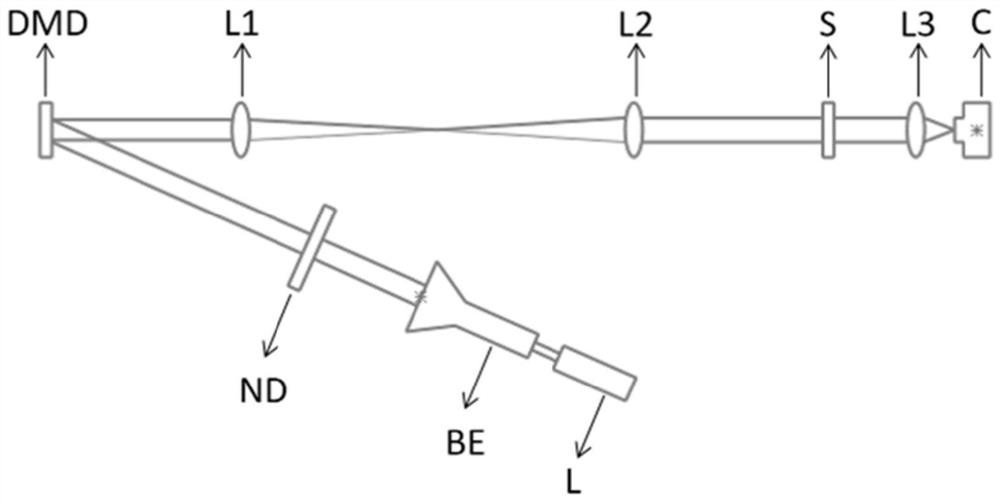
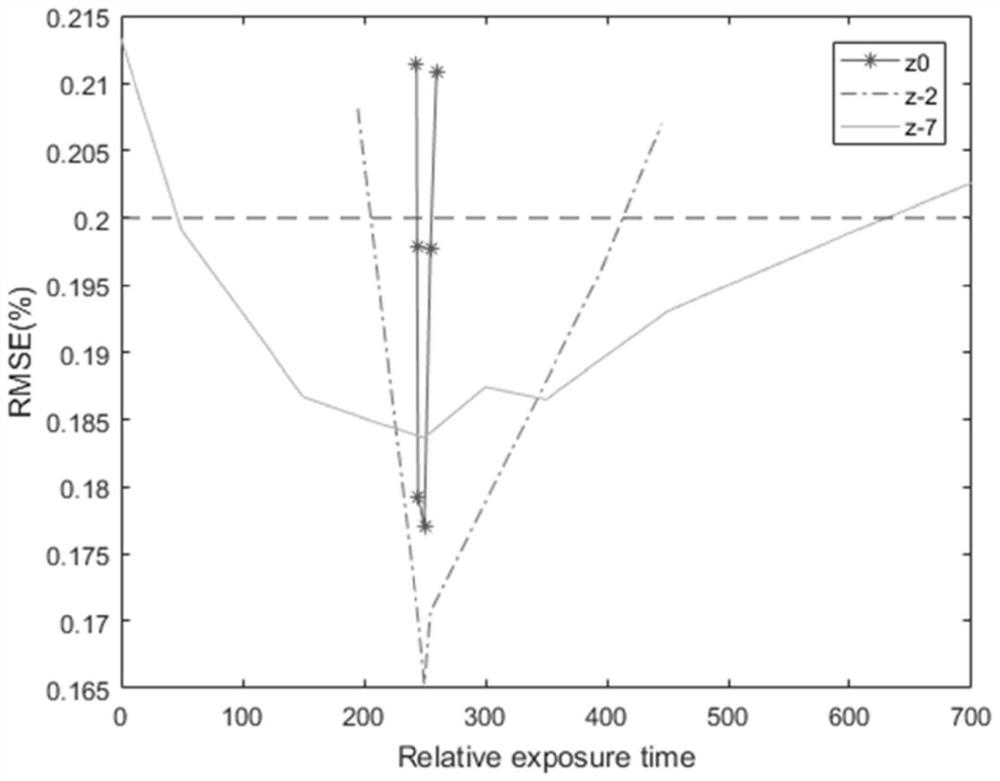
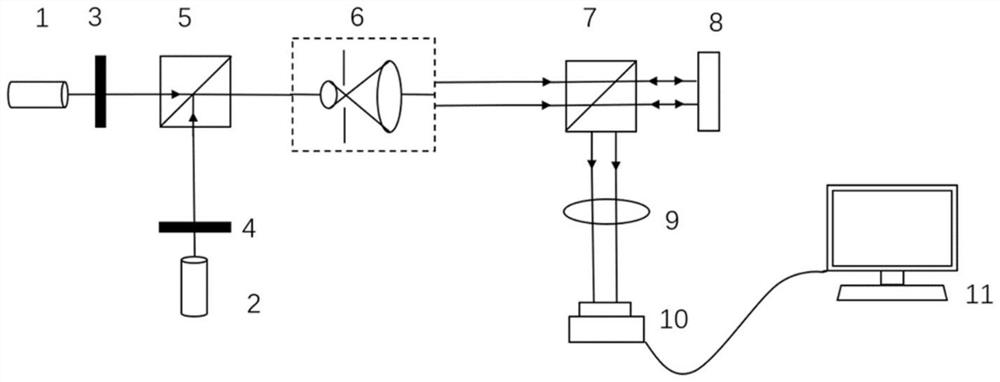
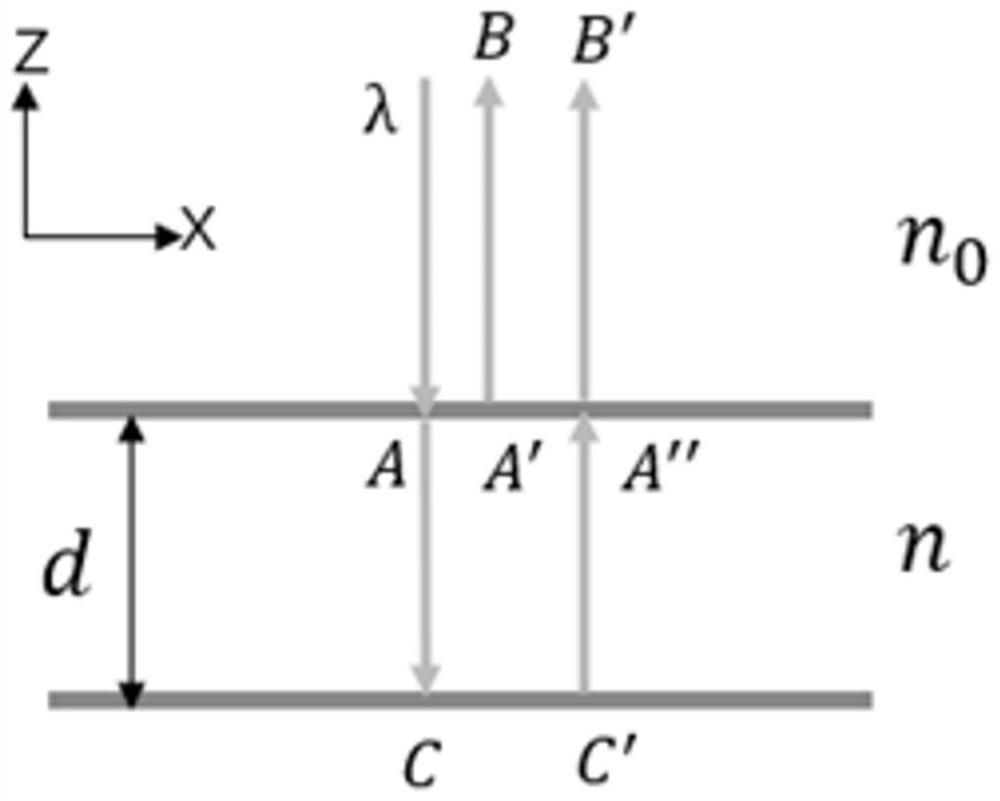
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Coherent diffraction imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
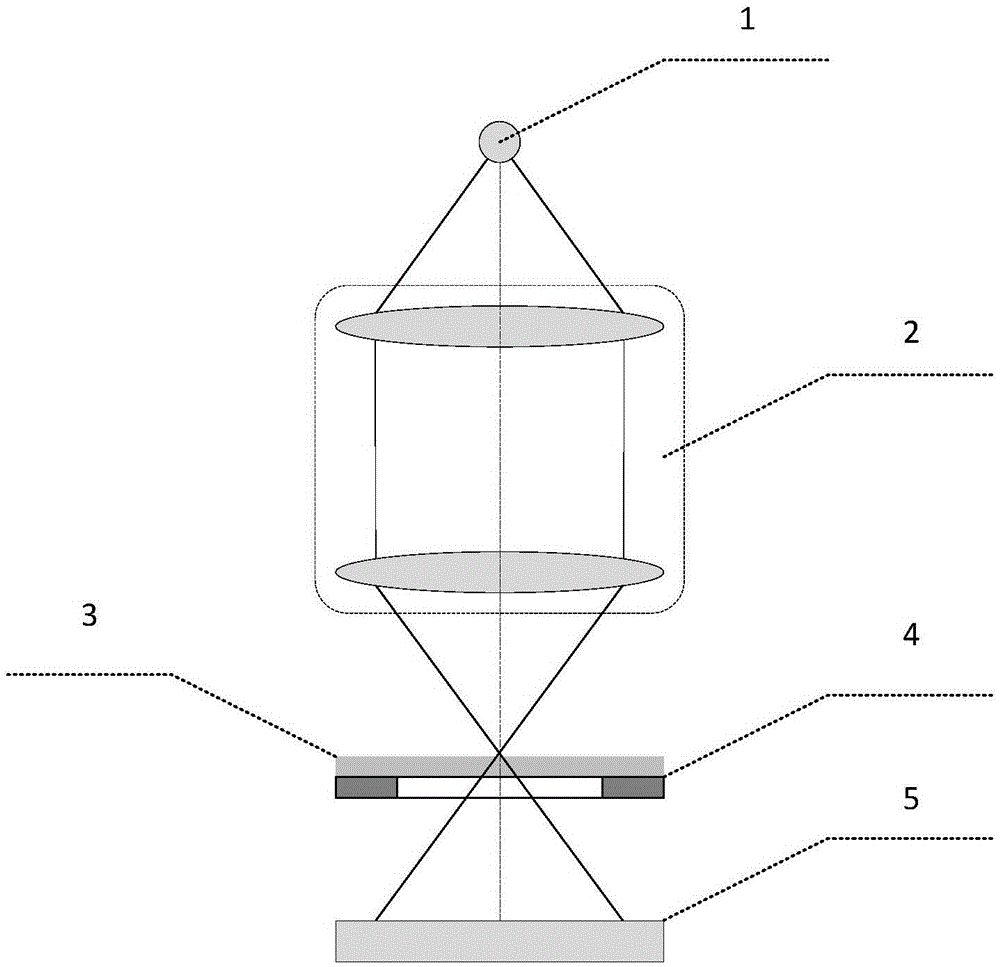
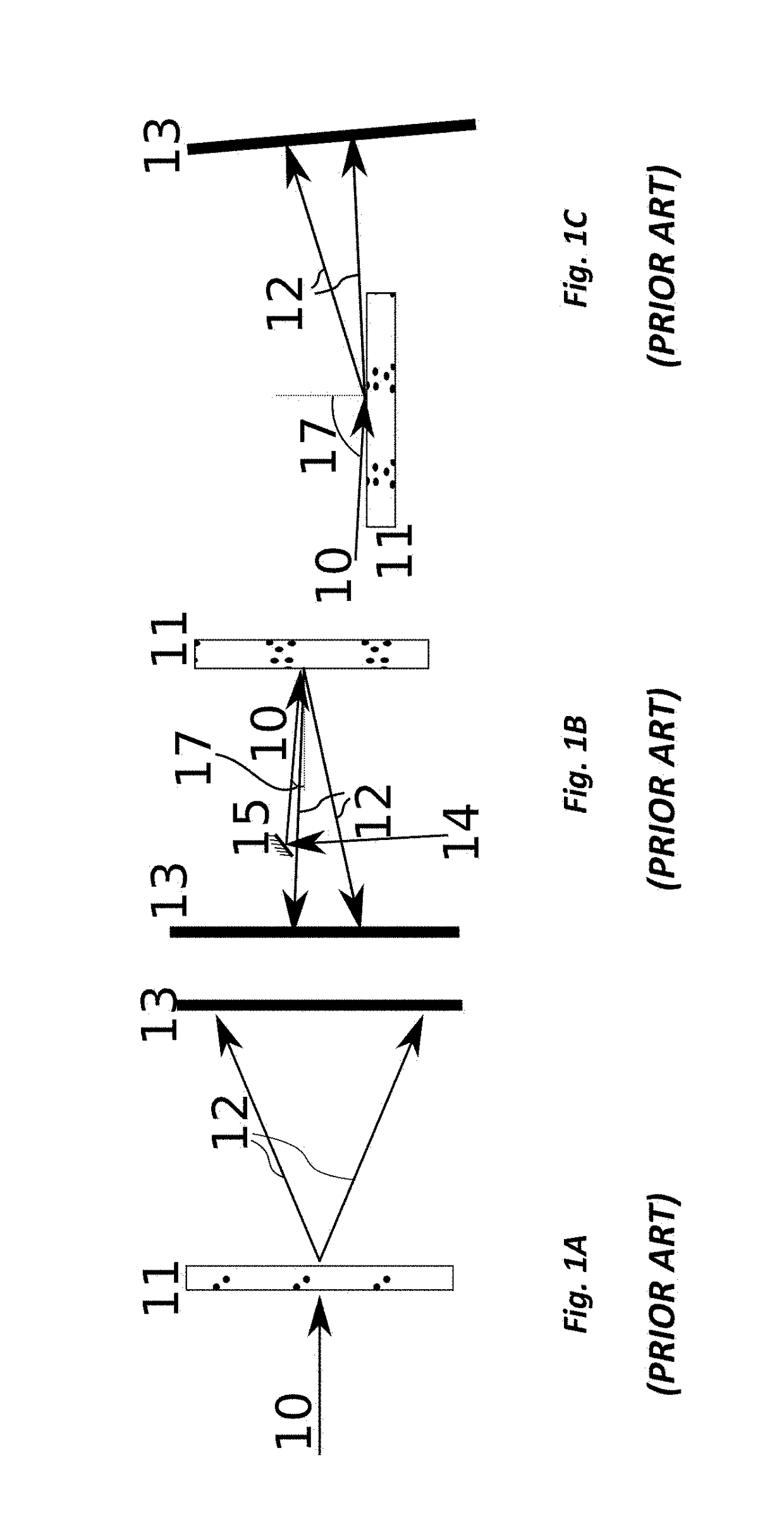
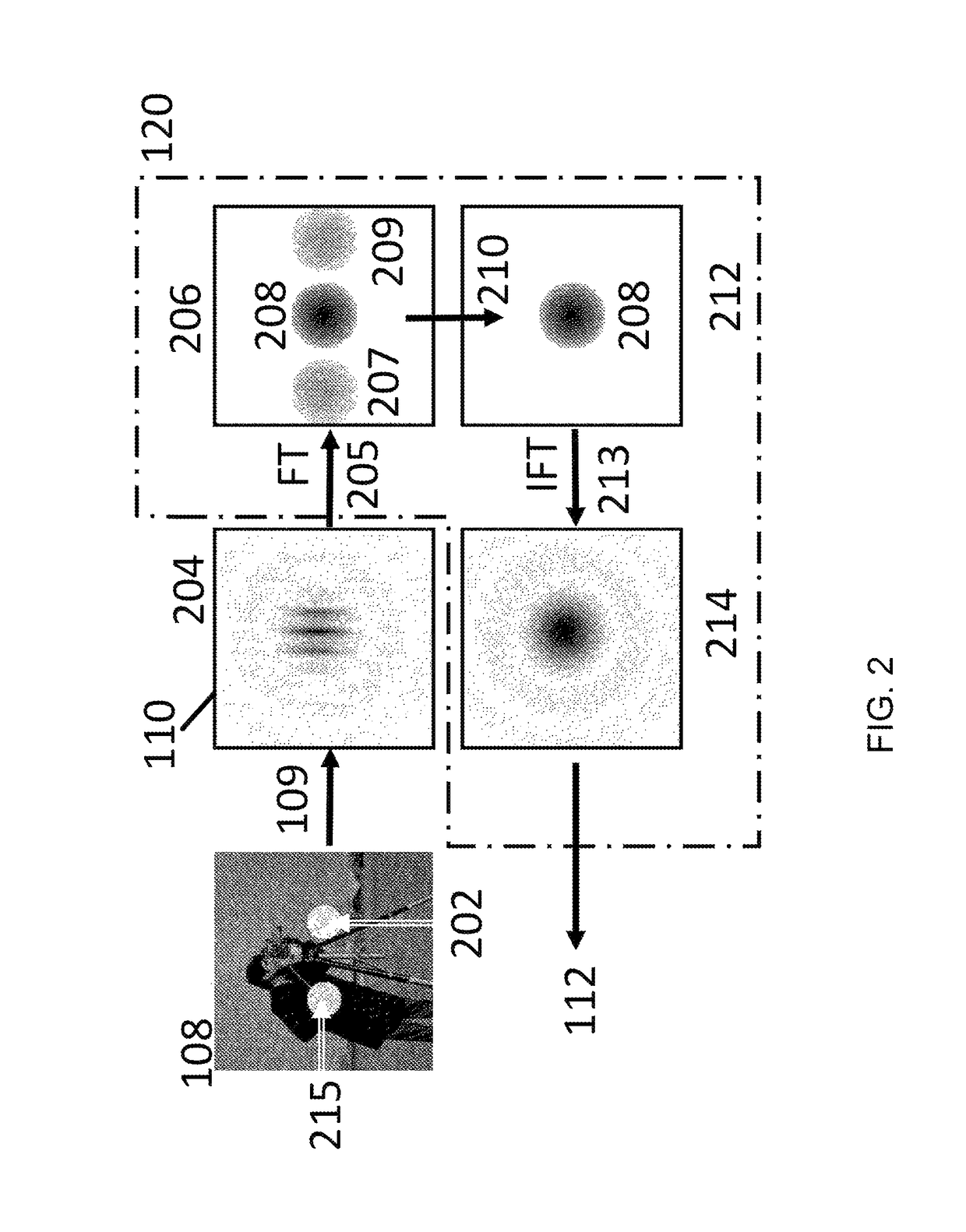
Coherent diffractive imaging (CDI) is a “lensless” technique for 2D or 3D reconstruction of the image of nanoscale structures such as nanotubes, nanocrystals, porous nanocrystalline layers, defects, potentially proteins, and more. In CDI, a highly coherent beam of x-rays, electrons or other wavelike particle or photon is incident on an object.
