Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Degradation pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological systems for manufacture of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers containing 4-hydroxyacids
The gene encoding a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA transferase has been isolated from bacteria and integrated into the genome of bacteria also expressing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, to yield an improved production process for 4HB-containing polyhydroxyalkanoates using transgenic organisms, including both bacteria and plants. The new pathways provide means for producing 4HB containing PHAs from cheap carbon sources such as sugars and fatty acids, in high yields, which are stable. Useful strains are obtaining by screening strains having integrated into their genomes a gene encoding a 4HB-CoA transferase and / or PHA synthase, for polymer production. Processes for polymer production use recombinant systems that can utilize cheap substrates. Systems are provided which can utilize amino acid degradation pathways, α-ketoglutarate, or succinate as substrate.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Biological systems for manufacture of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers containing 4-hydroxyacids
InactiveUS20060084155A1Increase productionHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyDegradation pathway
The gene encoding a 4-hydroxybutyryl-Co A transferase has been isolated from bacteria and integrated into the genome of bacteria also expressing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, to yield an improved production process for 4HB-containing polyhydroxyalkanoates using transgenic organisms, including both bacteria and plants. The new pathways provide means for producing 4HB containing PHAs from cheap carbon sources such as sugars and fatty acids, in high yields, which are stable. Useful strains are obtaining by screening strains having integrated into their genomes a gene encoding a 4HB-CoA transferase and / or PHA synthase, for polymer production. Processes for polymer production use recombinant systems that can utilize cheap substrates. Systems are provided which can utilize amino acid degradation pathways, α-ketoglutarate, or succinate as substrate.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Stabilization of self-assembled monolayers
InactiveUS20050221081A1Ability to retard and preventRetard and prevent degradationMaterial nanotechnologyBiological material analysisResistAmphiphile
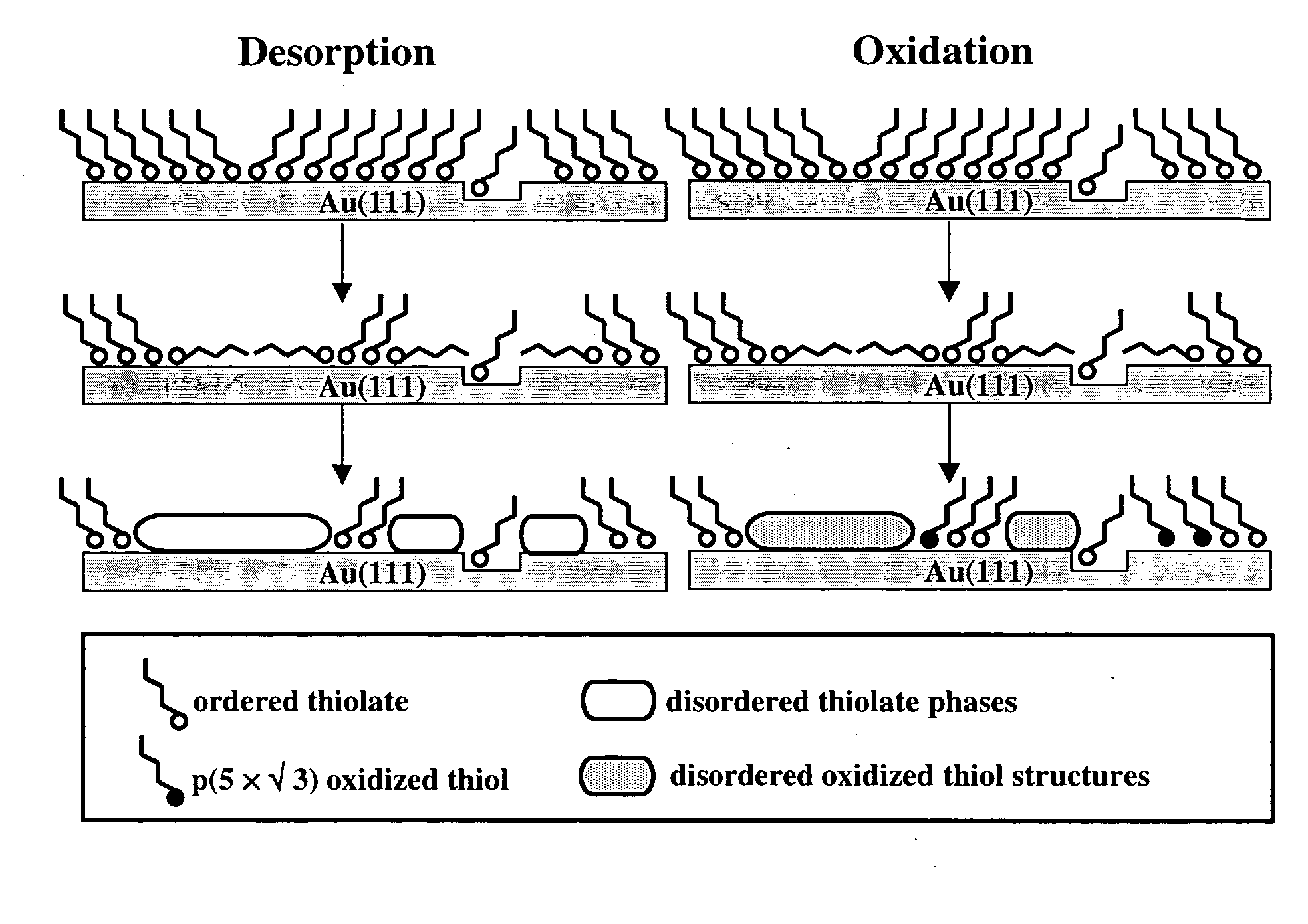
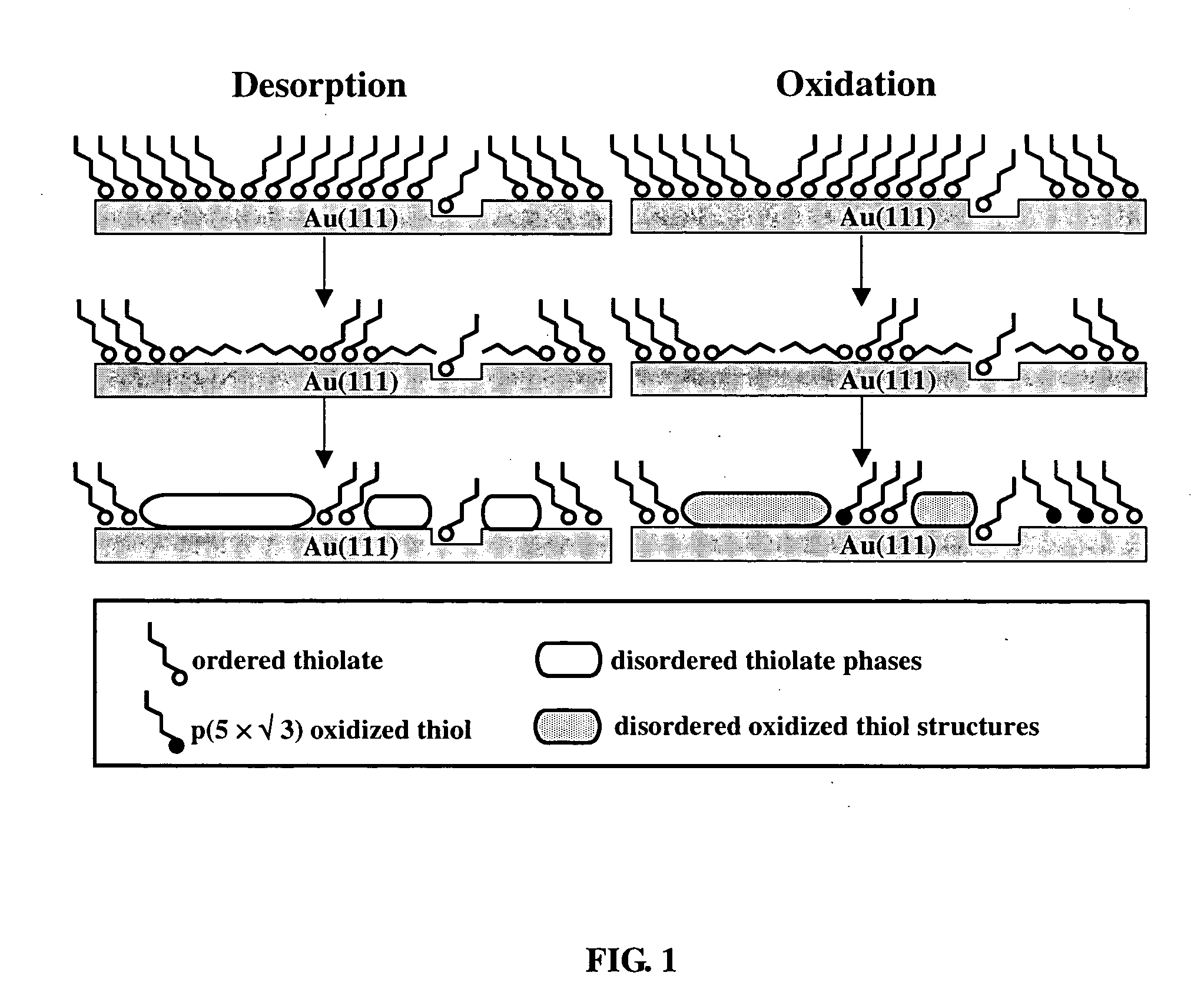
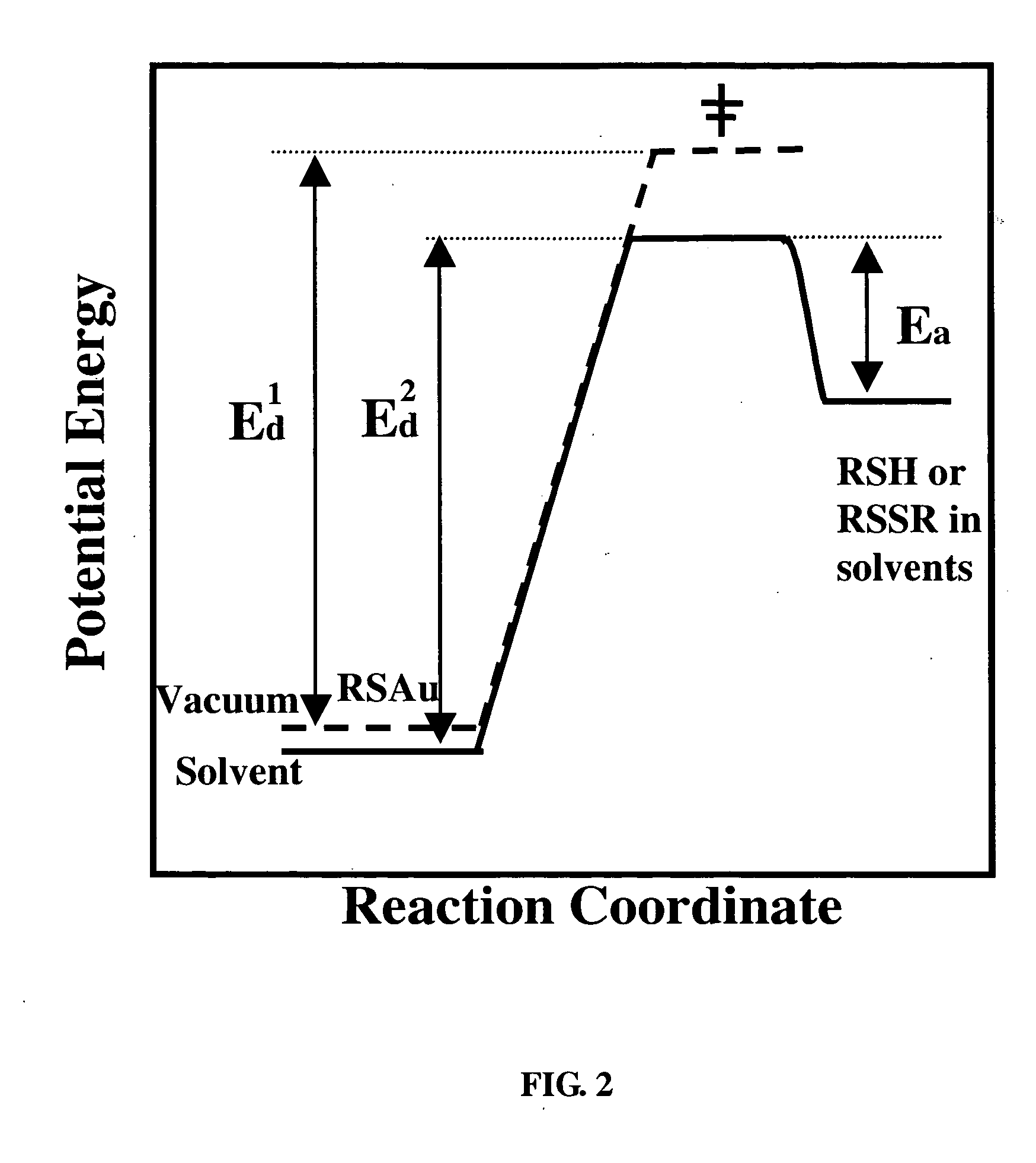
Self-assembled monolayers and other solid support / surface-layer systems are widely used as resists for nanofabrication because of its closely packed structure, low defect density, and uniform thickness. However these resists suffer the drawback of low stability in liquid due to desorption and / or oxidation induced desorption. Stabilized solid support / surface-layer systems and methods of preserving the integrity and structure of self-assembled monolayers on solid surfaces are provided. The method involves adding small amount of amphiphilic molecules, such as DMF and DMSO, into aqueous solutions as preserving media. These molecules adhere favorably to defect sites within monolayers and inhibit the initiation of both known degradation pathways: oxidation and desorption. Also provided are stabilized systems including the solid support / surface-layer system and stabilizing solution, as well as kits of stabilizing solutions for use with various systems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
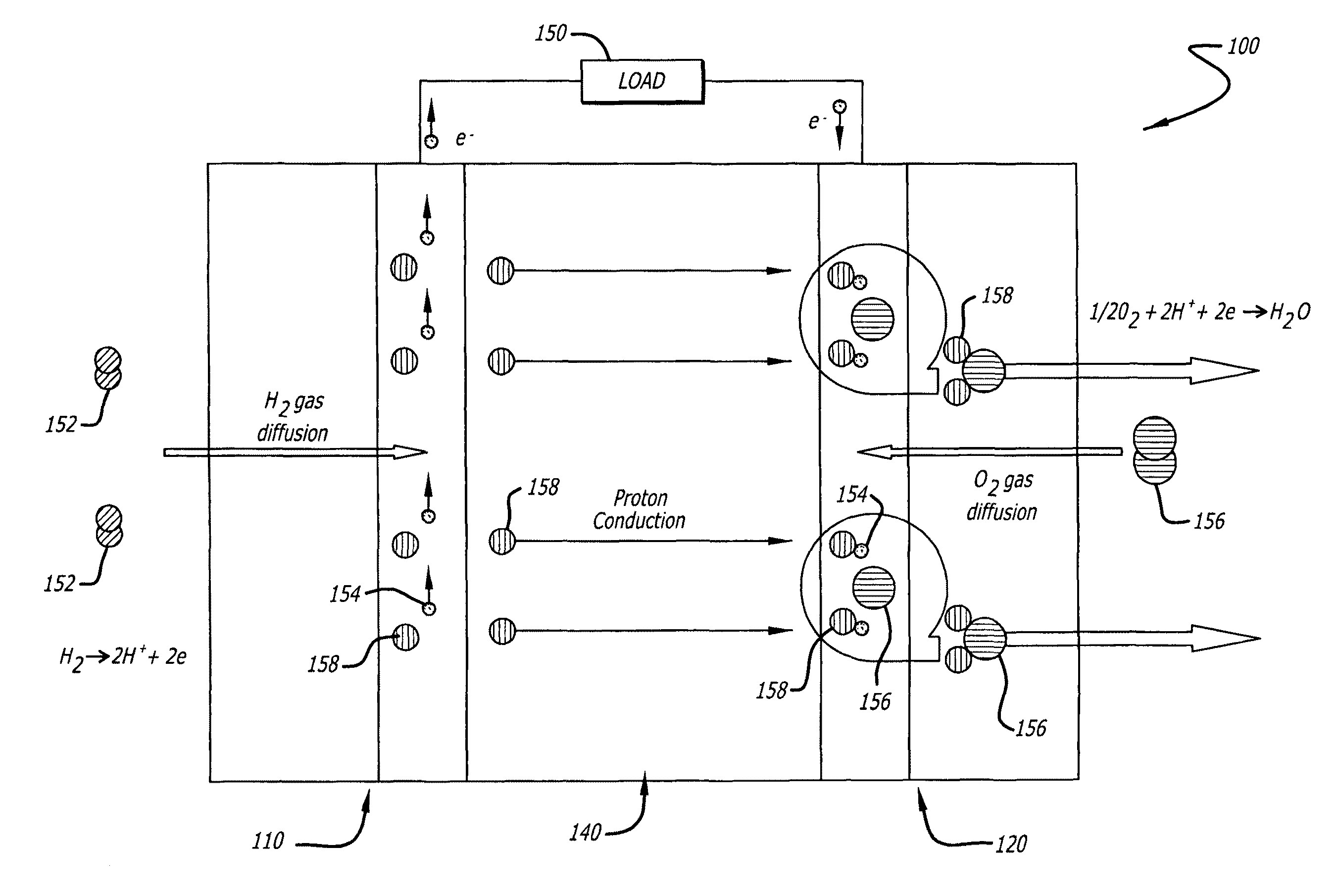
Platinum and Platinum Based Alloy Nanotubes as Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells
