Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about How to "Maximize resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
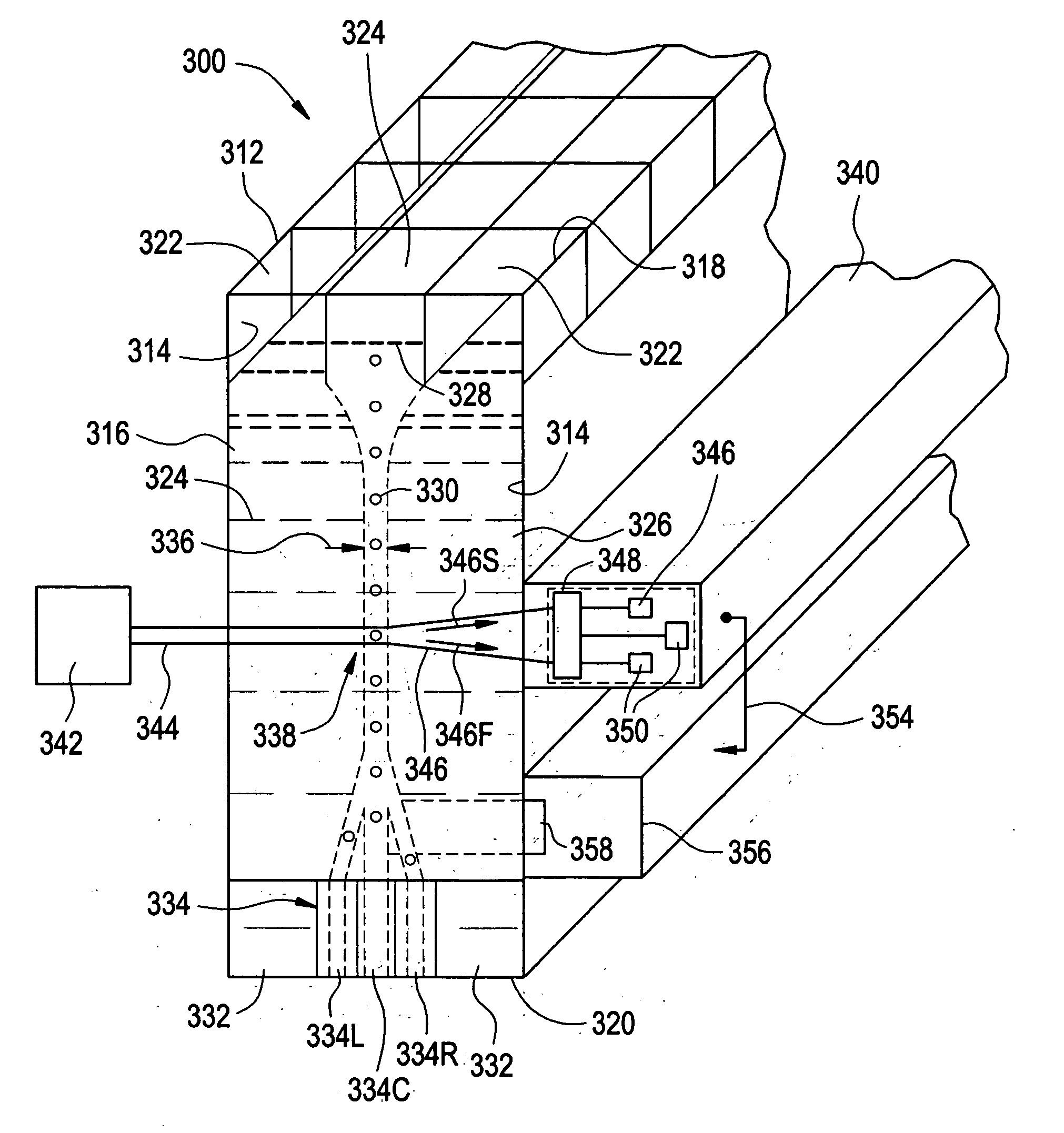
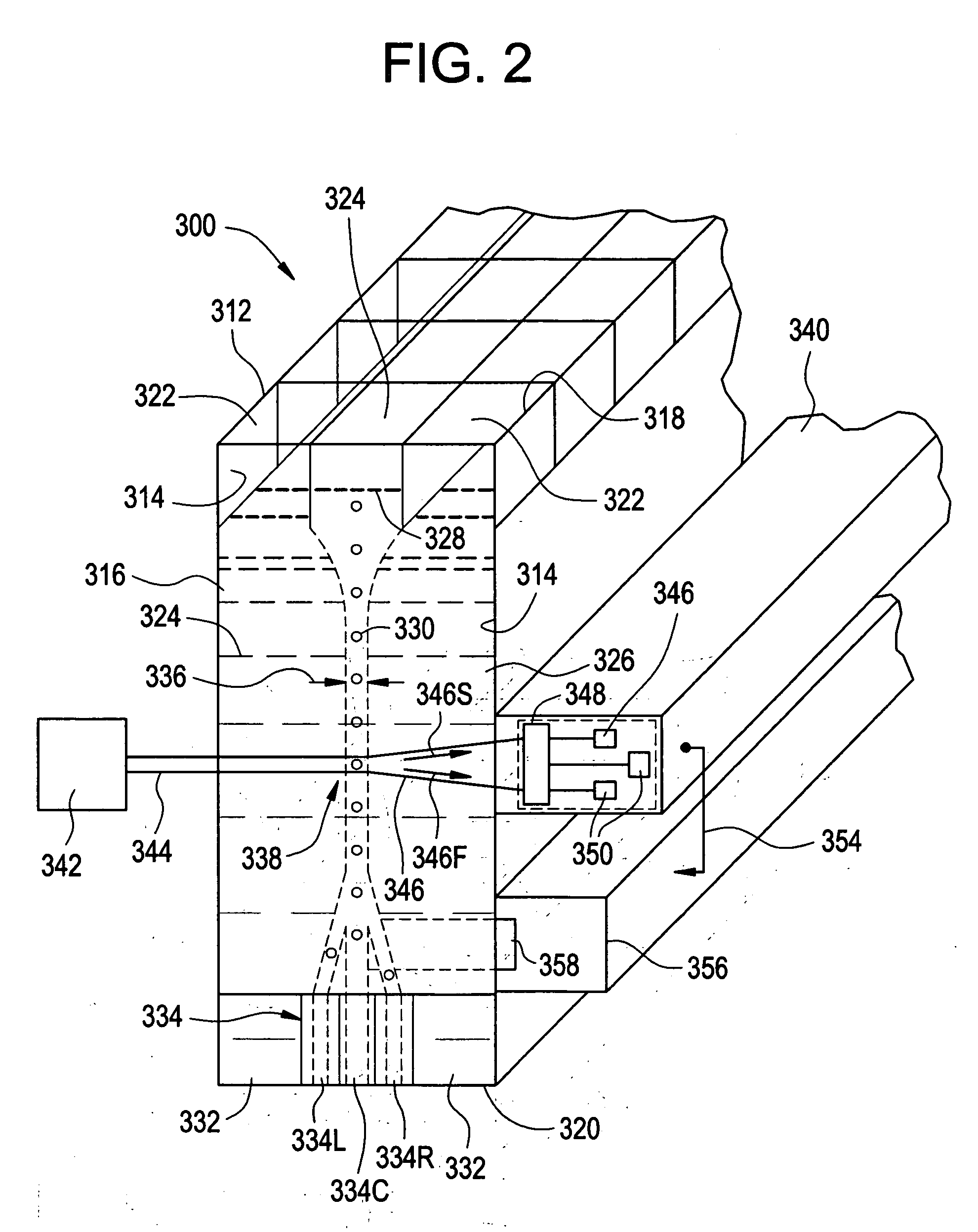
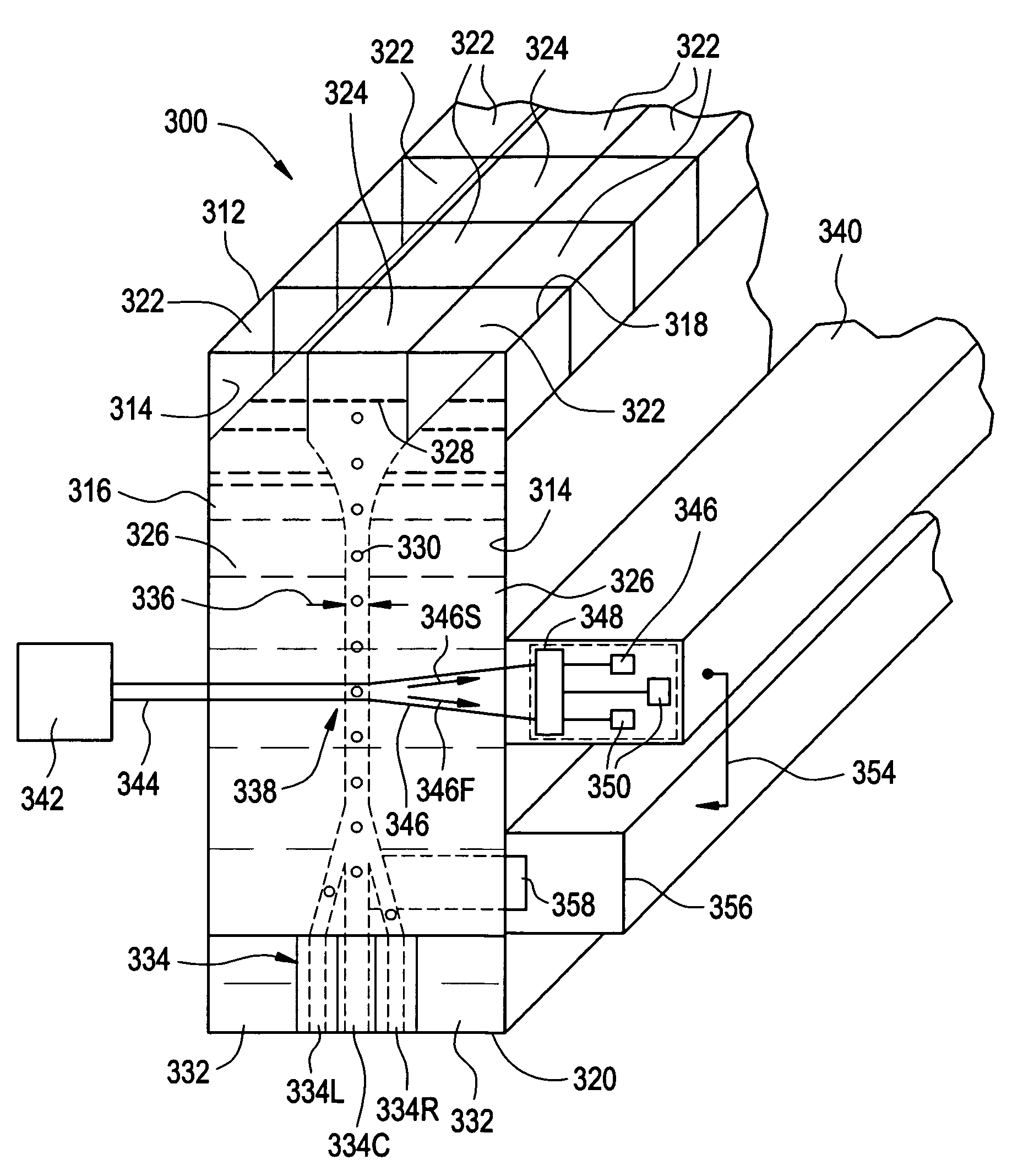
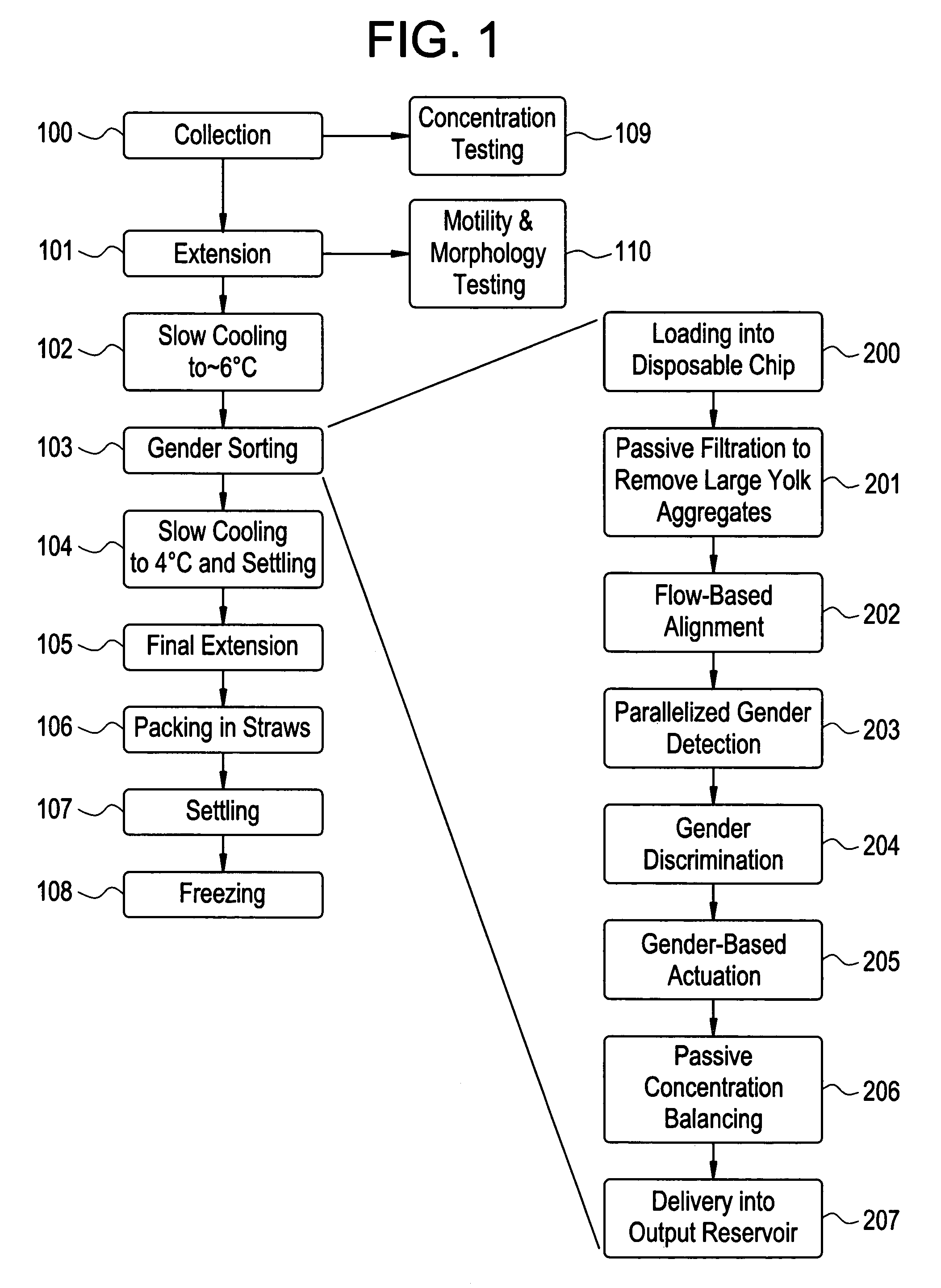
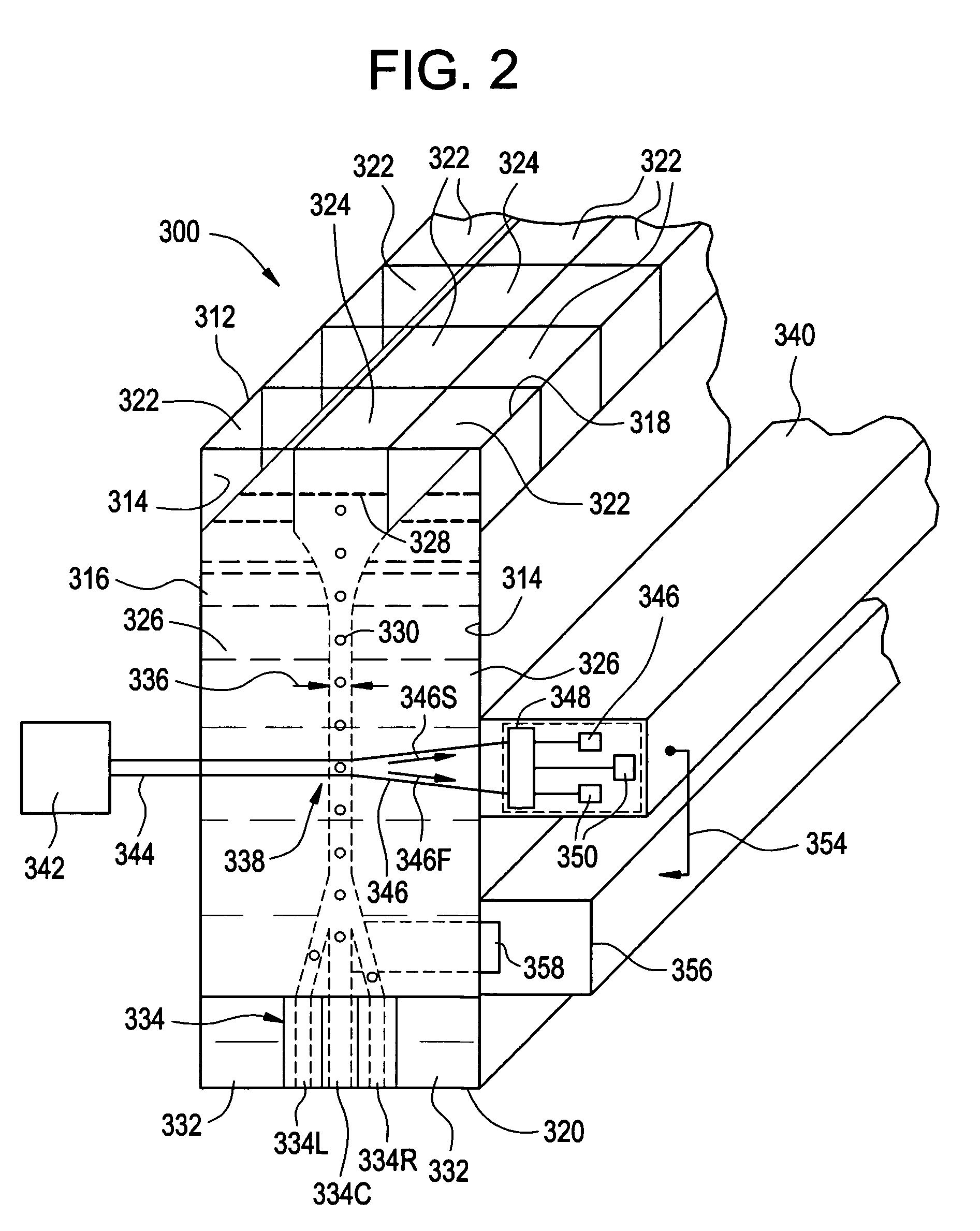
Method and apparatus for sorting cells
ActiveUS20060170912A1Improve collection efficiencyMaximize resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSperm cellPhysics
Apparatus for sorting and orienting sperm cells has a pair or walls in confronting relationship forming a flow chamber having inlet, a downstream outlet, and intermediate detector region. The inlet receives first and second spaced apart streams of input fluid and a third stream of sample fluid containing the cells to be sorted. The first and second streams have respective flow rates relative to third stream, such that the third stream is constricted forming a relatively narrow sample stream, so that the cells are oriented parallel to the walls. A detector detect desired cells and a sorter downstream of the detector for sorting the desired cells from the stream.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
Method and apparatus for sorting cells
ActiveUS7355696B2Improve collection efficiencyMaximize resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSperm cellPhysics
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
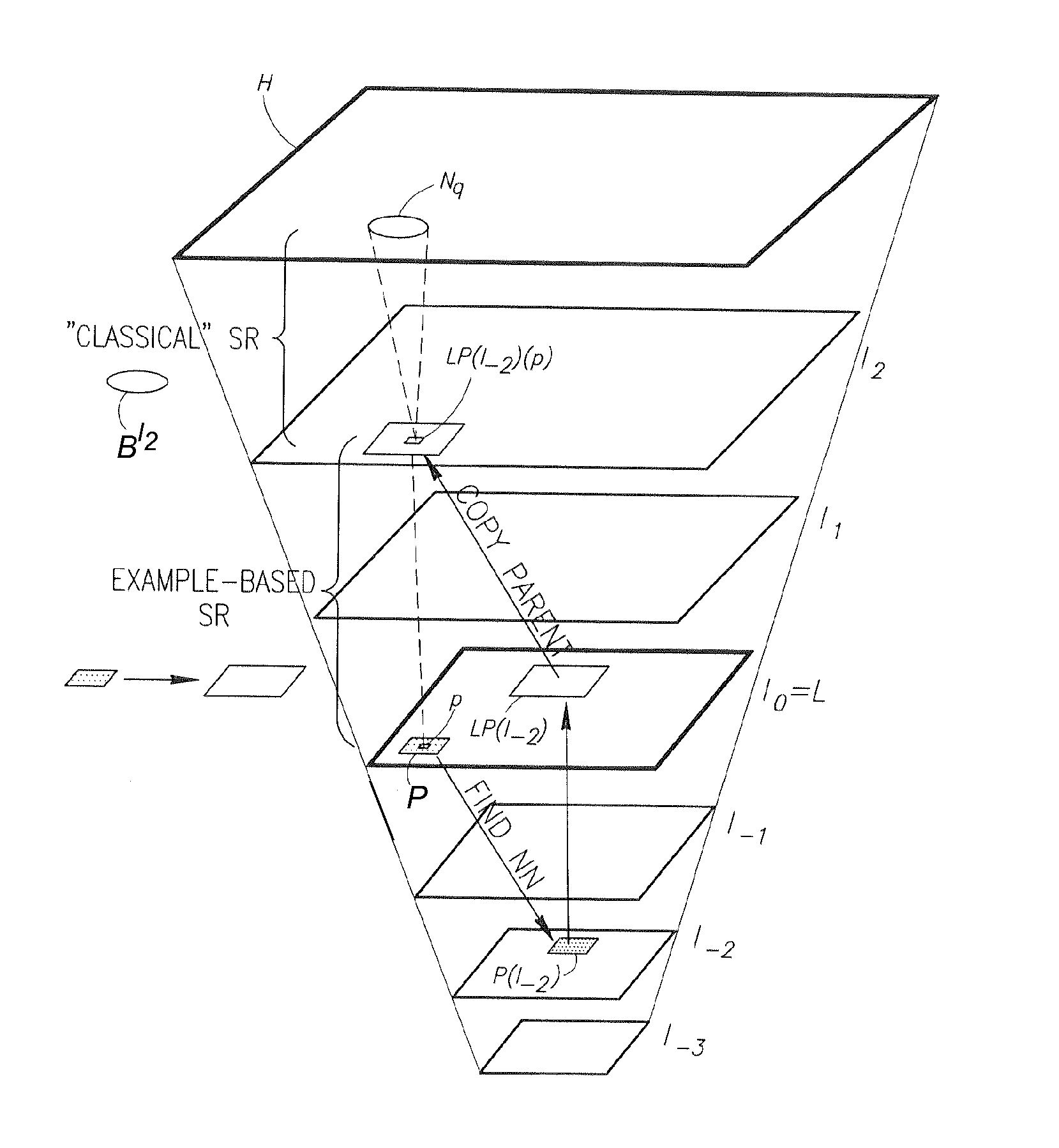
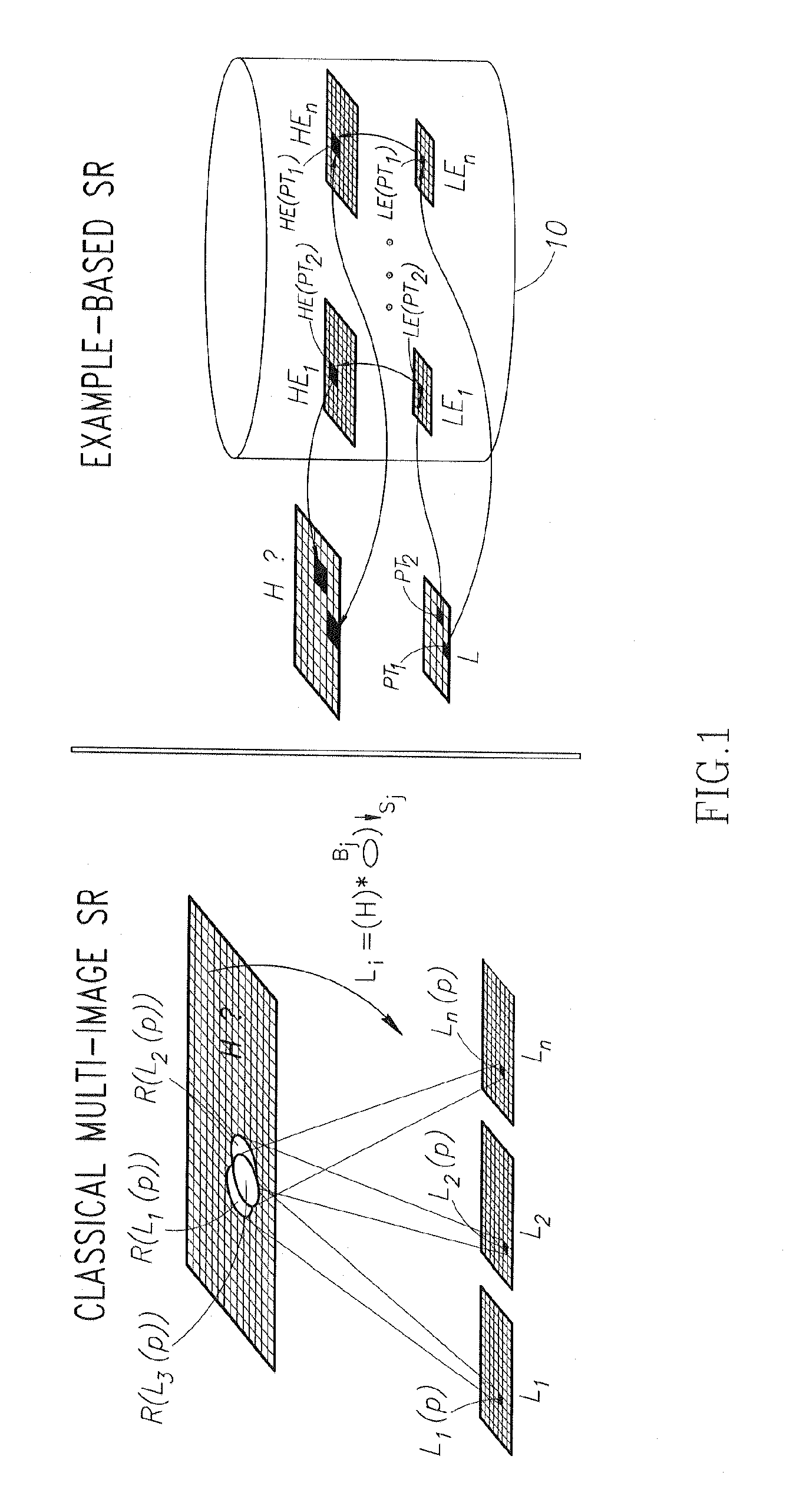
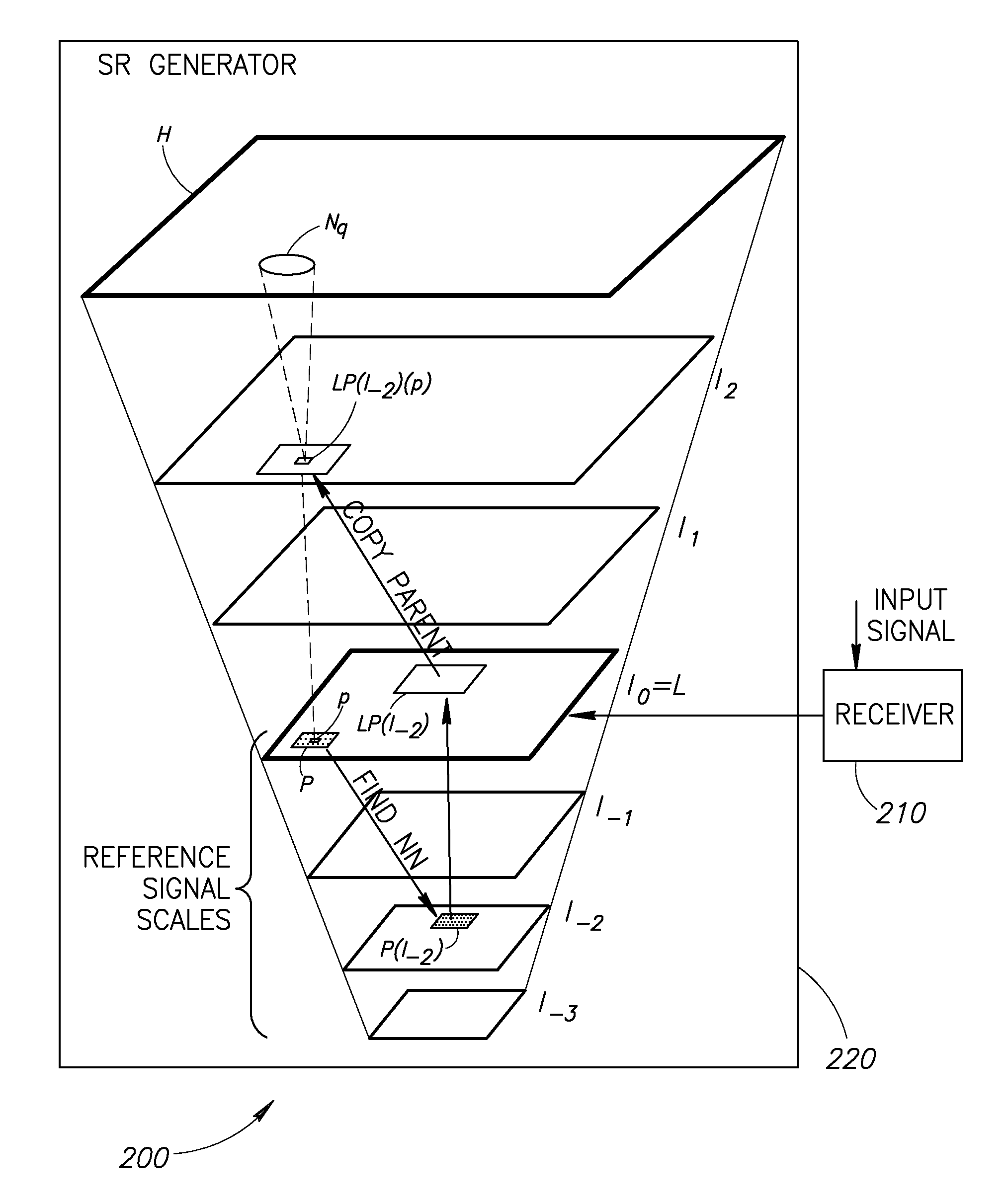
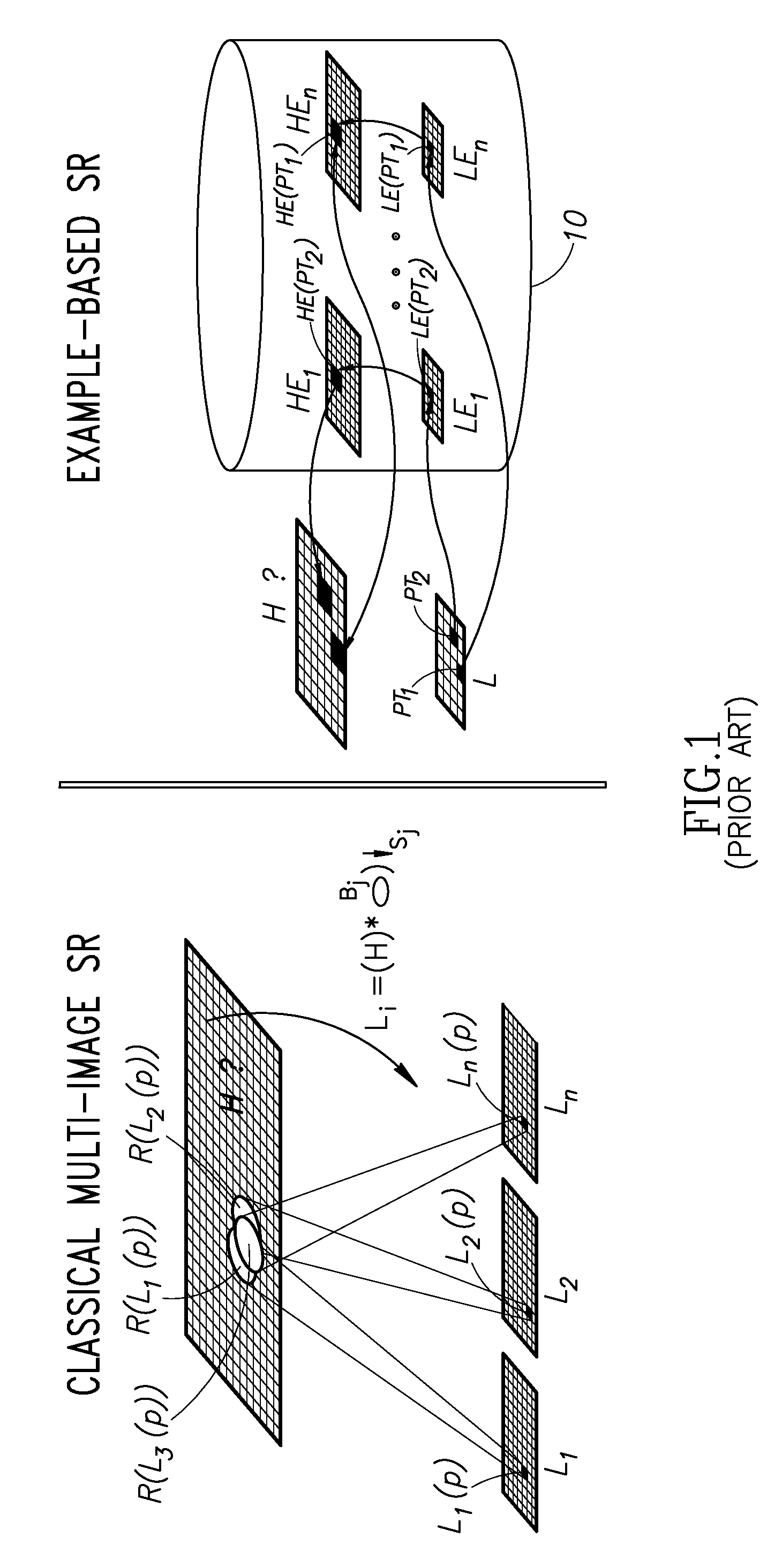
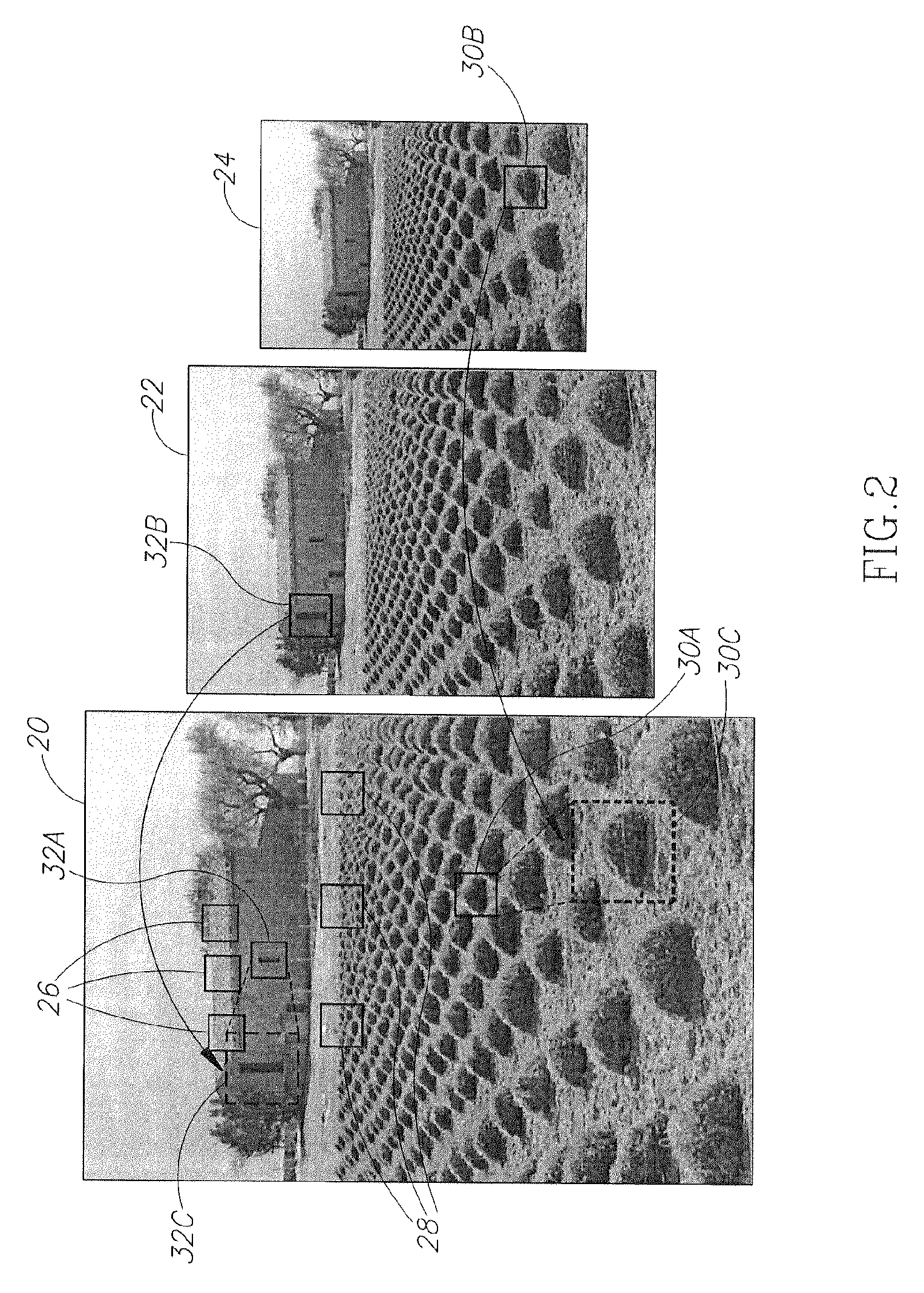
Super resolution from a single signal
ActiveUS20120086850A1Improve dynamic rangeMaximize resolutionStatic indicating devicesGeometric image transformationVideo sequenceAlternative methods
A method implementable on a computing device includes exploiting data redundancy to combine high frequency information from at least two different scales of an input signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes exploiting recurrence of data from an input signal in at least two different scales of at least one reference signal to extract and to combine high frequency information from a plurality of scales of said at least one reference signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes generating a super resolution version of a single input video sequence in at least the temporal dimension by exploiting data recurrence within the input video sequence or with respect to an external database of example video sequences. A signal may be an image, a video sequence, an audio signal, etc.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
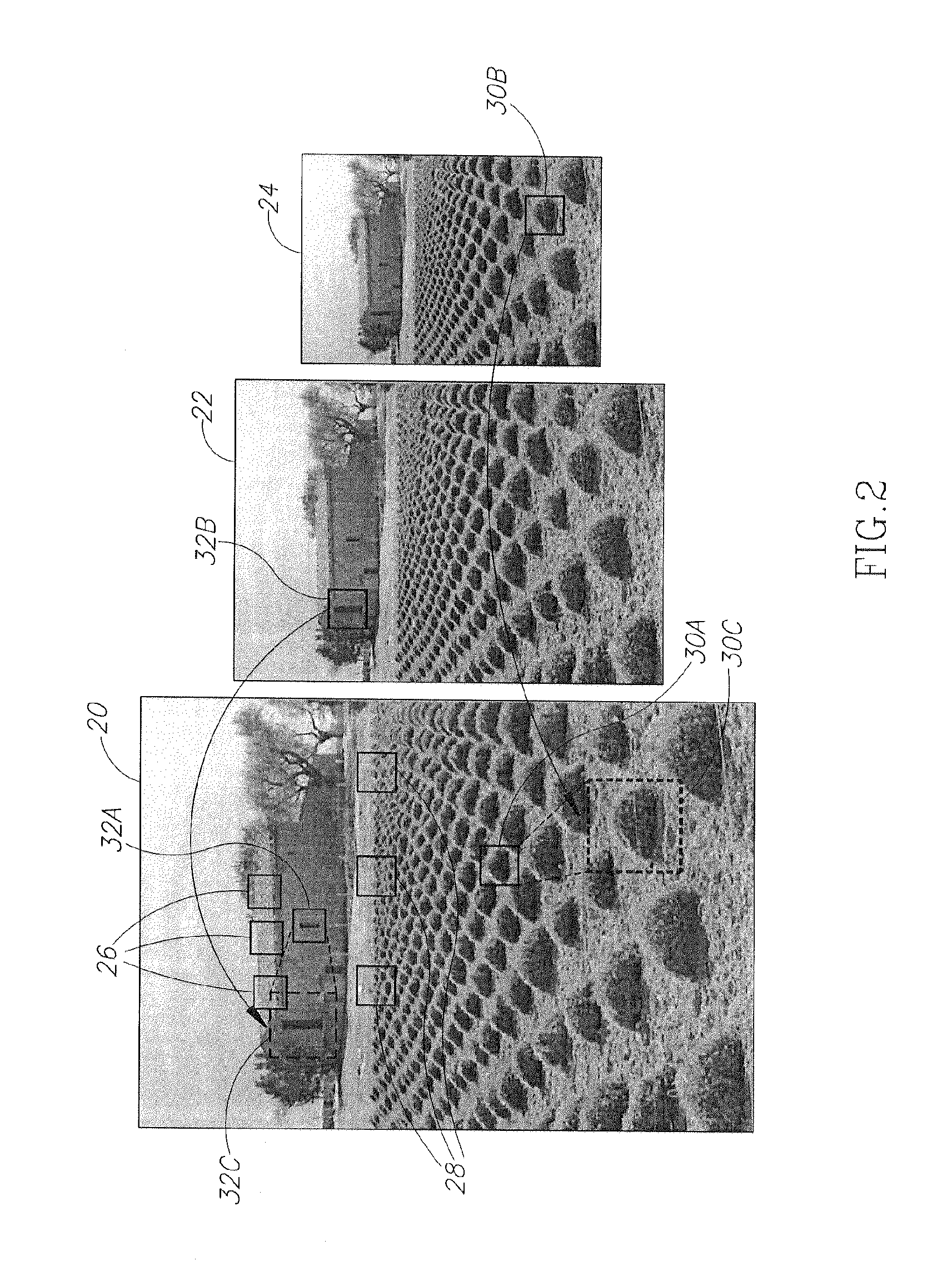
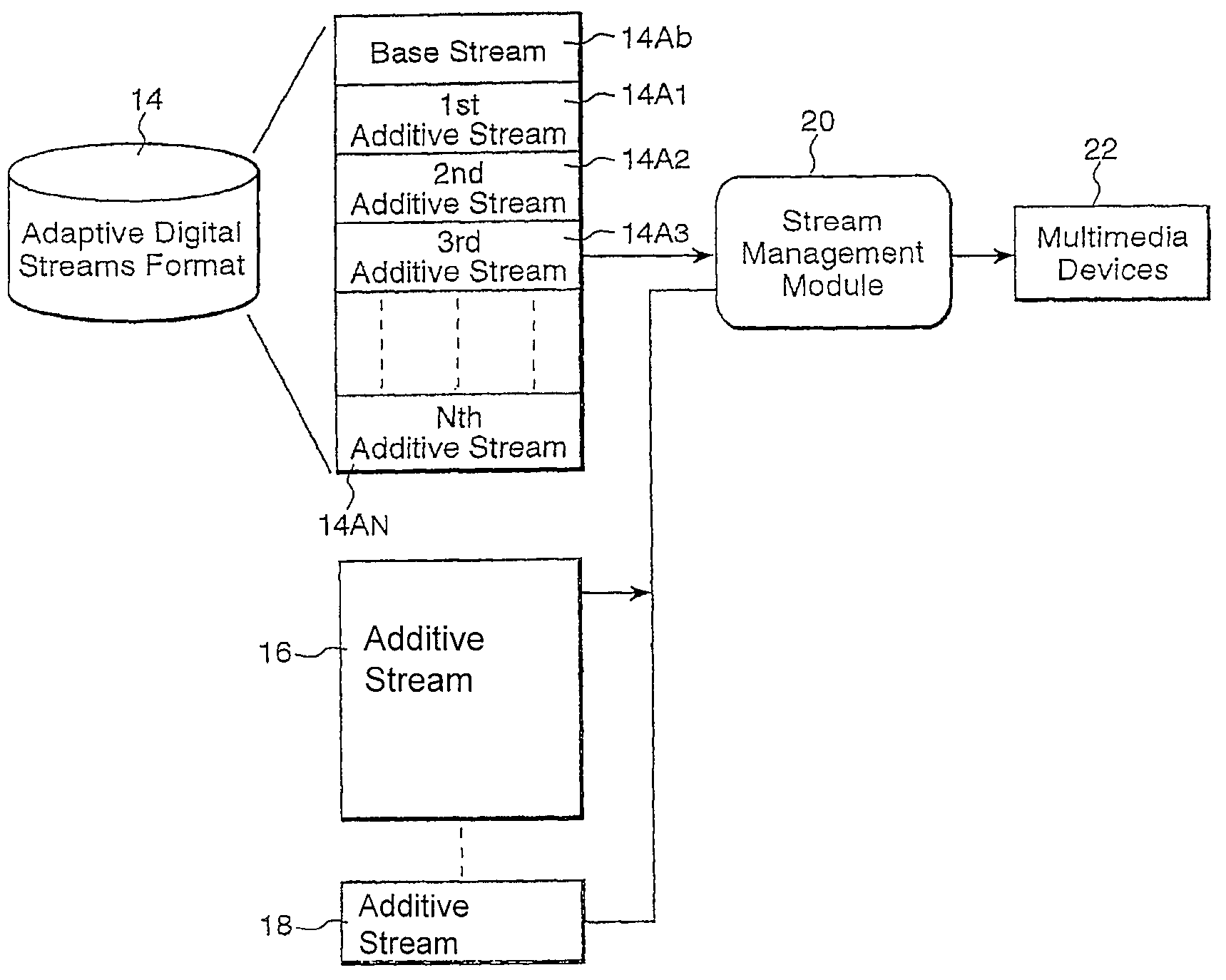
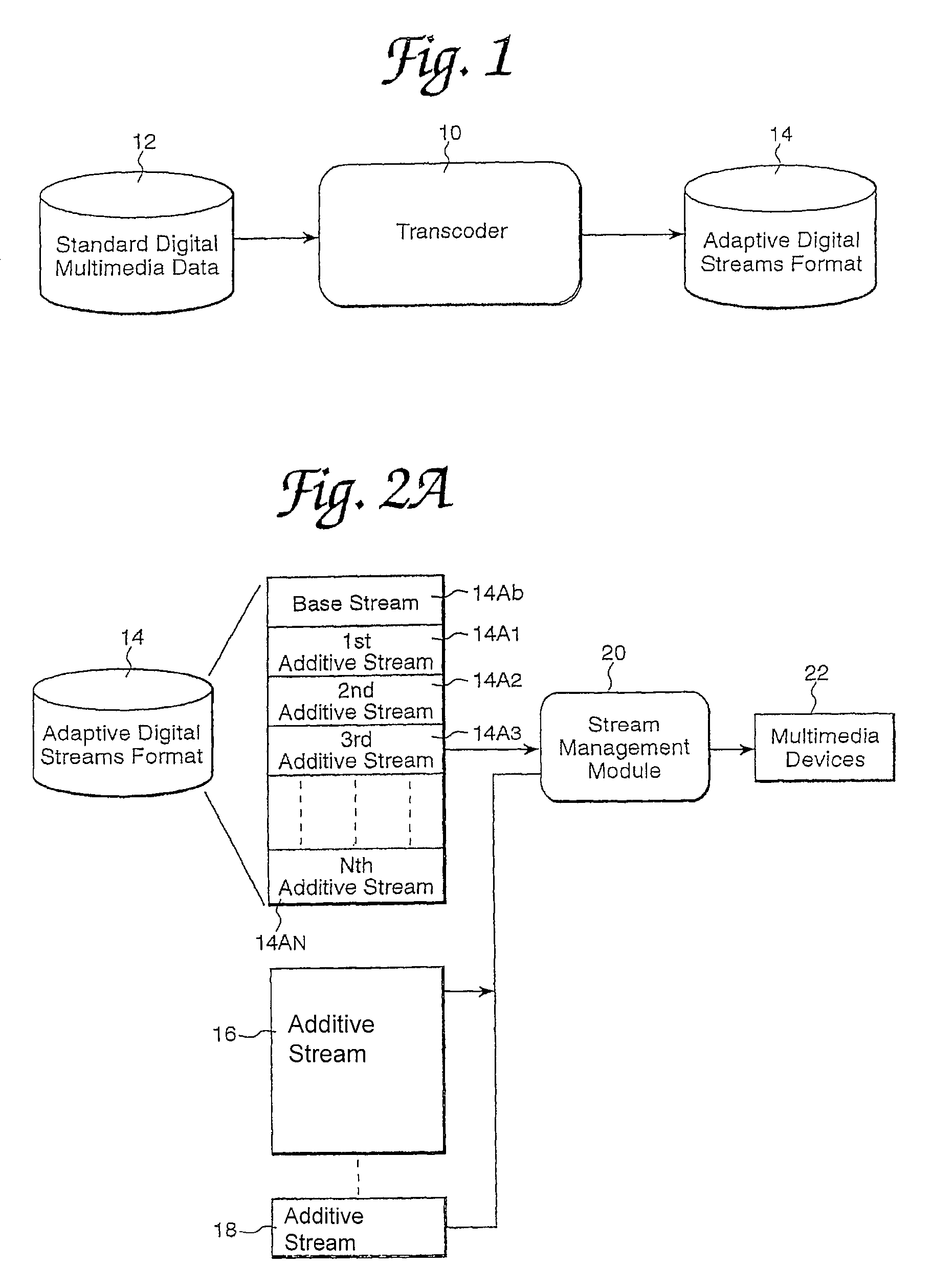
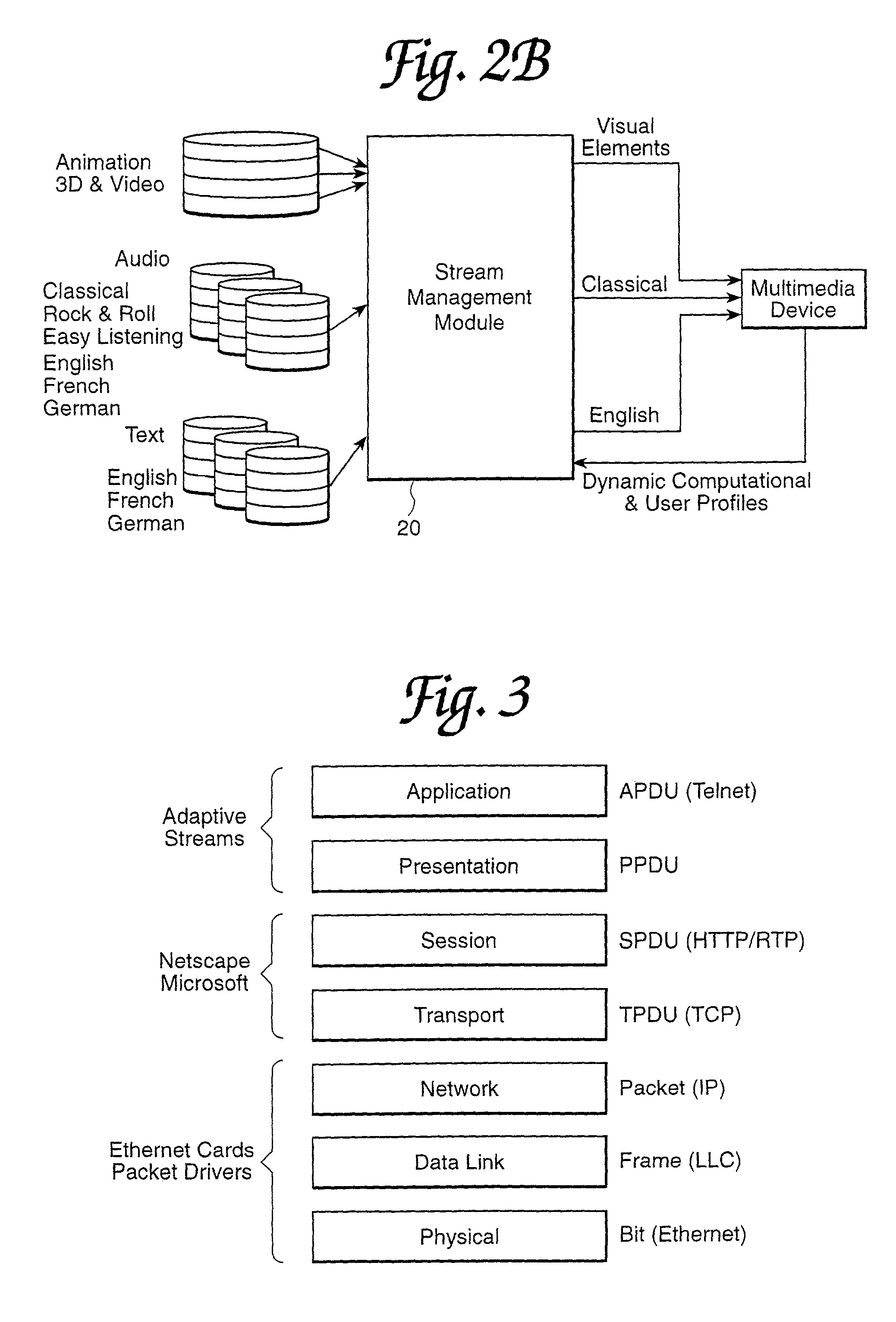
Method and apparatus for storing base and additive streams of video
