Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Cell geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
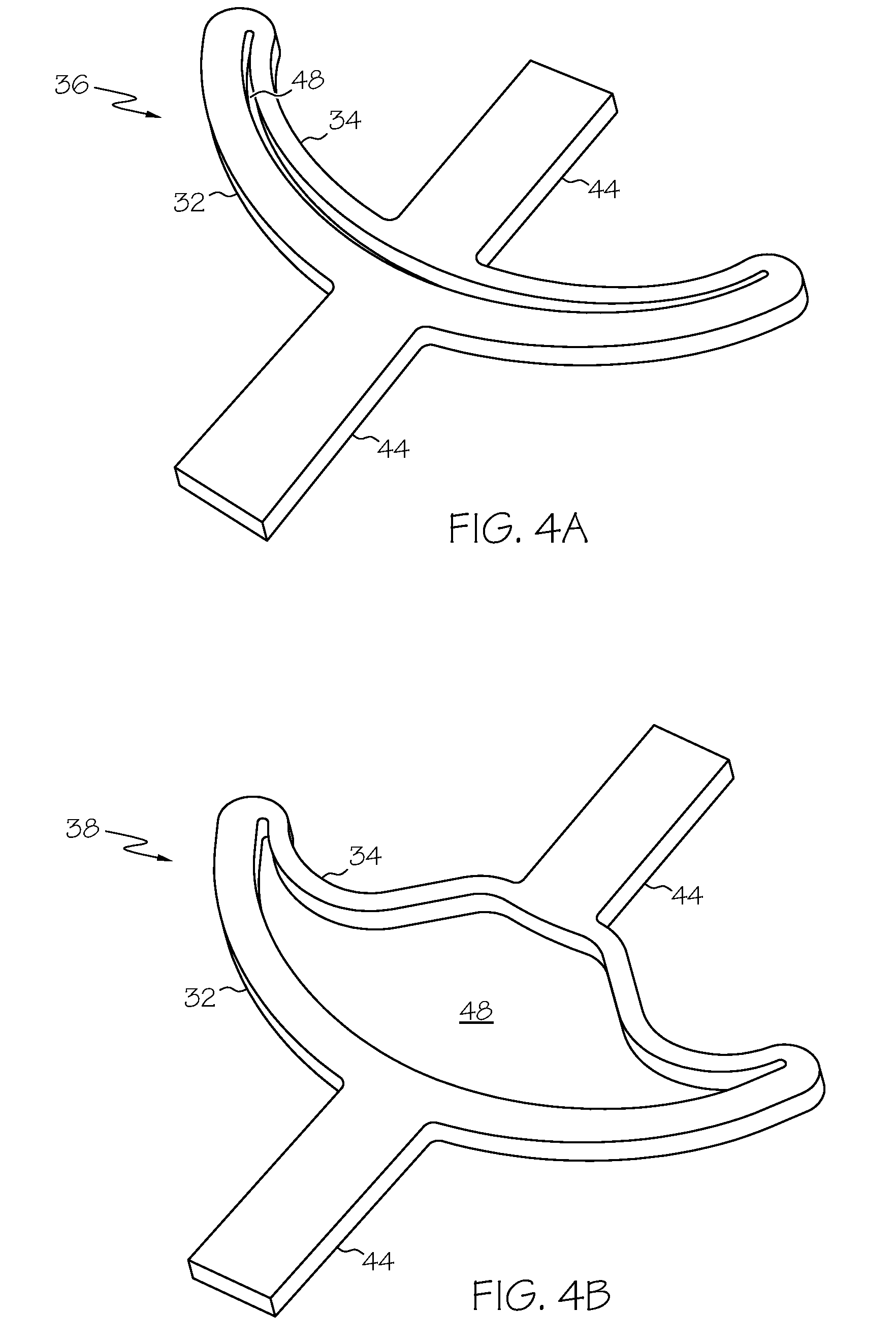
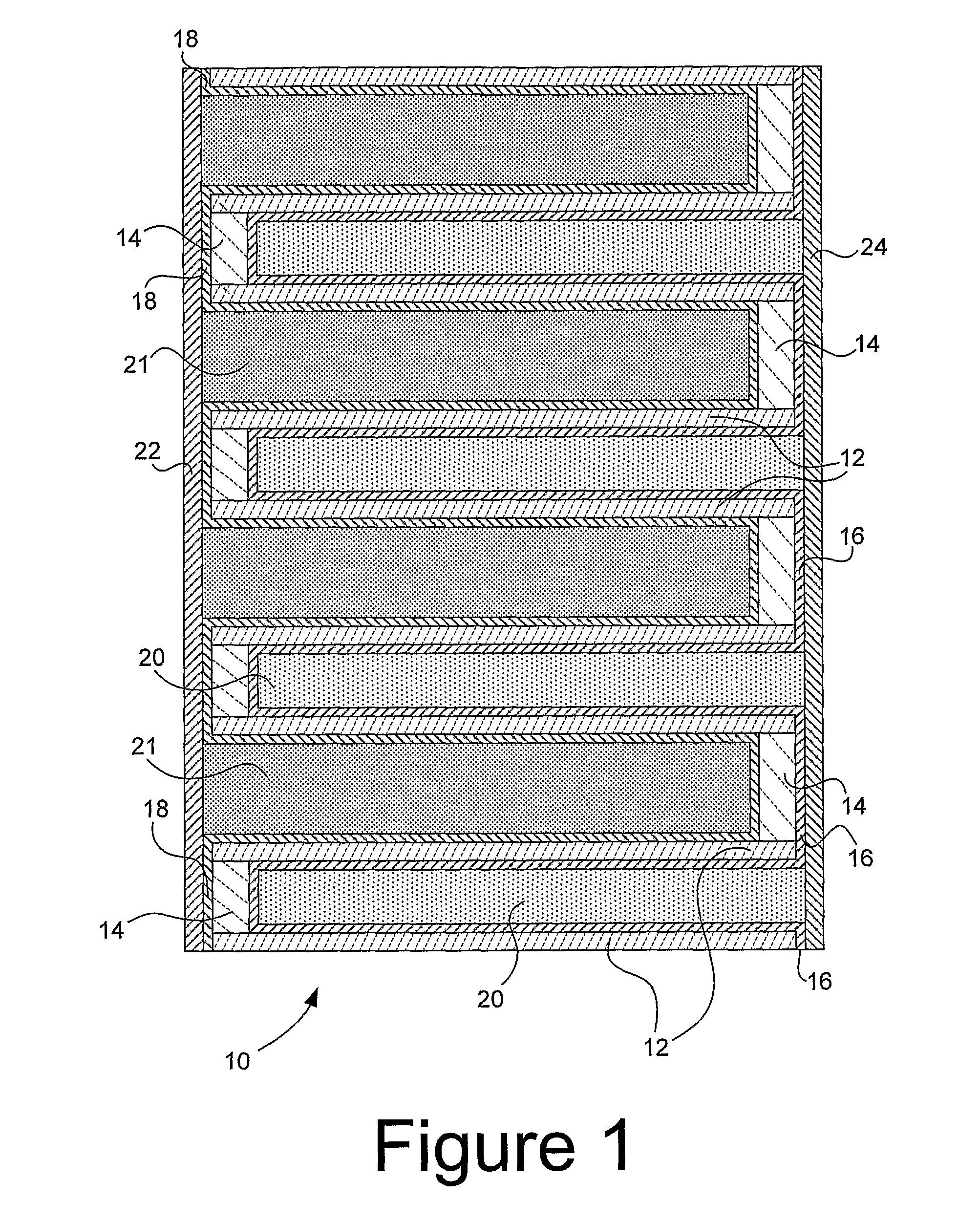
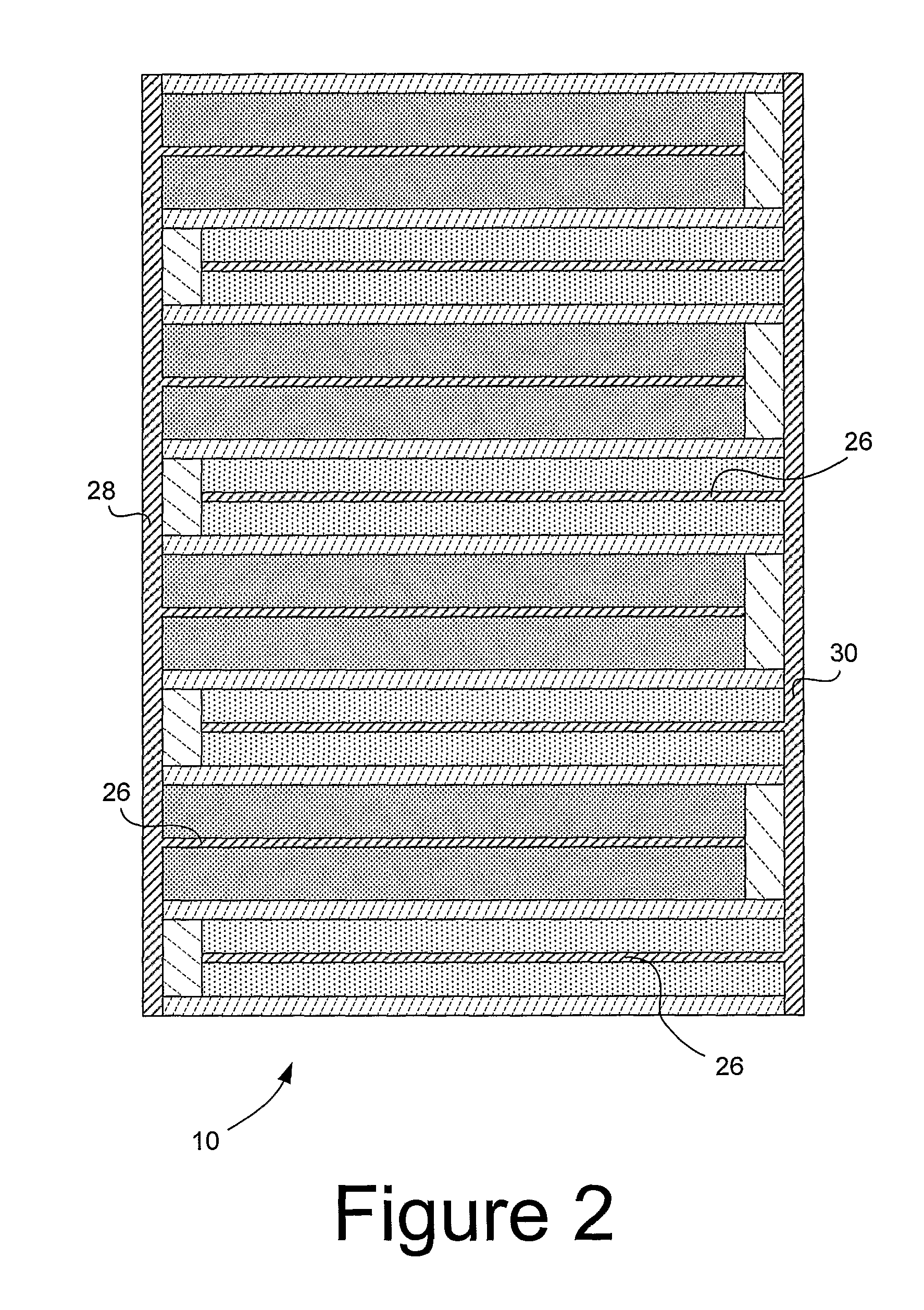
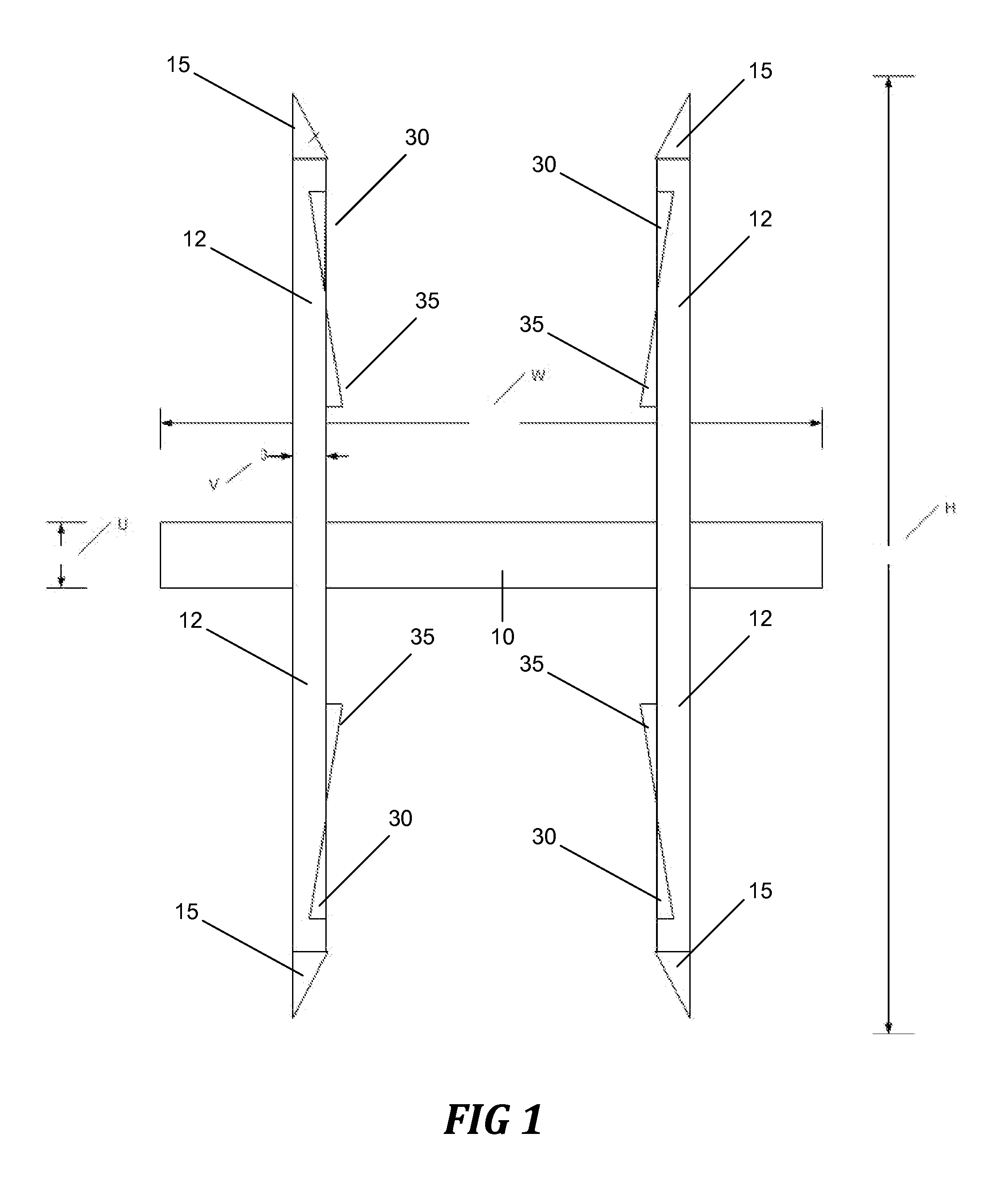
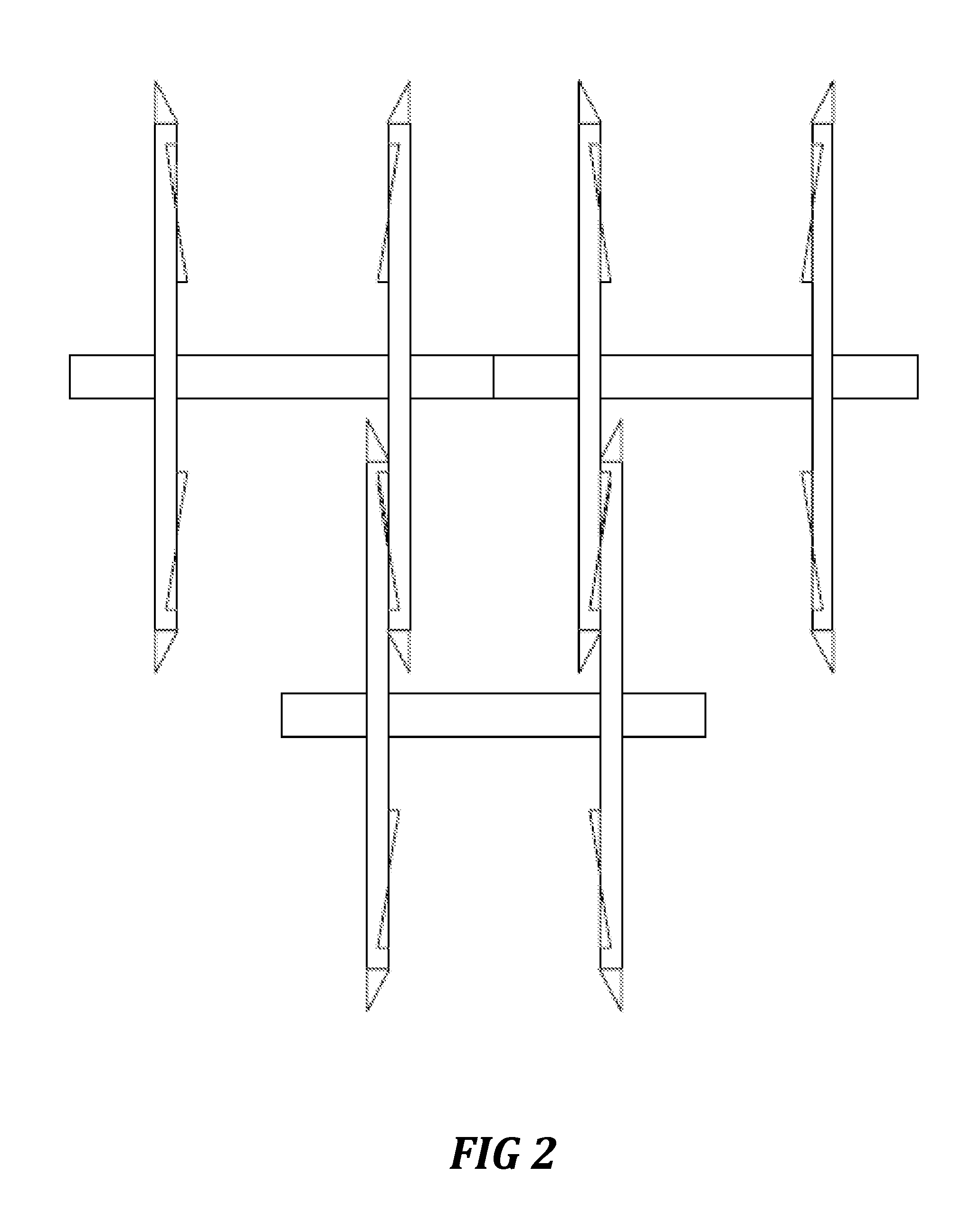
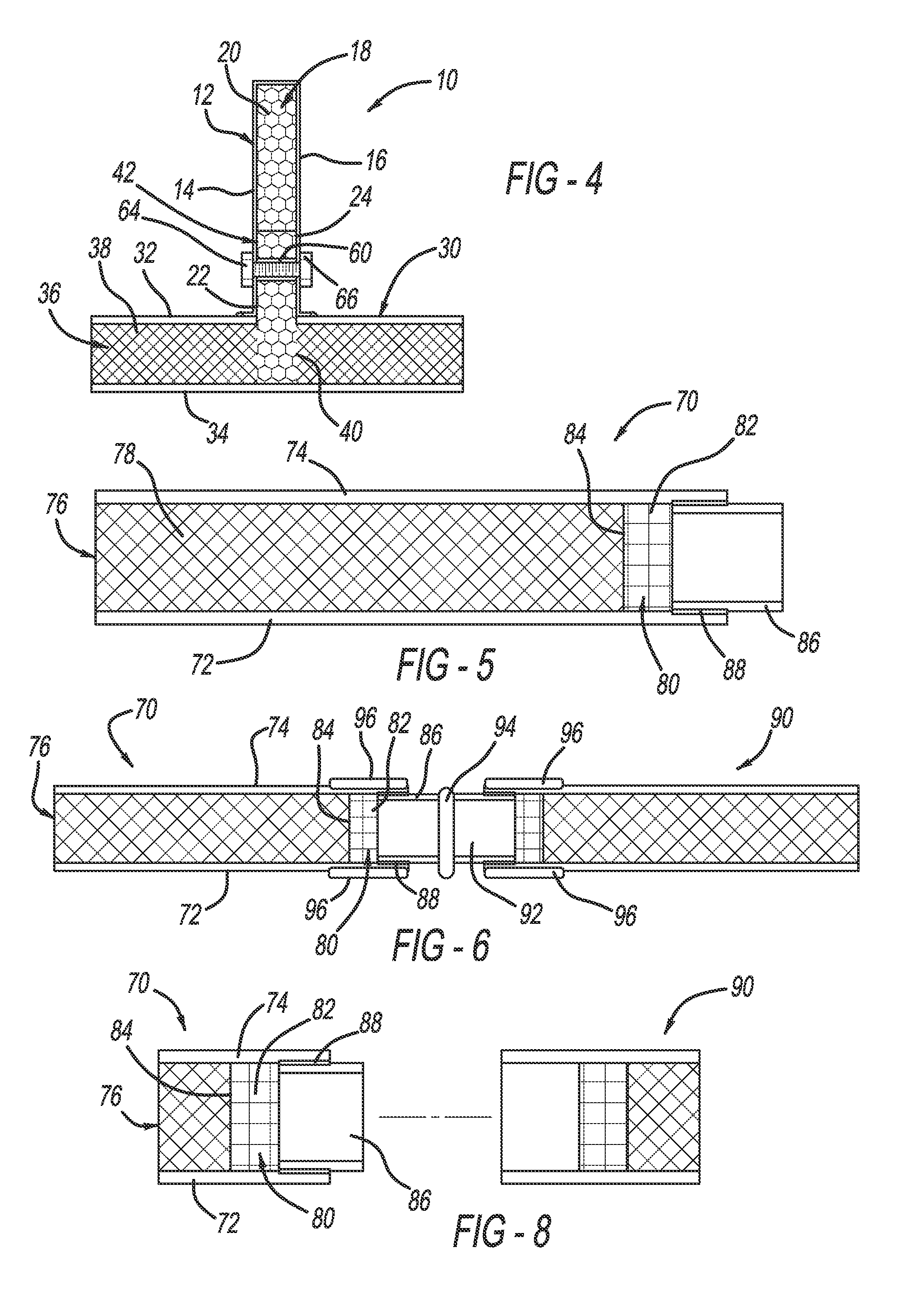
Bi-stable bifurcated stent petal geometry
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Non-latitude and vertically mounted solar energy concentrators
InactiveUS20130312811A1Maximum possible benefitImprove performancePV power plantsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusMultiplexingLength wave
A solar-energy concentrator optimized for operating in a substantially vertical orientation and method for collecting sunlight with such concentrator. The concentrator includes a photovoltaic (PV) module having a PV cell and layers containing diffraction gratings that may be spatially stacked or multiplexed. Diffraction gratings define corresponding diffraction patterns optimized for solar energy harvesting depending on which direction the concentrator is facing. Additionally, a method of designing a hologram for concentrating solar energy onto an adjacent photovoltaic chip is provided. The method includes selecting a photovoltaic chip material, selecting a photovoltaic cell geometry, selecting a first construction angle, selecting an installation latitude, selecting an installation tilt angle, and modeling hologram performance as a function of a second construction angle and a design wavelength.
Owner:PRISM SOLAR TECH
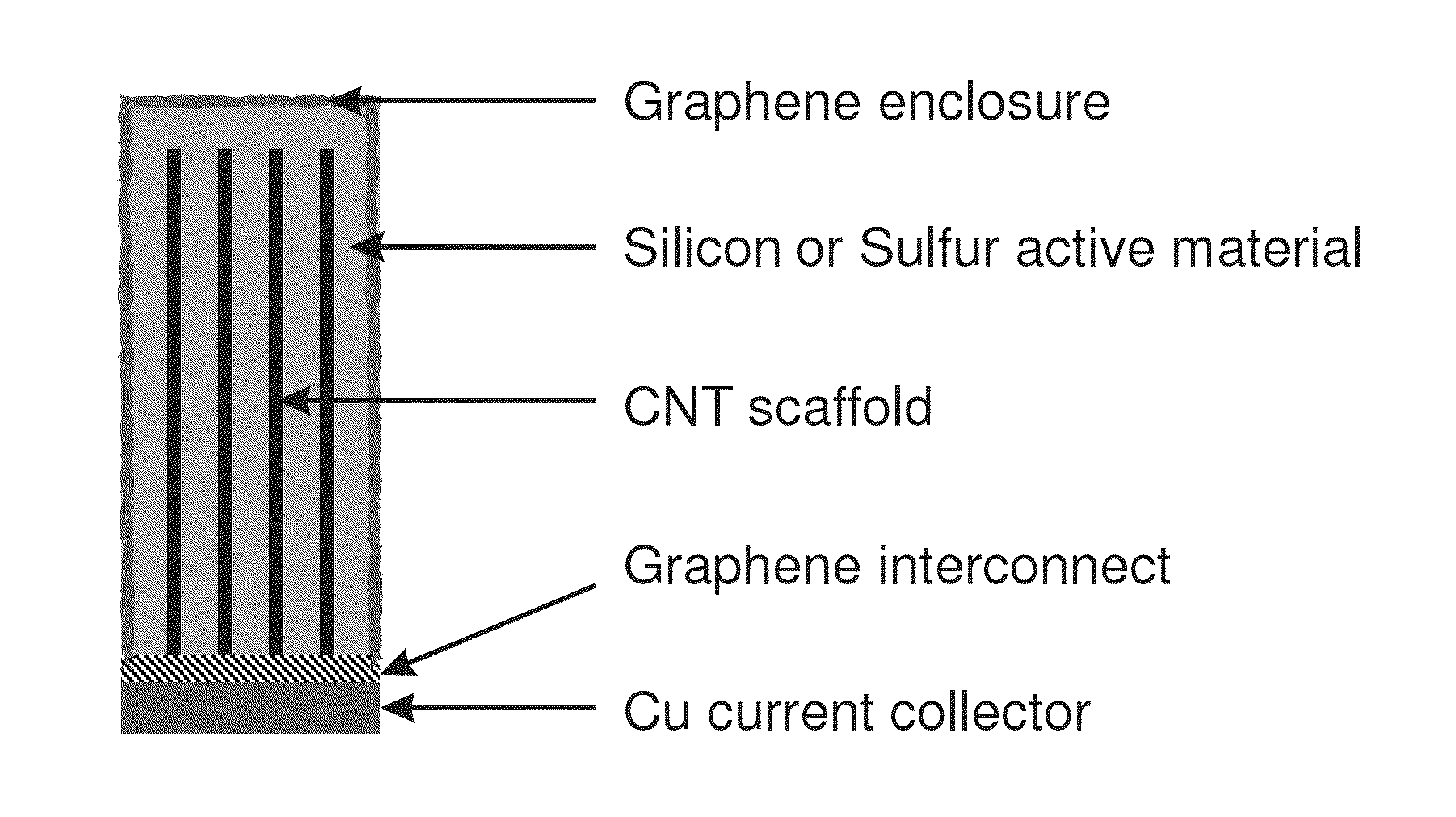
Carbon Nanotubes - Graphene Hybrid Structures for Separator Free Silicon - Sulfur Batteries
ActiveUS20150010788A1Improve power performanceImprove cycle lifeMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureMetallic lithiumDischarge rate
Provided herein are electrochemical systems and related methods of making and using electrochemical systems. Electrochemical systems of the invention implement novel cell geometries and composite carbon nanomaterials based design strategies useful for achieving enhanced electrical power source performance, particularly high specific energies, useful discharge rate capabilities and good cycle life. Electrochemical systems of the invention are versatile and include secondary lithium ion cells, such as silicon-sulfur lithium ion batteries, useful for a range of important applications including use in portable electronic devices. Electrochemical cells of the present invention also exhibit enhanced safety and stability relative to conventional state of the art lithium ion secondary batteries by using prelithiated active materials to eliminate the use of metallic lithium and incorporating carbon nanotube and / or graphene, composite electrode structures to manage residual stress and mechanical strain arising from expansion and contraction of active materials during charge and discharge.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Multifunctional periodic cellular solids and the method of making same
