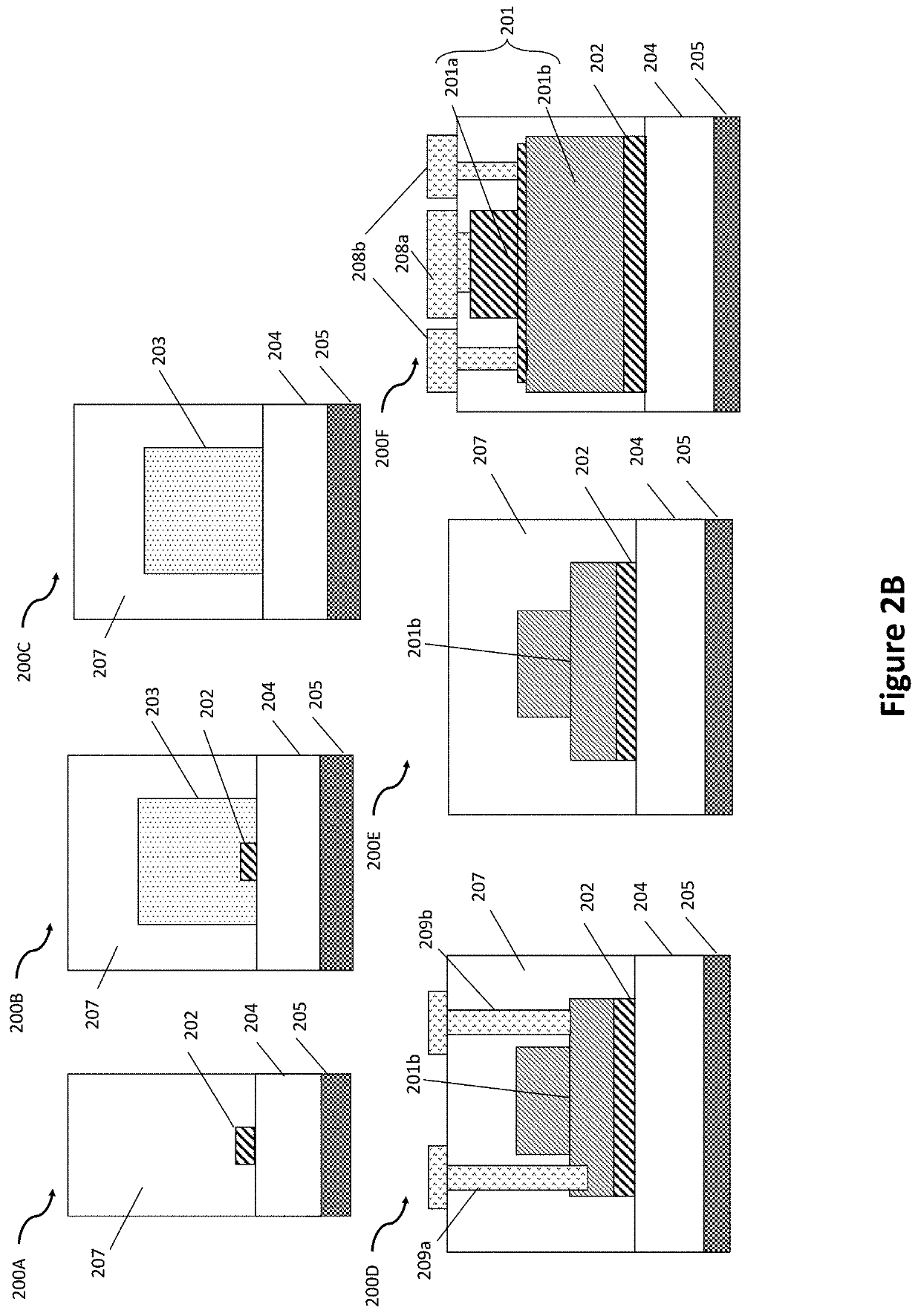
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Butt coupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
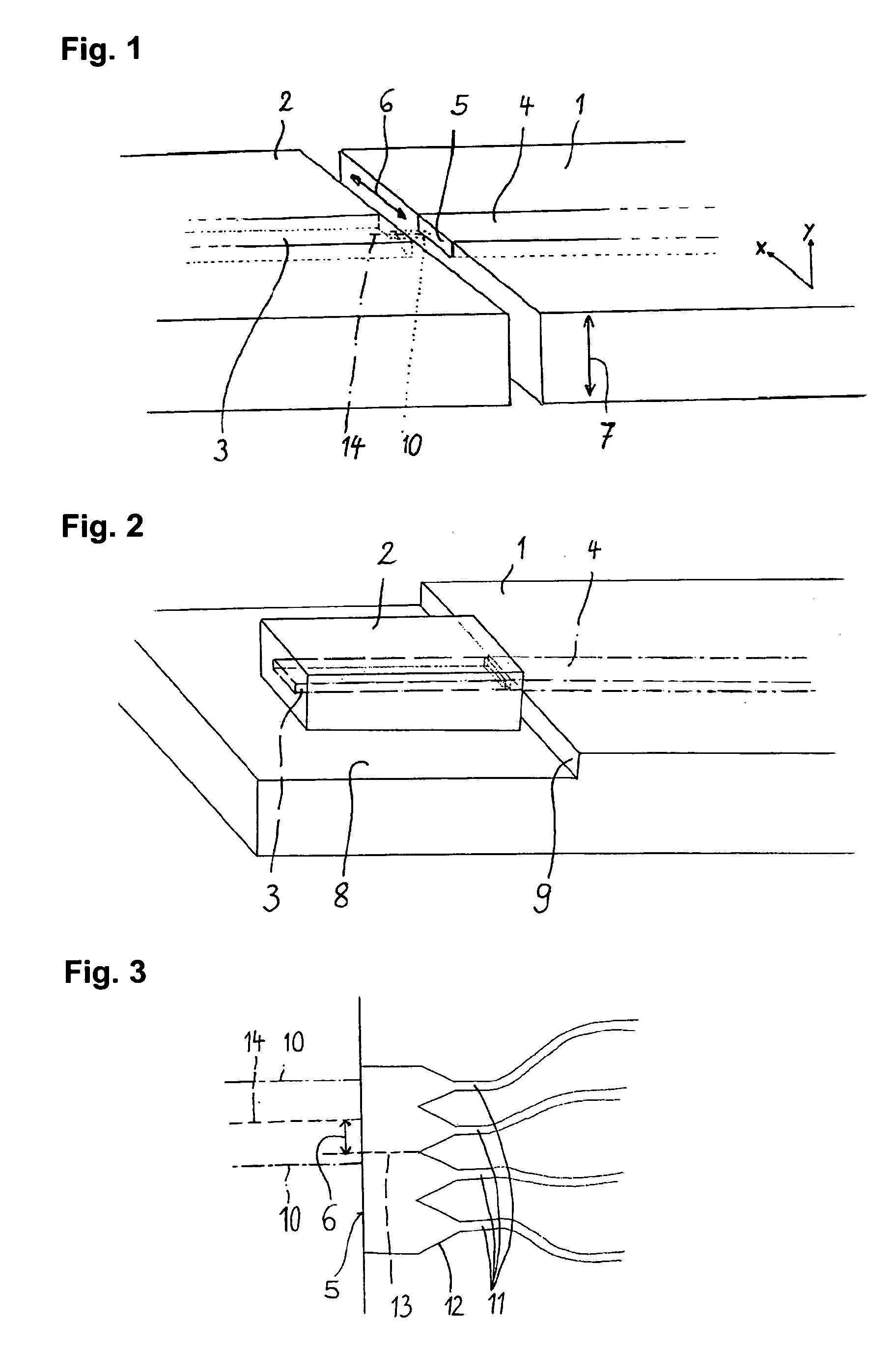
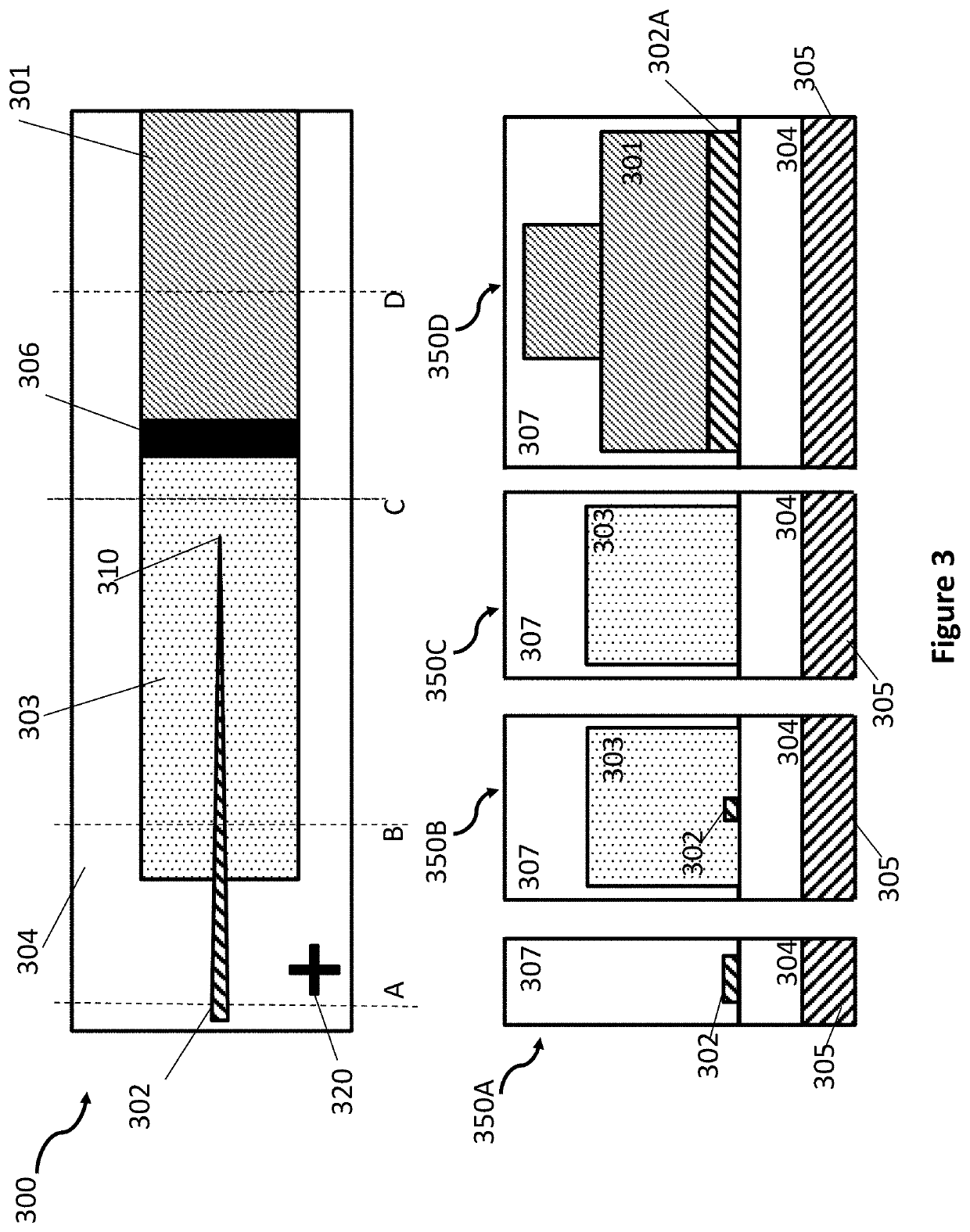
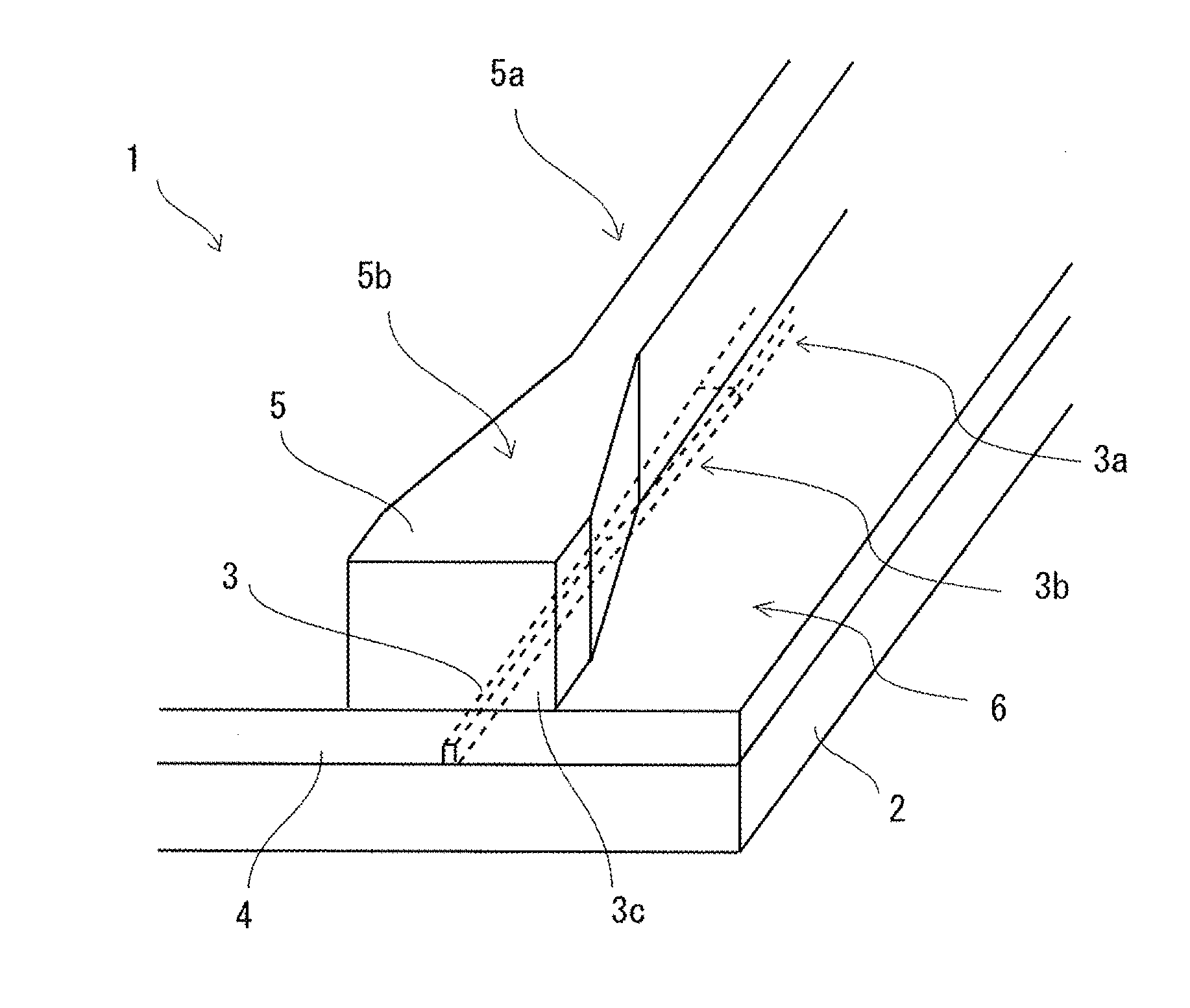
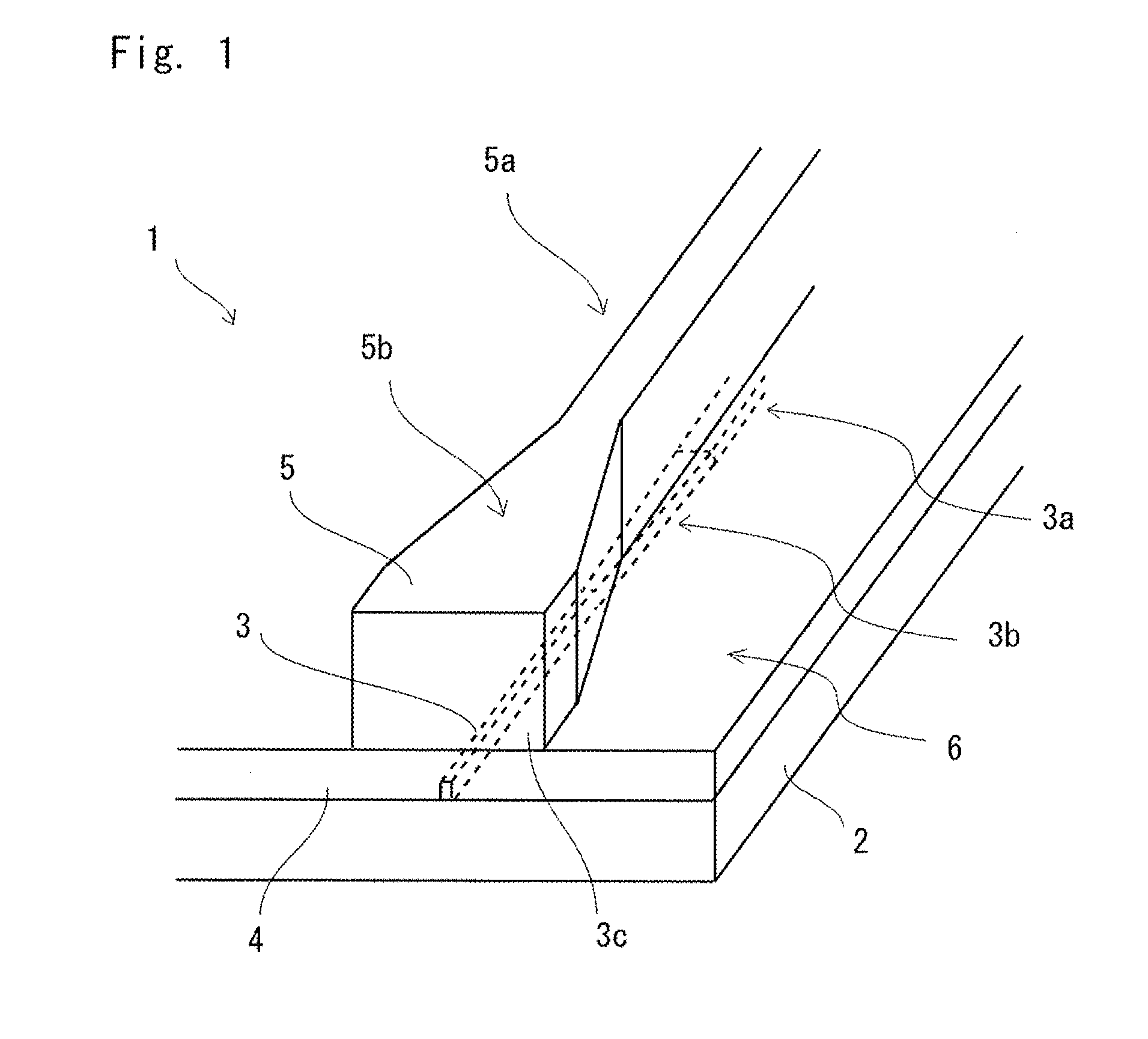
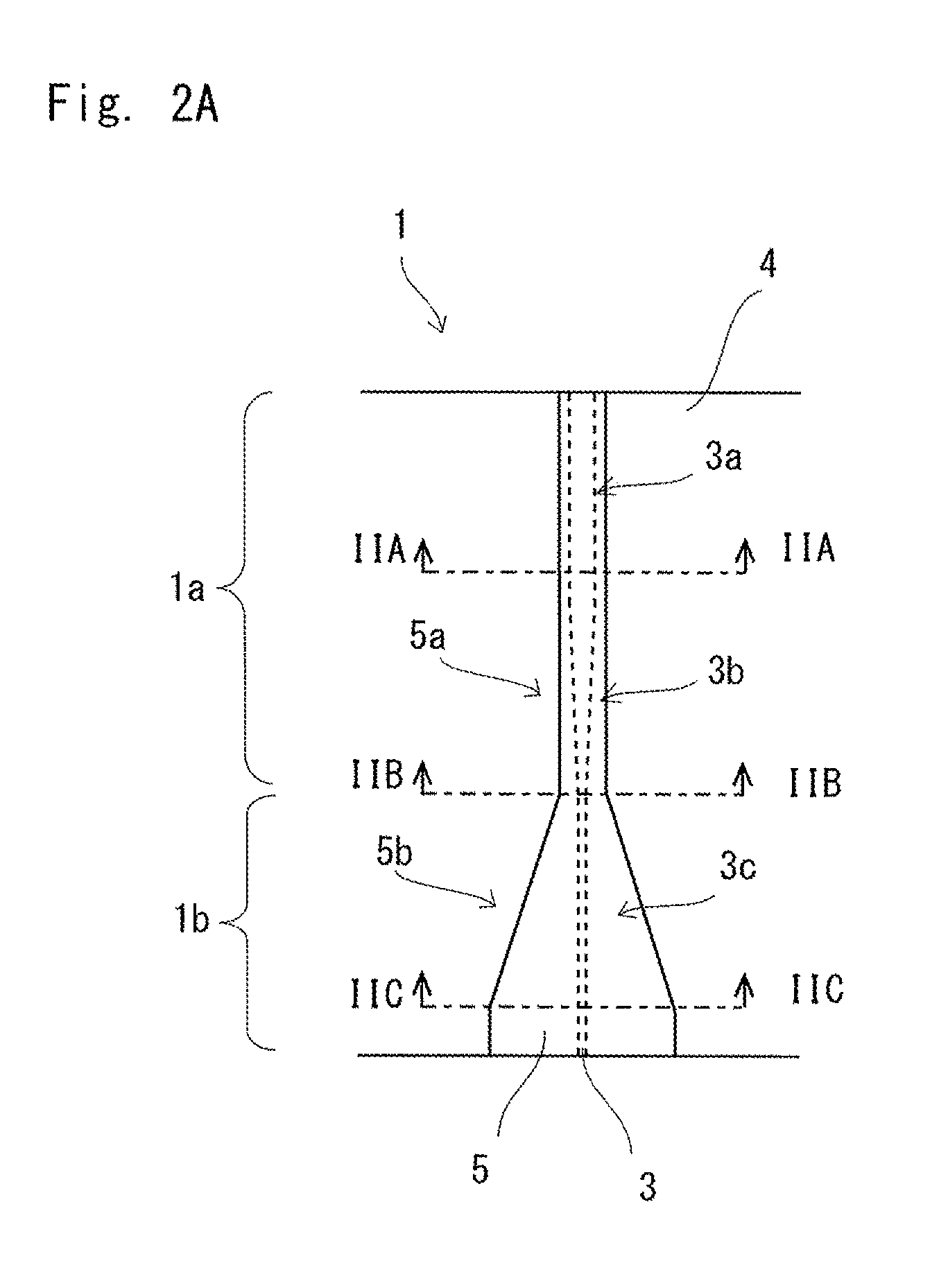
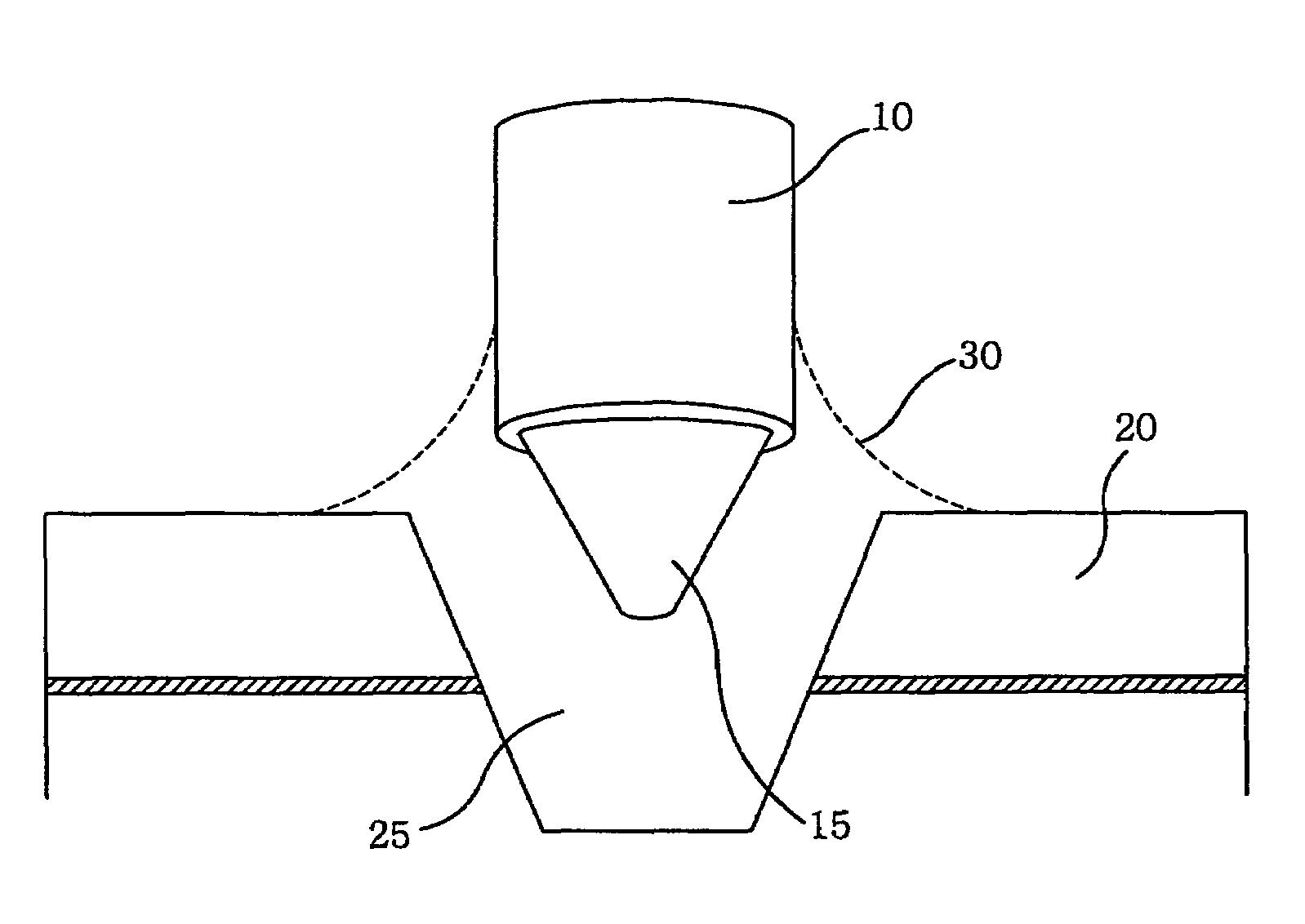
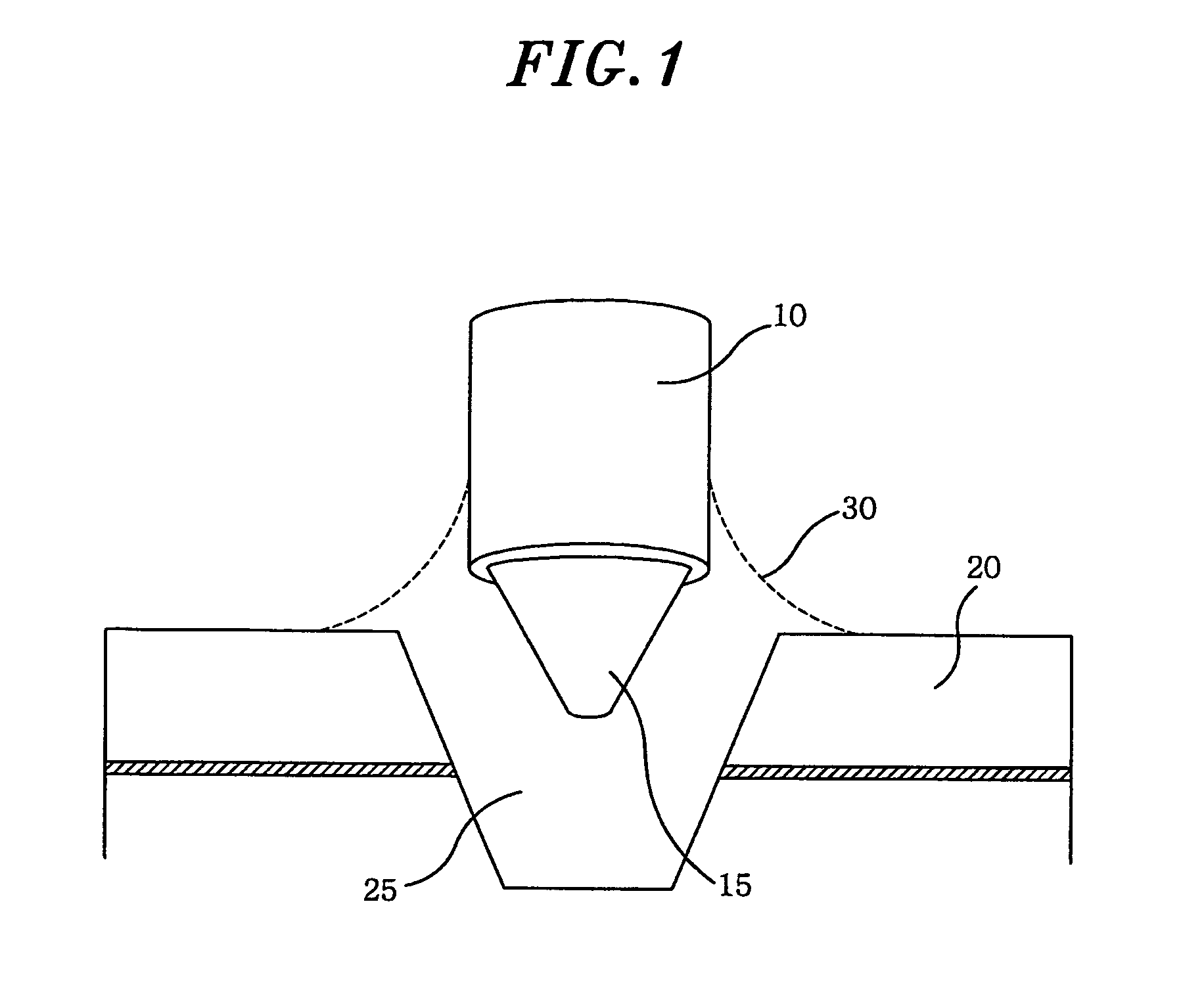
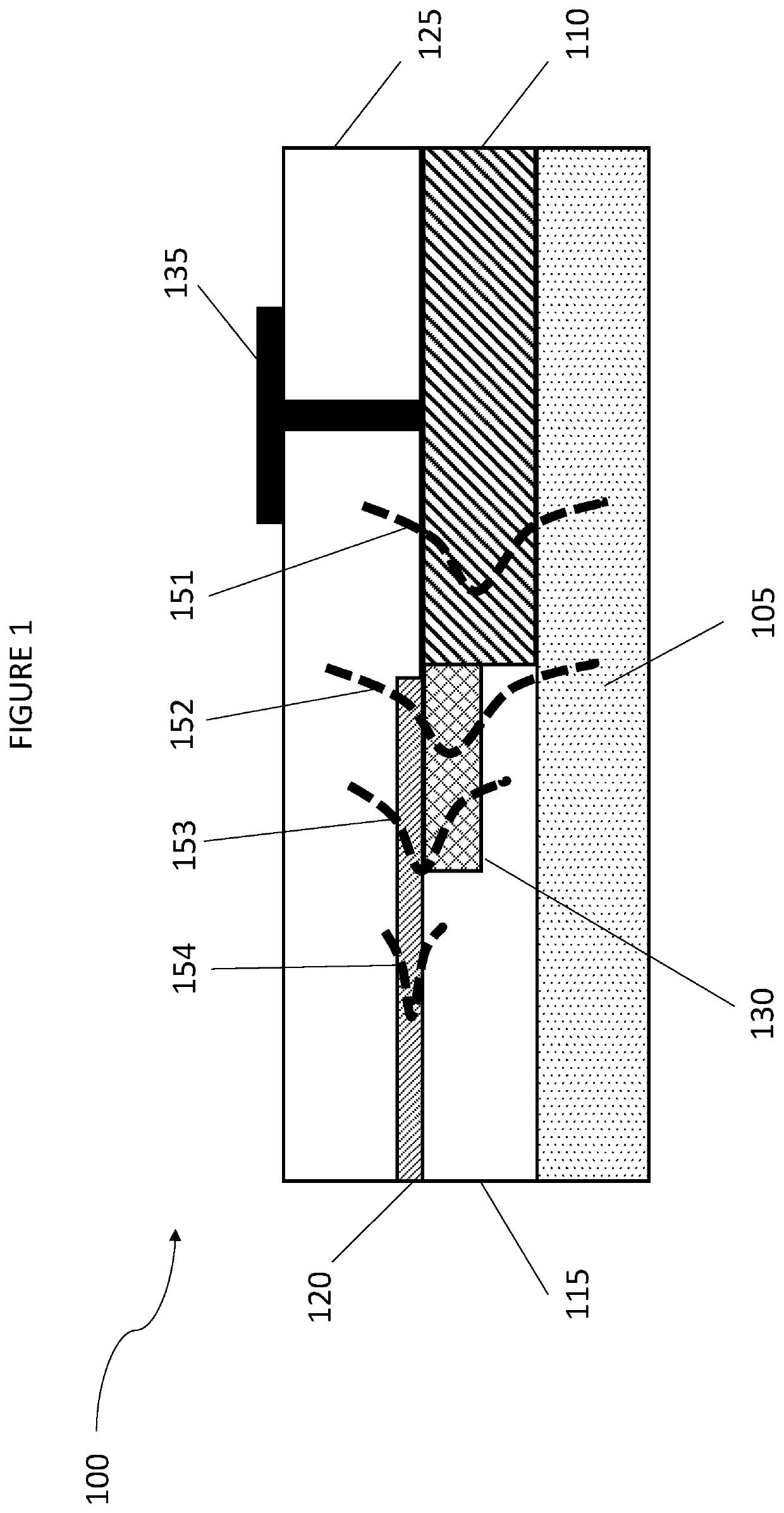
Laser to Chip Coupler
ActiveUS20130209112A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic receiversPhotonic ChipLight beam
A method and an apparatus for butt-coupling an input beam incoming from a photonic device of a second optical element to a primary photonic chip at an input interface of the primary photonic chip is disclosed. The primary photonic chip comprises a coupling apparatus. The light from the input beam is butt-coupled to the coupling apparatus. The coupling apparatus comprises a plurality of more than one single mode optical paths on the primary photonic chip. The single mode optical paths are strongly coupled to each other at the input interface of the primary photonic chip. Regions of strongly coupled single mode optical paths can correspond to one or both of distinct but highly coupled waveguides or waveguides fully merged into a multi-mode section.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
Laser to chip coupler
ActiveUS9316788B2Improve efficiencyHigh yieldLaser detailsCoupling light guidesPhotonic ChipCoupling
A method and an apparatus for butt-coupling an input beam incoming from a photonic device of a second optical element to a primary photonic chip at an input interface of the primary photonic chip is disclosed. The primary photonic chip comprises a coupling apparatus. The light from the input beam is butt-coupled to the coupling apparatus. The coupling apparatus comprises a plurality of more than one single mode optical paths on the primary photonic chip. The single mode optical paths are strongly coupled to each other at the input interface of the primary photonic chip. Regions of strongly coupled single mode optical paths can correspond to one or both of distinct but highly coupled waveguides or waveguides fully merged into a multi-mode section.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
Waveguide-optical fibre automatic core regulating method and device based on multi-target evolution algorithmic
InactiveCN101047449AReduce the number of operationsHigh degree of automationWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionGenetic populationRelationship - Father