ActiveUS20090220835A1Easy to chargeEnhances mass transportationMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsDegradation pathwayAlloy
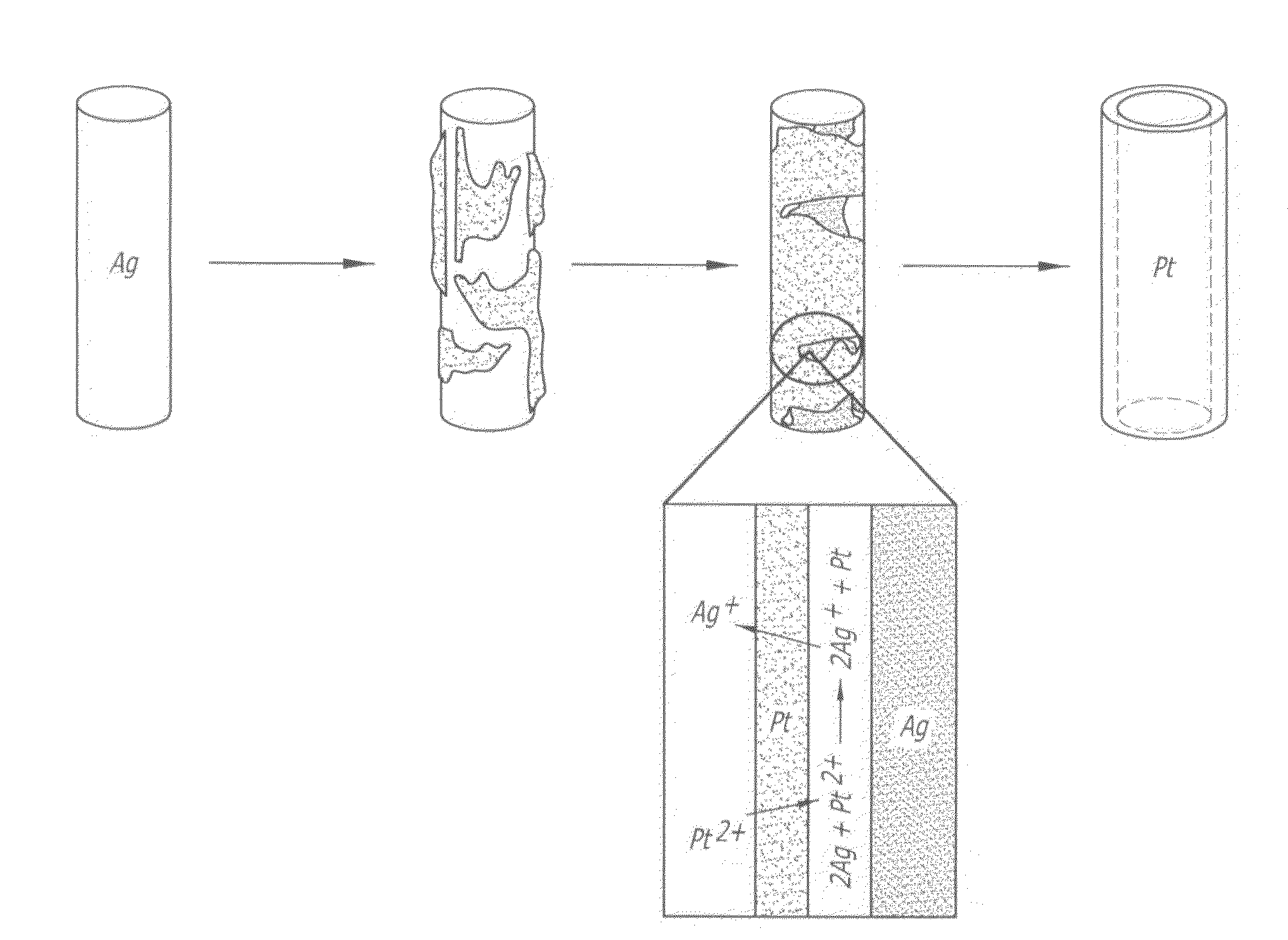
Electrocatalyst durability has been recently recognized as one of the most important issues that have to be addressed before the commercialization of the proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). The present invention is directed to a new class of cathode catalysts based on supportless platinum nanotubes (PtNTs) and platinum alloy nanotubes, for example, platinum-palladium nanotubes (PtPdNTs), that have remarkable durability and high catalytic activity. Due to their unique combination of dimensions at multiple length scales, the platinum nanotubes of the present invention can provide high platinum surface area due to their nanometer-sized wall thickness, and have the potential to eliminate or alleviate most of the degradation pathways of the commercial carbon supported platinum catalyst (Pt / C) and unsupported platinum-black (PtB) as a result of their micrometer-sized length. The platinum nanotube catalysts of the present invention asymptotically approach a maximum of about twenty percent platinum surface area loss in durability test, while the commercial PtB and Pt / C catalysts lose about fifty-one percent and ninety percent of their initial surface area, respectively. Moreover, the PtNT and PtPdNT catalysts of the present invention show higher mass activity and much higher specific activity than commercial Pt / C and PtB catalysts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of acetylglucosamine and application thereof
ActiveCN103060252AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDegradation pathwayGram
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of acetylglucosamine and application of the bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria with high yield of the acetylglucosamine. Bacillus subtilisi 168 serves as an original strain. On the basis that homologous recombination knocks out acetylglucosamine glucose transporter protein coding gene (nagP), acetylglucosamine deacetylation enzyme coding gene (nag A) and acetylglucosamine deamination enzyme coding gene (nag B) are further knocked out so as to block up acetylglucosamine degradation pathway in host bacteria. In the host bacteria without the nag A and the nag B, acetylglucosamine acetylase coding gene (GNA1) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C is overly expressed, an acetylglucosamine synthetic route is strengthened to produce recombination bacillus subtilis for producing acetylglucosamine, yield reaches 1.23 grams per liter, and the method is a basis for metabolic engineering to further modify bacillus subtilis to produce glucosamine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods and compositions for nucleic acid and protein payload delivery
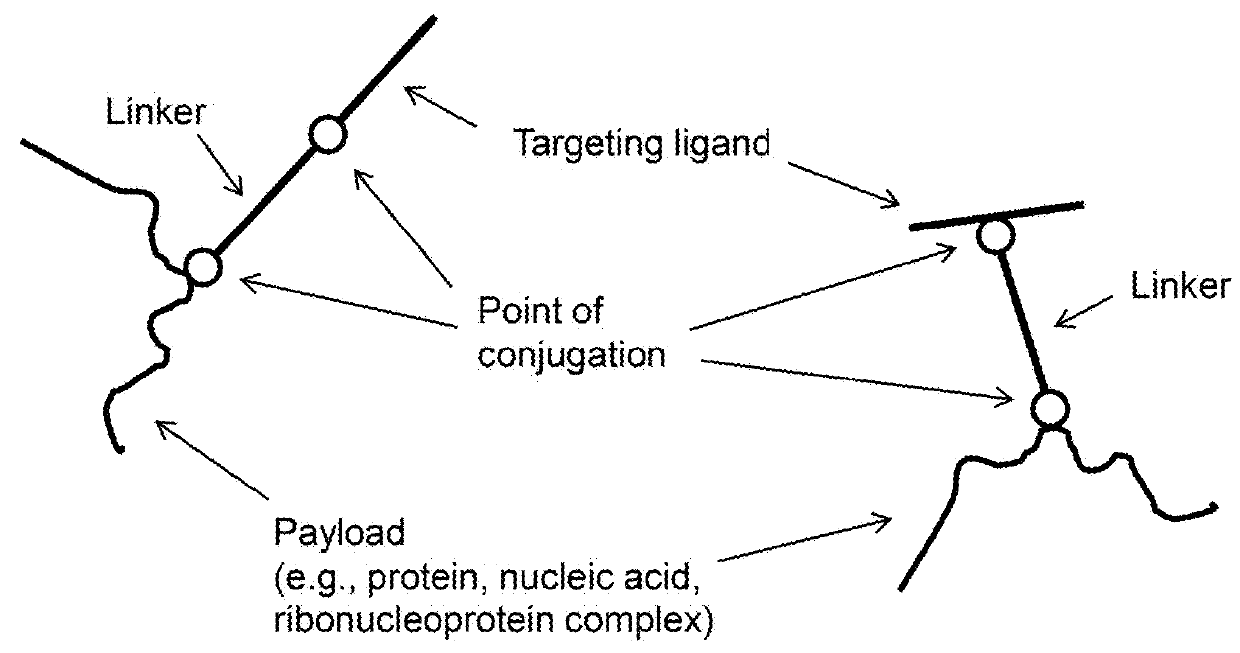
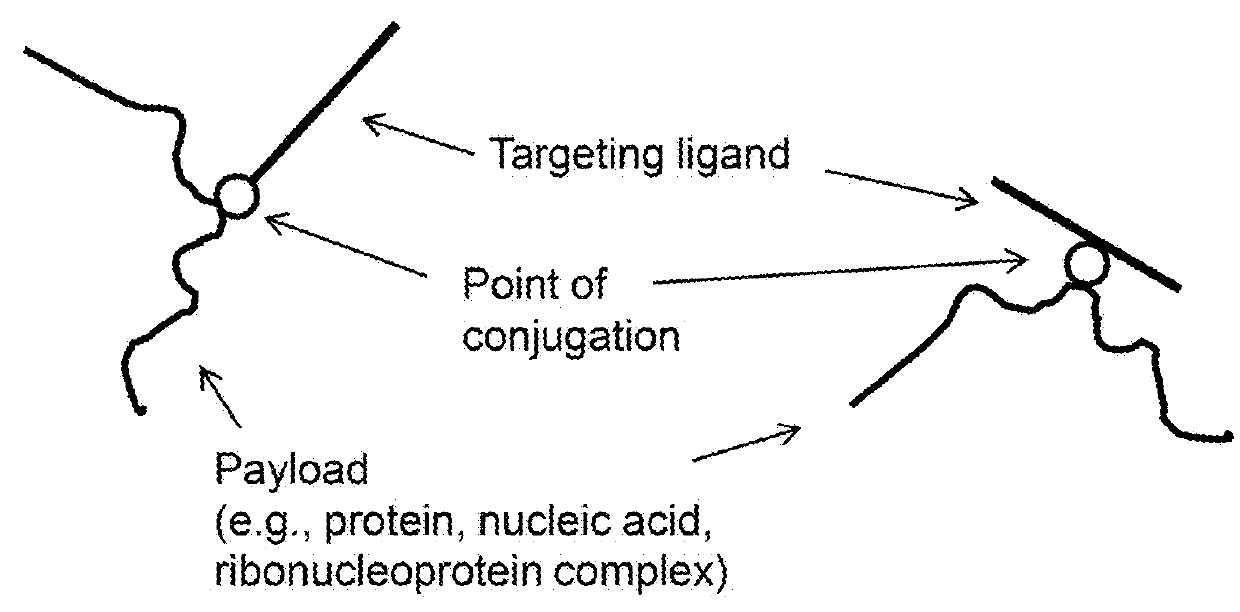
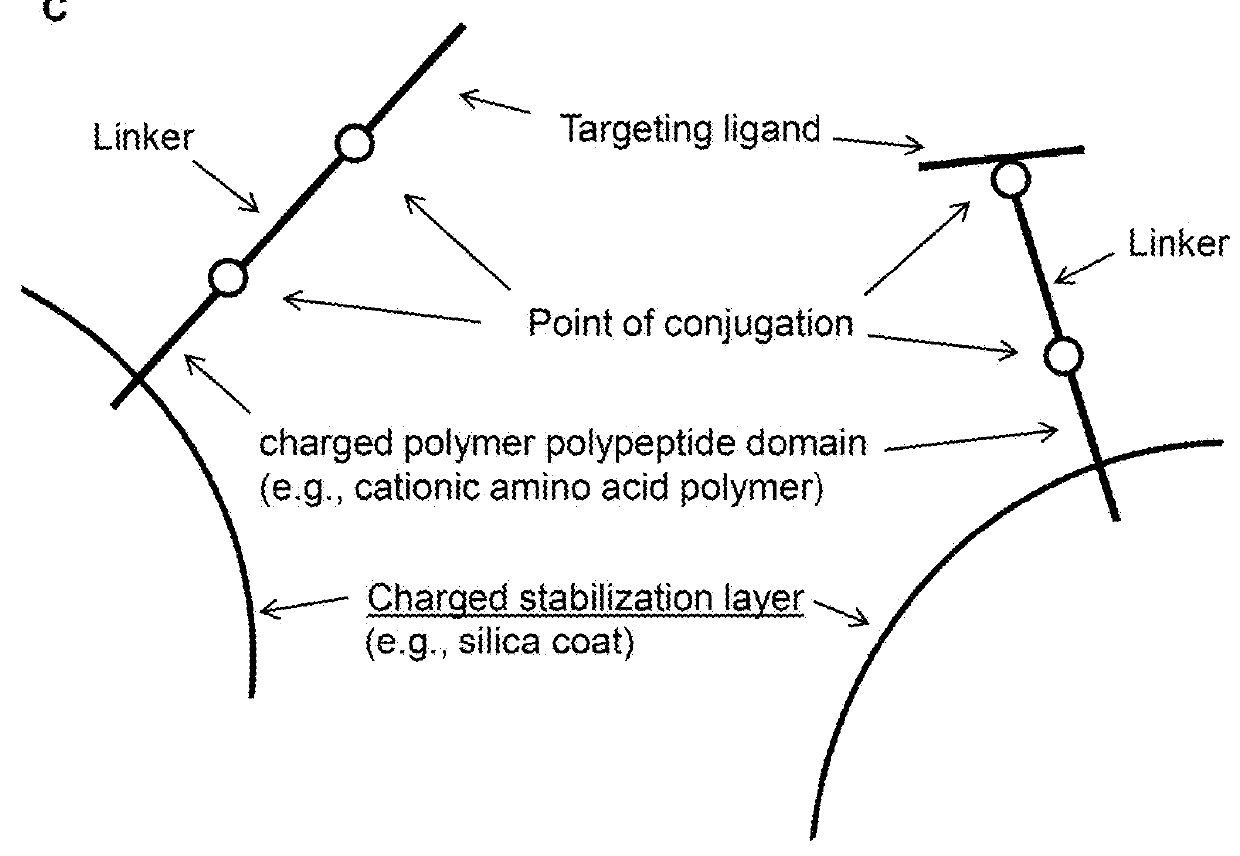
Provided are methods and compositions for delivering a nucleic acid, protein, and / or ribonucleoprotein payload to a cell. Also provided are delivery molecules that include a peptide targeting ligand conjugated to a protein or nucleic acid payload (e.g., an siRNA molecule), or conjugated to a charged polymer polypeptide domain (e.g., poly-arginine such as 9R or a poly-histidine such as 6H, and the like). The targeting ligand provides for (i) targeted binding to a cell surface protein, and (ii) engagement of a long endosomal recycling pathway. As such, when the targeting ligand engages the intended cell surface protein, the delivery molecule enters the cell (e.g., via endocytosis) but is preferentially directed away from the lysosomal degradation pathway.
Owner:LIGANDAL INC
Sewage treatment assessment method and device guided by tracing analysis of particular pollutants