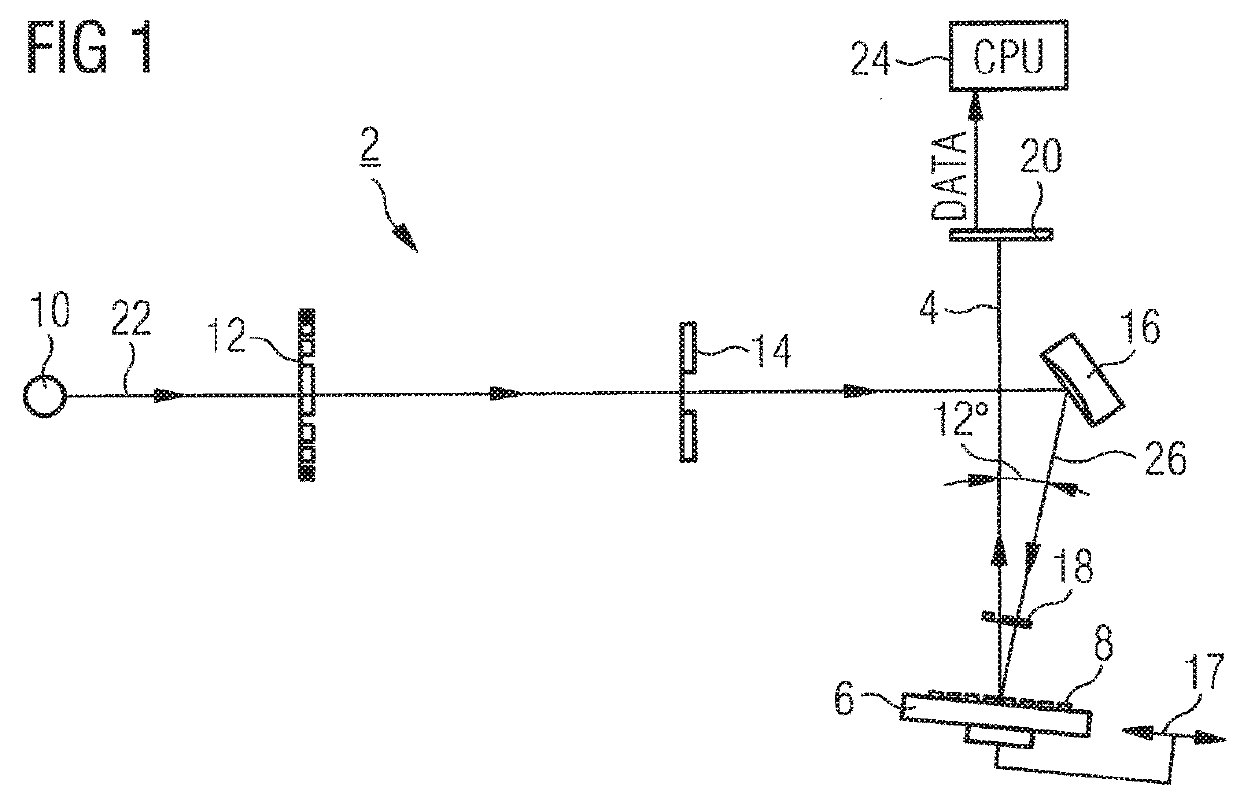
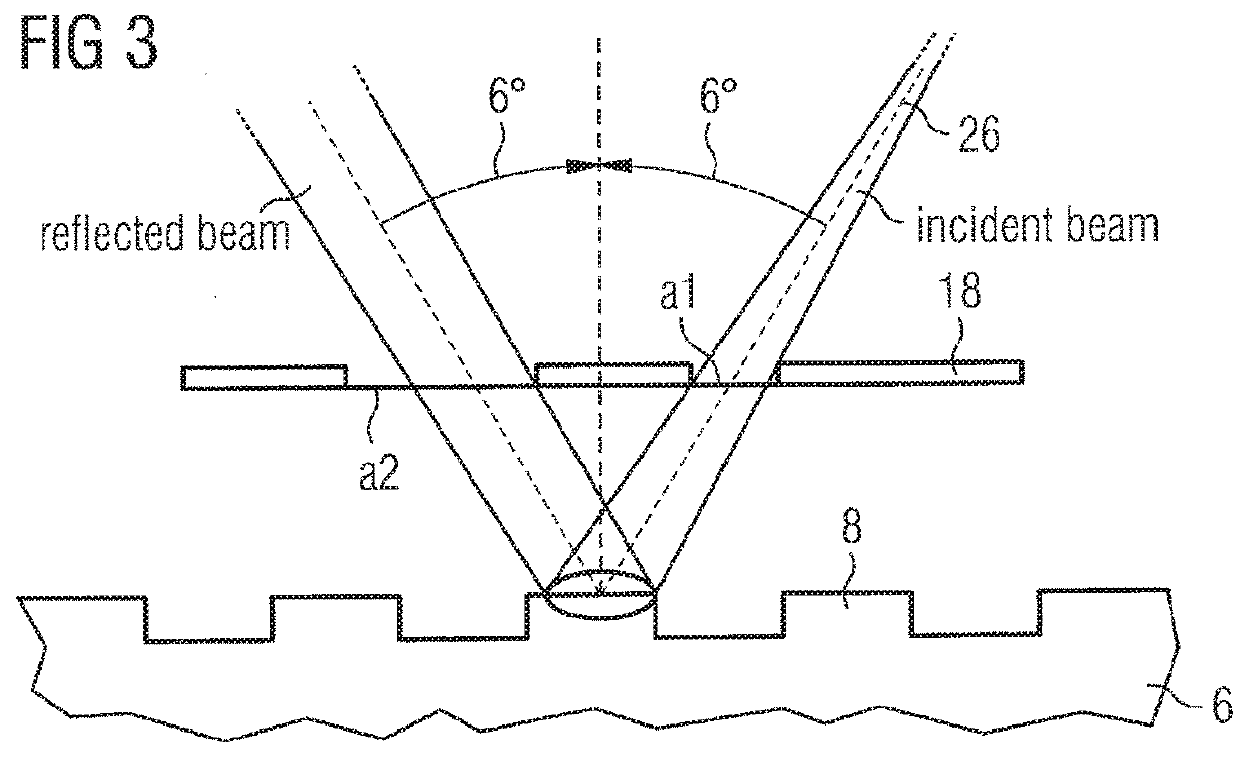
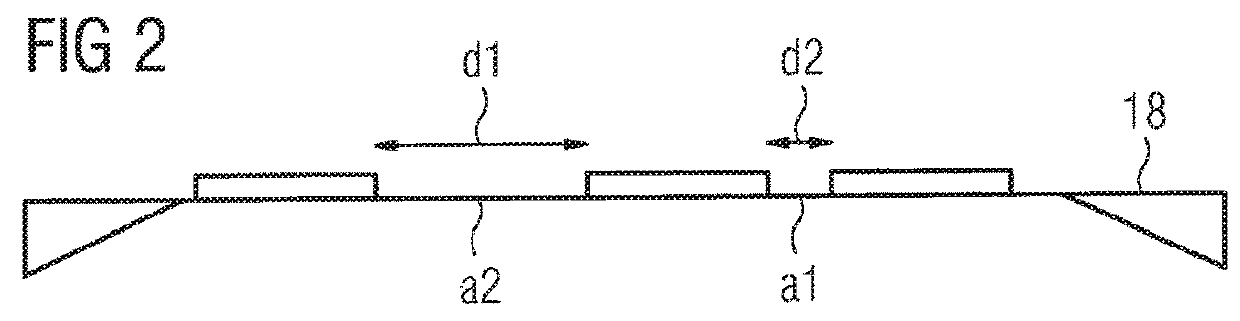
Inspection Apparatus, Inspection Method and Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20170031246A1Avoid difficultyScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansPtychographyLength wave
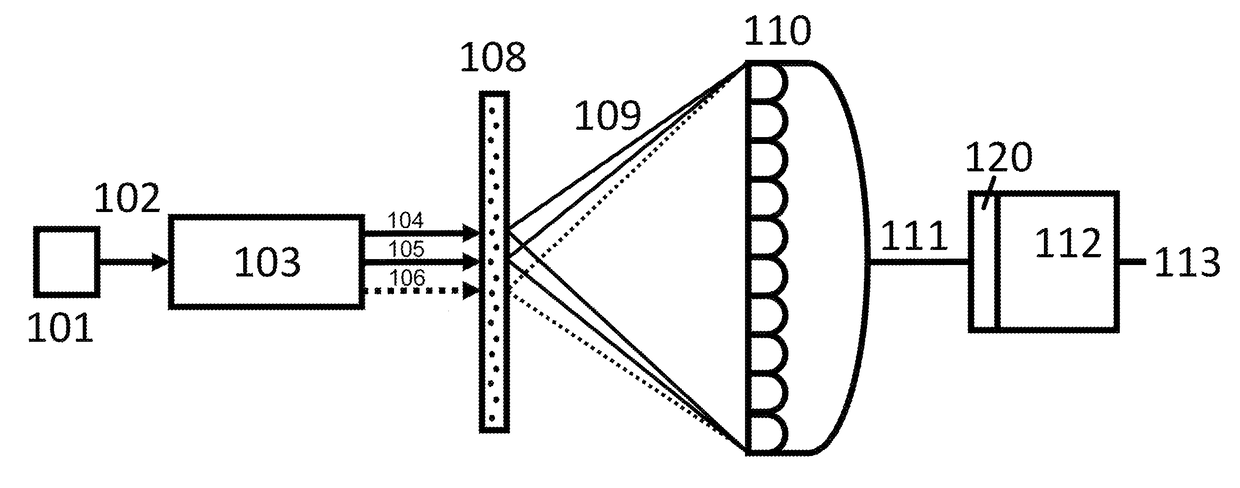
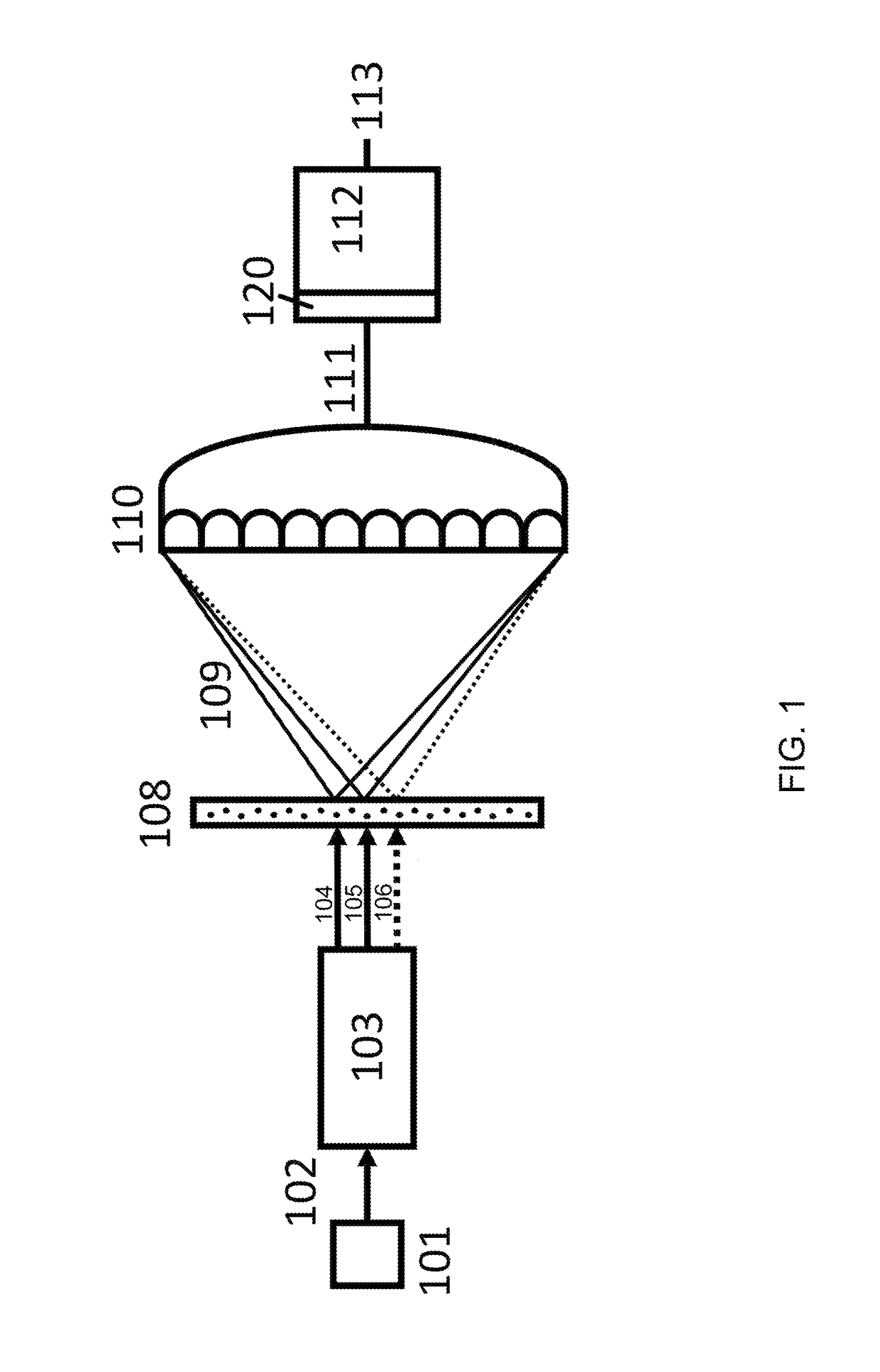
An inspection apparatus is provided for measuring properties of a non-periodic product structure (500′). A radiation source (402) and an image detector (408) provide a spot (S) of radiation on the product structure. The radiation is spatially coherent and has a wavelength less than 50 nm, for example in the range 12-16 nm or 1-2 nm. The image detector is arranged to capture at least one diffraction pattern (606) formed by said radiation after scattering by the product structure. A processor receives the captured pattern and also reference data (612) describing assumed structural features of the product structure. The process uses coherent diffraction imaging (614) to calculate a 3-D image of the structure using the captured diffraction pattern(s) and the reference data. The coherent diffraction imaging may be for example ankylography or ptychography. The calculated image deviates from the nominal structure, and reveals properties such as CD, overlay.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
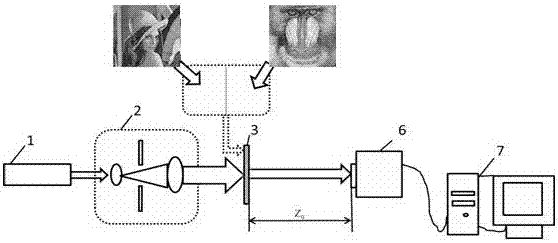
Coherent diffraction imaging method and its processing equipment
InactiveCN101482503AImprove efficiencyHigh speedPhase-affecting property measurementsCorrelation functionFourier transform on finite groups
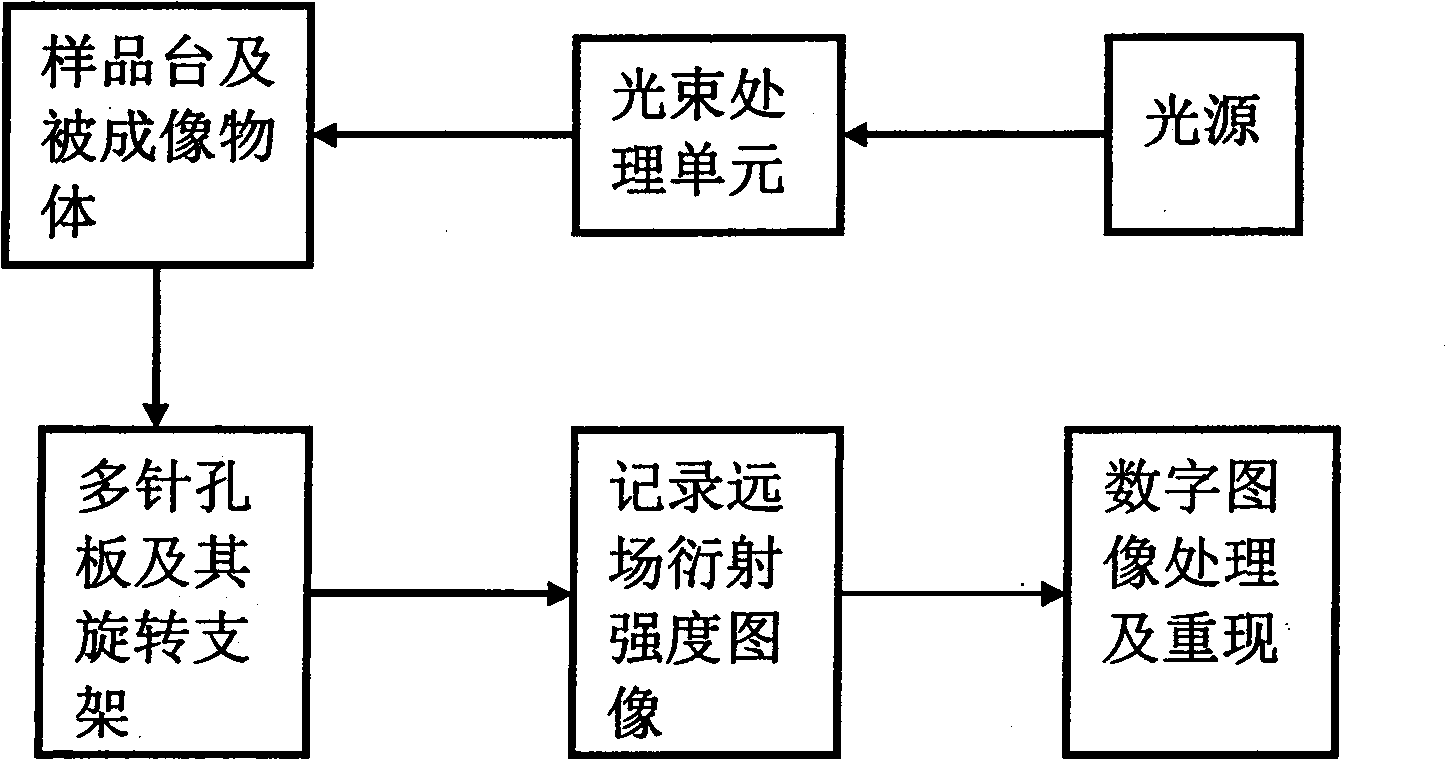
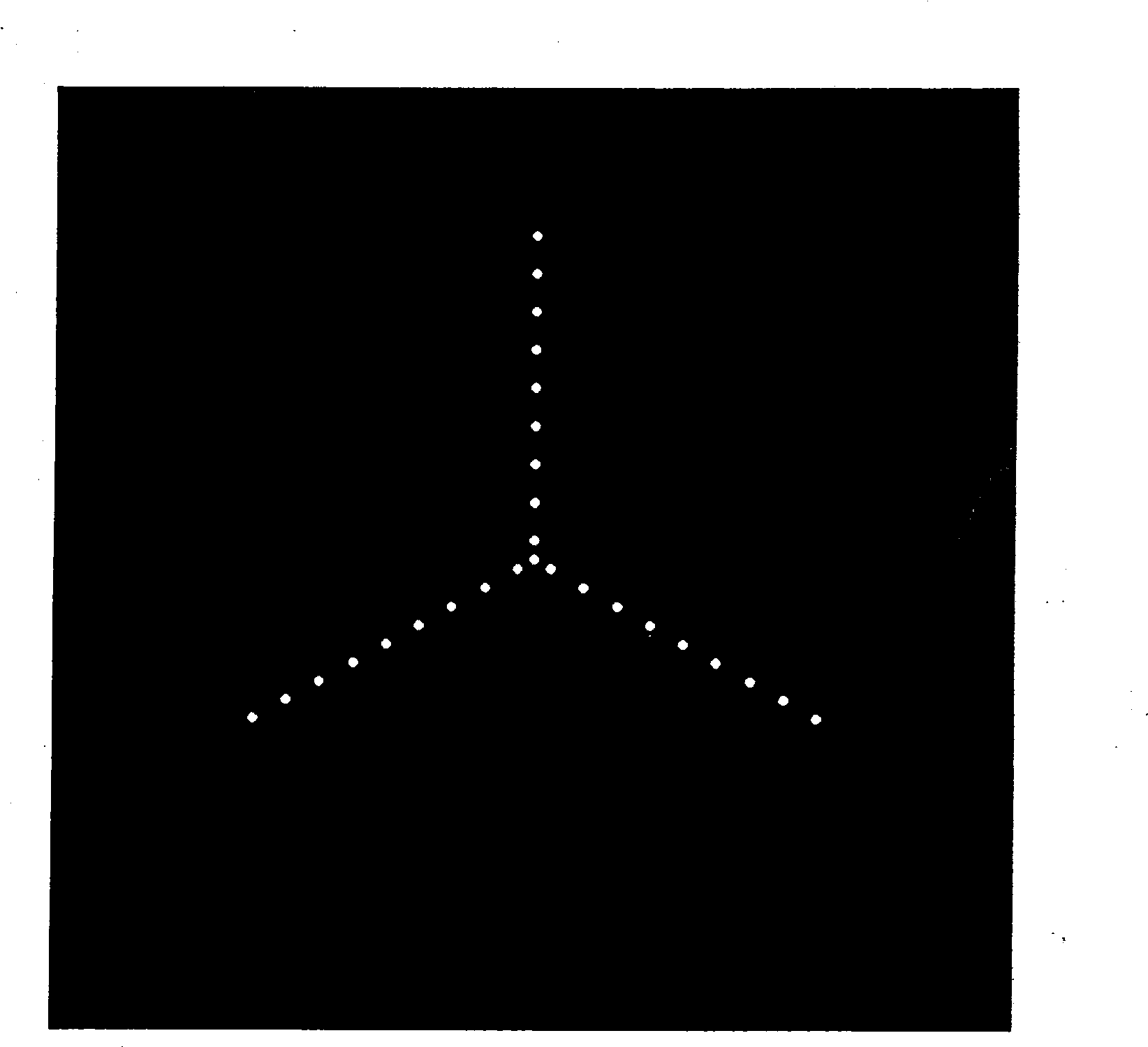
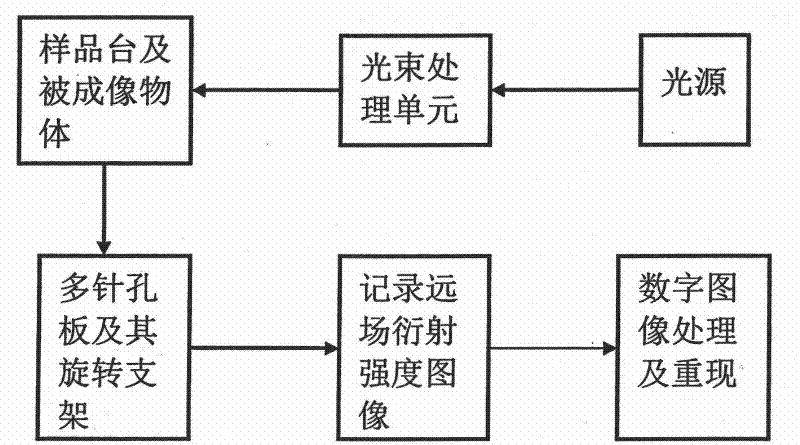
The invention discloses a coherent diffraction imaging method and processing device thereof. The object wave passes through a rotary multi-pinhole plate. The Fraunhofer diffraction intensity distribution pattern of the object wave passing through the multi-pinhole plate is recorded by an image sensor. The diffraction intensity distribution is subjected to inverse Fourier transformation to obtain the correlation function pattern of the recorded object wave, the amplitude and phase information of the object wave to be measured are directly extracted from the points corresponding with each measurement pinhole center position coordinate in the correlation function pattern and the diffraction imaging of the complex amplitude object is realized in the computer. The coherent diffraction imaging method has no need of any iterative process and greatly reduces the requirement of the scanning recording process and positioning accuracy and increases the diffraction imaging speed, with other features of simple processing device, convenient adjustment, lower cost, suitable of various different light source, and the imaging of the complex object or three-dimensional object can be realized without imaging lens, especially suitable for the situation that it is difficult to prepare high-quality X-ray using the imaging lens.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
High-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method
ActiveCN104808469AHigh resolutionFast convergenceInstrumentsTarget surfaceDigital holographic microscopy
The invention discloses a high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and a high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method. Based on a normal holographic device, the high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device is improved by adding a distribution-known random phase plate between a small-hole diaphragm and an imaging device, so that more object light information can be scattered on a target surface of the imaging device after a sample to be tested is added. The high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method includes the steps of collecting a group of holographic data, processing the holographic data by a filtering method to obtain distribution of object diffraction spots on the target surface of the imaging device, processing the diffraction spots by an improved iterative restoration algorithm similar to coherent diffractive imaging, and finally restoring a restructured image with the resolution rate much higher than that of a normal holographic image. The high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and the high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method have the advantage that a solution for current low-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
