Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Botryosphaeria rhodina" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
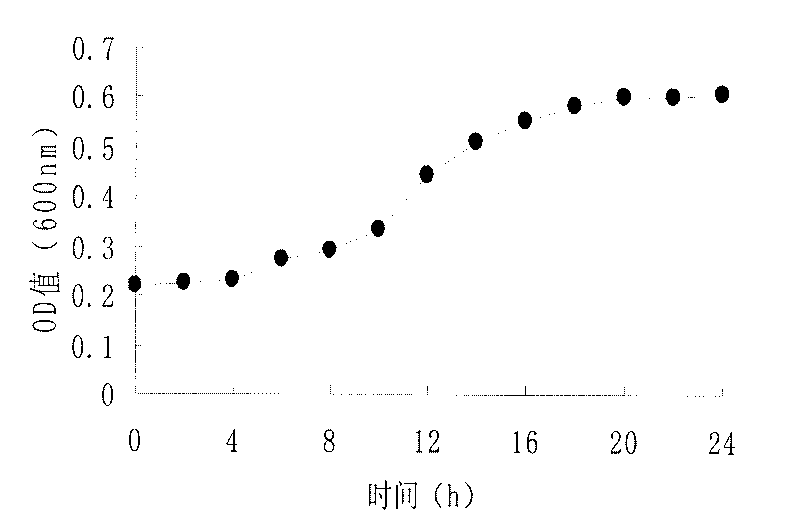
Botryosphaeria rhodina is a fungal plant pathogen that causes cankers on many plant species.
Technological process for preparing fermentation dehydrated beef using composite leaven
InactiveCN101248884AImprove organizational structureEnhance sensory effectFood preparationLactobacillusOrganoleptic
The invention provides a method for producing fermented beef jerky with compound leaven. The bacteria strain used in fermentation is lactobacillus casei and staphylococcus xylosus with volume ratio of 1:3 and volume of addition of 1-1.5%, the fermentation temperature is 20 DEG C, and the fermentation time is 5 days. The addition of lactobacillus casei reduces pH value of the product, improves safety, improves the texture of the product, and shortens fermentation period. At the same time, the addition of staphylococcus xylosus generates a large amount of flavoring substances during fermentation process, improves sensing effect of the product, and the final product has thick fragrance, good taste, and infinitive aftertaste. The inventive method is especially suitable for producing fermented beef jerky, as well as air dried sausage and sausage.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Crystalline form of r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin- 5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate
ActiveUS20100227839A1Reduce filter timeImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphateAntibacterial activity
A crystalline form of crystalline (R)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate, methods of making the crystalline form and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the crystalline form are useful antibiotics. Further, the derivatives of the present invention may exert potent antibacterial activity versus various human and animal pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococi, Enterococci and Streptococi, anaerobic microorganisms such as Bacteroides and Clostridia, and acid-resistant microorganisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Accordingly, the compositions comprising the crystalline form may be used in antibiotics.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Collagen-binding proteins from Enterococcal bacteria
InactiveUS20050180986A1Inhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCell-Extracellular MatrixBinding site
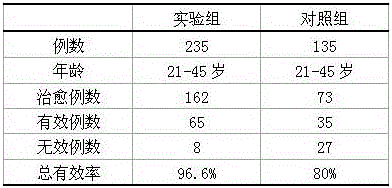
A collagen-binding MSCRAMM entitled Ace from enterococcal bacteria is provided which was homologous to the ligand-binding region of Cna, the collagen-binding MSCRAMM from Staphylococcus aureus, and which can be utilized to inhibit adhesion of enterococcal bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins. The N-terminal region of Ace contained a region (residues 174-319), or A domain, contains several 47-residue tandem repeat units between the collagen-binding site and cell wall-associated regions. The Ace protein can be utilized in methods of preventing and / or treating enterococcal infection, and in addition, antibodies raised against Ace, or its A domain, can be used to effectively inhibit the adhesion of enterococcal cells to a collagen substrate.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
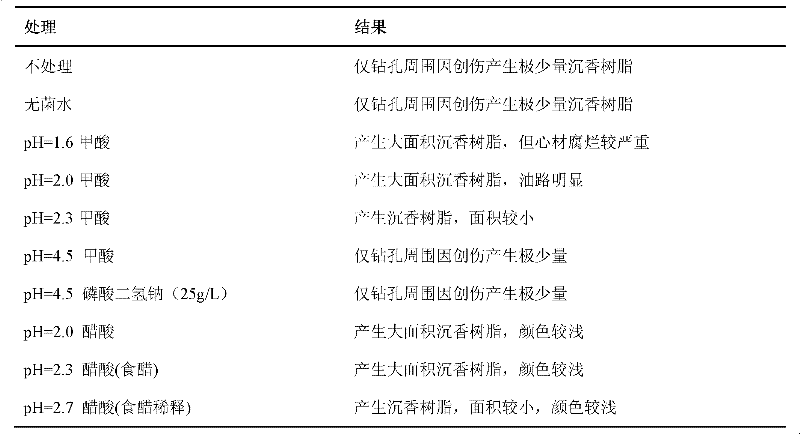
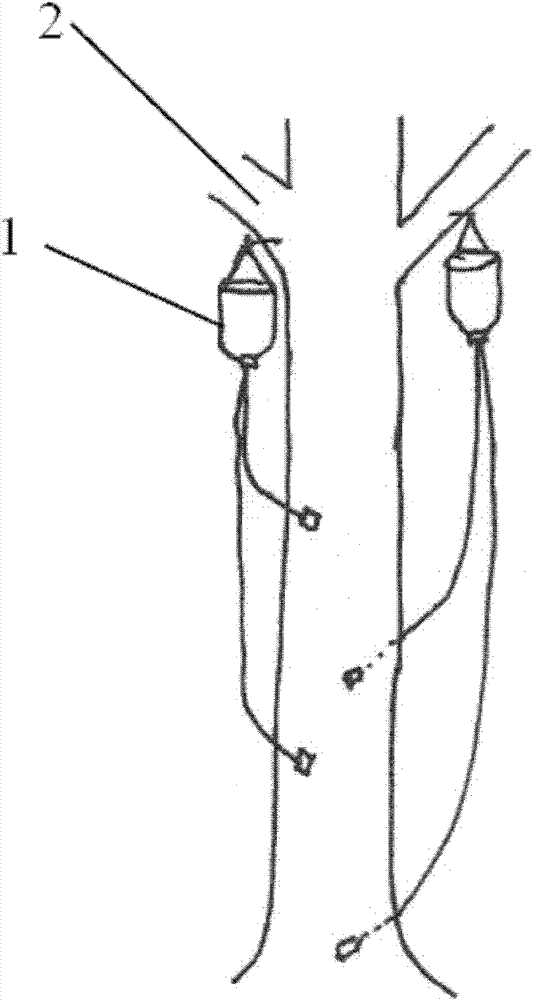
Method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood
ActiveCN102302041AShorten the cycle of producing agarwoodSimple and fast operationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFusariumAquilaria sinensis
The invention discloses a method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood. The method comprises the following steps of: injecting a methanoic acid or acetic acid solution with pH value of 1.5-3 or a mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid into xylem of Aquilaria sinensis [Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg]; respectively injecting the solution together with fungi, suchas Botryosphaeria rhodina, Hypocrea jecorina, Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Ampelomyces sp, Khuskia sp, Fungal endophyte sp.A 16, Pestalotiopsis sp., Hypocrea lixii and Chaetomium sp.or injecting the solution and the fungi in a mixed way; and inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood. According to the invention, the methanoic acid or acetic acid solution or the mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid is injected into the xylem of the Aquilaria sinensis to induce the Aquilaria sinensis to generate defense reaction so as to generate the agilawood; and alarge amount of agilawood are generated by using the method. The method for manually inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost and suitability for manually making agilawood on a large scale by using Aquilaria sinensis trees; and a large amount of agilawood can be effectively generated by the Aquilaria sinensis. According to the invention, the agilawood producing period of the Aquilaria sinensis is largely reduced, the agilawood can be generally obtained after 6-24 months, the production cost is reduced, the market requirements are satisfied, and important economic, social and ecological benefits are obtained in aspects of protection and sustainable utilization of the Aquilaria sinensis, economic development of mountainous regions and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Culture medium and method for detecting thermonuclease-positive staphylococci
ActiveUS7087401B2Promote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelect agentStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
The present invention provides a method of detecting thermonuclease-positive staphylococci that does not require inactivation of DNase-positive / TNase-negative bacteria with heat. The method includes (a) providing a culture medium selective for growing staphylococci; (b) inoculating the culture medium with a sample; (c) incubating the inoculated culture medium under conditions effective to promote the growth of staphylococci; (d) providing an indicator system that produces a differentiable, detectable signal in the presence of thermonuclease-positive staphylococci; (e) contacting the indicator system with the inoculated, incubated culture medium, thereby forming a detection assembly; (f) incubating the detection assembly under conditions effective for generating the differentiable, detectable signal; and (g) detecting the detectable signal.The present invention also provides a culture medium for the selective identification of Staphylococcus aureus. The culture medium includes at least one first selective agent that selects for growth of staphylococci; at least one second selective agent for differentiating Staphylococcus aureus from other staphylococci; at least one first indicator for indicating the presence of staphylococci; and at least one second indicator for differentially indicating the presence of non-staphylococci bacteria. The present invention also provides a method of selectively identifying Staphylococcus aureus in a sample by using the culture medium of the present invention.
