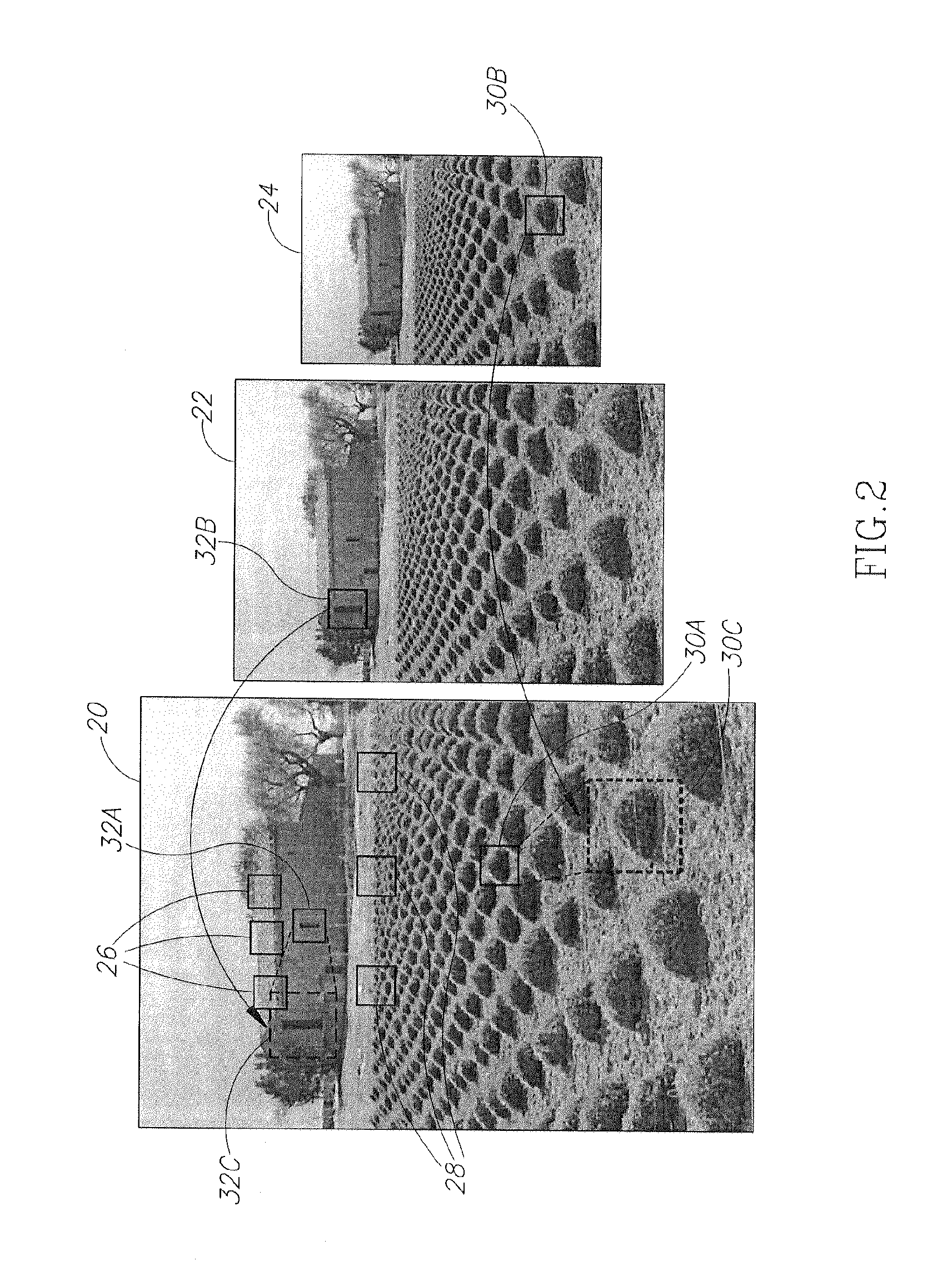
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1614 results about "Data redundancy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer main memory, auxiliary storage and computer buses, data redundancy is the existence of data that is additional to the actual data and permits correction of errors in stored or transmitted data. The additional data can simply be a complete copy of the actual data, or only select pieces of data that allow detection of errors and reconstruction of lost or damaged data up to a certain level.
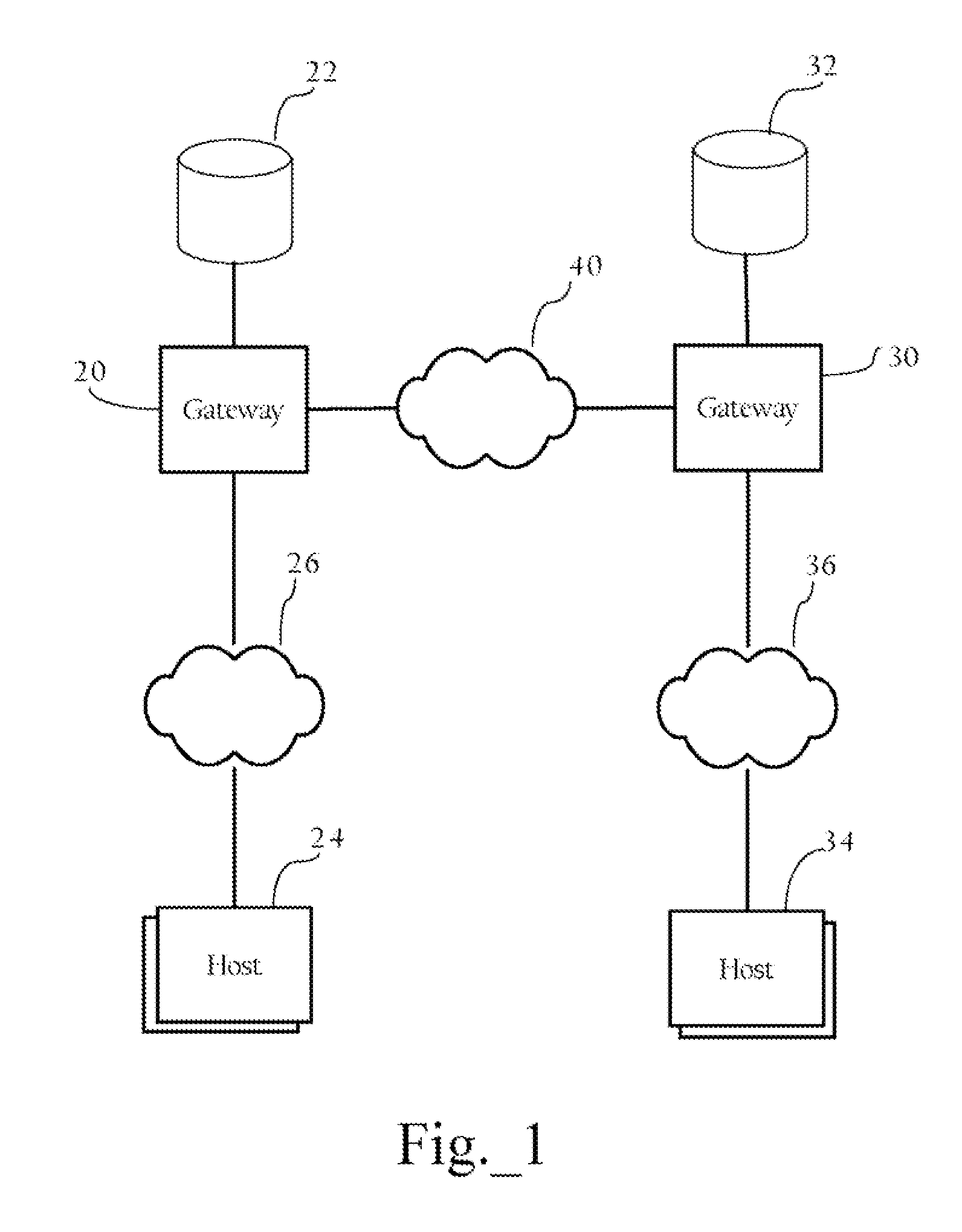
Parallel data redundancy removal
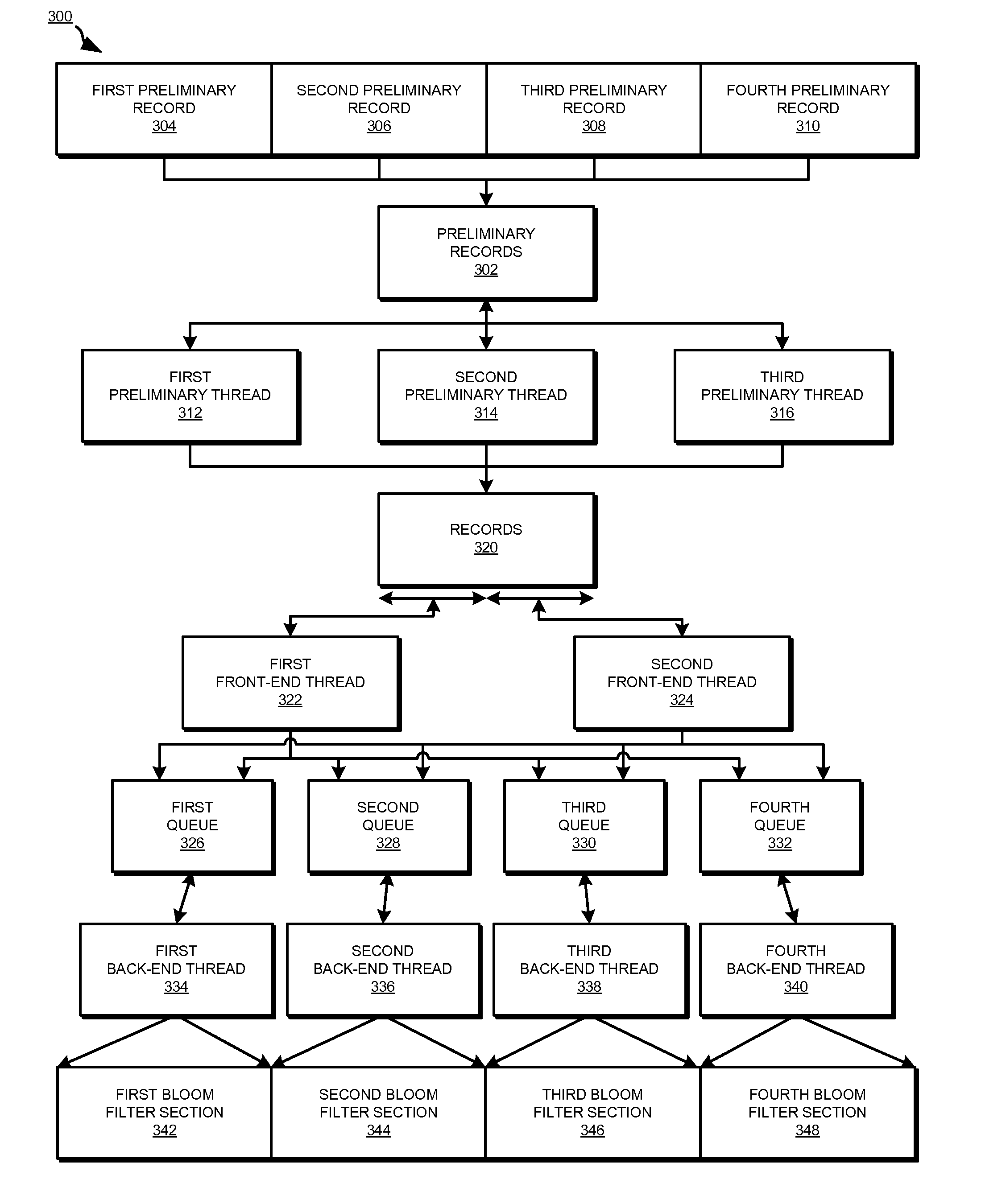
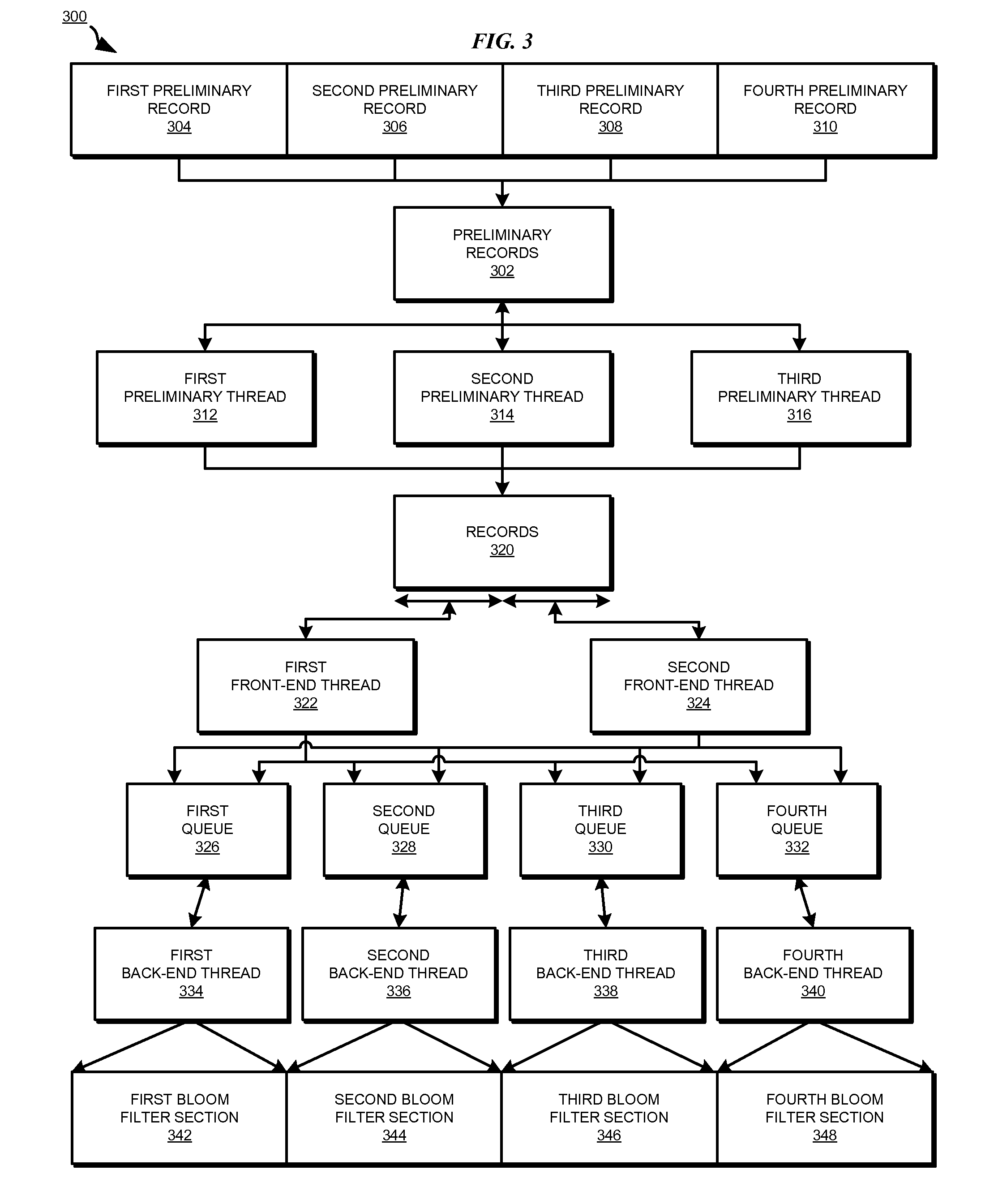
InactiveUS8332367B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRedundant codeBloom filter
A method, system, and computer usable program product for parallel data redundancy removal are provided in the illustrative embodiments. A plurality of values is computed for a record in a plurality of records stored in a storage device. The plurality of values for the record is distributed to corresponding queues in a plurality of queues, wherein each of the plurality of queues is associated with a corresponding section of a Bloom filter. A determination is made whether each value distributed to the corresponding queues for the record is indicated by a corresponding value in the corresponding section of the Bloom filter. The record is identified as a redundant record in response to a determination that each value distributed to the corresponding queues for the record is indicated by a corresponding value in the corresponding section of the Bloom filter.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Methods and systems for quick and efficient data management and/or processing
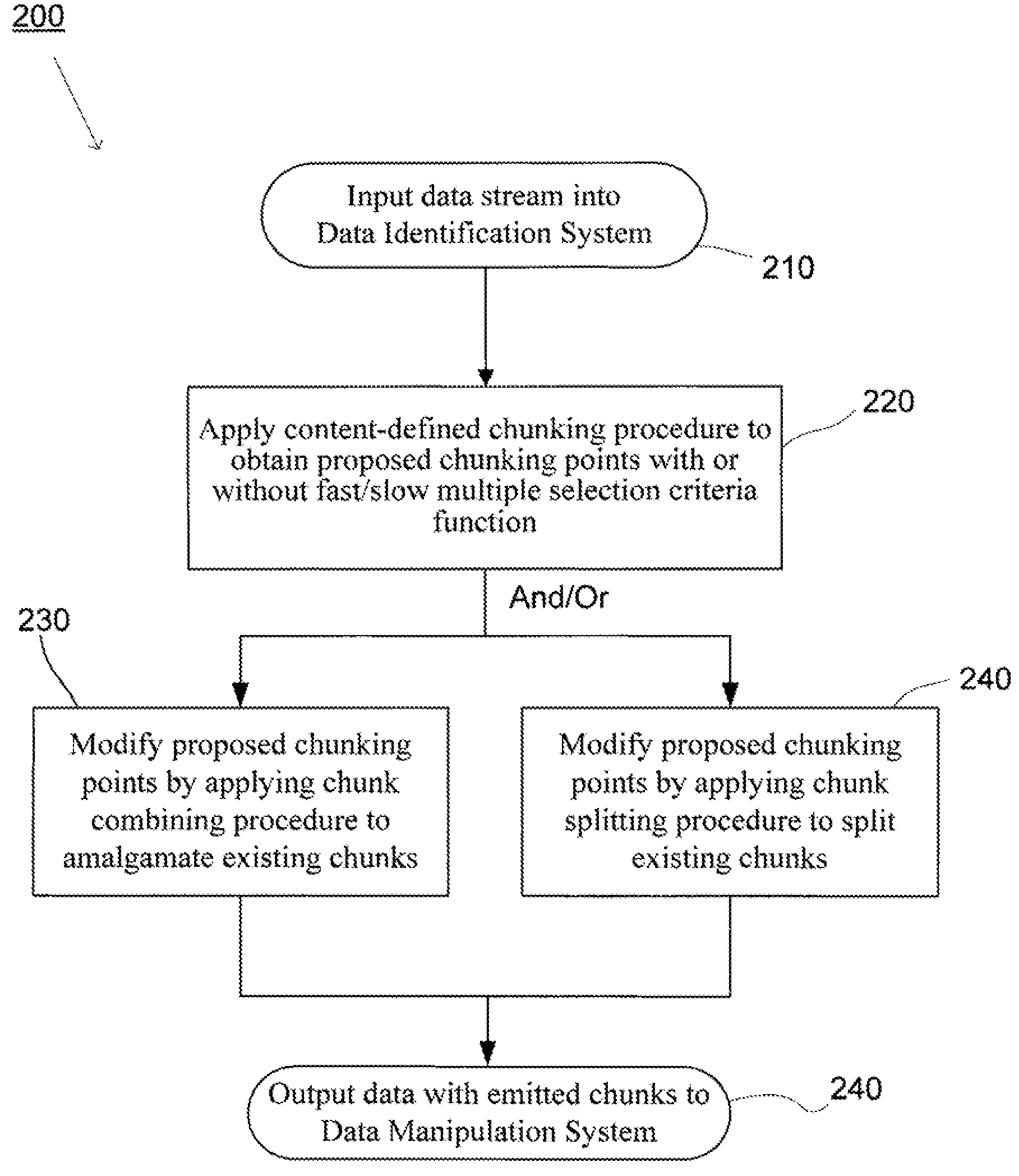
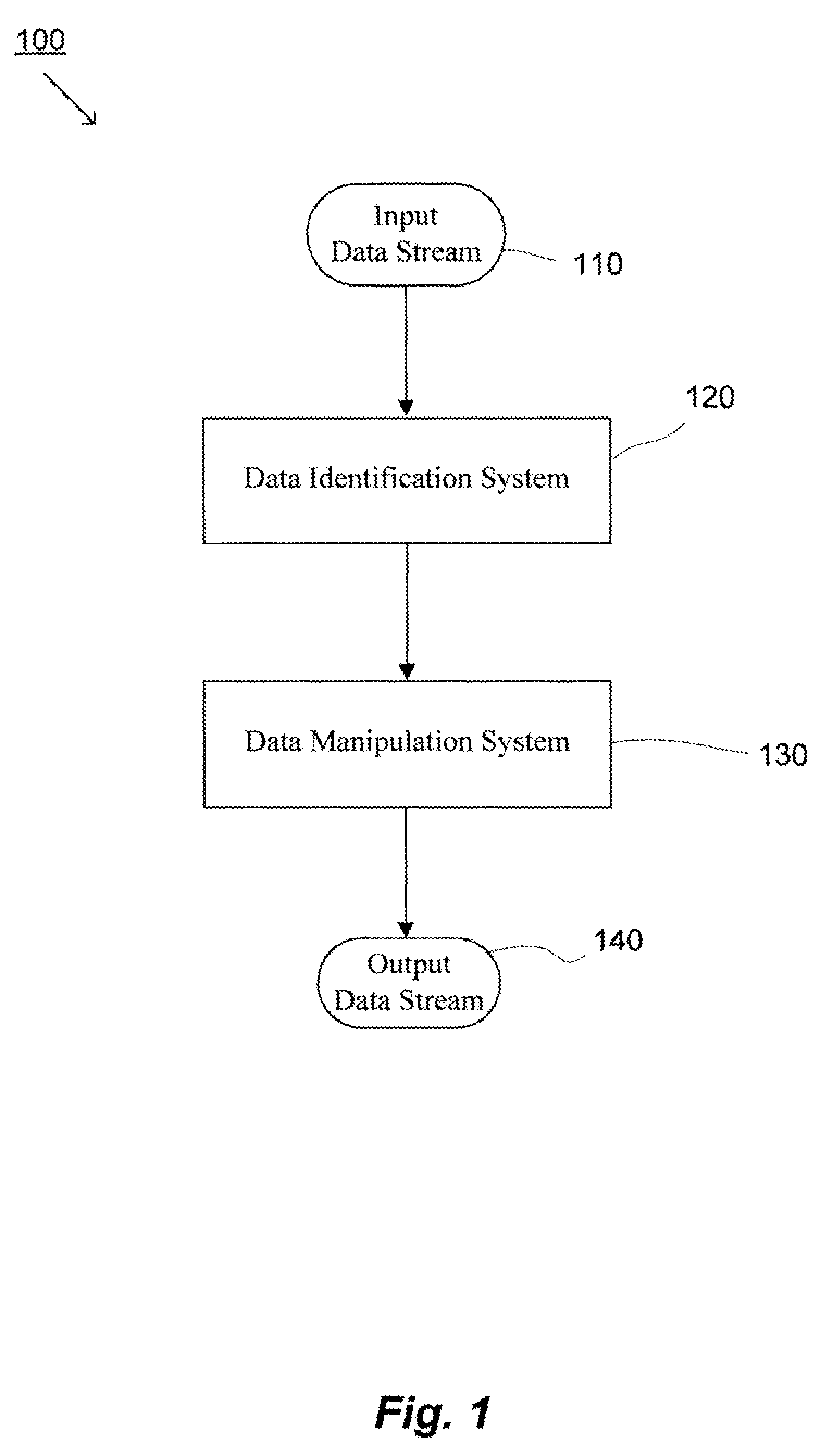
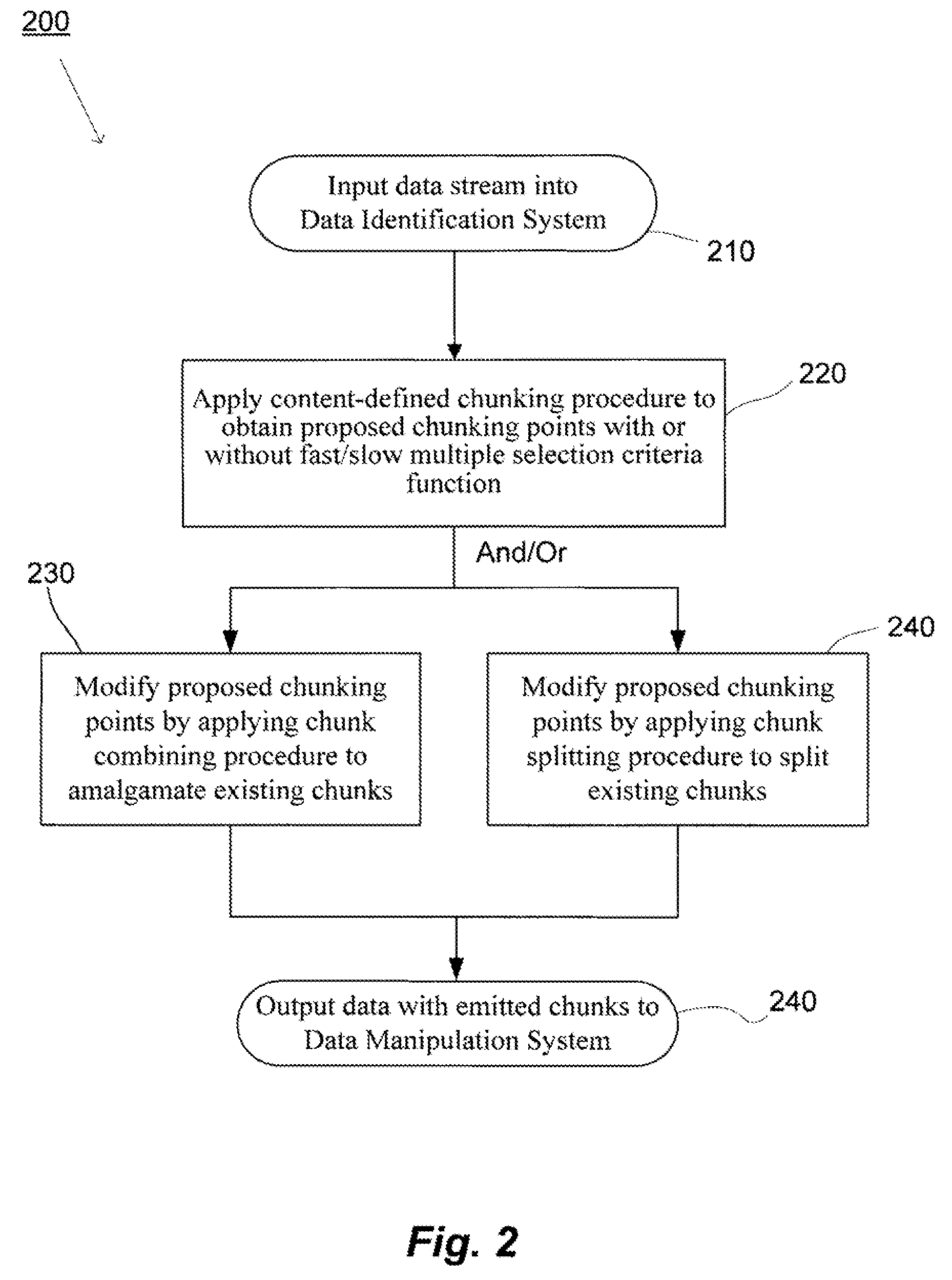
ActiveUS20080133561A1Improve data processing efficiencyReduce quality problemsDigital data information retrievalProgram control using stored programsData managementCombined technique
System(s) and method(s) are provided for data management and data processing. For example, various embodiments may include systems and methods relating to relatively larger groups of data being selected with comparable or better performing selection results (e.g., high data redundancy elimination and / or average chunk size). In various embodiments, the system(s) and method(s) may include, for example a data group, block, or chunk combining technique or / and a data group, block, or chunk splitting technique. Various embodiments may include a first standard or typical data grouping, blocking, or chunking technique and / or data group, block, or chunk combining technique or / and a data group, block, or chunk splitting technique. Exemplary system(s) and method(s) may relate to data hashing and / or data elimination. Embodiments may include a look-ahead buffer and determine whether to emit small chunks or large chunks based on characteristics of underlying data and / or particular application of the invention (e.g., for backup).
Owner:NEC CORP
Storing data with different specified levels of data redundancy
