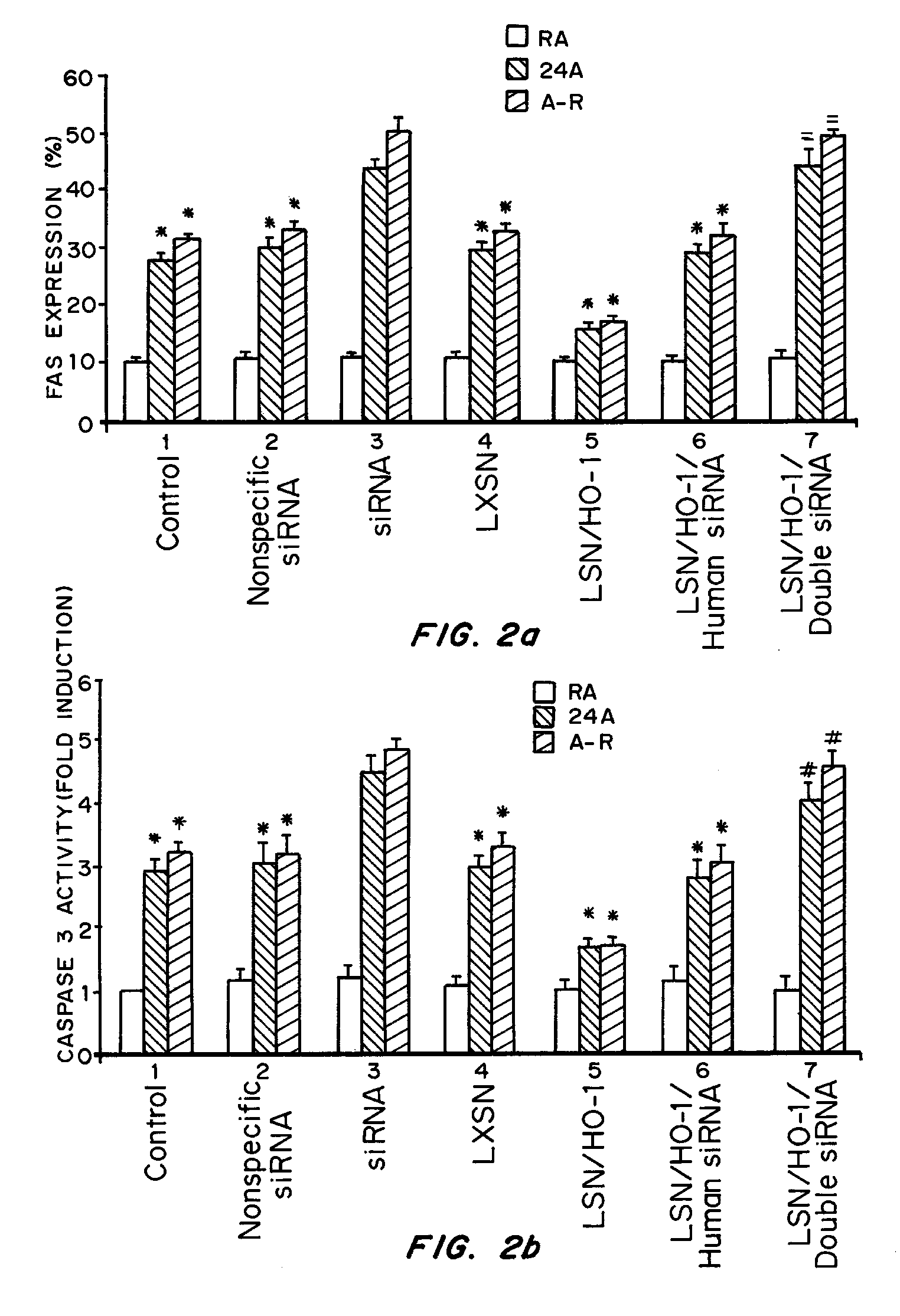
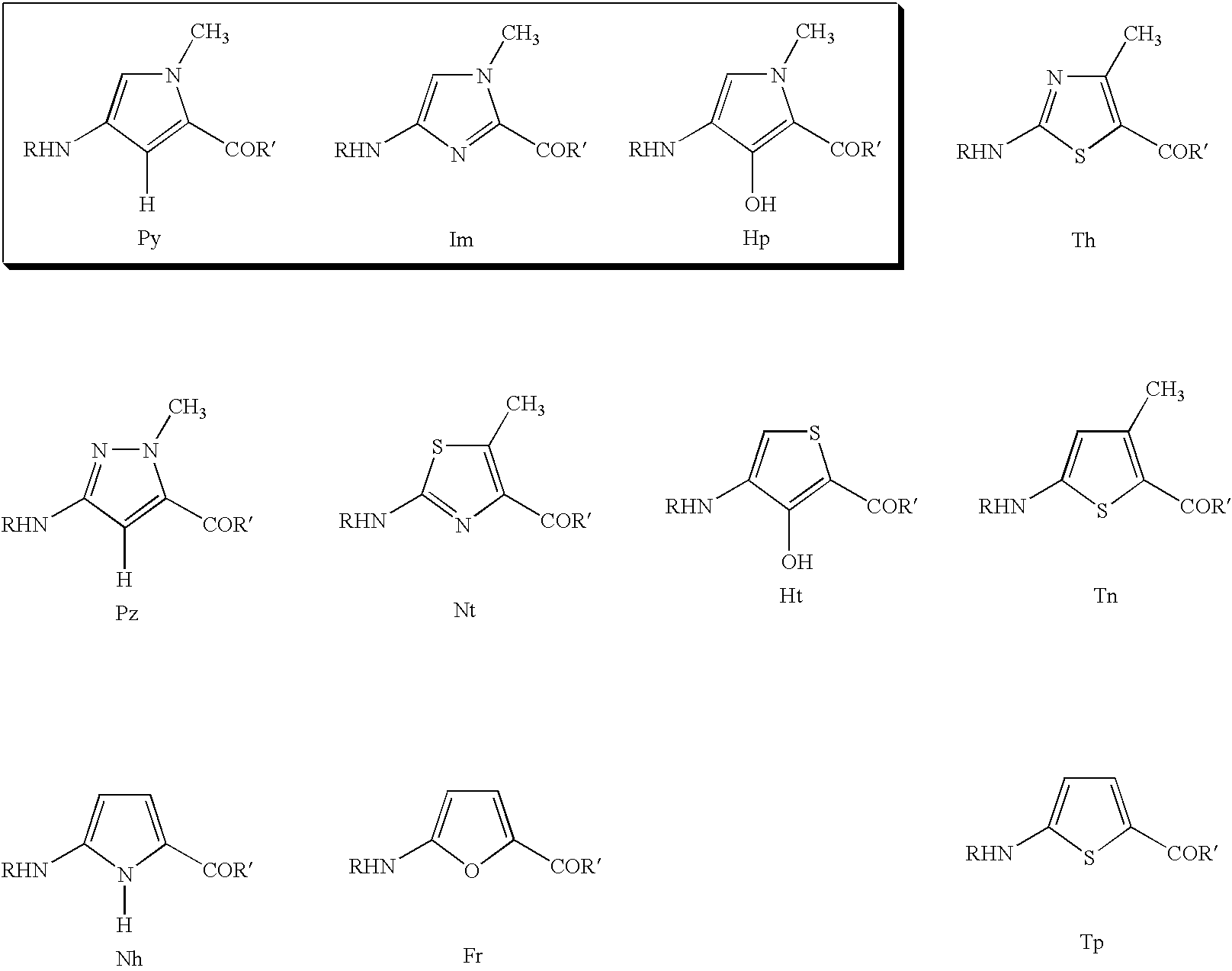
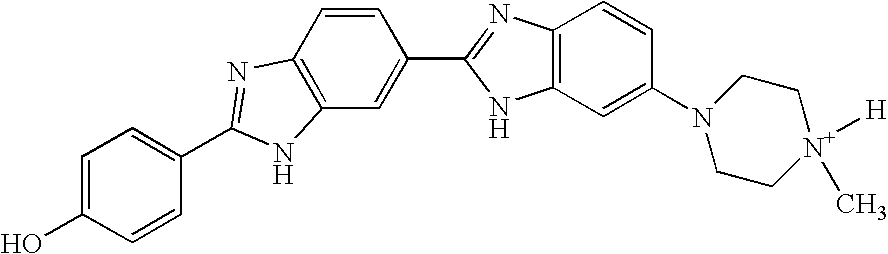
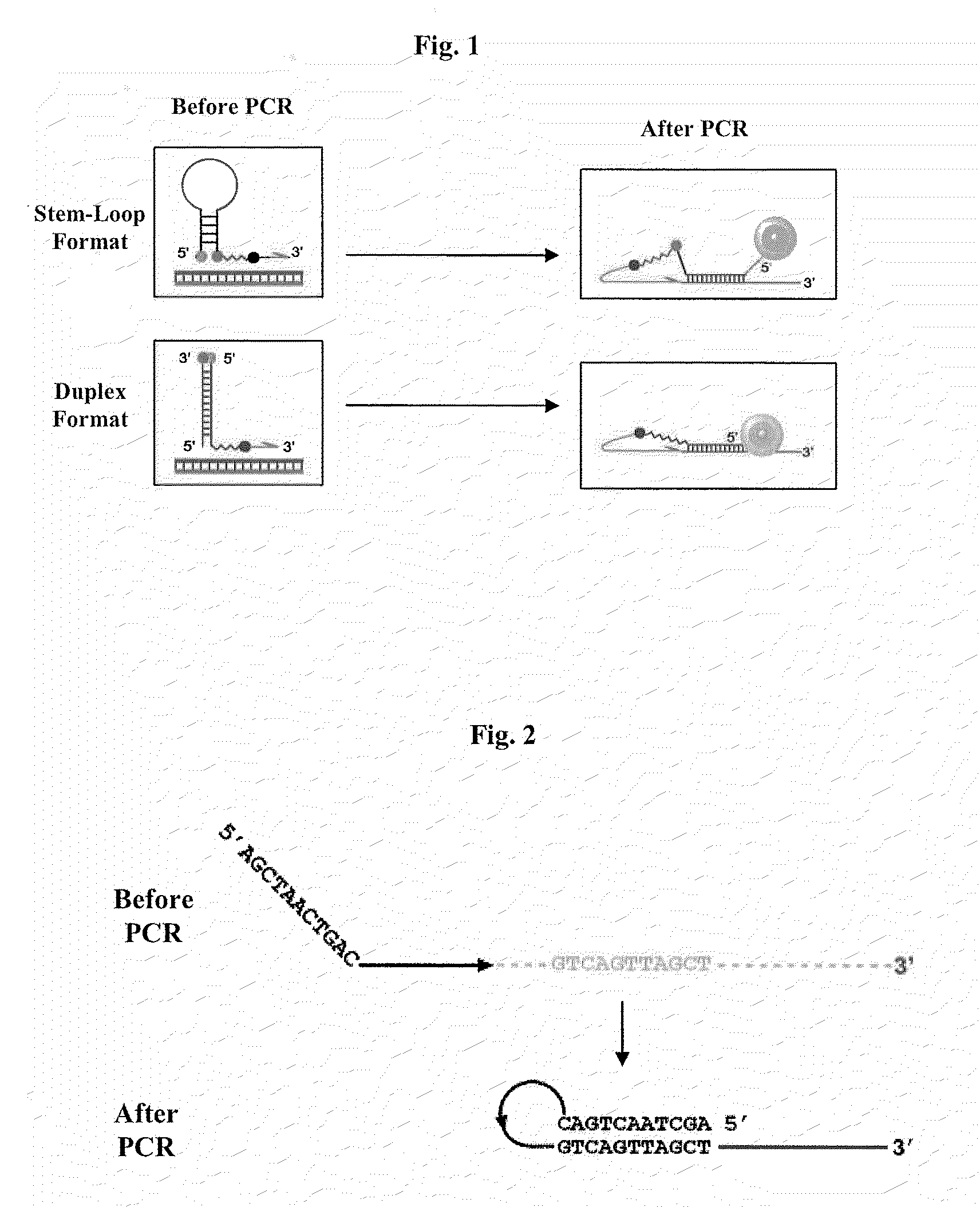
InactiveUS7452730B2Reduced transcript levelsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase pairDNA formation
Methods and compositions are provided for forming complexes between dsDNA and novel DNA-binding polymers comprising N-terminal thiophene-containing moieties which exhibit selectivity for T-A base pairs. By appropriate choice of target sequences and DNA-binding polymers, complexes comprising polymer-DNA are obtained with high association constants. The formation of complexes can be used for identification of specific dsDNA sequences, for inhibiting gene transcription, and as a therapeutic for inhibiting proliferation of undesired cells or modulation of expression of specific genes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Single molecule dsDNA microarray chip preparation method
InactiveCN1590559APromote commercial applicationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological studiesPolymerase L