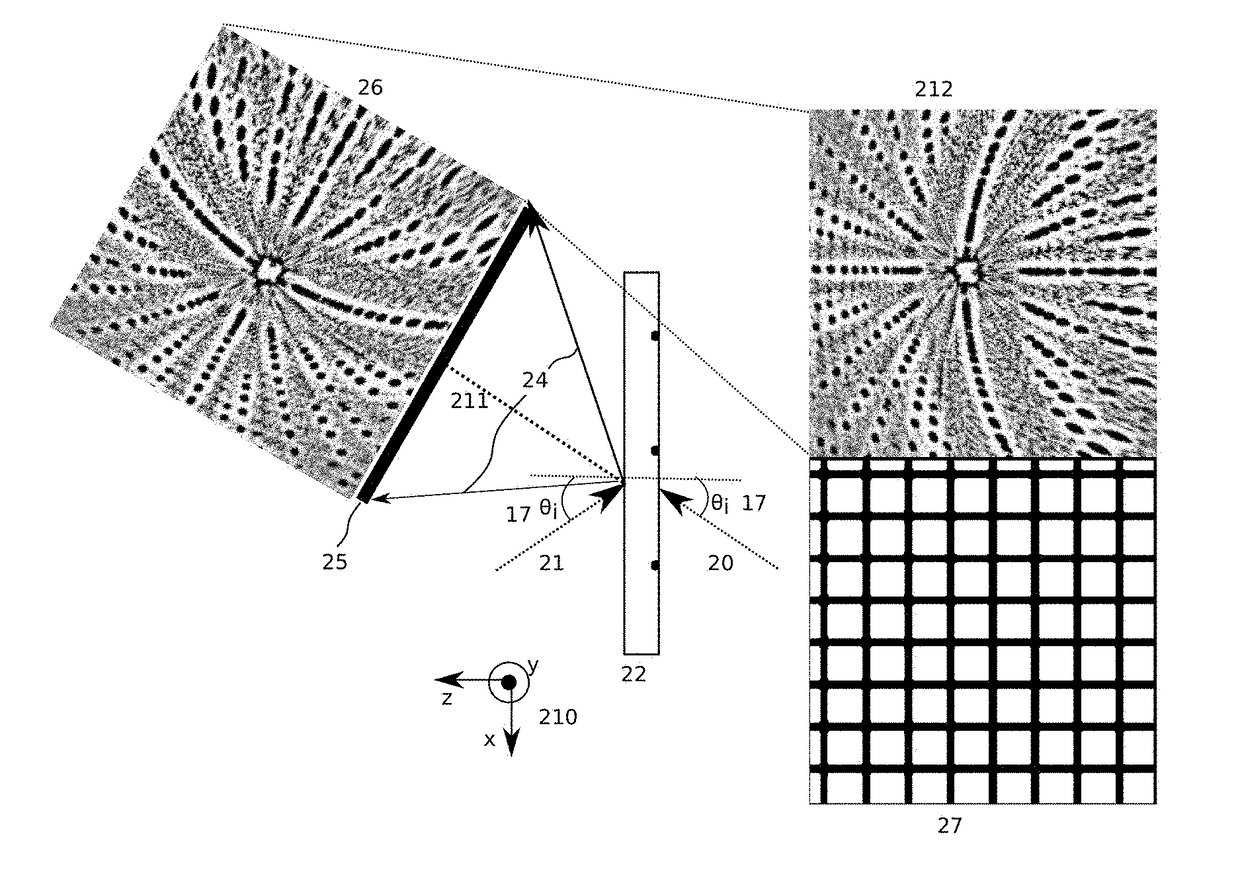
Coherent Diffractive Imaging With Arbitrary Angle of Incidence
ActiveUS20160187849A1Enhance the imageFast numerical methodImaging devicesPhotomechanical apparatusAngle of incidenceAngular degrees
Apparatus and methods for coherent diffractive imaging with arbitrary angle of illumination incidence utilize a method of fast remapping of a detected diffraction intensity pattern from a detector pixel array (initial grid) to a uniform spatial frequency grid (final grid) chosen to allow for FFT on the remapped pattern. This is accomplished by remapping the initial grid to an intermediate grid chosen to result in a final grid that is linear in spatial frequency. The initial grid is remapped (generally by interpolation) to the intermediate grid that is calculated to correspond to the final grid. In general, the initial grid (x,y) is uniform in space, the intermediate grid ({tilde over (x)},{tilde over (y)}) is non-uniform in spatial frequency, and the final grid ({tilde over (f)}x,{tilde over (f)}y) is uniform in spatial frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device
InactiveCN102903591AImprove time resolutionLow costElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionBack calculation
The invention discloses an ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device. The method is combined with the electronic pulse which is in precise synchronization with process exciting sources (such as femtosecond laser pulses) and a lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging technology, and comprises the steps of analyzing the strength distribution of the diffracted coherent electronic pulses, and carrying out back calculation to determine the electronic scattering phase, so as to achieve the reconstruction of the structure and the appearance of three-dimensional transient atomic scale. By adopting the method and device disclosed by the invention, the technical problem that the conventional electronic microimaging method has no high time resolution or the existing ultrafast electronic imaging time and space resolution are limited can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
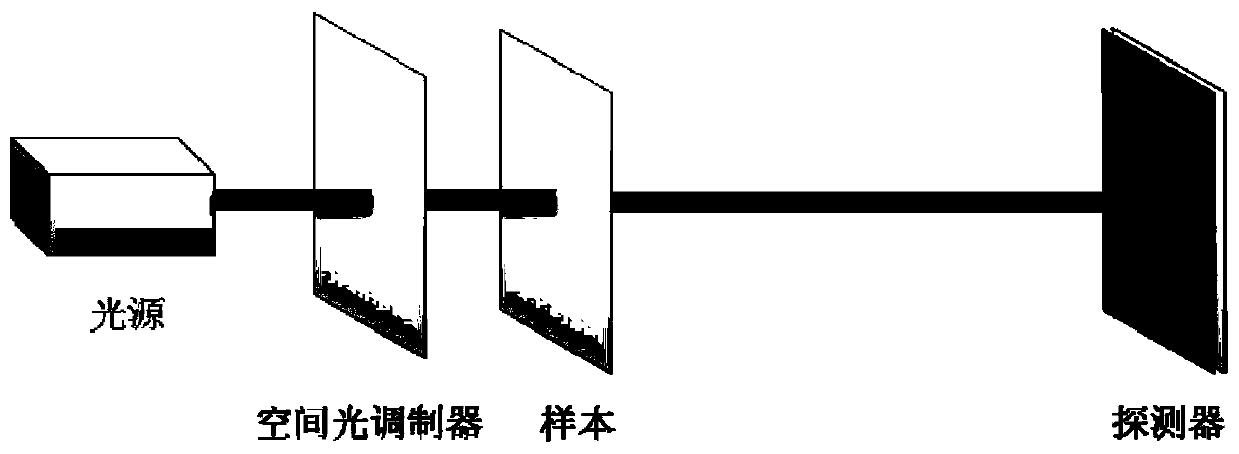
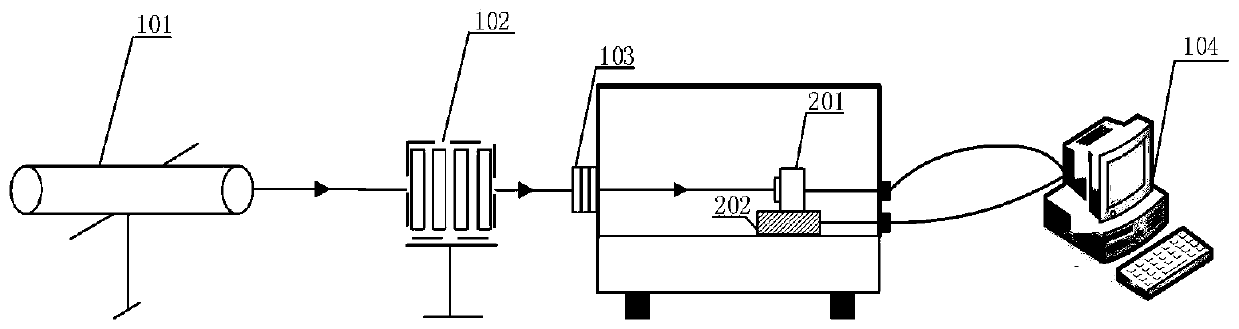
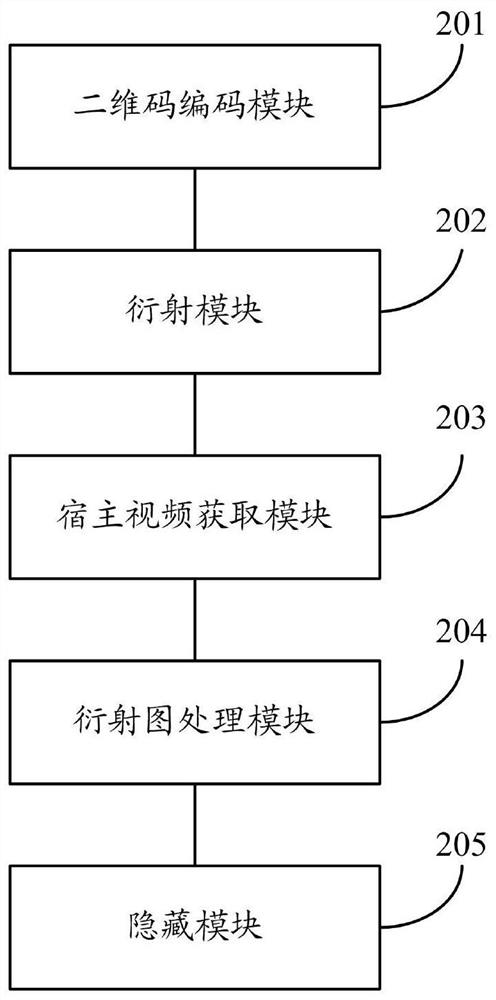
High-capacity optical information hiding method and system and high-capacity optical information extracting method and system
ActiveCN110942413AImprove privacyEnsure safetyImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial light modulatorInformation transmission
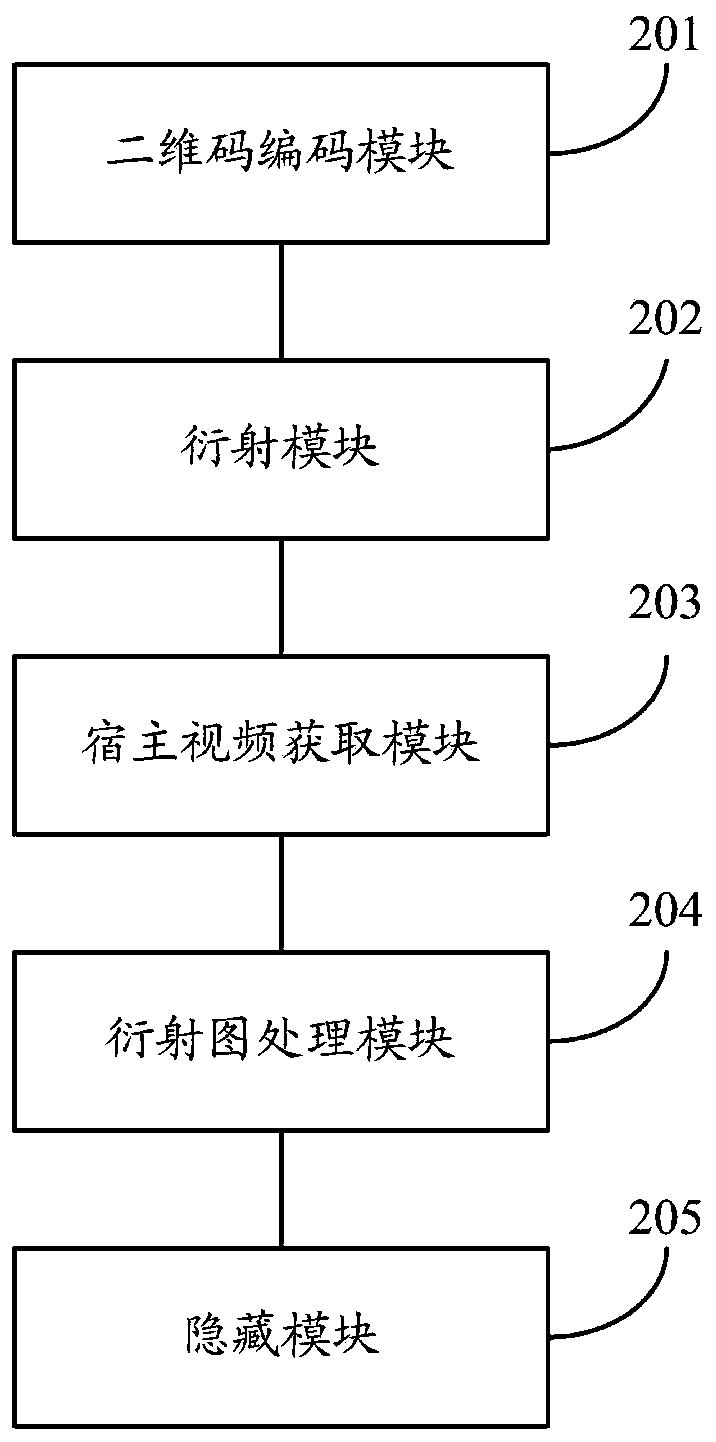
The invention relates to a high-capacity optical information hiding method and system and a high-capacity optical information extracting method and system. The hiding method comprises the steps of performing two-dimensional code encoding on to-be-hidden information to obtain a two-dimensional code set, wherein the two-dimensional code set comprises a plurality of two-dimensional codes corresponding to the to-be-hidden information; diffracting the two-dimensional codes in the two-dimensional code set through a reflective coherent diffraction imaging system comprising a spatial light modulator to obtain a diffraction pattern set, wherein the diffraction pattern comprises a diffraction pattern corresponding to each two-dimensional code; obtaining a host video; processing diffraction patternsin the diffraction pattern set according to a host video to obtain a processed image; and hiding the processed video file in the host video to obtain a to-be-transmitted video file with hidden information. According to the invention, the security of information transmission can be improved.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
A phase recovery image reproduction method for lensless imaging
InactiveCN109472842AAccurate reconstructionReduce mistakes2D-image generationOptical elementsNormalized root mean square errorPtychography
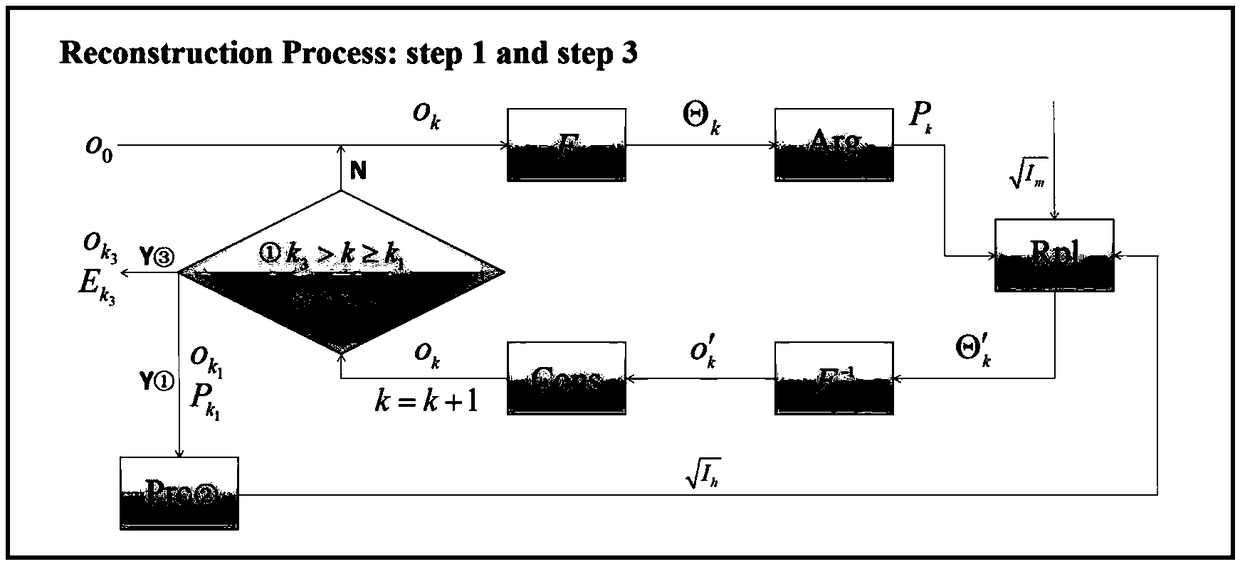
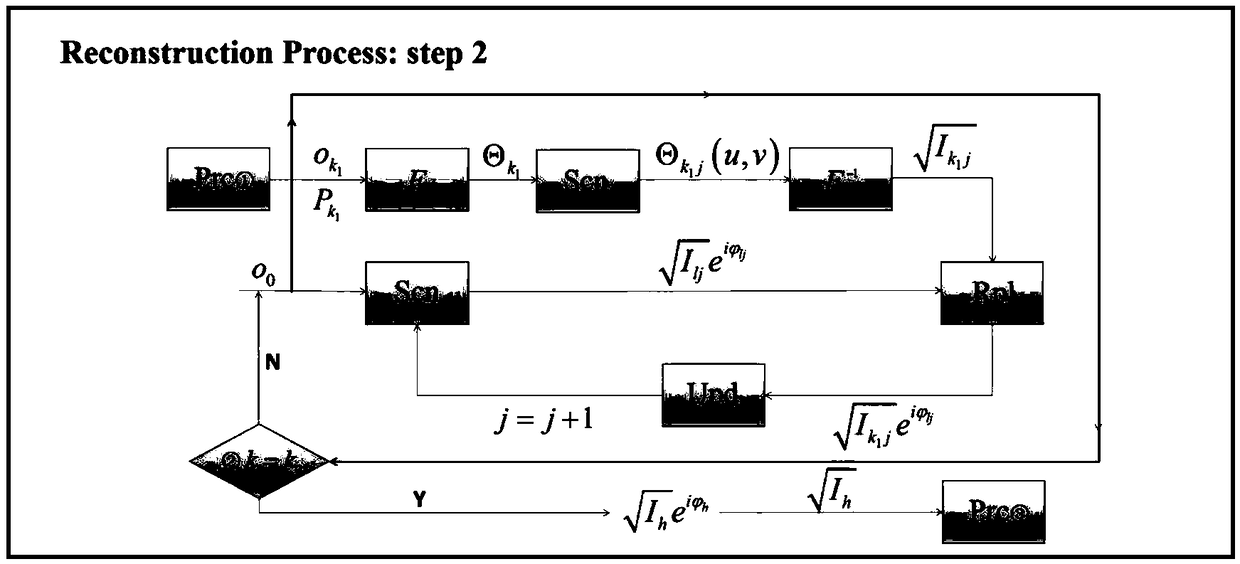
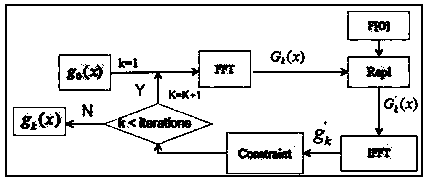