Methods of storing data with different specified levels of data redundancy are disclosed. In one aspect, a method may include receiving sets of data to be stored on a set of storage devices and information that specifies different levels of data redundancy for the sets of data. Then, the sets of data may be stored on the set of storage devices with different levels of data redundancy based, at least in part, on the information. Apparatus, software, and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamically controlling temporary compromise on data redundancy
InactiveUS9513820B1Avoid lostInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionHybrid storage systemComputer science
Systems and methods for determining when to allow a temporary compromise on redundancy in a storage system. When servicing write requests, the storage system may utilize data redundancy techniques when writing data to backend storage devices. The operating conditions of the storage system are tracked and early acknowledgements for write requests may be permitted when the storage system is healthy enough. If the number of unacknowledged writes is greater than a programmable threshold, then early acknowledges may be prohibited. Also, if the number of ongoing rebuild processes is greater than a programmable threshold, then early acknowledges may be prohibited.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
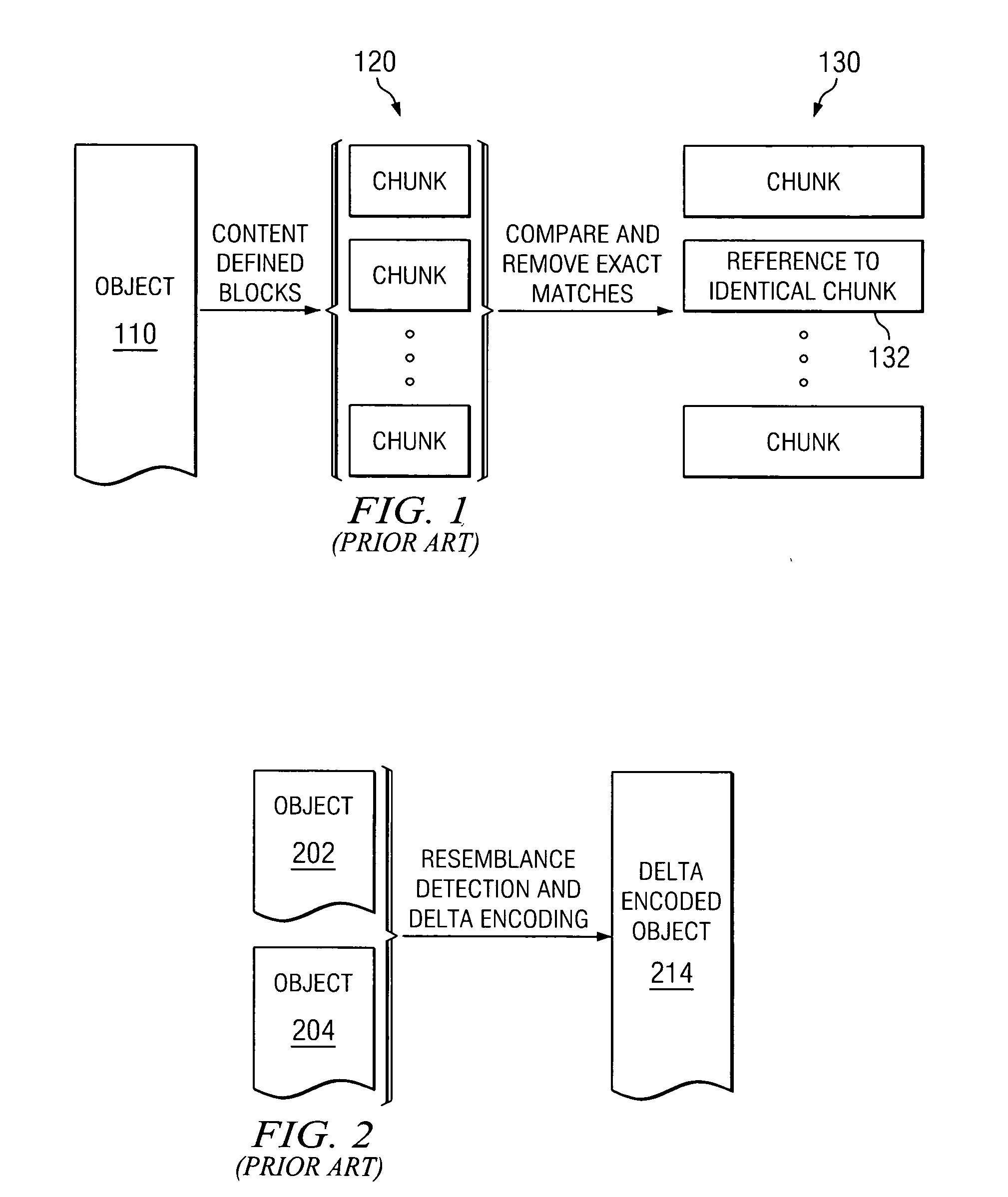
Method and apparatus for data redundancy elimination at the block level
InactiveUS20050131939A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsIncremental encodingComputer science
A redundancy elimination mechanism is provided, which applies aspects of duplicate block elimination and delta encoding at the block level. The redundancy elimination mechanism divides file objects into content-defined blocks or “chunks.” Identical chunks are suppressed. The redundancy elimination mechanism also performs resemblance detection on remaining chunks to identify chunks with sufficient redundancy to benefit from delta encoding of individual chunks. Any remaining chunks that do not benefit from delta encoding are compressed. Resemblance detection is optimized by merging groups of fingerprints into super fingerprints. This merging can be constructed to ensure that if two objects have a single super fingerprint in common, they are extremely likely to be substantially similar.
Owner:IBM CORP
Location independent scalable file and block storage
InactiveUS20120011176A1Fast and therefore expensiveSmall sizeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemBlock level
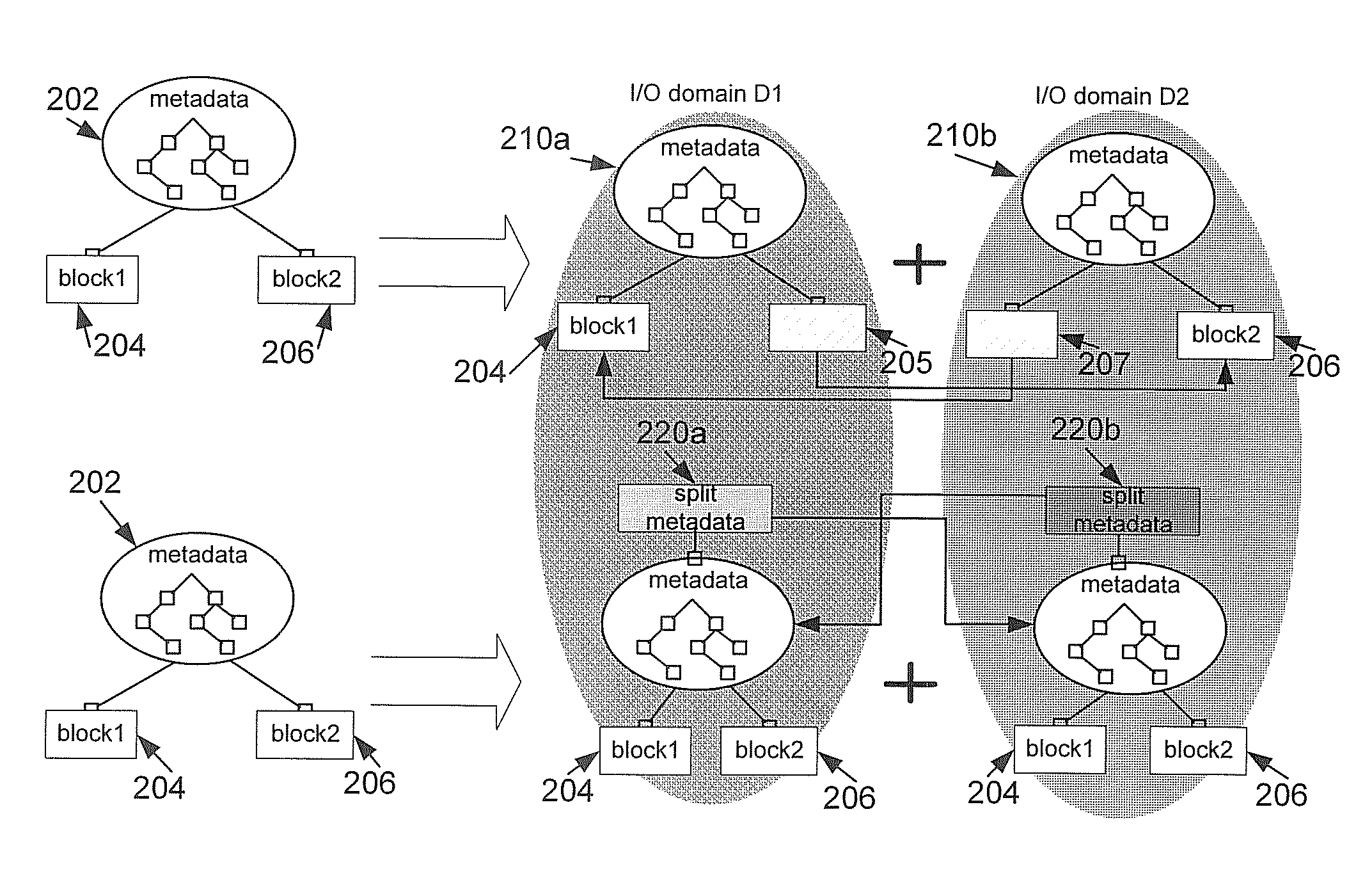
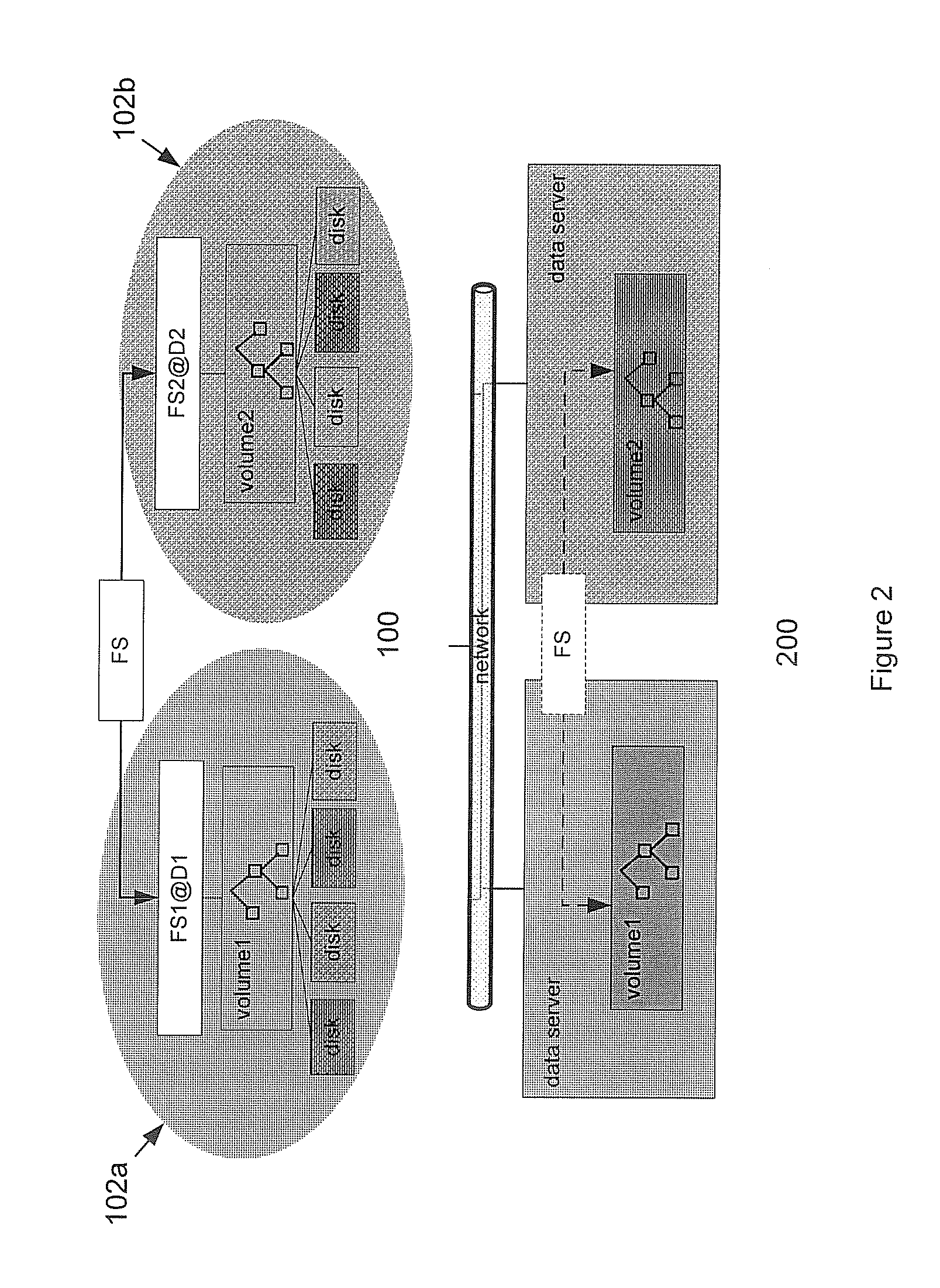
A method and system is disclosed for resolving a single server bottleneck. Logically associated data is typically collocated within a single filesystem or a single block device accessible via a single storage server. A single storage server can provide a limited I / O bandwidth, which creates a problem known as “single I / O node” bottleneck. The method and system provides techniques for spreading I / O workload over multiple I / O domains, both local and remote, while at the same time increasing operational mobility and data redundancy. Both file and block level I / O access are addressed.