A process for preparing the unimolecular ds DNA microarray on the surface of solid carrier includes chemically synthesizing target oligonucleotide and universal oligonucleotide, renaturation of them, linking them to the surface of solid carrier to become oligonucleotide microarray, on-chip polymerase elongation reaction to become bimolecular dsDNA microarray, modifying to become ssDNA microarray, renaturation to form hairpin structure, and on-chip polymerase elongation reaction.
Owner:王进科 +2
Double stranded nucleic acid biochips
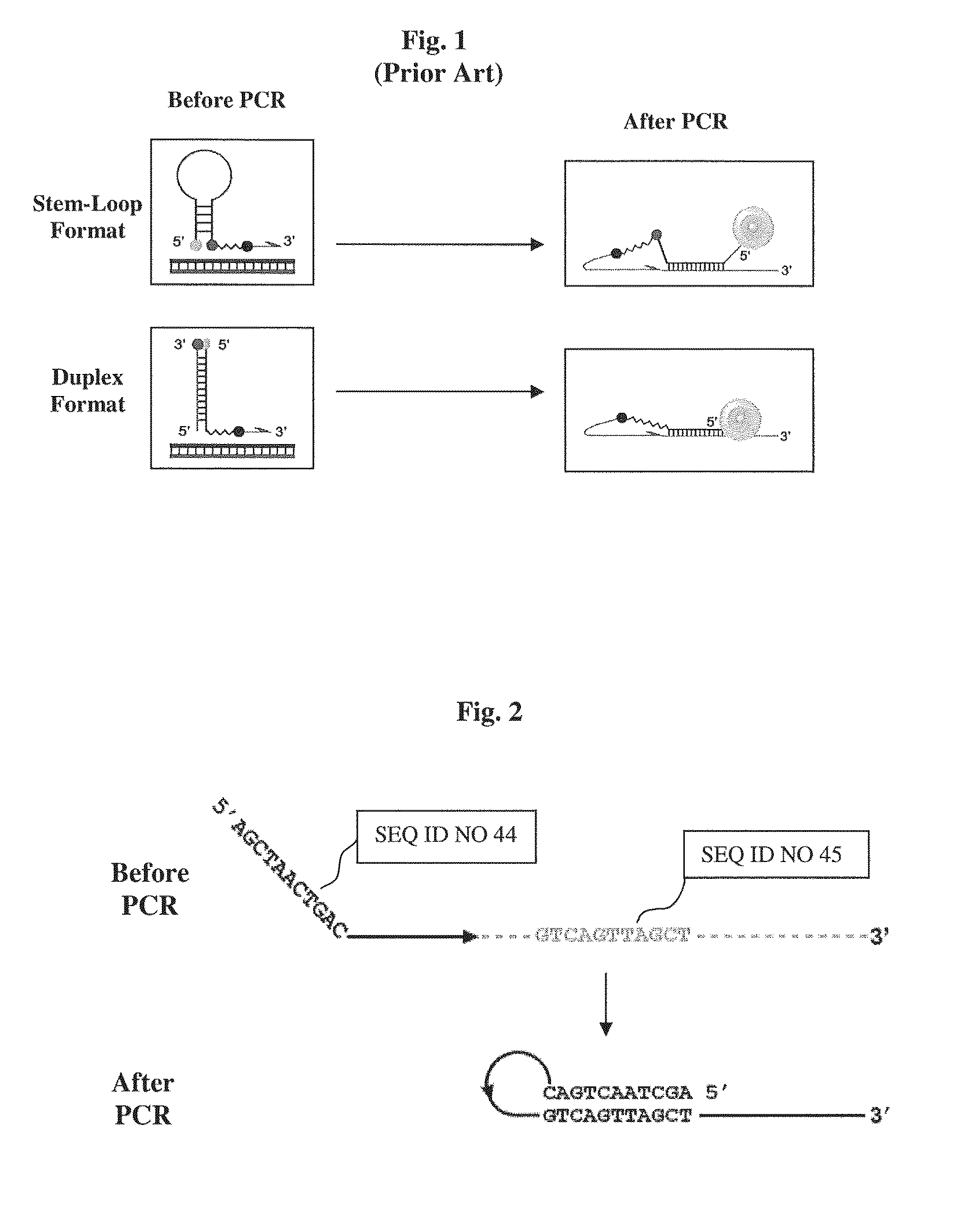
InactiveUS7049073B2Convenience to mergeSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesDouble strandNon enzymatic
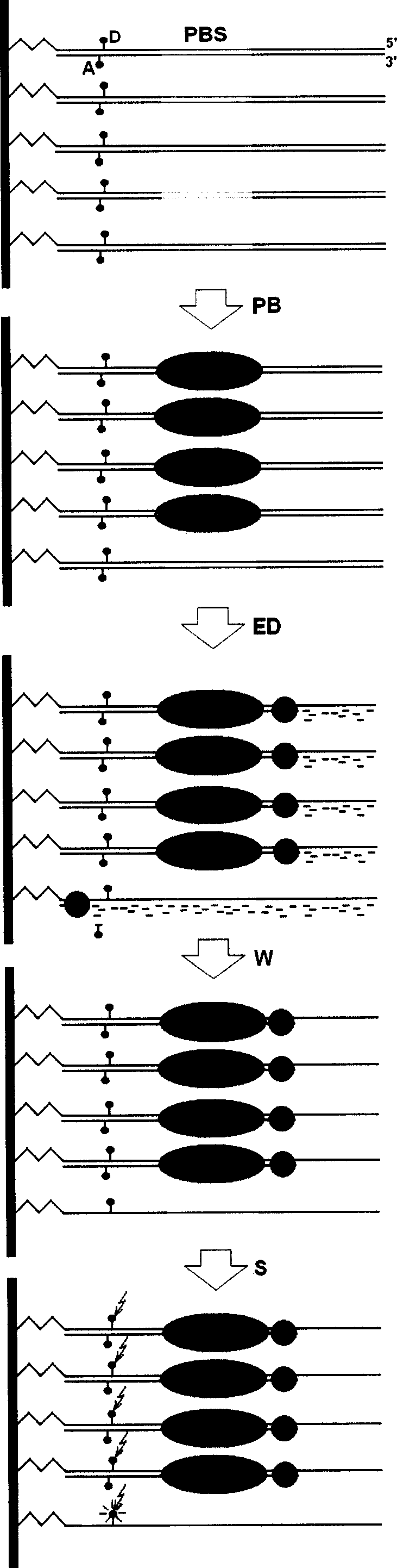
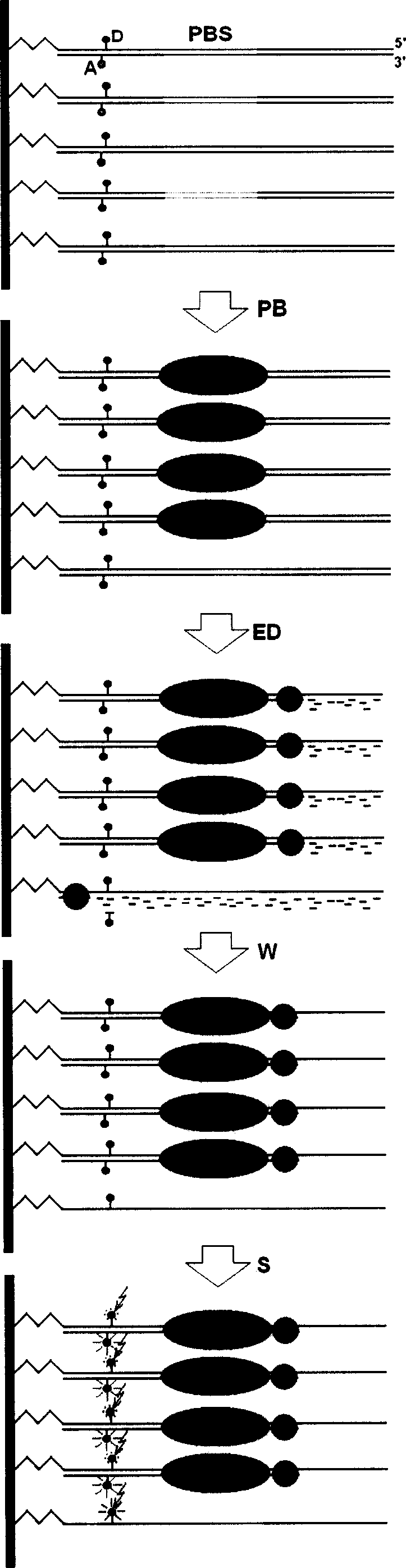
This invention describes a new method of constructing double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) microarrays based on the use of pre-synthesized or natural DNA duplexes without a stem-loop structure. The complementary oligonucleotide chains are bonded together by a novel connector that includes a linker for