ActiveUS7733956B1Exact reproductionQuality improvementGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital dataImage resolution
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for encoding, storing, transmitting and decoding multimedia information in the form of scalable, streamed digital data. A base stream containing basic informational content and subsequent streams containing additive informational content are initially created from standard digital multimedia data by a transcoder. Client computers, each of which may have different configurations and capabilities are capable of accessing a stream server that contains the scalable streamed digital data. Each different client computer, therefore, may access different stream combinations according to a profile associated with each different client computer. Thus, the streams accessed from the server are tailored to match the profile of each client computer so that the best combination of streams can be provided to maximize the resolution of the 3D, audio and video components.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Variable pitch electrode array
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
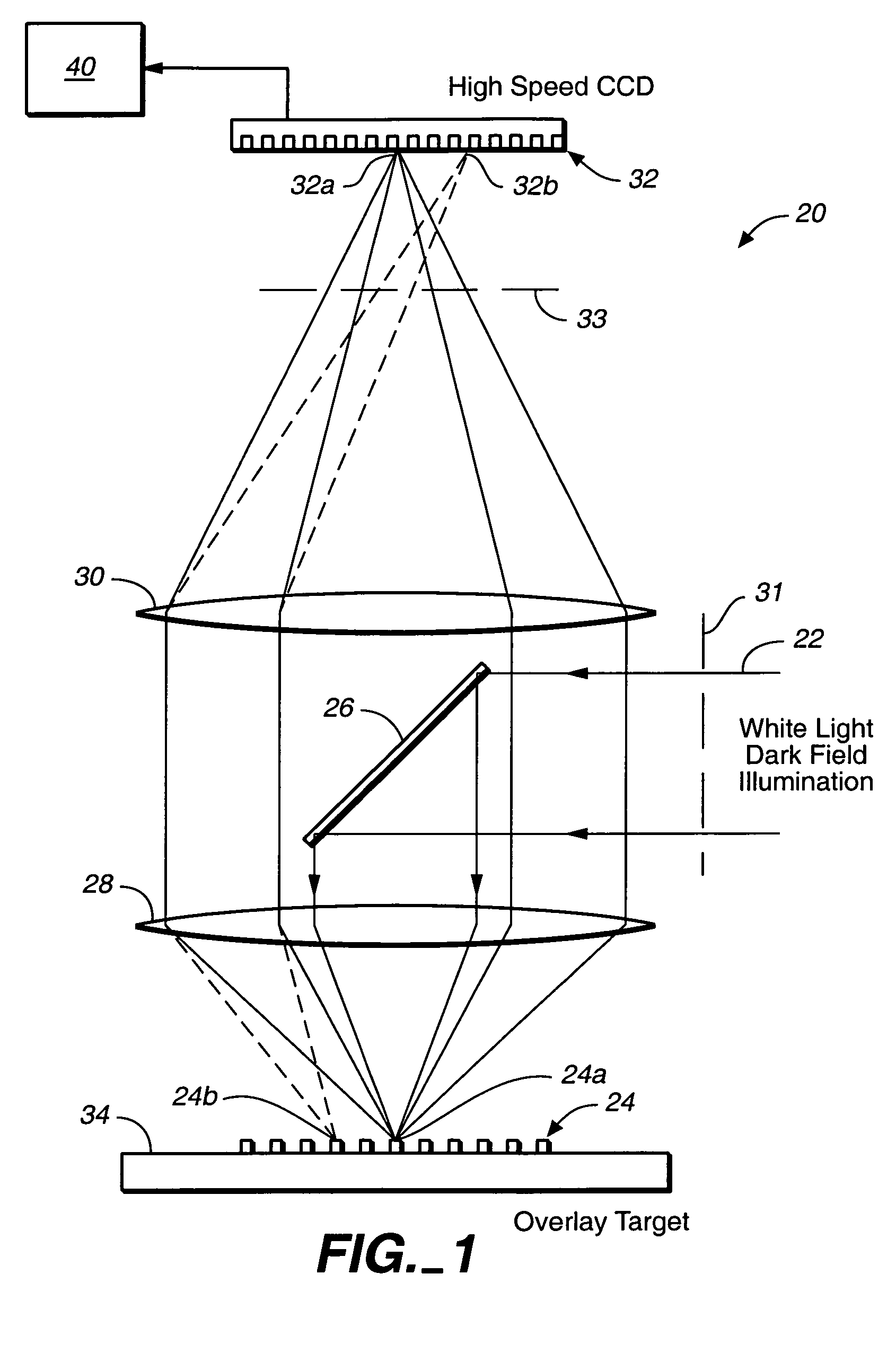
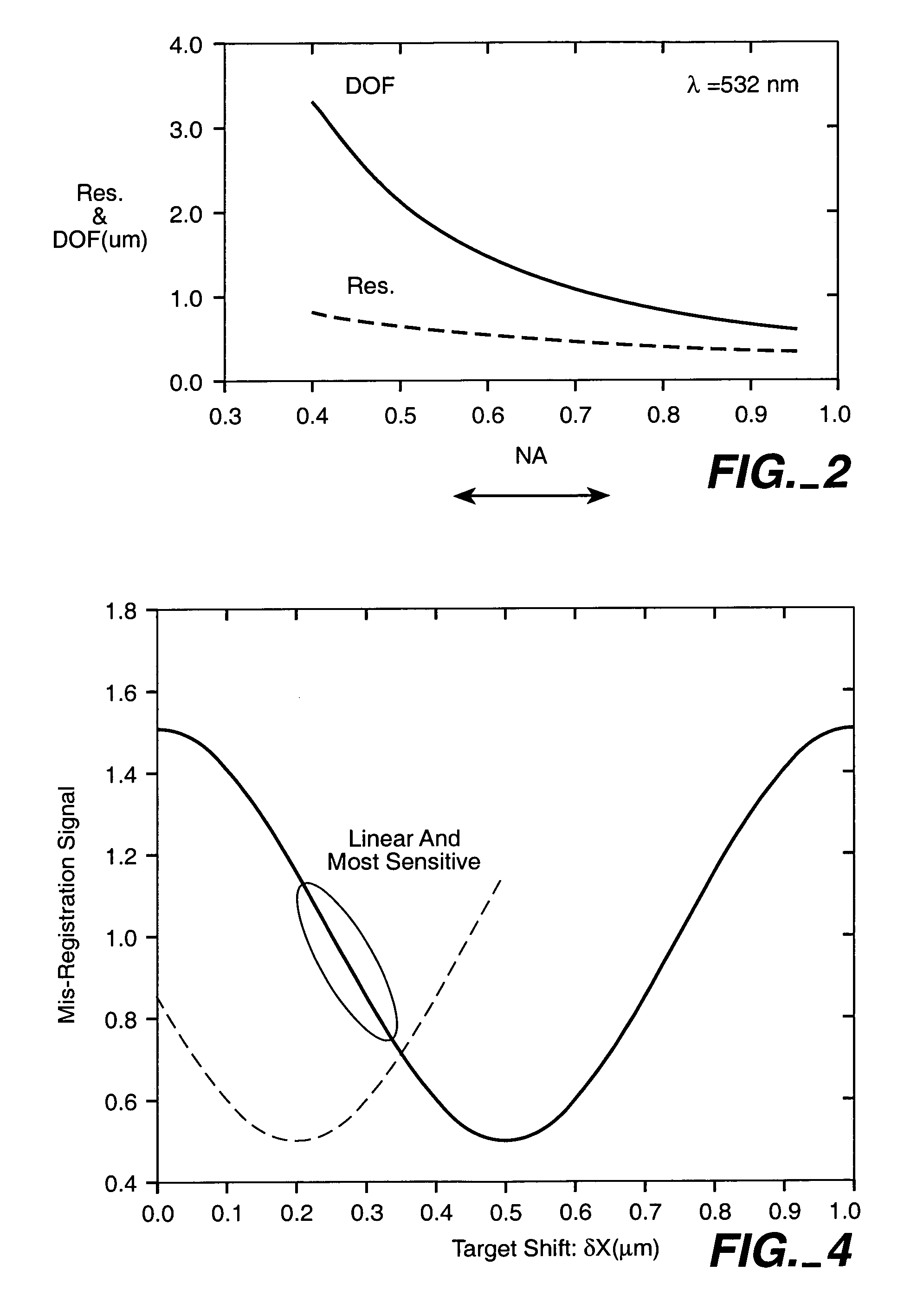
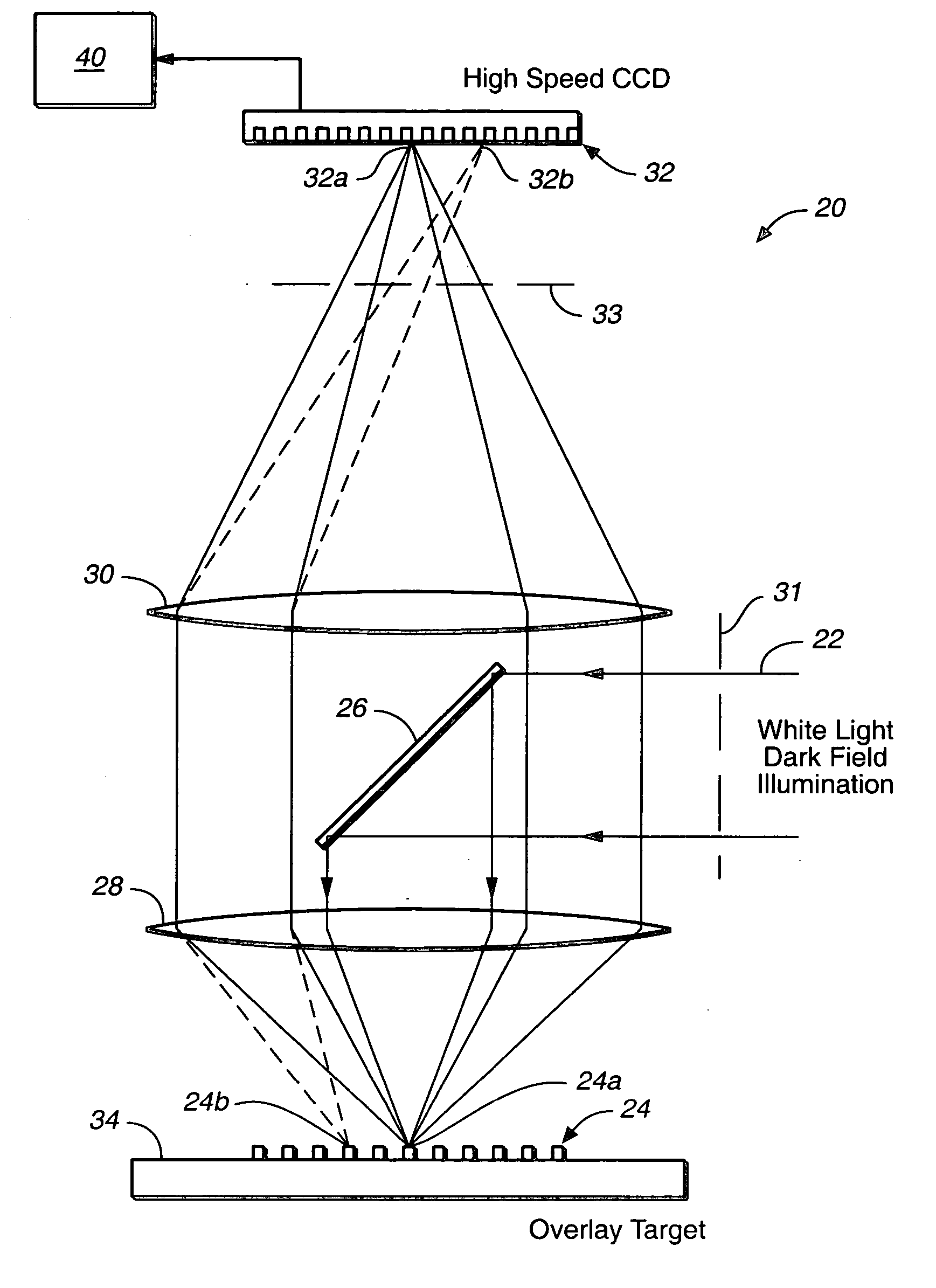
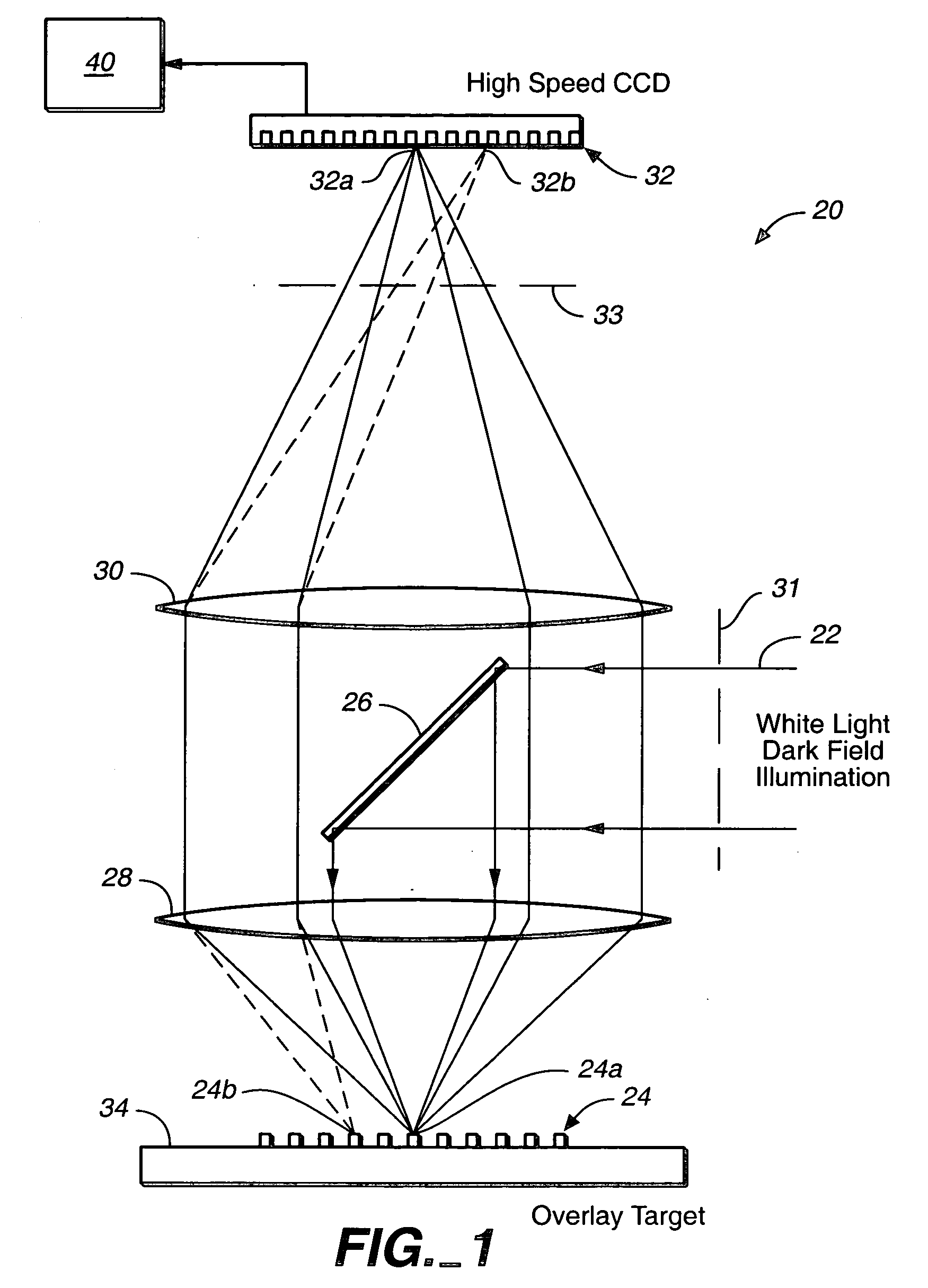
Overlay error detection
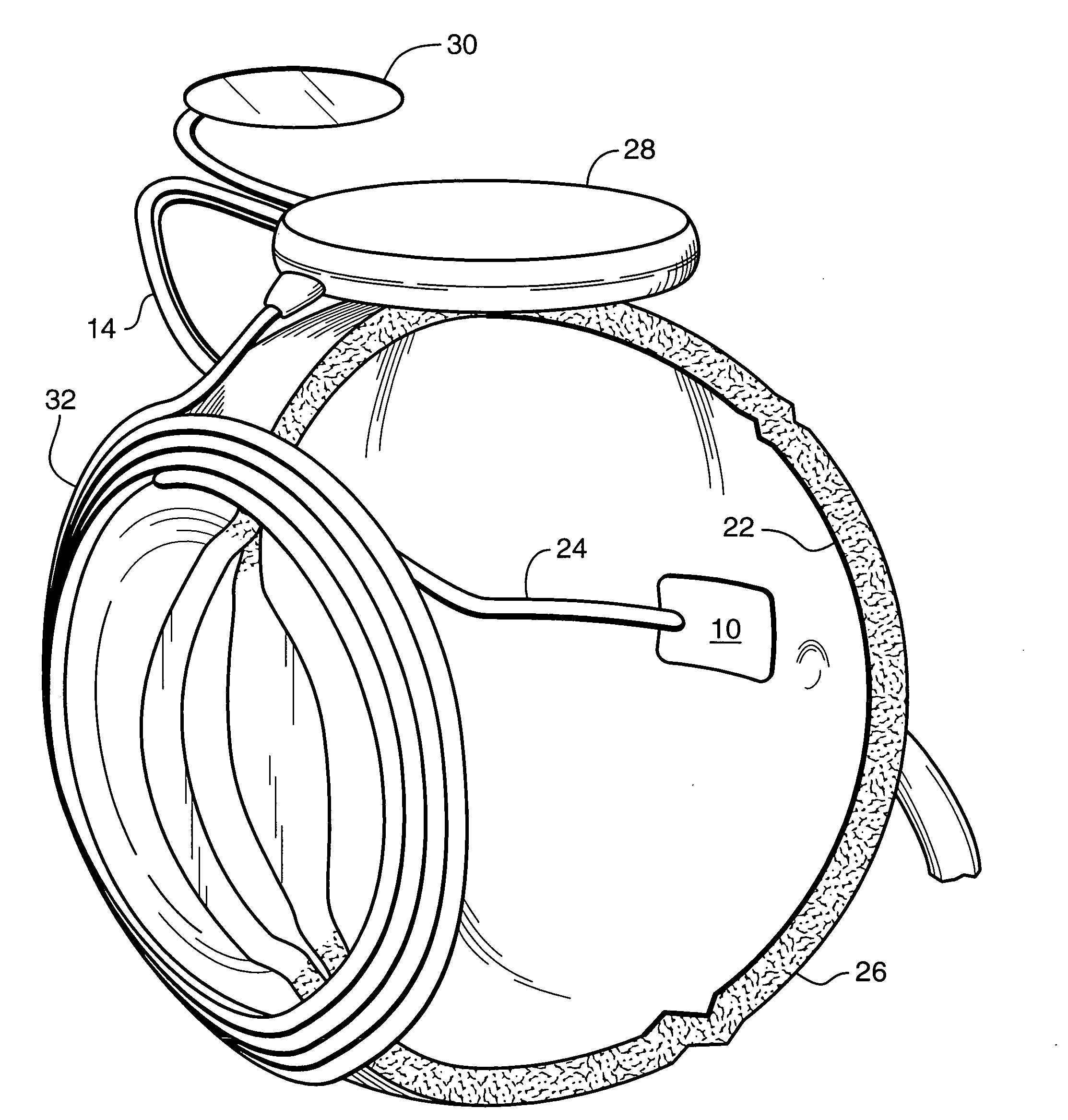
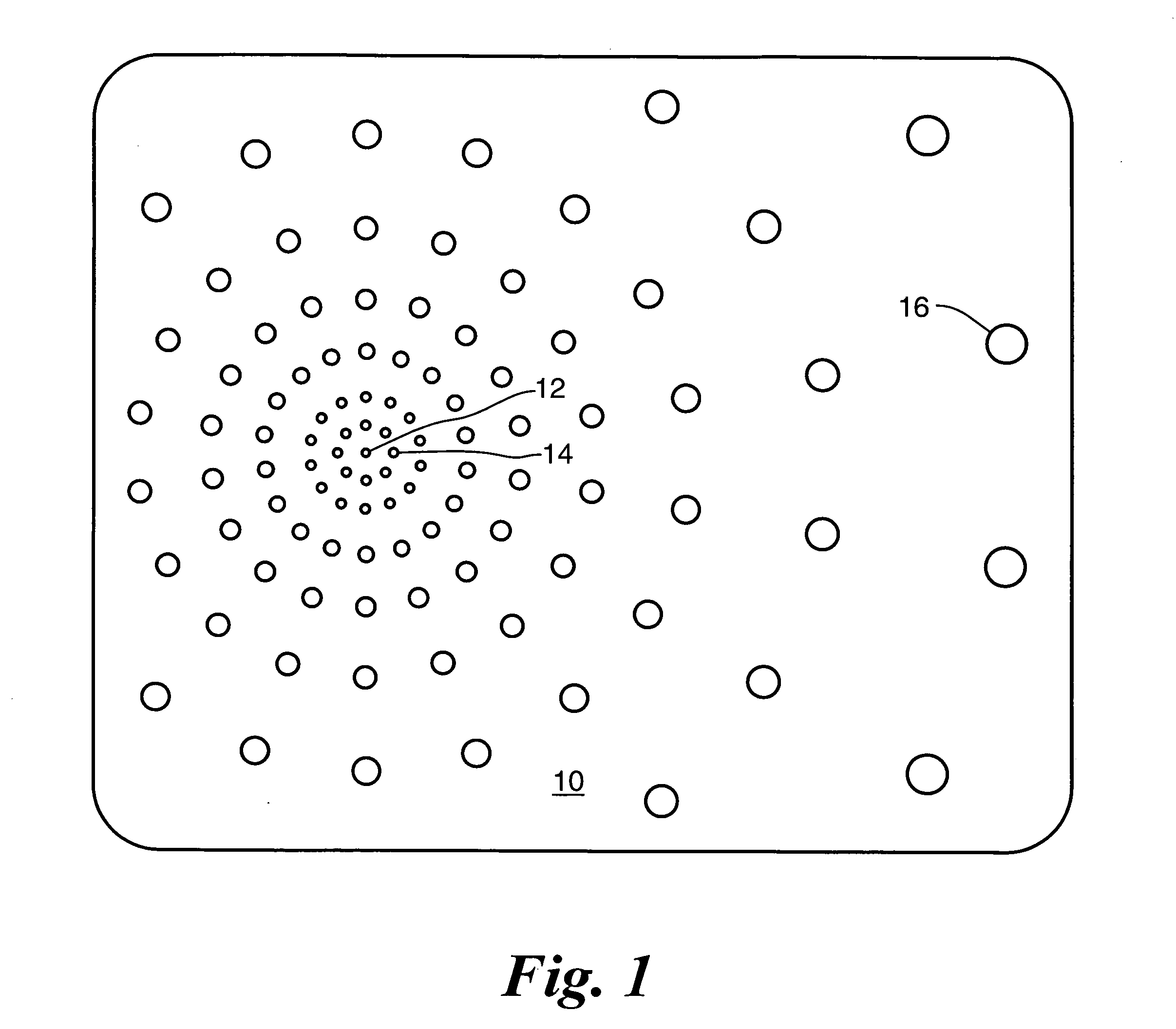
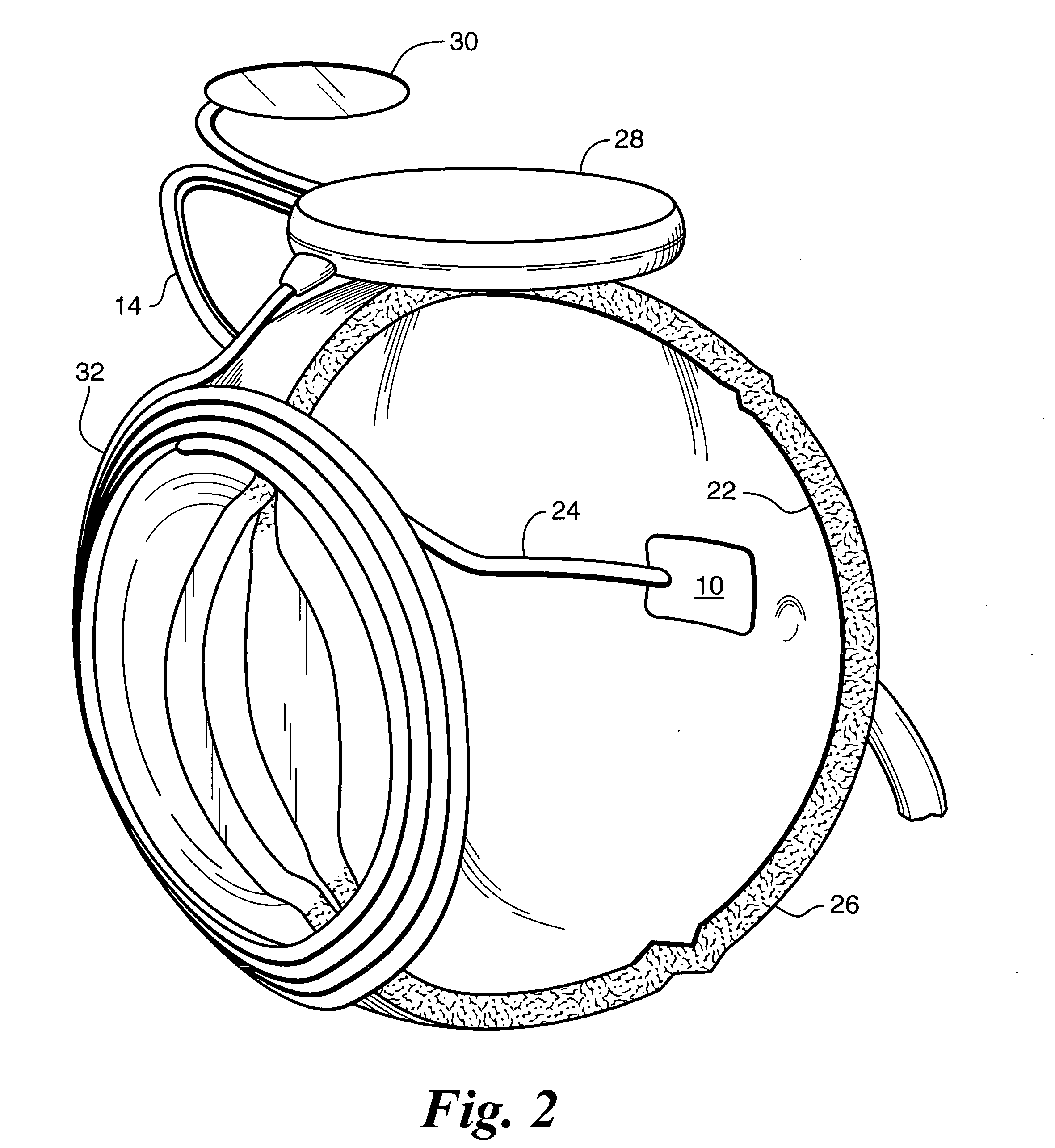
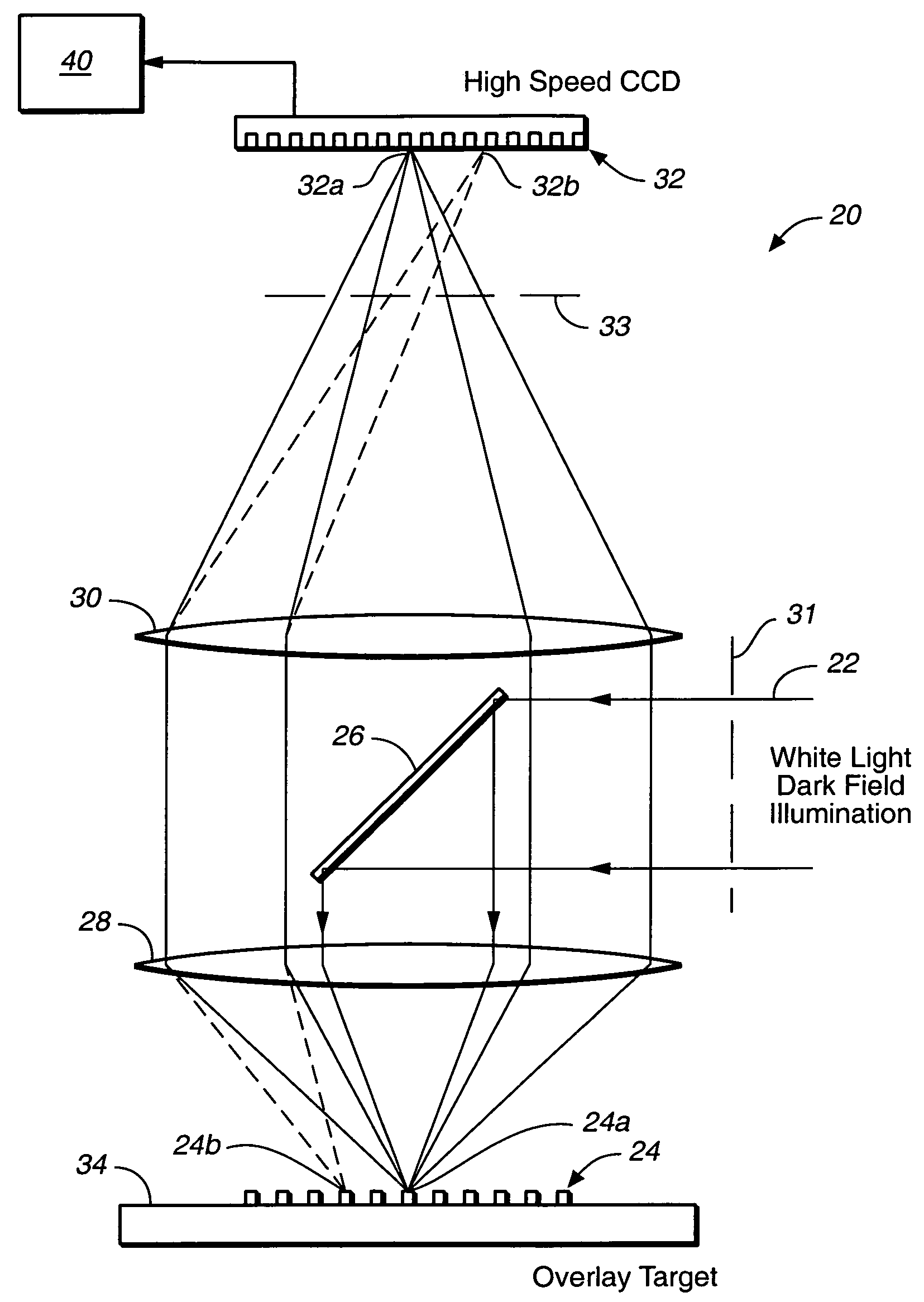
InactiveUS7009704B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce contrastPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingData pointSpecular reflection
An overlay target with gratings thereon is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors. A phase difference is then detected between the outputs of the detectors to find the mis-alignment error. In another aspect, an overlay target with gratings or box-in-box structures is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors located away from the specular reflection direction of the illumination in a dark field detection scheme. Medium numerical aperture optics may be employed for collecting the radiation from the overlay target in a bright or dark field configuration so that the system has a larger depth of focus and so that the two structures of the target at different elevations can be measured accurately at the same time. Analytical functions are constructed for the grating type targets. By finding the phase difference between the two gratings at different elevations, misalignment errors can be detected. Analytical functions are constructed as a model for box-in-box type targets where data points away from the edges of the box or bars can be used in the curve fitting. Symmetrical functions are employed to further reduce noise.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
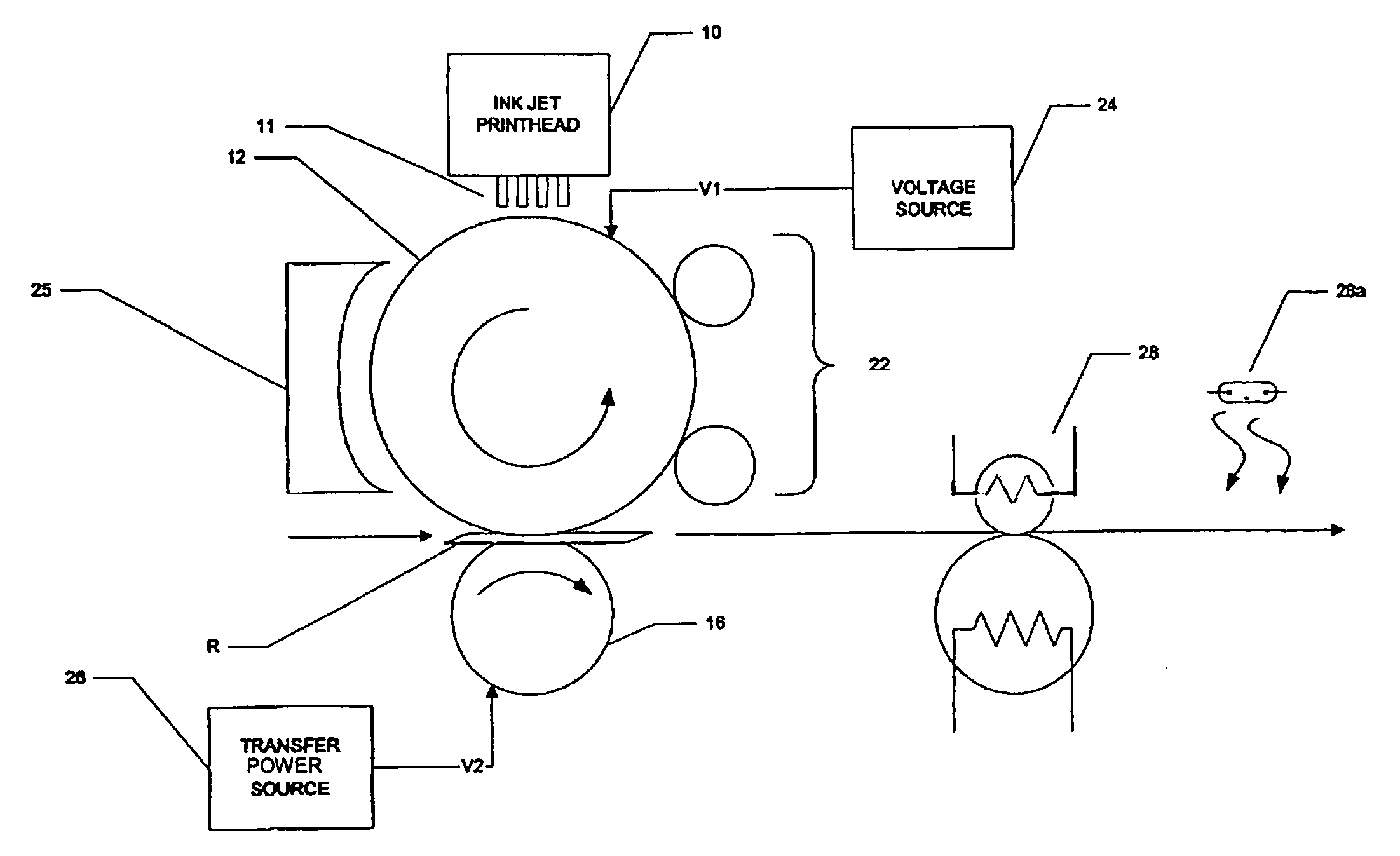
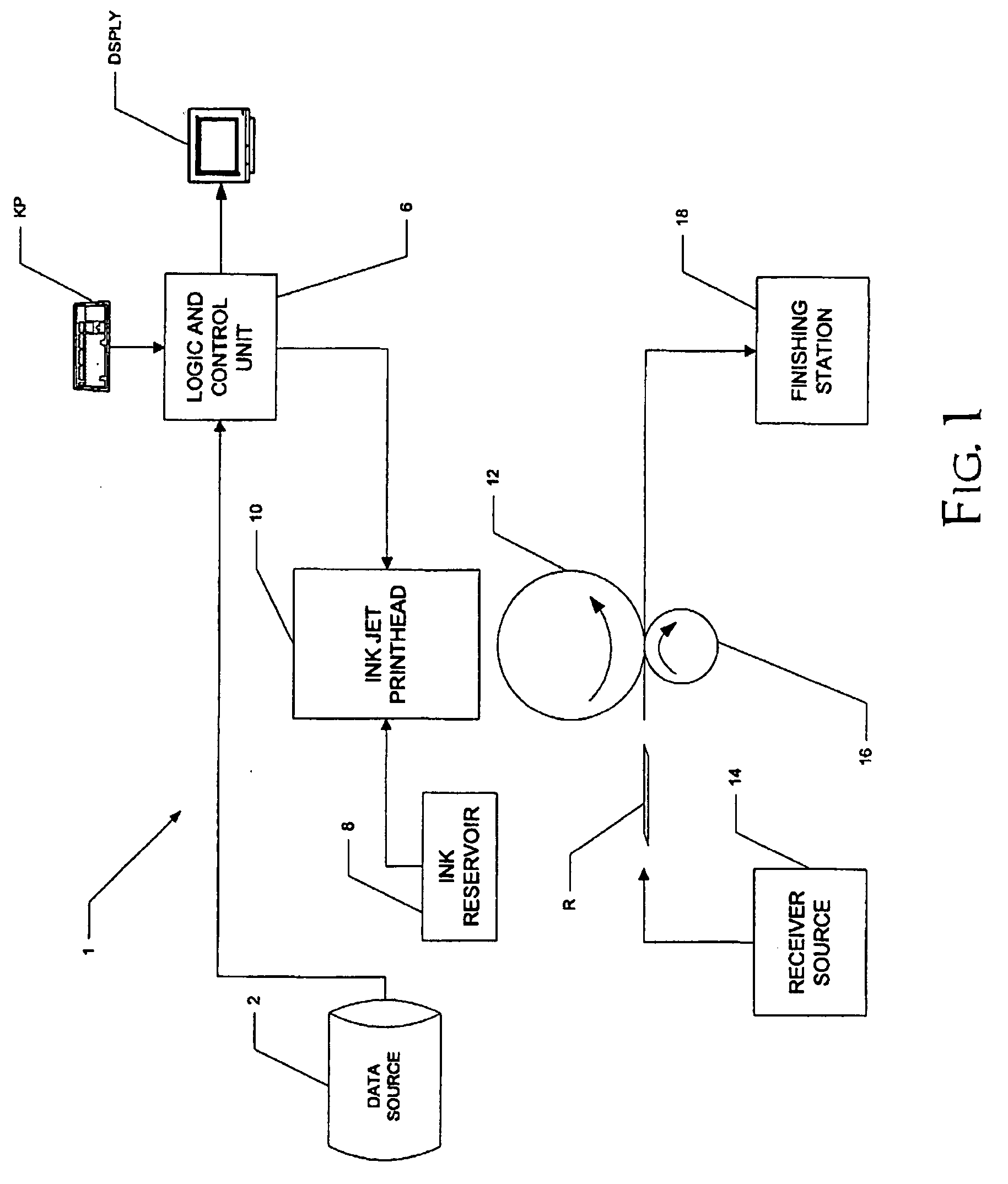
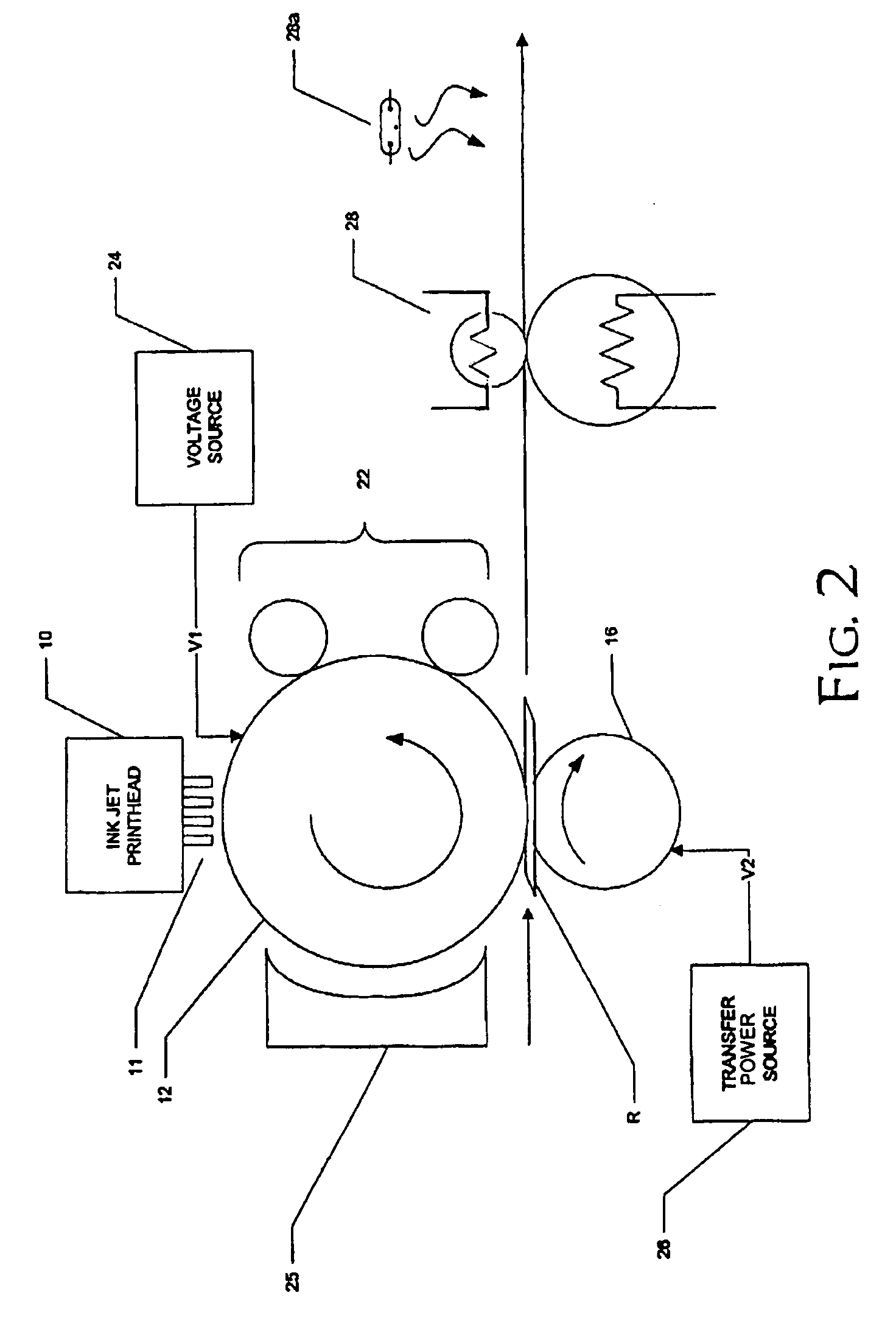
