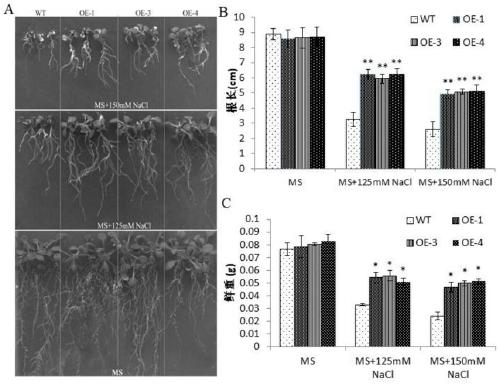
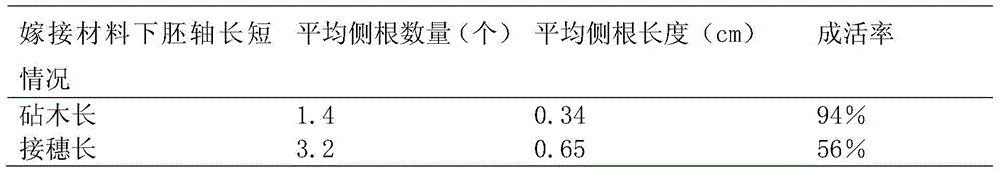
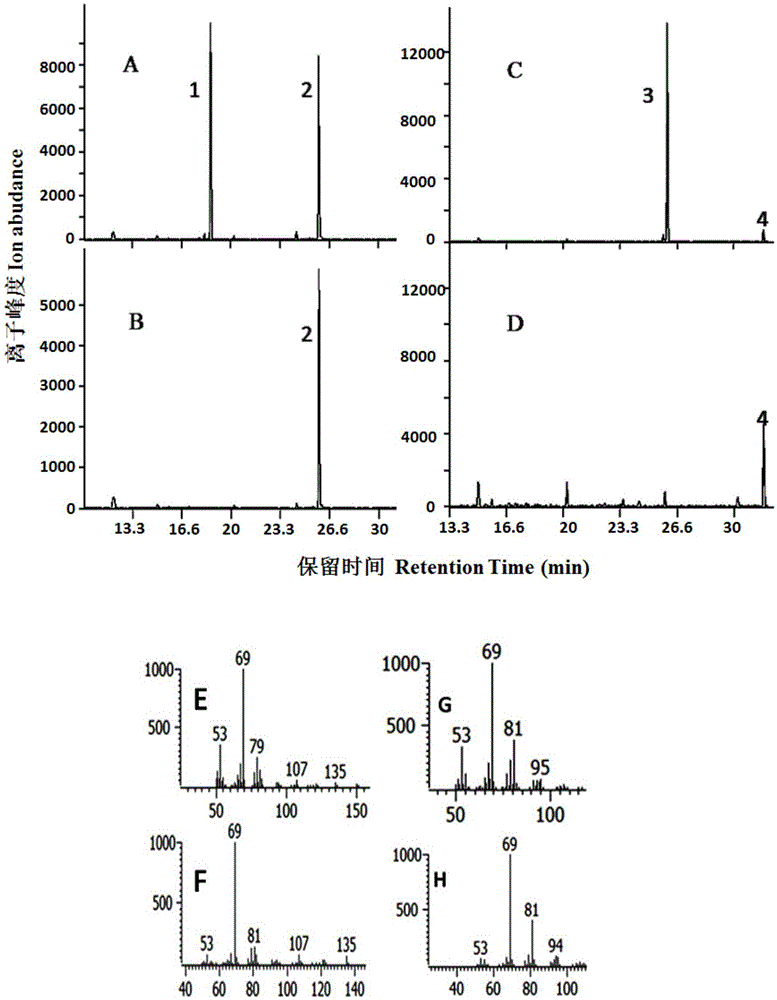
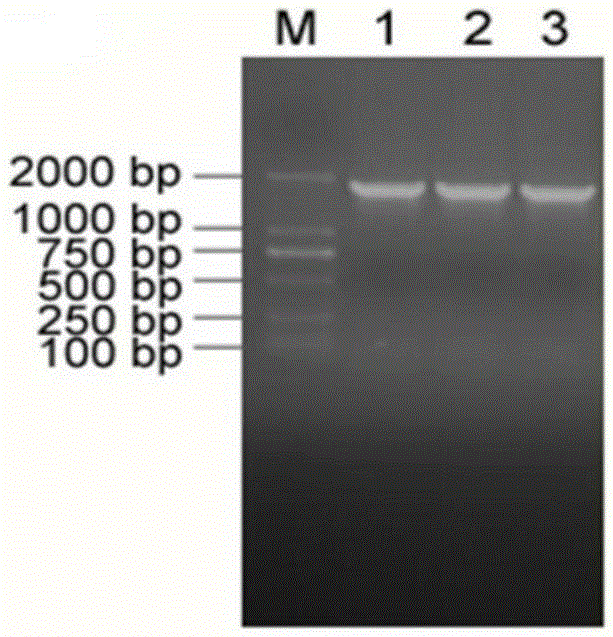
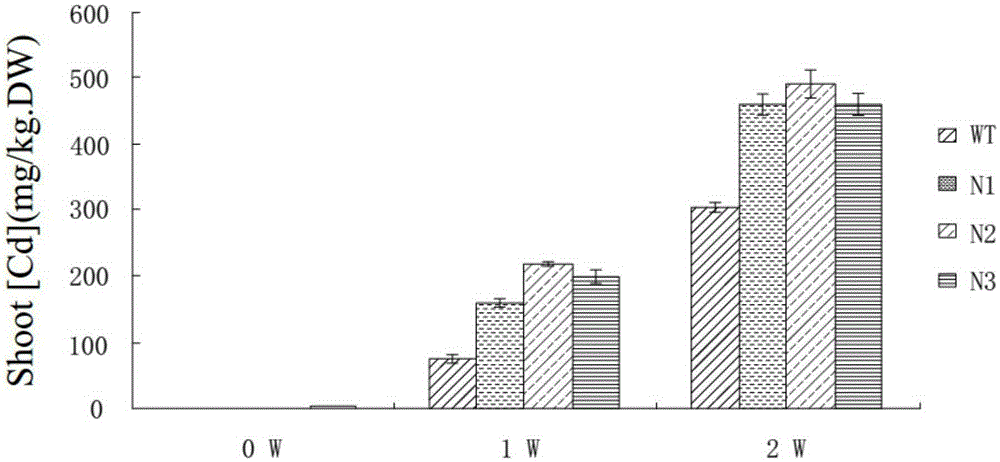
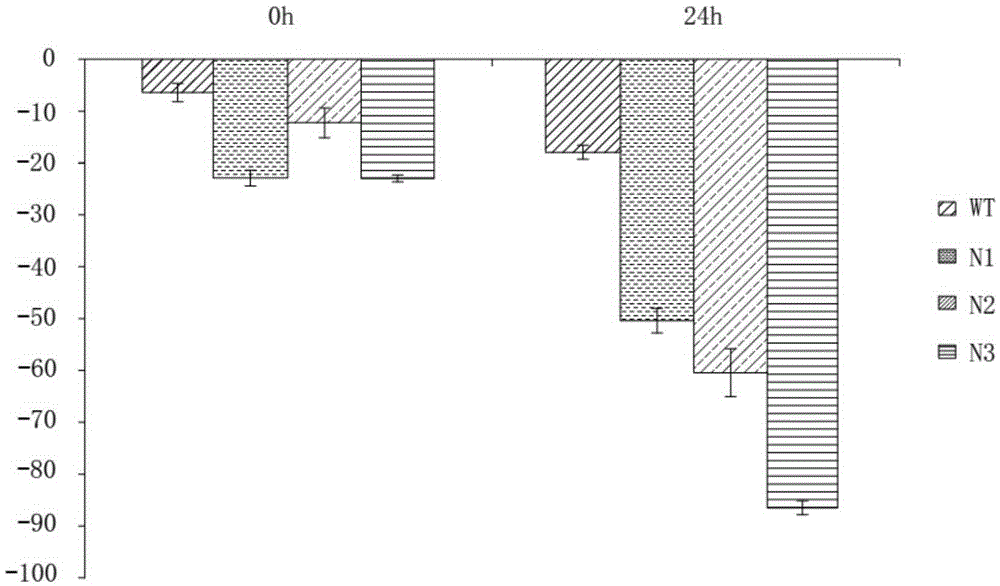
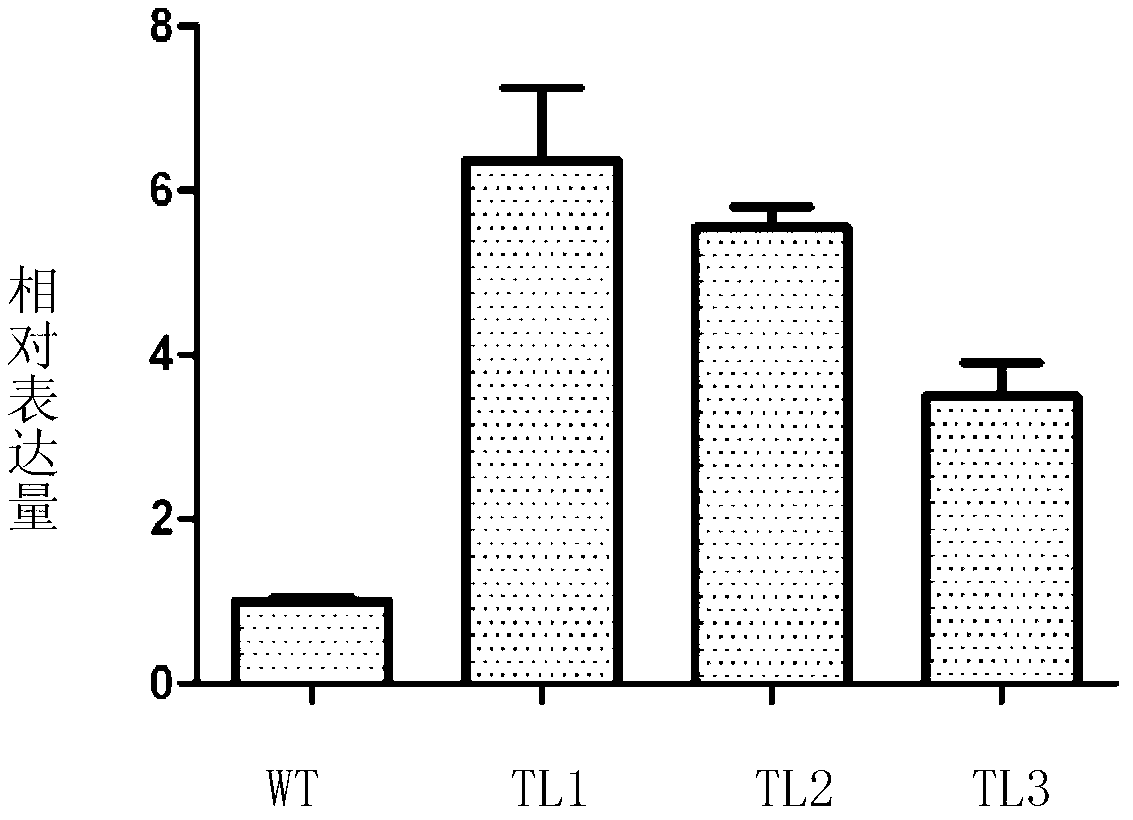
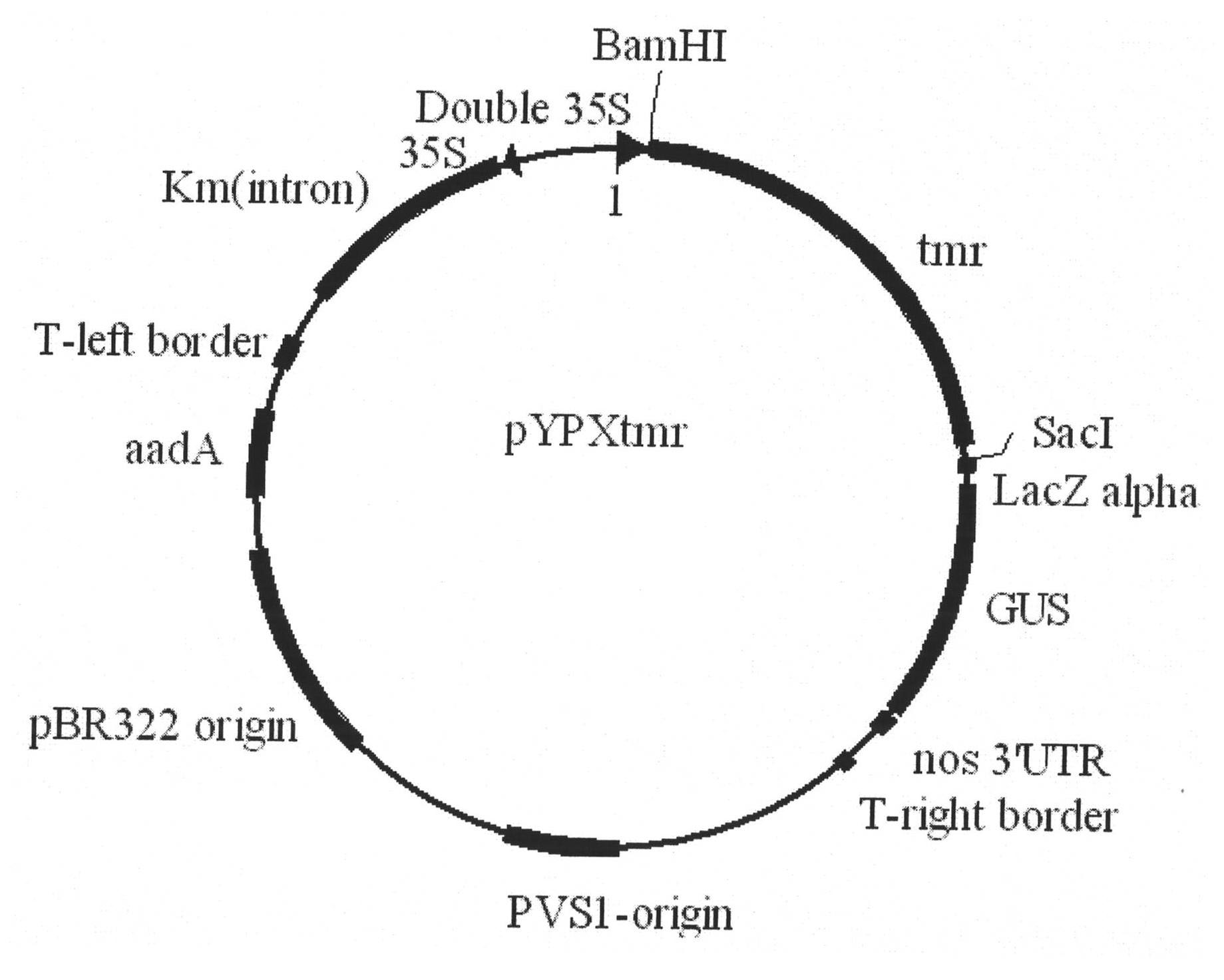
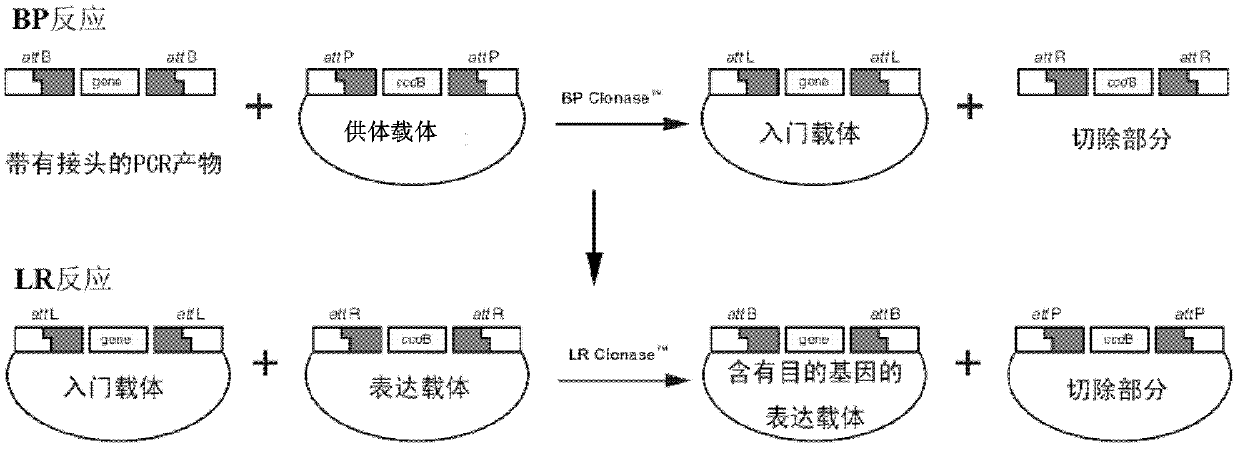
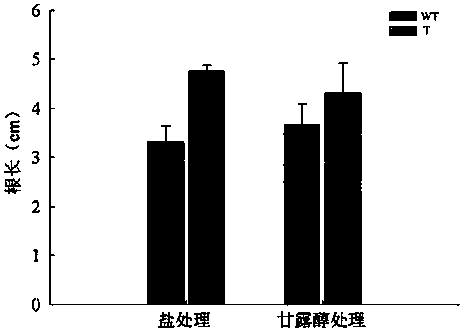
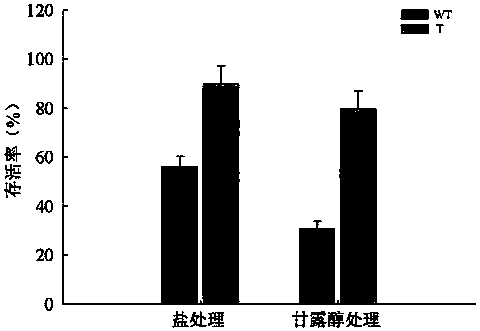
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114 results about "Arabidopsis thaliana <plant>" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arabidopsis thaliana is a small flowering plant that is widely used as a model organism in plant biology. Arabidopsis is a member of the mustard (Brassicaceae) family, which includes cultivated species such as cabbage and radish.