Owner:NEXENTA SYSTEMS
Virtually infinite reliable storage across multiple storage devices and storage services
InactiveUS20060230076A1Improve reliabilityImprove scalabilityError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsFile systemDistributed File System
A logical file system is described that distributes copies of files across various different physical storage resources yet provides a consistent view to the user of his or her data, regardless of which machine the user is accessing the files from, and even when the user's computer is offline. The distributed file system uses smart data redundancy to enable a virtually infinite amount of storage as long as additional storage resources are made available to the distributed file system. The result is a reliable storage system that does not necessarily tie the user's data to the user's particular computer. Instead, the user's data is associated with the user—for life—or for however long the user would like the data to be maintained, regardless of whether the user's computer or data storage components are replaced or destroyed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Detection and correction of block-level data corruption in fault-tolerant data-storage systems
ActiveUS20080115017A1Eliminate needEfficient detectionStatic storageRedundant data error correctionRAIDDisk controller
Various embodiments of the present invention provide fault-tolerant, redundancy-based data-storage systems that rely on disk-controller-implemented error detection and error correction, at the disk-block level, and RAID-controller-implemented data-redundancy methods, at the disk and disk-stripe level, in order to provide comprehensive, efficient, and system-wide error detection and error correction. Embodiments of the present invention use disk-level and stripe-level data redundancy to provide error detection and error correction for stored data objects, obviating the need for certain costly, intermediate levels of error detection and error correction commonly employed in currently available fault-tolerant, redundancy-based data-storage systems.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
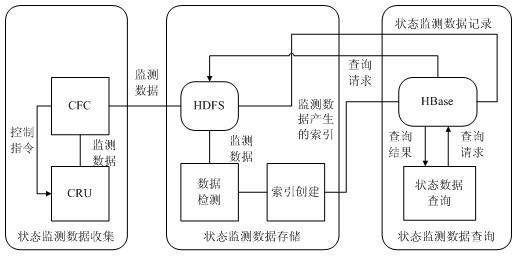
Distributed storage and parallel mining method for state monitoring data
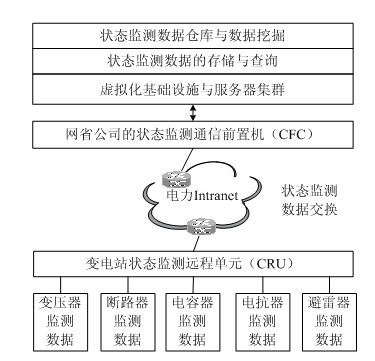
InactiveCN102685221AEnsure operabilityReduce construction costsData switching networksService modelData warehouse
A distributed storage and parallel mining method for state monitoring data includes the steps: defining function service models of a remote substation state monitoring unit and a state monitoring communication front-end processor by means of Web service description language, and exchanging the state monitoring data of electric power equipment in an electric power wide area network environment by a simple object access protocol; storing large-scale state monitoring data redundancy in a distributed file system, creating an index table for a state monitoring data file, inserting the index table into a large-scale structural data table and querying the state monitoring data according to a query request; and generating basic data and multi-dimensional analytical data by extracting, converting and loading to built a data warehouse, and parallelly executing association rules, classification and clustered data mining algorithm by means of MapReduce task decomposition and result summary. The distributed storage and parallel mining method can be used for effectively realizing distributed data exchange, redundant storage and rapid parallel processing for state monitoring information of the mass electric power equipment in an intelligent power network environment.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Methods and systems for eliminating data redundancies
