Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1181 results about "Arabidopsis sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid molecules encoding WRINKLED1-like polypeptides and methods of use in plants
InactiveUS8217223B2High oil contentImprove the level ofBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFatty acid
Isolated nucleic acids and proteins associated with lipid and sugar metabolism regulation are provided. In particular, lipid metabolism proteins (LMP) and encoding nucleic acids originating from Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus, Glycine max, Oryza sativa, and Triticum aestivum are provided. The nucleic acids and proteins are used in methods of producing transgenic plants and modulating levels of seed storage compounds. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches, or seed storage proteins. The nucleic acids and proteins also are used in methods of modulating the seed size, seed number, seed weight, root length, and leaf size of plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
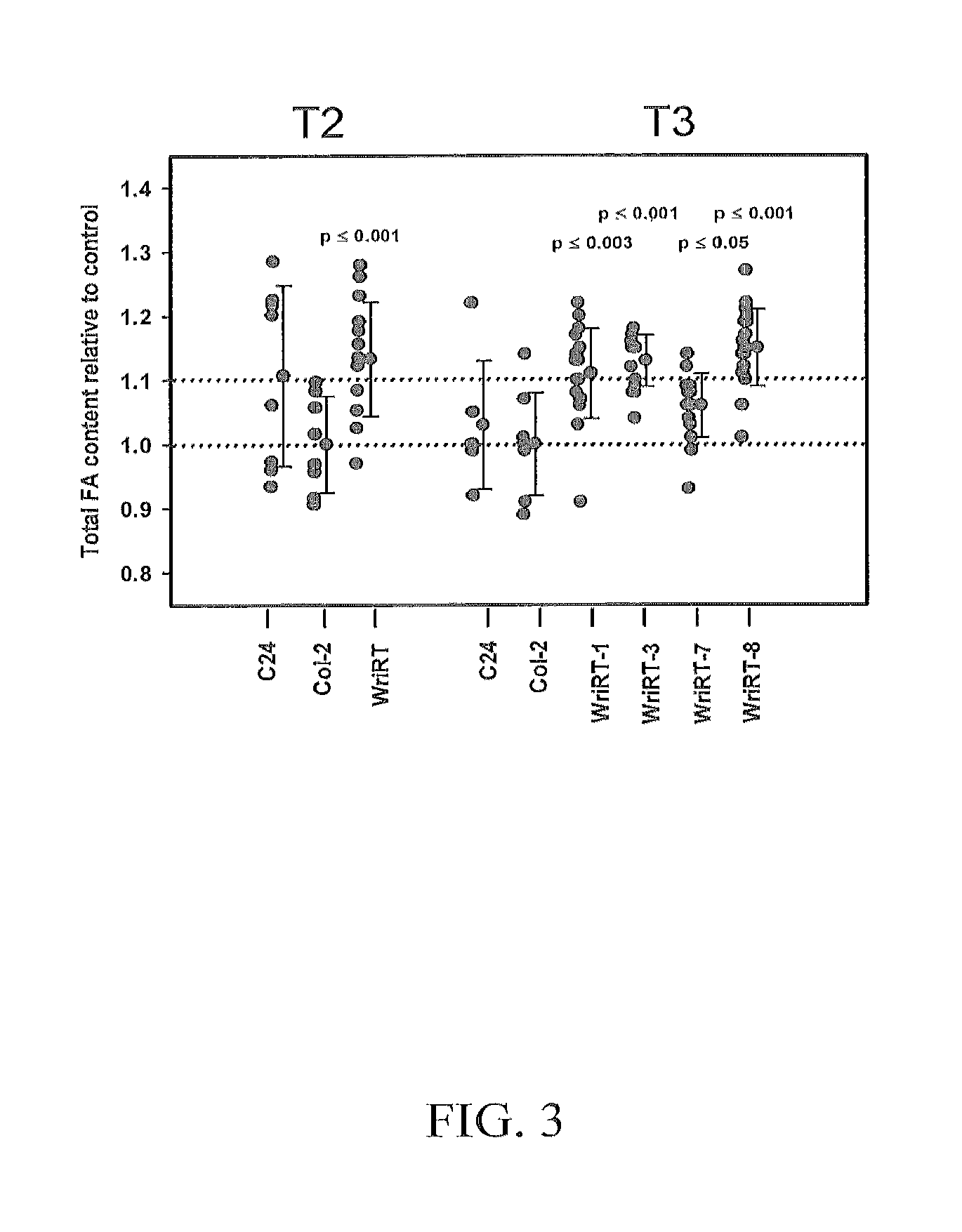
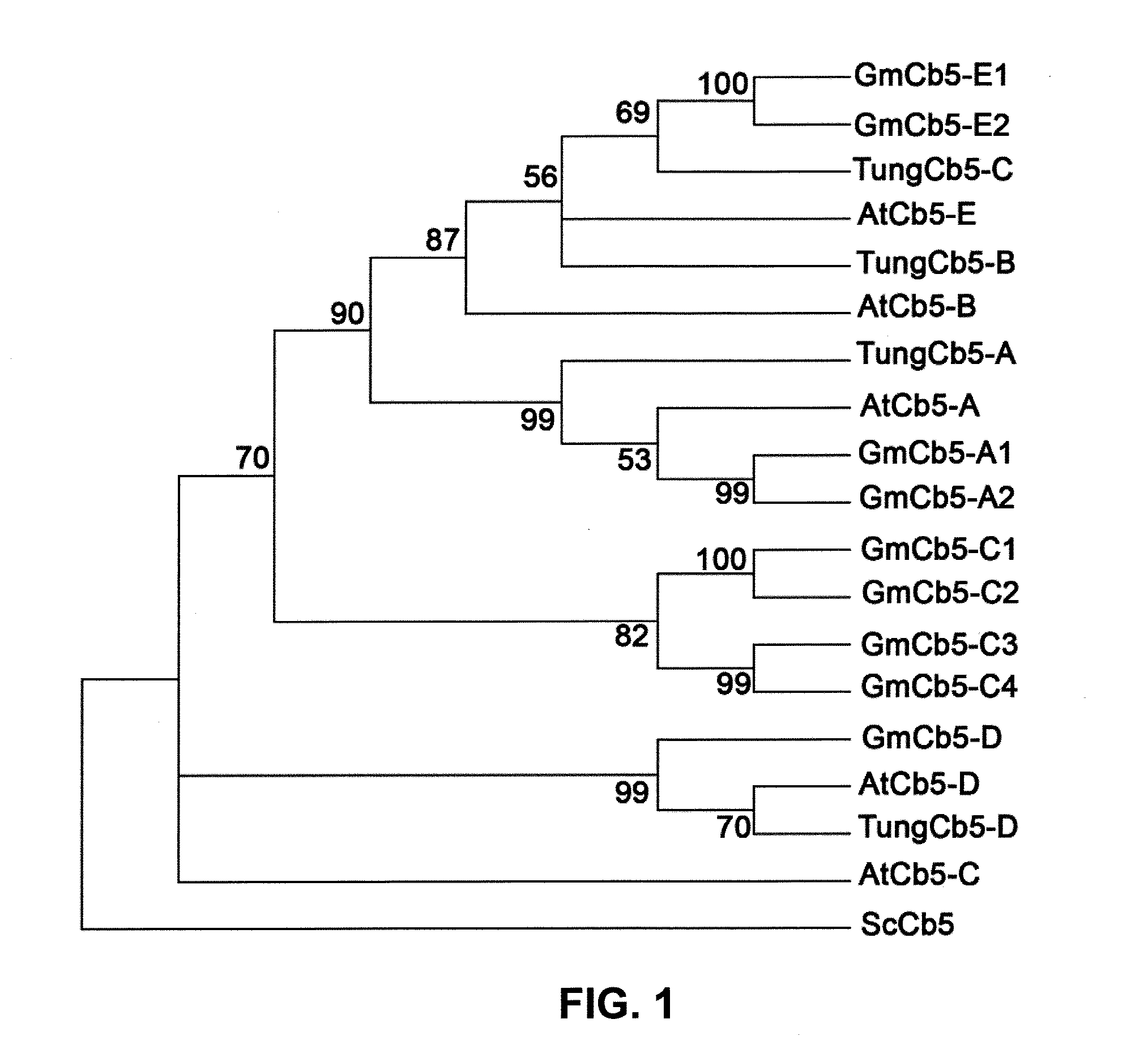
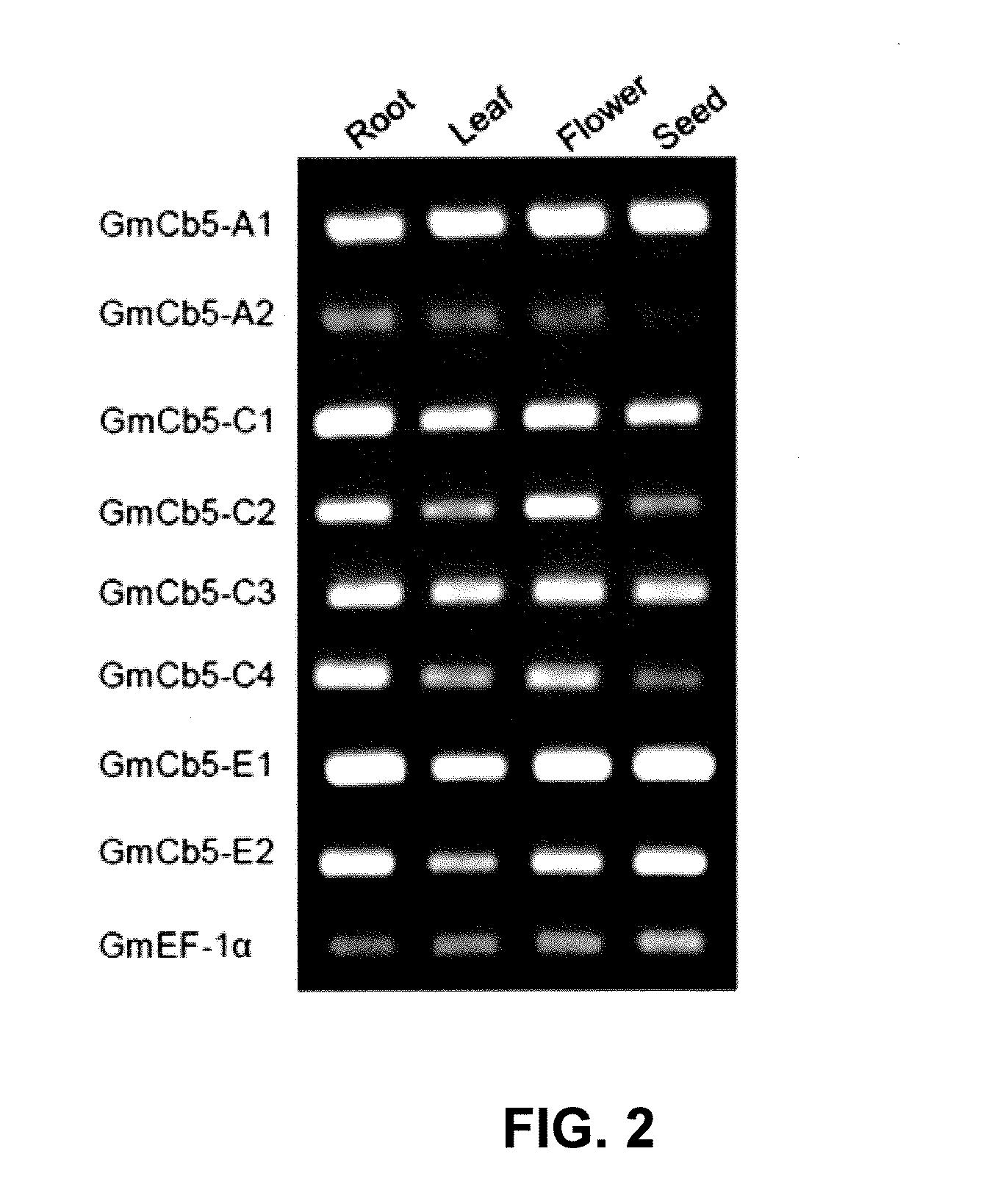
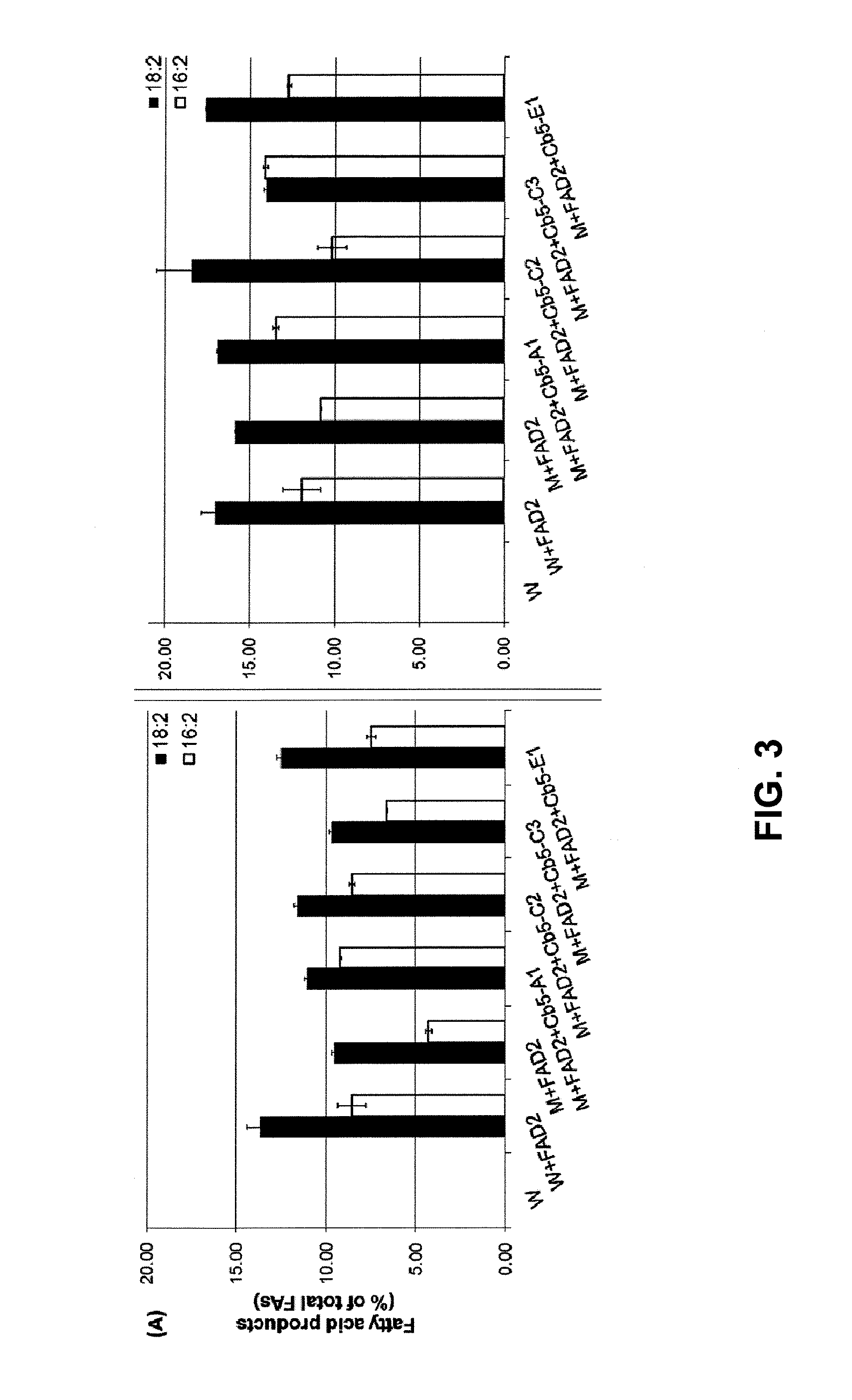
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Nematode-inducible plant gene promoter
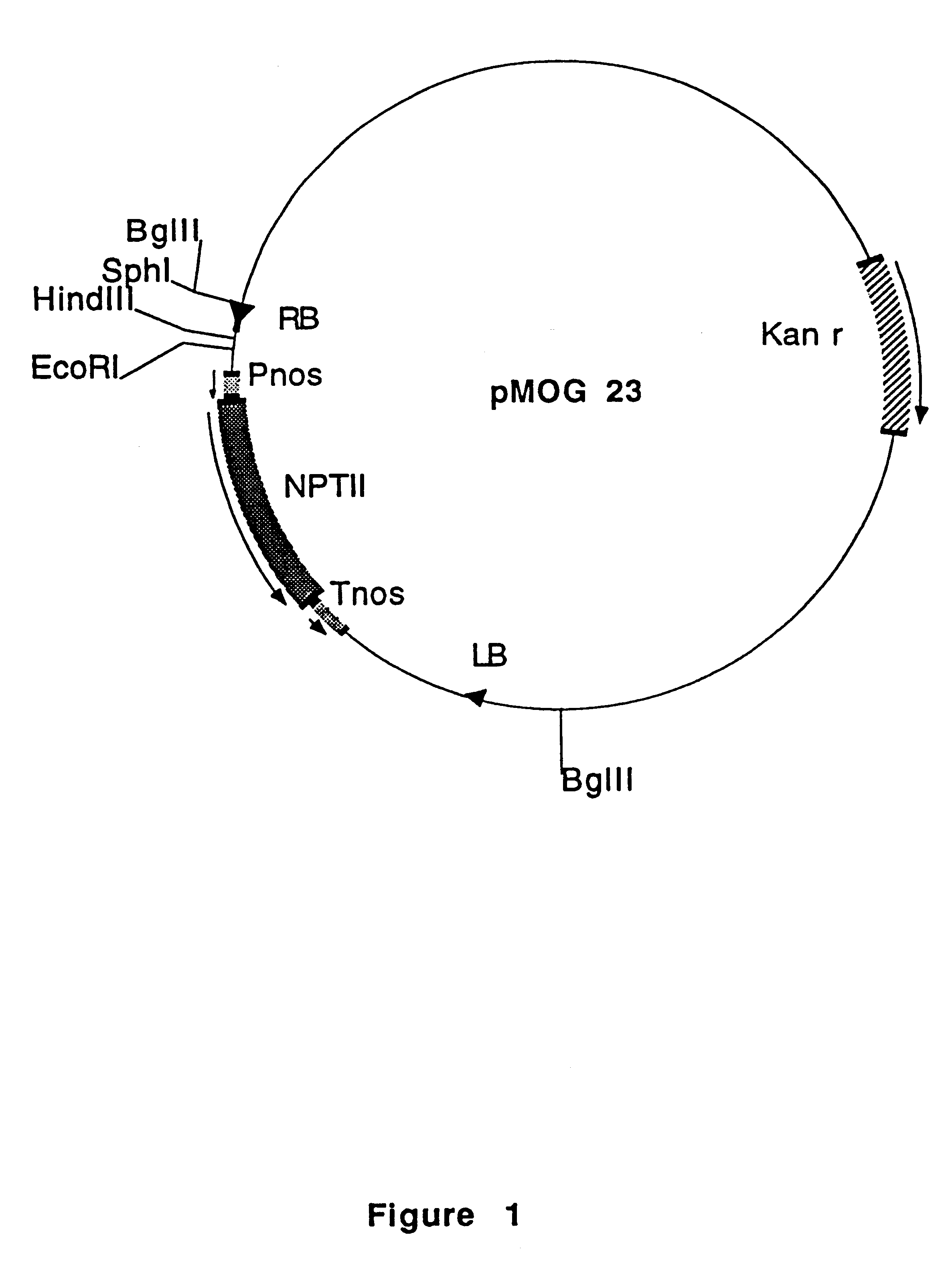
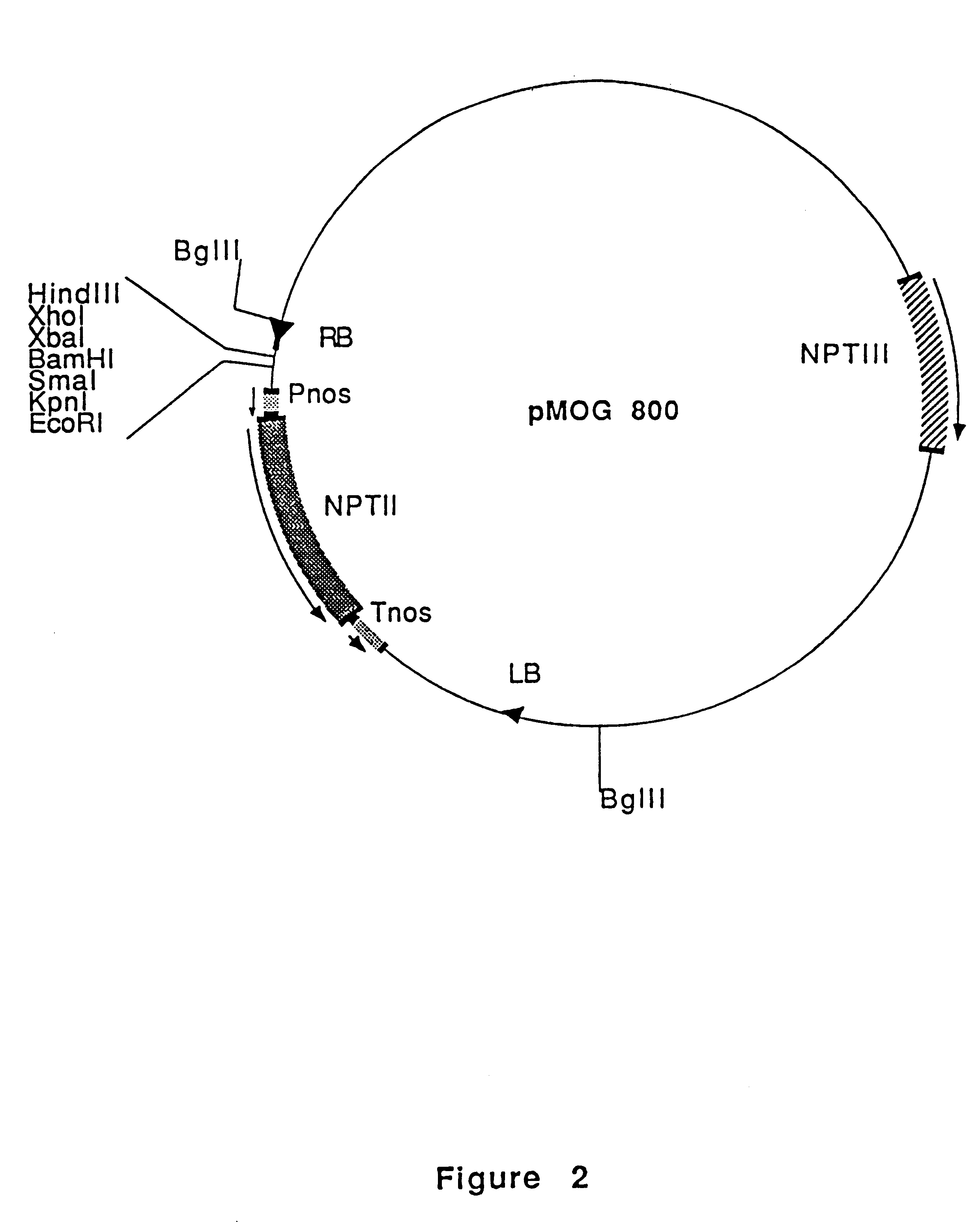
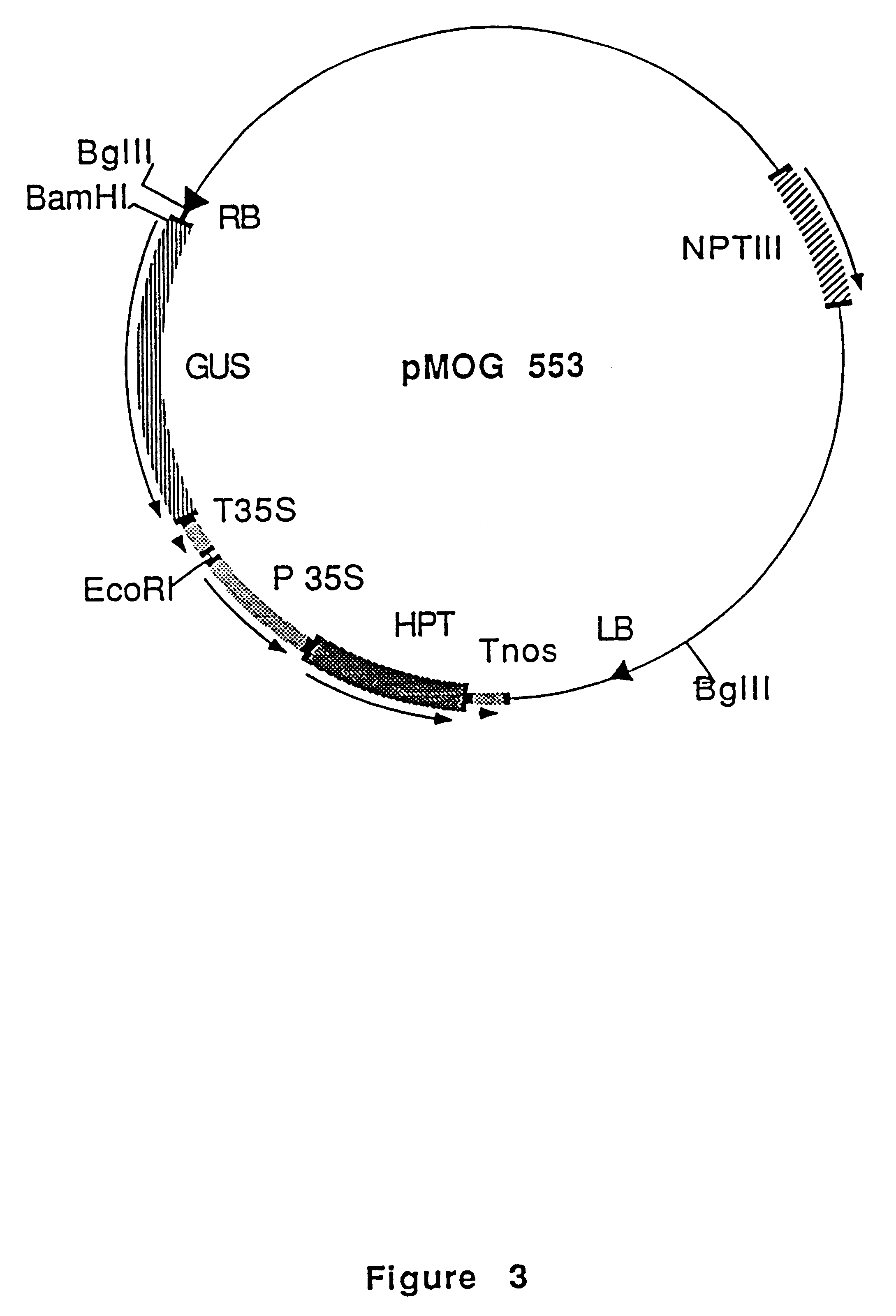
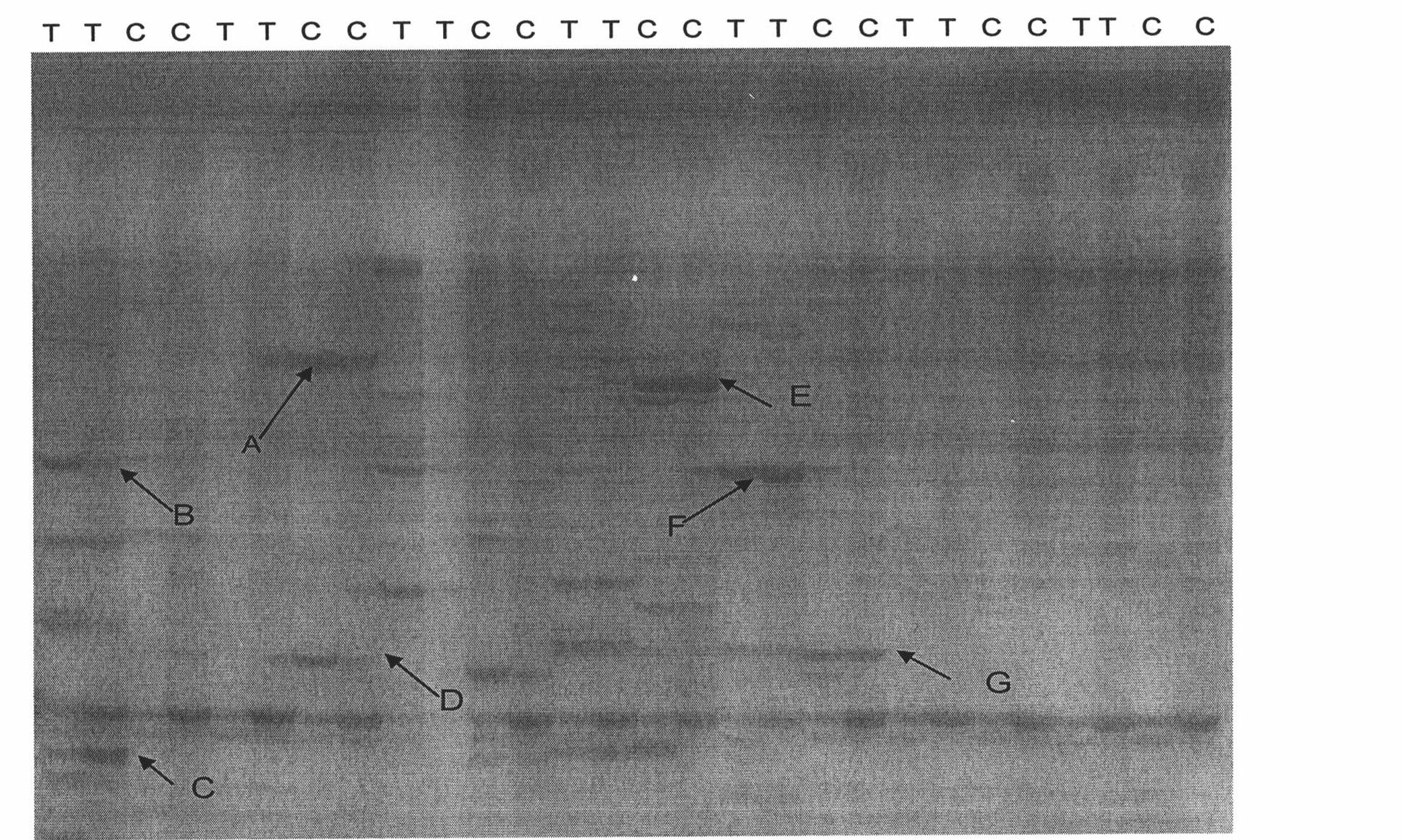
An isolated DNA fragment that promotes root knot or cyst nematode indcuible transcription of a coding sequence downstream of and operably linked to the fragment in at least an Arabidopsis thaliana plant and a chimeric DNA sequence including the DNA fragment. Also, methods for the use of the DNA fragment.
Owner:SYNGENTA MOGEN BV
Plant stress tolerance correlative protein kinase, encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101775381AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses plant stress tolerance correlative protein kinase, an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein refers to the protein of 1) or 2): 1) the protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown by a second sequence in a sequence table; or 2) the plant stress tolerance correlative protein which is formed through the substitution and / or lack and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residue radicals on the amino acid residue radical sequence of the second sequence in the sequence table and is derived from the protein of 1). The encoding gene of the protein is introduced into arabidopsis mutant sos2-1 or wild type arabidopsis for improving the salt tolerance and the drought tolerance of transgenic plants.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Plant genome sequences and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:CAO YONGWEI +1
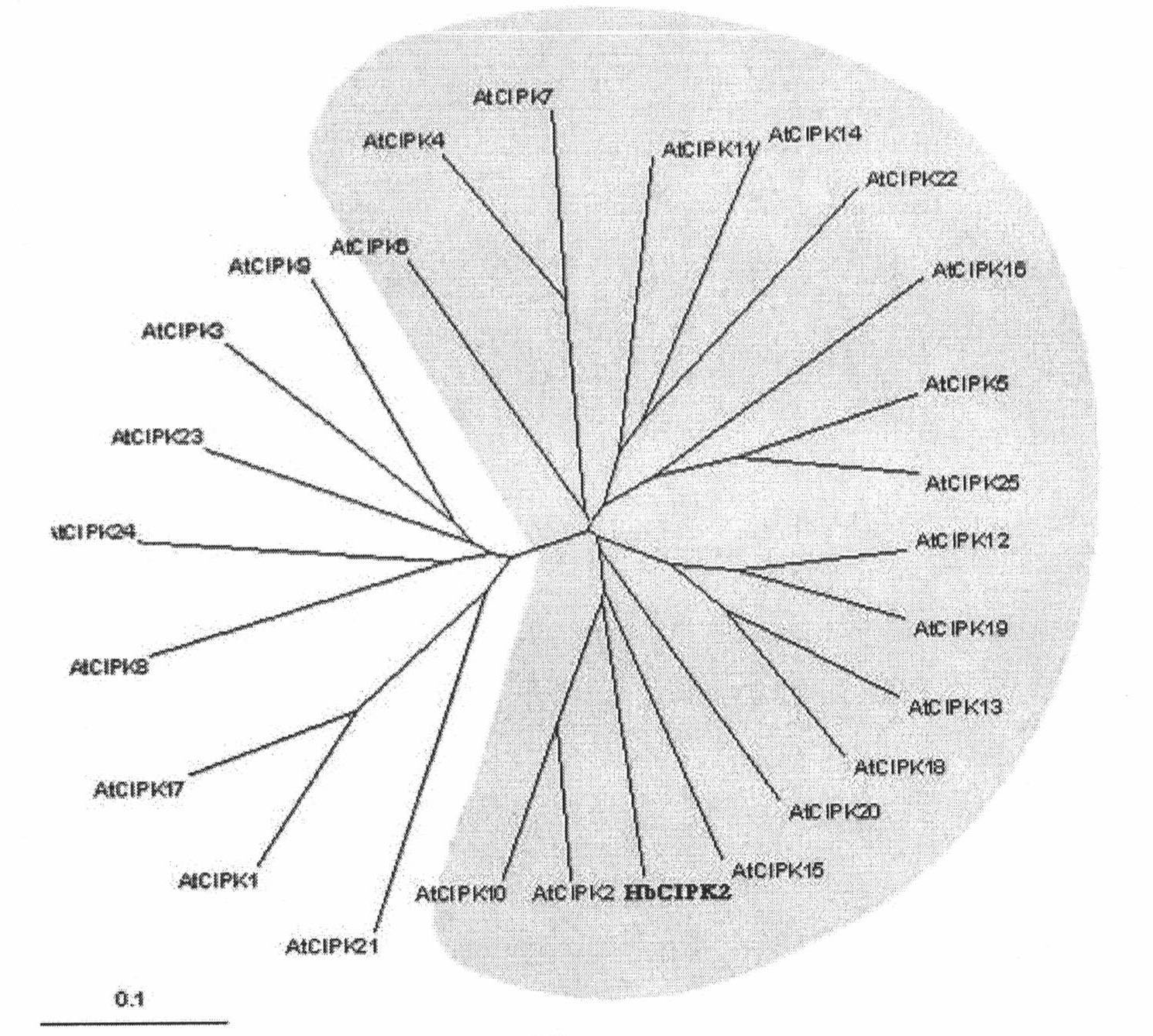
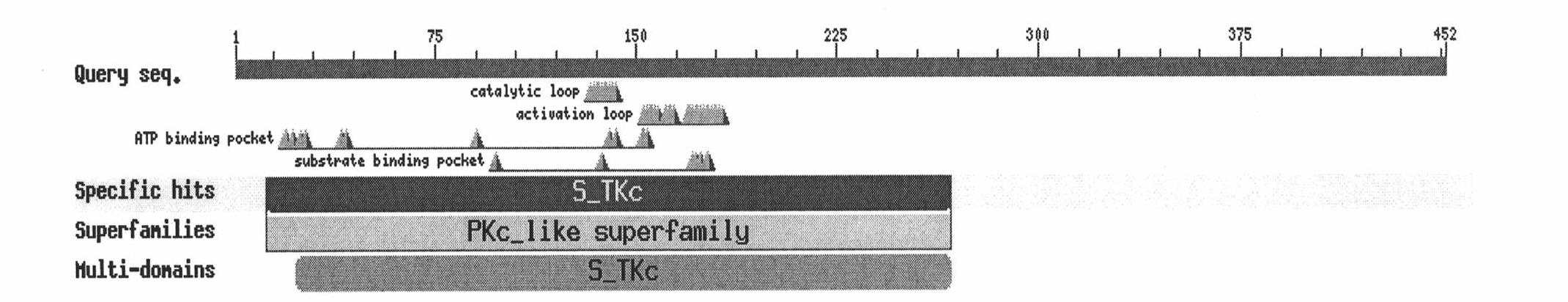
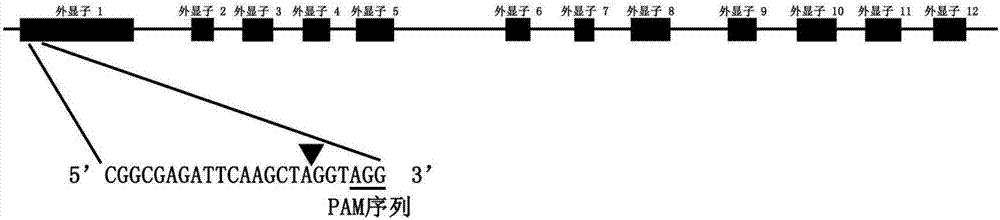
sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of sgRNA sequence
InactiveCN107236737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingArabidopsis thaliana