A method for automatically regulating core of waveguide-optical fiber based on multi-object evolution algorithm includes treating discrete genetic screening process by stable culling policy, applying father generation cross and real value variation in searching process, only change two individual bodies in each generation of genetic population and having no relationship to artificial weight-setting in process of realizing multi-object optimization.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
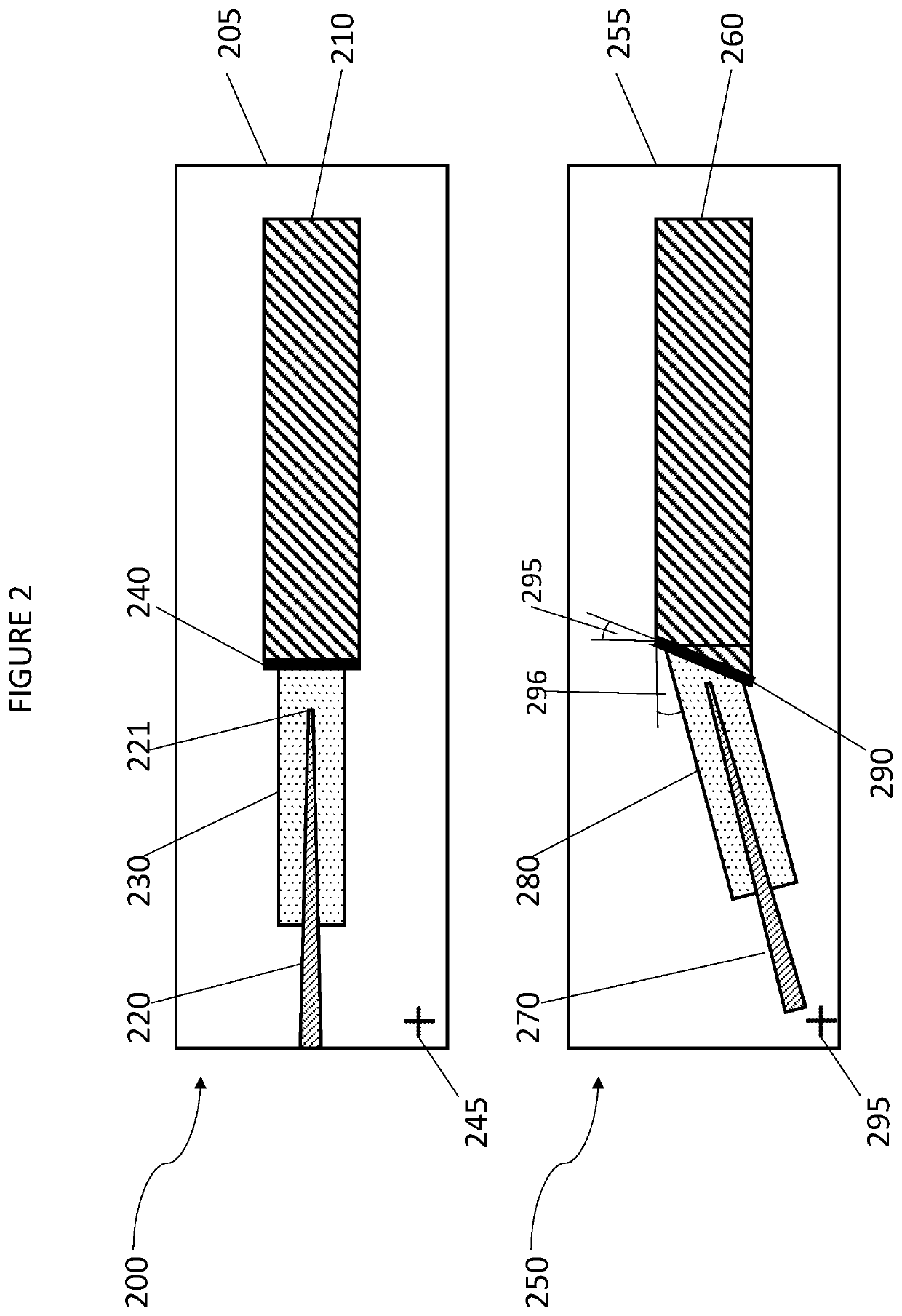
Optical conversion element and optical conversion element manufacturing method
InactiveUS20130188910A1Highly efficient optical couplingThe implementation process is simpleOptical articlesCoupling light guidesAnti-reflective coatingDual core
Disclosed is an optical conversion element capable of highly efficient optical coupling between a silicon waveguide and a general single-mode optical fiber only by butt-coupling without requiring anti-reflective coating. One embodiment is an optical conversion element that includes a waveguide structure and converts a mode field of guided light and is characterized in that at least a dual core is included, an innermost core of the dual core is a silicon inverse tapered thin wire core, a first outer core is a forward tapered ridge core having a ridge structure formed of an oxide film with only width of the ridge core changing. The first outer core is positioned on a narrow width side of the innermost core.
Owner:NEC CORP
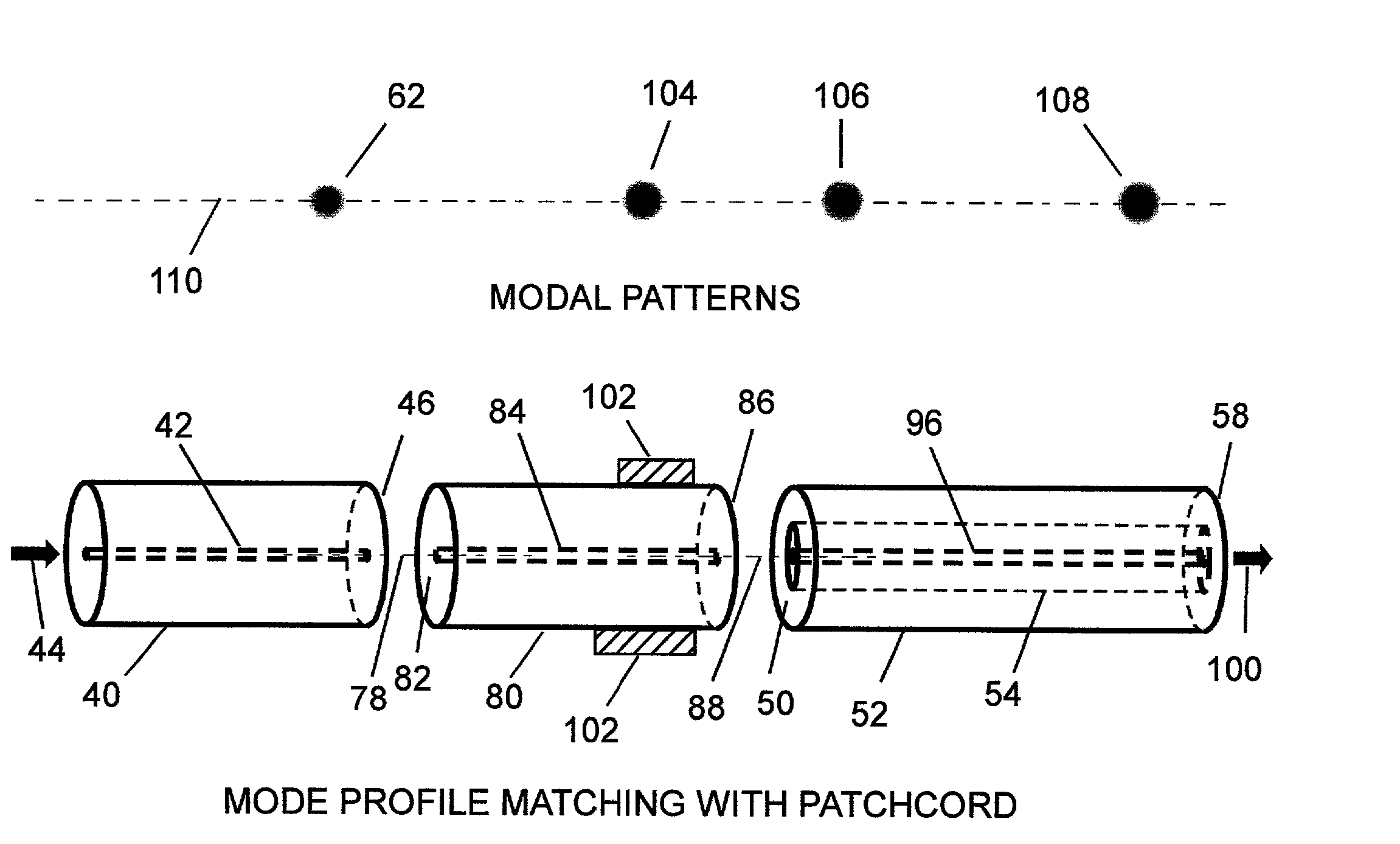
Profile matching fiber patchcord for fundamental mode excitation in graded-index multimode fiber
InactiveUS20020126954A1The right amountOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexCommunication link
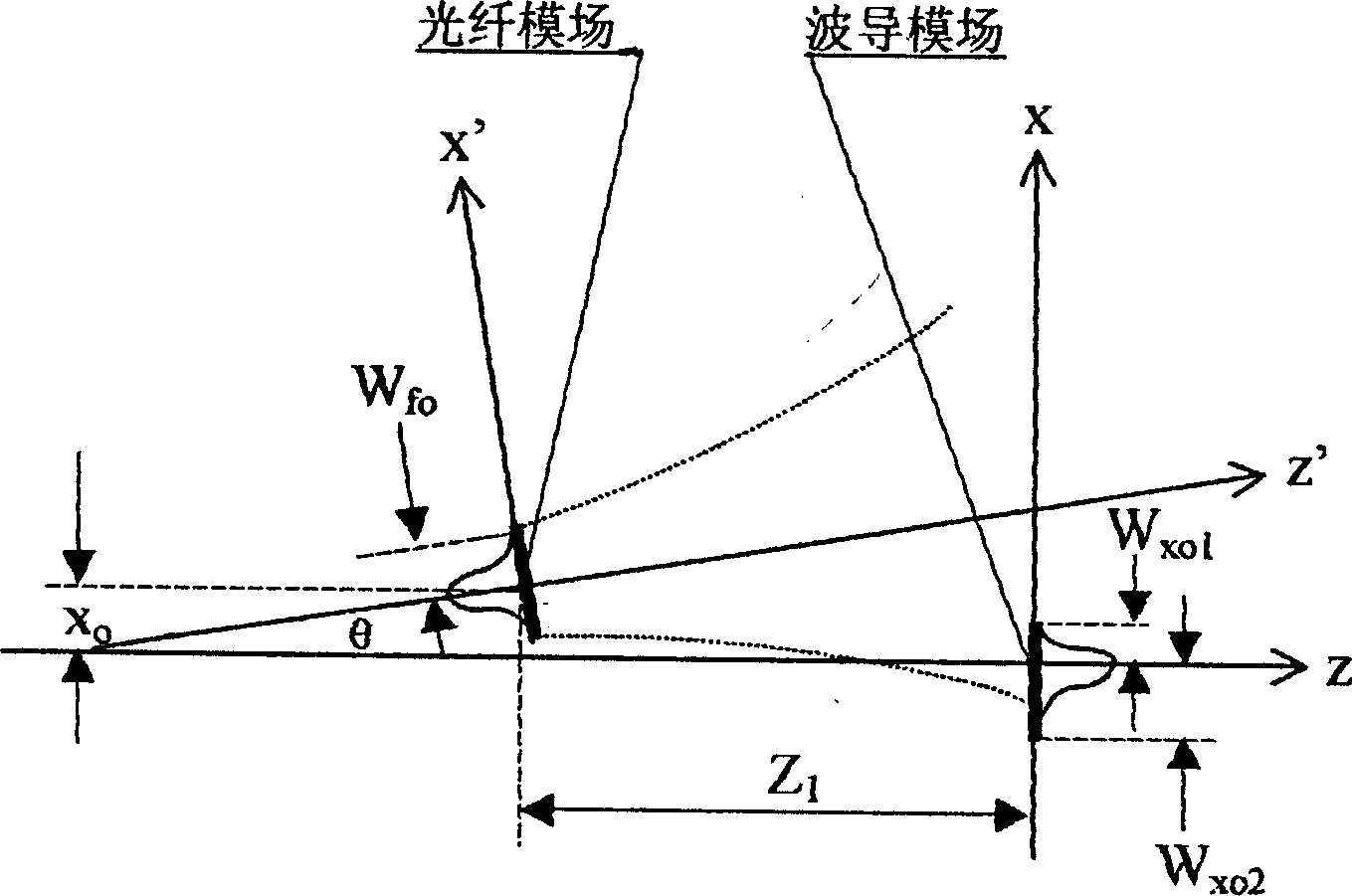
This invention relates to optical fiber systems where light is launched into and propagated in the fundamental mode of graded-index multimode fiber. Generally, it is not possible to launch light exclusively into the fundamental mode of graded-index multimode fiber by butt-coupling the multimode fiber to an arbitrary fiber carrying light from a source; several other modes may be launched. By inserting a length of a special singlemode fiber between an arbitrary fiber carrying light from a source and the graded-index multimode fiber, light can be launched exclusively into the fundamental mode of the graded-index multimode fiber. The special singlemode fiber has a modal pattern that matches the fundamental Gaussian modal pattern of the graded-index multimode fiber, which permits launching of the light into only the fundamental mode of the multi mode fiber. Several applications for propagation in the fundamental mode of graded-index multimode fiber arises. These include: fiber optic sensor systems, high data rate communication links, low modal noise links, high security links, etc.