The invention provides a phase recovery image reproduction method for lensless imaging, Fast power spectra were captured by the experimental device of coherent diffraction imaging, the imaging devicerequires only one collimated beam-spreading laser, A Fourier lens and a CCD detector, the detected power spectrum is reconstructed in three steps, the first step is to calculate an initial phase by using a hybrid input-output algorithm, Soft aperture scanning is then performed, instead of scanning in the target plane and the spatial spectral plane, The second step combines the Ptychography algorithm to enhance the Fourier domain constraints, and uses the phase iterative restoration algorithm to achieve the reconstruction of the target image. In the third step, in order to further reduce the normalized root mean square error, the error reduction algorithm is used to reconstruct the target image. The imaging device of the invention is simple, and the algorithm can quickly reconstruct an accurate target image from a power spectrum diagram, thereby realizing the function of image reproduction.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Wave aberration detecting system and method with knife edge as detection marker
ActiveCN105651493ASimple structureEasy to operateGeometric properties/aberration measurementSurface patternPtychography
The invention discloses a wave aberration detecting system with a knife edge as a detection marker and a wave aberration detecting method based on the knife-edge testing technology and the Ptychography technology. The wave aberration detecting system comprises a coherent point light source, a knife-edge graph serving as the detection marker, a detection-marker adjusting displacement platform for fixing the knife-edge graph and a two-dimensional photoelectric sensor. As the wave aberration of a to-be-detected projection lens is detected through the wave aberration detecting system, the system structure can be simplified, the collecting times of an observation surface pattern are decreased, and the detecting speed and the detecting accuracy of the system are increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
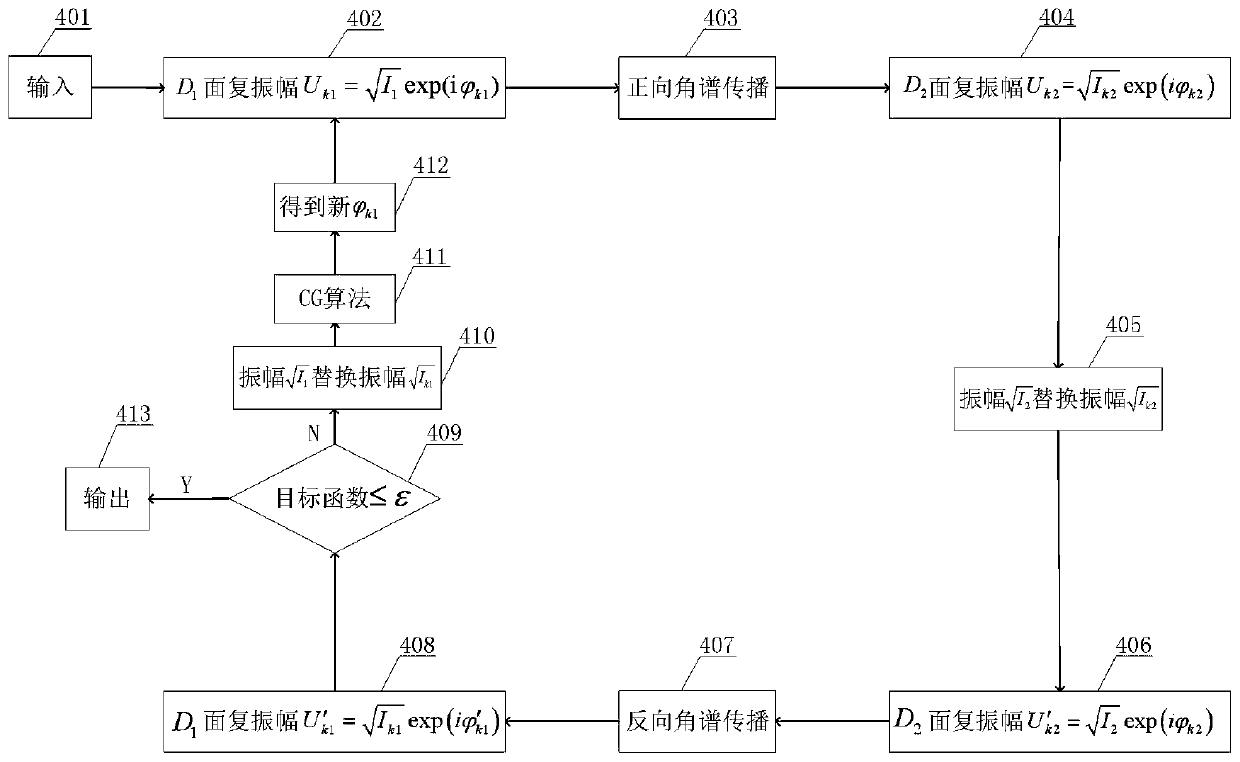
Laser complex amplitude measuring method and system based on coherent diffraction imaging
ActiveCN108760056AImproved sampling resolutionLarge dynamic rangeOptical measurementsUltrasound attenuationComplex amplitude
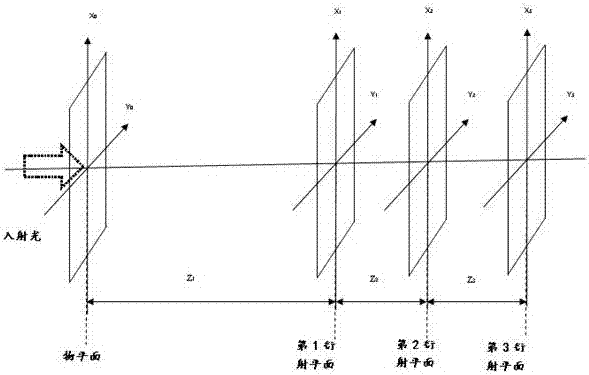
The invention discloses a laser complex amplitude measuring method and system based on coherent diffraction imaging. The measuring method comprises the following steps: establishing an optical measuring system, wherein the optical measuring system comprises a laser, an optical attenuation group, an attenuator, a camera and a motorized translation stage; controlling the camera to move to a positionz1 by the motorized translation stage, and acquiring a D1 surface light spot image of the position z1 by the camera so as to acquire a first light spot image; controlling the camera to move to a position z2 at which the light spot size change can be seen clearly by the motorized translation stage, and acquiring a D2 surface light spot image of the position z2 by the camera so as to acquire a second light spot image; calculating an actual wavefront inclination of the laser; calculating complex amplitude of the first light spot image according to the actual wavefront inclination, an objective function and the second light spot image. The measuring method disclosed by the invention is high in sampling resolution and wide in dynamic range, and the laser complex amplitude can be accurately measured.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
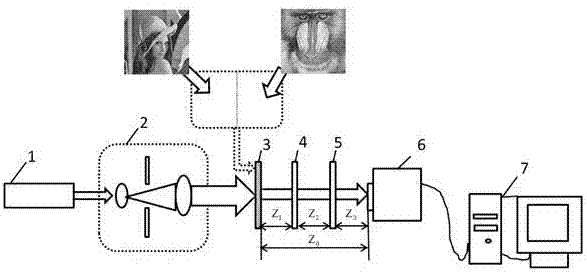
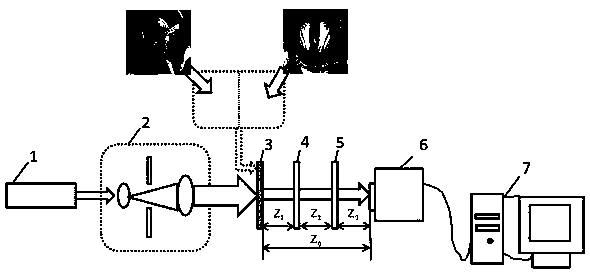
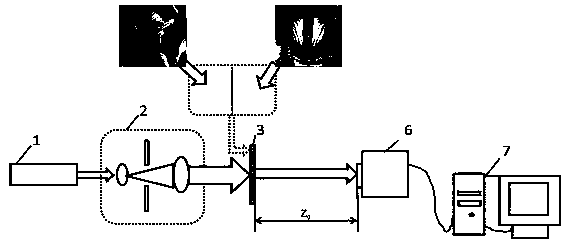
Novel three-step lens-free coherent diffractive imaging method
ActiveCN107101974AImprovement of Experimental ImplementationAvoid random errorsScattering properties measurementsComplex amplitudeImaging algorithm