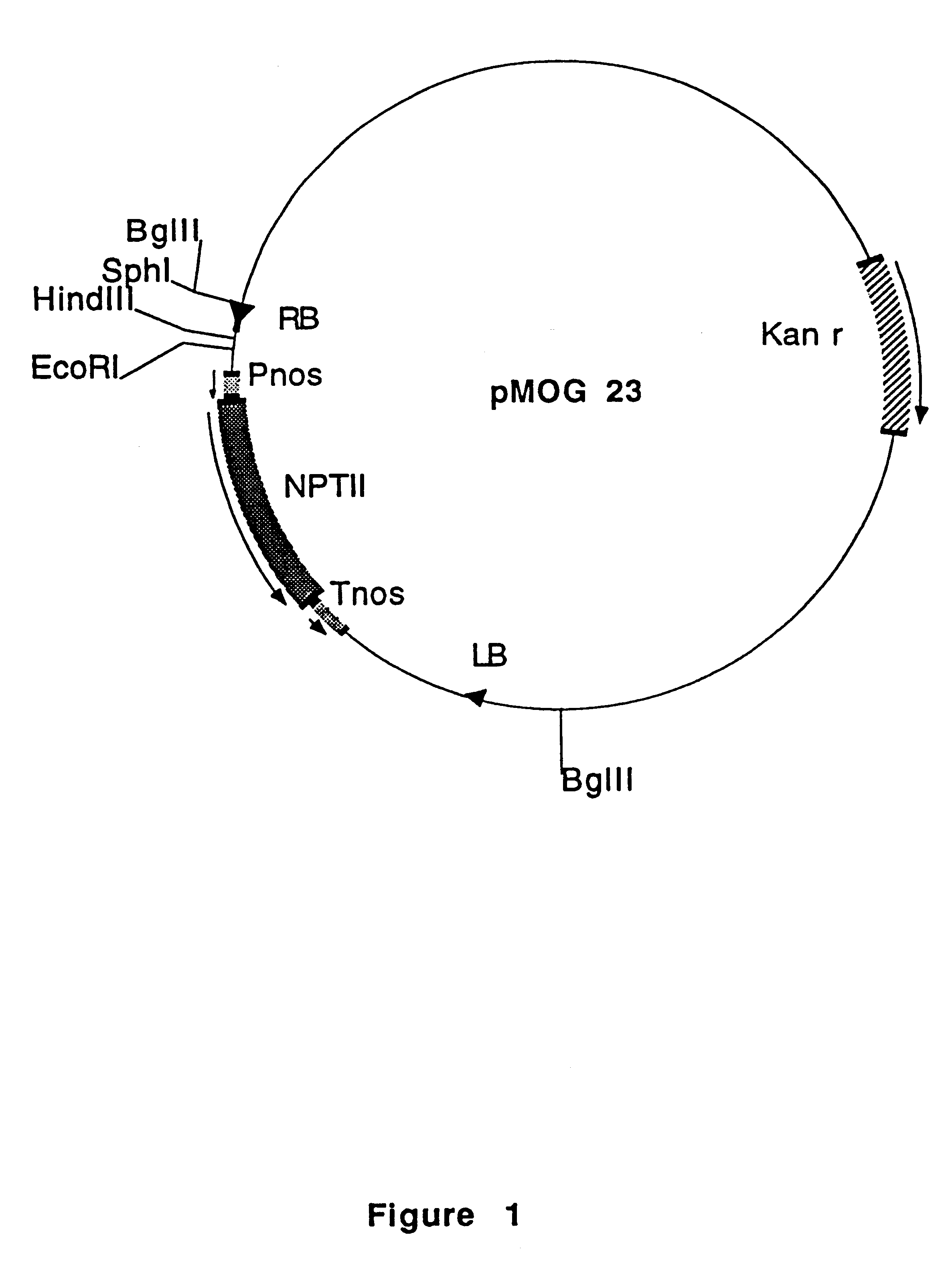
Nematode-inducible plant gene promoter
An isolated DNA fragment that promotes root knot or cyst nematode indcuible transcription of a coding sequence downstream of and operably linked to the fragment in at least an Arabidopsis thaliana plant and a chimeric DNA sequence including the DNA fragment. Also, methods for the use of the DNA fragment.
Owner:SYNGENTA MOGEN BV
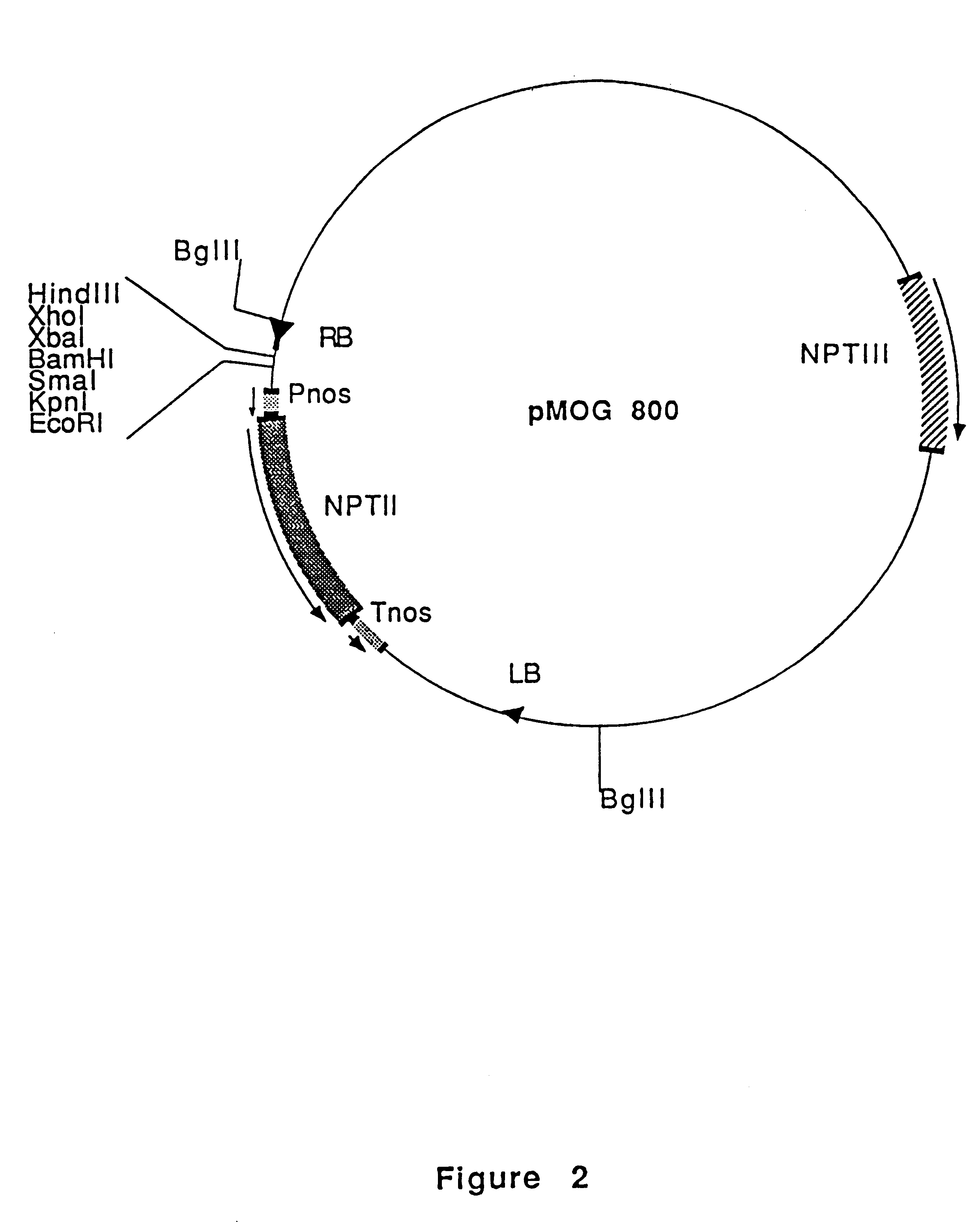
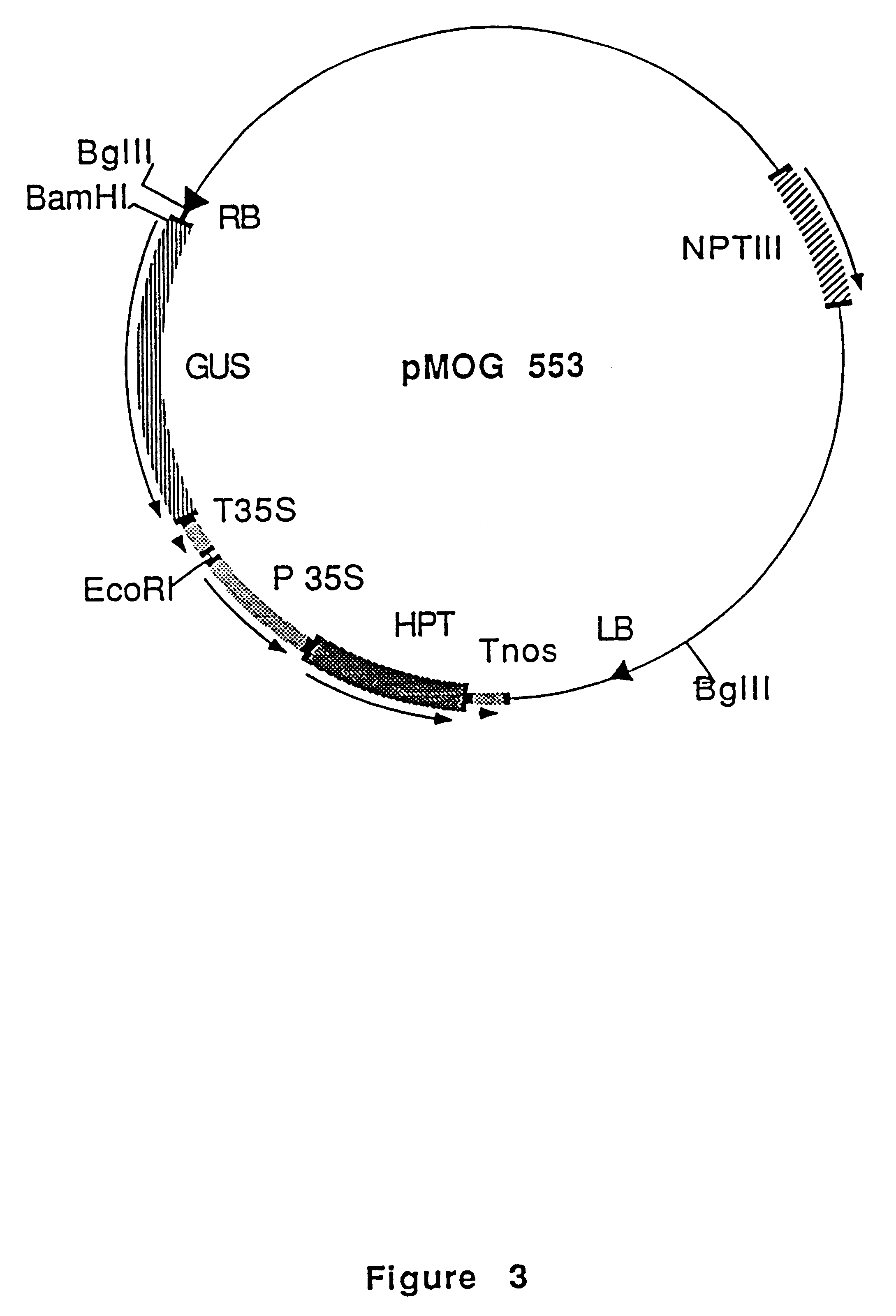
Plant genome sequences and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:CAO YONGWEI +1
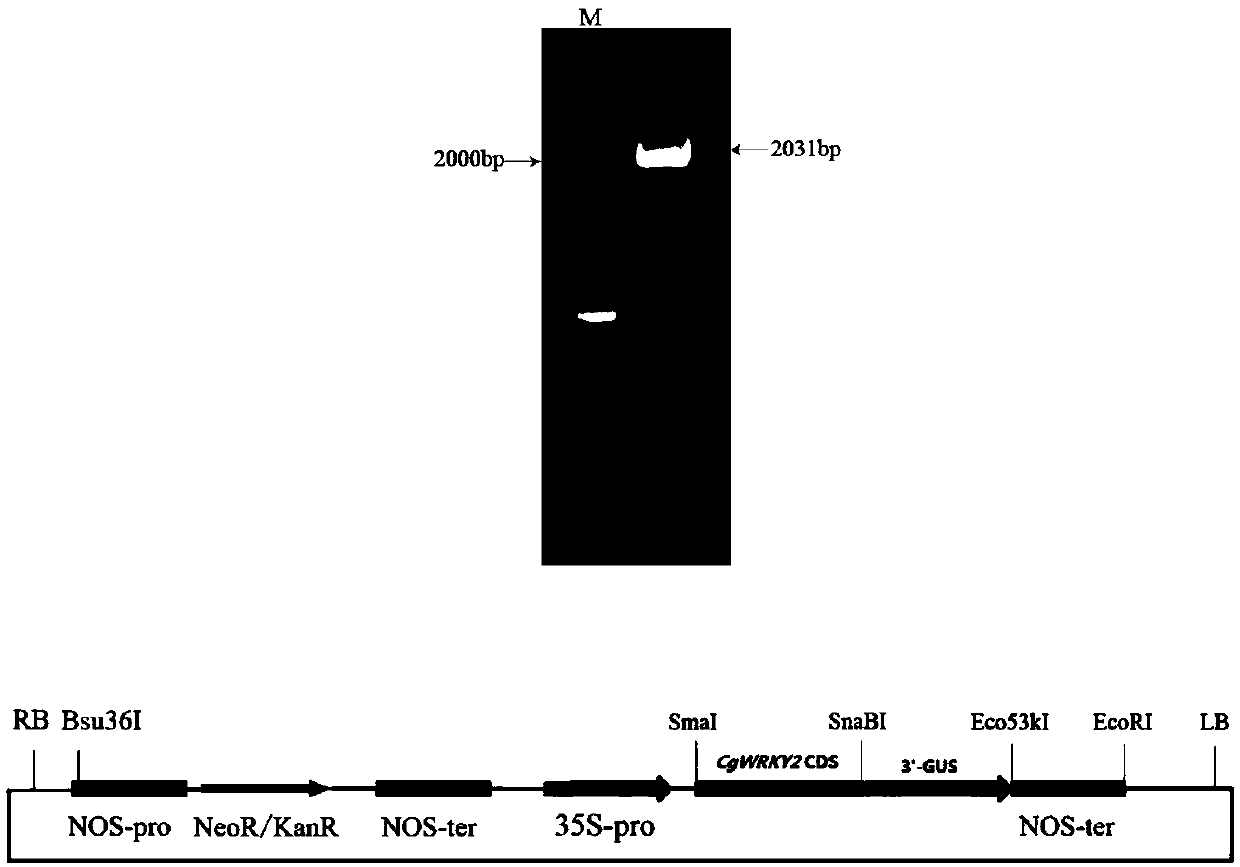
Spring orchid CgWRKY2 gene and application thereof
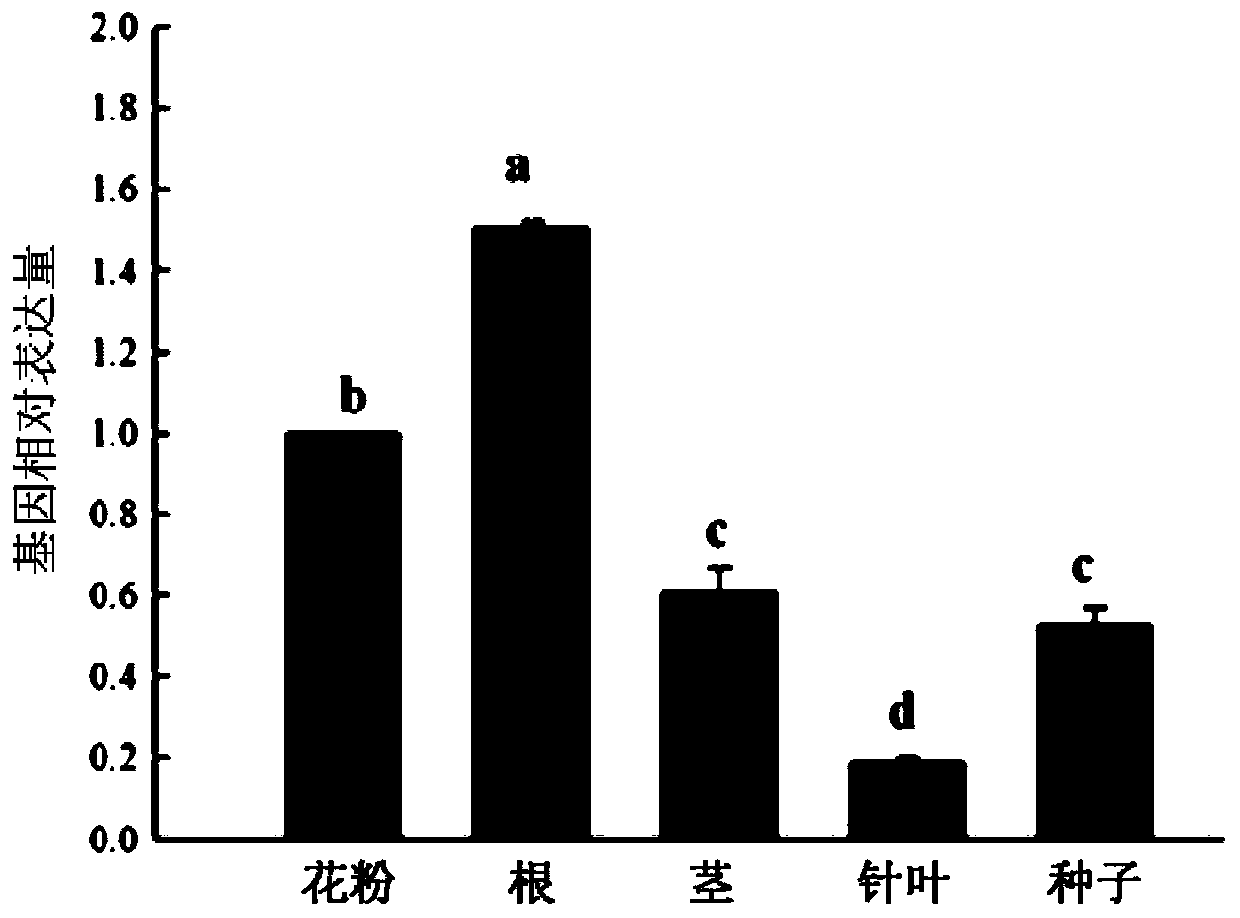
The invention discloses a spring orchid CgWRKY2 encoding gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the CgWRKY2 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of an expressedprotein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. According to cloning and identification of the CgWRKY2 gene of a spring orchid variety 'Song Mei', gene expression analysis and function verification, it's found thatan arabidopsis thaliana plant over expressing the CgWRKY2 gene grows slowly and is dwarfed with the phenotype of premature aging like early blight of leaves, thereof, the gene has a wide range of usesin production and breeding of the orchid and other plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
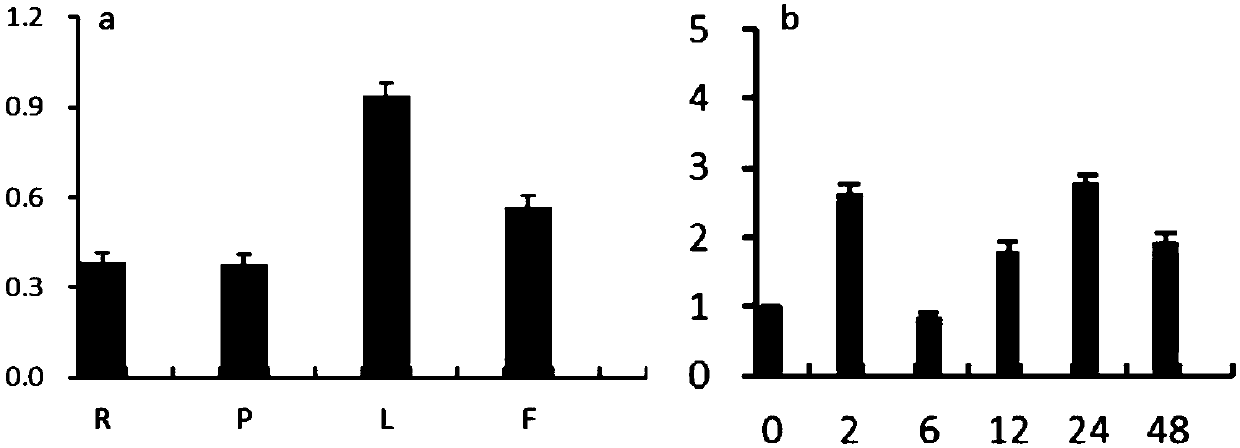
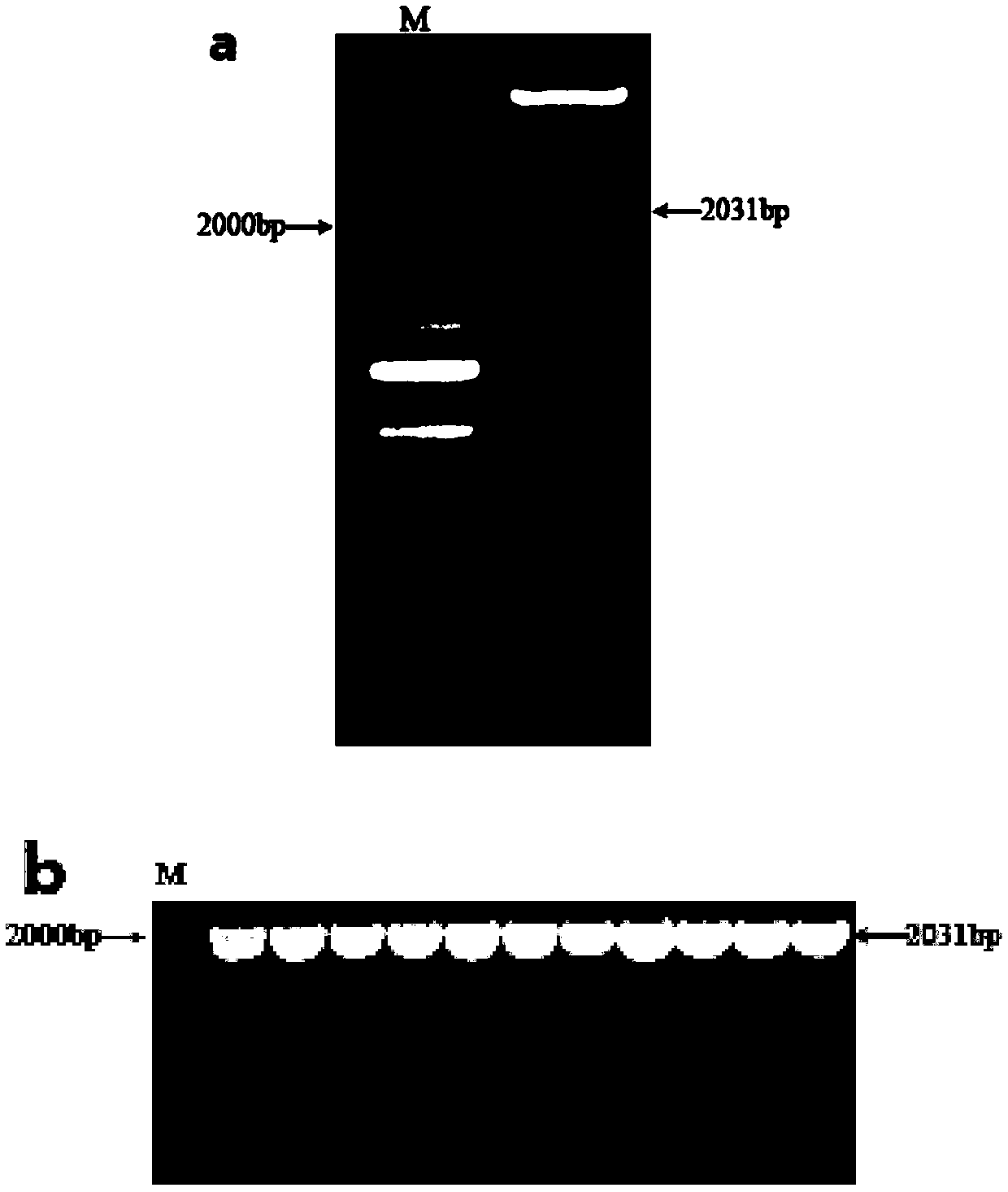
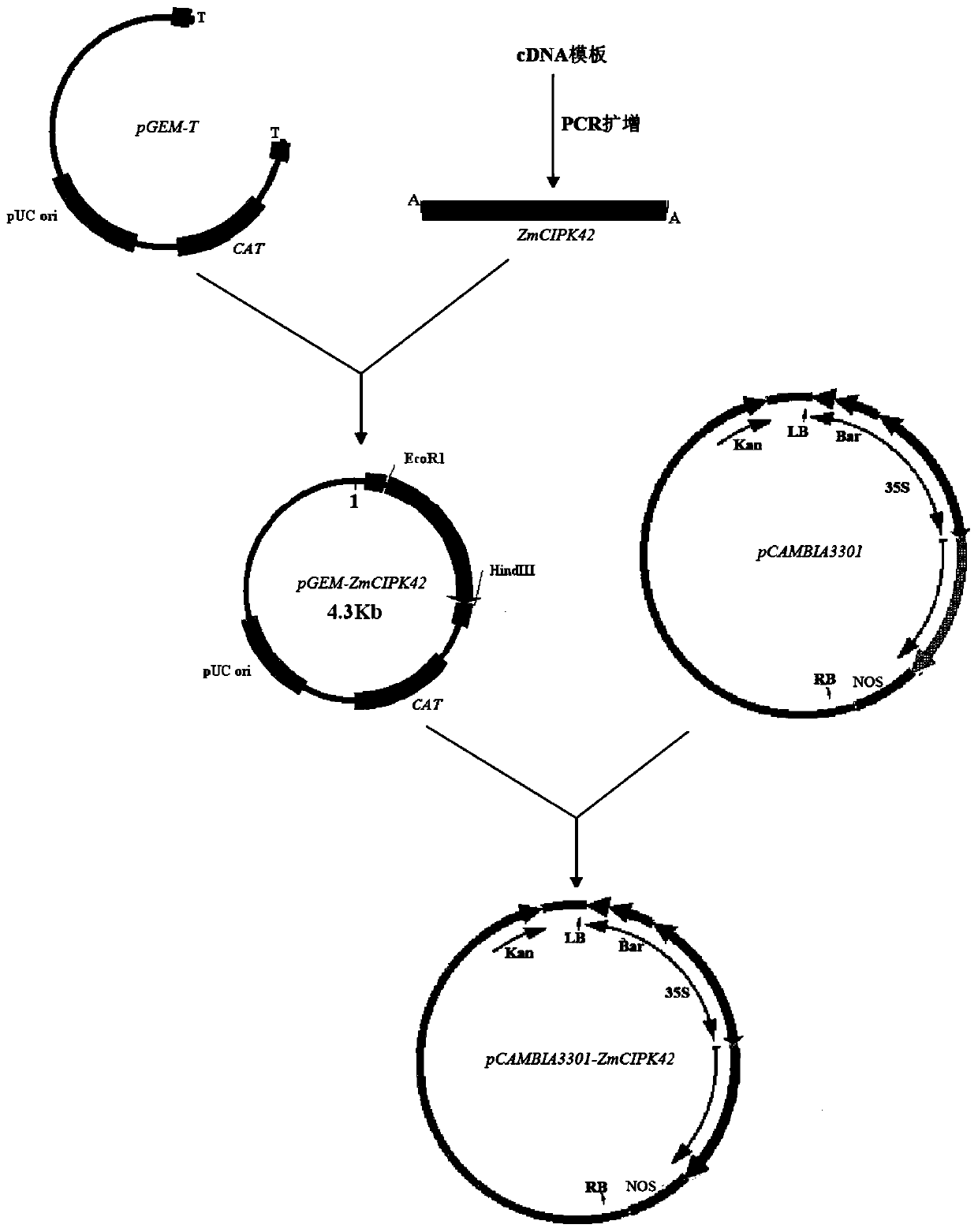
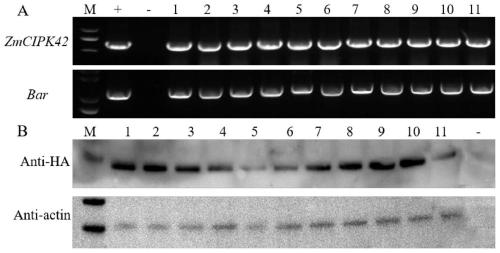
Application of corn CIPK42 protein and coding gene of corn CIPK42 protein in regulation and control of salt stress tolerance of plants
ActiveCN111172131AImprove salt toleranceImprove growth performanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologySalt Tolerant Plants
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly discloses an application of a corn CIPK42 protein and a coding gene of the corn CIPK42 protein in regulationand control of salt stress tolerance of plants. The corn ZmCIPK42 gene is found to be able to positively regulate and control the salt tolerance of the plants; and the salt tolerance of the plants can be effectively improved by increasing of the expression quantity of the ZmCIPK42 gene. According to the invention, transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants with ZmCIPK42 overexpression are constructed; and compared with a non-transgenic wild type, the transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants are significantly improved in salt tolerance and growth. Discovery of the salt-tolerant function of the ZmCIPK42 gene provides a novel gene target and resource for cultivation of salt-tolerant plant varieties, is of great significance to research of a salt-tolerant molecular mechanism of the plants, and lays a certain theoretical foundation for research of a salt stress response mechanism of the plants and a molecular mechanism of resisting adverse environments.
Owner:新疆农业科学院核技术生物技术研究所(新疆维吾尔自治区生物技术研究中心)
Grafting method for model arabidopsis thaliana
InactiveCN105706873AReduced germinationPromote growthGraftingGrowth substratesHypocotylCulture mediums
The invention discloses a grafting method for model arabidopsis thaliana.The method comprises the following steps that an arabidopsis thaliana plant with the seedling age of 6-8 days, thick and strong hypocotyl explant, consistent growth vigour and a main leaf emerging newly is used for grafting; stock and scion materials used for grafting are placed in the middle of 1.2% sepharose gel, the hypocotyl explant is transversely cut, and it is ensured that the hypocotyl explant part of the scion material is short and the hypocotyl explant part of the stock material is long; material notches are in tight contact on the sepharose gel, a 1 / 2MS+3% saccharose solid culture medium with the area larger than the stock root area is cut to cover the stock root, and a grafting body is formed; the grafting body is placed in the environment under the temperature of 21 DEG C to be vertically cultured for 7 days; after grafting notches are healed, the grafting body is transferred into a water culture device with 1 / 4MS as a liquid culture medium to be cultured.The problems that operation is difficult, notches are not round or normal, scion side roots are frequently produced, and the grafting survival rate is low due to the fact that arabidopsis thaliana plants are thin and weak are solved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
CYP450 gene participating in DMNT and TMTT biosynthesis and coding product and application of CYP450 gene