InactiveCN107944601AQuick identificationRealize the whole process traceabilityWater treatment parameter controlGeneral water supply conservationDegradation pathwayWater quality
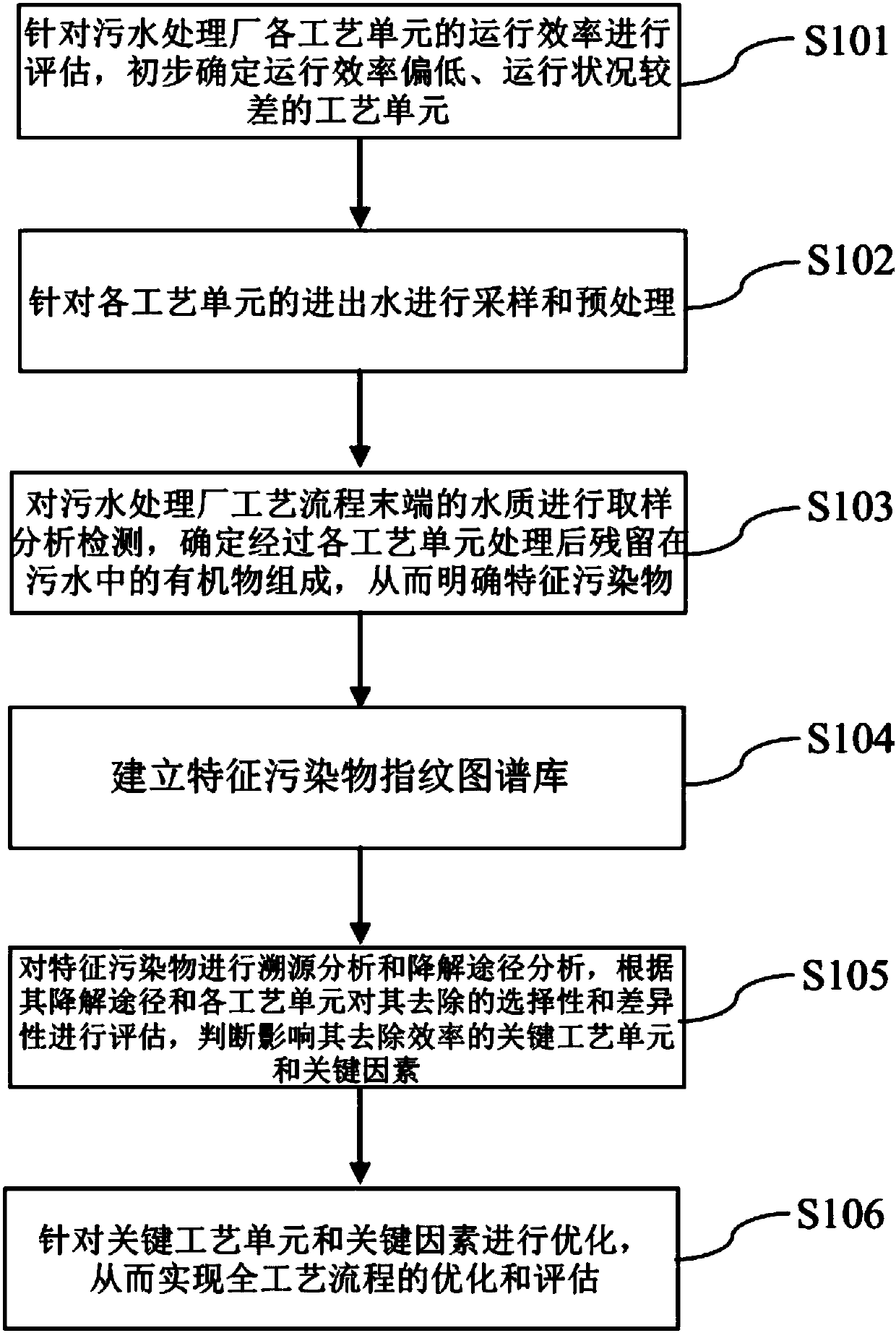
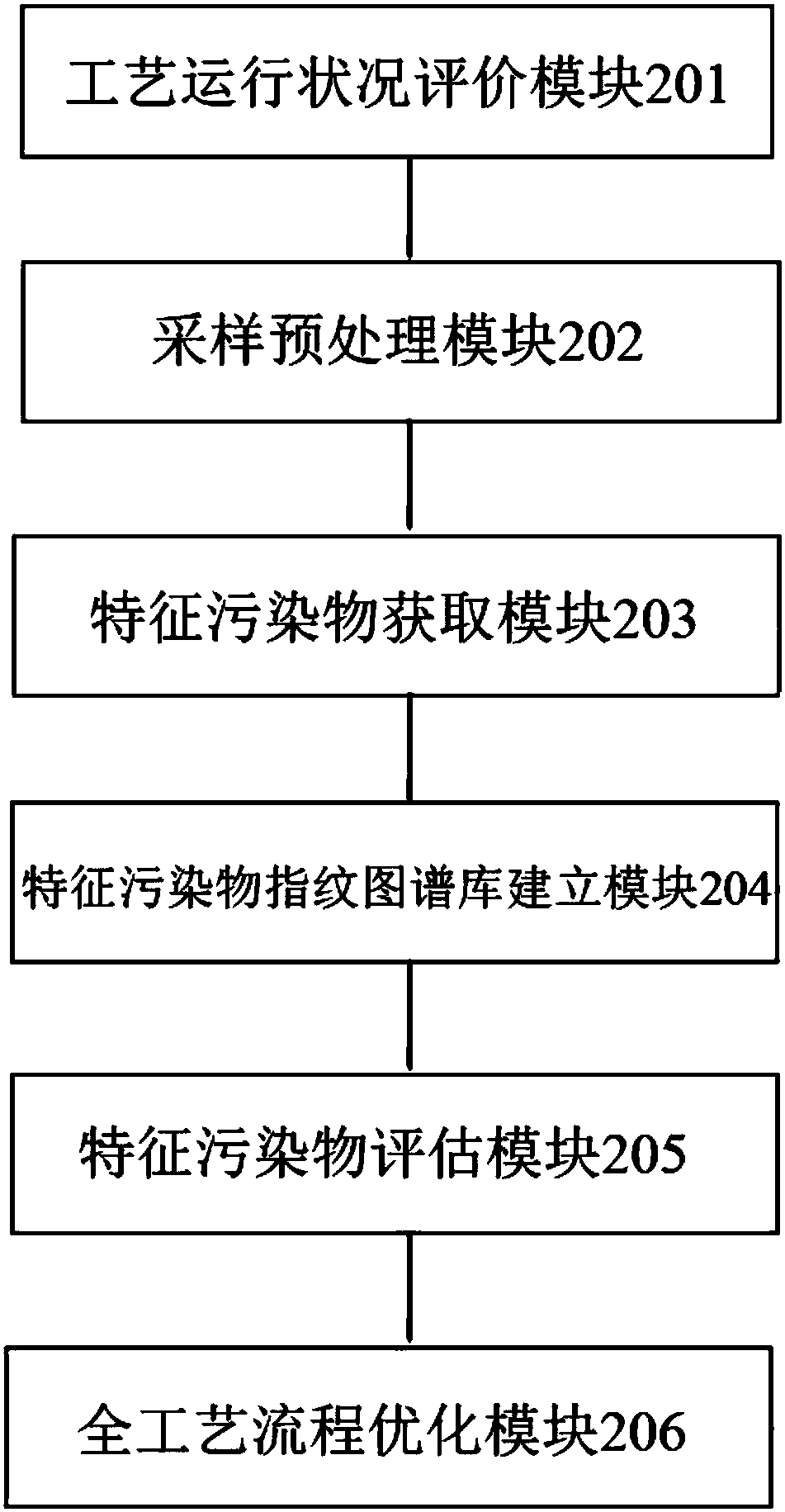
The invention provides a sewage treatment assessment method and device guided by tracing analysis of particular pollutants. The method comprises the steps that assessment is performed according to operation efficiency of all process units of a sewage treatment plant; sampling and preprocessing are performed according to inflow water and outflow water of all the process units; sampling analysis detection is performed on water quality at the tail end of the process flow of the sewage treatment plant, so that the particular pollutants are clarified; a particular pollutant fingerprint graph library is established; tracing analysis and degradation pathway analysis are performed on the particular pollutants, and key process units and key factors influencing removal efficiency of the particular pollutants are judged; and optimization is performed according to the key process units and the key factors, so that optimization and assessment of the whole process flow are realized. Through the sewage treatment assessment method and device, key pollution factors restricting efficiency improvement in the sewage treatment process can be accurately positioned, degradation efficiency changes of various pollutants along the sewage treatment flow are determined, process operation optimization measures and source reduction and control measures are proposed pertinently, and therefore the timelinessand effectiveness of sewage treatment system assessment are improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
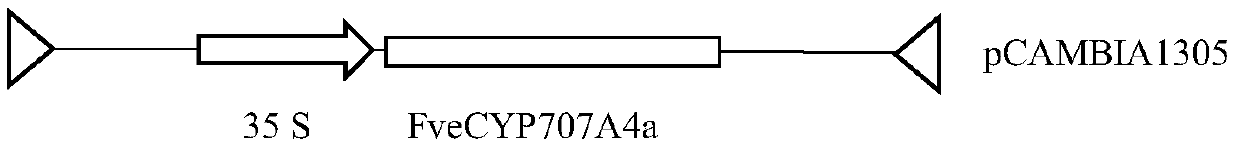
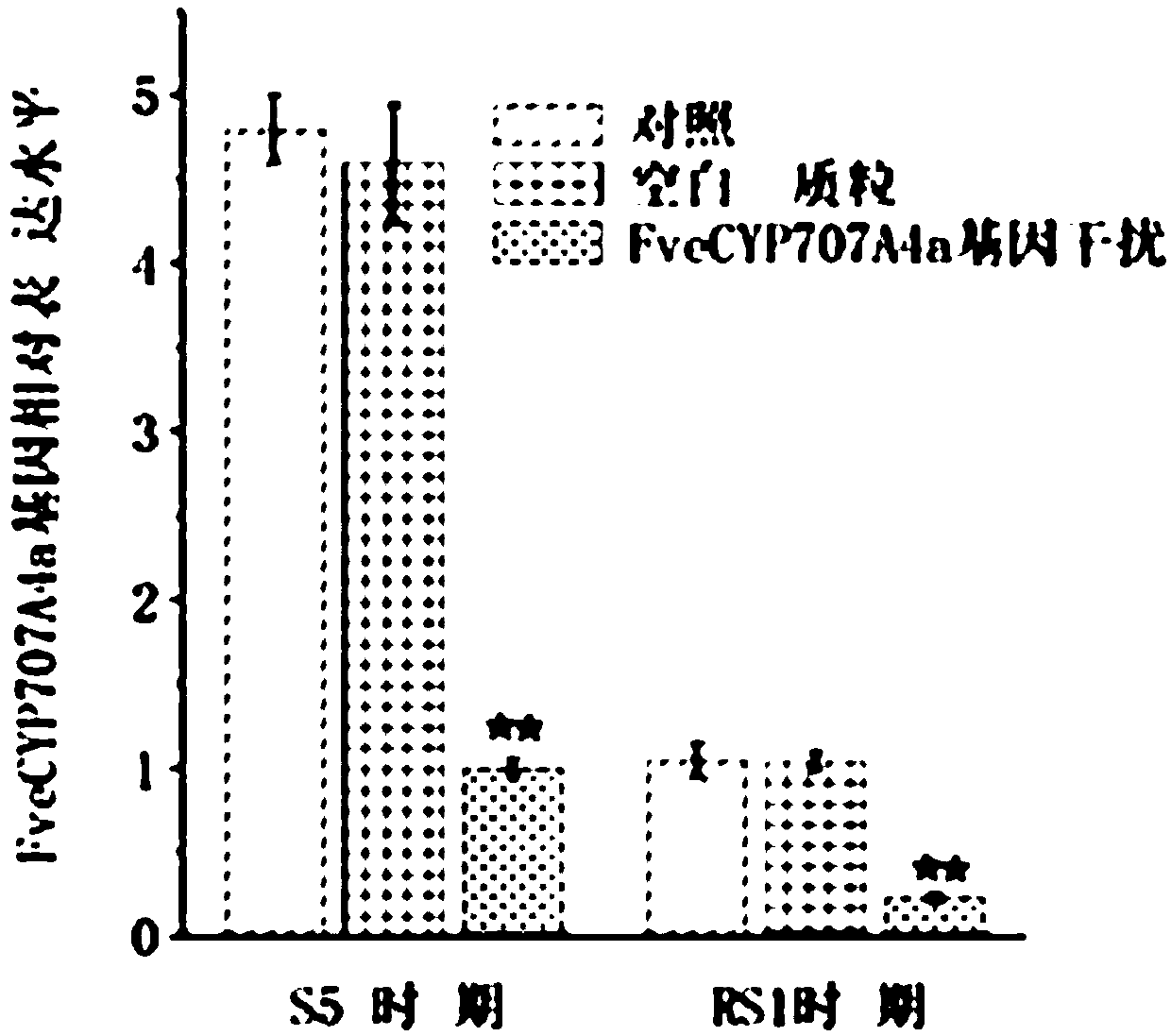
Fragaria X ananassa ABA degradation pathway key enzyme FveCYP707A4a gene and application thereof
InactiveCN109576288AReduce sizeAvoid expansionOxidoreductasesFermentationFragariaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a fragaria X ananassa ABA degradation pathway key enzyme FveCYP707A4a gene and application thereof. The application is characterized in that a PCR amplification primer pair isdesigned according to a CDS sequence of the fragariaX ananassa ABA degradation pathway key enzyme FveCYP707A4a gene; PCR amplification is implemented to obtain a FveCYP707A4a gene complete sequence bytaking Fragaria vesca achene cDNA as a template and using the PCR amplification primer pair; a gene for controlling the fragaria X ananassa fruit size is obtained; a silent vector or an overexpression vector is built by using the FveCYP707A4a gene complete sequence; the vector is mixed with an agrobacterium for soaking fragaria X ananassa, so that fragaria X ananassa fruit expansion is restrained, and free ABA content in fragaria X ananassa fruit is lowered in order to adjust the development and maturation of the fragaria X ananassa fruit.
Owner:浙江五合生物科技有限公司
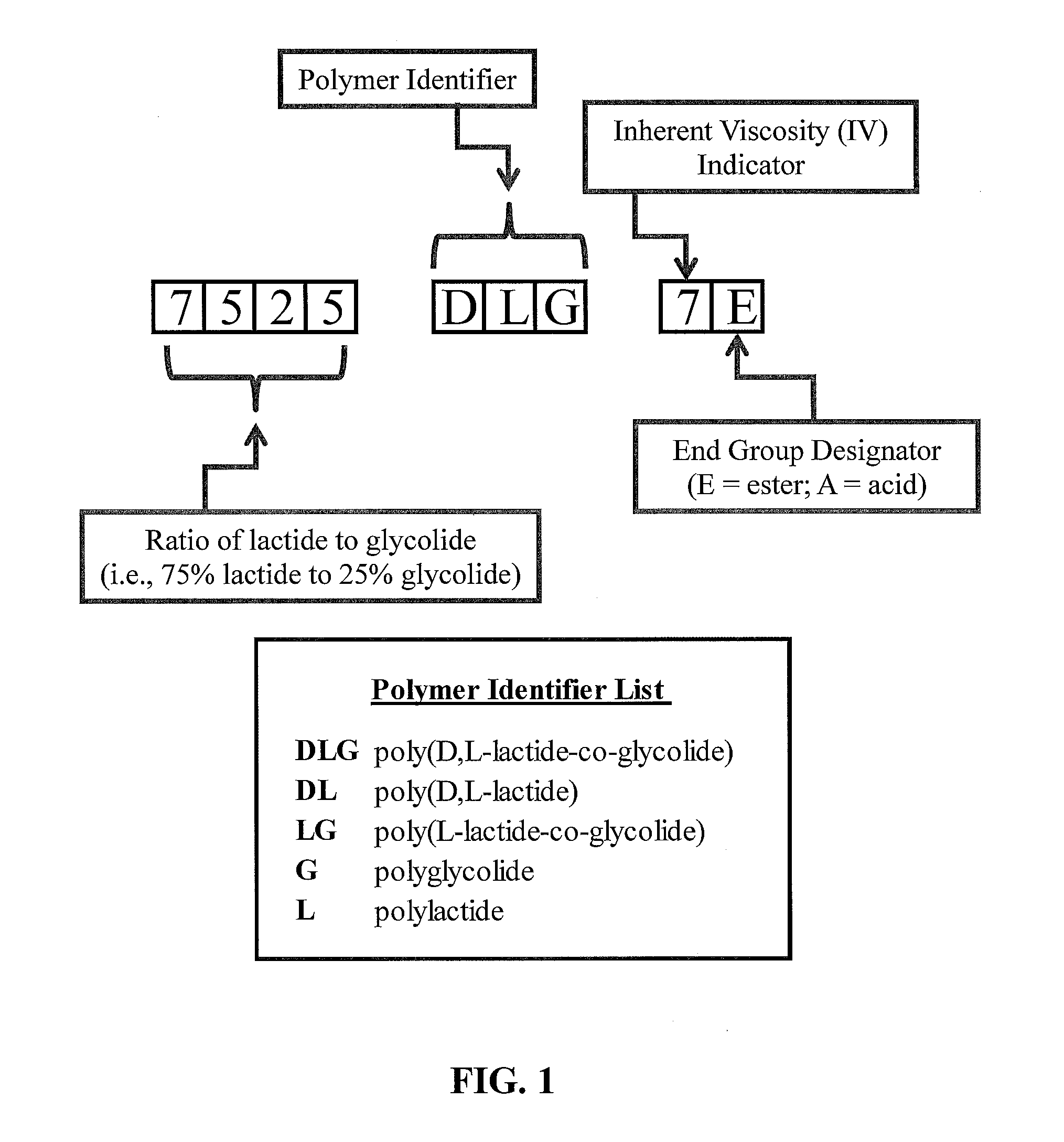
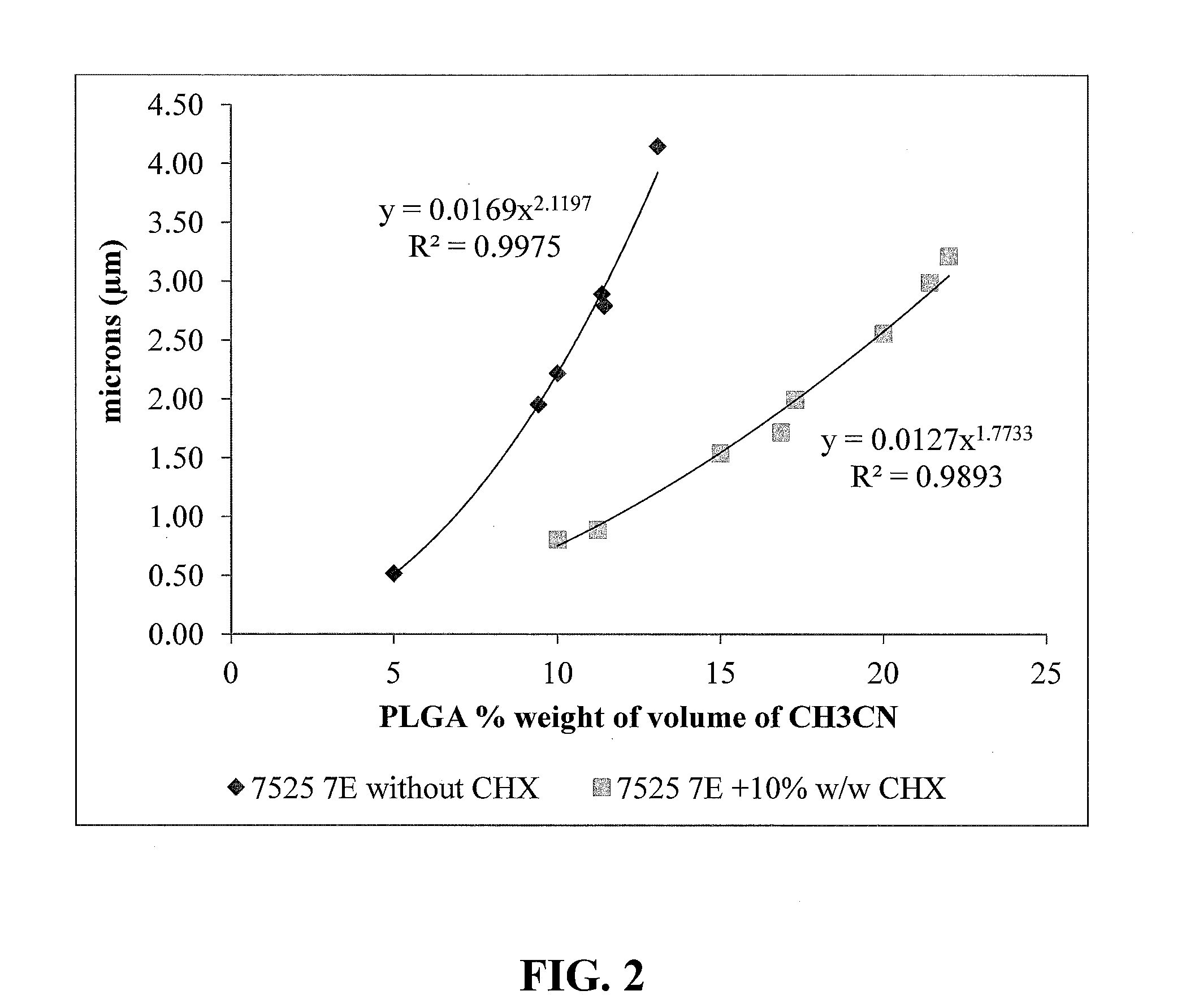
Composition of and method for forming reduced viscosity polymeric coatings
The present invention is directed to polymeric coating formulations in which addition of an antimicrobial to a solution, containing solvent and polymer, significantly alters polymer entanglements. Benefits include alternative routes to, and customization of the polymer's degradation pathways. The dramatic entanglement changes also provide manufacturing advantages such as ease of stirring, pumping, and spraying. Furthermore, the coatings may have faster drying times, less shrinkage, more complete fill, and a more even coat for a given thickness. Methodology for production of coating formulations of the desired properties and their use to provide antimicrobial coatings is also described.