The invention discloses a sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting an arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of the sgRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Two single-chain oligo DNA sequences are designed and synthesized according to a sgRNA guide sequence, a double chain is formed through annealing and is linked with a Cas9 carrier, a sgRNA coding sequence and a CRISPR system are introduced into Arabidopsis by using an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation technique, a target sequence is shorn by a Cas9 protein under the guidance of sgRNA, and therefore, the knockout of an ILK2 gene is realized. According to the sgRNA sequence provided by the invention, the ILK2 gene can be knocked out or edited by virtue of a CRISPR-Cas9 system, so as to analyze the functions of the arabidopsis ILK2 gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Plant artificial chromosome compositions and methods
InactiveUS6900012B1Confer susceptibilityEnhanced advantageOther printing matterMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure and functionArabidopsis
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited plant artificial chromosomes (PLACs) which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
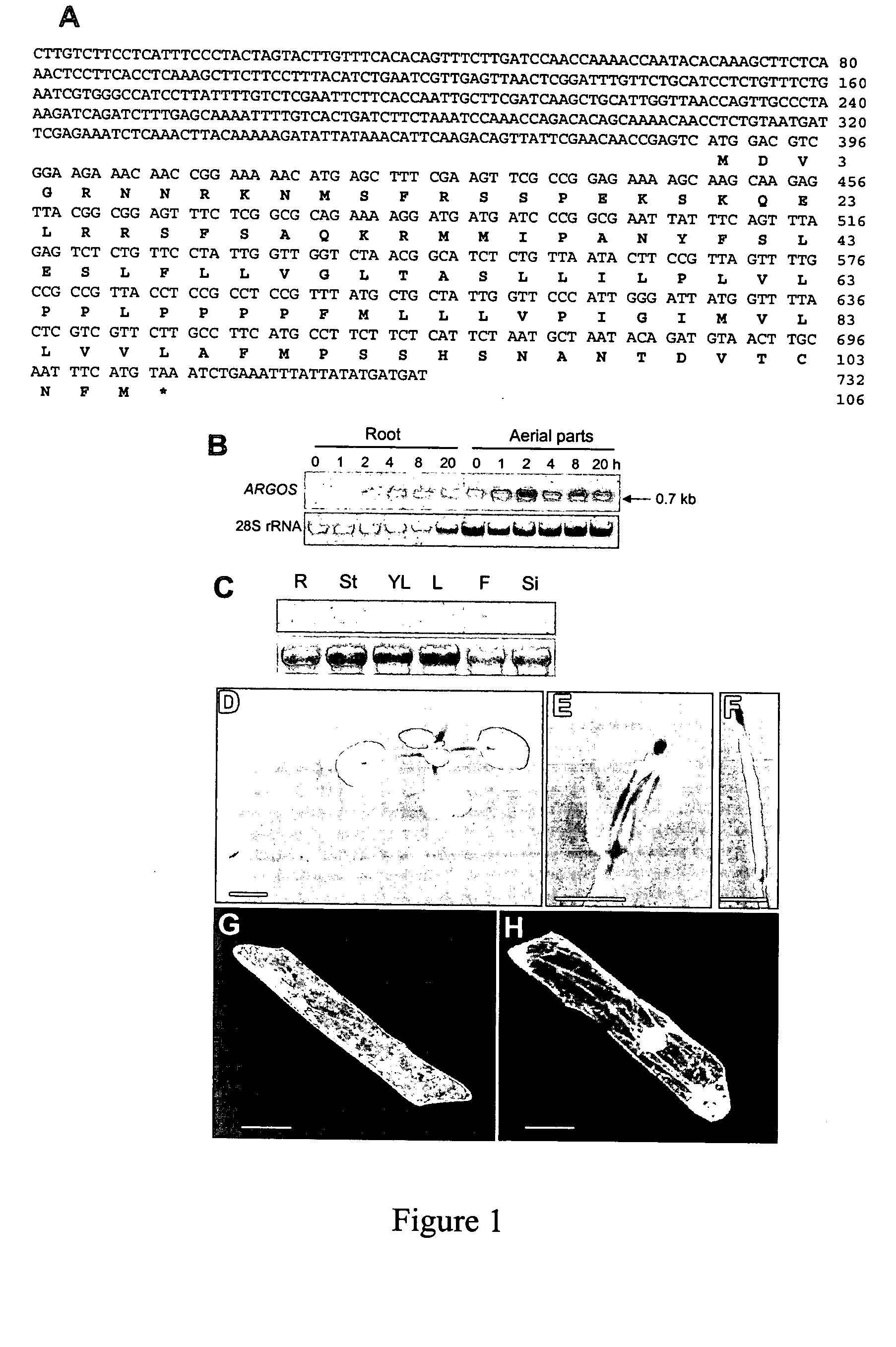
Arabidopsis argos, a novel gene involved in organ development
The present invention is directed to a novel auxin-inducible gene, ARGOS, that is involved in organ development, including size control, in plants. Methods of influencing this development are also described, as are transformed cells and transgenic plants comprising the described sequences.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Transcriptional factor relevant to resistant adversity from Arabidopsis thaliana, coded gene, and application
This invention discloses stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor, its coding gene and application. The stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor is derived from Arabidoesis thaliana, and can be applied in culturing stress-tolerant plants that can resist abscisic acid, high salt and draught. The transcription factor is one of the following amino acid residue sequences: (1) SEQ ID NO.1; (2) protein by substituting, deleting or adding 1-10 amino acid residues of SEQ ID NO.1, which can regulate the stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have important meaning to research on plant stress-tolerant mechanism, and method for improving draught, salt and stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have potential application in stress-tolerant genetic engineering of plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
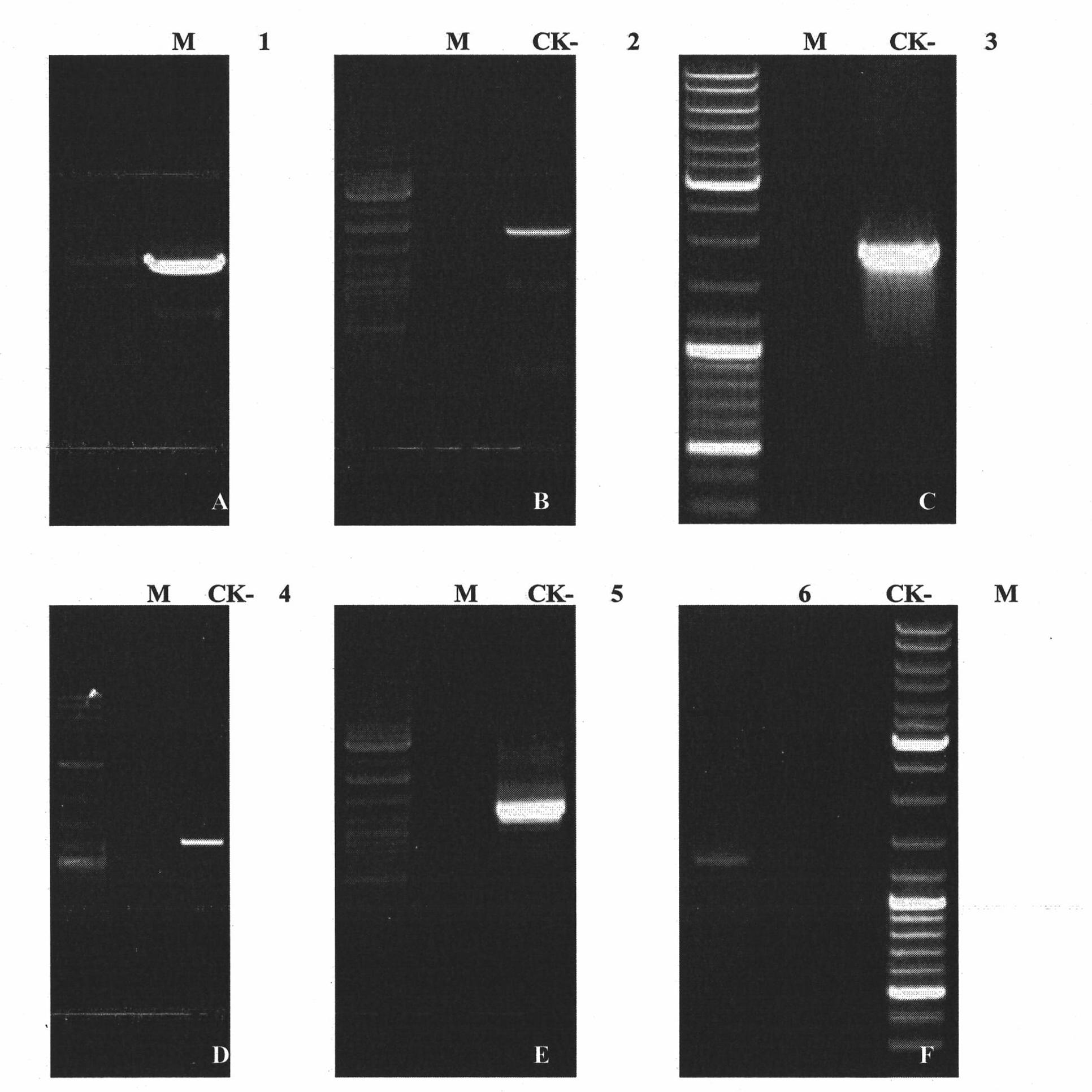
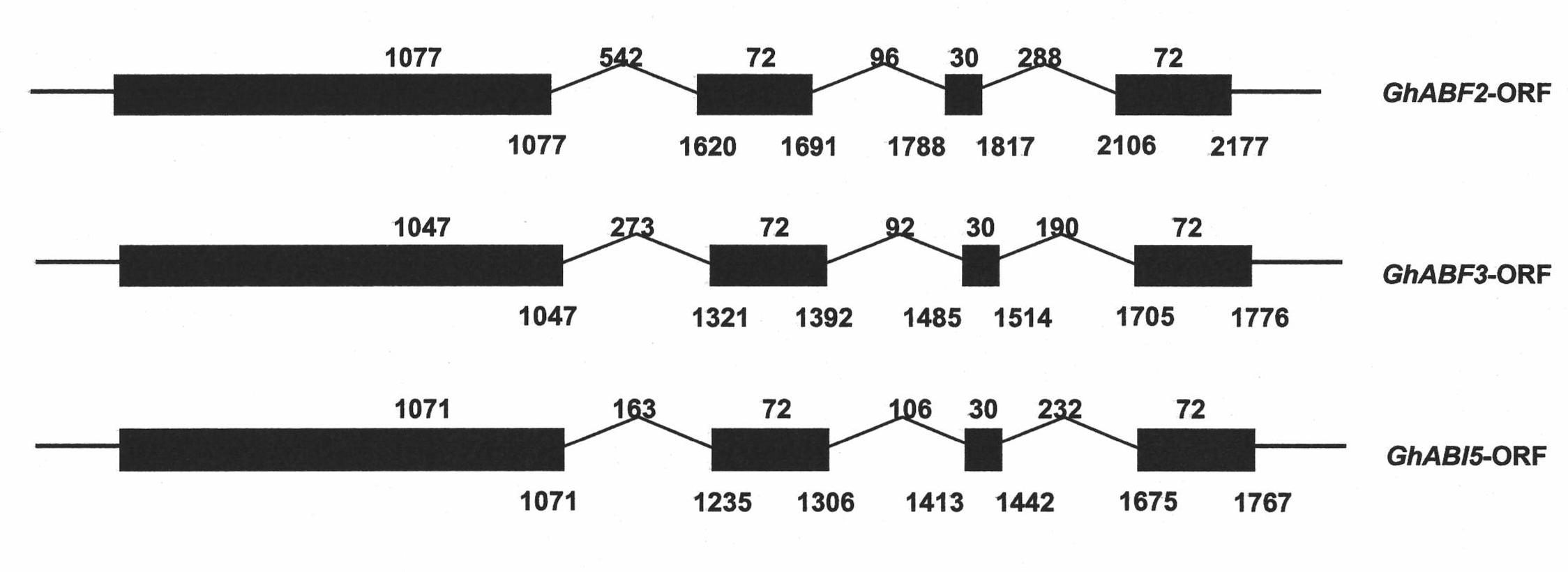
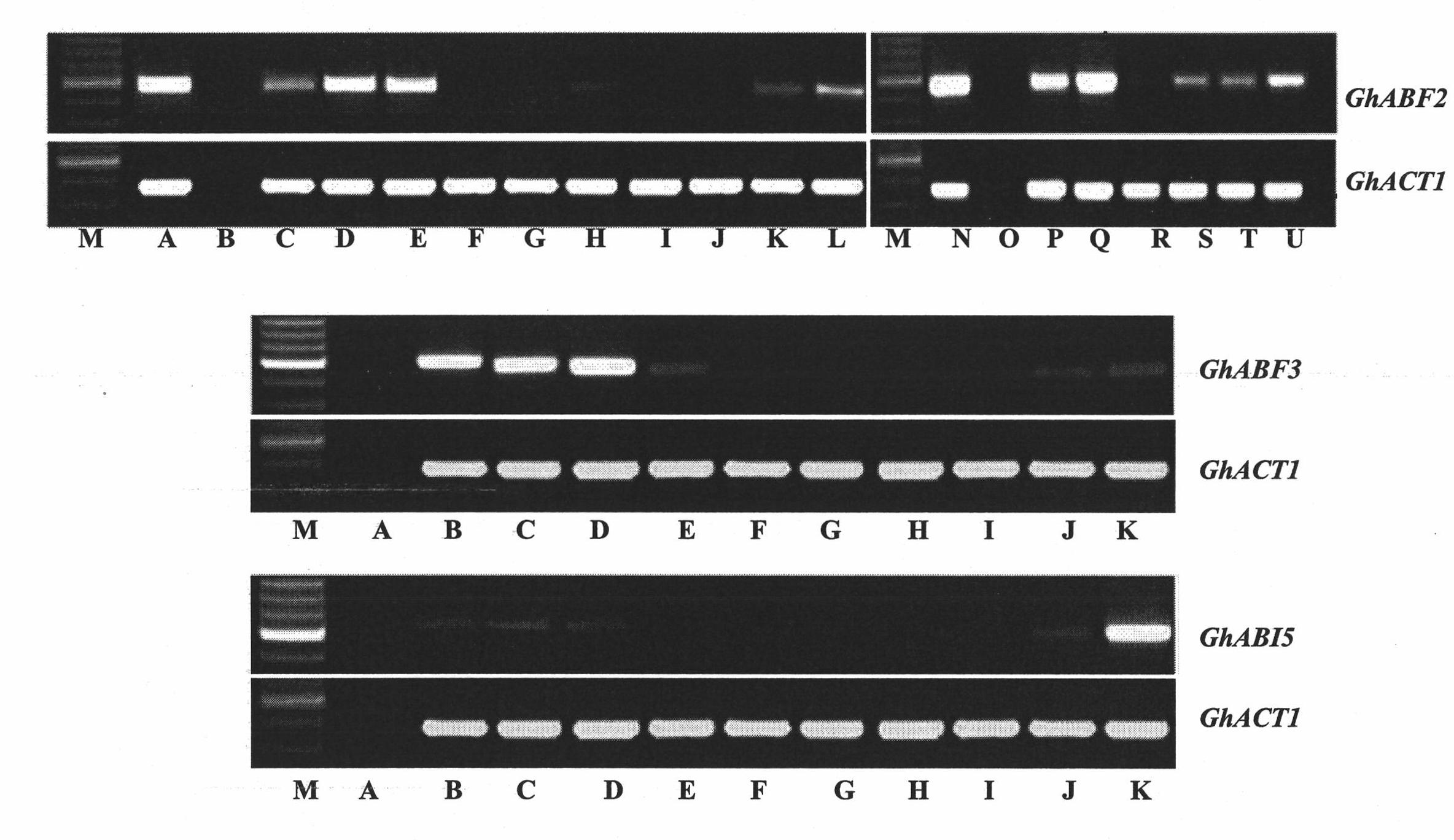
Three cotton ABF/AREB/ABI5/DPBF type transcription factors and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN102060919AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses three novel cotton ABF / AREB / ABI5 / DPBF type transcription factors GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5, and coding genes and application thereof. Amino acid sequences of the GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, 5 and 8 respectively. Nucleotide sequences of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, 4 and 7 respectively. The invention also discloses the structural characteristics on genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and a ribonucleic acid (RNA) editing law of reading frame regions of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5. The invention also discloses the cotton expression characteristics and yeast expression characteristics of the three genes and the characteristic that the three genes can improve the drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana. The genes provide gene resources for culturing a plant variety resistant to abiotic stress, and have great significance for improving the abiotic stress resistance of plants.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 and application thereof
InactiveCN101760439AGood control effectPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46, which is preserved in CGMCC with preservation date as November 2, 2009, and preservation number as CGMCC No.3378. The Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 CGMCC No.3378 in the invention is a biological control bacillus separated from grass root surrounding soil near Namco Lake in Tibet, which can grow at 10 DEG C, is favorable for exerting growth promotion and biological control effects, can restrain soybean root pythium myriotylum and saccharomycetes, can boost growth of Arabidopsis and soybean, has a prevention and control effects on soybean root pythium myriotylum as high as 85%, can increase yield of soybean to 24%, and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING HOUJI BIO TECH
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT (Asparatate AminoTransferase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides hitherto unknown ASPAT-encoding nucleic acids and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for increasing various plant yield-related traits by increasing expression in a plant of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a MYB91 like transcription factor (MYB91 ) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having increased expression of a nucleic acid sequence encoding an MYB91 polypeptide, which plants have increased yield- related traits relative to control plants. The invention additionally relates to nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and plants containing said nucleic acid sequences. Even furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA (Gibberellic Acid-Stimulated Arabidopsis). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Yet furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an AUX / IAA (auxin / indoleacetic acid) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding IAA polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising AUX / IAA-encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice
The invention relates to application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. Nucleotide sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Encoded protein sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Conditions that are met for the nucleotide sequences and the encoded protein sequences include: first, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1, or the sequences highly homologous to the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1; second, other encodable sequencecs with the same protein as the DNA sequences shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.2; third, the