The invention relates to a CYP450 gene participating in DMNT and TMTT biosynthesis and a coding product and application of the CYP450 gene, and belongs to the field of plant molecular biology. The protein has amino acid sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Experiments prove that the PlCYP82 protein obtained in the mode that the obtained cDNA nucleotide sequences and PlCYP82 coding protein sequences of lima beans PlCYP82 are expressed in yeast WAT21 cells has the activity of catalyzing (E)-nerolidol and (E,E)-geranyl linalool; PlCYP82 gene-transferred arabidopsis thaliana is obtained through a floral-dip method, and a result shows that PlCYP82 gene-transferred arabidopsis thaliana plants can significantly attract female cotesia plutellae.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene capable of promoting cadmium accumulation and application of gene
InactiveCN105274121AIncrease contentFast absorptionPlant peptidesFermentationSedum alfrediiComplementary pair
The invention discloses a gene capable of promoting cadmium accumulation and application of the gene. The gene capable of promoting cadmium accumulation is separated from super accumulation type sedum alfredii hance, the polynucleotide sequence is shown by (a) or (b), (a) is a polynucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1; (b) is a polynucleotide sequence which is complementary with the polynucleotide sequence in the (a) according to a base complementary pairing rule. The gene is derived from a super accumulation type sedum alfredii hance plant, an expression vector of the gene is constructed, agrobacterium is converted with an expression vector electric shock method, arabidopsis thaliana is soaked with a mature agrobacterium transformation method, and finally, a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant is obtained. The content of cadmium in the blade of the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant can be remarkably increased by over expression of the gene on the blade of the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant, compared with an ordinary arabidopsis thaliana plant, the content of cadmium in the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana subjected to cadmium treatment is improved by 50%-64%, and the absorption rate of the cadmium in the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant under heavy metal cadmium stress is remarkably higher than that of the cadmium in the ordinary arabidopsis thaliana plant.
Owner:RES INST OF SUBTROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Application of protein AtbHLH122 of arabidopsis thaliana and coding gene of protein AtbHLH122 for regulating and controlling stress tolerance of plants
InactiveCN103320470AImprove stress toleranceGenetic engineeringFermentationAgricultural scienceWild type
The invention discloses application of protein AtbHLH122 of Arabidopsis thaliana and a coding gene of the protein AtbHLH122 for regulating and controlling the stress tolerance of plants. The amino acid sequence of the protein is shown in a sequence 1 of a sequence table and can be used for regulating and controlling the stress tolerance of the plants, or substances and methods, capable of adjusting the expression level of the protein shown in the sequence 1 of the sequence table, can be used for regulating and controlling the stress tolerance of the plants. Shown by experiments, after the coding gene of the protein AtbHLH122, which is shown in a sequence 2 of the sequence table, is over-expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana, a transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant is obtained, the survival rate after drought treatment, the germination rate and leafy rate after 140mM NaCl treatment and the root length after 250mM mannitol treatment of the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant are remarkably lower than those of the wild plants, and furthermore, after the treatments, gene AtbHLH122 knockout mutants are less than those of the wild plants; and thus, the protein AtbHLH122 shown in the sequence 1 of the sequence table has the function of regulating and controlling the stress tolerance of the plants and has an important significance on the aspects of stress tolerance research and breeding of the plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
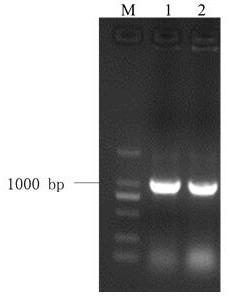
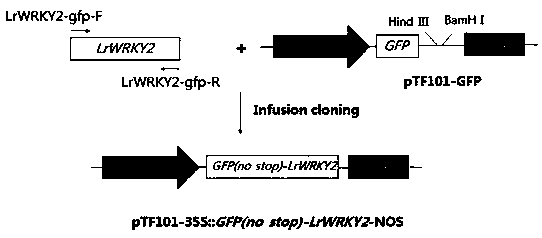
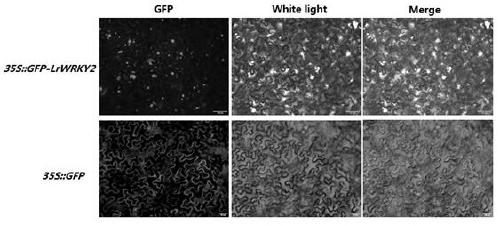
Lilium regale wilson LrWRKY2 gene and application