immobilization on a matrix. A non-enzymatic method for synthesizing double-stranded nucleic acids with this novel connector enables the construction of inexpensive and robust dsDNA / dsRNA microarrays. DNA-DNA and DNA-protein interactions are investigated using the microarrays.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF +1
Methods for obtaining directionally truncated polypeptides
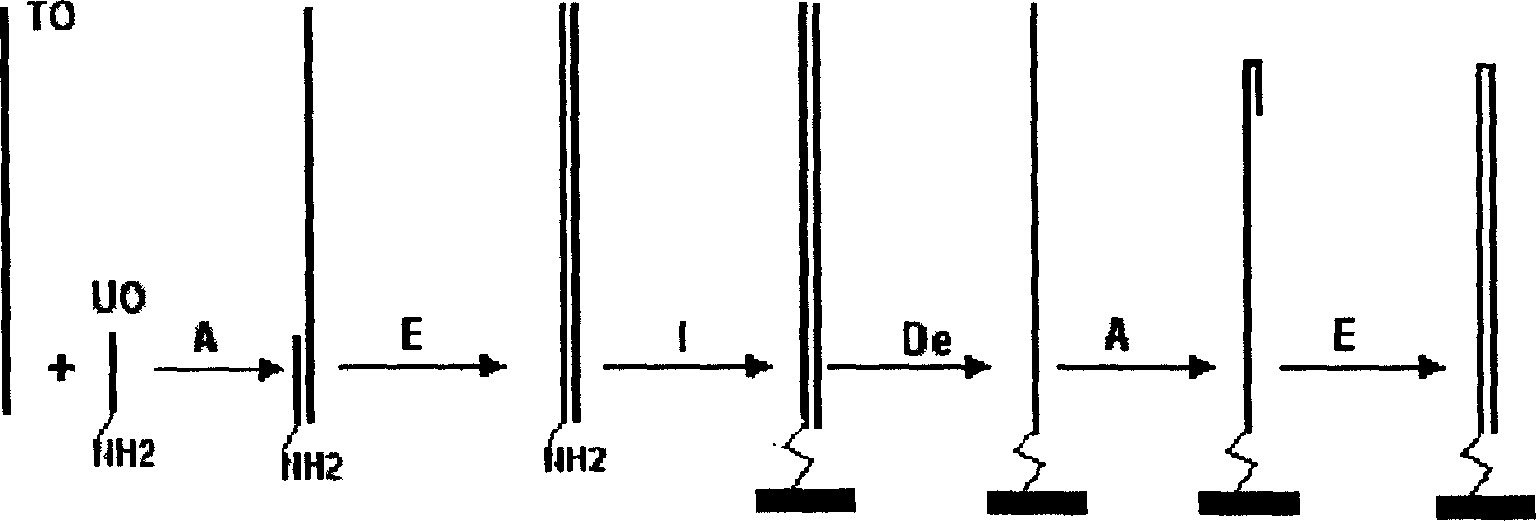
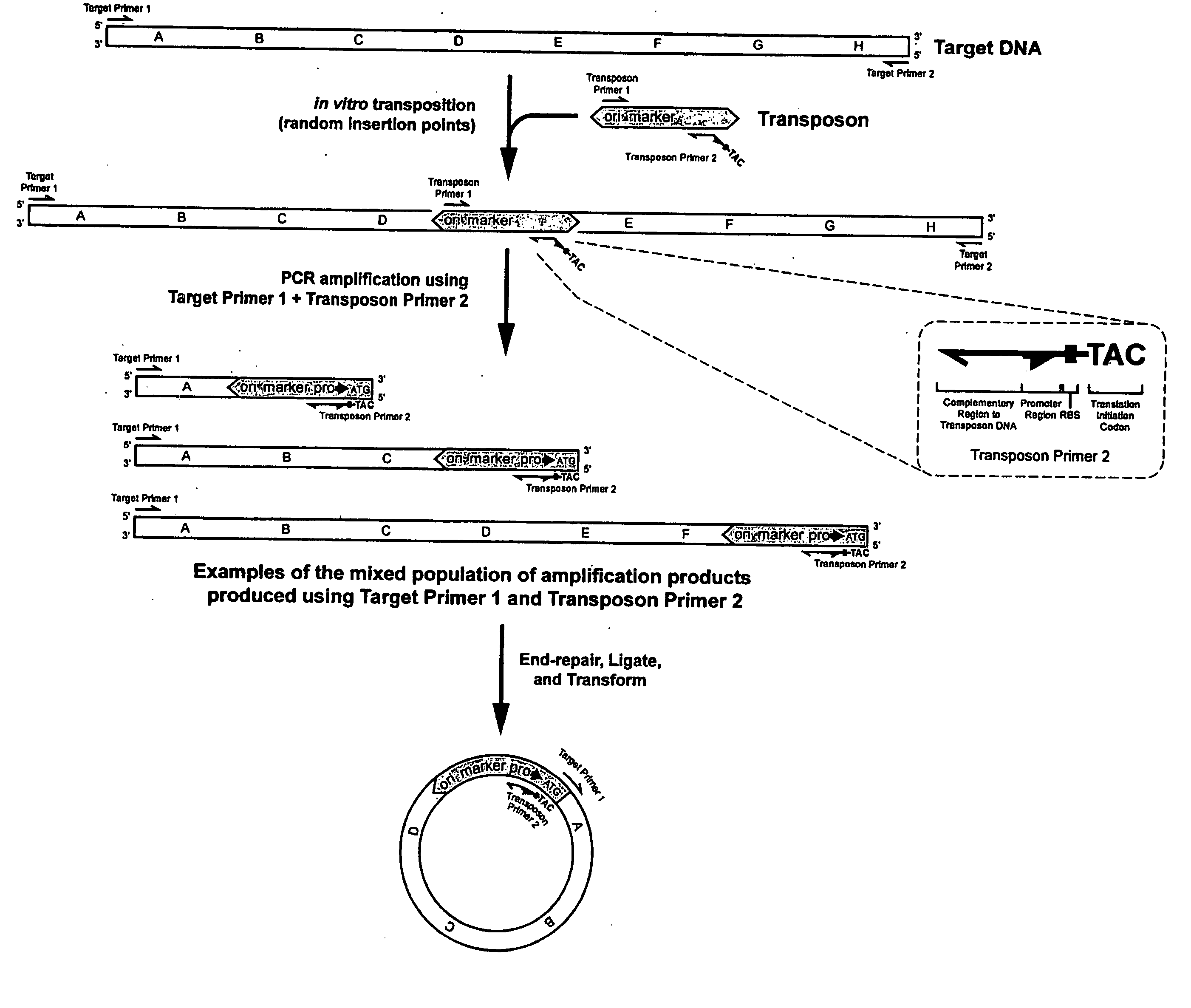
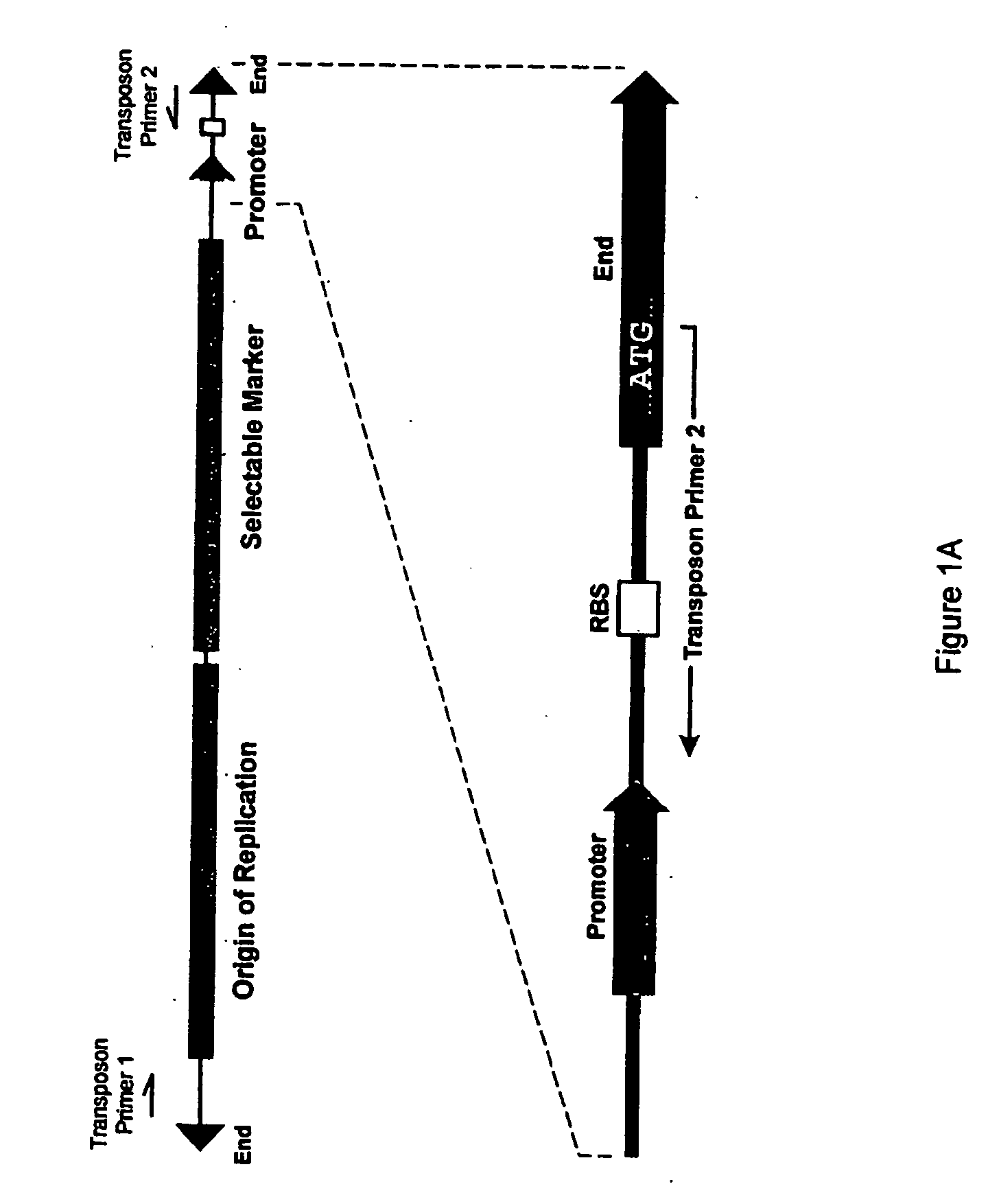
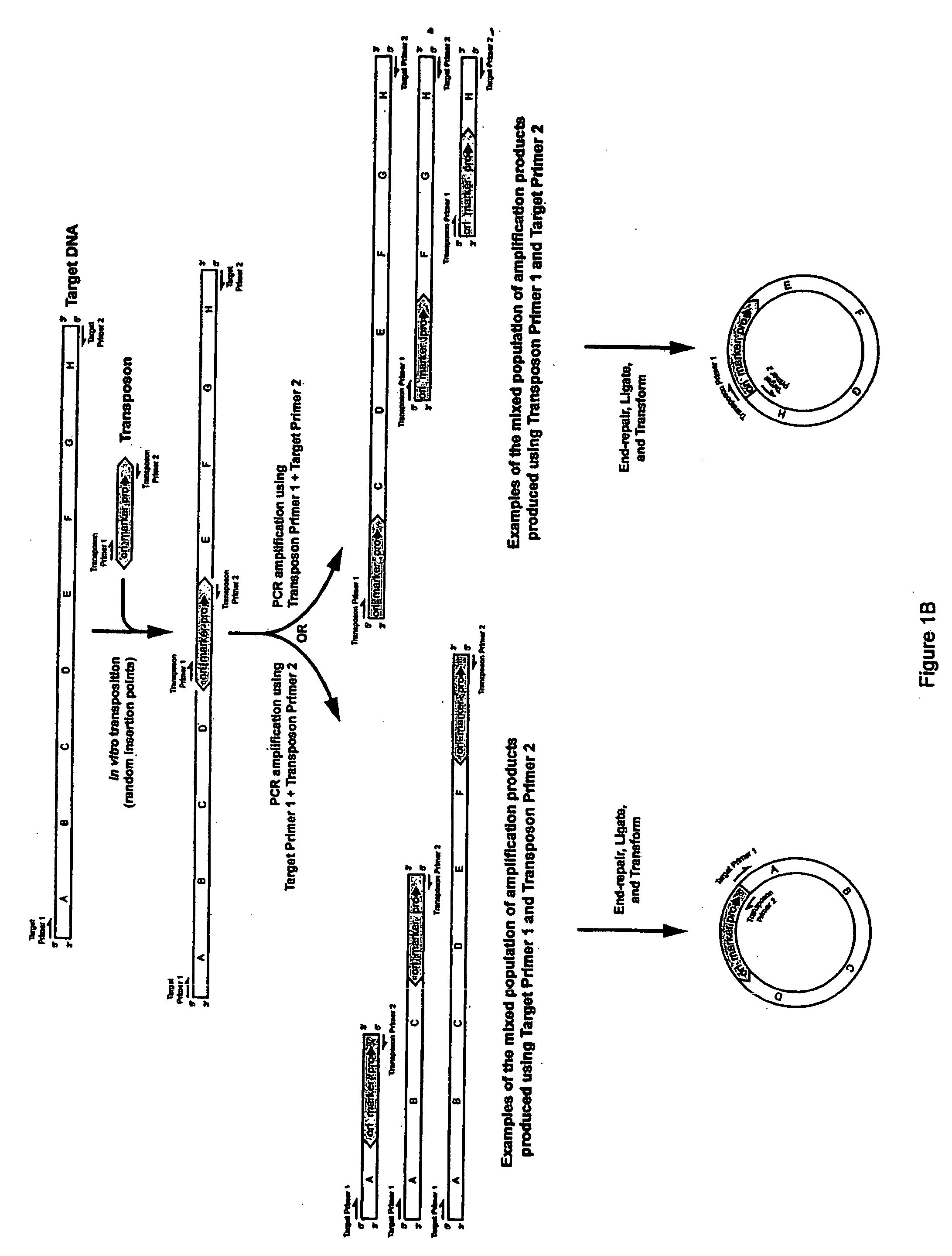
Methods, compositions and kits are disclosed for obtaining directionally truncated polypeptides by inserting a transposon. Preferably the transposon comprises a selectable marker and an ori, and optionally a promoter, a ribosome binding site and a translation start codon, into a target sequence in vitro or in vivo. Amplification products, varying in length depending on the transposon insertion site, are obtained using one primer that anneals to the target sequence and a second primer that anneals to the transposon. Amplification products are ligated