Owner:NEOGEN FOOD SAFETY US HOLDCO CORP
3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN101613362ANovel structureSimple manufacturing methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMinimum inhibitory concentrationSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and a synthesis method and application thereof. The compound has a right structure formula. The 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound serving as an inhibiting agent of YyCG histidine kinase protein for a staphylococcus epidermidis signal transduction system has a novel structure, and the adopted method for preparing the compound is simple and easy to implement. The test results of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) show that the compound has excellent inhibitory action on the formation of a staphylococcal biological film and can effectively kill and wound the bacteria in the staphylococcal biological film.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Primers useful in polymerase chain reaction for the identification of subtypes c1, c2 and c3 of staphylococcal enterotoxin type c
InactiveUS20060257864A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcal EnterotoxinsPcr method
The invention provides primers designed on base of the difference of sequences among staphylococcal enterotoxin subtypes, i.e., C1, C2 and C3. The invention also provides a PCR method for detecting subtypes of staphylococcal enterotoxin type C by using the above-mentioned primers. The invention relates also to DNA probes useful for the identification of subtypes C1, C2 and C3 of staphylococcal enterotoxin type C in various food and clinical samples. The primers of the invention comprises following sequences: ENTC15′-ACAGA GTTAT TAAAT GAAGG-3′;ENTC25′-GTATC AGCAA CTAAA GTTAT-3′;ENTC35′-AAGAG ATTAT TTATT TCACGT-3′;ENTCR5′-ATCAT ACCAA AAAGT ATTGC-3′.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG HSING UNIVERSITY