InactiveCN109825510AAltered growth and development phenotypePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a lilium regale wilson LrWRKY2 gene and application. A nucleotide sequence of the LrWRKY2 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the coded amino acid sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. According to the gene, an expression carrier with the LrWRKY2 gene is transferred into an arabidopsis thaliana plant, the acquired transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant shows creep growth, and the original growth form of wild arabidopsis thaliana is thoroughly changed; multiple lotus-throne-shaped basal leaves grow up on the arabidopsis thaliana stems with creep growth, the edges ofthe leaves have a special regular-protruding form, the arabidopsis thaliana is extremely suitable for large-scale cultivation and application in a courtyard and landscaping, and meanwhile the gene provides the theoretical basis and technical support for preparation of a novel ground cover plant and has potential application prospects.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
CgWRKY57 gene of cymbidium goeringii, and application of gene
The invention discloses a CgWRKY57 encoding gene of cymbidium goeringii, and application of the encoding gene. The nucleotide sequence of the CgWRKY57 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, the amino acid sequence of the expressed protein of the CgWRKY57 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By cloning and identifying the CgWRKY57 gene of 'Song Mei' which is a cultivated variety of the cymbidium goeringii, analyzing the gene expression and verifying the functions of the gene, an arabidopsis thaliana plant with the overexpressed CgWRKY57 gene is found to have phenotypes such as growth retardation and plant dwarf; therefore, the gene has a broad application prospect in the production and breeding of the cymbidium goeringii and other plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
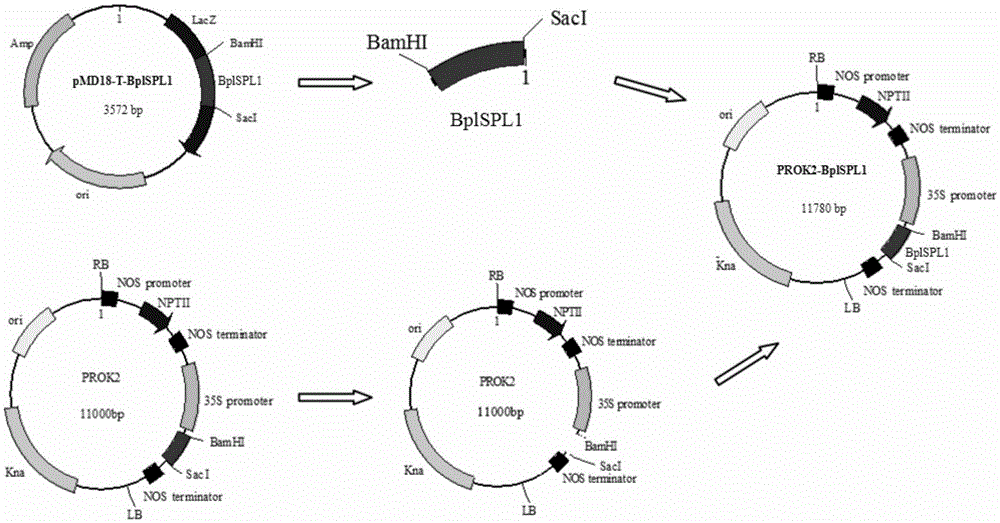
Betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering and encoded protein thereof
InactiveCN106591320AEarly floweringShorten flowering timePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringGenetic engineeringFlowering time
Belonging to the field of gene technology in molecular biology, the invention relates to a betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering and an encoded protein thereof. The invention is characterized in that the betula platyphylla BplSPL1 gene for promoting precocious flowering has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table, and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention provides the betula platyphylla flowering gene BplSPL1 and applies the gene to construction of a BplSPL1 gene's plant expression vector, and the constructed plant expression vector is subjected to agrobacterium impregnation of an arabidopsis thaliana plant so as to obtain a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant and achieve precocious flowering. Therefore, the gene has the function of inducing precocious flowering of arabidopsis thaliana and can regulate plant leaf development. The gene provided by the invention utilizes genetic engineering technology to regulate betula platyphylla flowering time and leaf development, provides gene resources and theoretical basis, and has great application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +3
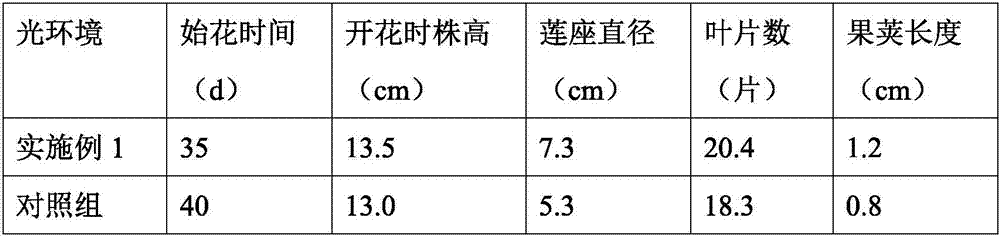
Artificial light environment cultivation method for Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN106973787AStrong plantA large amountPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsNutrient solutionCulture mediums
The invention discloses an artificial light environment cultivation method for Arabidopsis thaliana, the artificial light environment cultivation method for Arabidopsis thaliana comprises the following steps: (1) after disinfection treatment, Arabidopsis thaliana seeds are applied to a MS culture medium by a micro sampling syringe; (2) after the Arabidopsis thaliana seeds are completely applied to the MS culture medium, the MS culture medium is sealed and cultured in a dark room; (3) the MS culture medium is 55 to 65-degree inclined for culturing at 24 to 26 DEG C for 15-20d to obtain seedlings; (4) the seedlings obtained from the MS culture medium in the step (3) are taken out, and transplanted to a seeding tray with a mixed matrix; after the transplantation, the seeding tray is covered with a film, when plant leaves obviously elongate, and stems begin to develop, the plastic film is taken off, and a nutrition solution is regularly poured to ensure an adequate nutrition matrix; and (5) when pods turn yellow and mature, seeds are harvested. According to the cultivation method, in seedling raising and field planting phases, specific light environmental conditions are given to plants, the planted arabidopsis thaliana plants are strong, flowering time is early, the number of the pods is great, and the pods are full.