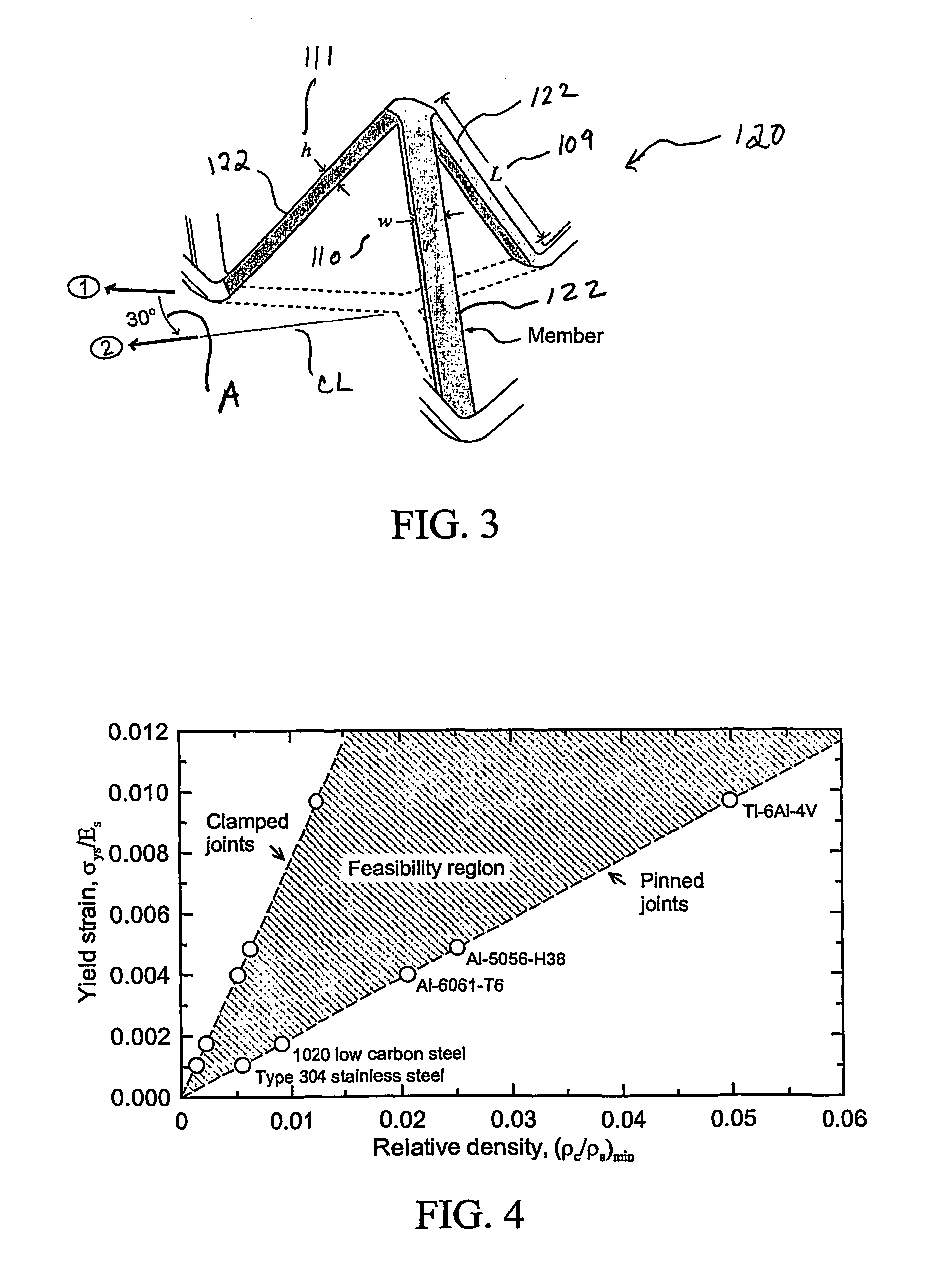
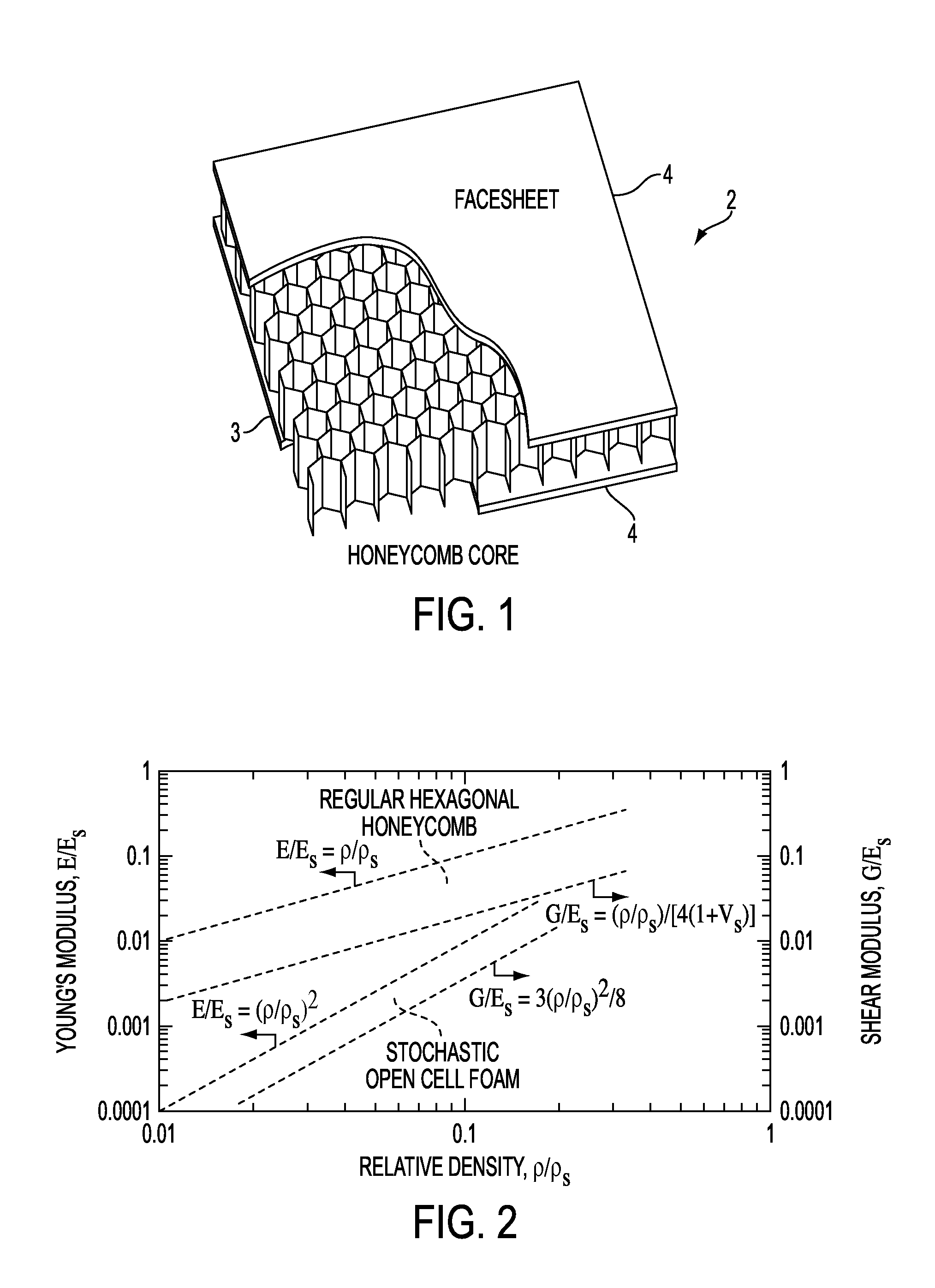
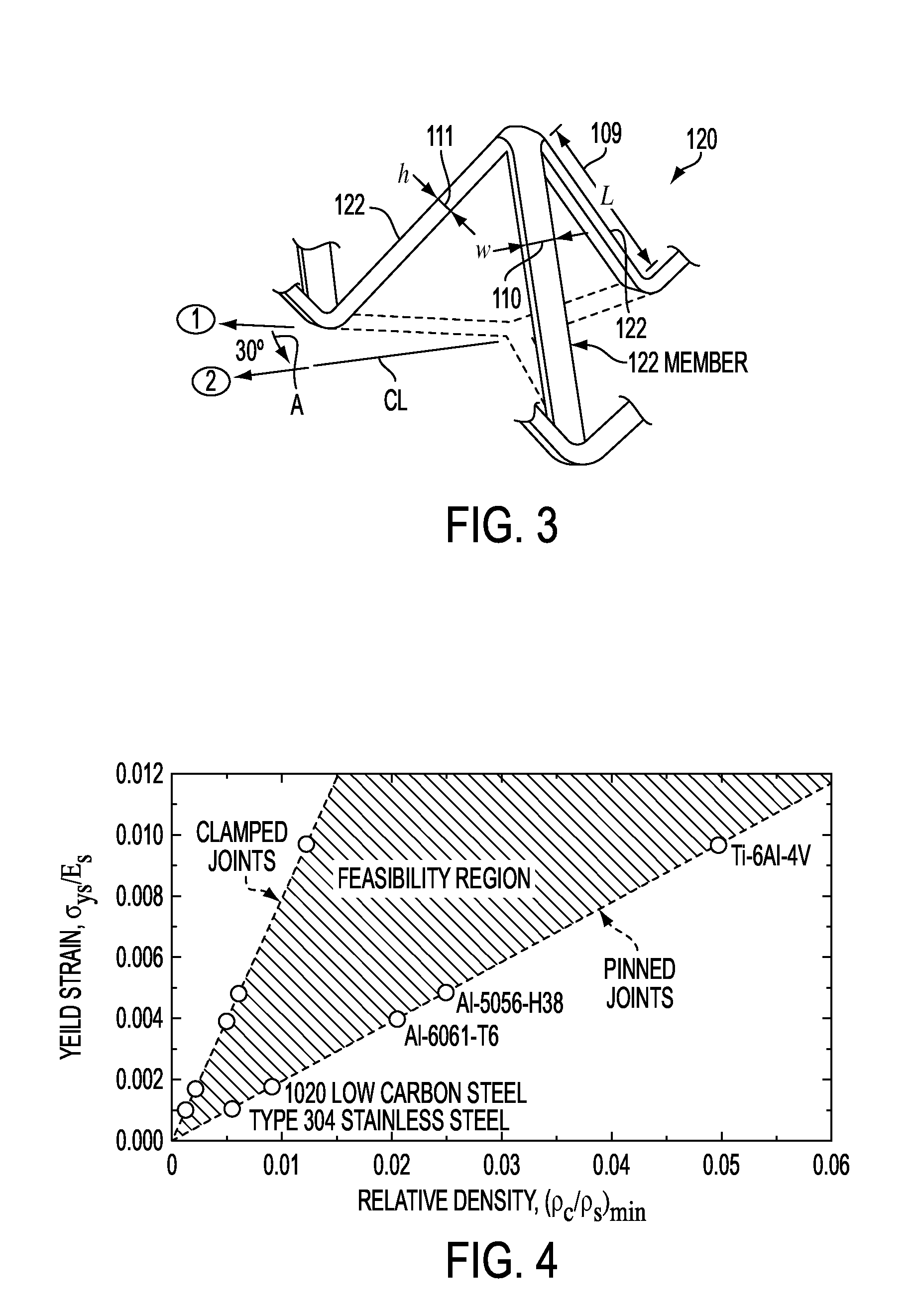
Methods of making truss-based periodic cellular solids that have improved structural properties and multifunctional design. Many materials (metals, ceramics, glasses, polymers, composites and even semiconductors) can be shaped into cellular, truss-like architectures with open, closed or mixed types of porosity and then very uniformly arranged in controlled, three-dimensional space-filling arrays. The truss-like elements do not necessarily have a constant cross-section, nor are they necessarily straight or solid throughout (they could be hollow). Their cross sections can be circular, square, triangular, I-beam or other shapes of interest depending on multifunctional needs. When bonded together by solid state, liquid phase, pressing or other methods at points of contact, a cellular structure of highly repeatable cell geometry and few imperfections results. The bonds hold the truss elements together in a desired configuration, allow load to be efficiently transferred amongst them and make the resulting structure significantly more rigid when bent, compressed or sheared. These constructed cellular solids offer a broad range of multifunctional structural uses with a tremendous freedom for choosing the truss type, orientation and distribution. Multiple materials can be intermixed.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Composite conformable pressure vessel
InactiveUSRE41142E1Trend downIncrease pressureGas handling applicationsLarge containersLine tubingCompressed natural gas
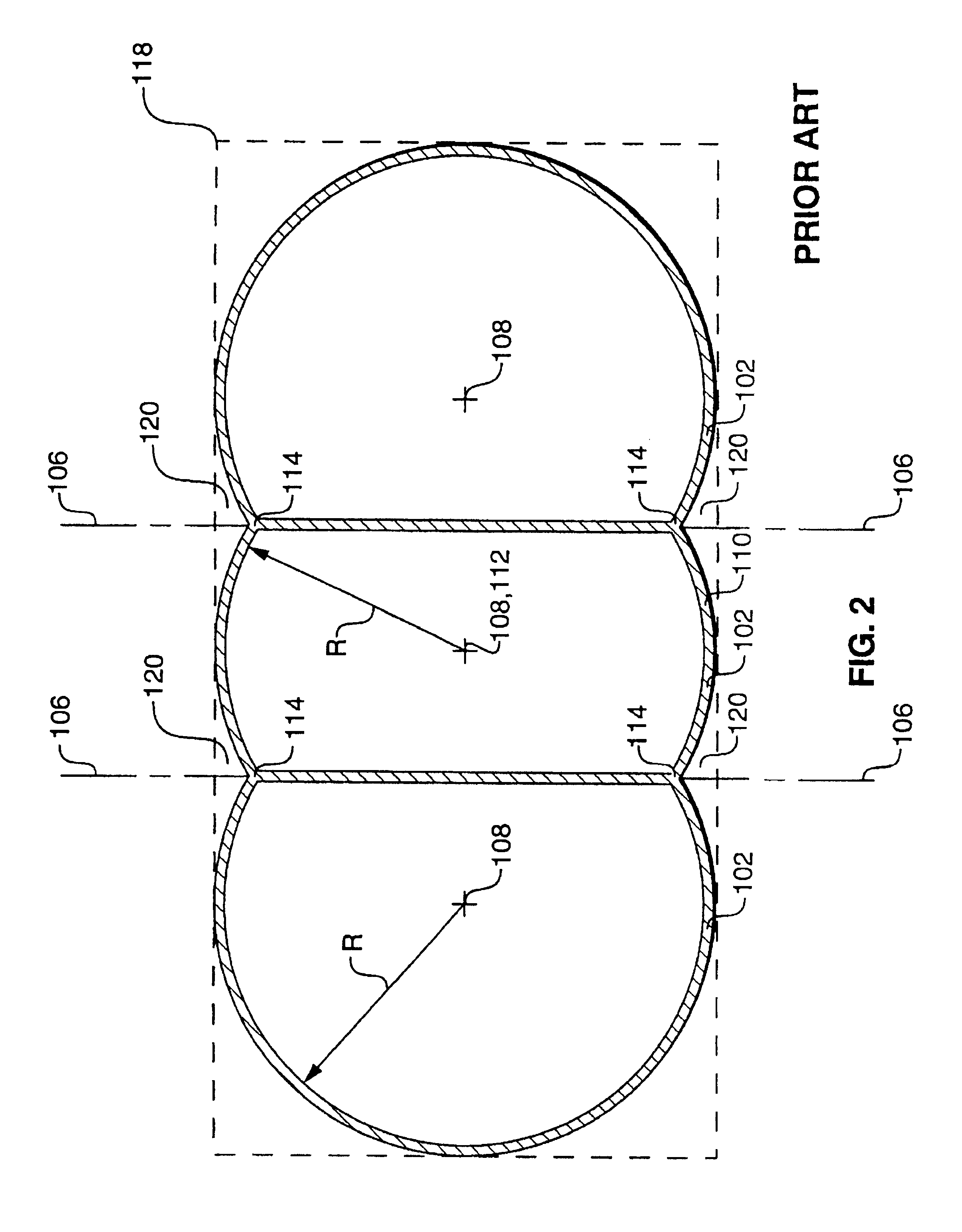
A pressure vessel for holding a pressurized fluid such as compressed natural gas (“CNG”) includes two end cells and zero or more interior cells. The cell geometry ensures that the cells meet one another at tangential circular surfaces, thereby reducing the tendency of adjacent cells to peel apart. A web secured about the cells includes two sheets that are tangent to the cells. Unused volumes between the cells and the web contain wedges of foam or rubber. A valve provides fluid communication between the interior of the pressure vessel and a pressurized fluid line. The filled weight of one pressure vessel does not exceed the filled weight of a conventional gasoline tank that occupies substantially the same space as the pressure vessel. The pressure vessel may be configured with exterior recesses for engaging conventional gasoline tank straps.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Multifunctional Periodic Cellular Solids and the Method of Making the Same
InactiveUS20110250385A1Efficient transferSimple designLaminationLamination apparatusPorosityMulti-function structure