2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof
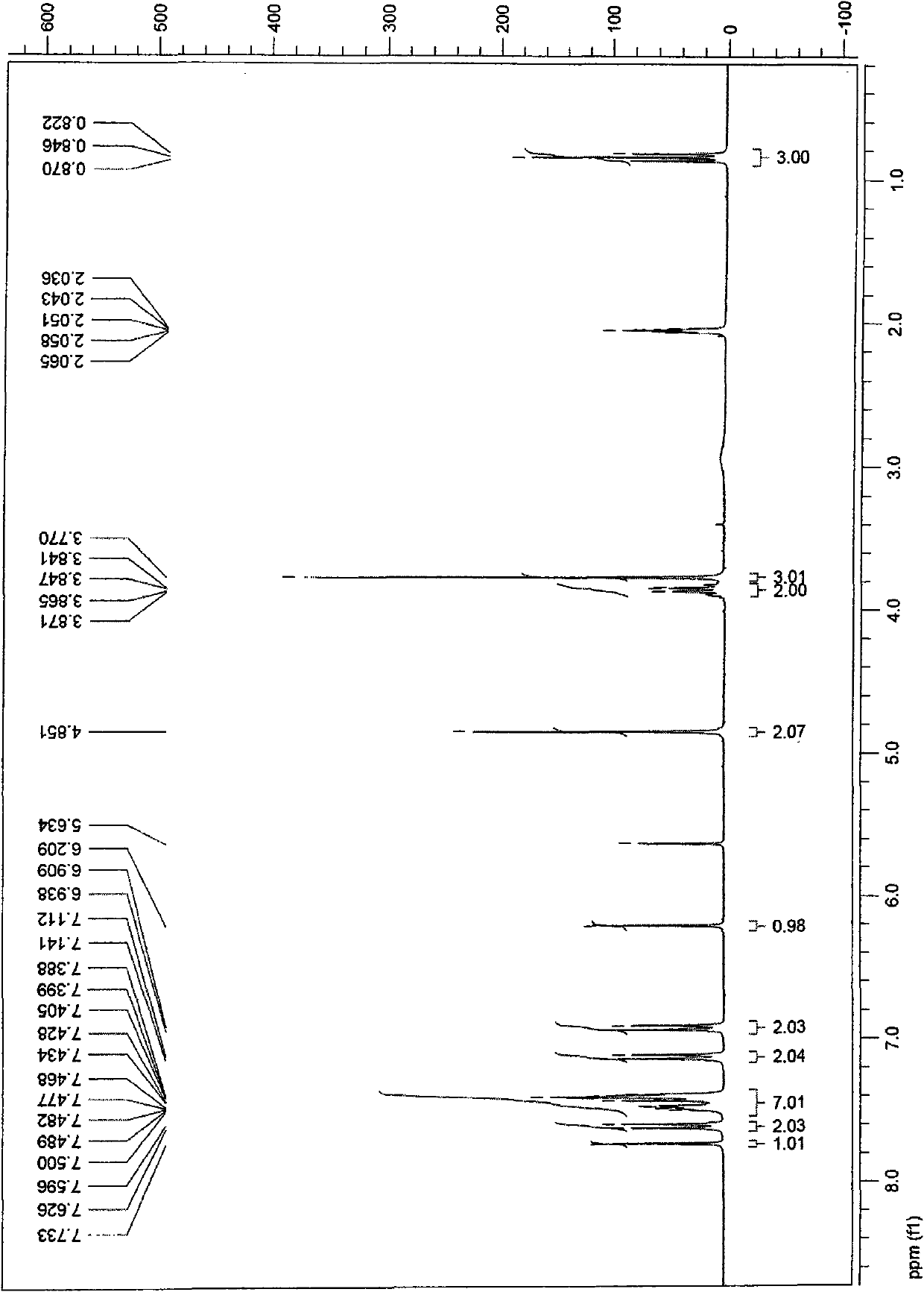
The invention discloses an application of a 2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative in antibacterial drugs, wherein the 2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative has the general formula (I), wherein in the formula I, R1 and R3 independently are hydrogen, methyl, halogen, hydroxyl, methoxyl, nitro, acetyl, propionyl or alkoxy, and R2 is methyl or ethyoxyl. The compound has an obvious inhibiting effect on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa and various bacteria and can be used in preparation of the antibacterial drugs.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
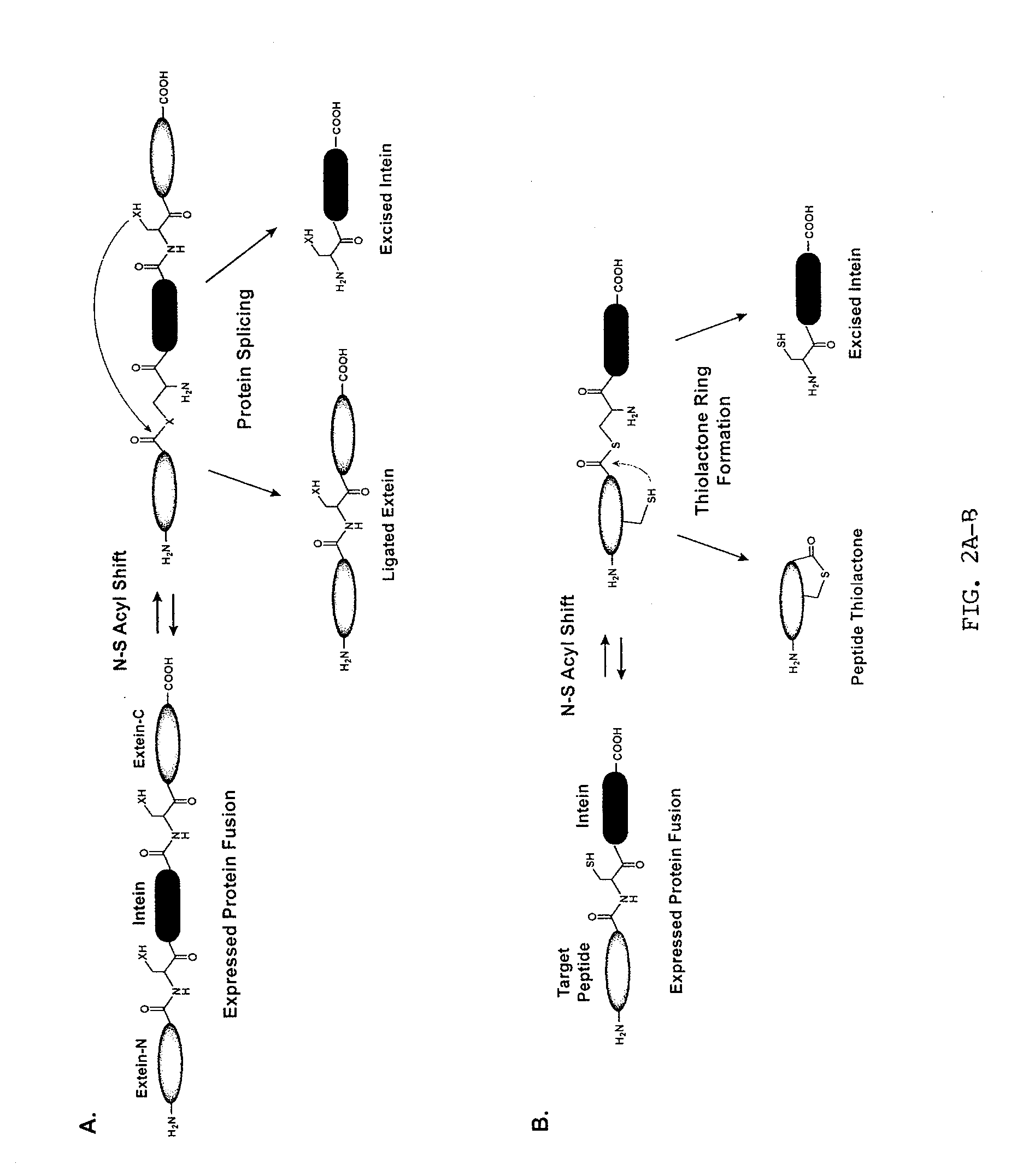
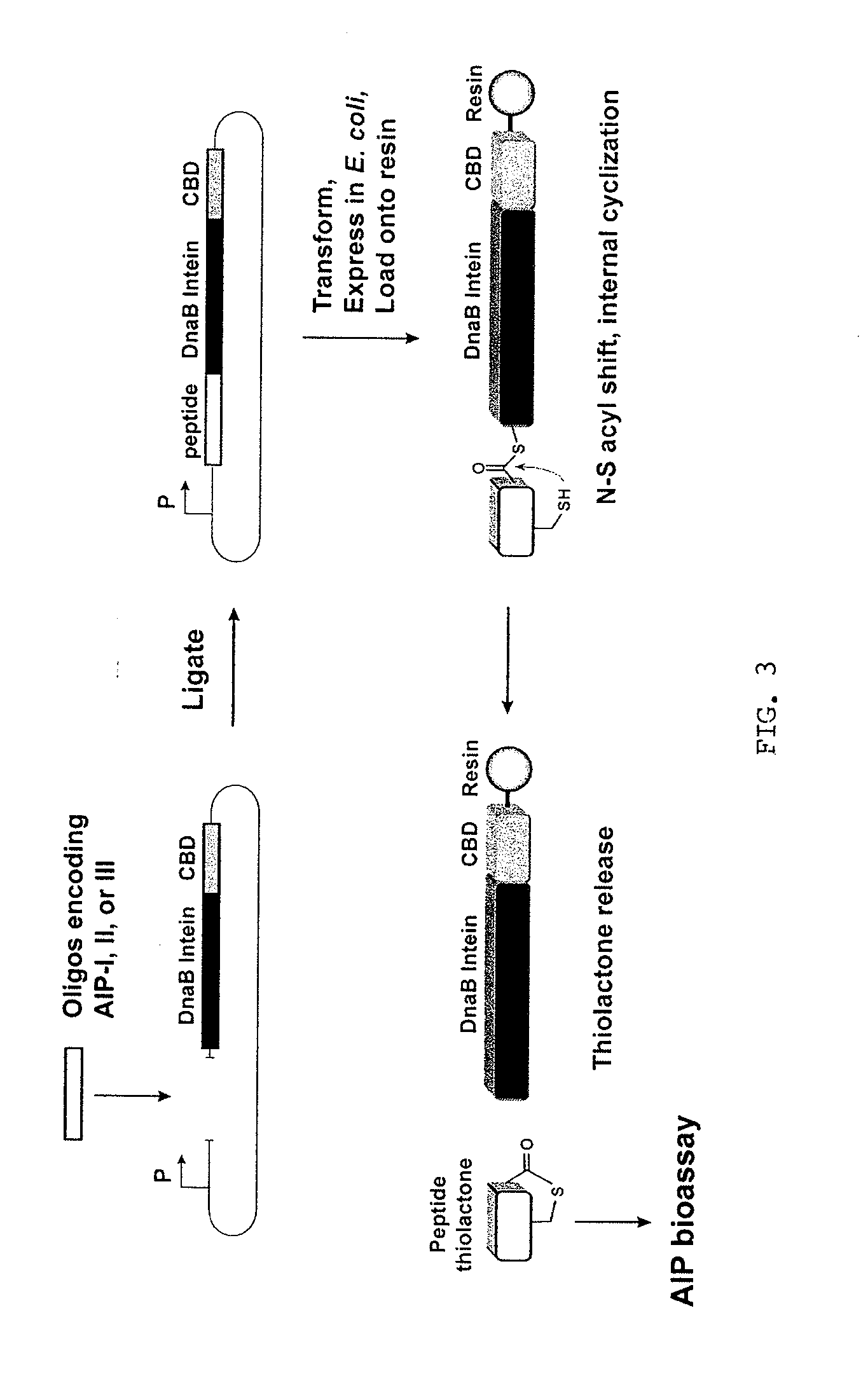
Method of Making Cyclic Polypeptides with Inteins
InactiveUS20100143972A1Bacteria peptidesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingCyclic peptideIntein
Methods for producing cyclic polypeptides comprising a lactone or thiolactone ring. In certain cases, intein fusion proteins may be used in a method for biologically producing internally cyclized polypeptides. The new methods enable the construction of cyclic polypeptide libraries that may be screened for the biological activity of cyclic polypeptides. Methods provided may be used, for instance, to produce and optimize novel cyclic peptides for use in treating Staphylococcal infections.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Botryosphaeria rhodina polypeptide
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Heavy metal adsorbent composition