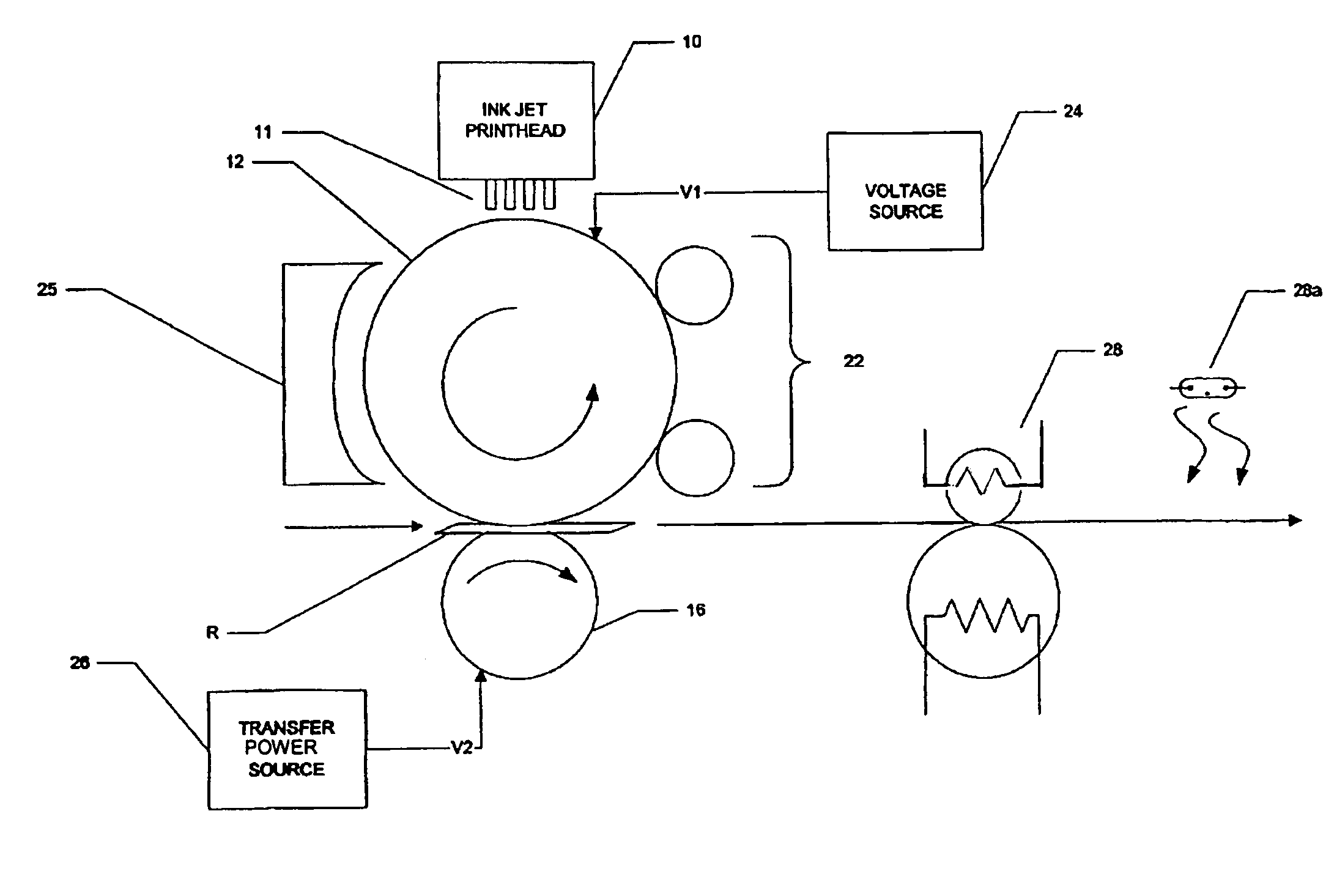
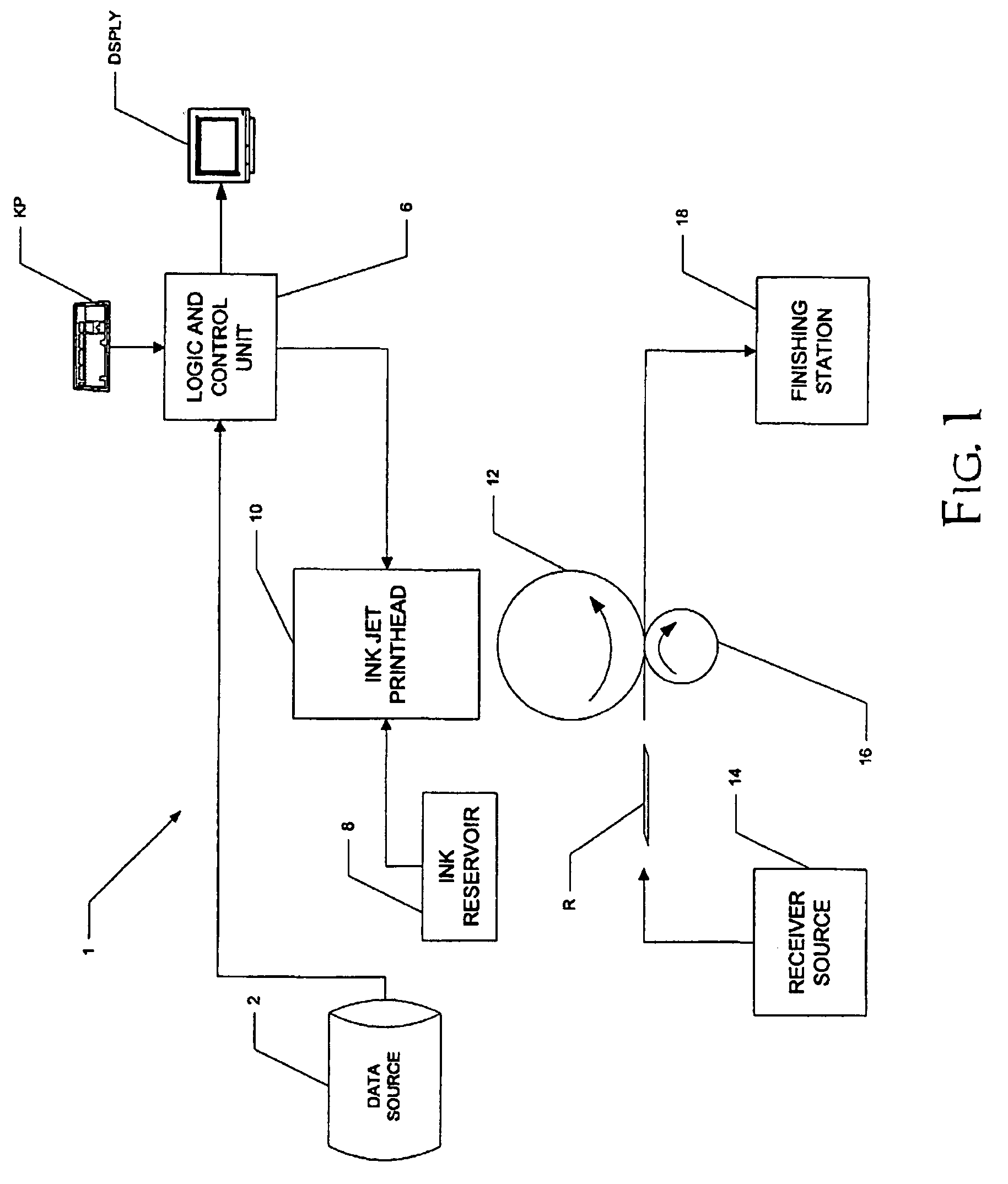
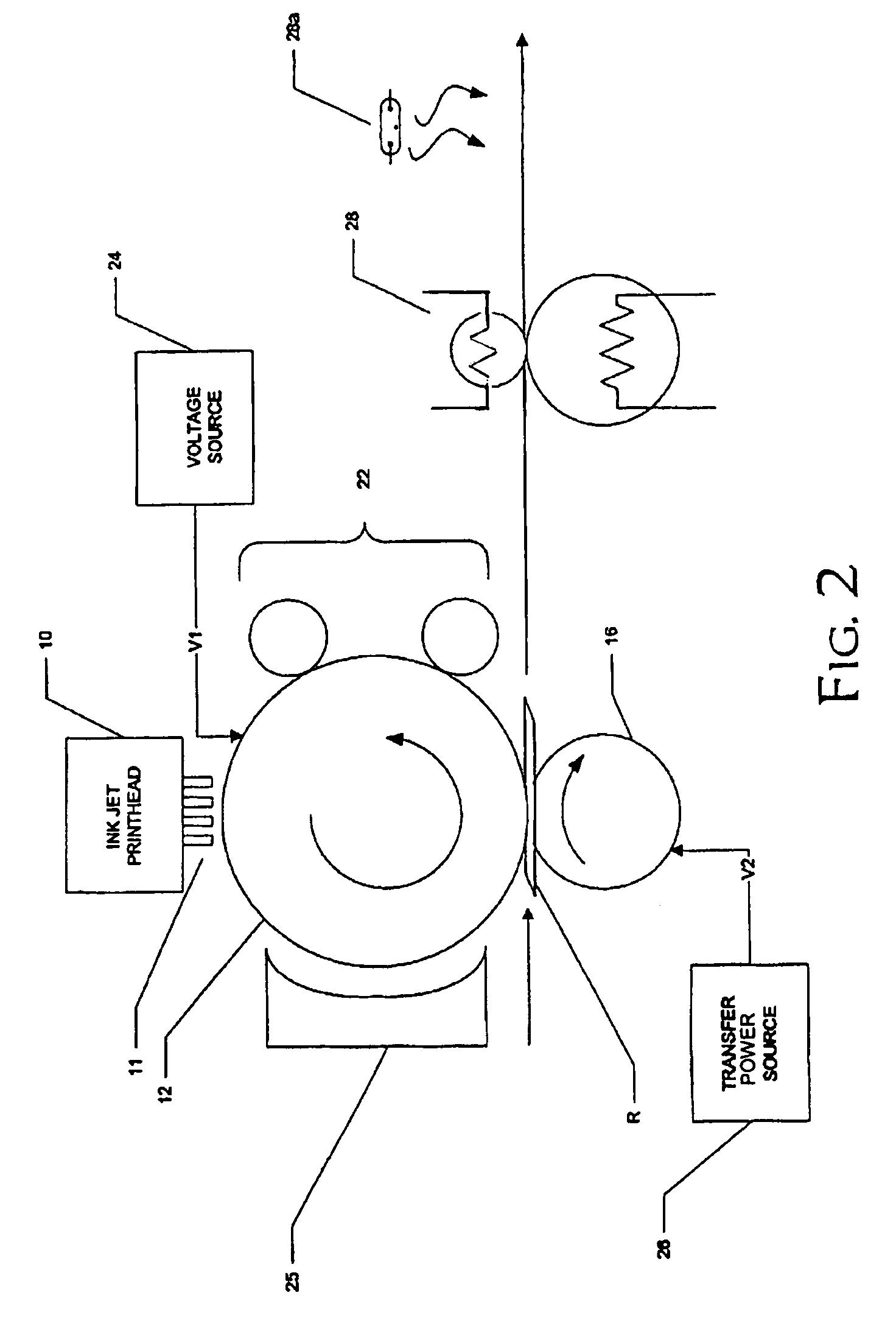
Phase-change ink jet printing with electrostatic transfer
A printing machine, comprising an intermediate medium; an ink jet printhead, for dispensing phase-change ink droplets at selected locations of a surface of the intermediate medium, the selected locations corresponding to an image to be printed; a receiver source, for providing a receiver; and a transfer station, for electrostatically transferring the dispensed phase-change ink droplets to the receiver.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
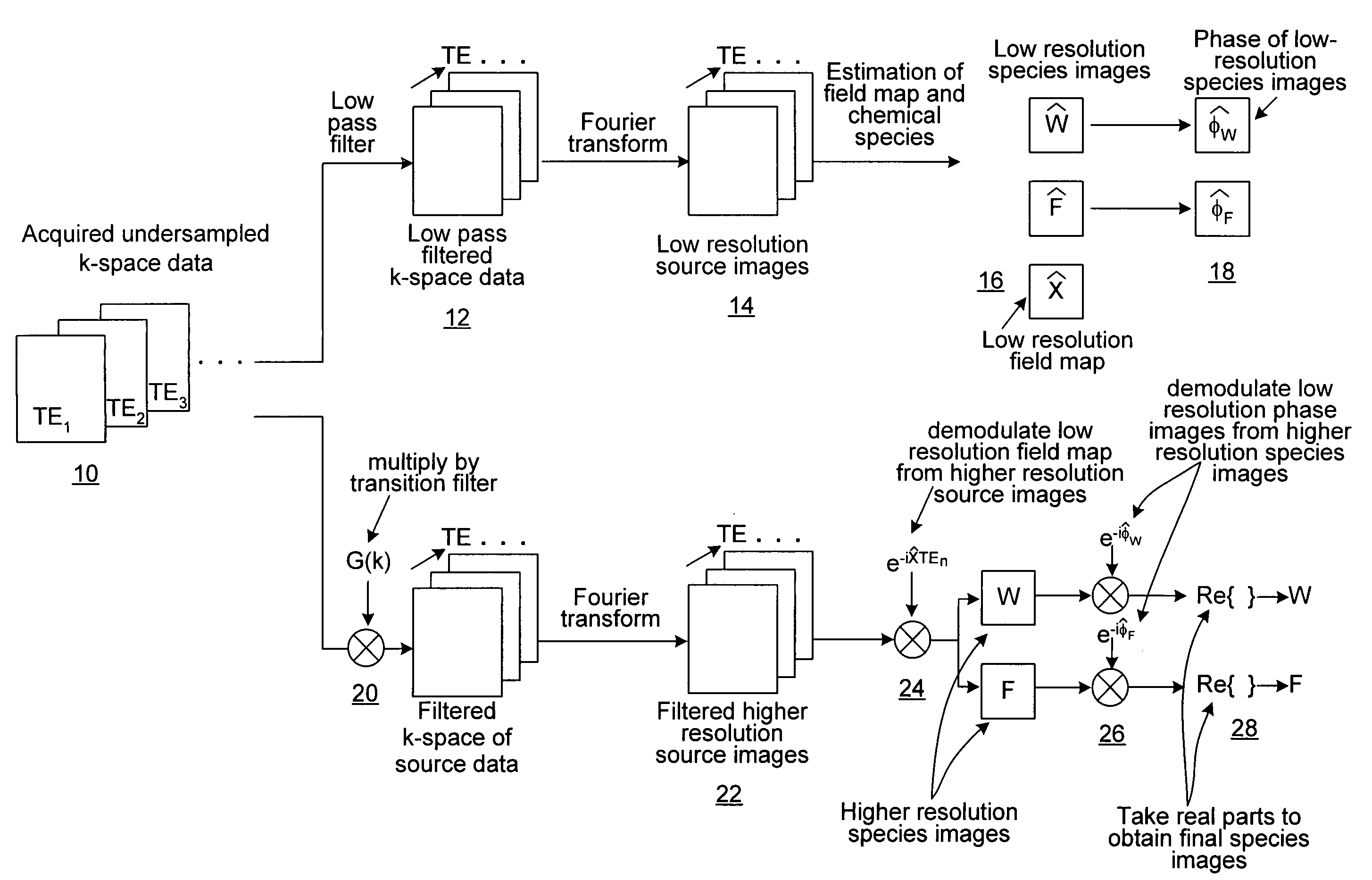
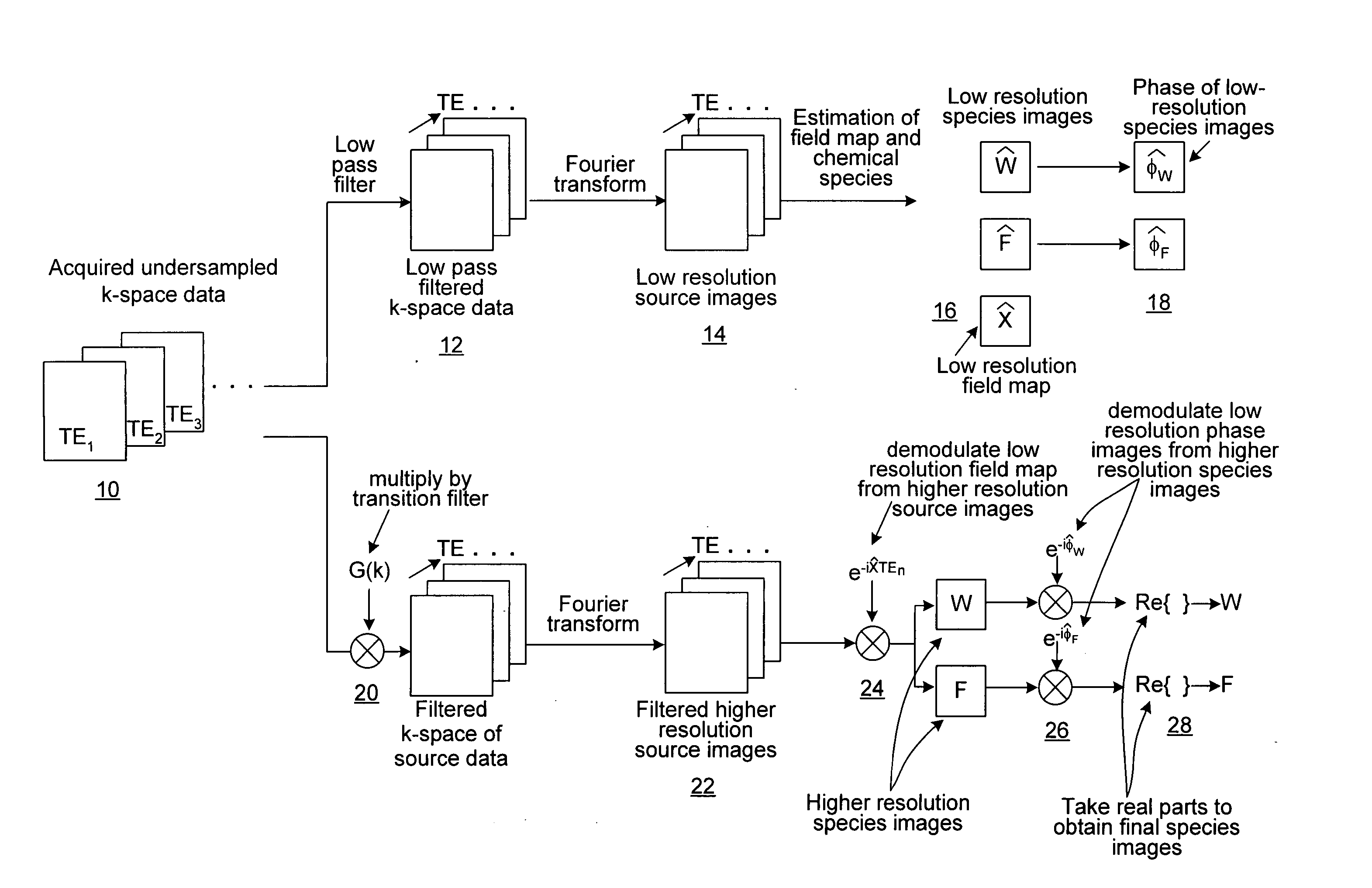
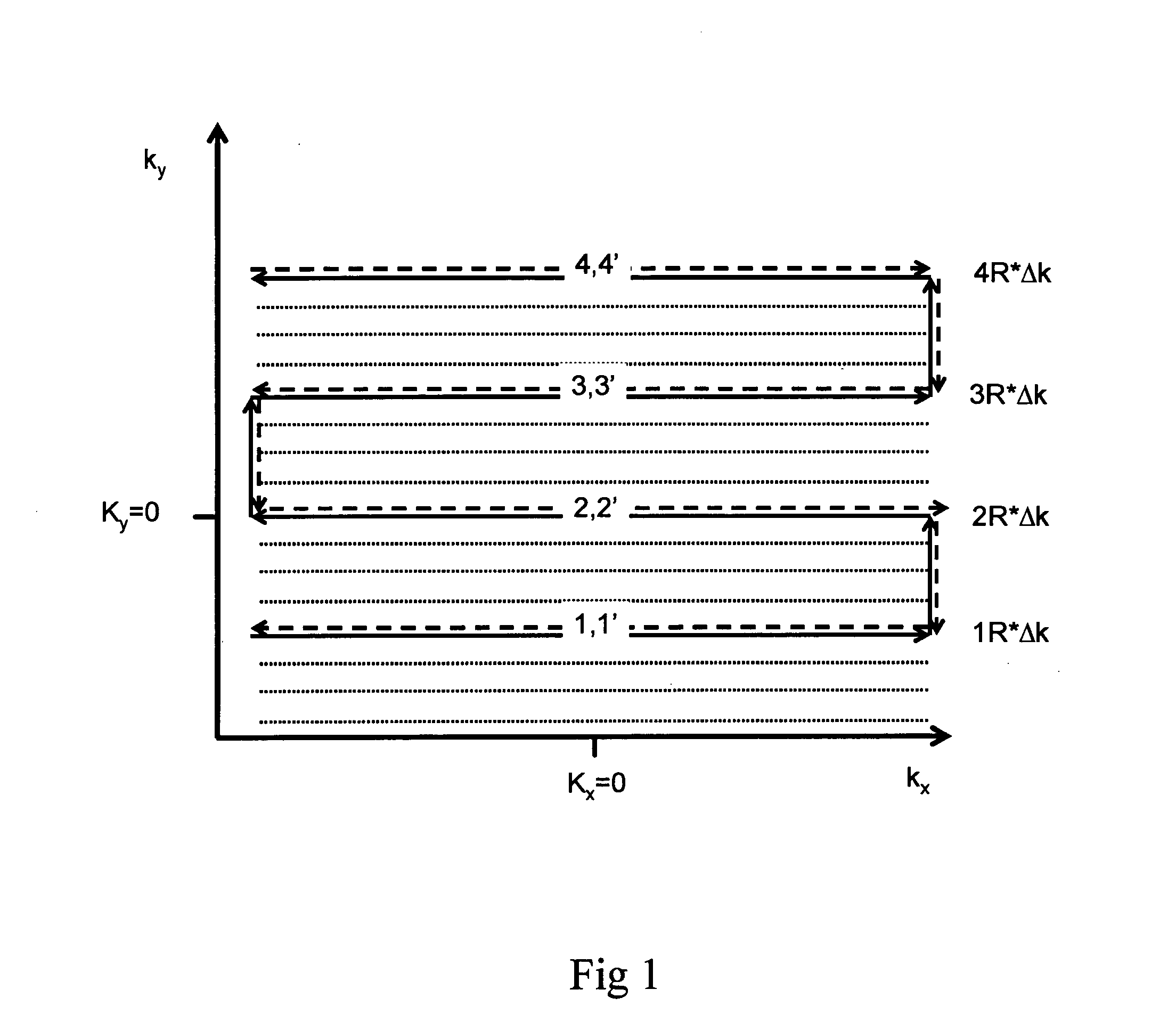
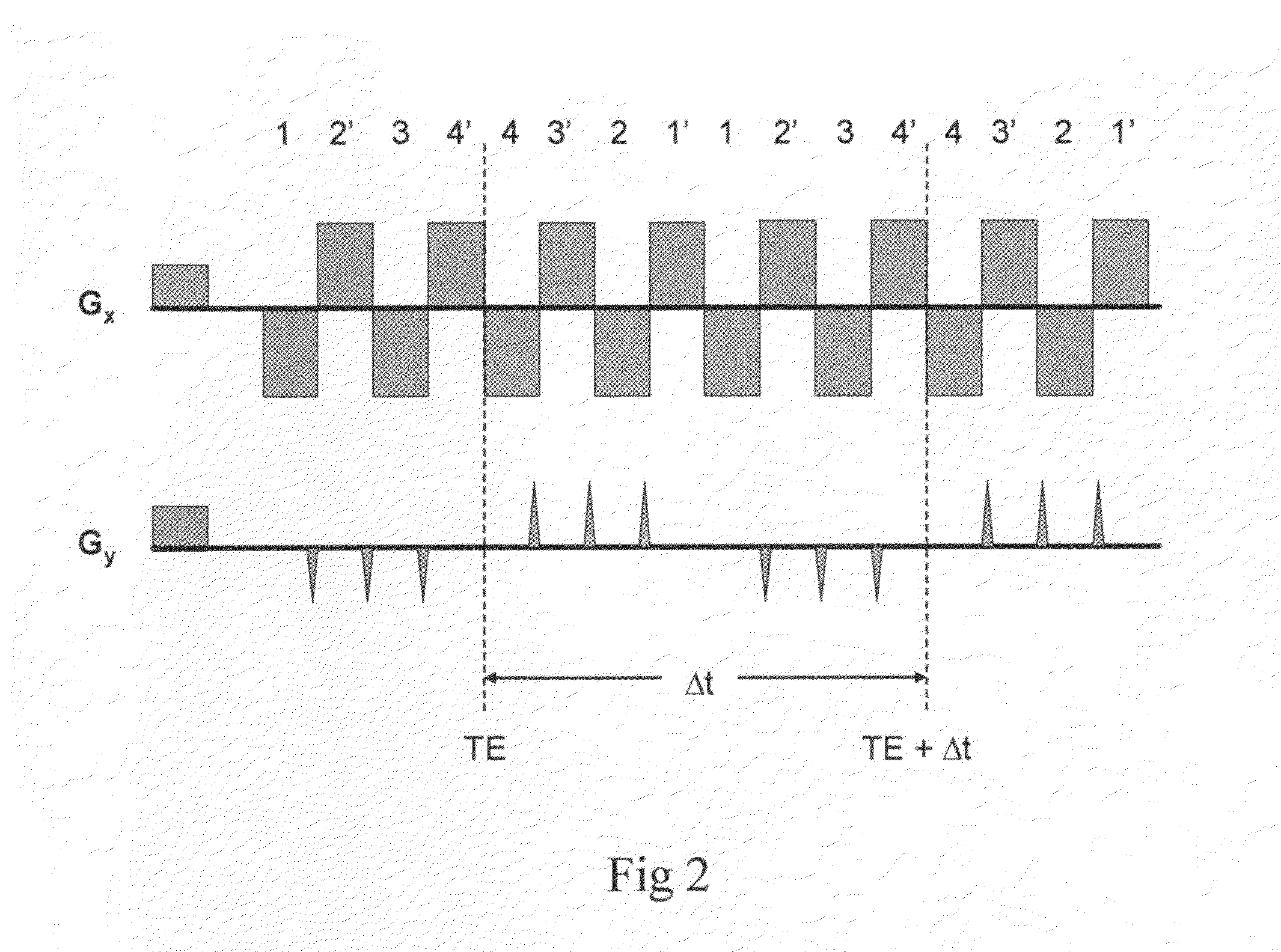
Homodyne reconstruction of water and fat images based on iterative decomposition of MRI signals
ActiveUS7298144B2Maximize resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionDecomposition
Homodyne image reconstruction is combined with an iterative decomposition of water and fat from MR signals obtained from a partial k-space signal acquisition in order to maximize the resolution of calculated water and fat images. The method includes asymmetrical acquisition of under-sampled MRI data, obtaining low resolution images, and then estimating a magnetic field map and phase maps of water and fat image signals from the low resolution images. The acquired data is again filtered and Fourier transformed to obtain an estimate of combined fat and water signals using the estimated magnetic field map and phase maps. Water and fat images are then estimated from which phases of the water and fat images are determined. The real parts of the water and fat images are then used in calculating water and fat images using a homodyne process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Homodyne reconstruction of water and fat images based on iterative decomposition of MRI signals
ActiveUS20060250132A1Maximize resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionDecomposition
Homodyne image reconstruction is combined with an iterative decomposition of water and fat from MR signals obtained from a partial k-space signal acquisition in order to maximize the resolution of calculated water and fat images. The method includes asymmetrical acquisition of under-sampled MRI data, obtaining low resolution images, and then estimating a magnetic field map and phase maps of water and fat image signals from the low resolution images. The acquired data is again filtered and Fourier transformed to obtain an estimate of combined fat and water signals using the estimated magnetic field map and phase maps. Water and fat images are then estimated from which phases of the water and fat images are determined. The real parts of the water and fat images are then used in calculating water and fat images using a homodyne process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