to circular dsDNA, transformed into host cells, and individual colonies, each containing a directionally truncated clone of the target sequence, are obtained by plating on medium for which the selectable marker encodes resistance. Directionally truncated polypeptides encoded by the target sequence are obtained in vivo by inducing an RNAP in the host cells that uses the promoter or, in vitro by cell-free transcription and translation.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Intranasal delivery of nucleic acid molecules
Aerosol delivery of nucleic acids to the lungs using viral vectors, polymers, surfactants, or excipients has been described. Compositions for intranasal administration are described that contain nucleic acids without viral or plasmid vectors and with little to no polymers, surfactants, or excipients. In one embodiment, the composition for intranasal delivery consists essentially of at least one nucleic acid and an aqueous solution. Suitable nucleic acids for intranasal delivery include, but are not limited to, dsDNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, ssRNA, short interfering RNA, micro-RNA, and antisense RNA Methods for treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of at least one symptom or manifestation of a lung disease are also described consisting of administration by intranasal delivery an effective amount of a composition containing a nucleic acid. The composition may be formulated as a liquid or aerosol or other acceptable formulation for intranasal administration.
Owner:YALE UNIV
DNA-binding polymers
InactiveUS20060014163A1Reduced transcript levelsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase pairPolymer
Methods and compositions are provided for forming complexes between dsDNA and novel DNA-binding polymers comprising N-terminal thiophene-containing moieties which exhibit selectivity for T-A base pairs. By appropriate choice of target sequences and DNA-binding polymers, complexes comprising polymer-DNA are obtained with high association constants. The formation of complexes can be used for identification of specific dsDNA sequences, for inhibiting gene transcription, and as a therapeutic for inhibiting proliferation of undesired cells or modulation of expression of specific genes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