Methods of making truss-based periodic cellular solids that have improved structural properties and multifunctional design. Many materials (metals, ceramics, glasses, polymers, composites and even semiconductors) can be shaped into cellular, truss-like architectures with open, closed or mixed types of porosity and then very uniformly arranged in controlled, three-dimensional space-filling arrays. The truss-like elements do not necessarily have a constant cross-section, nor are they necessarily straight or solid throughout (they could be hollow). Their cross sections can be circular, square, triangular, I-beam or other shapes of interest depending on multifunctional needs. When bonded together by solid state, liquid phase, pressing or other methods at points of contact, a cellular structure of highly repeatable cell geometry and few imperfections results. The bonds hold the truss elements together in a desired configuration, allow load to be efficiently transferred amongst them and make the resulting structure significantly more rigid when bent, compressed or sheared. These constructed cellular solids offer a broad range of multifunctional structural uses with a tremendous freedom for choosing the truss type, orientation and distribution. Multiple materials can be intermixed.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
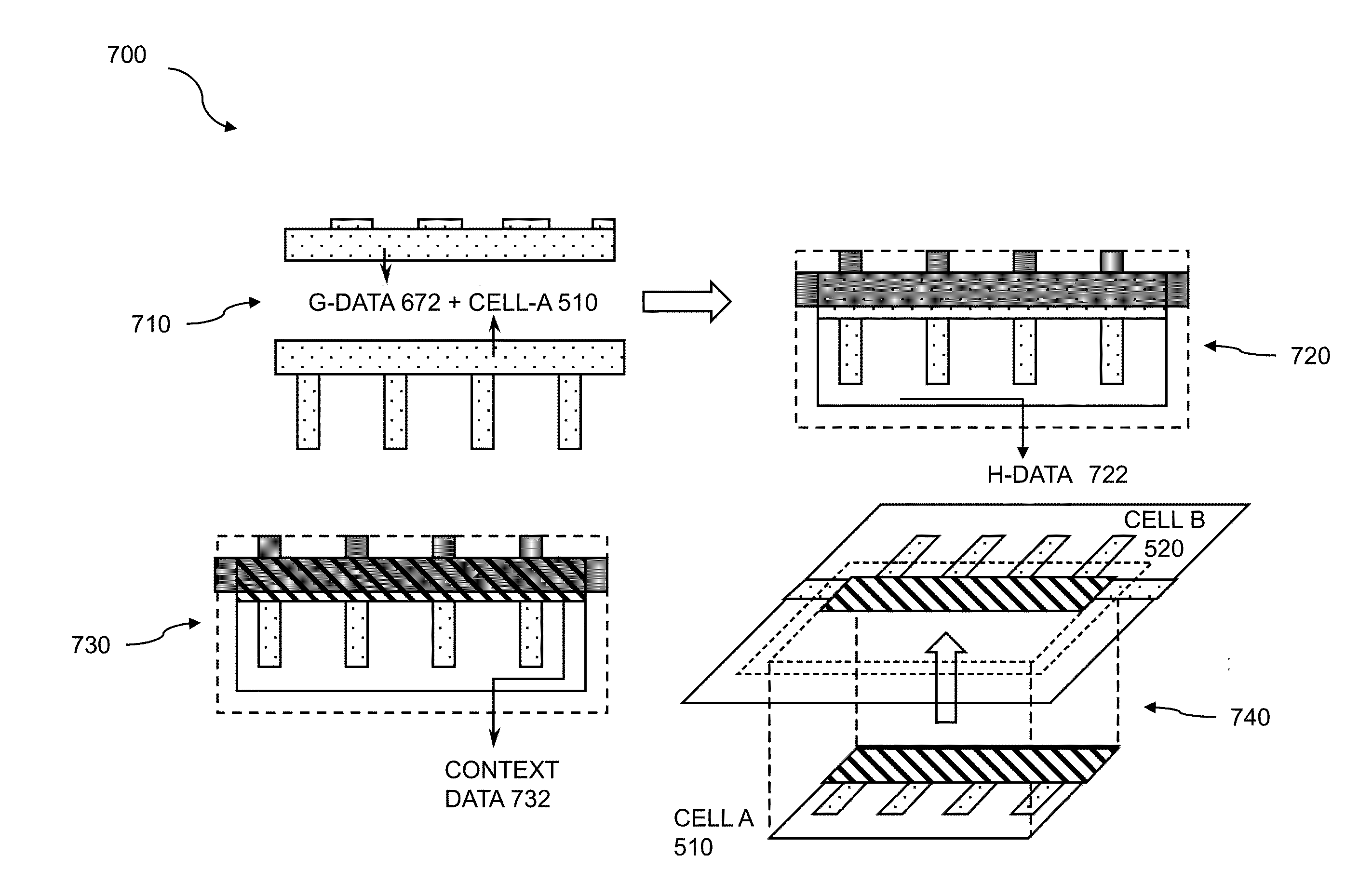
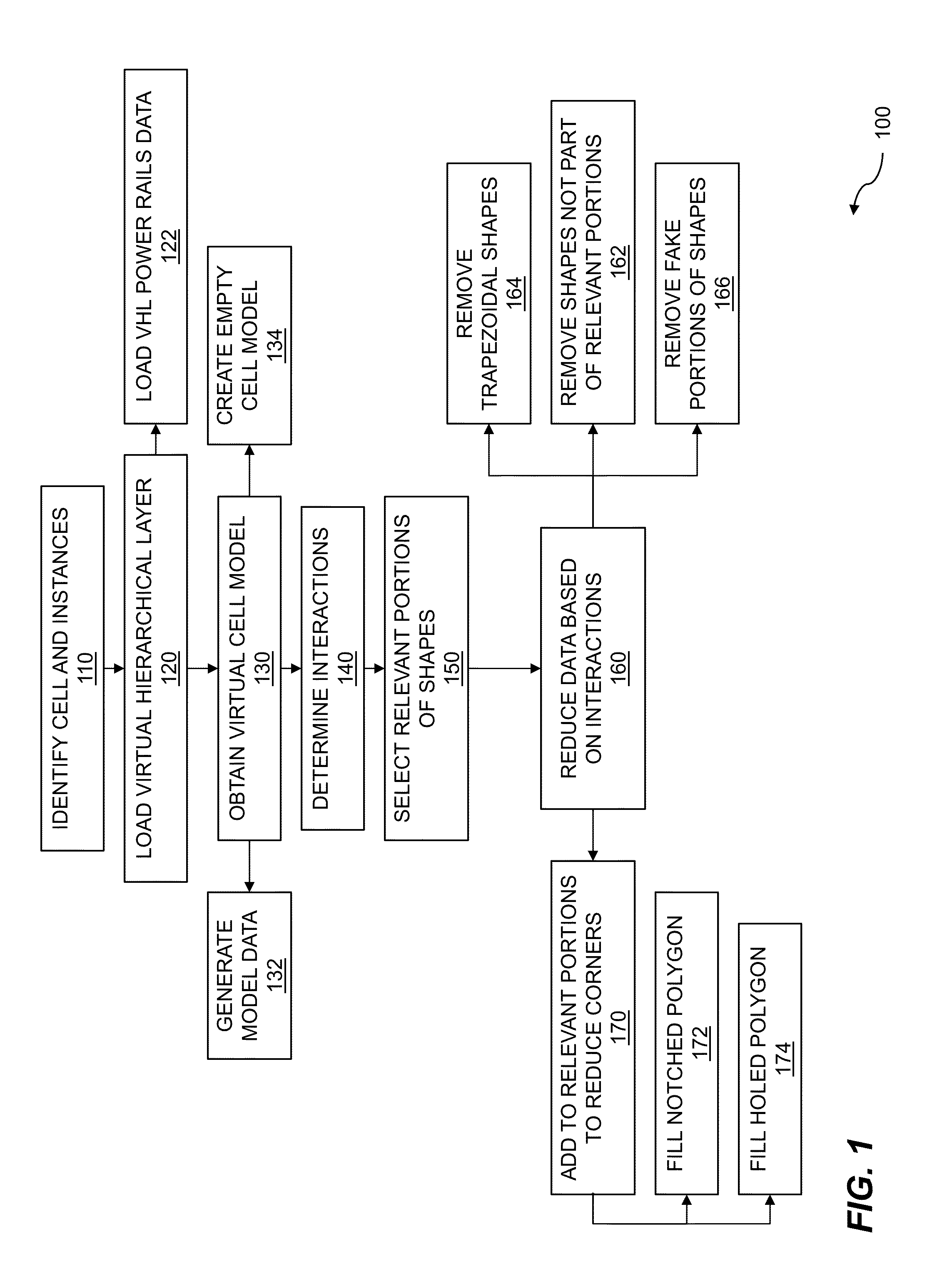
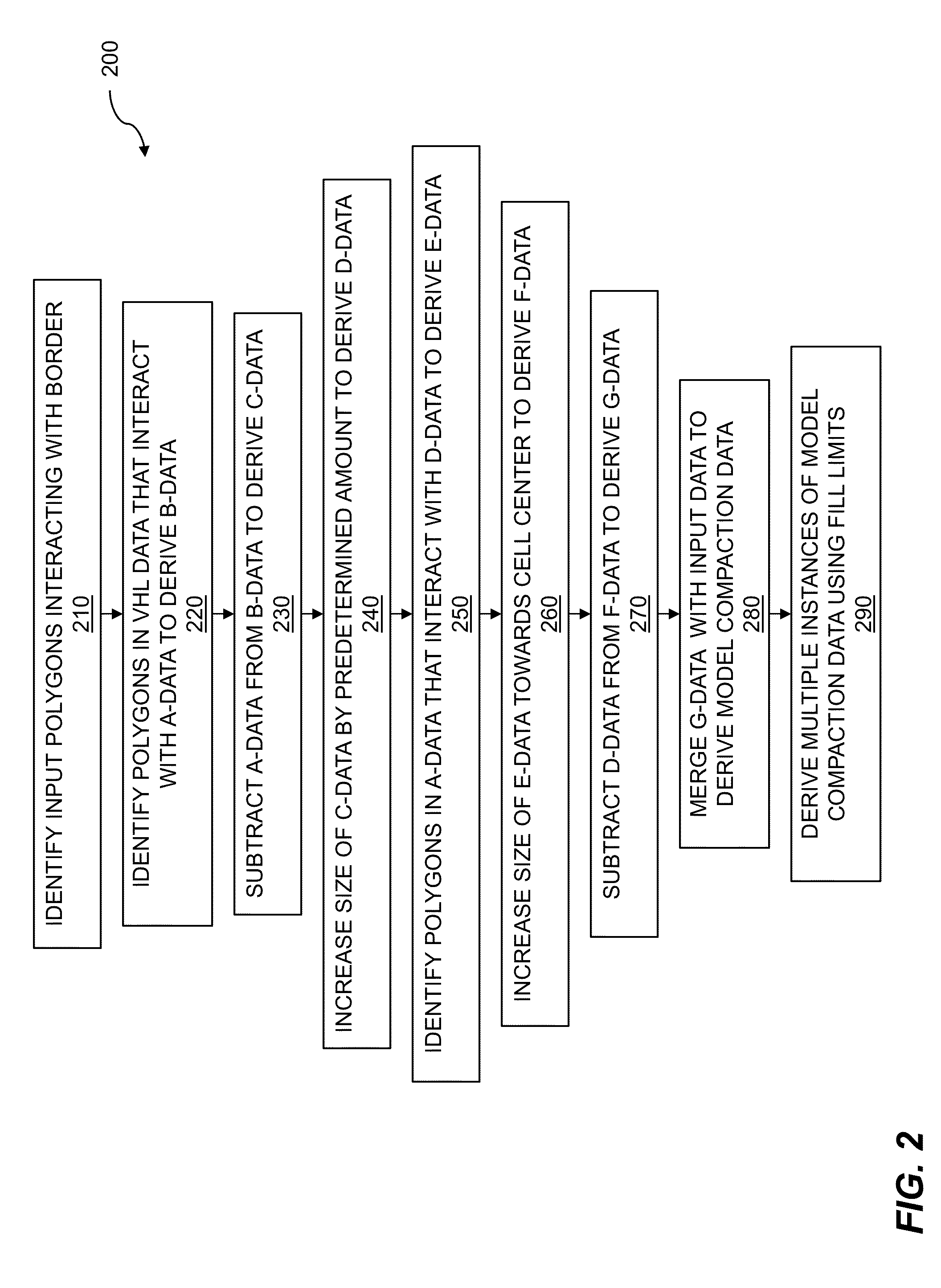
Virtual cell model geometry compression
ActiveUS20150339432A1Small sizeReduce in quantityDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designGeometry compressionComputer architecture
Semiconductor designs are large and complex, typically consisting of numerous circuits called cells. To handle complexity, hierarchical structures are imposed on the semiconductor design to help accomplish analysis, simulation, verification, and so on. The hierarchical structures define architecture, behavior, function, structure, etc. of the semiconductor design. Virtual cells are constructed to compress cell geometries and ease the various design tasks. A cell and multiple instances of the cell are identified within the semiconductor design and the virtual hierarchical levels describing the design. Virtual hierarchical layer (VHL) data based on the cell is loaded. A virtual cell model representative of the cell is obtained. Interactions between cell data and VHL data are determined, and relevant portions of shapes are selected. Data within the virtual cell model is reduced based on the determined interactions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
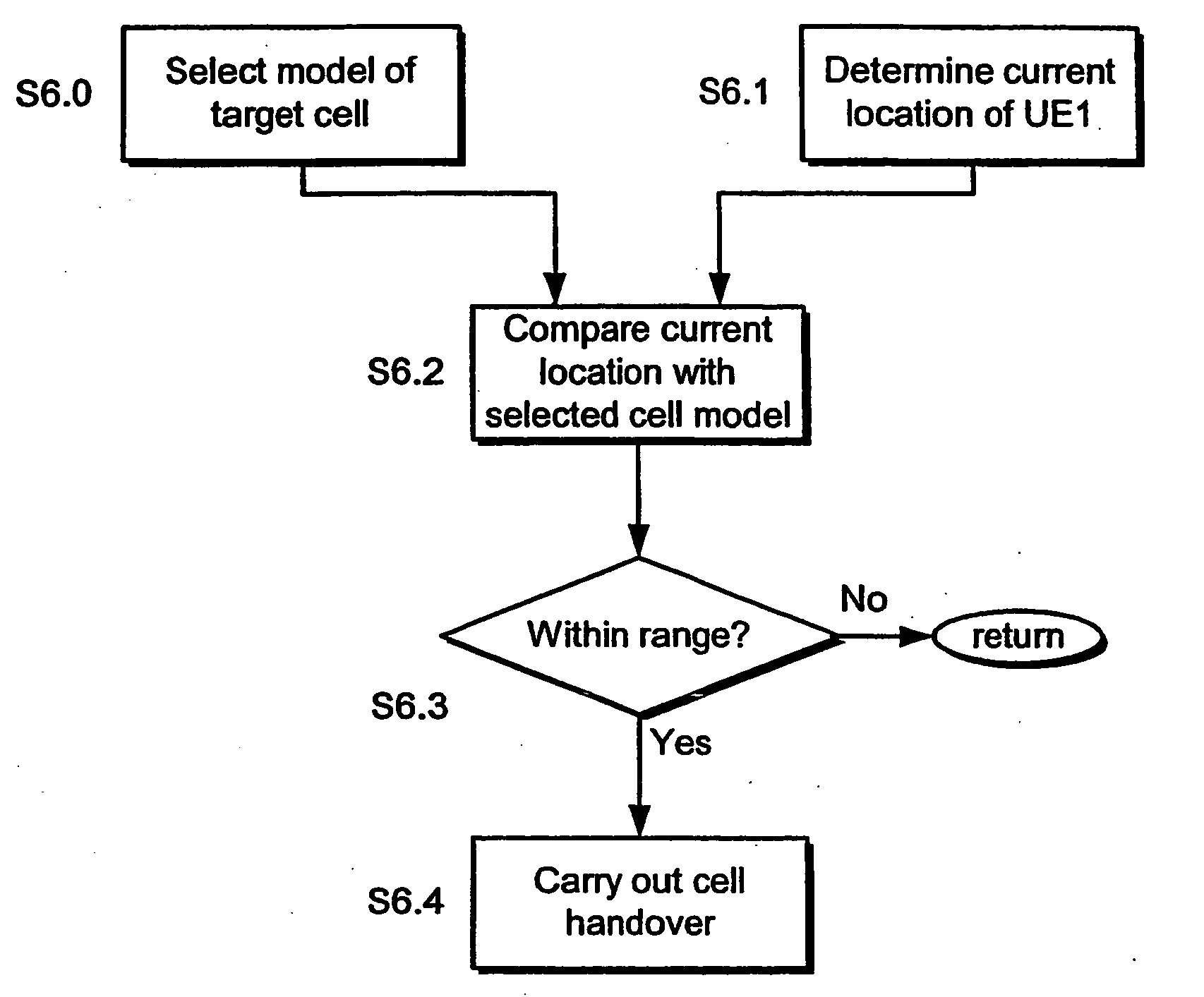
Approximating cell geometry in a cellular transmission system
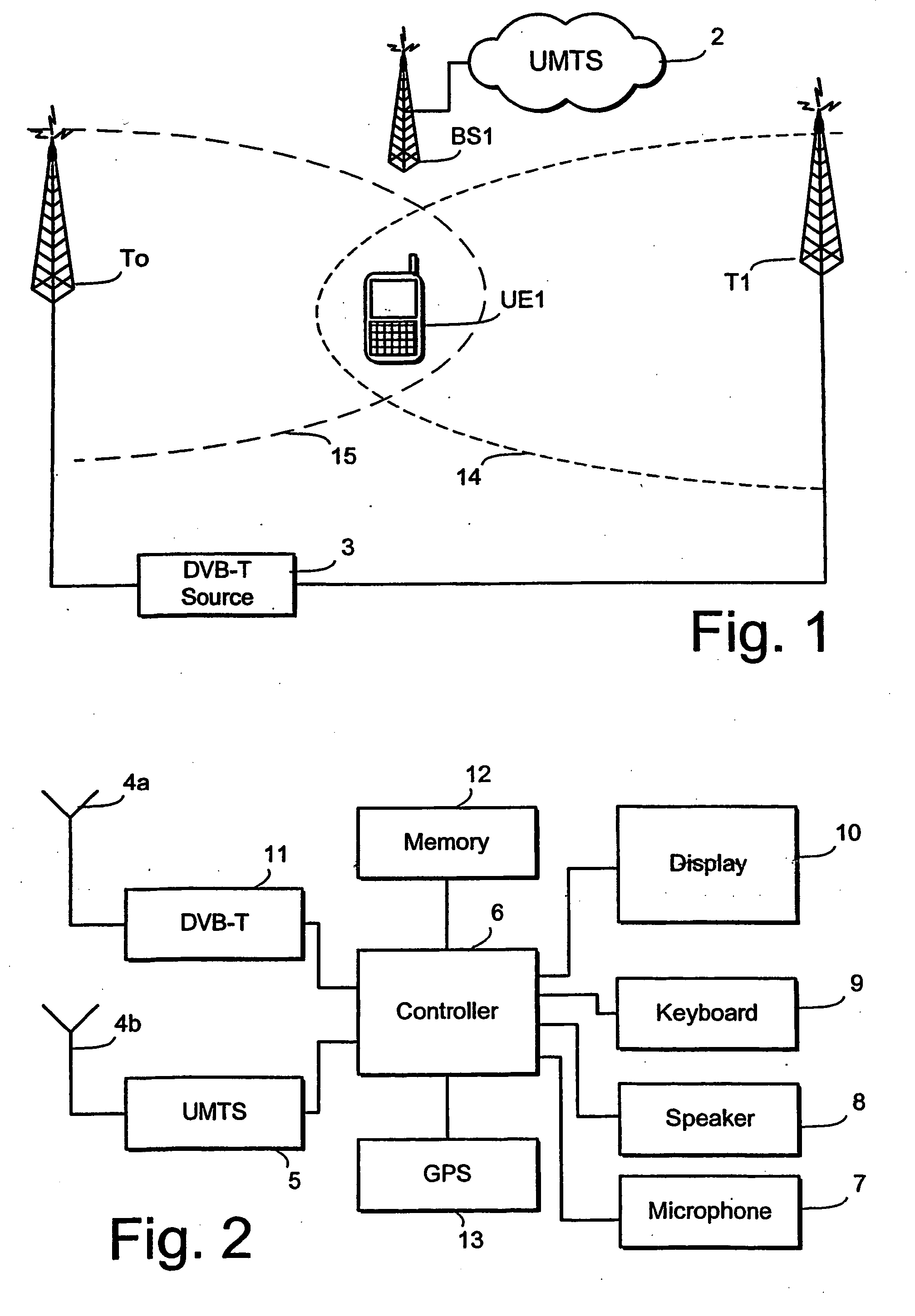
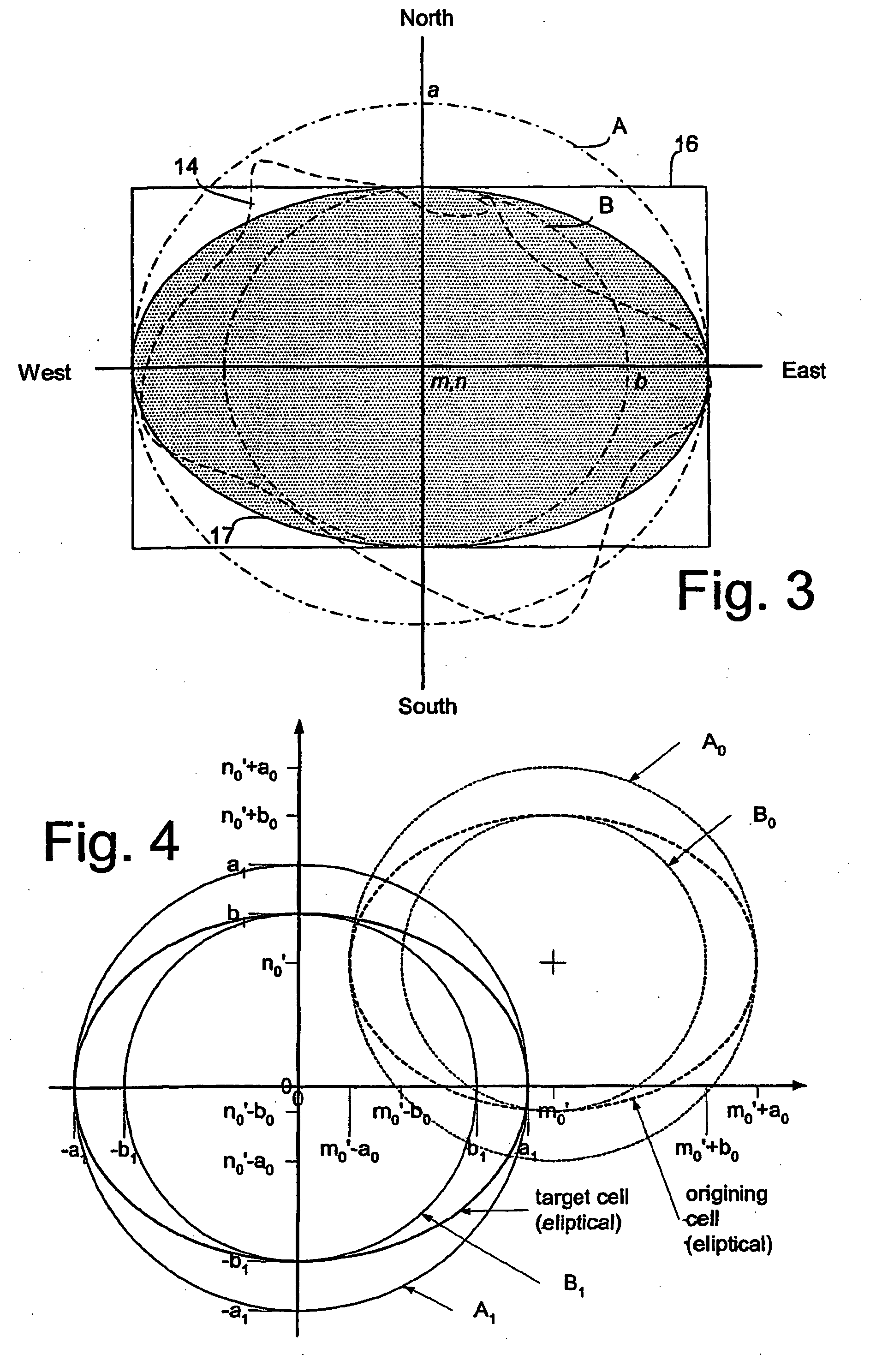
InactiveUS20050272429A1Improve handover processingImproves the accuracy of cell approximationBroadcast-related systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransfer systemComputer science