InactiveUS6889297B2Removing data redundancySave memory spaceData processing applicationsError detection/correctionData miningData redundancy
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
File system driven raid rebuild technique
In one embodiment, a file system driven RAID rebuild technique is provided. A layered file system may organize storage of data as segments spanning one or more sets of storage devices, such as solid state drives (SSDs), of a storage array, wherein each set of SSDs may form a RAID group configured to provide data redundancy for a segment. The file system may then drive (i.e., initiate) rebuild of a RAID configuration of the SSDs on a segment-by-segment basis in response to cleaning of the segment (i.e., segment cleaning). Each segment may include one or more RAID stripes that provide a level of data redundancy (e.g., single parity RAID 5 or double parity RAID 6) as well as RAID organization (i.e., distribution of data and parity) for the segment. Notably, the level of data redundancy and RAID organization may differ among the segments of the array.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
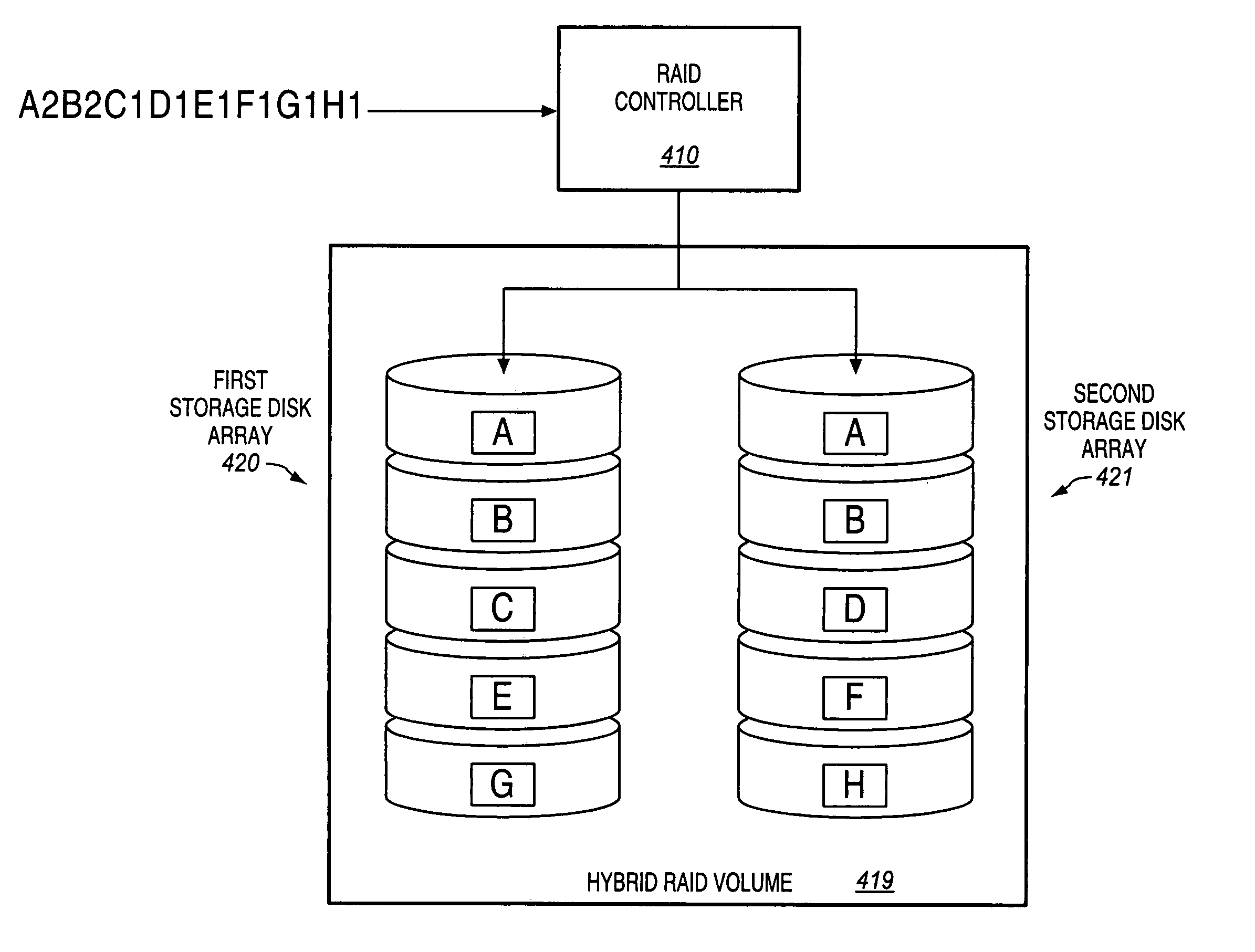
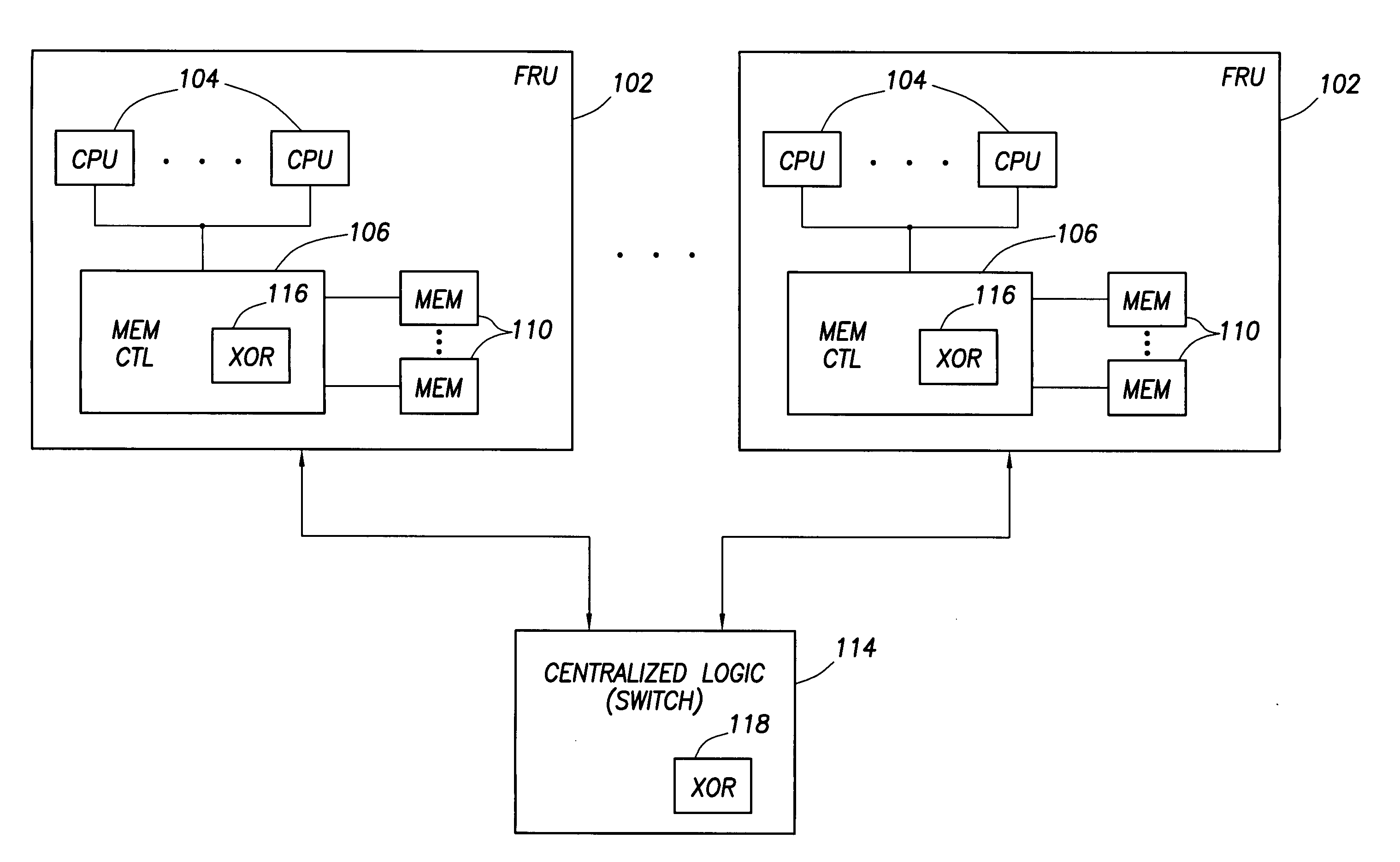
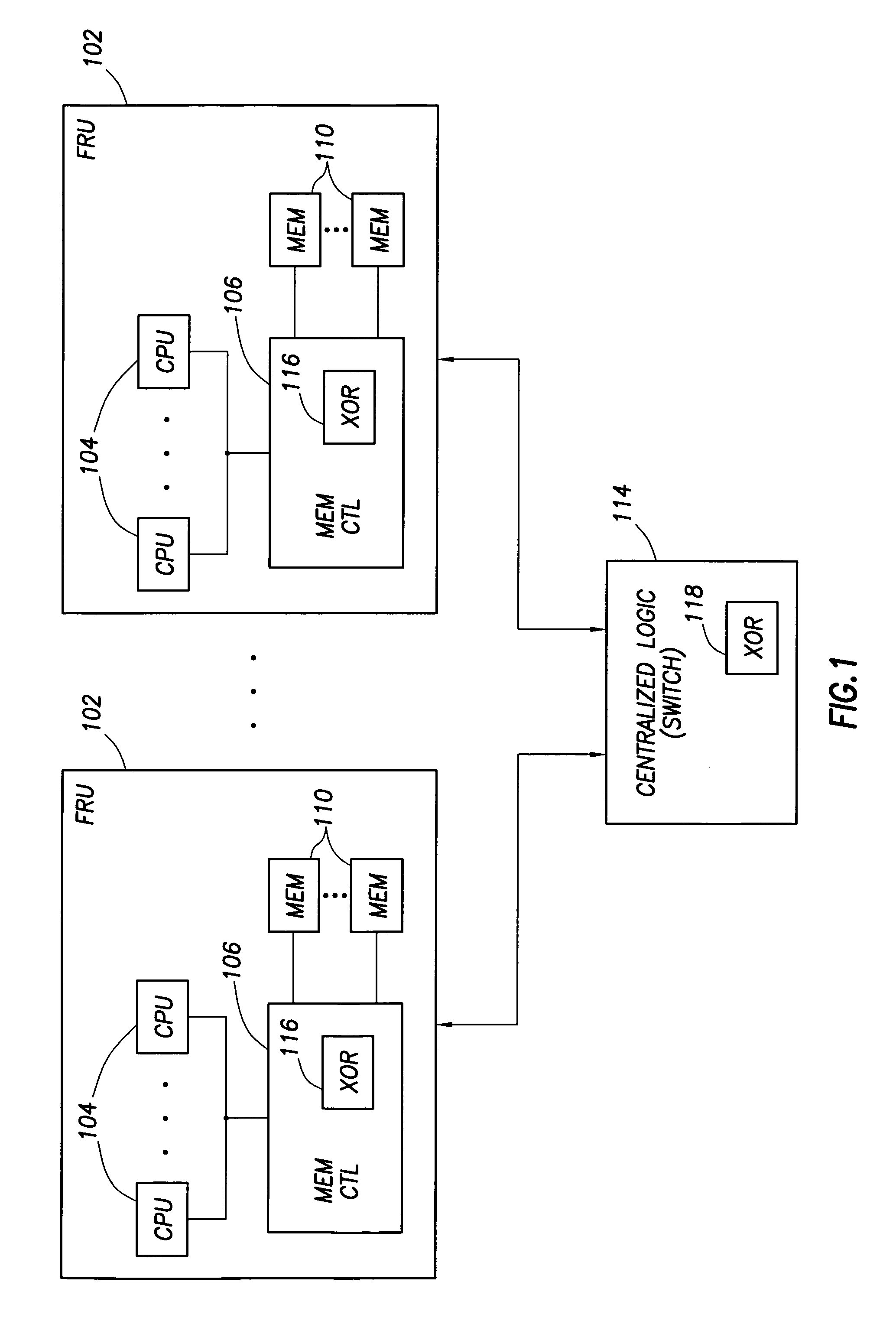
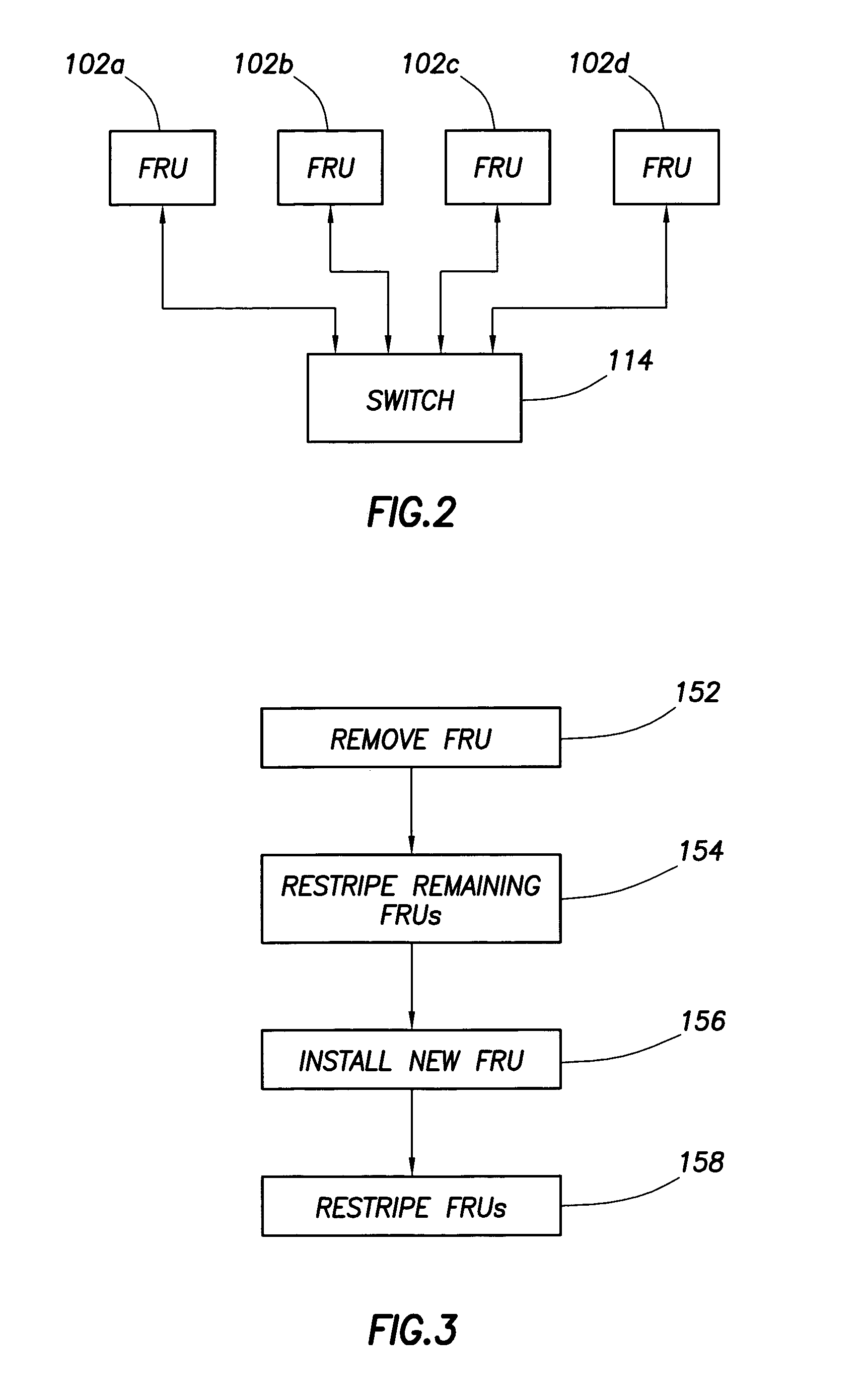
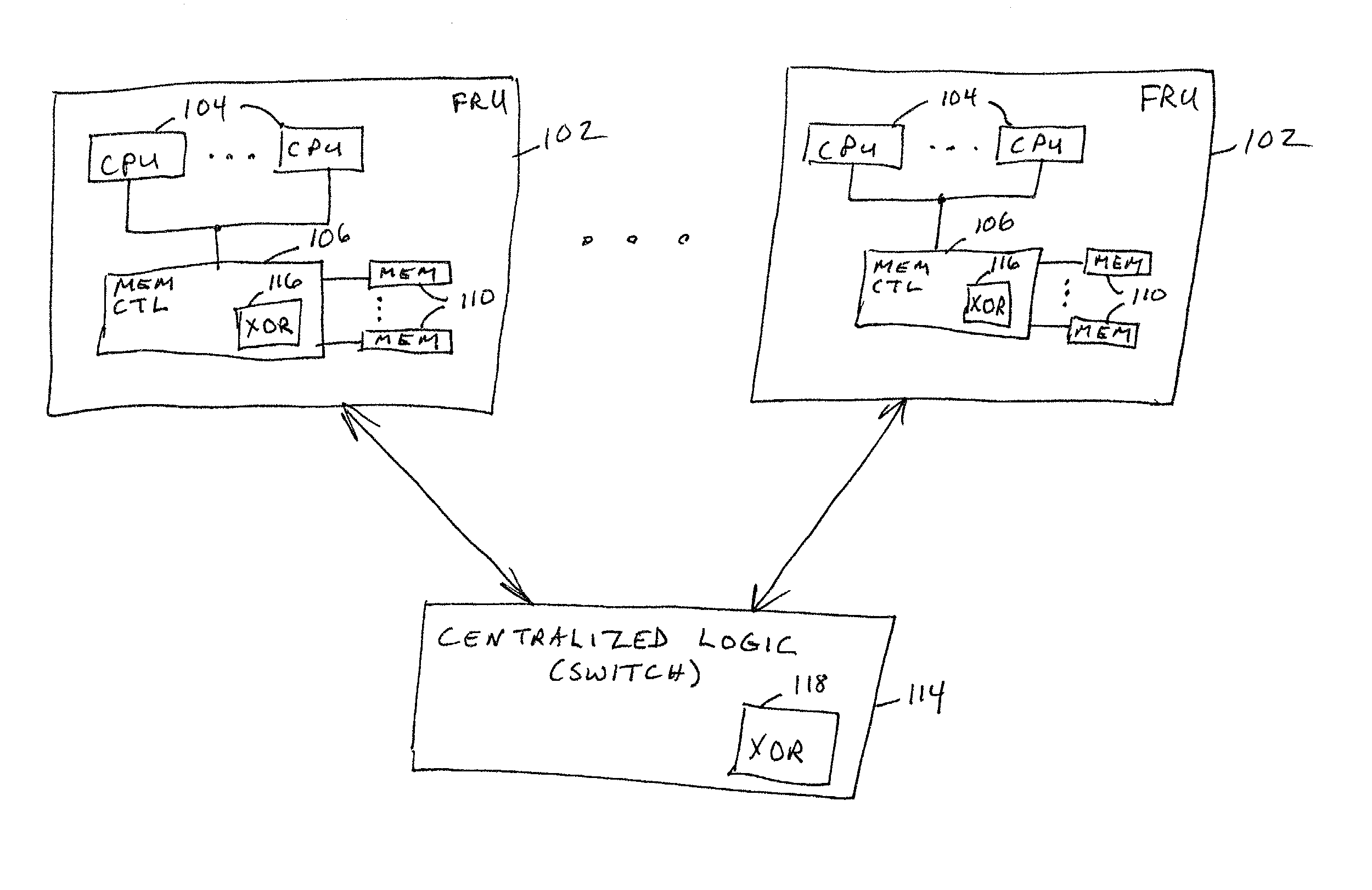
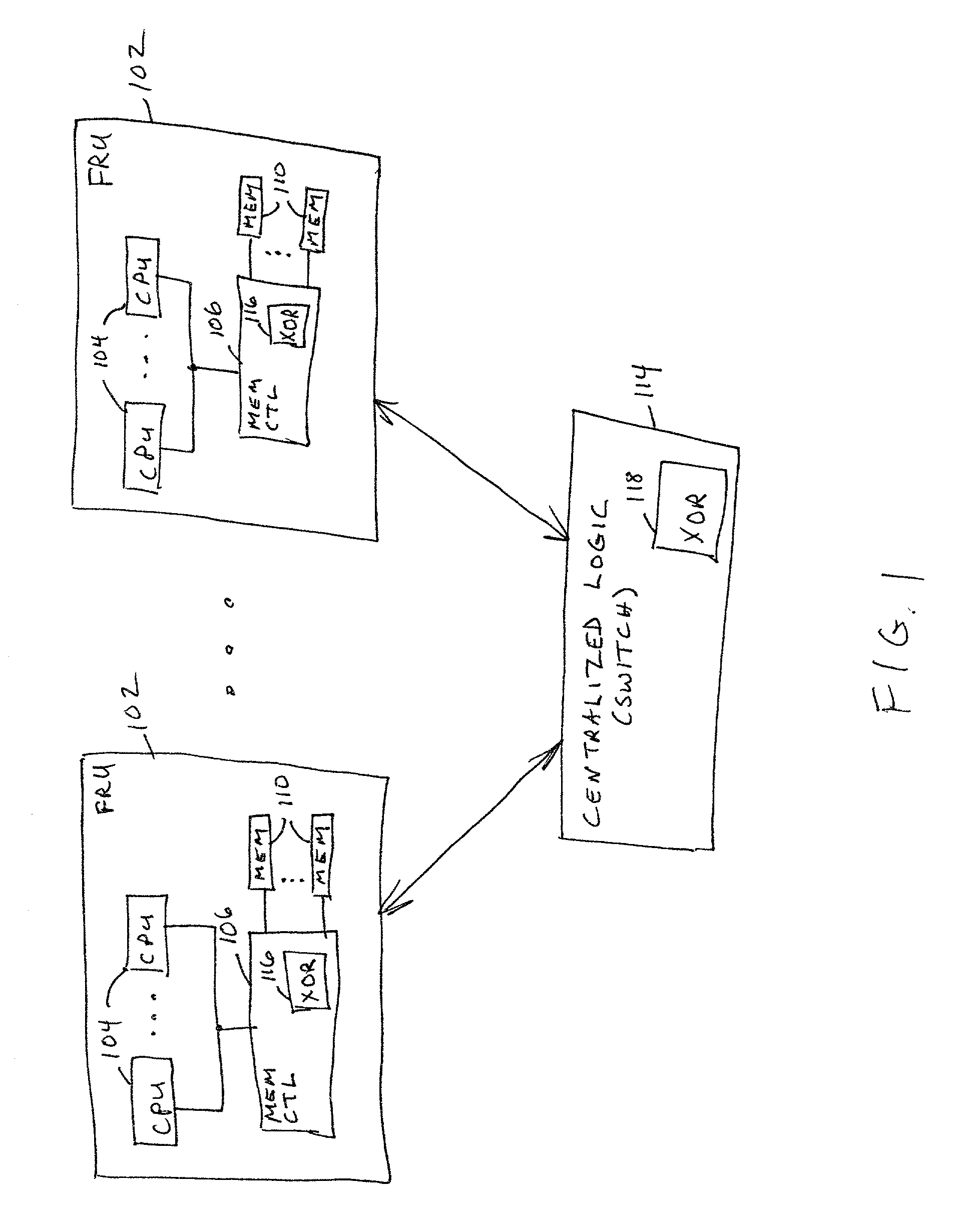
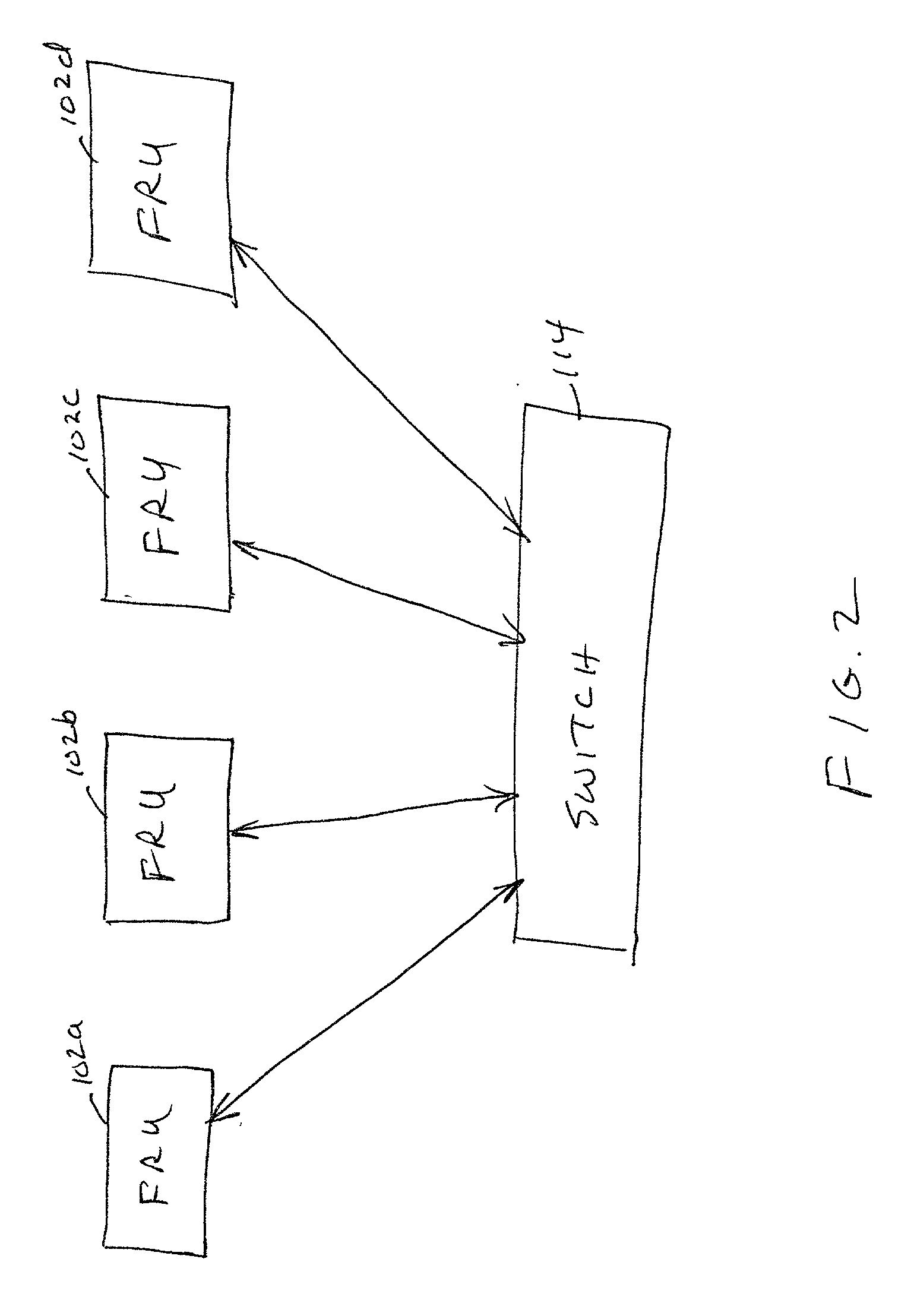
Data redundancy in a hot pluggable, large symmetric multi-processor system
ActiveUS20030172330A1Fault toleranceReduce the numberStatic storageRedundant data error correctionFault toleranceRAID
A computer system includes a plurality of field replaceable units, each having volatile memory and at least one CPU. The FRUs communicate with each other via centralized logic. A RAID data fault tolerance technique is applied to the system so that an FRU can be lost or removed without loss of its data. An exclusive OR engine is included in the centralized logic or distributed among the FRUs. The RAID logic can restripe itself upon removal or addition of a FRU.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
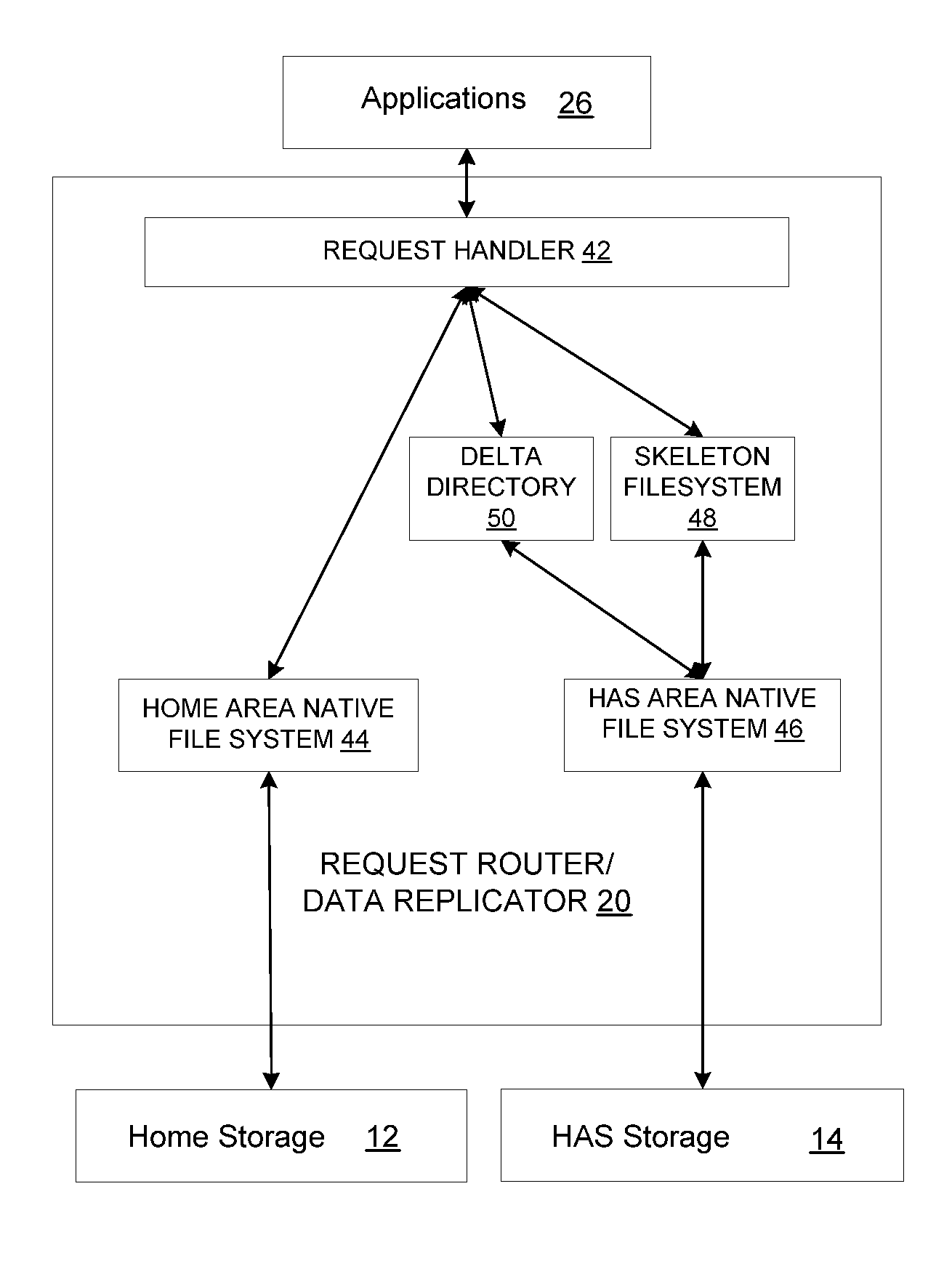
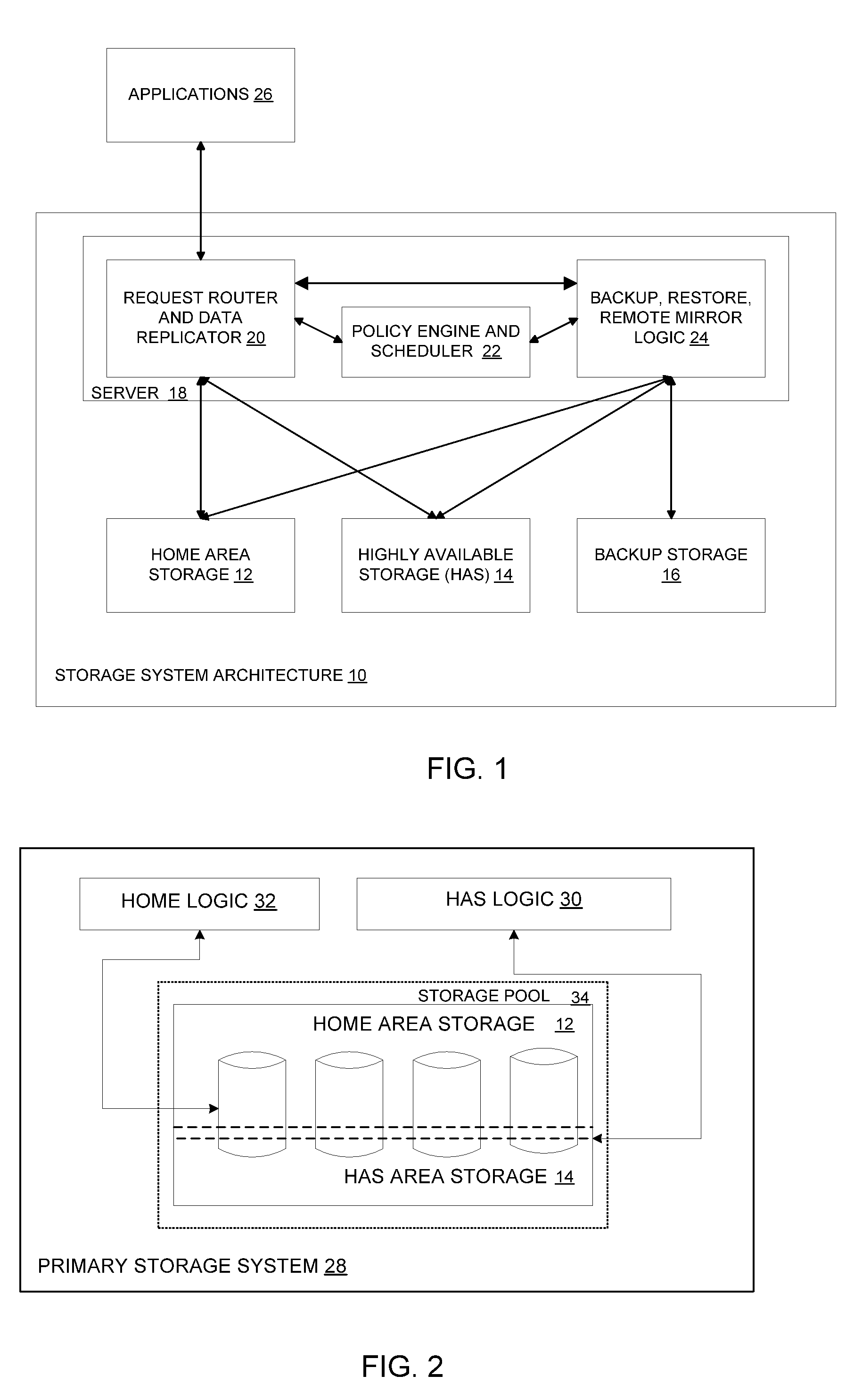
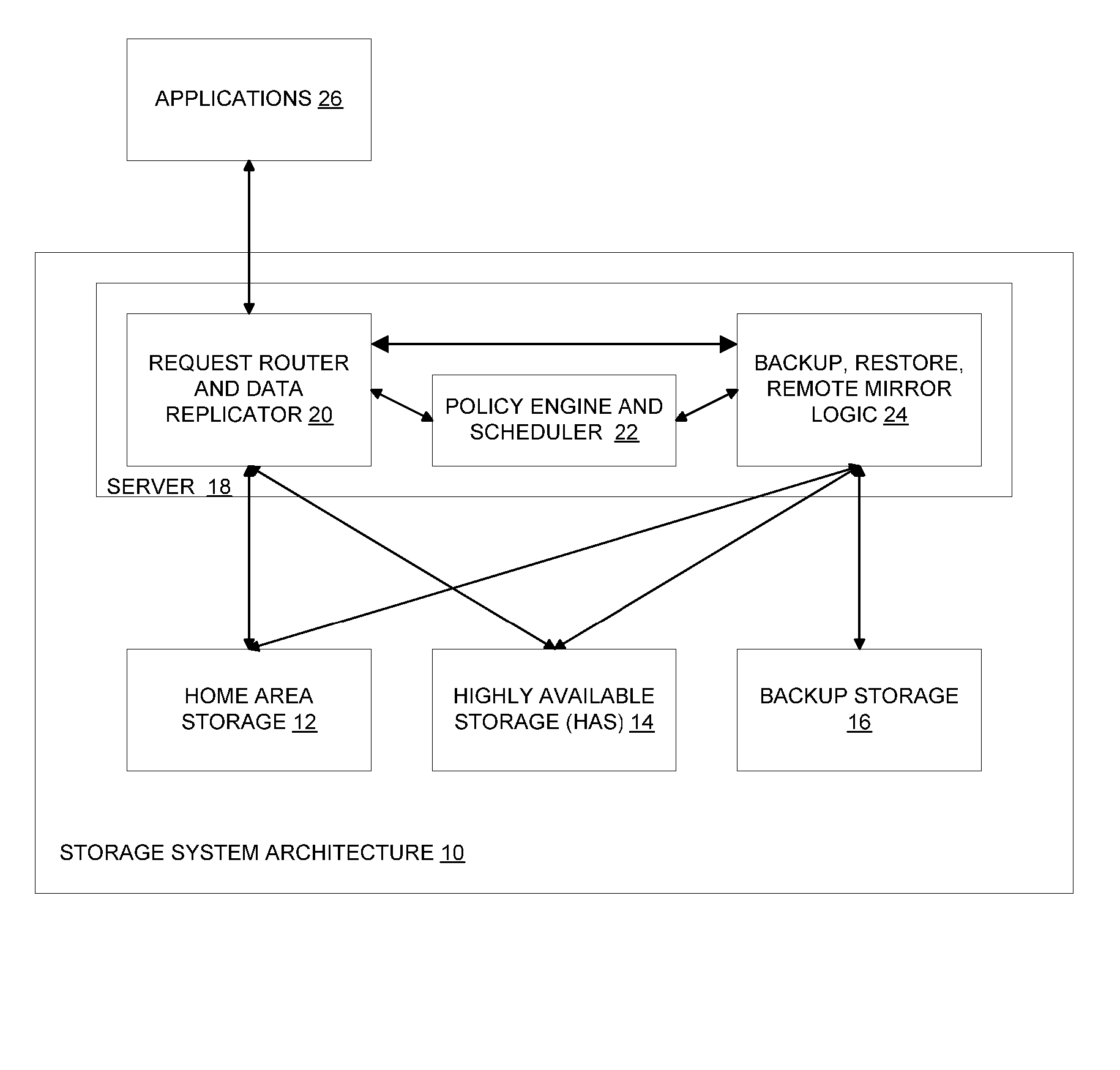
System and method for reliably storing data and providing efficient incremental backup and asynchronous mirroring by preferentially handling new data