A heavy metal adsorbent composition containing bacterial cells which are obtained by acid-treating a bacterium selected from among Bacillus sp. KRI-02 and its analogs, Bacillus licheniformis and Staphylococcus sp. KRI-04 and its analogs; and a method of removing a heavy metal from a heavy metal-containing medium with the use of the composition. Thus, heavy metals can be removed from rivers, lakes, ponds, industrial waste waters, etc.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Novel oxazolidinone derivative with difluorophenyl moiety, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, preparation method thereof and antibiotic composition containing the same as an active ingredient
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives with a difluorophenyl moiety, represented by Chemical Formula 1, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient are provided. Exhibiting potent inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacteria including Haemophilus influenza and Coagulase negative staphylococci and resistant bacteria including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), the pharmaceutical composition is useful as an antibiotic.(wherein, R is as defined in the specification)
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
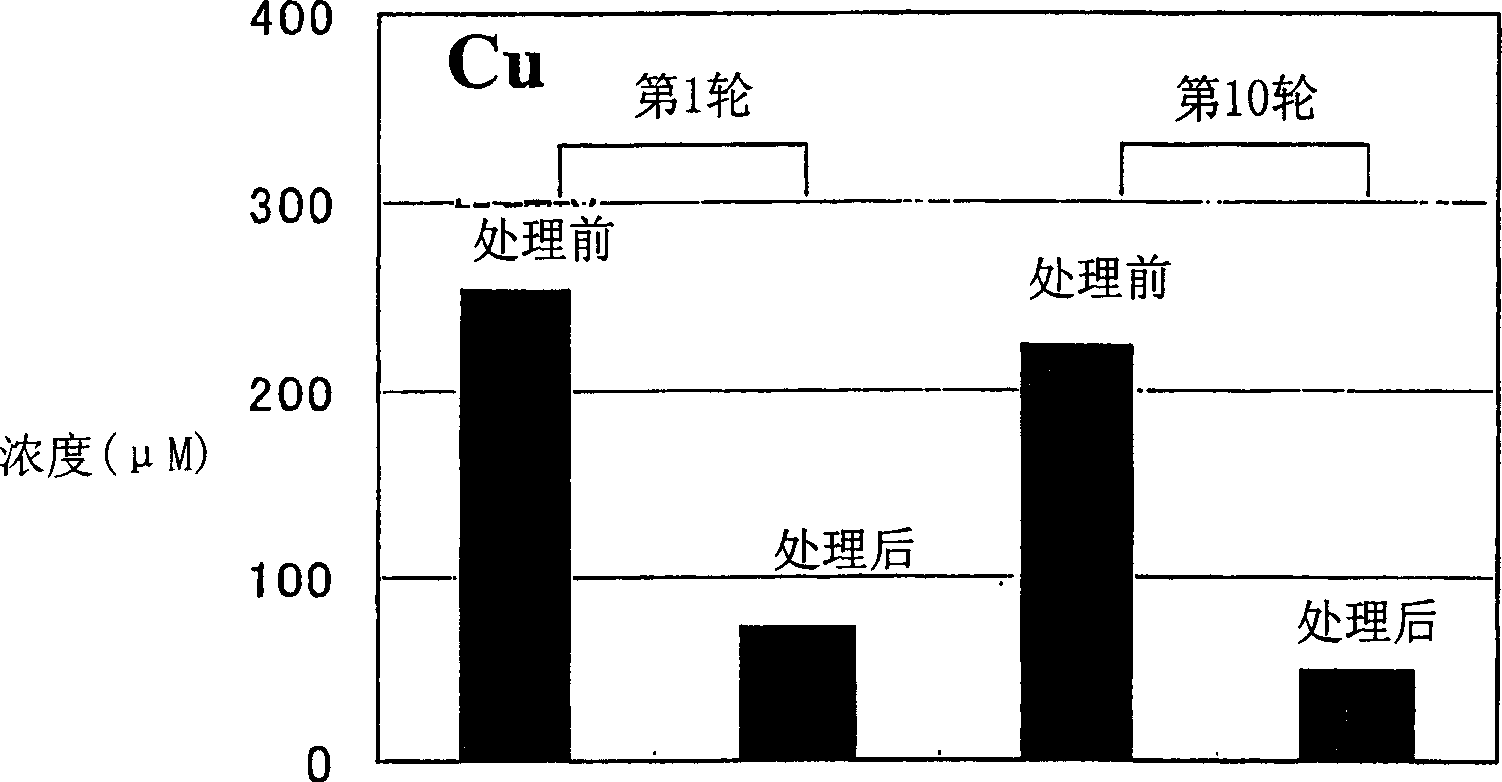
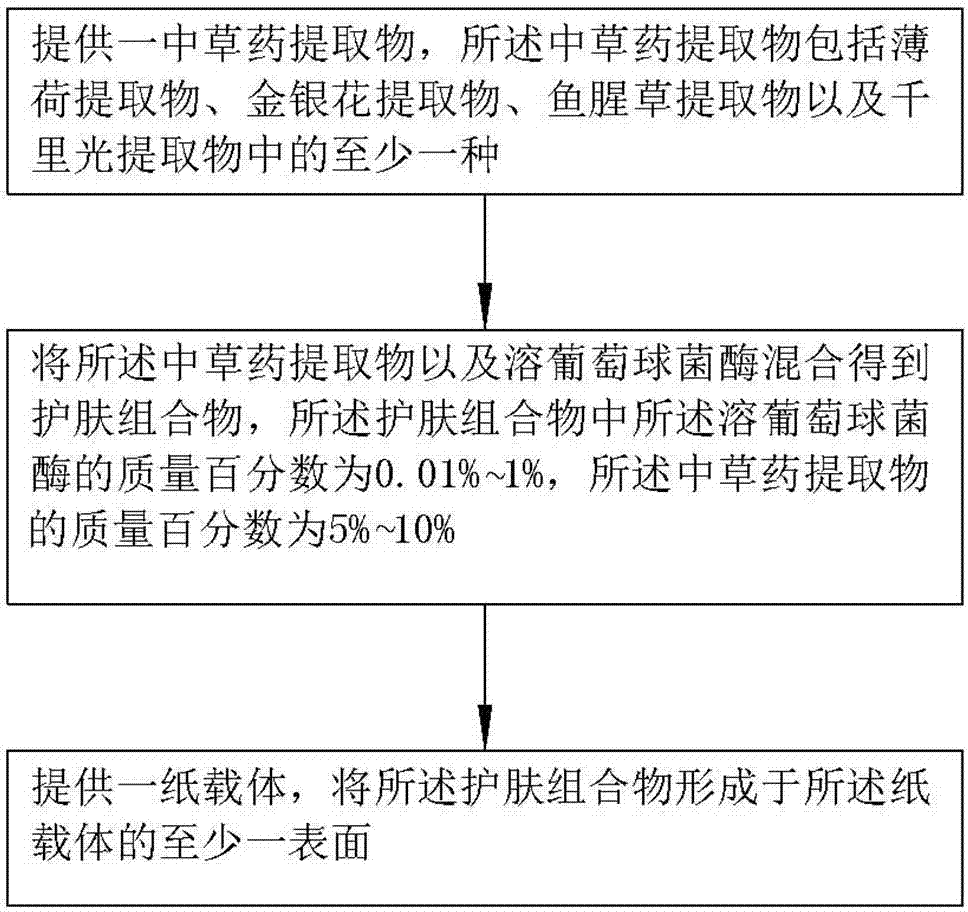
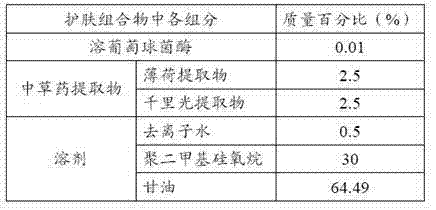
Skin care composition, paper towel and preparation method of paper towel
ActiveCN103861092ALower resistanceWill not cause harm to the bodyPeptide/protein ingredientsDomestic applicationsMint extractMedicine
The invention relates to a skin care composition which contains 0.01-1 percent by mass of lysostaphin and 5-10 percent by mass of Chinese herbal extracts, wherein the Chinese herbal extracts include at least one of a mint extract, a honeysuckle extract, a houttuynia cordata extract and a groundsel extract. The skin care composition has a function of preventing and removing prickly heat, does not contain powder carriers and has no damage to the organisms. The invention also provides a paper towel comprising the skin care composition and a preparation method of the paper towel.