The invention relates to a novel three-step lens-free coherent diffractive imaging method. The method is characterized in that laser beams subjected to collimation and beam expansion are used to illuminate a to-be-measured sample, and recording a diffraction pattern when the front end of CCD has no optical parallels, a diffraction pattern when the front end of the CCD has one optical parallel and a diffraction pattern when the front end of the CCD has two optical parallels; using an algorithm combining wave filtering and coherent diffractive imaging to process the three diffraction patterns, and rebuilding the complex amplitude image of the to-be-measured sample. The novel three-step lens-free coherent diffractive imaging method has the advantages that the bottleneck problem that a traditional coherent diffractive imaging method needs to move the CCD or the to-be-measured sample for multiple times is solved effectively, the problems of random errors during moving and experiment operability are solved at the same time, the method is simple and fast in experiment operation and high in operability, the coherent diffractive imaging algorithm is effectively combined with wave filtering, and convergence rate and a sample recovery effect are increased.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
Imaging method for target hidden in opaque scattering medium
InactiveCN110231310AUniqueness guaranteedMeet imaging real-time requirementsPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsFrequency spectrumReconstruction algorithm
The invention provides an imaging method for a target hidden in an opaque scattering medium. An imaging light path is formed on the basis of a conventional coherent diffraction imaging principle, whenthe target is blocked by the opaque scattering medium, an object is radiated by laser, and the target hidden behind the scattering medium is reconstructed. Imaging devices only comprise a laser, a scattering device, a Fourier lens and a CCD detector. According to the method, a reconstruction algorithm is a hybrid input-output phase retrieval algorithm; the target can be reconstructed only by collecting a single power spectrum image; in the reconstruction algorithm, an initial guess for the target employs an image obtained by carrying out inverse Fourier transform on the power spectrum image collected in an experiment, so convergence of the algorithm is accelerated; feedback parameters (which are 0.3-0.8, 0.8-1.0 and 1.0-1.25 respectively selected in an underexposure state, a correct exposure state and an overexposure state ) of the algorithm are adjusted for the power spectrum images which are collected in real time in different exposure degrees; and finally, the target hidden in thescattering medium is reconstructed.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Coherent diffractive imaging with arbitrary angle of incidence
ActiveUS9891584B2Enhance the imageFast numerical methodImaging devicesScattering properties measurementsAngle of incidenceComputational physics
Apparatus and methods for coherent diffractive imaging with arbitrary angle of illumination incidence utilize a method of fast remapping of a detected diffraction intensity pattern from a detector pixel array (initial grid) to a uniform spatial frequency grid (final grid) chosen to allow for FFT on the remapped pattern. This is accomplished by remapping the initial grid to an intermediate grid chosen to result in a final grid that is linear in spatial frequency. The initial grid is remapped (generally by interpolation) to the intermediate grid that is calculated to correspond to the final grid. In general, the initial grid (x,y) is uniform in space, the intermediate grid ({tilde over (x)},{tilde over (y)}) is non-uniform in spatial frequency, and the final grid ({tilde over (f)}x,{tilde over (f)}y) is uniform in spatial frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Coherent Diffractive Imaging With Spaced-Apart Beams
ActiveUS20170069116A1Reconstruction from projectionHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesLight beamComputational physics
Apparatus and methods for Coherent Diffractive Imaging with multiple, simultaneous, spatially distinct beams chosen and configured to isolate incoherent sums of beam diffraction such that interference between the multiple beams is not present in the data prior to computationally reconstructing the image. This is accomplished through selecting the multiple beams to be non-interfering modes, or through designing the apparatus such that the interference is not recorded, or through processing the collected data to filter the interference before reconstructing the image.