Owner:FUJIAN SANAN SINO SCI PHOTOBIOTECH CO LTD
Strawberry transcription factor for promoting precocious flowering of plants and application thereof
ActiveCN107056911AEarly boltingEarly floweringPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionFragariaGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a strawberry transcription factor for promoting precocious flowering of plants and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering in molecular biology. The strawberry transcription factor is characterized in that a full-length coding region sequence of the strawberry WRKY46 gene for promoting precocious flowering of the plants is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1; an amino acid sequence is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:2. The strawberry FvWRKY46 gene for promoting precocious flowering of the plants is used for constructing plant expression vectors of the FvWRKY46 gene, the constructed plant expression vectors transform arabidopsis thaliana through agrobacteria, genetically modified arabidopsis thaliana plants are obtained and flower early, and it is shown that the FvWRKY46 gene has the function of inducing precocious flowering of arabidopsis thaliana. According to the strawberry transcription factor for promoting precocious flowering of the plants, a genetic engineering technology is adopted, technical means and theoretical bases are provided for regulating the flowering time of strawberries, and the strawberry transcription factor has great application value.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Application of TGA7 gene in regulation and control of flowering period of plant
ActiveCN111996200AProlong flowering periodPrecise control of flowering timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyWild type
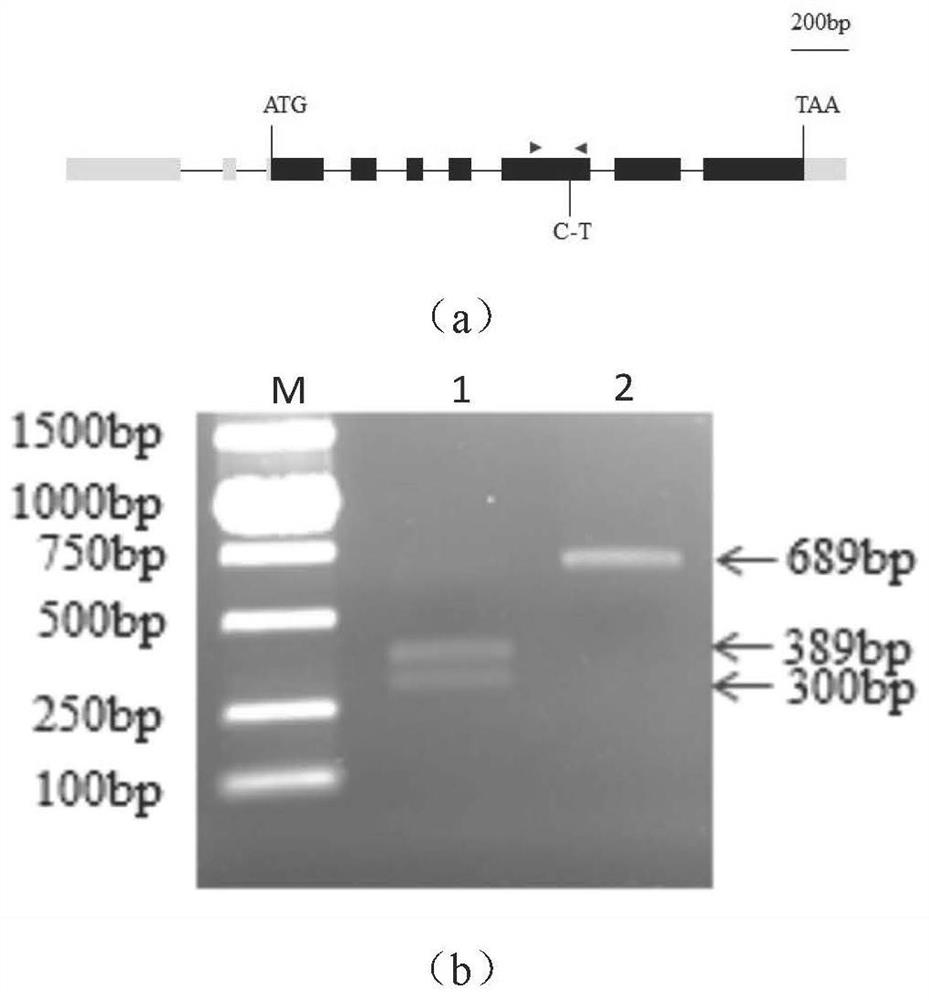
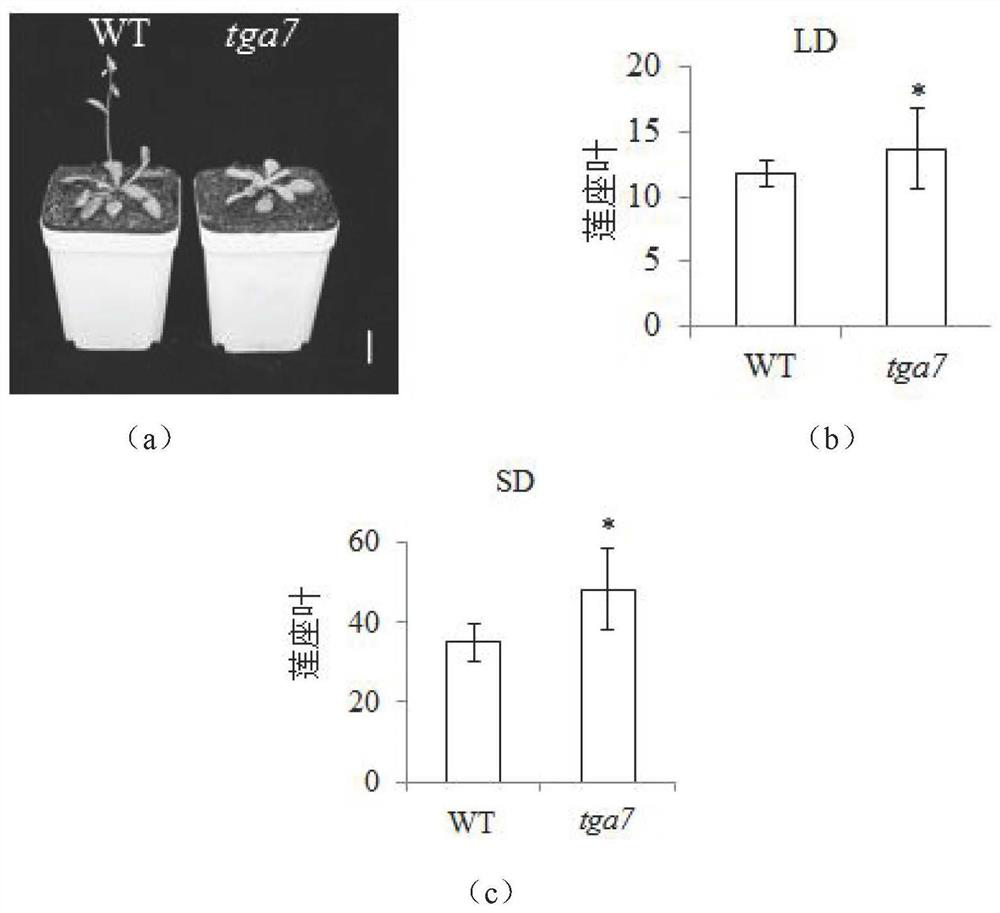
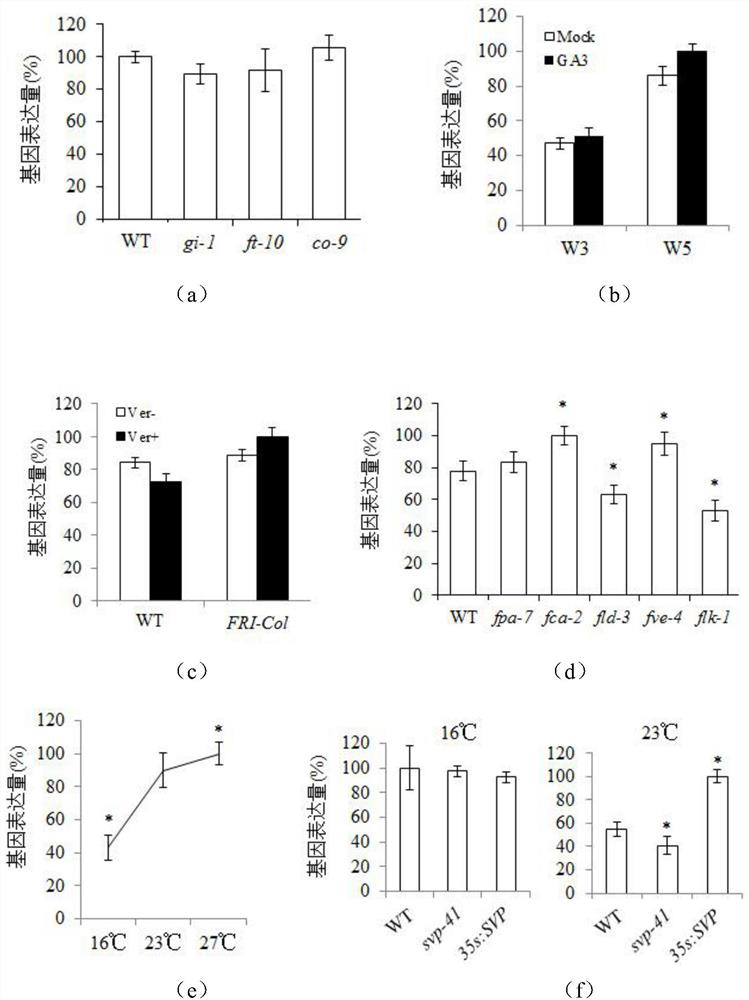
The invention discloses application of a TGA7 gene in regulation and control of a flowering period of a plant. Compared with a wild type plant, a plant with a point mutation of the TGA7 gene of arabidopsis thaliana delays flowering. A single base in the TGA7 gene of the arabidopsis thaliana is mutated. The number of lotus-base leaves of the arabidopsis thaliana plant with the mutated TGA7 gene ismore than that of the wild type plant under long-day and short-day conditions. In an autonomous pathway mutant, expression of the TGA7 in fca-2 and fv-4 is increased, and expression of the TGA7 in fld-3 and flk-1 is reduced. The expression amounts of the TGA7 gene in the wild type WT plant are sequentially and remarkably increased at the temperature of 16-27 DEG C, the expression of the TGA7 in ansvp-41 plant is remarkably reduced at the temperature of 23 DEG C, and the expression of the TGA7 in a 35S:SVP plant is remarkably increased. The expression amounts of key genes FLC, MAF5 and SMZ ina flowering regulation autonomous pathway in the arabidopsis thaliana plant with the mutated TGA7 gene are remarkably increased, and the expression amount of NF-YC2 is remarkably reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
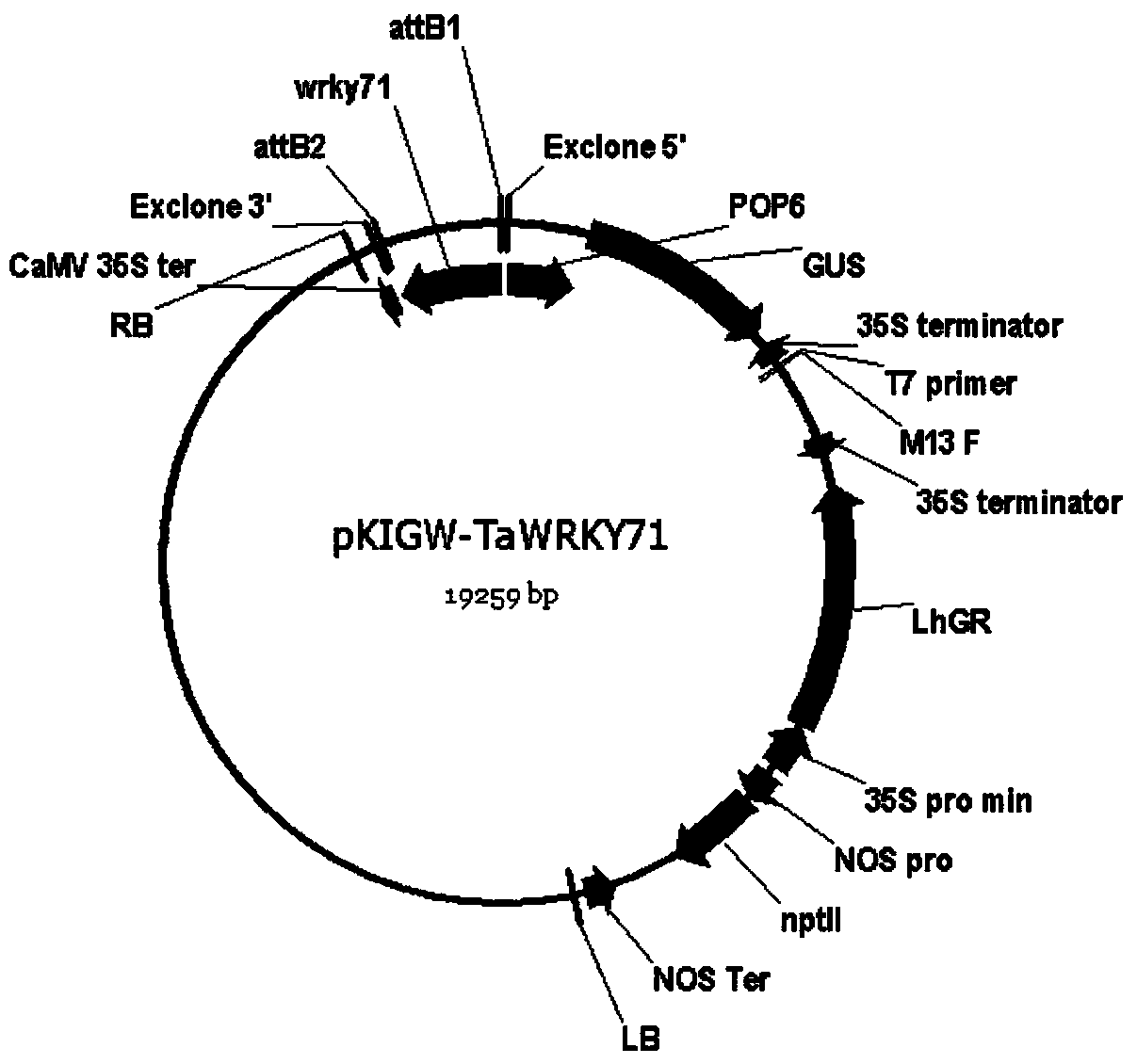
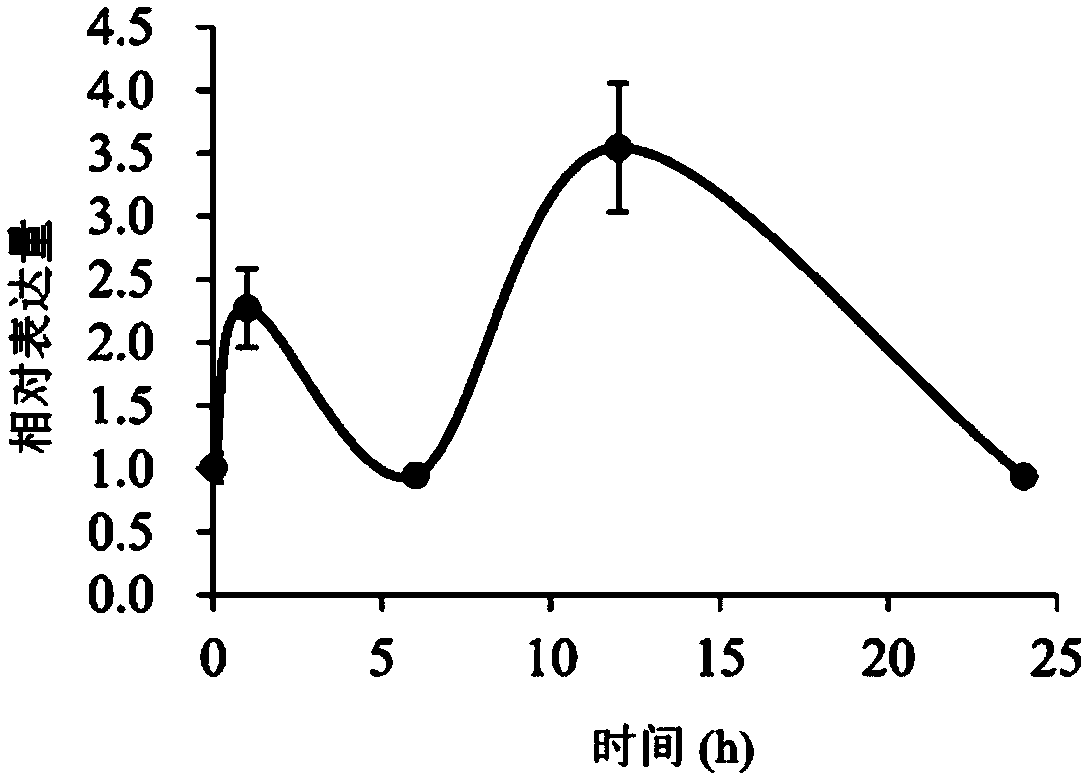
Triticum aestivum WRKY transcription factor gene and application thereof in high-temperature stress response of Arabidopsis thaliana
InactiveCN104046634AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionResponse processTemperature stress
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, provides a triticum aestivum WRKY transcription factor gene and further relates to application of the gene in high-temperature stress response of Arabidopsis thaliana. The nucleotide sequence of the triticum aestivum WRKY transcription factor gene is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1. Arabidopsis thaliana plants transformed with the gene have obvious phenotypic changes during the stressing of adverse situations, such as high temperature, and the gene participates in a stress-resisting defense signal transduction response process, so that excellent genetic resources are provided for the genetic improvement of triticum aestivum.
Owner:天津农兴源农业科技发展有限公司
Cloning and application of maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR
The invention discloses application of a maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR in maize breeding, and the application is the application of the maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR to the improvement on the drought stress tolerance of a maize variety. A protein encoded by the maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR hasa nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention also provides a plant expression vector for improving the drought tolerance of maize, and a main active ingredient of the vector is the protein encoded by the maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR, or an element expressing the protein, or an element expressing the maize drought-resistant gene ZmDSR. An overexpression vector of ZmDSR is constructed by amplifying the ZmDSR gene with a primer ZmDSR-Cloning to perform genetic transformation on arabidopsis thaliana. The overexpression of the gene in arabidopsis thaliana plants can significantly improve the drought tolerance of the plants, thereby providing a new way for cultivating new varieties of drought-tolerant maize.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Halogeton glomeratus salt tolerant gene HgS2 and application thereof