sequences the same functional as the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1, or sub-segments contained in the highly homologous DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is applied to breeding of the drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. An expression vector of the MYB44 gene can be introduced into plant cells by biotechnology. Transforming hosts, available to use the expression vector containing the MYB44 gene, can be monocotyledons such as rice, corn and wheat. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is also applicable to dicotyledons such as tobacco and soybean. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is used to breed drought-resistant salt-tolerant plant varieties.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
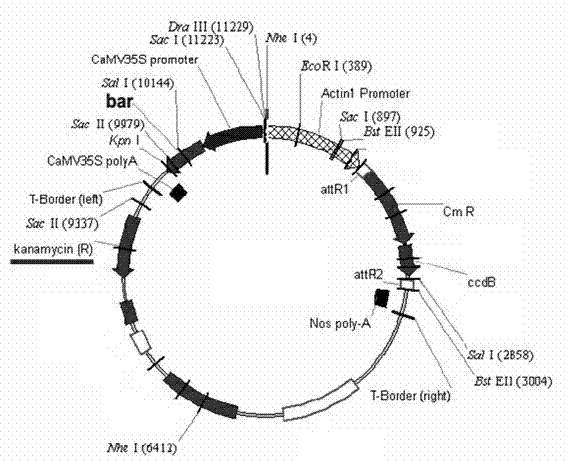
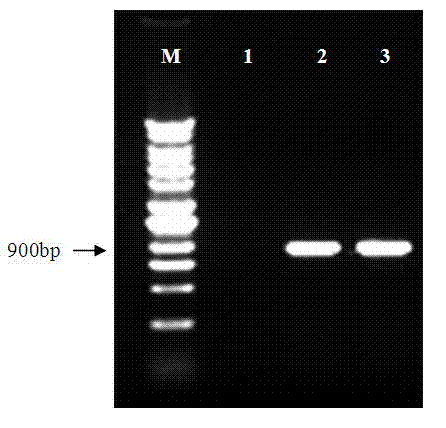
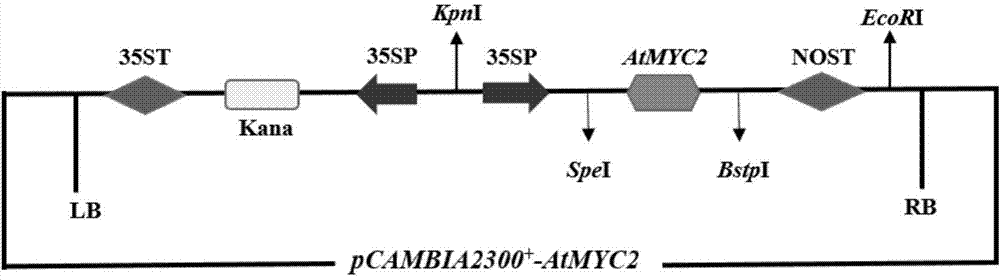
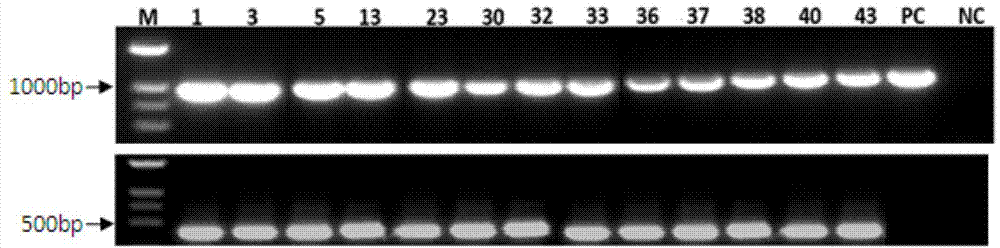
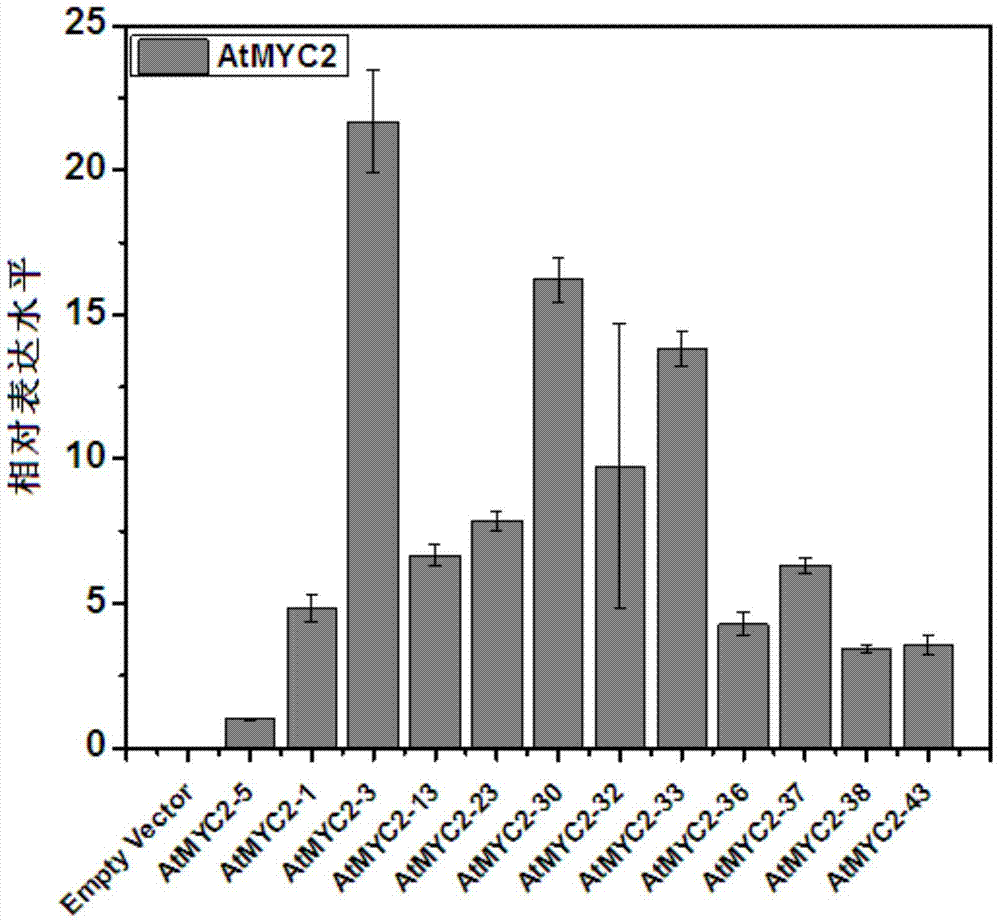
Method for increasing contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using transgene AtMYC2
InactiveCN104726485AIncrease contentGood effectFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSalvianolic acidBiology
The invention relates to a method for increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in a salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a transgene AtMYC2, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the steps of constructing a high-efficiency expression vector of a plant by using an arabidopsis transcription factor AtMYC2, and carrying out genetic transformation on salvia miltiorrhiza leaves to obtain a gene AtMYC2 overexpressed transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root; analyzing the expression of AtMYC2 in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and related genes in biosynthetic pathways of tanshinone and salvianolic acid through qRT-PCR; measuring the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); and measuring the antioxidant activity of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a DPPH free radical scavenging method. The invention provides the method for simultaneously increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and also provides a novel high-quality raw material for producing tanshinone and salvianolic acid with important clinic demands so as to have the positive promoting significance and application value for relieving the problem that the drug resources of tanshinone and salvianolic acid are short.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
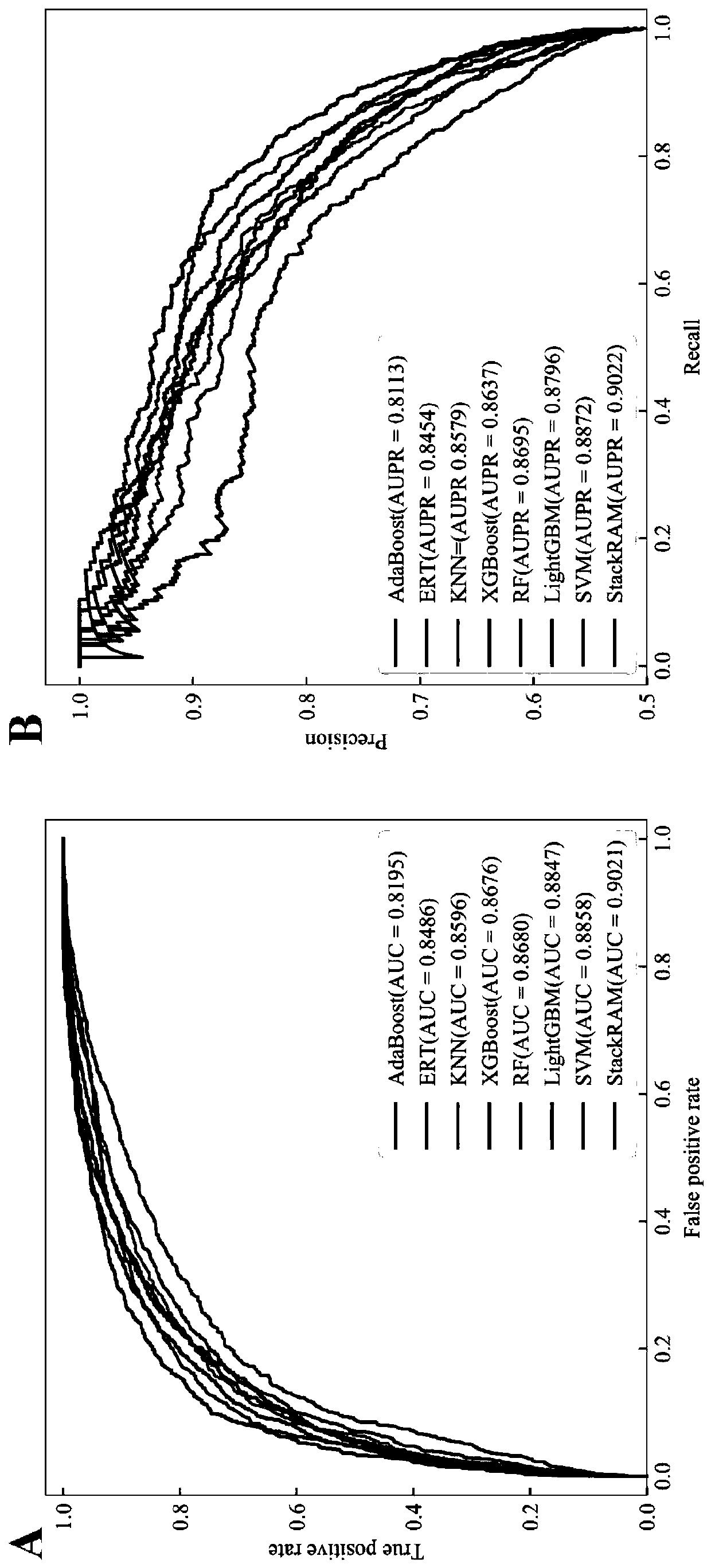
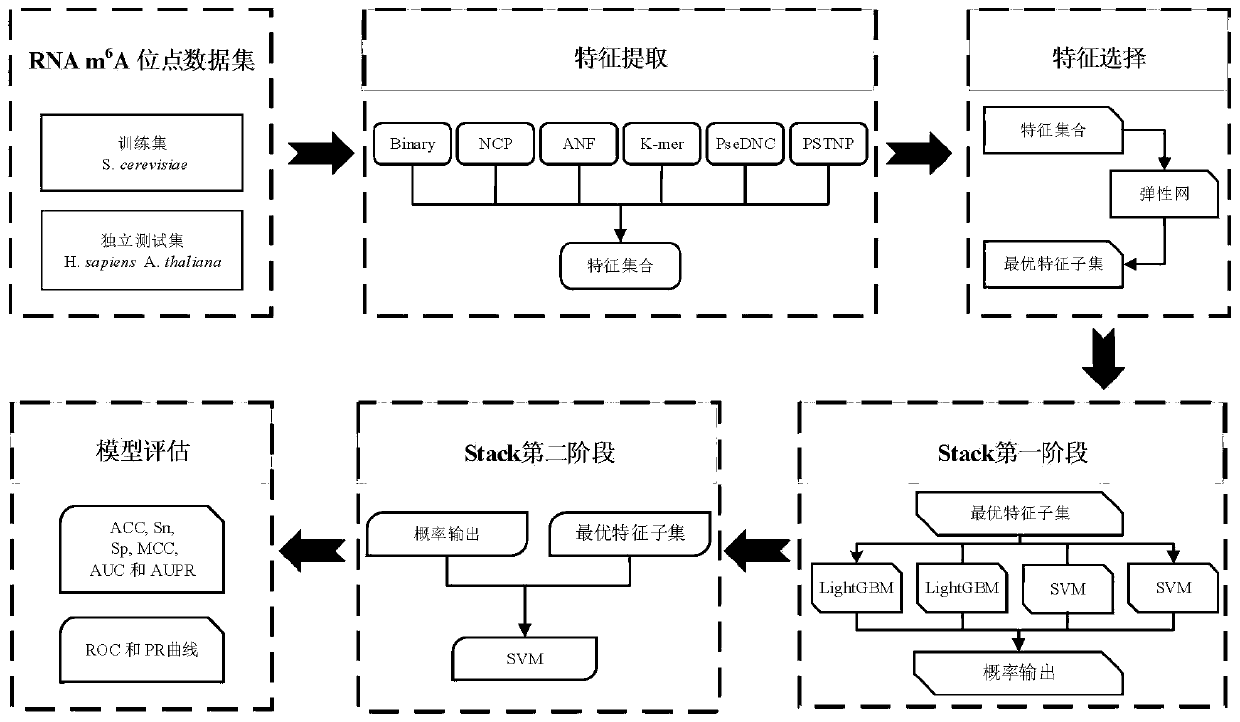
Method for predicting N6-methyladenosine modification site in RNA based on stacking integration
ActiveCN111161793APredictableIncrease computing speedBiostatisticsProteomicsDimensionality reductionRNA Sequence