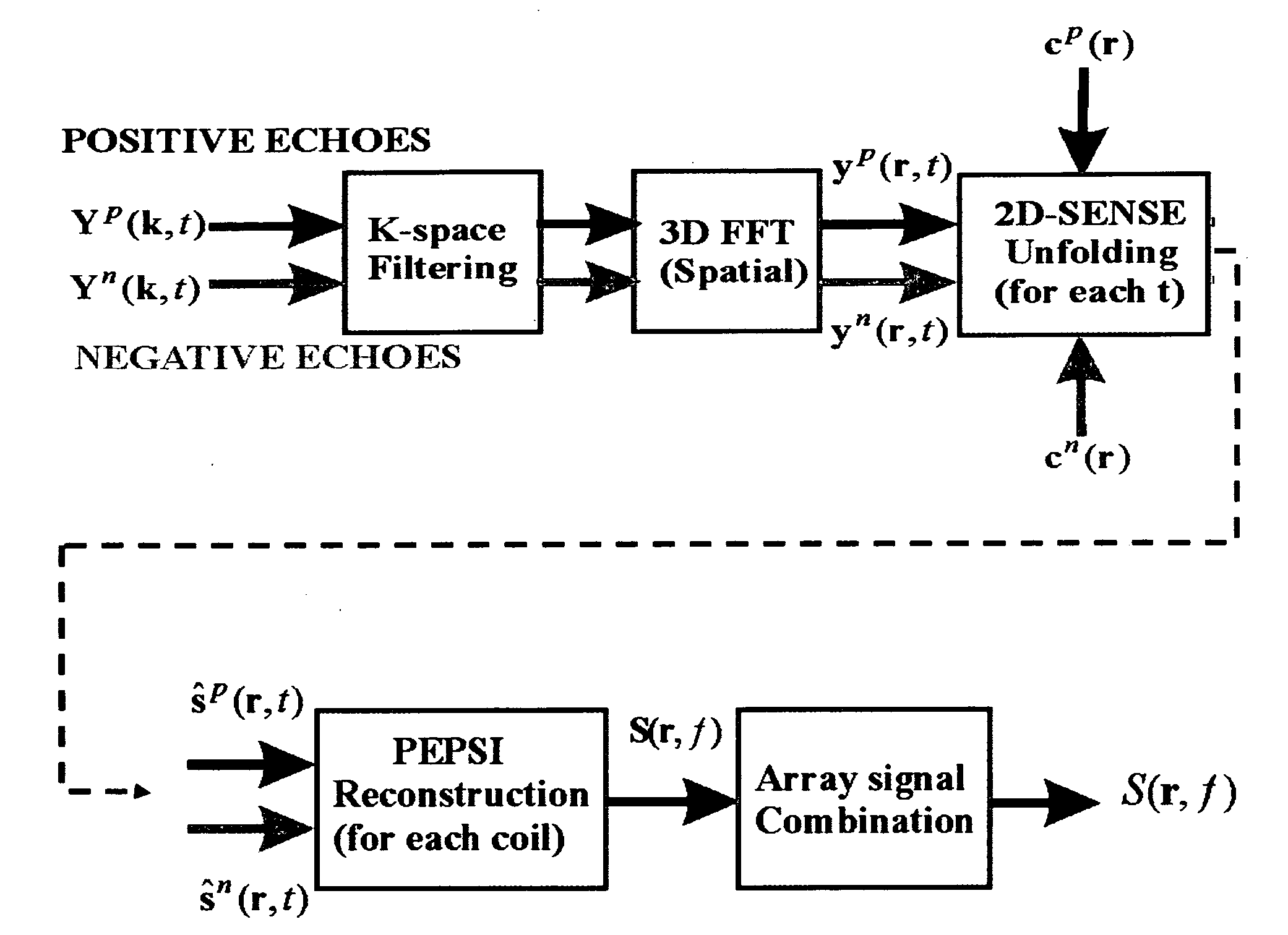
Single-shot magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging with partial parallel imaging
InactiveUS20090091322A1Large spectral width and spatial resolutionMaximize resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePhysicsParallel imaging
The present invention has a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method that allows collecting a complete spectroscopic image with one spectral dimension and up to three spatial dimensions in a single signal excitation. The method employs echo-planar spatial-spectral encoding combined with phase encoding interleaved into the echo-planar readout train and partial parallel imaging to reconstruct spatially localized absorption mode spectra. This approach enables flexible tradeoff between gradient and RF encoding to maximize spectral width and spatial resolution. Partial parallel imaging (e.g. SENSE or GRAPPA) is employed with this methodology to accelerate the phase encoding dimension. A preferred implementation is with the recently developed superresolution parallel MRI method, which accelerates along both the readout and phase encoding dimensions and thus enables particularly large spectral width and spatial resolution. The symmetrical k-space trajectory of this methodology is designed to compensate phase errors due to convolution of spatial and spectral encoding. This method is suitable for hyperpolarized MRSI, spatial mapping of the diffusion coefficients of biochemicals and functional MRI using quantitative mapping of water relaxation.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Overlay error detection
InactiveUS20060098199A1Accurate measurementLarge depth of fieldPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingPhase difference
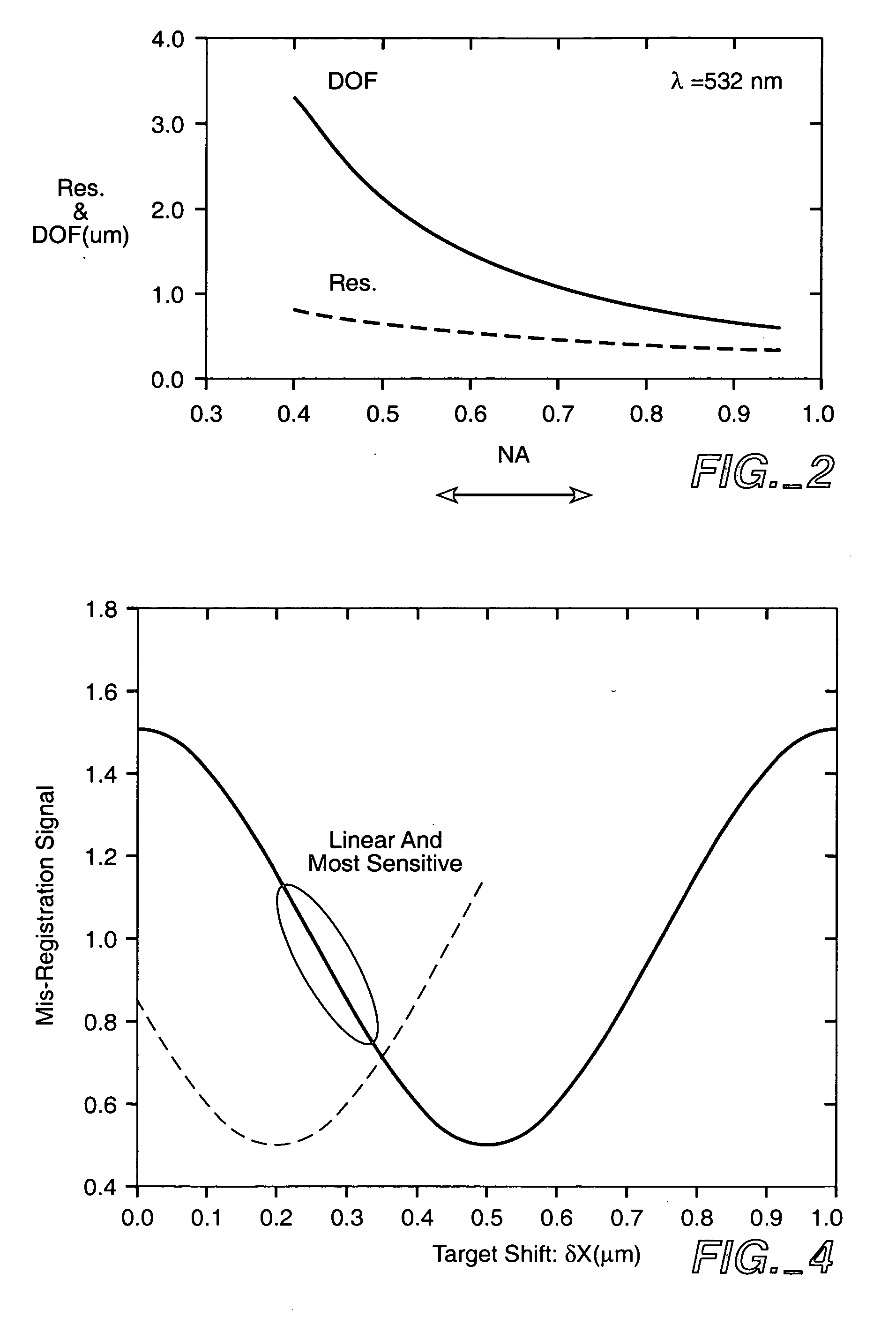
An overlay target with gratings thereon is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors. A phase difference is then detected between the outputs of the detectors to find the mis-alignment error. In another aspect, an overlay target with gratings or box-in-box structures is illuminated and radiation scattered by the target is imaged onto detectors located away from the specular reflection direction of the illumination in a dark field detection scheme. Medium numerical aperture optics may be employed for collecting the radiation from the overlay target in a bright or dark field configuration so that the system has a larger depth of focus and so that the two structures of the target at different elevations can be measured accurately at the same time. Analytical functions are constructed for the grating type targets. By finding the phase difference between the two gratings at different elevations, misalignment errors can be detected. Analytical functions are constructed as a model for box-in-box type targets where data points away from the edges of the box or bars can be used in the curve fitting. Symmetrical functions are employed to further reduce noise.