Owner:BACTERIN INT
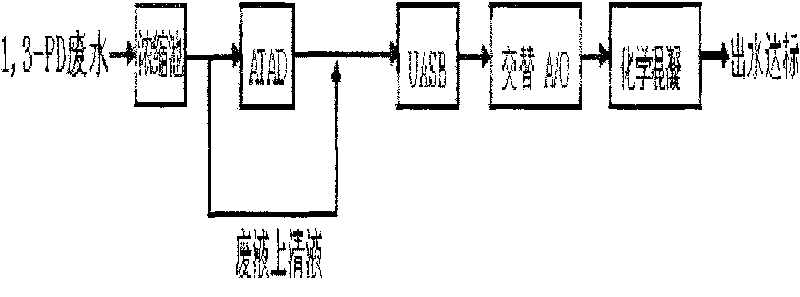
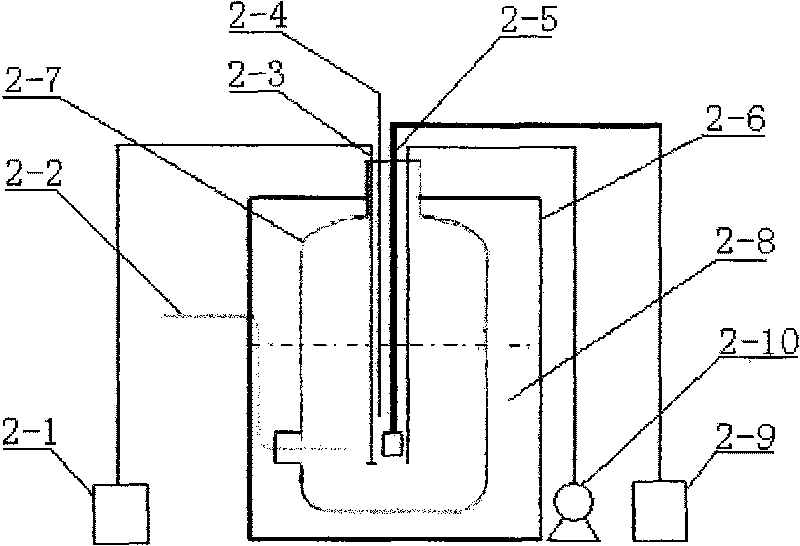
Biochemical comprehensive treatment method for 1, 3-propylene glycol fermentation organism waste water
InactiveCN101693583AHigh removal rateHighlight substantiveTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteActivated sludge
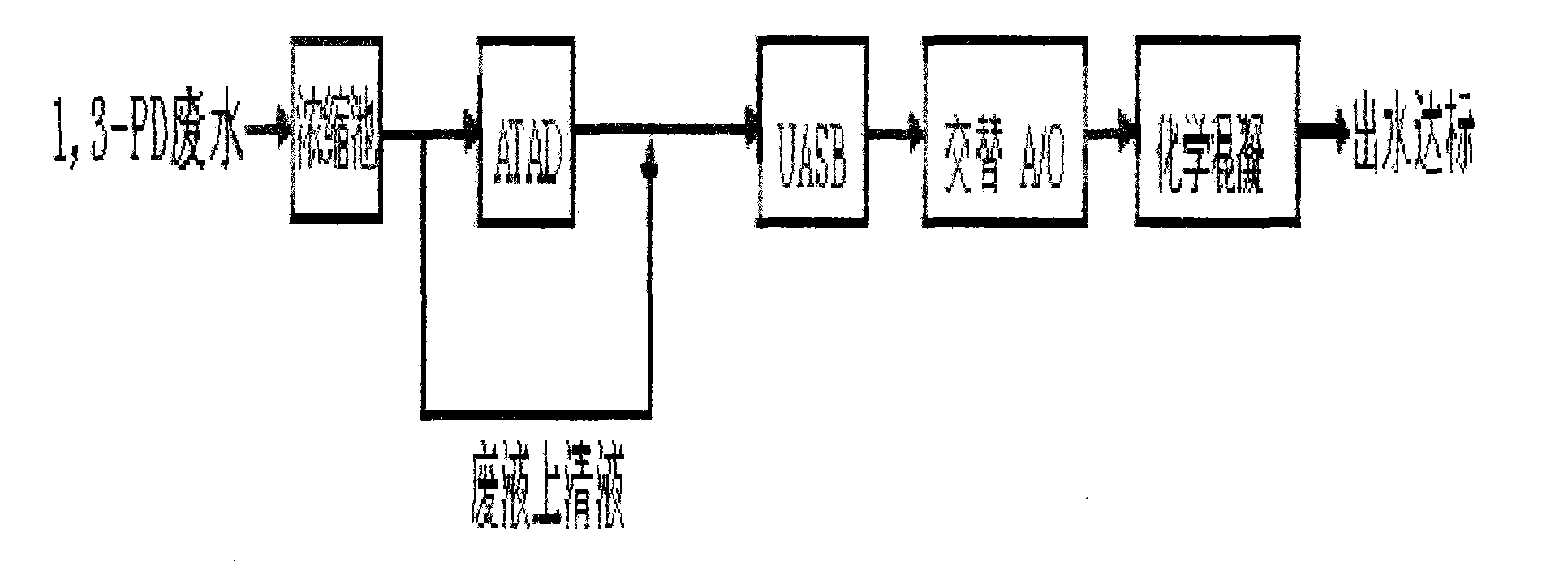
Disclosed is a biochemical comprehensive treatment method for 1, 3-propylene glycol fermentation organism waste water. The biochemical comprehensive treatment method includes concentration of fermentation organism, ATAD, UASB, alternating A / O and chemical coagulation; culturing and domesticating thermophilic bacteria inside an ATAD reactor first, then culturing and domesticating anaerobic activated sludge inside a UASB reactor, and finally culturing and domesticating aerobic activated sludge inside an alternating A / O pool. During a formal experiment, waste water is treated by the ATAD first so as to improve biochemical property of waste liquor and enable viral fermentation organism to be converted into substances with biochemical energy, ATAD effluent is treated by the UASB so as to further lower down concentration of organism, methane produced in the process is recycled, and final UASB effluent can achieve the B standard of first-class emission standards of national standard GB18918-2002 after treated by the alternating A / O technique and the chemical coagulation, thereby realizing safe emission and providing a novel degradation pathway for the 1, 3-propylene glycol fermentation organism waste water.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
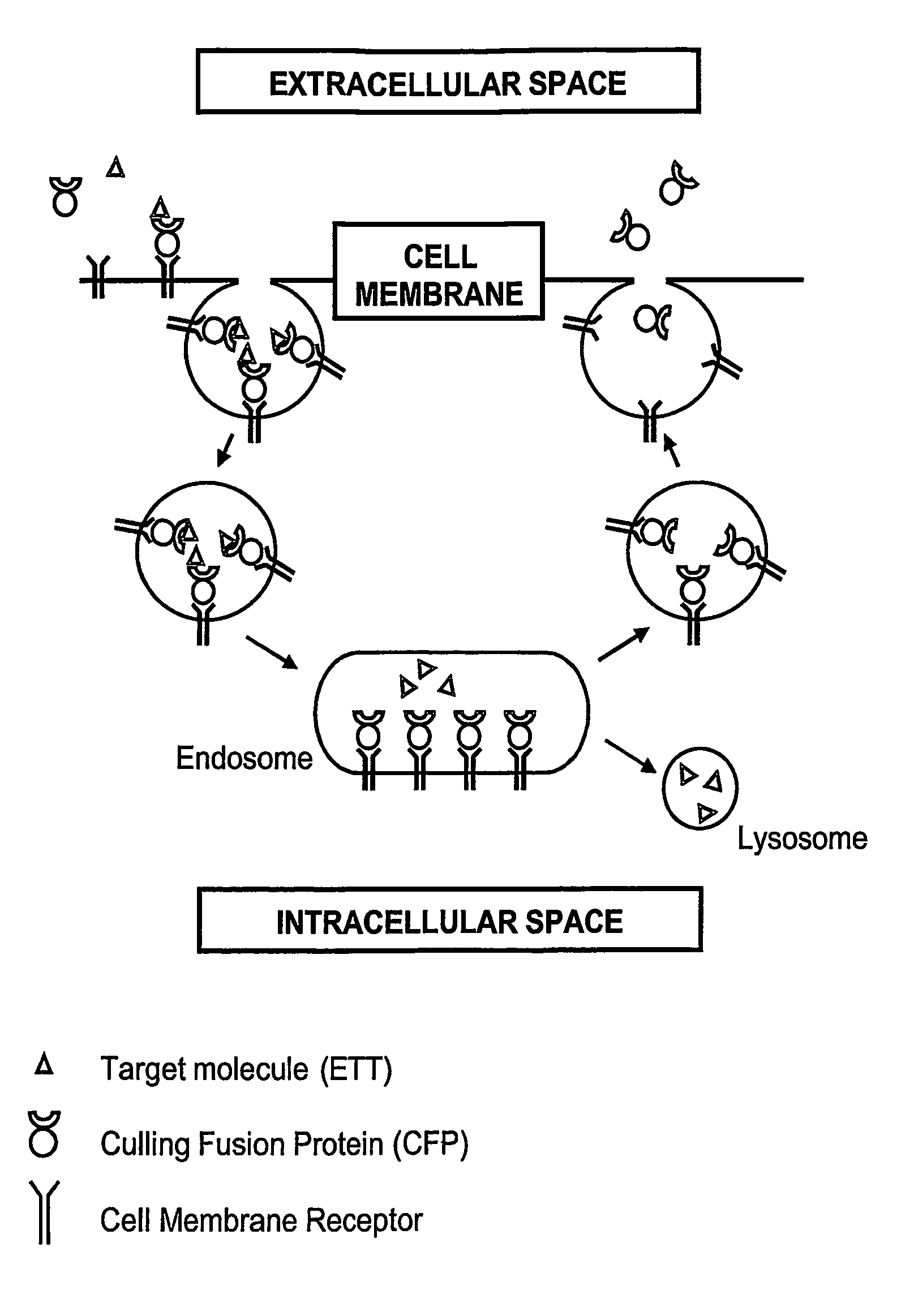
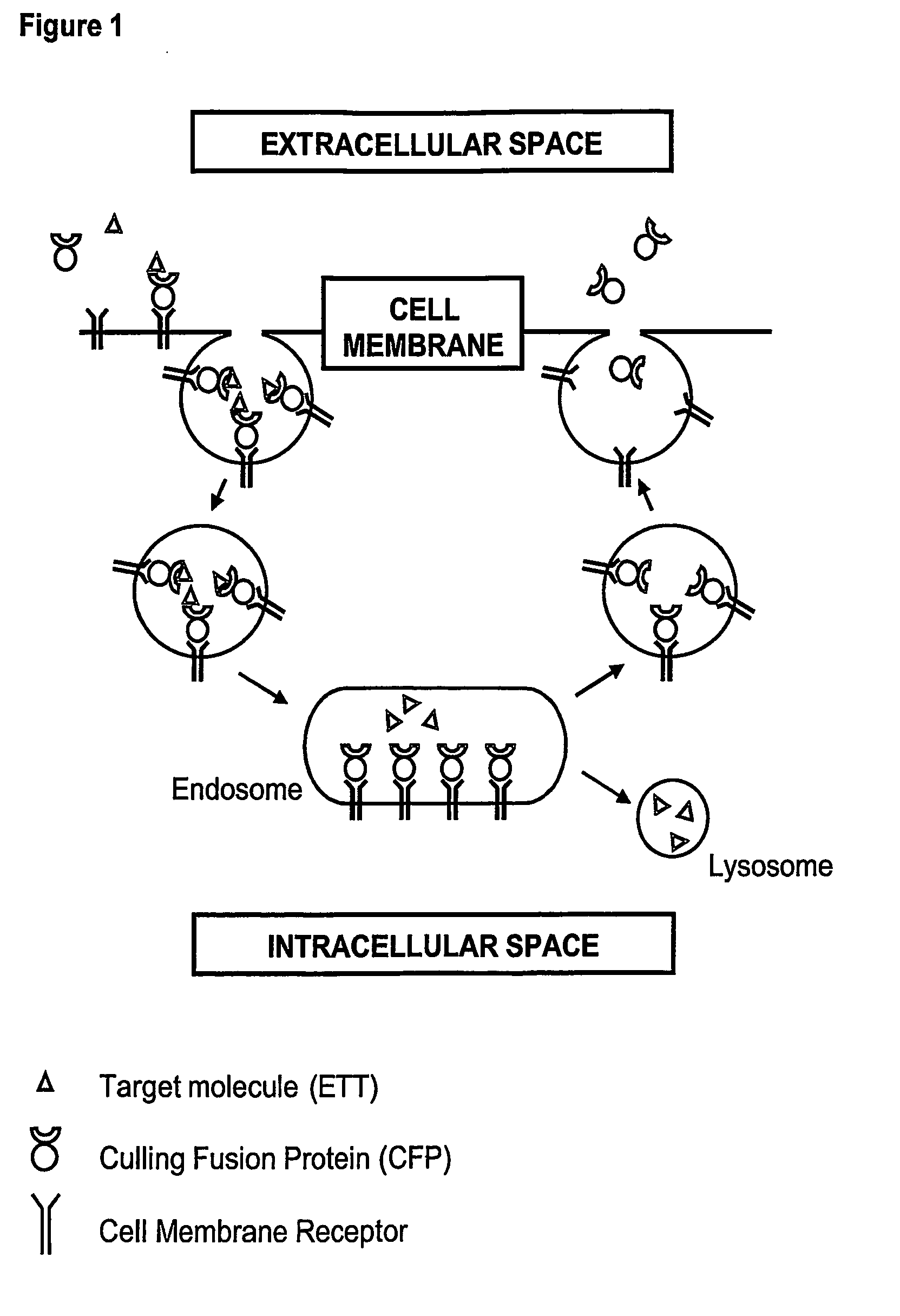
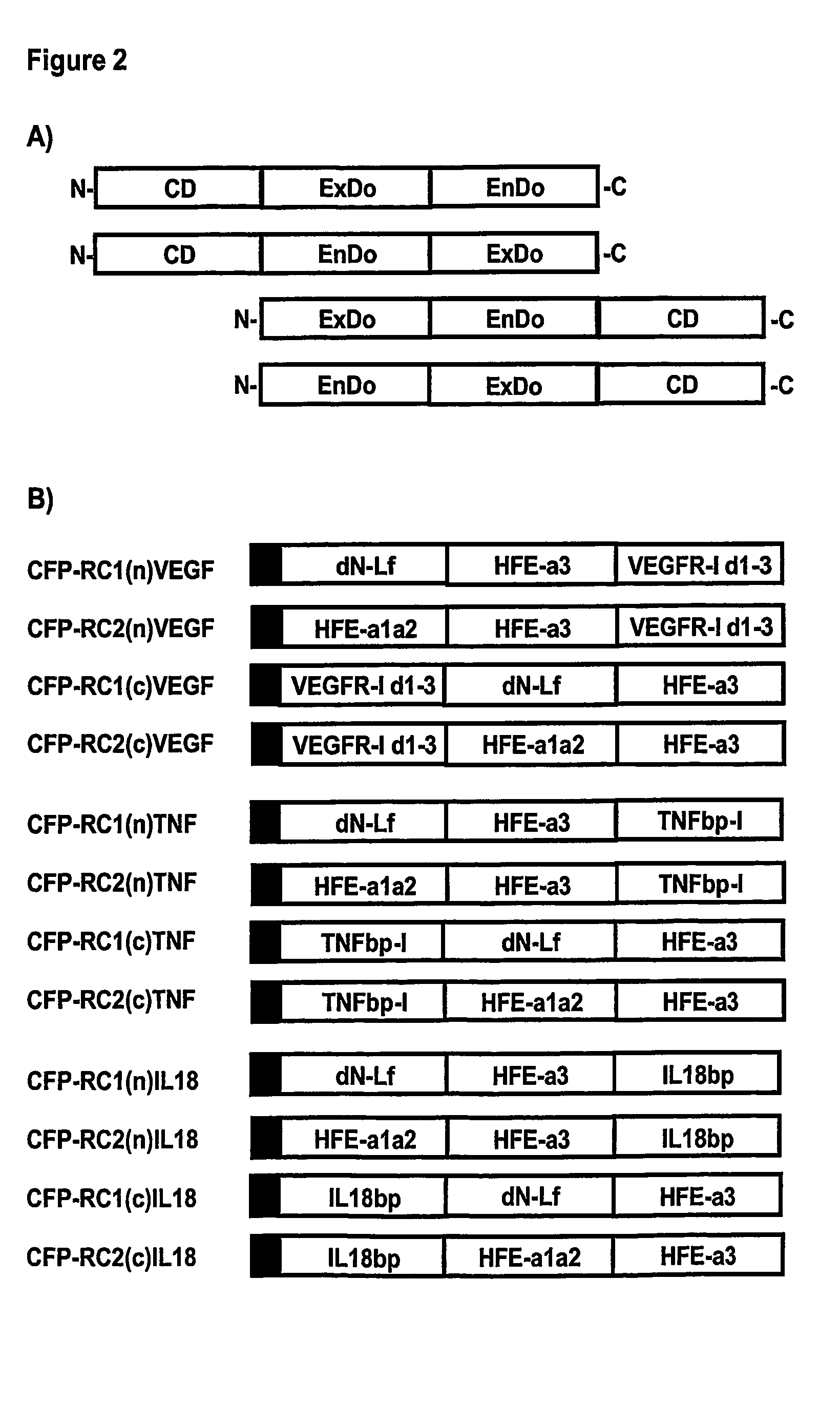
Novel Therapeutic Fusion Proteins
InactiveUS20070264236A1Reduce concentrationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDegradation pathwayExocytosis
The present invention provides novel therapeutic molecules called Culling Fusion Proteins (CFPs) that allow the continuous removal of therapeutic targets from extracellular space by exploiting the endosome / lysosome intracellular degradation pathway, and the exocytotic pathway in a combined manner. The products of the invention, by appropriately utilizing the cellular endocytosis and exocytosis mechanism, can be recycled multiple times by cells to eliminate undesired molecules, therefore such therapeutic molecules can be administered at low concentration.
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Method for producing long-chain binary acid by using recombinant escherichia coli strain
InactiveCN107022513AHigh yieldOvercome the conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDegradation pathway
The invention discloses a method for producing long-chain binary acid by using a recombinant escherichia coli strain. The method comprises the following steps of knocking out or weakening a fatty acid beta-oxidation and degradation pathway gene in escherichia coli to establish the recombinant escherichia coli; using the recombinant escherichia coli to express fatty acid synthetase and a fatty acid synthesizing regulatory gene, and utilizing sustained carbon source glucose as a raw material to enable a cell to accumulate long-chain fatty acid; finally, expressing fatty acid hydroxylase, fatty alcohol, aldehyde reductase and the like on the basis, and gradually converting the accumulated long-chain fatty acid step by step, so as to obtain the long-chain binary acid. The method has the advantages that the defects of the prior art are overcome; in the whole preparation process, the reaction conditions are mild, the technology is simple, the environment-friendly effect is realized, and the product yield is higher.
Owner:河北美邦工程科技股份有限公司
Fermentation process research of bacillus laterosporus capable of degrading organophosphorus pesticide
InactiveCN109321631AThe effect of the research experiment is obviousExperiment operation is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementDegradation pathwayBacillus laterosporus
The invention provides a fermentation process research of bacillus laterosporus capable of degrading organophosphorus pesticide. The fermentation process research is finished by adopting the followingsteps: firstly, preparing seed liquid; secondly, preparing a culture medium of a isocarbophos-containing pesticide and inoculating; thirdly, determining the degradation rate of the isocarbophos; fourthly, researching the characteristics of experimental strains for degrading the organophosphorus pesticide; fifthly, researching the condition of degrading the isocarbophos by using the experimental strains; sixthly, researching the degradation of organophosphorus pesticide enzymes by using the experimental strains; seventhly, researching degradation products and a degradation pathway of the isocarbophos; eighthly, carrying out use safety experiment of the strain. The research provided by the invention researches the degradation effect of the strain on the organophosphorus pesticide accordingto the concentration of pesticide sprayed in farmland, so that the influence of pesticide spraying dose on strain production through biologic bacterial fertilizer and the degradation ability of the strain to the organophosphorus pesticide are further known.