Approximating cell geometry in a cellular transmission system User equipment (UE1) for use in a cellular transmission system comprising a processor configuration (6) to provide data corresponding to first and second parameters (a, b) for dimensional extents of the cell, and to select one of a plurality of different approximate geometrical configurations for the cell in dependence on the relationship between the values of said parameters. The selected cell approximation is then compared with the UE's current location to determine if a cell handover is to be made. The cell approximation technique is described in relation to a DVB-T network.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Bi-Stable Bifurcated Stent Petal Geometry
A stent has a substantially cylindrical tubular body with at least one expandable side branch that has a plurality of members. The plurality of members includes at least one first member having a first width and at least one second member having a second width, where the first width is greater than the second width. Each of the at least one first members and each of the at least one second members define a cell that has at least two stable cell geometries.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Improved electric current sensing and management system for electrolytic plants
Owner:KHETCH PTI LTD
Microstructure biomaterials and fabrication methods therefor
ActiveUS9631171B2Additive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMicromirror arrayPolymer
Methods and systems for fabricating a micro-structured biomaterial include printing a three-dimensional structure using polymerizing radiation modulated by a digital micromirror array to project microstructure patterns into a pre-polymer material to form one or more porous scaffold sheets. The microstructure patterns have a unit-cell geometry that exhibits a negative Poisson ratio that is tunable in magnitude.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cellular honeycomb hybrid capacitors with non-uniform cell geometry
InactiveUS20090303663A1High densityHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrodesNon oxide ceramicsCordierite
An hybrid capacitor includes an electrically non-conductive rigid or semi-rigid porous honeycomb structure having cells extending along a common direction, the cells having a plurality of cross-sectional shapes. The honeycomb structure is desirably formed of a material that is stable at temperatures of 3000 or more, such that high temperature processing can be used to help ensure high purity of the final product. The material of the structure may desirably be an oxide or non-oxide ceramic, such as cordierite, silicon nitride, alumina, aluminum titanate, zircon, glass, or glass-ceramic. The plurality of shapes of the cells includes larger shapes in which cells are disposed non-galvanic electrodes, with galvanic electrodes disposed in cells of other shapes.