Owner:ASAWA CHARLES K +2
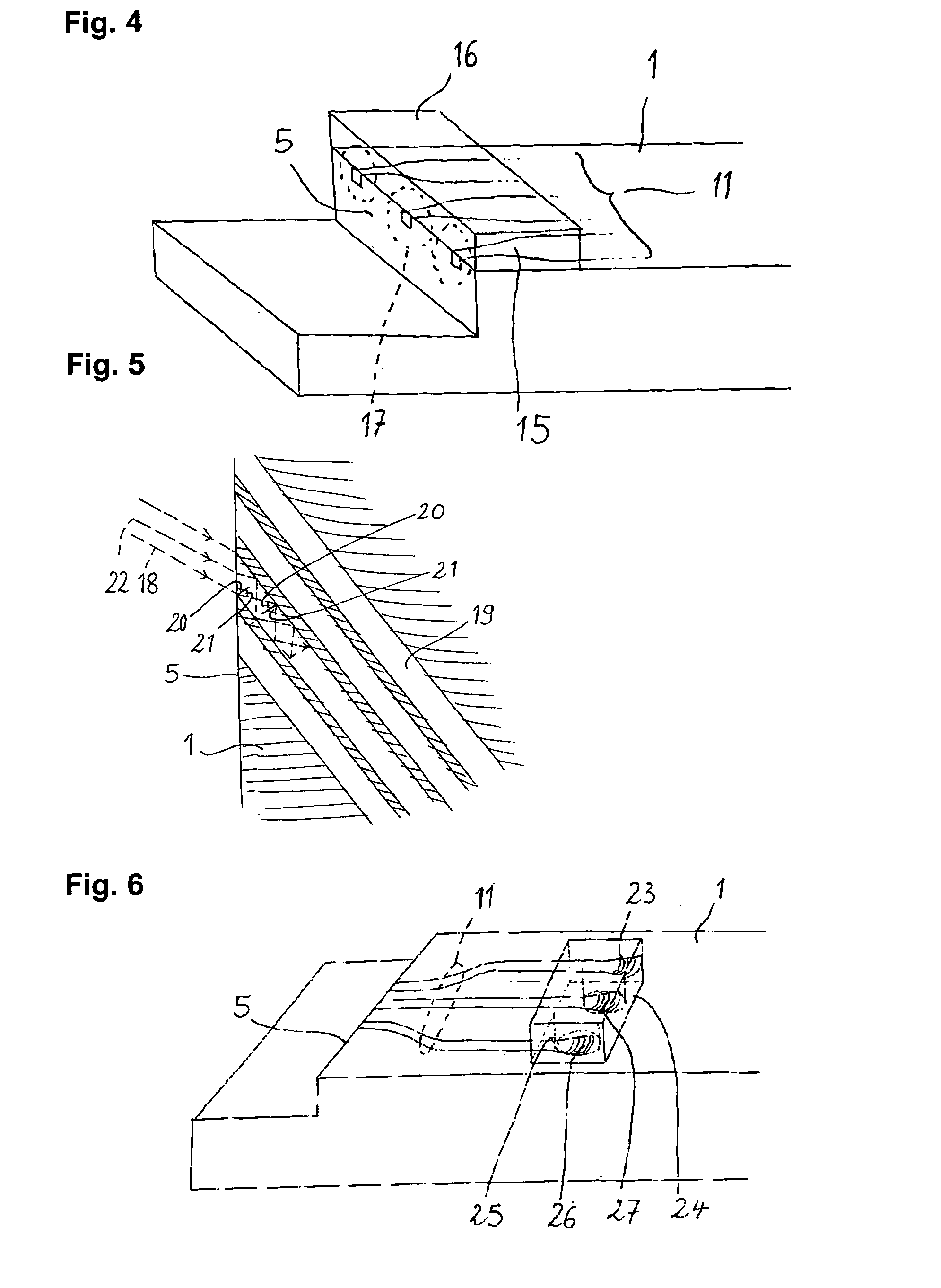
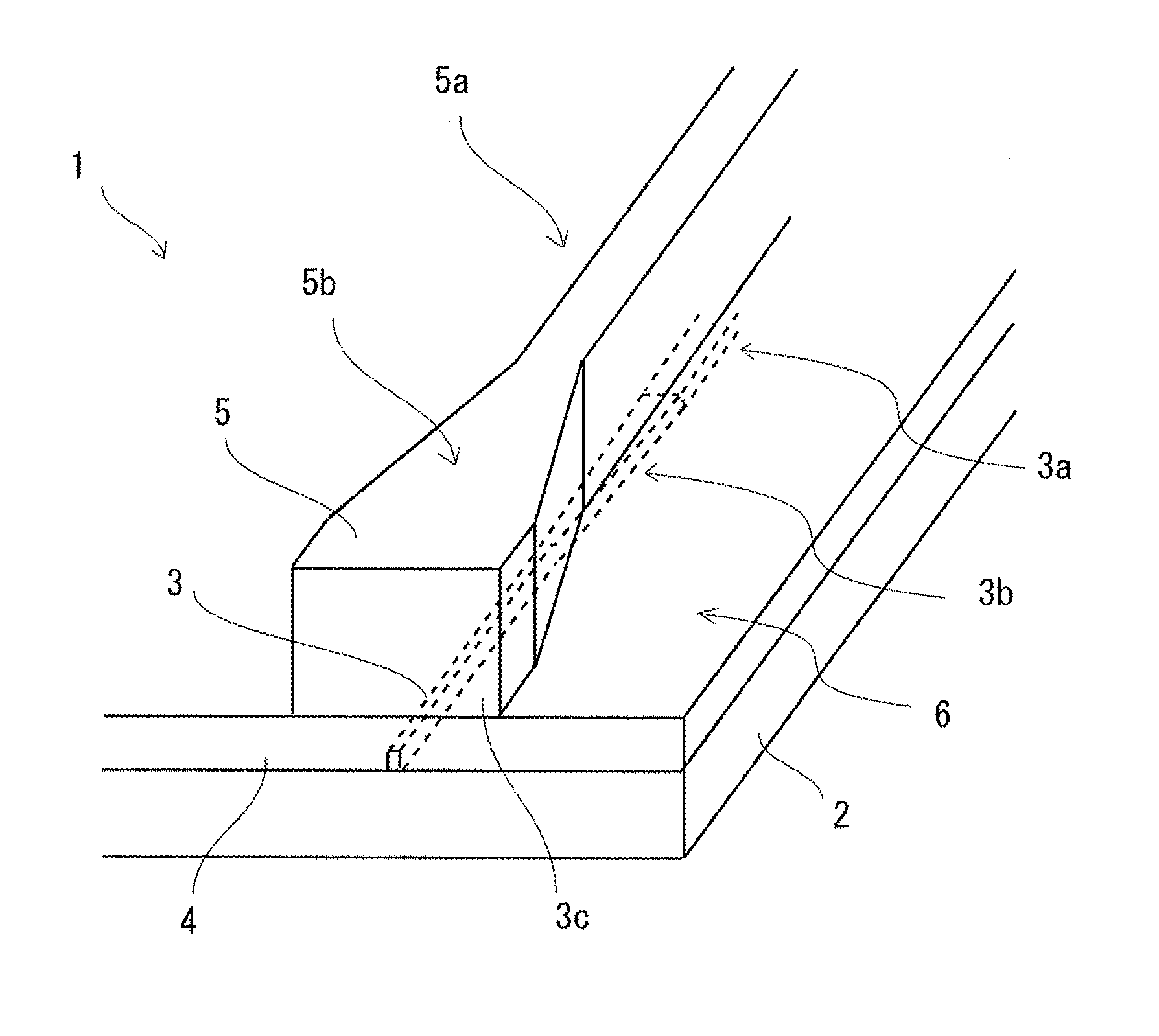
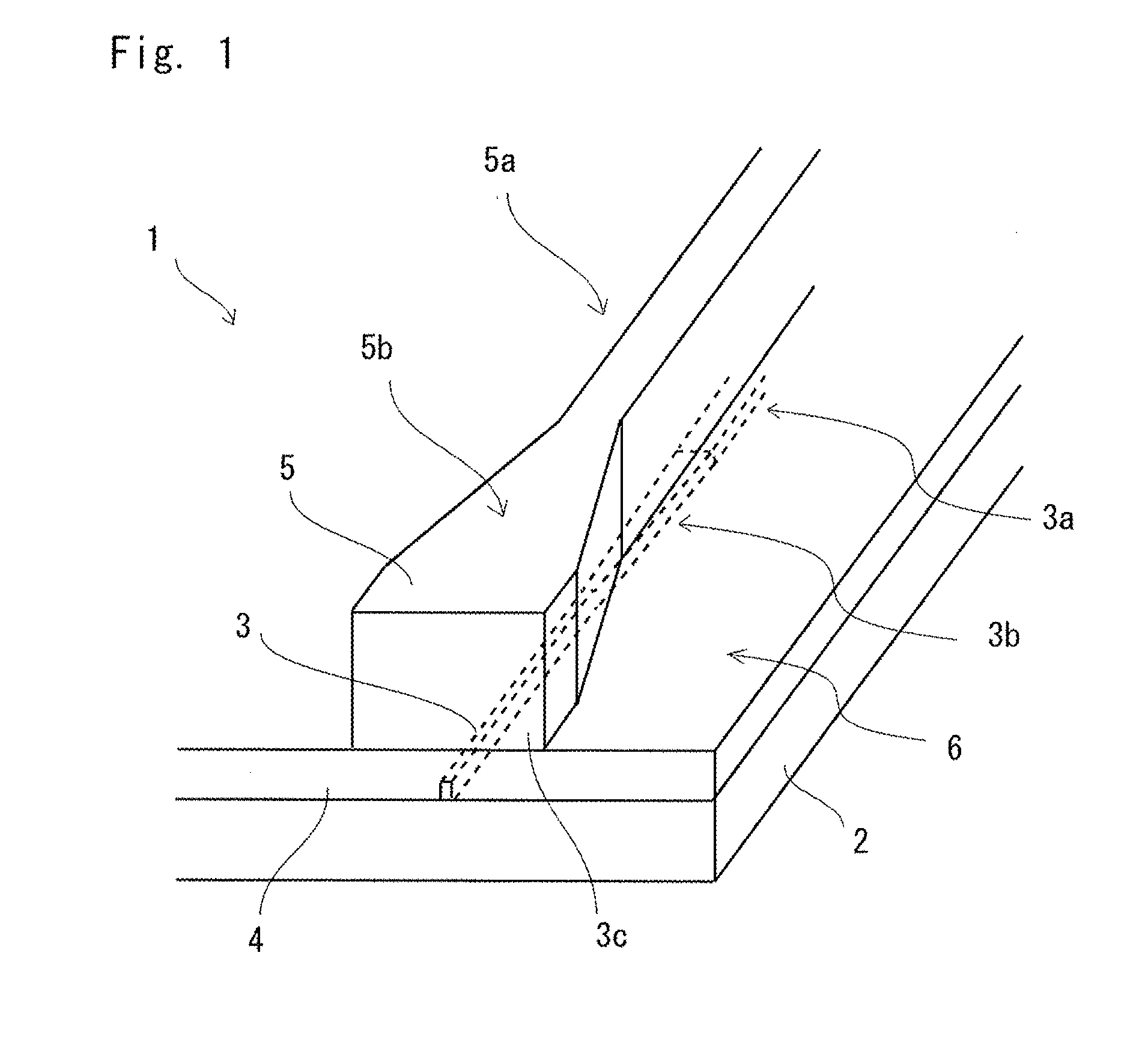
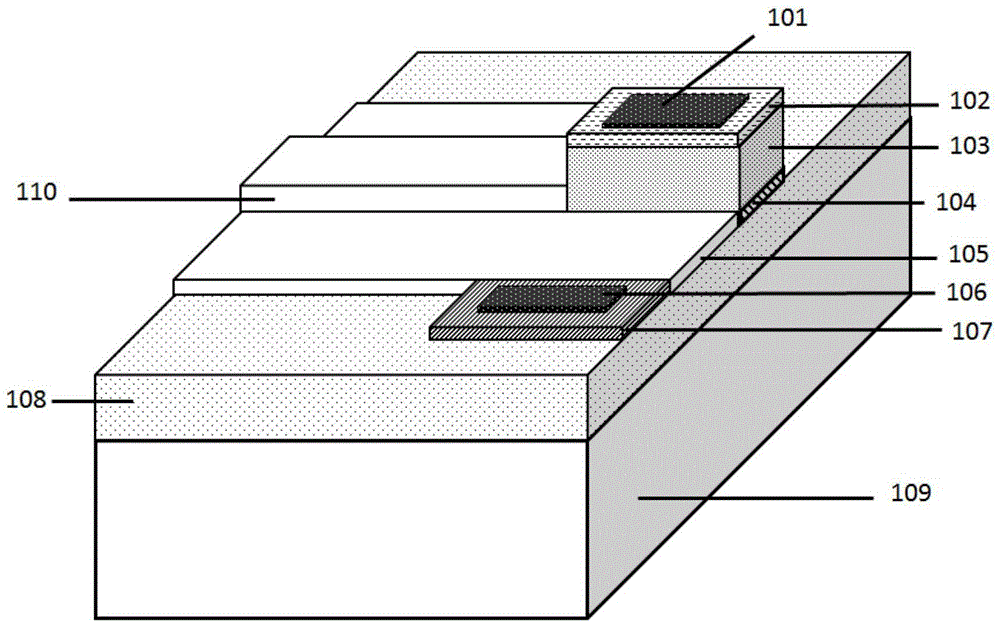
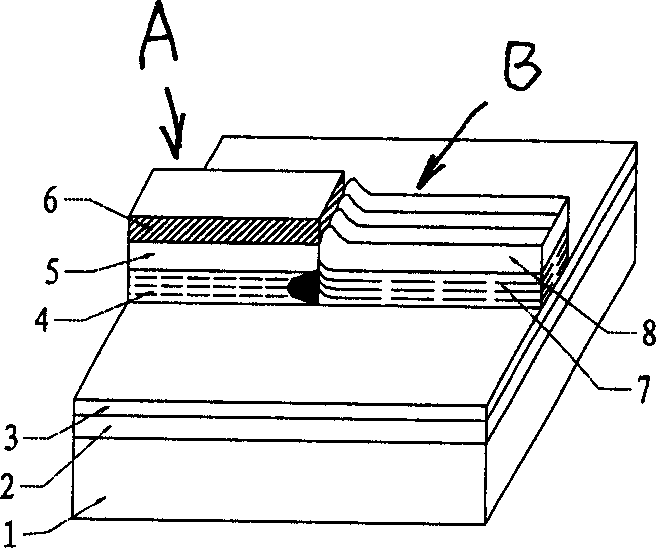
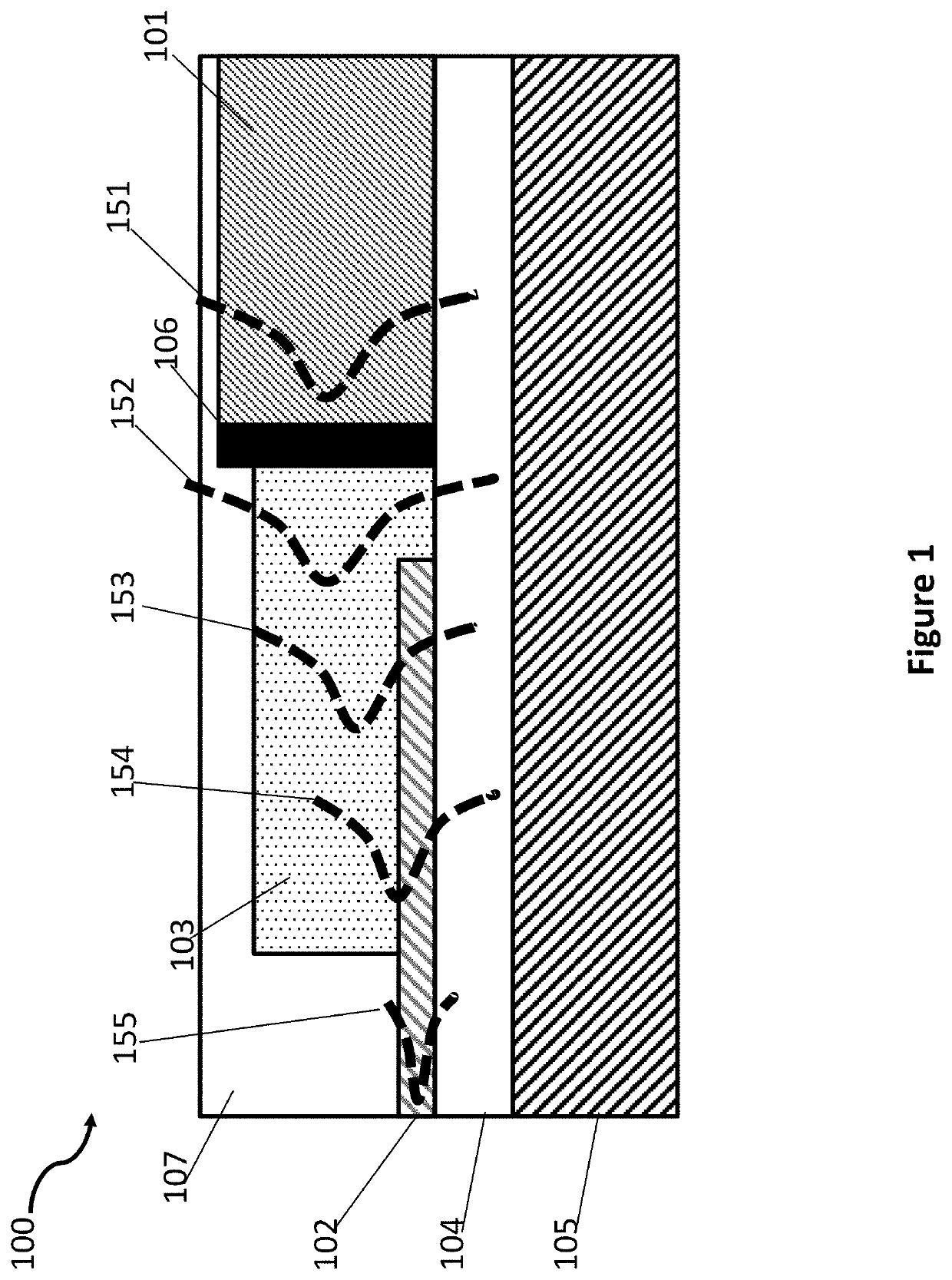
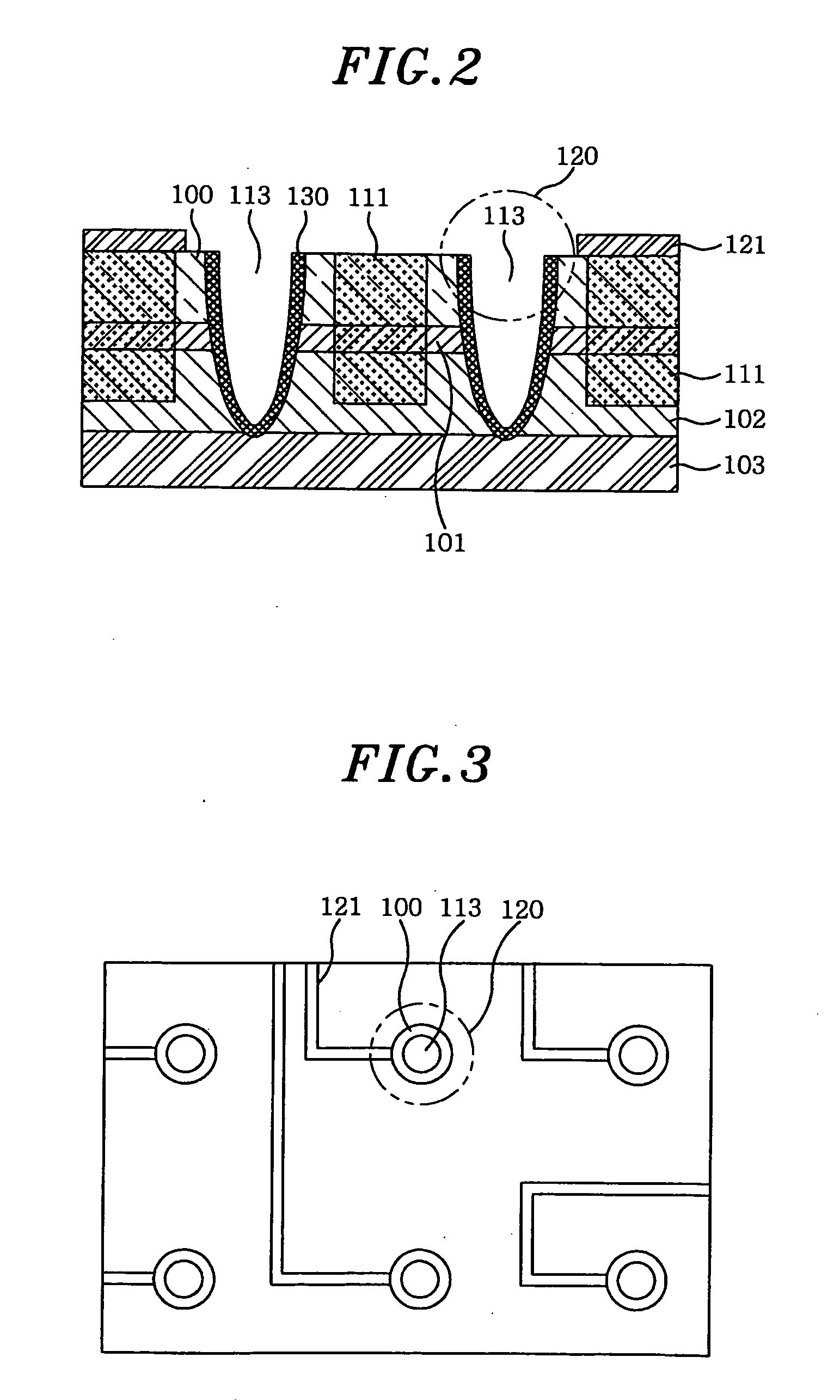
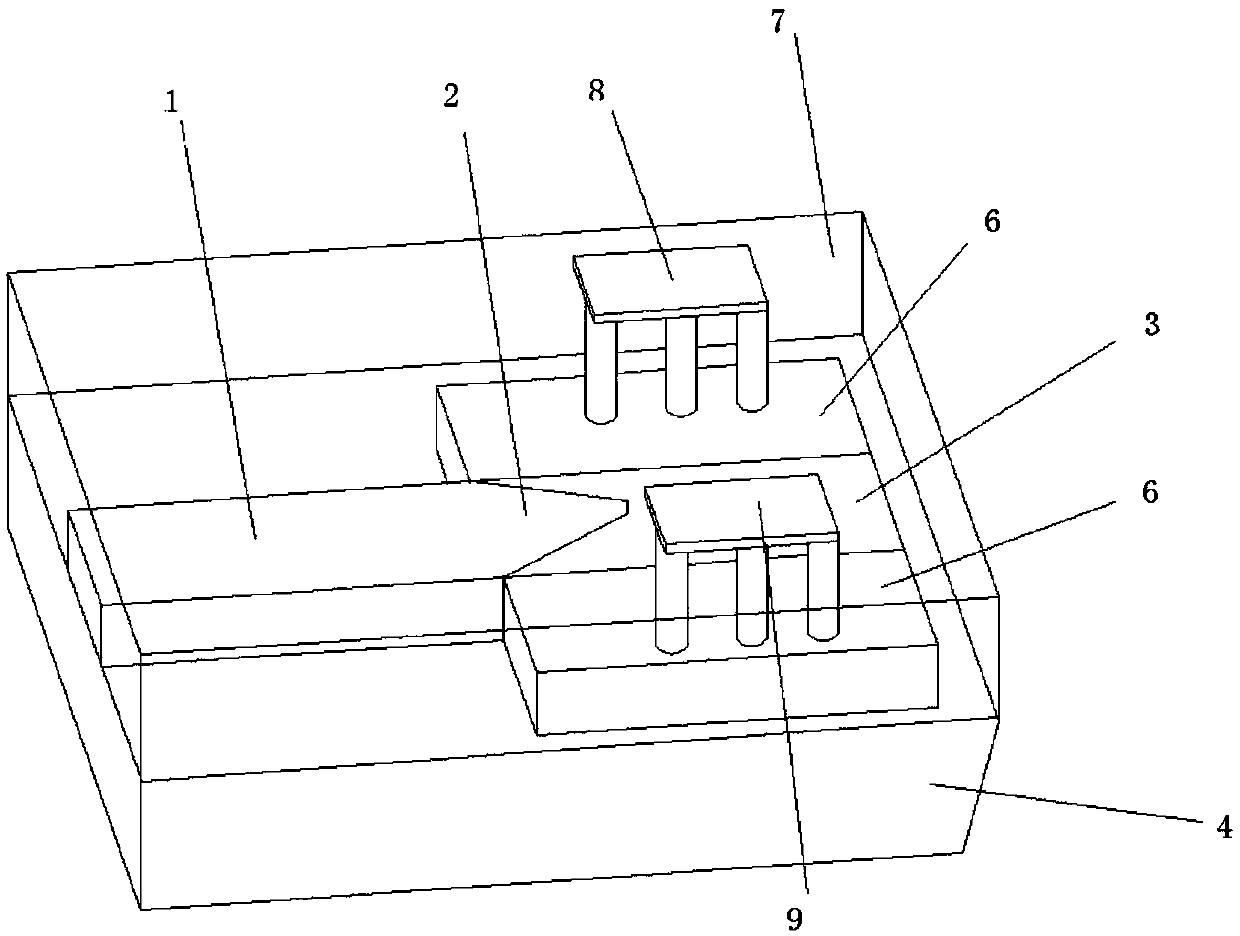
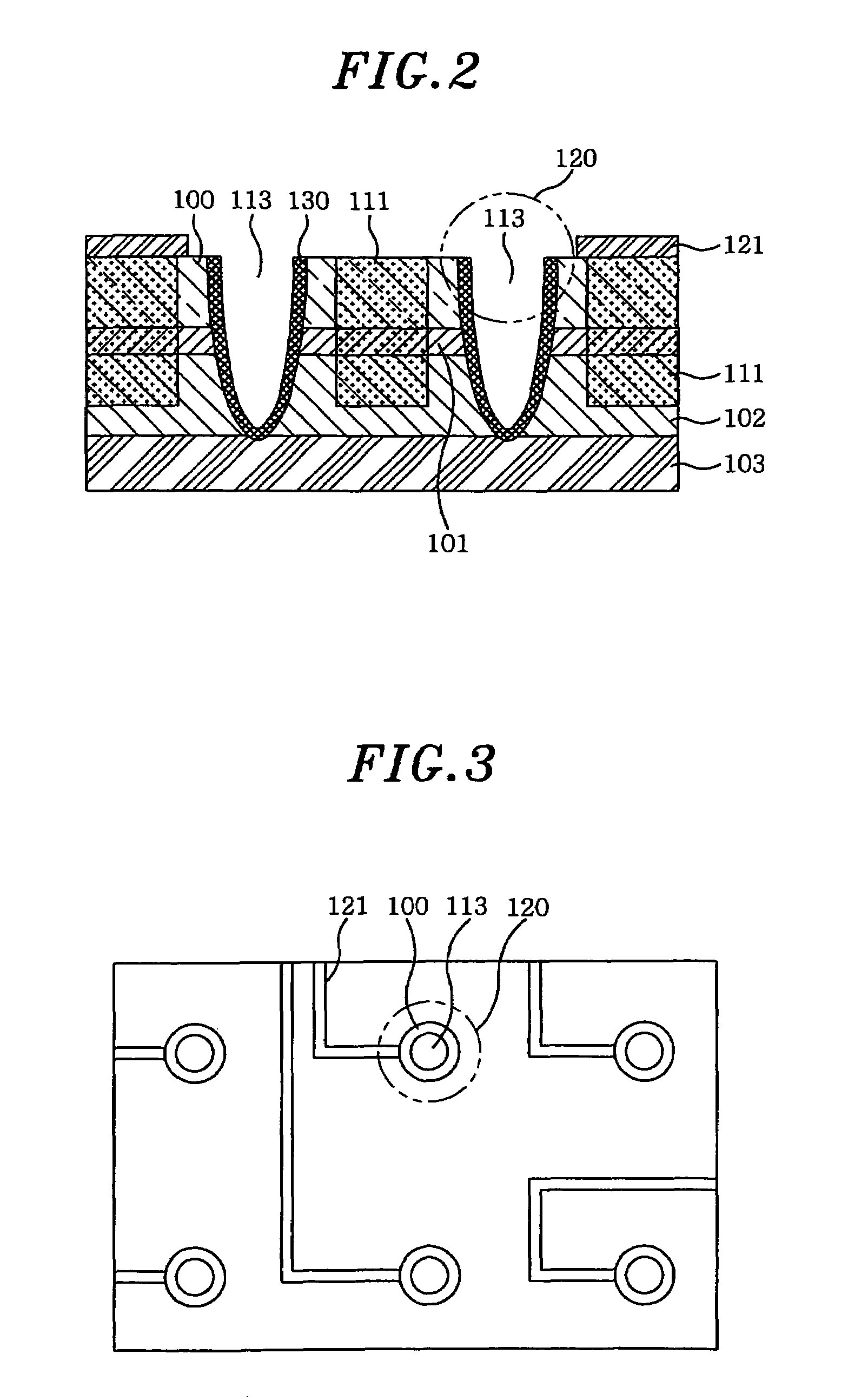
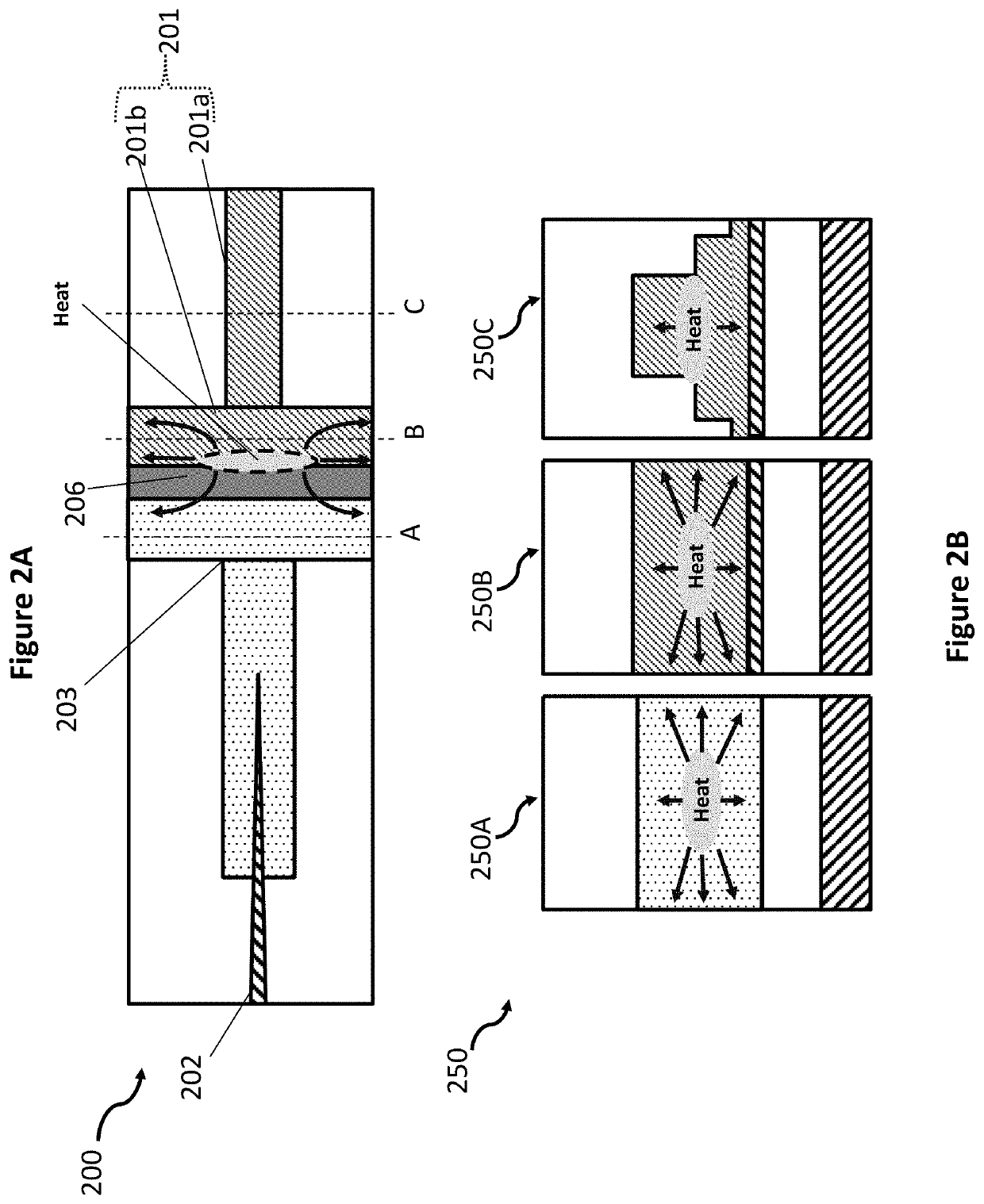
Waveguide butt-coupling type separated absorption multiplication avalanche diode
ActiveCN104882509AAvoid disturbance phenomenonImprove optical coupling efficiencySemiconductor devicesRidge waveguidesOhmic contact
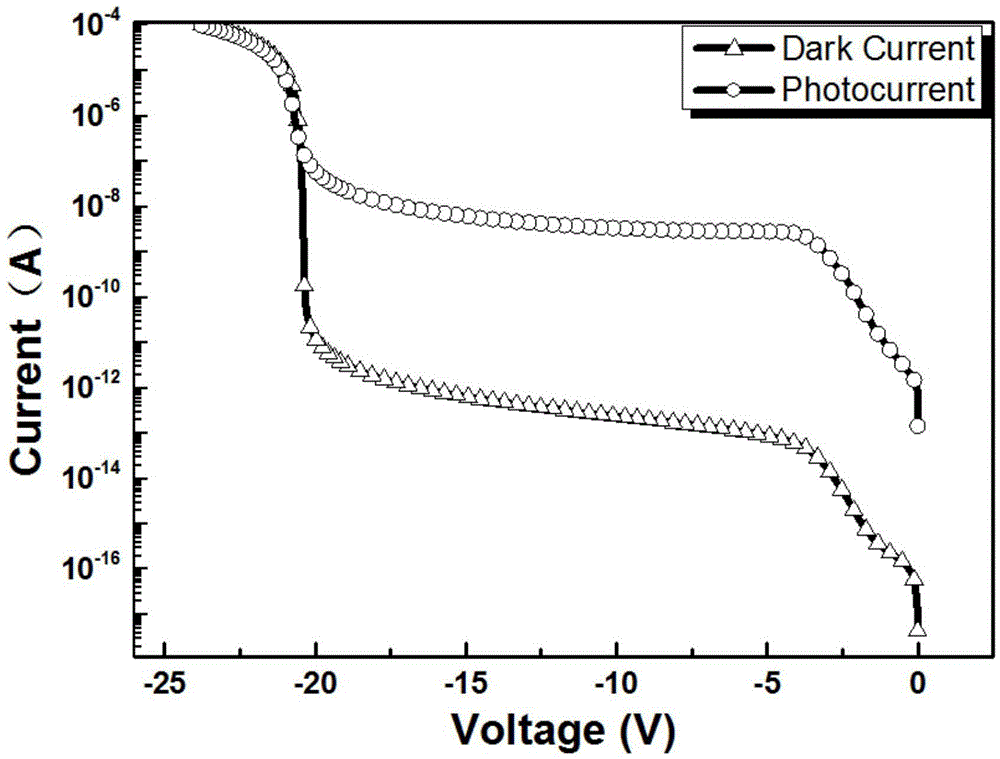
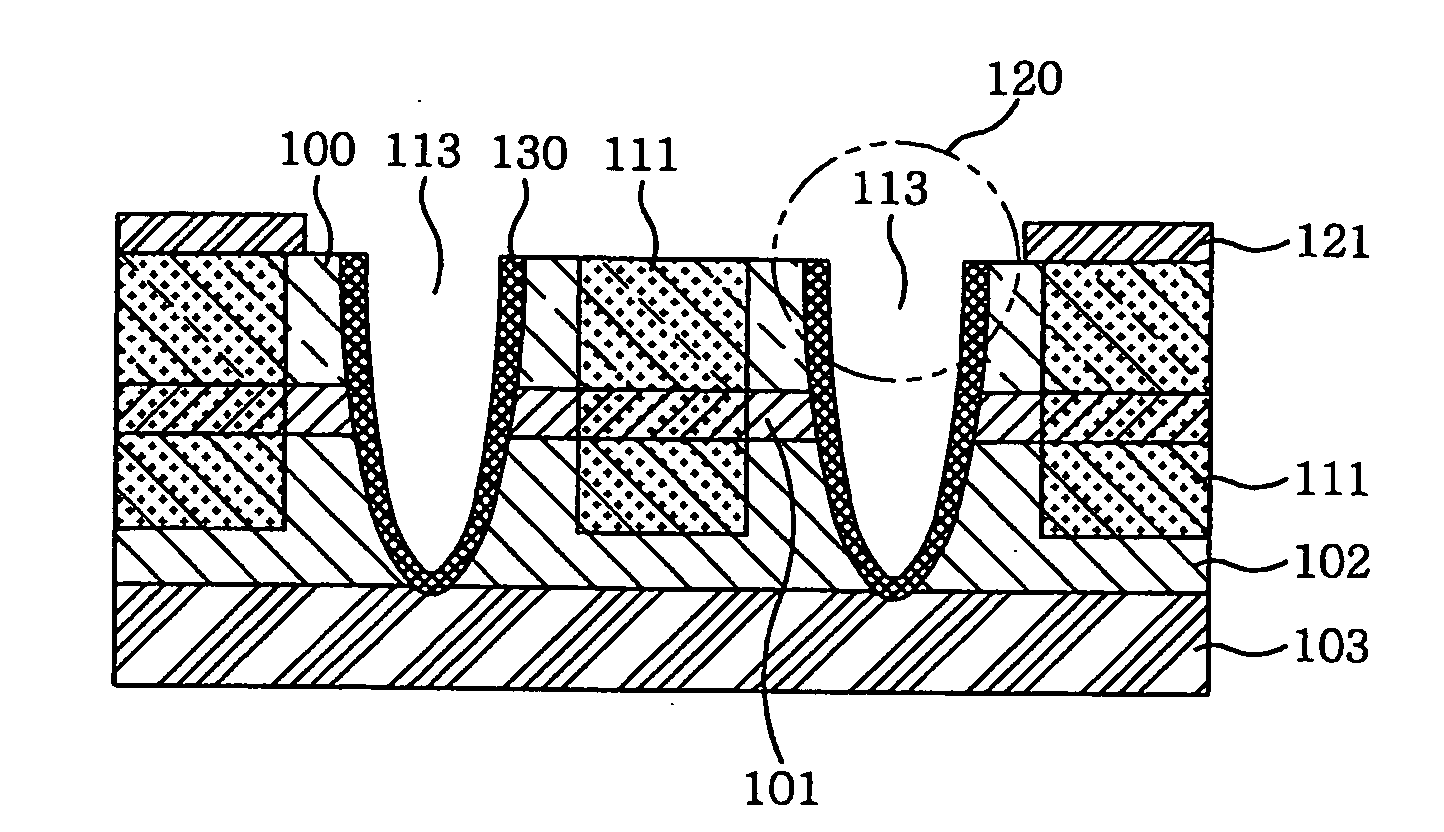
The invention discloses a waveguide butt-coupling type separated absorption multiplication avalanche diode which is capable of detecting weak communication optical signals, and relates to the fields of semiconductor photoelectric devices and optical interconnects. The waveguide butt-coupling type separated absorption multiplication avalanche diode comprises a p+ type ohmic contact electrode (101), p+ type ohmic contact layer (102), an absorption layer (103), a p type charge region (104), a high field multiplication region (105), a n+ type ohmic contact electrode (106), a n+ type ohmic contact region (107), an insulating buried layer (108), a substrate (109) and a ridge waveguide (110). The waveguide butt-coupling type separated absorption multiplication avalanche diode is characterized in that the p type charge region (104) is located at the terminal bottom of the ridge waveguide (110), and the absorption layer (103) is located at the top of the p type charge region (104) and is connected with a terminal inner ridge region of the ridge waveguide (110); and the high field multiplication region (105) and the n+ ohmic contact region (107) are sequentially arranged close to the p type charge region (104), have the same thickness as that of an outer ridge of the ridge waveguide (110), and extend perpendicular to the optical transmission direction of the ridge waveguide (110). As it can be seen from a schematic diagram of an I-V curve corresponding to the diode, excellent multiplication is achieved for the device.
Owner:BEIJING KANGGUAN SHIJI OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
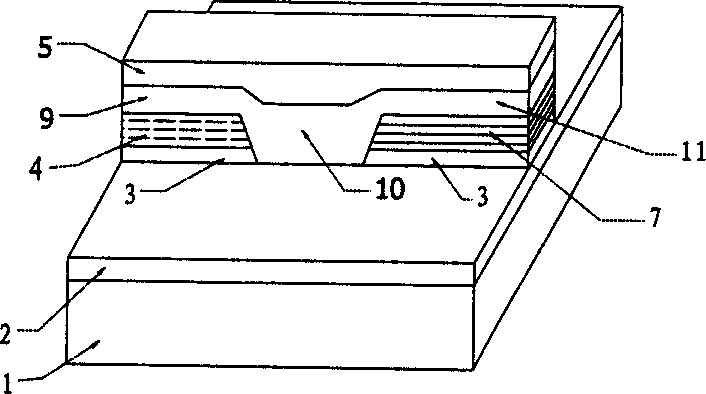