Owner:KLA CORP
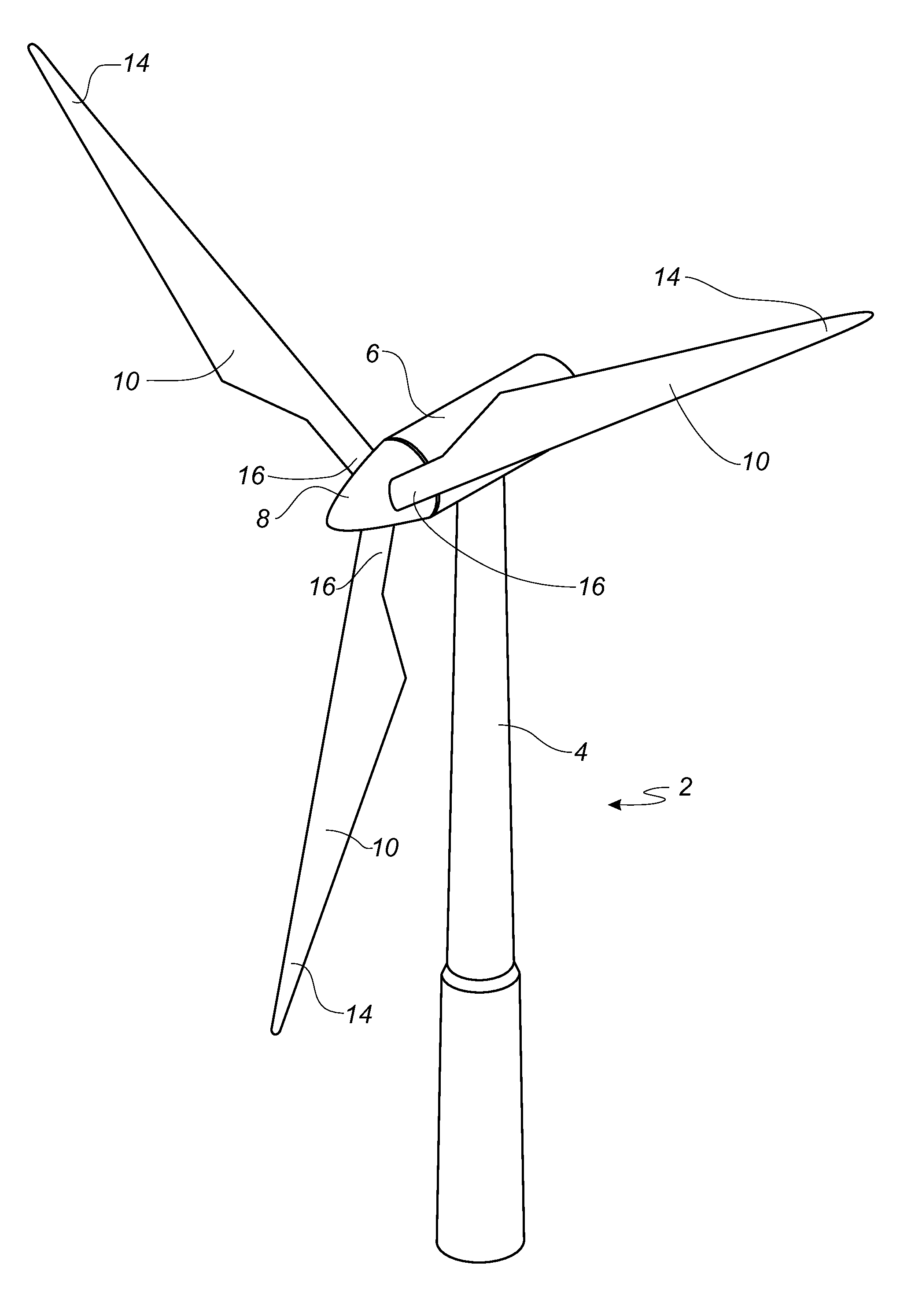
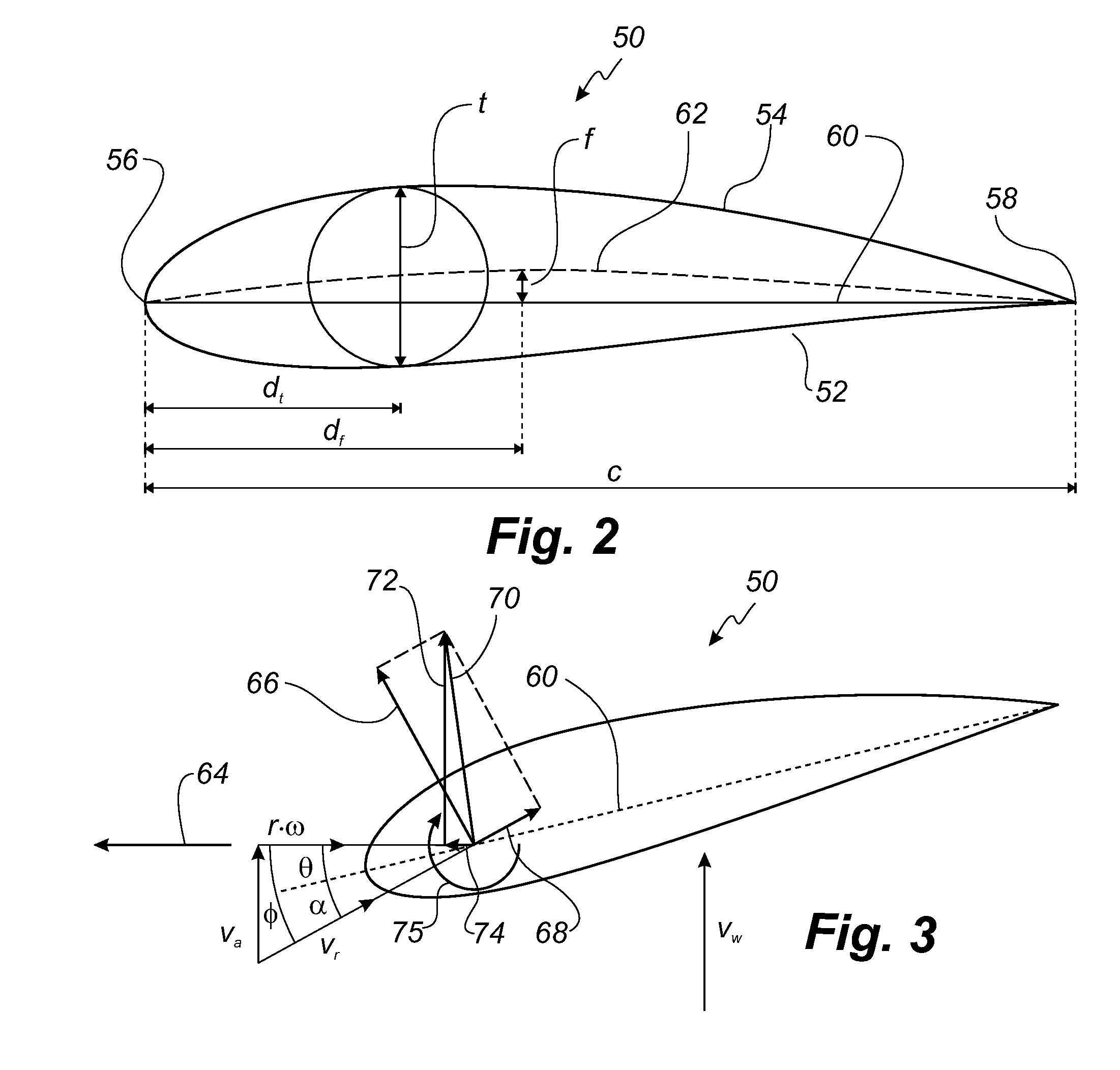
Wind turbine blade provided with optical wind velocity measurement system
ActiveUS20120229792A1Easy to adaptFacilitates optical measurementWind motor controlEngine fuctionsTurbine bladeOptical measurements
A wind turbine includes a number of blades and an optical measurement system comprising a light source, such as a laser, an optical transmitter part, an optical receiver part, and a signal processor. The light source is optically coupled to the optical transmitter part, which includes an emission point for emitting light in a probing direction. The optical receiver part comprises a receiving point and a detector. The optical receiver part is adapted for receiving a reflected part of light from a probing region along the probing direction and directing the reflected part of light to the detector to generate a signal used to determine a first velocity component of the inflow. The emission point is located in a first blade at a first radial distance from a center axis, and the receiving point is located in the first blade at a second radial distance from the center axis.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Optical resonance scanner
ActiveUS20160178894A1Improve prevention efficiencyMinimize occurrenceOptical elementsSuperimpositionEngineering
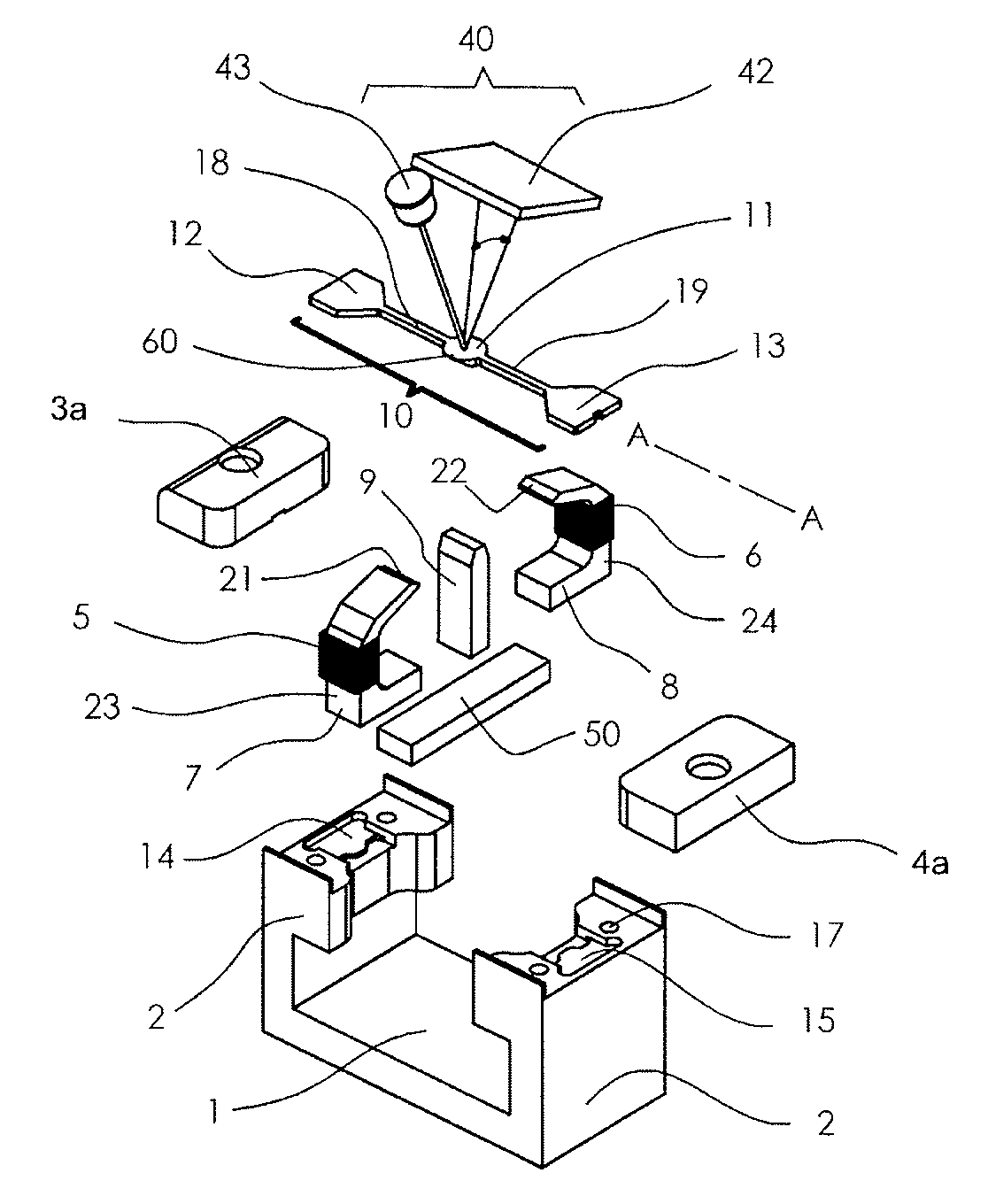
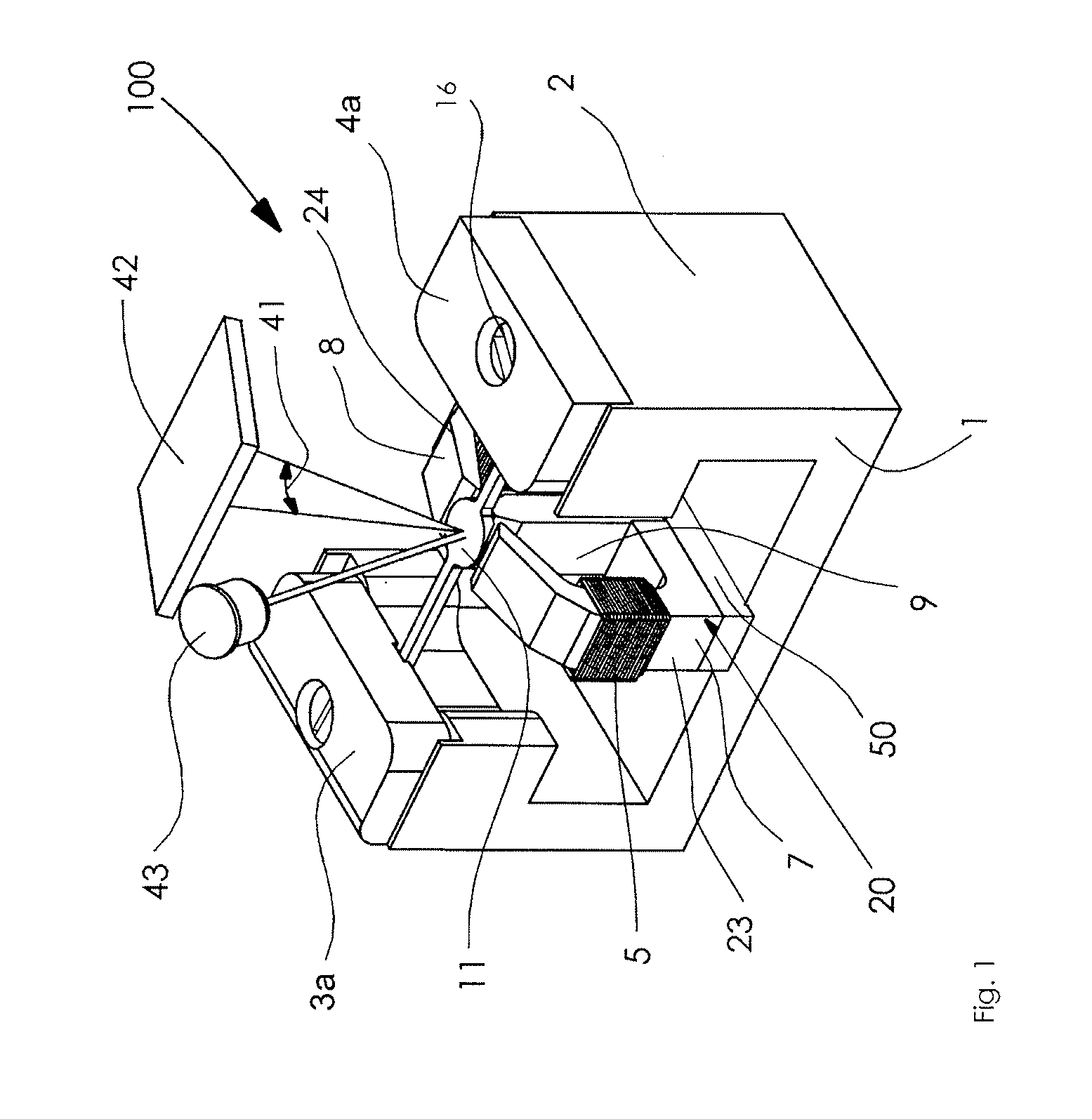
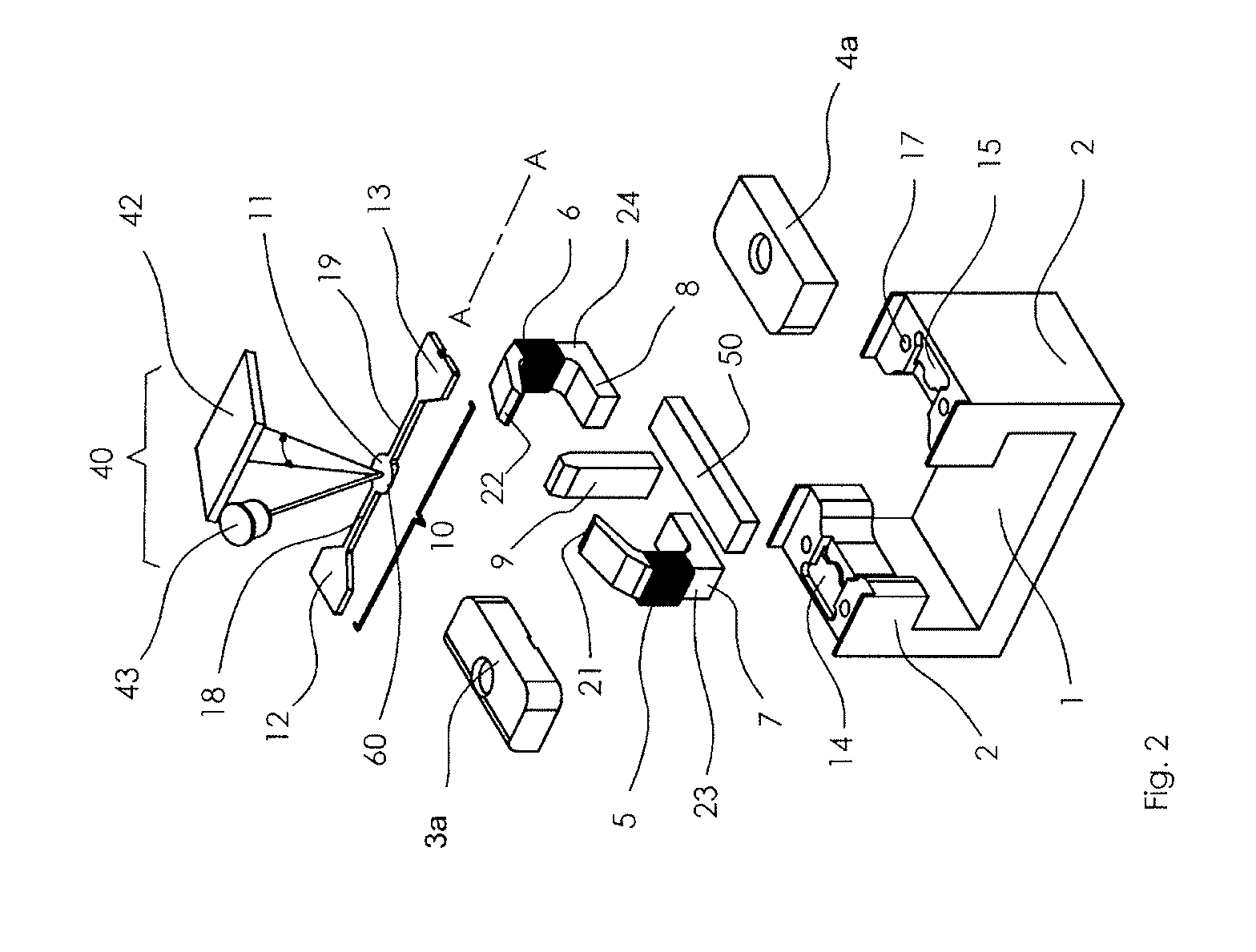
An optical resonance scanner has a spring-elastic bending element (10) excitable to effect rotational oscillations about a longitudinal axis (A-A) using a stationary magnet (9) and a stationary drive coil (5) that is wound around a pole shoe (20). The pole shoe (20) is magnetically coupled to the magnet (9) and has two mutually opposite free ends (21, 22) between which the bending element (10) is arranged symmetrically so that a magnetic flux can be transferred substantially perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis (A-A). In superimposition of the magnet- and coil-induced magnetic fluxes the magnet (9) and a first half (23) of the pole shoe (20) form a first magnetic circuit (30), and the magnet (9) and a second half (24) of the pole shoe (20) form a second magnetic circuit (31), which run in opposite senses with respect to one another in a plane perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis (A-A) through a magnetizable section (6) of the bending element (10).
Owner:FEMOTECH
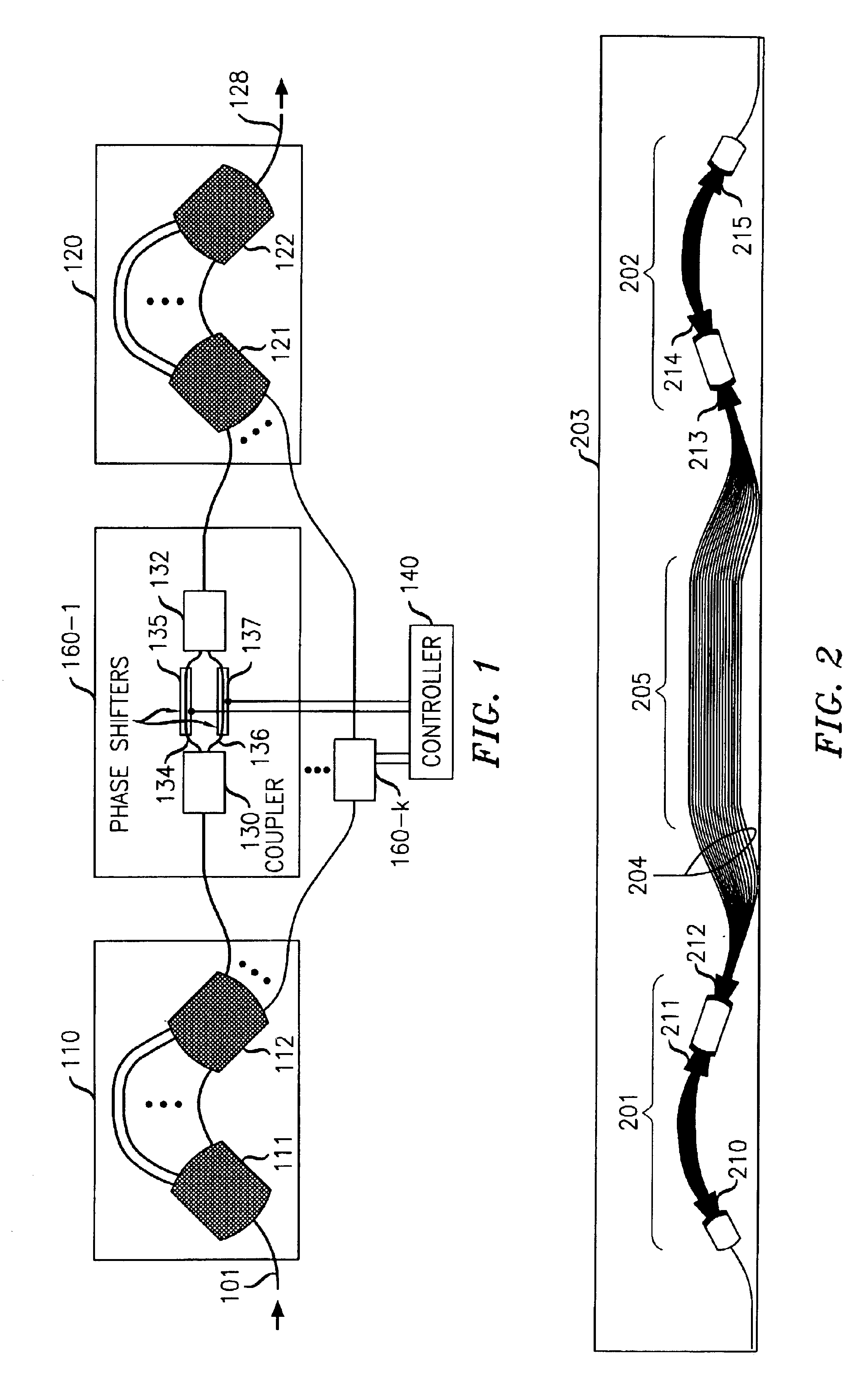
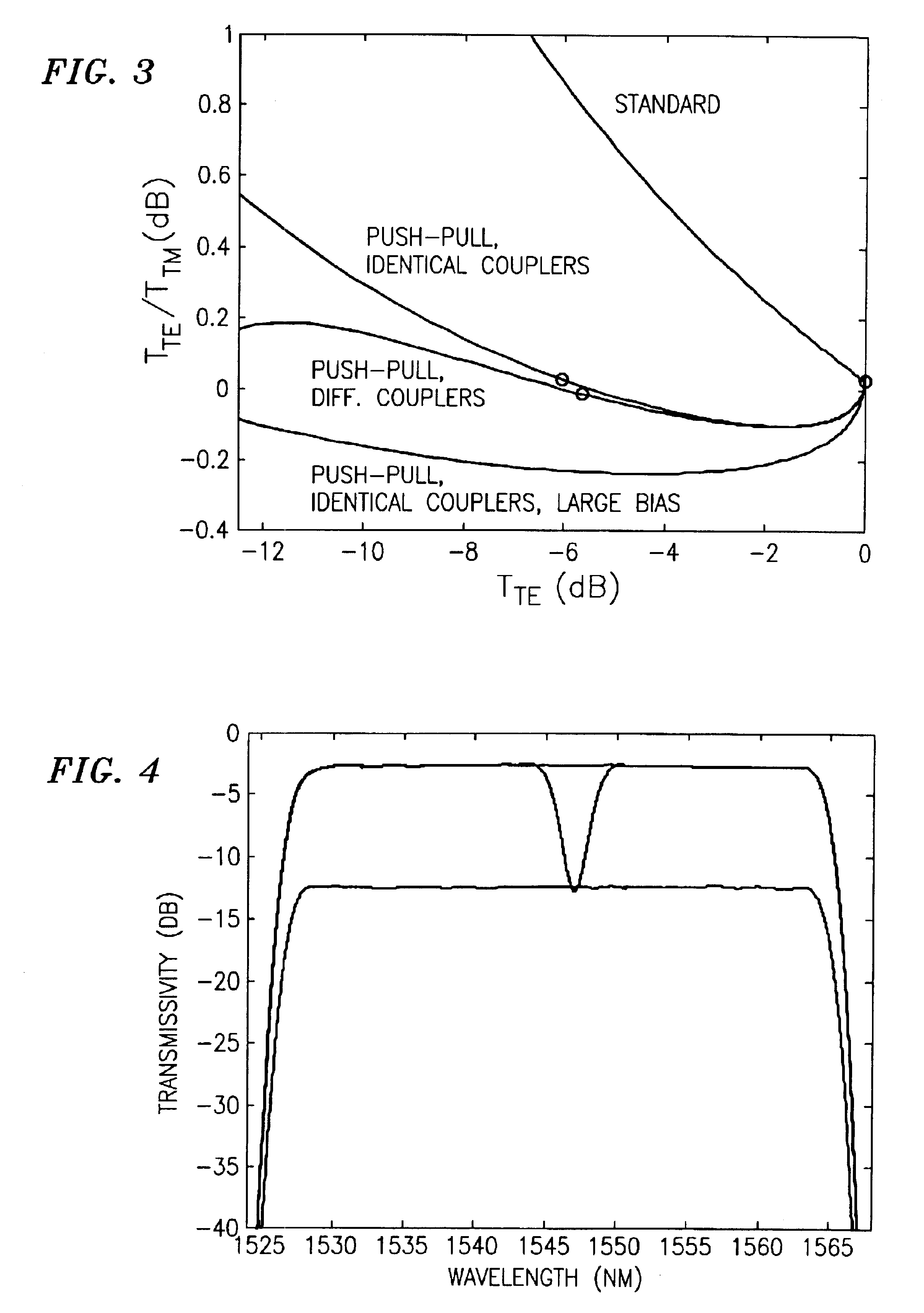
Dynamic gain equalization arrangement for optical signals
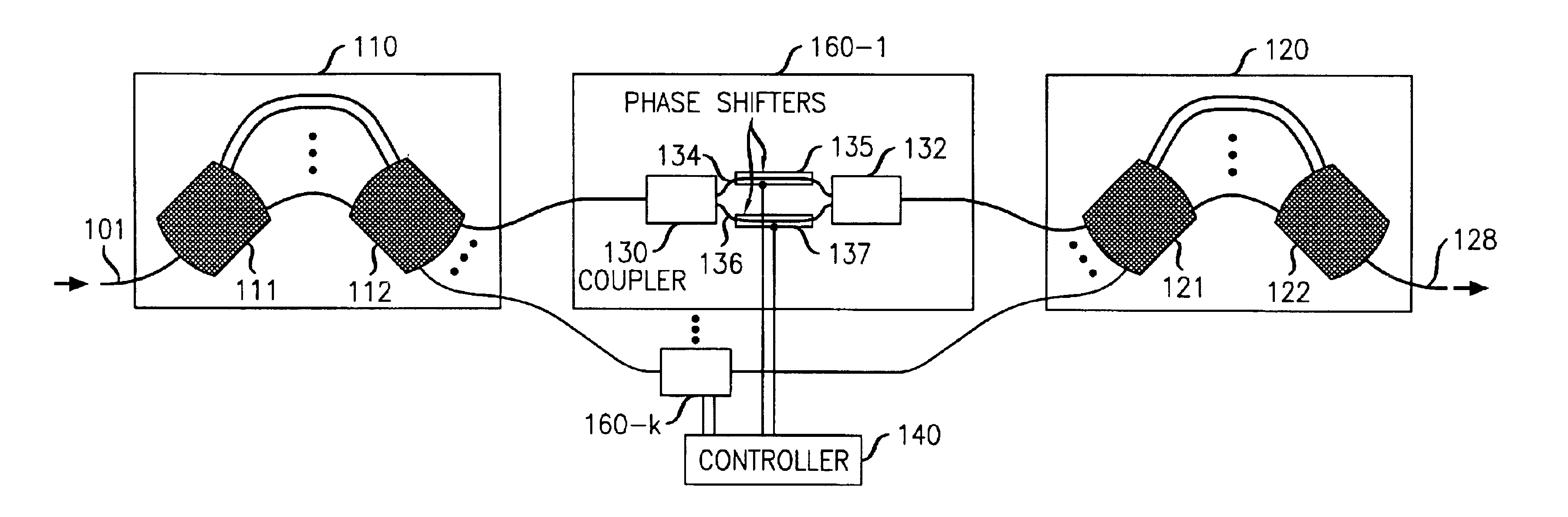
InactiveUS6892021B2Maximizes DGEF spectral resolutionMinimize rippleCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationNegative phase
An optical dynamic gain equalization filter (DGEF) comprises a planar arrangement of preferably “perfectly sampled” (or alternatively oversampled) waveguide grating routers (WGR's) connected by individual optical paths each containing a Mach-Zehnder interferometer operated in a push-pull fashion so that a positive phase change in one interferometer arm and a corresponding negative phase change in the other interferometer arm produces a desired change in attenuation while, at the same time, the overall phase of the optical signals after passing through the Mach-Zehnder interferometer is kept constant with respect to the adjacent paths. Alternatively, the above-described arrangement is effectively “cut in half”, and its size effectively also reduced accordingly, using a mirror placed at the midpoint of the device and an appropriate circulator to separate the input and output optical signals.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Flow cell and system for simultaneous measurement of absorbance and emission in a sample
ActiveUS20170370826A1Reduce trafficMinimize turbulenceMaterial analysis by optical meansFlow cellFluorescence
The flow cell of the present application simultaneously monitors and measures light absorbance and fluorescence of particles in a flowing liquid. The flow cell comprises a housing having a light input face, an absorbance output face and first and second emission output faces; a fluid flow section within the housing that comprises a bottom funnel through which fluid enters the flow cell, a core chamber into which fluid flows from the bottom funnel, and a top funnel into which fluid flows from the core chamber, wherein the bottom and top funnels each comprise a first end which extends at an angle to a second end that is wider in diameter than the first end, and said second end of each is adjacent to and aligned with the core chamber; and a center section within the housing center having a recess formed therein which houses the core chamber of the fluid flow section, wherein said center section comprises a first pair of opposing channels formed in the light input face and the absorbance output face, respectively, and a second pair of opposing channels formed in the first emission output face and the second emission output face and which are perpendicular to the first pair of opposing channels, and wherein the first pair of opposing channels and second pair of opposing channels are in communication with the core chamber. An apparatus comprising the flow cell is also provided.