Owner:CORNING INC
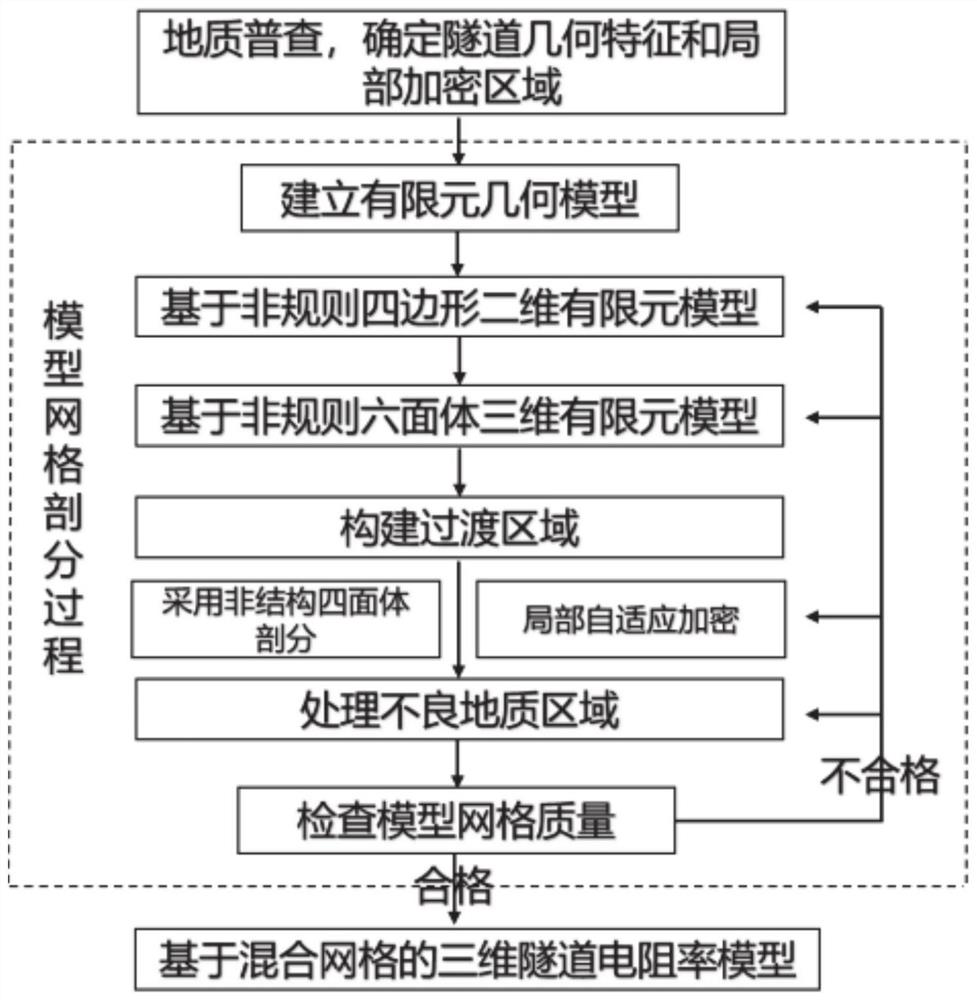
Tunnel resistivity modeling method and system based on hybrid grid
PendingCN114117861AReduce discretization errorReduce in quantityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention provides a tunnel resistivity modeling method and system based on a hybrid grid. The method comprises the following steps: determining the physical size, the actual shape, the power supply and acquisition electrode position and the possible unfavorable geological area of a tunnel to be modeled; establishing a finite element geometric model according to the actual shape and size of the tunnel; carrying out mesh generation on the finite element geometric model, carrying out non-structural tetrahedral mesh local encryption subdivision on power supply and acquisition electrode positions and possible unfavorable geological areas, and carrying out mesh generation on other uniform surrounding rock media by adopting an irregular hexahedron to form an optimized model; quality parameters of all units of the optimized model are checked, iterative optimization is carried out on the shapes of the units, so that transition between the units of different sizes and different types is uniform until all the units meet the quality requirements, and the method can well fit a complex structure type and is high in practicability. The discretization error of the model is reduced to a great extent; and the forward modeling precision of an actual tunnel complex environment resistivity method is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of replenishing cells damaged by treatment for cancer
A method of replenishing cells damaged by treatment for cancer comprising removing a sample of peripheral blood containing CD34+ pluripotent adult stem cells from a primate mammal, controllably expanding the cells without differentiation at a rate which produces an expansion factor of at least seven times within seven days while maintaining their three-dimensional geometry and their cell-to-cell support and cell-to-cell geometry, removing any toxic materials from the expanded undifferentiated CD34+ pluripotent adult stem cells, and reintroducing the CD34+ pluripotent adult stem cells into the primate mammal within a time period sufficient to prevent the primate mammal from suffering decreased mobility due to loss of hematopoietic or other cells from a treatment for cancer.
Owner:REGENETECH INC
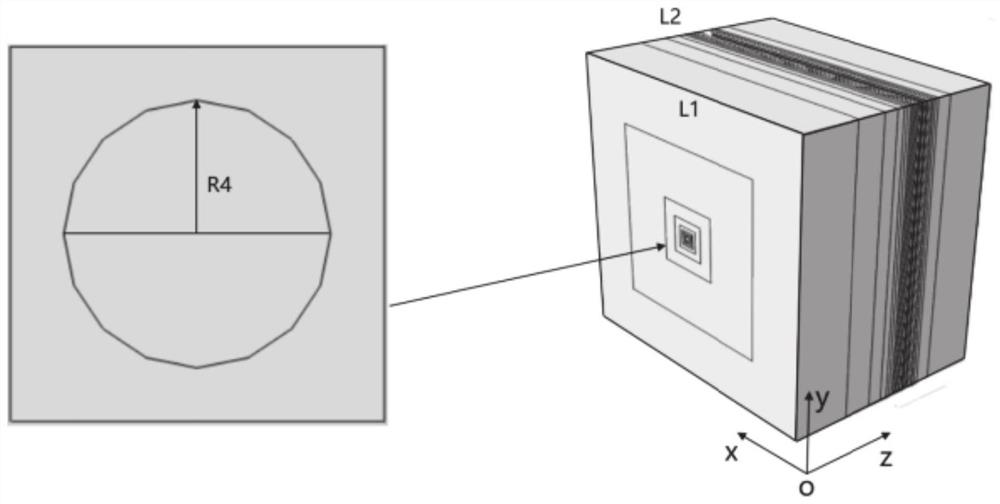
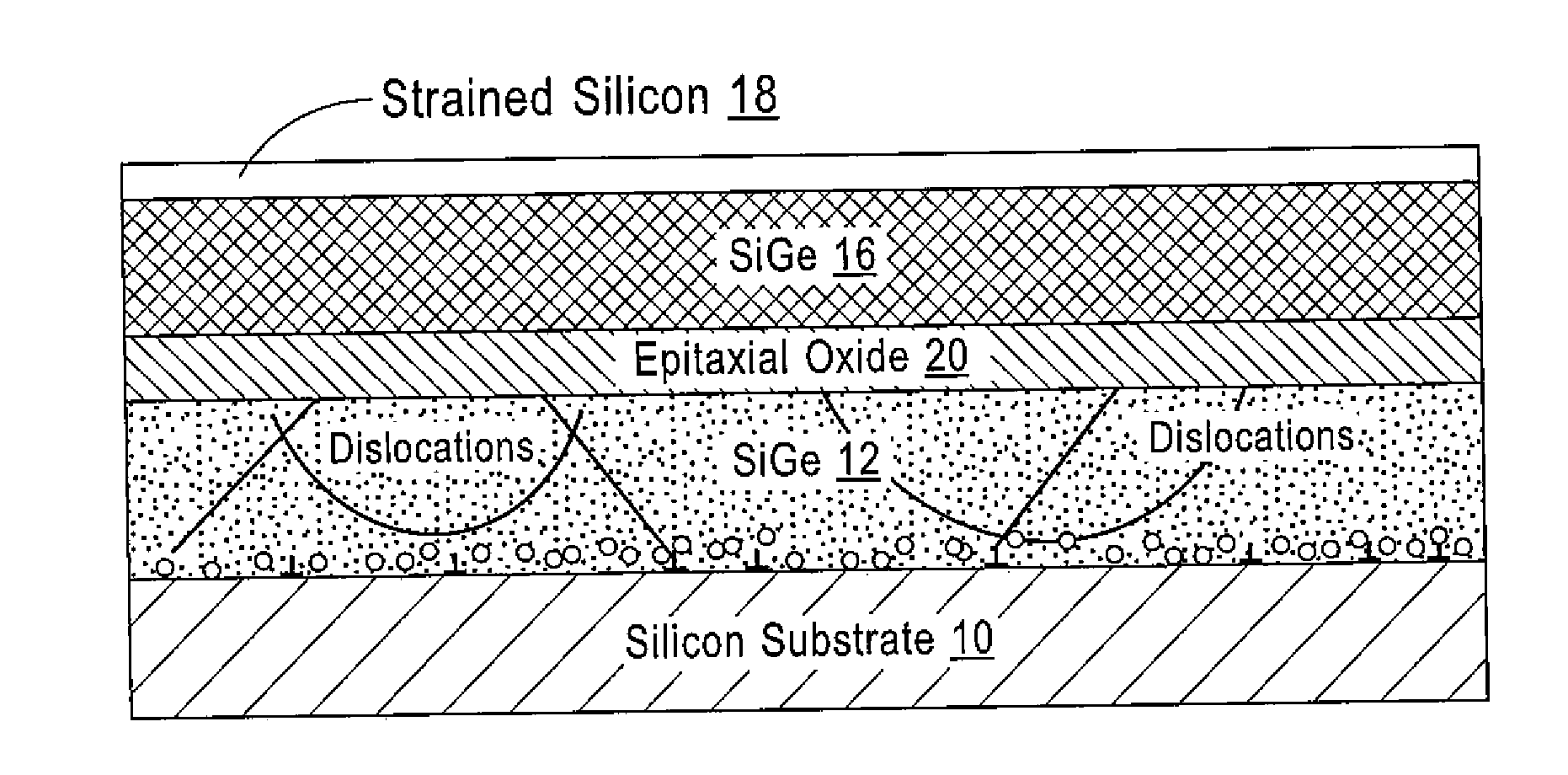
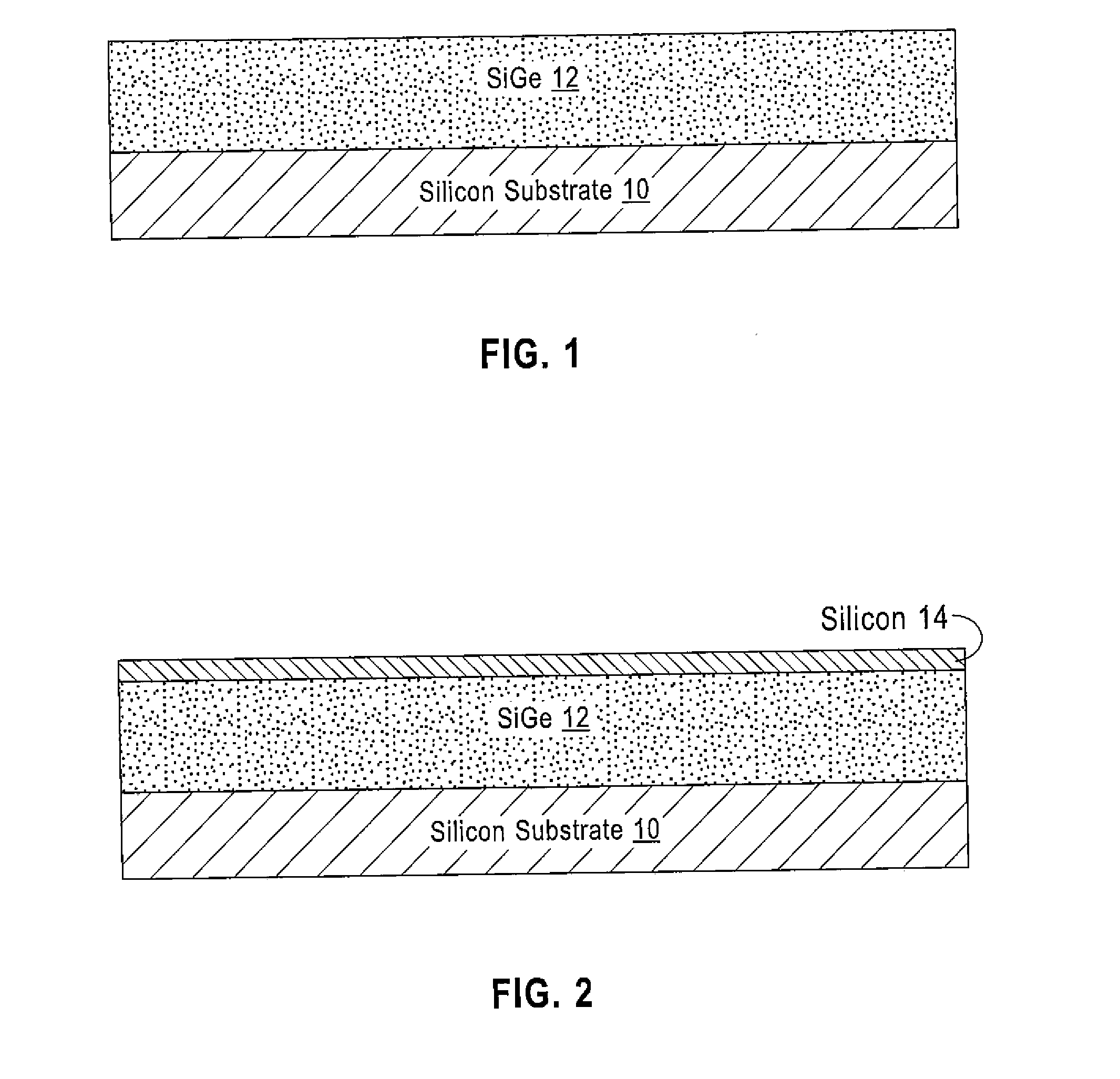
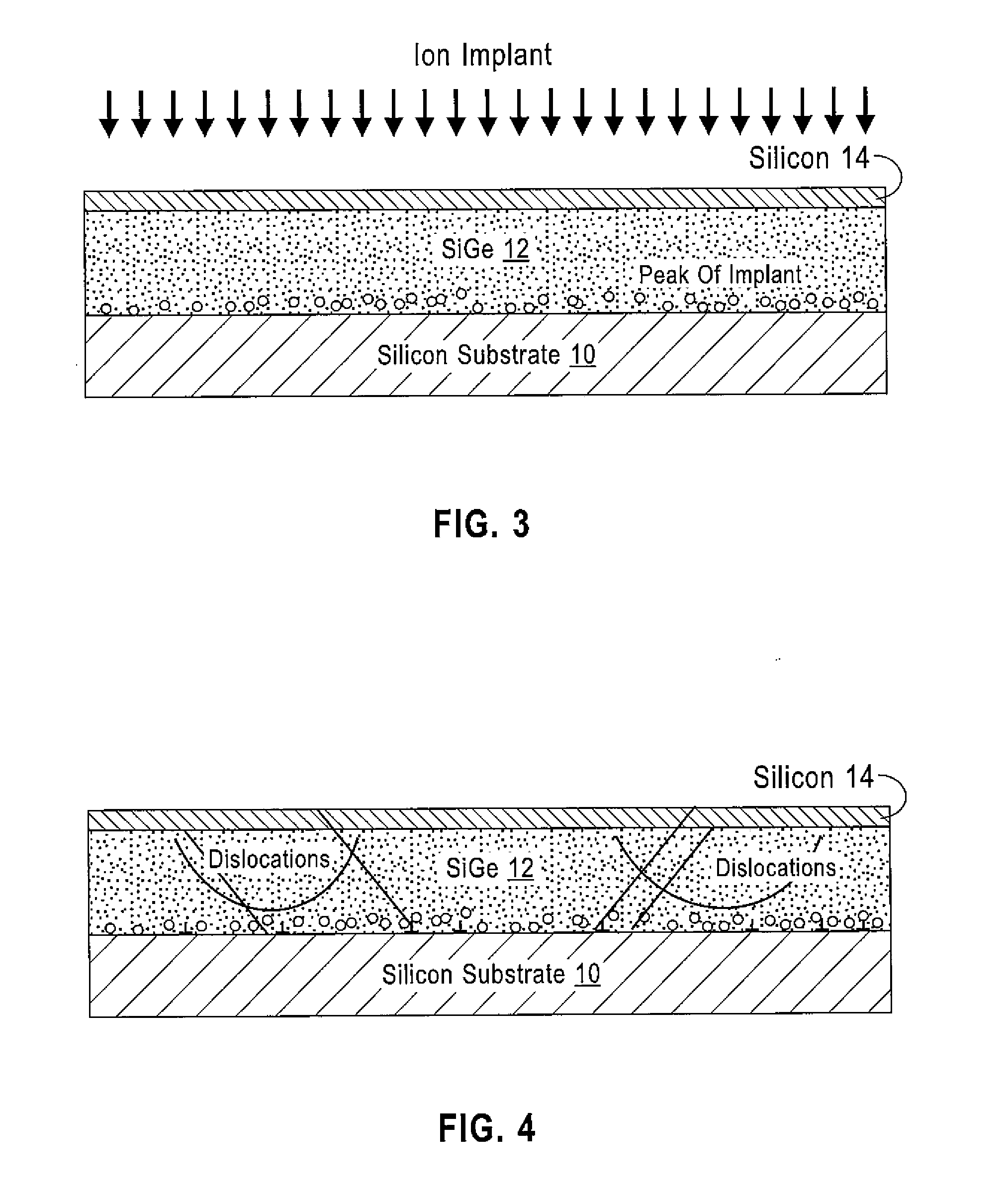
LOW DEFECT RELAXED SiGe/STRAINED Si STRUCTURES ON IMPLANT ANNEAL BUFFER/STRAIN RELAXED BUFFER LAYERS WITH EPITAXIAL RARE EARTH OXIDE INTERLAYERS AND METHODS TO FABRICATE SAME
ActiveUS20160322220A1Hinders its propagationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorRare earth
A method provides a substrate having a top surface; forming a first semiconductor layer on the top surface, the first semiconductor layer having a first unit cell geometry; epitaxially depositing a layer of a metal-containing oxide on the first semiconductor layer, the layer of metal-containing oxide having a second unit cell geometry that differs from the first unit cell geometry; ion implanting the first semiconductor layer through the layer of metal-containing oxide; annealing the ion implanted first semiconductor layer; and forming a second semiconductor layer on the layer of metal-containing oxide, the second semiconductor layer having the first unit cell geometry. The layer of metal-containing oxide functions to inhibit propagation of misfit dislocations from the first semiconductor layer into the second semiconductor layer. A structure formed by the method is also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electric current sensing and management system for electrolytic plants
InactiveUS20150211136A1Increase heightEnhancement of the electrolytic cell and/or tankhouse behaviourCellsPhotography auxillary processesEngineeringManagement system
The present invention relates to an electric current management (ECM) system and method comprising at least one electrolytic cell having at least two electrodes in contact with electrolyte media; a plurality of sensor means for measuring the current passing through one or more electrodes, said sensor means being located inside at least one ECM bar installed in one or more operating electrolytic cells; a support means for supporting at least one ECM bar in each cell; wherein the support means is adapted to avoid disruption to normal electrode movements and damage to the ECM bar. The present invention introduces improvements for minimizing the effects that several types of variables have on current measurement, such as magnetic field interference, cell geometry and contact configuration, in order to provide a reliable approximation of the current passing through each electrode. The present invention can be applied to real time monitoring of each cathode, or anode, constituting a metal electrowinning or electrorefining cell or other electrolytic cell.