Owner:山东蔚蓝绿源生物科技有限公司
Culture medium additive for preparing autophagosomes-type tumor vaccine and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106635994AInhibition of degradation pathwaysInhibitory activityCulture processCell culture active agentsAntigenDegradation pathway
The invention discloses a culture medium additive for preparing autophagosome-type tumor vaccine. A freeze-dried powder preparation comprises one group of compositions, and the compositions comprise a proteasome inhibitor, an autophagy inducer, a lysosomal alkalifier, an excipient, and an antioxidant. The culture medium additive for preparing autophagy small-body-type tumor vaccine and a preparing method thereof have the remarkable advantages that the additive compositions comprise the proteasome inhibitor, the lysosomal alkalifier and the autophagy inducer which synthesize with one another, on one hand, a proteasome degradation pathway and an autolysosome degradation pathway of a tumour cell can be inhibited simultaneously so that tumour antigens can be preserved; on the other hand, autophagosomes are induced to take shape, thus a large quantity of tumour antigens are preserved in the autophagosomes, and then the autophagosomes-type tumor vaccine can be prepared by extracting the autophagosomes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
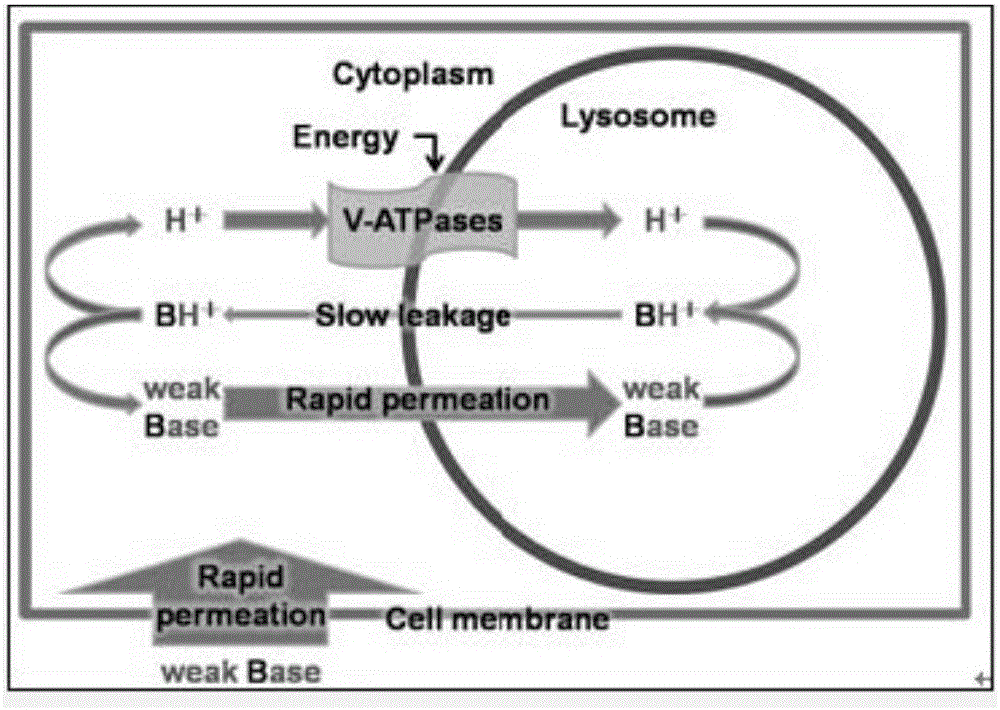
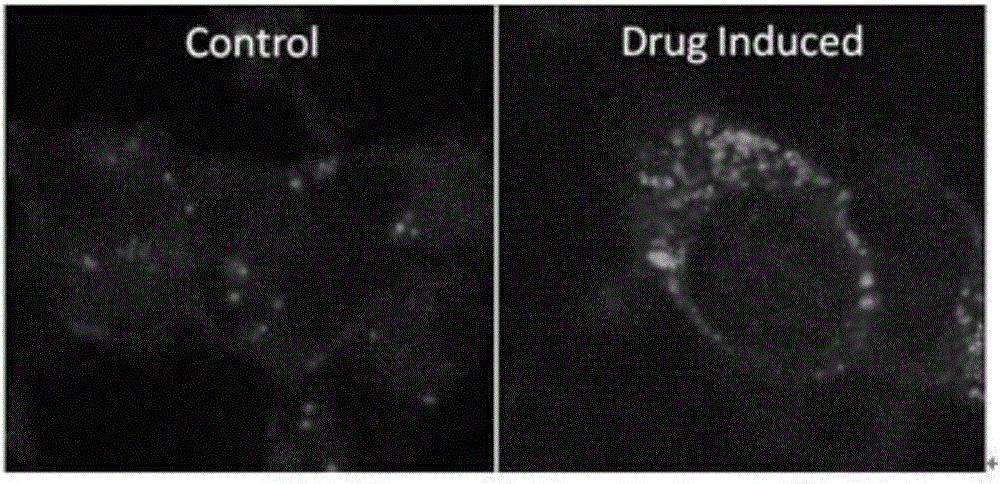
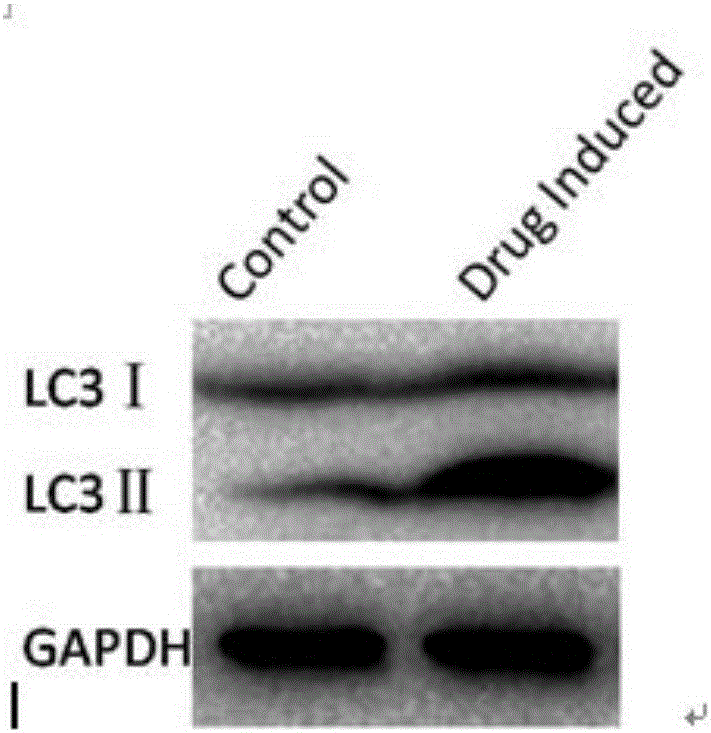
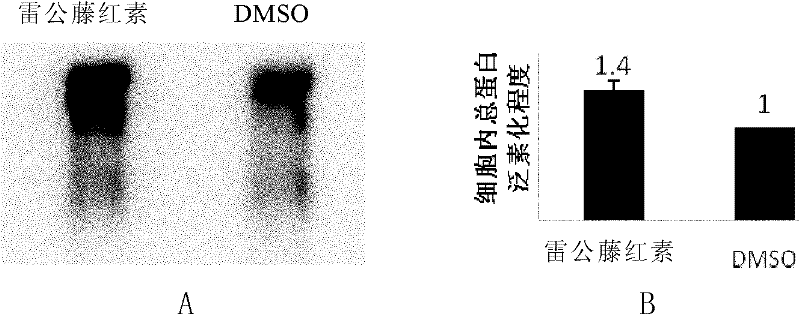
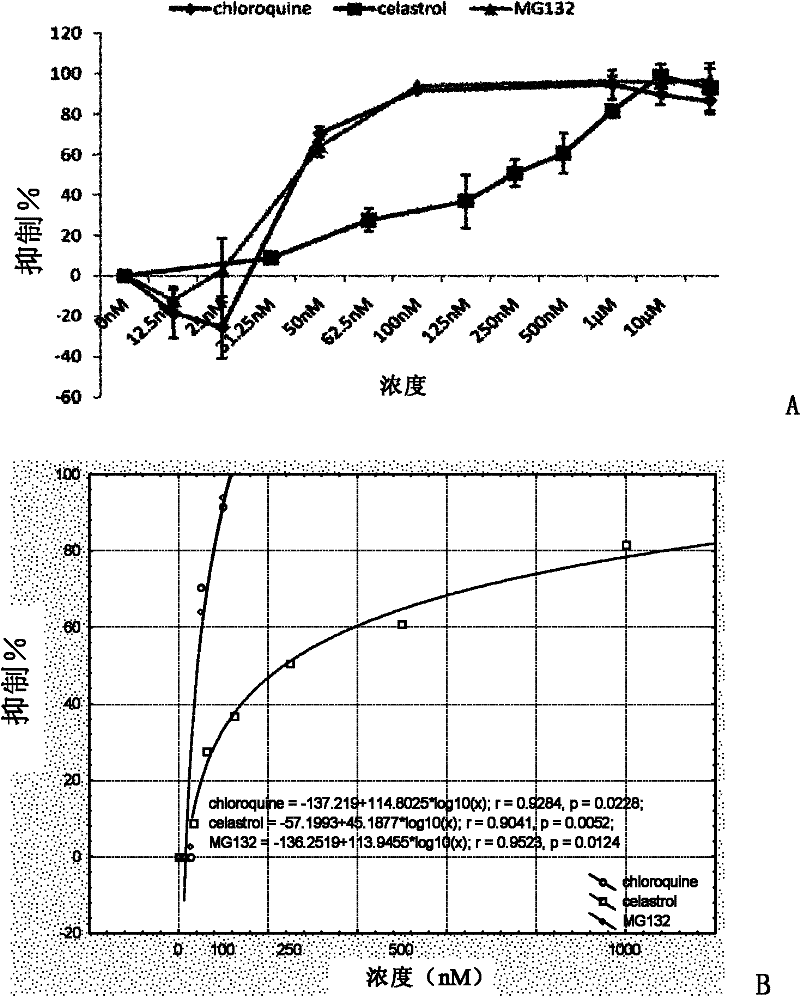
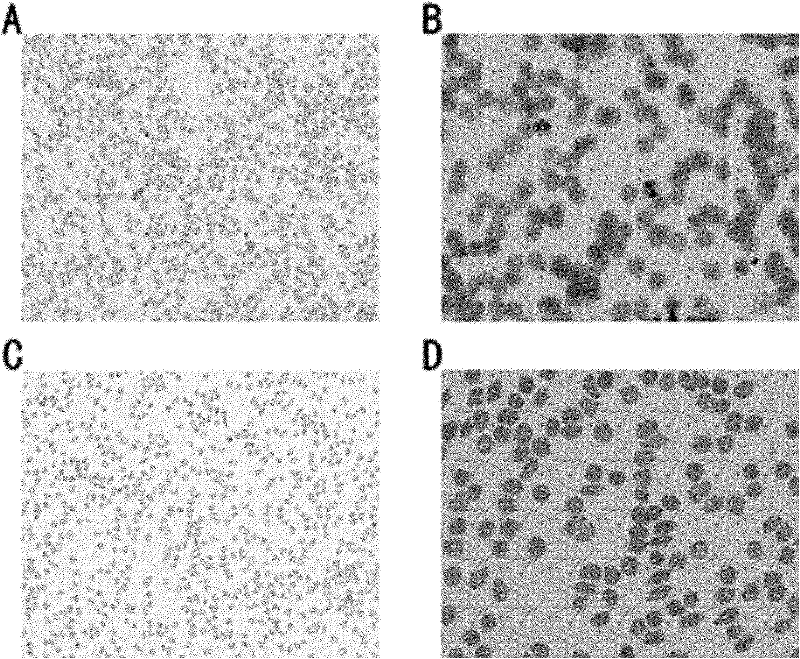
Antimalarial drug taking protein degradation pathway as target
The invention relates to an antimalarial drug taking a protein degradation pathway as a target. Particularly, the invention relates to use of tripterine or derivatives of the tripterine in the preparation of drugs for treating malaria and use of the tripterine or the derivatives of the tripterine in the preparation of drugs for the inhibition of proteasome. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing the tripterine or the derivatives of the tripterine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
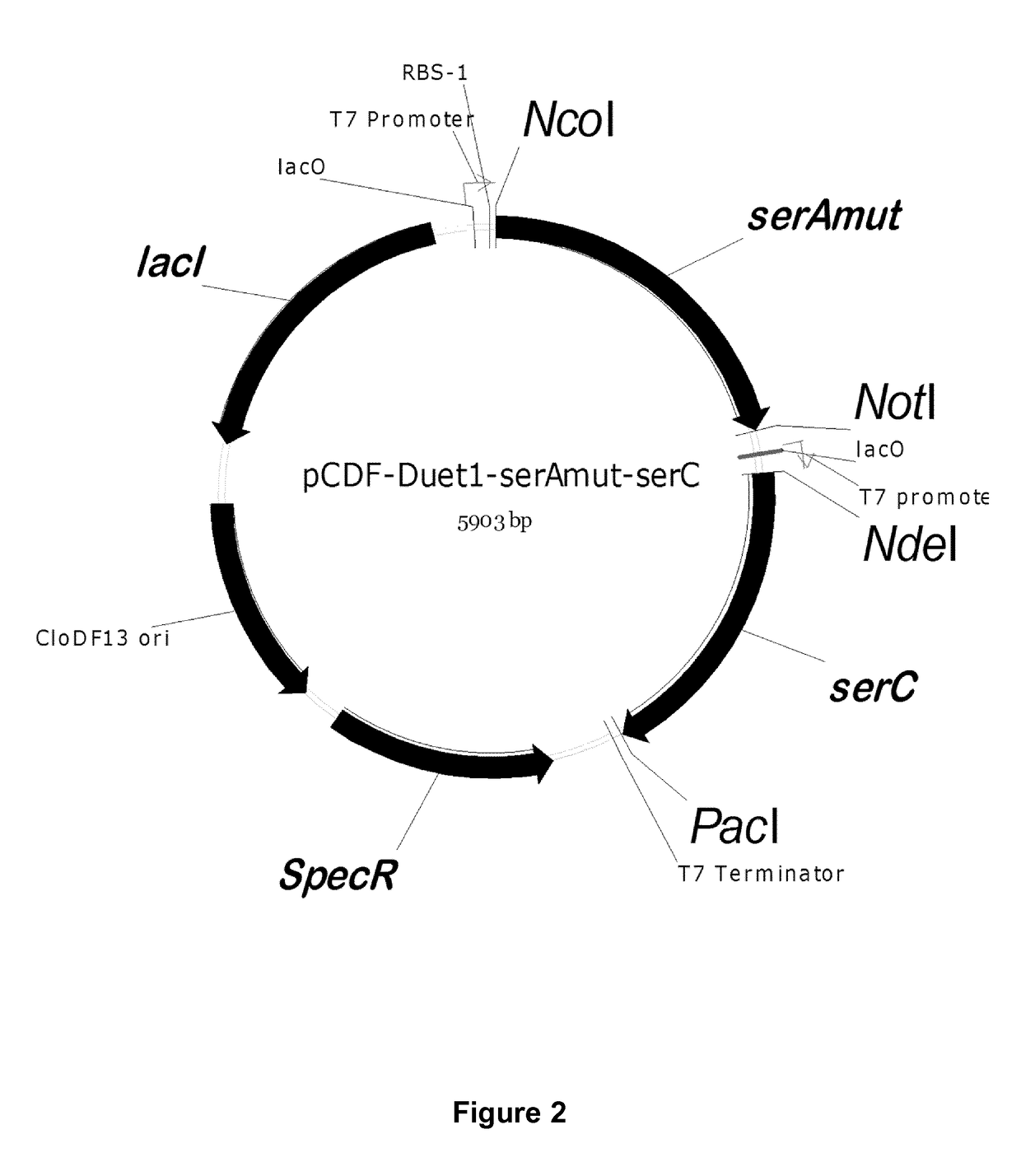
Method for the production of l-serine using genetically engineered microorganisms deficient in serine degradation pathways
ActiveUS20180016546A1Efficient production of L-serineHigh yieldCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBacteroidesHigh concentration
The present invention generally relates to the microbiological industry, and specifically to the production of L-serine using genetically modified bacteria. The present invention provides genetically modified microorganisms, such as bacteria, wherein the expression of genes encoding for enzymes involved in the degradation of L-serine is attenuated, such as by inactivation, which makes them particularly suitable for the production of L-serine at higher yield. The present invention also provides means by which the microorganism, and more particularly a bacterium, can be made tolerant towards higher concentrations of serine. The present invention also provides methods for the production of L-serine or L-serine derivative using such genetically modified microorganisms.