The invention discloses a method for predicting an N6-methyladenosine modification site in RNA based on stacking integration, belonging to the field of systems biology. The method comprises the following steps: extracting RNA sequence features of three species, namely saccharomyces cerevisiae, homo sapiens and arabidopsis thaliana through six feature extraction methods, and conducting feature fusion to obtain an initial feature space of an original data set; performing dimensionality reduction on the initial feature space by using an elastic network, eliminating redundant and noise features, and reserving important features related to model classification so as to obtain an optimal feature set; inputting optimal feature subsets and corresponding category labels into stacking integration for model training, and evaluating the prediction performance of a model in combination with evaluation indexes to obtain a prediction model; and inputting a to-be-predicted RNA sequence in a test set into the prediction model, predicting the m6A site and outputting the m6A site. The prediction accuracy of the model on the test set reaches 92.30% and 87.06% respectively, and the model has good development potential in the aspect of cross-species prediction and is expected to become a useful tool for identifying the m6A site.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Paddy rice fragile straw controlling gene BC1 and use thereof
InactiveCN1488643AReduce pollutionImprove lodging resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellFragility
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Homogentisate prenyl transferase gene (HPT2) from arabidopsis and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant genetics and biochemistry. More specifically, the present invention relates to genes and polypeptides associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway, namely those encoding homogentisate prenyl transferase activity, and uses thereof. In particular, the sequence of the HPT2 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is disclosed for expression in any plant species to increase the levels of tocopherol.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Expression cassettes for seed-preferential expression in plants
The present invention relates to expression cassettes comprising transcription regulating nucleotide sequences with seed-preferential or seed-specific expression profiles in plants obtainable from a tonoplast intrinsic protein, said gene being selected from the group consisting of the Arabidopsis thaliana tonoplast intrinsic protein alpha described by the GenBank Arabidopsis thaliana genome loci At1g73190 and its orthologous genes from Brassica napus and Linum usitatissimum.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
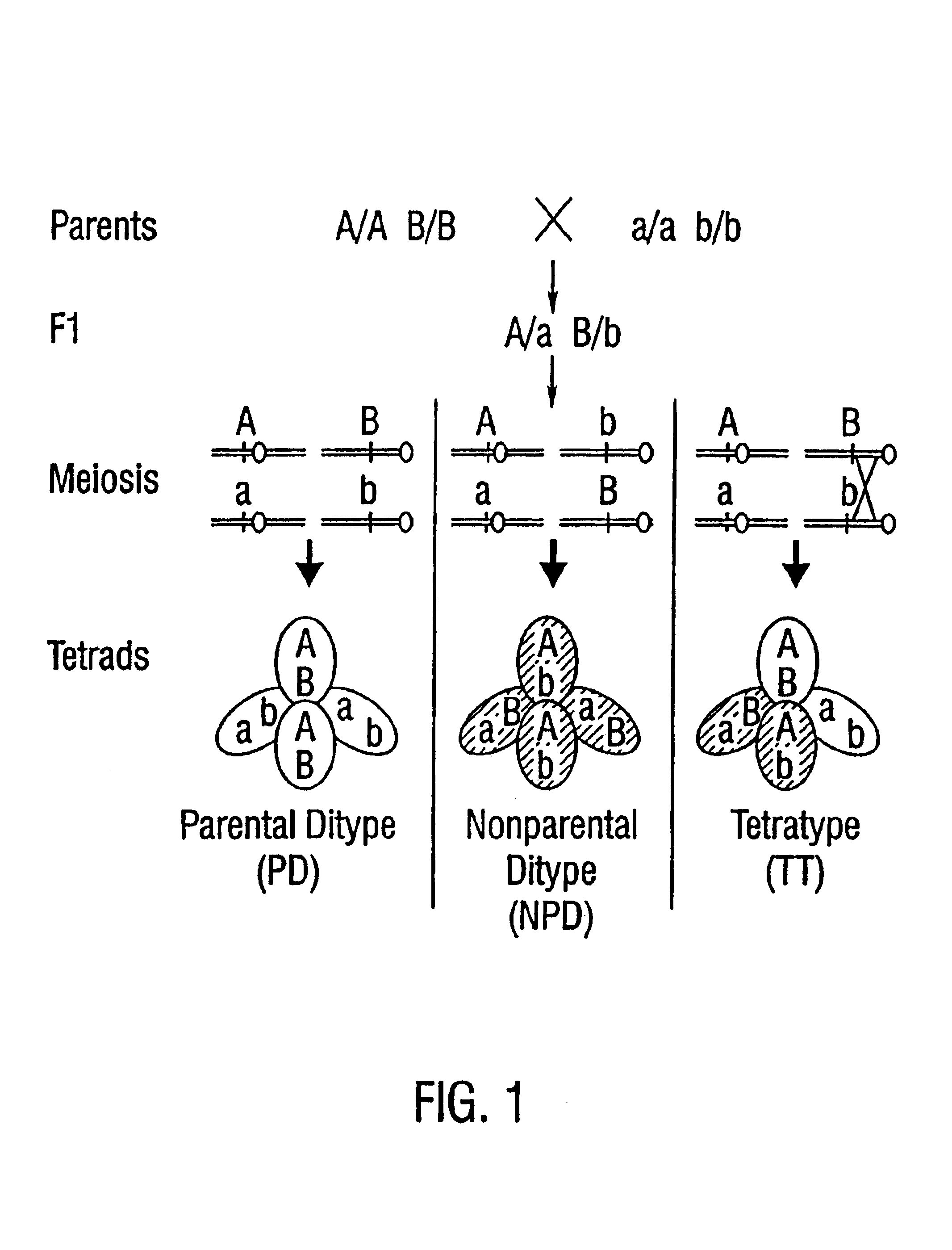
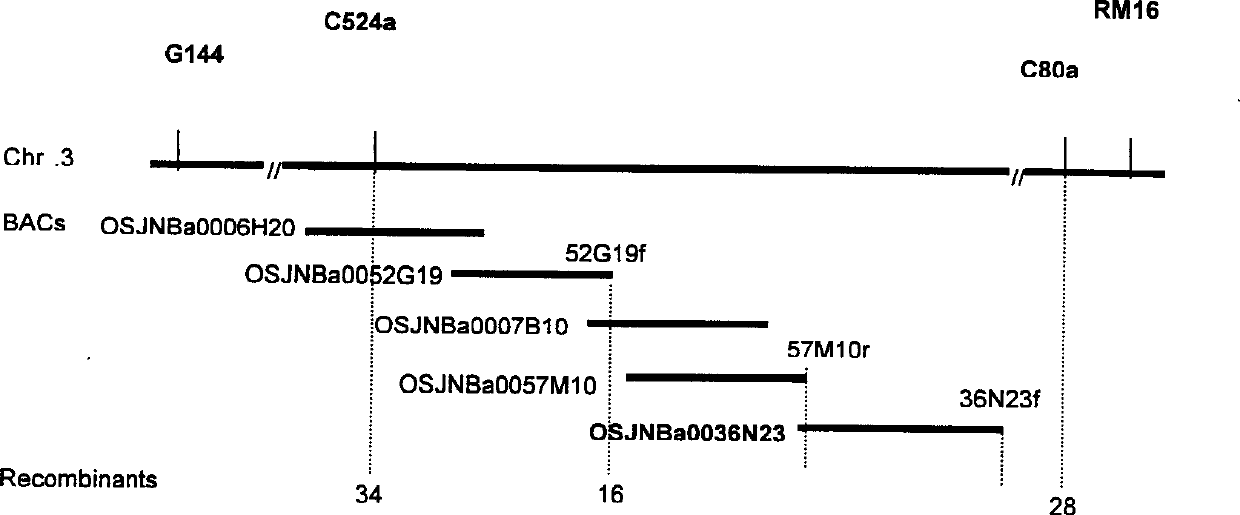
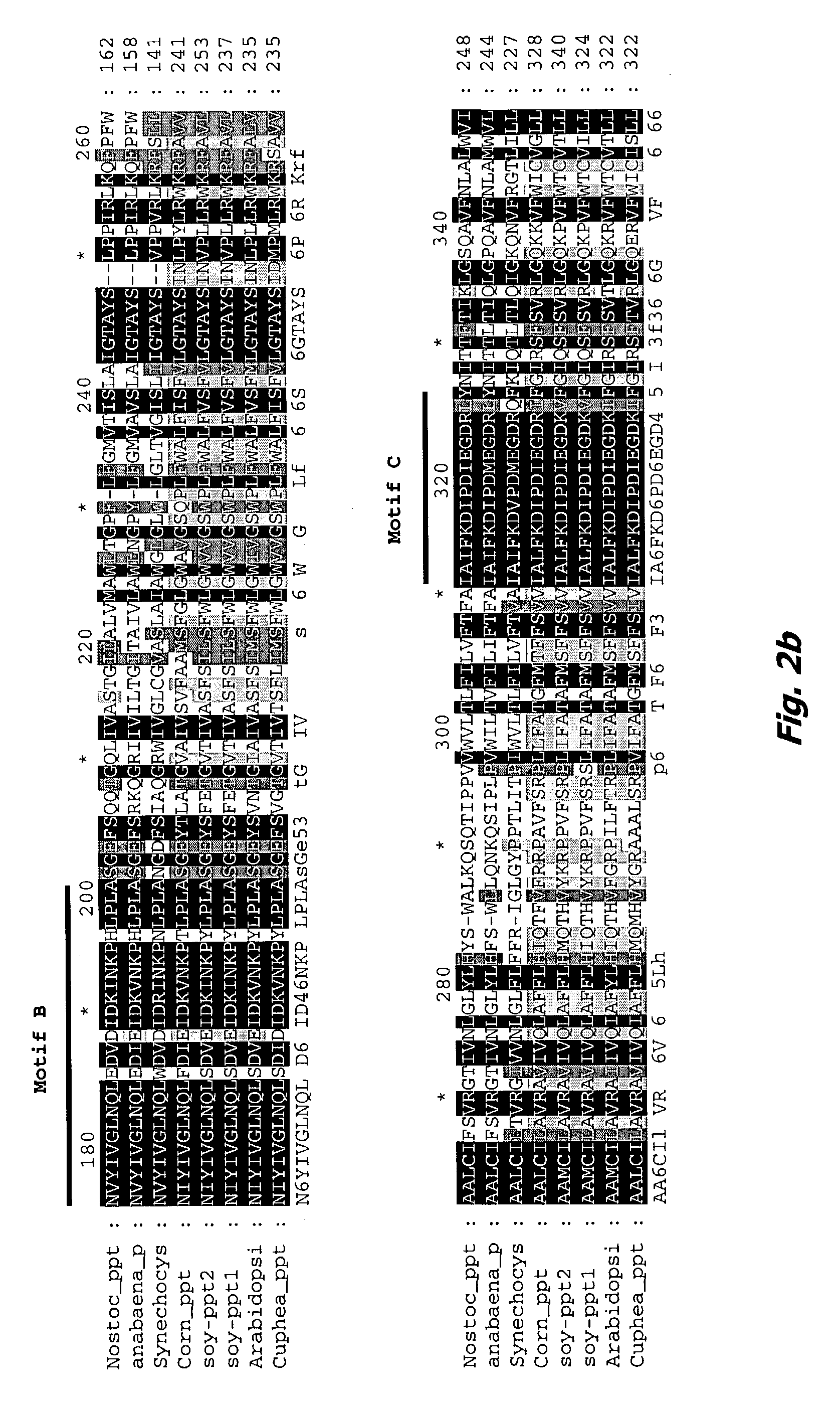
Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides with 95% identity to a Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptide from Arabidopsis thaliana for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +1
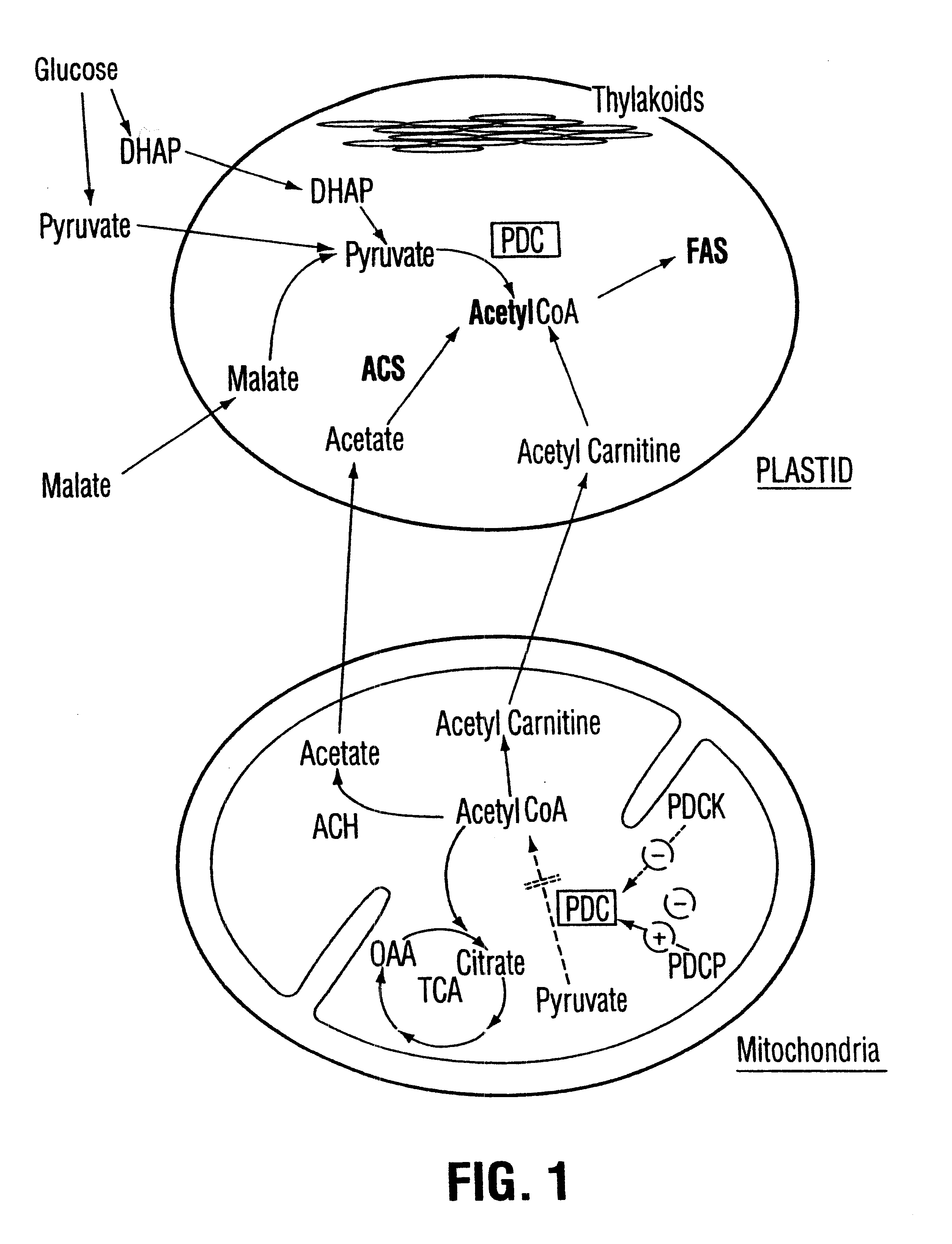
Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene
InactiveUS6500670B1High activityImprove availabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBrassicaceaePlanting seed