Owner:HATCH LTD
Method of replenishing cells damaged by treatment for cancer
InactiveCN1826125AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsExpansion factorHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein is a method of replenishing cells damaged by treatment for cancer. The method comprises removing blood cells from a primate mammal, controllably expanding the cells at a rate which produces an expansion factor of at least 700% within 7 days while maintaining their three-dimensional geometry and their cell-to-cell support and cell-to-cell geometry, removing any toxic materials from the blood cells, and reintroducing the cells into the primate mammal within a time period sufficient to prevent the primate mammal from suffering decreased mobility due to loss of hematopoietic or other cells.
Owner:REGENETECH INC
Building structured material using cell geometry
Owner:WENNBERG PAUL
Manufacturing method of grid combined type graphic model based on magnetic principle
PendingCN111597599AMeet lightweight requirementsFlexible disassemblyGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatus3d printModelSim
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a grid combined type graphic model based on a magnetic principle. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out 3D modeling ona basic unit geometry; according to the model data, enabling the basic geometry to be subjected to 3D printing forming manufacturing forming; magnetizing the surface of the unit basic geometry model;carrying out grid-type modular free combination on the magnetization unit body models to generate a new combination body model; and observing the forming process of related intersection lines and intersecting lines of the inner surface and the outer surface of the new assembly model, and analyzing the view projection characteristics. The manufacturing method has the advantages that: due to the modular design characteristic, flexible disassembly and assembly, free combination and convenience in carrying can be realized by utilizing a magnetic principle; due to the detachable characteristic, theinner structure and the outer structure can be observed in all directions, and the forming process of the intersection lines and the intersecting lines of the three-dimensional surface can also be observed and analyzed through model combination; and each basic unit body is of a thin-wall hollow structure and is manufactured through the 3D printing technology, and the requirement for light weightis met.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
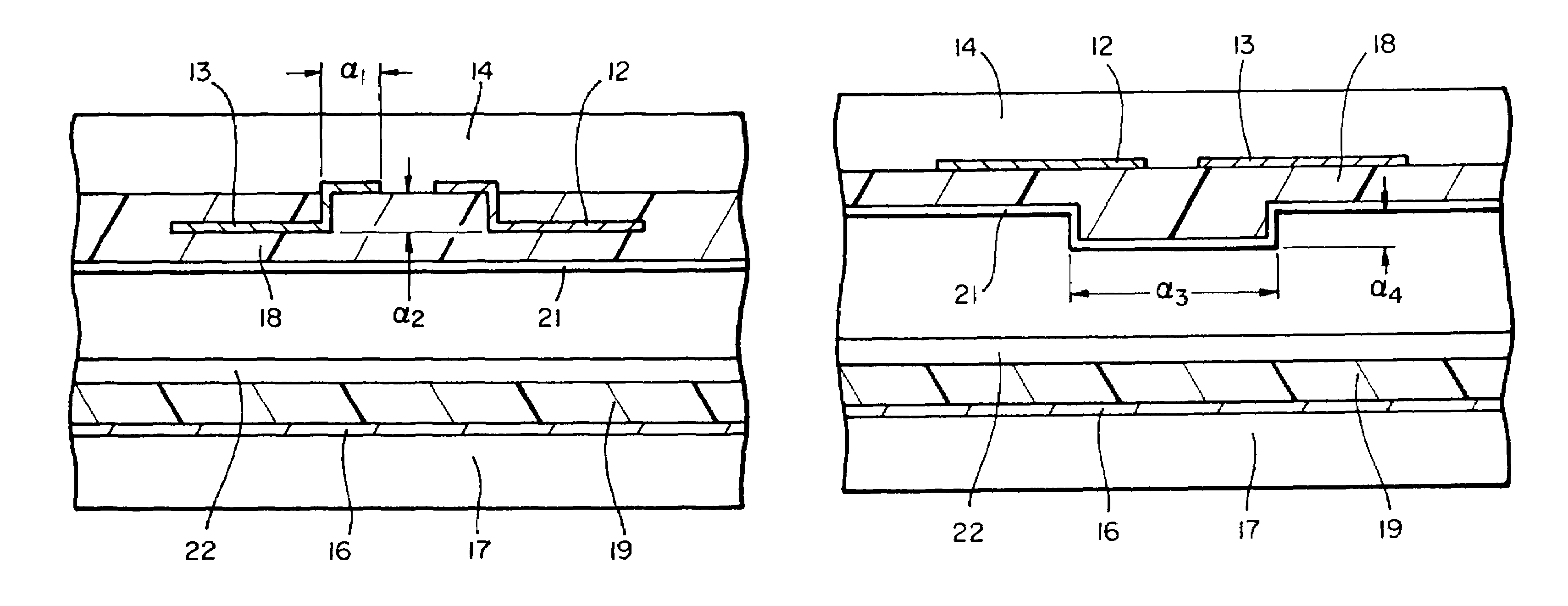
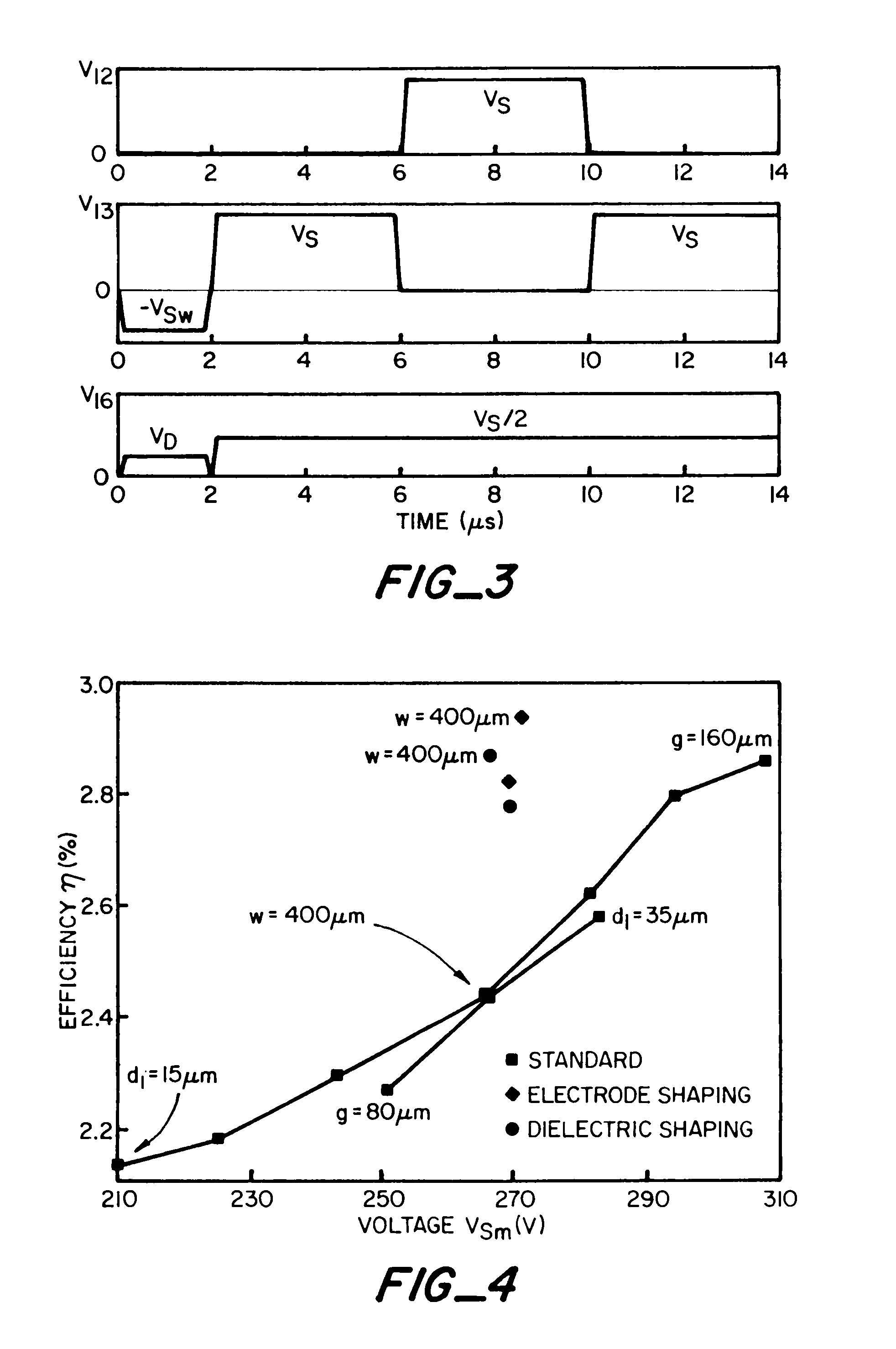
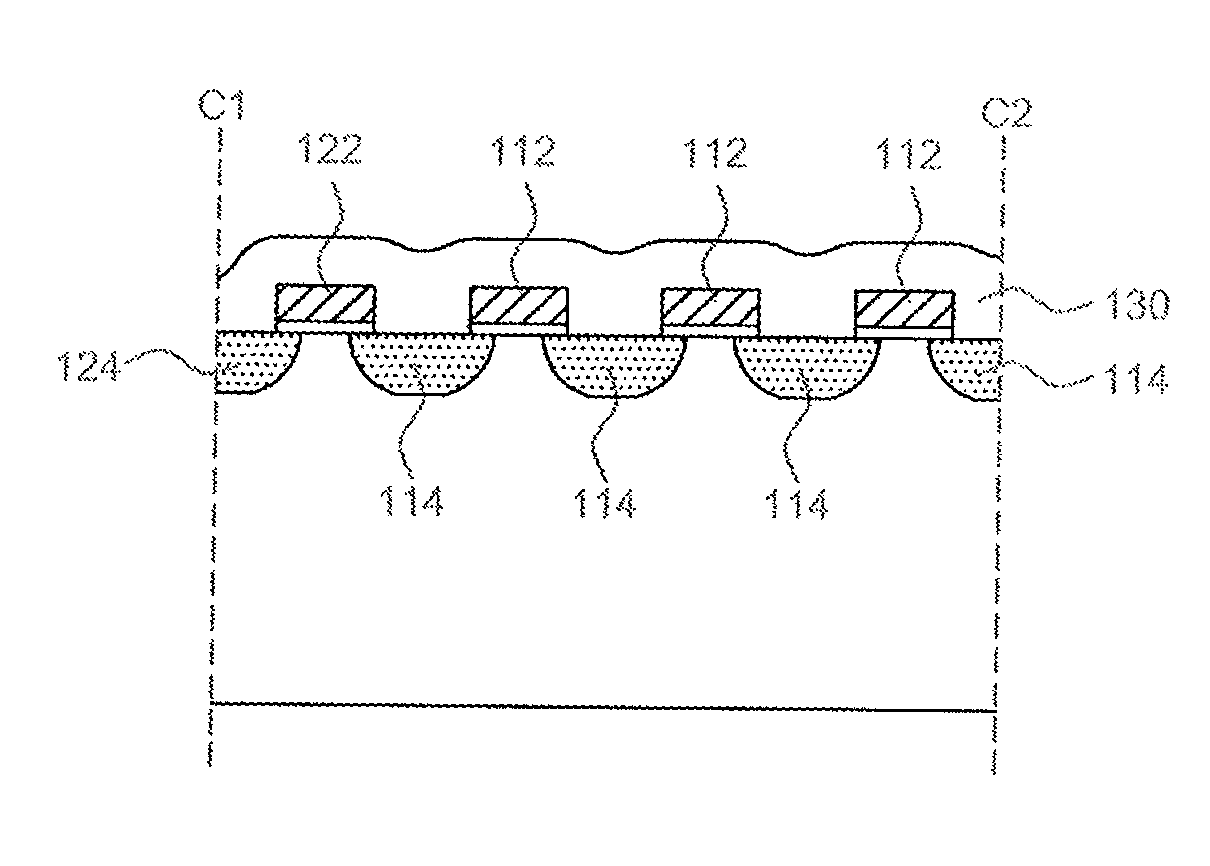
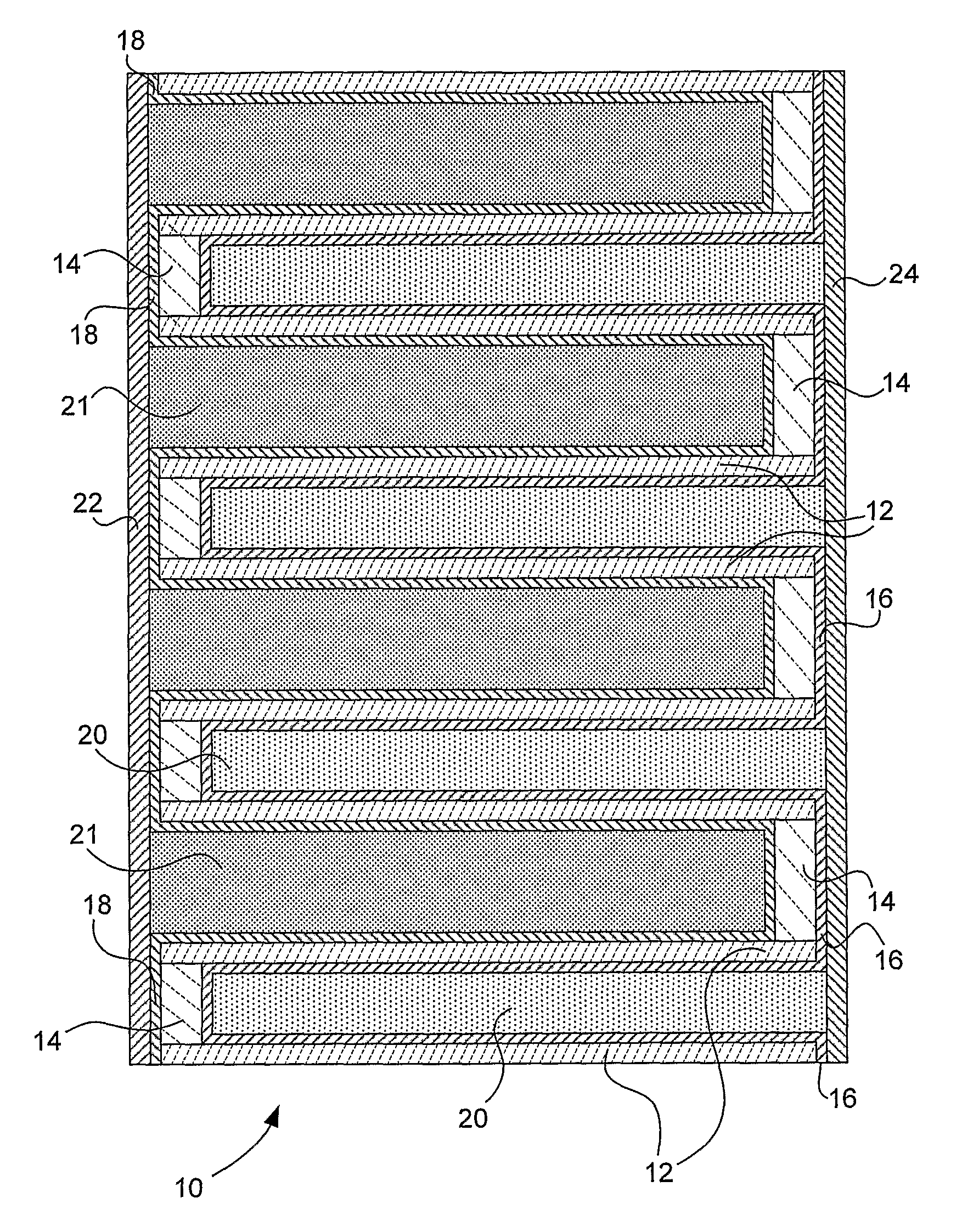
Plasma display panel with improved cell geometry
InactiveUS7288892B2Improve luminous efficiencyLarge equivalent capacitanceSustain/scan electrodesAlternating current plasma display panelsDielectricPhosphor
A cell geometry for a coplanar electrode plasma display panel consisting of two transparent plates, one with parallel sustain electrodes, and the other with address electrodes deposited on their surface. The electrodes are covered with a dielectric film. A protective MgO layer is deposited on the dielectric film adjacent the sustain electrodes. A phosphor layer is deposited on the other dielectric film. The plates are scaled together with their electrodes at right angles and the gap between the plates is filled with an inert gas mixture. The geometry of the sustain electrodes and / or associated dielectric film provides a larger equivalent capacitance at the outer part of the sustain electrodes to provide larger luminous efficiencies.