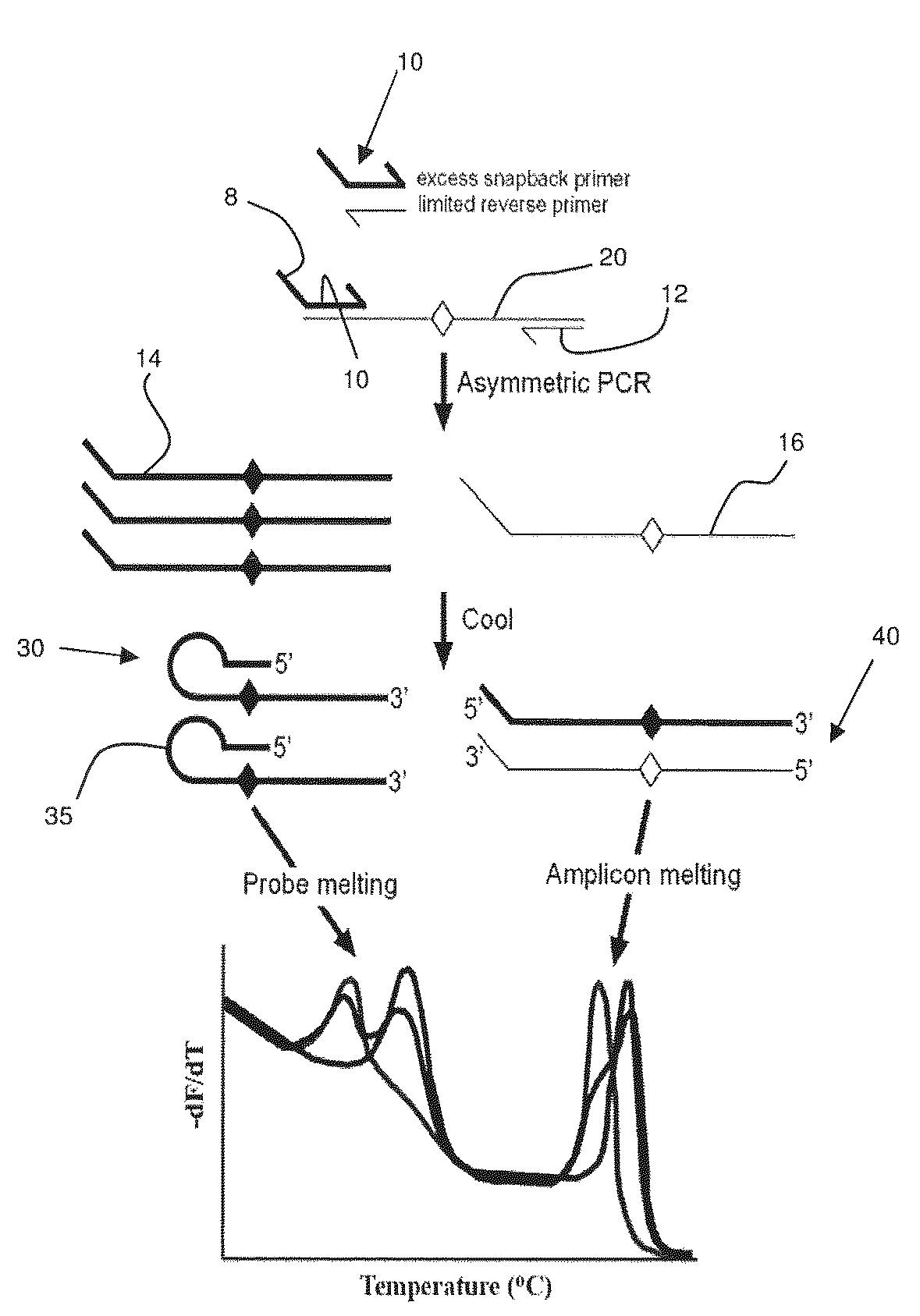
Primers for melting analysis
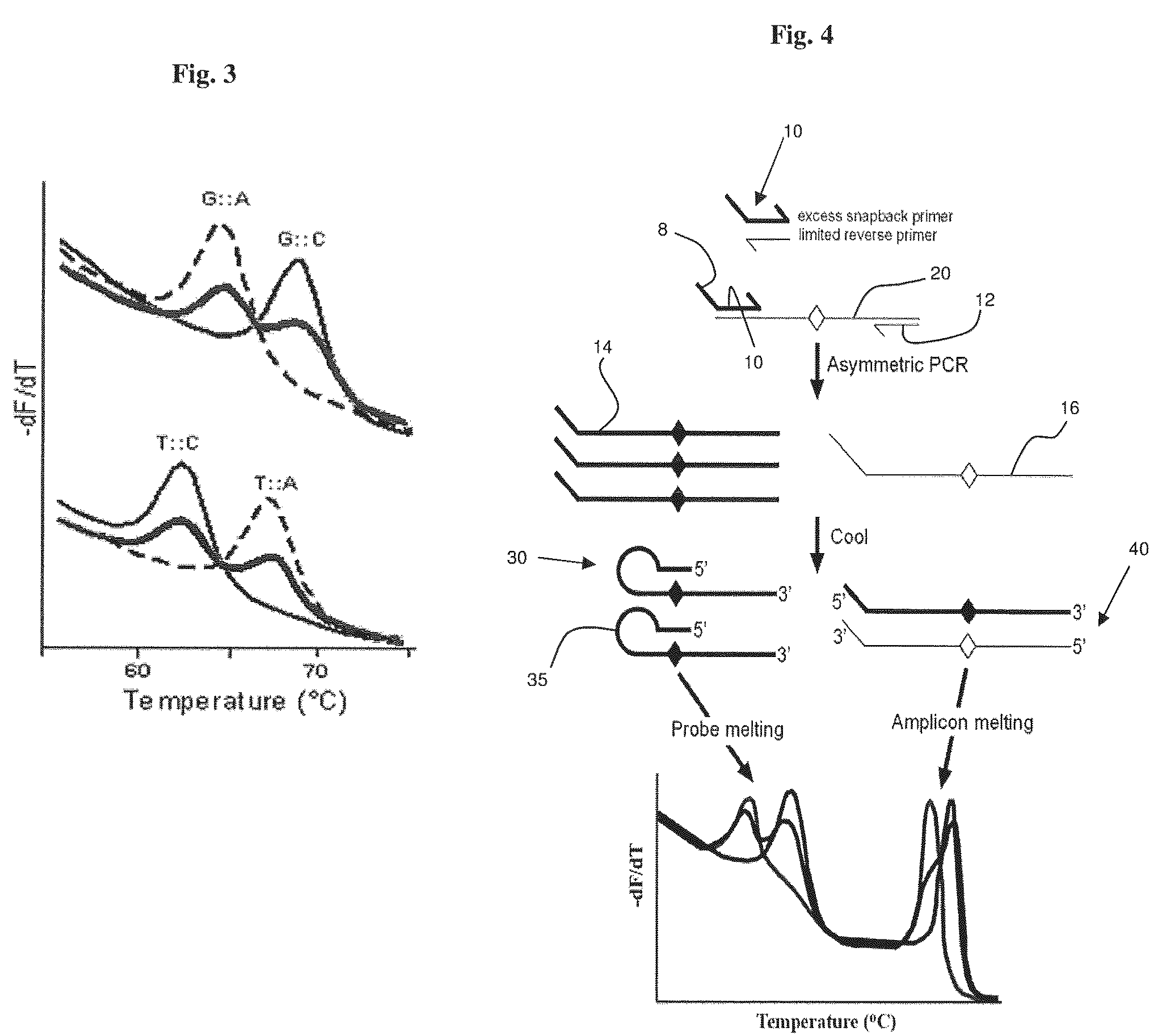
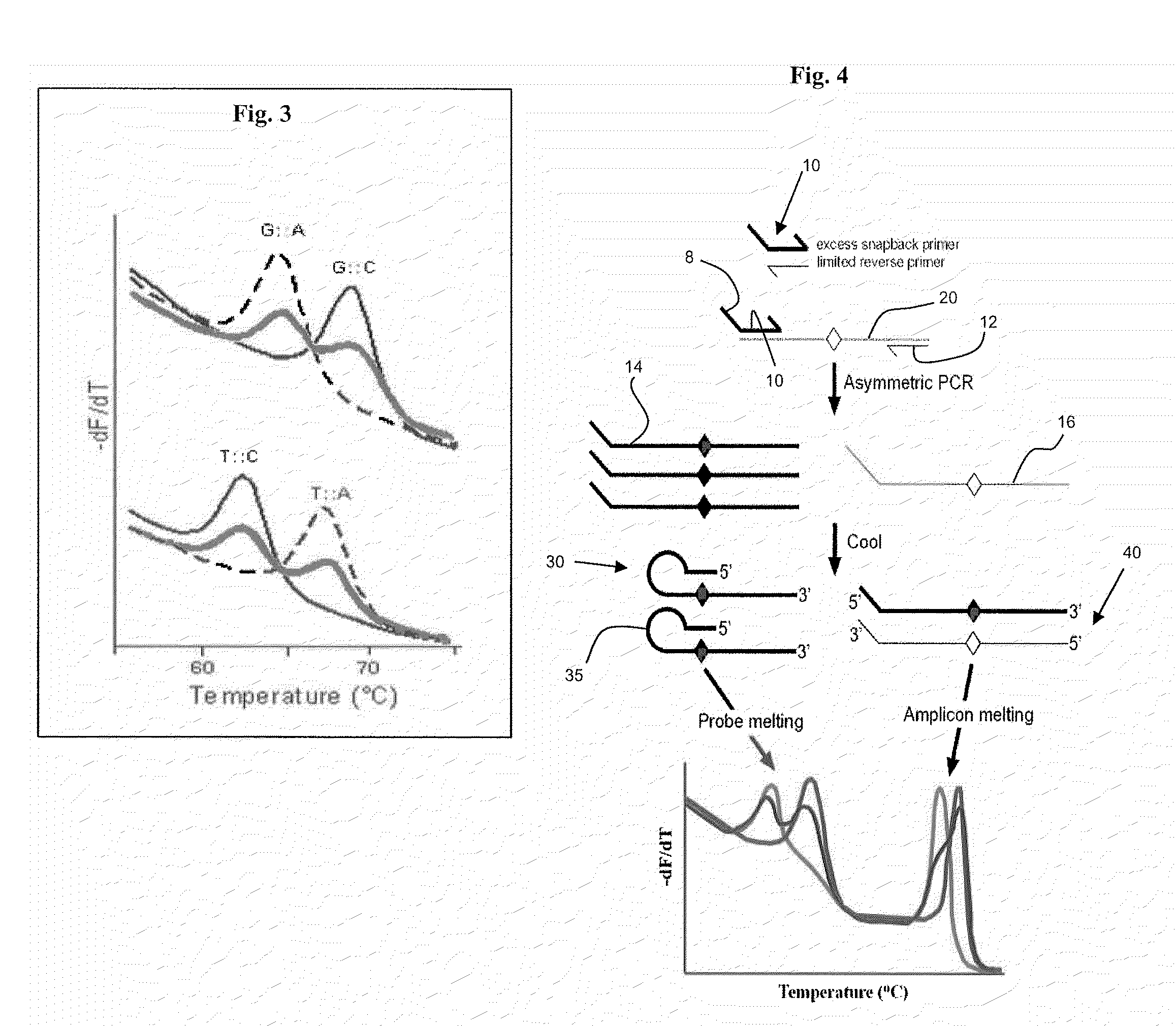
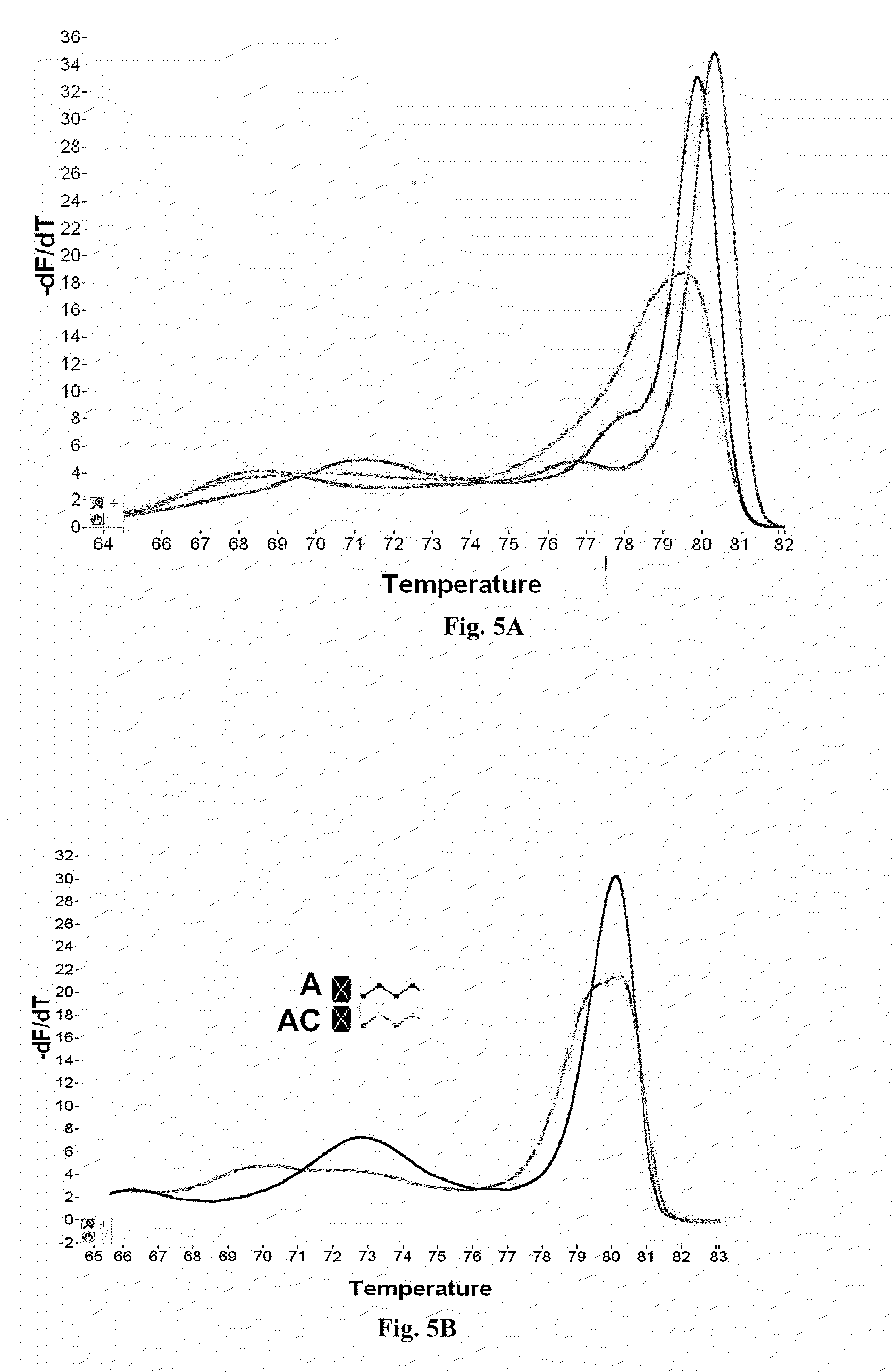
Methods and kits are provided for nucleic acid analysis. In an illustrative method a target nucleic acid is amplified using a first primer and a second primer, wherein the first primer comprises a probe element specific for a locus of the target nucleic acid and a template-specific primer region, and the probe element is 5′ of the template-specific primer region, subsequently allowing the probe element to hybridize to the locus to form a hairpin, generating a melting curve for the probe element by measuring fluorescence from a dsDNA binding dye as the mixture is heated, wherein the dye is not covalently bound to the first primer, and analyzing the shape of the melting curve. Kits may include one or more of the first and second primers, the dsDNA binding dye, a polymerase, and dNTPs.