Owner:CYSBIO APS
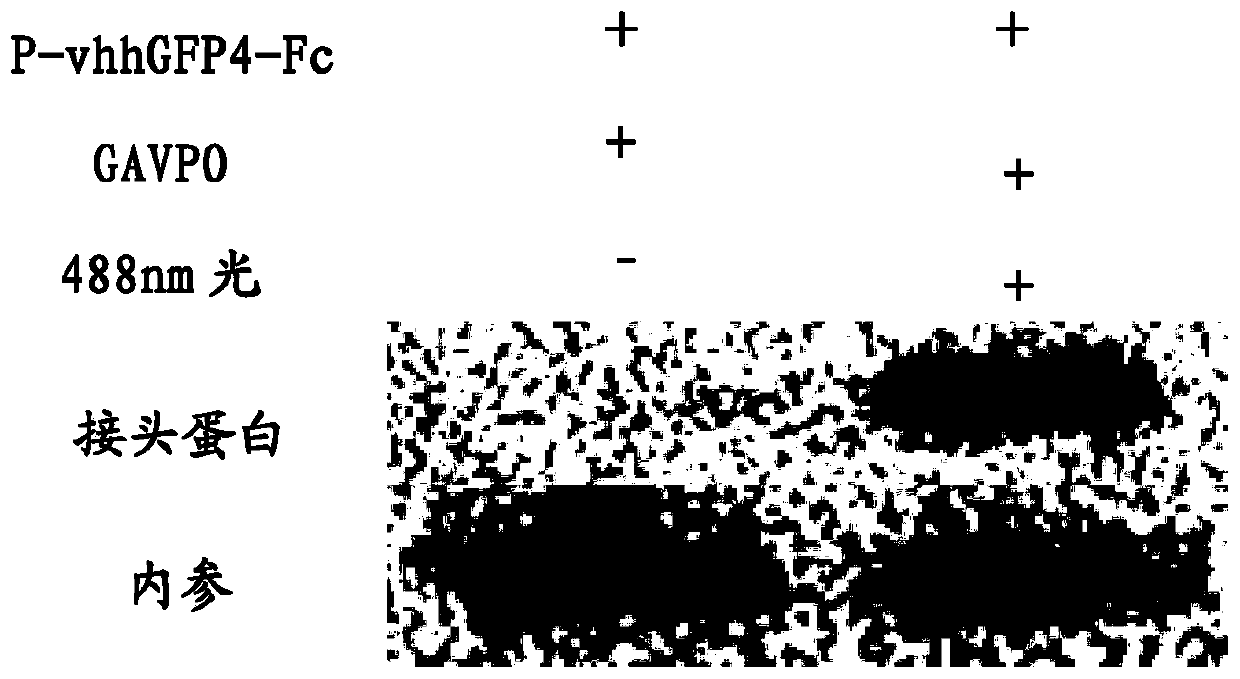
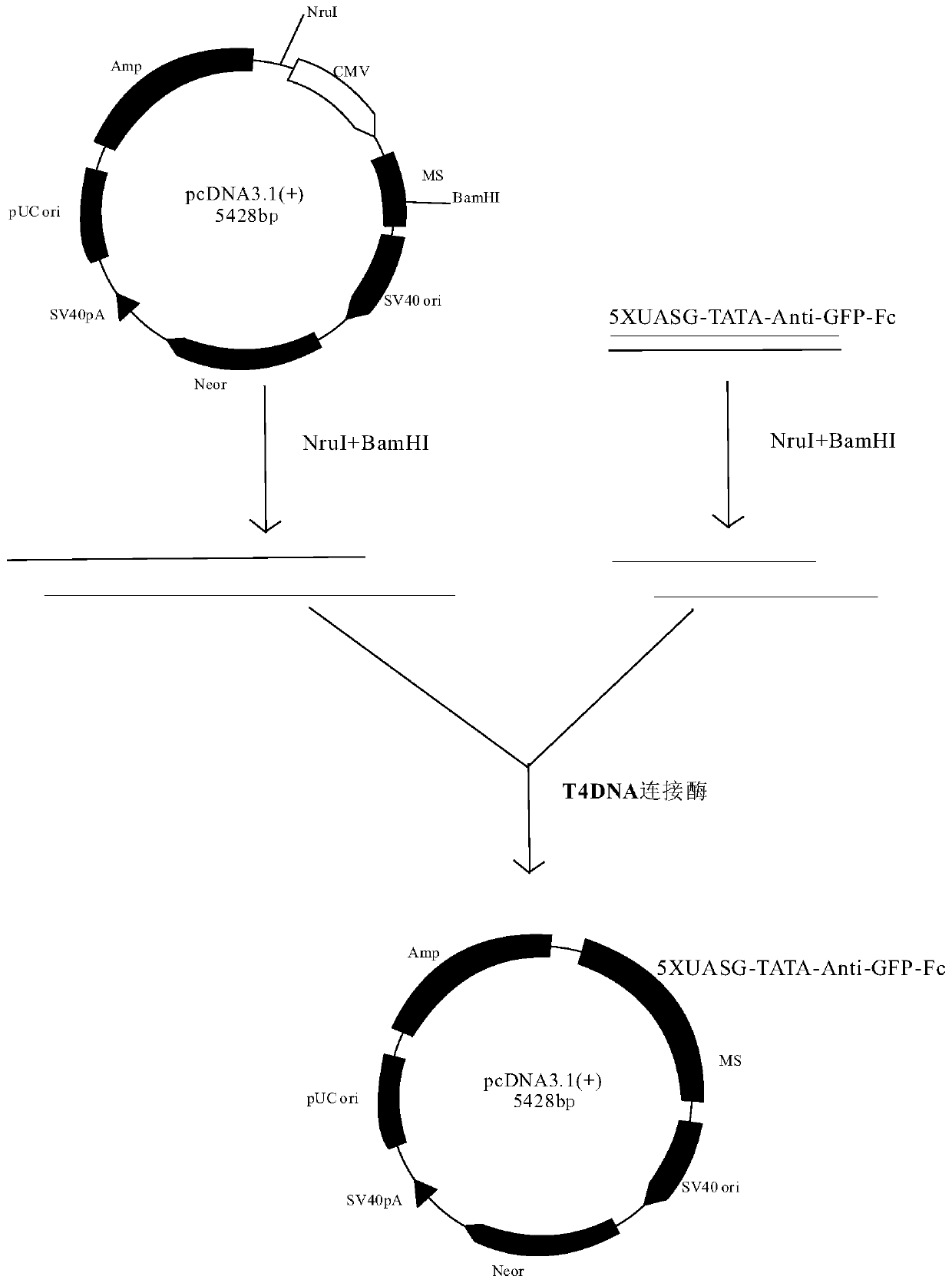
Light-controlled protein degrading system and construction method, and light adjusted and controlled protein degrading method
PendingCN110551755AAchieve degradationControl the degree of degradationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLigasesDegradation pathwayUbiquitin ligase
The invention relates to a light-controlled protein degrading system. The system comprises p-vhhGFP4-Fc, GAVPO and TRIM21 plasmid expression vectors, wherein the GAVPO is a light-controlled promoter constituent part, the TRIM21 is a kind of E3 ubiquitin ligase which can recruit proteasome and participate in a ubiquitination degradation pathway, and the p-vhhGFP4-Fc is a kind of fusion protein which can express vhhGFP4-Fc fusion protein under the illumination condition and induce GFP to generate degradation. The system can degrade particular protein in cells through adjusting illumination time,illumination frequency and illumination intensity, and is simple and efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
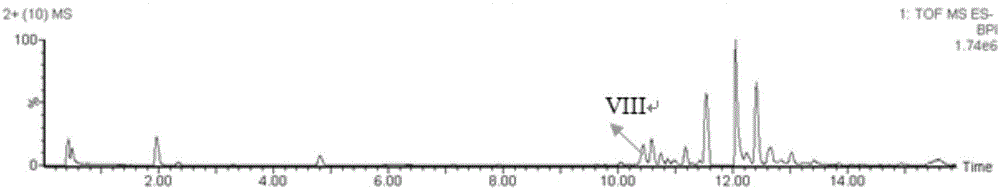
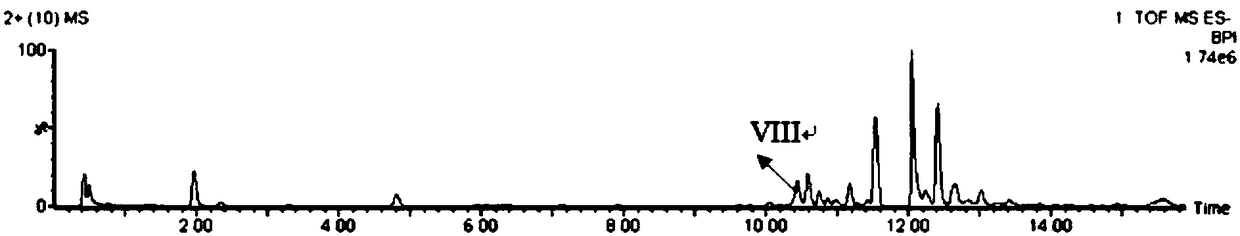
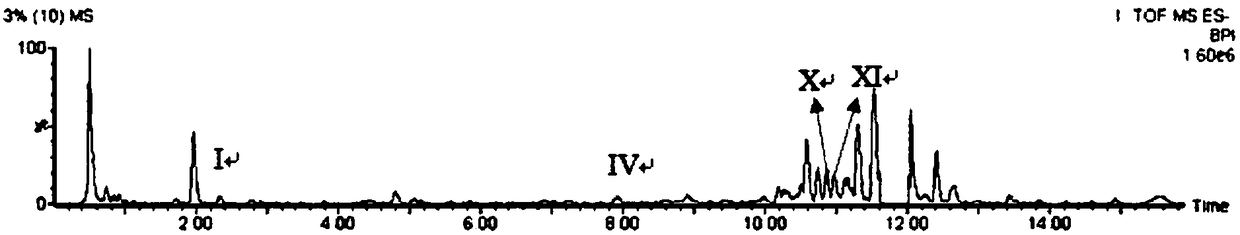
Researching method for stability of salvianolic acid used for injection, and analytical method for degradation pathway of salvianolic acid
InactiveCN106093223AIncrease coverageSpeed up the flowComponent separationDegradation pathwayStudy methods
The invention discloses a researching method for stability of salvianolic acid used for injection. The researching method comprises the following steps: separately subjecting salvianolic acid used for injection to high-temperature degradation test, oxydative degradation test, metal ion degradation test and illumination degradation test so as to obtain degradation products; detecting the degradation products of the degradation test by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry so as to obtain mass spectra and analyzing fragment ions in the mass spectra so as to determine degradation products; enriching the degradation products and simultaneously detecting a salvianolic acid raw material and the degradation products by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography so as to obtainultra-high performance liquid chromatograms; and carrying out indicating analysis on a random to-be-detected sample and determining degradation products of the sample according to the mass spectra and the chromatograms. The invention also discloses an analytical method for the degradation pathway of salvianolic acid. The methods provided by the invention can simultaneously determine active components in and degradation products of salvianolic acid used for injection, and have the characteristics of high sensitivity, small external interference, a fast testing speed, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for effectively improving proline conversion rate in system for producing Cis-3-hydroxy-L-proline according to biosynthesis method
InactiveCN105543265AImprove conversion rateNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyBiological cell
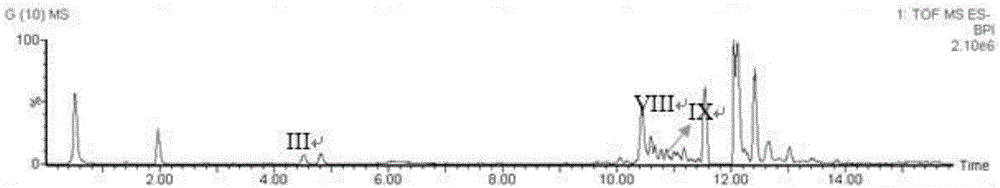
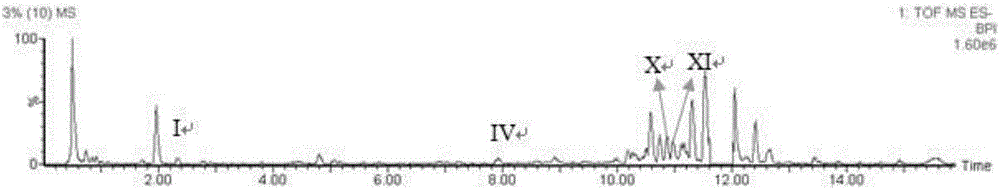
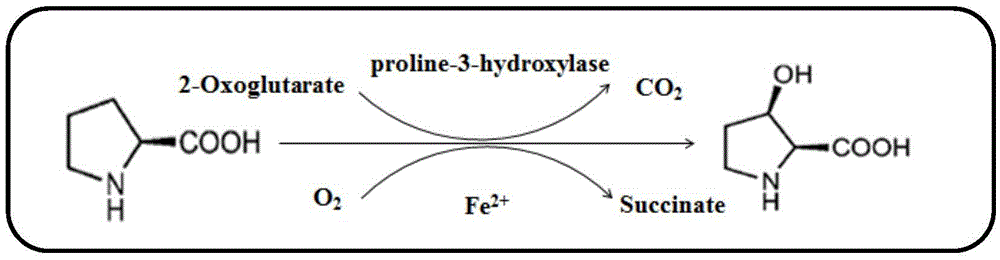
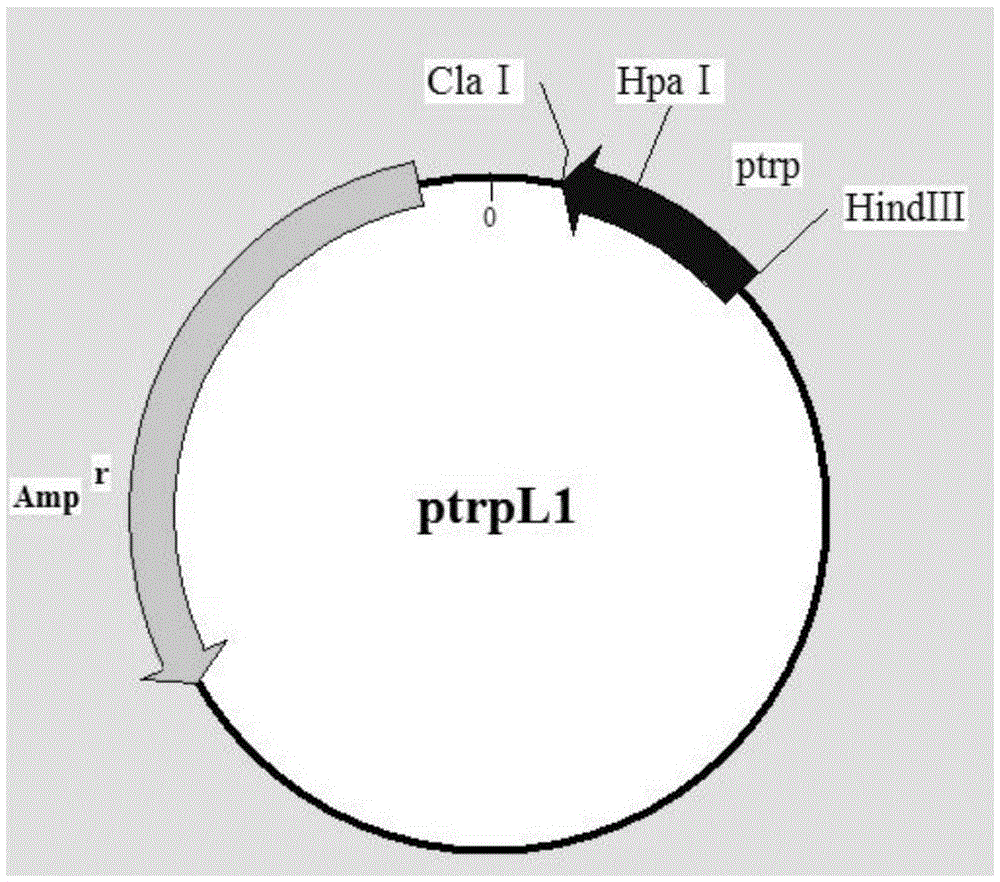
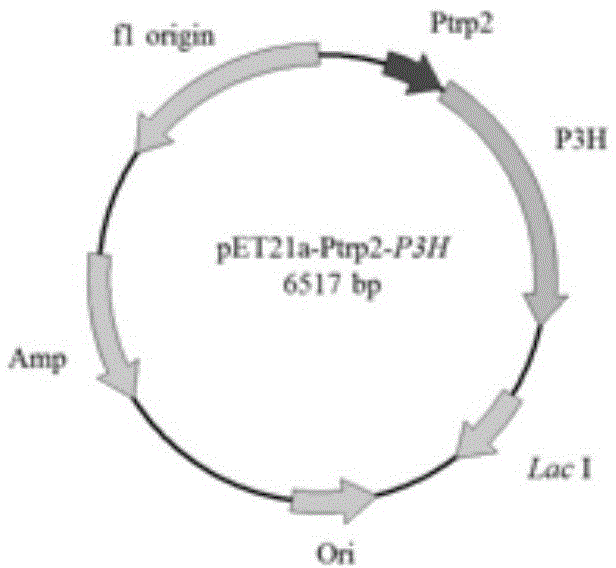
The invention discloses a method for effectively improving proline conversion rate in a system for producing Cis-3-hydroxy-L-proline according to a biosynthesis method. The system for producing the Cis-3-hydroxy-L-proline according to the biosynthesis method is a production method that in biological cells, free L-proline is converted into the Cis-3-hydroxy-L-proline by utilizing proline-4-hydroxylase under the existence of alpha-oxoglutarate and ferrous ions. The method for improving the proline conversion rate is to interrupt a degradation pathway of the proline in the biological cells. With the adoption of the method, the conversion rate of the Cis-3-hydroxy-proline-L-proline reaches 100 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A research method for the stability of salvianolic acid for injection and an analysis method for its degradation pathway
InactiveCN106093223BIncrease coverageSpeed up the flowComponent separationDegradation pathwayStudy methods
The invention discloses a researching method for stability of salvianolic acid used for injection. The researching method comprises the following steps: separately subjecting salvianolic acid used for injection to high-temperature degradation test, oxydative degradation test, metal ion degradation test and illumination degradation test so as to obtain degradation products; detecting the degradation products of the degradation test by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry so as to obtain mass spectra and analyzing fragment ions in the mass spectra so as to determine degradation products; enriching the degradation products and simultaneously detecting a salvianolic acid raw material and the degradation products by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography so as to obtainultra-high performance liquid chromatograms; and carrying out indicating analysis on a random to-be-detected sample and determining degradation products of the sample according to the mass spectra and the chromatograms. The invention also discloses an analytical method for the degradation pathway of salvianolic acid. The methods provided by the invention can simultaneously determine active components in and degradation products of salvianolic acid used for injection, and have the characteristics of high sensitivity, small external interference, a fast testing speed, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Antibody to SNIP1