Owner:BIOCOMP INSTR
System and Method for Image Reconstruction by Using Multi-Sheet Surface Rebinning
ActiveUS20110091007A1Improve approximationMaximize resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
The present application is directed toward the generation of three dimensional images in a tomography system having X-ray sources offset from detectors, in particular in a system where the sources are located on a plane, while detectors are located on multiple parallel planes, parallel to the plane of sources and all the planes of detectors lie on one side of the plane of sources. A controller operates to rebin detected X-rays onto a non-flat surface, perform two dimensional reconstruction on the surface, and generate the three dimensional image from reconstructed images on the plurality of surfaces.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Super resolution from a single signal
ActiveUS8989519B2Improve dynamic rangeMaximize resolutionGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionVideo sequence
A method implementable on a computing device includes exploiting data redundancy to combine high frequency information from at least two different scales of an input signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes exploiting recurrence of data from an input signal in at least two different scales of at least one reference signal to extract and to combine high frequency information from a plurality of scales of said at least one reference signal to generate a super resolution version of said input signal. An alternative method includes generating a super resolution version of a single input video sequence in at least the temporal dimension by exploiting data recurrence within the input video sequence or with respect to an external database of example video sequences. A signal may be an image, a video sequence, an audio signal, etc.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
System and method for image reconstruction by using multi-sheet surface rebinning
ActiveUS8204173B2Maximize resolutionImprove approximationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
The present application is directed toward the generation of three dimensional images in a tomography system having X-ray sources offset from detectors, in particular in a system where the sources are located on a plane, while detectors are located on multiple parallel planes, parallel to the plane of sources and all the planes of detectors lie on one side of the plane of sources. A controller operates to rebin detected X-rays onto a non-flat surface, perform two dimensional reconstruction on the surface, and generate the three dimensional image from reconstructed images on the plurality of surfaces.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Optical System for a Thin, Low-Chin, Projection Television
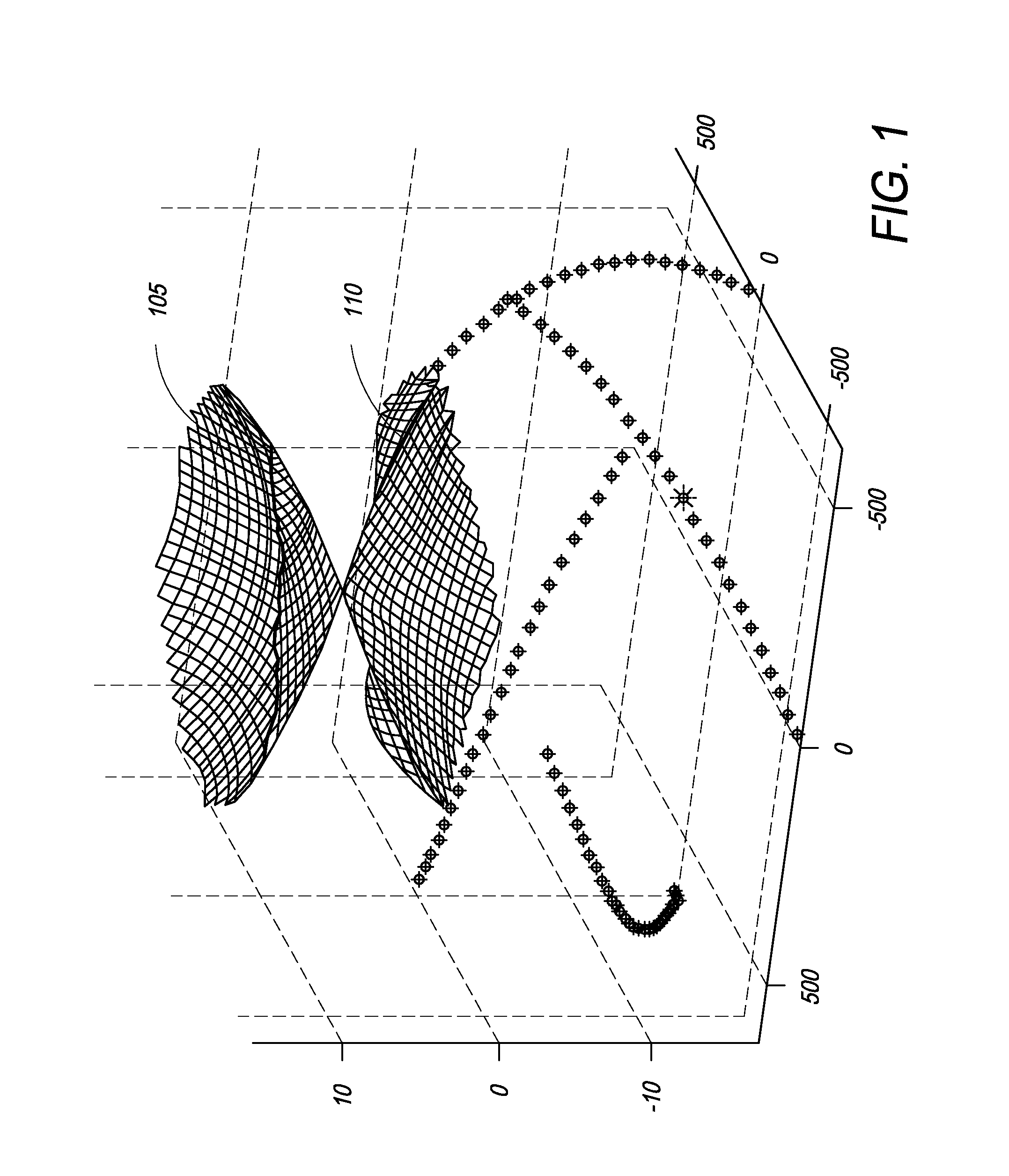
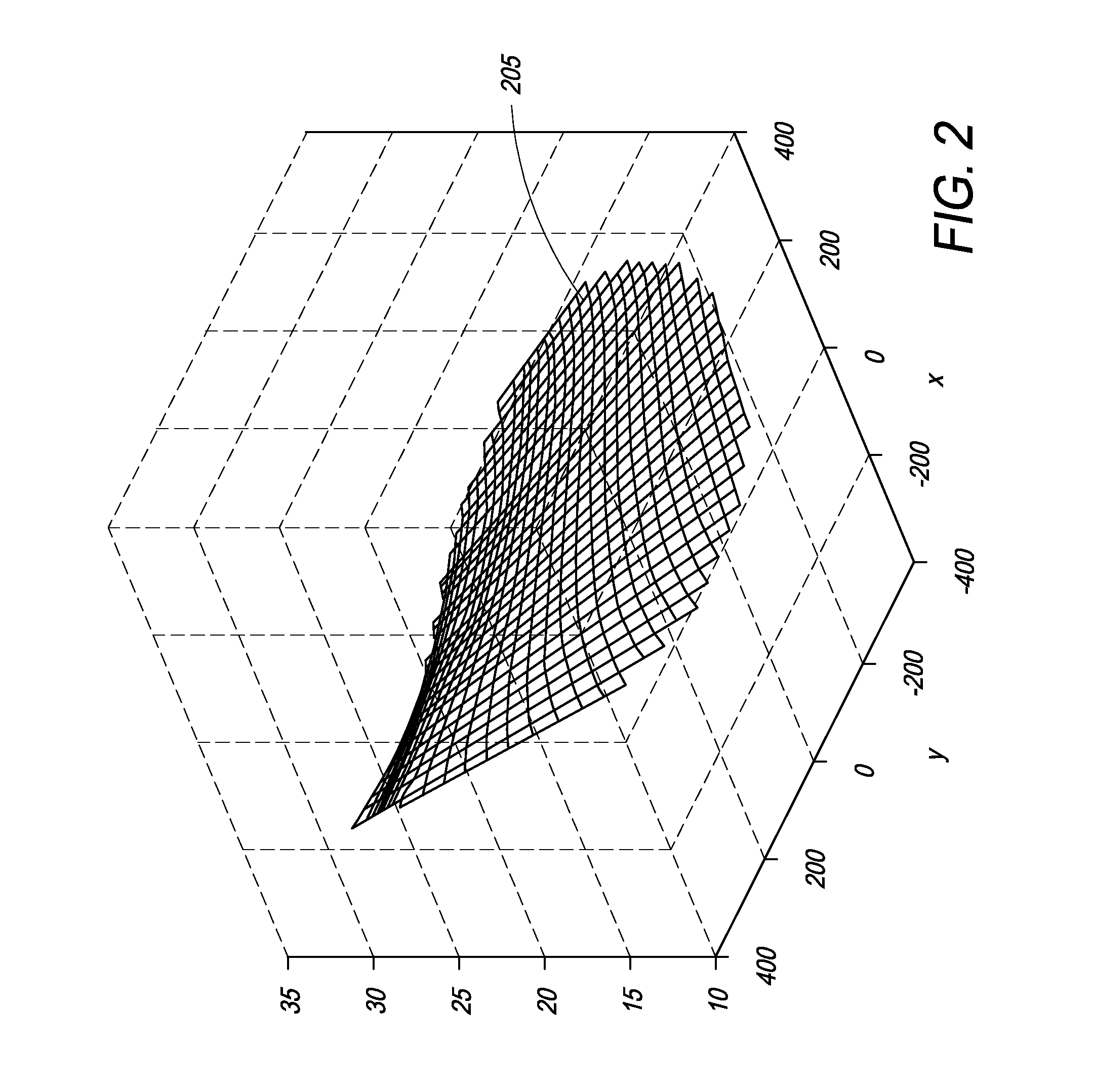
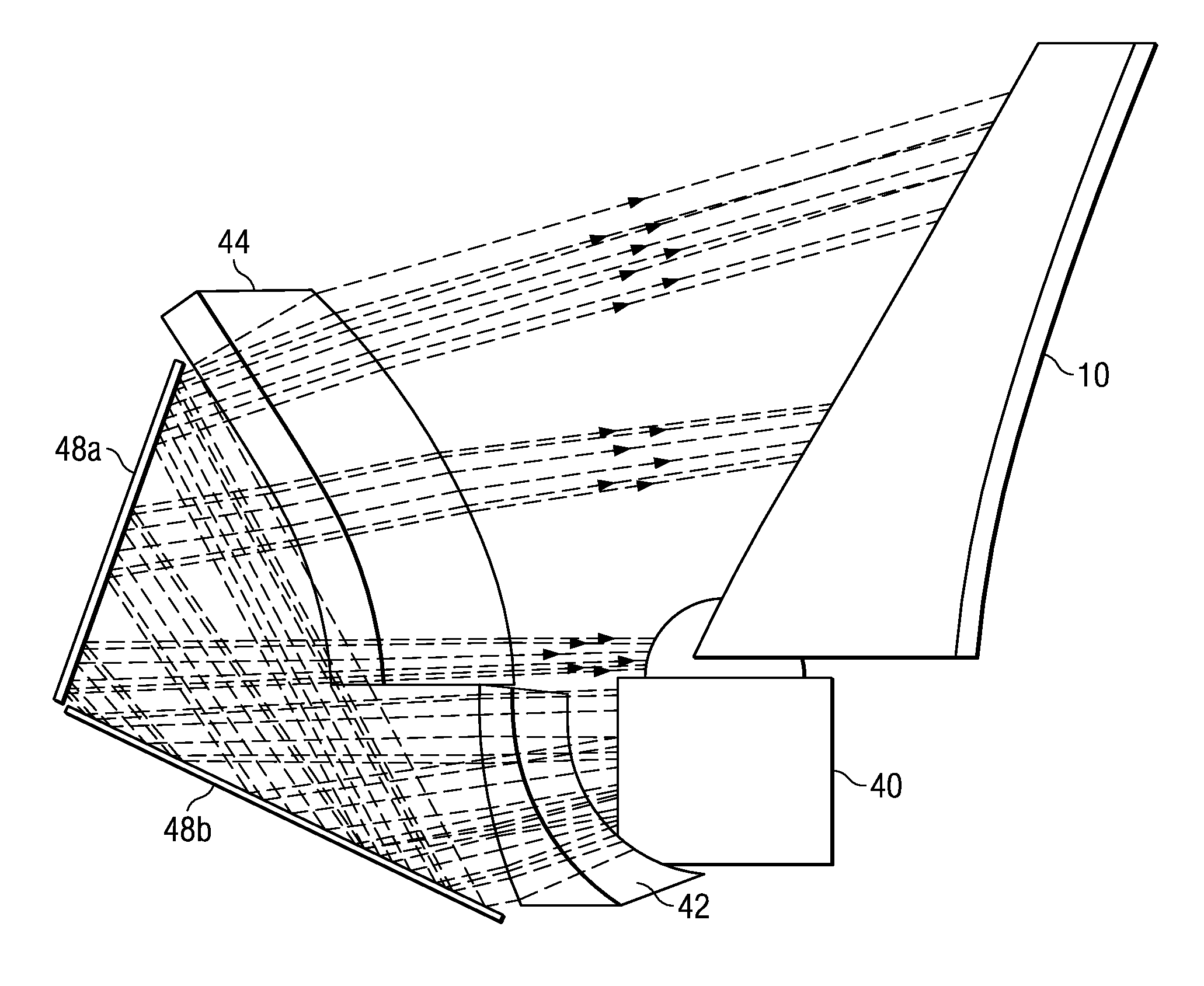
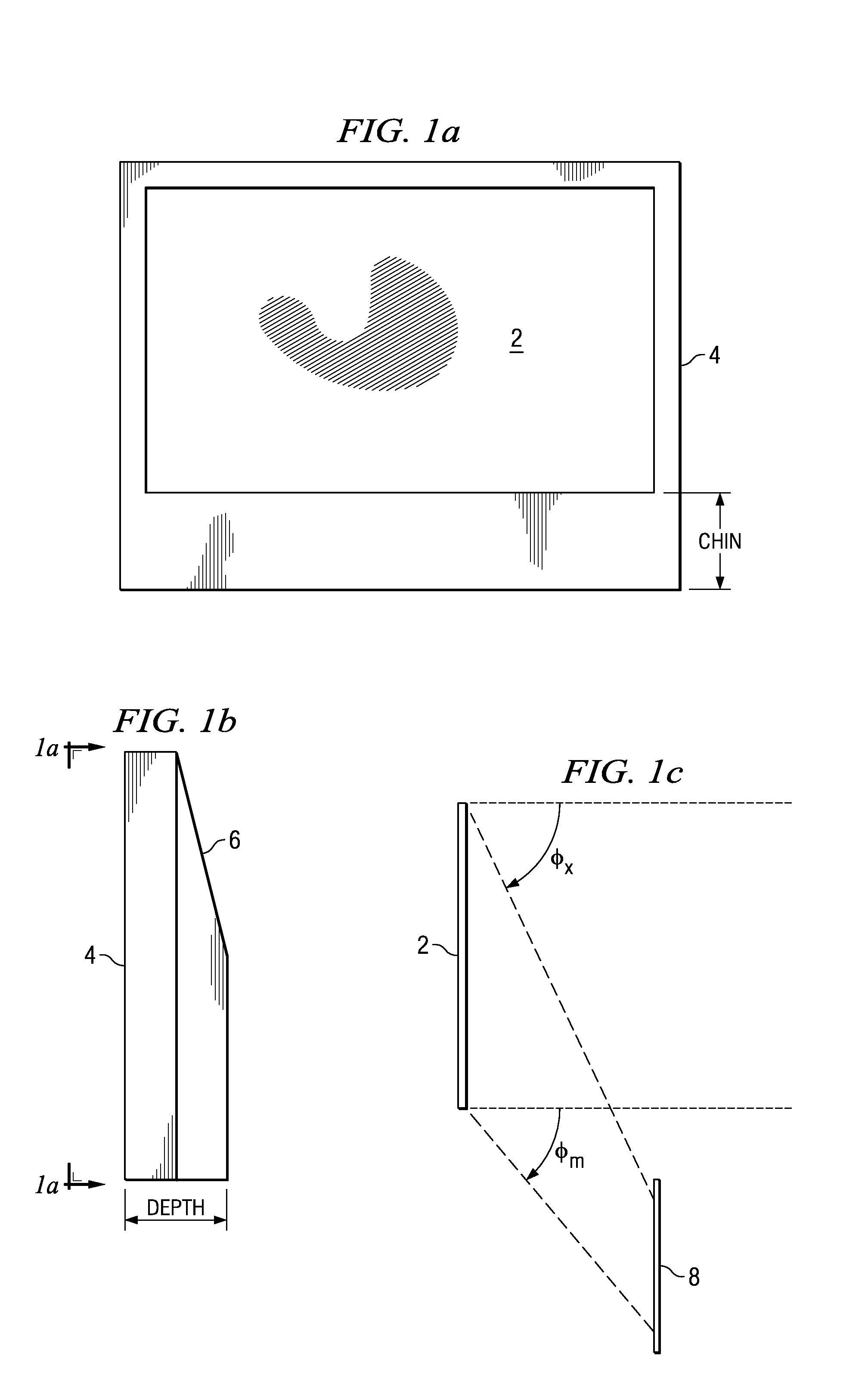
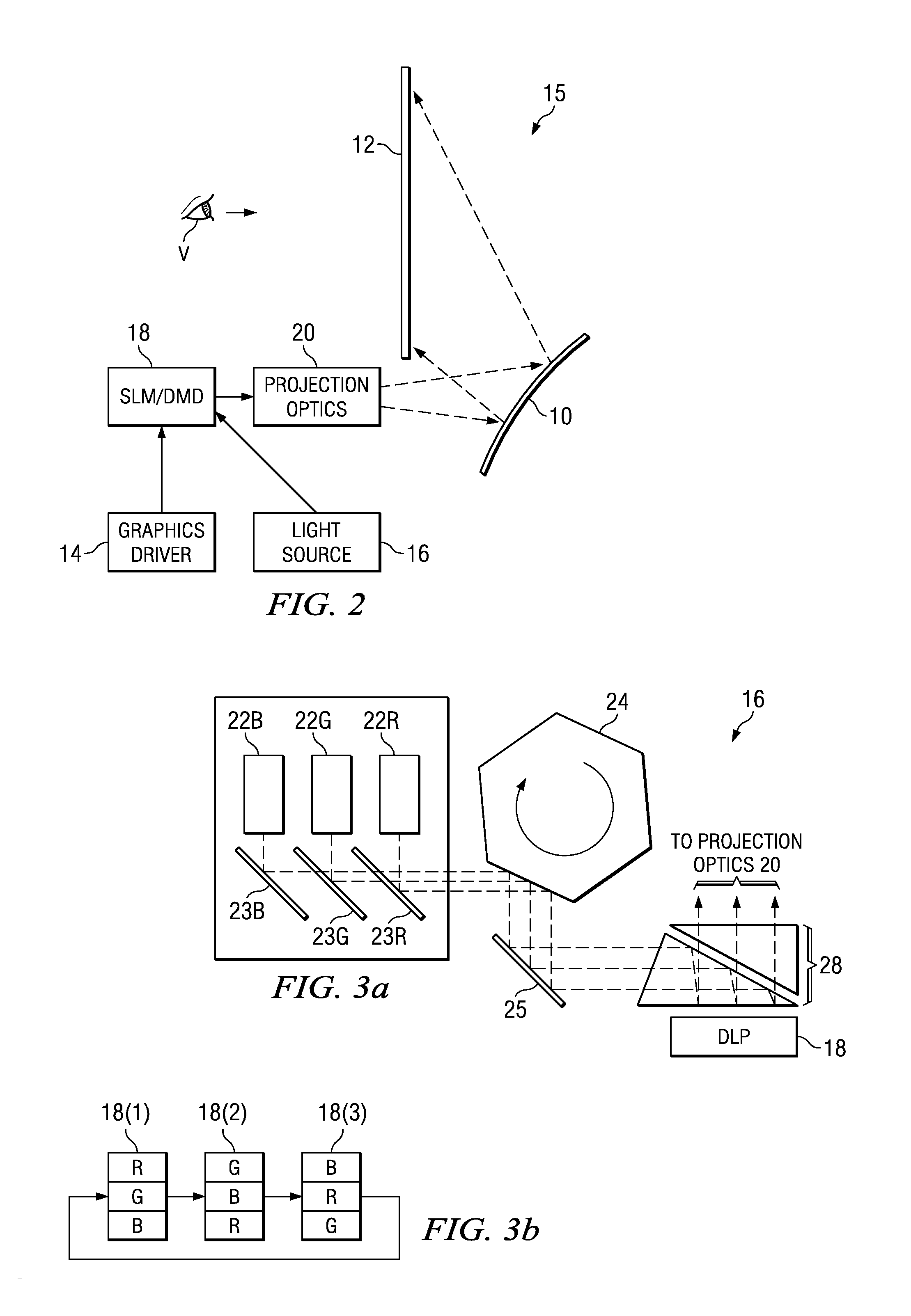
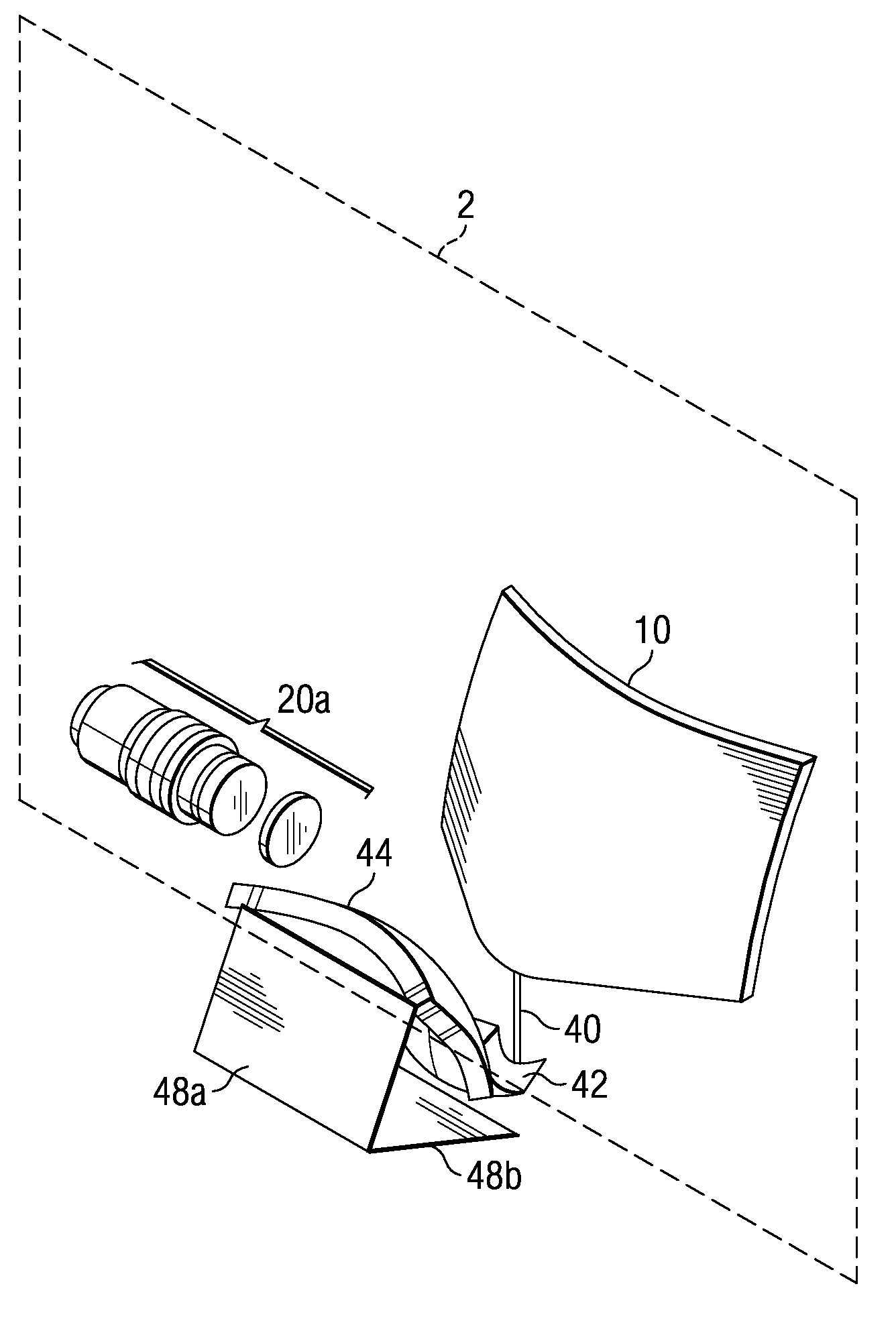
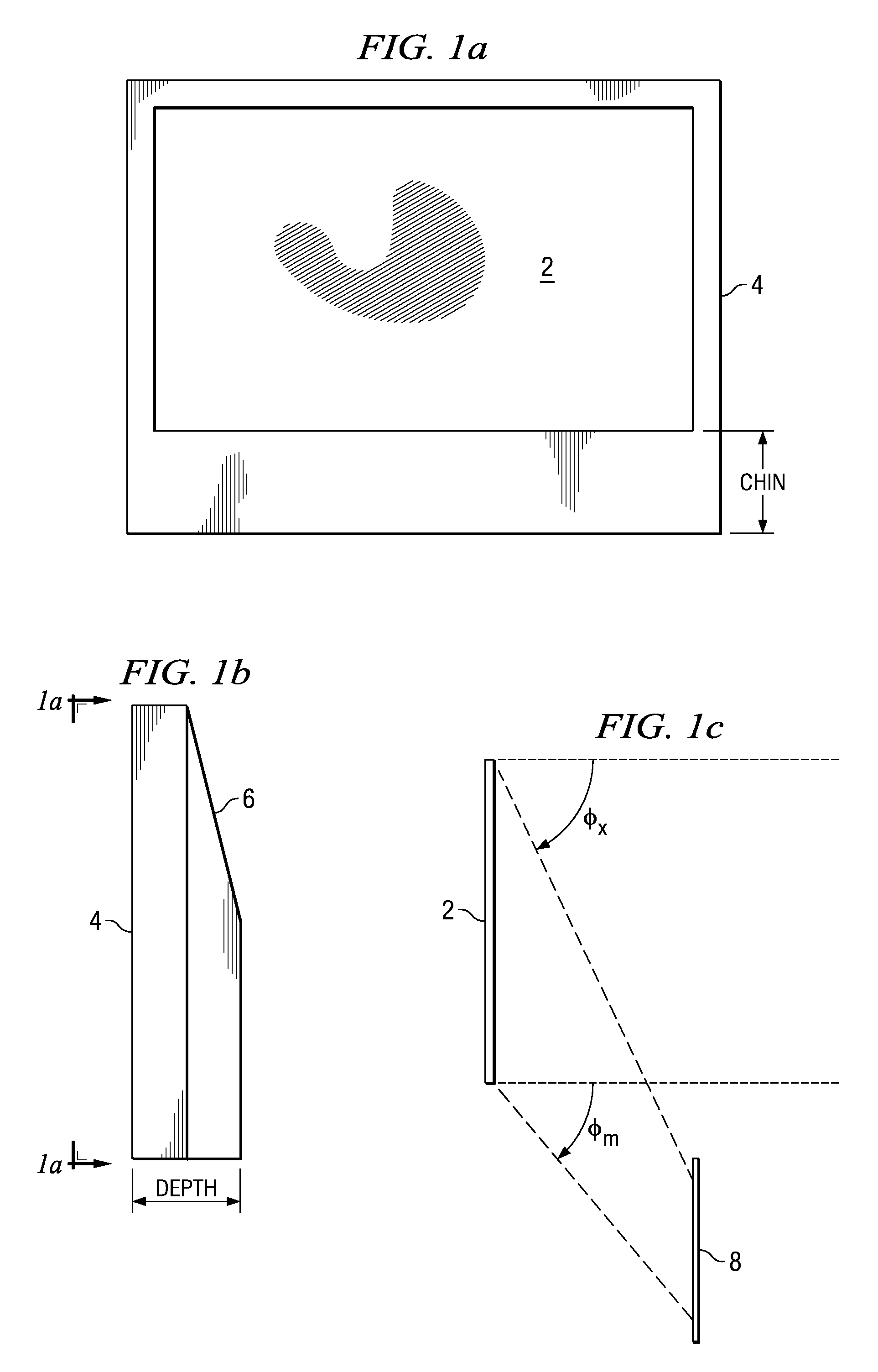
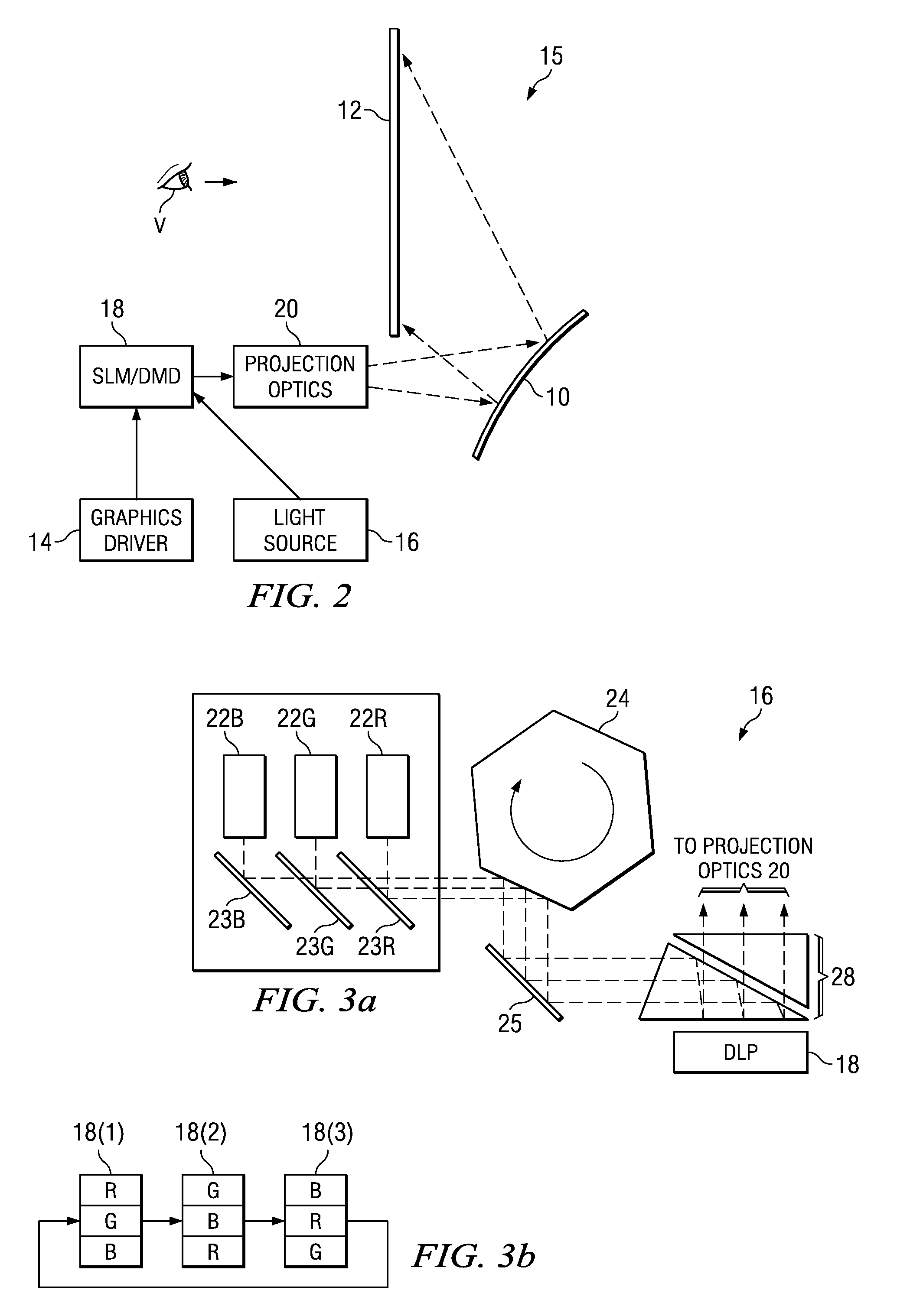
ActiveUS20080239251A1Minimize distortionMaximize resolutionProjectorsColor television detailsCamera lensDigital micro mirror device
A micro-mirror based projection display system in an enclosure with minimum chin and depth measurements is disclosed. A solid-state laser light source generates light of multiple primary colors that is modulated by a digital micro-mirror device. The projection optics of the system include a telecentric rear group of glass lenses with spherical surfaces, followed by a pair of aspheric lenses formed of plastic. A folding mirror is disposed between the aspheric lenses, to reduce the depth of the enclosure, and an aspheric mirror projects the image onto a TIR Fresnel projection screen. The aspheric lenses are magnifying, to reduce the magnification required of the aspheric mirror, and the aspheric lenses and mirror are clipped to reduce enclosure volume.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
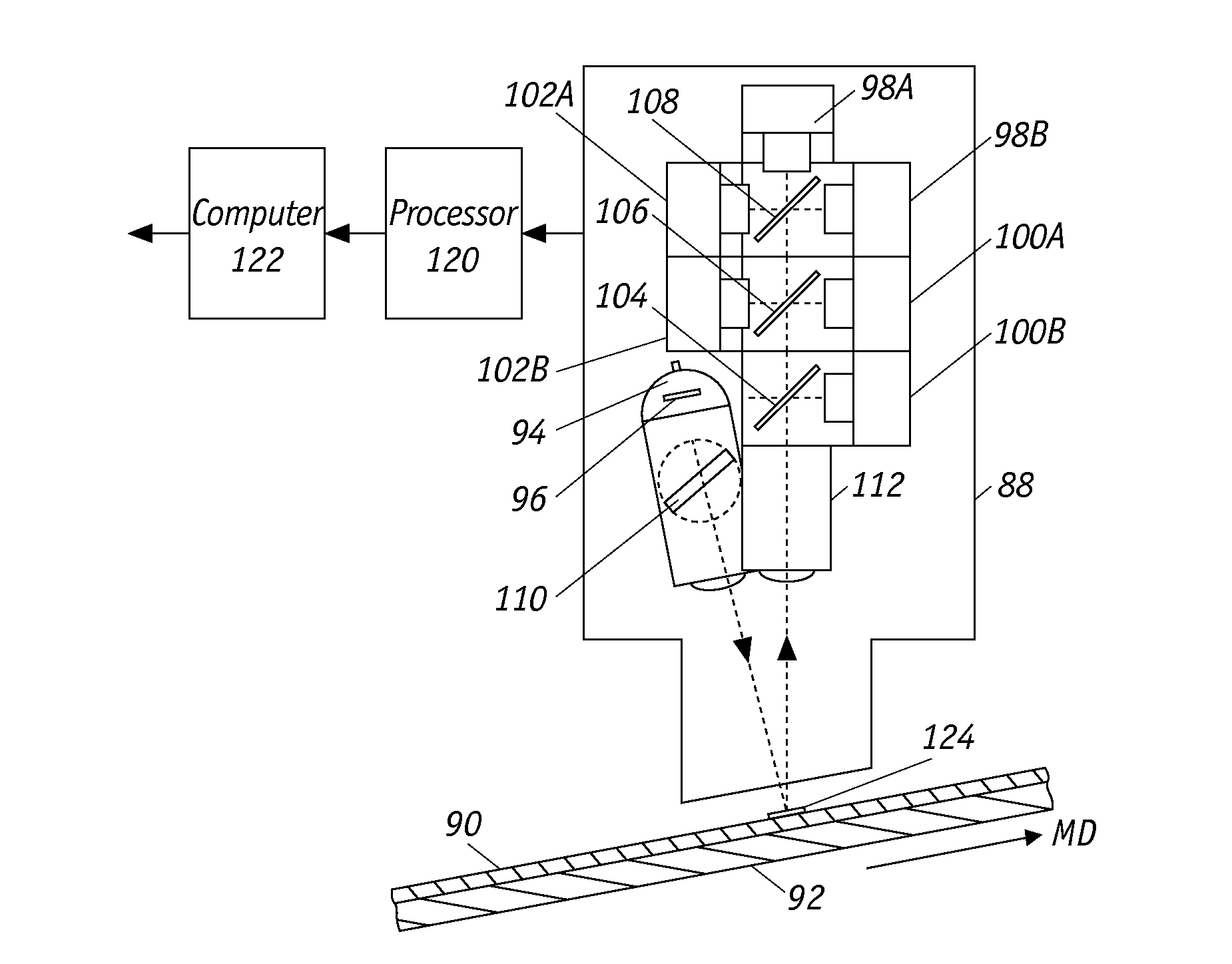
Optimized Spatial Resolution for a Spectroscopic Sensor
ActiveUS20150177155A1Simple designMaximize cross direction resolutionRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving sheetsImage resolutionEngineering