Owner:GOLD HONG YE PAPER
Staphylococcus epidermidis and application thereof in producing fermented segmental pork
InactiveCN101717741AMeet the requirementsSmall weightBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus epidermidisBotryosphaeria rhodina
The invention relates to Staphylococcus epidermidis CGMCC 3472 and application thereof in producing fermented segmental pork. The mouthfeel and other qualities of pork blocks of the fermented segmental pork produced by the strain approach or are superior to those of naturally-fermented hams; in addition, the fermented segmental pork has short production period and can be manufactured into small packages; meanwhile, the quality stability of products can be improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood
ActiveCN102302041BShorten the cycle of producing agarwoodSimple and fast operationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFusariumAquilaria sinensis
The invention discloses a method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood. The method comprises the following steps of: injecting a methanoic acid or acetic acid solution with pH value of 1.5-3 or a mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid into xylem of Aquilaria sinensis [Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg]; respectively injecting the solution together with fungi, suchas Botryosphaeria rhodina, Hypocrea jecorina, Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Ampelomyces sp, Khuskia sp, Fungal endophyte sp.A 16, Pestalotiopsis sp., Hypocrea lixii and Chaetomium sp.or injecting the solution and the fungi in a mixed way; and inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood. According to the invention, the methanoic acid or acetic acid solution or the mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid is injected into the xylem of the Aquilaria sinensis to induce the Aquilaria sinensis to generate defense reaction so as to generate the agilawood; and alarge amount of agilawood are generated by using the method. The method for manually inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost and suitability for manually making agilawood on a large scale by using Aquilaria sinensis trees; and a large amount of agilawood can be effectively generated by the Aquilaria sinensis. According to the invention, the agilawood producing period of the Aquilaria sinensis is largely reduced, the agilawood can be generally obtained after 6-24 months, the production cost is reduced, the market requirements are satisfied, and important economic, social and ecological benefits are obtained in aspects of protection and sustainable utilization of the Aquilaria sinensis, economic development of mountainous regions and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Test method for main necrosis microorganism of tomato paste
InactiveCN101270383ASeparation fitValid inspectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcid-fastInternational market
The invention discloses a detection method of main spoilage microorganism in tomato paste and aims at no report about the detection method of main spoilage microorganism in tomato paste at home and abroad. The method is carried out as follows: by adopting the pre-breeding cultivation, the 8 to 12 percent by weight in volume of tomato paste is taken, and physiological saline of 200 to 250 mililiter is added into the tomato paste and well-mixed to form suspension; 8 to 12 percent of the culture suspension solution is respectively inoculated into the breeding culture solution of flatsour bacterium or the agar culture solution of thermophilic acid-fast bacillus and tryptic soytone broth or BCP modified culture solution, cultivated in 35 to 37 DEG C for about 24 to 48 hours, then the culture solution of being same to that of pre-breeding is isolated and cultivated; by a series of biochemical test, spore bacteria and Staphylococci is identified to mainly exist in the tomato paste and as the main spoilage microorganism. The invention takes very important role in promoting the rapid development of tomato paste industry and keeping the dominant position of the tomato paste trade in international market.
Owner:新疆出入境检验检疫局检验检疫技术中心
Novel oxazolidinone derivative with difluorophenyl moiety, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, preparation method thereof and antibiotic composition containing the same as an active ingredient
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives with a difluorophenyl moiety, represented by Chemical Formula 1, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same as an active ingredient are provided. Exhibiting potent inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacteria including Haemophilus influenza and Coagulase negative staphylococci and resistant bacteria including vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), the pharmaceutical composition is useful as an antibiotic.(wherein, R is as defined in the specification)
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Biological agent for preventing and treating respiratory passage diseases of livestock and poultry
InactiveCN101428075ANo side effectsNo drug resistanceBacteria material medical ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyRespiratory disease
The invention relates to a biological preparation for preventing and curing the respiratory illnesses in livestock. The biological preparation is characterized in that the biological preparation comprises non-pathogenic bacillus coli and non-pathogenic staphylococcus albus which are completely wiped out through biological liquid deep fermentation, innoxious fermentation ganoderma lucidum mycelium and natural Chinese goldthread powder. The biological preparation can be prepared into emulsion or medicinal powder. The invention has the advantages that the raw materials are form the non-pathogenic bacteria, the biofermentation fungal powder of the fungus and the natural Chinese goldthread by fine finishing, and no any chemical drug, antibiotics and prohibited article are added, therefore, the biological preparation is safe, effective and environmental-friendly, has no toxicity and side-effect, no residual and no drug resistance, is the pure natural, pollution-free and environmental-friendly biological preparation of new generation, and plays the important role of providing the green food and protecting the food safety and sanitation.
Owner:胡鹏
Disinfection method of goose shed
The invention discloses a disinfection method of a goose shed. The method includes the steps: a, cleaning the goose shed and clearing goose dung; b, uniformly locating braziers and firing the braziers; c, putting appropriate Chinese mugwort leaves in the braziers above the charcoal fire; d, after disinfection and cooling, carrying out the braziers. The Chinese mugwort leaves need to be dried in the sun after harvesting; the Chinese mugwort leaves put in the braziers should keep in producing a lot of smoke, but without producing naked flame; the Chinese mugwort leaves can be added into the braziers for multiple times to enable fumigation to last for 30-90 minutes. By the disinfection method of the goose shed, various germs can be effectively inhibited from spreading in air, typhoid bacteria, mycobacterium tuberculosis, staphylococcus and the like in air can be killed, inhibiting effect on many kinds of pathogenic bacteria, funguses and viruses leading to different kinds of infectious and epidemic diseases is achieved, and plague is prevented.