Mass center method for adjusting core making automatic end to end joint for wave-guide and optical fiber
InactiveCN1462891AAvoid direct searchAlleviating demanding precision requirementsFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesHeat stabilityPeak value
A centroidal centralizing method for automatic butt coupling between waveguide and optical fibre features that the peak position can be determined by measuring the calculating the mass center near the peak, and includes initializing, coarse steps, fine steps, integration to find mass center, and repeating said steps for finding out the mass center of another dimension. Its equipment is composed of voltage-stabilized power supply, heat-stability light source, two sets of 6D precise regulator, regulator for fixing waveguide, drive controller of step motor, microscopic photography and observing system, high-resolution optical powermeter, and computer.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Multiple-quantum well waveguide butt-coupling method
ActiveCN102545047AInterface corrosion morphology is goodPrecise control of corrosion depthOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureCoupling lossEtching
The invention relates to a multiple-quantum well waveguide butt-coupling method comprising the following steps of: A, carrying out primary epitaxy on a substrate to obtain a multiple-quantum well structure; B, after a dielectric film is deposited, carrying out mask photoetching, and removing a waveguide part of a first region requiring secondary epitaxy by using a three-step etching method; C, placing an epitaxial wafer into metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment for high-temperature treatment; and D, carrying out secondary epitaxial growth to obtain a second multiple-quantum well structure. By using the method, an attractive interface etching appearance can be achieved, cavities caused during growth can be avoided, the butting quality can be effectively improved, the coupling loss can be reduced, and good repeatability can be obtained. The multiple-quantum well waveguide butt-coupling method can be used for manufacture and batch production of various photoelectronic integrated chips.
Owner:WUHAN HUAGONG GENUINE OPTICS TECH
Multi-quantum well waveguide butt coupling method