Owner:BIOFIRE DEFENSE +1
Exonuclease III digesting FRET-dsDNA microarray chip for detecting transcription factor protein
InactiveCN1733934ASolve application problemsEnable high-throughput detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein detectionFluorescence
Disclosed is a transcription factor protein detection method through exonuclease III digestion FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, wherein the expression and activation levels of the transcription factor are analyzed through the following steps: (1) preparing FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (2) reacting the transcription factor with FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (2) reacting the exonuclease III with FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (1) proceeding detection and analysis to the FRET-dsDNA micro array chips.
Owner:王进科 +1
Primers for melting analysis
ActiveUS20100196890A1High melting temperatureIncrease signal strengthSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePolymerase L
Methods and kits are provided for nucleic acid analysis. In an illustrative method a target nucleic acid is amplified using a first primer and a second primer, wherein the first primer comprises a probe element specific for a locus of the target nucleic acid and a template-specific primer region, and the probe element is 5′ of the template-specific primer region, subsequently allowing the probe element to hybridize to the locus to form a hairpin, generating a melting curve for the probe element by measuring fluorescence from a dsDNA binding dye as the mixture is heated, wherein the dye is not covalently bound to the first primer, and analyzing the shape of the melting curve. Kits may include one or more of the first and second primers, the dsDNA binding dye, a polymerase, and dNTPs.
Owner:BIOFIRE DEFENSE +1
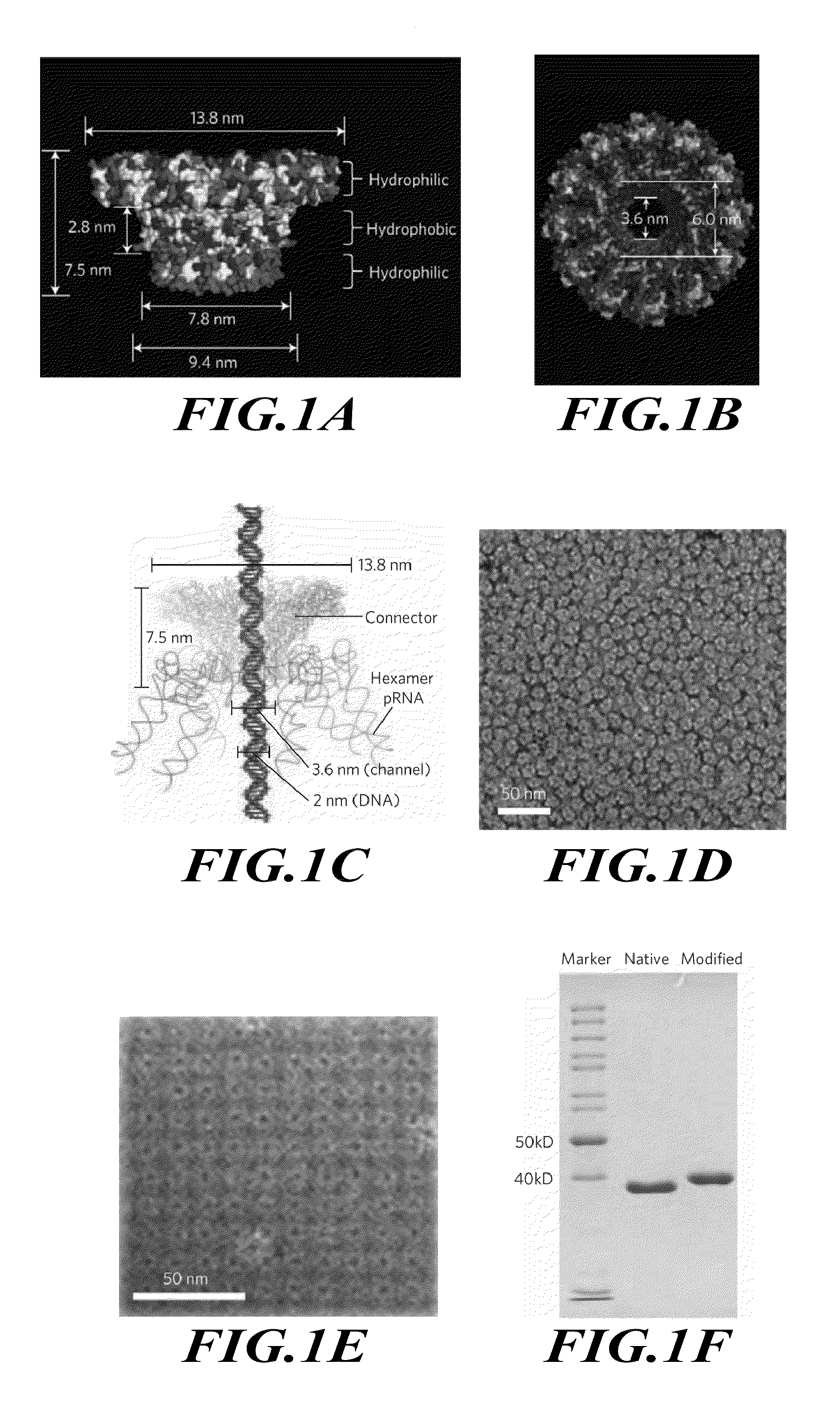
Membrane-integrated viral DNA-packaging motor protein connector biosensor for DNA sequencing and other uses
ActiveUS20150267253A1Improve throughputVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsGene deliveryLipid formation
Compositions and methods are disclosed that exploit the unprecedented modification of double-stranded DNA virus DNA-packaging motor protein connector polypeptides to render them capable of stable incorporation into lipid membranes as a self-assembled homodocamer that forms an aperture through which conductance can occur when an electrical potential is applied across the membrane. The aperture permits use of the modified protein as a biosensor, for dsDNA sequencing, SNP detection and highly sensitive affinity capture and fingerprinting of analytes, and also finds use in electropotential-driven solute translocation, such as for liposomal loading to form therapeutic nanoparticles (e.g., gene delivery) and bioreactors, and for other uses. The aperture can further be used in optical detection of dsDNA or other acceptor labeled analytes in a fluorophore donor labeled single pore channel.