ActiveCN107022552ASmall molecular weightImprove salt toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesHalophyteAgricultural science
The invention relates to a salt tolerant gene HgS2 derived from halophyte halogeton glomeratus, and application thereof. The invention aims at providing a novel salt tolerant gene HgS2, encoding protein of the salt tolerant gene HgS2, and application of the salt tolerant gene HgS2 to improve the plant salt tolerance and culture a salt tolerant new variety (strain). The salt tolerant gene HgS2 contains a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO.1cDNA, and the molecular weight is 678bp; the cDNA coding sequence is the nucleotide sequence from the 30th site to the 290th site in the SEQ ID NO.1, and the molecular weight is 261bp; the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.3 and consists of 86 amino acids. The salt tolerant gene HgS2 can obviously improve the salt tolerance of arabidopsis thaliana plants. The salt tolerant gene provided by the invention is favorable for the culture of salt tolerant crops and plant new varieties (strains).
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Flowering regulating gene AcFT and application thereof
The invention relates to a flowering regulating gene AcFT obtained from pineapple by cloning and application thereof in flowering regulation of arabidopsis thaliana. The nucleotide sequence of the AcFT gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 (sequence identity number 1) and the sequence of amino acid encoded by the AcFT gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The AcFT gene is obtained by cloning through the homologous sequence method, the arabidopsis thaliana is transformed by adopting the pollen tube channel method, and the results prove that a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant flowers in advance in comparison with a wild type arabidopsis thaliana plant. The invention is conductive to further understanding the flowering mechanism of pineapple so that the regulation of the flowering phase of pineapple and breeding of new varieties of pineapple can be realized by using a biotechnical means.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Application of cotton GhMADS41-A04 gene in plant flowering promotion
InactiveCN110373417AEarly floweringFavorable genetic resourcesPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceTransgenic technology
The invention discloses application of a cotton GhMADS41-A04 gene in plant flowering promotion and belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The GhMADS41-A04 gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 and an encodable amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The flowering time of an arabidopsis thaliana plant with the transgenic GhMADS41-A04 gene obtained by a transgenictechnology is remarkably advanced. Furthermore, by silencing the GhMADS41-A04 gene in cotton, results suggest that the GhMADS41-A04 gene plays a key role in cotton flowering promotion. Favorable generesources are provided for short-season cotton cultivation.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Phyllostachys edulis senescence related NAP (neutrophil alkaline phosphatase) transcription factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
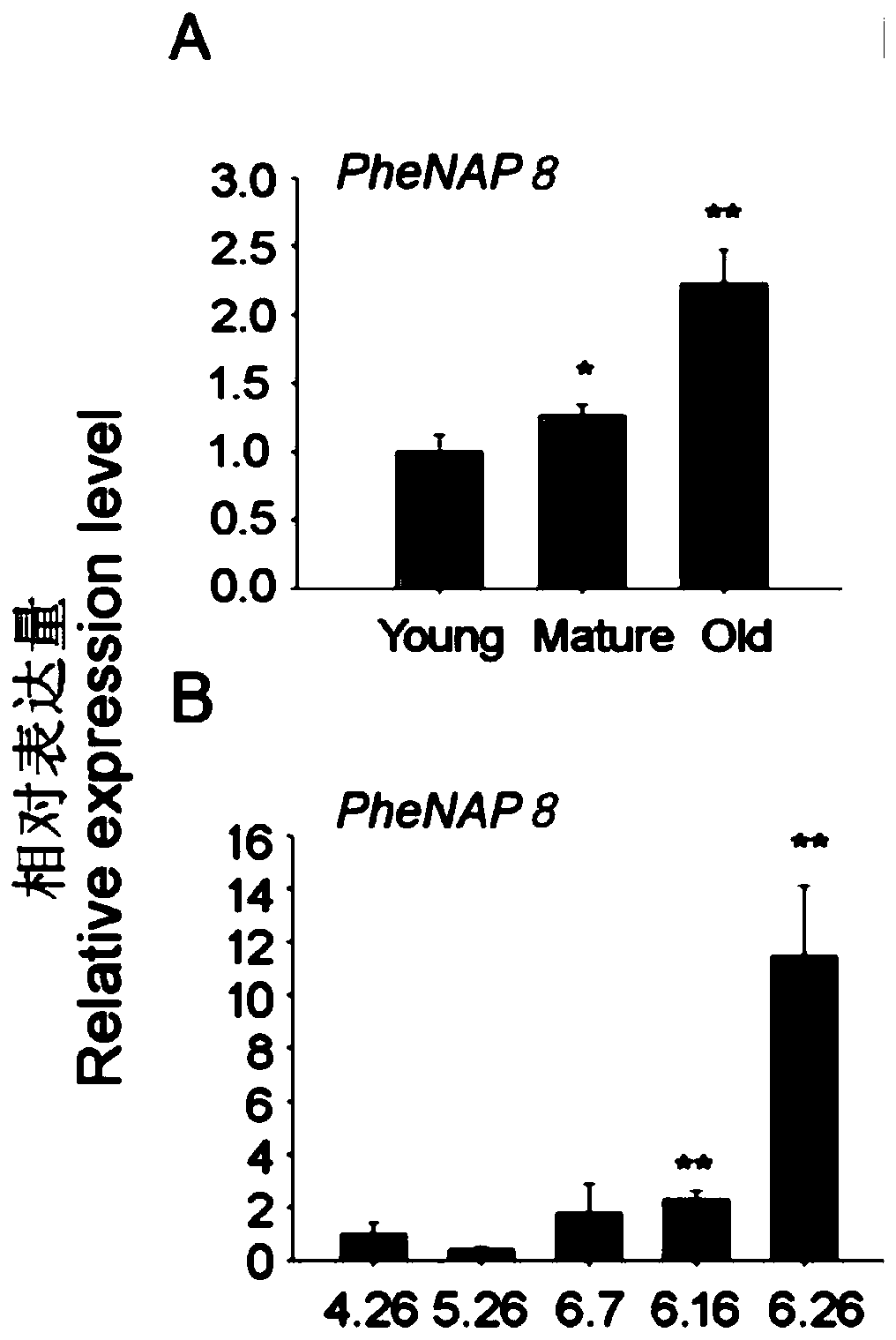
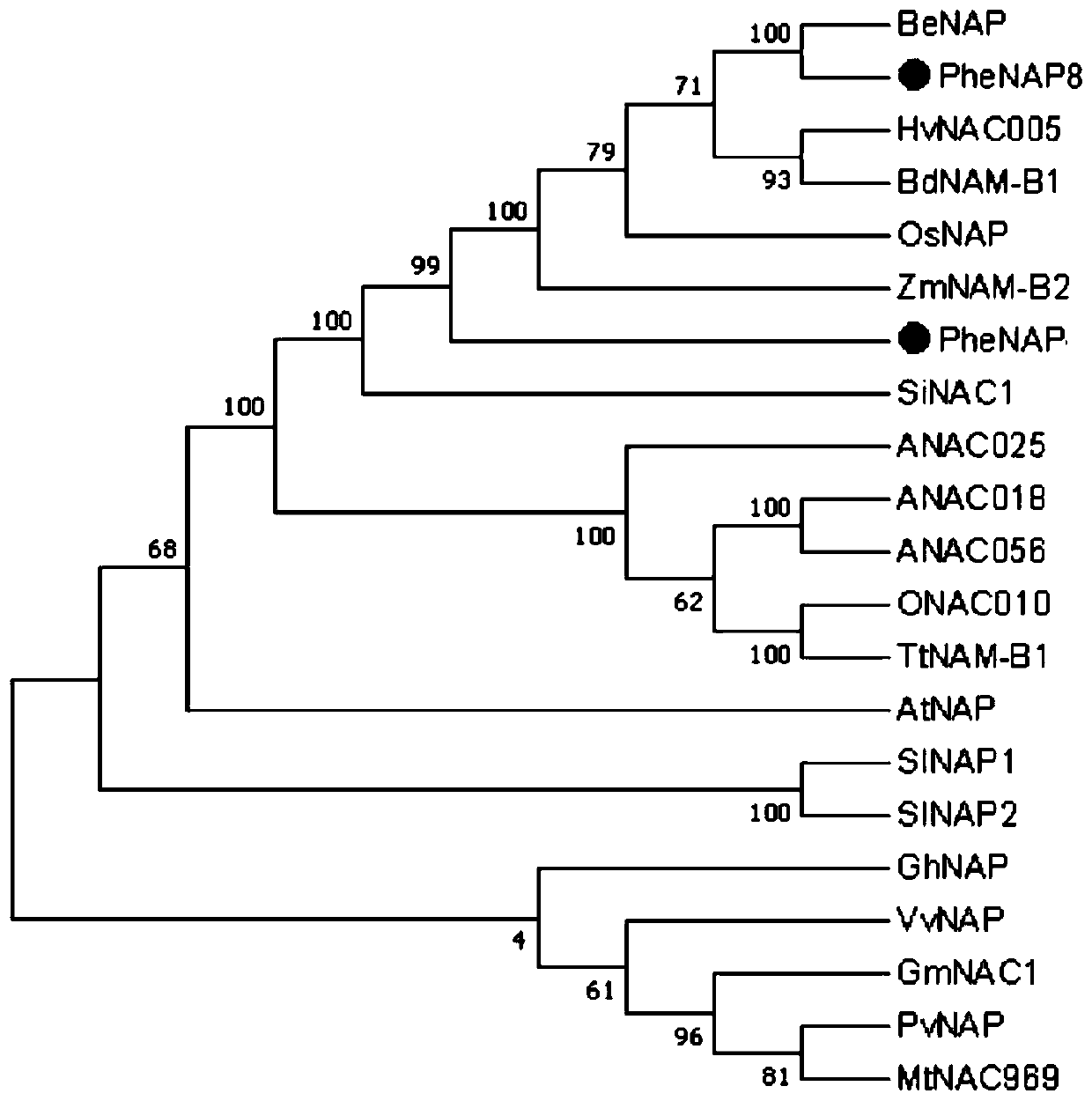
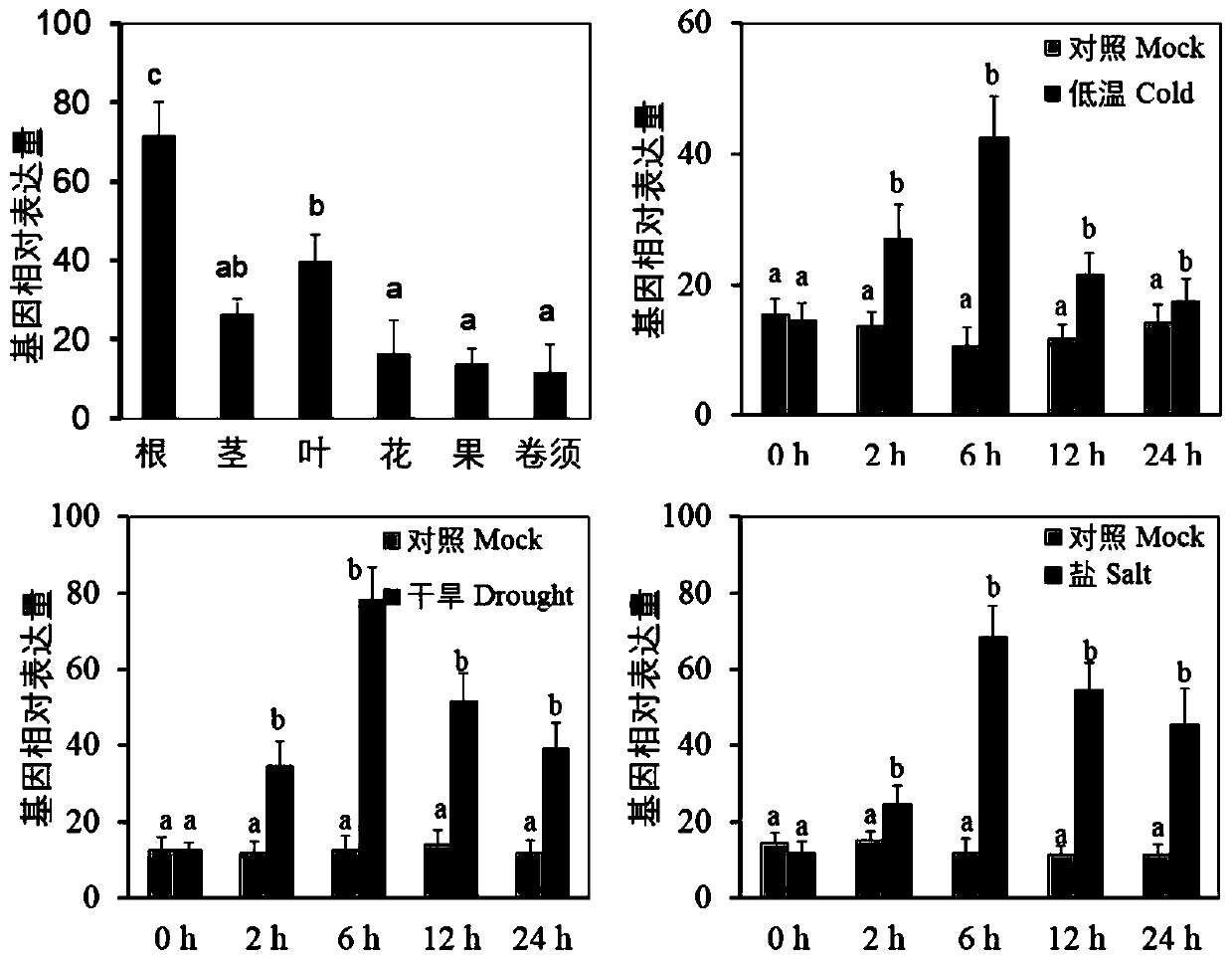
ActiveCN111072762ARegulated developmentAccelerated agingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a phyllostachys edulis senescence related NAP (neutrophil alkaline phosphatase) transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the factor is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in the description, and the protein sequence of the factor is shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the description. Through cloning and expression of a PheNAP8 gene of phyllostachys edulis and allogenic transformation of arabidopsis thaliana, it finds that a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plant with over-expressed PheNAP8 has remarkable phenotypes of growth retardationand pro-senescence, and it means that the gene has significant functions in senescence regulation and breeding of the phyllostachys edulis, can be applied to screening and identification on phyllostachys edulis varieties prone to senescence, and is applicable to industrial application.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
Wild grape VyGOLS gene and application of coding protein of wild grape VyGOLS gene to drought coercion
ActiveCN110452917AImprove drought resistanceFermentationGlycosyltransferasesBiotechnologyCauliflower mosaic virus
The invention relates to a wild grape VyGOLS gene and an application of coding protein of the wild grape VyGOLS gene to drought coercion, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. A genetically modified technique of a strong promoter (cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter) driving principle is adopted, an overexpression vector of a V.yanshanensis VyGOLS gene is transferred to arabidopsis thaliana, and a genetically modified arabidopsis thaliana plant is obtained. Experiment verifies that compared with an arabidopsis thaliana plant for transforming an empty vector, the overexpression VyGOLS gene can cause the accumulation of stress tolerance relevant substances in the genetically modified arabidopsis thaliana and expression of drought tolerance related genes, and thegenetically modified plant is high in drought resistance. Therefore, the wild grape VyGOLS gene and the recombinant expression vector thereof can be used for breeding of plant drought-resistant varieties.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of arabidopsis transcription factor AT3G46090 gene in cultivation of disease-resistant transgenic plants