InactiveCN1464603AImprove coupling efficiencyImprove stack bending phenomenonLaser detailsCoupling light guidesCoupling lossElectron
The invention discloses a multiple quantum well wave-guide end-to-end coupling process comprising, (1) epitaxially growing the multiple quantum well structure of the device A on the substrate, (2) depositing a layer of dielectric-coating, and mask photo-etching, etching the multiple quantum structure besides the A strips, (3) epitaxially growing the multiple quantum well structure of the device B, (4) mask photo-etching the less satisfying growing quality portion of the A and B interface. (5) extending optimization of the designed body material to the larger area, to serve simultaneously as both the up waveguide of device A and B, and the coupling waveguide between them. The process of the invention may be used to eliminate the inanity and multiple quantum well bending caused by direct linkage, to lower coupling loss and to increase optical output power. The invention can be applied to the making of a plurality of photoelectron integrated device.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
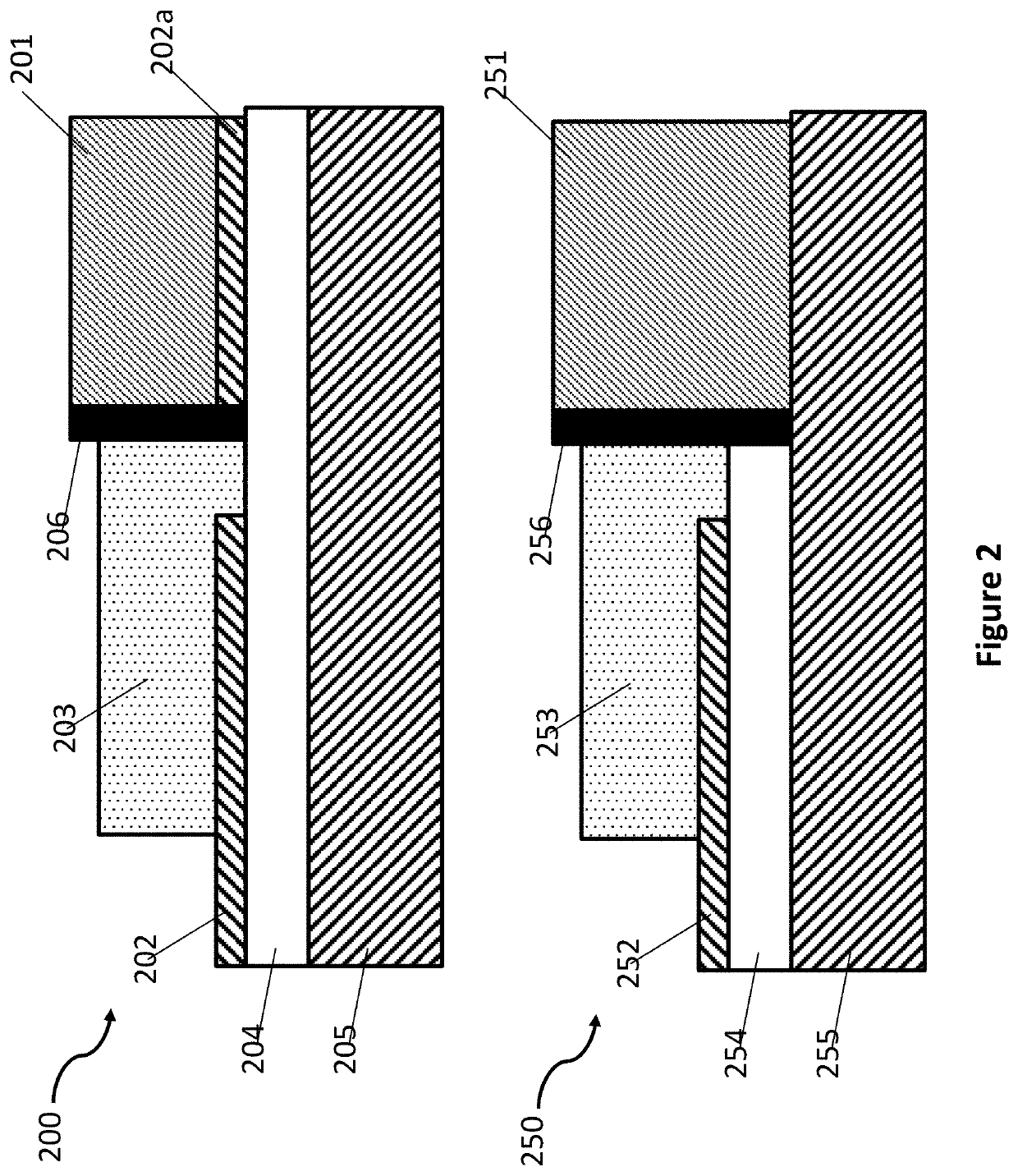
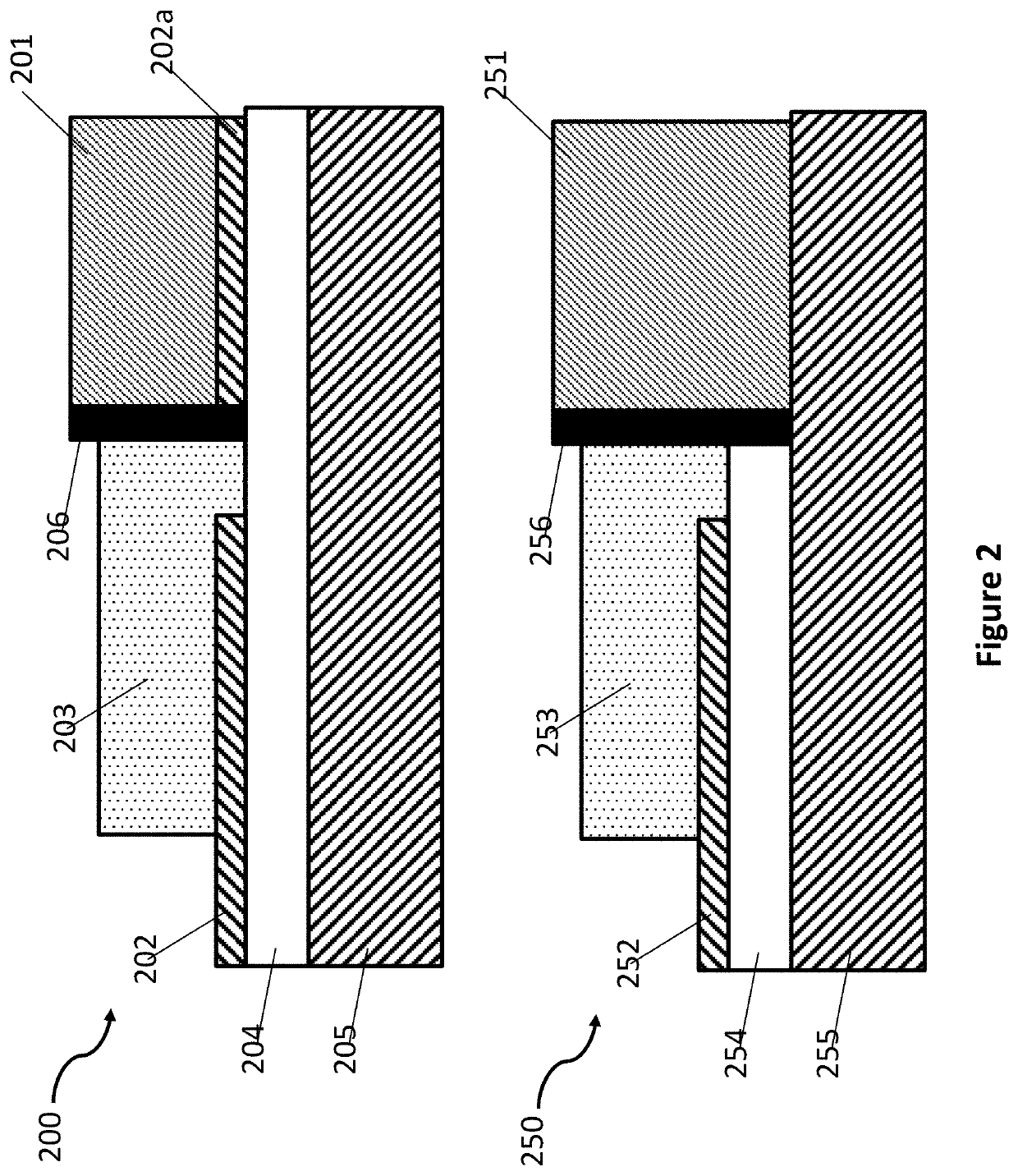
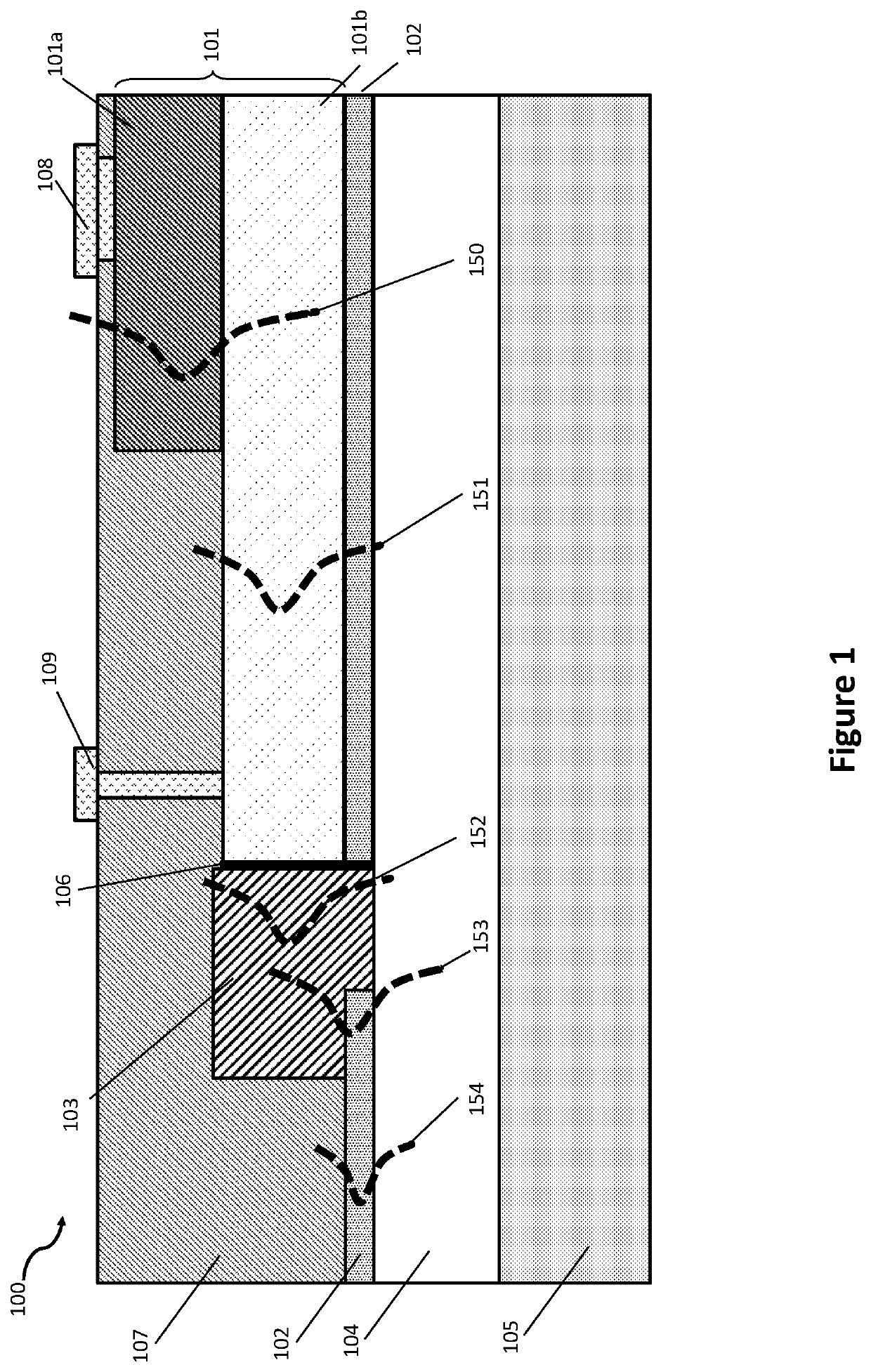
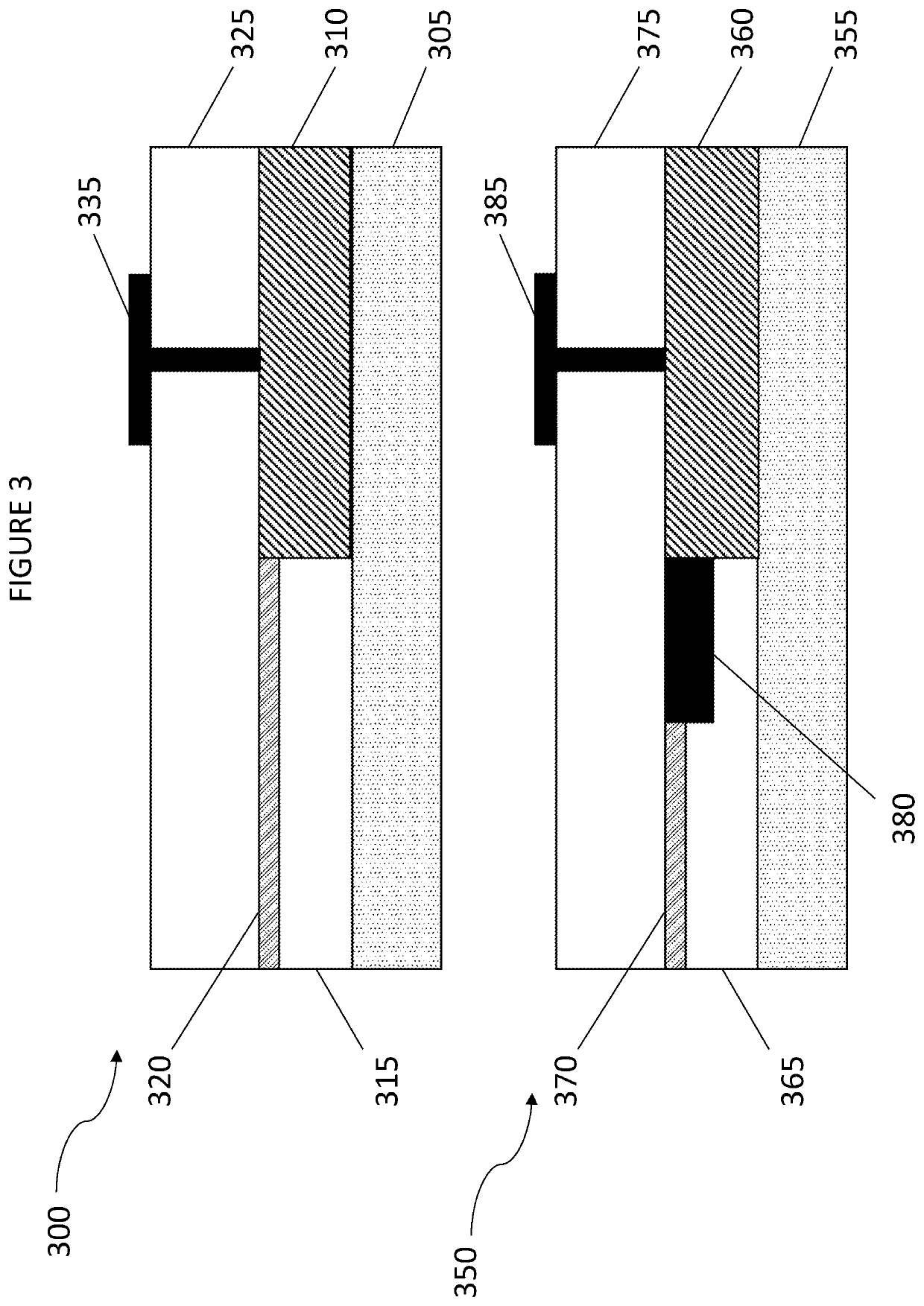
Integrated active devices with improved optical coupling to dielectric waveguides
ActiveUS10718898B1Facilitates efficient adiabatic transformationOptical waveguide light guideOptical couplingMaterials science
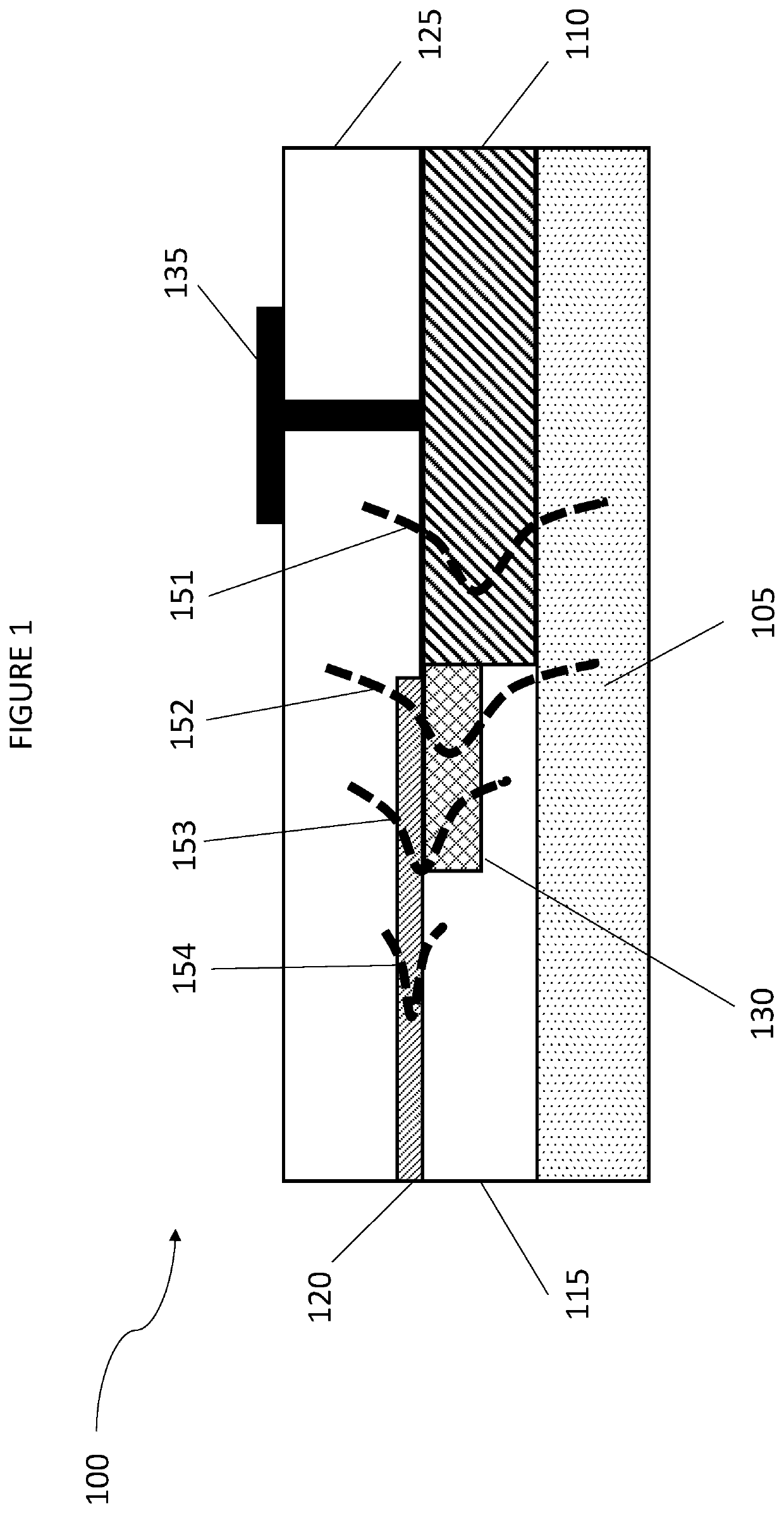
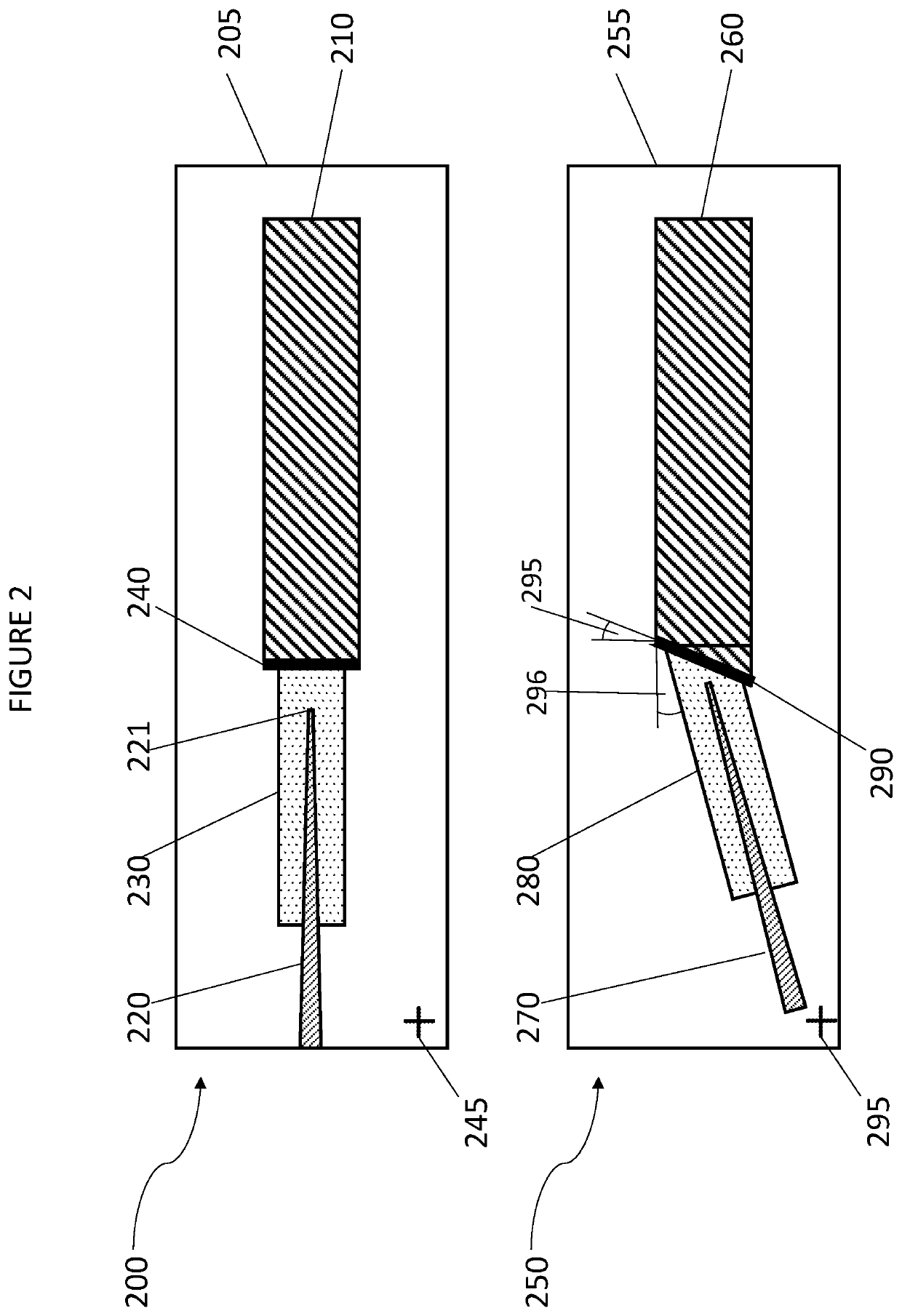
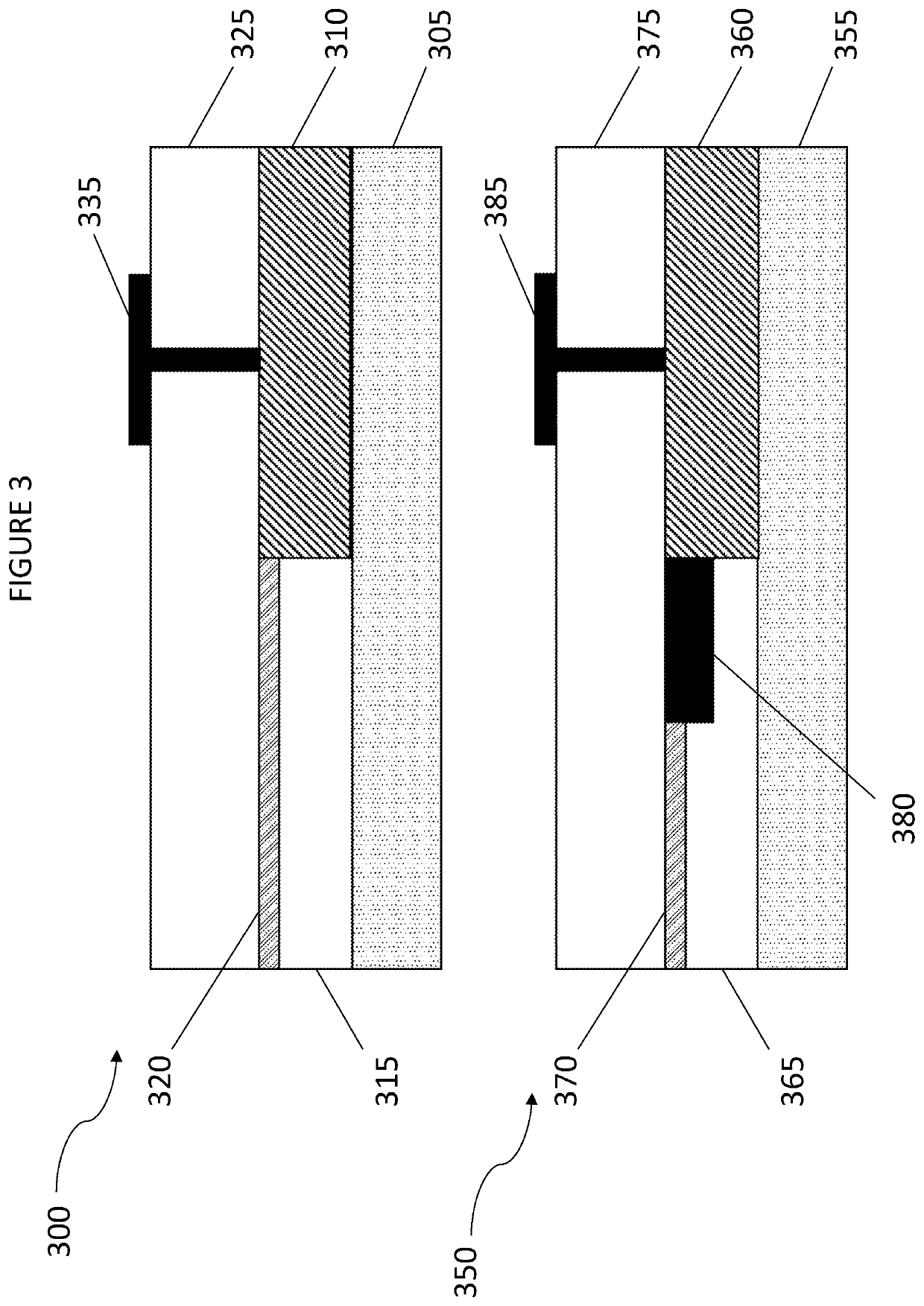
An optical device comprises first, second and third elements fabricated on a common substrate. The first element comprises an active waveguide structure supporting a first optical mode, the second element comprises a passive waveguide structure supporting a second optical mode, and the third element, at least partly butt coupled to the first element, comprises an intermediate waveguide structure. If the first optical mode differs from the second optical mode by more than a predetermined amount, a tapered waveguide structure in at least one of the second and third elements facilitates efficient adiabatic transformation between the first optical mode and the second optical mode. Mutual alignments of the first, second and third elements are defined using lithographic alignment marks.