Owner:KM LABS INC
Quantum-limited Extreme Ultraviolet Coherent Diffraction Imaging
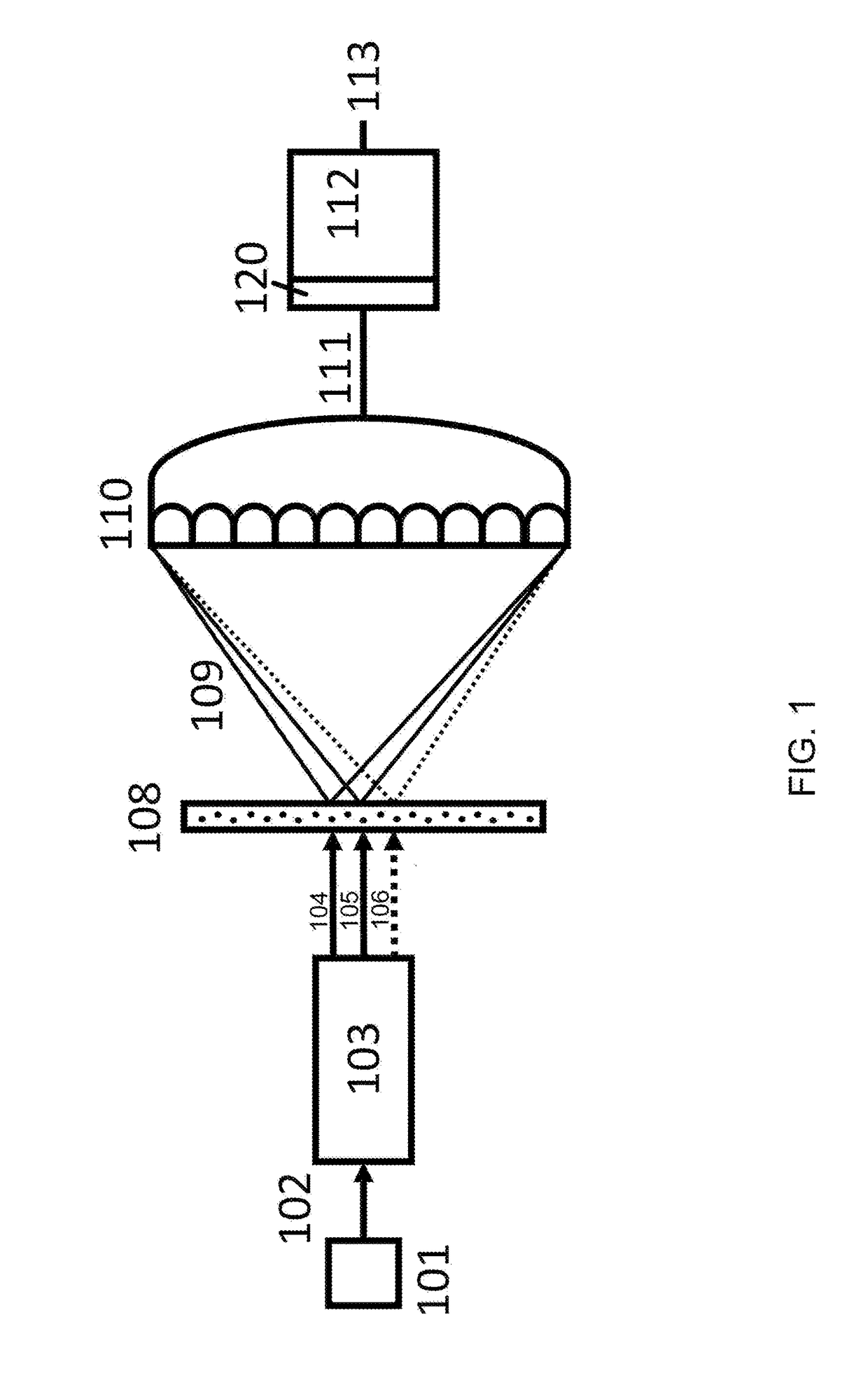
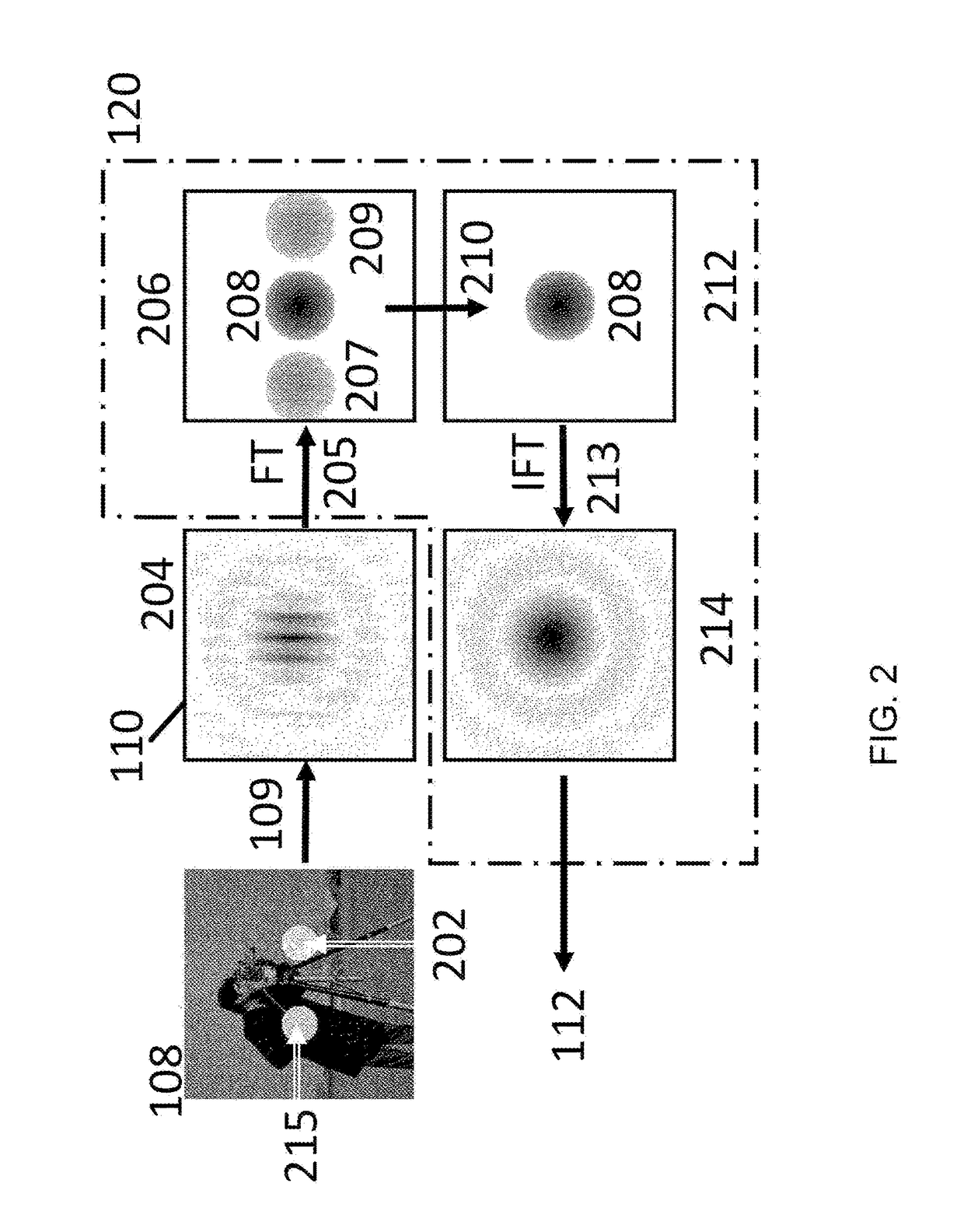
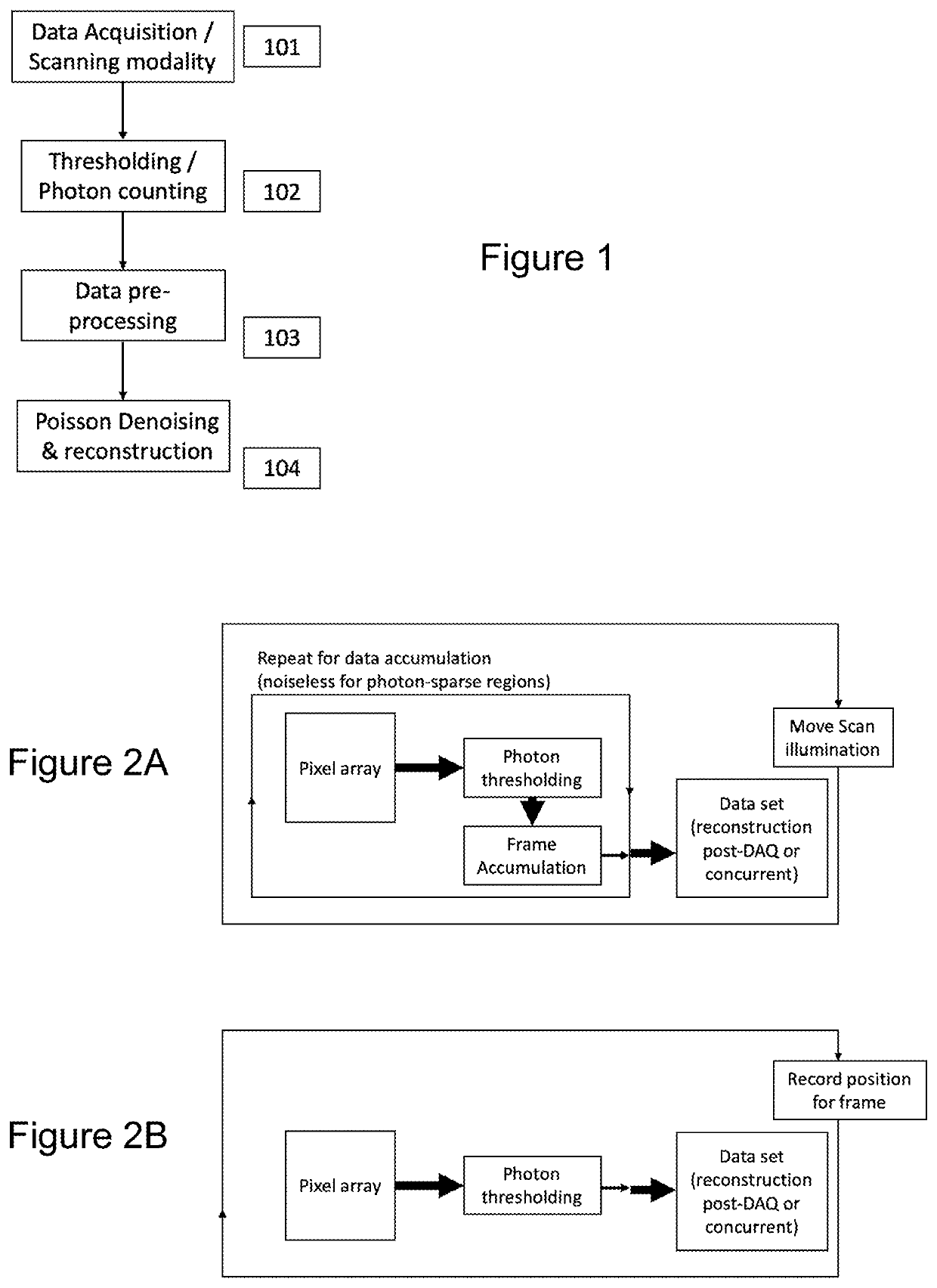
PendingUS20220100094A1Better accuracy-itContinuous scanPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusCMOSCoherent diffraction imaging
Apparatus and methods for coherent diffraction imaging This is accomplished by acquiring data in a CDI setup with a CMOS or similar detector. The object is illuminated with coherent light such as EUV light which may be pulsed. This generates diffraction patterns which are collected by the detector, either in frames or continuously (by recording the scan position during collection). Pixels in the CDI data are thresholded and set to zero photons if the pixel is below the threshold level. Pixels above the threshold may be set to a value indicating one photon, or multiple thresholds may be used to set pixels values to one photon, two photons, etc. In addition, multiple threshold values may be used to detect different photon energies for illumination at multiple wavelengths.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Ultra-short pulse laser-based extreme ultraviolet light generation system with high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength
InactiveCN110289538AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityLaser detailsGratingOptical parametric amplifier
The invention discloses an ultra-short pulse laser-based extreme ultraviolet light generation system with high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength. The method comprises the steps that fundamental frequency light output by an ultra-short pulse laser is subjected to wavelength conversion through an optical frequency multiplier or an optical parameter amplifier; and the converted pulse laser is focused on an inert gas through a higher harmonic generator to be radiated to generate higher harmonics, wavelength selection is carried out through an extreme ultraviolet monochromator, and finally high-energy and high-luminous flux monochromatic extreme ultraviolet light is output. The invention has high stability, signal to noise ratio is good, an optical frequency multiplier or an optical parameter amplifier is adopted to carry out wavelength conversion on ultra-short pulse fundamental frequency light; high-order harmonics with specific photon energy are selected from high-order harmonic spectrums through a light splitting grating, a reflector and a multi-dimensional adjusting structure, high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength are achieved, and generated high-energy and high-luminous-flux extreme ultraviolet light can be used for research of a time resolution and angle resolution photoelectron spectroscopy system and an extreme ultraviolet light coherent diffraction imaging system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Imaging system in reflection mode using coherent diffraction imaging methods and using micro-pinhole and aperture system
ActiveUS10042270B2Improve throughputQuiet simplePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam diameterLight beam
A reflective sample, such as a mask, is imaged in an optics system. A radiation source emits a light beam with relatively low coherence. A first focusing element focuses the beam before a mirror reflects the focused beam towards the sample at an incidence angle of between 2 and 25° A pinhole aperture plate upstream of the sample has a first aperture to focus and cut-off the beam diameter to form a more monochromatic beam. The sample is displaced by a mechanism in a direction perpendicular to the normal vector of the sample surface while it reflects the light beam. The reflected beam passes a second aperture in the pinhole aperture plate next to the first aperture on its way to a pixel detector. The second aperture limits the diameter of the reflected beam, thereby adjusting the diameter of the light beam before it reaches the pixel detector.
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Imaging method and device based on narrow dynamic range acquisition and adaptive phase recovery
ActiveCN111556257ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsTwo dimensional detectorDomain imaging
The invention discloses an imaging method and device based on narrow dynamic range acquisition and adaptive phase retrieval, and the method comprises the steps: establishing a complex domain imaging optical path; modulating the sample light field for multiple times; performing coherent diffraction imaging through a complex domain imaging light path, keeping a two-dimensional detector of the complex domain imaging light path in a preset state, and collecting a plurality of narrow dynamic range light intensity images of an optical Fourier plane; and reconstructing complex domain information of the observation sample by using an adaptive phase retrieval algorithm according to the acquired multiple narrow dynamic range light intensity images. According to the imaging method, the purpose of complex field imaging can be achieved based on narrow dynamic range collection and self-adaptive phase recovery, the exposure time of single measurement is shortened, photothermal damage caused by measurement is reduced, and the reliability and accuracy of imaging are effectively guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Large-aperture optical element surface shape detection method based on stacked coherent diffraction imaging
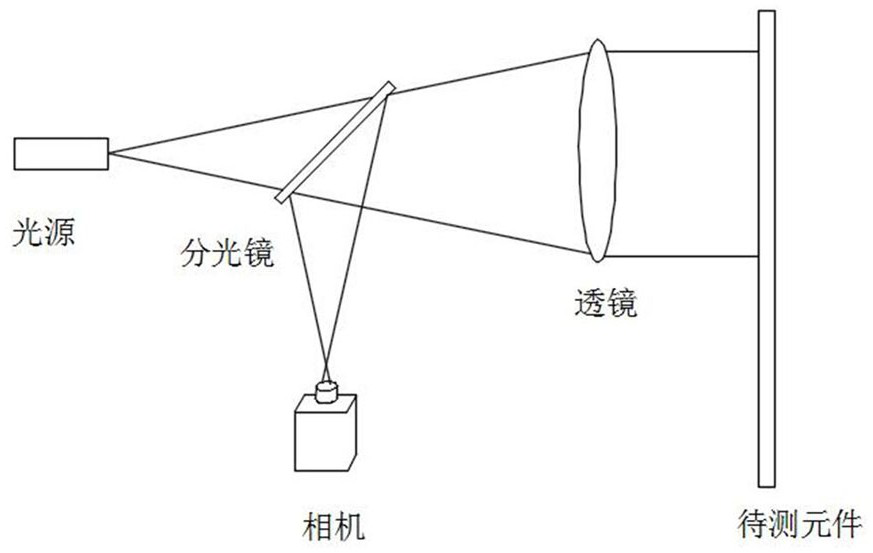
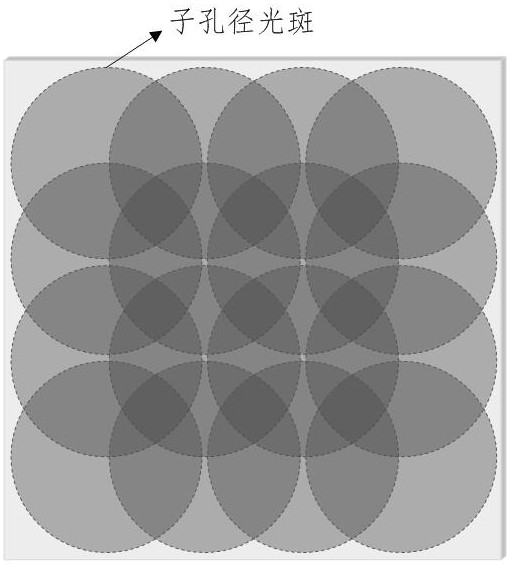
ActiveCN113091644ALarge field of viewLarge measuring rangeImage analysisUsing optical meansLight spotCoherent diffraction imaging
The invention discloses a large-aperture optical element surface shape detection method based on stacked coherent diffraction imaging, relates to the technical field of optical detection and digital image processing, solves the technical problem of small measurement view field in the existing stacked coherent diffraction imaging technology, and realizes surface shape measurement of a large-aperture optical element. Comprising the following steps: moving a to-be-measured element to an initial sub-aperture scanning position and performing alignment; acquiring diffraction spots by using a camera; the element to be measured is translated to the next sub-aperture scanning position, diffraction spots are collected, and sub-apertures at the adjacent sub-aperture scanning positions need to have a certain overlapping area; the scanning sub-aperture light spot covers the to-be-detected area of the optical element; processing the collected series of diffraction images, and recovering the surface shape distribution of the to-be-measured element by adopting a stacked coherent diffraction imaging iterative algorithm; the device is used for detecting the surface shape of the large-aperture optical element, and has the advantages of large measuring aperture, simple optical path and low cost.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
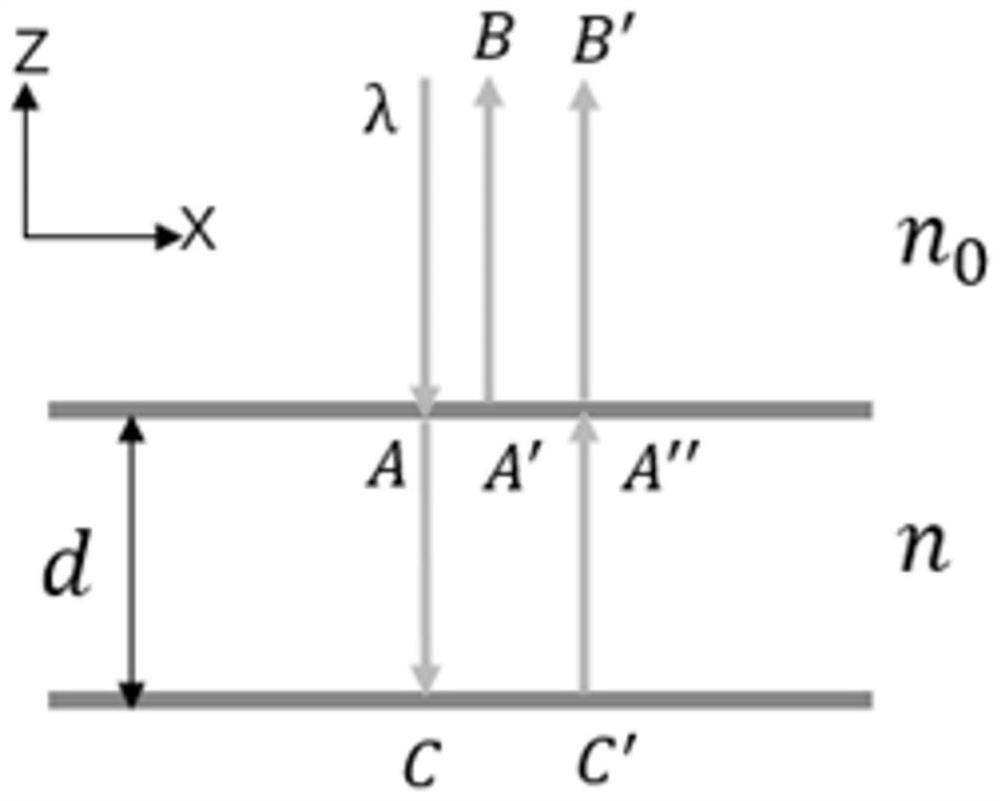
Analytic dual-wavelength phase decoupling method
PendingCN114112075AAvoid destructionReduce complexityOptical measurementsEngineeringComputational physics