Owner:合肥皖高特种家禽养殖科技有限公司
Novel microorganism rhizobium sp. kb10 having properties of promoting growh of botryococcus braunii and increasing fatty acid content
InactiveUS20140087420A1Promote cell growthIncrease contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismBiodiesel
The present invention relates to Rhizobium sp. KB10 strain having properties of promoting growth of Botryococcus braunii, which is an alga capable of producing biodiesel, and also enhancing production performance of biodiesel. Mores specifically, it relates to novel Rhizobium sp. KB10 strain which has properties of promoting growth of Botryococcus braunii used for biodiesel production and also enhancing content of C18 (i.e., oleate) corresponding to high quality biodiesel component as much as 900%. By using root colonizing bacteria like Rhizobium, it is possible to promote effectively the slow cell growth of Botryococcus braunii and increase as much as possible the oleate amount, which is a high quality biodiesel component. Further, by carrying out mixture culture using such bacteria, problems associated with contamination by other microorganisms during a process of producing biodiesel by culture in an outside environment can be dramatically solved.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Cross-reactive displacing antibodies from collagen-binding proteins and method of identification and use
InactiveUS20070122416A1Avoid stickingTreat and prevent staphylococcal infectionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteroidesCell-Extracellular Matrix
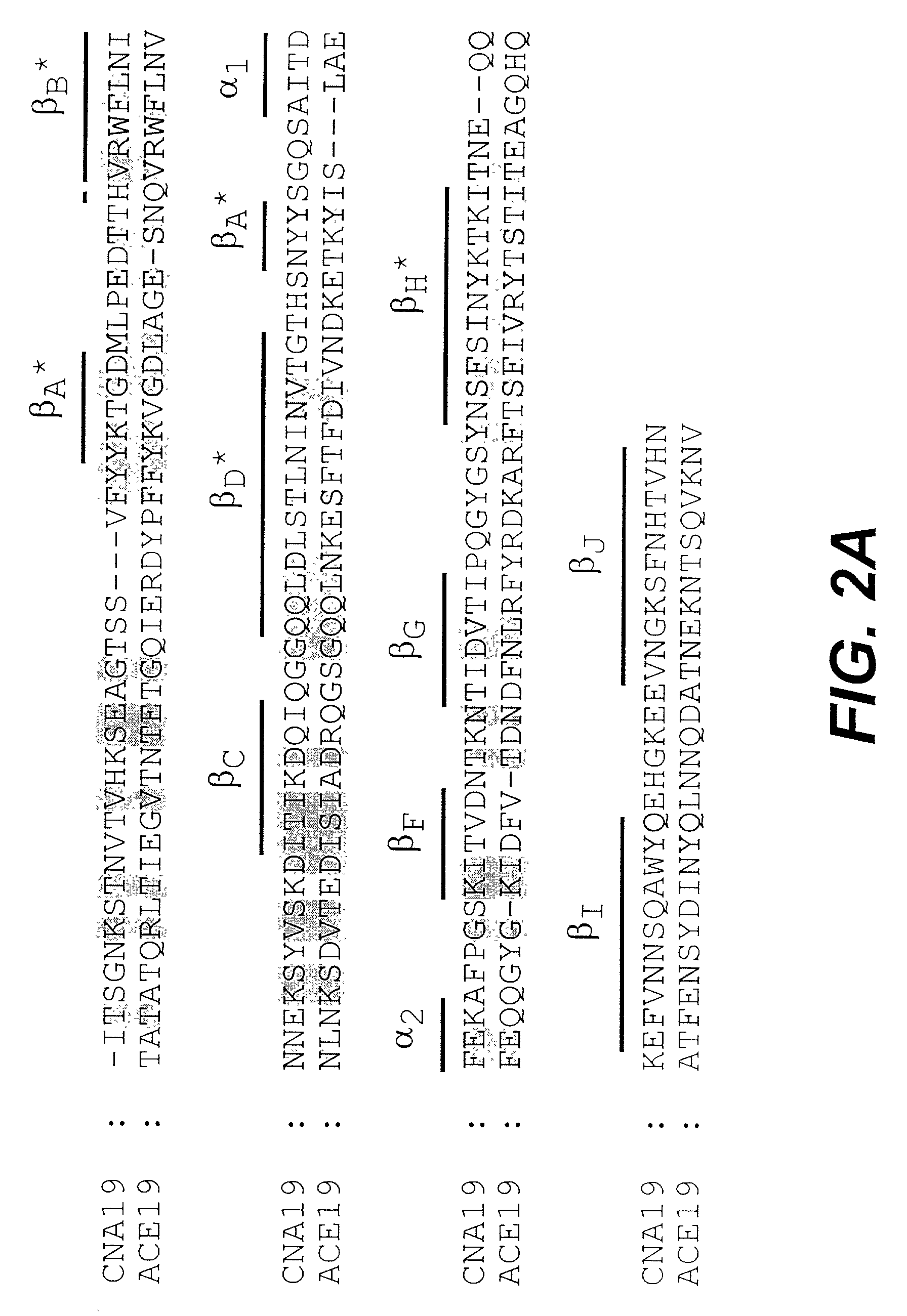
Antibodies to the CNA protein and to other regions from the collagen binding domain, including domain CNA19, are provided, and antibodies produced in this manner have been shown to be cross reactive to both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria and which can thus be used in the prevention and treatment of infections caused by both of these types of bacteria. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the antibodies of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the proteins are advantageous because they are cross-reactive and may thus be administered to patients so as to reduce or prevent severe infection by staphylococcal bacteria of more than one species. Antibodies generated in this manner have also been shown to exhibit displacement activity and can thus be utilized advantageously in methods wherein these antibodies will be administered to patients having pre-existing staphylococcal infections because of the ability to displace bacterial proteins from binding sites on the extracellular matrix. Finally, a method of identifying, isolating and utilizing displacing antibodies is also provided.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC +2
Regulating the production of long chain hydrocarbons
InactiveUS9090880B2Improve the level ofHigh expressionUnicellular algaeTransferasesWild typeEngineered genetic
The invention relates to isolated polypeptides that include amino acid sequences within botryococcene synthase from different algal species. In another aspect, the invention relates to a method for increasing the production level of a botryococcene hydrocarbon molecule in a cell. The method includes increasing expression of a polynucleotide sequence that encodes botryococcene synthase in the cell. In a further aspect, the invention relates to an algal cell having a polynucleotide sequence that is genetically engineered to express a higher level of botryococcene synthase than a corresponding wild type algal cell, wherein the cell produces an increased level of a botryococcene hydrocarbon molecule than a corresponding wild type algal cell.
Owner:THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK REPRESENTED BY THE RES FOUND OF THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Vulva lotion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105663722AEasy to useInhibitionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsMonilinia laxaRhaphidophora
The invention discloses vulva lotion, which is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 7 to 12 parts of Ecdysanthera rosea Hook. et Arn, 6 to 9 parts of spike of fungus-infected rice, 10 to 14 parts of ramose scouring rush herb, 12 to 16 parts of lobelia sessilifolia, 4.5 to 8.5 parts of mile swertia herb, 5 to 9 parts of radix cynanchi atrati, 5 to 10 parts of callicarpa longissima (hemsl.)merr., 8.5 to 13.5 parts of beautiful sweetgum fruit, 6 to 11 parts of Wusuli dragonflyorchis rhizome, 10 to 13 parts of wild tobacco, 7 to 10 parts of snake bramble seed, 5 to 8 parts of rhaphidophora peepla, and 3 to 6 parts of Arundina graminifolia (D. Don) Hochr.. The vulva lotion has the excellent effects that the vulva lotion can effectively inhabit the generation of microbial strains such as escherichia coli, staphylococcus, candida albicans and the like, and can protect and promote the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria at the same time; the vulva lotion obtained by the invention is simple in preparation method, low in cost, short in course of treatment, remarkable in curative effect, and convenient for popularization and use.
Owner:史春艳
Processing method of astroconger myriaster fermented preserved product
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic products, in particular to a processing method of an astroconger myriaster fermented preserved product. The processing method comprises the following steps: (1) killing and cleaning astroconger myriaster; (2) soaking the cleaned astroconger myriaster with an aqueous solution containing 10% of maltose, 5% of lemon and 3% of edible salt for 1-2h; (3) taking out and draining the astroconger myriaster, and inoculating lactic acid bacteria, staphylococcus, yeast and aspergillus oryzae in a ratio of 8:3:5:4:1, performing fermentation at 31-35DEG C for 5-10 h, and then performing fermentation at 20-25 DEG C for 10-13 days; (4) soaking the astroconger myriaster in a skipjack enzymatic hydrolysate for 10-13 min; (5) performing baking at 110-120 DEG C for 20-30 min to obtain the astroconger myriaster fermented preserved product. The preserved product prepared with the method has full fragrance, rich taste and high amino acid content, andpeople's choice of the astroconger myriaster is enriched.