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS LLC
Optical conversion element and optical conversion element manufacturing method
InactiveUS8873906B2Highly efficient optical couplingImprove performanceOptical articlesCoupling light guidesAnti-reflective coatingDual core
Disclosed is an optical conversion element capable of highly efficient optical coupling between a silicon waveguide and a general single-mode optical fiber only by butt-coupling without requiring anti-reflective coating. One embodiment is an optical conversion element that includes a waveguide structure and converts a mode field of guided light and is characterized in that at least a dual core is included, an innermost core of the dual core is a silicon inverse tapered thin wire core, a first outer core is a forward tapered ridge core having a ridge structure formed of an oxide film with only width of the ridge core changing. The first outer core is positioned on a narrow width side of the innermost core.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical waveguide array-optical fiber array automatic butt-coupling parallel index optimization method
InactiveCN104836620AImproving the Insufficiency of Automatic Aligning MethodReduce the number of operationsCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionFiber arrayOptical power
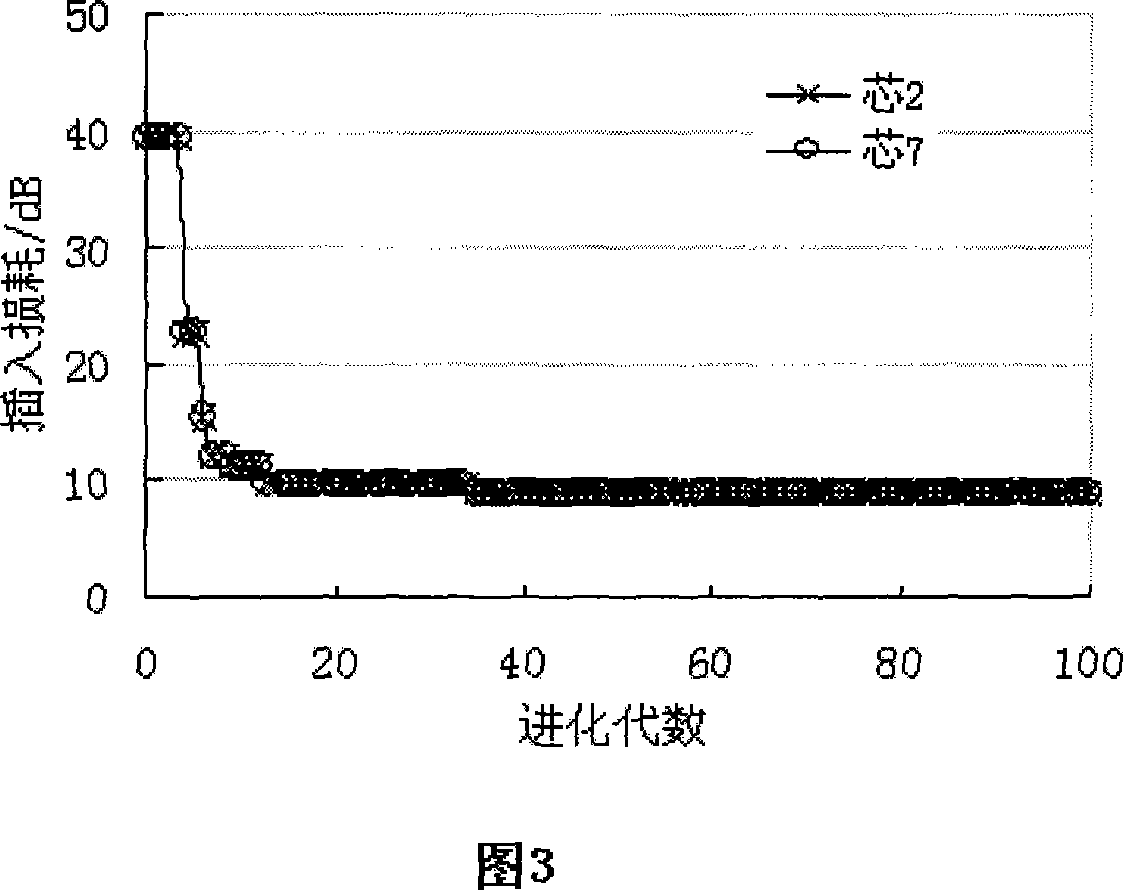
The invention provides an optical waveguide array-optical fiber array automatic butt-coupling parallel index optimization method. The optical waveguide array-optical fiber array automatic butt-coupling parallel index optimization method comprises that mapping between an optical waveguide array-optical fiber array auto-aligning physical parameter and a parallel index optimization model is established, and a first objective function and a second objective function are obtained; a maximum evolutional generation is set, input single-mode fiber arrays and output single-mode fiber arrays enter specified spatial positions in a specified direction and attitude according to the regulation of each individual, optical power values of two or more than two waveguide channels are read, recorded and stored, and the Pareto sequence and the crowding distance are calculated; evaluation of each individual in one generation cluster is completed, a next generation cluster is generated by means of intersection, variation and lowliest place elimination, the evolutional generation is accumulated, whether the evolutional generation reaches the maximum evolutional generation or not is determined, if the evolutional generation reaches the maximum evolutional generation, the process is finished; if the evolutional generation does not reach the maximum evolutional generation, the intersection step is returned. According to the invention, the low-loss rapid butt-coupling automation degree and the working efficiency of an optical fiber array-waveguide device-optical fiber array system are effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC CABLE RES INST
Integrated active devices with improved optical coupling to dielectric waveguides
ActiveUS20200233149A1Facilitates efficient adiabatic transformationOptical waveguide light guideOptical couplingMaterials science
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS LLC
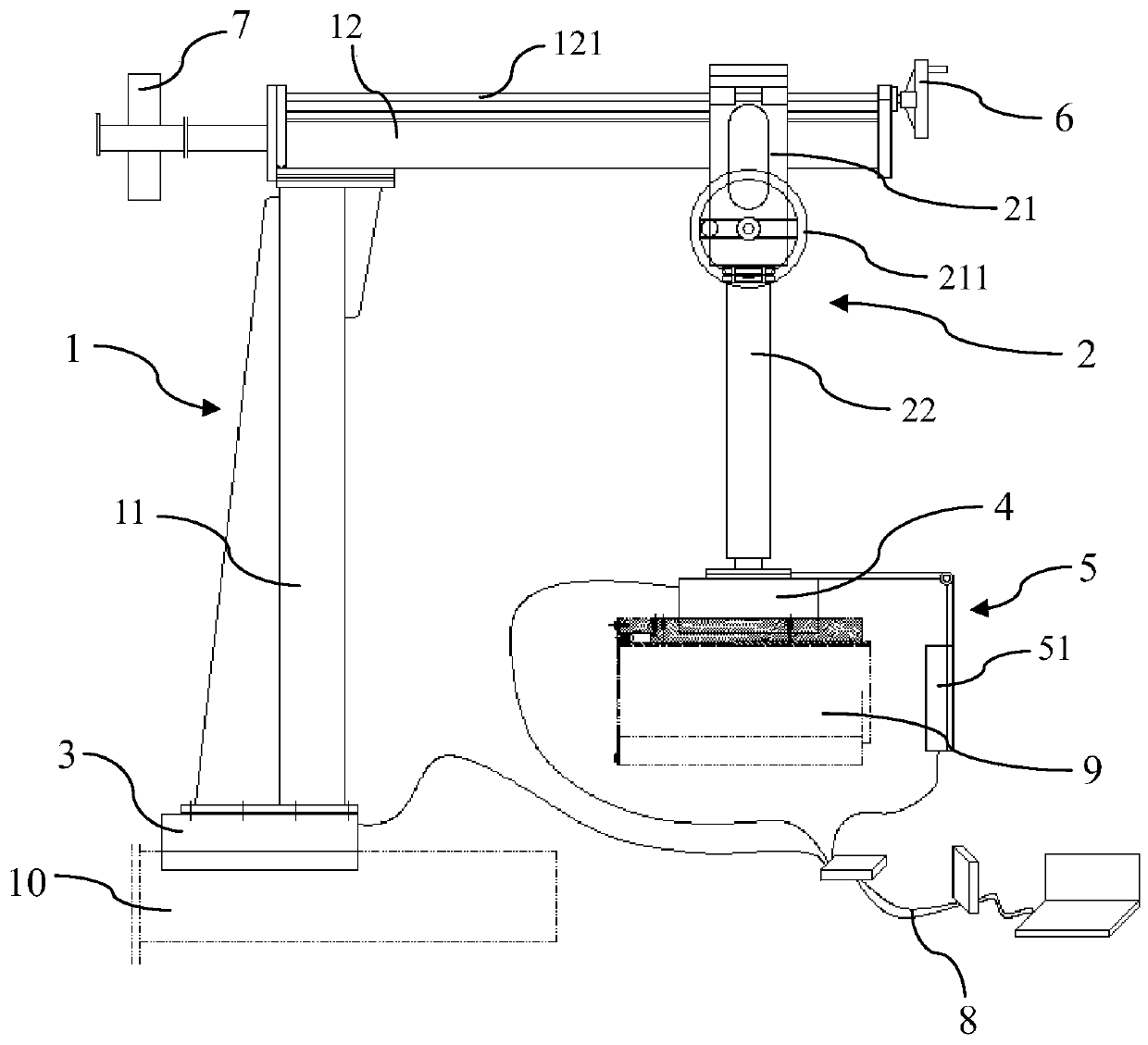
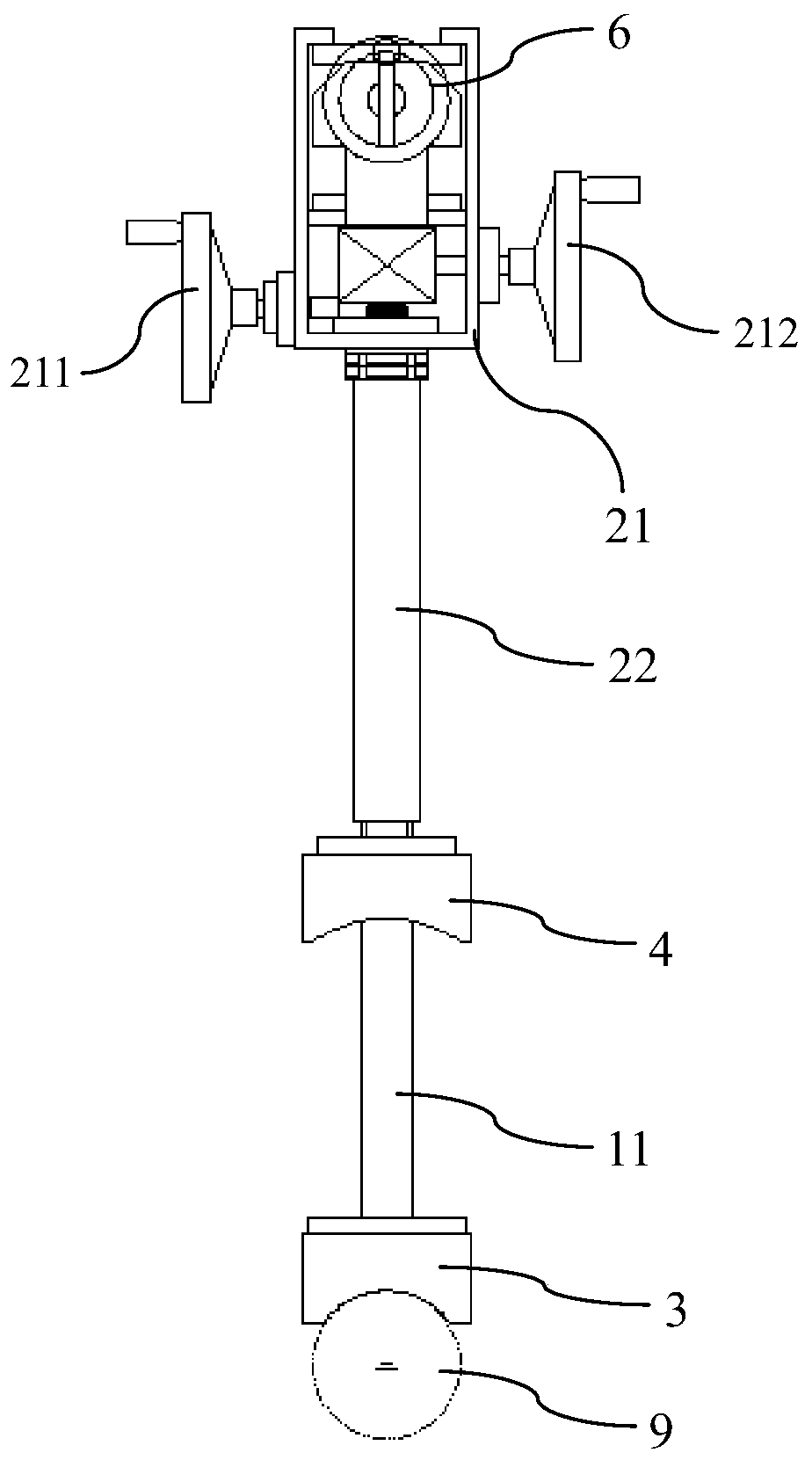
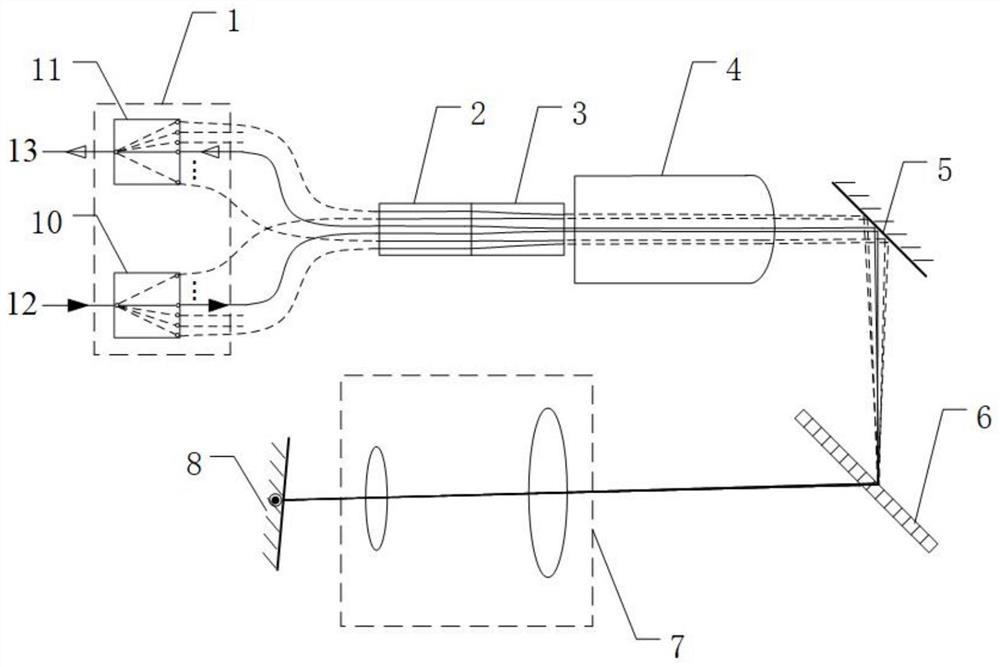
Small-diameter polarization-maintaining fiber and micro-chip fixed-shaft coupling system and method
ActiveCN106324750AConvenient coupling and dockingEasy to operateOptical fibre with polarisationFiberManufacturing technology
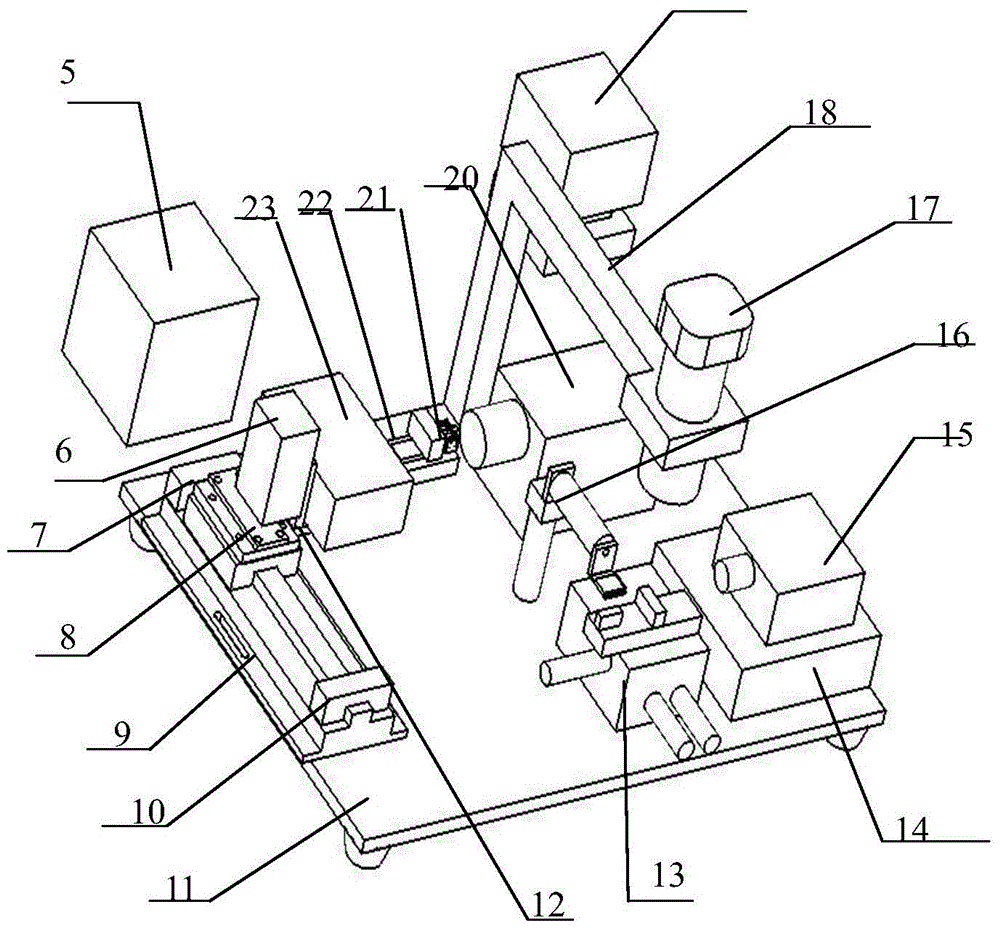
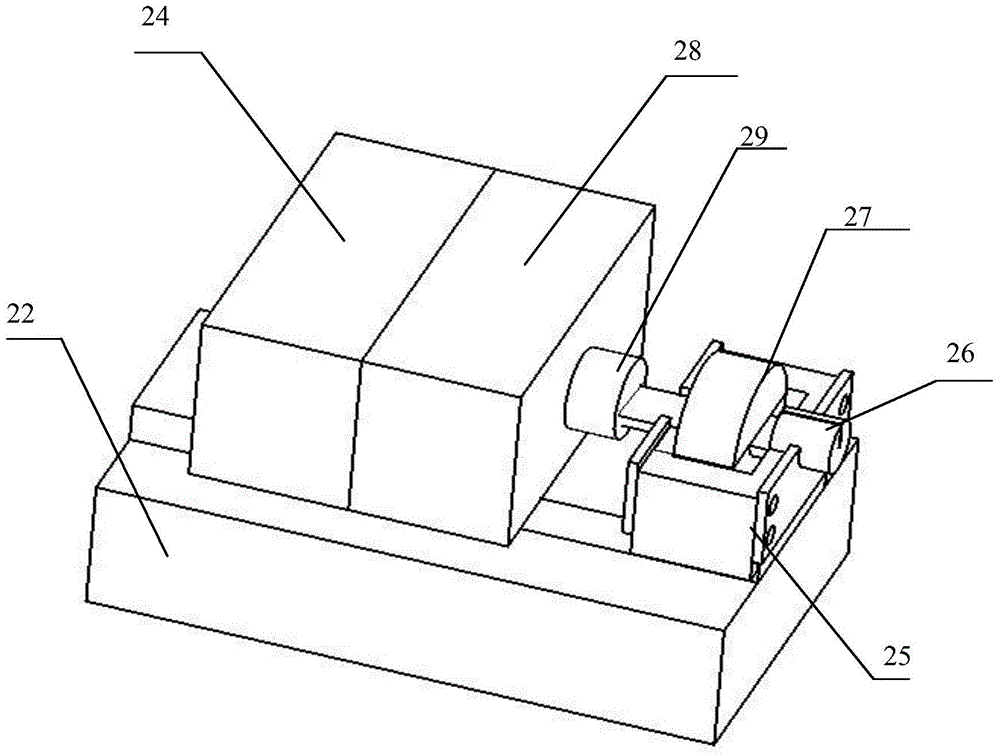
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-device fabrication and relates to a small-diameter polarization-maintaining fiber and micro-chip fixed-shaft coupling system and method. The coupling system includes an optical platform (11), a three-dimensional adjustment table I (6), a sliding block (8), a guide rail (9), a fixed base (12), a precise three-dimensional butt coupling table (13), a control processing system (19), a microscope III (20), a shaft fixing device (21), a two-dimensional fine adjustment platform (22), and a photoelectric converter (23). According to the technical scheme of the invention, a small-diameter polarization-maintaining fiber can be conveniently coupled to be in butt joint with a micro-chip while the small-diameter polarization-maintaining fiber is accurately controlled in the fixed-shaft manner at the same time. Therefore, the advantages of accurate shaft alignment, convenient operation and simple system are realized.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Butt coupling structure and method of photonic quantum ring hole emitter
InactiveUS20080138017A1Improve coupling strengthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionResistRefractive index matching
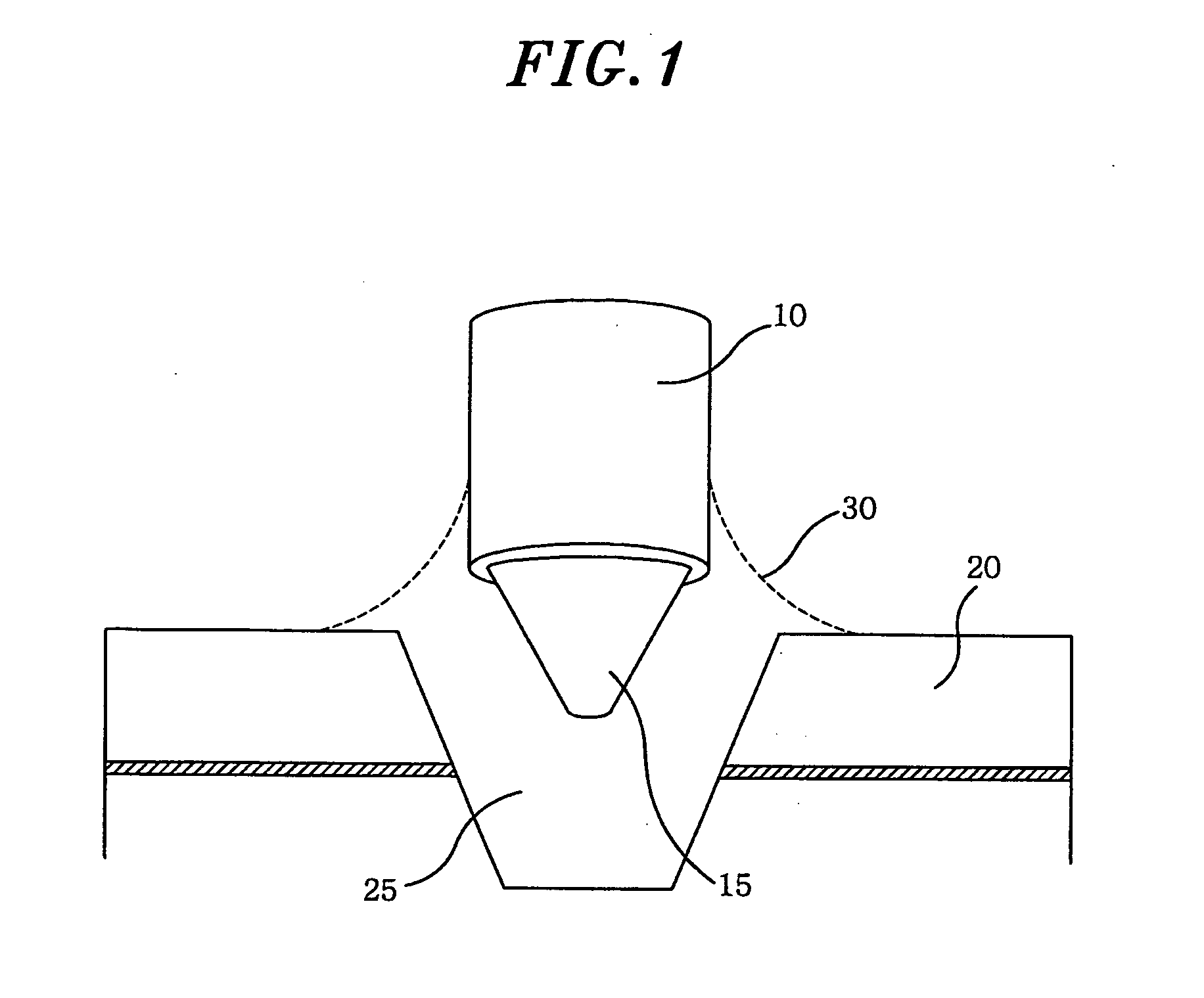
An optical coupling structure includes a PQR hole emitter having a PQR hole, and an optical fiber whose one side is tapered into the PQR hole. An index-matching solution such as a photo-resist or a photo-resist diluted solution is injected into the PQR hole to adhere the optical fiber and the PQR hole.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Mounting tool and mounting method of ship shafting case butt coupling
ActiveCN110525577AImprove securityEasy to operateVessel partsLoad-engaging elementsCouplingButt coupling
The invention discloses a mounting tool of a ship shafting case butt coupling. The mounting tool comprises a frame body and a derrick assembly, wherein the bottom end of the frame body is vertically and fixedly connected to a shaft body through a first permanent magnetic chuck, a guide rail is arranged on the frame body in the X axis direction, the derrick assembly comprises a base capable of moving along the guide rail back and forth and a derrick fixedly connected to the bottom of the base, and a Y-direction hand wheel for adjusting the derrick to move in the Y-axis direction and a Z-direction hand wheel for adjusting the derrick to move in the Z-axis direction are arranged on the base; and a second permanent magnetic chuck is arranged at the bottom end of the derrick to adsorb the coupling, and a camera device used for shooting the real-time position of the coupling is arranged on the derrick. The invention further provides a mounting method of the ship shafting case butt coupling.According to the mounting tool of the ship shafting case butt coupling, the hoisting safety of the coupling is high, besides, centering during mounting of the coupling is simple and accurate, the labor intensity is reduced, the working efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:CSSC HUANGPU WENCHONG SHIPBUILDING COMPANY
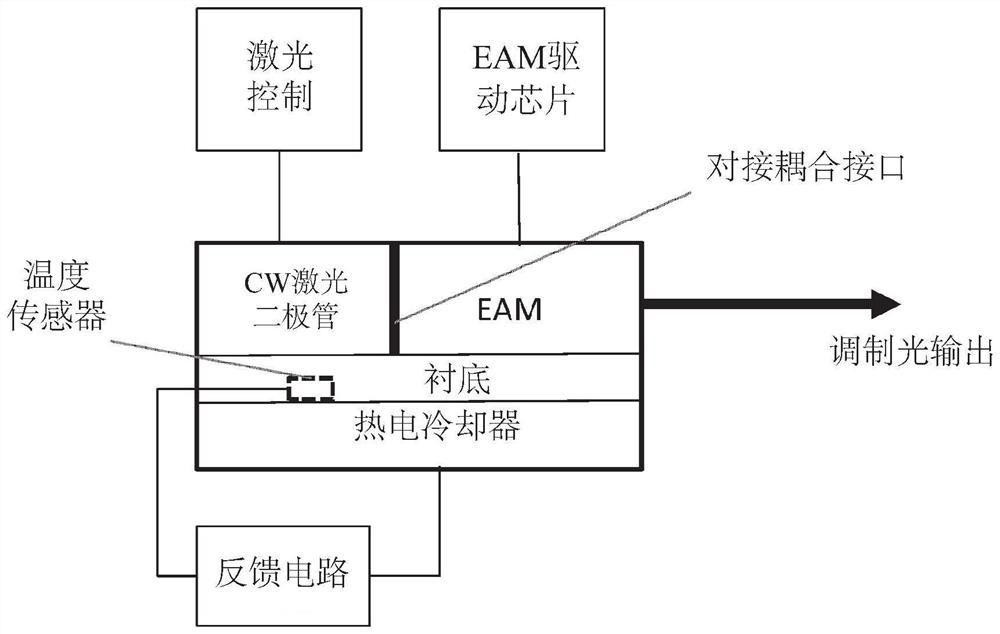
Vertically integrated electro-absorption modulated laser and method of manufacture
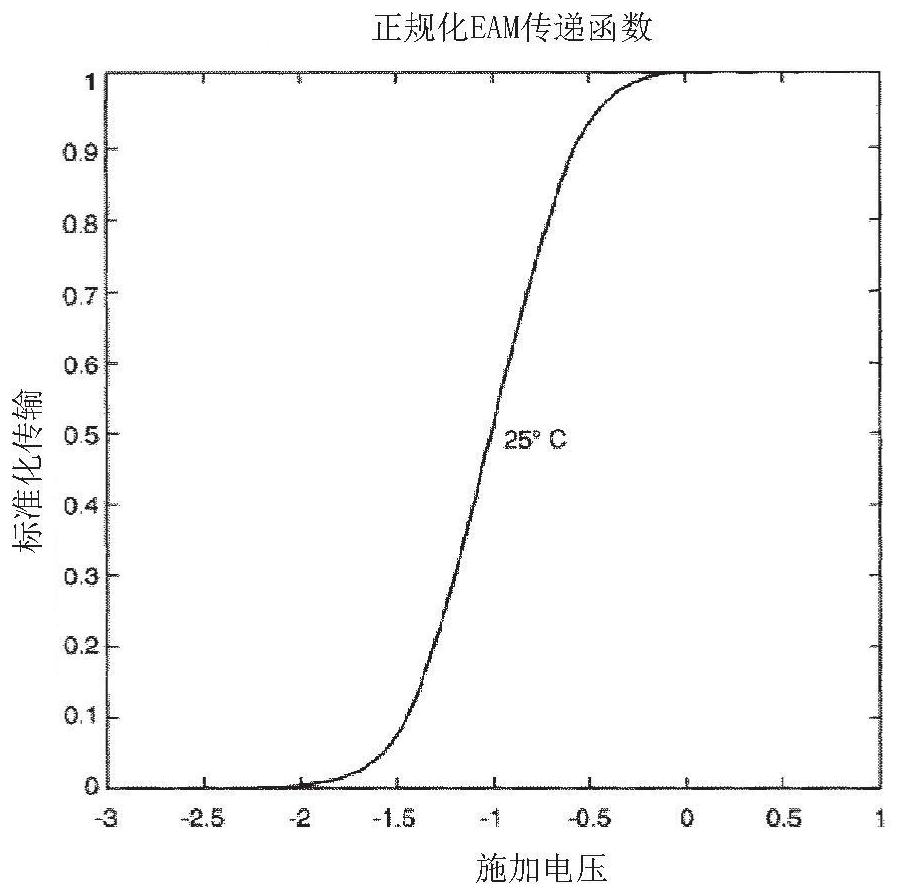
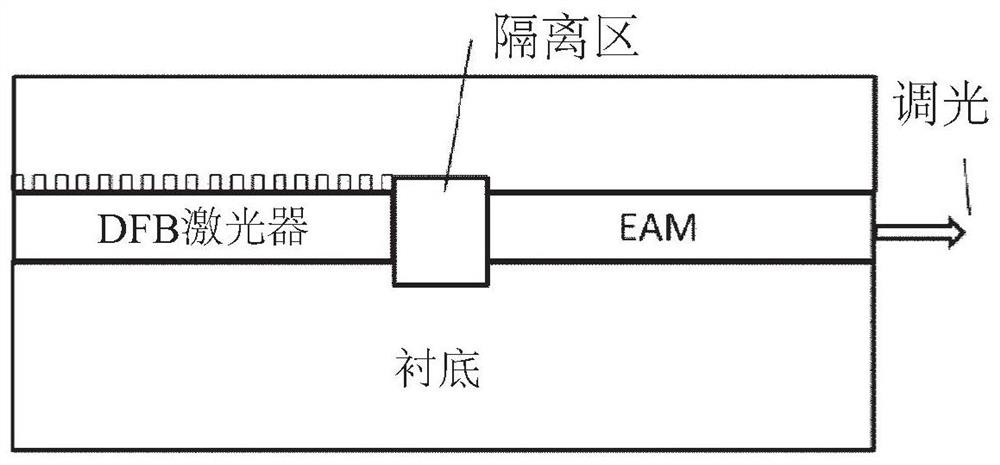
Monolithically integrated electro-absorption modulated lasers (EMLs) and methods of manufacture are disclosed. A vertical stacked waveguide vertical integration for a distributed feedback (DFB) laser, an electro-absorption modulator (EAM), and a passive output waveguide, the DFB laser, the EAM, and the output waveguide being optically coupled using a lateral tapered vertical optical coupler. Vertical integration using transverse tapered vertical optical couplers provides an alternative for traditional docking coupling of lasers and EAMs, which is possible to improve reliability of high power operation with extended lifetime. Optionally, the EML includes monolithic integrated electronic circuitry, such as drive and control electronics of the DFB laser and EAM. Advantageously, the integrated EAM drive and control circuit includes a high speed electro-optic control loop for very high speed linearization and temperature compensation, e.g., enabling advanced modulation schemes, such as PAM-4 and DP-QPSK, for analog optical data center interconnect applications. Some embodiments are compatible with fabrication using a single epitaxial growth.