Scanning sensor for measuring properties of continuous flat sheet, that is moving in the machine direction, employs an IR radiation source for directing a beam of incident IR radiation that impinges the sheet. The IR source has elongated lamp filament that generates IR radiation and the corresponding spot size formed on the sheet has elongated dimensions with its long axis being aligned with the machine direction. Aligned with the MD maximizes sensor spatial resolution in the cross direction. The sensor can employ a receiver having rectangular geometry with its long axis being aligned also in the MD. Scanning sensor can operate in the reflective, transmissive, or offset transmission mode to monitor characteristics of flat sheets, particularly of paper or plastic products.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
Phase-change ink jet printing with electrostatic transfer
A printing machine, comprising an intermediate medium; an ink jet printhead, for dispensing phase-change ink droplets at selected locations of a surface of the intermediate medium, the selected locations corresponding to an image to be printed; a receiver source, for providing a receiver; and a transfer station, for electrostatically transferring the dispensed phase-change ink droplets to the receiver.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
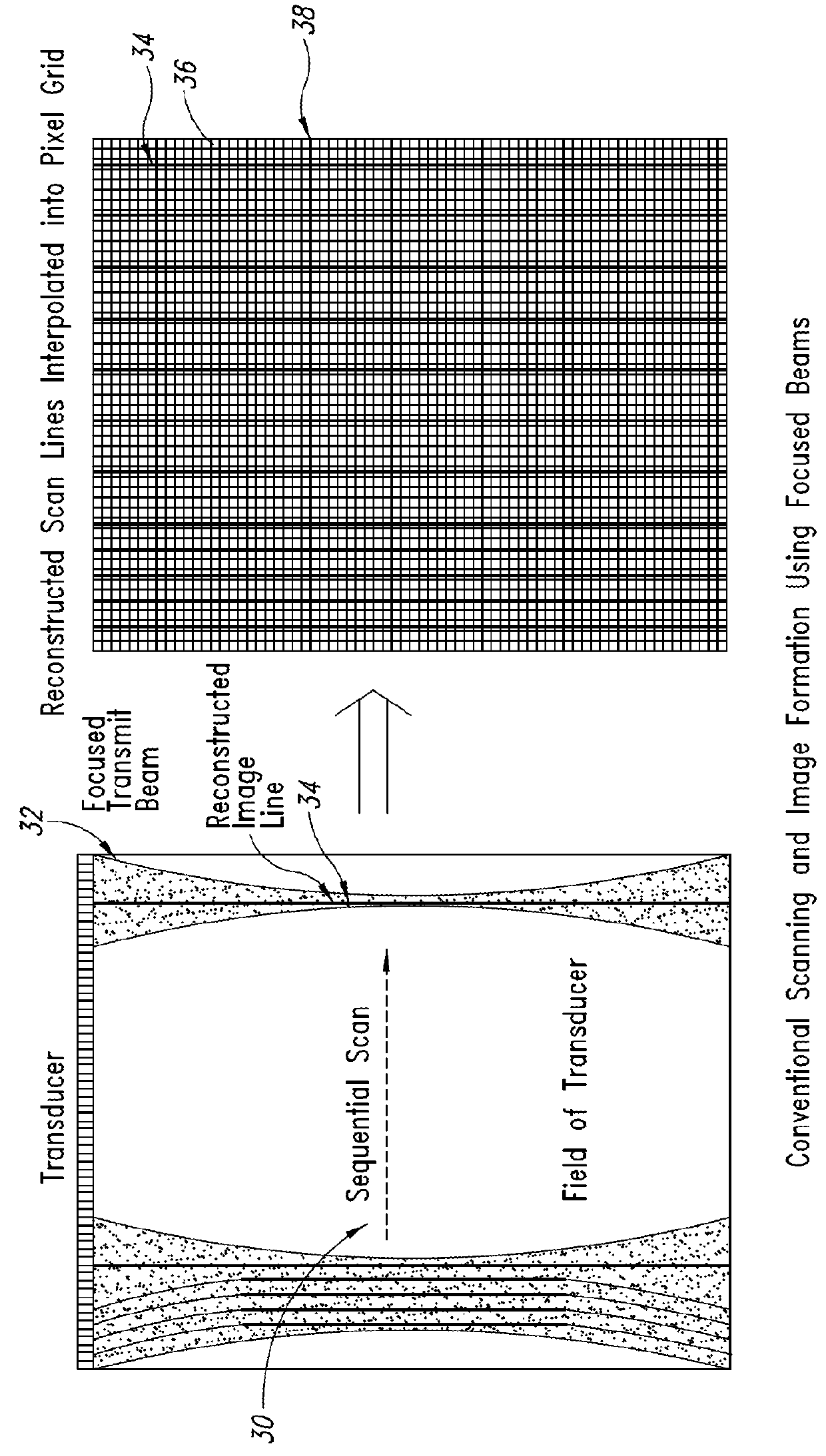
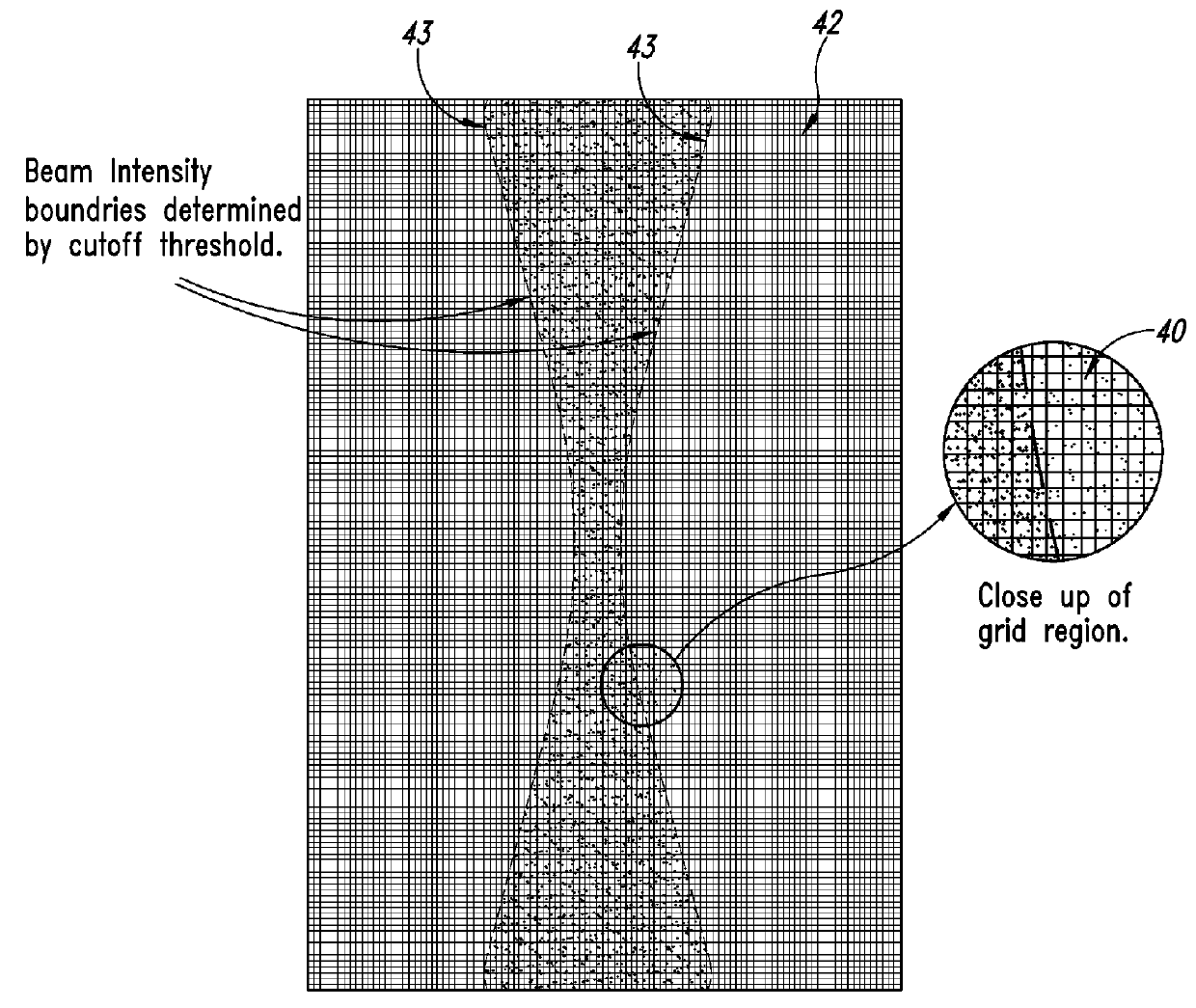
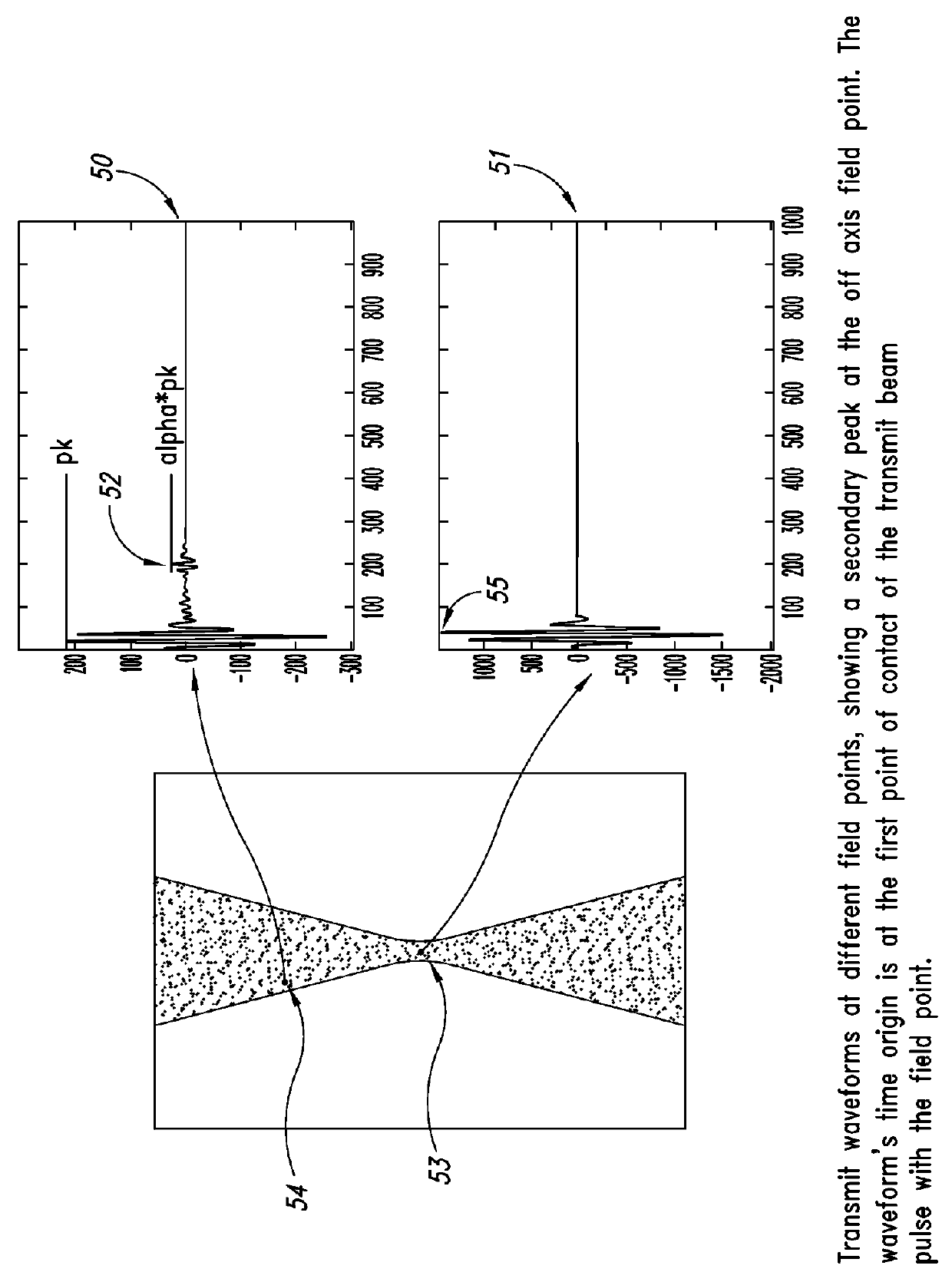
Enhanced ultrasound image formation using qualified regions of overlapping transmit beams
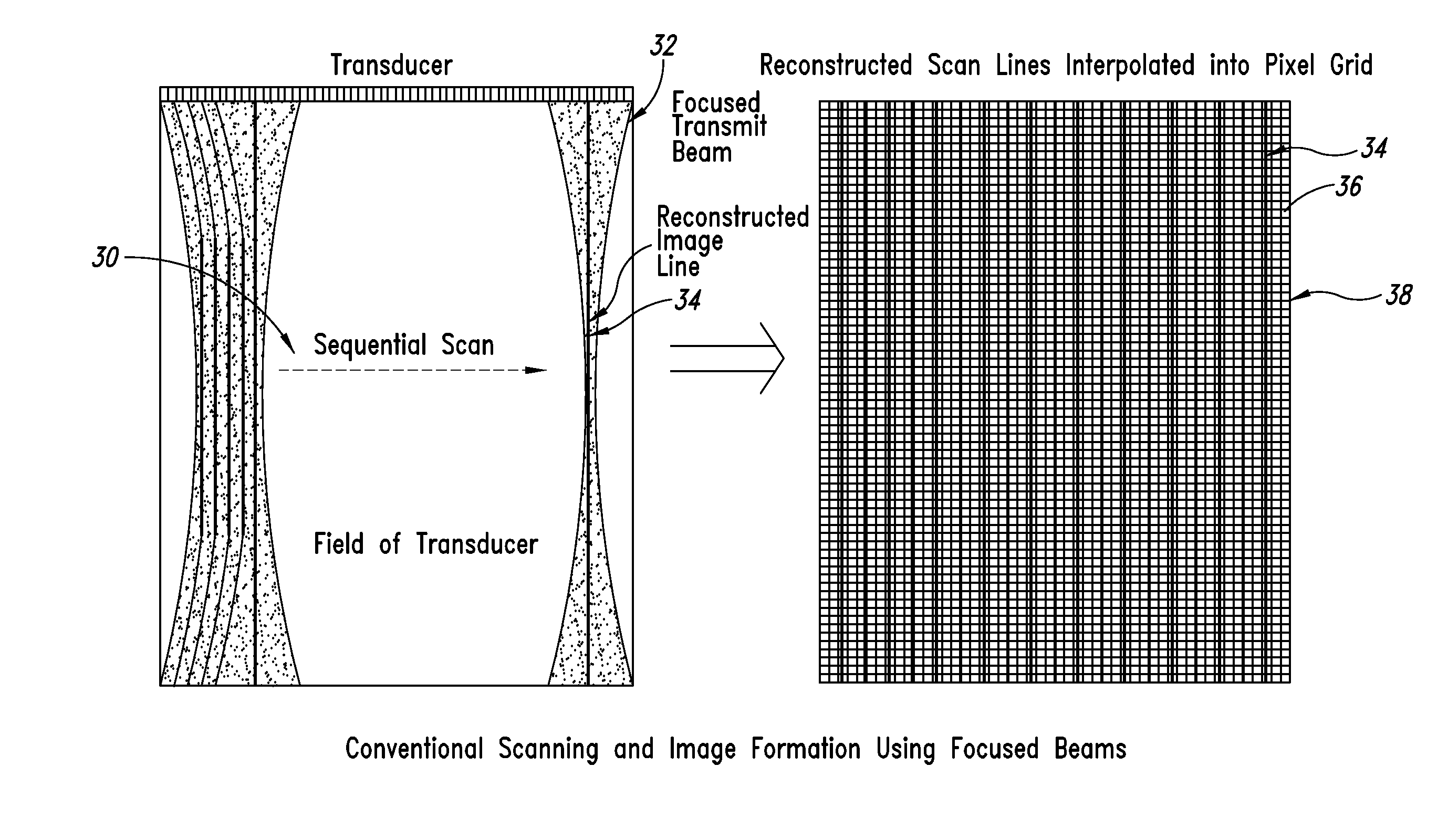
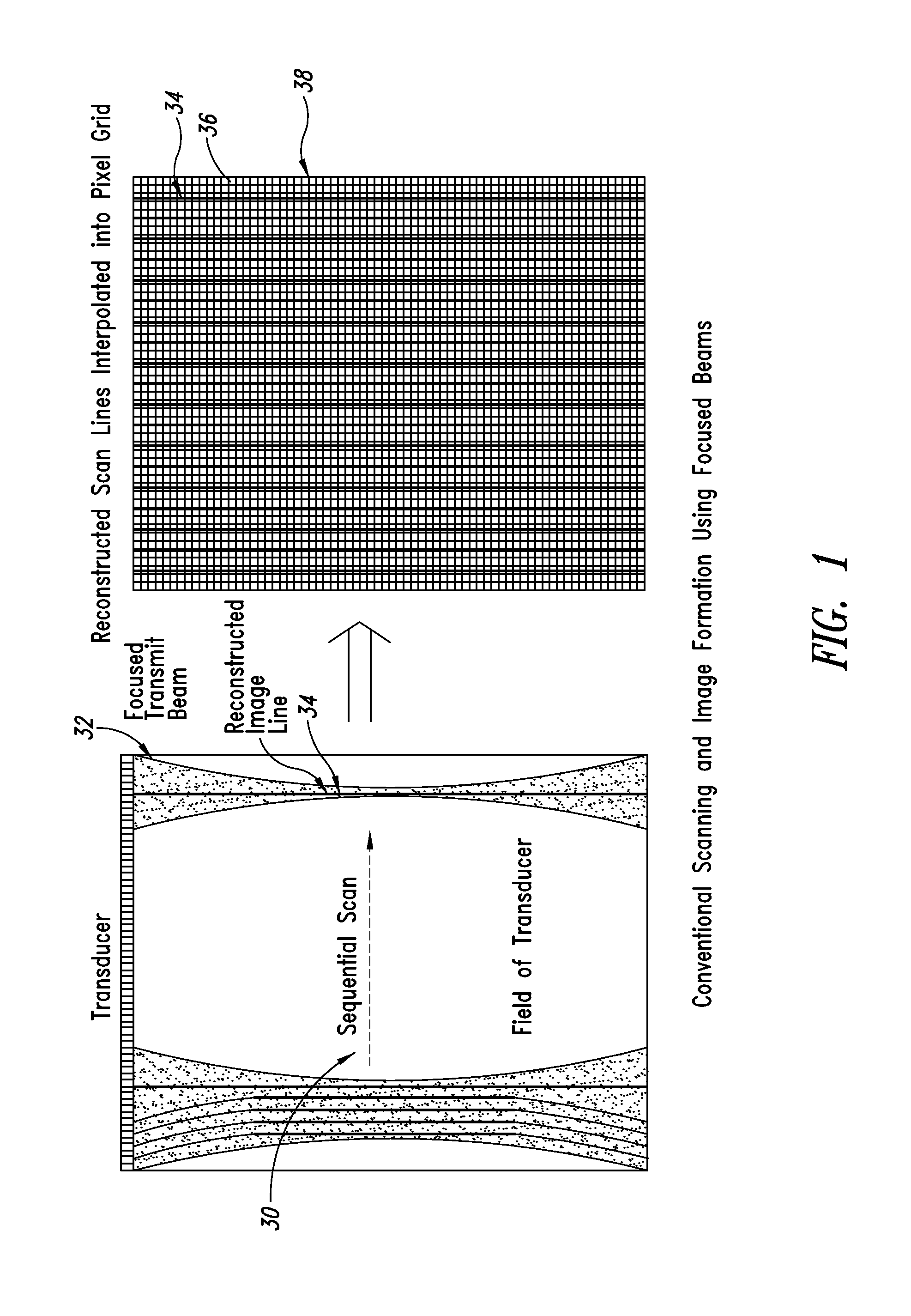
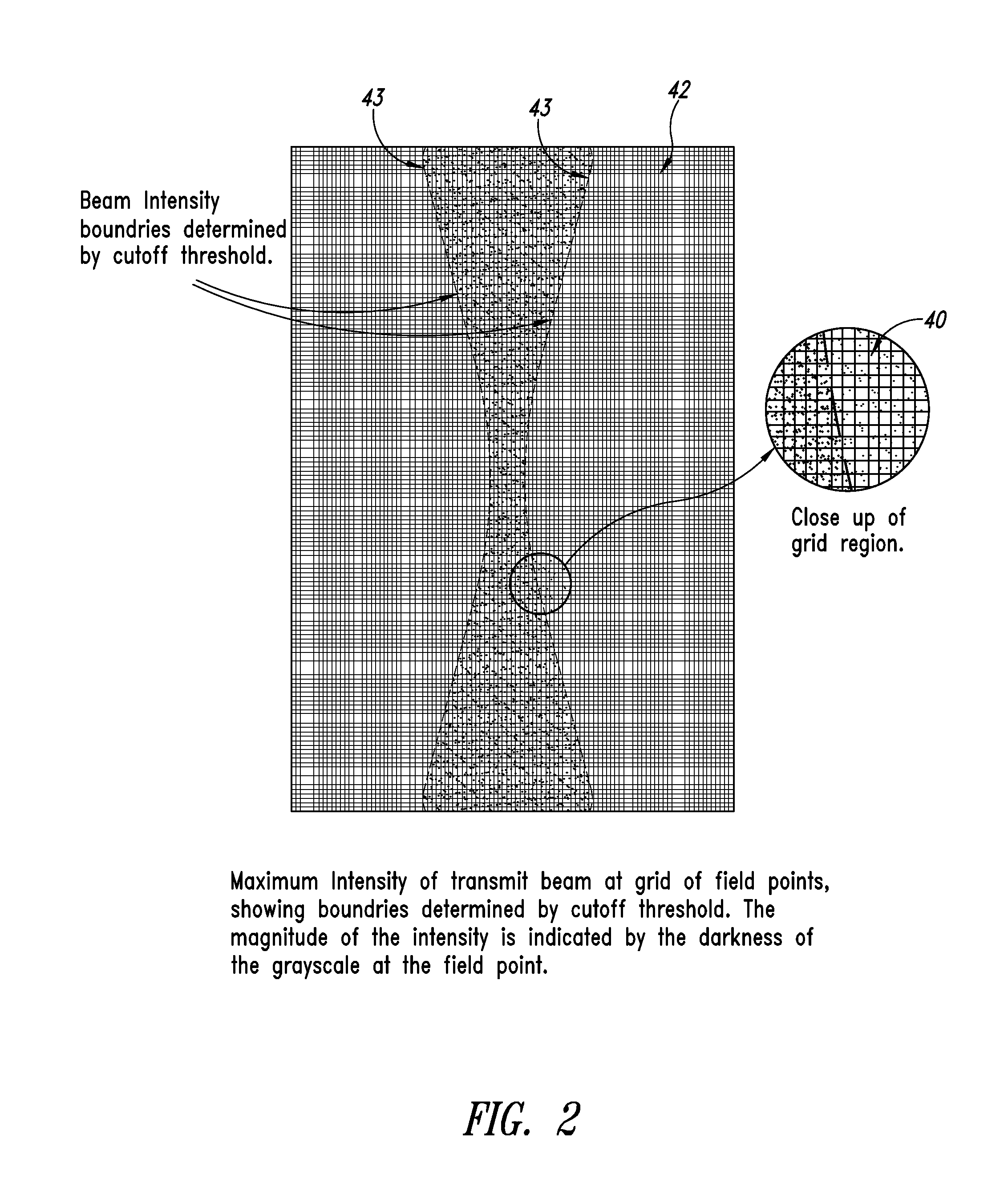
ActiveUS20140140600A1Increase ratingsImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationImage resolution
A method and related system for improving resolution and frame rate of ultrasound images that includes specifying individual element transmit characteristics for each transmit beam in a set of transmit beams; determining various attributes of the transmit beams at field points in the field of view; using one or more of the attributes to determine if received ultrasound echo signals contributed by each transmit beam are qualified for use in image formation, and if so, how the signal should be processed; storing the determined information for each field point for repeated use with each new image frame; using the stored information to select and process subsequent received echo signals for each field point to produce an image parameter at the field point for each qualified echo signal; and combining multiple image parameters from overlapping transmit beams for a field point to produce a final image parameter that constitutes the field point value for the image frame.
Owner:VERASONICS
Optical system for a thin, low-chin, projection television
ActiveUS7857463B2Minimize distortionMaximize resolutionProjectorsColor television detailsCamera lensDigital micro mirror device
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Design method for choosing spectral selectivity in multispectral and hyperspectral systems
InactiveUS20180293331A1Fast learningAdaptableConstraint-based CADTotal factory controlHigh rateEngineering
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Wind turbine blade provided with optical wind velocity measurement system
ActiveUS8917383B2Facilitates optical measurementMaximize resolutionWind motor controlEngine fuctionsEngineeringOptical measurements
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Enhanced ultrasound image formation using qualified regions of overlapping transmit beams
ActiveUS9384530B2Increase ratingsImprove resolutionImage enhancementOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationImage resolution
A method and related system for improving resolution and frame rate of ultrasound images that includes specifying individual element transmit characteristics for each transmit beam in a set of transmit beams; determining various attributes of the transmit beams at field points in the field of view; using one or more of the attributes to determine if received ultrasound echo signals contributed by each transmit beam are qualified for use in image formation, and if so, how the signal should be processed; storing the determined information for each field point for repeated use with each new image frame; using the stored information to select and process subsequent received echo signals for each field point to produce an image parameter at the field point for each qualified echo signal; and combining multiple image parameters from overlapping transmit beams for a field point to produce a final image parameter that constitutes the field point value for the image frame.