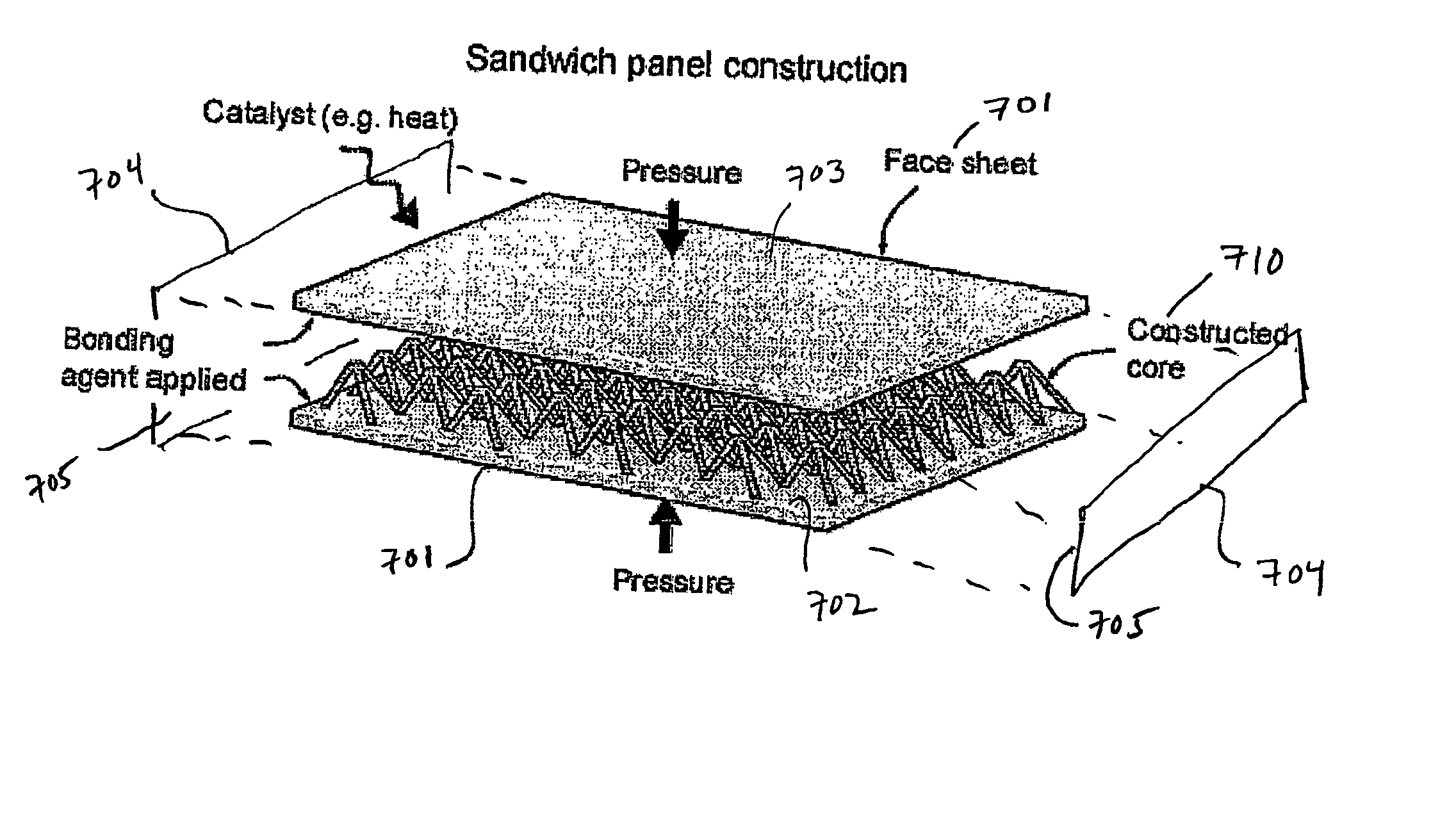
Joining approaches for sandwich structures
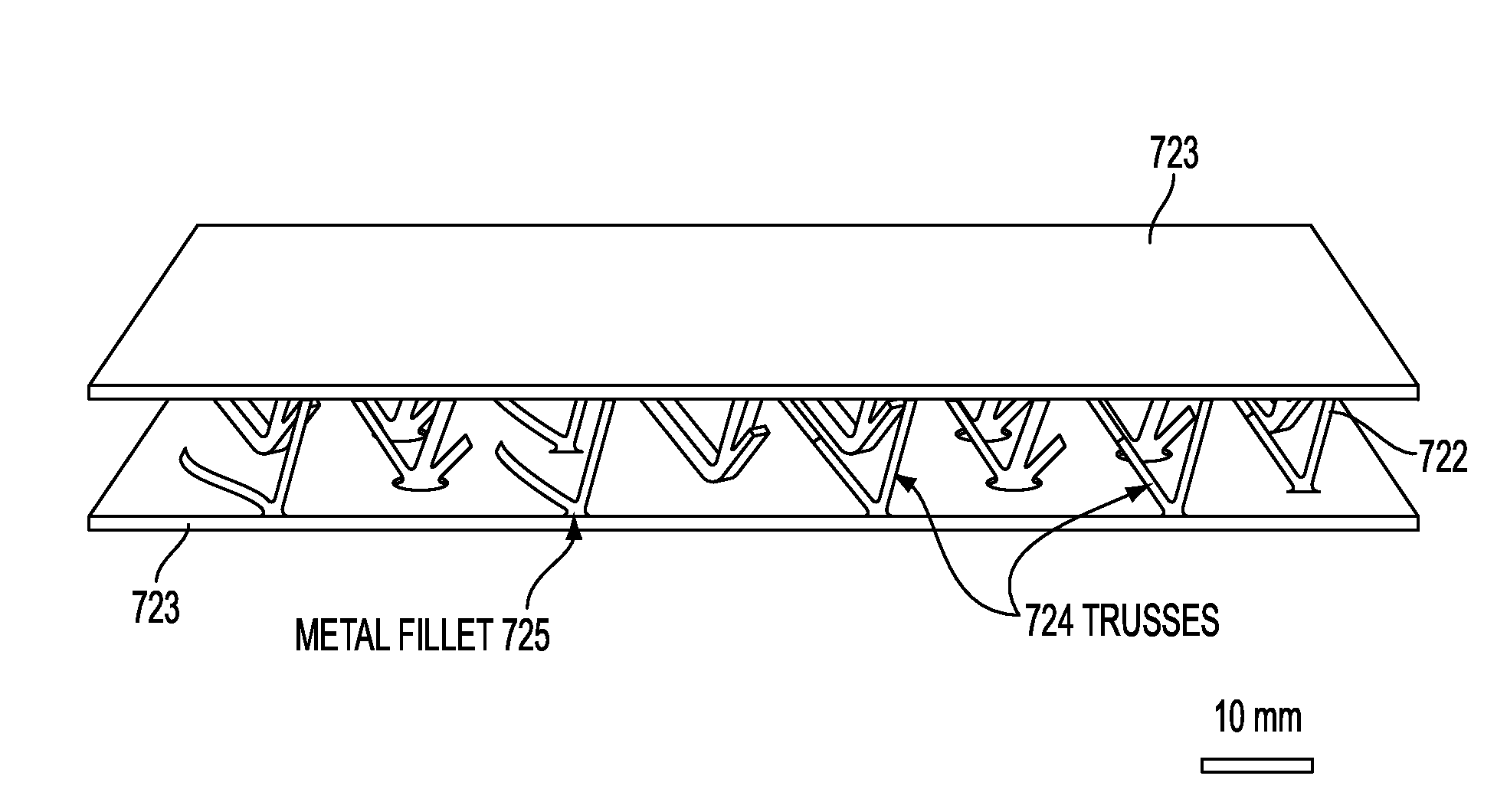
ActiveUS9457434B2Welding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesFace sheetMechanical engineering
A method for securing sandwich structures together, especially vehicle structures. In one embodiment, two sandwich structures are perpendicularly secured together, where a first one of the sandwich structures includes a micro-truss core having one unit cell geometry and second one of the sandwich structures includes a micro-truss core having different unit cell geometry. The micro-truss core of the second sandwich structure includes a micro-truss extension fabricated at the same time as the micro-truss core and having the same unit cell geometry as the micro-truss core for the first sandwich structure. The extension is inserted in an open area between face sheets in the first sandwich structure so that it abuts against the micro-truss core in the first sandwich structure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Power Semiconductor Device of Stripe Cell Geometry
A power semiconductor device of stripe cell geometry including a substrate, a plurality of striped power semiconductor units, and a guard ring structure is provided. The substrate has an active area and a termination area surrounding the active area defined thereon. The striped semiconductor unit includes a striped gate conductive structure. The striped semiconductor units are located in the active area. The guard ring structure is located in the termination area and includes at least a ring-shaped conductive structure surrounding the striped power semiconductor units. The ring-shaped conductive structure and the striped gate conductive structures are formed on the same conductive layer, and at least one of the striped gate conductive structures is separated from the nearby ring-shaped conductive structure and electrically connected to the nearby ring-shaped conductive structure through the gate metal pad.
Owner:UPI SEMICON CORP
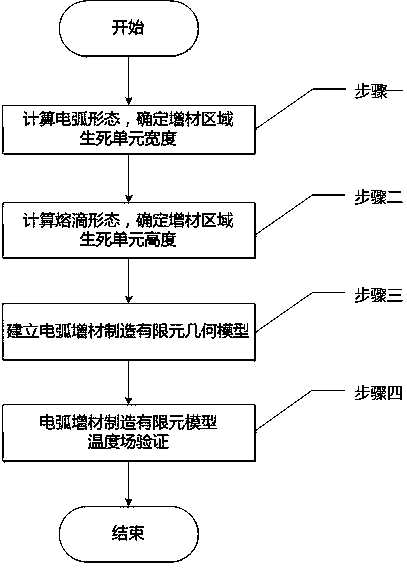
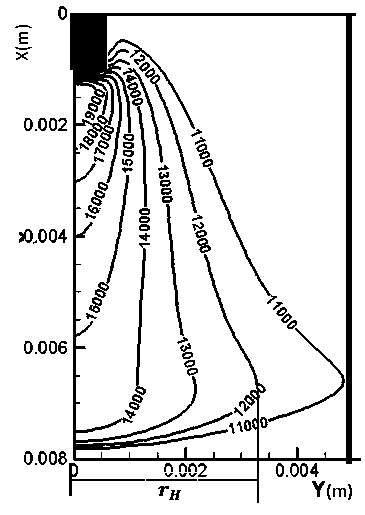
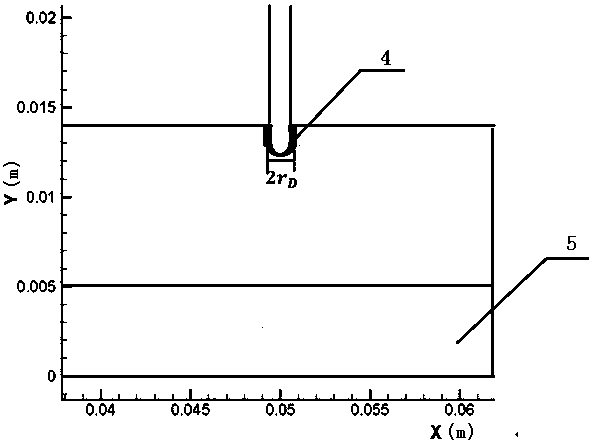
A Finite Element Modeling Method for Arc Additive Manufacturing
ActiveCN107066700BReduce the amount of experimentsImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModelSimGeometric modeling
The invention discloses an arc additive manufacturing finite element modeling method. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating an arc shape and determining the width of an additive area birth-death element; calculating a molten drop shape and determining the height of the additive area birth-death element; establishing an arc additive manufacturing finite element geometric model according to the width of the additive area birth-death element and the height of the additive area birth-death element; correcting the arc shape and the molten drop shape through verifying the temperature distribution of the arc additive manufacturing finite element geometric model, so as to correct the arc additive manufacturing finite element geometric model. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the geometric size of the additive area birth-death element can be determined before the arc additive manufacturing finite modeling by adopting an arc additive manufacturing simulation process, combining an arc shape simulation technology, a molten drop shape simulation technology and a finite element simulation technology and carrying out experimental verification, so as to realize the correct calculation of arc additive manufacturing finite element simulation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
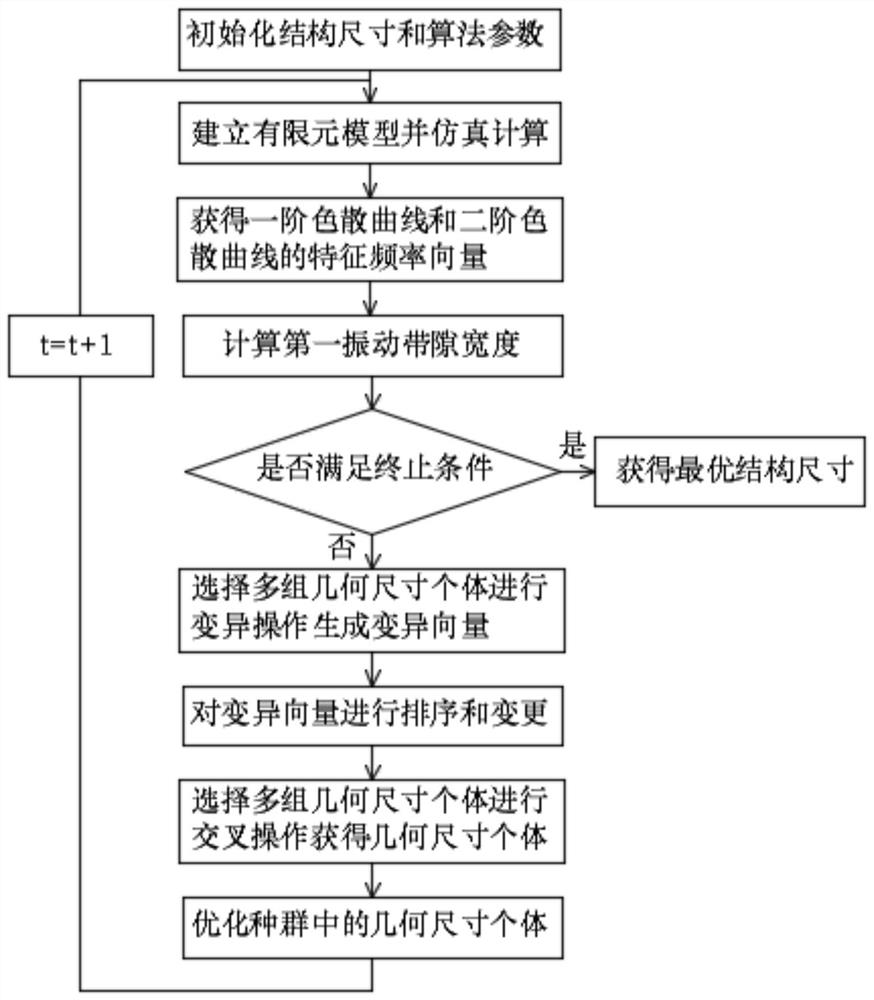
A topology optimization method for vibration energy harvesting piezoelectric metamaterial thin plate structure
ActiveCN111291515BSimple calculationEasy to implementDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelVibrational bands
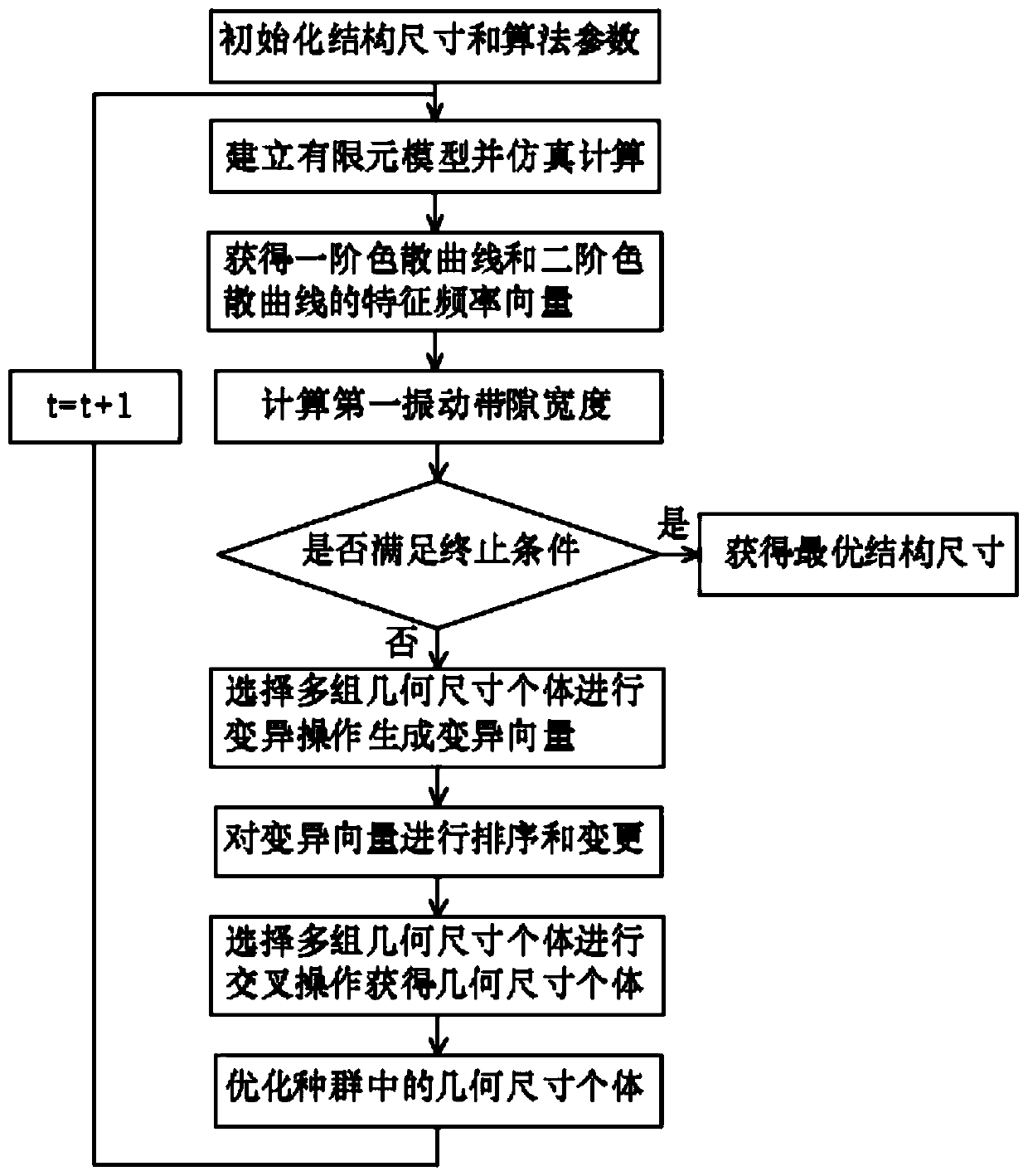
This application relates to a topology optimization method for vibration energy harvesting piezoelectric metamaterial thin plate structure, including: obtaining the D-dimensional structure size and algorithm parameter value of the unit cell unit and performing initialization processing; establishing a parameterized finite element model and performing simulation calculation; calculation The first vibration bandgap of the piezoelectric metamaterial thin plate, when the number of iterations exceeds a predetermined value or the decrease of the first vibration bandgap is less than a set threshold, the optimization process is terminated; otherwise, multiple groups of geometric size individuals are selected for variation The operation generates a variation vector group; multiple groups of geometric size individuals are selected and sorted; multiple groups of geometric size individuals are selected for crossover operation; better geometric size individuals are selected as the new D-dimensional structure size, and all optimizations are gradually achieved. The physical meaning of the method of the invention is clear, the established objective function is directly related to the geometric size of the unit cell, the geometric size of each component of the unit cell structure can be optimized simultaneously, and the calculation process is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Syntactic rigid PUR/PIR foam boardstock
The present invention relates to the use of hollow microspheres filled with a hydrocarbon, to introduce uniform cell geometries in syntactic foams having a bimodal cell structure. The rigid foam product includes from 20 to 80 percent by weight of the hollow microspheres, the microspheres having average diameters ranging from 80 to 200 microns. The microspheres are encapsulated from 80 to 20 percent by weight of a closed cell polyurethane foam, the cells of the foam having average diameters from 0.01 to 40 microns.