Owner:ELECTROPHOTONIC IC INC
Narrow linewidth laser
ActiveCN114552378ASimple structureEasy to tuneLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionCoupling lossResonant cavity
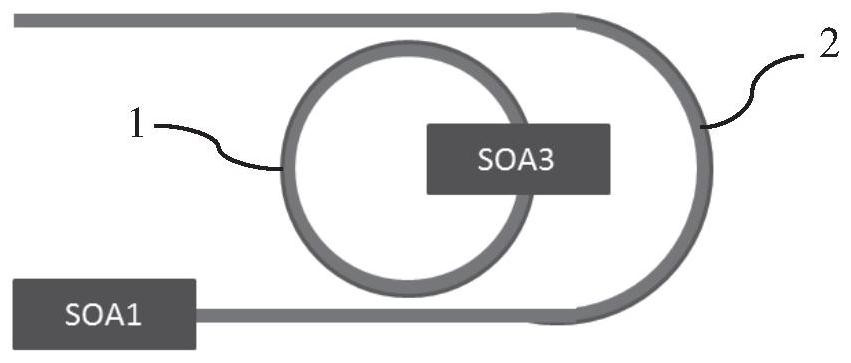
The invention discloses a narrow linewidth laser which comprises a passive annular resonant cavity, an FP resonant cavity and a first gain region, the passive annular resonant cavity and the FP resonant cavity are matched to form an M-Z (Mach-Zehnder Interference Structure) composite outer cavity structure, and the M-Z composite outer cavity structure is at least used for providing wavelength selection and narrowing the linewidth of the laser. And the first gain region is arranged on the outer side of the M-Z composite outer cavity structure and is at least used for providing gain for the whole laser. The narrow linewidth laser provided by the embodiment of the invention is simple in structure, high in side mode rejection ratio, narrow in linewidth and high in output power; by further integrating the third gain region, wide-spectrum, low-consumption and fast tuning can be realized, and tuning management is simple; in the prior art, for example, monolithic integration is adopted, butt joint coupling loss of the gain area and the waveguide area and narrow linewidth limitation caused by the butt joint coupling loss can be further avoided, meanwhile, the device can be manufactured through an integrally-formed semiconductor process, and the device is low in cost, higher in stability and reliability and higher in severe environment resistance.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Heterogeneously integrated photonic devices with improved optical coupling between waveguides
ActiveUS11287573B1Facilitates efficient adiabatic transformationOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringOptical coupling
An optical device comprises first, second and third elements fabricated on a common substrate. The first element comprises an active waveguide structure supporting a first optical mode, the second element, fabricated on a planarized top surface of the first element, comprises a passive waveguide structure supporting a second optical mode, and the third element, at least partly butt-coupled to the first element, comprises an intermediate waveguide structure, positioned such that a top surface of the intermediate structure underlies a bottom surface of the passive waveguide structure. If the first optical mode differs from the second optical mode by more than a predetermined amount, a tapered waveguide structure in at least one of the second and third elements facilitates efficient adiabatic transformation between the first optical mode and the second optical mode. Mutual alignments of the first, second and third elements are defined using lithographic alignment marks.
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS LLC
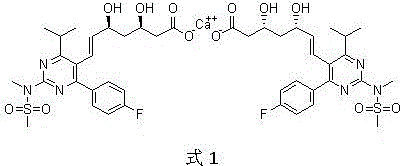
Method for preparing heptenoic acid cyclopentyl ester derivative
InactiveCN106478518AHigh yieldThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic chemistryTert-Butyl acetateSuperbase
The invention discloses a method for preparing a heptenoic acid cyclopentyl ester product by taking (4R-cis)-6-[(acetoxy)methyl]-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-tert butyl acetate as an initial raw material, and the product is prepared through steps of hydrolysis, replacement and oxidation. The synthesis step is simple, an intermediate can be subjected to a next reaction without refining and purifying steps, for a butt-coupling reaction, the conventional mild technology condition can replace ultralow temperature reaction condition, superbase with high danger is simultaneously replaced, reaction security is increased, the route total yield is high, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANTONG CHANGYOO PHARMATECH CO LTD
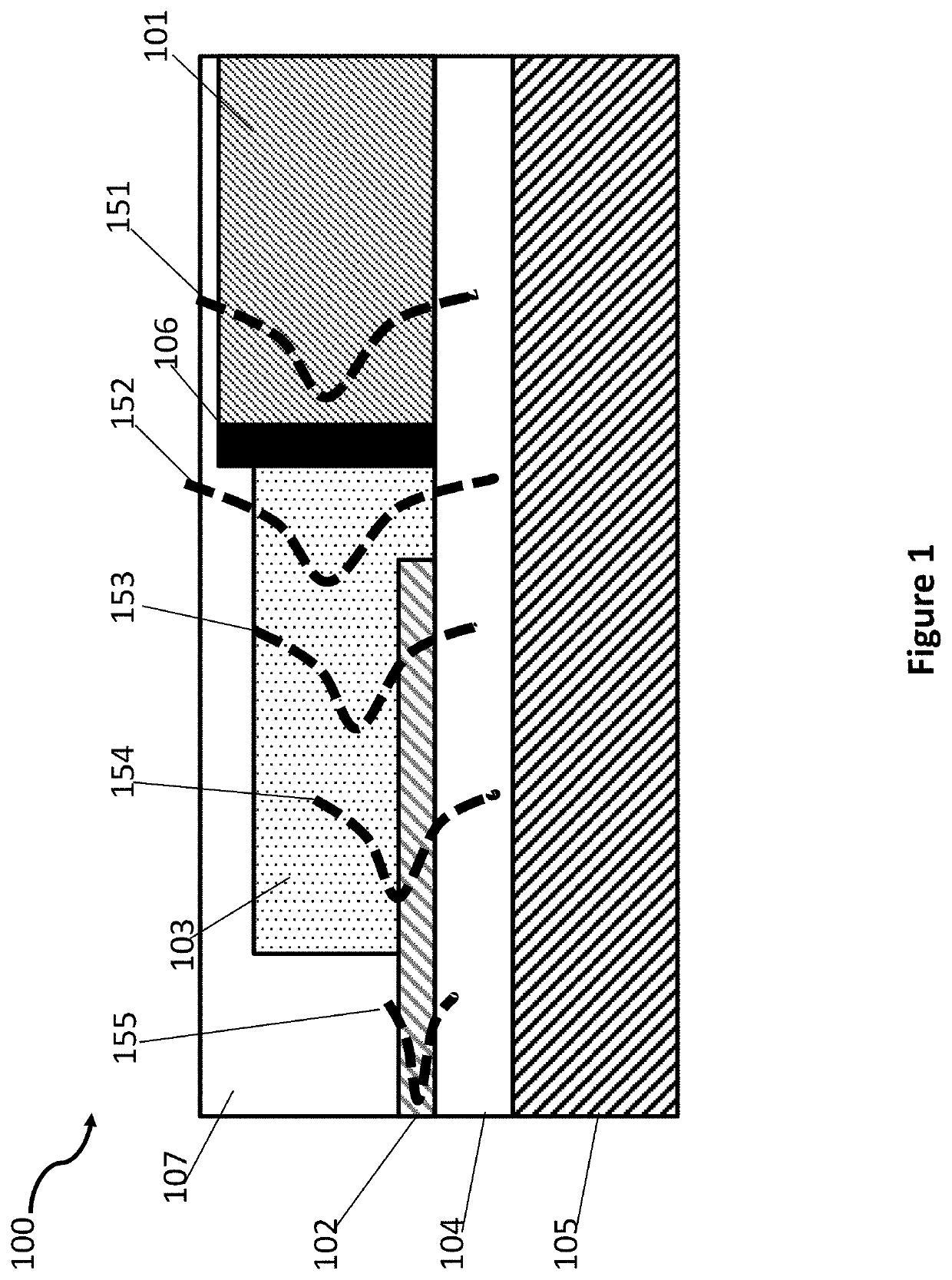
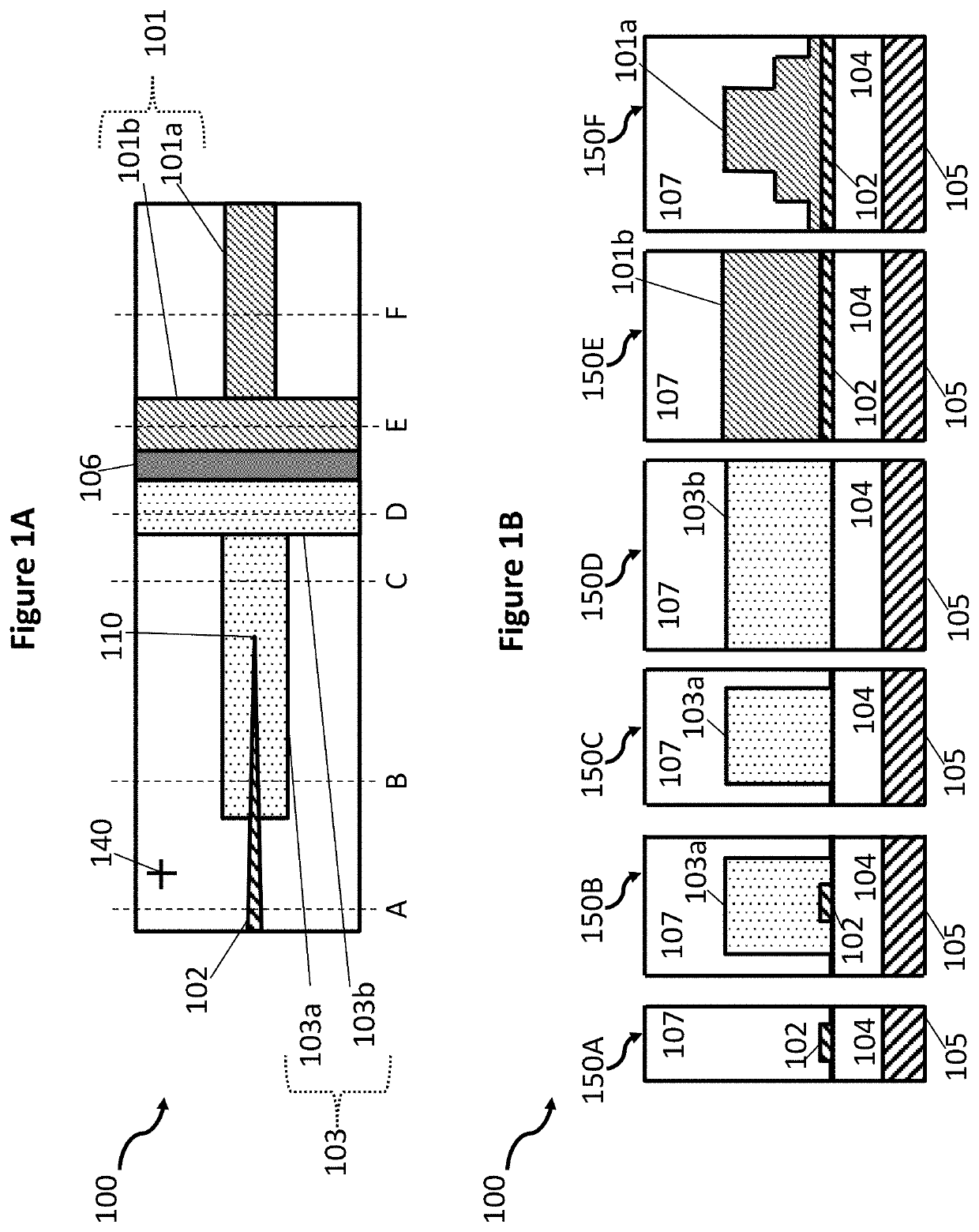
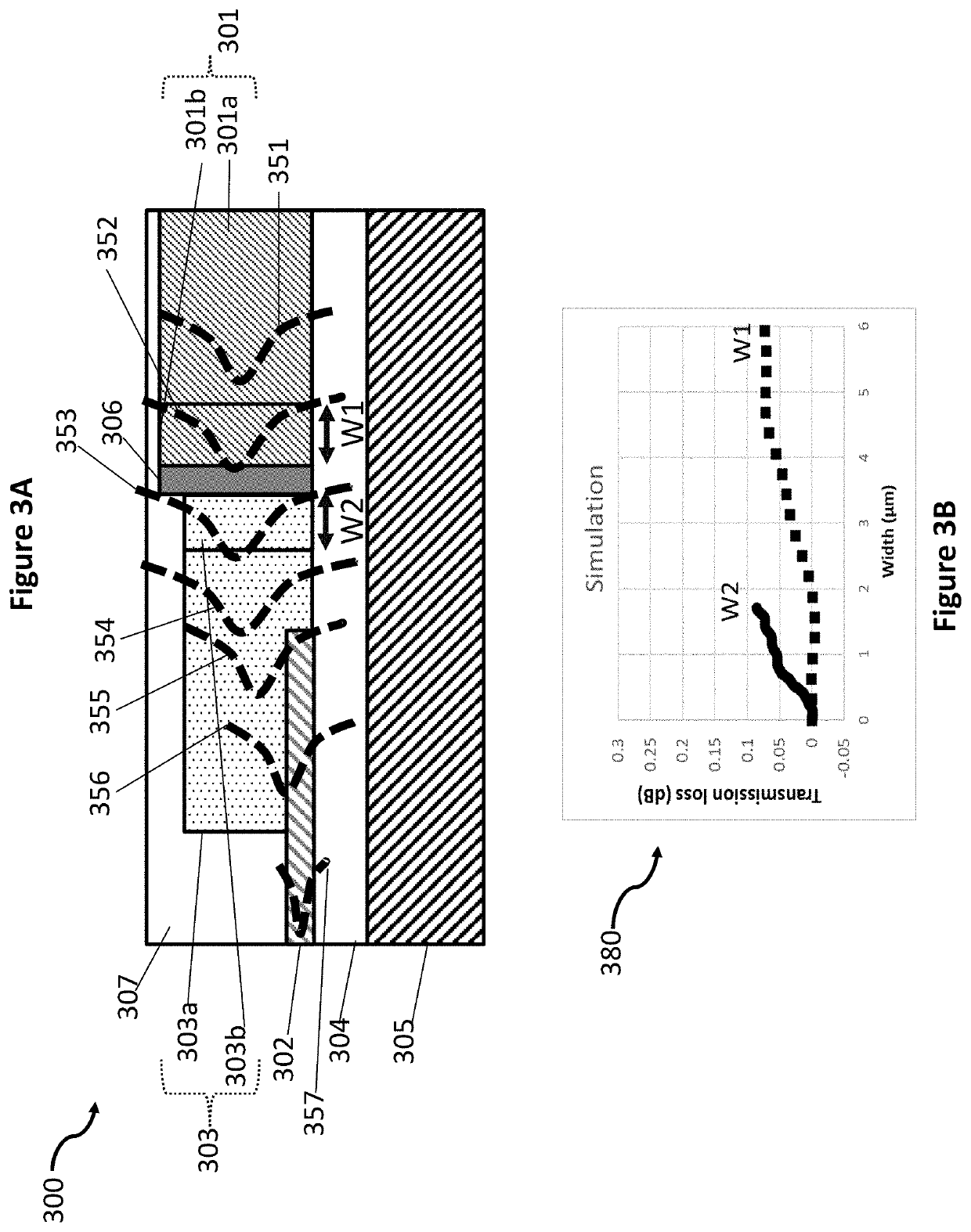
Butt coupling detector and method for manufacturing butt coupling detector
PendingCN109585610AReduce areaIncrease saturated output powerFinal product manufactureRadiation controlled devicesHigh bandwidthCoupling efficiency
The invention discloses a butt coupling detector and a method for manufacturing the butt coupling detector. The butt coupling detector comprises: a substrate, and a passive waveguide region, a butt coupling region and an absorption region, which are sequentially arranged on the substrate one the same layer along the propagation direction of the incident light, wherein the butt coupling region is embedded in the absorption region and coupled with the same, and the cross-sectional area of the butt coupling region along the propagation direction of the incident light is gradually reduced. By implementing the butt coupling detector provided by the invention, the light is evenly coupled into the absorption region through the butt coupling region by changing the pattern distribution of light atthe butt interface between the passive waveguide region and the absorption region in the prior art by the butt coupling region, thereby solving the problem of premature saturation of the butt couplingdetector. The method can significantly improve the saturated output power of the butt coupling detector while maintaining the high coupling efficiency and high bandwidth of the butt coupling detector.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
Butt coupling structure and method of photonic quantum ring hole emitter
InactiveUS7520681B2Improve coupling strengthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionResistRefractive index matching
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
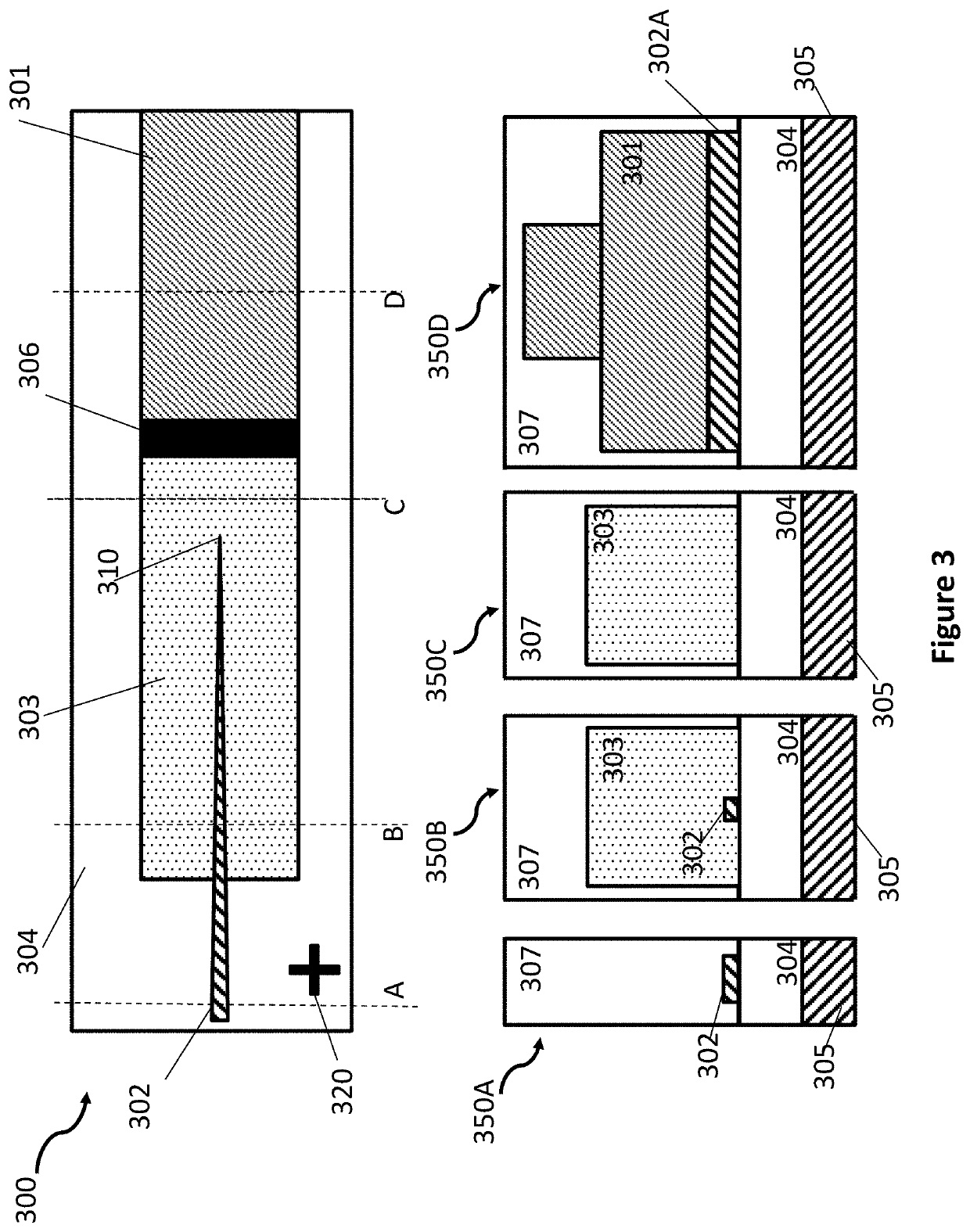
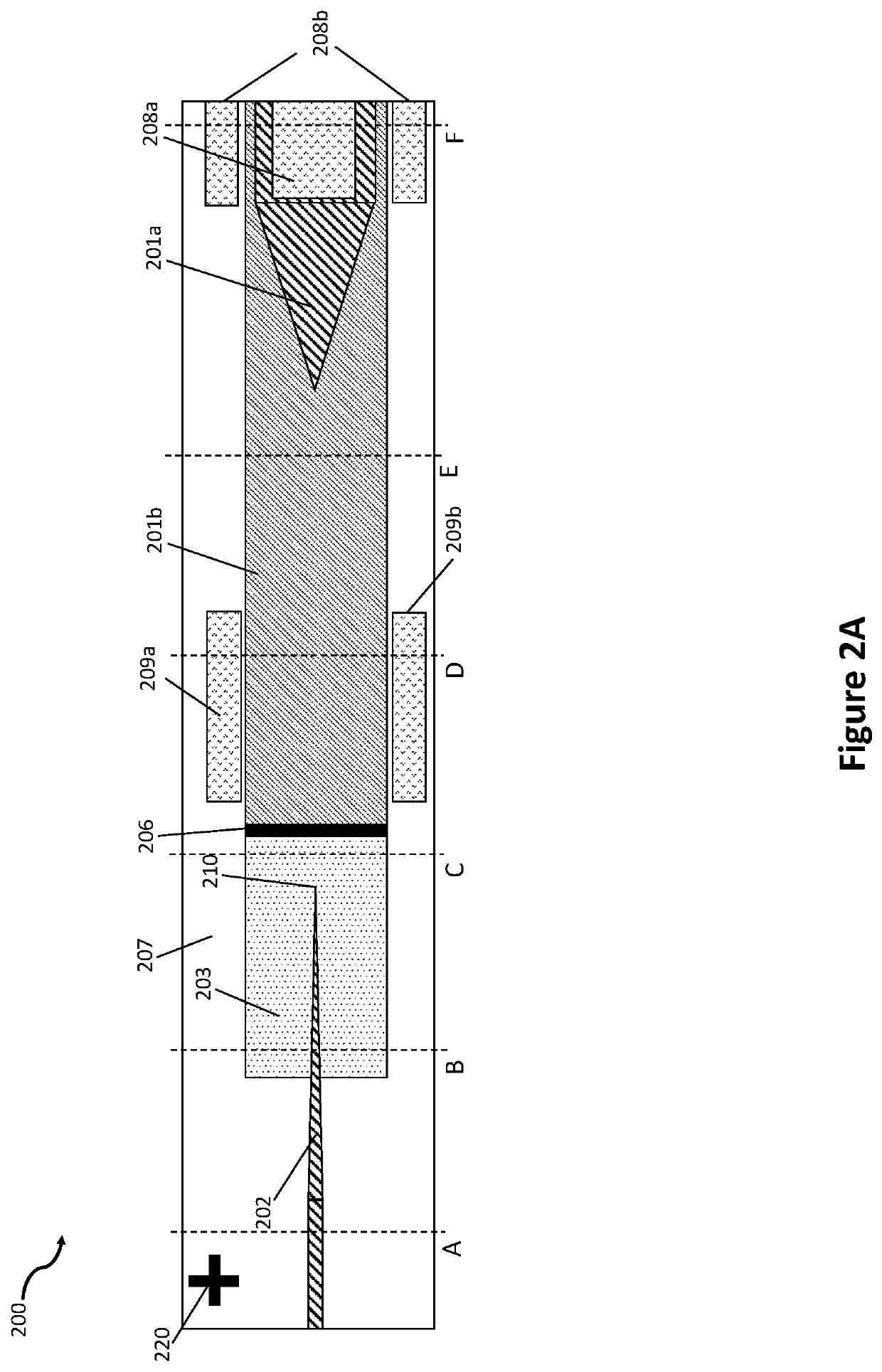
Integrated active devices with enhanced optical coupling to dielectric waveguides
ActiveUS11209592B2Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical couplingMaterials science
A device comprises first, second and third elements fabricated on a common substrate. The first element comprises an active waveguide structure comprising: one portion, of effective cross-sectional area A1, supporting a first optical mode; and a second portion, butt-coupled to the first portion, of effective cross-sectional area A2>A1. The second element comprises a passive waveguide structure supporting a second optical mode. The third element, at least partly butt-coupled to the second portion, comprises an intermediate waveguide structure supporting intermediate optical modes. If the first optical mode differs from the second optical mode by more than a predetermined amount, a tapered waveguide structure in at least one of the second and third elements facilitates efficient adiabatic transformation between the first optical mode and one intermediate optical mode. No adiabatic transformation occurs between any intermediate optical mode and the first optical mode. Mutual alignments of the elements are defined using lithographic marks.