Owner:GUO PEIXUAN
dsDNA (double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) high-sensitivity detection method based on monochrome fluorescence off-on switching system
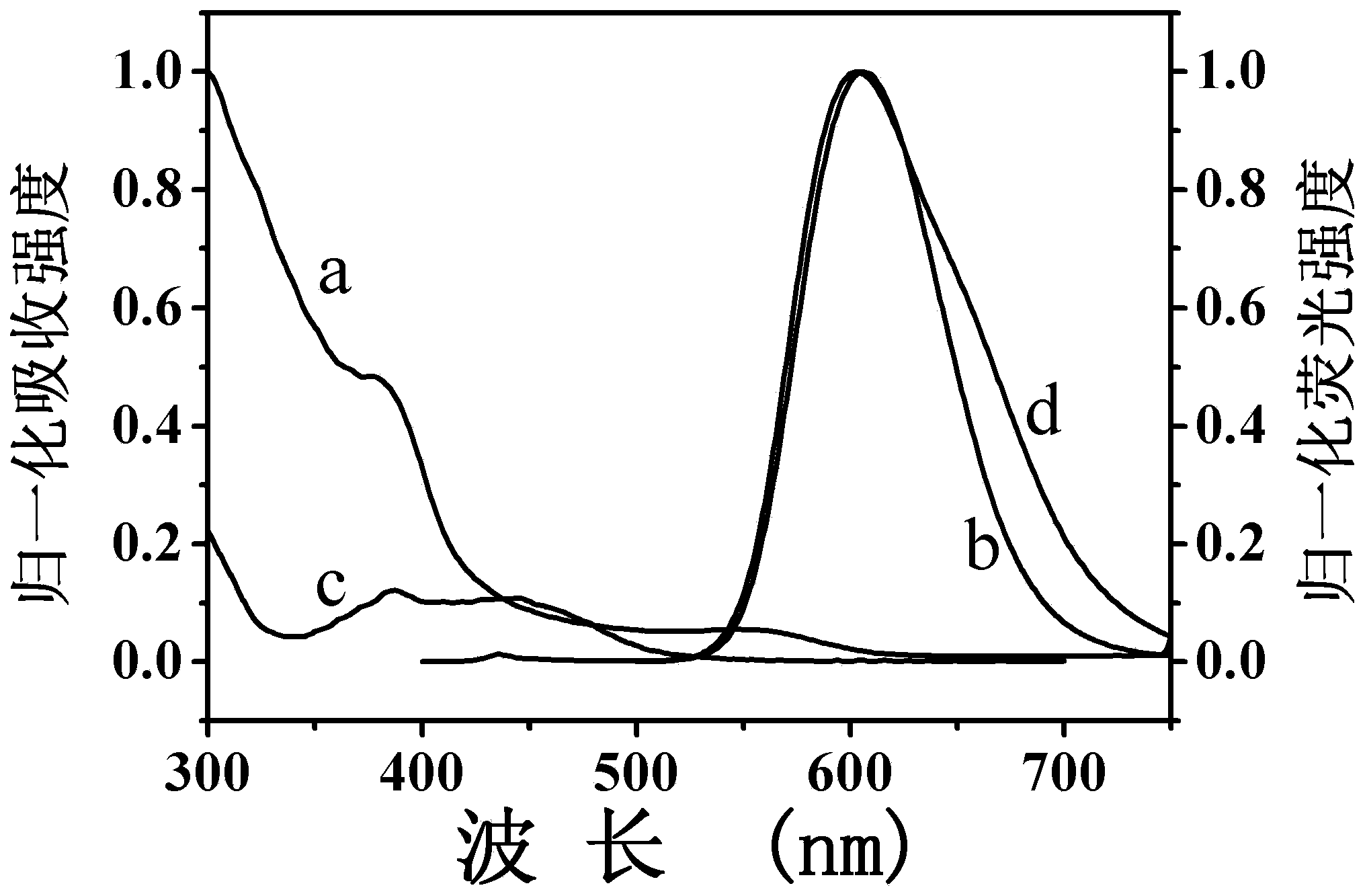
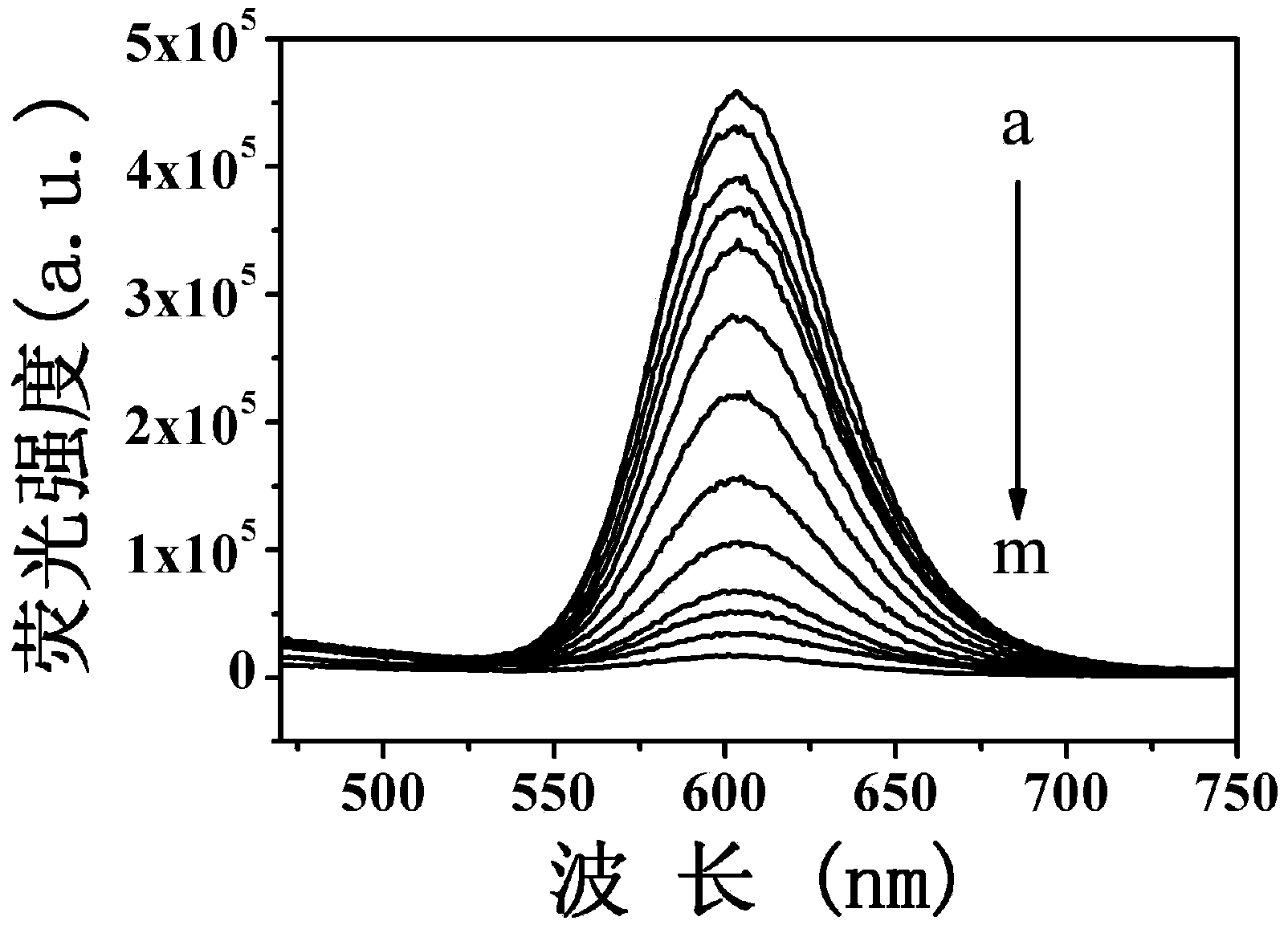
InactiveCN103529001AFluorescence recoveryHigh sensitivity detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceGradual increase
The invention relates to a dsDNA (double-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid) high-sensitivity detection method based on a monochrome fluorescence off-on switching system and belongs to the field of chemistry and biomedicine. The dsDNA high-sensitivity detection method comprises the following steps: synthesizing CdTe quantum dots (QDs) coated by water-soluble glutathione (GSH); controlling the fluorescence-emission wavelength of the quantum dots to be 605mm; mixing the CdTe quantum dots coated by the water-soluble glutathione with a metal ruthenium coordination compound [Ru(phen)2(dppz)]2+(Ru) to enable the fluorescence of the CdTe quantum dots coated by the water-soluble glutathione to be completely quenched, so as to obtain a QDs-Ru assembling group; adding dsDNA into the QDs-Ru assembling group and gradually enhancing the monochrome fluorescence strength at the wavelength of 605mm along with gradual increase of the concentration of the dsDNA so as to rapidly and flexibly defect the dsDNA. The detection system can be used for enabling the detection limit of the dsDNA to reach 10pg / mL. Compared with the prior art in a background technology, the sensitivity is improved by 500 times; the operation is simple and rapid; the specificity is good and the cost is low; the whole process can be finished within 30 minutes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com