According to the present invention, there is provided a method for reliably storing data in a computer system. The method includes receiving a piece of data to be stored at a storage system. In addition, the method includes writing a first copy of the data to the storage system according to a first data redundancy scheme. Also, the method includes writing a second copy of the data to the storage system according to a second data redundancy scheme. Also, the system includes maintaining metadata of the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme. In addition, the method includes copying the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme to a backup storage system, wherein the copying is performed in response to a defined condition being met. Moreover, removing the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme after it has been copied to the backup storage system.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
System and Method for Reliably Storing Data and Providing
According to the present invention, there is provided a method for reliably storing data in a computer system. The method includes receiving a piece of data to be stored at a storage system. In addition, the method includes writing a first copy of the data to the storage system according to a first data redundancy scheme. Also, the method includes writing a second copy of the data to the storage system according to a second data redundancy scheme. Also, the system includes maintaining metadata of the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme. In addition, the method includes copying the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme to a backup storage system, wherein the copying is performed in response to a defined condition being met. Moreover, removing the data written to the storage system according to the second data redundancy scheme after it has been copied to the backup storage system.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
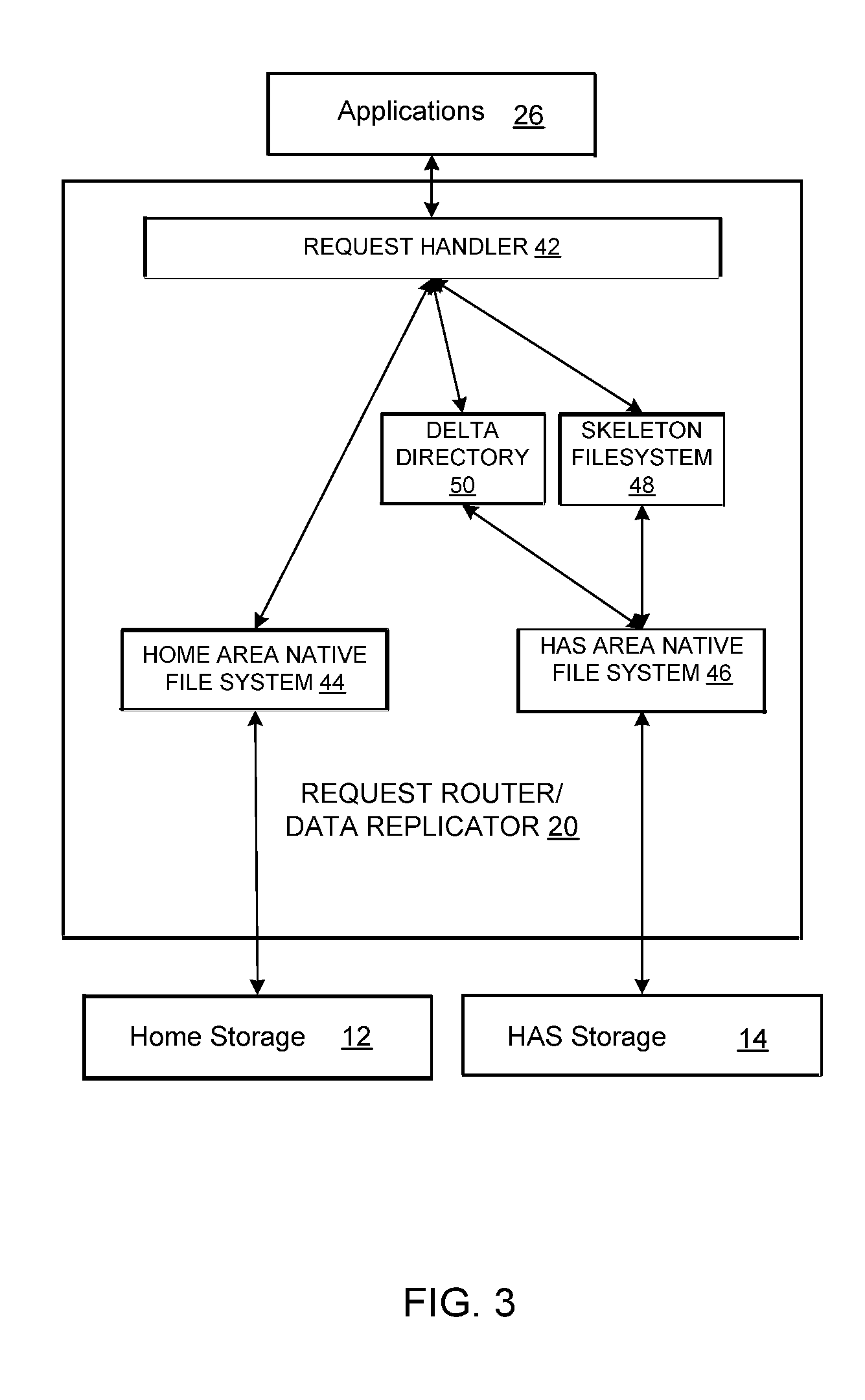
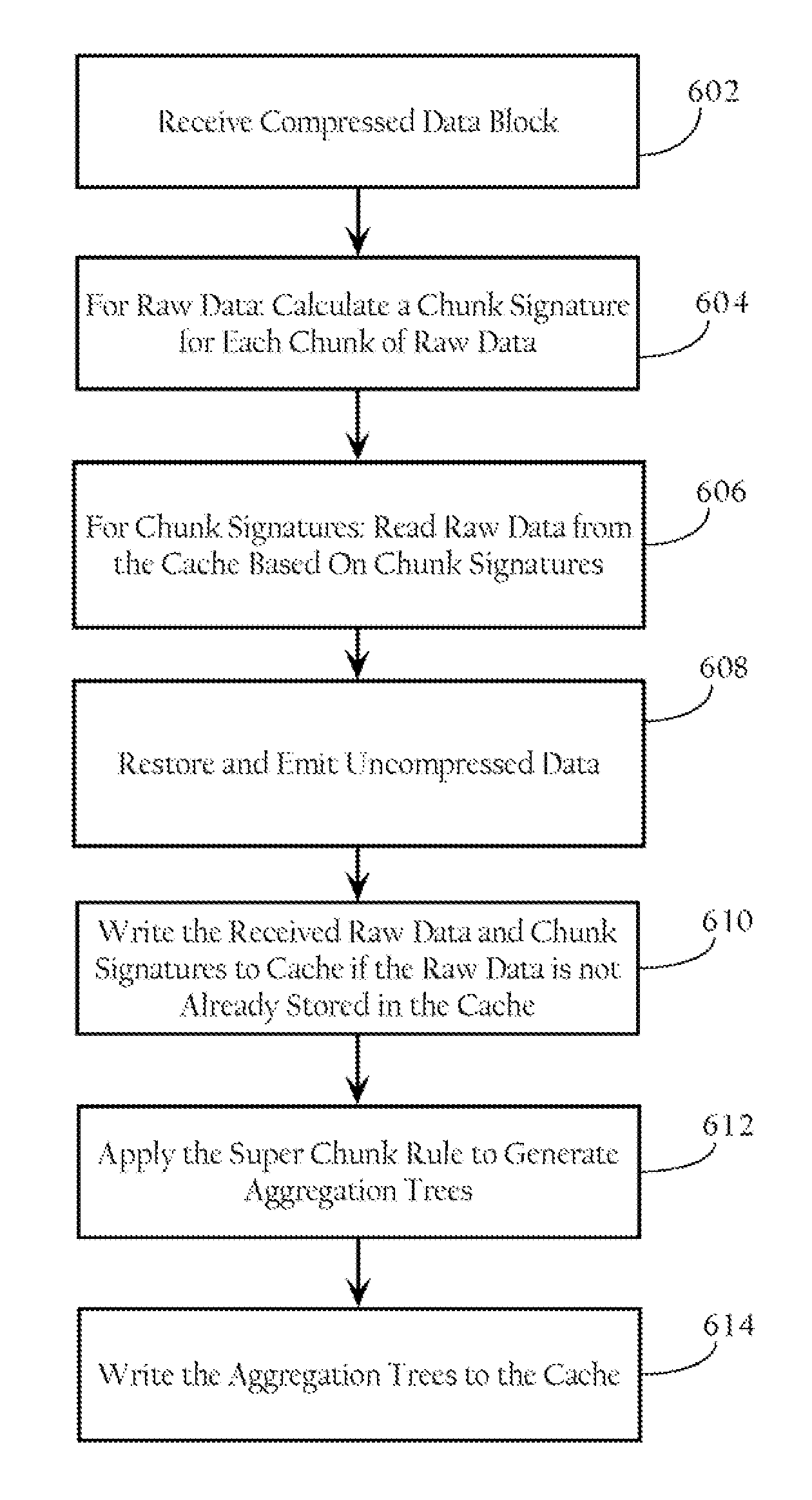
Redundancy elimination by aggregation of multiple chunks
A data redundancy elimination system. In particular implementations, a method includes storing in a memory one or more aggregation trees, each aggregation tree comprising one or more base chunk nodes and one or more super chunk nodes, wherein each base chunk node comprises a chunk signature and corresponding raw data, and wherein super chunk nodes correspond to child base chunk nodes and include a chunk signature; receiving a data block; dividing the data block into a plurality of base chunks, each base chunk having a degree value characterizing the occurrence probability of the base chunk; computing chunk signatures for the plurality of base chunks; applying a super chunk rule to contiguous sequences of base chunks of the plurality of base chunks to create one or more aggregation trees, wherein the super chunk rule aggregates base chunks based on the respective occurrence probabilities of the base chunks; identifying one or more nodes in the one or more created aggregation trees that match corresponding nodes of the aggregation trees in the memory; compressing the received data block based on the identified nodes; and conditionally adding the one or more created aggregation trees to the memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
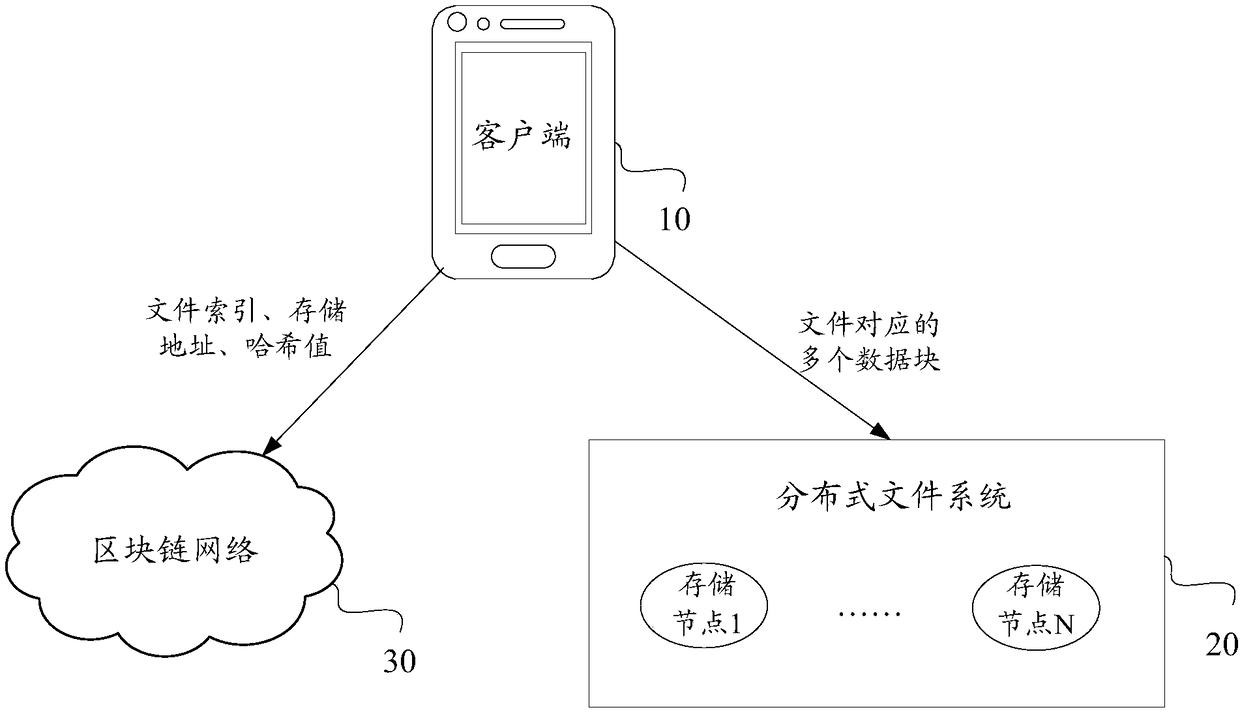
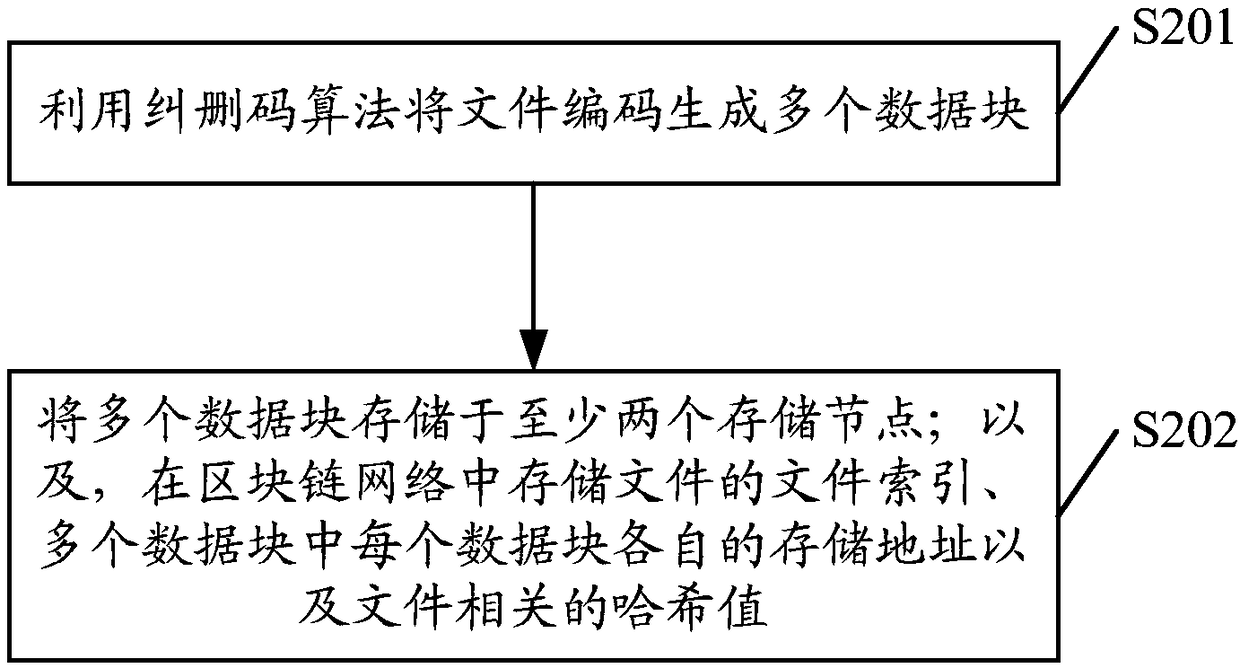
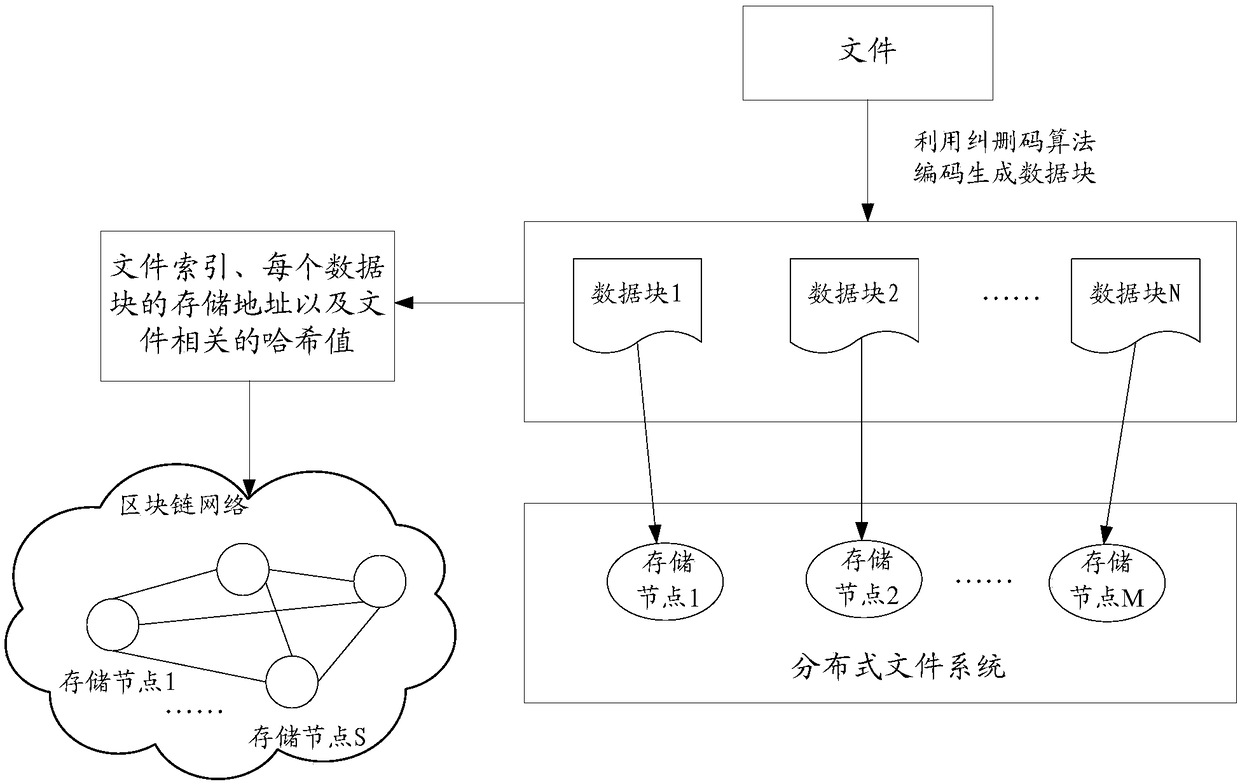
File processing method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN109491968AReduce storage pressureReduce data redundancyFile access structuresRedundant data error correctionDistributed File SystemChain network