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of a mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK) gene [SEQ ID NO:1](pYA5; ATCC No 209562) from the Brassicaceae (specifically Arabidopsis thaliana). The invention includes isolated and purified DNA of the stated sequence and relates to methods of regulating fatty acid synthesis, seed oil content, seed size / weight, flowering time, vegetative growth, respiration rate and generation time using the gene and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1; or a part of SEQ ID NO:1 characterized in that said sequence has been introduced into an antisense or sense orientation, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds. The invention also relates to substantially homologous DNA sequences from plants encoding proteins with deduced amino acid sequences of 25% or greater identity, and 50% or greater similarity, isolated and / or characterized by known methods using the sequence information of SEQ ID NO:1, and to parts of reduced length that are still able to function as inhibitors of gene expression by use in an anti-sense, co-suppression or other gene silencing technologies.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Genetic engineering salt tolerance in crop plants
InactiveUS7041875B1Improve salt toleranceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCytosolCrop species
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides for extrusion of monovalent cations (preferably lithium ions and postassium ions, most preferably sodium ions) from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. In a preferred embodiment, the nucleic acid is obtained from Arabidopsis thaliana. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +3
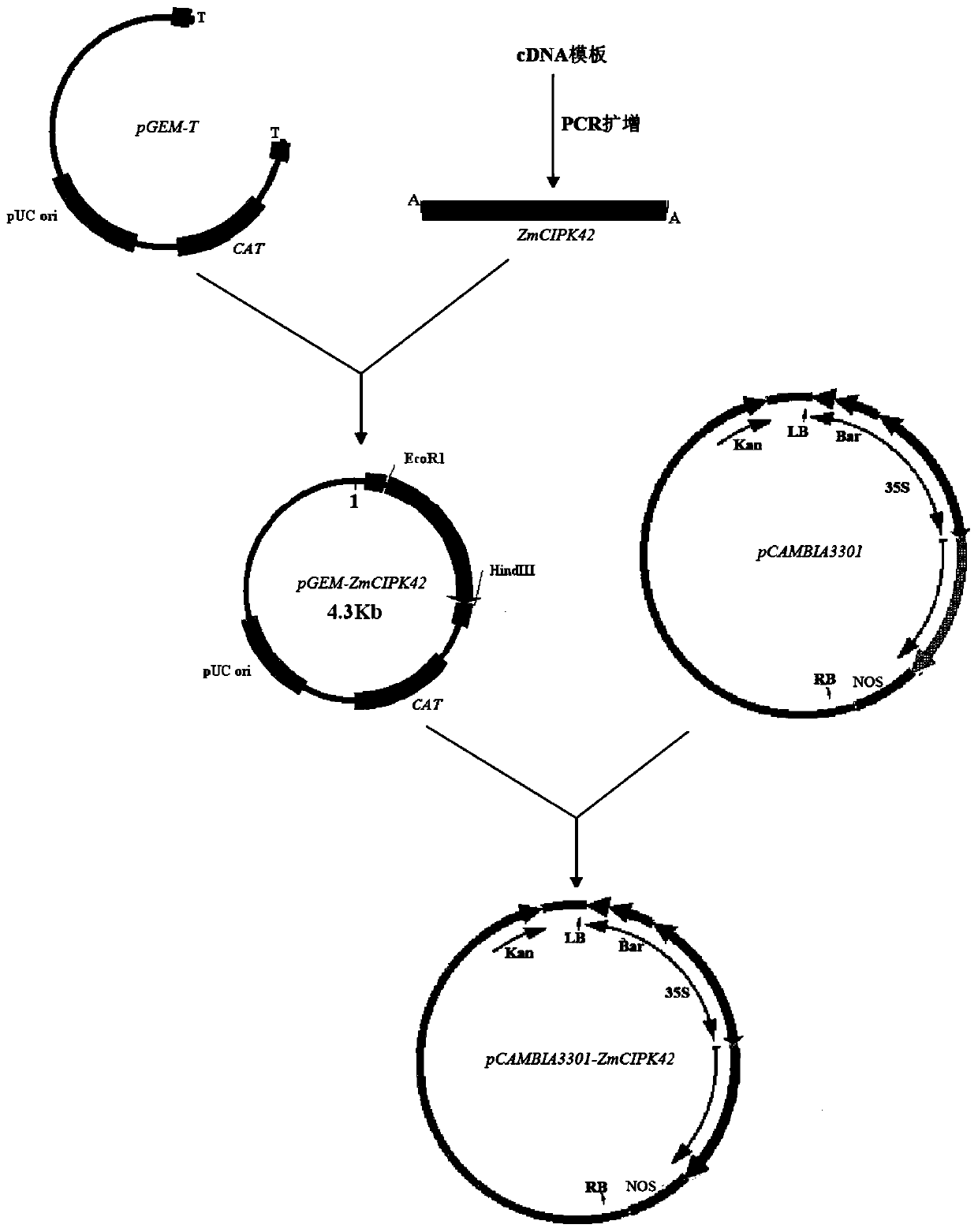
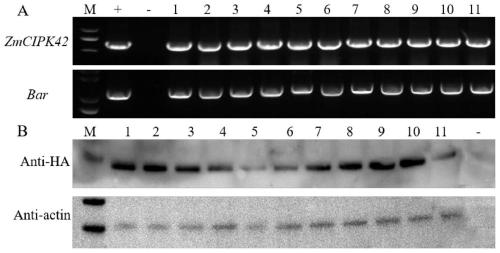
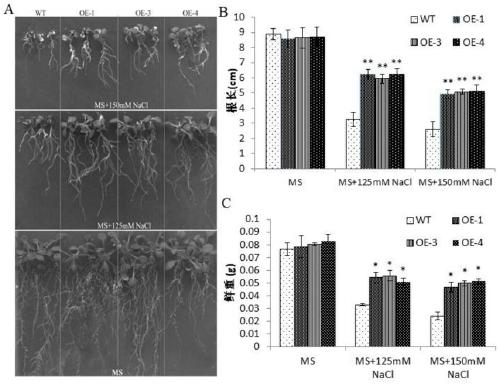
Application of corn CIPK42 protein and coding gene of corn CIPK42 protein in regulation and control of salt stress tolerance of plants
ActiveCN111172131AImprove salt toleranceImprove growth performanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologySalt Tolerant Plants
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly discloses an application of a corn CIPK42 protein and a coding gene of the corn CIPK42 protein in regulationand control of salt stress tolerance of plants. The corn ZmCIPK42 gene is found to be able to positively regulate and control the salt tolerance of the plants; and the salt tolerance of the plants can be effectively improved by increasing of the expression quantity of the ZmCIPK42 gene. According to the invention, transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants with ZmCIPK42 overexpression are constructed; and compared with a non-transgenic wild type, the transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants are significantly improved in salt tolerance and growth. Discovery of the salt-tolerant function of the ZmCIPK42 gene provides a novel gene target and resource for cultivation of salt-tolerant plant varieties, is of great significance to research of a salt-tolerant molecular mechanism of the plants, and lays a certain theoretical foundation for research of a salt stress response mechanism of the plants and a molecular mechanism of resisting adverse environments.
Owner:新疆农业科学院核技术生物技术研究所(新疆维吾尔自治区生物技术研究中心)
A transcription factor PwNAC2 related to plant stress tolerance, a coding gene thereof and applications of the transcription factor
ActiveCN107827964AImprove germination rateImprove drought tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationWAS PROTEINAgricultural science