The invention relates to coherent diffraction imaging, in particular to an analytic dual-wavelength phase decoupling method, which is used for overcoming the defects that the complexity of a measurement system is increased and the measurement speed is reduced due to a scanning technology or the original state of a sample is damaged due to a perfusion technology in the conventional phase decoupling method. According to the analytical dual-wavelength phase decoupling method, a scanning technology or a perfusion technology is not used any more, an imaging detector is used for recording intensity information of diffraction images under different wavelengths, and a high-order equation set is solved through a design algorithm, so that refractive index distribution and thickness distribution of a sample are obtained.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Detection method for bottom morphology of phase defect in multilayer film with extreme ultraviolet lithography mask
ActiveCN109031894BPrevent movementEliminate detection errorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial imageCoherent diffraction imaging
A method for detect that bottom topography of a phase-type defect of an EUV photolithography mask multilayer film is disclosed. The method includes modeling and detection. In the modeling phase, firstly, the spatial images of blank mask with multilayer phase defects under different illumination conditions are simulated by photolithography simulation software. Fourier transform coherent diffractionimage (FPI) is used to recover that phase of the spatial image, Finally, an artificial neural network is used to establish the detection model, which takes the spatial image information as input andthe mask multilayer phase defect bottom topography parameters as output. In the detection phase, the actual mask space image is collected, and the bottom topography parameters of the actual mask defects are calculated by using the detection model, and the bottom topography of the mask multilayer phase defects is detected. The invention can quickly and accurately detect the topography of the bottomof the phase type defect of the extreme ultraviolet photolithography mask multilayer film.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extreme ultraviolet light generating system with high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength based on ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveCN109638624AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityLaser detailsGratingOptical parametric amplifier
The invention discloses an extreme ultraviolet light generating system with high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength based on an ultrashort pulse laser. The fundamental frequency light outputted by the ultrashort pulse laser passes through an optical frequency multiplier or an optical parametric amplifier for wavelength conversion, converted pulsed laser is focused on inert gas by ahigher harmonic generator to radiate and generate higher harmonics, the wavelength is selected by an extreme ultraviolet monochromator, and finally monochromatic extreme ultraviolet light with high energy and high luminous flux is outputted. The extreme ultraviolet light generating system has the advantages of high stability, good signal-to-noise ratio, the wavelength conversion of an ultrashort pulse fundamental frequency light is carried out by using the optical frequency multiplier or the optical parametric amplifier, the higher harmonics of specific photon energy is selected from a higherharmonic spectrum by using a spectroscopic grating, a mirror and a multi-dimensional adjustment structure, the high efficiency and continuously adjustable wavelength are achieved, the generated high energy and extreme ultraviolet light can be used for the research of a time-resolved and angular-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy system and an extreme ultraviolet coherent diffraction imaging system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
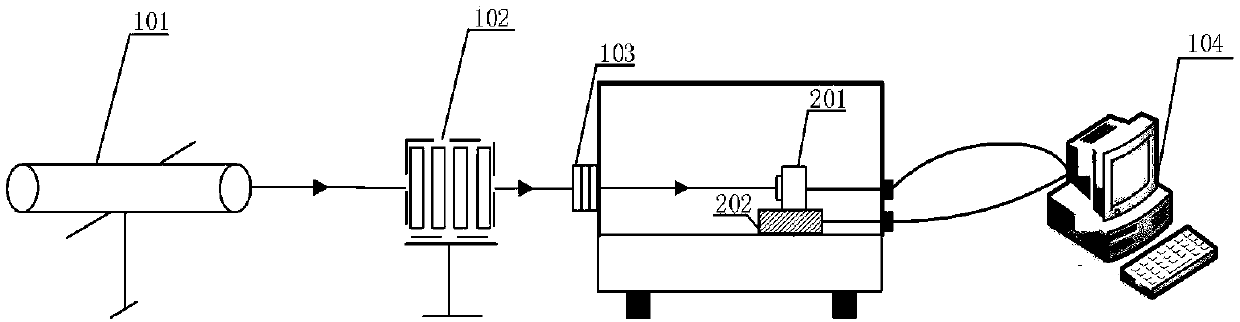
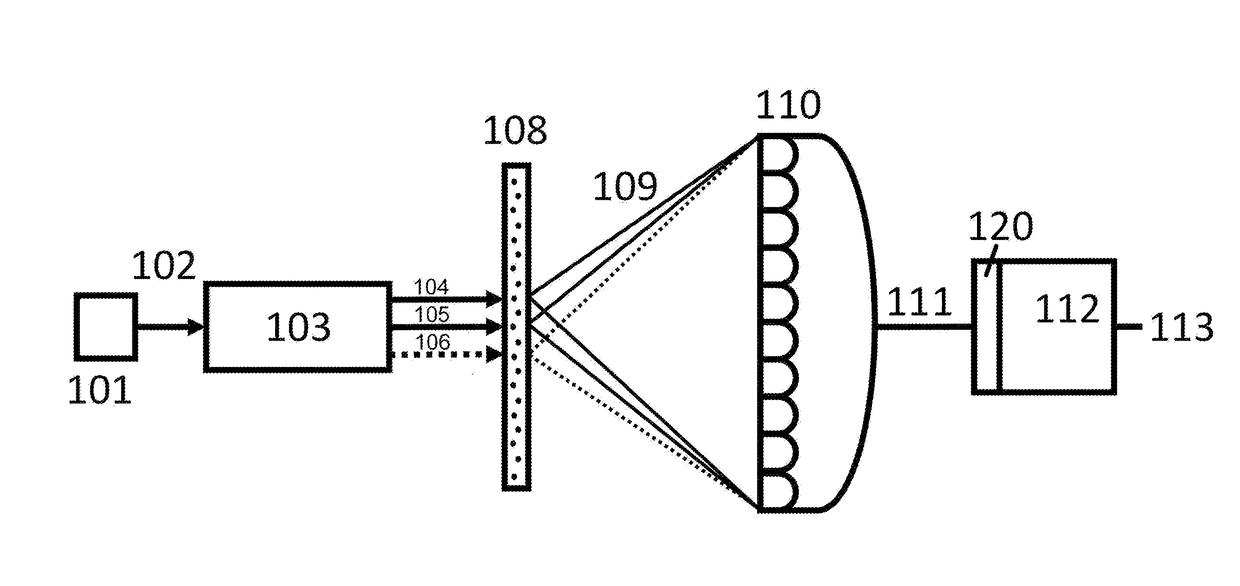
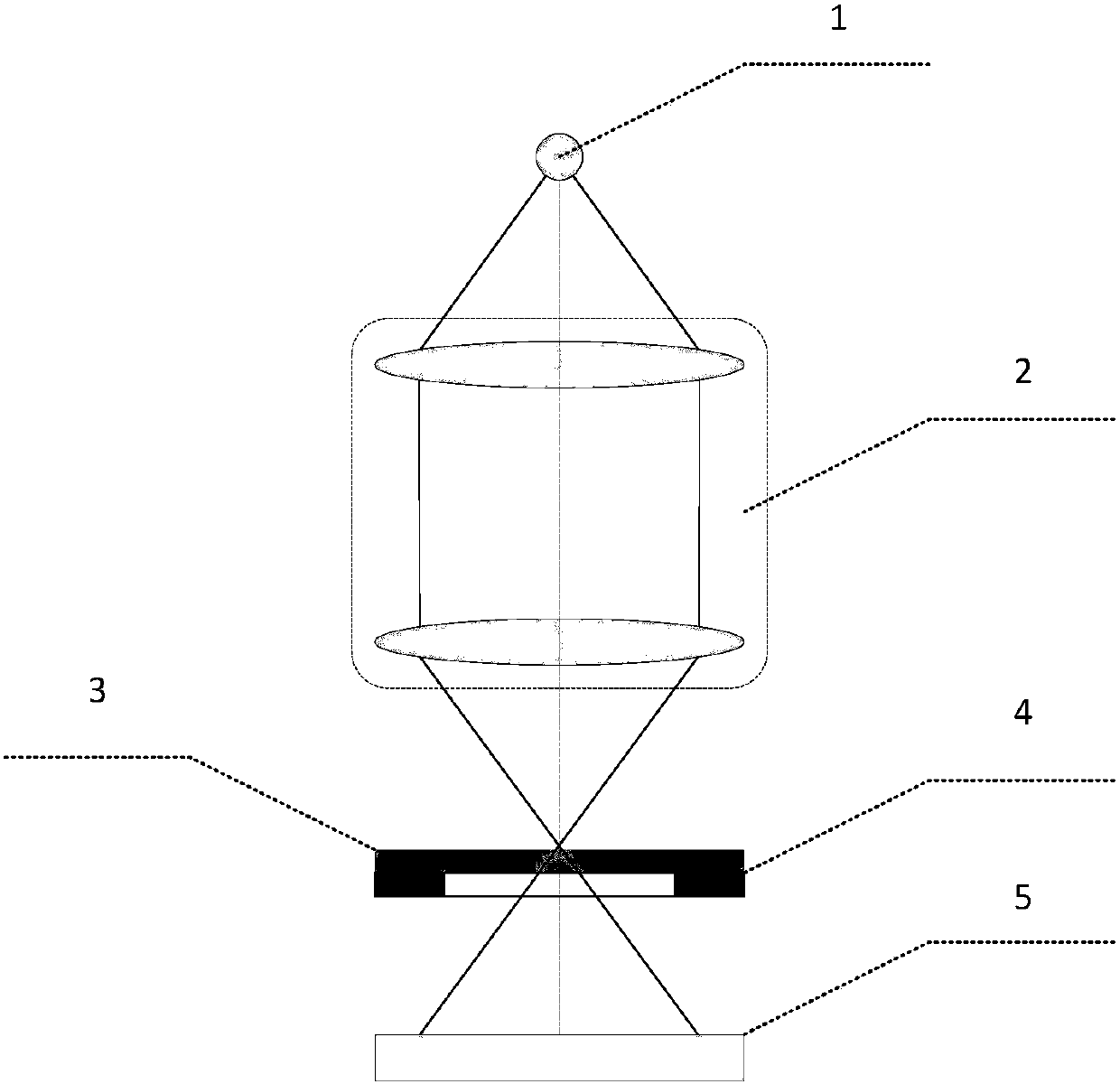
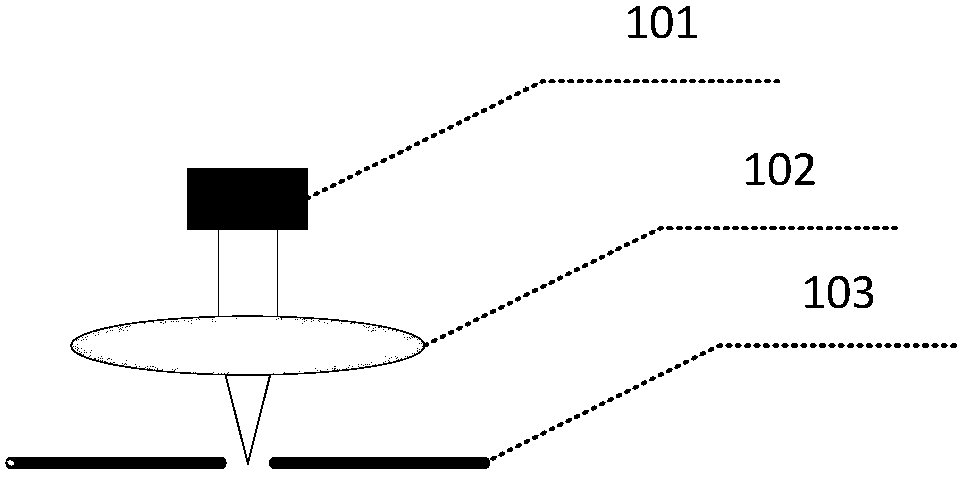
Single exposure high numerical aperture pulsed laser coherent diffraction imaging device and method of use
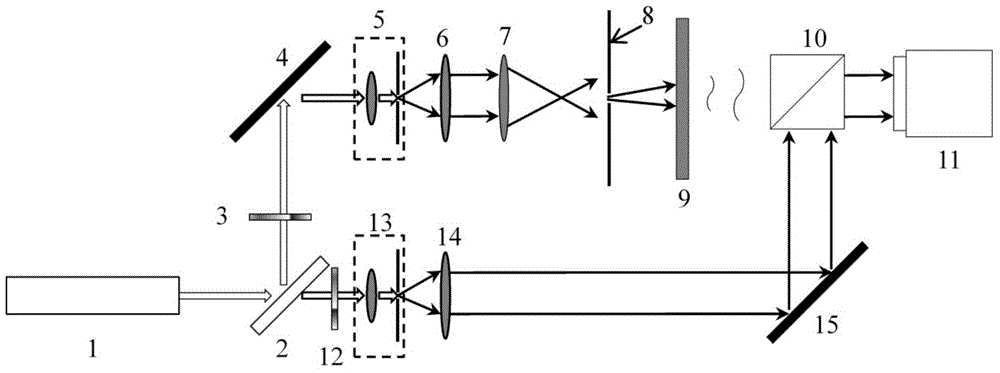
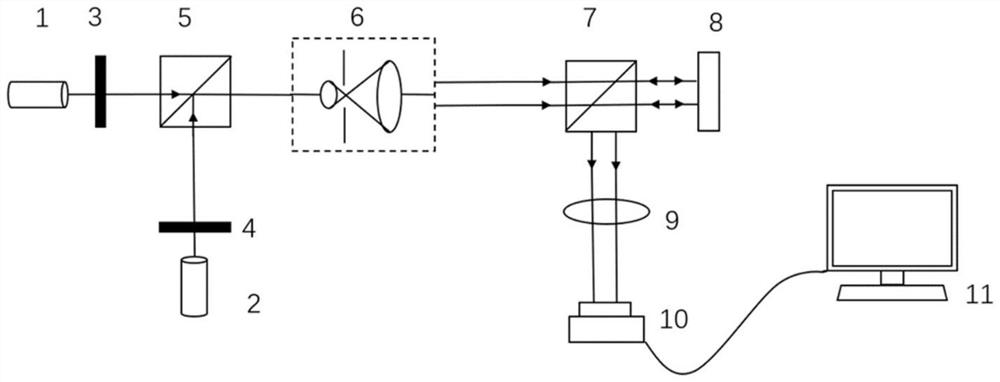
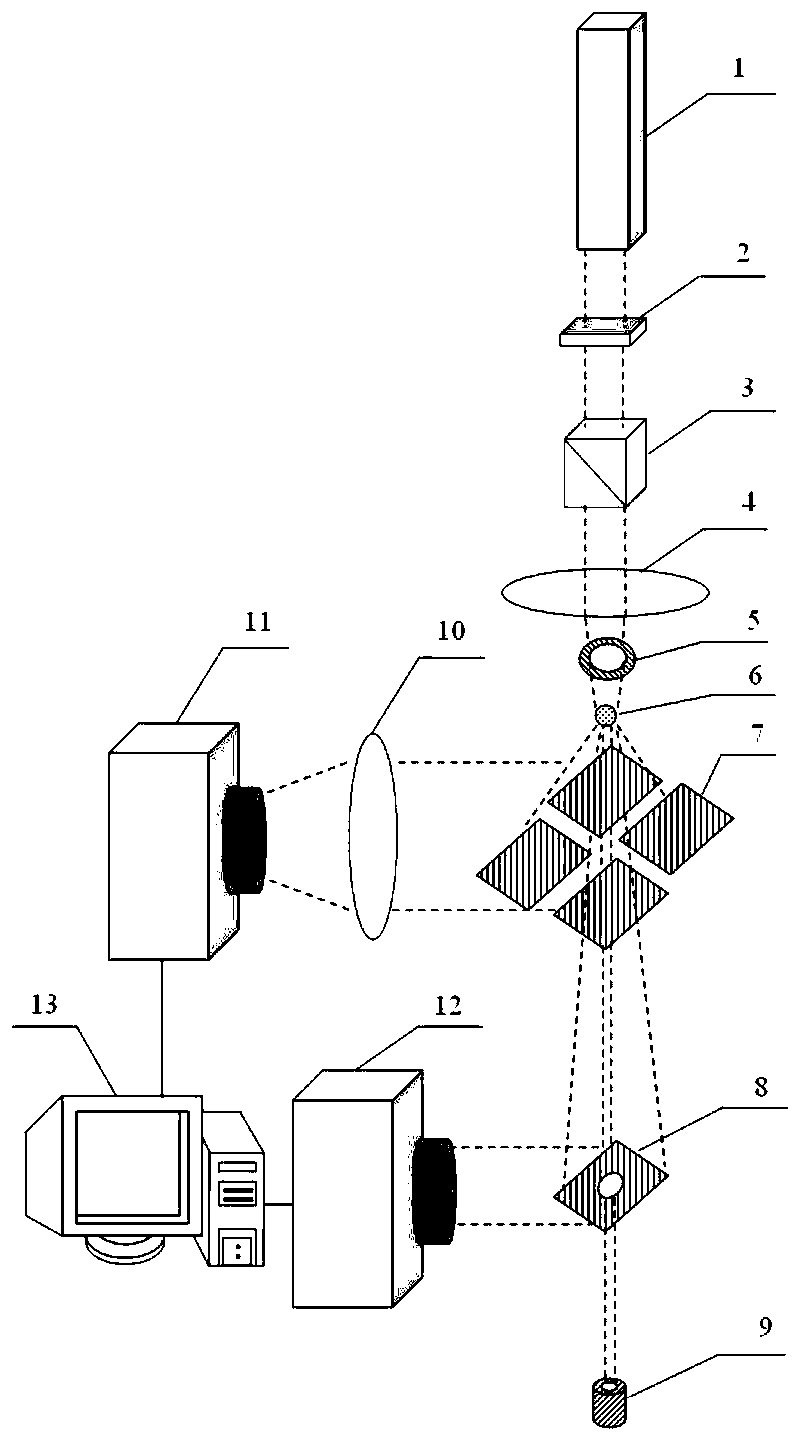
ActiveCN107703642BImprove accuracyGuaranteed luminous fluxOptical elementsLight spotLiquid nitrogen cooling
The invention discloses a single exposure high numerical aperture pulse laser coherent diffractive imaging apparatus and method. The apparatus herein includes a pulse laser 1, an attenuation sheet 2,a polarizer 3, a first lens 4, a diaphragm 5, a sample bench 6, a reflector group 7, a reflector 8 with a hole therein, a light beam collector 9 which are successively and coaxially disposed in the progressing direction of a light beam. The apparatus is provided with a second lens 10, and a liquid nitrogen cooling CCD image sensor 11 which are successively disposed in the progressing direction ofa reflection light beam of the reflector group 7. The reflector 8 with the hole therein is provided with a common CCD image sensor 12 in the progressing direction of the reflection light beam. The liquid nitrogen cooling CCD image sensor 11 and the common CCD image sensor 12 are both in connection to a computer 13. According to the invention, the apparatus herein can simultaneously acquire high angles and central diffraction light spots, and increases 3D reconstruction precision.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A laser complex amplitude measurement method and system based on coherent diffraction imaging
ActiveCN108760056BAccurate measurementImproved sampling resolutionOptical measurementsUltrasound attenuationComplex amplitude
The invention discloses a laser complex amplitude measuring method and system based on coherent diffraction imaging. The measuring method comprises the following steps: establishing an optical measuring system, wherein the optical measuring system comprises a laser, an optical attenuation group, an attenuator, a camera and a motorized translation stage; controlling the camera to move to a positionz1 by the motorized translation stage, and acquiring a D1 surface light spot image of the position z1 by the camera so as to acquire a first light spot image; controlling the camera to move to a position z2 at which the light spot size change can be seen clearly by the motorized translation stage, and acquiring a D2 surface light spot image of the position z2 by the camera so as to acquire a second light spot image; calculating an actual wavefront inclination of the laser; calculating complex amplitude of the first light spot image according to the actual wavefront inclination, an objective function and the second light spot image. The measuring method disclosed by the invention is high in sampling resolution and wide in dynamic range, and the laser complex amplitude can be accurately measured.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method and system for hiding and extracting large-capacity optical information
ActiveCN110942413BImprove privacyEnsure safetyImage enhancementImage analysisInformation transmissionSpatial light modulator
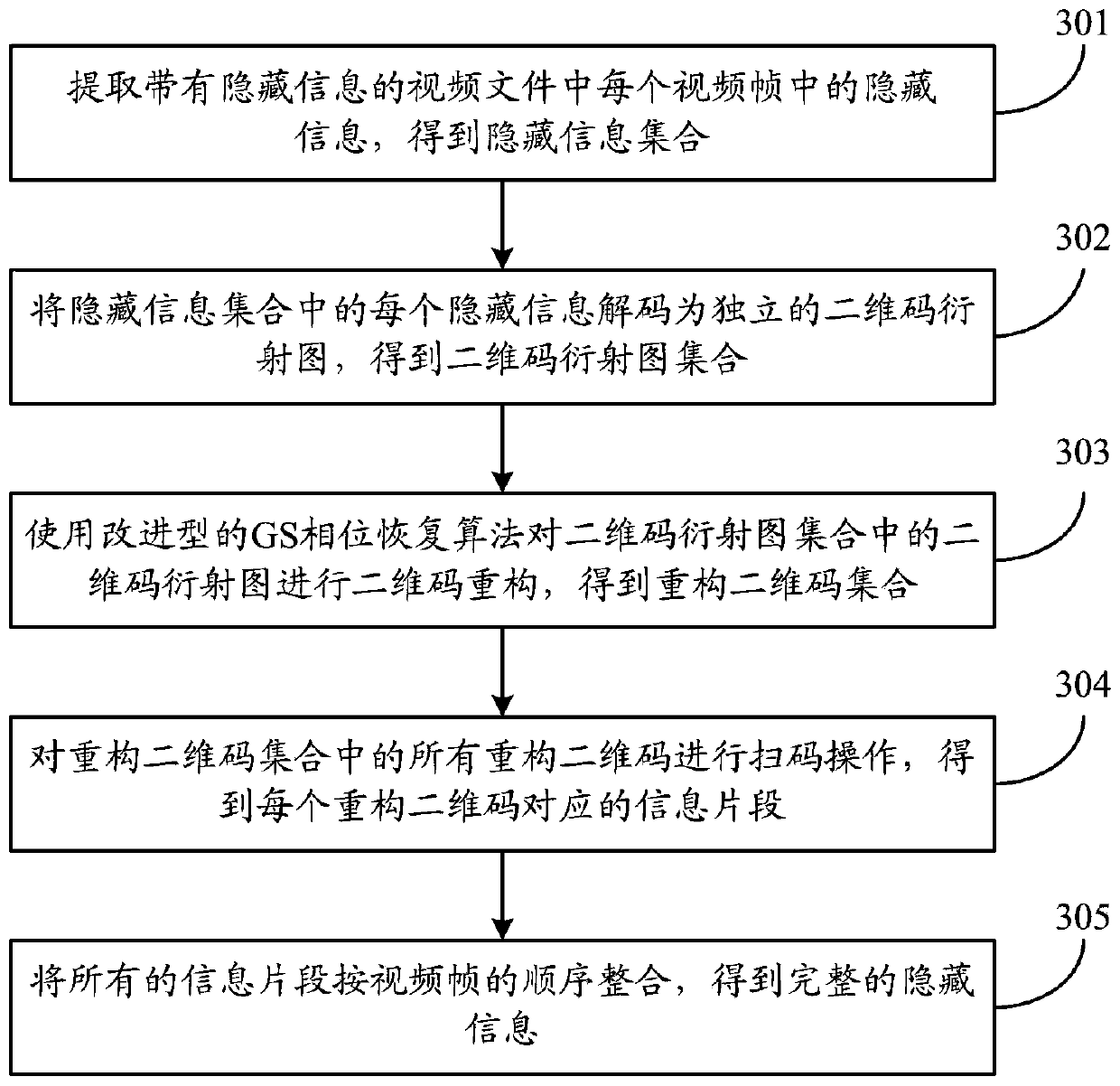
The invention relates to a method and system for hiding and extracting large-capacity optical information. The hiding method includes: encoding the information to be hidden with a two-dimensional code to obtain a two-dimensional code set; the two-dimensional code set includes a plurality of two-dimensional codes corresponding to the information to be hidden; by including a spatial light modulator A reflective coherent diffraction imaging system, which diffracts the two-dimensional codes in the two-dimensional code set to obtain a set of diffraction patterns; the diffraction pattern includes the diffraction pattern corresponding to each two-dimensional code; obtains the host video; according to the host video , processing the diffraction patterns in the diffraction pattern set to obtain processed images; hiding the processed images in the host video to obtain a video file with hidden information to be transmitted. The invention can improve the security of information transmission.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Wave aberration detection system and detection method using knife edge as detection mark