The invention discloses a file processing method, which comprises the following steps of: encoding a file into a plurality of data blocks by utilizing an erasure code algorithm, and storing the plurality of data blocks in at least two storage nodes which at least comprise storage nodes in a distributed file system; wherein one data block is only stored once; and storing the file index of the file,the respective storage address of each data block in the plurality of data blocks and the hash value related to the file in a block chain network. Therefore, the data redundancy is greatly reduced, higher data reliability is obtained with lower data redundancy, and the utilization rate of the storage space is improved. Moreover, the method adopts a mode of combined storage of the block chain network and the out-of-chain distributed storage system, so that the storage pressure of the block chain network is reduced, and the storage capacity is expanded by introducing the distributed file system. The invention further discloses a file processing device, equipment, a medium and a computer program product.
Owner:HUNDSUN TECH
Memory redundancy oriented virtual machine migration device and method
InactiveCN102103524ASave bandwidthImprove migration speedResource allocationTransmissionData compressionData center
The invention discloses a memory redundancy oriented virtual machine migration device and method, wherein the method comprises the following steps: integrating the characteristics of a virtual machine with memory data redundancy by using a data center, and before the virtual machine is subjected to formal migration, scanning a memory page of the virtual machine so as to obtain a memory descriptor of the virtual machine which is required to be migrated; comparing the obtained memory descriptor with a targeted-node memory page so as to obtain part of memory page list of the virtual machine which is required to be migrated; and according to the obtained memory page list, canceling the transmission of redundant memories, and reducing the transmission quantity of data for migration by using a data compression technology. Therefore, by using the device and method disclosed by the invention, in the process of virtual machine migration with the purpose of saving the memory resources of the data center, the network load can be reduced as far as possible, and the overall resource utilization ratio of the data center can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Data redundancy methods and apparatus
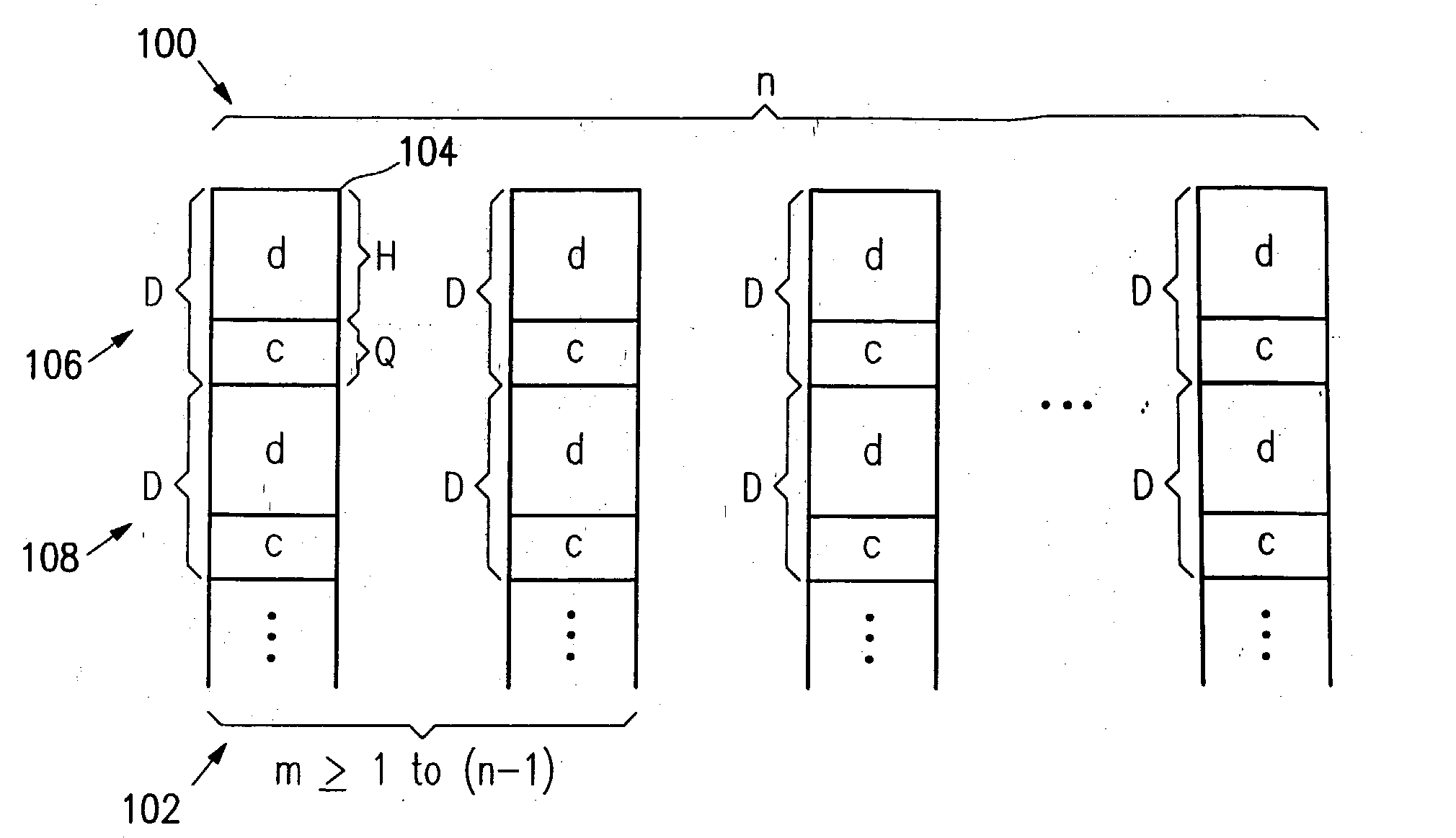
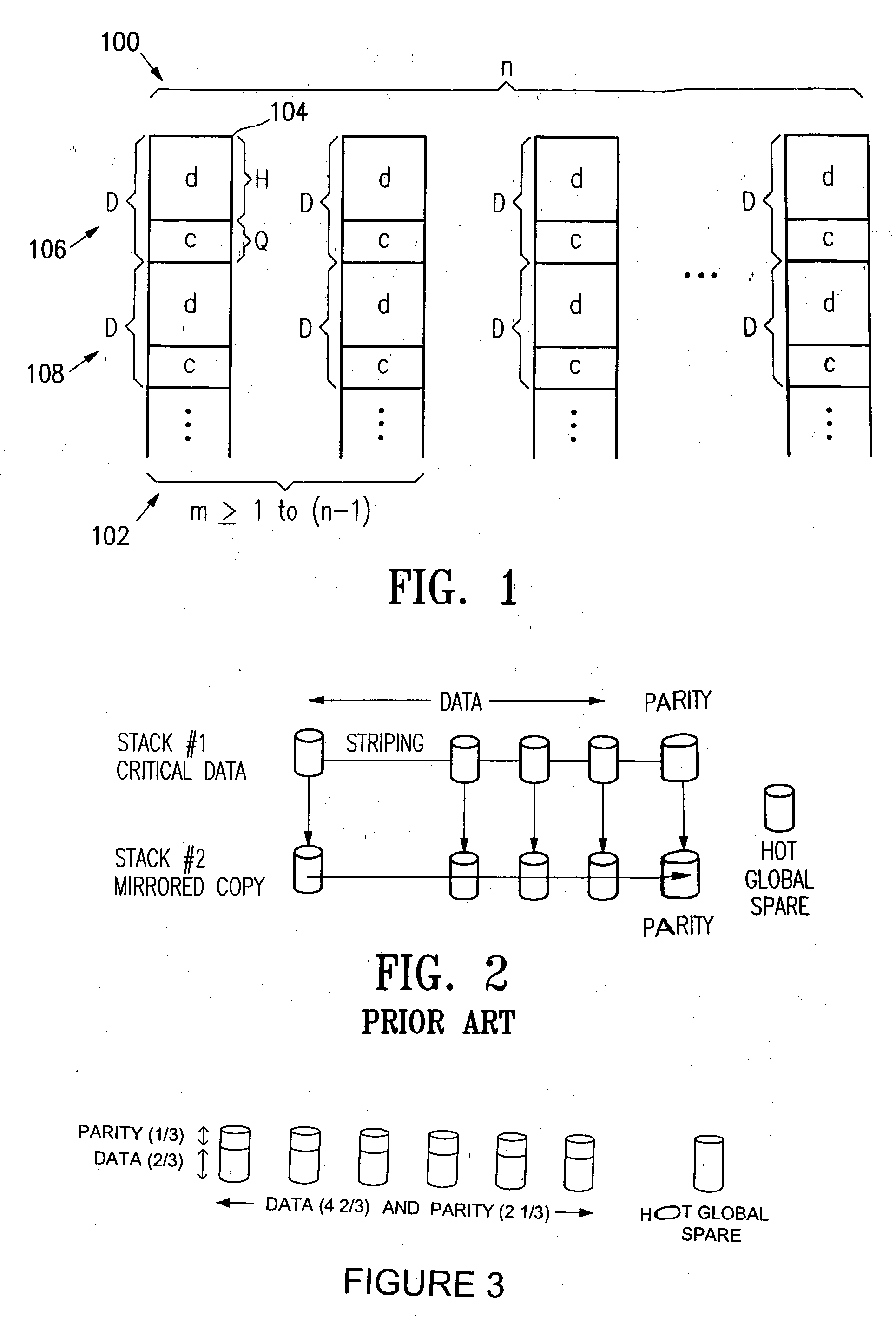
Method and apparatus for providing data recovery in a one or multiple disk loss situation in a RAID5 like system. A data storage apparatus has a plurality of n disks storing data comprising a plurality of n data groupings stored across the plurality of n disks. Each one of the n data groupings comprises a data portion and a redundancy portion. The size of the data portion relative to the redundancy portion is as H to Q, where H / Q<(n-m) / m, where m is the maximum number of disks that may be lost at any given time. Advantageously, the n data portions are recoverable from any and all combinations of n-m data grouping(s) on n-m disk(s) when the other m data grouping(s) are unavailable, where 1<=m<n.