A transcription factor PwNAC2 related to plant stress tolerance, a coding gene thereof and applications of the transcription factor are disclosed. Protein provided by the invention is a), b), c) or d), wherein the a) is protein the amino acid sequence of which is shown as a sequence 2; the b) is fusion protein obtained by connecting a label to the N end and / or C end of the protein shown as the sequence 2; the c) is protein having same functions and obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues to the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 2; and the d) is protein which has functions same to functions of the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 2, and which has 75% or 75% or above of homology with the amino acid sequence shownas the sequence 2. The new gene PwNAC2 is found and is introduced into arabidopsis thaliana to obtain a PwNAC2-transgenicarabidopsis thaliana plant. Experiments prove that drought tolerance and salt tolerance of the PwNAC2-transgenicarabidopsis thaliana plant are significantly improved, thus proving that the PwNAC2 or the protein coded by the PwNAC2 has stress tolerance.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
WRKY45 gene of paddy rice, preparation method and application
InactiveCN101003808AImprove disease resistanceImprove drought resistancePlant peptidesFermentationDiseaseAgricultural science
This invention discloses a method for preparing rice gene WRKY45 and its applications. This invention successfully separates gene WRKY45 from rice, determines its nucleotide sequence, and deduces its amino acid sequence. Gene functional analysis shows that rice gene WRKY45 can effectively improve the disease and drought resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana, rice, economic crops, horticultural plants, and pasture grass, thus has wide potential applications.
Owner:XISHUANGBANNA TROPICAL BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Drought resistant correlative protein of plant and coding gene and application thereof
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sesame drought resisting and salt-tolerant gene SiMYB75 as well as encoded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN109337915AIncreased drought and salt toleranceImprove drought and salt toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringDrought resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and provides a sesame drought resisting and salt-tolerant gene SiMYB75 as well as encoded protein and application thereof. The sesame drought resisting and salt-tolerant gene SiMYB75 is a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 or a nucleotide sequence with drought resistance and salt tolerance, generated by adding, displacing, inserting or deleting one or more nucleotides. The gene SiMYB75 disclosed by the invention is constructed to an expression vector and is transferred into arabidopsis by a agrobacterium tumefaciens medicated transformation method to obtain transgenic arabidopsis; by overexpression of the drought resisting and salt-tolerant gene SiMYB75 in the arabidopsis, the gene is found to remarkably improve thedrought resistance and the salt tolerance of plants. Therefore, the sesame drought resisting and salt-tolerant gene SiMYB75 has a good application prospect in improving the properties of the plants, such as the drought resistance and the salt tolerance.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of Arabidopis thaliana AtGDSL gene in prevention of sclerotinia rot and promotion of seed germination of rape