The invention provides the application of an Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor, namely the AT3G46090 gene in cultivation of disease-resistant transgenic plants. The CDS sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana AT3G46090 gene is constructed to upper stream with an FLAG protein tag through the Gateway technology, Arabidopsis thaliana plants are transformed, screened and identified, and finally, the transgenic plants are obtained. The screened plants are analyzed, and it is found that the AT3G46090 gene has the effect of enhancing the resistance of the plants to the pseudomonas syringae tomato subspecies, the expression of the gene affects the disease resistance phenotype of the plants, and homologous genes in crops possibly have the same function, so the gene has important significance in production.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
DNA fragment related to drought tolerance and alkali resistance of plant and application thereof
The invention discloses a DNA fragment related to drought tolerance and alkali resistance of a plant and application thereof. The DNA fragment is originated from Boea hygromettica(Bunge)R. Br and composed of a nucleotide sequence ranging from site 7 to site 6375 in a sequence 1 in a sequence table. Under the condition of osmotic stress of PEG with a concentration of 25%, the main root of a T3-generation homozygous transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant which transfers the DNA fragment is substantially longer than the main root of a wild Arabidopsis thaliana plant; and under the condition of alkaline stress of the pH value of 8.0, the number of lateral roots of the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant is substantially more than the number of lateral roots of the wild Arabidopsis thaliana plant, and the overground part of the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant is more thriving. The DNA fragment provided by the invention has critical theoretical and practical significance to breeding of novel species of drought-tolerant and alkali-resistant crops, forests and grass, is applicable to cultivation and identification of plant varieties with resistance desired in farming and animal husbandry and in ecological environment treatment and provides a specific anti-adversity resource gene which cannot be provided by model plants and crops for cultivation of plants with high stress tolerance.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
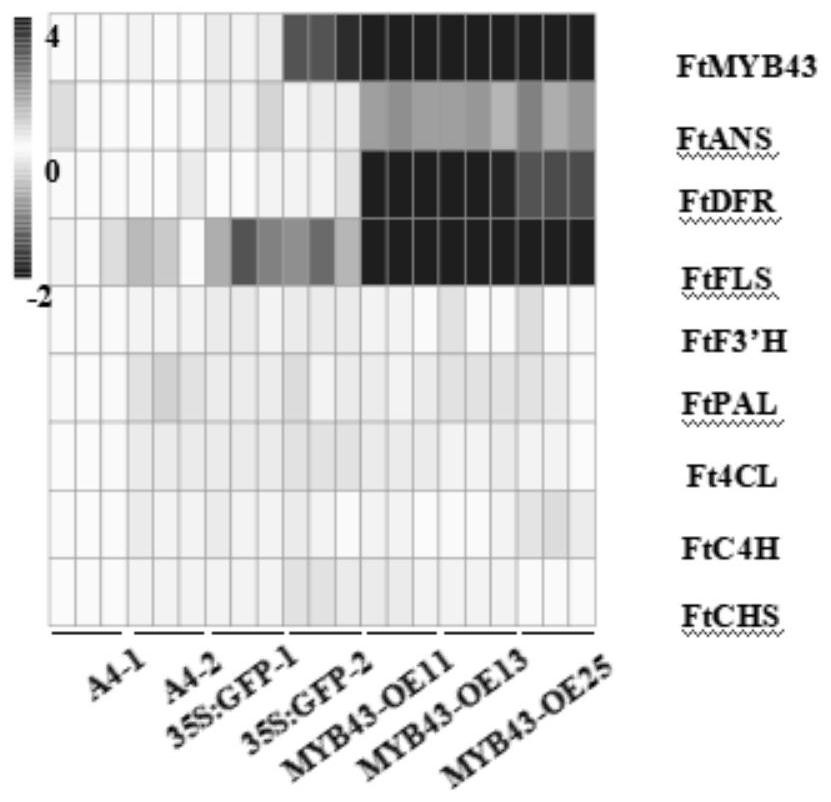
MYB transcription factor for regulating and controlling synthesis of plant procyanidine as well as coding gene and application of MYB transcription factor
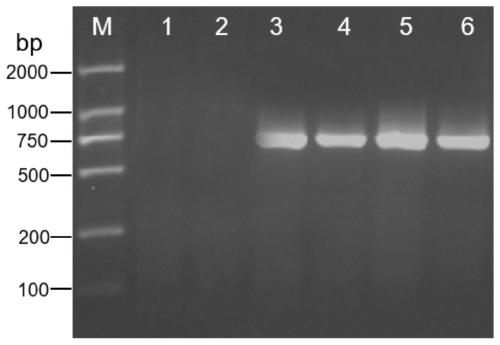
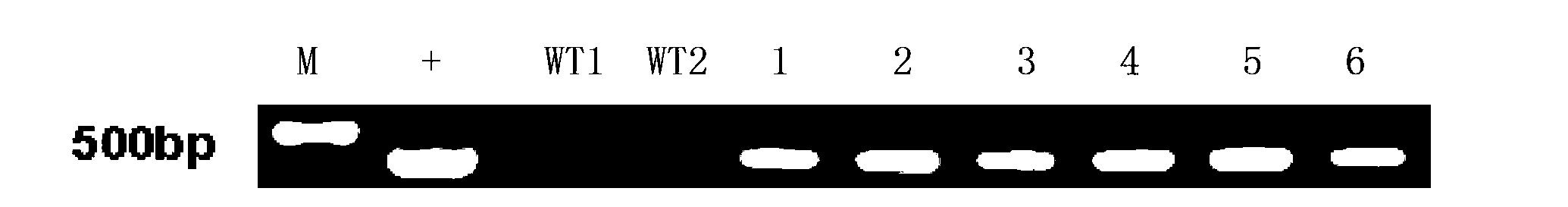
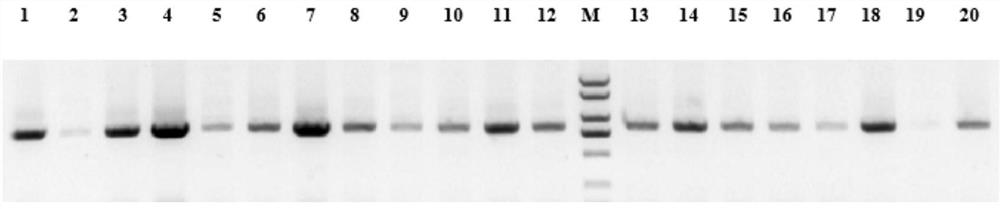
The invention discloses an MYB transcription factor for regulating and controlling plant procyanidine synthesis as well as a coding gene and application of the MYB transcription factor. The MYB transcription factor FtMYB43 is cloned from tartary buckwheat, and the amino acid sequence of the MYB transcription factor FtMYB43 is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. The transcription factor FtMYB43 gene is respectively subjected to genetic transformation of buckwheat and arabidopsis thaliana to obtain transgenic buckwheat hairy roots and arabidopsis thaliana, the expression quantity of an enzyme gene of a proanthocyanidins pathway in the obtained positive arabidopsis thaliana is detected, and the content of proanthocyanidins after the FtMYB43 gene is transformed into arabidopsis thaliana for ectopic expression is detected. Test results display that the FtMYB43 gene is beneficial for improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes of a flavonoid metabolic pathway part in hairy roots, so that the biosynthesis of procyanidine is promoted; the content of procyanidine in a transgenic line is remarkably increased, which indicates that the FtMYB43 gene participates in biosynthesis of procyanidine in an up-regulated arabidopsis thaliana plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene as well as expression and application thereof
InactiveCN102108362AGrowth impactVerify degradation functionMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene as well as an expression and an application thereof. The triphenylmethane reductase gene in citric acid bacillus is transformed by a plant preference codon to get the optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene with the full length of 864bp, the nucleotide sequence of the optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene is as shown in SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) No.1, and the sequence of a coded protein is as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The optimized triphenylmethane reductase gene is constructed into a plant vector, agrobacterium-mediated transformation is further performed, and a transformed arabidopsis thaliana plant can continuously express triphenylmethane reductase and induce the plant to participate in degradation of crystal violet and malachite green, thereby providing broad application prospects for restoring pollution caused by triphenylmethane dyes through the plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Plant root hair