Owner:TANDBERG DATA
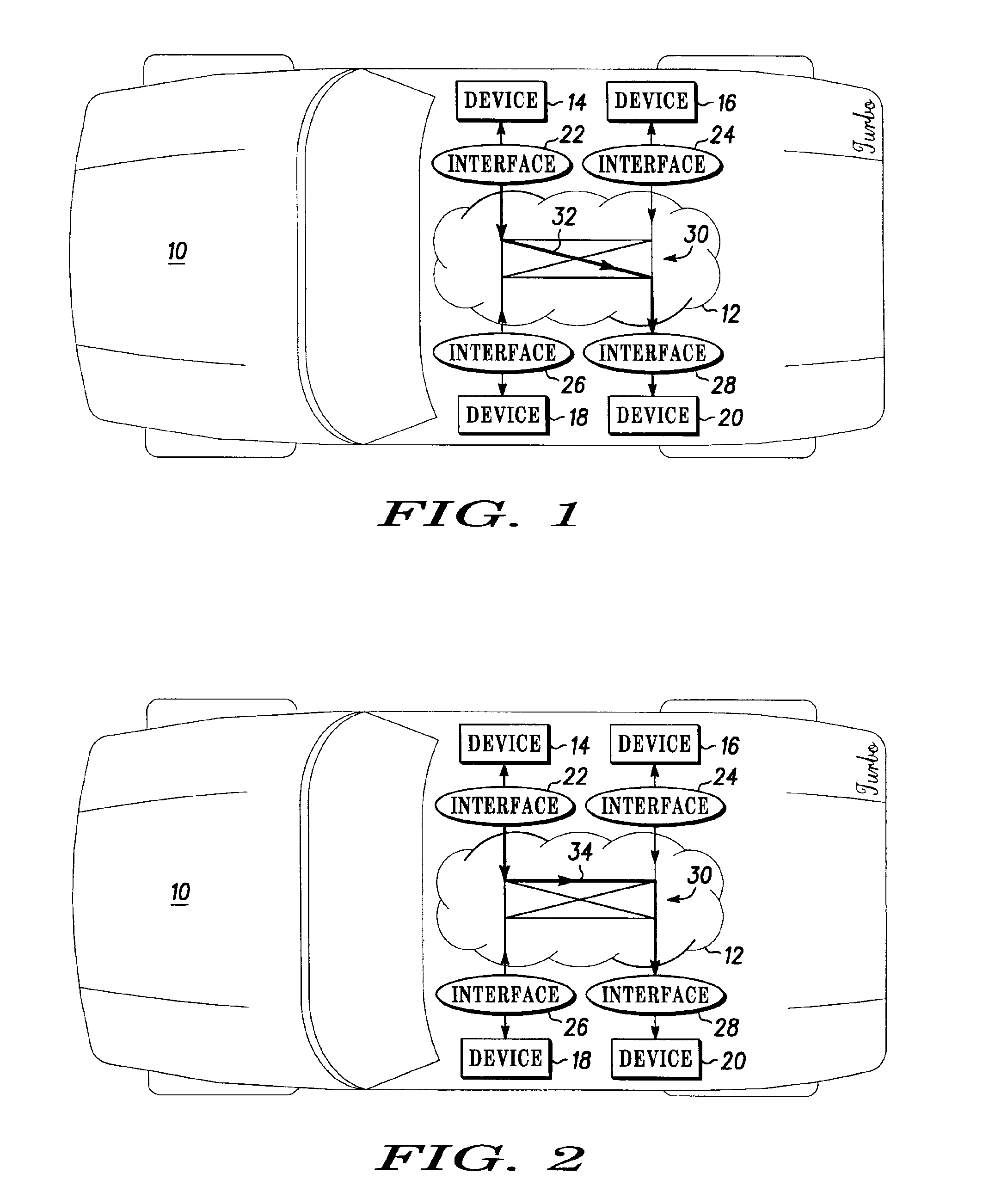
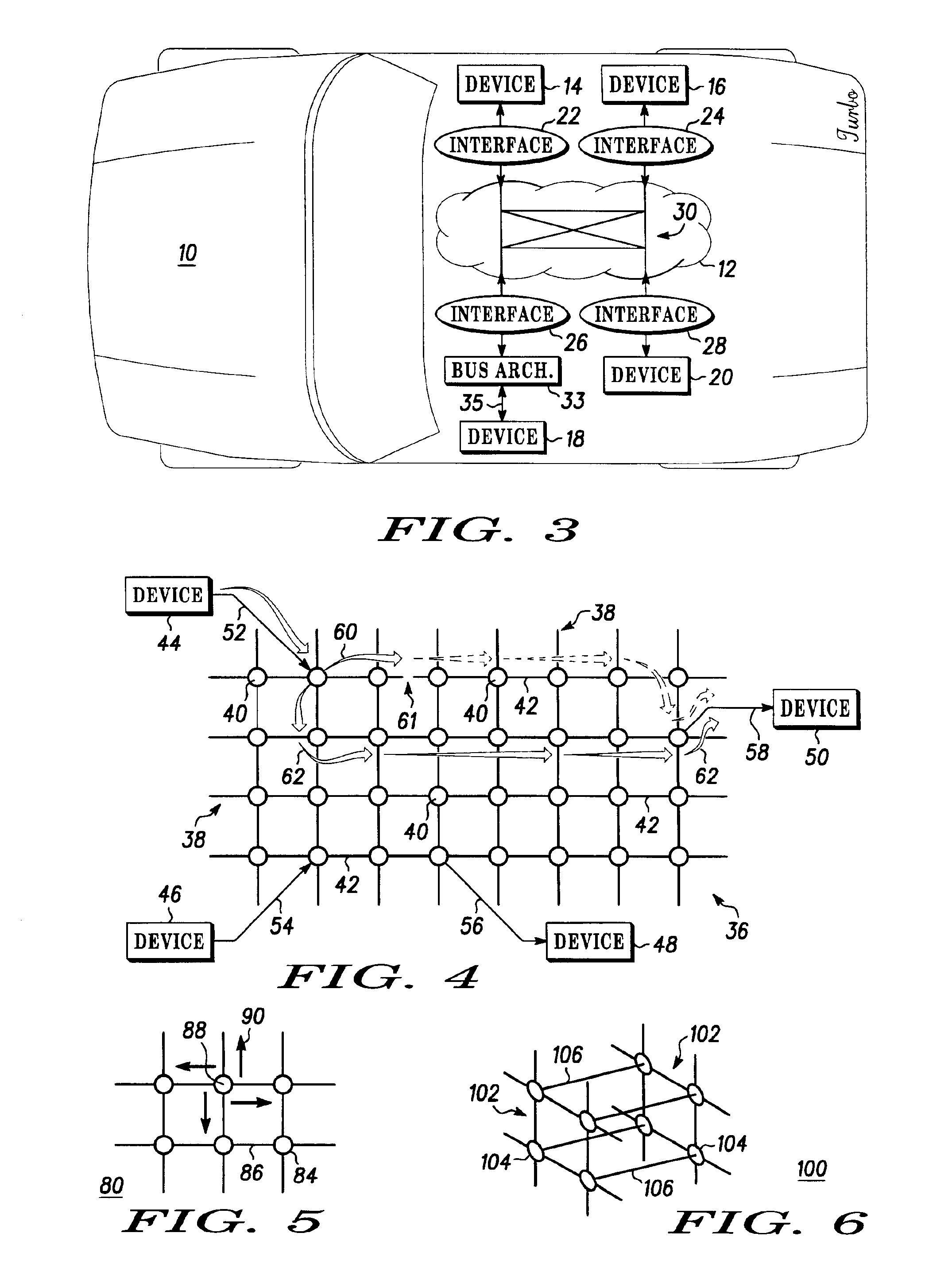
Vehicle active network with data redundancy
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Open type cloud computing monitoring system for large scale cluster and method thereof
ActiveCN103024060AReal-time monitoring serviceReliable and detailed monitoring serviceData switching networksDynamic monitoringMonitoring system
The invention belongs to the technical field of cloud computing, and particularly relates to an open type cloud computing monitoring system for large scale cluster and method thereof. The open type cloud computing monitoring system for large scale cluster comprises a monitoring terminal, a function server cluster and a cloud platform server cluster, wherein the monitoring terminal is used to select the object which is needed to be monitored for users, the function server cluster is used to receive dynamic monitoring levels and monitoring objects needed and selected by the monitoring terminal and sends out the monitoring instructions, the cloud platform server cluster is used to receive the monitoring instructions of the function server cluster and transfer the monitored node information to the function server cluster. The open type cloud computing monitoring system for large scale cluster dynamically monitors a physical machine and a virtual machine, which operate in the cluster, in real time and provide cluster administrators with more reliable, real time, and detailed monitoring service; besides, the monitoring system reports the node monitoring information and uniformly stores the monitoring information to prevent mass data redundancy.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection and correction of block-level data corruption in fault-tolerant data-storage systems
ActiveUS8145941B2Efficient detectionEliminate needStatic storageRedundant data error correctionRAIDDisk controller
Various embodiments of the present invention provide fault-tolerant, redundancy-based data-storage systems that rely on disk-controller-implemented error detection and error correction, at the disk-block level, and RAID-controller-implemented data-redundancy methods, at the disk and disk-stripe level, in order to provide comprehensive, efficient, and system-wide error detection and error correction. Embodiments of the present invention use disk-level and stripe-level data redundancy to provide error detection and error correction for stored data objects, obviating the need for certain costly, intermediate levels of error detection and error correction commonly employed in currently available fault-tolerant, redundancy-based data-storage systems.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
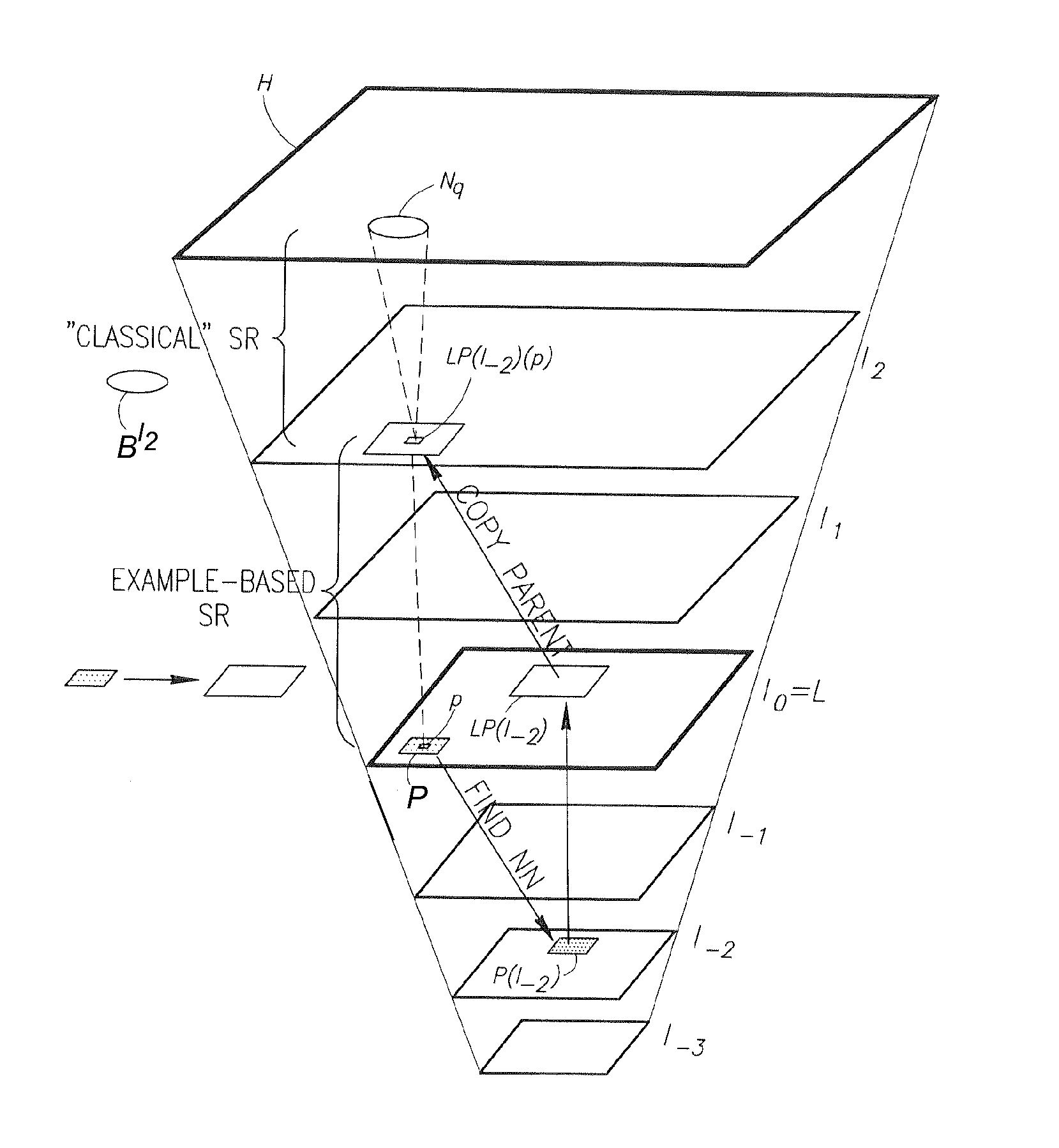
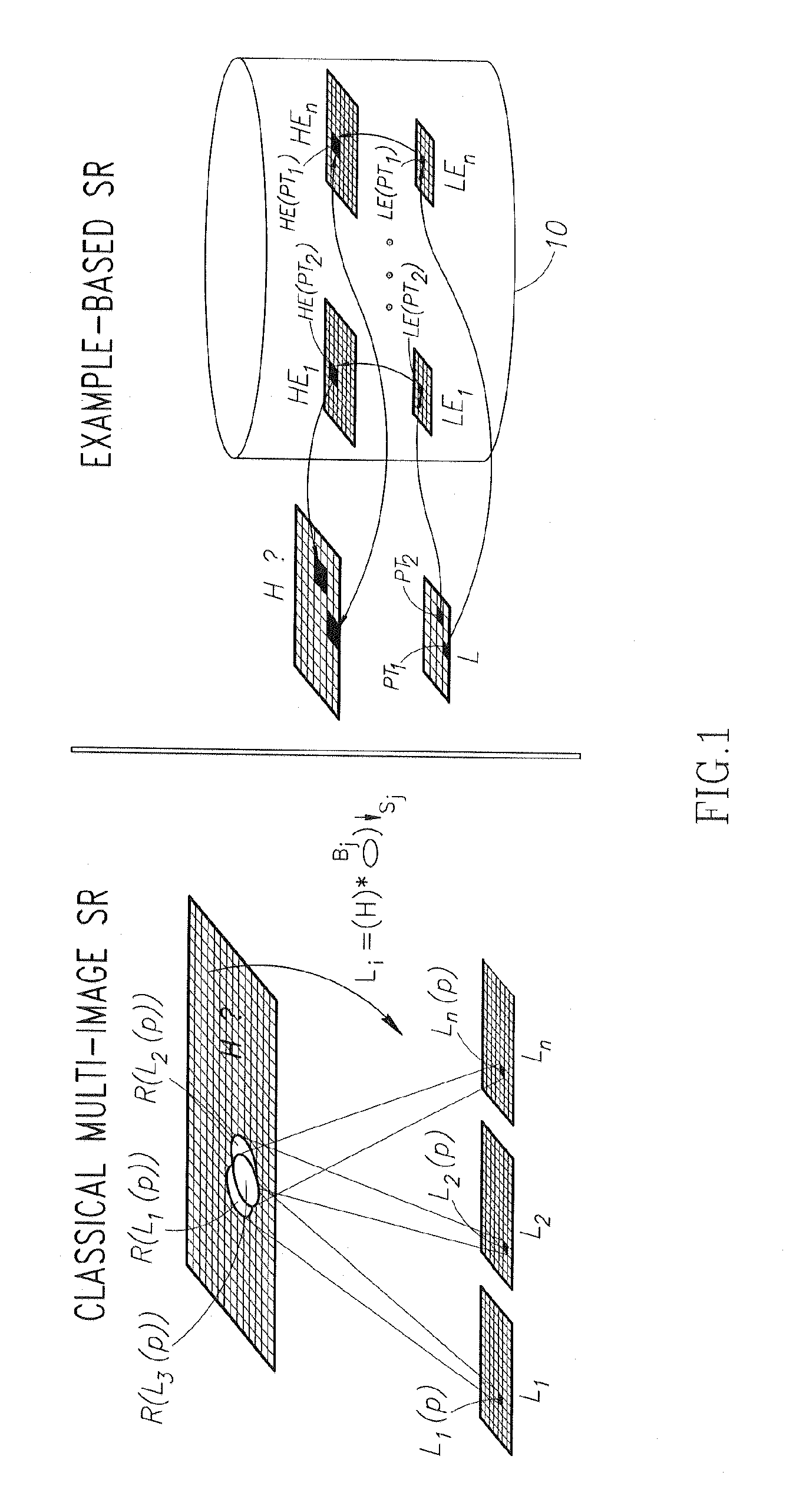
Super resolution from a single signal
ActiveUS20120086850A1Improve dynamic rangeMaximize resolutionStatic indicating devicesGeometric image transformationVideo sequenceAlternative methods
A method implementable on a computing device includes exploiting data redundancy to combine high frequency information from at least two different scales of an input signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes exploiting recurrence of data from an input signal in at least two different scales of at least one reference signal to extract and to combine high frequency information from a plurality of scales of said at least one reference signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes generating a super resolution version of a single input video sequence in at least the temporal dimension by exploiting data recurrence within the input video sequence or with respect to an external database of example video sequences. A signal may be an image, a video sequence, an audio signal, etc.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
State machine and system for data redundancy
A state machine and system for redundantly backing up data. A first storage facility is controlled by a first state machine having a finite number of states, each state having a set of allowed operations. The first state machine includes at least one state for controlling the first storage facility to operate as a primary storage facility for storing and updating a primary copy of the data. A second storage facility is controlled by a second state-machine that has least one state for controlling the second storage facility to operate as a secondary storage facility for storing redundant data. The second state machine also has at least one state for controlling the second storage facility to operate as the primary storage facility. The second storage facility assumes the role of primary in response to a fault at the first storage facility or based on the origin of request traffic. The first and second state machines may also include states for responding to various fault conditions and may include substantially the same states as the other.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
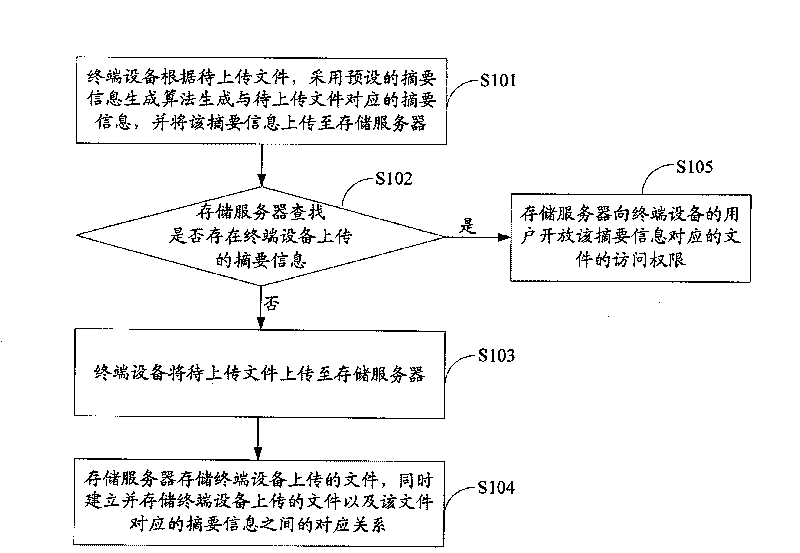
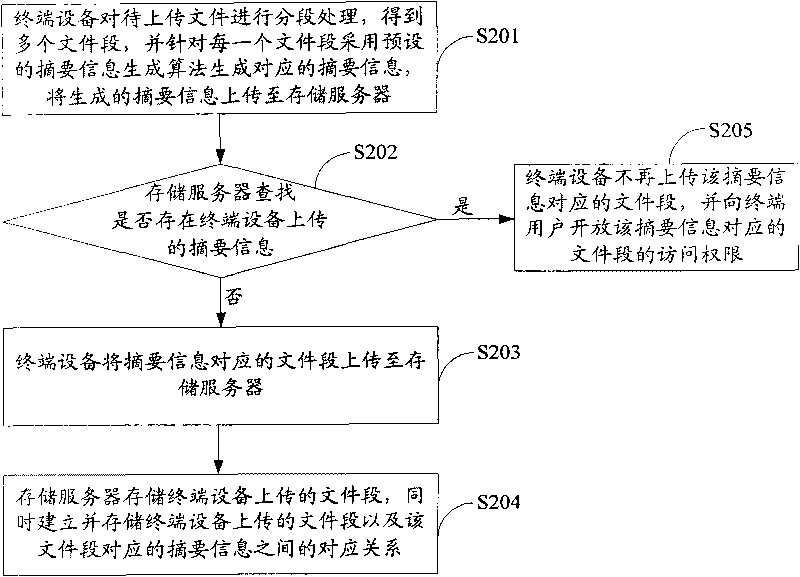
File uploading method and device, and mass storage system
InactiveCN101699822AReduce data redundancyIncrease upload speedTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsTerminal equipmentOperating system
The invention is suitable for the field of storage and provides a file uploading method and device, and a mass storage system. The method comprises the following steps: a terminal device generates summary information corresponding to the file to be uploaded by using a preset summary information generating algorithm according to the file to be uploaded, and uploads the summary information to a storage server; the storage server searches whether the summary information uploaded by the terminal device exists or not; and when the storage server does not find the summary information, the terminal device uploads the file to be uploaded to the storage server. In the embodiment of the invention, the terminal device needs to upload the file to the storage server only when the file to be uploaded does not exist in the storage server, thereby reducing the data redundancy in the storage server, saving the network resources while uploading files and increasing the file uploading speed.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and system for striping spares in a data storage system including an array of disk drives