The invention discloses a gene for resisting sclerotinia rot of cabbage type rape and promoting rape seed germination and application thereof and specifically relates to an AtGDSL gene capable of improving resistance of plants to sclerotinia sclerotiorum biotic stress and promoting rape seed germination. Verification is carried out on the function of the AtGDSL gene in improvement of resistance of plants to sclerotinia sclerotiorum biotic stress and promotion of rape seed germination, and application of the gene is also verified. According to the invention, the exogenous Arabidopis thaliana AtGDSL gene is introduced into a rape plant through a genetic engineering technological means, and after excess expression of the exogenous Arabidopis thaliana AtGDSL gene in the cabbage type rape, the rape plant has substantially improved sclerotinia rot resistance and seed germination capability; and the AtGDSL gene exerts obvious resistance effect on sclerotinia sclerotiorum, can be applied to stress resistance breeding of plants, improves stress resistance of the plants and improves the speed of seed germination, thereby providing excellent breeding materials for large-scale mechanical production of rape.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Paraquat resistance gene and a vascular tissue-and trichome-specific promoter
A paraquat resistance gene and a vascular tissue- and trichome-specific promoter are provided. The paraquat resistance gene and the vascular tissue- and trichome-specific promoter are isolated by identifying and analyzing genes of Arabidopsis thaliana.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of repressing flowering in a plant
ActiveUS20060070141A1Reducing and substantially preventing floweringReducing and preventing floweringImmunoglobulinsFermentationArabidopsisTransgene
The isolation and function of a plant LpTFL1 from Lolium perenne (perennial ryegrass) are described, along with generation of transgenic Arabidopsis ryegrass, and red fescue plants. Thc gene prevents or represses flowering of transgenic plants. Methods for using the gene to repress or prevent flowering are described.
Owner:DLF SEEDS AS
Synthesis and structure of high potency RNA therapeutics
ActiveUS20190002906A1Increased cytoplasmic half-lifeExtended half-lifeApolipeptidesFibrinogenProtein targetArabis
This invention provides expressible polynucleotides, which can express a target protein or polypeptide. Synthetic mRNA constructs for producing a protein or polypeptide can contain one or more 5′ UTRs, where a 5′ UTR may be expressed by a gene of a plant. In some embodiments, a 5′ UTR may be expressed by a gene of a member of Arabidopsis genus. The synthetic mRNA constructs can be used as pharmaceutical agents for expressing a target protein or polypeptide in vivo.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com











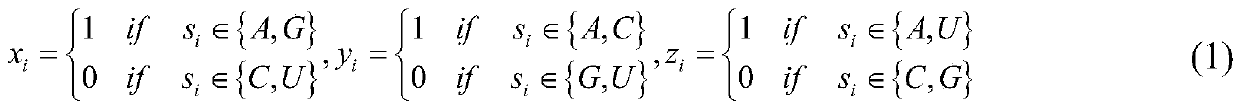





![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00001.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00002.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00003.png)