InactiveUS6906179B2Improve responseSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDegradation pathwayProteasome degradation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Platinum and platinum based alloy nanotubes as electrocatalysts for fuel cells
ActiveUS9214680B2Improve overall utilizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesDegradation pathwayAlloy
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of KPNB1 inhibitor and protein degradation pathway inhibitor in preparation of anti-tumor drugs
The invention relates to an application of a KPNB1 inhibitor and a protein degradation pathway inhibitor in the preparation of anti-tumor drugs. According to the invention, the KPNB1 inhibitor and theprotein degradation pathway inhibitor are used in combination so as to have extremely excellent inhibition effect on treating tumors, particularly glioma. The aim of killing more tumor cells can be achieved by drug combination.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
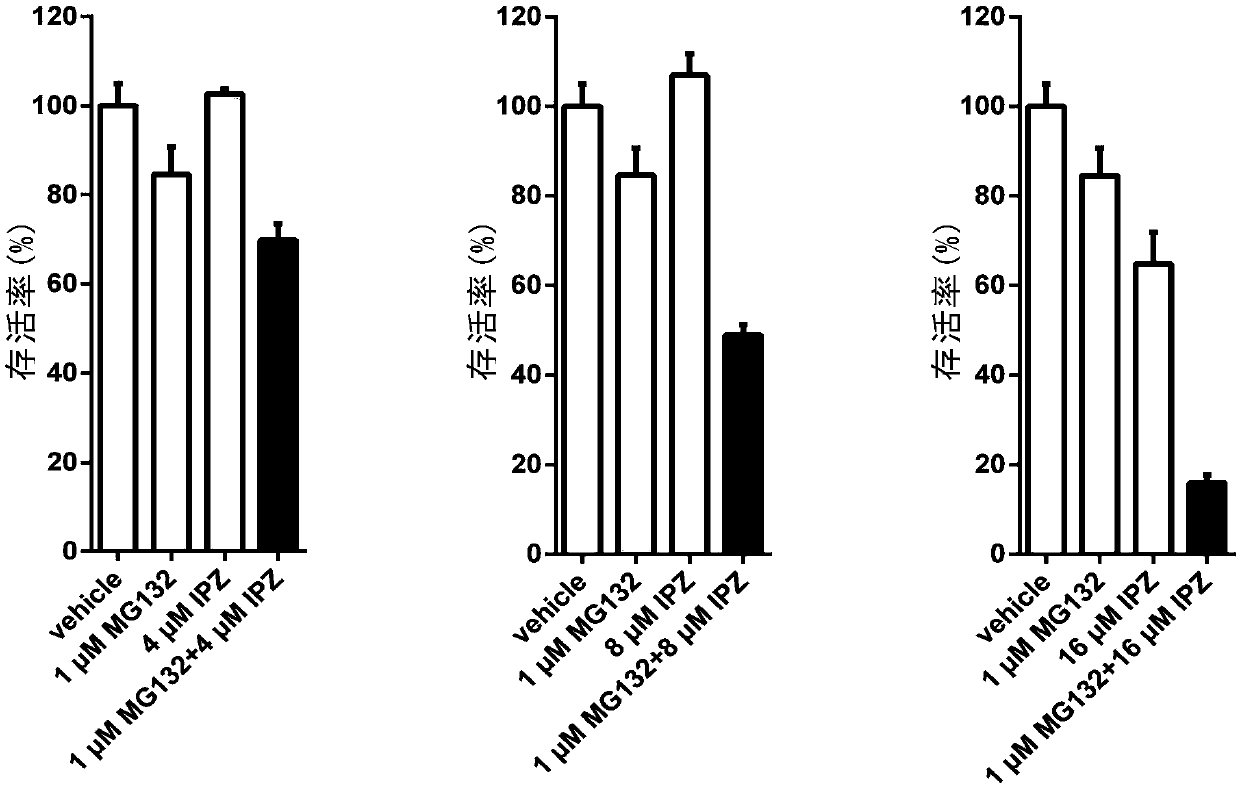
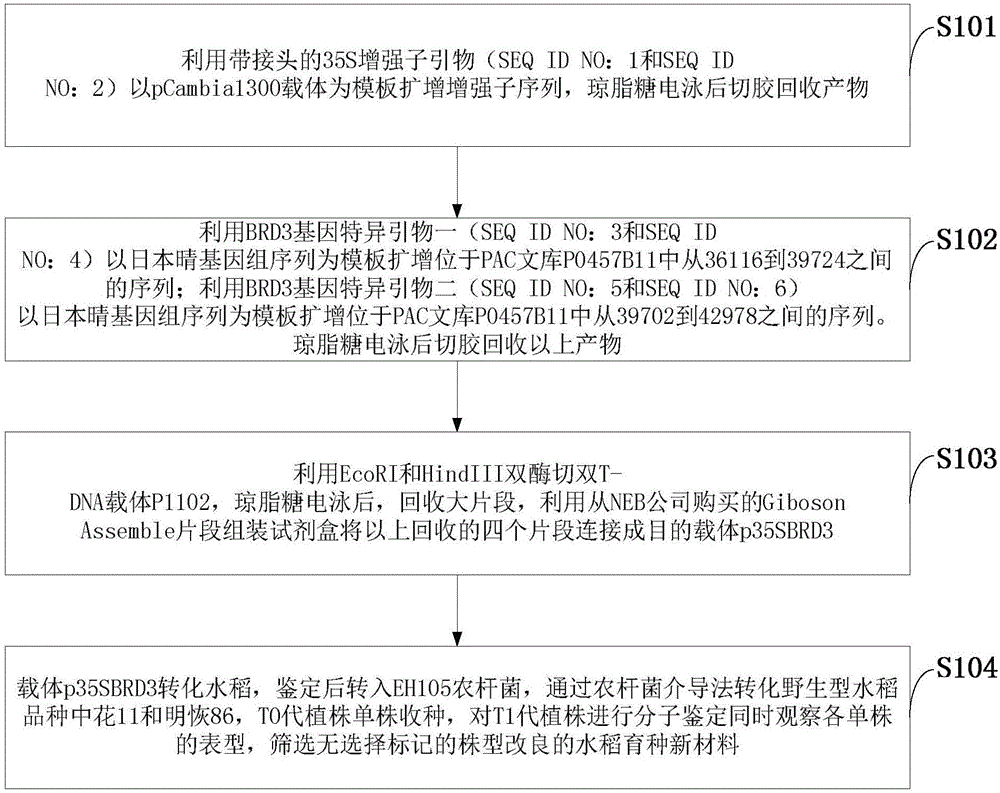
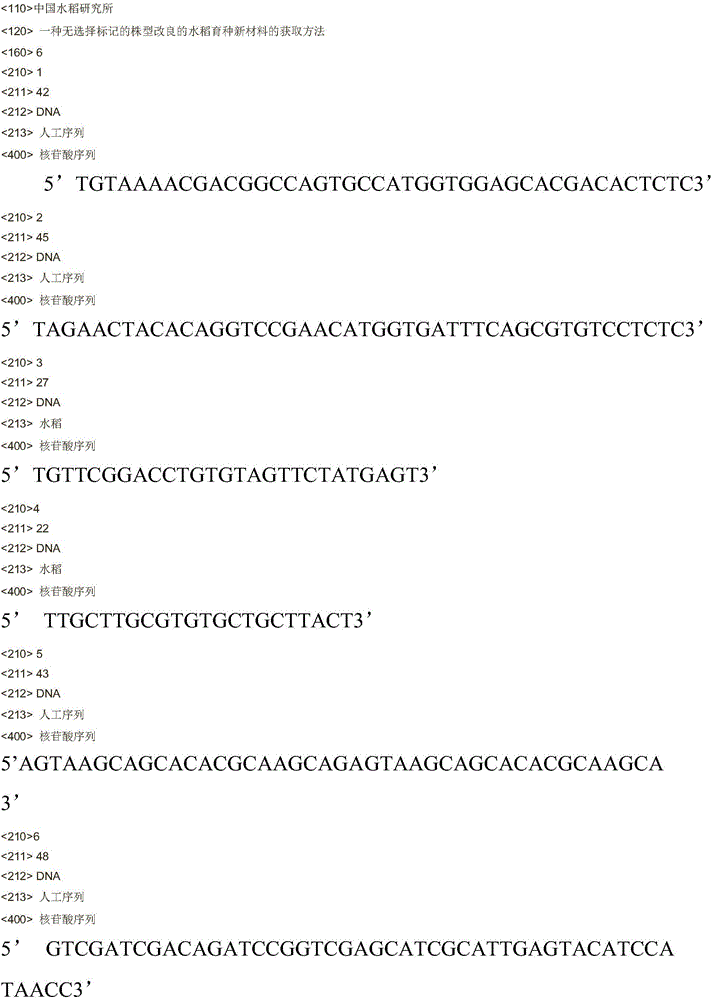
Method for obtaining plant-type-improved new rice breeding materials without selectable markers
InactiveCN106222198AFast aggregationIncrease productionNucleic acid vectorGenetic engineeringDegradation pathwayTransgenic technology
The invention discloses a method for obtaining plant-type-improved new rice breeding materials without selectable markers. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an amplification enhanced subsequence which uses pCambia1300 vector as a template; using a Giboson Assemble fragment assembling kit to connect four recovered fragments into a target vector p35SBRD3; using the vector p35SBRD3 for rice transforming. The method provided by the invention can realize the rapid polymerization of genes through transgenosis; however, the presently available genes are extremely limited; compared with OsDWARF4 gene and OsBRI1 gene reported at present, BRD3 gene is involved in the degradation pathway of BR metabolism so as to more easily realize the fine adjustment of BR at different parts; the expression levels of the BRD3 gene at different parts can be finely adjusted by transgenic technology, so that the ideal plant type can be shaped and the yield of crops can be increased.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
L-ornithine production in eukaryotic cells
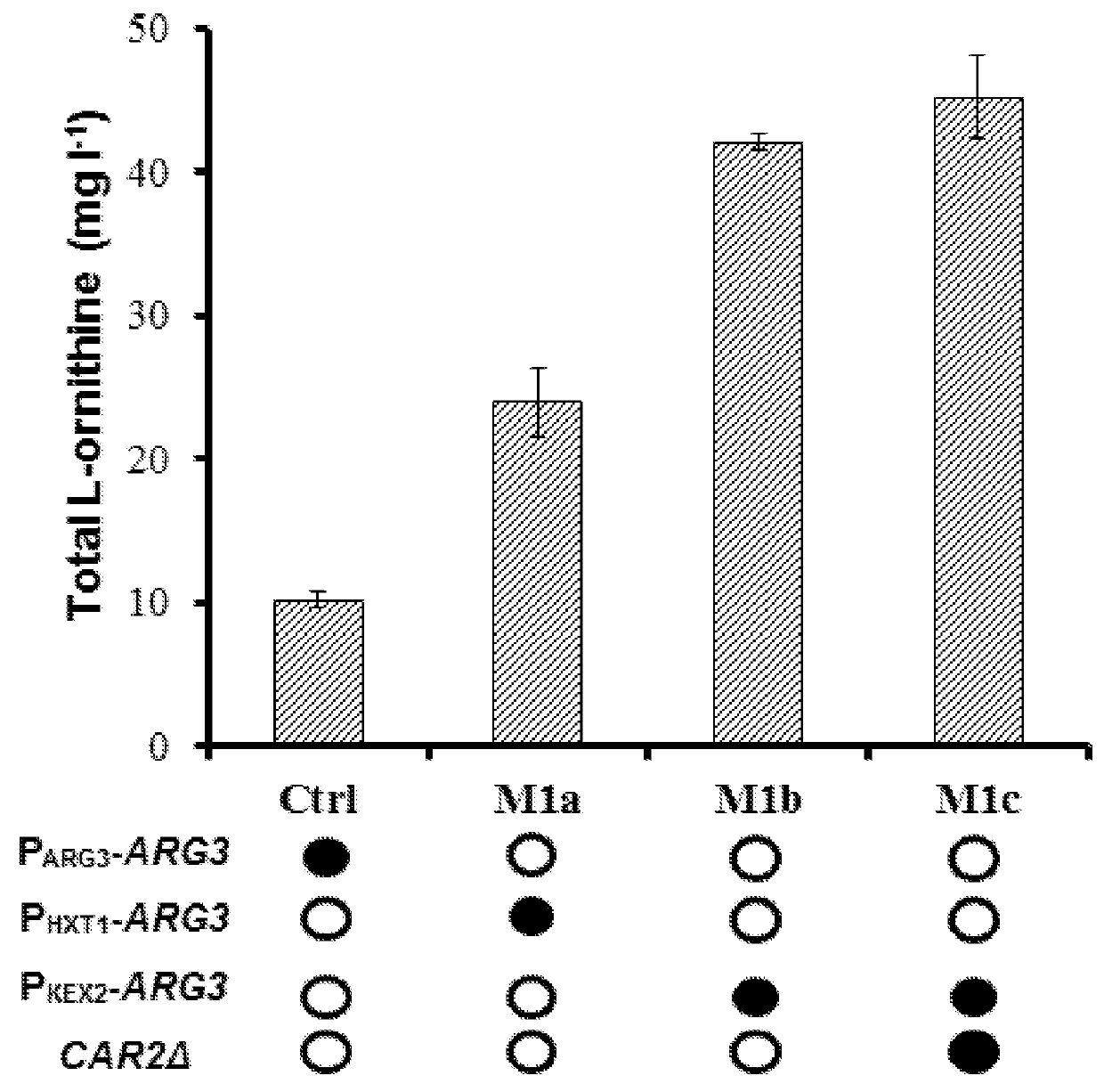
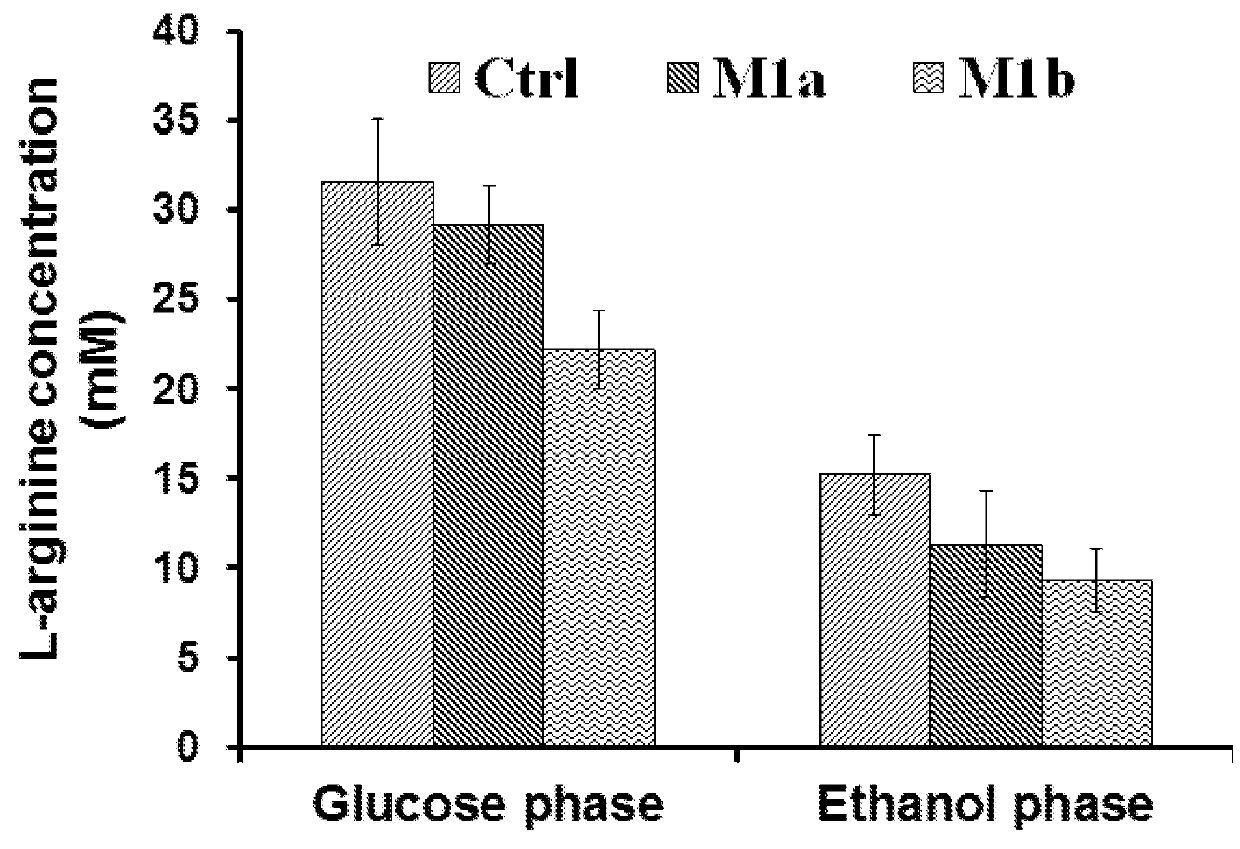
ActiveUS20180105850A1Improve toleranceExemption stepsCarbon-nitrogen lyasesHydrolasesDegradation pathwayL-glutamate synthesis
The present invention relates to the provision of genetically modified microbial cells, such as yeast cells with an improved ability for producing L-ornithine and its derivatives. Overproduction of L-ornithine is obtained in the first place by the down-regulation or attenuation of specially selected genes, wherein said genes encode enzymes involved in the L-ornithine consumption and / or degradation pathways. Further L-ornithine production ability is improved by down-regulation, attenuation, deletion or overexpression of specially selected genes, wherein said genes encode enzymes and / or proteins involved in the L-ornithine ‘acetylated derivatives cycle’, L-glutamate synthesis pathways, subcellular trafficking, TCA cycle, pyruvate carboxylation pathway, respiratory electron-transport chain, and the carbon substrates' assimilation machinery. The invention additionally provides a method to produce L-ornithine with said modified eukaryotic cells.
Owner:CHRYSEA LTD
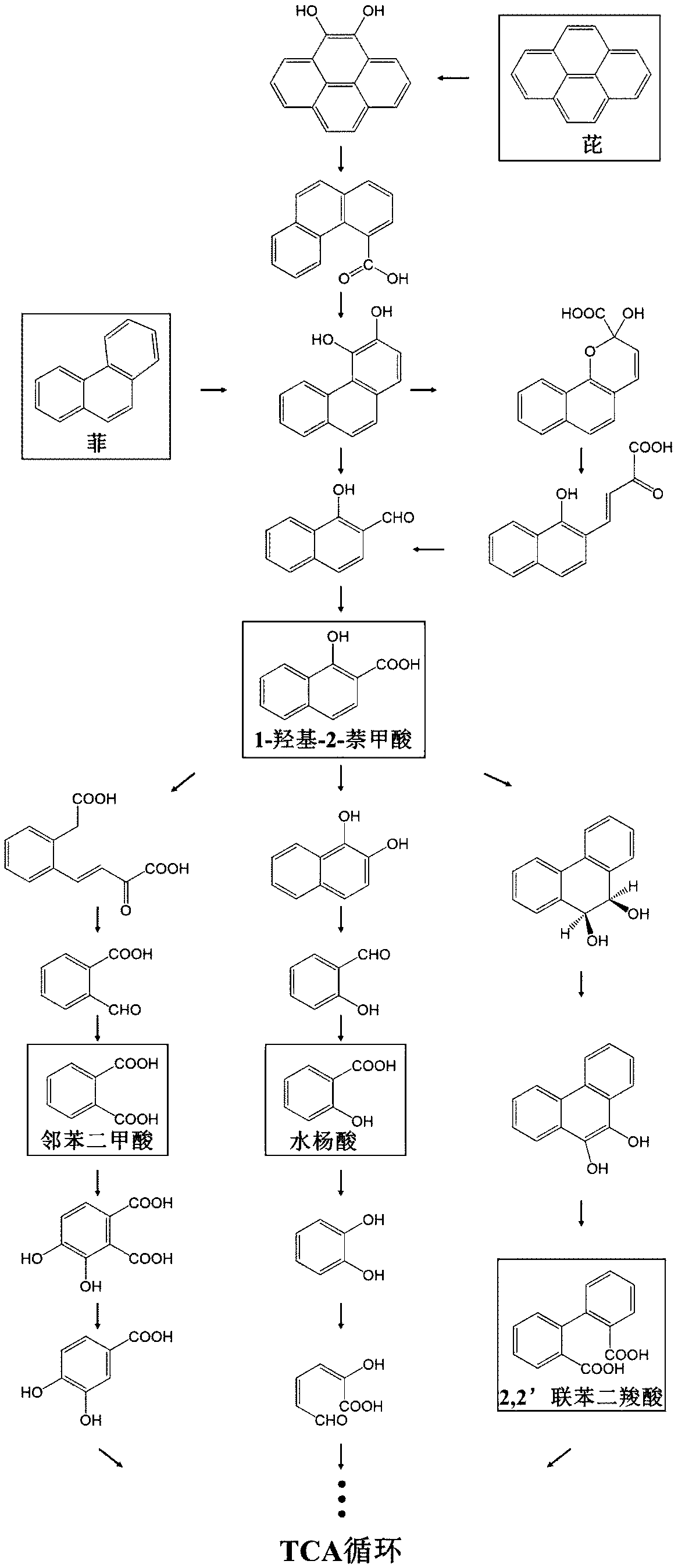
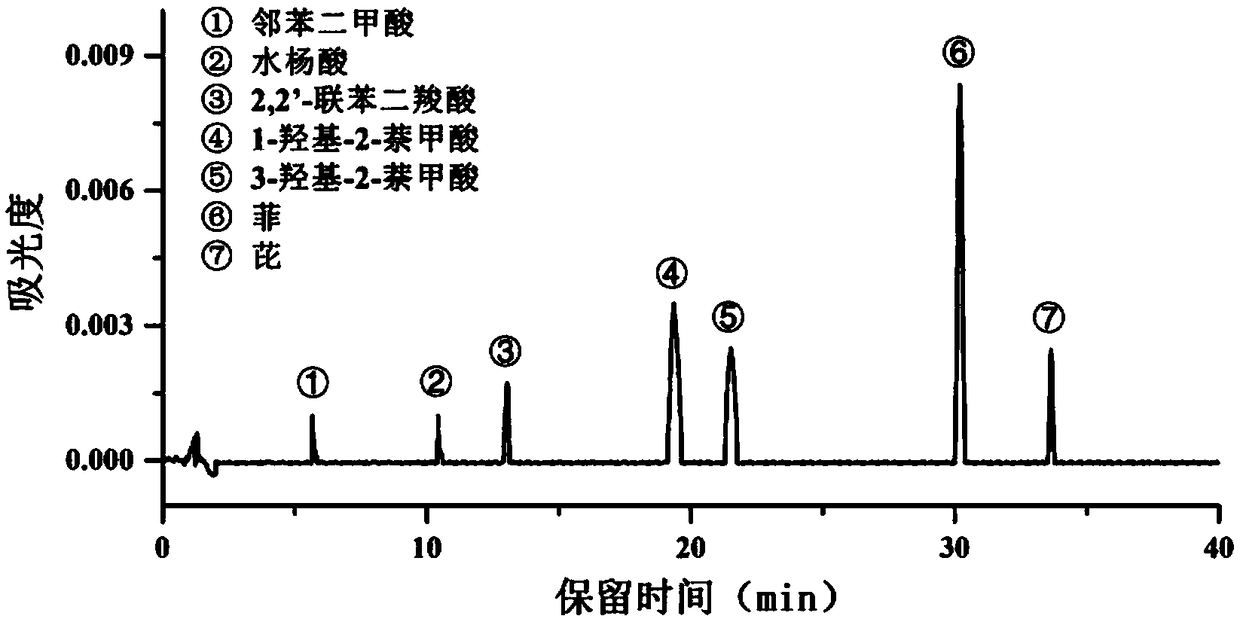
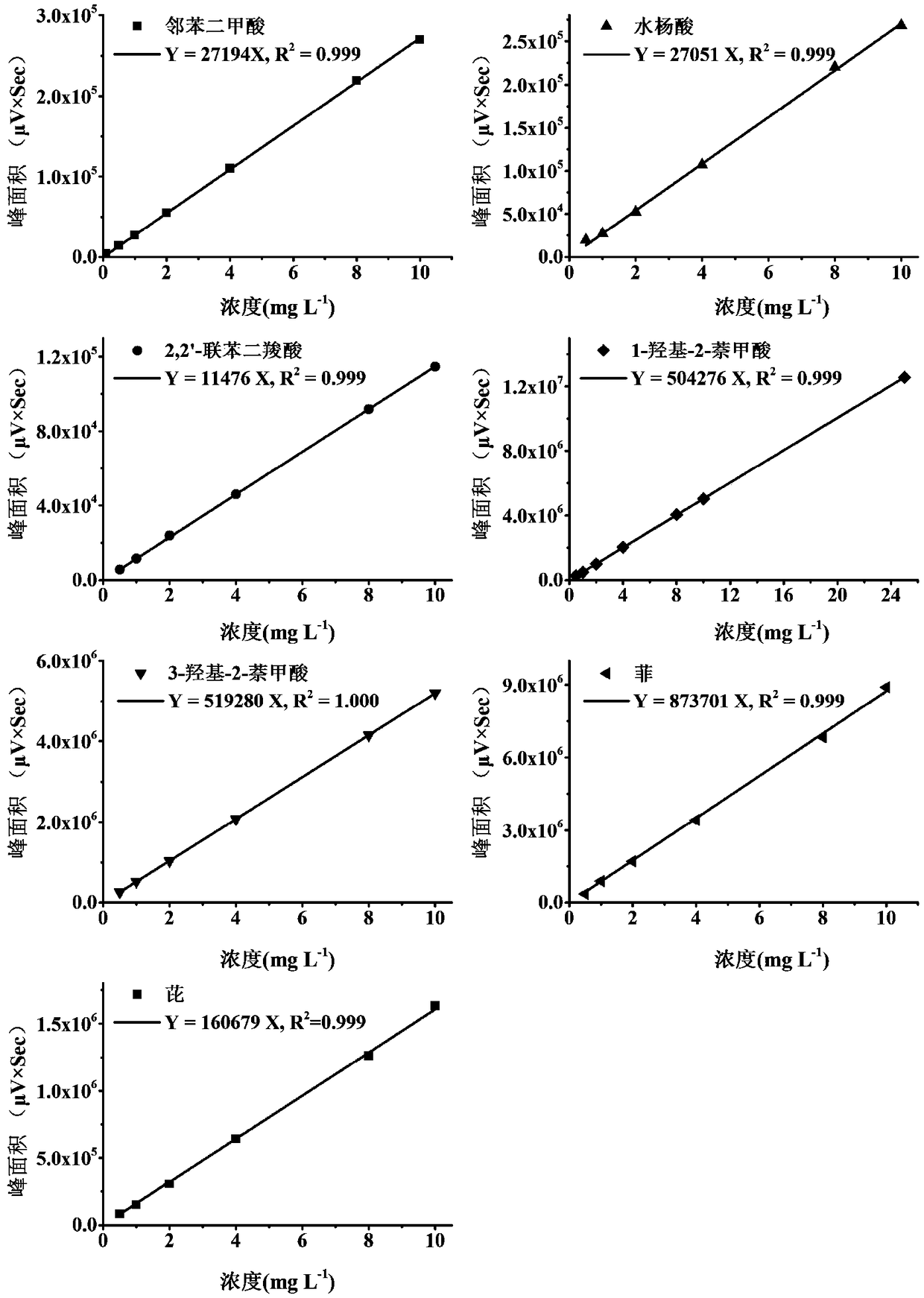
High-efficiency extraction of bacterial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites and identification of degradation pathways
ActiveCN107941938BFull peak shapeEasy to separateComponent separationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMetabolite
The invention discloses a method for high-efficiency extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites in bacteria and determination of degradation approaches. The method comprises the following steps: culturing degrading bacteria with phenanthrene / pyrene as a sole carbon source; extracting degradation products; and carrying out HPLC detection, determining the peak appearance time of substances and lower detection limit by using a standard sample, carrying out conversion via marked lines so as to obtain the contents of the degradation products, and calculating the proportion of pollutant degradation approaches. The method provided by the invention can be used for assessing the possibility that a bacterial strain has novel degradation approaches and provides a theoretical basis forfurther exploration of degradation approaches and treatment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution with microbes.