InactiveUS6934804B2Improve reliabilityImprove performanceMemory loss protectionRedundant data error correctionGranularityData store
Method and apparatus for striping spare storage in a data storage system. Specifically the present invention describes a method and apparatus for storing data and spare storage in a data storage system having a plurality of physical storage devices. The plurality of physical storage devices is partitioned into a plurality of slices. Logical units of storage (LUNs) are created, wherein each LUN contains data, spare, and data redundancy. Each of the plurality of slices is assigned to one of the plurality of LUNs so as to distribute storage of data, data redundancy, and spare across all of the plurality of physical storage devices. Distribution of spare storage is concentrated at the inner zone of each of the plurality of physical storage devices. The data and spare storage can be distributed uniformly or with varying granularities across all of the plurality of physical storage devices.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data storage using disk drives in accordance with a schedule of operations
ActiveUS7734867B1Save powerLow heat generationEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionData integrityData store
Techniques for data storage using disk drives. To conserve power and reduce heat generation so that higher packaging density is possible, only some of the disk drives in an array may be powered on at any one time. Disk accesses may then be scheduled so that appropriate drives are powered on and off at appropriate times. In addition, various levels of storage services may be provided depending, for example, upon how accessible the drives are to individual clients and upon a level of data redundancy provided. Another advantage includes off-loading of tasks to a controller or processor included within the disk drives themselves. For example, the disk drives themselves may compute error detection or error correction representations and perform data integrity checks based on those representations. Failure simulation may also be performed to verify the ability to recover lost data and the disk drives may be used to convert the data into general formats that may be expected to be more easily read in the future.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Data redundancy processing method, device and distributed storage system
ActiveCN102279777AImplement redundant processingReduce loadInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionComputer scienceData recovery
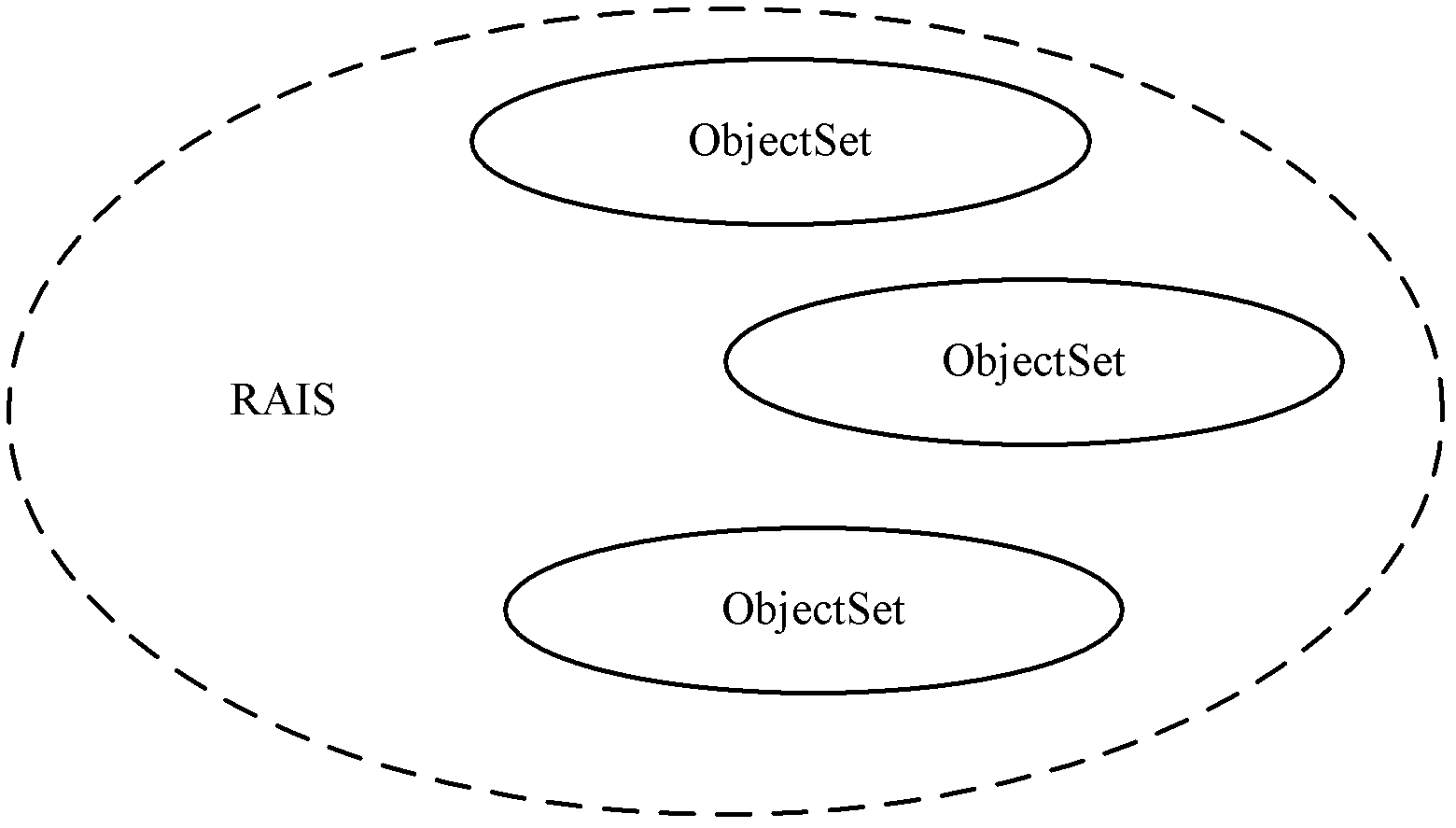
A method and device for processing data redundancy and distributed storage system are provided. The method comprises: generating M pieces of slice data and N pieces of redundancy slice data of data to be written by using a redundancy algorithm (403), wherein when at most N pieces of data among said M pieces of slice data and N pieces of redundancy slice data are arbitrarily damaged, the damaged data can be recovered by using the undamaged data, with M being a natural number which is more than 1, and N being a natural number which is not less than 1; and respectively storing said M pieces of slice data and N pieces of redundancy slice data into objects located in at least two storage nodes (404), wherein each storage node contains at least one object set, and each object set contains s at least one object. The method can improve utilization rates of storage spaces and storage loads are reduced, moreover, different redundancy algorithms can be supported, thus different requirements for reliability of customers can be met and the flexibility is relatively higher.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
Data redundancy for writes using remote storage system cache memory
A technique for using a remote array cache memory for data redundancy. A computer system includes a first storage system having cache memory and mass storage. Data to be written to the mass storage is written to the cache memory. Redundant data is stored elsewhere in case the cache experiences a fault before the data can be written to mass storage. Otherwise, data not yet written to the mass storage may be lost. The first storage system is in communication with a second storage system which is typically located remotely from the first storage system. When the first storage system receives a write request, the first storage system forwards the data to the second storage system for redundant storage. Where the data is forwarded to the second storage system, this is referred to herein as "remote mode."The first storage system may include redundant cache memories and enters remote mode only in the event a fault affects one of the cache memories. The data can then be recovered from the second storage system if needed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
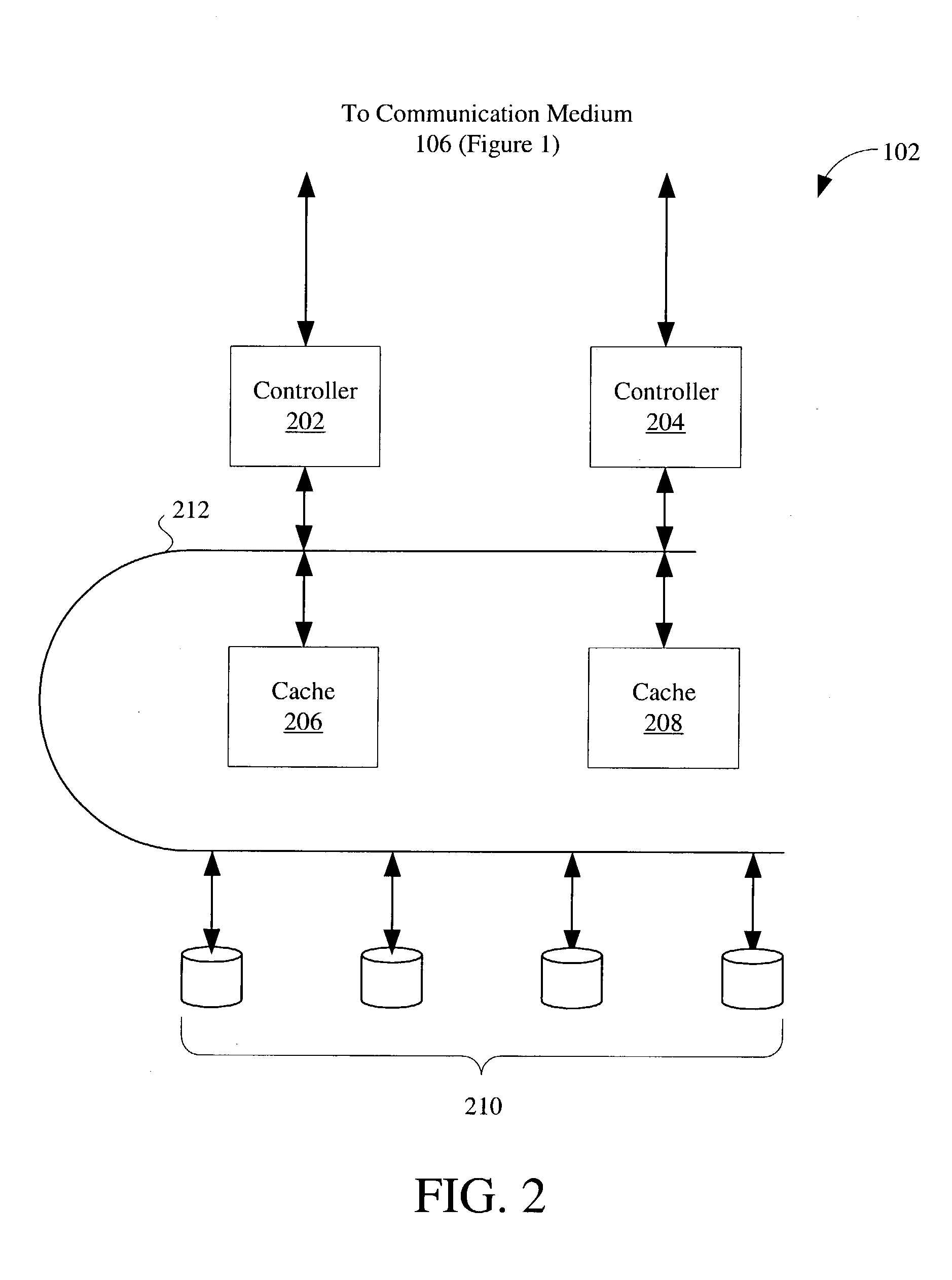
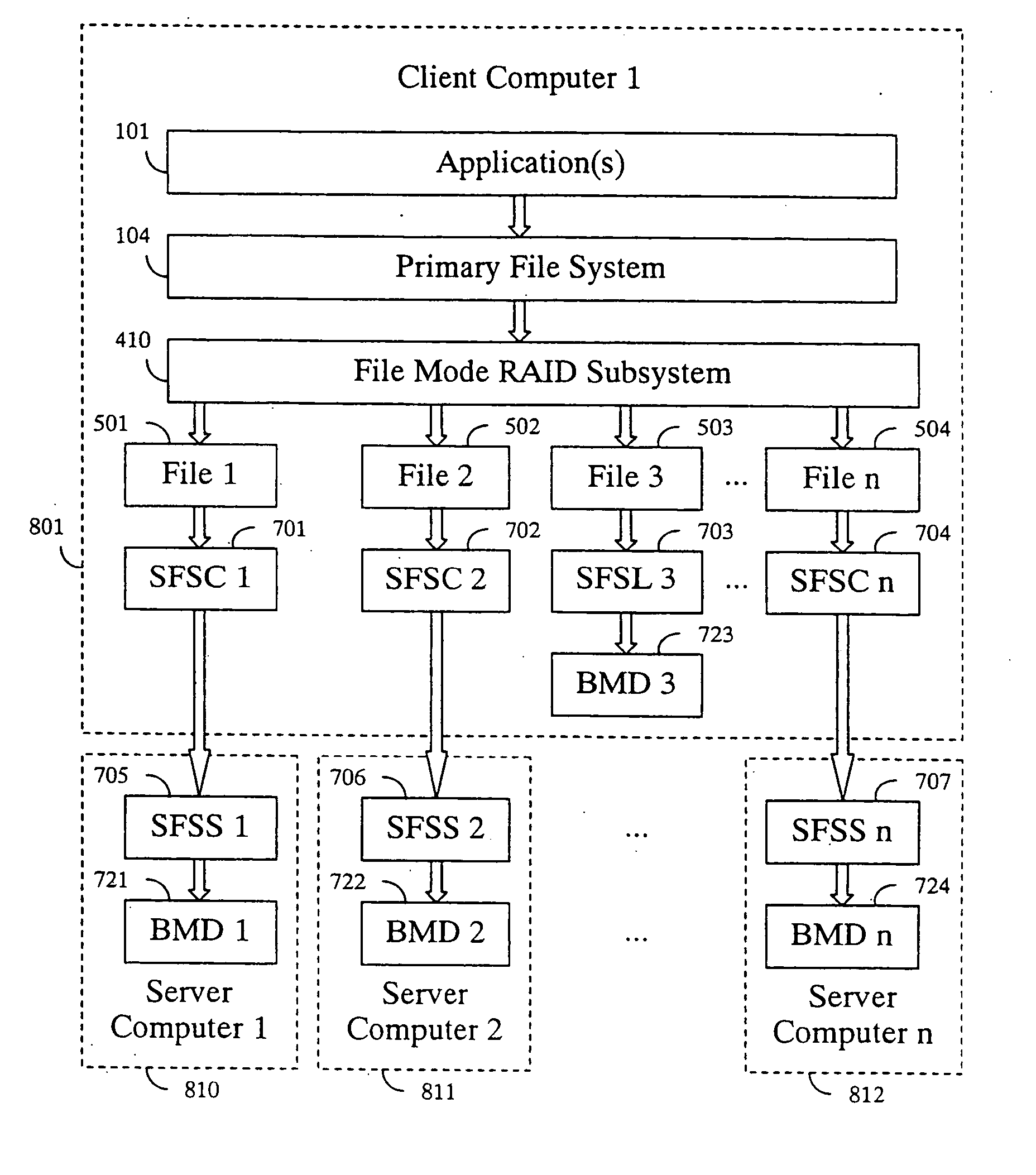
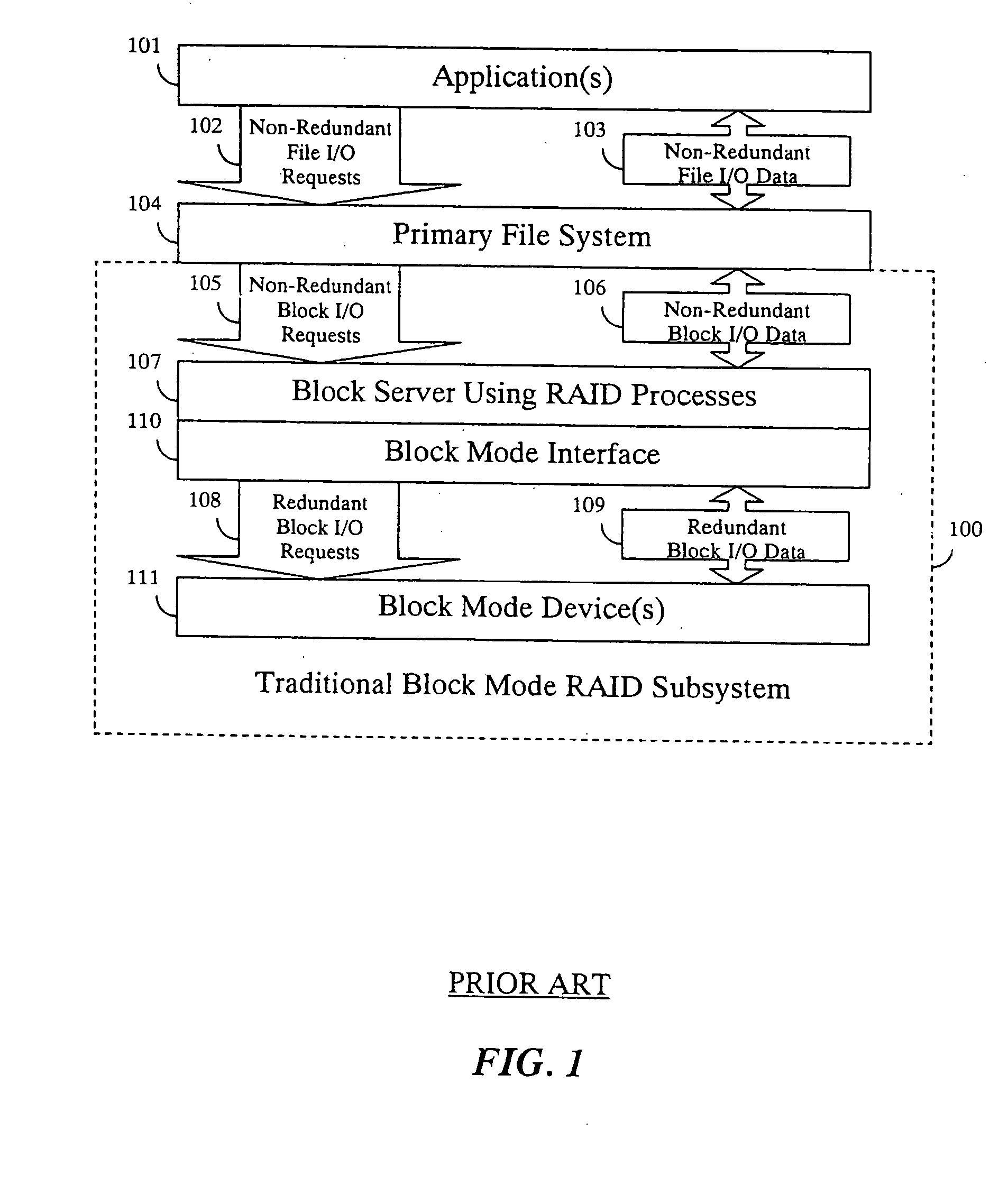
File mode RAID subsystem
InactiveUS20050021615A1Avoid less flexibilityLow costInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsRAIDFile system
A method and system enables data redundancy across servers, networks, and controllers by using standard redundant files as underlying storage for RAID subsystem configurations. A redundant array of independent disk (RAID) subsystem includes a front-end interface configured to process non-redundant requests received from a primary file system communicating with an application program. A back-end interface of the RAID subsystem is configured to process redundant requests corresponding to the non-redundant requests. The redundant requests to be issued to a secondary file system communicates with a block mode device including multiple physical storage devices.
Owner:RAIDCORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com