Owner:舟山市福瑞达食品有限公司
Method for oxygen regulated production of recombinant staphylokinase
InactiveUS7524644B2Efficient and economicalOverall system can be economically viableSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliNucleotide
The present invention relates to a nucleotide sequence of expression cassette OXY-1 of SEQ ID No. 1, a modified staphylokinase SAK-2 gene of SEQ ID No. 2, a peptide sequence of modified staphylokinase SAK-2 gene, of SEQ ID No. 3, three plasmids having International Deposition Nos. BPL-0019, BPL-0020, and BPL-0021, and their corresponding three recombinant E. Coli; also invention relates to a process for over-producing staphylokinase and its analogues by modulating level of oxygen of its growth medium in a host system, and lastly, a method of dissolving blood clot in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications
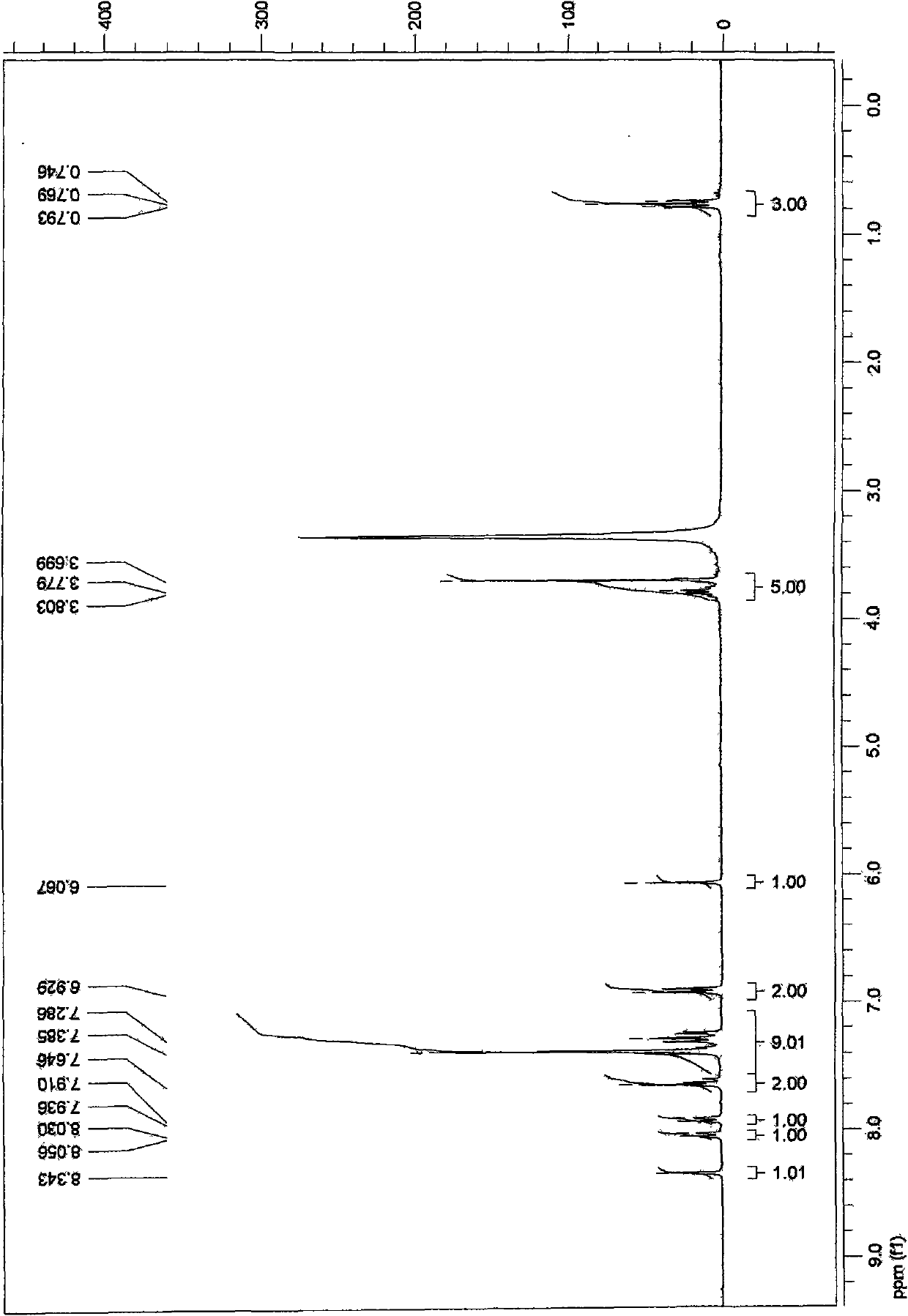
The invention discloses application of 3-benzoyl-5, 7-diphenyl-5H-thiazole [3, 2-a] pyrimidine derivatives shown in a general formula to antibacterial drugs, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are hydrogen, methyl, halogen, hydroxyl, methoxyl, nitryl, ethanoyl, propionyl or alkoxyl which are separated from each other respectively. The compound has an obvious inhibiting effect in the plurality of bacteria such as meticillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, escherichia colim, pseudomonas aeruginosa and the like, and can be used for preparing the antibacterial drugs.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN101613362BNovel structureSimple manufacturing methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHistidine kinaseMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention relates to a 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound and a synthesis method and application thereof. The compound has a structure formula as below. The 3-carbonyl-6-ethoxycarbonyl-thiazole pyrimidine compound serving as an inhibiting agent of YyCG histidine kinase protein for a staphylococcus epidermidis signal transduction system has a novel structure, and the adopted method for preparing the compound is simple and easy to implement. The test results of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) show that the compound has excellent inhibitory action on the formation of a staphylococcal biological film and can effectively kill and wound the bacteria in the staphylococcal biological film.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV +1
Process for curing meat using a starter culture
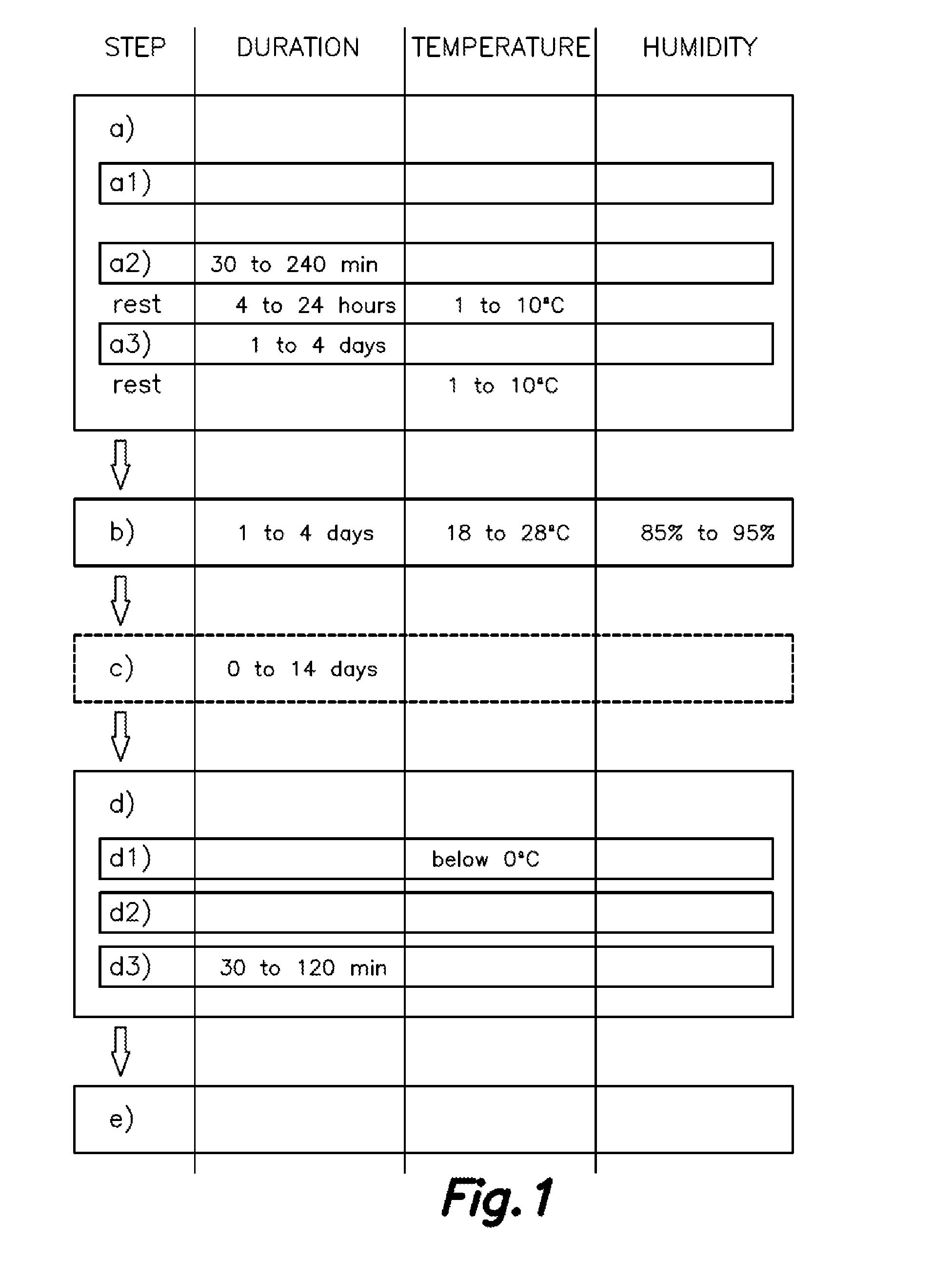
ActiveUS20160366901A1Improve permeabilityAid in preservationMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsBiotechnologyYeast
The present invention relates to a method for the application and implantation of starter cultures in products of animal origin for curing same, which comprises:a) introducing one or more starter cultures of Staphylococcus and yeasts in a whole muscle product of animal origin by means of sprinkling, tumbling and massaging;b) subjecting said product after step a) to maturation treatment with heat and humidity to favor starter culture growth;d1) freezing the product after step b), stopping the starter culture biological activity; andd2) cutting or slicing the frozen product; andd3) subjecting cutted or sliced product to a rapid drying process for between 30 and 120 minutes; ande) packing the dried product of animal origin.