Owner:BAYER CORP
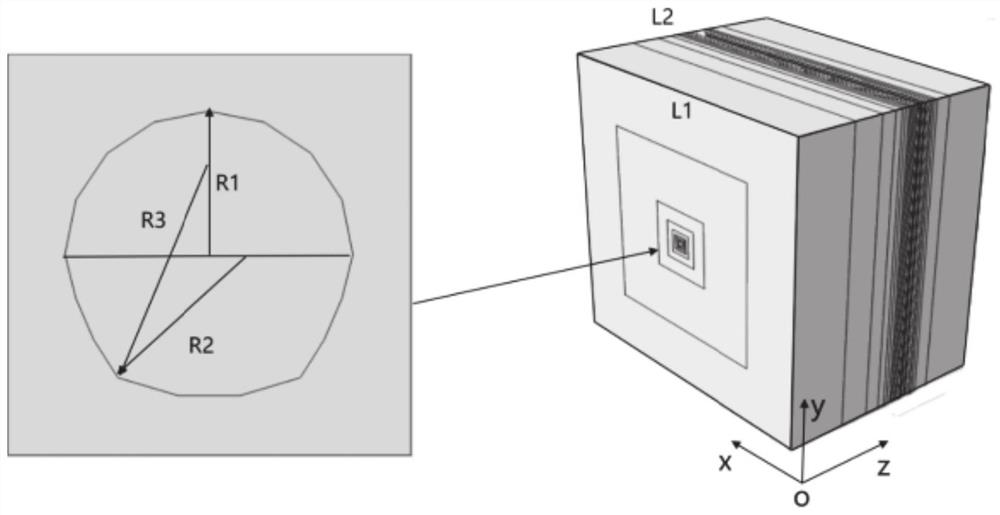
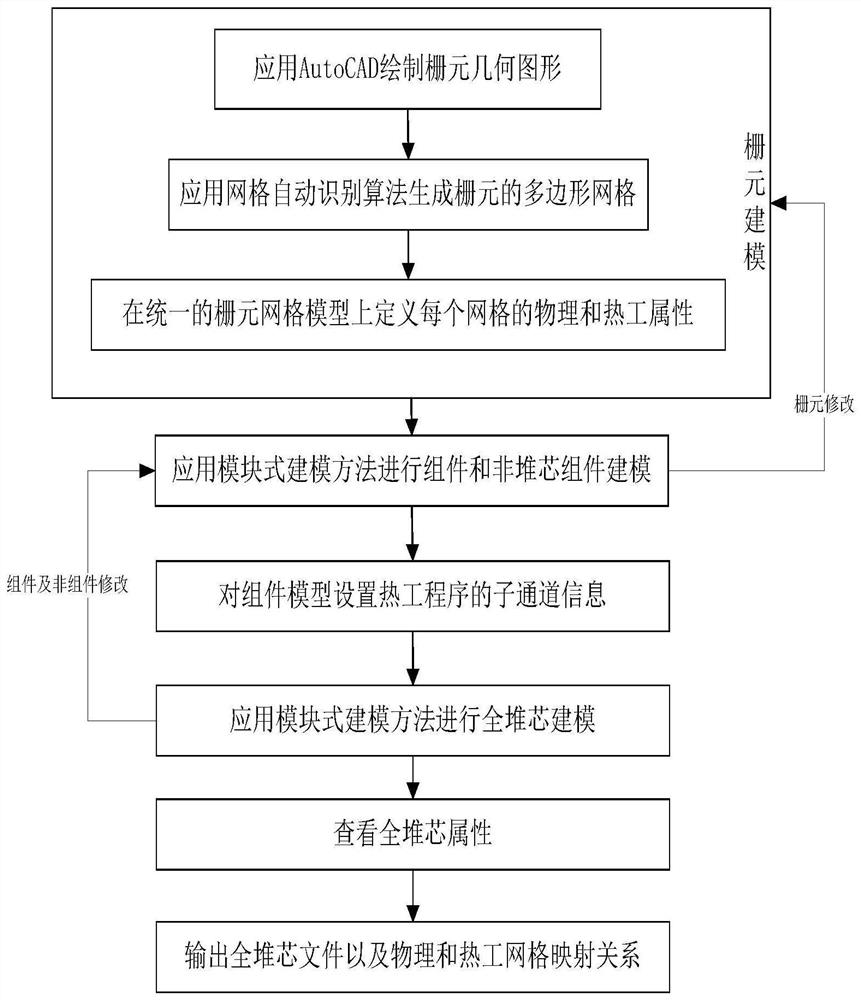
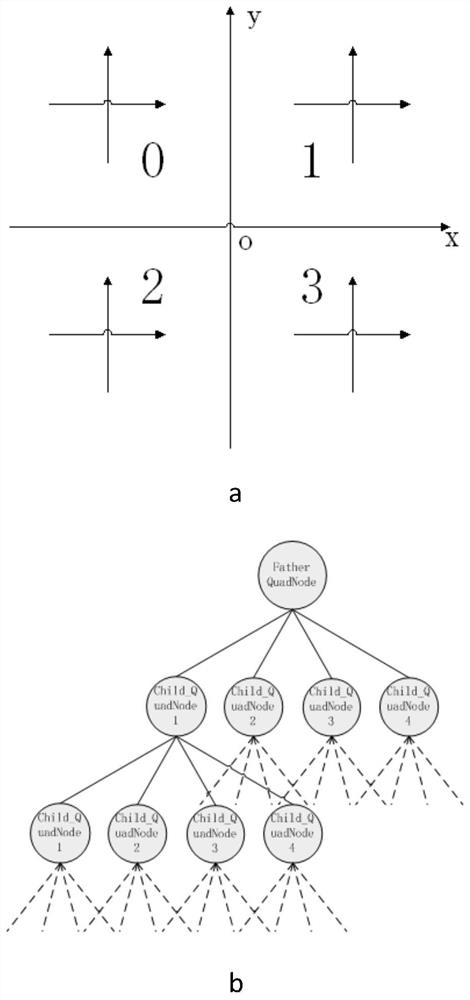
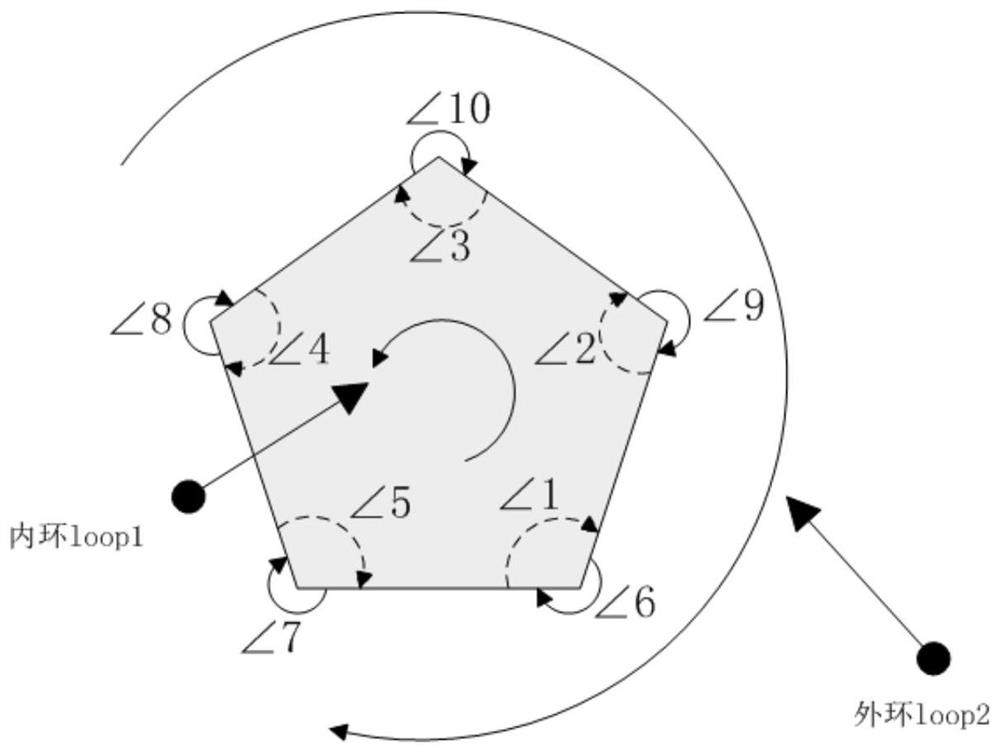
Physical and thermotechnical coupling visualization full-reactor-core complex geometric modeling method and physical and thermotechnical coupling visualization full-reactor-core complex geometric modeling system
ActiveCN113673006ATimely error checkingRapid modelingGeometric CADSustainable transportationNuclear reactor coreGrid mapping
The invention discloses a physical and thermal coupling visualization full-reactor-core complex geometric modeling method and system, and relates to the technical field of nuclear reactor core design, and the technical scheme is characterized in that the method comprises the steps: acquiring the lattice cell geometry through drawing; carrying out automatic identification on lattice cell geometry to obtain a polygonal mesh; carrying out physical and thermal attribute definition processing on the basis of grids divided by a physical program to obtain corresponding lattice cell grids; performing integration processing on the plurality of lattice cell grids to complete component and reflecting layer structure construction, and obtaining a component model; establishing sub-channel information of a thermal program on the basis of a component model established by a physical program to obtain a component lattice cell model; carrying out integrated processing on the plurality of assembly lattice cell models to obtain a full-reactor-core model; and outputting full-core information and a mapping relation between grids of a physical program and a thermal program in a specific format. According to the method, grid mapping and data transmission between the physical program and the thermotechnical program can be quickly, simply and conveniently carried out, and the coupling difficulty of the physical calculation program and the thermotechnical calculation program is reduced.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Cellular honeycomb hybrid capacitors with non-uniform cell geometry
InactiveUS8456801B2Hybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrodesNon oxide ceramicsCordierite
A hybrid capacitor includes an electrically non-conductive rigid or semi-rigid porous honeycomb structure having cells extending along a common direction, the cells having a plurality of cross-sectional shapes. The honeycomb structure is desirably formed of a material that is stable at temperatures of 300° or more, such that high temperature processing can be used to help ensure high purity of the final product. The material of the structure may desirably be an oxide or non-oxide ceramic, such as cordierite, silicon nitride, alumina, aluminum titanate, zircon, glass, or glass-ceramic. The plurality of shapes of the cells includes larger shapes in which cells are disposed non-galvanic electrodes, with galvanic electrodes disposed in cells of other shapes.
Owner:CORNING INC
Building structured material using cell geometry
Owner:B BRAUN MEDIZINELEKTRONIK
Semiconductor Switching Device with Different Local Cell Geometry
ActiveCN105206654ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceOhmic contact
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate having an outer rim, a plurality of switchable cells defining an active area, and an edge termination region arranged between the switchable cells defining the active area and the outer rim. Each of the switchable cells includes a body region, a gate electrode structure and a source region. A source metallization is in ohmic contact with the source regions of the switchable cells. A gate metallization is in ohmic contact with the gate electrode structures of the switchable cells. The active area defined by the switchable cells includes at least a first switchable region having a specific gate-drain capacitance which is different to a specific gate-drain capacitance of a second switchable region.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Topological optimization method for vibration energy collection piezoelectric metamaterial sheet structure
ActiveCN111291515ASimple calculationEasy to implementDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelComputation process
The invention relates to a topological optimization method for a vibration energy collection piezoelectric metamaterial sheet structure. The topological optimization method comprises the following steps: acquiring a D-dimensional structure size and an algorithm parameter value of a cell unit and performing initialization processing; establishing a parameterized finite element model and carrying out simulation calculation; calculating a first vibration band gap of the piezoelectric metamaterial thin plate, and terminating the optimization process when the number of iterations exceeds a preset value or the decrement of the first vibration band gap is smaller than a set threshold value; otherwise, selecting a plurality of groups of geometric dimension individuals to perform mutation operationto generate a mutation vector group; selecting a plurality of groups of geometric dimension individuals and sorting; selecting a plurality of groups of geometric dimension individuals for crossover operation; and selecting an individual with an optimal geometric dimension as a new D-dimensional structure dimension, and gradually achieving all the optimal dimensions. By adopting the method, the physical significance is clear, the established target function is directly related to the geometric dimension of the unit cell, the geometric dimension of each component of the unit cell structure canbe optimized at the same time, and the calculation process is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com