ActiveCN105651493BSimple structureEasy to operateGeometric properties/aberration measurementSurface patternPtychography
The invention discloses a wave aberration detecting system with a knife edge as a detection marker and a wave aberration detecting method based on the knife-edge testing technology and the Ptychography technology. The wave aberration detecting system comprises a coherent point light source, a knife-edge graph serving as the detection marker, a detection-marker adjusting displacement platform for fixing the knife-edge graph and a two-dimensional photoelectric sensor. As the wave aberration of a to-be-detected projection lens is detected through the wave aberration detecting system, the system structure can be simplified, the collecting times of an observation surface pattern are decreased, and the detecting speed and the detecting accuracy of the system are increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coherent diffraction imaging device and method based on low dynamic range spectrogram
InactiveCN113030024AImproving Imaging AccuracyLow costPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsOptical axisCoherent diffraction imaging
The invention provides a coherent diffraction imaging device and method based on a low dynamic range spectrogram, and the device comprises: a light source module which is used for generating a beam of monochromatic parallel light to provide a light source for a to-be-detected sample; a modulation module which is used for loading n coding patterns to modulate the to-be-detected sample so as to obtain n low dynamic range spectrograms corresponding to different parts of the to-be-detected sample, wherein n is an integer greater than 2; an image acquisition module which comprises an acquisition lens and a camera which are sequentially arranged in the optical axis direction, wherein the sample plane of the to-be-detected sample is strictly located on the imaging front focal plane of the acquisition lens due to the arrangement position of the acquisition lens, and the n low-dynamic-range spectrograms are acquired through the camera; and a data processing module which is used for calculating the n collected low-dynamic-range spectrograms through a self-adaptive iteration phase retrieval algorithm to obtain the complex amplitude of the to-be-detected sample. The problem that a conventional coherent diffraction imaging technology needs to collect a high-dynamic-range and low-dynamic-range spectrogram to ensure the recovery precision is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Analytic dual-wavelength phase recovery method
PendingCN114092588AAccurate recoveryAvoid uniquenessReconstruction from projectionComplex mathematical operationsCoherent diffraction imagingIterative refinement
The invention relates to coherent diffraction imaging, in particular to an analytic dual-wavelength phase recovery method, which is used for solving the defect of high data redundancy caused by the fact that an existing iterative phase recovery algorithm needs a large amount of intensity data in order to improve convergence performance. According to the analytic dual-wavelength phase recovery method, an iterative optimization algorithm is not used any more, but an analytic solution of the phase is obtained in a mode of solving a high-order equation set, and the problems of non-uniqueness, convergence stagnation and the like of an iterative algorithm solution are avoided.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A Novel Three-Step Lensless Coherent Diffraction Imaging Method
ActiveCN107101974BImprovement of Experimental ImplementationAvoid random errorsScattering properties measurementsImaging algorithmCoherent diffraction imaging
The invention relates to a novel three-step lens-free coherent diffractive imaging method. The method is characterized in that laser beams subjected to collimation and beam expansion are used to illuminate a to-be-measured sample, and recording a diffraction pattern when the front end of CCD has no optical parallels, a diffraction pattern when the front end of the CCD has one optical parallel and a diffraction pattern when the front end of the CCD has two optical parallels; using an algorithm combining wave filtering and coherent diffractive imaging to process the three diffraction patterns, and rebuilding the complex amplitude image of the to-be-measured sample. The novel three-step lens-free coherent diffractive imaging method has the advantages that the bottleneck problem that a traditional coherent diffractive imaging method needs to move the CCD or the to-be-measured sample for multiple times is solved effectively, the problems of random errors during moving and experiment operability are solved at the same time, the method is simple and fast in experiment operation and high in operability, the coherent diffractive imaging algorithm is effectively combined with wave filtering, and convergence rate and a sample recovery effect are increased.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
Coherent diffractive imaging with spaced-apart beams
ActiveUS9911207B2Reconstruction from projectionHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesLight beamComputational physics
Apparatus and methods for Coherent Diffractive Imaging with multiple, simultaneous, spatially distinct beams chosen and configured to isolate incoherent sums of beam diffraction such that interference between the multiple beams is not present in the data prior to computationally reconstructing the image. This is accomplished through selecting the multiple beams to be non-interfering modes, or through designing the apparatus such that the interference is not recorded, or through processing the collected data to filter the interference before reconstructing the image.
Owner:KM LABS INC
Coherent diffraction imaging method and its processing equipment
InactiveCN101482503BImprove efficiencyHigh speedPhase-affecting property measurementsCorrelation functionFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a coherent diffraction imaging method and processing device thereof. The object wave passes through a rotary multi-pinhole plate. The Fraunhofer diffraction intensity distribution pattern of the object wave passing through the multi-pinhole plate is recorded by an image sensor. The diffraction intensity distribution is subjected to inverse Fourier transformation to obtain the correlation function pattern of the recorded object wave, the amplitude and phase information of the object wave to be measured are directly extracted from the points corresponding with each measurement pinhole center position coordinate in the correlation function pattern and the diffraction imaging of the complex amplitude object is realized in the computer. The coherent diffraction imaging method has no need of any iterative process and greatly reduces the requirement of the scanning recording process and positioning accuracy and increases the diffraction imaging speed, with other features of simple processing device, convenient adjustment, lower cost, suitable of various different light source, and the imaging of the complex object or three-dimensional object can be realized without imaging lens, especially suitable for the situation that it is difficult to prepare high-quality X-ray using the imaging lens.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com