Owner:杭州质谱检测技术有限公司
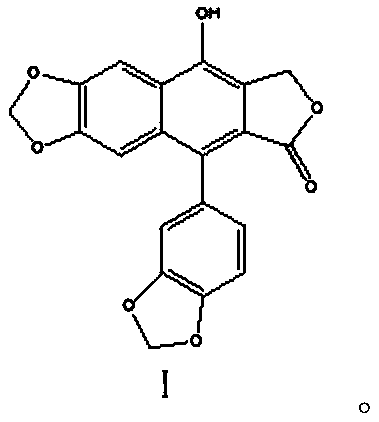
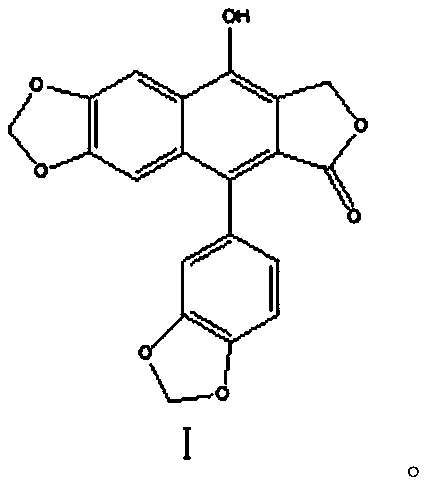
Application of Taiwanin E in preparation of herbicides
ActiveCN110583673AGrowth inhibitionSmooth degradation pathwayBiocideAnimal repellantsDegradation pathwayRoot growth
The invention discloses an application of Taiwanin E in preparation of herbicides. The Taiwanin E compound, a structural analog thereof and / or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is prepared asherbicides for application, and a structure of the Taiwanin E is shown in a formula I. The Taiwanin E is derived from plants, has a smooth degradation pathway in nature, and has low residue, low pollution, and high environmental protection. The invention finds for the first time that the Taiwanin E can inhibit growth of weeds, growth of roots of the weeds treated by the Taiwanin E becomes slow, afresh-weight inhibition rate is significant, and thereby normal growth of the weeds is inhibited, so that the Taiwanin E can be prepared as herbicides for application. At the same time, the TaiwaninE shows relatively good effects of inhibiting root growth on a variety of dicotyledonous, monocotyledonous and aquatic weeds, has broad-spectrum properties, and has a wide application range. Moreover,the structure of the Taiwanin E is different from existing herbicides, and can provide a template for creation of herbicides, so that the Taiwanin E has obvious significance both in theory and in practice.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
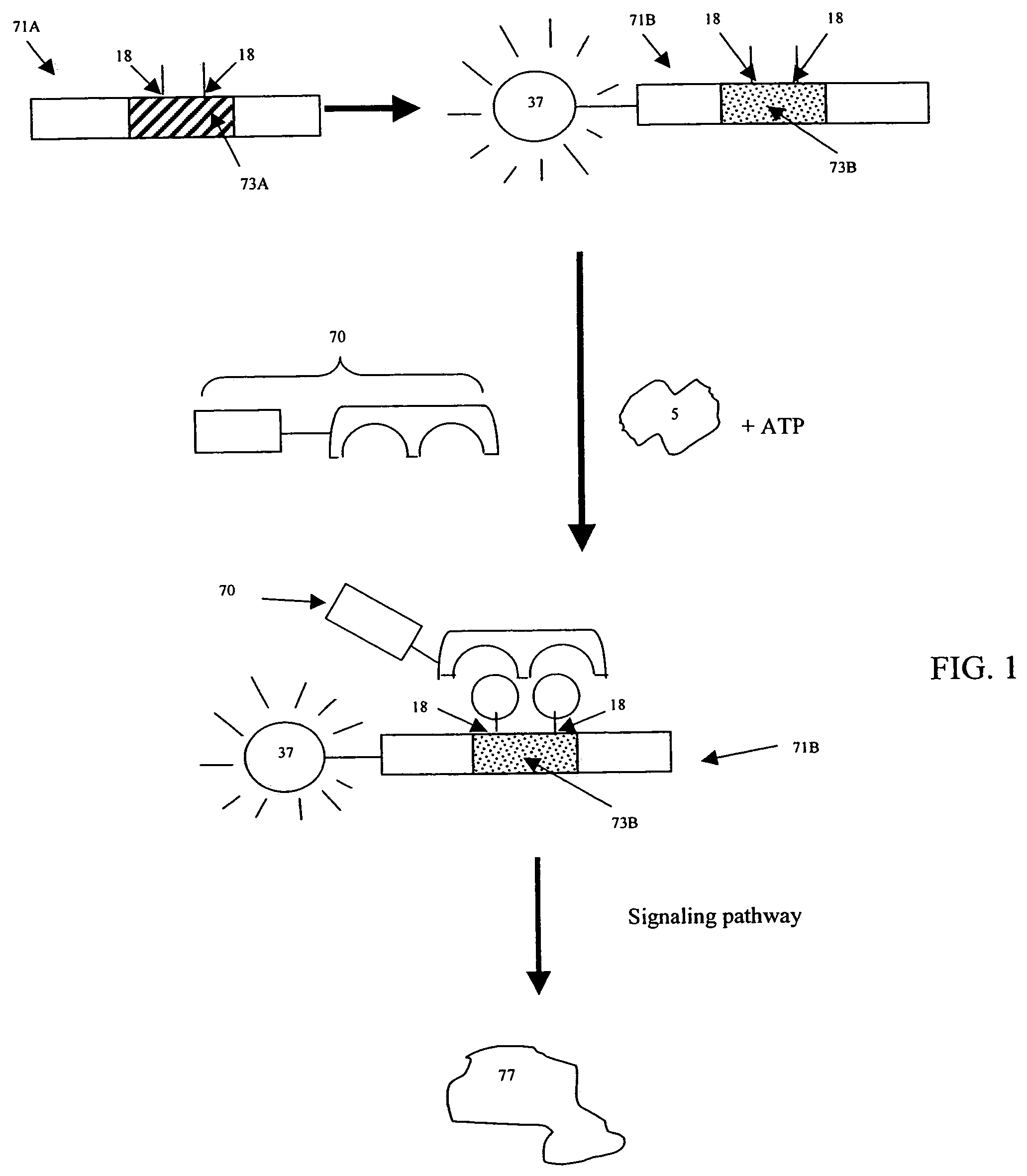
Cell-based screening methods
InactiveUS7083938B2Activity can be delayedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCellular pathwaysKinase activity
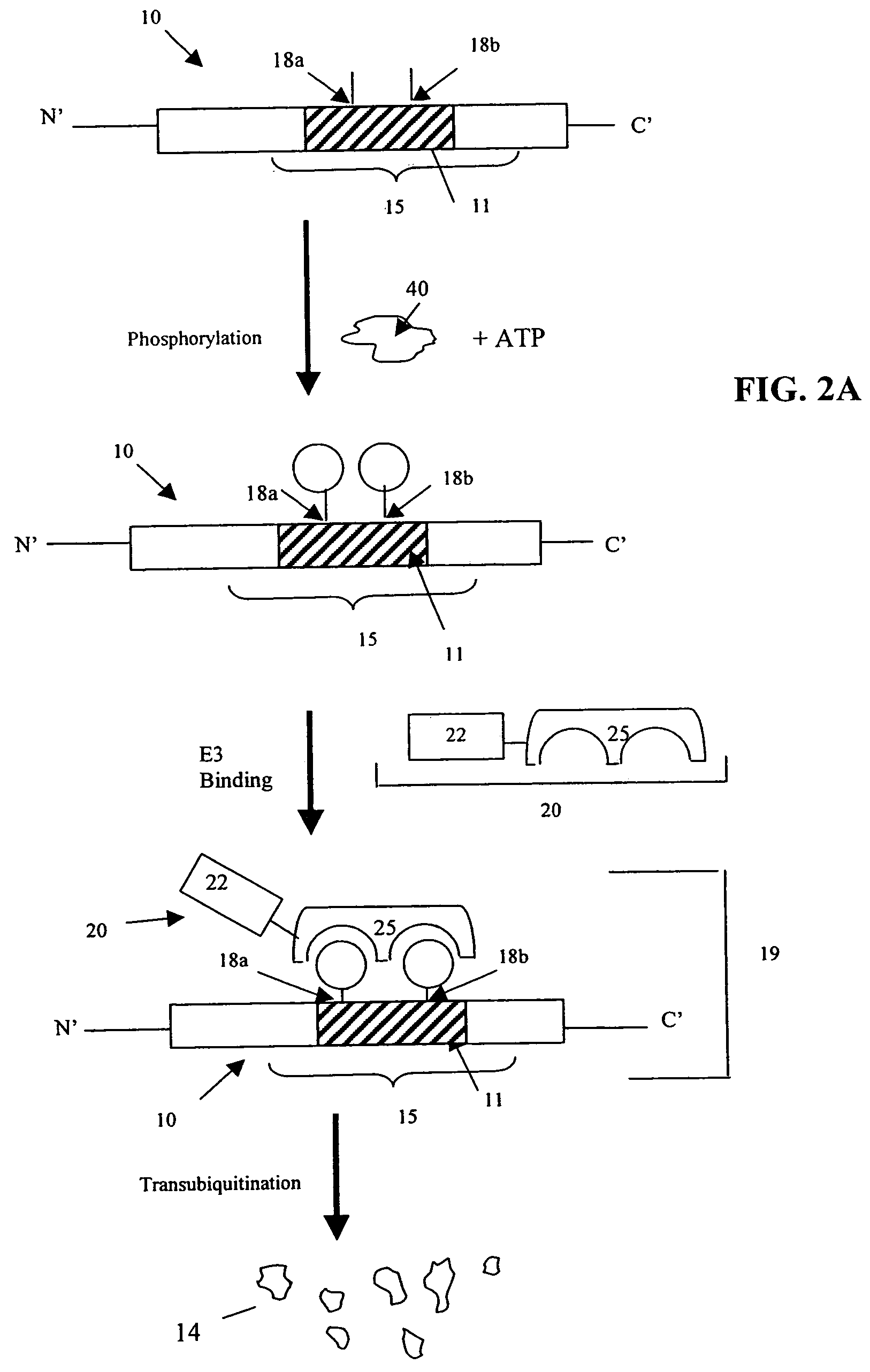
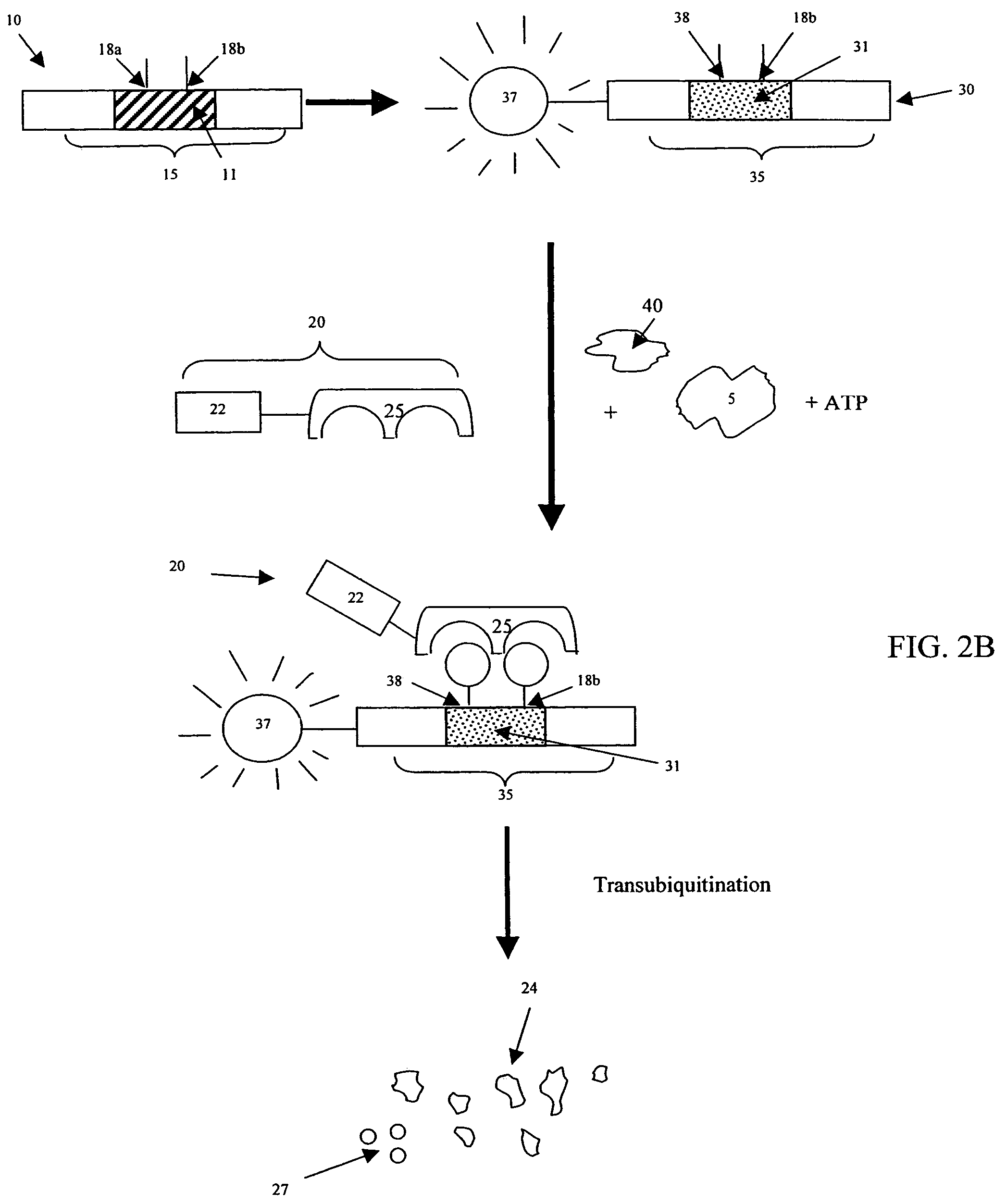
Cell-based screening methods for determining kinase activity are provided. The methods utilize existing cellular pathways that are regulated by kinases. In one embodiment, various components of a ubiquitin-mediated degradation pathway are modified to create an assay that can be used to screen for a molecule that modulates the activity of a kinase of interest that otherwise does not regulate the degradation pathway. In another embodiment, various components of a protein translocation pathway are modified to screen for a molecule that modulates the activity of a kinase of interest that otherwise does not regulate the translocation pathway.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method for controlling noisome decomposition byproducts from human efflux retained in personal hygiene products
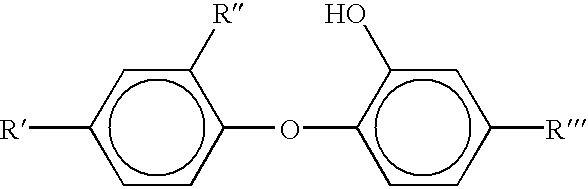
The present invention is directed to the control of noisome odors created by the decomposition of human waste in a personal hygiene product. Control of the decomposition process is by the pre-application of an odor control compound comprising a hydroxydiphenyl ether in a modified acidic environment to one or more components of the personal hygiene product. The odor control compound exhibits a multi-functional performance, affecting not only the odiferous decomposition byproducts, but the biochemical decomposition and degradation pathways.
Owner:POLYMER GROUP INC
Biochemical comprehensive treatment method for 1, 3-propylene glycol fermentation organism waste water
InactiveCN101693583BHigh removal rateHighlight substantiveTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteActivated sludge
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com