development related protein TaRHD6, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a plant root hair development related protein TaRHD6, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein disclosed by the invention is derived from wheat and named TaRHD6, and is composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table. The experiment proves that compared with a wild Arabidopsis thaliana plant under the same conditions, the phenotype of a T3-generation homozygous transgenic plant obtained by transforming Arabidopsis thaliana with a recombinant expression vector pB2GW7.0-TaRHD6 of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule (the coding gene of the protein) disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table has obviously increased root hair length; and under normal and nutrient stress conditions, the plant types and fresh weight of the overground plant are obviously increased. The invention has important meanings in the aspects of increasing the plant root hair length and further enhancing the biological yield of the plant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Protein PwRBP1 related to stress tolerance of plants, and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109971766AImprove germination rateImprove drought tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationWoody plantArabidopsis thaliana <plant>
The invention discloses an RNA binding protein PwRBP1 related to stress tolerance of plants, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The PwRBP1 encoding gene discovered in woody plants is introduced into arabidopsis thaliana to obtain PwRBP1 transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plants. Experiments prove that the PwRBP1 transgenic arabidopsis thaliana plants have higher drought tolerance and salttolerance than receptor plants, indicating the stress tolerance of the PwRBP1 and the encoding gene thereof, so that the PwRBP1 and the encoding gene thereof are suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Application of cymbidium goeringii miR390a for controlling plant root system development
ActiveCN110951771AFast formingFast growthVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyPlant roots
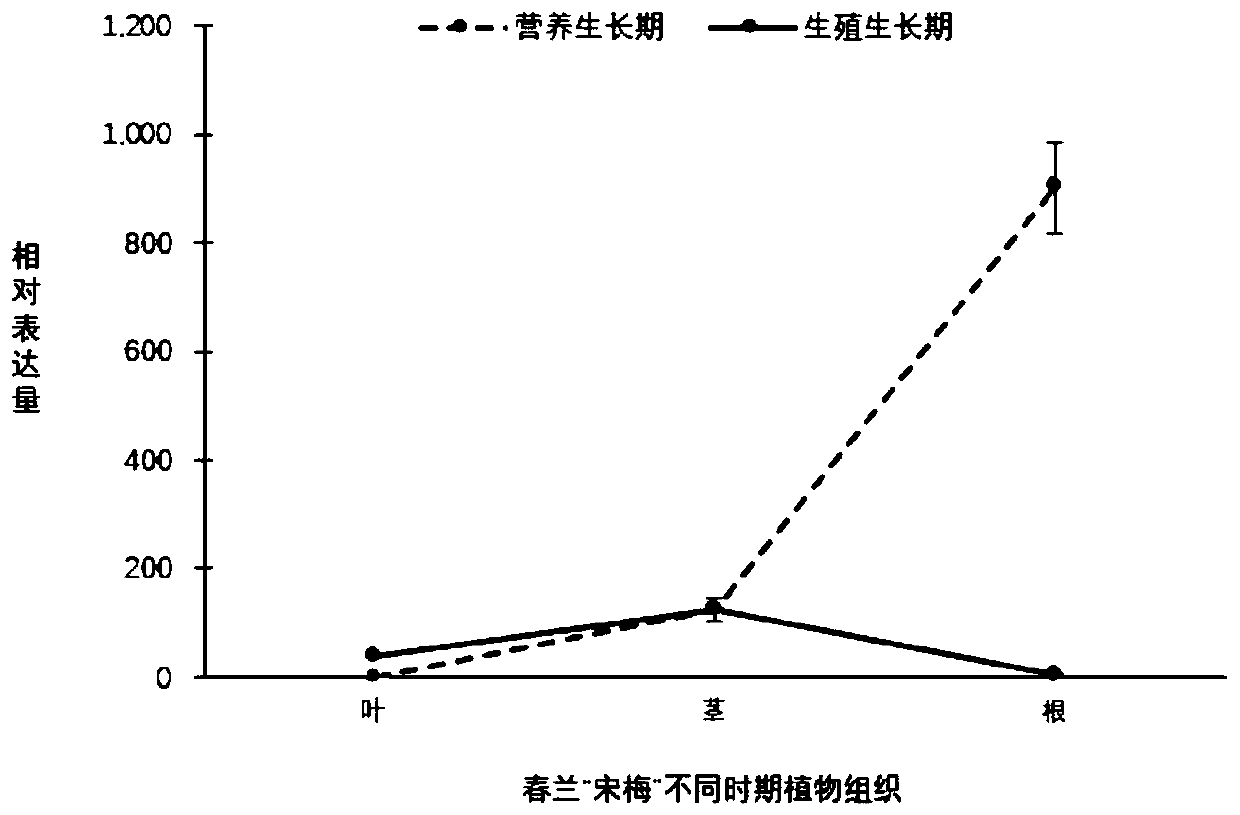
The invention discloses a cymbidium goeringii miR390a gene and application of the cymbidium goeringii miR390a gene for controlling plant root system development. The precursor sequence segment encoding gene of the miR390a is obtained from a cymbidium goeringii cultivated variety "Song Mei", expression analysis is carried out in the cymbidium goeringii, then, the precursor sequence segment encodinggene is constructed to an overexpression vector, the overexpression vector is imported into an objective plant to verify the function of the overexpression vector so as to discover the phenotypes ofan arabidopsis thaliana plant that an overexpression miR390a gene has a high root system growth speed in a seedling stage and a euphylla formation speed is quickened, and therefore, the gene has a wide purpose in the production and the seed breeding of orchids and other horticultural plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Application of grape VlKNOX gene in promoting cytokinin synthesis and regulating fruit setting
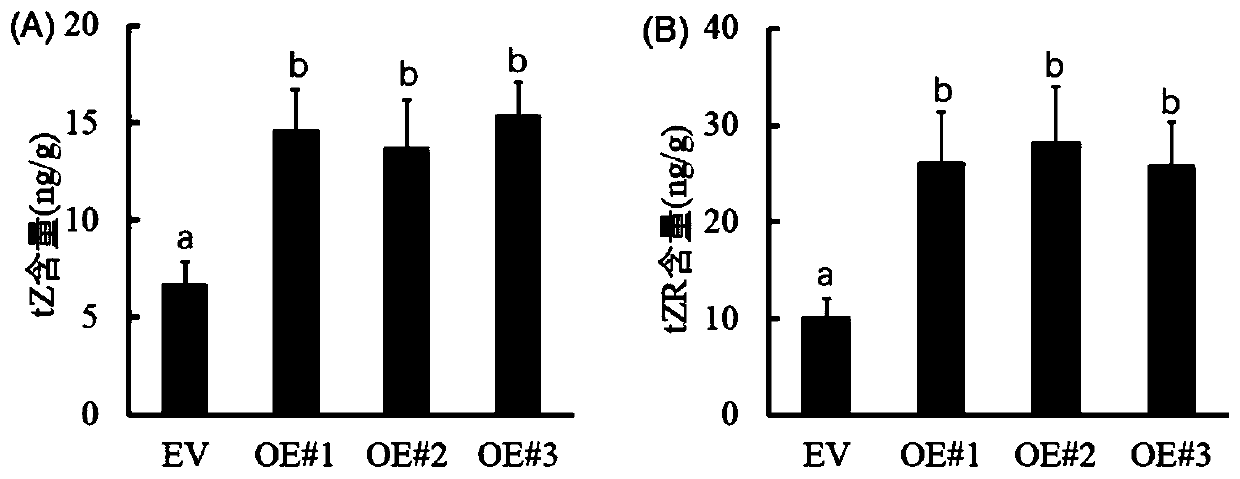
ActiveCN110452915AIncrease productivityIncreased mitogen contentPlant peptidesFermentationVitis viniferaFruit set
The invention relates to an application of grape VlKNOX gene for promoting cytokinin synthesis and regulating fruit setting, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. In the invention, a transgenic technology of a strong promoter (cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter) driving principle is utilized to transfer an excess-expression vector of a VlKNOX gene into Arabidopsis thaliana so as to obtain a transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plant. Experiments prove that: compared with an Arabidopsis thaliana transformed with an empty vector, excessive expression of the VlKNOX gene leads to large accumulation of cytokinins in the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana, and the fruit setting rate of fruits is obviously improved. Therefore, the grape VlKNOX gene and the recombinant expression vector thereof can be used for breeding high-yield plant variety.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
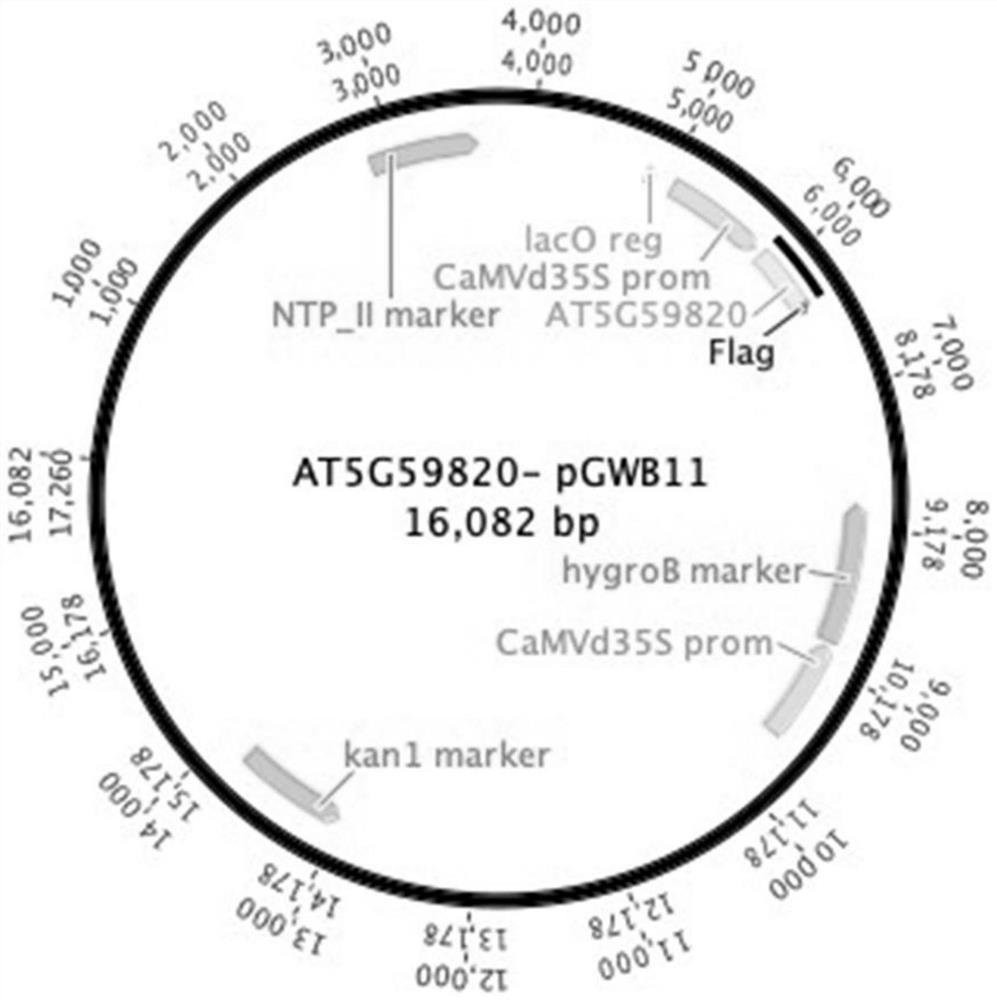
Application of arabidopsis transcription factor AT5G59820 gene in cultivation of disease-resistant transgenic plants
ActiveCN112795570AImprove disease resistanceBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyProtein tag
The invention relates to an application of arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor AT5G59820 gene in cultivation of disease-resistant transgenic plants, the CDS sequence of the arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor AT5G59820 gene is constructed to the upstream with an FLAG protein tag through the Gateway technology, the arabidopsis thaliana plant is transformed, screened and identified, and finally the transgenic plants are obtained. The screened plants are analyzed and found to have the effect of enhancing the resistance of arabidopsis thaliana to tomato pseudomonas syringae subspecies, that is, the gene affects the disease resistance phenotype of the plants, and homologous genes in crops possibly have the same or similar functions, so that the gene has important significance in production.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com