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS INC
Active-passive photonic integrated circuit platform
ActiveUS11480734B2Facilitates efficient transformationEfficient conversionCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideMode transformationPhotonic integrated circuit
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS INC
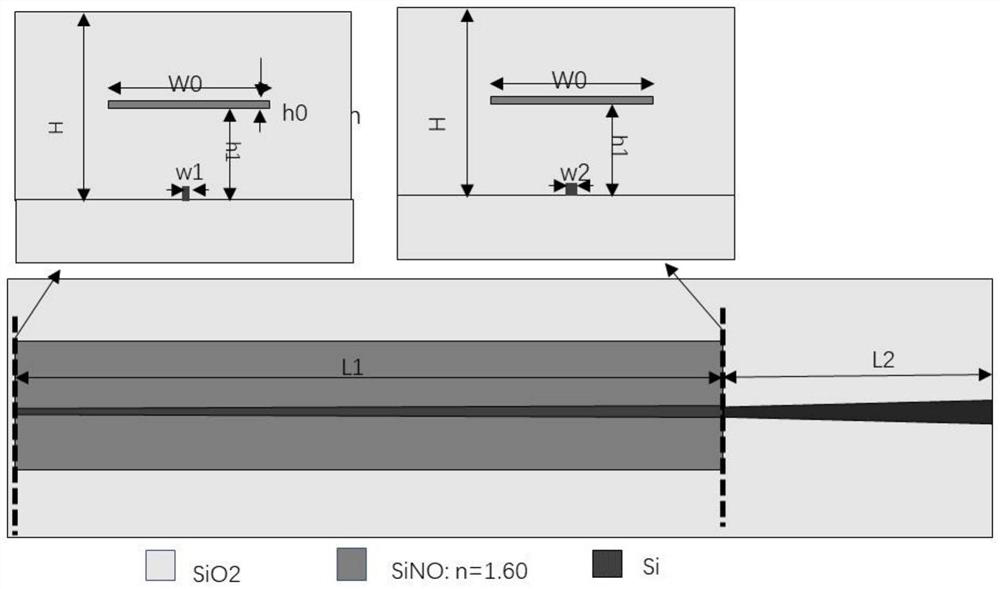
Planar optical waveguide chip and waveguide type single-mode fiber laser
PendingCN111580216ACoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionLaser technologyErbium lasers
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser, in particular to a planar optical waveguide chip and a waveguide type single-mode fiber laser. The planar optical waveguide chip comprises a planar optical waveguide chip main body, wherein the planar optical waveguide chip main body is used for butting and coupling laser emitted by a semiconductor laser. The planar optical waveguide chip mainbody comprises a light inlet end and a light outlet end. Waveguide width is in gradient reduction from the light inlet end to the light outlet end. The waveguide thickness is unchanged from the lightinlet end to the light outlet end. The waveguide thickness and waveguide width of the light outlet end are equal. The planar optical waveguide chip is different from a complex optical component of atraditional optical fiber laser. According to the single-mode fiber laser, multimode laser emitted by the high-power semiconductor laser can be coupled into the single-mode fiber with a small fiber core diameter in a lossless manner through the planar optical waveguide chip which is a simple optical device, so that the high-power laser can be directly output through the single-mode fiber.
Owner:SHANDONG MINGCAN PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Heterogeneously integrated photonic devices with improved optical coupling between waveguides
ActiveUS20220120970A1Facilitates efficient adiabatic transformationOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringOptical coupling
An optical device comprises first, second and third elements fabricated on a common substrate. The first element comprises an active waveguide structure supporting a first optical mode, the second element, fabricated on a planarized top surface of the first element, comprises a passive waveguide structure supporting a second optical mode, and the third element, at least partly butt-coupled to the first element, comprises an intermediate waveguide structure, positioned such that a top surface of the intermediate structure underlies a bottom surface of the passive waveguide structure. If the first optical mode differs from the second optical mode by more than a predetermined amount, a tapered waveguide structure in at least one of the second and third elements facilitates efficient adiabatic transformation between the first optical mode and the second optical mode. Mutual alignments of the first, second and third elements are defined using lithographic alignment marks.
Owner:NEXUS PHOTONICS INC
A MEMS-based ultra-broadband tunable optical filter
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical communication and particularly discloses an MEMS-based ultra-wide band adjustable optical filter which comprises a 1*N port optical switch group, an optical fiber array, an array optical waveguide, a collimating lens, a diffraction grating, a light beam compression unit and an MEMS micromirror, the optical switch group is connected with the optical fiber array, one side of the array optical waveguide is in butt coupling with the optical fiber array, the other side of the array optical waveguide is arranged on a front focal plane of the collimating lens, the diffraction grating is arranged on a rear focal plane of the collimating lens, and the diffraction grating and the MEMS micromirror are arranged on a front focal plane and a rear focal plane of the light beam compression unit respectively. Through the combination of the 1*N port optical switch group and the array optical waveguide, a working waveband is divided into N sub-wavebands, and the expansion of a tuning range is realized. According to the invention, the problem of narrow tuning range caused by the limitation of an MEMS manufacturing process in the prior art can besolved, and specifically, the tuning range of the filter can be expanded to N times through a band segmentation technology.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
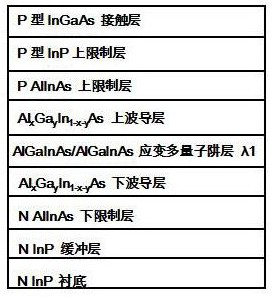
Optical communication semiconductor laser and aluminum-containing quantum well active layer butt joint growth method thereof
InactiveCN112217097AImprove performanceSolve Oxidation ProblemsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to an optical communication semiconductor laser and an aluminum-containing quantum well active layer butt joint growth method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: growing an aluminum-free passive waveguide layer on a substrate to complete first epitaxy; removing the aluminum-free passive waveguide layer in a first aluminum-containing quantum well active layer area preset on the primary epitaxial wafer, performing secondary epitaxy, and growing a first aluminum-containing quantum well active layer; and continuously removing the aluminum-free passive waveguidelayer in a preset second aluminum-containing quantum well active layer region on the secondary epitaxial wafer, performing third epitaxy, and growing a second aluminum-containing quantum well activelayer, the aluminum-free passive waveguide layer being spaced between the first aluminum-containing quantum well active layer and the second aluminum-containing quantum well active layer. The epitaxial growth of the aluminum-containing quantum well active layer is carried out on the aluminum-free passive waveguide layer, so that the problem of oxidation of an aluminum-containing material is avoided, and the butt coupling growth quality is improved. And meanwhile, the active layer is made of a high-performance aluminum-containing material, so that the performance of the component can be improved.
Owner:武汉云岭光电股份有限公司
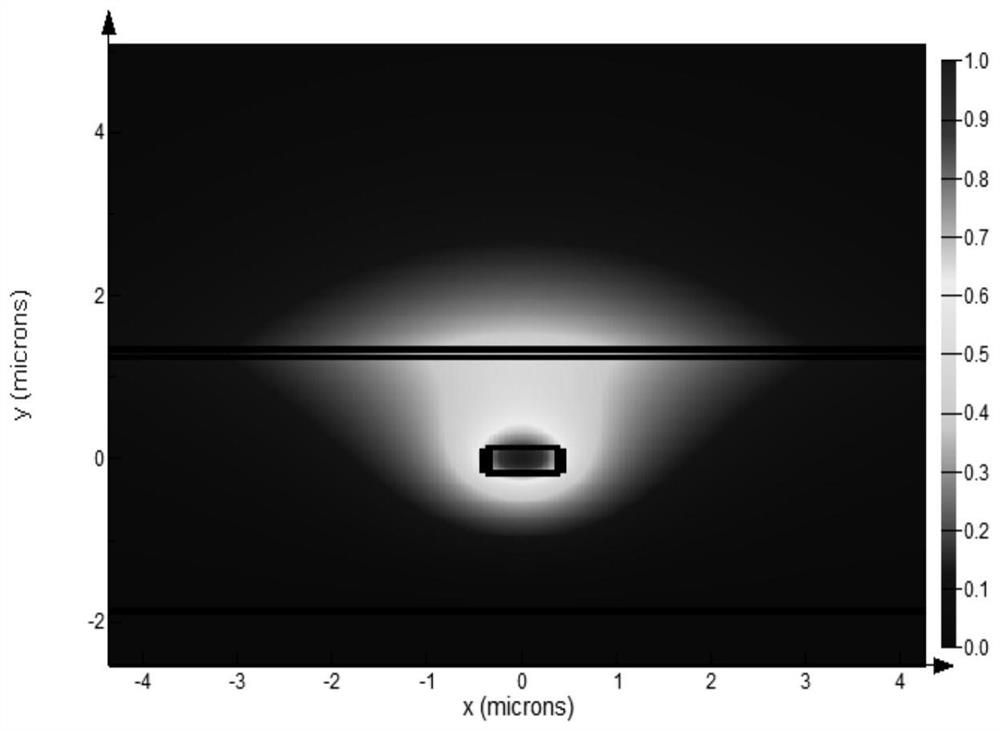
Optoelectronic integrated chip and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN114156731AAccuracy meetsSolve the problem of small end-face coupling tolerancesOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsQuantum wellEngineering
The invention provides a photoelectronic integrated chip and a manufacturing method thereof. The photoelectronic integrated chip comprises a gain chip and a silicon optical chip spot-size converter, the gain chip comprises a passive waveguide part and an active waveguide part; a first thin film layer is grown below a passive waveguide region of the passive waveguide part, and a second thin film layer is grown below a quantum well gain region of the active waveguide part; a third thin film layer grows above a silicon waveguide of the silicon optical chip spot size converter; a TE fundamental mode supported by the passive waveguide part is greater than a mode field of a first threshold value; the TE fundamental mode supported by the active waveguide part is greater than a mode field of a second threshold value; the TE fundamental mode supported by the silicon optical chip spot size converter is larger than a mode field of a third threshold value. The problem that in the prior art, the end face coupling tolerance of an integrated light source on a silicon substrate is small through a hybrid integration technology is solved, high-efficiency coupling can be achieved, the butt joint tolerance is greatly increased, the tolerance can meet the precision of an automatic chip mounter, and passive end face butt joint coupling can be achieved.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CENT CO LTD
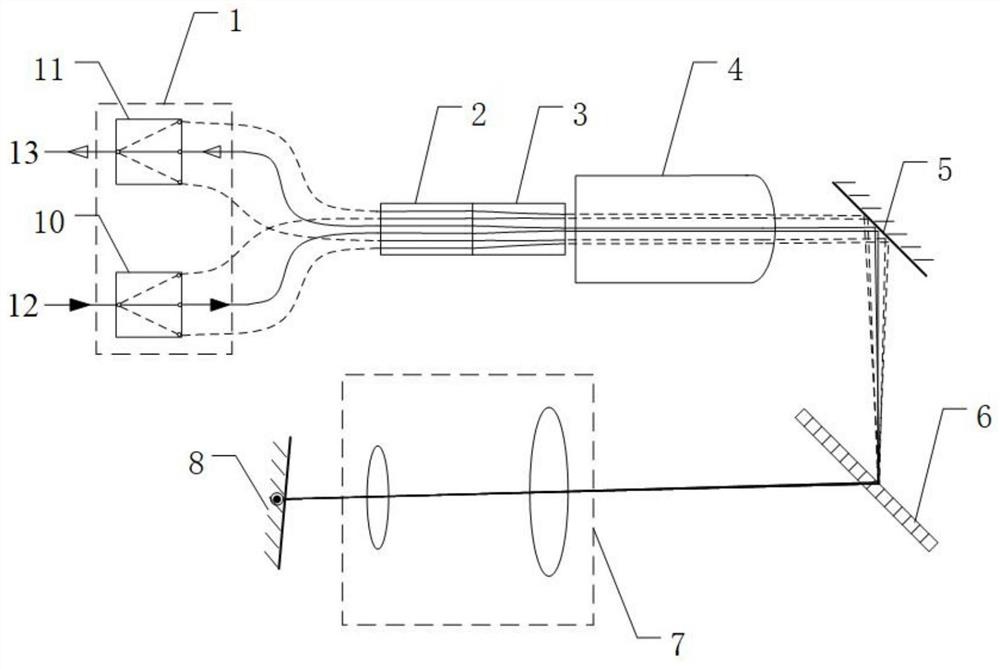
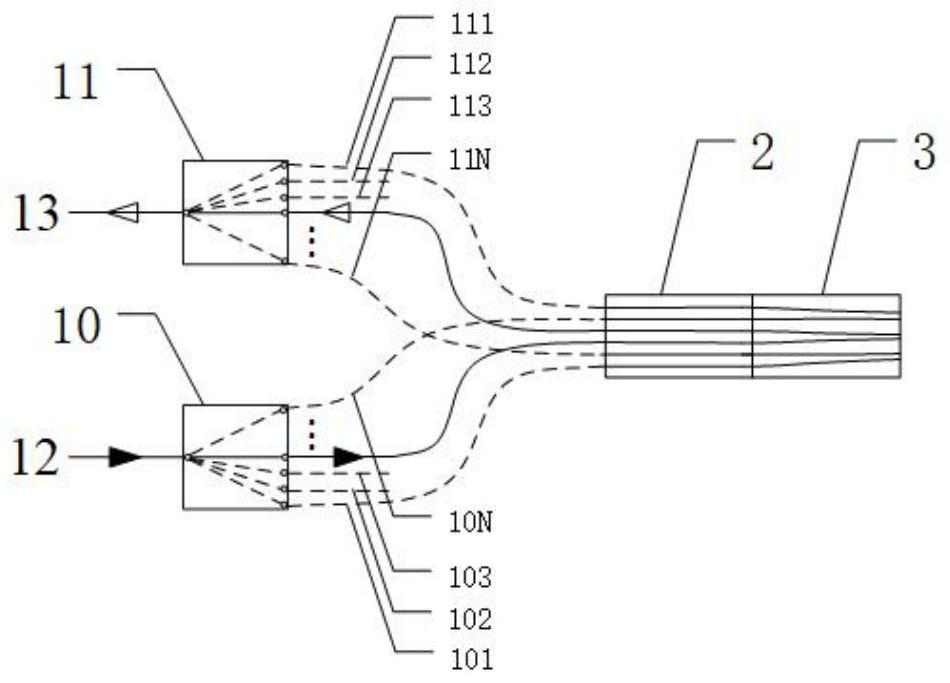
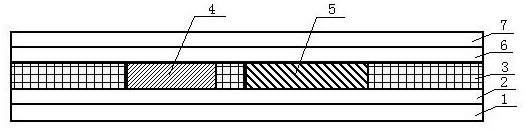
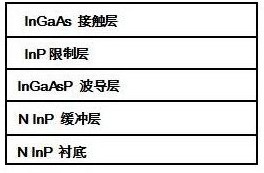
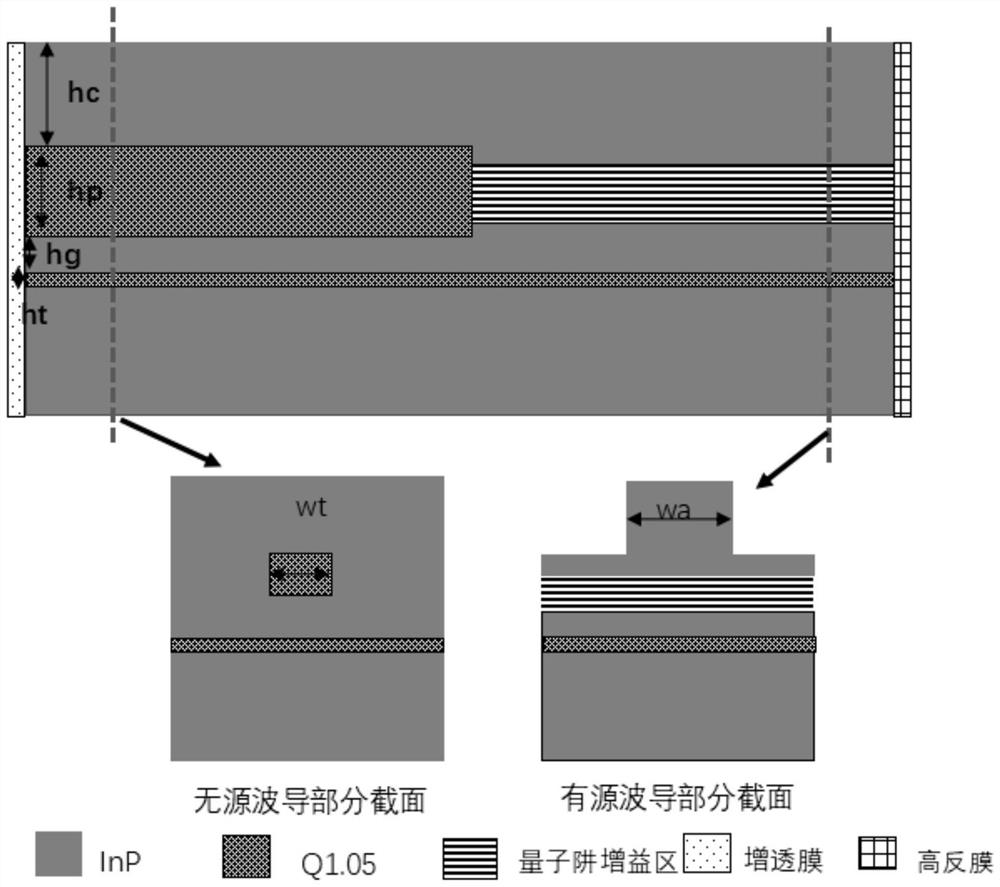
A butt coupling method for monolithic integrated chips
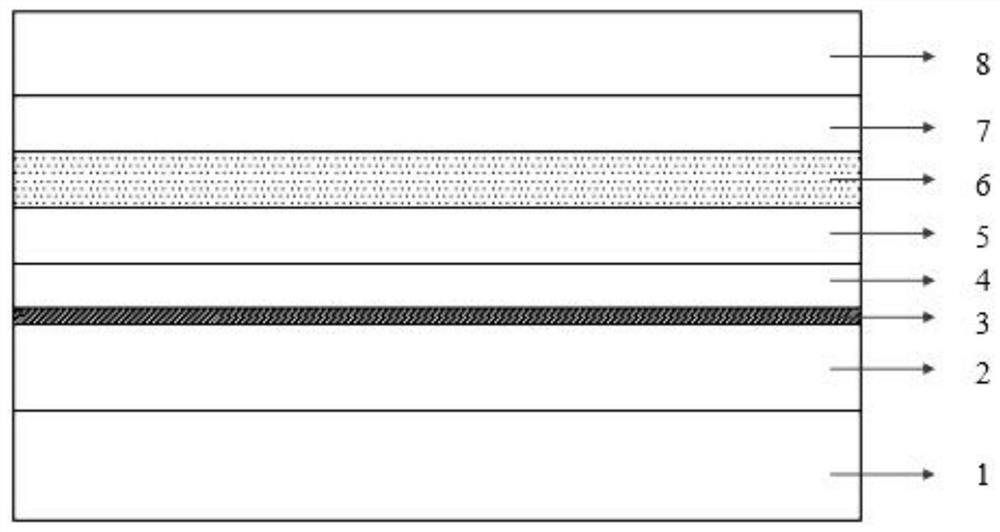
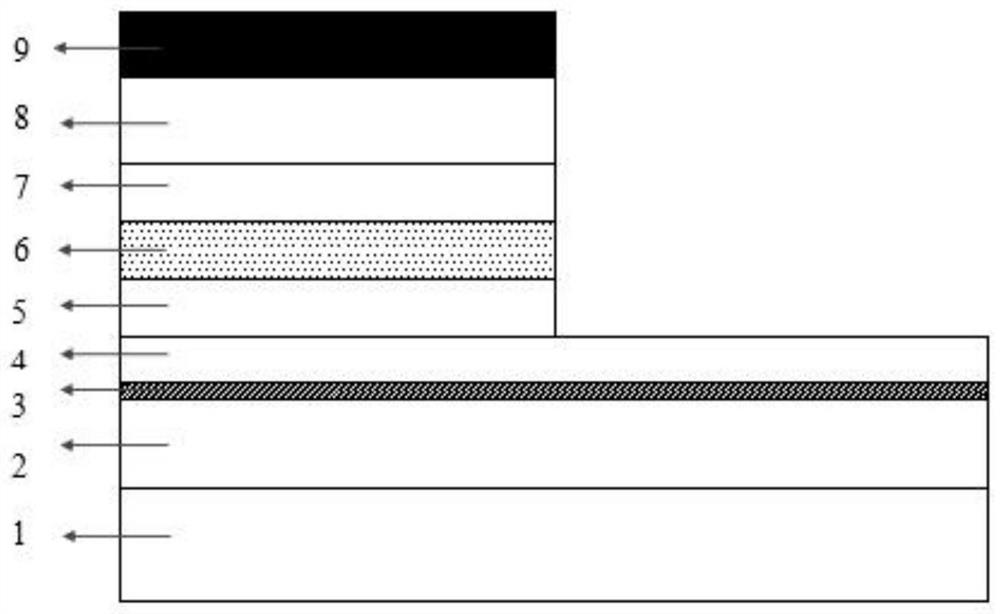
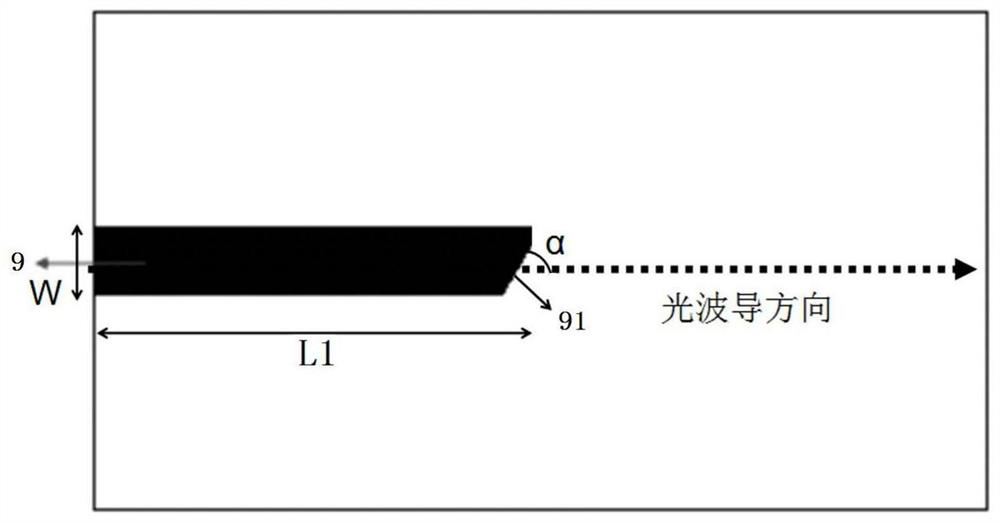
ActiveCN110718849BAffect the light output powerAffect chirpLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersThin membraneSingle chip
Owner:湖北光安伦芯片有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com