Owner:VERASONICS
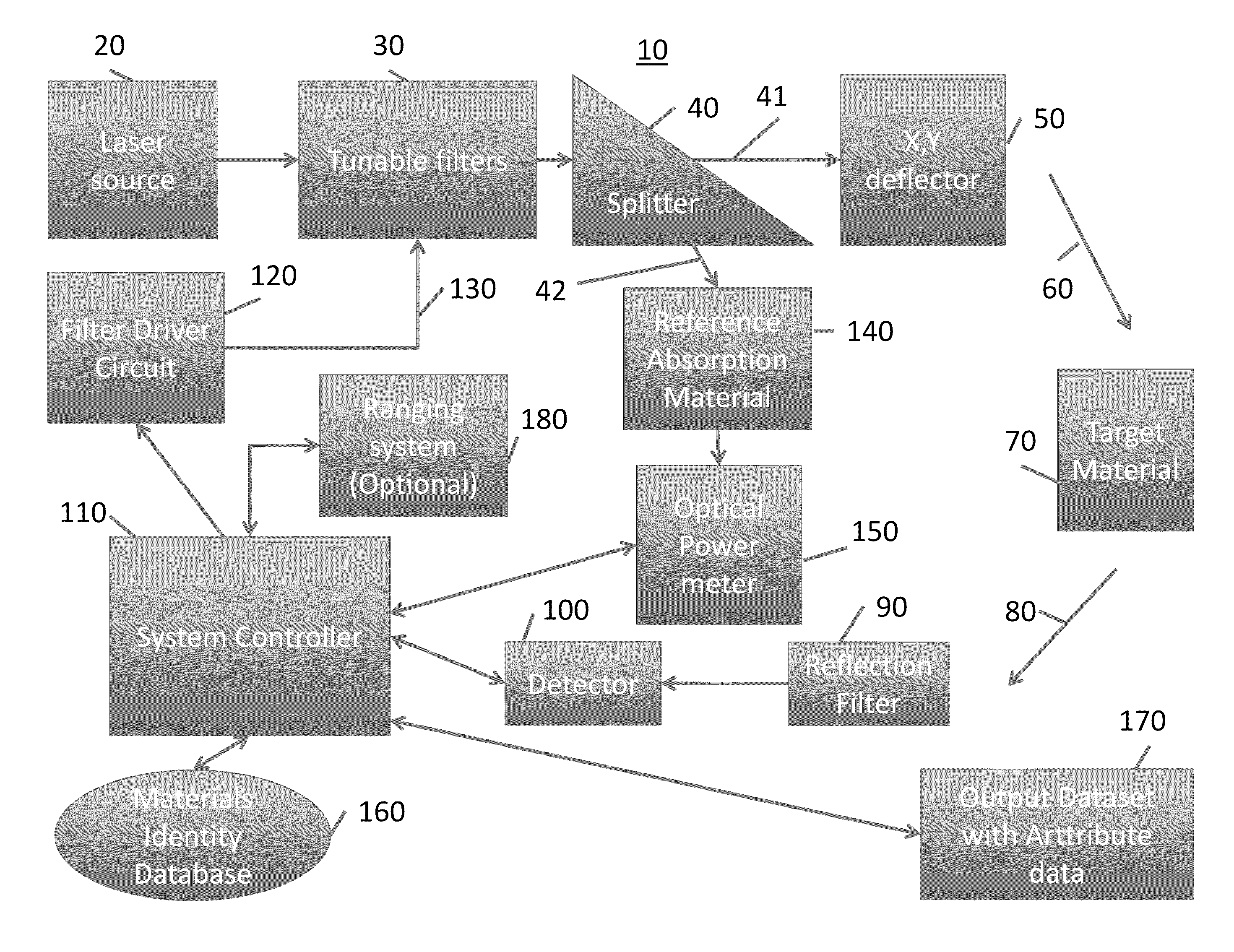
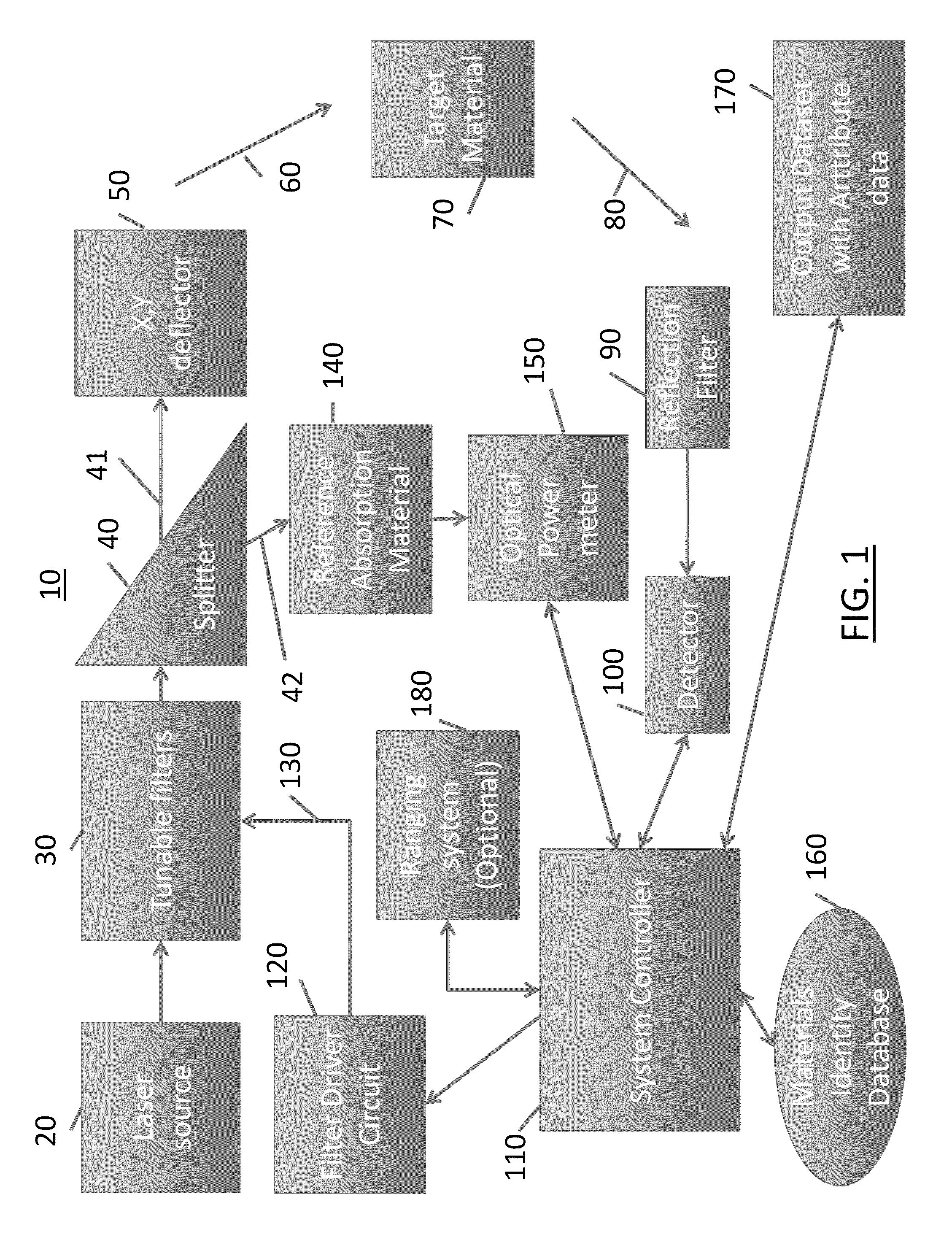
System and method for interrogation of target material in situ
ActiveUS9140643B2Adapt quicklyMaximize resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationImage resolutionLaser source
A system for remotely sensing a target material in situ include a broad-band laser source, at least one tunable filter coupled to the source laser for generating a swept-frequency signal an optical device for splitting the swept-frequency signal into a first illumination signal and second illumination signal, a first optical path for directing the first illumination signal unto the target material and receiving a reflected signal from the target material, a second optical path for receiving the second illumination signal and generating a spectral reference signal, and a controller coupled to the first optical path and the second optical path for adjusting the frequency and spatial resolution of the laser source based at least in part on a comparison of the spectral reference signal and the reflected signal.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
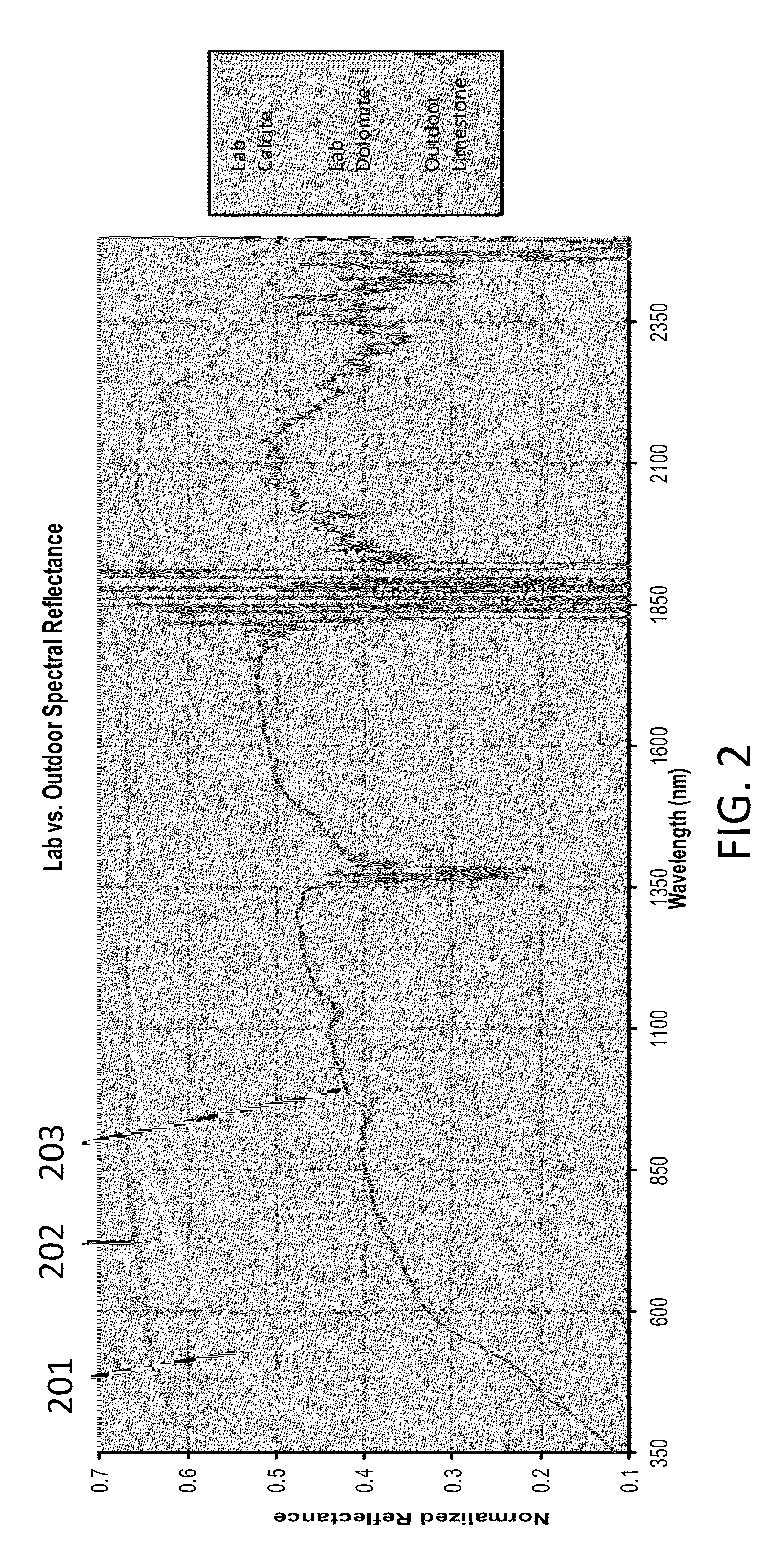
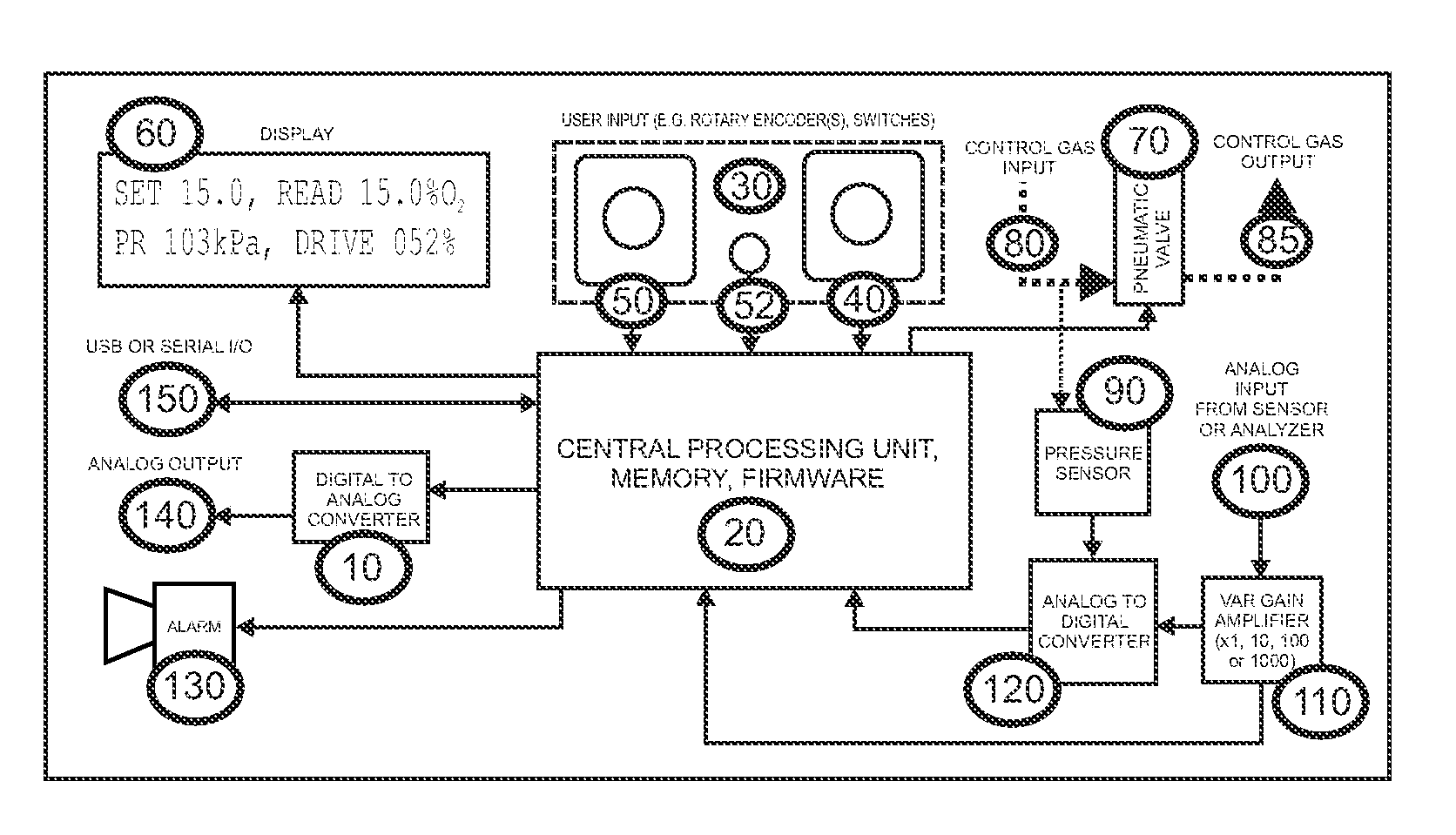
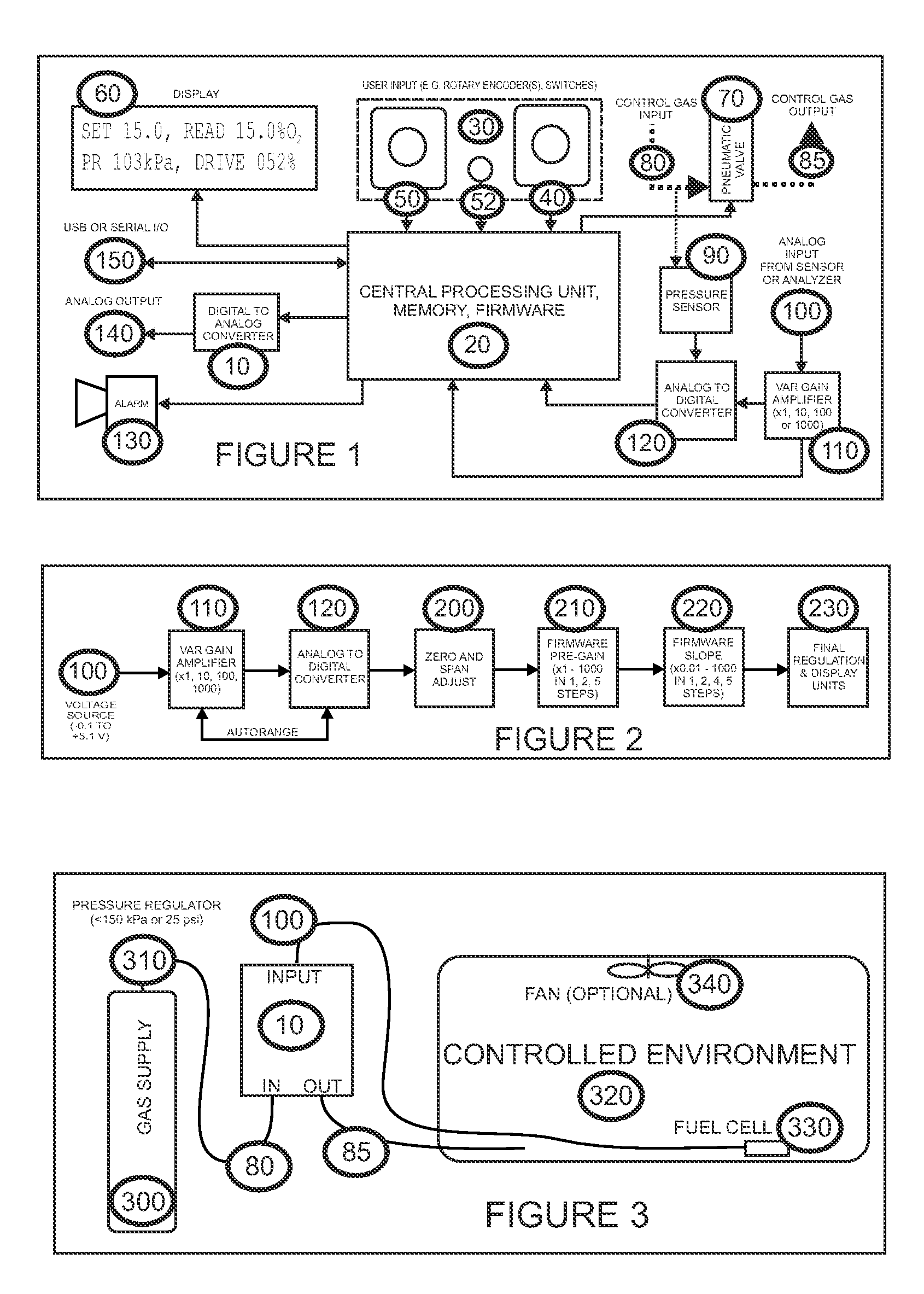
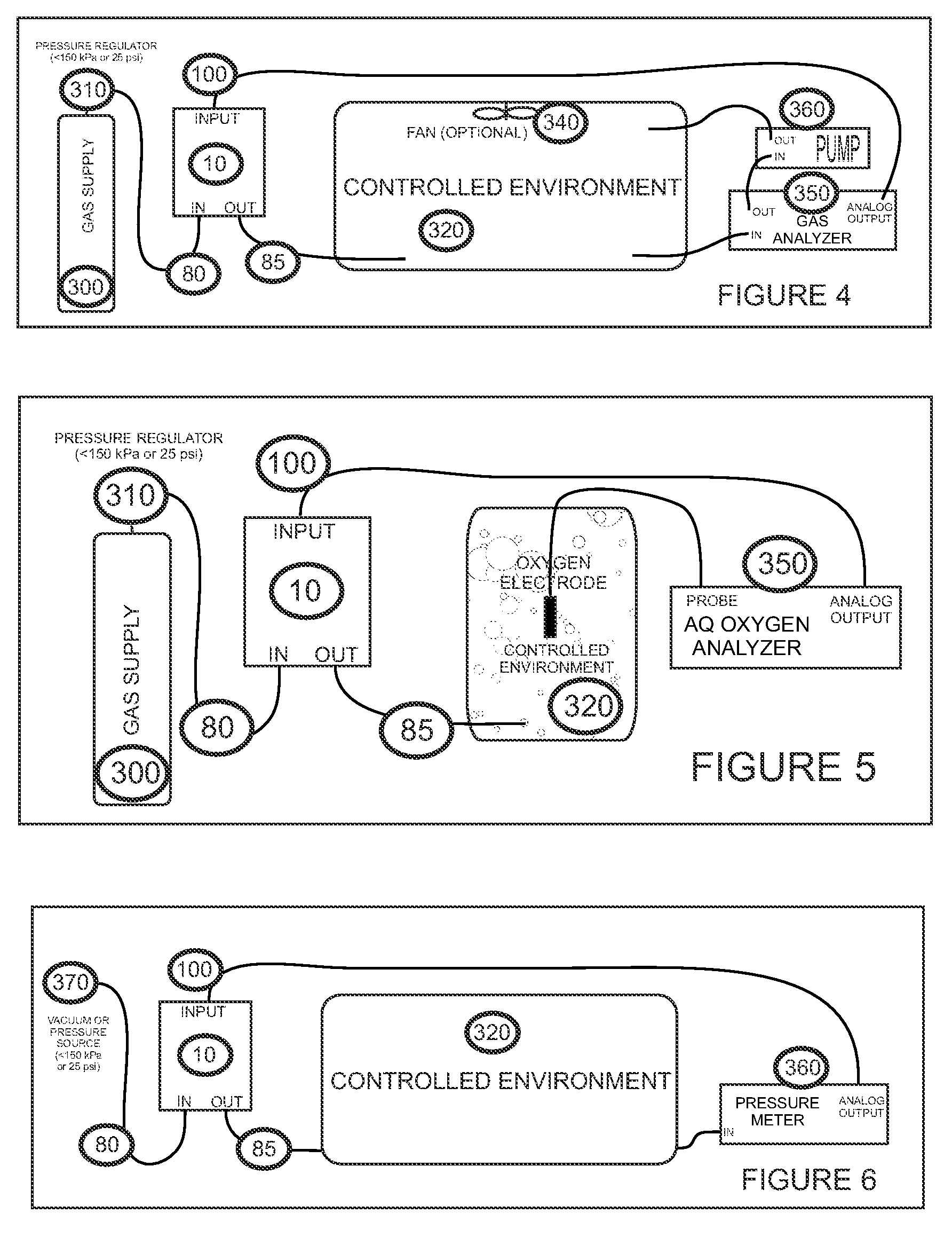
Universal Regulatory Apparatus for Controlled Environments for Use with Added Sensors and Analyzers
InactiveUS20080089810A1Maximize resolutionMaximising voltageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansControlling environmentComputer science
A gas-based regulatory apparatus has an electrical input, optionally connected to an analog to digital converter; a central processing unit (CPU) comprising a non-volatile memory for storing and retrieving program and configuration data and a random access memory for storing and retrieving other data; a visible alphanumeric display means connected thereto; a user input means adjacent to the display and connected to the processing means; an alarm driven directly or indirectly from the CPU; a pneumatic valve having an input port and an output port, and being driven directly or indirectly from the CPU; and a program that runs on the CPU, for receiving user input, measuring input voltages and pressure voltages from the analog to digital converter, displaying data, converting measured voltages to gas and pressure units, implementing a control algorithm, and driving the pneumatic valve and alarm.
Owner:LIGHTON JOHN R B
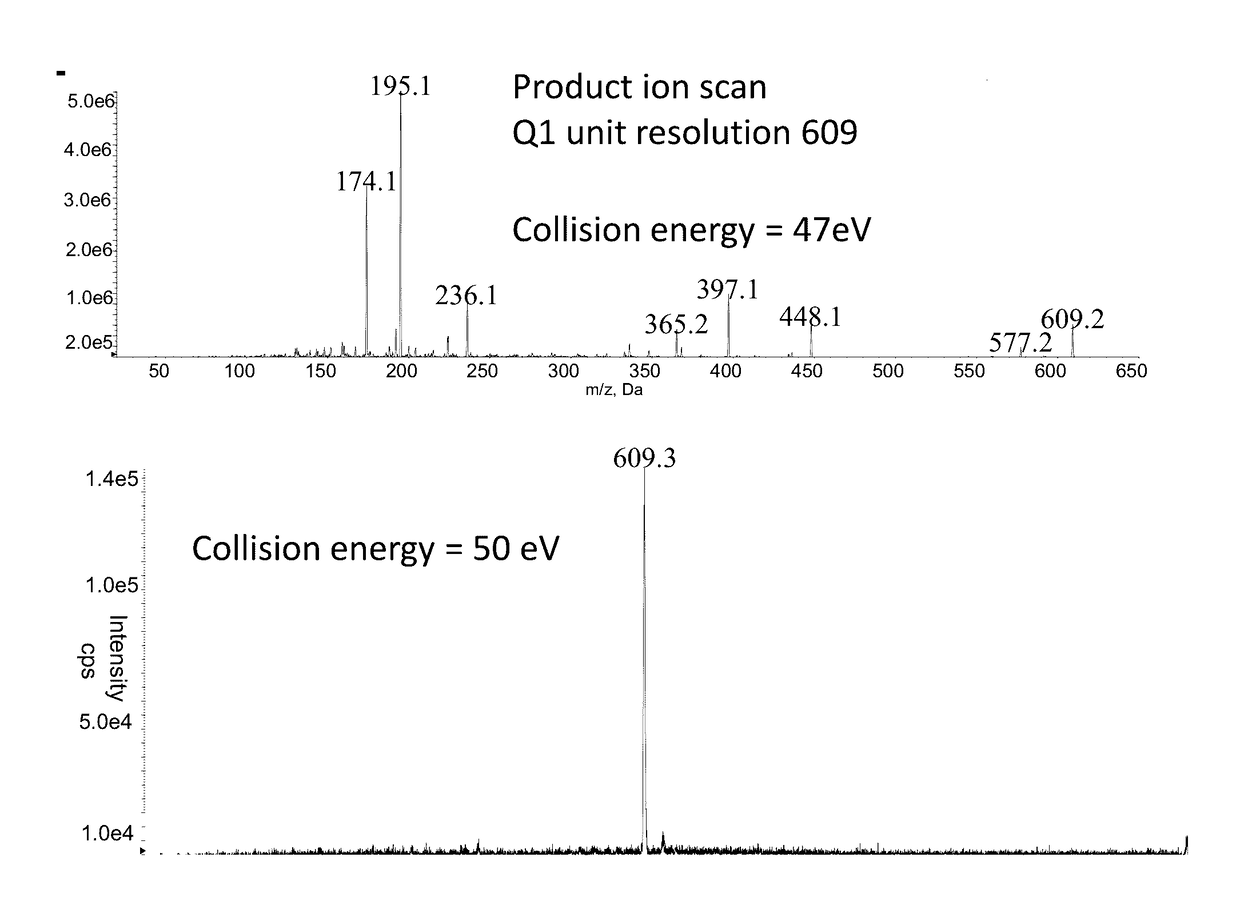
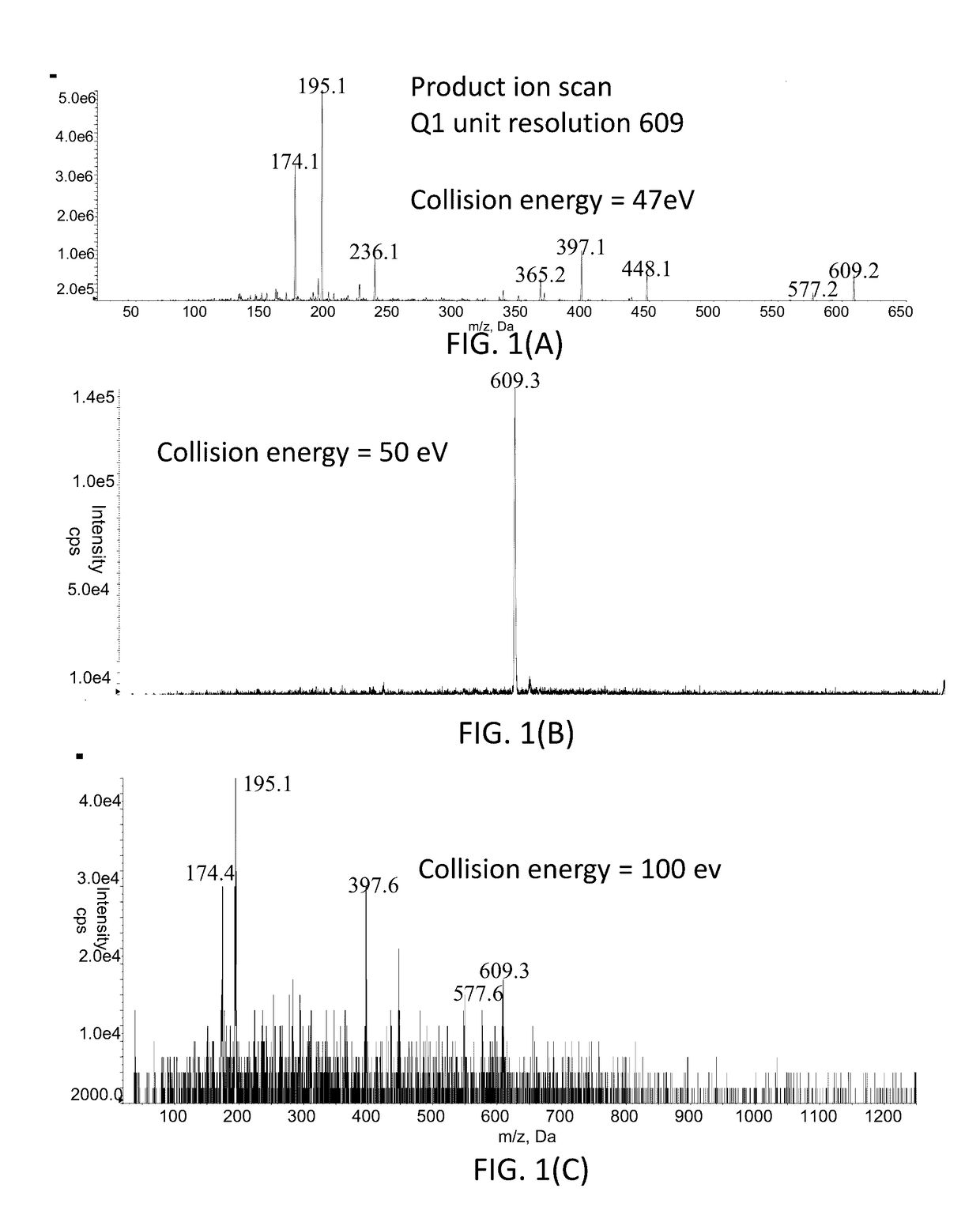
Contamination Filter for Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20170122908A1Increased signal noiseReduce the amount requiredSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Methods and systems for performing mass spectrometry are provided herein. In accordance with various aspects of the applicants' teachings, the methods and systems can utilize an ion mobility spectrometer operating at atmospheric or low-vacuum pressure to remove the major contributors to the contamination and degradation of critical downstream components of a mass spectrometer located within a high-vacuum system (e.g., ion optics, mass filters, detectors), with limited signal loss.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Mass spectrometer and method of use
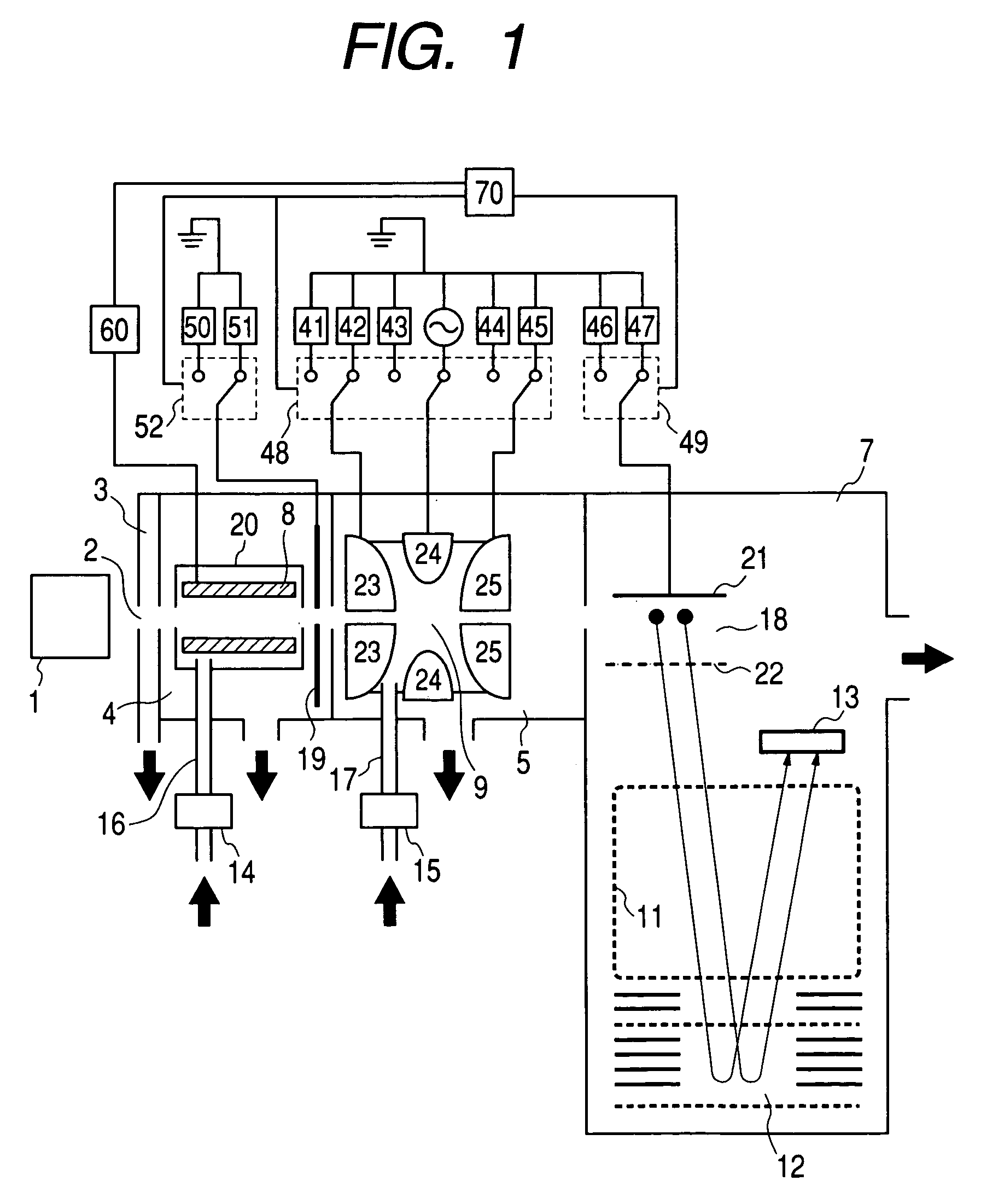
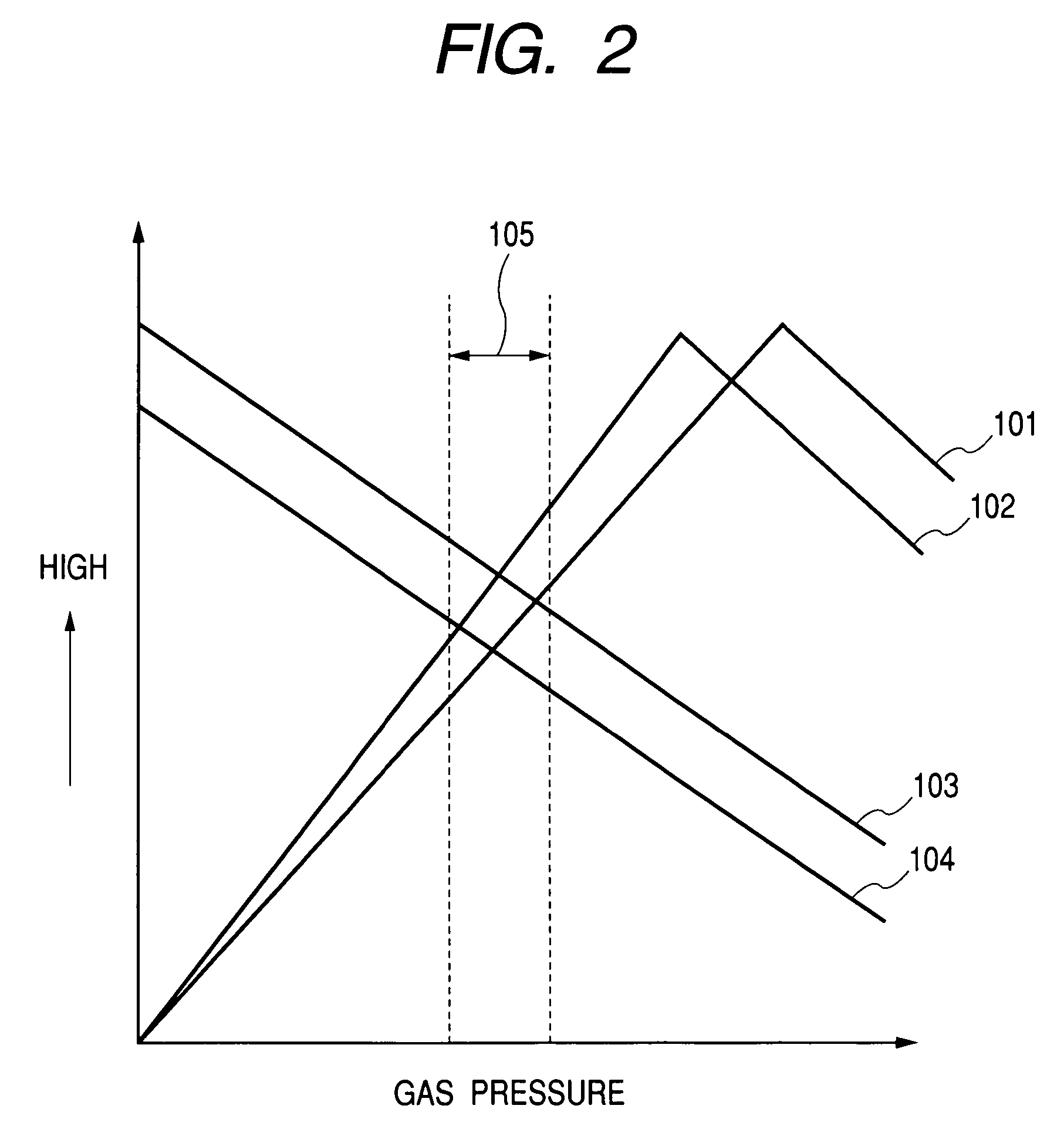
ActiveUS7034287B2Maximum efficiencyMaximize resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryImage resolution
Disclosed is a mass spectrometer combining an ion trap and a TOFMS non-coaxially, wherein ion trapping efficiency, mass resolution, and CID efficiency can be maximized. The present invention relates to the mass spectrometer combining the ion trap and the TOFMS non-coaxially, having a mass filter disposed between an ion source and an ion trap and a controller for controlling the gas pressure inside the ion trap and the gas pressure inside the mass filter independently, wherein the gas pressure inside the ion trap is set to the level higher than that inside the mass filter.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com