Owner:METALQUIMIA SA
Special feed capable of preventing dysentery in piglets
InactiveCN108936022AAvoid Weaning StressLower pHFood processingAnimal feeding stuffEscherichia coliLactic acid bacterium
The invention discloses a special feed capable of preventing dysentery in piglets. The special feed capable of preventing dysentery in piglets comprises the following ingredients in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of corn powder, 20-30 parts of millet powder, 20-30 parts of bean cake powder, 5-8 parts of fish meal, 3-6 parts of bone meal, 0.2-0.4 part of edible salt, 0.3-0.5 part of calcium formate,and 1-3 parts of a plant extract. The ingredients of the special feed are ideally matched, so that the special feed is balanced in nutrient matches and beneficial for preventing risk of dysentery in piglets. The plant extract has the functions of clearing away heat, detoxifying, cooling the blood and relieving dysentery; moreover, the plant extract is also capable of enhancing body immunity of piglets. The calcium formate has the functions of reducing gastrointestinal pH value of piglets, increasing gastrointestinal acidity and digestive enzyme activity, promoting lactic acid bacterium propagation, inhibiting growth of Escherichia coli and staphylococci, recovering physiological characteristics of gastrointestinal tract of the piglets, and greatly decreasing incidence of dysentery.
Owner:无为县旺盛饲料加工厂
Streptomyces flavotricini for antagonizing botryosphaeria dothidea
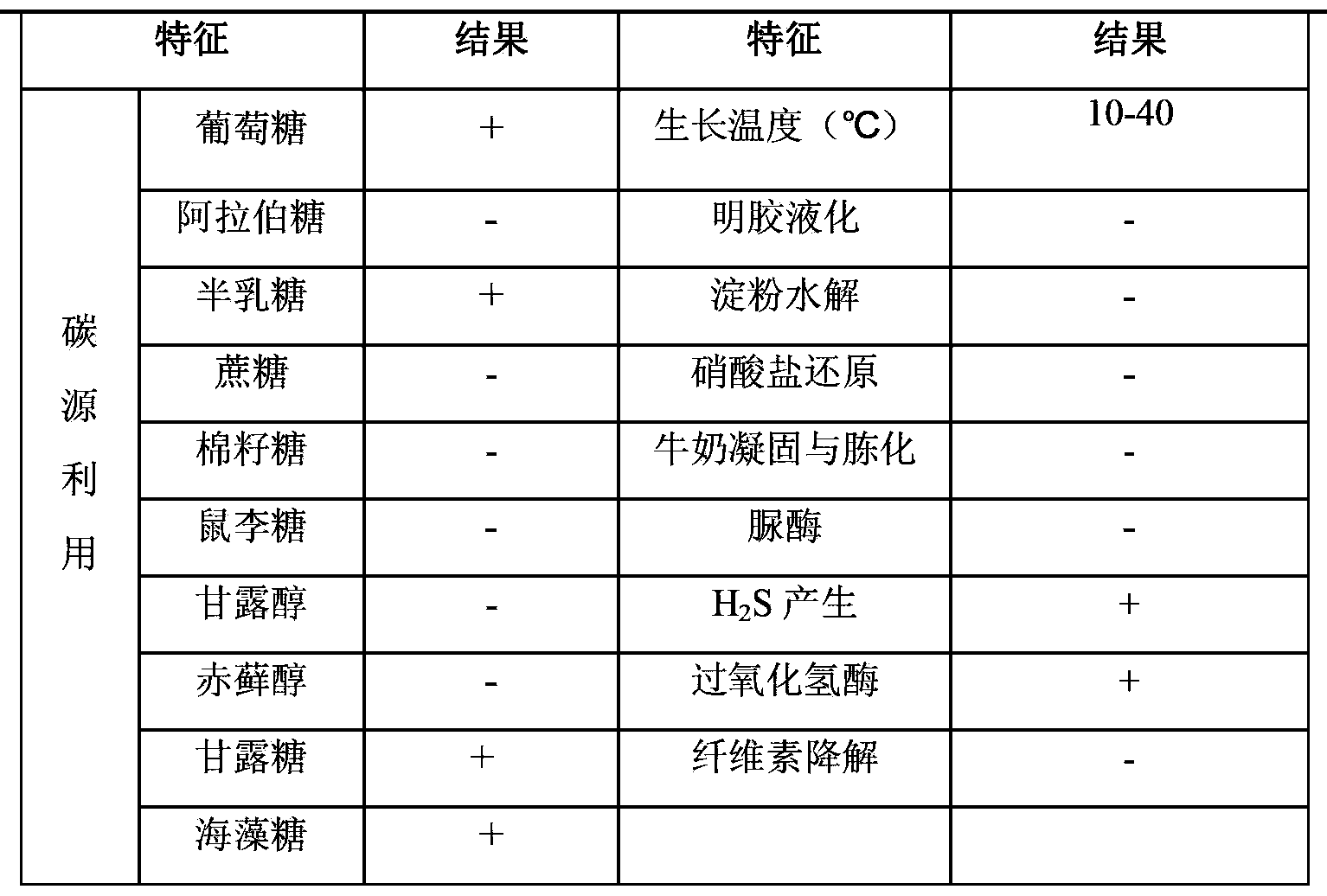
The invention relates to biological prevention of plant diseases and belongs to the field of biological prevention research and application in a plant protection subject. The invention discloses streptomyces flavotricini YZF3 for antagonizing botryosphaeria dothidea, with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7529. The strain can effectively inhibit the botryosphaeria dothidea and the effect is obviously better than that of bismerthiazol and is equivalent to agricultural streptomycin; and the strain has the potential of preventing and treating the botryosphaeria dothidea. Compared with a chemical medicament, the YZF3 strain is used for preventing and treating the plant diseases and has no problems of environmental pollution, pesticide residues and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com









![2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof 2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bab1c640-7043-4456-a794-14b5a1cfda16/246389DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.PNG)
![2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof 2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bab1c640-7043-4456-a794-14b5a1cfda16/518287DEST_PATH_IMAGE004.PNG)
![2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof 2H,6H-pyrimido[2,1-b][1,3]thiazine derivative and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/bab1c640-7043-4456-a794-14b5a1cfda16/703915DEST_PATH_IMAGE003.PNG)























![3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications 3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/48208799-14ee-4bad-b028-8ed83a3e8682/151727DEST_PATH_IMAGE003.png)
![3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications 3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/48208799-14ee-4bad-b028-8ed83a3e8682/212404DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.png)
![3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications 3‑Benzoyl‑5,7‑diphenyl‑5h‑thiazolo[3,2‑a]pyrimidine derivatives and their applications](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/48208799-14ee-4bad-b028-8ed83a3e8682/867377DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.png)